JP5258222B2 - Camera with shake correction function - Google Patents
Camera with shake correction function Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5258222B2 JP5258222B2 JP2007204937A JP2007204937A JP5258222B2 JP 5258222 B2 JP5258222 B2 JP 5258222B2 JP 2007204937 A JP2007204937 A JP 2007204937A JP 2007204937 A JP2007204937 A JP 2007204937A JP 5258222 B2 JP5258222 B2 JP 5258222B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- shake correction
- signal
- output
- unit
- abnormal signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Studio Devices (AREA)
- Adjustment Of Camera Lenses (AREA)
Description
本発明は、ビデオカメラやスチルカメラ等の撮影装置の振動によって生ずる像振れを検出し、この像振れを低減するための振れ補正機能付き撮影装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a photographing apparatus with a blur correction function for detecting image blur caused by vibration of a photographing apparatus such as a video camera or a still camera and reducing the image blur.
近年の撮影装置は、オートフォーカスや自動露出を始めとする自動化及び電子化が著しく進んでいる。その中でも、撮影時に生ずる手振れ等の振動を検出し、像振れを低減する振れ補正機能を備えた撮影装置が一般的になりつつある。 2. Description of the Related Art In recent years, photographing apparatuses are remarkably advanced in automation and computerization including autofocus and automatic exposure. Among them, photographing apparatuses having a shake correction function that detects vibrations such as camera shake occurring during photographing and reduces image shake are becoming popular.
一方、携帯電話や無線LAN等の普及により、撮影装置がこれらの電波に晒される機会が増えており、このような電磁波によって振れ補正機能が誤動作してしまう可能性が生じている。 On the other hand, with the widespread use of mobile phones, wireless LANs, and the like, there are increasing opportunities for the photographing apparatus to be exposed to these radio waves, and there is a possibility that the shake correction function malfunctions due to such electromagnetic waves.
機器の振動を検出するためのセンサには、角速度センサや加速度センサが用いられているが、これらのセンサは微弱な信号により振動を検出するため、電磁波や強い衝撃等の外乱に弱いという欠点を持っている。特許文献1では、角速度センサとそれに隣接して配置された加速度センサとを有する装置であって、加速度センサの信号からジャイロセンサの誤出力を判定する提案がされている。
Angular velocity sensors and acceleration sensors are used as sensors for detecting the vibrations of equipment, but these sensors detect vibrations with weak signals, so they are vulnerable to disturbances such as electromagnetic waves and strong impacts. have.
従来、電磁波による外乱から振動検出センサを守るためには、導電性部材や高透磁率部材、電波吸収材によるセンサの保護を行っている。このような機構的な対策では、専用のシールド部品を追加しなければならず、コストアップの要因となる。また、特許文献1のように2種類の振れ検出センサがあれば、互いのセンサの異常状態を把握することが可能であるが、撮影装置では1種類の振れ検出センサにより振動を検出する場合が多く実用的ではない。
Conventionally, in order to protect the vibration detection sensor from disturbance due to electromagnetic waves, the sensor is protected by a conductive member, a high permeability member, or a radio wave absorber. In such a mechanistic measure, it is necessary to add a dedicated shield part, which increases the cost. In addition, if there are two types of shake detection sensors as in
本発明の目的は、上述の課題を解消し、異常信号を検出しても正常な像振れ補正を行い得る振れ補正機能付き撮影装置を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to solve the above-described problems and provide an imaging apparatus with a shake correction function that can perform normal image shake correction even when an abnormal signal is detected.
上記課題を解決するために本発明に係る振れ補正機能付き撮影装置の技術的特徴は、振れ信号を検出する振れ信号検出手段と、前記振れ信号検出手段とは別のレンズ制御に関する信号を検出する信号検出手段と、前記振れ信号検出手段および前記信号検出手段に重畳した異常信号を検出する異常信号検出手段と、振れ補正特性を変更する振れ補正特性変更手段とを有し、前記異常信号検出手段により前記振れ信号検出手段からの出力および前記信号検出手段からの出力に異常信号が検出された場合に、前記振れ補正特性変更手段により焦点距離に応じて前記振れ補正特性を変更することを特徴とする。 Technical characteristics of the shake correcting function imaging apparatus according to the present invention in order to solve the above problems, the vibration signal detecting means for detecting a vibration signal, from said vibration signal detecting means for detecting a signal relating to another lens control a signal detecting means, and the abnormal signal detecting means for detecting an abnormality signal superimposed on the vibration signal detecting means and the signal detecting unit, and a shake correction characteristic changing means changes the shake correction characteristics, the abnormal signal detecting means When the abnormal signal is detected in the output from the shake signal detecting means and the output from the signal detecting means , the shake correction characteristic changing means changes the shake correction characteristic according to a focal length. To do.
本発明の振れ補正機能付き撮影装置によれば、レンズ制御に利用している既存のせンサを用いて電磁波等による機器の異常を検出することが可能であり、振れ補正の異常動作を低減することができる。また、複数のセンサにより異常信号を検出しているため、異常信号の検出精度を向上でき誤検出がない。 According to the photographing apparatus with a shake correction function of the present invention, it is possible to detect an abnormality of a device due to an electromagnetic wave or the like using an existing sensor used for lens control, and to reduce an abnormal operation of shake correction. Can do. In addition, since the abnormal signal is detected by a plurality of sensors, the detection accuracy of the abnormal signal can be improved and there is no erroneous detection.
本発明を図示の実施例に基づいて詳細に説明する。 The present invention will be described in detail based on the embodiments shown in the drawings.
図1は実施例1の振れ補正機能のブロック回路構成図を示している。図1において、光軸に沿って可変頂角プリズム1、固定のフロントレンズユニット2、光軸方向に移動して変倍を行うズームレンズユニット3、光量調整を行う絞りユニット4が配列されている。絞りユニット4の後方には、固定レンズユニット5、光軸方向に移動して焦点調節を行うフォーカスレンズユニット6、CCDセンサやCMOSセンサ等から成る撮像素子7が配列されている。また、撮像素子7の出力は、映像信号処理回路8を介して表示デバイスVTRに接続されている。
FIG. 1 is a block circuit configuration diagram of a shake correction function according to the first embodiment. In FIG. 1, a variable
撮影装置の角度振れを検出するジャイロセンサ9の出力は、DCカットフィルタ10、増幅器11を介して、パンニング制御部12、可変HPF(ハイパスフィルタ)13に接続され、パンニング制御部12の出力は可変HPF13に接続されている。可変HPF13の出力は位相・ゲイン補償部14、積分処理部15を介して減算器16に接続されている。また、積分処理部15の出力はパンニング制御部12にも接続されている。減算器16の他端には、可変頂角プリズム1の変位を検出するエンコーダ17の出力が信号処理回路18、増幅器20を介して接続されている。減算器16の出力は位相・ゲイン補償部21、駆動回路22を経て、可変頂角プリズム1のアクチュエータ23に接続されている。
The output of the
被写体からの光束は、可変頂角プリズム1及びレンズユニット2、ズームレンズユニット3、絞りユニット4、固定レンズユニット5、フォーカスレンズユニット6を通過して、撮像素子7の受光面上で結像する。撮像素子7では光電変換された電荷が蓄積され、所定のタイミングで電荷が読み出される。撮像素子7から出力された信号は映像信号処理回路8に送られ、撮像素子7からの出力信号に対して所定の増幅やガンマ補正などの各種処理を施して映像信号が生成され、映像信号は液晶ディスプレイパネル等の表示デバイスVTRに出力される。
The light flux from the subject passes through the
ジャイロセンサ9は撮影装置の角速度振れを検出し、撮影装置の振動を物理的又は機械的に検出する。本実施例ではジャイロセンサとしているが、加速度センサを用いて撮影装置の振動を検出してもよい。カットオフ周波数0.1Hz程度のDCカットフィルタ10は、ジャイロセンサ9からの出力信号のうち、直流成分を遮断して振動成分のみを通過させる。
The
増幅器11はDCカットフィルタ10から出力された角速度信号を所要のレベルに増幅し、増幅された角速度信号は可変HPF13に入力される。可変HPF13はパンニング制御部12による指令信号によりカットオフ周波数が変更され、入力される角速度信号のうちの所望の周波数帯域を得るために用いられる。
The
例えば、可変HPF13のカットオフ周波数が0.1Hz程度である場合には、手振れや体の揺れなどの振れ信号を通過させる。また、カットオフ周波数が100Hz以上の十分高い周波数である場合は振れ信号は通過されず、ジャイロセンサ9のリファレンス電位が出力され、振れ補正系はセンタリングされた状態となる。可変HPF13を経た角速度信号は位相・ゲイン補償部14に入力され、位相補償とゲイン設定が行われ、積分処理部15に送られる。積分処理部15を通過した信号は角変位信号となり、像振れ補正を行うための目標角変位信号となる。
For example, when the cut-off frequency of the
可変頂角プリズム1は光学式振れ補正を行い、対向配置された平板ガラス間に高屈折率の透明な弾性体又は不活性液体が封入されて構成され、平板ガラスを傾けることで光路を変位させることができる。可変頂角プリズム1の頂角或いは光軸振れ角を示す位置は、エンコーダ17により検出される。検出信号は信号処理回路18で積分処理部15の出力と同次元の位置信号に変換された後に、減算器16にフィードバックされる。減算器16の出力は、可変頂角プリズム1の目標角変位信号と実際の可変頂角プリズム1の位置信号との偏差値である。この偏差値に応じた信号が、位相・ゲイン補償部21で位相及びゲインの補償がなされることにより、振れ補正制御信号として駆動回路22に入力される。駆動回路22からの駆動信号に基づいて、アクチュエータ23は可変頂角プリズム1を駆動し振れ補正を行う。
The variable
パンニング制御部12は角速度信号や角変位信号を用いて、撮影装置がパンニング中であるかを判定し、この判定結果に応じて可変HPF13のカットオフ周波数を変更する。これにより、可変頂角プリズム1の機械端位置への突き当たりを防止したり、振れ補正を用いた撮影によって生じてしまう撮影者の船酔い現象を低減したり、振れ補正に係るパンニング制御を行っている。
The
図2は撮影装置の絞り制御機能のブロック回路構成図である。図1と同じ符号は同じ部材を示している。映像信号処理回路8の出力は目標絞り位置設定部31を介して減算器32に接続され、目標絞り位置設定部31には絞り操作部33の出力が接続されている。一方、絞りユニット4の絞り位置検出を行う絞り位置センサ34の出力は、増幅器35を経て減算器32に接続され、減算器32の出力は位相・ゲイン補償部36、駆動回路37を介して絞りユニット4のアクチュエータ38に接続されている。
FIG. 2 is a block circuit configuration diagram of the aperture control function of the photographing apparatus. The same reference numerals as those in FIG. 1 denote the same members. The output of the video
絞り位置センサ34は例えばホール効果により位置を検出するホールセンサや、可変抵抗式のポテンショメータやパルス発生を用いた検出センサ等が用いられている。絞り位置センサ34の出力は微弱であるため、増幅器35で増幅し、減算器32にフィードバックされる。目標絞り位置設定部31は映像信号処理回路8からの輝度情報、或いは絞り操作部33からの信号に応じて所望の絞り位置になるように目標絞り位置信号を生成する。減算器32の出力は、絞りユニット4の目標絞り位置信号と実際の絞りユニット4の位置信号との偏差値である。
As the
この偏差値に応じた信号が、位相・ゲイン補償部36で位相及びゲインの補償がされることにより、絞りユニット4を目標位置に駆動するための絞り制御信号として駆動回路37に入力される。アクチュエータ38では駆動回路37からの駆動信号に基づいて、絞りユニット4を駆動し光量調整を行う。
A signal corresponding to the deviation value is compensated for the phase and gain by the phase /
図3は異常信号検出機能及びその際の振れ補正動作機能のブロック回路構成図である。撮影装置の振動を角速度として検出するジャイロセンサ9の出力はDCカットフィルタ10と異常信号検出部41に接続されている。図1と同様に、DCカットフィルタ10の出力は増幅器11、可変HPF13、位相・ゲイン補償部14、積分処理部15に接続されている。異常信号検出部41の出力は振れ補正特性変更部42と絞り位置補正部43に接続されている。また、パンニング制御部12の出力が振れ補正特性変更部42、可変HPF13に接続されている。
FIG. 3 is a block circuit configuration diagram of the abnormal signal detection function and the shake correction operation function at that time. The output of the
また、ズーム操作部44の出力は焦点距離検出部45を経て振れ補正特性変更部42に接続されている。更に、絞り位置センサ34の出力は増幅器35を経て、異常信号検出部41と絞り位置補正部43に接続されている。
The output of the
異常信号検出部41はジャイロセンサ9及び絞り位置センサ34の重畳した異常信号を検出する。異常信号が検出された場合に、振れ補正特性変更部42は振れ補正動作の停止や焦点距離に応じた振れ補正動作の制限を行う。
The
焦点距離の情報はズーム操作部44及び焦点距離検出部45から得る。また、絞り位置補正部43は異常信号が大きい場合に、絞り位置も誤検出されてしまうので、絞り位置補正部43により補正を行うことで、異常信号検出時においても撮影が可能となる。
The focal length information is obtained from the
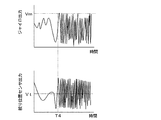
図4〜図6はジャイロセンサ9及び絞り位置センサ34の出力波形の一例を示している。図4は通常状態での出力波形である。閾値Vmによりジャイロセンサ9のジャイロ出力信号の異常ドリフト信号を判定する。時間T1〜T2の期間において、ジャイロセンサ9の出力信号には閾値Vmを超える異常ドリフト信号が発生している。しかし、絞り位置センサ34の出力信号は目標値Vtで安定しており、異常信号は認められず、このような場合では撮影装置はパンニング状態にあると判断し、通常のパンニング制御を行う。
4 to 6 show examples of output waveforms of the
図5では、時間T3以降においてジャイロセンサ9の出力信号に異常ドリフト信号が発生しており、絞り位置センサ34の出力信号も目標位置に対して異常ドリフトVnが発生している。このときには、撮影装置が異常な環境下に置かれていると判断し、振れ補正の停止や制限を行う。また、異常ドリフトVnが絞り目標位置に対して、数%程度のドリフト量ならば撮影には影響がないが、所定の例えば5%の閾値を超える場合には異常な光量変化が発生する懸念があるため、前述した絞り位置補正部43による位置補正処理を行うことになる。
In FIG. 5, an abnormal drift signal is generated in the output signal of the
図6では、時間T4以降にジャイロセンサ9、絞り位置センサ34の出力に異常周波数が重畳している。異常周波数の検出には周波数−電圧変換器(FVコンバータ)が用いられ、変換された電圧値から特定の異常周波数を容易に検知することができる。この場合も、図5での説明と同様に、撮影装置が異常な環境下に置かれていると判断し、振れ補正の停止や制限、絞り位置の補正処理を行う。
In FIG. 6, the abnormal frequency is superimposed on the outputs of the
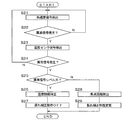
図7は前述した異常信号検出時における動作のフローチャート図である。 FIG. 7 is a flowchart of the operation when the abnormal signal is detected.
(ステップS11)ジャイロセンサ9の出力である角速度信号を検出する。
(Step S11) An angular velocity signal that is an output of the
(ステップS12)角速度信号に図4〜図6に示したような異常ドリフトや異常周波数の重畳がないかの判断を行う。異常信号がない場合にはスタートに戻り、異常信号が検出された場合には次のステップS13に進む。 (Step S12) It is determined whether or not there is an abnormal drift or an abnormal frequency superposition as shown in FIGS. If there is no abnormal signal, the process returns to the start, and if an abnormal signal is detected, the process proceeds to the next step S13.
(ステップS13)絞り位置センサ34の出力信号を検出する。
(Step S13) The output signal of the
(ステップS14)角速度信号の検出の際と同様に、絞り位置センサ34の出力に異常信号の重畳がないかの判断を行う。異常信号がない場合にはスタートに戻り、異常信号が検出された場合には、次のステップS15に進む。
(Step S14) Similarly to the detection of the angular velocity signal, it is determined whether or not an abnormal signal is superimposed on the output of the
(ステップS15)異常信号レベルの判定を行う。例えば、異常ドリフトの場合にはドリフト量からレベルを判定し、異常周波数の場合には振幅からレベルの判定を行う。 (Step S15) The abnormal signal level is determined. For example, in the case of abnormal drift, the level is determined from the drift amount, and in the case of abnormal frequency, the level is determined from the amplitude.
(ステップS16)ステップS15の判定で異常信号レベルが大きいと判定された場合に、光量変化も異常となってしまうため、絞り位置の信号補正を行い、適正な光量となるように制御を行う。 (Step S16) If it is determined in step S15 that the abnormal signal level is high, the light amount change also becomes abnormal. Therefore, the signal of the diaphragm position is corrected, and control is performed so as to obtain an appropriate light amount.
(ステップS17)異常信号が検出された際に、この異常な角速度信号を用いて振れ補正動作を行うと誤動作を招くため、振れ補正動作を停止する。 (Step S <b> 17) If a shake correction operation is performed using this abnormal angular velocity signal when an abnormal signal is detected, the shake correction operation is stopped because a malfunction occurs.
(ステップS18)ステップS15の判定で異常信号レベルが小さいと判定された場合に、焦点距離を検出する。この際に、光量変化は十分に小さいと判断し、絞り位置信号の補正は行わなくともよい。 (Step S18) When it is determined in step S15 that the abnormal signal level is low, the focal length is detected. At this time, it is determined that the change in the amount of light is sufficiently small, and the aperture position signal need not be corrected.
(ステップS19)異常信号レベルが小さい場合に、振れ補正の誤動作回避と正常な振れ補正動作の両立を図るため、前のステップS18で検出した焦点距離に応じて振れ補正特性を変更し、異常信号による悪影響がない範囲で振れ補正動作を行う。 (Step S19) When the abnormal signal level is small, in order to achieve both the avoidance of the shake correction malfunction and the normal shake correction operation, the shake correction characteristic is changed according to the focal length detected in the previous step S18, and the abnormal signal The shake correction operation is performed within the range where there is no adverse effect due to.
例えば、焦点距離が広角側にある場合には、感覚的に像振れが少なく感ずる。そのため、異常信号による影響をなくすように、振れ補正は殆ど行わない程度のゲイン或いはカットオフ周波数に可変HPF13の特性を変更する。
For example, when the focal length is on the wide-angle side, the image blur is felt sensibly. For this reason, the characteristic of the
一方、焦点距離が望遠側にある場合には、感覚的に像振れが大きく感ずる。そのため、異常信号による悪影響が出ない範囲で可変HPF13のゲイン又はカットオフ周波数を下げ、振れ補正を少しでも利かせるようにする。
On the other hand, when the focal length is on the telephoto side, the image blur is sensed greatly. For this reason, the gain or cut-off frequency of the
上述したように、ジャイロセンサ9及び絞り位置センサ34の2つのセンサの検出信号を基により、電磁波等による機器の異常を検出することができ、振れ補正の異常動作を低減することが可能となる。また、複数のセンサにより異常信号を検出しているため、異常信号の検出精度を向上でき誤検出が生ずることがない。
As described above, based on the detection signals of the two sensors, the
図8は実施例2のブロック回路構成図である。図3と同じ符号は同一の回路部材を示している。温度検出を行う温度センサ51の出力は、増幅器52を介して異常信号検出部41と温度情報補正部53に接続されている。また、異常信号検出部41の出力は温度情報補正部53に接続されている。
FIG. 8 is a block circuit configuration diagram of the second embodiment. The same reference numerals as those in FIG. 3 denote the same circuit members. The output of the
サーミスタや感温抵抗器等である温度センサ51からの温度信号は、増幅器52で増幅され、この温度信号は環境温度の変化に伴って発生するフォーカスレンズのピント移動や振れ補正駆動系の特性変化を補正するために用いられる。温度センサ51は測定すべきユニットの近くに配置しなければならず、増幅器52まで或いは増幅器52後の信号ライン距離が長くなる場合が多い。そのため、電磁波が信号ラインに飛び込み、図6の場合と同様の異常信号が発生し易くなる。そこで、実施例1のジャイロセンサ9と絞り位置センサ34による異常信号検出の場合と同様に、ジャイロセンサ9と温度センサ51とにより異常信号の検出を行う。
A temperature signal from a
異常信号が検出された場合に、振れ補正特性変更部42は振れ補正動作の停止や焦点距離に応じた振れ補正動作の制限を行う。焦点距離の情報はズーム操作部44及び焦点距離検出部45から得る。また、温度情報補正部53は異常信号が大きい場合に、温度情報も誤検出されてしまうので、温度情報補正部53により補正を行うことで、異常信号検出時においても撮影が可能となる。
When an abnormal signal is detected, the shake correction characteristic changing
図9はジャイロセンサ9と温度センサ51を用いた異常信号検出動作及び制御動作のフローチャート図である。
FIG. 9 is a flowchart of an abnormal signal detection operation and a control operation using the
(ステップS21)ジャイロセンサ9の出力である角速度信号を検出する。
(Step S21) An angular velocity signal that is an output of the
(ステップS22)角速度信号に異常周波数の重畳がないかの判断を行う。異常信号がない場合にはスタートに戻り、異常信号が検出された場合には次のステップS23に進む。 (Step S22) It is determined whether or not there is an abnormal frequency superimposed on the angular velocity signal. If there is no abnormal signal, the process returns to the start, and if an abnormal signal is detected, the process proceeds to the next step S23.
(ステップS23)温度センサ51の出力信号を検出する。
(Step S23) The output signal of the
(ステップS24)角速度信号の検出の場合と同様に、異常信号の重畳がないかの判断を行う。温度センサ51の場合に、出力信号の変化が環境温度の変化によるドリフトなのか、異常状態の発生によるドリフトなのかの区別が難しい。そこで、単位時間毎の温度変化の傾きを測定し、傾きが所定値よりも急である場合には、異常ドリフトが発生していると判断するようにするとよい。
(Step S24) As in the case of detecting the angular velocity signal, it is determined whether or not there is an abnormal signal superposition. In the case of the
異常信号がない場合にはスタートに戻り、異常信号が検出された場合には、ステップS25に進む。 If there is no abnormal signal, the process returns to the start, and if an abnormal signal is detected, the process proceeds to step S25.
(ステップS25)異常信号レベルの判定を行う。例えば、異常ドリフトの場合にドリフト量からレベルを判定し、異常周波数の場合には振幅からレベルの判定を行う。 (Step S25) The abnormal signal level is determined. For example, the level is determined from the drift amount in the case of an abnormal drift, and the level is determined from the amplitude in the case of an abnormal frequency.
(ステップS26)ステップS25の判定により、異常信号レベルが大きいと判定された場合に、検出される温度を誤認識してしまうため、温度情報の補正を行う。 (Step S26) If it is determined in step S25 that the abnormal signal level is high, the detected temperature is erroneously recognized, so that the temperature information is corrected.
(ステップS27)異常な角速度信号を用いて振れ補正動作を行った場合に、誤動作を招くため、振れ補正動作を停止する。 (Step S27) When the shake correction operation is performed using the abnormal angular velocity signal, the shake correction operation is stopped to cause a malfunction.
(ステップS28)ステップS25の判定で異常信号レベルが小さいと判定された場合に、焦点距離を検出する。この際に、電磁波等による外乱ノイズによる温度信号の異常変化は十分小さいと判断し、温度補正は行わなくてもよい。 (Step S28) When it is determined in step S25 that the abnormal signal level is low, the focal length is detected. At this time, it is determined that the abnormal change of the temperature signal due to disturbance noise due to electromagnetic waves or the like is sufficiently small, and the temperature correction may not be performed.
(ステップS29)異常信号レベルが小さい場合に、僅かでも像振れを軽減するために、ステップS26で検出した焦点距離に応じて振れ補正特性を変更し、異常信号による悪影響がない範囲で振れ補正動作を行う。 (Step S29) When the abnormal signal level is small, in order to reduce the image blur even slightly, the shake correction characteristic is changed according to the focal length detected in Step S26, and the shake correction operation is performed in a range where there is no adverse effect due to the abnormal signal. I do.
上述したように、ジャイロセンサ9と絞り位置センサ34を用いたときと同様に、ジャイロセンサ9及び温度センサ51の2つのセンサの検出信号を基に電磁波等による機器の異常を検出することできる。これにより、振れ補正の異常動作を低減することが可能となり、複数のセンサにより異常信号を検出しているため、異常信号の検出精度を向上でき、誤検出のない振れ補正機能付き撮影装置が得られる。
As described above, similarly to the case where the
本実施例では、可変頂角プリズム1を用いた振れ補正について説明したが、光軸と垂直な平面方向にレンズを移動し、光路を変位させて振れ補正を行うシフト方式の振れ補正等の他の振れ補正機構にも適用可能である。
In this embodiment, the shake correction using the variable
1 可変頂角プリズム
4 絞りユニット
9 ジャイロセンサ
12 パンニング制御部
13 可変HPF
17 エンコーダ
23、38 アクチュエータ
31 目標絞り位置設定部
34 絞り位置センサ
41 異常信号検出部
42 振れ補正特性変更部
43 絞り位置補正部
45 焦点距離検出部
51 温度センサ
53 温度情報補正部
1 Variable
Claims (10)
振れ信号を検出する振れ信号検出手段と、
前記振れ信号検出手段とは別のレンズ制御に関する信号を検出する信号検出手段と、
前記振れ信号検出手段および前記信号検出手段に重畳した異常信号を検出する異常信号検出手段と、
振れ補正特性を変更する振れ補正特性変更手段とを有し、
前記異常信号検出手段により前記振れ信号検出手段からの出力および前記信号検出手段からの出力に異常信号が検出された場合に、前記振れ補正特性変更手段により焦点距離に応じて前記振れ補正特性を変更することを特徴とする振れ補正機能付き撮影装置。 In an imaging device with shake correction function,
A shake signal detecting means for detecting a shake signal;
Signal detection means for detecting a signal related to lens control different from the shake signal detection means;
An abnormal signal detecting means for detecting an abnormal signal superimposed on the shake signal detecting means and the signal detecting means;
And a shake correction characteristic changing means for changing the shake correction characteristic,
When an abnormal signal is detected in the output from the shake signal detecting means and the output from the signal detecting means by the abnormal signal detecting means, the shake correction characteristic changing means changes the shake correction characteristic according to the focal length. An imaging apparatus with a shake correction function, characterized in that:
前記異常信号のドリフト量が所定の値以下である場合、前記絞り位置検出手段からの出力の補正を行わず、前記振れ補正特性変更手段により焦点距離に応じて前記振れ補正特性を変更することを特徴とする請求項3に記載の振れ補正機能付き撮影装置。 When an abnormal signal is detected in the output from the shake signal detecting means and the output from the aperture position detecting means, and the drift amount of the abnormal signal exceeds a predetermined value, the aperture position detecting means detects the aperture position. Correcting the output from the means, and stopping the shake correction by the shake correction characteristic changing means,
When the drift amount of the abnormal signal is not more than a predetermined value , the shake correction characteristic is changed according to the focal length by the shake correction characteristic changing unit without correcting the output from the aperture position detecting unit. The photographing apparatus with a shake correction function according to claim 3 .
前記異常信号の振幅が前記所定の値以下であった場合、前記絞り位置検出手段からの出力の補正を行わず、前記振れ補正特性変更手段により焦点距離に応じて前記振れ補正特性を変更することを特徴とする請求項3に記載の振れ補正機能付き撮影装置。 When an abnormal signal exceeding a predetermined frequency is detected in the output from the shake signal detecting unit and the output from the aperture position detecting unit, and the amplitude of the abnormal signal exceeds a predetermined value, the aperture position correcting unit While correcting the output from the aperture position detecting means, and stopping the shake correction by the shake correction characteristic changing means,
When the amplitude of the abnormal signal is less than or equal to the predetermined value, the shake correction characteristic is changed according to the focal length by the shake correction characteristic changing unit without correcting the output from the aperture position detecting unit. The photographing apparatus with a shake correction function according to claim 3 .
前記異常信号のドリフト量が所定の値以下であった場合、前記温度検出手段からの出力の補正を行わず、前記振れ補正特性変更手段により焦点距離に応じて前記振れ補正特性を変更することを特徴とする請求項7に記載の振れ補正機能付き撮影装置。 When an abnormal signal is detected in the output from the shake signal detecting means and the output from the temperature detecting means, and the drift amount of the abnormal signal exceeds a predetermined value, the temperature correcting means While correcting the output, stop the shake correction by the shake correction characteristic changing means,
When the drift amount of the abnormal signal is less than or equal to a predetermined value, the shake correction characteristic is changed according to the focal length by the shake correction characteristic changing unit without correcting the output from the temperature detecting unit. The photographing apparatus with a shake correction function according to claim 7 , wherein:
前記異常信号の振幅が前記所定の値以下であった場合、前記温度検出手段からの出力の補正を行わず、前記振れ補正特性変更手段により焦点距離に応じて前記振れ補正特性を変更することを特徴とする請求項7に記載の振れ補正機能付き撮影装置。 When an abnormal signal exceeding a predetermined frequency is detected in the output from the shake signal detecting means and the output from the temperature detecting means, and the amplitude of the abnormal signal exceeds a predetermined value, the temperature correcting means While correcting the output from the detection means, stop the shake correction by the shake correction characteristic change means,
When the amplitude of the abnormal signal is equal to or less than the predetermined value, the shake correction characteristic is changed according to the focal length by the shake correction characteristic changing unit without correcting the output from the temperature detecting unit. The photographing apparatus with a shake correction function according to claim 7 , wherein:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007204937A JP5258222B2 (en) | 2007-08-07 | 2007-08-07 | Camera with shake correction function |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007204937A JP5258222B2 (en) | 2007-08-07 | 2007-08-07 | Camera with shake correction function |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009042332A JP2009042332A (en) | 2009-02-26 |
| JP2009042332A5 JP2009042332A5 (en) | 2010-08-12 |
| JP5258222B2 true JP5258222B2 (en) | 2013-08-07 |
Family
ID=40443153
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007204937A Expired - Fee Related JP5258222B2 (en) | 2007-08-07 | 2007-08-07 | Camera with shake correction function |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5258222B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5276535B2 (en) * | 2009-07-15 | 2013-08-28 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image blur correction apparatus, optical apparatus including the same, image pickup apparatus, and image blur correction apparatus control method |
| JP6046931B2 (en) * | 2011-08-18 | 2016-12-21 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof |
| JP7305464B2 (en) * | 2019-07-02 | 2023-07-10 | キヤノン株式会社 | Optical device and its control method |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2517576B2 (en) * | 1987-01-12 | 1996-07-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | Camera system |
| JPH04308823A (en) * | 1991-04-05 | 1992-10-30 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Camera provided with jiggle correction function |
| JPH06281989A (en) * | 1993-03-26 | 1994-10-07 | Canon Inc | Image blurring correcting device |
| JPH11231389A (en) * | 1998-02-16 | 1999-08-27 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Controller for camera |
| JP4627144B2 (en) * | 2004-02-25 | 2011-02-09 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Display device |
| US7124632B2 (en) * | 2004-07-26 | 2006-10-24 | Bei Technologies, Inc. | Electronically configurable rate sensor circuit and method |
| JP2007065592A (en) * | 2005-09-02 | 2007-03-15 | Nikon Corp | Camera system and lens barrel |
-
2007
- 2007-08-07 JP JP2007204937A patent/JP5258222B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009042332A (en) | 2009-02-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2458426B1 (en) | Image pickup apparatus including image shake correction | |
| US8811809B2 (en) | Image stabilization apparatus, control method therefor, optical apparatus and imaging apparatus | |
| US9170429B2 (en) | Optical apparatus and image capturing apparatus, and method of controlling the same and storage medium | |
| US7634181B2 (en) | Image stabilizing system and optical apparatus | |
| US20150036011A1 (en) | Image shake correcting apparatus and control method for same, lens barrel, optical apparatus, and imaging apparatus | |
| JP2012037778A (en) | Image pickup apparatus | |
| KR101117010B1 (en) | Vibration correction control circuit and imaging device using the same | |
| JP2011139167A5 (en) | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP6769696B2 (en) | Position detector | |
| US8488955B2 (en) | Optical device and control method therefor | |
| JP2015185925A (en) | Imaging device and control method thereof | |
| JP6039212B2 (en) | Image blur correction apparatus, imaging apparatus, and image blur correction apparatus control method | |
| JP5258222B2 (en) | Camera with shake correction function | |
| JP2012128356A (en) | Shake correction device and optical apparatus | |
| JP2013210614A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JP6930049B2 (en) | Control method of drive device and image pickup device | |
| JP5241019B2 (en) | Lens device with shift lens for vibration isolation | |
| JP4689328B2 (en) | Shooting system | |
| JP2007140064A (en) | Optical equipment with image blur correcting function | |
| JP5383216B2 (en) | Optical instrument with shake correction function | |
| JP5276535B2 (en) | Image blur correction apparatus, optical apparatus including the same, image pickup apparatus, and image blur correction apparatus control method | |
| JP4679236B2 (en) | Camera shake detection device and photographing device | |
| JP2017194531A (en) | Vibration proof control device | |
| JP4530910B2 (en) | Camera shake detection device and photographing device | |
| KR20080088521A (en) | Vibration correction device and method, manufacturing method of the vibration correction device, and imaging device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20100218 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20100630 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20111227 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120117 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120319 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120529 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130228 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130423 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160502 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 5258222 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |