JP5340332B2 - Rotating electric machine - Google Patents
Rotating electric machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5340332B2 JP5340332B2 JP2011045312A JP2011045312A JP5340332B2 JP 5340332 B2 JP5340332 B2 JP 5340332B2 JP 2011045312 A JP2011045312 A JP 2011045312A JP 2011045312 A JP2011045312 A JP 2011045312A JP 5340332 B2 JP5340332 B2 JP 5340332B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- rotor
- magnetic
- stator
- field
- winding
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、回転子が界磁巻線により界磁される回転電機に関する。 The present invention relates to a rotating electrical machine in which a rotor is fielded by a field winding.
回転子が界磁巻線により界磁される回転電動機として、回転軸が高速回転した際に回転軸の半径方向の振れが大きくなるのを抑制したホモポーラ形リラクタンスモータが提案されている(特許文献1参照)。このホモポーラ形リラクタンスモータは、図12に示すように、突極51を有する一対の回転子52A,52Bが所定の間隔を有して直列に、かつ各回転子52A,52Bの突極51同士が互いにずれた状態で回転軸53に固定されている。固定子54A,54Bは、それぞれ回転子52A,52Bを囲繞するように配置され、回転子52A,52Bにトルクを発生させるトルク発生用駆動コイル(図示せず)を備えている。固定子54A,54Bの外側には突極51を励磁する界磁コイル55が設けられている。そして、界磁コイル55に通電すると、図12に示すように一方の回転子52Aの突極51から他方の回転子52Bの突極51に通じる磁束が形成され、一方の回転子52Aの4個の突極51が例えばN極となり、他方の回転子52Bの4個の突極51が例えばS極になる。
A homopolar reluctance motor has been proposed as a rotary motor in which a rotor is fielded by a field winding, which suppresses an increase in radial deflection of the rotating shaft when the rotating shaft rotates at high speed (Patent Document). 1). In this homopolar reluctance motor, as shown in FIG. 12, a pair of
特許文献1のホモポーラ形リラクタンスモータは、回転軸53に固定された一対の回転子52A,52Bのうちの一方の回転子52Aの全ての突極51がN極になり、他方の回転子52Bの全ての突極51がS極になる。そのため、回転軸53に作用するラジアル力のバランスが取り易い。しかし、回転子及び固定子をそれぞれ2個ずつ設ける必要があり、構成が複雑で小型化し難い。
In the homopolar reluctance motor of
回転子が界磁巻線により界磁され、かつ単極となる回転電機で回転子及び固定子を1個ずつにした場合、構成が簡単になり小型化し易くなる。ところが、その際、固定子の巻線に集中巻を採用すると、固定子(ステータ)及び回転子(ロータ)の突極数の組み合わせにより、通電時に回転子に働くラジアル力が不均一に作用する状態となり、回転軸を支持するベアリングの負担が大きくなり、振動増や寿命低下を招くという問題が生じる。 When the rotor is fielded by the field winding and has only one rotor and one stator in the rotating electric machine having a single pole, the configuration is simplified and the size is easily reduced. However, if concentrated winding is employed for the stator winding, the radial force acting on the rotor when energized acts unevenly due to the combination of the number of salient poles of the stator (stator) and rotor (rotor). This causes a problem that the load on the bearing that supports the rotating shaft increases, resulting in increased vibration and reduced life.
本発明は前記の問題に鑑みてなされたものであって、その目的は、回転子が界磁巻線により単極となるように界磁される回転電機において、回転シャフトに加わるラジアル力のアンバランスをなくすことができる回転電機を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object of the present invention is to reduce the radial force applied to the rotating shaft in a rotating electric machine in which a rotor is fielded so as to have a single pole by a field winding. An object of the present invention is to provide a rotating electrical machine that can eliminate the balance.
前記の目的を達成するため、請求項1に記載の発明は、回転子が界磁巻線により界磁される回転電機である。そして、回転シャフトに一体回転可能に固定され、かつ周方向に一定間隔で磁気的突極が形成されたロータコアを有する回転子と、筒状に形成されるとともに前記ロータコアの外周側に配置され、かつ三相交流電流で励磁される固定子巻線が集中巻で巻き付けられたティースが内周面に一定間隔で形成された固定子と、前記固定子の外側に設けられるとともに、軸方向両側においてベアリングを介して前記回転シャフトを回転可能に支持する界磁ヨークと、前記回転子が単極となる磁気回路を形成するための界磁巻線とを備えている。また、前記磁気的突極、前記ティースがそれぞれ前記回転シャフトを中心とした回転対称に配置され、前記固定子巻線の相配置が前記回転シャフトを中心とした回転対称に設定され、かつ前記磁気的突極の数をPn、前記固定子のスロットの数をPsとした場合、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有し、且つPn:Psが4:9、5:12のいずれかを満足する。ここで、「回転子が単極となる」とは、ロータコアに複数形成された磁気的突極の固定子側端部が、界磁巻線に励磁電流が供給された状態では全てN極又はS極の同じ磁極になることを意味する。また、「磁気的突極」とは、ロータコアの内側から外面に向かって磁束が流れ易い部分を意味し、ロータコアとして突部を一定間隔で有する形状に限らず、磁性材で形成された突部の間が非磁性材で埋められる、もしくは磁気的突極性を有するようロータコアに非磁性部を配し、全体として平坦な形状のロータコアであってもよい。
In order to achieve the above object, an invention according to
この発明では、固定子(ステータ)のティースに集中巻で巻き付けられた固定子巻線が励磁されると回転磁界が発生し、回転磁界による磁束により回転子(ロータ)にトルクが作用する。一方、界磁巻線に励磁電流が供給された状態では、回転子のロータコアに複数形成された全ての磁気的突極の固定子側端部が同じ磁極になる。そして、回転磁界による磁束と、界磁巻線による磁束との相互作用によって回転シャフトにラジアル力が加わる。磁気的突極、ティースがそれぞれ回転シャフトを中心とした回転対称に配置され、前記固定子巻線の相配置が前記回転シャフトを中心とした回転対称に設定され、かつ前記磁気的突極の数をPn、前記固定子のスロットの数をPsとした場合、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有するため、回転シャフトに加わるラジアル力のアンバランスがなくなる。 In this invention, when the stator winding wound by concentrated winding on the teeth of the stator (stator) is excited, a rotating magnetic field is generated, and torque acts on the rotor (rotor) by the magnetic flux generated by the rotating magnetic field. On the other hand, in a state in which the exciting current is supplied to the field winding, the stator side end portions of all the magnetic salient poles formed on the rotor core of the rotor become the same magnetic pole. A radial force is applied to the rotating shaft by the interaction between the magnetic flux generated by the rotating magnetic field and the magnetic flux generated by the field winding. Magnetic salient poles and teeth are arranged rotationally symmetrical around the rotating shaft, the phase arrangement of the stator windings is set rotationally symmetrical around the rotating shaft, and the number of magnetic salient poles Is Pn, and the number of slots of the stator is Ps, Pn and Ps have a common divisor other than 1, so that there is no unbalance of the radial force applied to the rotating shaft.
請求項2に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の発明において、前記ロータコアは、複数枚積層された電磁鋼板で形成されている。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the first aspect of the present invention, the rotor core is formed of a plurality of laminated electromagnetic steel sheets.
請求項3に記載の発明は、請求項2に記載の発明において、前記回転シャフトは、外周側の磁気抵抗が内周側の磁気抵抗より小さい2重構造に形成されている。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the second aspect of the present invention, the rotary shaft is formed in a double structure in which the magnetic resistance on the outer peripheral side is smaller than the magnetic resistance on the inner peripheral side.
請求項4に記載の発明は、請求項2に記載の発明において、前記ロータコアは、筒状コアと前記筒状コアの外側に形成された積層コアとで構成され、前記筒状コアの材質は磁気抵抗が前記積層コアの材質より小さく構成されている。 The invention according to claim 4 is the invention according to claim 2 , wherein the rotor core is composed of a cylindrical core and a laminated core formed outside the cylindrical core, and the material of the cylindrical core is The magnetic resistance is configured to be smaller than the material of the laminated core.
本発明によれば、回転子が界磁巻線により単極となるように界磁される回転電機において、回転シャフトに加わるラジアル力のアンバランスをなくすことができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the unbalance of the radial force added to a rotating shaft can be eliminated in the rotary electric machine by which a rotor is fielded so that it may become a single pole by a field winding.
以下、本発明を三相の回転電動機に具体化した一実施形態を図1〜図4にしたがって説明する。なお、図2(a),(b)及び図3の模式断面図において図示の都合上、断面のハッチングを省略している。 Hereinafter, an embodiment in which the present invention is embodied in a three-phase rotary motor will be described with reference to FIGS. In addition, in the schematic cross-sectional views of FIGS. 2A and 2B and FIG. 3, the cross-sectional hatching is omitted for convenience of illustration.
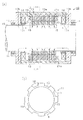
図1(a)に示すように、回転電機としての回転電動機10は、ロータ(回転子)11と、ロータ11の外側に配置された筒状のステータ(固定子)12と、ステータ12の外側に設けられた界磁ヨーク13と、ロータ11を界磁する界磁巻線14とを備えている。界磁ヨーク13は回転電動機10のケースとしても機能し、ステータ12の外周と対向する円筒部13aと、円筒部13aの両端に固定された一対の円板部13bとを有する。
As shown in FIG. 1A, a rotary
ロータ11は、回転シャフト15に一体回転可能に固定されたロータコア16を有し、回転シャフト15は円板部13bを貫通する状態でベアリング17を介して円板部13bに回転可能に支持されている。回転シャフト15は磁性材で形成されている。
The
図1(b)に示すように、ロータコア16は、径方向に突出する突部が周方向に一定間隔で形成されており、突部が磁気的突極18を構成する。磁気的突極18は、ロータコア16を軸方向から見た場合に回転シャフト15を中心とした回転対称となるように配置されている。この実施形態では磁気的突極18は8個設けられ、各磁気的突極18はロータコア16の軸方向全長に亘って延設されている。ロータコア16は、電磁鋼板を複数枚(例えば数十枚)積層して構成されており、軸方向の磁気抵抗が、径方向及び周方向の磁気抵抗より大きくなっている。このため、ロータコア16内においては、磁束は軸方向に流れ難く、径方向及び周方向に流れ易くなる。
As shown in FIG. 1B, the
ステータ12は、電磁鋼板を積層して略円筒状に形成されており、ステータ12の径方向及び周方向の磁気抵抗は、軸方向の磁気抵抗より小さくなっている。このため、ステータ12内においては、磁束はステータ12の周方向及び径方向に流れ易く、軸方向に流れ難くなる。
The
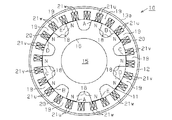
図2に示すように、ステータ12の内側には複数のティース19が周方向に一定間隔で形成されるようにスロット20が等間隔で設けられている。ティース19及びスロット20は、ステータ12を軸方向から見た場合に回転シャフト15を中心とした回転対称となるように配置されている。この実施形態ではティース19及びスロット20がそれぞれ18個設けられている。したがって、ロータコア16の磁気的突極18の数をPn、ステータ12のスロット20の数をPsとした場合、Pn=8、Ps=18となり、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有し、かつPn:Psが4:9を満足する。
As shown in FIG. 2,
各ティース19には、固定子巻線としてのU相巻線21u、V相巻線21v、W相巻線21wがそれぞれ集中巻で巻き付けられている。U相巻線21u、V相巻線21v、W相巻線21wは、図2において時計方向にU相、V相、W相の順で、かつ同じ相の巻線が巻き付けられたティース19が3個ずつ隣り合うように巻き付けられている。即ち、固定子巻線を構成するU相巻線21u、V相巻線21v、W相巻線21wの相配置が回転シャフト15を中心とした回転対称に設定されている。
A U-phase winding 21u, a V-phase winding 21v, and a W-phase winding 21w as stator windings are wound around each
界磁ヨーク13の両円板部13bには、円環状の突条13cがロータコア16に向かって突出するように形成され、突条13cには外周部に界磁巻線14が巻き付けられたボビン23が嵌合固定されている。突条13c及びボビン23は、ロータ11が単極となる磁気回路を形成するための界磁巻線14が巻き付けられた界磁巻線巻回部を構成する。ロータ11が単極となるとは、ロータコア16に複数形成された磁気的突極18のステータ12側端部が、界磁巻線14に励磁電流が供給された状態では全てN極又はS極の同じ磁極になることを意味する。
An
この実施形態では、各界磁巻線14に電流が供給されると、界磁ヨーク13とロータコア16との間にロータコア16の磁気的突極が全て同じ磁極(N極)となる磁気回路が形成されるようになっている。詳述すると、図1(a)において左側に位置する一方の界磁巻線14においては、磁束が環状の界磁巻線14の左側から内周側に進入して右側から界磁巻線14の外部へ出るように発生する。また、図1(a)において右側に位置する他方の界磁巻線14においては、磁束が環状の界磁巻線14の右側から内周側に進入して左側から界磁巻線14の外部へ出るように発生する。その結果、両界磁巻線14から発生した磁束の経路は、回転シャフト15内を対向する方向に進んだ後、ロータコア16の内側から磁気的突極18内を通ってステータ12のティース19内へ進み、界磁ヨーク13の円筒部13a及び円板部13bを通って再び回転シャフト15内に進入する経路となる。
In this embodiment, when a current is supplied to each field winding 14, a magnetic circuit is formed in which the magnetic salient poles of the
次に前記のように構成された回転電動機10の作用を説明する。
回転電動機10は、U相巻線21u、V相巻線21v、W相巻線21wが三相インバータに接続され、界磁巻線14が直流電源に接続された状態で使用される。そして、制御装置により三相インバータから出力される制御電流量と、直流電源から界磁巻線14に供給される電流量が制御される。
Next, the operation of the rotary
The
界磁巻線14に直流が供給されると、界磁巻線14から発生した磁束(磁力線)が、図1(a)に破線で示すように、界磁ヨーク13の円板部13b→回転シャフト15→ロータコア16→磁気的突極18→ステータ12→界磁ヨーク13の円筒部13a→界磁ヨーク13の円板部13bの経路で通過する磁気回路が形成される。その結果、界磁巻線14に励磁電流が供給された状態では、図2に示すように、ロータコア16に複数形成された磁気的突極18のステータ12側端部が、全てN極になってステータ12が単極となる。
When a direct current is supplied to the field winding 14, the magnetic flux (line of magnetic force) generated from the field winding 14 is rotated from the
一方、ステータ12のU相巻線21u、V相巻線21v、W相巻線21wには所定周波数の三相交流が順次供給されてステータ12に回転磁界が発生し、ロータ11に回転磁界が作用する。そして、回転磁界と磁気的突極18の磁束との間の磁気的な吸引力及び反発力によりロータ11が回転磁界と同期して回転する。また、界磁巻線14に供給する電流量を調整することにより、生成する磁束量を調整することができる。そのため、界磁巻線14に供給する電流量を調整することにより、所謂「弱め界磁制御」や「強め界磁制御」、自在な界磁磁束制御を行うことができる。
On the other hand, the U-phase winding 21u, the V-phase winding 21v, and the W-phase winding 21w of the
図2(a)に示すように、Aで示す180度の機械角をなす一対の磁気的突極18が、U相巻線21uが巻き付けられた隣接する3個のティース19の中央のティース19と対向する状態において、それぞれ180度の機械角をなす他の3対の磁気的突極18のティース19との位置関係も、対毎に同じ状態となる。詳述すると、Bで示す磁気的突極18は、V相巻線21vが巻き付けられた隣接する3個のティース19のうちU相巻線21uが巻き付けられたティース19寄りのティース19と対向する。Cで示す磁気的突極18は、V相巻線21vが巻き付けられた隣接する3個のティース19のうちW相巻線21wが巻き付けられたティース19寄りのティース19と、W相巻線21wが巻き付けられた隣接する3個のティース19のうちV相巻線21vが巻き付けられたティース19寄りのティース19とに対向する。Dで示す磁気的突極18はW相巻線21wが巻き付けられた隣接する3個のティース19のうちU相巻線21uが巻き付けられたティース19寄りのティース19と対向する。したがって、この状態では180度の機械角をなすA,B,C,Dで示す各一対の磁気的突極18に作用するラジアル方向の力は、各一対の磁気的突極18毎に同じとなり、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力はバランスした状態になる。
As shown in FIG. 2A, a pair of magnetic
また、図2(a)に示す状態からロータ11が任意の角度回転した場合、例えば、図2(b)に示す状態においても、180度の機械角をなすA,B,C,Dで示す各一対の磁気的突極18のティース19及び固定子巻線の相配置に対する位置関係は、各一対の磁気的突極18毎に同じとなり、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力はバランスした状態になる。
Further, when the
一方、磁気的突極18、ティース19がそれぞれ回転シャフト15を中心とした回転対称に配置され、かつ固定子巻線の相配置が回転シャフト15を中心とした回転対称に設定されていても、磁気的突極18の数Pnとステータ12のスロット20の数Psとが1以外の公約数を有しない場合は、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力はアンバランスになる。
On the other hand, even if the magnetic
例えば、図3に、Pn=5、Ps=12の場合を示す。磁気的突極18は360/5度で回転対称であり、ティース19(相配置)は360/2度で回転対称であるが、PnとPsが1以外の公約数を有していない。図3に示す状態において、A、B、C、D、Eで示す各磁気的突極18は、U相巻線21u、V相巻線21v及びW相巻線21wが巻き付けられたティース19との位置関係がそれぞれ異なり、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力はアンバランスになる。
For example, FIG. 3 shows a case where Pn = 5 and Ps = 12. The magnetic
図4に、Pn=8、Ps=18の場合(8突極18スロットの場合)と、Pn=5、Ps=12の場合(5突極12スロットの場合)の回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力のシミュレーション結果を示す。図4においてラジアル力を表す縦軸の値はラジアル力の平均値に対する相対的な値を示し、1.0が平均値となる。
FIG. 4 shows the radial force applied to the
図4に示すように、実施形態の回転電動機10である8突極18スロットの場合は、電気角0〜360度の範囲に亘ってラジアル力は0、即ち回転シャフト15に特定方向へのラジアル力が作用しないこと、即ち回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力のアンバランスがないこと確認された。一方、図3に示す比較例、即ち5突極12スロットの場合は、電気角0〜360度の範囲において、特定方向へのラジアル力が60度周期で変動することが確認された。
As shown in FIG. 4, in the case of the eight salient poles and 18 slots which are the rotary
この実施形態によれば、以下に示す効果を得ることができる。
(1)回転電動機10は、回転シャフト15に一体回転可能に固定され、かつ周方向に一定間隔で磁気的突極18が形成されたロータコア16を有するロータ11と、筒状に形成されるとともにロータコア16の外周側に配置され、かつ固定子巻線が集中巻で巻き付けられたティース19が内周面に一定間隔で形成されたステータ12とを備えている。また、回転電動機10は、ステータ12の外周に設けられた界磁ヨーク13と、ロータ11が単極となる磁気回路を形成するための界磁巻線14とを備えている。磁気的突極18、ティース19がそれぞれ回転対称に配置され、固定子巻線の相配置が回転対称に設定され、かつ磁気的突極18の数をPn及びステータ12のスロット20の数Psが1以外の公約数を有する。したがって、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力のアンバランスをなくすことができる。
According to this embodiment, the following effects can be obtained.
(1) The rotary
(2)固定子巻線(U相巻線21u、V相巻線21v及びW相巻線21w)は三相交流電流で励磁される。したがって、ロータコア16にトルクを発生させるための回転磁界を発生させる構成が一般に使用される三相回転電動機と同じで簡単になる。
(2) The stator windings (U-phase winding 21u, V-phase winding 21v and W-phase winding 21w) are excited by a three-phase alternating current. Therefore, the configuration for generating a rotating magnetic field for generating torque in the
(3)回転電動機10は、磁気的突極18の数Pnが8、ステータ12のスロット20の数Psが18であるため、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有し、かつPn:Psが4:9を満足する。したがって、トルクバランスも良好になる。
(3) In the
(4)界磁巻線14は界磁ヨーク13の両端部にそれぞれ設けられているため、各磁気的突極18に所望の量の磁束を円滑に流すために必要な円筒部13aの断面積を小さくすることができ、回転電動機10の小型化に寄与する。
(4) Since the
(5)界磁巻線巻回部はボビン23を円板部13bに形成された円環状の突条13cに嵌合固定することで構成されている。したがって、界磁巻線14を巻き付けたボビン23を突条13cに固定することができ、界磁巻線14を円板部13bに突設された突条13cに直接巻き付ける場合に比べて、界磁巻線14の巻き付け作業が簡単になる。
(5) The field winding portion is configured by fitting and fixing the
実施形態は前記に限定されるものではなく、例えば、次のように具体化してもよい。
○ 磁気的突極18、ティース19がそれぞれ回転対称に配置され、固定子巻線の相配置が回転対称に設定され、かつ磁気的突極18の数Pn及びステータ12のスロットの数Psが1以外の公約数を有していれば、磁気的突極18の数Pnとスロット20の数Psとの組み合わせはPn=8、Ps=18に限らない。例えば、図3に示した磁気的突極18の数Pnが5、スロット20の数Psが12の回転電動機10ではPn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有せず、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力がアンバランスになったが、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有する組み合わせにすると、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力のアンバランスをなくすことができる。例えば、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有するように、Pn=10、Ps=24にすると、図5に示すように、180度の機械角をなすA,B,C,D,Eで示す各一対の磁気的突極18に作用するラジアル方向の力は、各一対の磁気的突極18毎に同じとなり、回転シャフト15に加わるラジアル力はバランスした状態になる。
The embodiment is not limited to the above, and may be embodied as follows, for example.
The magnetic
○ 磁気的突極18の数Pnとスロット20の数Psとの組み合わせはPn=8、Ps=18及びPn=10、Ps=24に限らず、例えば、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有し、かつPn:Psが1:3、2:3、4:3、4:9、5:3、5:6、5:9、5:12、8:9、8:15、8:21のいずれかを満足すればよい。しかし、そのうち、Pn:Psが1:3、4:3、5:3、5:6、5:9、8:9、8:15、8:21の組み合わせは、トルク変動が大きい。したがって、トルクバランスも良好になるPn:Psが2:3、4:9、5:12のいずれかの組み合わせが好ましい。
The combination of the number Pn of the magnetic
○ 回転電動機10は、界磁巻線14が界磁ヨーク13の片側(一端側)に設けられた構成でもよい。例えば、図6に示すように、界磁ヨーク13は円板部13bが円筒部13aの一端側にのみ設けられ、他端側には非磁性材で形成された支持円板24が設けられる。支持円板24は界磁ヨーク13と共に回転電動機10のケースを構成し、ベアリング17を介して回転シャフト15の他端を支持する。この実施形態では、界磁巻線14に電流が供給されると、磁束が界磁ヨーク13の円板部13b→回転シャフト15→ロータコア16→磁気的突極18→ステータ12→界磁ヨーク13の円筒部13a→界磁ヨーク13の円板部13bの経路で通過する磁気回路が形成され、各磁気的突極18がN極になる。この場合、界磁巻線14が円筒部13aの両側に設けられた実施形態と異なり、各磁気的突極18を流れた磁束が円筒部13aを経て円板部13bに戻るために必要な円筒部13aの断面積が2倍になる。
The rotary
○ 図7に示すように、ロータコア16を、円筒状に形成されて回転シャフト15に固設された筒状コア16aと、筒状コア16aの外周に設けられた積層ロータコア16bとで構成し、突条13cの先端を筒状コア16aの端面近傍まで延設するとともに突条13cの厚さを厚くして、その分、回転シャフト15の径を小さくしてもよい。磁気的突極18は積層ロータコア16bに形成する。筒状コア16aは、一体の磁性材料で形成されており、具体的には粉末成形磁性体(SMC:Soft Magnetic Composites)で形成されている。粉末成形磁性体の磁気抵抗は、積層ロータコア16bや回転シャフト15の材質より小さい。この場合、界磁巻線14で発生した磁束が回転シャフト15より筒状コア16a内を流れ易くなり、磁束が回転シャフト15を流れる場合に比べて磁束の経路長が短くなる。その結果、界磁電流量を低減させることができる。また、積層ロータコア16b内においては、磁束は、軸方向に流れ難く、径方向及び周方向に流れ易くなるのに対して、筒状コア16a内では積層ロータコア16b内より軸方向に磁束が流れ易くなる。このため、筒状コア16aが無い構成に比べて、磁束の経路が積層ロータコア16bを構成する全ての電磁鋼板に分散して流れ易くなる。
As shown in FIG. 7, the
○ ロータコア16、16bは電磁鋼板を積層して形成したが、鉄塊やSMCで形成しても良い。
○ 図8に示すように、回転シャフト15を、外周側の磁気抵抗が内周側の磁気抵抗より小さい2重構造に形成してもよい。この場合、界磁巻線14に電流が供給されて界磁巻線14から発生した磁束がロータコア16に向かって流れる際、磁束は磁気抵抗の小さい外周側を流れるため、磁束の経路長が短くなる。その結果、界磁電流量を低減させることができる。
The
As shown in FIG. 8, the
○ 図8に示すように、回転電動機10に専用のケース25を設け、ケース25で回転シャフト15をベアリング17を介して支持するようにしてもよい。この場合、界磁ヨーク13の円板部13bの形状が簡単になる。また、界磁ヨーク13がケースを兼用する場合に比べてケース25の形状や材質の自由度が大きくなる。図8では回転シャフト15が2重構造の場合を図示しているが、2重構造の場合に限らない。
As shown in FIG. 8, a
○ 図9に示すようにシャフトの径をそのベアリング部において細くするようにしても良い。この場合、ベアリングの小径化が可能になる。
○ ティース19に巻き付けられるU相巻線21u、V相巻線21v及びW相巻線21wの配置は、各巻線が巻き付けられたティース19がそれぞれ二つのグループ(360/2度で回転対称)に分けられる構成に限らない。例えば、図10(a)に示すように、Pn=10、Ps=24の回転電動機10において、各巻線が巻き付けられたティース19がそれぞれ四つのグループ(360/4度で回転対称)に分けられた構成にしてもよい。
As shown in FIG. 9, the shaft diameter may be reduced at the bearing portion. In this case, it is possible to reduce the diameter of the bearing.
○ The arrangement of the U-phase winding 21u, the V-phase winding 21v and the W-phase winding 21w wound around the
○ ロータコア16の形状は、磁気的突極18となるための突部を有する形状に限らない。例えば、図10(b)に示すように、ロータコア16として突部を一定間隔で有する形状の部分を磁性材で形成し、突部の間を非磁性材26で埋めて全体として平坦な形状としたものであってもよい。また、図11に示すように突部の先端のみを隣接する突部の先端とつなげても、実質的に磁気的突極になればよい。
The shape of the
○ ボビン23を設けずに、突条13cの外周に界磁巻線14を直接巻き付けて、突条13cを界磁巻線巻回部としてもよい。
○ 固定子巻線としてのU相巻線21u、V相巻線21v及びW相巻線21wは、一つのスロット20に2本の巻線の一部がそれぞれ収容される状態ではなく、一つのスロット20に1本の固定子巻線の一部が収容される構成であってもよい。
O Without providing the
○ The U-phase winding 21u, the V-phase winding 21v, and the W-phase winding 21w as the stator windings are not in a state in which a part of the two windings are accommodated in one
○ ロータ11が単極となる場合、各磁気的突極18のステータ12側端部が、全てN極になるのではなく、全てS極になる構成にしてもよい。
○ 磁気的突極18はロータコア16の全長に亘って延設されずに、全長より短く形成されていてもよい。
When the
The magnetic
○ 回転電動機10は三相交流で駆動されるものに限らず、単相交流や二相交流あるいは四相以上の多相交流で駆動されるものであってもよい。
○ 電動機ではなく発電機に適用してもよい。
The rotary
○ It may be applied to a generator instead of an electric motor.
以下の技術的思想(発明)は前記実施形態から把握できる。
(1)前記界磁巻線は前記界磁ヨークの両端部にそれぞれ設けられている。
The following technical idea (invention) can be understood from the embodiment.
(1) Before Symbol field winding are provided at both ends of the field magnet yoke.
(2)前記回転シャフトは、外周側の磁気抵抗が内周側の磁気抵抗より小さい2重構造に形成されている。 (2) pre-Symbol rotating shaft, the magnetic resistance of the outer peripheral side is formed on the magnetoresistive smaller double structure of the inner circumferential side.
(3)前記ロータコアは、筒状コアと前記筒状コアの外側に形成された積層コアとで構成され、前記筒状コアの材質は磁気抵抗が前記積層コアの材質より小さく構成されている。 (3) pre-Symbol rotor core is composed of a laminated core formed on the outside of the cylindrical core and the cylindrical core, the material of the tubular core is composed reluctance is smaller than the material of the laminated core .
10…回転電機としての回転電動機、11…ロータ(回転子)、12…ステータ(固定子)、13…界磁ヨーク、14…界磁巻線、15…回転シャフト、16…ロータコア、18…磁気的突極、19…ティース、20…スロット、21u…固定子巻線としてのU相巻線、21v…同じくV相巻線、21w…同じくW相巻線。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (4)
回転シャフトに一体回転可能に固定され、かつ周方向に一定間隔で磁気的突極が形成されたロータコアを有する回転子と、
筒状に形成されるとともに前記ロータコアの外周側に配置され、かつ三相交流電流で励磁される固定子巻線が集中巻で巻き付けられたティースが内周面に一定間隔で形成された固定子と、
前記固定子の外側に設けられるとともに、軸方向両側においてベアリングを介して前記回転シャフトを回転可能に支持する界磁ヨークと、
前記回転子が単極となる磁気回路を形成するための界磁巻線と
を備え、
前記磁気的突極、前記ティースがそれぞれ前記回転シャフトを中心とした回転対称に配置され、前記固定子巻線の相配置が前記回転シャフトを中心とした回転対称に設定され、かつ前記磁気的突極の数をPn、前記固定子のスロットの数をPsとした場合、Pn及びPsが1以外の公約数を有し、且つPn:Psが4:9、5:12のいずれかを満足する回転電機。 A rotating electric machine in which a rotor is fielded by a field winding,
A rotor having a rotor core fixed to a rotating shaft so as to be integrally rotatable and having magnetic salient poles formed at regular intervals in the circumferential direction;
A stator that is formed in a cylindrical shape and arranged on the outer peripheral side of the rotor core, and teeth in which a stator winding excited by a three-phase alternating current is wound in a concentrated manner is formed on the inner peripheral surface at regular intervals. When,
Rutotomoni provided outside the stator, the field yoke for rotatably supporting the rotary shaft via the bearing in the axial direction on both sides,
A field winding for forming a magnetic circuit in which the rotor has a single pole;
The magnetic salient poles and the teeth are arranged rotationally symmetrical about the rotary shaft, the phase arrangement of the stator windings is set rotationally symmetrical about the rotary shaft, and the magnetic salient when the number of poles Pn, the number of the stator slots and Ps, Pn and Ps are have a common divisor other than 1, and Pn: Ps 4: 9,5: 12 satisfies either Rotating electric machine.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011045312A JP5340332B2 (en) | 2011-03-02 | 2011-03-02 | Rotating electric machine |
| CN201210047825.XA CN102655363B (en) | 2011-03-02 | 2012-02-27 | Rotary electric machine |
| EP20120157225 EP2495851A2 (en) | 2011-03-02 | 2012-02-28 | Rotary electric motor |
| US13/407,472 US9083225B2 (en) | 2011-03-02 | 2012-02-28 | Rotary electric machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011045312A JP5340332B2 (en) | 2011-03-02 | 2011-03-02 | Rotating electric machine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012182943A JP2012182943A (en) | 2012-09-20 |
| JP5340332B2 true JP5340332B2 (en) | 2013-11-13 |
Family
ID=47013668
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011045312A Expired - Fee Related JP5340332B2 (en) | 2011-03-02 | 2011-03-02 | Rotating electric machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5340332B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109417342A (en) * | 2016-06-30 | 2019-03-01 | 安珀动力能源公司 | Unipolar motor for flywheel energy storage system |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS4857113A (en) * | 1971-11-18 | 1973-08-10 | ||
| JPS4911207U (en) * | 1972-05-02 | 1974-01-30 |
-
2011
- 2011-03-02 JP JP2011045312A patent/JP5340332B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2012182943A (en) | 2012-09-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5449892B2 (en) | Permanent magnet excitation type radial magnetic bearing and magnetic bearing device including the radial magnetic bearing | |
| JP4926107B2 (en) | Rotating electric machine | |
| US8847464B2 (en) | Electrical machine with improved stator flux pattern across a rotor that permits higher torque density | |
| JP4644832B2 (en) | Rotating electrical machine | |
| JP2010025342A6 (en) | Permanent magnet excitation type radial magnetic bearing and magnetic bearing device including the radial magnetic bearing | |
| JP2013005683A (en) | Stator and motor | |
| JP2013074743A (en) | Rotary electric machine | |
| JP5610989B2 (en) | Rotating motor | |
| JP6388611B2 (en) | Hybrid field double gap synchronous machine | |
| CN110268610B (en) | Synchronous machine with magnetic rotating field reduction and flux concentration | |
| JP2013215021A (en) | Electromagnetic induction device | |
| US9000648B2 (en) | Asymmetrical reluctance machine | |
| JP6327221B2 (en) | Rotating electric machine | |
| WO2014195999A1 (en) | Synchronous motor | |
| JP2009153305A (en) | Brushless motor | |
| JP2008252979A (en) | Axial-gap type rotating machine | |
| JP2018082600A (en) | Double-rotor dynamoelectric machine | |
| JP2012182942A (en) | Rotary electric machine | |
| JP5340332B2 (en) | Rotating electric machine | |
| JP2018148675A (en) | Stator for rotary electric machine | |
| JP2006025486A (en) | Electric electric machine | |
| JP6483300B1 (en) | Synchronous reluctance motor | |
| JP2017063594A (en) | Brushless motor | |
| JP2018516532A (en) | Single pole composite type asynchronous motor | |
| JP6830073B2 (en) | Rotating machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20121206 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130424 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130507 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130708 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130730 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130806 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |