JP5330486B2 - Bearing device - Google Patents
Bearing device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5330486B2 JP5330486B2 JP2011242733A JP2011242733A JP5330486B2 JP 5330486 B2 JP5330486 B2 JP 5330486B2 JP 2011242733 A JP2011242733 A JP 2011242733A JP 2011242733 A JP2011242733 A JP 2011242733A JP 5330486 B2 JP5330486 B2 JP 5330486B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- elastic body
- gradient
- load
- bearing device
- restraining
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、例えば建築物や橋梁等の各種構造物を支承する支承装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a support device for supporting various structures such as buildings and bridges.
建築物や橋梁等の構造物の支承装置には、ゴム板と鉄板とを交互に積層し、これらが加硫接着によって相互に接着されて構成されたゴム支承がある(特許文献1参照)。ゴム支承では、ゴムの変位を拘束することで、鉛直バネ剛性を高める工夫や回転追従性能を向上させる工夫がなされている。例えば、ゴム支承では、ゴム板と鉄板とを交互に積層し、これらを加硫接着することによって、ゴムの流動性を低減し、鉛直バネ剛性を高めるようにしている。 2. Description of the Related Art A bearing device for a structure such as a building or a bridge includes a rubber bearing in which rubber plates and iron plates are alternately stacked and bonded together by vulcanization bonding (see Patent Document 1). In the rubber bearing, by constraining the displacement of the rubber, a device for improving the vertical spring rigidity and a device for improving the rotation follow-up performance are made. For example, in rubber bearings, rubber plates and iron plates are alternately laminated and vulcanized and bonded to reduce the fluidity of rubber and increase the rigidity of the vertical spring.
また、密閉ゴム支承では、ゴム板が下沓となる金属製ポット内に配置され、ゴム板の上にピストン状の上沓が載置され、ゴム板が非圧縮性の流体的に振る舞うように拘束されることで、回転追従性能が得られるように構成されている(特許文献2参照)。なお、この密閉ゴム支承は、鉛直可撓性がないことから金属支承の扱いとなる。 Also, in the sealed rubber bearing, the rubber plate is placed in the metal pot that serves as the lower shell, and the piston-shaped upper flange is placed on the rubber plate so that the rubber plate behaves in an incompressible fluid. It is comprised so that rotation tracking performance may be acquired by being restrained (refer patent document 2). This sealed rubber bearing is handled as a metal bearing because it does not have vertical flexibility.
更に、所謂コンパクト支承では、大きな鉛直荷重を支持するため、上沓と下沓の相対する面にそれぞれ凹部を設け、それぞれの凹部内にゴム層が配設され、鉛直荷重が加わった際にゴムが撓み変形によって半径方向外方に膨出しないようにして、鉛直バネ剛性の向上を図るようにしている(特許文献3参照)。 Furthermore, in so-called compact bearings, in order to support a large vertical load, a concave portion is provided on each of the opposing surfaces of the upper and lower collars, and a rubber layer is disposed in each concave portion. Is prevented from bulging outward in the radial direction due to bending deformation, thereby improving the vertical spring rigidity (see Patent Document 3).
本発明は、載荷物からの荷重に応じて適度な鉛直可撓性を発現しながら高荷重を支持することが出来る支承装置を提供することを目的とする。 An object of this invention is to provide the support apparatus which can support a high load, expressing moderate vertical flexibility according to the load from a load.
詳しくは、低荷重から高荷重に至る広範な入力に適する鉛直バネ性能を発現させることが出来る支承装置を提供することを目的とする。 Specifically, it is an object of the present invention to provide a bearing device capable of expressing vertical spring performance suitable for a wide range of inputs from low loads to high loads.
また、本発明は、高面圧化させながらも、良好な回転追従性を実現出来る支承装置を提供することを目的とする。 It is another object of the present invention to provide a bearing device that can realize good rotation followability while increasing surface pressure.
本発明に係る支承装置は、建築物や橋梁等の各種構造物を支承する支承装置として用いられるものであり、第一剛性体と、第二剛性体と、前記第一剛性体と前記第二剛性体との間に配設される弾性体と、前記弾性体を囲繞する拘束体とを備えている。前記拘束体と前記弾性体との間には、隙間が設けられている。そして、鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性が比較的低い荷重域において近似直線としてあらわれる低荷重域の一次勾配と、比較的高い荷重域において近似直線としてあらわれる高荷重域の二次勾配とを有し、前記二次勾配の近似直線の傾きが前記一次勾配の近似直線の傾きより大きいことを特徴としている。具体的に、前記一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率は、1.43以上であり、また、3.72以下であることが好ましい。 The bearing device according to the present invention is used as a bearing device for supporting various structures such as buildings and bridges, and includes a first rigid body, a second rigid body, the first rigid body, and the second rigid body. And an elastic body disposed between the rigid body and a restraining body surrounding the elastic body. A gap is provided between the restraining body and the elastic body. And a primary gradient of a low load region that appears as an approximate straight line in a load region where the characteristic of the vertical load relative to the vertical displacement is relatively low, and a secondary gradient of a high load region that appears as an approximate straight line in a relatively high load region. The slope of the approximate line of the secondary gradient is larger than the slope of the approximate line of the primary gradient. Specifically, the gradient factor of the secondary gradient with respect to the primary gradient is 1.43 or more, and preferably 3.72 or less.
これにより、本発明に係る支承装置は、低荷重域では鉛直面内における回転に必要とされる撓みを満足する鉛直撓み量を確保しつつ、高荷重域では1mm以下の鉛直撓み量となって、連続的に配置された被支承物同士の間の鉛直方向における段差を1mm以下とする鉛直ばね特性を実現出来る。即ち、本発明に係る支承装置は、金属支承装置の扱いではなく、弾性支承装置に属する扱いとし得ると共に、段差を規定内に抑えることが出来る。 As a result, the bearing device according to the present invention has a vertical deflection amount of 1 mm or less in the high load region while ensuring a vertical deflection amount that satisfies the deflection required for rotation in the vertical plane in the low load region. Moreover, the vertical spring characteristic which makes the level | step difference in the perpendicular direction between the to-be-supported articles arrange | positioned continuously 1 mm or less is realizable. That is, the bearing device according to the present invention can be handled as belonging to the elastic bearing device, not handled as a metal bearing device, and can suppress a step within a specified range.
前記支承装置では、例えば最大許容荷重が500kNの場合、前記一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率が1.65−3.37の範囲にあり、最大許容荷重が1000kNの場合、前記一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率が1.73−3.62の範囲にあり、最大許容荷重が3000kNの場合、前記一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率が1.43−3.72の範囲にあり、最大許容荷重が10000kNの場合、前記一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率が1.74−2.83の範囲にある。 In the bearing device, for example, when the maximum allowable load is 500 kN, the gradient factor of the secondary gradient with respect to the primary gradient is in the range of 1.65 to 3.37, and when the maximum allowable load is 1000 kN, the secondary gradient with respect to the primary gradient is When the gradient factor of the secondary gradient is in the range of 1.73-3.62, and the maximum allowable load is 3000 kN, the gradient factor of the secondary gradient with respect to the primary gradient is in the range of 1.43-3.72, and the maximum When the allowable load is 10,000 kN, the gradient factor of the secondary gradient with respect to the primary gradient is in the range of 1.74-2.83.
以上のような支承装置は、所定以上の入力がなされると、前記弾性体が前記隙間の容積を縮小するように弾性変形し、且つ、変形した当該弾性体が拘束体に当接及び/又は圧接して当該弾性体の変形が拘束されるように構成される。例えば、前記弾性体は、前記第一剛性体と前記第二剛性体と前記拘束体とによって囲繞されて略密閉状態とされ、前記弾性体への荷重の増大に伴って、より高度な密閉状態へと変化する。このような支承装置において、荷重が入力されたときには、入力の大きさに伴って、前記弾性体の側面又は前記拘束体の拘束面の前記凸部間の凹部により構成された隙間を埋めるように前記弾性体が変形しながら、凸部が前記拘束体の拘束面に圧接する程度が増大する。前記拘束体は、このような前記弾性体の変形を拘束する。 In the above-described support device, when an input exceeding a predetermined value is made, the elastic body elastically deforms so as to reduce the volume of the gap, and the deformed elastic body abuts on the restraining body and / or The elastic body is configured to be restrained from being deformed by pressure contact. For example, the elastic body is surrounded by the first rigid body, the second rigid body, and the restraining body to be in a substantially sealed state, and as the load on the elastic body increases, a more advanced sealed state To change. In such a support device, when a load is input, the gap formed by the concave portions between the convex portions of the side surface of the elastic body or the constraining surface of the constraining body is filled with the magnitude of the input. While the elastic body is deformed, the degree to which the convex portion comes into pressure contact with the restraining surface of the restraining body increases. The restraint body restrains such deformation of the elastic body.
ここで、前記弾性体は、弾性層と補強板とが積層された積層構造で構成されていても良いし、補強板を含まず単層の弾性層で構成されていても良い。前記弾性体を積層構造としたときには、前記補強板の位置又は前記補強板の間の位置の一方に前記凸部又は凹部を形成し、他方に凹部又は凸部を形成すると良い。前記補強板がある場合、前記弾性体は、荷重入力があると、前記補強板の間において、前記弾性体の厚さ方向と略直交する方向に膨出する。前記補強板の間の位置に前記凸部を設けた場合には、弾性変形した前記弾性体の凸部が最初に前記拘束体の拘束面に圧接されることで、前記弾性体が変形し過ぎることを防止出来る。特に、前記補強板間に相当する弾性体周面の局部歪みによる損傷を防止出来る。 Here, the elastic body may be constituted by a laminated structure in which an elastic layer and a reinforcing plate are laminated, or may be constituted by a single elastic layer without including the reinforcing plate. When the elastic body has a laminated structure, the convex portion or the concave portion may be formed at one of the position of the reinforcing plate or the position between the reinforcing plates, and the concave portion or the convex portion may be formed at the other. When there is the reinforcing plate, the elastic body bulges between the reinforcing plates in a direction substantially orthogonal to the thickness direction of the elastic body when there is a load input. When the convex portion is provided at a position between the reinforcing plates, the elastic body is deformed excessively because the elastic convex portion of the elastic body is first pressed against the restraining surface of the restraining body. It can be prevented. In particular, it is possible to prevent damage due to local distortion of the elastic peripheral surface corresponding to the space between the reinforcing plates.
前記凸部又は凹部は、例えば、前記弾性体の側面又は前記拘束体の拘束面の周回り方向に連続及び/又は断続的に形成することで、前記作用を効果的に実現することが出来る。 The said effect | action can be effectively implement | achieved by forming the said convex part or a recessed part continuously and / or intermittently in the surrounding direction of the side surface of the said elastic body or the restraint surface of the said restraint body, for example.
前記弾性体の側面と前記拘束体の拘束面との間に隙間が形成されていても良い。すなわち、本発明は、少なくとも、大きい荷重が加わったとき、前記弾性体の凸部が拘束体の拘束面に当接しているように構成する。なお、支承装置の組立時等において、前記拘束体の拘束面と前記弾性体の凸部とが当接する程度であっても好い。この場合、前記拘束体内において、組立時に、前記弾性体の位置を容易に位置決め出来る。 A gap may be formed between the side surface of the elastic body and the restraining surface of the restraining body. That is, the present invention is configured such that at least when a large load is applied, the convex portion of the elastic body is in contact with the restraining surface of the restraining body. It is also preferable that the restraint surface of the restraint body and the convex portion of the elastic body are in contact with each other during assembly of the support device. In this case, the position of the elastic body can be easily positioned in the restraint body during assembly.
前記拘束体は、前記第一剛性体と一体的に設けられていても良く、また、前記第二剛性体と一体的に設けられていても良い。 The restraining body may be provided integrally with the first rigid body, or may be provided integrally with the second rigid body.
本発明では、弾性体を、第一剛性体と第二剛性体と拘束体とで囲繞することで、略密閉された空間部を構成して、密閉ゴム支承のように小さな支承面積にして高荷重支承を実現しながら、拘束体と弾性体との間に隙間を設けるようにしている。そして、鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性が低荷重域の一次勾配と高荷重域の二次勾配とを有し、二次勾配の近似直線の傾きが一次勾配の近似直線の傾きより大きい。 In the present invention, the elastic body is surrounded by the first rigid body, the second rigid body, and the restraint body, thereby forming a substantially sealed space portion, and a small bearing area such as a sealed rubber bearing. A gap is provided between the restraining body and the elastic body while realizing the load support. The characteristic of the vertical load with respect to the vertical displacement amount has a primary gradient in the low load region and a secondary gradient in the high load region, and the inclination of the approximate line of the secondary gradient is larger than the inclination of the approximate line of the primary gradient.
これにより、本発明に係る支承装置は、金属支承装置の扱いではなく、弾性支承装置に属する扱いとし得る。そして、鉛直荷重に対する鉛直可撓変位を実現することが出来、また、回転作用の際には、隙間により弾性体が変形し、良好な回転追従性を実現出来る。 As a result, the bearing device according to the present invention can be handled as belonging to an elastic bearing device, not as a metal bearing device. Further, it is possible to realize a vertical flexible displacement with respect to a vertical load, and in the case of a rotating action, the elastic body is deformed by the gap, and a good rotation followability can be realized.
また、拘束体と弾性体との間に間隙を設けたことにより、鉛直荷重が大きくなるに連れて鉛直変位量も大きくなるが、その特性は非線形で、鉛直変位に対する鉛直荷重反力の大きさを表すグラフの傾き(拘束度又はバネ定数)は、鉛直変位又は鉛直荷重が大きくなるほど大きくなる。このように、本発明では、拘束体と弾性体との間に設けた隙間を設定したことで、荷重が大きくなるほど、鉛直変位量の増加量が小さくなるような特性で、即ち拘束度を可変として、上部構造物を支承することが出来る。 In addition, by providing a gap between the restraining body and the elastic body, the vertical displacement increases as the vertical load increases, but its characteristics are non-linear and the magnitude of the vertical load reaction force against the vertical displacement. The inclination (constraint degree or spring constant) of the graph representing the value increases as the vertical displacement or the vertical load increases. As described above, in the present invention, by setting the gap provided between the restraining body and the elastic body, the amount of increase in the vertical displacement amount decreases as the load increases, that is, the degree of restraint is variable. As above, the superstructure can be supported.
そして、本発明は、一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率が1.43−3.72の範囲にある。したがって、低荷重域では鉛直面内における回転に必要とされる撓みを満足する鉛直撓み量を確保しつつ、高荷重域では1mm以下の鉛直撓み量となって、連続的に配置された被支承物同士の間の鉛直方向における段差を1mm以下とする鉛直ばね特性を実現出来る。即ち、本発明に係る支承装置は、金属支承装置の扱いではなく、弾性支承装置に属する扱いとし得ると共に、段差を規定内に抑えることが出来る。 In the present invention, the gradient factor of the secondary gradient with respect to the primary gradient is in the range of 1.43-3.72. Therefore, in a low load region, a vertical deflection amount that satisfies the deflection required for rotation in the vertical plane is ensured, while in a high load region, the vertical deflection amount is 1 mm or less, and the continuously mounted bearings. A vertical spring characteristic in which the step in the vertical direction between the objects is 1 mm or less can be realized. That is, the bearing device according to the present invention can be handled as belonging to the elastic bearing device, not handled as a metal bearing device, and can suppress a step within a specified range.
具体的に、例えば、支承装置の最大許容荷重が500kNの場合、一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率を1.65−3.37の範囲とすることで、上記効果を得ることが出来る。更に、支承装置の最大許容荷重が1000kNの場合、一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率を1.73−3.62の範囲とすることで、上記効果を得ることが出来る。更に、支承装置の最大許容荷重が3000kNの場合、一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率を1.43−3.72の範囲とすることで、上記効果を得ることが出来る。更に、支承装置の最大許容荷重が10000kNの場合、一次勾配に対する二次勾配の勾配倍率を1.74−2.83の範囲とすることで、上記効果を得ることが出来る。 Specifically, for example, when the maximum allowable load of the bearing device is 500 kN, the above effect can be obtained by setting the gradient factor of the secondary gradient to the primary gradient in the range of 1.65 to 3.37. Furthermore, when the maximum allowable load of the bearing device is 1000 kN, the above effect can be obtained by setting the gradient magnification of the secondary gradient to the primary gradient in the range of 1.73-3.62. Furthermore, when the maximum allowable load of the bearing device is 3000 kN, the above effect can be obtained by setting the gradient factor of the secondary gradient to the primary gradient in the range of 1.43-3.72. Furthermore, when the maximum allowable load of the bearing device is 10,000 kN, the above effect can be obtained by setting the gradient factor of the secondary gradient to the primary gradient in the range of 1.74-2.83.
以下、本発明に係る支承装置について図面を参照して説明する。なお、以下、支承装置について、以下の順に沿って説明する。 Hereinafter, a support device according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Hereinafter, the support device will be described in the following order.
1.支承装置の説明
2.弾性体及び拘束体の説明
3.支承装置の動作説明
4.積層型弾性体の説明
5.補強板の変形例の説明
6.支承装置の変形例1
7.支承装置の変形例2
8.支承装置の変形例3
9.支承装置の変形例4
10.鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性の説明
10−1.最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置について
10−2.最大許容荷重が1000kNの支承装置について
10−3.最大許容荷重が3000kNの支承装置について
10−4.最大許容荷重が10000kNの支承装置について
11.その他の変形例
1. 1. Explanation of
7).
8).
9.
10. Explanation of characteristics of vertical load with respect to vertical displacement 10-1. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 500 kN 10-2. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 1000 kN 10-3. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 3000 kN 10-4. 10. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 10,000 kN Other variations
[1.支承装置の説明]
図1に示すように、支承装置10は、橋桁等の上部構造物1と橋脚や橋台といった下部構造物2との間に装着して水平荷重や鉛直荷重、回転荷重等の各種の荷重を支えると共に、地震や風、動的又は静的交通荷重等による揺動や振動、応力を吸収、分散しつつ、支承する橋梁用支承装置である。この支承装置10は、第一剛性体としての上沓11と第二剛性体としての下沓12との間に支承体となる弾性体13が介在されている。また、弾性体13は、上沓11又は下沓12(ここでは上沓11)に固定された拘束体16によって囲繞されている。
[1. Description of bearing device]
As shown in FIG. 1, a bearing
上沓11は、金属やセラミックス、或いは硬質樹脂やFRPの如くの強化樹脂等の剛性素材によって構成することが好ましいが、必ずしも剛性素材に限定されるものではなく、弾性素材や剛性素材と弾性素材との組合せによって構成される材料によっても構成することが出来る。各種素材から構成される上沓11は、平面形状が略多角形、略円形、略長円径、略楕円形等の適宜の形状に設定することが出来るが、方形又は円形とすることが製造上、或いは施工上、交換上有利である。なお、上沓11は、外表面を全体的に弾性体等の被覆層で覆って、耐候性、防錆効果を得るように構成しても良い。
The
上部構造物1に対する上沓11の固定手段は、例えばボルト、ナット等の締結手段を用いて上沓11を上部構造物に対して直接的に固定しても良いが、ここでは、上沓11よりも広面積の板状をなす上部プレート3を用いて上沓11を上部構造物1に対して間接的に固定している。上沓11の上部構造物1への固定方法は、これらの例に限定されるものではない。
As a means for fixing the
なお、可動支承装置として用いるとき等は、上沓11の上部、例えば上沓11と上部プレート3との間に摺滑部材4を配設して、上部構造物1と支承装置10とを相対変位可能に固定しても良い。この摺滑部材4としては、例えば、フッ化炭素樹脂の一種であるポリテトラフルオロエチレン(PTFE)の如くの低摩擦係数の表面を有するプレート等を、上沓11の上面に固定したり、又は上部構造物1や上部構造物1に固定される取付手段側の下面に固定することによって構成することが可能である。
When used as a movable support device, the sliding
下沓12は、上沓11同様、金属やセラミックス、或いは硬質樹脂やFRPの如くの強化樹脂等の剛性素材によって構成することが好ましいが、必ずしも剛性素材に限定されるものではなく、弾性素材や剛性素材と弾性素材との組合せによっても構成される材料によって構成することが出来る。各種素材から構成される下沓12は、平面形状が略多角形、略円形、略長円径、略楕円形等の適宜の形状に設定することが出来るが、方形又は円形とすることが製造上、又は施工上、交換上で有利である。下沓12の平面形状等は、必ずしも上沓11と一致させる必要はないが、各部のサイズと、凸部や凹部の形状や位置等は下沓12の設定と上沓11の設定を互いに整合させる必要がある。なお、下沓12は、外表面を全体的に弾性体等の被覆層で覆って、耐候性、防錆効果を得るように構成することも出来る。
The
下部構造物に対する下沓12の固定手段は、例えばボルト、ナット等の締結手段を用いて下沓12を下部構造物2に対して直接的に固定しても良いが、ここでは、下沓12よりも広面積の板状をなす下部プレート5の如くの下部固定手段を用いて下沓12を下部構造物2に対して間接的に固定している。下沓12の下部構造物2への固定方法は、これらの例に限定されるものではない。
As a fixing means of the
なお、可動支承装置として用いるとき等は、下沓12の下部、例えば下部プレート5と下沓12との間に摺滑部材6を配設して、下部構造物2と支承装置10とを相対変位可能に固定しても良い。この摺滑部材6としては、例えば、PTFEの如くの低摩擦係数の表面を有するプレート等を、下沓12の下面に固定したり、又は下部構造物2や下部構造物2に固定される取付手段側の上面に固定することが可能である。
When used as a movable bearing device, a sliding
尚、上沓11や下沓12の直接的又は間接的な固定は、着脱可能な方法とするのが好ましく、ボルト、ナット等による締結はその一例である。
The direct or indirect fixing of the
[2.弾性体及び拘束体の説明]
弾性体13は、天然ゴムや合成ゴム、熱可塑性エラストマや熱硬化性エラストマを用いることができ、これらの中でも天然ゴムを主成分として使用することが好ましい。具体的なエラストマ成分としては、例えば、天然ゴム(NR)、ポリイソプレンゴム(IR)、ポリブタジエンゴム(BR)、スチレン−ブタジエンゴム(SBR)、クロロプレンゴム(CR)、エチレン−プロピレンゴム、ブチルゴム(IIR)、ハロゲン化ブチルゴム(臭素化、塩素化等)、アクリルゴム、ポリウレタン、シリコーンゴム、フッ化ゴム、多硫化ゴム、ハイパロン、エチレン酢酸ビニルゴム、エピクロルヒドリンゴム、エチレン−メチルアクリレート共重合体、スチレン系エラストマ、ウレタン系エラストマ、ポリオレフィン系エラストマ、アクリロニトリル−ブタジエンゴム(NBR)、スチレン・イソプレン・スチレンブロック共重合体(SIS)、エポキシ化天然ゴム、trans−ポリイソプレン、ノルボルネン開環重合体(ポリノルボルネン)、スチレンブタジエンゴム(SBR)、ハイスチレン樹脂、イソプレンゴム等のゴムを一種単独、或いは二種以上を併用することが出来る。
[2. Explanation of elastic body and restraint body]
As the
図2に示す弾性体13aは、例えば、円柱状をなし、内部に鉄板といった剛性の補強板が設けられていない弾性層が一つ(単層)のものを示している。この弾性体13aの側面には、周回り方向に、凸部14と凹部15とが設けられている。凸部14と凹部15は、図2の例では、互いに平行に、周回り方向に連続して設けられている。
The
なお、凸部14と凹部15は、周回り方向に断続的に設けられていても良い。更に、凸部14と凹部15は、厚さ方向の間隔も、等間隔でも、等間隔でなくても良い。更に、図3に示すように、弾性体13としては、高さ(厚さ)方向に、凸部14や凹部15を設けたものであっても良い。更に、図4に示すように、弾性体13としては、側面に凸部14や凹部15を有しないものであってもよい。
The
以上のような弾性体13は、図1に示す例では、下沓12上に配設され、下沓12によって支持される。弾性体13は、上沓11と下沓12との間を接着して高支圧化しても良いが、接着しないことにより、良好な回転追従性を実現することも出来る。
In the example shown in FIG. 1, the
また、弾性体13は、図1に示すように、拘束体16によって囲繞されている。拘束体16は、弾性体13の外径よりやや大きい内径を有する円筒体であり、上沓11又は下沓12の何れか、図1では上沓11の外周部に固定されている。例えば、上沓11と拘束体16との結合は、ボルト・ナット等の固定手段16bを用いても良い。なお、固定手段16bとしては、上沓11と拘束体16の何れか一方に雄ねじを設け、他方に雌ねじを設け、これらを互いに螺合して結合するねじ締結によったり、溶接したり、従来公知の結合方法等で行うことも出来る。拘束体16の下沓12側の先端部は、下沓12の外周部の外側に位置し、固定されていない。これにより、上沓11は、鉛直荷重の入力があっとき、弾性体13を圧縮しながら鉛直下向きに移動することが出来る。すなわち、拘束体16の下沓12側の先端部が下沓12の外周部の外側に位置することで、上沓11と下沓12の間に配設される弾性体13の剪断変形を抑制する機能や、弾性体13を略密閉状態に拘束して高支圧化させるピストンの役割を実現する。かくして、下沓12に支持された弾性体13は、上面が上沓11、側面が拘束体16によって包囲され、略密閉された空間に配設されることになる。支承装置10は、略密閉ゴム支承となり、小さな支承面積にして高荷重を支承することが可能となる。
Moreover, the
ここで、弾性体13と拘束体16との大きさの関係について説明すると、図1の例では、支承装置10が上部構造物1と下部構造物2との間に設置され、支承装置10に対して上部構造物1の荷重によって弾性体13が変形している状態において、弾性体13の側面の凸部14が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aに当接した状態となっている。つまり、図5に示すように、上部構造物1と下部構造物2との間に設置される前は、弾性体13の側面の凸部14が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aとの間が非接触の状態で、隙間が設けられた状態となっており、上部構造物1と下部構造物2との間に設置されると、上部構造物1の死荷重によって、弾性体13の側面の凸部14が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aに当接した状態となる。なお、通常の使用範囲での荷重の際には、弾性体13の側面の凸部14が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aと非接触で、通常の使用範囲を超える高い荷重があった際に、弾性体13の側面の凸部14が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aと当接し、更なる高荷重の入力によって拘束面16aに凸部14、並びに、凹部15の膨出変形した部分が圧接されるようにしても良い。
Here, the size relationship between the
更に、図6に示すように、上部構造物1と下部構造物2との間に設置される前において、弾性体13の側面の凸部14が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aに当接した状態であっても良い。この場合、弾性体13を拘束体16内に配設する際、拘束体16内における弾性体13を正確に位置決めすることが出来る。
Further, as shown in FIG. 6, the
以上のように、本発明で用いる弾性体13は、弾性体13の側面に凸部14を設け、凸部14以外を凹部15とすることによって、弾性体13に鉛直荷重が加わった際に、鉛直下向きに変位するようにし、更に、拘束体16によって、弾性体13の変形量が制限される構成となっている。従って、このような作用を実現出来るのであれば、弾性体13の側面に設ける凸部14と凹部15を設ける位置や大きさは、上述の例に限定されるものではない。
As described above, when the
[3.支承装置の動作説明]
以上のような支承装置10では、上部構造物1と下部構造物2との間に設置されると、図1に示すように、弾性体13が、通常の使用範囲の荷重(例えば死荷重や死荷重+車両通行時の活荷重)によって、圧縮され、弾性体13の凸部14は、弾性体13を囲繞した拘束体16の拘束面16aに近接又は当接した位置となる。支承装置10は、弾性体13が鉛直荷重の大きさに応じた弾性変形をし、この弾性変形によって側面の凸部14が凹部15により構成された隙間を埋めるように変形しながら、拘束体16の拘束面16aに圧接される。すなわち、弾性体13の変位量は、拘束体16によって制限される。
[3. Explanation of operation of bearing device]
In the
このような支承装置10では、下沓12に支持された弾性体13を、上沓11と拘束体16によって囲繞し、弾性体13の側面と拘束面16aとの間に所定の隙間を有する略密閉された空間部を設けて構成することで、重入力の初期や低荷重の入力時には、鉛直荷重に対する鉛直可撓変位を可能としながら入力の高荷重化に伴って、徐々に鉛直変位量の増加量が小さくなって弾性率が高くなり、大きな荷重の入力に対しては密閉ゴム支承のように挙動して、小さな支承面積にして高荷重支持を実現する。また、低荷重から高荷重の入力に亘って鉛直面内における回転力の作用時には、弾性体13が拘束体16によって部分的に支持されながらも弾性体13と拘束体16との間の隙間により弾性体13が変形し、弾性体への極端な負荷なく、良好な回転追従性を実現出来る。
In such a
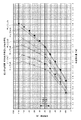
ここで、図7に、鉛直方向の変位量と鉛直荷重との関係を示す。
線A・・・密閉ゴム支承ではなく、荷重が加わった際の変位が拘束されていないゴム支承。
線B・・・拘束体16の内径(ポット部の内径)に対して弾性体13の外形を小さくし、凸部14と凹部15を大きく形成して、拘束面16aと弾性体13の側面との間の隙間を大きくしたときの特性を示す。(隙間大)
線C・・・拘束面16aと弾性体13の側面との間の隙間を線Bの場合より小さくしたときの特性を示す。(隙間中)
線D・・・拘束面16aと弾性体13の側面との間の隙間を最も小さくしたときの特性を示す。(隙間小)
線E・・・拘束面16aと弾性体13の側面との間の隙間を設けない密閉ゴム支承。回転追従性能を有するが、鉛直方向の弾性変位はほとんど無く、金属支承の扱いとなる。
Here, FIG. 7 shows the relationship between the amount of displacement in the vertical direction and the vertical load.
Line A: Not a sealed rubber bearing, but a rubber bearing whose displacement when a load is applied is not constrained.
Line B: The outer shape of the
Line C: Characteristic when the gap between the restraining
Line D: shows characteristics when the gap between the restraining
Line E: A sealed rubber bearing that does not provide a gap between the restraining
図7の線Aで示すゴム支承では、鉛直荷重が大きくなるに連れて鉛直変位量もほぼ比例的に大きくなり、グラフの傾き(拘束度又はバネ定数)はほぼ一定である。弾性体13の側面に凸部14と凹部15を設けた線B−Dの例によれば、鉛直荷重が大きくなるに連れて鉛直変位量も大きくなるが、その特性は非線形となる。すなわち、鉛直変位に対する鉛直荷重反力の大きさを表すグラフの傾き(拘束度又はバネ定数)は、鉛直変位が大きくなるほど大きくなる。このように、弾性体13の側面に凸部14と凹部15を設けたときには、大きな荷重が入力されたときほど、より高度な密閉状態に変化して鉛直変位量の増加量が小さくなるような特性で、すなわち拘束度を可変として、上部構造物1を支承することが出来る。すなわち、この支承装置10では、適度な鉛直可撓性を有しながら高荷重を支持することが出来る。また、線B−Dの例を見ると、隙間が小さい程、鉛直変位に対する鉛直荷重反力の大きさを表すグラフの傾きの緩やかな範囲(一次勾配)を狭く設定することが出来る。すなわち、鉛直変位が小さくなる。更に、線Eの密閉ゴム支承では、鉛直方向の弾性変位はほとんど見られない。
In the rubber bearing shown by line A in FIG. 7, as the vertical load increases, the amount of vertical displacement increases substantially proportionally, and the slope (constraint or spring constant) of the graph is substantially constant. According to the example of the line BD in which the
特に、弾性体13の側面に凸部14と凹部15を設けた線B−Dの例によれば、高荷重が加わると、鉛直可撓変位が小さくなり、密閉ゴム支承のように挙動する。したがって、線B−Dの例では、支承する上部構造物1の種類、用途等に応じて、線B−Dの使用範囲を設定していくことになる。例えば、死荷重に活荷重が加わったとき、グラフの急勾配の範囲(二次勾配)の領域に含まれるようにすることで、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来るようになる。なお、鉛直撓みがあるため、線B−Dの支承装置は、弾性支承装置に属する扱いとし得る。
In particular, according to the example of the line BD in which the
[4.積層型弾性体の説明]
以上の例では、弾性層が単層の弾性体13を用いた支承装置10を説明したが、弾性体13としては、図8に示すように、弾性層と補強板とが積層された積層構造の弾性体17であっても良い。弾性体17は、内部に補強板17aが設けられ、弾性層17bが複数設けられ、補強板17aと弾性層17bとが加硫接着によって相互に接着されている。単層の弾性体13は、荷重が加わると、自由側面が側方に押し出され、特に厚さ方向の中央部を中心として膨出する。積層型の弾性体17では、補強板17aがあることで、弾性体17の自由側面の膨出が抑制され、耐荷力が増大する。但し、補強板17aの間の弾性層17bの側面も、自由側面であるから荷重の大きさに応じて、側方に僅かに膨出する。しかし、支承装置10では、拘束体16が弾性体17の変形を拘束するので膨出量は僅かとなる。
[4. Explanation of laminated elastic body]
In the above example, the supporting
つまり、図8に示すように、積層型の弾性体17では、側面において、自由側面の弾性層17bの位置に凸部18を設け、補強板17aの位置に凹部19を設けるようにしている。この場合、凸部18は、荷重が加わった際、弾性層17bの自由側面が膨出することで、凹部19より先に拘束体16の拘束面16aに強く圧接されることになる。勿論、本発明では、図9に示すように、補強板17aの位置を凸部18とし、弾性層17bの位置を凹部19としても良い。この場合、凹部19となっている弾性層17bの自由側面が僅かに膨出することで、凸部18と凹部19の部分が同じように拘束体16の拘束面16aと当接され均等に圧接されるようにすることが出来る。積層型の弾性体17は、従来最も膨出量が多い補強板間位置の弾性部であるが、この部位に凸部18を設けた上、拘束体16の拘束面16aによってこの凸部18周辺の膨出量が拘束されているので、高荷重が入力されている際でも内部の補強板17aの周囲における弾性層17bに対する局部応力が緩和される。また、内部の補強板17aが高荷重によってもつぶれにくくなり、補強板17aを薄くすることが出来、支承装置10の全体の厚さの薄型化を実現出来る。
That is, as shown in FIG. 8, in the laminated
積層型弾性体17と拘束体16との大きさの関係については、弾性体13の場合と同様で、図5や図6を用いて説明したように、設置前において、弾性体17の側面の凸部18が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aとの間が非接触の状態であっても良いが、接触した状態としても良く、この場合、組立時に、弾性体17の側面の凸部18が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aと接触するようになり、位置決め性が向上するので好ましい。しかしながら入力が無い時点での弾性体と拘束体との接触の有無は特に限定されるものではなく、例えば、大きな荷重が入力されたときに、弾性体17の側面の凸部18が拘束体16の内周面の拘束面16aと接触するようにしても良い。
The size relationship between the laminated
なお、図8及び図9の例では、上沓11と拘束体16とを一体に構成している。また、積層型の弾性体17は、鉛直荷重支持性能や水平荷重支持性能、並びに鉛直回転性能は、弾性層の面積や厚さ、材質、数、補強板の面積や厚さ、数等によって調節することが出来る。また。拘束体16は、上沓11の下面の外周側に固定されている。例えば、上沓11と拘束体16との結合は、ボルト・ナット等の固定手段16bを用いても良い。また、固定手段16bとしては、上沓11と拘束体16の何れか一方に雄ねじを設け、他方に雌ねじを設け、これらを互いに螺合して結合するねじ締結によったり、溶接したり、従来公知の結合方法等で行うことも出来る。
In the example of FIGS. 8 and 9, the
[5.補強板の変形例の説明]
積層型の弾性体17に用いる補強板17aは、具体的に、図10に示すように構成することが出来る。図10(A)に示す例では、上沓11の弾性体17が配設される側の面の中央部に、突出部21aを設け、突出部21aの周囲に環状の凹部21bを設けている。また、下沓12の弾性体17が配設される側の面の中央部に、突出部22aを設け、突出部22aの周囲に凹部21bを設けている。したがって、上沓11と下沓12との間に配設される弾性体17は、中央部が薄肉部で、周囲が環状に厚肉部となっている。この弾性体17の内部には、厚肉部となる外周領域に、環状の補強板17aが設けられる。この弾性体17において、側面には、補強板17aの位置に凹部19が設けられ、弾性層17bの位置に凸部18が連続して又は断続的に設けられている。勿論、補強板17aの位置に凸部18を設け、弾性層17bの位置に凹部19を設けるようにしても良い。また、弾性体17の中央部には、拘束度調節のため、空隙部23aを設けるようにしても良い。このような弾性体17は、中央部が薄肉部で、周囲が環状の厚肉部となっているので、回転追従性を向上させることが出来る。
[5. Description of modification of reinforcing plate]
Specifically, the reinforcing
図10(B)は、図10(A)の変形例で、下沓12の弾性体17が配設される側の面が平坦に形成され、上沓11側のみに、突出部21aと凹部21bとが設けられている。この弾性体17では、下沓12の弾性体17が配設される側の面が平坦に形成されているので、下沓12や弾性体17の形状を簡素化することが出来、加工コストを削減出来る。この例でも、弾性体17の中央部に、空隙部23aを設けるようにしても良い。また、弾性体17の側面には、補強板17aの位置に凹部19が設けられ、弾性層17bの位置に凸部18が連続して又は断続的に設けられている。勿論、補強板17aの位置に凸部18を設け、弾性層17bの位置に凹部19を設けるようにしても良い。
FIG. 10 (B) is a modification of FIG. 10 (A), in which the surface on the side where the
図10(C)は、弾性体17に同心に、環状の複数の補強板17aが同心円状に設けられている。この例では、上沓11と下沓12の相対する面、すなわち弾性体17が配設される面は平坦に形成されている。この例では、上沓11と下沓12の弾性体17が配設される面に突出部21a,22aや凹部21b,22b(図10(A),(B)参照)が設けられていないので、構成が簡素化され、加工コストを削減することが出来る。なお、複数の環状の補強板17aは、内周側に一つでも良く、また、外周側に一つでも良く、その数も特に限定されるものではない。また、図10(C)では、同じ高さに同心に環状の補強板17aを複数設けているが、各補強板17aの設けられる高さは、必ずしも同じで無くて良い。この例においても更に、弾性体17の中央部には、空隙部23aを設けるようにしても良い。更に、弾性体17の側面には、補強板17aの位置に凸部18が設けられ、弾性層17bの位置に凹部19が連続して又は断続的に設けられている。勿論、補強板17aの位置に凹部19を設け、弾性層17bの位置に凸部18を設けるようにしても良い。
In FIG. 10C, a plurality of annular reinforcing
図10(D)は、複数の補強板17aが互いに離間して平行に設けられている。この例において、補強板17aの枚数は一枚でも複数枚でも良い。この例では、側面に、補強板17aの位置に凸部18が設けられ、弾性層17bの位置に凹部19が連続して又は断続的に設けられている。勿論、補強板17aの位置に凹部19を設け、弾性層17bの位置に凸部18を設けるようにしても良い。
In FIG. 10D, a plurality of reinforcing
図10(E)は、補強板17aの表裏に、複数の環状突出部17cが同心円状に設けられている。この例において、補強板17aの枚数は一枚でも複数枚でも良い。また、環状突出部17cの数は、特に限定されるものではなく、例えば一つであっても良い。また、環状突出部17cは、連続した突条部ではなく、断続的なものであっても良い。この例では、弾性体17の側面の補強板17aの位置に凸部18が設けられ、弾性層17bの位置に凹部19が連続して又は断続的に設けられている。勿論、補強板17aの位置に凹部19を設け、弾性層17bの位置に凸部18を設けるようにしても良い。また、環状突出部17cは、表裏の何れか一方の面のみに設けても良く、また、補強板17aは複数枚設けるようにしても良い。
In FIG. 10E, a plurality of
[6.支承装置の変形例1]
図11に示す支承装置30は、下沓12に、芯材31が取り付けられ、上揚防止部と水平変位防止部とを設けたものである。また、この支承装置30は、第一剛性体としての上沓11と第二剛性体としての下沓12との間に弾性層と補強板とが積層された積層構造の弾性体17が介在されている。支承装置30の上沓11は、表裏面に貫通した貫通孔32が穿設されている。貫通孔32には、上沓11の上面側から芯材31が挿入され、芯材31の先端部が上沓11の上面から突出することなく、上沓11が鉛直下向きに変位する分を考慮して、先端部が一段低くなるように収容されている。この貫通孔32の開口端には、上揚防止片32aがフランジ状に形成されている。
[6.
A
貫通孔32に挿通される芯材31は、大径部33となる頭部を有する金属性のボルト状部材からなり、先端部である大径部33が上沓11の貫通孔32の内部に収容可能な大きさに設定されている。この芯材31は、上沓11の貫通孔32より弾性体17の略中央部に形成された挿通孔34に挿通され、更に、下沓12の弾性体17の支持面側に形成されたネジ穴35に螺合されることによって固定される。芯材31は、貫通孔32より挿入され、ネジ穴35に固定されたとき、大径部33が貫通孔32内に一段低くなるように収容される。この芯材31は、下沓12に固定されることで、上沓11と下沓12とが水平方向に相対変位しようとした際に、芯材31が上揚防止片32aの先端面又は貫通孔32の側面に突き当たり、下沓12に固定された芯材31によって上沓11の変位が規制される。すなわち、芯材31は、水平変位防止部として機能して、過剰に上沓11と下沓12とが水平方向において相対変位することを防止する。更に、芯材31の大径部33は、貫通孔32の上揚防止片32aの開口径より大きく、上揚防止片32aと係合する。芯材31は、上沓11に上揚力、すなわち上沓11が下沓12に対して相対的に上揚しようとする力が加わったとき、下沓12に固定された芯材31の大径部33に上揚防止片32aが係止されることによって、上沓11と下沓12とが乖離することを防止することが出来る。すなわち、大径部33は、上揚防止部としても機能することになる。
The
また、弾性体17は、図11に示すように、拘束体16によって囲繞されている。拘束体16は、弾性体13の平均外径よりやや大きい内径を有する円筒体であり、上沓11の外周部に固定されている。例えば、上沓11と拘束体16との結合は、ボルト・ナット等の固定手段16bを用いても良い。なお、固定手段16bとしては、上沓11と拘束体16の何れか一方に雄ねじを設け、他方に雌ねじを設け、これらを互いに螺合して結合するねじ締結によったり、溶接したり、従来公知の結合方法等で行うことが出来る。
Moreover, the
拘束体16の下沓12側の先端部は、下沓12の外周部の外側に位置し、固定されていない。これにより、上沓11は、鉛直荷重の入力があっとき、弾性体13を圧縮しながら鉛直下向きに変位することが出来る。すなわち、拘束体16の下沓12側の先端部が下沓12の外周部の外側に位置することで、芯材31と協働して、上沓11と下沓12の間に配設される弾性体17の剪断変形を抑制する機能や、弾性体17を略密閉状態に拘束して高支圧化させるシリンダの役割を果たす。かくして、下沓12に支持された弾性体17は、上面が上沓11、側面が拘束体16によって包囲され、略密閉された空間に配設されることになる。すなわち、支承装置10は、略密閉ゴム支承となり、小さな支承面積にして高荷重を支承することが可能となる。
The tip of the restraining
このような支承装置30にあっても、上述した支承装置10と同様に、下沓12に支持された弾性体17を、上沓11と拘束体16によって囲繞することで、略密閉された空間部を構成して、略密閉ゴム支承のようにして小さな支承面積にして高荷重支承を実現しながら、弾性体17の側面と拘束面16aとの間に隙間を設けることで、鉛直荷重に対する鉛直可撓変位を実現することが出来る。また、回転作用の際には、隙間により弾性体17が変形し良好な回転追従性を実現出来る。そして、上記図7で示したように、拘束面16aと弾性体17の側面との間に隙間を設けることで、大きな荷重が入力されたときほど、より高度な密閉状態に変化して鉛直変位量の増加量を小さくすることが出来る。
Even in such a
なお、この支承装置30において、支承体となる弾性体17は、弾性層が単層の弾性体13であっても良い(図2−4参照)。また、上下を逆にして、上沓11を下沓とし、下沓12を上沓として用いても良い。更に、上部構造物1と下部構造物2に設置するにあたっては、上述したように、上部プレート3や下部プレート5を介在させて固定しても良いし、更に、摺滑部材4,6を介在させて固定しても良い(図1参照。)。また、図12に示すように、支承装置30は、拘束体16を上沓11ではなく、下沓12の外周部に固定手段16bによって固定するようにしても良い。この場合、拘束体16の先端部は、上沓11の外周部の外側に位置し固定されていない。これにより、上沓11は、鉛直荷重の入力があっとき、弾性体13を圧縮しながら鉛直下向きに変位することが出来る。
In the
[7.支承装置の変形例2]
図13に示す支承装置40は、芯材41が上沓11と下沓12とを非貫通としたものである。この支承装置40は、下沓12に、芯材41が取り付けられ、上揚防止部と水平変位防止部とを設けたものである。また、この支承装置40は、第一剛性体としての上沓11と第二剛性体としての下沓12との間に弾性層と補強板とが積層された積層構造の弾性体17が介在されている。
[7.
In the
上沓11は、弾性体17の上面に配設されるものであって、外周部に、拘束体16が固定される。例えば、上沓11と拘束体16との結合は、ボルト・ナット等の固定手段16bを用いて良い。また、固定手段16bとしては、上沓11と拘束体16の何れか一方に雄ねじを設け、他方に雌ねじを設け、これらを互いに螺合して結合するねじ締結によったり、溶接したり、従来公知の結合方法等で行うことが出来る。拘束体16の下沓12側の先端部は、フランジ状の上揚防止片42が内側に張り出して形成されている。
The
芯材41は、大径部43となる頭部を有する金属製のボルト状部材からなり、先端部が下沓12の弾性体17の支持面側に形成されたネジ穴44に螺合されることによって固定される。この芯材41は、上端部が大径部43となっており、弾性体17を支持する支持面となっている。また、この大径部43は、上沓11の外周部に固定された拘束体16の上揚防止片42に係合する。下沓12に固定された芯材41の大径部43は、上揚防止部ともなって、上沓11に上揚力が加わったとき、上沓11側の上揚防止片42が係止されることで、上沓11と下沓12とが乖離することを防止する。また、この芯材41の大径部43は、拘束体16の拘束面16aを摺動するような大きさに形成され、弾性体17を略密閉状態に拘束して高支圧化させるピストンのように機能して、鉛直方向の変位を許容し、また、水平変位防止部となって、芯材41で水平方向の変位を制限する。これにより、過剰に上沓11と下沓12とが水平方向において相対変位することを防止することが出来る。更に、上揚防止片42と下沓12との間は、間隙が設けられており、鉛直下向き上沓11が変位した際に、上揚防止片42が下沓12に突き当たらないようにしている。
The
このような支承装置40にあっても、上述した支承装置10,30と同様に、下沓12に支持された弾性体17を、上沓11と拘束体16によって囲繞することで、略密閉された空間部を構成して、略密閉ゴム支承のようにして小さな支承面積にして高荷重支持を実現しながら、弾性体17の側面と拘束面16aとの間に隙間を設けることで、鉛直荷重に応じた鉛直可撓変位を可能とすることが出来る。また、回転作用の際には、隙間により弾性体17がより一層変形し易くなり、良好な回転追従性を実現出来る。そして、上記図7で示したように、拘束面16aと弾性体17の側面との間に隙間を設けることで、大きな入力があったときほど、より高度な密閉状態に変化して高支圧化させ鉛直変位量の増加量を小さくすることが出来る。
Even in such a
なお、この支承装置40において、支承体となる弾性体17は、弾性層が単層の弾性体13であっても良い(図2−4参照)。また、上下を逆にして、上沓11を下沓とし、下沓12を上沓として用いても良い。更に、上部構造物1と下部構造物2に設置するにあたっては、上述したように、上部プレート3や下部プレート5を介在させて固定しても良いし、更に、摺滑部材4,6を介在させて固定しても良い(図1参照)。
In the
[8.支承装置の変形例3]
図14に示す支承装置50は、図13の支承装置40を更に変形したものである。この支承装置50は、下沓12に、芯材51が取り付けられ、上揚防止部と水平変位防止部とを設けたものである。この支承装置50は、第一剛性体としての上沓11と第二剛性体としての下沓12との間に弾性層17bと補強板17aとが積層された積層構造の弾性体17が介在されている。
[8.
A
上沓11は、弾性体17の上面に配設されるものであって、外周部に、拘束体16が固定される。例えば、上沓11と拘束体16との結合は、ボルト・ナット等の固定手段16bを用いることが出来る。また、固定手段16bとしては、上沓11と拘束体16の何れか一方に雄ねじを設け、他方に雌ねじを設け、これらを互いに螺合して結合するねじ締結によったり、溶接したり、従来公知の結合方法等で行うことが出来る。拘束体16の下沓12側の先端部は、フランジ状の上揚防止片52が内側に張り出して形成されている。
The
芯材51は、ベースプレートとなる下沓12に下端部が固定される。芯材51の下端面は、位置決め凸部51aが設けられ、位置決め凸部51aが下沓12側の位置決め凹部51bに嵌合されることで、位置決めされる。また、下沓12には、挿通孔55aが形成され、固定ボルト55bが芯材51の下端部に設けられた固定孔55cに締め付けられることで固定される。芯材51の上端部には、弾性体17を支持する支持面となる大径部53が一体的に設けられる。大径部53は、裏面中央部にネジ穴53aが設けられており、ネジ穴53aに、芯材51の先端部に形成されたネジ部54が締め付けられることで一体化される。なお、固定ボルト55bのボルト頭部は、下沓12の挿通孔55aと連通した凹部55dに突出することなく収容されている。
The lower end portion of the
芯材51と一体の大径部53は、外周部下面が上沓11の外周部に固定された拘束体16の上揚防止片52と係合する。下沓12との一体の芯材51の大径部53は、上揚防止部ともなって、上沓11に上揚力が加わったとき、上沓11側の上揚防止片52が係止されることで、上沓11と下沓12とが乖離することを防止する。また、この芯材51の大径部53は、拘束体16の拘束面16aを摺動するような大きさに形成され、弾性体17を略密閉状態に拘束して高支圧化させるピストンのように機能して、鉛直方向の変位を許容し、また、水平変位防止部となって、芯材51で水平方向の変位を規制する。これにより、過剰に上沓11と下沓12とが水平方向において相対変位することを防止することが出来る。更に、上揚防止片52と下沓12との間は、間隙が設けられており、鉛直下向きに上沓11が変位した際に、上揚防止片52が下沓12に突き当たらないようにしている。
The large-
このような支承装置50にあっても、上述した支承装置10,30,40と同様に、下沓12に支持された弾性体17を、上沓11と拘束体16によって囲繞することで、略密閉された空間部を構成して、密閉ゴム支承のようにして小さな支承面積にして高荷重支承を実現しながら、弾性体17の側面と拘束面16aとの間に隙間を設けることで、鉛直荷重に対する鉛直可撓変位を実現することが出来る。また、回転作用の際には、隙間により弾性体17がより一層変形し易くなり、良好な回転追従性を実現出来る。そして、上記図7で示したように、拘束面16aと弾性体17の側面との間に隙間を設けることで、大きな荷重があったときほど、より高度な密閉状態に変化して鉛直変位量の増加量を小さくすることが出来る。
Even in such a
なお、この支承装置50において、支承体となる弾性体17は、弾性層が単層の弾性体13であっても良い(図2−4参照)。また、上下を逆にして、上沓11を下沓とし、下沓12を上沓として用いても良い。更に、上部構造物1と下部構造物2に設置するにあたっては、上述したように、上部プレート3や下部プレート5を介在させて固定しても良いし、更に、摺滑部材4,6を介在させて固定しても良い(図1参照)。
In the
[9.支承装置の変形例4]
以上の例では、弾性体13,17の側面に凸部14,18と凹部15,19を設けた場合を説明したが、図15に示すように、弾性体13,17の側面には、凸部14,18と凹部15,19を設けず、代わりに、拘束体16の拘束面16aに凸部61又は凹部62を設けるようにしても良い。なお、支承装置の構造は、図13に示した支承装置40と同一であるため詳細は省略する。なお、ここでは、一例として、積層型弾性体17を用いるようにしている。図15では、拘束体16の下沓12側の先端部には、フランジ状の上揚防止片52が内側に張り出すように、ボルト・ナット等の固定手段16cによって固定されている。
[9.
In the above example, the case where the
図15に示す拘束体16の拘束面16aには、自由側面の弾性層17bの位置に凸部61を設け、補強板17aの位置に凹部62を設けるようにしている。この場合、凸部61は、荷重が加わった際、弾性層17bの自由側面が膨出することで、凹部62より先に、補強板17a,17a間の側方に膨出した側面が圧接されることになる。勿論、本発明では、図16に示すように、補強板17aの位置を凸部61とし、弾性層17bの位置を凹部62としても良い。この場合、凹部62となっている弾性層17bの自由側面が僅かに膨出することで、凸部61と凹部62の部分が同じように拘束体16の拘束面16aに圧接されるようにすることが出来る。このように、拘束体16の拘束面16aに凸部61と凹部62を設けた場合にも、弾性体13,17の側面に凸部14,18と凹部15,19を設けた場合と類似した作用効果を得ることが出来る。しかし、拘束体16の内周面側に凸部や凹部を設けて弾性体13,17との間に隙間を設けるようにすると、荷重が入力された際に、鉛直変位を生じ、これによって弾性体13,17内部に配設された各補強板17aの位置が鉛直下方に変位し、補強板17aと凸部61との位置関係が設定位置からズレてしまい所要の性能を発揮できなくなる虞がある上、拘束体16の剛性内周面を加工するのは、弾性体13,17の自由側面(弾性周面)を加工するよりも高コスト化する。このため、凸部や凹部は弾性体13,17側に設ける方が好ましい。
The constraining
[10.鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性の説明]
図7に示す鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性について更に詳細に説明する。ここでは、最大許容荷重毎に、弾性体13の側面と拘束体16の拘束面16aとの間の隙間の容積を異ならせて、上沓11又は下沓12の何れかと拘束体16とによって構成された弾性体13を収納するポット部16dに対する隙間容積を異ならせた支承装置10を作製し、作製した支承装置10について、鉛直荷重を付加して鉛直撓み量を測定した(図5参照)。なお、ここでは、図4に示すような側面に凸部14や凹部15を有しない弾性体13を用いた。
[10. Explanation of vertical load characteristics with respect to vertical displacement]
The characteristics of the vertical load with respect to the vertical displacement amount shown in FIG. 7 will be described in more detail. Here, for each maximum permissible load, the volume of the gap between the side surface of the
そして、各最大許容荷重の支承装置において、下記表1に示すように、弾性体13の側面と拘束体16の拘束面16aとの間の隙間容積を異ならせた最大許容荷重の異なる支承装置10を作製し、作製した支承装置10について、鉛直荷重を付加して鉛直撓み量を測定した。
In each maximum allowable load bearing device, as shown in Table 1 below, the bearing
ここで、表1中の弾性体13の体積とは、例えば、図5に示すように、支承装置10が上部構造物1と下部構造物2との間に設置される前の弾性体13の外径d1及び高さh1より算出した弾性体13の体積を示している。更に、隙間の容積とは、弾性体13の体積と、拘束体16の拘束面16aの内径d2及び高さh2より算出した拘束体16の拘束面16a内(ポット部16d)の容積との差を示している。
Here, the volume of the
ここで、図17は、最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置における鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性を示し、図18は、最大許容荷重が1000kNの支承装置における鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性を示し、図19は、最大許容荷重が3000kNの支承装置における鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性を示し、図20は、最大許容荷重が10000kNの支承装置における鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性を示している。 Here, FIG. 17 shows the characteristic of the vertical load with respect to the vertical displacement amount in the bearing device with the maximum allowable load of 500 kN, and FIG. 18 shows the characteristic of the vertical load with respect to the vertical displacement amount in the bearing device with the maximum allowable load of 1000 kN. FIG. 19 shows the characteristic of the vertical load with respect to the vertical displacement amount in the bearing device having the maximum allowable load of 3000 kN, and FIG. 20 shows the characteristic of the vertical load with respect to the vertical displacement amount in the bearing device having the maximum allowable load of 10,000 kN. .
図17では、最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置においては、鉛直荷重が250kNより小さいときを、低荷重域と定義し、250kNより大きいときを高荷重域と定義している。また、図18では、最大許容荷重が1000kNの支承装置においては、鉛直荷重が500kNより小さいときを、低荷重域と定義し、500kNより大きいときを高荷重域と定義している。更に、図19では、最大許容荷重が3000kNの支承装置においては、鉛直荷重が1500kNより小さいときを、低荷重域と定義し、1500kNより大きいときを高荷重域と定義している。更に、図20では、最大許容荷重が10000kNの支承装置においては、鉛直荷重が5000kNより小さいときを、低荷重域と定義し、5000kNより大きいときを高荷重域と定義している。そして、図17−図20の各図のサンプルについて、低荷重域の近似直線と高荷重域の近似直線を最小二乗法を用いて作成し、各サンプルの低荷重域での一次勾配(傾き)と高荷重域での二次勾配(傾き)を算出した。 In FIG. 17, in a bearing device having a maximum allowable load of 500 kN, a case where the vertical load is smaller than 250 kN is defined as a low load region, and a case where the vertical load is larger than 250 kN is defined as a high load region. In FIG. 18, in a bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 1000 kN, a case where the vertical load is smaller than 500 kN is defined as a low load region, and a case where the vertical load is larger than 500 kN is defined as a high load region. Further, in FIG. 19, in the bearing device having a maximum allowable load of 3000 kN, a case where the vertical load is smaller than 1500 kN is defined as a low load region, and a case where the vertical load is larger than 1500 kN is defined as a high load region. Further, in FIG. 20, in the bearing device having the maximum allowable load of 10,000 kN, a case where the vertical load is smaller than 5000 kN is defined as a low load region, and a case where the vertical load is larger than 5000 kN is defined as a high load region. Then, for the samples shown in FIGS. 17 to 20, an approximate straight line in the low load region and an approximate straight line in the high load region are created using the least square method, and the primary gradient (slope) in the low load region of each sample is created. The secondary gradient (slope) in the high load range was calculated.
上述したように、本発明の支承装置では、弾性体13の外周面と拘束体16の拘束面16aとの間に隙間を設定することによって、荷重入力の初期や低荷重の入力時、鉛直荷重に対する鉛直可撓変位を可能としながら入力の高荷重化に伴って、徐々に鉛直変位量の増加量が小さくなって弾性率が高くなり、大きな荷重の入力に対しては密閉ゴム支承のように挙動して、小さな支承面積にして高荷重支持を実現するようにし、また、低荷重から高荷重の入力に亘って鉛直面内における回転力の作用時、弾性体13が拘束体16によって部分的に支持されながらも弾性体13と拘束体16との間の隙間により弾性体13が変形し、弾性体への極端な負荷なく、良好な回転追従性を実現するようにしている。すなわち、この支承装置では、一次勾配の低荷重の載荷では鉛直撓みがあるため弾性支承装置に属する扱いとすることができ、更に、弾性体13が急勾配の範囲(二次勾配)の領域において撓み量を所定量以内に抑えることで、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。
As described above, in the support device of the present invention, by setting a gap between the outer peripheral surface of the
本発明の支承装置では、このような作用効果を実現するため、低荷重域での一次勾配(傾き)に対する高荷重域での二次勾配(傾き)の勾配倍率が1.43−3.72の範囲となるようにしている。道路橋支承便覧(平成16年4月:社団法人日本道路協会)には、段差の照査上、圧縮変位量(段差)の許容値が1mm以内とされている。即ち、支承装置が上部構造物1と下部構造物2との間に設置され、死荷重を支持している状態から活荷重による撓み量を1mm以内に抑える必要がある。本発明では、低荷重域での一次勾配(傾き)に対する高荷重域での二次勾配(傾き)の勾配倍率を1.43−3.72の範囲とすることで、死荷重を支持している状態から活荷重による撓み量を1mm以内に抑え、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減するようにしている。
In the bearing device of the present invention, in order to realize such an effect, the gradient magnification of the secondary gradient (inclination) in the high load region with respect to the primary gradient (inclination) in the low load region is 1.43-3.72. To be in the range. In the road bridge support manual (April 2004: Japan Road Association), the allowable value of the amount of compressive displacement (step) is set to 1 mm or less for checking the step. That is, it is necessary to suppress the deflection amount due to the live load within 1 mm from the state in which the support device is installed between the
[10−1.最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置について]
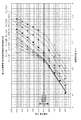
図17は、最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置10における鉛直荷重と鉛直撓み量の関係を示している。縦軸は、鉛直荷重[kN]を示し、横軸は、鉛直撓み量[mm]を示している。図17によれば、サンプル1−5の何れも、低荷重域、高荷重域の両方で、鉛直荷重が大きくなるに連れて鉛直変位量も大きくなり、低荷重域の一次勾配より高荷重域の二次勾配の方が勾配が急なものになっている。一般に、最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置10においては、死荷重が300−350kNに設定され、活荷重が200−150kNに設定される。サンプル1−5では、低荷重域での一次勾配(傾き)に対する高荷重域での二次勾配(傾き)の勾配倍率(二次勾配/一次勾配)が1.65−3.37の範囲となっているので、活荷重域における鉛直変位量が1mm以内となり、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。例えば、最も勾配の緩やかなサンプル5を例に見ても、鉛直荷重(死荷重)が約300kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約1.04mmであり、約500kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約1.34mmであり、撓み量の差が約0.3mmである。したがって、活荷重域における鉛直変位量を1mm以内に抑えることを実現することが出来る。
[10-1. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 500kN]
FIG. 17 shows the relationship between the vertical load and the amount of vertical deflection in the
なお、上記道路橋支承便覧によれば、支承装置10について、回転撓みの照査上、1/150rad程度撓むことが出来ることが望ましいとされている。回転撓みの照査上において撓み量が足りないと、金属支承の扱いとなってしまい問題が生じる。即ち、最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置10においては、撓み量δ=有効直径÷2÷150の式より、撓み量が0.53mm以上有ることが必要である。サンプル1−5の何れも、死荷重(例えば死荷重が300−350kN)が加わった際、撓み量が0.53mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来る。なお、ここで言う有効直径は、弾性体13の外周端部(面圧を受けない部分)を考慮して、設定直径より若干(直径で10mm以下程度)小さめの寸法としている。
In addition, according to the above-mentioned road bridge support manual, it is desirable that the
以上のように、最大許容荷重が500kNの支承装置10(サンプル1−5)では、勾配倍率を1.43−3.72の範囲、好ましくは1.65−3.37の範囲にすることで、荷重が載荷された際の変位量を1mm以内の段差に抑えることが出来、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。また、サンプル1−5の何れも、少なくとも死荷重(例えば300−350kN)が加わった際に、撓み量を0.53mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来、金属支承装置の扱いではなく、弾性支承装置に属する扱いに出来る。 As described above, in the bearing device 10 (sample 1-5) having a maximum allowable load of 500 kN, the gradient magnification is set to a range of 1.43-3.72, preferably 1.65 to 3.37. The amount of displacement when a load is loaded can be suppressed to a level difference of 1 mm or less, and vibration and noise when passing through the vehicle can be reduced. In addition, in any of the samples 1-5, when at least a dead load (for example, 300-350 kN) is applied, the deflection amount can be 0.53 mm or more, and the conditions for the above-mentioned road bridge support manual can be satisfied. It can be handled as belonging to an elastic bearing device, not a metal bearing device.
[10−2.最大許容荷重が1000kNの支承装置について]
図18は、最大許容荷重が1000kNの支承装置10における鉛直荷重と鉛直撓み量の関係を示している。縦軸は、鉛直荷重[kN]を示し、横軸は、鉛直撓み量[mm]を示している。図18によれば、サンプル6−11の何れも、低荷重域、高荷重域の両方で、鉛直荷重が大きくなるに連れて鉛直変位量も大きくなり、低荷重域の一次勾配より高荷重域の二次勾配の方が勾配が急なものになっている。一般に、最大許容荷重が1000kNの支承装置10においては、死荷重が600−700kNに設定され、活荷重が400−300kNに設定される。サンプル6−11では、低荷重域での一次勾配(傾き)に対する高荷重域での二次勾配(傾き)の勾配倍率(二次勾配/一次勾配)が1.73−3.62の範囲となっているので、活荷重域における鉛直変位量が1mm以内となり、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。例えば、最も勾配の緩やかなサンプル11を例に見ても、鉛直荷重が約600kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約1.28mmであり、約1000kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約1.62mmであり、撓み量の差が約0.34mmである。したがって、活荷重域における鉛直変位量を1mm以内に抑えることを実現することが出来る。
[10-2. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 1000kN]
FIG. 18 shows the relationship between the vertical load and the vertical deflection amount in the
なお、上記道路橋支承便覧によれば、上述のように、金属支承の扱いとならないように、回転撓みの照査上、1/150rad程度撓むことが必要であり、撓み量が0.75mm以上有ることが必要である。サンプル6−11の何れも、死荷重(例えば死荷重が600−700kN)が加わった際、撓み量が0.75mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来る。 In addition, according to the above-mentioned road bridge support manual, as described above, it is necessary to bend about 1/150 rad on the basis of the rotational deflection so that it is not handled as a metal bearing, and the deflection amount is 0.75 mm or more. It is necessary to be. In any of the samples 6-11, when a dead load (for example, a dead load is 600 to 700 kN) is applied, the amount of deflection can be set to 0.75 mm or more, and the conditions for the road bridge support manual can be satisfied.
以上のように、最大許容荷重が1000kNの支承装置10(サンプル6−11)では、勾配倍率を1.43−3.72、好ましくは1.73−3.62の範囲の範囲にすることで、荷重が載荷された際の変位量を1mm以内の段差に抑えることが出来、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。また、サンプル6−11の何れも、少なくとも死荷重(例えば600−700kN)が加わった際、撓み量を0.75mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来、金属支承装置の扱いではなく、弾性支承装置に属する扱いに出来る。 As described above, in the bearing device 10 (sample 6-11) having a maximum allowable load of 1000 kN, the gradient magnification is set to a range of 1.43-3.72, preferably 1.73-3.62. The amount of displacement when a load is loaded can be suppressed to a level difference of 1 mm or less, and vibration and noise when passing through the vehicle can be reduced. In addition, in any of the samples 6-11, when at least a dead load (for example, 600-700 kN) is applied, the amount of deflection can be set to 0.75 mm or more, and the conditions for the road bridge support manual can be satisfied. It can be handled as belonging to an elastic bearing device, not a metal bearing device.
[10−3.最大許容荷重が3000kNの支承装置について]
図19は、最大許容荷重が3000kNの支承装置10における鉛直荷重と鉛直撓み量の関係を示している。縦軸は、鉛直荷重[kN]を示し、横軸は、鉛直撓み量[mm]を示している。図19によれば、サンプル12−21の何れも、低荷重域、高荷重域の両方で、鉛直荷重が大きくなるに連れて鉛直変位量も大きくなり、低荷重域の一次勾配より高荷重域の二次勾配の方が勾配が急なものになっている。一般に、最大許容荷重が3000kNの支承装置10においては、死荷重が1800−2100kNに設定され、活荷重が1200−900kNに設定される。サンプル12−21では、低荷重域での一次勾配(傾き)に対する高荷重域での二次勾配(傾き)の勾配倍率(二次勾配/一次勾配)が1.43−3.72の範囲となっているので、活荷重域における鉛直変位量が1mm以内となり、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。例えば、最も勾配の緩やかなサンプル21を例に見ても、鉛直荷重が約1800kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約2.15mmであり、約3000kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約2.7mmであり、撓み量の差が約0.55mmである。したがって、活荷重域における鉛直変位量を1mm以内に抑えることを実現することが出来る。
[10-3. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 3000kN]
FIG. 19 shows the relationship between the vertical load and the vertical deflection amount in the
なお、上記道路橋支承便覧によれば、上述のように、金属支承の扱いとならないように、回転撓みの照査上、1/150rad程度撓むことが必要であり、撓み量が1.3mm以上有ることが必要である。サンプル12を除くサンプル13−21は、少なくとも死荷重(例えば1800−2100kN)が加わった際、撓み量が1.30mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来る。
In addition, according to the above-mentioned road bridge support manual, as described above, it is necessary to bend about 1/150 rad on the basis of the rotational deflection so that it is not handled as a metal bearing, and the deflection amount is 1.3 mm or more. It is necessary to be. The sample 13-21 except the
以上のように、最大許容荷重が3000kNの支承装置10(サンプル12−21)では、勾配倍率を1.43−3.72の範囲にすることで、荷重が載荷された際の変位量を1mm以内の段差に抑えることが出来、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。また、サンプル12を除くサンプル13−21は、少なくとも死荷重(例えば1800−2100kN)が加わった際、撓み量を1.30mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来、金属支承装置の扱いではなく、弾性支承装置に属する扱いに出来る。
As described above, in the bearing device 10 (sample 12-21) having a maximum allowable load of 3000 kN, the displacement amount when the load is loaded is 1 mm by setting the gradient magnification in the range of 1.43-3.72. It is possible to suppress the level difference within the range, and vibration and noise when passing through the vehicle can be reduced. In addition, the sample 13-21 except the
[10−4.最大許容荷重が10000kNの支承装置について]
図20は、最大許容荷重が10000kNの支承装置10における鉛直荷重と鉛直撓み量の関係を示している。縦軸は、鉛直荷重[kN]を示し、横軸は、鉛直撓み量[mm]を示している。図20によれば、サンプル22−31の何れも、低荷重域、高荷重域の両方で、鉛直荷重が大きくなるに連れて鉛直変位量も大きくなり、低荷重域の一次勾配より高荷重域の二次勾配の方が勾配が急なものになっている。一般に、最大許容荷重が10000kNの支承装置10においては、死荷重が6000−7000kNに設定され、活荷重が4000−3000kNに設定される。サンプル22−31では、低荷重域での一次勾配(傾き)に対する高荷重域での二次勾配(傾き)の勾配倍率(二次勾配/一次勾配)が1.74−2.83の範囲となっているので、活荷重域における鉛直変位量が1mm以内となり、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。例えば、サンプル31を例に見ても、鉛直荷重が約6000kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約3.0mmであり、約10000kNのとき、鉛直変位量が約3.4mmであり、撓み量の差が約0.4mmである。したがって、活荷重域における鉛直変位量を1mm以内に抑えることを実現することが出来る。
[10-4. Bearing device with a maximum allowable load of 10,000 kN]
FIG. 20 shows the relationship between the vertical load and the amount of vertical deflection in the
なお、上記道路橋支承便覧によれば、上述のように、金属支承の扱いとならないように、回転撓みの照査上、1/150rad程度撓むことが必要であり、撓み量が2.4mm以上有ることが必要である。サンプル22を除くサンプル23−31は、少なくとも死荷重(例えば6000−7000kN)が加わった際、撓み量が2.4mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来る。 In addition, according to the above-mentioned road bridge support manual, as described above, it is necessary to bend about 1/150 rad on the basis of the rotational deflection so that it is not handled as a metal bearing, and the deflection amount is 2.4 mm or more. It is necessary to be. The sample 23-31 except the sample 22 can have a deflection amount of 2.4 mm or more when at least a dead load (for example, 6000-7000 kN) is applied, and can also satisfy the conditions of the road bridge support manual.
以上のように、最大許容荷重が10000kNの支承装置10(サンプル22−31)では、勾配倍率を1.43−3.72、好ましくは1.74−2.83の範囲の範囲にすることで、荷重が載荷された際の変位量を1mm以内の段差に抑えることが出来、車両通過時の振動や騒音を低減することが出来る。また、サンプル22を除くサンプル23−31は、少なくとも死荷重(例えば6000−7000kN)が加わった際、撓み量を2.4mm以上にすることが出来、上記道路橋支承便覧の条件も満たすことが出来、金属支承装置の扱いではなく、弾性支承装置に属する扱いに出来る。 As described above, in the bearing device 10 (sample 22-31) having a maximum allowable load of 10,000 kN, the gradient magnification is set to a range of 1.43-3.72, preferably 1.74-2.83. The amount of displacement when a load is loaded can be suppressed to a level difference of 1 mm or less, and vibration and noise when passing through the vehicle can be reduced. In addition, the sample 23-31 excluding the sample 22 can have a deflection amount of 2.4 mm or more when at least a dead load (for example, 6000-7000 kN) is applied, and can also satisfy the conditions of the road bridge support manual. Yes, it can be handled as belonging to an elastic bearing device, not a metal bearing device.
[11.その他の変形例]
上述の説明では、本発明の支承装置として橋梁用支承装置について説明したが、本発明は橋梁用支承装置に限定されることはなく、各種の構造物の制震、免震用の支承装置として採用することが出来る。
[11. Other variations]
In the above description, the bridge support device has been described as the support device of the present invention. However, the present invention is not limited to the bridge support device, but as a support device for vibration control and seismic isolation of various structures. It can be adopted.
1 上部構造物、2 下部構造物、3 上部プレート、4 摺滑部材、5 下部プレート、6 摺滑部材、10 支承装置、11 上沓、12 下沓、13 弾性体、13 凸部13(13a,13b,13c) 弾性体、14 凸部、15 凹部、16 拘束体、16b,16c 固定手段、16d ポット部、17 貫通孔、17a 上揚防止片、18 芯材、19 大径部、21 挿通孔、22 ネジ穴、23 積層型弾性体、23a 補強板、23b 弾性層、23c 環状突出部、24 凸部、25 凹部、25,27a 突出部、27b 凹部,28a 空隙部、30 支承装置、31 芯材、32 上揚防止片、33 大径部、34 ネジ穴、40 支承装置、41 芯材、41a 位置決め凸部、41b 位置決め凹部、42 上揚防止片、43 大径部、43a ネジ穴、44 ネジ部、45a 挿通孔、45b 固定ボルト、45c 固定孔、45d 凹部、61 凸部、62 凹部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (16)
前記拘束体と前記弾性体との間に、隙間が設けられ、
鉛直変位量に対する鉛直荷重の特性が低荷重域の一次勾配と高荷重域の二次勾配とを有し、
前記二次勾配の近似直線の傾きが前記一次勾配の近似直線の傾きより大きく、
所定以上入力されると、前記拘束体は、変形した前記弾性体が当接及び/又は圧接され、前記弾性体の変形を拘束することを特徴とする支承装置。 A first rigid body, a second rigid body, an elastic body disposed between the first rigid body and the second rigid body, and a restraining body surrounding the elastic body,
A gap is provided between the restraining body and the elastic body,
The characteristic of the vertical load with respect to the vertical displacement amount has a primary gradient in the low load region and a secondary gradient in the high load region,
The gradient of the approximate line of the secondary slope is rather greater than the slope of the approximate line of the primary gradient,
The support device according to claim 1, wherein when the input is greater than or equal to a predetermined amount, the deformed elastic body is brought into contact with and / or pressed against the deformed elastic body to restrain deformation of the elastic body .
前記弾性体への荷重の増大に伴って、より高度な密閉状態へと変化することを特徴とする請求項1−7の何れかに記載の支承装置。 The elastic body is surrounded by the first rigid body, the second rigid body, and the restraining body to be in a substantially sealed state,
The bearing device according to any one of claims 1 to 7 , wherein the bearing device changes to a higher sealed state as the load on the elastic body increases.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011242733A JP5330486B2 (en) | 2011-11-04 | 2011-11-04 | Bearing device |
| PCT/JP2012/073098 WO2013035879A1 (en) | 2011-09-08 | 2012-09-10 | Support device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011242733A JP5330486B2 (en) | 2011-11-04 | 2011-11-04 | Bearing device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013096195A JP2013096195A (en) | 2013-05-20 |
| JP2013096195A5 JP2013096195A5 (en) | 2013-07-04 |
| JP5330486B2 true JP5330486B2 (en) | 2013-10-30 |
Family
ID=48618447
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011242733A Active JP5330486B2 (en) | 2011-09-08 | 2011-11-04 | Bearing device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5330486B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6062907B2 (en) * | 2014-10-29 | 2017-01-18 | 東京ファブリック工業株式会社 | Rubber bearing body and rubber bearing apparatus provided with the rubber bearing body |
| AT524177B1 (en) * | 2020-09-14 | 2022-05-15 | Engel Austria Gmbh | Plasticizing unit for a molding machine and molding machine with a corresponding plasticizing unit |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3018291B2 (en) * | 1997-11-21 | 2000-03-13 | 株式会社カイモン | Sliding elastic bearing device for structures |
-
2011
- 2011-11-04 JP JP2011242733A patent/JP5330486B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013096195A (en) | 2013-05-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5373274B2 (en) | Anti-vibration structure | |
| JP5330463B2 (en) | Elastic body restraint degree variable structure | |
| US20190120321A1 (en) | Seismic isolation apparatus | |
| JP5330486B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| CA2907567A1 (en) | Disc and spring isolation bearing | |
| JP5390565B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP5244220B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP5330485B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP5390574B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP5690112B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP5330472B2 (en) | Elastic body restraint variable structure and bearing device | |
| JP2018136000A (en) | Seismic isolator | |
| JP5186589B1 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP2018071602A (en) | Lower cushion rubber for upper support | |
| JP5330475B2 (en) | Bearing structure | |
| JP6809951B2 (en) | Connection vibration isolation device for seismic isolation bearings | |
| JP2018132175A (en) | Upper support | |
| JP5390583B2 (en) | Bearing structure | |
| JP5703035B2 (en) | Seismic isolation device | |
| JP5702643B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP5392685B2 (en) | Isolator protection device and method of assembling the same | |
| JP2015052354A (en) | Vibration prevention support device | |
| JP6030289B2 (en) | Bearing device | |
| WO2013008828A1 (en) | Bearing device | |
| JP5651429B2 (en) | Bearing device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130516 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130516 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20130516 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20130604 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130702 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130725 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5330486 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |