JP5073782B2 - Information transmission method, apparatus and system - Google Patents
Information transmission method, apparatus and system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5073782B2 JP5073782B2 JP2010118057A JP2010118057A JP5073782B2 JP 5073782 B2 JP5073782 B2 JP 5073782B2 JP 2010118057 A JP2010118057 A JP 2010118057A JP 2010118057 A JP2010118057 A JP 2010118057A JP 5073782 B2 JP5073782 B2 JP 5073782B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- spatial area
- divergence
- degree
- boundary
- cumulative
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 58
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 title 1
- 230000001186 cumulative effect Effects 0.000 claims description 151
- 238000002716 delivery method Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 13
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010365 information processing Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
本発明は、情報処理に関し、特に、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を発信するための方法、装置及びシステムに関する。 The present invention relates to information processing, and more particularly to a method, apparatus, and system for transmitting information associated with a spatial area to an object.
ロケーション情報は、ユーザと環境間の地理的関係を特定するための基本的なコンテキストの一種であり、これによりユーザの行動をより深く理解することが可能になる。近年、位置情報を提供する方法とシステムは、ますます多くの注目を集めてきている。特に、室内の環境および市街地の環境にとってより一層多くの注目を集めている。 Location information is a kind of basic context for specifying a geographical relationship between a user and an environment, and this enables a deeper understanding of user behavior. In recent years, methods and systems for providing location information have received more and more attention. In particular, it has attracted more attention for indoor environments and urban environments.
現在、例えば、オフィス、医療機関、鉱山、地下鉄、スマートビルディング、あるいはホテル等のような様々な適用状況において、リアルタイムの正確な位置追跡に対する市場要求はますます高まってきている。
多くの位置情報に基づいた用途においては、通常、空間を空間エリアあるいは空間グリッドと呼ばれる複数のエリアに区分けする必要がある。
ユーザがある特定の空間エリアに位置する場合、情報配信システムは、ユーザの位置を検出することにより、ユーザの携帯型端末に対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を自動的に配信する。その結果として、ユーザに快適な体験を供給する。
Currently, there is an increasing market demand for real-time accurate location tracking in various applications such as offices, medical institutions, mines, subways, smart buildings, or hotels.
In applications based on a lot of position information, it is usually necessary to divide a space into a plurality of areas called spatial areas or spatial grids.
When the user is located in a specific spatial area, the information distribution system automatically distributes information associated with the spatial area to the user's portable terminal by detecting the position of the user. As a result, it provides a comfortable experience to the user.
例えば、観光客が見知らぬ都市を観光する場合、観光客の位置に従って近くのホテルおよびレストランに関する情報を観光客に配信することは、観光客に利便性をもたらす。
参観者が博物館を見学する場合、展示された各展示品は、展示された展示品に対応する空間エリアにあるとみなすことができる。
参観者が閲覧するのに展示された展示品に近づけば、展示された展示品に関する情報が、参観者の位置に基づいて参観者に配信される。
顧客がショッピング・モールにおいて買い物をする場合、各商品はその商品に対応する空間エリアにあるとみなすことができる。顧客が興味のある商品に接近すれば、その商品に関する情報が顧客の携帯電話あるいは公共の公共のディスプレイに配信される。
For example, when a tourist tours a strange city, delivering information about nearby hotels and restaurants to the tourist according to the location of the tourist brings convenience to the tourist.
When the visitor visits the museum, each exhibited exhibit can be considered to be in a spatial area corresponding to the exhibited exhibit.
If the exhibitor approaches the exhibit displayed for viewing, information on the exhibited exhibit is distributed to the viewer based on the location of the exhibitor.
When a customer shop at a shopping mall, each product can be considered to be in a spatial area corresponding to that product. When a customer approaches an item of interest, information about the item is delivered to the customer's mobile phone or public public display.
これまで、空間エリアに関連付けた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するいくつかの方法が既に提案されている。
しかしながら、これらの関連技術による方法は、非常に限定的であり、例えば、比較的低い測位精度に適したものである。
オブジェクトが、比較的高い測位精度を有するシステムにおける空間エリアを頻繁に横断する場合、オブジェクトに配信される情報が頻繁に切り替えられる事態が引き起こされ、ユーザのにとって好ましくない影響をもたらすことになる。
So far, several methods for distributing information associated with a spatial area to an object have already been proposed.
However, these related art methods are very limited, for example, suitable for relatively low positioning accuracy.
If an object frequently traverses a spatial area in a system with relatively high positioning accuracy, the information delivered to the object will be frequently switched, which will have an undesirable effect on the user.
従って、高い測位精度を有するシステム内のオブジェクトに情報を配信するために適応された技術的解決法が、特にこの技術分野において必要とされている。 Therefore, there is a need in the art, particularly in the art, for technical solutions adapted to deliver information to objects in a system with high positioning accuracy.
本発明の目的は、空間エリアに関連付けた情報にオブジェクトに配信するために使用される技術的解決方法を提供し、特に、高い測位精度を有するシステムにおいてオブジェクトに情報を配信するのに適した情報配信方法、装置およびシステムを提供することにある。 The object of the present invention is to provide a technical solution used to deliver to an object information associated with a spatial area, in particular information suitable for delivering information to an object in a system with high positioning accuracy. It is to provide a distribution method, apparatus, and system.
本発明による情報配信方法は、情報配信装置による情報配信方法であって、受信手段が、1つ以上の空間エリアを含む空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータの受信するステップと、配信手段が、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップと、配信手段が備える即時的乖離度決定手段が、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定する即時的乖離度決定ステップと、配信手段が備える累積的乖離度取得手段が、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得する累積的乖離度取得ステップと、配信手段が備える配信制御手段が、累積的剥離度に基づいて、オブジェクトに対する配信を制御する配信制御ステップとを有し、乖離度が、即時的乖離度と累積的乖離度を含む。 An information distribution method according to the present invention is an information distribution method by an information distribution apparatus, in which a reception unit receives a position parameter of an object in a space including one or more spatial areas, and the distribution unit includes each space. Distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object by using the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area based on the degree of divergence of the area, and an immediate divergence determining means included in the distribution means However, based on the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area, an immediate divergence degree determining step for determining an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area, and a cumulative divergence degree acquisition means provided in the distribution means are provided for each spatial area. The cumulative divergence acquisition step for acquiring the cumulative divergence of each spatial area based on the immediate divergence of And a distribution control means included in the distribution means includes a distribution control step for controlling distribution to the object based on the cumulative degree of separation, and the degree of divergence includes the immediate degree of divergence and the degree of cumulative divergence .
本発明による情報配信装置は、1つ以上の空間エリアを含む空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータの受信する受信手段と、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信する配信手段とを備え、乖離度が、即時的乖離度と累積的乖離度を含み、配信手段が、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定する即時的乖離度決定手段と、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得する累積的乖離度取得手段と、累積的剥離度に基づいて、オブジェクトに対する配信を制御する配信制御手段とを含む。 The information distribution apparatus according to the present invention is configured to receive a position parameter of an object in a space including one or more spatial areas, and based on the degree of divergence between the spatial areas, the position parameter of the object and the boundary between the spatial areas. Using a distribution means for distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object , the divergence degree includes an immediate divergence degree and a cumulative divergence degree, and the distribution means includes the position parameter of the object and Based on the boundary of each spatial area, an immediate divergence determination means for determining an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area, and a cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the present time based on the immediate divergence degree of each spatial area A cumulative divergence acquiring unit that acquires the degree, and a distribution control unit that controls distribution to the object based on the cumulative peeling degree .
本発明の他の特徴と利点は、添付図面を参照する好適な実施の形態によって明らかとなるであろう。 Other features and advantages of the present invention will become apparent from the preferred embodiments with reference to the accompanying drawings.
本発明によれば、高い測位精度を有するシステムにおいてオブジェクトに情報を配信するのに適した情報配信方法、装置およびシステムを提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the information delivery method, apparatus, and system suitable for delivering information to an object in the system which has high positioning accuracy can be provided.
他の目的および本発明の効果は、添付図面を参照した詳細な説明の記述によって、本発明の好適な実施の形態についてのより総合的な理解をもってより明らとなり、かつ容易に理解できるであろう。
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施の形態について説明する。こられの実施の形態は例として説明するものであり、本発明の範囲を制限するものでないことは十分に理解されるべきである。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. It should be appreciated that these embodiments are described by way of example and do not limit the scope of the invention.
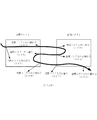
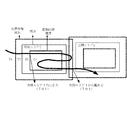
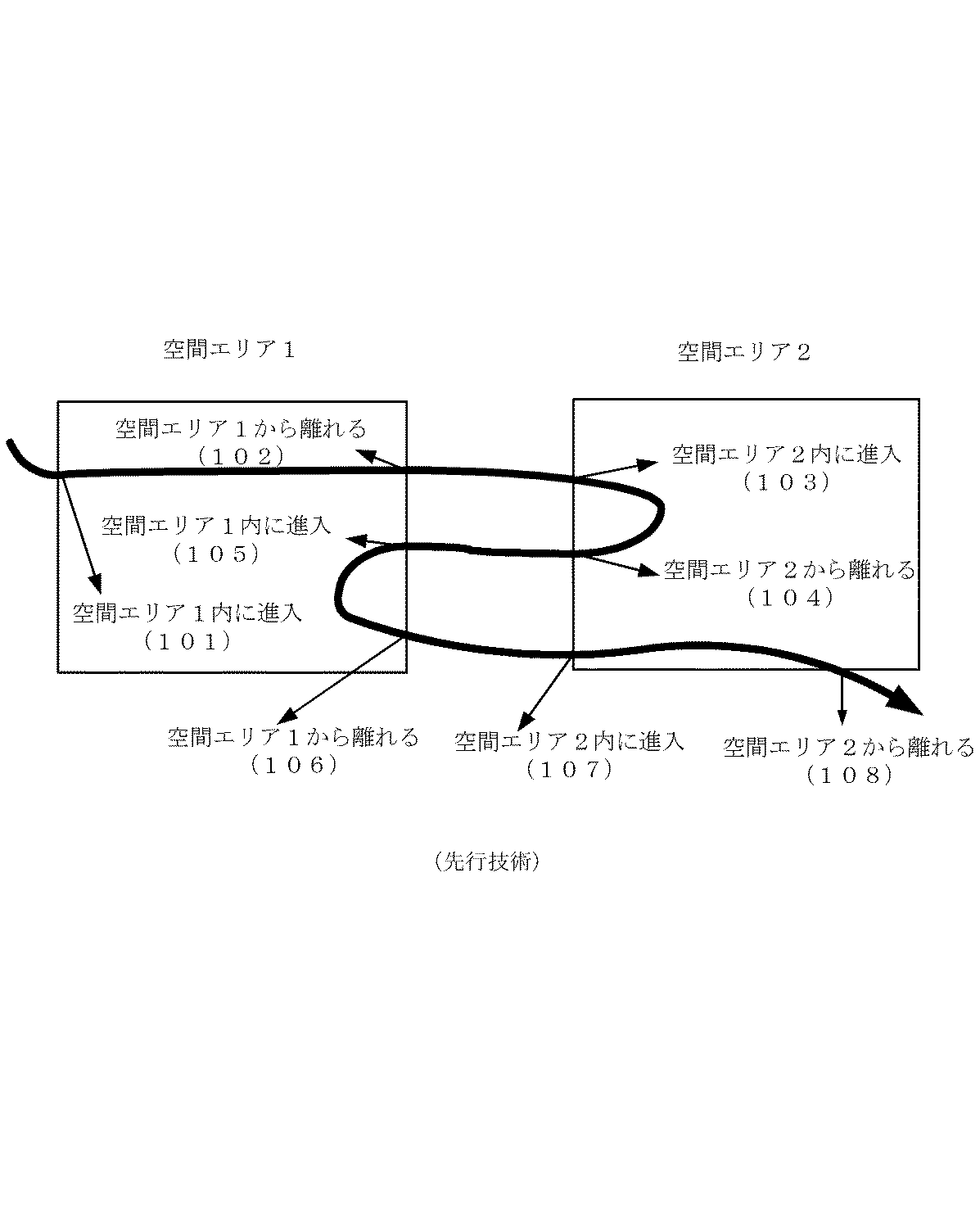
図1は、関連技術によるオブジェクトに対する空間エリアに関連付けた情報の提供の概要を示す図である。 FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an outline of provision of information associated with a spatial area for an object according to related technology.
非特許文献「ブルートゥースとWPAプッシュ型位置対応モバイル広告システム(Bluetooth and WAP Push Based Location-Aware
Mobile Advertising System)L. Aalto, N. Gothlin, J. Korhonen and T.
Ojala, In Proc of 2nd ACM MOBISYS, Boston, MA, June, 2004は、ブルートゥース測位とワイアレス・アプリケーション・プロトコル(WAP)を採用する正確な位置に基づく情報提供システムを提案する。図1に示すのはこの確実な位置に基づく情報配信方法である。この方法は、オブジェクトのリアルタイム位置に対して非常に敏感である。
Non-Patent Document “Bluetooth and WAP Push Based Location-Aware
Mobile Advertising System) L. Aalto, N. Gothlin, J. Korhonen and T.
Ojala, In Proc of 2nd ACM MOBISYS, Boston, MA, June, 2004 proposes an accurate location-based information provision system that employs Bluetooth positioning and Wireless Application Protocol (WAP). FIG. 1 shows an information distribution method based on this certain position. This method is very sensitive to the real-time position of the object.
図1は、例示とのして2つの空間エリア(すなわち、空間エリア1と空間エリア2)と、2つの空間エリア間のオブジェクトの移動の軌跡を示している。
101で、オブジェクトが外部から空間エリア1の境界に到達し、その後空間エリア1内に進入する。そのとき、オブジェクトに対する空間エリア1に関連付けた情報の配信が開始する。その後、オブジェクトは空間エリア1内を移動する。
空間エリア1内でのターゲットの移動中、空間エリア1に関連付けた情報は、常にターゲットに配信される。
102で、オブジェクトは空間エリア1の内部から境界に到達し、その結果空間エリア1から離れる。そのとき、空間エリア1に関連付けた情報のオブジェクトに対する配信が停止される。その後、オブジェクトがどの空間エリアにも進入しないので、何れの空間エリアに関連付けた情報もオブジェクトに対して配信されない。
103で、ターゲットが空間エリア2を進入すると、空間エリア2に関連付けた情報のターゲットに対する配信が開始する。
その後、ターゲットは空間エリア2内を移動する。
空間エリア2内でのターゲットの移動中、空間エリア1に関連付けた情報は、常にターゲットに配信される。
104で、ターゲットが空間エリア2から離れると、ターゲットに対する空間エリア2に関連付けた情報の配信が停止される。
105で、ターゲットが再び空間エリア1を進入すると、再びターゲットに対する空間エリア1に関連付けた情報の配信が開始する。
106で、ターゲットが再び空間エリア1から離れると、ターゲットに対する空間エリア1に関連付けた情報の配信が再び停止される。
107で、ターゲットが再度空間エリア2を進入すると、再びターゲットに対して空間エリア2に関連付けた情報の配信が開始する。
最後に、108で、ターゲットが再び空間エリア2から離れると、ターゲットに対する空間エリア2に関連づけた情報の配信が再び停止される。
FIG. 1 shows, by way of example, two spatial areas (namely, spatial area 1 and spatial area 2) and a trajectory of object movement between the two spatial areas.
In 101, the object reaches the boundary of the spatial area 1 from the outside, and then enters the spatial area 1. At that time, distribution of information associated with the spatial area 1 for the object starts. Thereafter, the object moves in the space area 1.
During the movement of the target in the space area 1, information associated with the space area 1 is always distributed to the target.
At 102, the object reaches the boundary from the inside of the spatial area 1 and consequently leaves the spatial area 1. At that time, distribution of the information associated with the space area 1 to the object is stopped. Thereafter, since the object does not enter any spatial area, information associated with any spatial area is not distributed to the object.
When the target enters the spatial area 2 at 103, distribution of information associated with the spatial area 2 to the target starts.
Thereafter, the target moves in the space area 2.
During the movement of the target in the space area 2, the information associated with the space area 1 is always delivered to the target.
When the target leaves the space area 2 at 104, distribution of information associated with the space area 2 to the target is stopped.
When the target enters the space area 1 again at 105, distribution of information associated with the space area 1 to the target starts again.
When the target leaves the space area 1 again at 106, the distribution of information associated with the space area 1 to the target is again stopped.
When the target enters the space area 2 again at 107, distribution of information associated with the space area 2 to the target starts again.
Finally, when the target leaves the spatial area 2 again at 108, the delivery of information associated with the spatial area 2 to the target is again stopped.
図1から分かるように、ターゲットに対してどの空間エリアに関する情報が配信されるかは、ターゲットの位置パラメータと空間エリアの境界に基づく。
ターゲットが複数空間エリアの境界を頻繁に横断する場合、ターゲットの位置の変更に伴ってターゲットに対する情報の配信が頻繁に切り替えられる。これは、ユーザにとって好ましくない体験をもたらす可能性がる。
As can be seen from FIG. 1, information about which spatial area is distributed to the target is based on the position parameter of the target and the boundary of the spatial area.
When the target frequently crosses the boundary of a plurality of spatial areas, the distribution of information to the target is frequently switched as the target position changes. This can lead to an undesirable experience for the user.
図1に示すような正確な位置に基づく情報提供方法は、システム内の空間エリアの範囲が比較的広い(例えば、数十平方メートルから数平方キロメートル)ことを前提として、ブルートゥースおよびGPSをベースとする情報提供システムに適応される。
しかしながら、図1に示した方法は、非常に正確な位置に基づいた情報配信システムには適応されない。その理由は、非常に正確な位置に基づく情報提供システムにおいて定義される空間エリアは比較的狭くかつ互いに密接してつながっているためである。
The information providing method based on an accurate position as shown in FIG. 1 is information based on Bluetooth and GPS on the premise that the range of the spatial area in the system is relatively wide (for example, several tens of square meters to several square kilometers). Adapted to the provision system.
However, the method shown in FIG. 1 is not applicable to a highly accurate location-based information distribution system. This is because the spatial areas defined in a highly accurate location-based information providing system are relatively narrow and closely connected to each other.
例えば、棚の上の商品の情報提供への用途において、商品は棚の上に非常に密接して置かれ、それらの間隔はほんの数センチメートルから数十センチメールである。
とても小さな空間エリアが各品物に対してのみ定義され、かつそれらの空間エリアは互いに密接につながっている。
そのような用途において、信号の送信機を保持するユーザ(すなわち、オブジェクト)がいくつかの空間エリアを無意識に通り抜ける時、もしこれまでの正確な位置に基づく情報提供方法を採用すれば、ユーザがそれらの空間エリア内の商品に興味を感じなくても、ユーザがこれらの商品に対応する空間エリアに進入するので、それらの商品に関連付けた情報がユーザの端末に配信されることになる。
そのような情報はユーザにとって無用である可能性があり、かつそのような用途に対してユーザの反感を引き起こす可能性がある。
For example, in informational applications for merchandise on shelves, merchandise is placed very closely on the shelves, and their spacing is only a few centimeters to tens of centimeters mail.
A very small spatial area is defined for each item only, and these spatial areas are closely connected to each other.
In such an application, when a user holding a signal transmitter (ie, an object) unconsciously passes through several spatial areas, if the user provides a method of providing information based on the accurate location so far, Even if the user does not feel interested in the products in these space areas, the user enters the space area corresponding to these products, so information associated with these products is distributed to the user's terminal.
Such information may be useless to the user and may cause the user to feel disliked for such use.
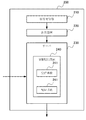
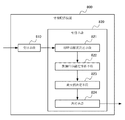
図2は、本発明の一実施の形態による情報配信システム200のブロック図である。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram of an
図2に示すように、情報配信システム200は、空間内のオブジェクトに位置し、測距信号を発するように構成された信号発信器210と、信号発信器から発された測距信号に基づいてオブジェクトの位置パラメータを取得するように構成された測位装置220と、空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを受信し、また、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの境界を使用して、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するように構成されたサーバ230とを備える。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
システム200の実現例について以下に詳細に説明する。
An implementation example of the
まず、信号発信器210はオブジェクトに設置可能である。例えば、ユーザが信号発信器210を手で持つことができる。また、信号発信器210は、測距信号を発信することができる。
一例では、サーバ230は、信号発信器210によって発信された測距信号と、測距信号を受信する測位装置200の位置パラメータを受信し、次に、サーバ230は、受信データに基づいて信号発信器210の位置パラメータを決定する。
他の例では、測位装置220が、信号発信器210によって発信された測距信号と、自身の位置パラメータによって、信号発信器210の位置パラメータを決定する。
信号発信器210自体は、本発明の技術分野において周知であり、ここでは詳細を説明しない。
First, the
In one example, the
In another example, the
The
測位装置220は、空間のどの場所にも設置することが可能である。
一例として、測位装置220は空間の頂部に設置される。その場合の最初の設置場所は任意であり、すなわち頂部のどの位置に設置してもよい。
測位装置220は、信号発信器210から測距信号を受信し、サーバ230が、信号発信器210によって発信された測距信号と測距信号を受信する測位装置220自身の位置パラメータによって、空間内の信号発信器210の位置を決定するために、その測距信号と測位装置220自身の位置パラメータをサーバ230に対して送信する。
他の実施例では、測位装置220は、信号発信器210によって発信された測距信号と自身の位置パラメータに基づいて、位置点シーケンス内の各位置点の位置パラメータを決定することができる。
The
As an example, the
The
In another embodiment, the
信号発信器210と測位装置220は、順番に設置する必要がないことを十分に理解すべきである。すなわち、信号発信器210と測位装置220を同時に配置しても、あるいは、最初に測位装置220を配置し、次に信号発信器210を空間特徴点に配置してもよい。
It should be appreciated that the
サーバ230は情報配信装置240を備える。この情報配信装置240は、空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを受信する受信手段241と、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信する配信手段242とを備える。
サーバ230は、さらに、信号発信器210によって発信された測距信号と測距信号を受信する測位装置220自身の位置パラメータを受信し、その結果として、受信データに基づいて信号発信器210の位置パラメータを決定する手段を備える。
The
The
図3は、図2に示す実施の形態による情報配信方法を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 3 is a flowchart for explaining an information distribution method according to the embodiment shown in FIG.
ステップ301において、空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを受信する。
In
ステップ302において、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、空間エリアに関連づけた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信する。
本発明は、乖離度に基づいてオブジェクトに対して情報を配信する種々の実施の形態を提供する。
In
The present invention provides various embodiments for distributing information to objects based on the degree of divergence.
本発明の一実施の形態において、乖離度は内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターを含んでいる。そして、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップは、各空間エリアの境界および各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および仮想の外部境界を取得することと、オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想の内部境界に入る時、オブジェクトが仮想外部境界を越えるまで、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信し始めることを含む。
図4〜図7は、そのような実施の形態による情報配信装置と方法を示し、その詳細については以下に説明する。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the degree of divergence includes an inner boundary factor and an outer boundary factor. Then, the step of distributing the information associated with the spatial area to the object is based on the boundary of each spatial area and the internal boundary factor and external boundary factor of each spatial area. Acquiring an external boundary includes starting to deliver information associated with the spatial area to the object until the object crosses the virtual external boundary when the object enters the virtual internal boundary of the spatial area.
4 to 7 show an information distribution apparatus and method according to such an embodiment, and details thereof will be described below.
本発明の他の実施の形態においては、乖離度は即時的乖離度と累積的乖離度を含んでいる。
オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップは、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定すること、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得すること、蓄積的乖離度をソートすることにより最大の累積的乖離度を決定すること、最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するのを停止すること、最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、最大の累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けられた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信することを含む。
図8および図9は、そのような情報配信のための装置および方法をそれぞれ示しており、その詳細については以下に説明する。
In another embodiment of the present invention, the divergence includes an immediate divergence and a cumulative divergence.
The step of distributing the information associated with the spatial area to the object is to determine the immediate divergence of each spatial area based on the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area, and the immediate divergence of each spatial area. To obtain the current cumulative divergence of each spatial area, to determine the maximum cumulative divergence by sorting the cumulative divergence, and to end the maximum cumulative divergence If it is greater than the value, stop delivering the same information as the information delivered at the previous time from the current time to the object, and if the maximum cumulative divergence is greater than the delivery threshold, Delivering information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence to the object.
FIG. 8 and FIG. 9 respectively show an apparatus and method for such information distribution, the details of which will be described below.
本発明のさらに他の実施の形態においては、乖離度が内部境界ファクター、外部境界ファクター、即時的乖離度および累積的乖離度を含んでいる。
オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップは、各空間エリアの境界と各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび(または)外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界を取得すること、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定すること、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得すること、蓄積的乖離度をソートすることにより最大の累積的乖離度を決定すること、最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するのを停止すること、最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、最大の累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けられた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信することを含んでいる。
In still another embodiment of the present invention, the divergence degree includes an internal boundary factor, an external boundary factor, an immediate divergence degree, and a cumulative divergence degree.
The step of distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object includes the virtual inner boundary of each spatial area and (or based on the boundary boundary of each spatial area and the internal boundary factor and / or external boundary factor of each spatial area. Or) obtaining a virtual external boundary, determining the immediate divergence of each spatial area based on the object's positional parameters and the virtual internal and / or virtual external boundary of each spatial area, and each spatial area Based on the immediate divergence level, obtain the cumulative divergence level of each spatial area at the present time, determine the maximum cumulative divergence level by sorting the cumulative divergence levels, and determine the maximum cumulative divergence level. If the degree is larger than the end threshold, the same information delivered at the previous time is delivered to the object from the current time. Stopping, if the maximum cumulative divergence is greater than the distribution threshold, from now on, delivering information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence to the object .
図4は、本発明の一実施の形態による情報配信装置400のブロック図である。
FIG. 4 is a block diagram of an
情報配信装置400は、空間(空間は1つ以上の空間エリアを含む)内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを受信する受信手段410と、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信する配信手段420とを備える。
配信手段420は、各空間エリアの境界と各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および仮想外部境界を取得する内部境界・外部境界取得手段421と、オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想の内部境界に入る時、オブジェクトが仮想外部境界を越えるまで、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信し始める決定手段422とを備える。
The
The
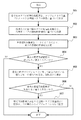
図5は、本発明の一実施の形態による情報配信方法を説明するフローチャートである。
本実施の形態においては、関連技術で使用されるような空間エリアの本当の境界を、空間エリアに関連付けた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するための判断基準として使用しない。その代わりに、図6に示されるような仮想の内部境界および仮想外部境界が使用される。
ここでは、オブジェクトに対して情報の配信を開始しオブジェクトに対する情報の配信を終了するタイミング(すなわち、情報配信開始タイミングと情報配信終了タイミング)が、仮想外部境界および仮想の内部境界に対するオブジェクト位置の関係によって決定される。
図5に示す情報配信方法が、図4に示す情報配信装置400によって実施される。
FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating an information distribution method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
In the present embodiment, the true boundary of the spatial area as used in the related art is not used as a criterion for distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object. Instead, virtual internal and virtual external boundaries as shown in FIG. 6 are used.
Here, the timing of starting the distribution of information to the object and ending the distribution of information to the object (that is, the information distribution start timing and the information distribution end timing) is the relationship of the object position with respect to the virtual outer boundary and the virtual inner boundary. Determined by.
The information distribution method shown in FIG. 5 is performed by the
ステップ501において、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および仮想外部境界が、各空間エリアの境界と各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて取得される。
In
図6は、本発明の一実施の形態による空間エリアの概要を示す図である。 FIG. 6 is a diagram showing an outline of a spatial area according to an embodiment of the present invention.
図6に示す実施の形態によれば、空間エリアの仮想の内部境界601および仮想外部境界603は、空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて空間エリアの境界602によって決定される。
本実施の形態において、空間エリアの乖離度は内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターを含む。境界602は空間エリアの本当の境界である。
仮想の内部境界601は、内部境界ファクターおよび境界602に基づいて決定される。
また、仮想外部境界603は、外部要因および境界602に基づいて決定される。
According to the embodiment shown in FIG. 6, the virtual
In the present embodiment, the degree of divergence of the spatial area includes an internal boundary factor and an external boundary factor. The
The virtual
The virtual
例えば、空間エリアの本当の境界は、
A=bound(x,y,z) (1)
として表すことができる。
ここで、bound(x,y,z)は、3次元座標系における空間エリアの境界関数を示す。
For example, the real boundary of the spatial area is
A = bound (x, y, z) (1)
Can be expressed as
Here, bound (x, y, z) represents a boundary function of the spatial area in the three-dimensional coordinate system.
仮想外部境界は、空間エリアを含んでおり、本当の境界より大きいか或いは等しい仮想的境界である。図6に示す仮想外部境界603は、境界602の外側にある。
仮想外部境界は、以下のように表すことができる。
ここで、lx、ly、lzは、それぞれ、空間エリアの外部境界ファクターであり、3次元座標系のx, y, z軸方向に沿った拡大係数を示す。外部境界ファクターlx、ly、lzが大きいほど、仮想外部境界は大きくなる。
A virtual outer boundary is a virtual boundary that includes a spatial area and is greater than or equal to a real boundary. A virtual
The virtual outer boundary can be expressed as follows:
Here, l x , l y , and l z are external boundary factors of the spatial area, respectively, and indicate enlargement factors along the x, y, and z axis directions of the three-dimensional coordinate system. The larger the outer boundary factors l x , l y , and l z , the larger the virtual outer boundary.
仮想内部境界は、本当の境界より小さいか或いは等しい仮想的境界である。
図6に示す仮想内部境界601は、境界602の内部にある。
仮想内部境界は、以下のように表すことができる。
AVSI=Bound(sxx,syy,szz)
(sx,sy,sz≧1) (3)
ここで、sx、sy、sz
は、それぞれ、空間エリアの内部境界ファクターであり、3次元座標系のx, y, z軸方向に沿った縮小係数を示す。内部境界ファクターsx、sy、sz
が大きいほど、仮想内部境界は小さくなる。
A virtual inner boundary is a virtual boundary that is less than or equal to the true boundary.
A virtual
The virtual inner boundary can be expressed as follows:
A VSI = Bound (s x x, s y y, s z z)
(s x , s y , s z ≧ 1) (3)
Where s x , s y , s z
Are internal boundary factors of the spatial area, and indicate reduction factors along the x, y, and z axis directions of the three-dimensional coordinate system. Internal boundary factors s x , s y , s z
The larger the, the smaller the virtual inner boundary.
基本的に、内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターは空間の測位精度に関係する。
測位精度がより高ければ(例えば、1cm)、内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターは、「1」に近くなる。
反対に、測位精度がより低ければ(例えば、1m)、内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターは、「1」より非常に大きくなる。
すなわち、測位精度が高くなるほど、内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターは「1」により近くなる。
Basically, the inner and outer boundary factors are related to the positioning accuracy of the space.
If the positioning accuracy is higher (for example, 1 cm), the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor are closer to “1”.
Conversely, if the positioning accuracy is lower (for example, 1 m), the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor are much larger than “1”.
That is, the higher the positioning accuracy, the closer the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor are to “1”.
仮想内部境界601、本当の境界602および仮想外部境界603は、空間エリアを、4つの子エリアT1、T2、T3およびT4に区分けする。
オブジェクトが、仮想内部境界601(すなわち、AVSI)内にいる時、オブジェクトは子エリアT1に位置する。
オブジェクトが仮想内部境界601の外側でかつ本当の境界602(すなわち、A)内にいる時、オブジェクトは子エリアT2に位置する。
オブジェクトが本当の境界602の外側でかつ仮想外部境界603(すなわち、AVSO)内にいる時、オブジェクトは子エリアT3に位置する。
また、オブジェクトが仮想外部境界603の外にいる時、オブジェクトは子エリアT4に位置する。
The virtual
When the object is within the virtual inner boundary 601 (ie, A VSI ), the object is located in the child area T1.
When the object is outside the virtual
When the object is outside the
When the object is outside the virtual
ステップ502において、空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータが受信される。
In
上述したように、空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータは、測位装置220によって決定するか、あるいは、オブジェクトが保持する信号発信器によって発信された測距信号と測位装置220の位置に従ってサーバ230によって決定することができる。
この位置パラメータは、空間内のオブジェクトの3次元座標を用いることができる。
As described above, the position parameter of the object in the space is determined by the
As the position parameter, the three-dimensional coordinates of the object in the space can be used.
ステップ503において、情報配信フラグが「1」に等しいかどうかを判断する。
In
この情報配信フラグは、直前の時点でオブジェクトに対して情報を発信するかどうか示すのための識別子であり、「YES」あるいは「NO」を区別して示すことができる文字、数字等のどのような識別子であってもよい。
例えば、情報配信フラグは、「1」と「0」、「YES」と「NO」、あるいは漢字の「是」と「否」などを含み、本実施の形態で使用する「1」と「0」に限定されない。
This information distribution flag is an identifier for indicating whether or not information is transmitted to the object at the previous time point, and can be any character, number, or the like that can distinguish between “YES” or “NO”. It may be an identifier.
For example, the information distribution flag includes “1” and “0”, “YES” and “NO”, or “k” and “no” in Chinese characters, and “1” and “0” used in the present embodiment. It is not limited to.
本実施の形態においては、オブジェクトに対して情報を配信することあるいはオブジェクトに対して情報を配信しないことを示すために、情報配信フラグとして数字の「1」と「0」を使用する。
情報配信フラグが「1」ならば、ある空間エリアに関連付けた情報が直前の時点でオブジェクトに対して配信されたと決定し、次に、処理はステップ507へ進む。
情報配信フラグが「0」ならば、ある空間エリアに関連付けた情報が直前の時点でオブジェクトに配信されていないと決定し、次に、処理はステップ504へ進む。
In the present embodiment, the numbers “1” and “0” are used as information distribution flags to indicate that information is distributed to an object or information is not distributed to an object.
If the information distribution flag is “1”, it is determined that the information associated with a certain spatial area has been distributed to the object at the previous time point, and the process then proceeds to step 507.
If the information distribution flag is “0”, it is determined that the information associated with a certain spatial area has not been distributed to the object at the previous time point, and the process then proceeds to step 504.
ステップ504において、オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想内部境界に進入するかどうかを判断する。
In
そのような判断を行うためには種々の方法が存在する。
例えば、オブジェクトと各空間エリアの仮想内部境界との間の距離は、ステップ502で受信したオブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの仮想内部境界に基づいて取得することができる。それらの距離の最小値に基づいて、オブジェクトが進入する空間エリアの仮想内部境界を決定することができる。
他の例では、オブジェクトと各空間エリアの仮想内部境界内のキーポイントとの間の平均距離は、ステップ502で受信したオブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの仮想内部境界内のいくつかのキーポイントの空間座標に基づいて取得することができる。その後、これらの平均距離の最小値に基づいてオブジェクトが進入する空間エリアの仮想の内部境界を決定することができる。
当業者が、様々な方法によって関連技術に従ってステップ504における判断を実行することができ、その方法は上記の特定の方法に限定されないことを十分に理解すべきである。
There are various ways to make such a determination.
For example, the distance between the object and the virtual internal boundary of each spatial area can be obtained based on the position parameter of the object received in
In another example, the average distance between the object and the keypoints within the virtual internal boundary of each spatial area is calculated by calculating the position parameter of the object received at
It should be appreciated that one skilled in the art can perform the determination in
オブジェクトがある空間エリアの仮想内部境界に進入すれば、処理はステップ505へ進む。そうでなければ、処理が終了する。 If the object enters the virtual internal boundary of a certain spatial area, the process proceeds to step 505. Otherwise, the process ends.
ステップ505において、情報配信フラグは、「1」に設定される。
In
直前の時点でオブジェクトに対して配信された情報がないことがステップ503で決定され、かつステップ504の判断で現時点でオブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想内部境界に進入するので、情報配信フラグは「1」にセットされる。
情報配信フラグの「0」から「1」への変化は、空間エリアに関連付けた情報が現時点からオブジェクトに対して配信され始めることを意味する。
In
The change of the information distribution flag from “0” to “1” means that information associated with the spatial area starts to be distributed to the object from the present time.
ステップ506において、空間エリアに関連付けた情報が、オブジェクトに対して配信され、その後処理が終了する。
In
ステップ507において、オブジェクトに配信される情報に関連付けた空間エリアが決定される。
In
ステップ503で情報配信フラグが「1」でないと判断されると、ステップ507において、配信された情報内の関連領域および識別子に従って情報が関連付けられたのがどの空間エリアであるかを決定する。
すなわち、直前の時点でオブジェクトに対して配信された情報がどの空間領域に関連付けられた情報であるかを決定することができる。
If it is determined in
That is, it is possible to determine to which spatial region the information distributed to the object at the immediately preceding time point is associated with information.
ステップ508において、オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想外部境界を越えるかどうかが判断される。
In
オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想外部境界を越えるかどうかを判断する複数の方法が存在する。 There are several ways to determine whether an object crosses the virtual external boundary of a spatial area.
例えば、仮想外部境界が複数の点で構成されると考えることができる。
仮想外部境界上のオブジェクトとその点との間の距離の最大値は、空間エリアの仮想外部境界上のオブジェクトと全てのポイントの位置パラメータに基づいて計算される。
距離の最大値が仮想外部境界の全ての点のうちのどの2点の間の距離より大きければ、オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想外部境界を越えると判定することができる。
For example, it can be considered that the virtual external boundary is composed of a plurality of points.
The maximum distance between the object on the virtual external boundary and the point is calculated based on the position parameters of the object on the virtual external boundary of the spatial area and all points.
If the maximum value of the distance is larger than the distance between any two of all the points on the virtual external boundary, it can be determined that the object exceeds the virtual external boundary of the spatial area.
当業者が、様々な方法によって関連技術に従ってステップ508における判断を実行することができ、その方法は上記の特定の方法に限定されないことを十分に理解すべきである。
It should be appreciated that one skilled in the art can perform the determination in
オブジェクトが、空間エリアの仮想外部境界を越えれば、処理はステップ509へ進む。そうでなければ、処理はステップ506へ進み、空間エリアに関連付けたオブジェクト情報のオブジェクトに対する配信が継続される。 If the object exceeds the virtual external boundary of the spatial area, processing proceeds to step 509. Otherwise, the process proceeds to step 506, and the distribution of the object information associated with the spatial area to the object is continued.
ステップ509において、オブジェクトに対する空間エリアに関連付けた情報の配信が停止され、そして情報配信フラグが「0」に設定される。
In
その後、処理が終了する。 Thereafter, the process ends.
図7は、図5に示す情報配信方法によってオブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信する例を示す概略図である。 FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram illustrating an example in which information associated with a spatial area is distributed to an object by the information distribution method illustrated in FIG.
テーブル1は、オブジェクトのリアルタイム位置ストリームと空間的状態ストリームを示す。リアルタイム位置ストリームは、異なる時点における空間エリア内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータxiを示す。ここで、i = 1, 2, …, n-1, nは、1からnの時点うちの任意の時点を示す。
空間的な状態ストリームは、オブジェクトが異なる時点に空間エリアの子エリアT1、T2、T3、T4のどの子エリアに位置するかを示す。
The spatial state stream indicates in which child area T1, T2, T3, T4 of the spatial area the object is located at different times.
図7に示すように、オブジェクトが、子エリアT4(リアルタイム位置ストリームのx1に対応)から、T3、T2を経由して、空間エリア1の仮想内部境界に到達した後、オブジェクトは、子エリアT1(リアルタイム位置ストリームのxwに対応)に進入し、ポイント701で空間エリア1に関連付けた情報がオブジェクトに対して配信され始める。その後、オブジェクトは、T1、T2およびT3の範囲内を移動するので、空間エリア1に関連付けた情報がオブジェクトに配信され続ける。
ポイント702で、オブジェクトは仮想外部境界に到達し、子エリアT4(リアルタイム位置ストリームのxn-1に対応)に進入し始める。そのとき、オブジェクトに対する空間エリア1に関連付けた情報の配信が停止する。
As shown in FIG. 7, after an object, from the child area T4 (corresponding to the x 1 real-time location stream) via the T3, T2, it reaches the virtual internal boundary of the space area 1, the object, the child area enters the T1 (corresponding to x w of real-time location stream), information associated with the space area 1 at the point 701 begins to be delivered to the object. Thereafter, since the object moves within the range of T1, T2, and T3, information associated with the spatial area 1 continues to be delivered to the object.
At point 702, the object reaches the virtual outer boundary and begins to enter child area T4 (corresponding to x n-1 in the real-time position stream). At that time, distribution of information associated with the space area 1 to the object stops.
このようにして、高精度位置に基づく情報配信システムにおいて情報の誤配信を回避できる。
例えば、信号発信器を保持するユーザ(すなわち、オブジェクト)が空間エリア1内を移動する過程で、無意識に空間エリア1の境界の外に出るとき、本発明の情報配信装置は、オブジェクトに対する空間エリア1に関連付けた情報の配信をすぐには停止しない。代わりに、情報配信装置は、ユーザが空間エリア1の仮想外部境界を越えるまでユーザに対して情報を配信し続ける。
たとえユーザが空間エリア2の仮想外部境界(本当の境界であっても)に入ったとしても、ユーザの位置が、空間エリア1の仮想外部境界を越えない限り、空間エリア2に関連付けた情報ではなく空間エリア1に関連付けた情報がオブジェクトに対して配信される。
このように、高測位精度の場合、他の空間エリアへのユーザの故意ではない進入によって引き起こされる情報の誤配信が防止される。
In this way, erroneous delivery of information can be avoided in an information delivery system based on a high-precision position.
For example, when a user (that is, an object) holding a signal transmitter unconsciously goes out of the boundary of the space area 1 in the process of moving in the space area 1, the information distribution apparatus of the present invention uses the space area for the object. The distribution of information associated with 1 is not immediately stopped. Instead, the information distribution device continues to distribute information to the user until the user crosses the virtual external boundary of the space area 1.
Even if the user enters the virtual external boundary of the spatial area 2 (even if it is a real boundary), as long as the user's position does not exceed the virtual external boundary of the spatial area 1, the information associated with the spatial area 2 The information associated with the spatial area 1 is distributed to the object.
In this way, in the case of high positioning accuracy, erroneous delivery of information caused by the user's unintentional entry into another spatial area is prevented.
図8は、本発明の他の実施の形態による情報配信装置800のブロック図である。
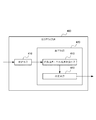
FIG. 8 is a block diagram of an
情報配信装置800は、空間(ここで、空間は1つ以上の空間エリアを含む)内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを受信するための受信手段810と、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの境界を用いることにより、空間エリアに関連付けた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するのための配信手段820とを備える。
配信手段820は、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて各空間エリアの即時的な乖離度を決定する即時乖離度決定手段821と、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得する累積的乖離度計算手段822と、累積的乖離度をソートすることにより、最大の累積的乖離度を決定する最大値決定手段823と、最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するのを停止し、最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、最大の累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けられた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信する決定手段824とを備える。
The
The
即時的乖離度決定手段821は、さらに、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアならば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の負の値に設定する手段と、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の時点の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の正の値に設定し、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離性を「0」に設定する手段を備える。 Further, the immediate divergence determining means 821 further sets the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas to a predetermined negative value if the spatial area where the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing. If the spatial area where the object is currently located is not the spatial area associated with the information distribution start timing at the immediately preceding time, the immediate divergence of the spatial area where the object is currently located is predetermined. And a means for setting the immediate divergence of the spatial area other than the spatial area where the object is currently located to “0”.
累積的乖離度計算手段822は、さらに、直前の瞬間での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での各空間エリアの即時的乖離度との合計を求める手段と、合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得する手段と、その最大値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定する手段とを備える。 The cumulative divergence calculation means 822 further includes a means for calculating the sum of the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the immediately previous moment and the immediate divergence degree of each spatial area at the present moment, and the total result is a predetermined maximum. Comparing with a value, means for obtaining a maximum value of the two values, and means for determining the maximum value as a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time.
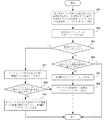
図9は、本発明の他の実施の形態による情報配信方法を説明するフローチャートである。
本実施の形態による情報配信方法は、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに基づいて、オブジェクトの位置ストリームからオブジェクトの移動の傾向を見つけ出し、それによって、情報配信終了タイミングと新たな情報配信開始タイミングを決定する。
FIG. 9 is a flowchart illustrating an information distribution method according to another embodiment of the present invention.
The information distribution method according to the present embodiment finds the tendency of the movement of the object from the object position stream based on the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, thereby determining the information distribution end timing and the new information distribution start timing. .
本発明の実施の形態において、情報配信開始タイミングは、ある空間エリアに関連付けた情報がオブジェクトに対して配信され始める時点を示し、その時点から、情報の情報配信終了タイミングまである空間エリアに関連付けた情報がオブジェクトに対して配信され始める。
情報配信終了タイミングは、ある空間エリアに関連付けた情報の配信が終了する時点を示し、その時点から、ある空間エリアに関連付けた情報のオブジェクトに対する配信が停止される。
In the embodiment of the present invention, the information distribution start timing indicates a point in time when information associated with a certain spatial area starts to be distributed to the object, and is associated with a certain spatial area from that point to the information distribution end timing of information. Information begins to be delivered to the object.
The information distribution end timing indicates a time point at which distribution of information associated with a certain spatial area ends, and distribution of information associated with a certain spatial area is stopped from that point.
この実施の形態において、{Ai, i=1,2,…L, …M}で示される合計Mの空間エリアが存在すると仮定する(ここで、Lは1からMの間の任意の数である)。
また、オブジェクトがxwに位置する時点が、空間エリアALに関連付けた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するための情報配信開始タイミングであると仮定する。
テーブル2は、リアルタイム位置ストリームとブジェクトのエリア索引ストリームを示す。
リアルタイム位置ストリームは、異なる時点での空間エリア内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを示す。ここで、i=1、2、・・・、nは、1からnの時点うちの任意の時点を表す。
エリア索引ストリームは、オブジェクトが異なる時点に空間エリアA1, A2, …, AL,…, AM-1, AMのうちどの空間エリアに位置するかを示す。
Further, assume that the object point is located in the x w is the information distribution start timing for distributing information associated with spatial areas AL for the object.
Table 2 shows the real-time position stream and the object area index stream.
The real-time position stream shows the position parameters of the objects in the spatial area at different times. Here, i = 1, 2,..., N represents an arbitrary point in time from 1 to n.
The area index stream indicates in which spatial area the spatial areas A1, A2,..., AL,.
テーブル2に示すように、オブジェクトは時点xwに空間エリアALに位置し、その前にオブジェクトは他の空間エリア(例えば、空間エリアA3)に位置するので、空間エリアALに関連付けた情報は、その時点にオブジェクトに対して配信され始める。すなわち、xwに対応する時点は、空間エリアALに関連付けた情報の情報配信開始タイミングである。
オブジェクトの新たな位置パラメータが間断なく受信されるに従って、空間エリアALを除く他の各空間エリアの空間エリアALに対する累積乖離度(ADS:Accumulate
Departing Significance)が、本実施の形態によって計算される。
As shown in Table 2, the object is located in the space area AL at time x w, objects before the other area of space (e.g., space area A3) so located, the information associated with the space area AL, At that time, it starts to be delivered to the object. That is, time corresponding to x w is information distribution start timing of information associated with the spatial area AL.
As new position parameters of the object are received without interruption, the cumulative divergence (ADS: Accumulate) of each of the other spatial areas excluding the spatial area AL with respect to the spatial area AL
Departing Significance) is calculated according to this embodiment.
オブジェクトが位置xwに位置する時点の後に、位置ストリームが、空間エリアALをわずかに外れれば(例えば、そのようなわずかな外れは測位エラーによって引き起こされる場合がある)、累積的乖離度は低レベルで安定を維持する。すなわち、ユーザは現在の情報配信エリアから外れていないとみなされる。 After the time the object is positioned at the position x w, position stream, if outside this space area AL slightly (e.g., such slight off may be caused by the positioning error), the cumulative deviation degree is low Stay stable at the level. That is, it is considered that the user has not left the current information distribution area.
ある時点で、ある空間エリアに対応する累積的乖離度が、情報配信終了タイミングに対応する終了しきい値を越えれば、その時点は情報配信終了タイミングと見なすことができる。その時点に、オブジェクトに対する空間エリアALに関連付けた情報の配信は直ちに終了する。 If, at a certain point in time, the cumulative divergence corresponding to a certain spatial area exceeds the end threshold corresponding to the information distribution end timing, that point can be regarded as the information distribution end timing. At that time, distribution of information associated with the space area AL for the object is immediately terminated.
ある時点で、ある空間エリアに対応する累積的乖離度が、情報配信開始タイミングに対応する配信しきい値を越えれば、その時点は新たな情報配信開始タイミングと見なすことができる。
その時点から、累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きな空間エリアに関連付けた情報が配信され始める。
終了するしきい値が配信しきい値より小さい値であることを認識すべきである。
If, at a certain point in time, the cumulative divergence corresponding to a certain spatial area exceeds the distribution threshold corresponding to the information distribution start timing, that point can be regarded as a new information distribution start timing.
From that point on, information associated with a spatial area in which the cumulative divergence degree is greater than the distribution threshold value starts to be distributed.
It should be appreciated that the termination threshold is less than the delivery threshold.
図9に示す情報配信方法は、図8において示す情報配信装置800によって実現される。
The information distribution method shown in FIG. 9 is realized by the
ステップ901において、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度は、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの境界に基づいて決定される。
In
本実施の形態において、以下の方法によって即時的乖離度を決定することができる。
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けた空間エリアであれば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離度を予め定めた負の値とする。
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離度を予め定めた正の値とし、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離度を「0」とする。
In the present embodiment, the immediate divergence degree can be determined by the following method.
If the spatial area in which the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence degree of all the spatial areas is set to a predetermined negative value.
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is not the spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area where the object is currently located is set to a predetermined positive value, and the object is Assume that the immediate divergence degree of a spatial area other than the spatial area located at is “0”.
空間エリアの即時的乖離度は相対的概念である。具体的は、即時的乖離度は、空間エリアALに対する空間エリアAiの関係を反映する。ここで、i=1、…M、かつi≠Lである。
例えば、空間エリアALに関する空間エリアAiの即時的乖離度(以下、空間エリアAiの即時的乖離度と称する)は、以下のDSのように表される。
For example, the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area A i with respect to the spatial area A L (hereinafter referred to as the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area A i ) is expressed as DS below.
式(4)において、αとβは両方とも予め定めた正の値である。
従って、(a)の場合、すなわち、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアAiが、直前の時点での情報配信開始タイミングに関連する空間エリアALである場合(すなわち、i=L)、空間エリアAiの即時的乖離度は所定の負の値−αであり、それと同時に、空間エリアALの即時的乖離度は、所定の負の値−αに設定される。
(b)と(c)の場合、すなわち、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアAiが、直前の時点での情報配信開始タイミングに関連する空間エリアALと異なる場合(すなわち、i=1,…M and i≠L)、空間エリアAiの即時的乖離度は、所定の正の値βとなり、空間エリアAjの即時的乖離度は、「0」となる(ここで、j=1,…M,j≠L and j≠i)。そして、同時に、空間エリアALの即時的乖離度は、「0」に設定される。
In Expression (4), α and β are both positive values determined in advance.
Therefore, In the case of (a), i.e., if the object space area A i which is located at the present time, a space area A L related to information distribution start timing at the time just before (i.e., i = L), the space The immediate deviation degree of the area A i is a predetermined negative value −α, and at the same time, the immediate deviation degree of the space area A L is set to a predetermined negative value −α.
In the cases (b) and (c), that is, the spatial area A i where the object is currently located is different from the spatial area A L related to the information distribution start timing at the previous time (ie, i = 1, ... M and i ≠ L), the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area A i is a predetermined positive value β, and the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area A j is “0” (where j = 1 , ... M, j ≠ L and j ≠ i). At the same time, immediate divergence of the spatial area A L is set to "0".
実施の形態において、空間エリアの即時的乖離度が相対的な概念であり、空間エリアALに対する空間エリアAiの関係を反映するので、空間エリアALの即時的乖離度(すなわち、空間エリアALのそれ自体に対する即時的乖離度)の具体的な値はどのような値でもよく、そのことは本発明の情報配信方法に影響を与えない。
また、本実施の形態において、空間エリアALの即時的乖離度は、設定する必要がなく、かつ、空間エリアALに関する空間エリアAiの即時的乖離度は、式(4)を利用することによってのみ決定される。
In embodiments, immediate divergence of the space area is a relative concept, reflect a relationship between the spatial area A i for the spatial area A L, immediate divergence of the spatial area A L (i.e., the space area The specific value of the immediate deviation degree of AL with respect to itself may be any value, and this does not affect the information distribution method of the present invention.
Further, in this embodiment, the immediate deviation of the spatial area A L, there is no need to set, and the immediate deviation of the spatial area A i on the spatial area A L, using Equation (4) Is determined only by
本実施の形態において、第1の情報配信タイミングが到来する前には、直前の時点の情報配信開始タイミングに関連する空間エリアALがないので、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度は、式(4)の(b)と(c)だけに従って計算されることを理解すべきである。
すなわち、オブジェクトが一定の空間エリアに位置する時、その空間エリアの累積的乖離度が配信しきい値を越えるまで、その空間エリアの累積的乖離度は増加する。
In this embodiment, before the first information distribution timing is reached, since there is no space area A L related to information distribution start timing of the time just before, immediate divergence of each space area, the formula ( It should be understood that the calculation is made only according to (b) and (c) of 4).
That is, when an object is located in a certain spatial area, the cumulative divergence of the spatial area increases until the cumulative divergence of the spatial area exceeds the distribution threshold.
ステップ902において、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度が、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて取得される。
In
本の実施の形態においては、直前の時点での空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での空間エリアの即時的乖離度との合計を求め、合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得し、その最大値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定する。 In the present embodiment, the total of the cumulative divergence degree of the spatial area at the previous time point and the immediate divergence degree of the current spatial area is obtained, and the total result is compared with a predetermined maximum value. The maximum value is acquired, and the maximum value is determined as the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time.
本実施の形態において、累積的乖離度は、直前の時点の情報配信開始タイミング(すなわち、xwに対応する時点)を起点とし、新しく受信したオブジェクトの位置パラメータを終点とする時間ウィンドーにおいて、集計され計算される。 In the present embodiment, the cumulative deviation degree is, just before the time point information distribution start timing (i.e., time corresponding to x w) and a starting point, the time window for the end point of the position parameters of the newly received object, aggregate And calculated.
本実施の形態において、直前の時点の情報配信開始タイミング(すなわち、xwに対応する時点)では、空間エリアAL以外の空間エリアに対応する累積的乖離度ADSは、すべて「0」に設定される。すなわち、
ADS(Ai,xw)=0,∀Ai,(i=1,...,M),i≠L
(5)
オブジェクトの位置パラメータxnを受信した場合は常に、xwからxnの時間帯における累積的乖離度ADSが、式(6)を利用することより、空間エリアAL以外の各空間エリアAi(i=1,…M and i≠L)ついて計算される。
ADS(Ai,xn)=max{0, ADS(Ai,xn-1)+DS(Ai|AL,xn)},∀Ai,(i=1,...,M),i≠L (6)
In this embodiment, the immediately preceding time information delivery start timing (i.e., time corresponding to x w), cumulative deviance ADS corresponding to the spatial area other than the area of space A L is set to all "0" Is done. That is,
ADS (Ai, x w ) = 0, ∀Ai, (i = 1, ..., M), i ≠ L
(Five)
Whenever the position parameter x n of the object is received, the cumulative divergence ADS in the time zone from x w to x n uses the equation (6), so that each spatial area A i other than the spatial area A L is obtained. (I = 1,... M and i ≠ L)
ADS (Ai, x n ) = max {0, ADS (Ai, x n-1 ) + DS (A i | A L , x n )}, ∀Ai, (i = 1, ..., M), i ≠ L (6)
式(6)において、まず、現時点で決定した即時的乖離度DSと直前の時点の累積的乖離度の合計が求められ、次に、合計結果が「0」と比較される。また、2つのうちの最大値が現時点での累積的乖離度として決定される。 In equation (6), first, the sum of the immediate divergence DS determined at the present time and the cumulative divergence at the previous time is obtained, and then the total result is compared with “0”. Further, the maximum value of the two is determined as the cumulative divergence degree at the present time.
ステップ903において、各累積的乖離度をソートすることにより、最大の累積的乖離度を決定する。
In
ステップ902に従って、現時点でのM個の空間エリアのそれぞれの累積的乖離度が取得され、また、M個の累積的乖離度が最大値を取得するためにソートされる。 According to step 902, the current cumulative divergence of the M spatial areas is obtained, and the M cumulative divergences are sorted to obtain a maximum value.
オブジェクトの位置パラメータが連続的に受信されるに従って、各時点での空間エリアの累積的乖離度ADS(Ai, xw)が、空間エリアAL以外の各空間エリアAi(i=1,…M and i≠L)について取得され、それが累積的乖離度の時系列ADS(Ai)を構成する。
具体的には、各時点での空間エリアAL以外の空間エリアの累積的乖離度ADS(Ai, xw)は、以下のように表される。
Specifically, cumulative deviance ADS space areas other than the space area A L at each time point (A i, x w) is expressed as follows.
式(7)において、式(7)において、各行は、各時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度ADS(Ai)を表わす。また、各列は、同じ時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度ADS(xn)を表わす。
式(7)から、オブジェクトのリアルタイム位置ストリームが空間エリアALから離れ、他の空間エリアAiの方へ移動する傾向にあれば、空間エリアAiの累積的乖離度ADS(Ai)は、単調に増加し、オブジェクトのリアルタイム位置ストリームのほとんどが空間エリアALの近くに集中すれば、他の空間エリアの累積的乖離度はより小さくなることが分かる。
In Expression (7), each line in Expression (7) represents the cumulative divergence ADS (A i ) of each spatial area at each time point. Each column represents the cumulative divergence level ADS (x n ) of each spatial area at the same time point.
From equation (7), if the trend of real-time location stream objects away from the space area A L, to move towards the other space areas A i, ADS cumulative deviation degree of the spatial area A i (Ai) is increases monotonically, if concentrated most real-time location stream objects in the space near the area a L, the cumulative deviation of the other space areas is can be seen that smaller.
以上のことから、各時点毎の各空間エリアの累積的乖離度の最大値は、以下のように計算される。
ステップ904において、最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きいかどうかを判断する。
In
最大の累積的乖離度M(xn)が終了しきい値より大きければ、その時点は情報配信終了タイミングと見なすことができる。
その時点から、オブジェクトに対する空間エリアALに関連する情報の配信が停止される。その後、処理はステップ905へ進む。
If the maximum cumulative divergence M (x n ) is larger than the end threshold value, the time point can be regarded as the information distribution end timing.
From that point, the distribution of information related to the spatial area A L to the object is stopped. Thereafter, the processing proceeds to step 905.
最大の累積的乖離度M(xn)が終了しきい値より大きくなければ、処理が終了する。 If the maximum cumulative divergence M (x n ) is not greater than the end threshold value, the process ends.
ステップ905において、直前の時点でオブジェクトに対して配信されている情報と同一の情報の配信は、現時点から停止される。
In
ステップ906において、最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きいかどうかを判断する。
In
最大の累積的乖離度M(xn)が配信しきい値より大きければ、その時点は情報配信開始タイミングと見なすことができる。
この時点から、その累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連する情報のオブジェクトに対する配信が開始する。その後、処理はステップ907へ進む。
If the maximum cumulative divergence degree M (x n ) is larger than the distribution threshold value, the time point can be regarded as the information distribution start timing.
From this point of time, distribution of information related to the spatial area corresponding to the cumulative divergence degree to the object starts. Thereafter, the processing proceeds to step 907.
最大の累積的乖離度M(xn)が配信しきい値より大きくなければ、処理が終了する。 If the maximum cumulative divergence degree M (x n ) is not greater than the distribution threshold value, the process ends.
ステップ907において、累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けた情報が、その時点からオブジェクトに対して配信される。
In
その後、処理が終了する。 Thereafter, the process ends.
終了しきい値と配信しきい値が予め設定され、情報配信システムの具体的な状況に従って異なる値が設定されることを理解すべきである。 It should be understood that the end threshold value and the distribution threshold value are set in advance, and different values are set according to the specific situation of the information distribution system.
本発明の他の実施の形態によれば、乖離度には、内部境界ファクター、外部境界ファクター、即時的乖離度および累積的乖離度を含めることができる。
仮想内部境界と仮想外部境界は、図8〜図9の実施の形態において使用される空間エリアの本当の境界の代わりに使用することができる。
オブジェクトが異なる空間エリア間で移動する時、図4の実施の形態に記述するような仮想内部境界および仮想外部境界は、オブジェクトと空間エリア間の関係を決定するために使用することができる。
オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想内部境界に進入する時、オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想外部境界を越えるまで、オブジェクトはその空間エリア内にあるとみなされる。
According to another embodiment of the present invention, the divergence degree may include an internal boundary factor, an external boundary factor, an immediate divergence degree, and a cumulative divergence degree.
The virtual inner boundary and the virtual outer boundary can be used instead of the real boundary of the spatial area used in the embodiment of FIGS.
When an object moves between different spatial areas, virtual internal and virtual external boundaries as described in the embodiment of FIG. 4 can be used to determine the relationship between the object and the spatial area.
When an object enters the virtual internal boundary of a spatial area, the object is considered to be within that spatial area until the object crosses the virtual external boundary of the spatial area.
実際上、この他の実施の形態では、図9に示す情報配信方法と異なり、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度は、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界に基づいて決定される。
例えば、まず、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界を、各空間エリアの境界、各空間エリアの外部境界ファクターおよび内部境界ファクターに基づいて取得し、その後、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を、オブジェクトの位置パラメータと、各空間エリアの仮想内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界に基づいて決定する。
Actually, in this other embodiment, unlike the information distribution method shown in FIG. 9, the immediate divergence of each spatial area is determined based on the virtual inner boundary and / or virtual outer boundary of each spatial area. Is done.
For example, first, the virtual inner boundary and / or virtual outer boundary of each spatial area is obtained based on the boundary of each spatial area, the outer boundary factor and the inner boundary factor of each spatial area, and then An immediate divergence is determined based on the position parameters of the object and the virtual internal and / or virtual external boundaries of each spatial area.
その後、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて取得し、累積的乖離度をソートすることにより最大の累積的乖離度を決定し、最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きければ、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報のオブジェクトに対する配信を現時点から停止し、最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きければ、最大の累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けた情報を現時点からオブジェクトに対して配信する。 After that, the current cumulative divergence of each spatial area is obtained based on the immediate divergence of each spatial area, and the maximum cumulative divergence is determined by sorting the cumulative divergence. If the cumulative divergence is greater than the end threshold, distribution to the object of the same information as the information distributed immediately before is stopped from the current time, and if the maximum cumulative divergence is greater than the distribution threshold, the maximum The information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the cumulative divergence degree is distributed to the object from the present time.
各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定する処理は、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の時点の情報配信開始タイミングに関連する空間エリアならば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離度を予め定めた負の値とすること、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の時点の情報配信開始タイミングに関連する空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離度を予め定めた正の値とし、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の空間エリアの即時的乖離度を「0」とすることを含む。
The process of determining the immediate divergence of each spatial area is
If the spatial area in which the object is currently located is a spatial area related to the information distribution start timing at the previous time, the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas should be set to a negative value that is determined in advance. If the spatial area is not a spatial area related to the information distribution start timing at the immediately previous time, the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area where the object is currently located is set to a positive value, and the object is located at the current time. Including setting the immediate divergence degree of a spatial area other than the spatial area to be “0”.
現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得する処理は、
直前の時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での各空間エリアの即時的乖離度の合計を求めること、合計結果と所定の最大値を比較して2つのうちの最大値を取得すること、また、その大きな値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定することを含む。
The process to get the cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the moment is
Find the sum of the cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the previous time point and the immediate divergence of each spatial area at the present time, and compare the total result with a predetermined maximum value to obtain the maximum value of the two And determining the large value as the cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the present time.
内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターは空間の測位精度に関係する。
測位精度がより高くなるほど、内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターは、「1」に近くなる。
The inner and outer boundary factors are related to the spatial positioning accuracy.
The higher the positioning accuracy, the closer the inner boundary factor and outer boundary factor are to “1”.
上記の実施の形態による情報配信装置は、空間(ここで、空間は1つ以上の空間エリアを含む)内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを受信するための受信手段と、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を利用して、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアと関連付けた情報を配信するための配信手段とを含む。 The information distribution apparatus according to the above-described embodiment is based on receiving means for receiving a position parameter of an object in a space (where space includes one or more spatial areas) and the degree of divergence between the spatial areas. And a distribution means for distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object using the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area.
配信手段は、
各空間エリアの境界および各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界を取得するための内部境界・外部境界取得手段と、
オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定するための即時的乖離度決定手段と、
各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得するのための累積的乖離度計算手段と、
累積的乖離度をソートすることにより最大の累積的乖離度を決定するのための最大値決定手段と、
最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するのを停止し、最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、最大の累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けられた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信する配信手段とを備える。
Distribution means
Internal boundary / external boundary acquisition means for acquiring the virtual internal boundary and / or virtual external boundary of each spatial area based on the boundary of each spatial area and the internal boundary factor and external boundary factor of each spatial area;
An immediate divergence determining means for determining an immediate divergence of each spatial area based on the position parameter of the object and the virtual internal boundary and / or virtual external boundary of each spatial area;
Based on the immediate divergence degree of each spatial area, a cumulative divergence degree calculating means for obtaining the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time;
A maximum value determining means for determining the maximum cumulative divergence by sorting the cumulative divergence;
If the maximum cumulative divergence is larger than the end threshold, the distribution of the same information as the information distributed at the previous time is stopped from the current time to the object, and the maximum cumulative divergence is distributed. If greater than the threshold value, a distribution means for distributing to the object information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence degree from the present time is provided.
即時的乖離度決定手段は、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアならば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の負の値に設定する手段と、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の正の値に設定し、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離性を「0」に設定する手段を備える。
Immediate divergence determination means is
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, means for setting the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas to a predetermined negative value, and the object If the spatial area is not a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence of the spatial area where the object is currently positioned is set to a predetermined positive value, and the object is positioned at the current time Means for setting the immediate divergence of other spatial areas other than the spatial area to be set to “0”.
累積的乖離度計算手段は、直前の時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での各空間エリアの即時的乖離度との合計を求める手段と、合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得する手段と、その大きな値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定する手段とを備える。 The cumulative divergence calculation means is a means for calculating the sum of the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the time immediately before and the immediate divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time, and compares the total result with a predetermined maximum value. And means for obtaining the maximum value of the two, and means for determining the large value as the cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the present time.
本発明による方法と装置は、ソフトウェア、ハードウェアあるいはソフトウェアとハードウェアの組合せによって実現することが可能である。ハードウェア部分は専用のロジックで実現され、ソフトウェア部分は記憶装置に格納され、適切な命令実行システム(例えばマイクロプロセッサ、パーソナルコンピュータ(PC)、大型コンピュータ)によって実行される。 The method and apparatus according to the present invention can be realized by software, hardware or a combination of software and hardware. The hardware part is realized by dedicated logic, and the software part is stored in a storage device and executed by an appropriate instruction execution system (for example, a microprocessor, a personal computer (PC), a large computer).
本発明の説明は、本発明を網羅的に示しあるいは本発明を開示された形態に限定するためではなく、例示と説明を目的として提示される。多くの変形や変更が可能なことは、当該技術に精通した当業者には明らかであろう。 The description of the present invention has been presented for purposes of illustration and description, and is not intended to be exhaustive or to limit the invention to the disclosed form. Many modifications and variations will be apparent to practitioners skilled in this art.
したがって、上記の実施の形態の選択と説明が、本発明の原理および実際の適用をより明快に説明するものであり、本発明の精神から逸脱することなくなされた全ての変形および変更は付記される請求項に定義される本発明の保護範囲に含まれることを当業者が理解することを可能にする。 Therefore, the selection and description of the above embodiments more clearly explain the principle and practical application of the present invention, and all modifications and changes made without departing from the spirit of the present invention will be appended. Enabling the person skilled in the art to understand that they fall within the protection scope of the invention as defined in the appended claims.
さらに、上記実施形態の一部又は全部は、以下の付記のようにも記載されうるが、これに限定されない。 Further, a part or all of the above-described embodiment can be described as in the following supplementary notes, but is not limited thereto.
(付記1)
1つ以上の空間エリアを含む空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータの受信するステップと、
各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップと
を有することを特徴とする情報配信方法。
(Appendix 1)
Receiving a positional parameter of an object in a space including one or more spatial areas;
Distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object by using the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area based on the degree of divergence of each spatial area. Method.
(付記2)
前記乖離度が、内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターを含み、
前記オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップが、
各空間エリアの境界と各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および仮想外部境界を取得するステップと、
前記オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想内部境界に進入すると、前記オブジェクトが仮想外部境界を越えるまで、前記オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報の配信を開始するステップとを含むことを特徴とする付記1に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 2)
The degree of divergence includes an internal boundary factor and an external boundary factor;
Delivering information associated with the spatial area to the object;
Obtaining a virtual inner boundary and a virtual outer boundary for each spatial area based on the boundary of each spatial area and the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor of each spatial area;
The method further includes the step of, when the object enters the virtual internal boundary of the spatial area, starting to distribute information associated with the spatial area to the object until the object crosses the virtual external boundary. Information distribution method described in 1.
(付記3)
前記内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターは空間の測位精度と関係し、
測位精度が高いほど、前記内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターは1により近くなることを特徴とする付記2に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 3)
The inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor are related to the positioning accuracy of space,
The information distribution method according to supplementary note 2, wherein the higher the positioning accuracy is, the closer the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor are to 1.
(付記4)
前記乖離度が、即時的乖離度と累積的乖離度を含み、
前記オブジェクトに空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップが、
前記オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定するステップと、
各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得するステップと、
前記累積的乖離度をソートすることにより、最大累積的乖離度を決定するステップと、
前記最大累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きい場合、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報の前記オブジェクトに対する配信を、現時点で停止するステップと、
前記最大累積的乖離度が配信するしきい値より大きい場合、前記最大累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けた情報を前記オブジェクトに対して、現時点から配信するステップとを含むことを特徴とする付記1に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 4)
The degree of deviation includes an immediate degree of deviation and a cumulative degree of deviation,
Delivering information associated with the spatial area to the object;
Determining the immediate divergence of each spatial area based on the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area;
Obtaining a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area based on an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area; and
Determining the maximum cumulative divergence by sorting the cumulative divergence; and
If the maximum cumulative divergence is greater than an end threshold, stopping the delivery of the same information as the information delivered at the previous time point at the current time;
Delivering the information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence degree to the object from the current time when the maximum cumulative divergence degree is larger than a distribution threshold value. The information delivery method according to appendix 1.
(付記5)
前記各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定するステップが、
前記オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けた空間エリアであれば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離度を所定の負の値に設定するステップと、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離度を予め定めた正の値とし、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離度を0に設定するステップとを含むことを特徴とする付記4に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 5)
Determining the immediate divergence of each spatial area,
If the spatial area in which the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information delivery start timing, setting the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas to a predetermined negative value;
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is not the spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area where the object is currently located is set to a predetermined positive value, and the object is And the step of setting the immediate divergence degree of other spatial areas other than the spatial area located at 0 to 0.
(付記6)
現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得するステップが、
直前の時点での空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での空間エリアの即時的乖離度との合計を求めるステップと、
合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得するステップと、
取得した前記最大値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定するステップとを含むことを特徴とする付記4に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 6)
The step of acquiring the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time,
Calculating the sum of the cumulative divergence of the spatial area at the previous time point and the immediate divergence of the current spatial area;
Comparing the total result with a predetermined maximum value and obtaining the maximum value of the two;
And determining the acquired maximum value as a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time.
(付記7)
前記乖離度が、内部境界ファクター、外部境界ファクター、即時的乖離度および累積的乖離度を含み、
前記オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップが、
各空間エリアの境界および各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想内部境界および/または仮想外部境界を取得するステップと、
オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および/または仮想外部境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定するステップと、
各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得するステップと、
累積的乖離度をソートすることにより最大の累積的乖離度を決定するステップと、
最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するのを停止するステップと、
最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、最大の累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けられた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するステップとを含むことを特徴とする付記1に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 7)
The degree of divergence includes an inner boundary factor, an outer boundary factor, an immediate divergence degree, and a cumulative divergence degree,
Delivering information associated with the spatial area to the object;
Obtaining a virtual internal boundary and / or a virtual external boundary for each spatial area based on the boundary of each spatial area and the internal and external boundary factors of each spatial area;
Determining the immediate divergence of each spatial area based on the object location parameters and the virtual internal and / or virtual external boundaries of each spatial area;
Obtaining a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area based on an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area; and
Determining the maximum cumulative divergence by sorting the cumulative divergence; and
If the maximum cumulative divergence is greater than the ending threshold, stopping the delivery of the same information to the object from the current time to the object,
Delivering the information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence from the current time to the object if the maximum cumulative divergence is greater than the distribution threshold. The information delivery method according to attachment 1.
(付記8)
前記各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定するステップが、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアならば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の負の値に設定するステップと、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の正の値に設定し、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離性を0に設定するステップとを含むことを特徴とする付記7に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 8)
Determining the immediate divergence of each spatial area,
If the spatial area in which the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information delivery start timing, setting the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas to a predetermined negative value;
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is not the spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence of the spatial area where the object is currently located is set to a predetermined positive value, and the object The method for delivering information according to claim 7, further comprising the step of setting the immediate divergence of a spatial area other than the spatial area currently located at 0 to 0.
(付記9)
現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得するステップが、
直前の時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での各空間エリアの即時的乖離度との合計を求めるステップと、
合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得するステップと、
前記最大値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定するステップとを含むことを特徴とする付記7に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 9)
The step of acquiring the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time,
Calculating the sum of the cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the previous time point and the immediate divergence of each spatial area at the current time;
Comparing the total result with a predetermined maximum value and obtaining the maximum value of the two;
And determining the maximum value as a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time.
(付記10)
前記内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターが空間の測位精度に関係し、測位精度がより高くなるほど、前記内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターが1に近くなることを特徴とする付記7に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 10)
The information distribution method according to appendix 7, wherein the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor relate to spatial positioning accuracy, and the higher the positioning accuracy, the closer the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor to 1. .
(付記11)
前記オブジェクトに、測距信号を送信する信号発信器が備えられ、
前記信号発信器から測位装置へ発された測距信号によってオブジェクトの位置パラメータが取得されることを特徴とする付記1に記載の情報配信方法。
(Appendix 11)
The object is provided with a signal transmitter for transmitting a ranging signal,
The information distribution method according to claim 1, wherein a position parameter of the object is acquired by a distance measurement signal transmitted from the signal transmitter to the positioning device.
(付記12)
1つ以上の空間エリアを含む空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータの受信する受信手段と、
各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信する配信手段と
を備えることを特徴とする情報配信装置。
(Appendix 12)
Receiving means for receiving a positional parameter of an object in a space including one or more spatial areas;
Distribution means for distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object by using the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area based on the degree of divergence of each spatial area Distribution device.
(付記13)
前記乖離度が、内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターを含み、
前記配信手段が、
各空間エリアの境界と各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および仮想外部境界を取得する内部境界・外部境界取得手段と、
前記オブジェクトが空間エリアの仮想内部境界に進入すると、前記オブジェクトが仮想外部境界を越えるまで、前記オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報の配信を開始する決定手段と
を備えることを特徴とする付記12に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 13)
The degree of divergence includes an internal boundary factor and an external boundary factor;
The delivery means is
An internal boundary / external boundary acquisition means for acquiring a virtual internal boundary and a virtual external boundary of each spatial area based on the boundary of each spatial area and the internal boundary factor and external boundary factor of each spatial area;
And a determination unit that starts distribution of information associated with the spatial area to the object until the object crosses the virtual external boundary when the object enters the virtual internal boundary of the spatial area. 12. The information distribution device according to 12.
(付記14)
前記内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターは空間の測位精度と関係し、
測位精度が高いほど、前記内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターは1により近くなることを特徴とする付記13に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 14)
The inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor are related to the positioning accuracy of space,
14. The information delivery apparatus according to appendix 13, wherein the higher the positioning accuracy, the closer the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor are to 1.
(付記15)
前記乖離度が、即時的乖離度と累積的乖離度を含み、
前記配信手段が、
前記オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定する即時的乖離度決定手段と、
各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得する累積的乖離度計算手段と、
前記累積的乖離度をソートすることにより、最大累積的乖離度を決定する最大値決定手段と、
前記最大累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きい場合、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報の前記オブジェクトに対する配信を、現時点で停止し、前記最大累積的乖離度が配信するしきい値より大きい場合、前記最大累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けた情報を前記オブジェクトに対して、現時点から配信する決定手段と
を備えることを特徴とする付記12に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 15)
The degree of deviation includes an immediate degree of deviation and a cumulative degree of deviation,
The delivery means is
Immediate divergence determination means for determining an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area based on the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area;
A cumulative divergence calculating means for obtaining a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area based on an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area; and
Maximum value determining means for determining the maximum cumulative divergence by sorting the cumulative divergence,
When the maximum cumulative divergence degree is larger than an end threshold value, the threshold value at which the distribution of the same information as the information distributed at the previous time point to the object is stopped at the present time and the maximum cumulative divergence degree is distributed. The information distribution apparatus according to appendix 12, further comprising: a determination unit that distributes information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence degree to the object from the present time when the value is larger.
(付記16)
前記即時的乖離度決定手段が、
前記オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けた空間エリアであれば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離度を所定の負の値に設定する手段と、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離度を予め定めた正の値とし、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離度を0に設定する手段とを備えることを特徴とする付記15に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 16)
The immediate divergence determination means is
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information delivery start timing, means for setting the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas to a predetermined negative value;
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is not the spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area where the object is currently located is set to a predetermined positive value, and the object is The information distribution apparatus according to claim 15, further comprising means for setting an immediate divergence degree of a spatial area other than the spatial area located at 0 to 0.
(付記17)
前記累積的乖離度計算手段は、さらに、
直前の時点での空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での空間エリアの即時的乖離度との合計を求める手段と、
合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得する手段と、
取得した前記最大値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定する手段とを備えることを特徴とする付記15に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 17)
The cumulative divergence calculating means further includes:
Means for calculating the sum of the cumulative divergence of the spatial area at the previous time point and the immediate divergence of the spatial area at the present time;
Means for comparing the total result with a predetermined maximum value and obtaining the maximum value of the two;
The information distribution apparatus according to claim 15, further comprising means for determining the acquired maximum value as a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time.
(付記18)
前記乖離度が、内部境界ファクター、外部境界ファクター、即時的乖離度および累積的乖離度を含み、
前記配信手段は、さらに、
各空間エリアの境界および各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界を取得するための内部境界・外部境界取得手段と、
オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および(または)仮想外部境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定するための即時的乖離度決定手段と、
各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得するのための累積的乖離度計算手段と、
累積的乖離度をソートすることにより最大の累積的乖離度を決定するのための最大値決定手段と、
最大の累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報をオブジェクトに対して配信するのを停止し、最大の累積的乖離度が配信しきい値より大きければ、現時点から、最大の累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けられた情報をオブジェクトに対して配信する配信手段とを備えることを特徴とする付記12に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 18)
The degree of divergence includes an inner boundary factor, an outer boundary factor, an immediate divergence degree, and a cumulative divergence degree,
The distribution means further includes:
Internal boundary / external boundary acquisition means for acquiring the virtual internal boundary and / or virtual external boundary of each spatial area based on the boundary of each spatial area and the internal boundary factor and external boundary factor of each spatial area;
An immediate divergence determining means for determining an immediate divergence of each spatial area based on the position parameter of the object and the virtual internal boundary and / or virtual external boundary of each spatial area;
Based on the immediate divergence degree of each spatial area, a cumulative divergence degree calculating means for obtaining the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time;
A maximum value determining means for determining the maximum cumulative divergence by sorting the cumulative divergence;
If the maximum cumulative divergence is larger than the end threshold, the distribution of the same information as the information distributed at the previous time is stopped from the current time to the object, and the maximum cumulative divergence is distributed. The information delivery apparatus according to appendix 12, further comprising: a delivery unit that delivers to the object information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence degree from the current time if greater than the threshold value. .
(付記19)
前記即時的乖離度決定手段が、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアならば、すべての空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の負の値に設定する手段と、
オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けられた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離性を所定の正の値に設定し、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離性を「0」に設定する手段とを備えることを特徴とする付記18に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 19)
The immediate divergence determination means is
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, means for setting the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas to a predetermined negative value;
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is not the spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence of the spatial area where the object is currently located is set to a predetermined positive value, and the object The information distribution apparatus according to appendix 18, further comprising means for setting the immediate divergence of a spatial area other than the spatial area currently located to “0”.
(付記20)
前記累積的乖離度計算手段が、
直前の時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度と現時点での各空間エリアの即時的乖離度との合計を求める手段と、
合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得する手段と、前記最大値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定する手段とを備えることを特徴とする付記18に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 20)
The cumulative divergence calculating means includes:
Means for calculating the sum of the cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the previous time point and the immediate divergence of each spatial area at the present time;
Comparing the total result with a predetermined maximum value, and means for obtaining the maximum value of the two, and means for determining the maximum value as a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time The information distribution device according to appendix 18.
(付記21)
前記内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターが空間の測位精度に関係し、測位精度がより高くなるほど、前記内部境界ファクターと外部境界ファクターが1に近くなることを特徴とする付記18に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 21)
The information distribution apparatus according to appendix 18, wherein the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor relate to spatial positioning accuracy, and the higher the positioning accuracy, the closer the inner boundary factor and the outer boundary factor to 1. .
(付記22)
前記オブジェクトに、測距信号を送信する信号発信器が備えられ、
前記信号発信器から測位装置へ発された測距信号によってオブジェクトの位置パラメータが取得されることを特徴とする付記12に記載の情報配信装置。
(Appendix 22)
The object is provided with a signal transmitter for transmitting a ranging signal,
13. The information distribution apparatus according to appendix 12, wherein a position parameter of the object is acquired by a distance measurement signal transmitted from the signal transmitter to the positioning apparatus.
(付記23)
1つ以上の空間エリアを含む空間内のオブジェクトに備えられる、測距信号を発する信号発信器と、
前記信号発信器から発された測距信号に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータを取得する測位装置と、
空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータを受信し、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するサーバと
を備えることを特徴とする情報配信システム。
(Appendix 23)
A signal transmitter that emits a ranging signal provided in an object in a space including one or more spatial areas;
A positioning device that acquires a position parameter of an object based on a ranging signal emitted from the signal transmitter;
Receives location parameters of objects in the space, and distributes information associated with the spatial area to the object by using the positional parameters of the objects and the boundaries of the spatial areas based on the degree of divergence of each spatial area An information distribution system comprising a server.
210:信号発信器
220:測位装置
230:サーバ
240:情報配信装置
241:受信手段
242:配信手段
410:受信手段
420:配信手段
421:内部境界・外部境界取得手段
422:決定手段
601:仮想内部境界
602:境界
603:仮想外部境界
810:受信手段
820:配信手段
821:即時乖離度決定手段
822:累積的乖離度計算手段
823:最大値決定手段
824:決定手段
210: Signal transmitter 220: Positioning device 230: Server 240: Information distribution device 241: Receiving means 242: Distribution means 410: Receiving means 420: Distribution means 421: Internal boundary / external boundary acquisition means 422: Determination means 601: Virtual internal Boundary 602: Boundary 603: Virtual external boundary 810: Receiving means 820: Distribution means 821: Immediate divergence degree determining means 822: Cumulative divergence degree calculating means 823: Maximum value determining means 824: Determination means
Claims (8)
受信手段が、1つ以上の空間エリアを含む空間内のオブジェクトの位置パラメータの受信するステップと、
配信手段が、各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信するステップと、
前記配信手段が備える即時的乖離度決定手段が、前記オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定する即時的乖離度決定ステップと、
前記配信手段が備える累積的乖離度取得手段が、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得する累積的乖離度取得ステップと、
前記配信手段が備える配信制御手段が、前記累積的剥離度に基づいて、前記オブジェクトに対する配信を制御する配信制御ステップとを有し、
前記乖離度が、即時的乖離度と累積的乖離度を含む
ことを特徴とする情報配信方法。 An information distribution method by an information distribution apparatus,
Receiving a position parameter of an object in a space including one or more spatial areas;
A delivery means for delivering information associated with the spatial area to the object by using the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area based on the degree of divergence of each spatial area ;
Immediate divergence determination means for determining the immediate divergence degree of each spatial area based on the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area,
The cumulative divergence degree acquisition means provided in the distribution means acquires a cumulative divergence degree acquisition step of acquiring the cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area at the present time based on the immediate divergence degree of each spatial area;
A distribution control unit included in the distribution unit, the distribution control step of controlling the distribution to the object based on the cumulative degree of separation,
The degree of deviation includes an immediate degree of deviation and a cumulative degree of deviation.
Information distribution method, wherein a call.
前記配信制御ステップで、
前記最大累積的乖離度に基づいて、前記オブジェクトに対する配信を制御する
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の情報配信方法。 The maximum value determining means provided in the distribution means has a maximum value determining step for determining a maximum cumulative divergence degree from the cumulative divergence degree,
In the delivery control step,
Control delivery to the object based on the maximum cumulative divergence
The information distribution method according to claim 1 .
前記最大累積的乖離度が終了しきい値より大きい場合、直前の時点で配信された情報と同じ情報の前記オブジェクトに対する配信を、現時点で停止する
ことを特徴とする請求項2に記載の情報配信方法。 In the delivery control step,
When the maximum cumulative divergence degree is larger than the end threshold, the distribution of the same information as the information distributed at the previous time point to the object is stopped at the present time.
The information delivery method according to claim 2, wherein:
前記最大累積的乖離度が配信するしきい値より大きい場合、前記最大累積的乖離度に対応する空間エリアに関連付けた情報を前記オブジェクトに対して、現時点から配信する
ことを特徴とする請求項2又は請求項3に記載の情報配信方法。 In the delivery control step,
When the maximum cumulative divergence degree is larger than a distribution threshold value, information associated with the spatial area corresponding to the maximum cumulative divergence degree is distributed to the object from the present time.
The information delivery method according to claim 2 or claim 3, wherein
前記即時的乖離度決定手段が、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアが、直前の情報配信開始タイミングに関連付けた空間エリアでなければ、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリアの即時的乖離度を予め定めた正の値とし、オブジェクトが現時点で位置する空間エリア以外の他の空間エリアの即時的乖離度を0に設定するステップと
を含むことを特徴とする請求項1から請求項4の何れか1項に記載の情報配信方法。 If the immediate divergence determination means is a spatial area in which the object is currently located is a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence of all the spatial areas is a predetermined negative value. Step to set to
If the spatial area where the object is currently located is not a spatial area associated with the immediately preceding information distribution start timing, the immediate divergence determining means determines in advance the immediate divergence degree of the spatial area where the object is currently located. A step of setting the immediate divergence degree to zero in a spatial area other than the spatial area where the object is currently located, and
The information distribution method according to claim 1, further comprising:
前記累積的乖離度取得手段が、合計結果を所定の最大値と比較し、2つのうちの最大値を取得するステップと、
前記累積的乖離度取得手段が、取得した前記最大値を現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度として決定するステップと
を含むことを特徴とする請求項1から請求項5の何れか1項に記載の情報配信方法。 The cumulative divergence acquisition means obtains the sum of the cumulative divergence of the spatial area at the previous time and the immediate divergence of the spatial area at the current time;
The cumulative divergence acquiring means compares the total result with a predetermined maximum value, and acquires the maximum value of the two;
The cumulative divergence acquiring means determines the acquired maximum value as the cumulative divergence of each spatial area at the present time; and
The information delivery method according to any one of claims 1 to 5, wherein the information delivery method includes:
前記配信手段が備える内部境界・外部境界取得手段が、各空間エリアの境界および各空間エリアの内部境界ファクターおよび外部境界ファクターに基づいて、各空間エリアの仮想内部境界および/または仮想外部境界を取得する内部境界・外部境界取得ステップを有し、
前記即時的乖離度決定ステップで、
オブジェクトの位置パラメータと各空間エリアの仮想の内部境界および/または仮想外部境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定する
ことを特徴とする請求項1から請求項6の何れか1項に記載の情報配信方法。 The degree of divergence includes an inner boundary factor, an outer boundary factor, an immediate divergence degree, and a cumulative divergence degree,
The internal boundary / external boundary acquisition means included in the distribution means acquires the virtual internal boundary and / or virtual external boundary of each spatial area based on the boundary of each spatial area and the internal boundary factor and external boundary factor of each spatial area. An internal boundary / external boundary acquisition step,
In the immediate divergence determination step,
Determine the immediate divergence of each spatial area based on the object's positional parameters and the virtual internal and / or virtual external boundaries of each spatial area
The information distribution method according to any one of claims 1 to 6, wherein the information distribution method is performed .
各空間エリアの乖離度に基づいて、オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界を使用することにより、オブジェクトに対して空間エリアに関連付けた情報を配信する配信手段とを備え、
前記乖離度が、即時的乖離度と累積的乖離度を含み、
前記配信手段が、
前記オブジェクトの位置パラメータおよび各空間エリアの境界に基づいて、各空間エリアの即時的乖離度を決定する即時的乖離度決定手段と、
各空間エリアの即時的乖離度に基づいて、現時点での各空間エリアの累積的乖離度を取得する累積的乖離度取得手段と、
前記累積的剥離度に基づいて、前記オブジェクトに対する配信を制御する配信制御手段とを含む
ことを特徴とする情報配信装置。 Receiving means for receiving a positional parameter of an object in a space including one or more spatial areas;
Distribution means for distributing information associated with the spatial area to the object by using the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area based on the degree of divergence of each spatial area;
The degree of deviation includes an immediate degree of deviation and a cumulative degree of deviation,
The delivery means is
Immediate divergence determination means for determining an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area based on the position parameter of the object and the boundary of each spatial area;
A cumulative divergence acquisition means for acquiring a cumulative divergence degree of each spatial area based on an immediate divergence degree of each spatial area;
Distribution control means for controlling distribution to the object based on the cumulative peeling degree.
An information distribution apparatus characterized by that .
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN200910203109.4 | 2009-05-27 | ||
| CN200910203109.4A CN101902683B (en) | 2009-05-27 | 2009-05-27 | Information publishing method, device and system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010277587A JP2010277587A (en) | 2010-12-09 |
| JP5073782B2 true JP5073782B2 (en) | 2012-11-14 |
Family
ID=43227811
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010118057A Expired - Fee Related JP5073782B2 (en) | 2009-05-27 | 2010-05-24 | Information transmission method, apparatus and system |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5073782B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101902683B (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5420704B2 (en) * | 2012-03-19 | 2014-02-19 | ヤフー株式会社 | Information processing apparatus and method |
| US20130268378A1 (en) * | 2012-04-06 | 2013-10-10 | Microsoft Corporation | Transaction validation between a mobile communication device and a terminal using location data |
| US9986375B2 (en) * | 2014-02-12 | 2018-05-29 | Google Llc | Energy-efficient location determination |
| JP6899505B2 (en) * | 2016-09-16 | 2021-07-07 | 株式会社日立国際電気 | Broadcasting device and received waveform evacuation method |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3151395B2 (en) * | 1995-10-16 | 2001-04-03 | 株式会社エヌ・ティ・ティ・ドコモ | Dual mode location registration method, mobile communication system using the same, and radio base station used in the mobile communication system |
| JP3462449B2 (en) * | 2000-06-02 | 2003-11-05 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | Information guidance method and mobile radio station |
| US6985588B1 (en) * | 2000-10-30 | 2006-01-10 | Geocodex Llc | System and method for using location identity to control access to digital information |
| JP2002175232A (en) * | 2000-12-05 | 2002-06-21 | Sony Corp | Information providing operation, device, information communication device and information providing system |
| JP2003288289A (en) * | 2002-03-27 | 2003-10-10 | Seiko Epson Corp | Ad distribution server, portable terminal, advertisement distribution system, advertisement distribution method, and recording medium |
| JP3712381B2 (en) * | 2002-04-18 | 2005-11-02 | 富士通株式会社 | Push distribution service providing method, information providing service system, server system, and user terminal |
| JP2007336311A (en) * | 2006-06-16 | 2007-12-27 | Hitachi Ltd | Communication device |
| JP2008259092A (en) * | 2007-04-09 | 2008-10-23 | Sony Ericsson Mobilecommunications Japan Inc | Broadcast receiving terminal |
-
2009
- 2009-05-27 CN CN200910203109.4A patent/CN101902683B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2010
- 2010-05-24 JP JP2010118057A patent/JP5073782B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101902683A (en) | 2010-12-01 |
| JP2010277587A (en) | 2010-12-09 |
| CN101902683B (en) | 2014-07-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11403797B2 (en) | Dynamic location based digital element | |
| US20220027948A1 (en) | Methods, systems, and media for presenting advertisements relevant to nearby users on a public display device | |
| US10826631B2 (en) | System and method for 3D tracking for ad-hoc cross-device interaction | |
| US9037407B2 (en) | Method and system for determining position of an inertial computing device in a distributed network | |
| US20240412434A1 (en) | Dynamic location based digital element | |
| CN105302916A (en) | Information recommendation method and device | |
| CN105260431A (en) | Electronic map based information acquisition method and apparatus | |
| US10621624B2 (en) | Live auction advertisements for smart signs | |
| JP2014153828A (en) | Server device, advertisement distribution system and program | |
| JP5073782B2 (en) | Information transmission method, apparatus and system | |
| CN103152375A (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, program, recording medium, and information processing system | |
| JP5920886B2 (en) | Server, system, program and method for estimating POI based on terminal position / orientation information | |
| US20150006461A1 (en) | Recommendation information providing device, mobile terminal, recommendation information providing method, recommendation information provision supporting method, and recording medium | |
| KR102148775B1 (en) | Method for displaying location of member for group driving, and apparatus for the same | |
| KR102200458B1 (en) | Method for displaying location of member for gorup driving, apparatus and system for the same | |
| CN104422438B (en) | Air navigation aid, system and equipment | |
| US20200084580A1 (en) | Location based information service application | |
| JP2012216087A (en) | Advertisement system and advertisement distribution method | |
| JP2014082580A (en) | Guide information distribution system | |
| JP6353190B2 (en) | Advertising display system | |
| JP5300833B2 (en) | Information distribution apparatus, information distribution system, and information distribution method | |
| US12182946B2 (en) | Mixed reality space sharing system, sharing information management server, mixed reality terminal, mixed reality space sharing method, and sharing information management program | |
| JP2014170451A (en) | Server device, advertisement display and program | |
| KR20150131803A (en) | Method and apparatus for processing message using user device's status information | |
| KR20150067464A (en) | Method for transmitting of voice for gorup driving, apparatus and system for the same |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101105 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120411 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120709 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120727 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120822 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150831 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |