JP5262829B2 - Developing apparatus and developing method - Google Patents
Developing apparatus and developing method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5262829B2 JP5262829B2 JP2009042961A JP2009042961A JP5262829B2 JP 5262829 B2 JP5262829 B2 JP 5262829B2 JP 2009042961 A JP2009042961 A JP 2009042961A JP 2009042961 A JP2009042961 A JP 2009042961A JP 5262829 B2 JP5262829 B2 JP 5262829B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- developer
- wafer
- substrate
- rotational speed
- nozzle
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 30
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 67
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 20
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 67
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 abstract description 5
- 235000012431 wafers Nutrition 0.000 description 110
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 20
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 19
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000007654 immersion Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000003028 elevating effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000003892 spreading Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 101100221835 Arabidopsis thaliana CPL2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100221836 Arabidopsis thaliana CPL3 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100221837 Arabidopsis thaliana CPL4 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100065702 Arabidopsis thaliana ETC3 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100536545 Arabidopsis thaliana TCL2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011109 contamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001276 controlling effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002079 cooperative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000012805 post-processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007781 pre-processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005871 repellent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Exposure Of Semiconductors, Excluding Electron Or Ion Beam Exposure (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、レジスト液が塗布され、露光処理された後の基板に対して、現像処理を行う現像方法及び現像装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a developing method and a developing apparatus for performing a developing process on a substrate after a resist solution is applied and subjected to an exposure process.
従来、半導体製造工程の一つであるフォトレジスト工程においては、基板である半導体ウエハ(以下、ウエハという)の表面にレジストを塗布し、このレジストを所定のパターンで露光した後に、現像してレジストパターンを形成している。このような処理は、一般にレジストの塗布・現像を行う塗布・現像装置に、露光装置を接続したシステムを用いて行われる。 Conventionally, in a photoresist process, which is one of semiconductor manufacturing processes, a resist is applied to the surface of a semiconductor wafer (hereinafter referred to as a wafer), which is a substrate, the resist is exposed in a predetermined pattern, and then developed to develop a resist. A pattern is formed. Such processing is generally performed using a system in which an exposure apparatus is connected to a coating / developing apparatus that performs resist coating / development.
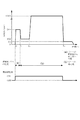
ところで、現像処理の手法には基板保持部であるスピンチャックにウエハを保持させ、当該ウエハを鉛直軸回りに回転させると共に現像液ノズルをウエハの周縁部より中心部へ移動させながら、現像液ノズルより現像液を吐出して現像処理を行う手法がある(特許文献1参照)。前記手法について図11を用いて具体的に説明すると、先ずウエハの回転数を例えば1000rpmとして前処理液を塗布し(時刻t0)、ウエハの表面の濡れ性を高め、後に塗布する現像液が広がり易い環境を整える(プリウェット工程)。次に、ウエハの周縁部から中心部へ現像液ノズルを移動させながら現像液を吐出し(時刻t1)、回転しているウエハの遠心力により現像液を螺旋状に広げ、ウエハの表面に現像液の液膜を形成する。このときウエハの回転数は例えば1000rpmである。その後、現像液の吐出を停止し(時刻t2)、ウエハの回転数を例えば50rpmまで減速することにより現像液をウエハの表面に保持し、現像処理を行う。そして、現像処理後にウエハへ洗浄液を供給して現像液を洗い流し、スピン乾燥を行う。 By the way, in the development processing method, the wafer is held by a spin chuck which is a substrate holding unit, the wafer is rotated about the vertical axis, and the developer nozzle is moved from the peripheral portion of the wafer to the center portion while developing the developer nozzle. There is a method of performing development processing by discharging more developer (see Patent Document 1). The method will be specifically described with reference to FIG. 11. First, a pretreatment liquid is applied at a wafer rotation speed of, for example, 1000 rpm (time t 0 ), the wettability of the wafer surface is improved, and a developer to be applied later Prepare an easy-to-expand environment (pre-wet process). Next, the developing solution is discharged while moving the developing solution nozzle from the peripheral edge of the wafer to the center (time t 1 ), and the developing solution is spirally spread by the centrifugal force of the rotating wafer, and is applied to the surface of the wafer. A liquid film of a developer is formed. At this time, the rotation speed of the wafer is, for example, 1000 rpm. Thereafter, the discharge of the developing solution is stopped (time t 2 ), and the developing solution is held on the surface of the wafer by reducing the number of rotations of the wafer to, for example, 50 rpm, and the developing process is performed. Then, after the developing process, a cleaning solution is supplied to the wafer to wash away the developing solution, and spin drying is performed.
一方、露光機においては、露光の解像度を上げるために例えば純水の液膜をウエハの表面に形成した状態で露光する液浸露光を行うものが知られている。この液浸露光では露光機液浸部(レンズ先端)のスキャンの追随性を高めて従来の露光装置と同等のスループットを確保するために露光処理するウエハの表面に撥水性の高い例えば水の接触角が80〜85度程度の保護膜を形成したり、また保護膜を形成せずに撥水性の高い例えば水の接触角が85度以上のレジストを用いてレジスト膜の形成を行うことが検討されている。なお、接触角とは水滴がウエハの表面に付着しているときに水滴の断面における水滴の外縁を形成する円弧について、基板の表面における接線と当該表面とのなす角度のことである。 On the other hand, an exposure machine is known that performs immersion exposure in which a liquid film of pure water is exposed on the surface of a wafer in order to increase exposure resolution. In this immersion exposure, the surface of the wafer to be exposed is contacted with, for example, water with high water repellency in order to improve the followability of scanning of the exposure unit immersion part (lens tip) and ensure the same throughput as that of a conventional exposure apparatus. Consider forming a protective film with an angle of about 80 to 85 degrees, or forming a resist film using a resist having a high water repellency, for example, a contact angle of water of 85 degrees or more without forming a protective film. Has been. The contact angle is an angle formed between a tangent line on the surface of the substrate and the surface of an arc that forms the outer edge of the water droplet in the cross section of the water droplet when the water droplet is attached to the surface of the wafer.
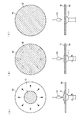
前述の現像手法においては、図12(a)に示すようにウエハWの中心位置に吐出された現像液Dは遠心力により広がっていくが、ウエハWの周縁に向かう程、液膜が薄くなるのでウエハWの表面の撥水性が高いと均一に広がりにくくなり、図12(b)に示すようにウエハの周縁付近にて現像液Dの液膜が形成されない露出部位Bが生じてしまう場合がある。また、仮にウエハの表面の全体に現像液Dの液膜が形成されたとしても、洗浄工程に移るまでの間に表面張力により液膜が破れてしまうおそれもある。この結果、液膜が形成されずに表面が露出する部位Bがあることによって現像欠陥が発生しやすいという課題がある。また、ウエハWの表面の撥水性が大きいと現像液Dをウエハへ吐出したときに、吐出された現像液Dがウエハの表面より跳ね返って、現像液ノズルの汚れの要因となり、また現像装置内部のパーティクルの原因となるおそれがある。 In the developing method described above, the developer D discharged to the center position of the wafer W spreads due to centrifugal force as shown in FIG. 12A, but the liquid film becomes thinner toward the periphery of the wafer W. Therefore, when the surface of the wafer W has high water repellency, it becomes difficult to spread uniformly, and as shown in FIG. 12B, an exposed portion B in which the liquid film of the developing solution D is not formed may occur near the periphery of the wafer. is there. Even if a liquid film of the developer D is formed on the entire surface of the wafer, there is a possibility that the liquid film may be broken by the surface tension before the cleaning process is started. As a result, there is a problem that development defects are likely to occur due to the presence of the portion B where the surface is exposed without forming a liquid film. Further, if the surface of the wafer W has a high water repellency, when the developer D is discharged onto the wafer, the discharged developer D rebounds from the surface of the wafer, causing contamination of the developer nozzle, and the inside of the developing device. There is a risk of causing particles.
本発明は、このような事情の下に基づいてなされたものであり、回転している基板の表面に現像液を塗布するにあたって、基板の表面の撥水性が大きくても基板の表面全体に亘って現像液の液膜を形成することができ、現像欠陥を低減することができる現像方法及び現像装置を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made under such circumstances, and when applying a developer to the surface of a rotating substrate, the entire surface of the substrate is covered even if the surface of the substrate is highly water-repellent. Another object of the present invention is to provide a developing method and a developing apparatus that can form a liquid film of a developer and reduce development defects.
本発明に係る現像方法は、基板保持部に保持された基板を回転させながら現像液ノズルから当該基板に現像液を吐出する現像方法において、
前記基板を第1の回転数で回転させながらかつ前記現像液ノズルから現像液を吐出させながら、前記現像液の吐出位置が基板の周縁部から中心部へ移動するように現像液ノズルを操作する工程と、
次いで前記現像液が基板の中心部に吐出されている状態で、少なくとも基板の中心部に液溜まりを形成するために基板の回転数を前記第1の回転数よりも低い第2の回転数で回転させる工程と、
その後、基板を前記第2の回転数より高い第3の回転数で回転させて、現像液を基板の表面に広げる工程と、を備えたことを特徴とする。
The developing method according to the present invention is a developing method in which the developer is discharged from the developer nozzle to the substrate while rotating the substrate held by the substrate holder.
The developer nozzle is operated so that the discharge position of the developer moves from the peripheral portion of the substrate to the central portion while rotating the substrate at the first rotation speed and discharging the developer from the developer nozzle. Process,
Next, in a state where the developer is discharged to the central portion of the substrate, the rotational speed of the substrate is set to a second rotational speed lower than the first rotational speed in order to form a liquid pool at least in the central portion of the substrate. Rotating, and
Then, the substrate is rotated at a third rotational speed higher than the second rotational speed to spread the developer on the surface of the substrate.
また、本発明に係る現像方法は以下の構成を取っても良い。
前記基板はその表面の水の接触角が85度以上である構成。
前記第1の回転数は500〜1500rpmである構成。
前記第2の回転数は50〜500rpmである構成。
前記第3の回転数は1000〜2500rpmである構成。
The developing method according to the present invention may take the following configuration.
The said board | substrate is the structure whose water contact angle of the surface is 85 degree | times or more.
The first rotation speed is 500 to 1500 rpm.
The second rotation speed is 50 to 500 rpm.
The third rotation speed is 1000 to 2500 rpm.
また本発明に係る現像装置は、基板保持部に保持された基板を回転させながら現像液ノズルから当該基板に現像液を吐出する現像装置において、
基板を保持する基板保持部と、
この基板保持部を鉛直軸回りに回転させる回転駆動部と、
前記基板保持部に保持された基板へ現像液を塗布する現像液ノズルと、
この現像液ノズルを操作する操作機構と、
前記基板を第1の回転数で回転させながらかつ前記現像液ノズルから現像液を吐出させながら、前記現像液の吐出位置が基板の周縁部から中心部へ移動するように現像液ノズルを操作するステップと、
次いで前記現像液が基板の中心部に吐出されている状態で、少なくとも基板の中心部に液溜まりを形成するために基板の回転数を前記第1の回転数よりも低い第2の回転数で回転させるステップと、
その後、基板を前記第2の回転数より高い第3の回転数で回転させて、現像液を基板の表面に広げるステップと、を実行するように制御信号を出力する制御部と、を備えたことを特徴とする。
The developing device according to the present invention is a developing device that discharges the developer from the developer nozzle to the substrate while rotating the substrate held by the substrate holder.
A substrate holder for holding the substrate;
A rotation drive unit that rotates the substrate holding unit around a vertical axis;
A developer nozzle for applying a developer to the substrate held by the substrate holder;
An operation mechanism for operating the developer nozzle;
The developer nozzle is operated so that the discharge position of the developer moves from the peripheral portion of the substrate to the central portion while rotating the substrate at the first rotation speed and discharging the developer from the developer nozzle. Steps,
Next, in a state where the developer is discharged to the central portion of the substrate, the rotational speed of the substrate is set to a second rotational speed lower than the first rotational speed in order to form a liquid pool at least in the central portion of the substrate. A rotating step;
And a step of rotating the substrate at a third rotational speed higher than the second rotational speed to spread the developer on the surface of the substrate, and a controller that outputs a control signal to perform It is characterized by that.
本発明によれば、現像液ノズルから基板の中心部に現像液を供給するときには基板の回転数を低くし、これにより少なくとも基板の中央部に液溜まりが形成され、その後基板の回転数を高くしている。このため少なくとも中央部に溜められた液が高速回転により広がるので液膜が厚い状態で周縁部へ向かうことから、基板の表面の撥水性が高くても均一に広がりやすくなり、現像欠陥の発生を抑制することができる。また、高速回転にしたときに十分に均一に広がることができる程度の液溜まりを低速回転で形成した後、そのまま低速回転で液を周縁部まで広げずに高速回転に移行すれば、スループットの低下を極力抑えることができる。 According to the present invention, when supplying the developing solution from the developing solution nozzle to the central portion of the substrate, the number of rotations of the substrate is lowered, thereby forming a liquid pool at least in the central portion of the substrate, and then increasing the number of rotations of the substrate. doing. For this reason, at least the liquid stored in the central part spreads by high-speed rotation, so the liquid film goes to the peripheral part in a thick state, so that even if the water repellency of the substrate surface is high, it tends to spread evenly, and development defects occur. Can be suppressed. In addition, if a liquid pool that can be spread sufficiently uniformly when rotating at high speed is formed at low speed, and then the liquid is transferred to high speed without spreading to the peripheral edge at low speed, the throughput decreases. Can be suppressed as much as possible.
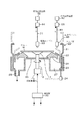
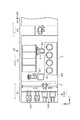
本発明に係る現像方法の実施の形態を説明する。図1及び図2はこの実施形態を実施するための現像装置を示す図であり、この現像装置は中央に基板例えばウエハWを吸着保持する基板保持部であるスピンチャック11を有している。このスピンチャック11は回転軸12を介して下方に設けられた例えばモータである回転駆動部13に接続されており、ウエハWを保持した状態で鉛直軸回りに回転することができ、また昇降することが可能である。また、現像装置には、スピンチャック11に保持されたウエハWを取り囲むようにカップ体20が設けられている。このカップ体20は、外カップ21と内カップ22とから成り、カップ体20の上方側は開口している。前記外カップ21は上部側が四角形状であり、下部側が円筒状である。また、外カップ21の下端部には段部23が形成されている。さらに、前記外カップ21は下方に設けられた昇降部24により昇降することが可能である。前記内カップ22は円筒状であり、上部側が内側に傾斜している。また、内カップ22は、その下端面が前記外カップ21の昇降時に段部23と当接することによって上方へ押し上げられる。
An embodiment of the developing method according to the present invention will be described. FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 are views showing a developing device for carrying out this embodiment, and this developing device has a
またスピンチャック11に保持されたウエハWの下方側には円形板25が設けられており、この円形板25の外側には縦断面形状が山形のガイド部材26が設けられている。前記ガイド部材26はウエハWよりこぼれ落ちた現像液や洗浄液を後述する液受け部27へ導くためのものである。また円形板25の外側には縦断面が凹部上に形成された液受け部27が全周に亘って設けられている。この液受け部27の底面には、下方より廃液管28が接続されている。また図示していないが廃液管28は廃液タンクに接続され、その途中には気液分離器が設けられ、排気と廃液の分離が行われる。また、図示していないが現像装置には円形板25を下方より貫通する例えば3本の昇降ピンが設けられており、この昇降ピンは図示しない基板搬送アームとの協働作用によってウエハWをスピンチャック11に受け渡すことが可能である。
A
また、現像装置にはスピンチャック11に保持されたウエハWの上方側に、現像液ノズル30及び洗浄液ノズル40が設けられている。前記現像液ノズル30には、図3に示すようにその下端面に例えば長さL1が8〜15mm、幅L2が0.1〜1mmである帯状の吐出口30aが設けられている。
Further, the developing device is provided with a developing
現像液ノズル30は現像液供給管31を介して現像液供給源32や液供給制御機器(バルブ、ポンプ等)を含む現像液供給系54に接続されている。また、図2に示すように現像液ノズル30は支持部材であるノズルアーム33の一端に支持されており、このノズルアーム33の他端は図示しない昇降機構を介して移動基体34に接続されている。この移動基体34は、X方向に伸びるガイドレール35沿って移動することが可能である。また、図中36は現像液ノズル30の待機部であり、この待機部36にて現像液ノズル30の先端部の洗浄等が行われる。
The
前記洗浄液ノズル40はウエハWへ洗浄液例えば純水を吐出するためのノズルであり、洗浄液供給管41を介して洗浄液供給源42や洗浄液供給制御機器(バルブ、ポンプ等)を含む洗浄液供給系55に接続されている。また、図2に示すように、洗浄液ノズル40はノズルアーム43の一端に支持されて図示しない昇降機構を介して移動基体44と接続されており、この移動基体44はガイドレール35に沿ってX方向に移動可能である。図中45は洗浄液ノズル40の待機部である。
The cleaning
図4は現像装置の各部を制御するための制御部50を示し、この制御部50は例えばCPU51、プログラム格納部52に格納されたプログラム52a、データバス53などから構成されるコンピュータである。前記プログラム52aはプロセスレシピに基づいて回転駆動部13、現像液供給系54、洗浄液供給系55及びノズル駆動系56を制御する。
FIG. 4 shows a
次に、上述の現像装置を用いてウエハWを現像する方法を説明する。現像装置に搬入されるウエハWには、塗布装置にてその表面に撥水性の高い例えば水の静的接触角が85度以上のレジストが塗布され、露光装置にて液浸露光が施されている。先ず、現像装置の外カップ21及び内カップ22が下方へ位置している状態にて、図示しない搬送アームにより現像装置内にウエハWを搬送する。このウエハWを搬送アームと昇降ピンとの協働作用によってスピンチャック11に載置され、吸着保持される。
Next, a method for developing the wafer W using the above-described developing device will be described. A wafer having a high water repellency, for example, a static contact angle of water of 85 degrees or more is applied to the surface of the wafer W carried into the developing device by the coating device, and immersion exposure is performed by the exposure device. Yes. First, with the
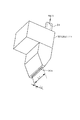
続いて、ウエハWを第1の回転数で回転させながら、現像液の吐出位置が当該ウエハWの周縁部から中心部へ移動するように現像液ノズル30を操作する工程を説明する。図5に示すようにウエハWを第1の回転数例えば500rpmで回転させ、現像液ノズル30をその吐出口30aの長さ方向がウエハWの中央部と周縁部を結ぶラインに一致するように、例えばウエハWの半径方向と一致するように、当該ウエハWの周縁部の上方に配置し(図6参照)、ウエハWへ現像液を吐出する(図5の時刻t0)。吐出された現像液はウエハWの回転による遠心力によって展伸される。この現像液を吐出している状態のまま現像液ノズル30をウエハWの中心部の上方へ移動させる(図6参照)。前記現像液ノズル30をウエハWの周縁部の上方から中央部の上方へ移動するのに要する時間は例えば1秒程度である。このように現像液ノズル30をウエハWの周縁部の上方から中央部の上方へ移動させながら、吐出口30aより現像液を帯状に吐出していることから、ウエハWの表面に隙間無く現像液を塗布することができ、現像液が塗布された部位では現像処理が行われる。
Next, a process of operating the
次に、現像液ノズル30がウエハWの中心部上方まで移動したときに(図5の時刻t1)、ウエハWの回転数を第2の回転数例えば100rpmまで落とし、例えば2秒間引き続き現像液の吐出を行う。そして、ウエハWの中心部へ現像液Dの供給を行っている状態で、ウエハWの回転数を第2の回転数より高い第3の回転数例えば2000rpmまで上昇させ(図5の時刻t2)、例えば10秒後に現像液Dの供給を停止する。そして、その直後にウエハWを例えば20000rpm/sの減速度で一気に減速して、第4の回転数例えば50rpmまで落とし(図5の時刻t3)、現像液ノズル30を待機部36へ退避させる。この第4の回転数は、現像液Dの周縁がその表面張力でウエハWの中央部へ引き戻されずにウエハWの周縁部に形成した状態とするのに十分な回転数である。この第4の回転数にて例えば2秒程度、ウエハWを回転させ、その後ウエハWの回転を例えば45秒間停止させる。
Next, when the
しかる後に洗浄液ノズル40からウエハWの中心部に洗浄液の吐出を行う。このときのウエハWの回転数は例えば500rpmであり、吐出された洗浄液はウエハWの中心から周縁へ向かって広げられて、現像液Dの洗浄が行われる。その後、洗浄液の供給を停止して、洗浄液ノズル40を待機部45へ退避させ、昇降機構によって外カップ21及び内カップ22を上昇させて、ウエハWを例えば2000rpmの回転数として所定の時間スピン乾燥させる。その後、ウエハWは現像装置より搬送アームによって搬出され現像処理を終了する。
Thereafter, the cleaning liquid is discharged from the cleaning
以上のように現像液ノズル30をウエハWの中心部の上方に位置させたときに、ウエハWの回転数を例えば100rpm程度の低速回転とすることにより、吐出された現像液DはウエハWの遠心力により徐々に外方へ広がってゆくが、低速回転であるためにウエハWの中央部に液溜まりができる(図7(a))。その後、ウエハWの回転数を例えば2000rpmの高速回転とすることで大きな遠心力により一気に広がろうとするが、中央部に液溜まりが存在するので広がっていく液膜の源の液量が多い。このため液膜が厚いことから、ウエハWの表面の撥水性が高くても液膜が途切れにくく、ウエハWの中心部から周縁部へ向かって均一に広がる(図7(b))。また、一部の現像液DはウエハWの周縁より外方へこぼれ落ちるが、前述のガイド部材26を伝って流れてゆき、液受け部27に一時的に溜められ、廃液管28より現像装置の外部へ排出される。
As described above, when the
前記第2の回転数は、ウエハWの中心部に現像液Dの液溜まりを形成するための回転数であるから、その回転数が高過ぎるとウエハWの遠心力が大きくなって、現像液の吐出が追いつかず液溜まりが形成されなくなる。逆に第2の回転数が低過ぎると、既にウエハWの表面に形成されている液膜が破れてしまうことから、50〜500rpmが好ましく、より好ましくは50〜200rpmである。また、ウエハWを第2の回転数で回転させている時間は、ウエハWの中央部に液溜まりが形成されるのに十分な時間以上であればよい。この時間が長くても処理に対する影響は無いが、中央部に液溜まりが形成されていれば、その後低速回転を維持させておく必要はないので、スループットを向上させる観点からは速やかに例えば既述のように1秒後に第3の回転数まで上昇させる(高速回転に移行する)ことが好ましい。従って、本発明は少なくともウエハWの中央部に液溜まりが形成されることが必要であると言える。 Since the second rotational speed is a rotational speed for forming a pool of the developer D at the center of the wafer W, if the rotational speed is too high, the centrifugal force of the wafer W increases, and the developer The discharge cannot catch up and no liquid pool is formed. On the other hand, if the second rotational speed is too low, the liquid film already formed on the surface of the wafer W is broken, so 50 to 500 rpm is preferable, and 50 to 200 rpm is more preferable. Further, the time during which the wafer W is rotated at the second number of rotations may be longer than the time sufficient for the liquid pool to be formed in the central portion of the wafer W. Even if this time is long, there is no effect on the processing, but if a liquid pool is formed at the center, there is no need to maintain low-speed rotation thereafter. Thus, it is preferable to increase to the third rotation number after 1 second (shift to high-speed rotation). Therefore, it can be said that the present invention requires that a liquid pool be formed at least in the central portion of the wafer W.
前記第3の回転数は現像液D(液溜まり)を瞬時にウエハWの周縁部まで広げるための回転数である。前記液溜まりを瞬時に広げる理由は、ウエハWの表面が高い撥水性例えば接触角85度にもなると、ウエハWの表面の乾燥速度が大きく乾燥しやすいため、液膜が薄い状態で現像液Dを広げるのに長い時間を費やすと液膜が部分的に乾燥して、引きちぎれ、均一に広がらないためである。従って、ここでいう瞬時とはウエハWの中央部の液溜まりが均一に広がる状態を確保できる程度に速やかに第3の回転数に移行するという意味である。 The third rotational speed is a rotational speed for instantly spreading the developer D (liquid reservoir) to the peripheral edge of the wafer W. The reason why the liquid pool is instantly expanded is that when the surface of the wafer W has a high water repellency, for example, a contact angle of 85 degrees, the surface of the wafer W has a high drying rate and is easily dried. This is because if a long time is taken to spread the film, the liquid film is partially dried, torn off, and does not spread uniformly. Therefore, the instant here means that the rotation speed is shifted to the third rotational speed as quickly as possible to ensure that the liquid pool in the central portion of the wafer W spreads uniformly.
上述の実施形態によれば、ウエハWを回転させながら周縁部から中心部へ現像液の吐出位置を移動させて現像を行うにあたって、現像液ノズル30よりウエハWの中心部へ現像液Dを吐出するときには、ウエハWを低速な第2の回転数とし少なくともウエハWの中心部に現像液Dの液溜まりを形成している。その後、ウエハWを高速な第3の回転数とし、中心部に溜められた現像液Dが、その液膜が厚い状態で周縁部まで広がることから、ウエハWの表面の撥水性が高くても均一に広がりやすく、現像欠陥の発生を抑制することができる。また、高速回転(第3の回転数)にしたときに十分に均一に広がることができる程度の液溜まりを低速回転(第2の回転数)で形成した後、そのまま低速回転で液を周縁部まで広げずに高速回転に移行すれば、スループットの低下を極力抑えることができる。
According to the above-described embodiment, the developing solution D is discharged from the developing
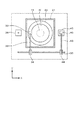
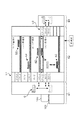
続いて本発明の現像装置を適用した塗布、現像装置の一例について簡単に説明する。図8は前記塗布、現像装置の平面図であり、図9は前記塗布、現像装置の斜視図である。この装置には、キャリアブロックS1が設けられており、このブロックS1では、載置台101上に載置された密閉型のキャリア100から受け渡しアームCがウエハWを取り出して、当該ブロックS1に隣接された処理ブロックS2に受け渡すと共に、前記受け渡しアームCが、処理ブロックS2にて処理された処理済みのウエハWを受け取って前記キャリア100に戻すように構成されている。
Next, an example of a coating and developing device to which the developing device of the present invention is applied will be briefly described. FIG. 8 is a plan view of the coating and developing apparatus, and FIG. 9 is a perspective view of the coating and developing apparatus. In this apparatus, a carrier block S1 is provided. In this block S1, the transfer arm C takes out the wafer W from the hermetically sealed
前記処理ブロックS2は、図9に示すように、この例では現像処理を行うための第1のブロック(DEV層)B1、レジスト膜の下層側に形成される反射防止膜の形成処理を行なうための第2のブロック(BCT層)B2、レジスト液の塗布処理を行うための第3のブロック(COT層)B3、レジスト膜の上層側に形成される反射防止膜の形成処理を行なうための第4のブロック(TCT層)B4を下から順に積層して構成されている。 As shown in FIG. 9, the processing block S2 is a first block (DEV layer) B1 for performing development processing in this example, and a processing for forming an antireflection film formed on the lower layer side of the resist film. The second block (BCT layer) B2, the third block (COT layer) B3 for applying the resist solution, and the antireflection film forming process formed on the upper layer side of the resist film. 4 blocks (TCT layers) B4 are stacked in order from the bottom.
前記第2のブロック(BCT層)B2と第4のブロック(TCT層)B4とは、各々反射防止膜を形成するための薬液をスピンコーティングにより塗布する液処理装置と、この液処理装置にて行われる処理の前処理及び後処理を行うための加熱・冷却系の処理ユニット群と、前記塗布処理装置と処理ユニット群との間に設けられ、これらの間でウエハWの受け渡しを行なう搬送アームA2,A4とを備えている。第3のブロック(COT層)B3においては、前記薬液がレジスト液であり、疎水化処理ユニットが組み込まれることを除けば同様の構成である。一方、第1の処理ブロック(DEV層)B1については、例えば一つのDEV層B1内に本発明の現像ユニットが2段に積層されている。そして当該DEV層B1内には、これら2段の現像ユニットにウエハWを搬送するための共通の搬送アームA1が設けられている。さらに処理ブロックS2には、図8及び図10に示すように、棚ユニットU1が設けられ、この棚ユニットU1の各部同士の間では、前記棚ユニットU1の近傍に設けられた昇降自在な受け渡しアームD1によってウエハWが搬送される。 The second block (BCT layer) B2 and the fourth block (TCT layer) B4 are respectively a liquid processing apparatus for applying a chemical solution for forming an antireflection film by spin coating, and this liquid processing apparatus. A heating / cooling system processing unit group for performing pre-processing and post-processing of the processing to be performed, and a transfer arm that is provided between the coating processing apparatus and the processing unit group and delivers the wafer W between them. A2 and A4 are provided. The third block (COT layer) B3 has the same configuration except that the chemical solution is a resist solution and a hydrophobic treatment unit is incorporated. On the other hand, for the first processing block (DEV layer) B1, for example, the developing units of the present invention are stacked in two stages in one DEV layer B1. In the DEV layer B1, a common transfer arm A1 for transferring the wafer W to the two-stage development units is provided. Further, as shown in FIG. 8 and FIG. 10, the processing block S2 is provided with a shelf unit U1, and between each part of the shelf unit U1, a transfer arm that can be raised and lowered is provided in the vicinity of the shelf unit U1. The wafer W is transferred by D1.
このような塗布、現像装置では、キャリアブロックS1からのウエハWは前記棚ユニットU1の一つの受け渡しユニット、例えば第2のブロック(BCT層)B2の対応する受け渡しユニットCPL2に受け渡しアームCによって順次搬送され、ここからウエハWは受け渡しユニットCPL3及び搬送アームA3を介して第3のブロック(COT層)B3に搬入され、疎水化処理ユニットにおいてウエハ表面が疎水化された後、液処理装置2にてレジスト膜が形成される。レジスト膜形成後のウエハWは、搬送アームA3により、棚ユニットU1の受け渡しユニットBF3に受け渡される。 In such a coating and developing apparatus, the wafer W from the carrier block S1 is sequentially transferred by the transfer arm C to one transfer unit of the shelf unit U1, for example, the corresponding transfer unit CPL2 of the second block (BCT layer) B2. From here, the wafer W is transferred into the third block (COT layer) B3 via the transfer unit CPL3 and the transfer arm A3, and the wafer surface is hydrophobized in the hydrophobizing unit, and then the liquid processing apparatus 2 A resist film is formed. The wafer W after the formation of the resist film is transferred to the transfer unit BF3 of the shelf unit U1 by the transfer arm A3.
その後、この場合はウエハWは受け渡しユニットBF3→受け渡しアームD1→受け渡しユニットCPL4を介して搬送アームA4に受け渡され、レジスト膜の上に反射防止膜が形成された後、搬送アームA4により受け渡しユニットTRS4に受け渡される。なおレジスト膜の上の反射防止膜を形成しない場合や、ウエハWに対して疎水化処理を行う代わりに、第2のブロック(BCT層)B2にて反射防止膜が形成される場合もある。 Thereafter, in this case, the wafer W is transferred to the transfer arm A4 via the transfer unit BF3 → the transfer arm D1 → the transfer unit CPL4, and after the antireflection film is formed on the resist film, the transfer arm A4 transfers the wafer W. Passed to TRS4. In some cases, an antireflection film is not formed on the resist film, or an antireflection film is formed in the second block (BCT layer) B2 instead of performing the hydrophobic treatment on the wafer W.
一方DEV層B1内の上部には、棚ユニットU1に設けられた受け渡しユニットCPL11から棚ユニットU2に設けられた受け渡しユニットCPL12にウエハWを直接搬送するための専用の搬送手段であるシャトルアームEが設けられている。レジスト膜やさらに反射防止膜が形成されたウエハWは、受け渡しアームD1により受け渡しユニットBF3、TRS4を介して受け渡しユニットCPL11に受け渡され、ここからシャトルアームEにより棚ユニットU2の受け渡しユニットCPL12に直接搬送され、インターフェイスブロックS3に取り込まれることになる。なお図10中のCPLが付されている受け渡しユニットは、温調用の冷却ユニットを兼ねており、BFが付されている受け渡しユニットは、複数枚のウエハWを載置可能なバッファユニットを兼ねている。 On the other hand, on the upper part in the DEV layer B1, a shuttle arm E which is a dedicated transfer means for directly transferring the wafer W from the transfer unit CPL11 provided in the shelf unit U1 to the transfer unit CPL12 provided in the shelf unit U2. Is provided. The wafer W on which the resist film and further the antireflection film are formed is delivered to the delivery unit CPL11 by the delivery arm D1 via the delivery units BF3 and TRS4, and from here to the delivery unit CPL12 of the shelf unit U2 directly by the shuttle arm E. It is conveyed and taken into the interface block S3. The delivery unit with CPL in FIG. 10 also serves as a cooling unit for temperature control, and the delivery unit with BF also serves as a buffer unit on which a plurality of wafers W can be placed. Yes.
次いで、ウエハWはインターフェイスアームBにより露光装置S4に搬送され、ここで液浸露光処理が行われた後、棚ユニットU2の受け渡しユニットTRS6に載置されて処理ブロックS2に戻される。戻されたウエハWは、第1のブロック(DEV層)B1にて現像処理が行われ、搬送アームA1により棚ユニットU5における受け渡しアームCのアクセス範囲の受け渡し台に搬送され、受け渡しアームCを介してキャリア100に戻される。なお図8においてU3は各々加熱部と冷却部等を積層した処理ユニット群である。
Next, the wafer W is transferred to the exposure apparatus S4 by the interface arm B, and after being subjected to immersion exposure processing, it is placed on the transfer unit TRS6 of the shelf unit U2 and returned to the processing block S2. The returned wafer W is developed in the first block (DEV layer) B1, and is transferred by the transfer arm A1 to the transfer table in the access range of the transfer arm C in the shelf unit U5. And returned to the
W ウエハ
11 スピンチャック
13 回転駆動部
20 カップ体
30 現像液ノズル
30a 吐出孔
32 現像液供給源
40 洗浄液ノズル
42 洗浄液供給源
50 制御部
52a プログラム
56 ノズル駆動系
D 現像液
Claims (6)
前記基板を第1の回転数で回転させながらかつ前記現像液ノズルから現像液を吐出させながら、前記現像液の吐出位置が基板の周縁部から中心部へ移動するように現像液ノズルを操作する工程と、
次いで前記現像液が基板の中心部に吐出されている状態で、少なくとも基板の中心部に液溜まりを形成するために基板の回転数を前記第1の回転数よりも低い第2の回転数で回転させる工程と、
その後、基板を前記第2の回転数より高い第3の回転数で回転させて、現像液を基板の表面に広げる工程と、を備えたことを特徴とする現像方法。 In the developing method of discharging the developer from the developer nozzle to the substrate while rotating the substrate held by the substrate holder,
The developer nozzle is operated so that the discharge position of the developer moves from the peripheral portion of the substrate to the central portion while rotating the substrate at the first rotation speed and discharging the developer from the developer nozzle. Process,
Next, in a state where the developer is discharged to the central portion of the substrate, the rotational speed of the substrate is set to a second rotational speed lower than the first rotational speed in order to form a liquid pool at least in the central portion of the substrate. Rotating, and
And a step of rotating the substrate at a third rotational speed higher than the second rotational speed to spread the developer on the surface of the substrate.
基板を保持する基板保持部と、
この基板保持部を鉛直軸回りに回転させる回転駆動部と、
前記基板保持部に保持された基板へ現像液を塗布する現像液ノズルと、
この現像液ノズルを操作する操作機構と、
前記基板を第1の回転数で回転させながらかつ前記現像液ノズルから現像液を吐出させながら、前記現像液の吐出位置が基板の周縁部から中心部へ移動するように現像液ノズルを操作するステップと、
次いで前記現像液が基板の中心部に吐出されている状態で、少なくとも基板の中心部に液溜まりを形成するために基板の回転数を前記第1の回転数よりも低い第2の回転数で回転させるステップと、
その後、基板を前記第2の回転数より高い第3の回転数で回転させて、現像液を基板の表面に広げるステップと、を実行するように制御信号を出力する制御部と、を備えたことを特徴とする現像装置。 In the developing device for discharging the developer from the developer nozzle to the substrate while rotating the substrate held by the substrate holder,
A substrate holder for holding the substrate;
A rotation drive unit that rotates the substrate holding unit around a vertical axis;
A developer nozzle for applying a developer to the substrate held by the substrate holder;
An operation mechanism for operating the developer nozzle;
The developer nozzle is operated so that the discharge position of the developer moves from the peripheral portion of the substrate to the central portion while rotating the substrate at the first rotation speed and discharging the developer from the developer nozzle. Steps,
Next, in a state where the developer is discharged to the central portion of the substrate, the rotational speed of the substrate is set to a second rotational speed lower than the first rotational speed in order to form a liquid pool at least in the central portion of the substrate. A rotating step;
And a step of rotating the substrate at a third rotational speed higher than the second rotational speed to spread the developer on the surface of the substrate, and a controller that outputs a control signal to perform A developing device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009042961A JP5262829B2 (en) | 2009-02-25 | 2009-02-25 | Developing apparatus and developing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009042961A JP5262829B2 (en) | 2009-02-25 | 2009-02-25 | Developing apparatus and developing method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010199323A JP2010199323A (en) | 2010-09-09 |
| JP5262829B2 true JP5262829B2 (en) | 2013-08-14 |
Family
ID=42823744
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009042961A Active JP5262829B2 (en) | 2009-02-25 | 2009-02-25 | Developing apparatus and developing method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5262829B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5315320B2 (en) * | 2010-11-09 | 2013-10-16 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Substrate processing method, program, computer storage medium, and substrate processing apparatus |
| JP6352230B2 (en) * | 2015-10-09 | 2018-07-04 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Substrate processing method, substrate processing apparatus, and recording medium |
| JP6769335B2 (en) * | 2017-02-22 | 2020-10-14 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Processing recipe evaluation method, storage medium, processing recipe evaluation support device, and liquid processing device |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS57198457A (en) * | 1981-06-01 | 1982-12-06 | Nec Corp | Developing method for photoresist |
| JPH0917723A (en) * | 1995-06-26 | 1997-01-17 | Dainippon Screen Mfg Co Ltd | Coating method for coating solution and its equipment |
| JP3451158B2 (en) * | 1996-01-19 | 2003-09-29 | 大日本スクリーン製造株式会社 | Method and apparatus for rotary development processing of substrate |
| JPH10232498A (en) * | 1997-02-19 | 1998-09-02 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | Developing device |
| JP2000232062A (en) * | 1999-02-12 | 2000-08-22 | Tokyo Electron Ltd | Developing method |
| JP4369325B2 (en) * | 2003-12-26 | 2009-11-18 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Development device and development processing method |
| JP2006203041A (en) * | 2005-01-21 | 2006-08-03 | Seiko Epson Corp | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device and spin coating device |
| JP4947711B2 (en) * | 2006-04-26 | 2012-06-06 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Development processing method, development processing program, and computer-readable recording medium recording the program |
| JP2009004597A (en) * | 2007-06-22 | 2009-01-08 | Sokudo:Kk | Substrate development method and developing apparatus |
| JP4985188B2 (en) * | 2007-07-30 | 2012-07-25 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Development method, development device, and storage medium |
| JP5308045B2 (en) * | 2008-03-24 | 2013-10-09 | 株式会社Sokudo | Development method |
-
2009
- 2009-02-25 JP JP2009042961A patent/JP5262829B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2010199323A (en) | 2010-09-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4947711B2 (en) | Development processing method, development processing program, and computer-readable recording medium recording the program | |
| JP5136103B2 (en) | Cleaning device and method, coating and developing device and method, and storage medium | |
| JP5151629B2 (en) | Substrate cleaning method, substrate cleaning apparatus, developing method, developing apparatus, and storage medium | |
| JP4324527B2 (en) | Substrate cleaning method and developing apparatus | |
| KR101184820B1 (en) | Developing apparatus, developing method and storage medium | |
| KR101347017B1 (en) | Developing device, developing method and storage medium | |
| KR101426665B1 (en) | Fluid processing device and fluid processing method | |
| JPWO2005050724A1 (en) | Substrate cleaning method, substrate cleaning apparatus, and computer-readable recording medium | |
| JP5098964B2 (en) | Wafer cleaning method and storage medium | |
| KR20100132915A (en) | Coating, developing apparatus and cleaning method for backside of substrate | |
| JP6301281B2 (en) | Substrate liquid processing method, substrate liquid processing apparatus, and storage medium | |
| CN108028195B (en) | Substrate processing method, substrate processing apparatus, and storage medium | |
| TW201919776A (en) | Substrate processing apparatus, substrate processing method and storage medium | |
| JP4900397B2 (en) | Liquid processing equipment | |
| JP5262829B2 (en) | Developing apparatus and developing method | |
| JP2008060104A (en) | Substrate treatment method and substrate-treating device | |
| JP7073658B2 (en) | Board processing method, board processing device, and storage medium | |
| TW202142321A (en) | Substrate processing method, and substrate processing device | |
| JP5541311B2 (en) | Substrate cleaning method, substrate cleaning apparatus, developing method, developing apparatus, and storage medium | |
| JP5183562B2 (en) | Coating film forming apparatus and coating film forming method | |
| JP5104994B2 (en) | Developing device, developing method, and storage medium | |
| JP2019047131A (en) | Coating and developing method, storage medium, and coating and developing apparatus | |
| JP2010141162A (en) | Method of processing substrate, program, computer storage medium and substrate processing system | |
| JP2008118042A (en) | Method for cleaning substrate | |
| JP6318012B2 (en) | Substrate processing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20101102 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20121226 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130108 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130311 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130402 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130415 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 5262829 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |