JP4974787B2 - Recording device - Google Patents
Recording device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4974787B2 JP4974787B2 JP2007172286A JP2007172286A JP4974787B2 JP 4974787 B2 JP4974787 B2 JP 4974787B2 JP 2007172286 A JP2007172286 A JP 2007172286A JP 2007172286 A JP2007172286 A JP 2007172286A JP 4974787 B2 JP4974787 B2 JP 4974787B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- recording
- roller
- recording medium
- period
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Ink Jet (AREA)
- Handling Of Sheets (AREA)
- Controlling Sheets Or Webs (AREA)
- Delivering By Means Of Belts And Rollers (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、記録媒体に記録を行う記録装置及び記録装置の制御方法に関し、記録媒体の搬送の制御及び記録手段の制御に関する。 The present invention relates to a recording apparatus that performs recording on a recording medium and a control method for the recording apparatus, and relates to control of conveyance of the recording medium and control of recording means.
近年の記録装置は、記録される画像の高画質化や画像の記録の高速化が進んでいる。記録装置の搬送系においては、例えば、搬送系に光学式のロータリーエンコーダーを備え、ロータリーエンコーダーからの信号を用いて搬送制御を行っている。搬送制御として、搬送ローラーによる搬送量の制御や、搬送速度の制御が行われる(特許文献1)。 In recent years, recording devices have been improved in the quality of recorded images and the speed of image recording. In the conveyance system of the recording apparatus, for example, an optical rotary encoder is provided in the conveyance system, and conveyance control is performed using a signal from the rotary encoder. As conveyance control, control of the conveyance amount by a conveyance roller and control of conveyance speed are performed (patent document 1).
また、転写ベルトの速度ムラを無くすために、転写ベルトにスケールを設け、スケールを検知する光学式のセンサーを用いて転写ベルトの速度を測定し、測定した速度によりベルトを駆動するモーターの速度を制御している(特許文献2)。 In order to eliminate the uneven speed of the transfer belt, a scale is provided on the transfer belt, the speed of the transfer belt is measured using an optical sensor that detects the scale, and the speed of the motor that drives the belt is determined by the measured speed. (Patent Document 2).
<ロータリーエンコーダーを用いた記録装置>
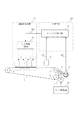
図2は従来の記録装置の一例である。1は記録ヘッドであり、搬送方向に並んでいる。2は記録を行う記録媒体であり、3は記録媒体2を搬送する搬送ベルトである。4は搬送ベルト3を回転移動させるための搬送ローラーであり、5は搬送ベルト3を支持する2つの従送ローラである。6は搬送ローラー4と一体化された搬送ローラ軸で、7は搬送ローラー軸6を駆動する搬送モーターである。8は搬送ローラ軸6に設けられているロータリーエンコーダーである。
<Recording device using a rotary encoder>
FIG. 2 shows an example of a conventional recording apparatus.
101は記録媒体2が搬送するタイミングに合わせて記録ヘッド1の駆動タイミングを制御するヘッド駆動制御部である。102は搬送モーター7の回転制御を行うモーター駆動部である。201はロータリーエンコーダーが出力する回転パルス信号である。搬送ローラの回転に応じて周期的なパルス信号が、ロータリーエンコーダーから出力される。202は記録タイミング基準信号である。103は回転パルス信号201から記録タイミング基準信号202を生成する記録タイミング生成手段である。
記録媒体2に対して記録を行う時は、搬送ベルト3を一定速度で周回するように搬送モーター7を駆動させた後、記録ヘッド1を駆動させて記録を行う。
When recording on the
図3(A)は搬送ベルト3を上から見下ろした図である。説明を簡単にするために記録ヘッド1は1本の場合で説明する。記録媒体2にはAという画像が記録されている状態を示している。記録媒体上に記録できるドット数は搬送方向12ドット、搬送方向に対して垂直方向(以降、搬送幅方向と記す)9ドットとする。搬送方向について一番左にある縦一列のドット列を“1st LINE”と呼び、左から2番目のドット列を”2nd LINE“と呼ぶ。一番右のドット列は”12th LINE”と呼ぶ。記録ヘッド1の数字1〜9はノズルの位置を示している。
FIG. 3A is a view of the
図3(B)は、ヘッド駆動制御部101に入力される記録タイミング基準信号202と記録ヘッド1の駆動タイミングを示す図である。”7th LINE”と”8th LINE”の記録のタイミングを説明する図である。
FIG. 3B is a diagram illustrating the recording
記録媒体が△Xの移動量に対応する△tの時間経過したタイミングで記録ヘッドを駆動させる制御を行う。 Control is performed to drive the recording head at the timing when the time Δt corresponding to the movement amount of the recording medium ΔX has elapsed.
例えば、搬送速度は300mm/s、搬送方向の記録解像度は2400dpiの場合、
△t=35.28μs((25.4mm÷2400dpi)÷300mm/s)
となる。
For example, when the conveyance speed is 300 mm / s and the recording resolution in the conveyance direction is 2400 dpi,
Δt = 35.28 μs ((25.4 mm ÷ 2400 dpi) ÷ 300 mm / s)
It becomes.
なお、図3(B)のタイミングチャートでは例えば、”7th LINE”について、2から9が駆動されていることを示す。 In the timing chart of FIG. 3B, for example, 2 to 9 are driven for “7th LINE”.
尚、実際には、記録装置には、複数の記録ヘッドが搬送方向に配列されており、ヘッドの距離に対応して、駆動タイミングを調整する。 Actually, a plurality of recording heads are arranged in the transport direction in the recording apparatus, and the drive timing is adjusted according to the distance of the heads.
この駆動タイミングの制御構成について図4を用いて説明する。 This drive timing control configuration will be described with reference to FIG.
図4(A)はタイミング生成手段11のブロック図であり、図4(B)はタイミングチャートである。回転パルス信号201は搬送解像度300dpi、搬送基準信号は搬送解像度1200dpiとする。
4A is a block diagram of the timing generation means 11, and FIG. 4B is a timing chart. The
図4において、161は回転パルス信号201が”0(ローレベル)”から”1(ハイレベル)”に変化したことを検知する立ち上がり検知部である。261はその立ち上がり検知信号である。162は立ち上がり検知信号261が入力される間隔をカウントするカウンタ部である。262はカウンタ部162でカウントされた結果であるカウント値である。
In FIG. 4, reference numeral 161 denotes a rise detection unit that detects that the
163はカウント値262を保持するパルス幅値保持部である。164はパルス幅値263を1/4倍した値を算出する搬送基準信号パルス周期算出部である。 Reference numeral 163 denotes a pulse width value holding unit that holds the count value 262. Reference numeral 164 denotes a carrier reference signal pulse period calculation unit that calculates a value obtained by multiplying the pulse width value 263 by ¼.
264は搬送基準信号パルス周期算出部164で算出された搬送基準周期値である。165は搬送基準周期値264に従ってパルス信号を生成する搬送基準信号生成部である。 Reference numeral 264 denotes a conveyance reference period value calculated by the conveyance reference signal pulse period calculation unit 164. Reference numeral 165 denotes a conveyance reference signal generation unit that generates a pulse signal according to the conveyance reference period value 264.
回転パルス信号201が”0”から”1”に変化すると立ち上がり検出部161からの立ち上がり信号261にパルスが出力される。このパルスによりカウント部162ではカウント値262を0に戻した後、本システムのシステムクロック等の常時安定して動作しているクロック信号によりカウントアップを行う。次に回転パルス信号201が”0”から”1”に変化し立ち上がり信号261にパルスが生成されると、この時のカウント部162のカウント値262の値をパルス幅値保持部163に保持される。このとき保持される値の例として、カウンタ部で使用しているクロック数を用いる。尚、カウント部162のカウント値262を保持すると同時にカウント値を0に戻し次のパルスのカウントを行う。保持された値はパルス幅値263にて搬送基準信号パルス周期算出部164にて直ちに1/4倍した値を搬送基準周期値264として搬送基準信号生成部165に出力する。搬送基準信号生成部165ではカウント部162で用いたクロック信号を使用し、搬送基準周期値264毎にパルスを出力することで搬送基準信号202を生成する。これを繰り返すことで搬送解像度300dpiの回転パルス信号201から搬送解像度1200dpiの搬送基準信号202が生成する。
When the
以上のようにしてロータリーエンコーダー8の回転パルス信号201に従って画像形成を行っていた。
As described above, image formation is performed according to the
<レーザードップラー式センサを用いた記録装置>
図5は、従来の別の形態の記録装置の例である。レーザードップラー式センサ(レーザードップラー式速度センサ)9を用いた記録装置である。レーザードップラー式センサ9を用いて搬送ベルトの移動量を検知する。
<Recording device using laser Doppler sensor>
FIG. 5 shows an example of another conventional recording apparatus. This is a recording apparatus using a laser Doppler type sensor (laser Doppler type speed sensor) 9. The amount of movement of the conveyor belt is detected using a laser Doppler sensor 9.
ロータリーエンコーダー8の代わりにレーザードップラー式センサ9を用いる点で図2と異なっている。他の構成は図2と同様であるので説明を省く。
2 is different from FIG. 2 in that a laser Doppler sensor 9 is used instead of the
<レーザードップラー式センサの説明>
図6はレーザードップラー式センサの原理を簡単に説明する。
<Description of laser Doppler sensor>
FIG. 6 briefly explains the principle of the laser Doppler sensor.
レーザ光源0301からレーザ光LAを発射する。発射されたレーザ光LAは、ビームスプリッタ0302において二分される。その二分された一方のレーザ光L1は、ビームスプリッタ0302を透過して被測定物0310に直接照射される。これに対して、二分された他方のレーザ光L2は、ビームスプリッタ0302で反射されて、更に反射用ミラー0303でも反射されて被測定物0310に照射される。レーザ光L1及びL2は、図6に示す通り、被測定物0310の垂線に対してそれぞれ入射角θの角度で入射し、かつ対称な軌道にて被測定物0310を照射する。
Laser light LA is emitted from the
ある速度Vで移動している被測定物0310に上記レーザ光L1及びL2が入射されると、当該被測定物0310は上記レーザ光L1、L2を散乱し、散乱光LBを発する。この散乱光LBは集光レンズ0304等の光学系を通過して受光センサ0305へ到達する。受光センサ0305は、上記散乱光LBを検出し、光電変換する。この変換された電気信号はアンプ0306に入力される。アンプ0306は、電気信号の振幅を増幅し、バンドパスフィルタ0307へ出力する。バンドパスフィルタは、ヘテロダイン検波を行い、アナログ信号であるドップラ信号Dを信号処理回路0308へ出力する。
When the laser beams L1 and L2 are incident on the object to be measured 0310 moving at a certain speed V, the object to be measured 0310 scatters the laser beams L1 and L2 and emits scattered light LB. The scattered light LB passes through the optical system such as the
信号処理回路0308では、上記の周波数をfDとするドップラー信号Dを、同じく周波数をfDとするパルス信号へと変換し、当該パルス信号を速度信号として出力する。
In the
このパルス信号の周期Tは被測定物0310が一定距離Lを進むための時間を示している。このようにして、レーザードップラー式センサ0300は、被測定物にスケールを設けること無く精密な変位を検知しうるパルス信号を速度信号としてリアルタイムに出力できる(特許文献3)。
上述したようなロータリーエンコーダーを用いた制御では、例えば、搬送ローラー4の偏心が原因となる搬送ベルトの速度変動に対応できなった。また、搬送ベルト3の厚みにムラがあった場合に、同様に、搬送ベルトの速度変動に対応できなかった。
In the control using the rotary encoder as described above, for example, it has been impossible to cope with the speed fluctuation of the transport belt caused by the eccentricity of the transport roller 4. Similarly, when the thickness of the
図7は搬送ローラの偏心を説明するためのローラの断面図である。400は回転軸の中心、401は搬送ローラ4の中心、rは搬送ローラ半径、△rは偏心量を示す。
FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view of the roller for explaining the eccentricity of the conveying roller.
例えば、半径rが8mm、偏心量△rが5μmの搬送ローラ4を頂点の速度が100mm/Sになるように定各速度で回転すると偏心△rの分、搬送ローラ半径が増減するため実際の速度は100±0.0625mm/sというように速度が変動する。 For example, if the conveyance roller 4 having a radius r of 8 mm and an eccentricity amount Δr of 5 μm is rotated at constant speeds so that the apex speed is 100 mm / S, the conveyance roller radius increases or decreases by the amount of the eccentricity Δr. The speed varies as 100 ± 0.0625 mm / s.
このような条件で図2の構成の記録装置で画像形成を行った時のドット位置ズレを示したのが図8で、486.8μm間隔でドットを記録したときの搬送方向の位置ズレを横軸に記録媒体上の位置、縦軸には位置ズレ量で表した図である。図8から解るように約50.3mm周期で位置ズレが周期的に変動している。この50.3mmは搬送ローラの半径r=8mmより求められる周長L=2*π*r=2*8mm*π=50.27mmと一致する。このように、図2の構成では制御できない搬送ローラ軸から記録媒体までの変動要因の中では搬送ローラの偏心が画像劣化に大きく影響している。 FIG. 8 shows the dot position deviation when an image is formed by the recording apparatus having the configuration shown in FIG. 2 under such conditions. The position deviation in the transport direction when dots are recorded at intervals of 486.8 μm is shown in FIG. The axis represents the position on the recording medium, and the vertical axis represents the amount of positional deviation. As can be seen from FIG. 8, the positional deviation periodically fluctuates at a cycle of about 50.3 mm. This 50.3 mm coincides with the circumferential length L = 2 * π * r = 2 * 8 mm * π = 50.27 mm obtained from the radius r = 8 mm of the conveying roller. As described above, the eccentricity of the conveyance roller greatly affects the image deterioration among the fluctuation factors from the conveyance roller shaft to the recording medium that cannot be controlled by the configuration of FIG.
背景技術の欄で説明したように、転写ベルトにスケールを設け、スケールを検知する光学式のセンサーを用いて転写ベルトの速度を測定する方法がある。しかし、ミストと呼ばれる微小なインク液滴や紙紛により搬送ベルトが汚れる場合には、搬送ベルトの移動速度を正確に読めない。 As described in the background art section, there is a method in which a scale is provided on the transfer belt and the speed of the transfer belt is measured using an optical sensor that detects the scale. However, when the transport belt is soiled by minute ink droplets or paper dust called mist, the moving speed of the transport belt cannot be read accurately.
レーザードップラー式速度センサ9は搬送ベルトの速度を直接測定できるが、以下のような欠点があった。 The laser Doppler type speed sensor 9 can directly measure the speed of the conveyor belt, but has the following drawbacks.
レーザードップラー式速度センサ9の動作中に、何らかの原因で、ドップラー信号が弱くなる期間(タイミング)があり、その期間においては、速度を正確に測定できないという問題がある。 During the operation of the laser Doppler speed sensor 9, there is a period (timing) in which the Doppler signal is weak for some reason, and there is a problem that the speed cannot be measured accurately during that period.
図9はレーザードップラー式速度センサ9から出力されるパルス波形である。この波形において、200μsecから800μsecは、ドップラー信号が弱くなる期間であり、ドロップアウトと呼ばれる。このドップラー信号が弱くなる期間は、搬送ベルトの移動速度を正確に検出できていない。 FIG. 9 shows a pulse waveform output from the laser Doppler type speed sensor 9. In this waveform, 200 μsec to 800 μsec is a period in which the Doppler signal becomes weak, and is called dropout. During the period when the Doppler signal is weak, the moving speed of the conveyor belt cannot be accurately detected.
本発明の目的は、上記各問題点を解決するために、搬送ローラ偏心の影響を抑制し、かつ装置内の汚れの影響を受けずに精度の高い搬送制御方法と記録制御方法を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a highly accurate conveyance control method and recording control method that suppresses the influence of eccentricity of the conveyance roller and is not affected by dirt in the apparatus, in order to solve the above problems. It is in.
上記目的を達成するため、本発明は以下を有することを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention is characterized by the following.
本発明の記録装置の一つの形態は、インクジェット方式の記録ヘッドと、ローラーを含み記録媒体を搬送するための搬送手段と、記録媒体の表面を検出することで、記録媒体の移動速度に応じてパルス周期が変化するパルス信号である第1信号を生成するレーザードップラー式センサと、前記ローラーの回転に応じてパルス信号である第2信号を生成するエンコーダと、前記レーザードップラー式センサで生成される前記第1信号の前記パルス周期が所定の範囲を越えた場合は前記第1信号を補正する補正手段と、前記補正手段を経た前記第1信号のパルス周期の成分であって、前記ローラーの1回転を1周期とする周期的な変動情報を取得する取得手段と、前記エンコーダで生成される前記第2信号により前記記録媒体に対する記録の制御を行う際に、前記ローラーの偏心による前記記録媒体の移動速度むらの影響を抑制するように前記変動情報を前記記録の制御に反映させる制御手段とを備えることを特徴とする。 According to one aspect of the recording apparatus of the present invention, an ink jet recording head, a conveying means including a roller for conveying the recording medium, and a surface of the recording medium are detected, so that the recording medium is moved according to the moving speed of the recording medium. Generated by a laser Doppler sensor that generates a first signal that is a pulse signal that changes in pulse period, an encoder that generates a second signal that is a pulse signal according to the rotation of the roller, and the laser Doppler sensor A correction means for correcting the first signal when the pulse period of the first signal exceeds a predetermined range; and a component of a pulse period of the first signal that has passed through the correction means, wherein Acquisition means for acquiring periodic fluctuation information with one period of rotation, and control of recording on the recording medium by the second signal generated by the encoder When performing, characterized in that it comprises a control means to be reflected in the control of the recording the variation information so as to suppress the influence of the moving speed fluctuation of the recording medium due to the eccentricity of the roller.
本発明の記録装置の別の形態は、ロール状の記録媒体の搬送方向の上流から下流に沿って複数配置されたインクジェット方式の記録ヘッドと、前記複数の記録ヘッドよりも上流に配置され、記録媒体を前記搬送方向に搬送するための第1ローラーと、前記複数の記録ヘッドよりも下流に配置され、記録媒体を前記搬送方向に搬送するための、前記第1ローラーよりも記録媒体を保持する圧力が小さく且つ前記第1ローラーよりも回転の速度が大きい第2ローラーと、記録媒体の表面を検出することで記録媒体の移動に応じた第1信号を生成するためのレーザードップラー式センサと、前記第1ローラーの回転に応じた第2信号を生成するためのエンコーダと、前記第1信号と前記第2信号に基づいて前記第1ローラーの偏心の影響を抑制するように前記記録媒体に対する記録の制御を行う制御手段とを備えることを特徴とする。 Another embodiment of the recording apparatus of the present invention includes a plurality of inkjet recording heads arranged from upstream to downstream in the conveyance direction of the roll-shaped recording medium, and an upstream side of the plurality of recording heads. A first roller for transporting the medium in the transport direction and a recording medium that is disposed downstream of the plurality of recording heads and holds the recording medium than the first roller for transporting the recording medium in the transport direction A second roller having a low pressure and a rotation speed larger than that of the first roller; a laser Doppler sensor for generating a first signal corresponding to the movement of the recording medium by detecting the surface of the recording medium; An encoder for generating a second signal corresponding to the rotation of the first roller, and the influence of eccentricity of the first roller is suppressed based on the first signal and the second signal. Characterized in that it comprises a control means for controlling recording on the sea urchin the recording medium.
本発明によれば、搬送ベルト等の搬送手段が汚れても、その汚れの影響を受けずに搬送手段の駆動制御が行うことができ、搬送変動による画像劣化を抑制できる。 According to the present invention, even if the conveyance means such as the conveyance belt becomes dirty, the drive control of the conveyance means can be performed without being affected by the contamination, and image deterioration due to conveyance fluctuation can be suppressed.
次に、本発明の実施形態について図面を参照して説明する。 Next, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
(第1の実施形態)
図1は第1の実施形態の構成図である。記録装置は、記録ヘッド1を記録媒体の搬送方向に複数配置した構成である。記録ヘッド1には、複数のノズルが配列され、その配列方向は記録媒体の搬送方向と交差する方向である。
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of the first embodiment. The recording apparatus has a configuration in which a plurality of recording heads 1 are arranged in the recording medium conveyance direction. A plurality of nozzles are arranged in the
搬送ベルトにて記録媒体を搬送しながら記録を行うインクジェット方式の記録ヘッド1を4本備えた記録装置について、搬送変動を画像形成にフィードバックする制御構成を説明する。 A control configuration that feeds back conveyance fluctuations to image formation will be described for a recording apparatus that includes four inkjet recording heads 1 that perform recording while conveying a recording medium with a conveyance belt.
図1に記載の各符号は図2および図3と同じであるため説明は省略する。また、以降の説明ではロータリーエンコーダー8を回転検知センサーと呼ぶ。
1 are the same as those in FIG. 2 and FIG. In the following description, the
画像の記録を行うために搬送モーター7を定速で回転させて搬送ベルト3を回転(周回)させると、タイミング生成手段11には回転パルス信号201と移動パルス信号203が入力される。
When the
回転パルス信号201は、搬送ローラー4の回転を検知するために搬送ローラ軸6に取り付けたロータリーエンコーダー(エンコーダセンサ)から出力される信号である。移動パルス信号203は、レーザードップラー式速度センサ(移動量検知センサ)9から出力される信号である。
The
そのうち、回転パルス信号201は搬送ベルト3の移動情報である搬送基準信号202を生成する時の基準信号として使用する。この回転パルス信号201は搬送モーター7から搬送ローラ軸6までの伝達時に生じる速度変動を含んでいる。しかし、搬送ローラ軸6から搬送ベルト3までの伝達時に生じる搬送ローラ偏心などの速度変動は含んでいない。
Among them, the
このため、このまま搬送基準信号202を生成すると、この搬送基準信号202に従ってヘッド駆動制御部101にて形成した画像には搬送ローラ偏心などによる搬送ムラが発生してしまう。
For this reason, if the
そこで、タイミング生成手段が入力する1つの情報である移動パルス信号203から搬送ローラ偏心による速度変動情報を取り出し、この速度変動情報を回転パルス信号201から搬送基準信号202を生成する時に補正を行う。この補正により、搬送ローラ偏心などの速度変動も含んだ搬送基準信号202が生成できる。この搬送基準信号202に従ってヘッド駆動制御部101にて画像形成のタイミング制御を行うことにより、搬送ローラ偏心等の速度変動の影響が無い画像形成が行われる。
Therefore, speed fluctuation information due to the conveyance roller eccentricity is extracted from the
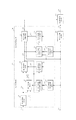
<タイミング生成手段11の処理の概要>
図10は図1に示したタイミング生成手段11のブロック図である。図11を用いて、タイミング生成手段11の処理の概要を説明する。
<Outline of Processing of
FIG. 10 is a block diagram of the timing generation means 11 shown in FIG. An outline of the processing of the
信号生成部113は、情報220と情報221を入力して、タイミング信号202を生成する。
The
情報(パルス信号)203を入力する第1信号補正部153と、第1信号補正部153の出力と情報(パルス信号)201とを入力する第1信号変動検出部154により周期の変動を示す情報220を生成する。第2信号周期検出部112は、情報201を入力し、周期情報221を出力する。
Information indicating a cycle variation by a first
第1信号補正部153は、信号203が正常か否かを判定する。情報203の状態が正常の場合、情報203を第1信号変動検出部154へ出力する。情報203の状態が正常でない場合、代わりの情報を第1信号変動検出部154へ出力する。
The first
これにより、例えば、ローラの偏心の影響をうける回転パルス信号201の周期を補正したタイミング信号220を、レーザードップラー式速度センサーの状態に係わらず、出力することができる。これは、移動パルス信号203のパルスが突然欠落する場合がある。この場合、第1信号補正部153は、移動検知センサー9からのパルス信号203のパルス欠落の有無を常に調べ、信号において欠落した部分の補完処理を行う。
Thereby, for example, the timing signal 220 obtained by correcting the period of the
第1信号変動検出部154は、第1信号補正部153から出力された情報(信号)214に基づき、周期的な変動情報を生成し、基準信号生成部113へ出力する。
The first signal fluctuation detection unit 154 generates periodic fluctuation information based on the information (signal) 214 output from the first
第1信号周期変動情報220の周期をf1、第2信号周期情報221の周期をf2、タイミング信号202の周期をfoutとすると、
fout=f2+Σf1(n=1〜m)で求めることができる。
If the period of the first signal period variation information 220 is f1, the period of the second signal period information 221 is f2, and the period of the
It can be obtained by fout = f2 + Σf1 (n = 1 to m).
ここで、m=搬送ローラ1回転あたりの期間の移動パルス信号のパルス数÷搬送ローラ1回転あたりの回転パルス信号のパルス数である。 Here, m = the number of pulses of the movement pulse signal during the period per rotation of the conveyance roller / the number of pulses of the rotation pulse signal per rotation of the conveyance roller.
ここで、後で説明するが、f1は基準の周期に対する差分値であるため、マイナスの値またはプラスの値となる。 Here, as will be described later, since f1 is a difference value with respect to the reference period, it is a negative value or a positive value.
<タイミング生成手段11の説明(図10)>
図10の第1信号補正部153について説明する。
<Description of Timing Generation Unit 11 (FIG. 10)>
The first
101は移動パルス信号203のパルス周期情報を検出する第1信号周期検出部である。この第1信号周期検出部101は、周期情報をカウントするカウンタと、カウンタの値を保持するラッチを備える。
ラッチされた値を第1信号周期情報210として、第1信号周期判定部102と第1信号周期補正部104へ出力する。
The latched value is output to the first signal
一方、第1信号周期検出部101のカウンタでカウントされた値は、第1信号周期カウント信号218として第1信号周期判定部102へ出力される。
On the other hand, the value counted by the counter of the first signal
212は第1信号周期判定部102で判定した結果を示す第1信号周期判定結果情報である。
Reference numeral 212 denotes first signal cycle determination result information indicating a result determined by the first signal
103は第1信号周期判定部102にて判定するための判定基準値を記憶する第1信号周期判定基準記憶部、211はその判定基準値の第1信号周期判定基準情報(基準値)である。
103 is a first signal cycle determination reference storage unit that stores a determination reference value for determination by the first signal
104は第1信号周期補正部であり、判定結果が正常と判断すれば第1信号周期情報210を第1信号変動検出部154へ出力し、判定結果が異常と判断すれば補正値に置き換えて第1信号変動検出部154へ出力する。 Reference numeral 104 denotes a first signal period correction unit that outputs the first signal period information 210 to the first signal fluctuation detection unit 154 if the determination result is determined to be normal, and replaces it with a correction value if the determination result is determined to be abnormal. It outputs to the 1st signal fluctuation | variation detection part 154.
214は第1信号周期補正部が出力する第1信号周期情報である。105は第1信号周期補正部104が補正に使用する情報(補正値)を記憶する第1信号周期補正値記憶部、213はその補正値である第1信号周期補正情報である。
Reference numeral 214 denotes first signal cycle information output from the first signal cycle correction unit.
次に、図10の第1信号変動検出部154について説明する。106は第1信号周期情報214の平均値を算出する第1信号周期平均値算出部、217は算出結果の第1信号周期平均値算出信号である。第1信号周期平均値算出部106は、第1信号周期情報214のうち期間T(搬送ローラ1周分)について平均値を算出する。この平均値は、図11のB1(24.9μS)である。この平均値を第1信号周期平均値記憶部110に格納する。この平均値は搬送ローラが1周する毎に、第1信号周期平均値記憶部110に格納される。
Next, the first signal fluctuation detection unit 154 in FIG. 10 will be described.
107は回転検知センサー8からの回転パルス数をカウントし、ローラ1回転の基準位置を示すローラ原点生成部である。215は生成されたローラ原点信号である。
A roller
219は第1信号周期平均値記憶部110から読み出された第1信号周期平均値情報(信号)である。111は第1信号周期変動検出部である。この第1信号周期変動検出部111には、搬送ローラのパルス周期は図11に示すように高周波成分を含んでいる。このため、期間△T毎に平均値を算出する。図11で示すように、C1、C2は平均値である。
Reference numeral 219 denotes first signal cycle average value information (signal) read from the first signal cycle average
第1信号周期変動検出部111はこのC2とB1との差分を△T毎に取得する。この結果(差分値)は第1信号周期変動情報220であり、信号生成部113へ出力する。
The first signal period variation detector 111 acquires the difference between C2 and B1 for each ΔT. This result (difference value) is the first signal period variation information 220 and is output to the
例えば、C2>B1では、パルス周期が平均より大きく、移動速度が平均速度より遅いことを示している。また、C2<B1では、パルス周期が平均より小さく、移動速度が平均速度より速いことを示している。このような周期むら(速度むら)の情報を、信号生成部113する。
For example, C2> B1 indicates that the pulse period is larger than the average and the moving speed is slower than the average speed. Further, C2 <B1 indicates that the pulse period is smaller than the average and the moving speed is faster than the average speed. Information on such period unevenness (speed unevenness) is sent to the
以上のように、移動パルス信号203の周期情報から回転パルス信号の周期ムラ(搬送ローラの速度ムラ)の情報(変動情報)を生成することができる。
As described above, it is possible to generate information (variation information) on the periodic unevenness (speed unevenness of the conveying roller) of the rotation pulse signal from the periodic information of the moving
図14はこの第1信号周期平均値算出信号217を格納するタイミングの説明図である。第1信号周期平均値算出部106は、搬送ローラの”N回転目”では、第1信号周期平均値算出信号217の加算を行う。次のN+1回転目の開始時に加算結果A1から平均値B1を算出し、この値を第1周期平均値記憶部110に記憶を行う。同様に、搬送ローラの”N+1回転目”で、第1信号周期平均値算出信号217の加算を行い、次のN+2回転目の開始時に加算結果A2から平均値B2)を算出する。以降、同様の処理を行う。
FIG. 14 is an explanatory diagram of the timing at which the first signal cycle average
タイミング生成手段11には、第1信号補正部153及び第1信号変動検出部154のほかに以下のブロックがある。112は回転パルス信号201のパルス周期情報(第2信号周期情報信号)221を検出する第2信号周期検出部である。113は搬送基準信号生成部である。この搬送基準信号生成部221は、第1信号周期変動情報220を用いて第2信号周期情報221から情報202を生成する。
The
<パルス信号の補間処理>
次に、第1信号補正部153における移動パルス信号203の補間処理の説明を行う。この第1信号補正部153は、移動パルス信号203の周期が上限値と下限値の範囲を超えたら異常と判断し、異常があった場合補正を行う。
<Pulse signal interpolation processing>
Next, the interpolation processing of the moving
上限値によりパルスの欠落の検知を行い、下限値により故障等による短い周期も検知する。 The missing pulse is detected by the upper limit value, and a short cycle due to a failure or the like is also detected by the lower limit value.
移動検知センサー9から入力された移動パルス信号203は第1信号周期検出部101にてシステムクロック等のクロック信号を用いてパルス周期をカウントする。
The moving
検出されたパルス周期が格納されている第1信号周期情報信号210は、第1信号周期判定部102にて第1信号周期判定基準記憶部103に記憶された上限値と下限値の情報を有する第1信号周期判定基準値信号211と比較を行う。即ち、検知したパルス周期について、周期の上限値と下限値と比較を行う。
The first signal period information signal 210 in which the detected pulse period is stored has information on the upper limit value and the lower limit value stored in the first signal period determination
この比較処理において、上限値と下限値の範囲内であれば正常と判定し、範囲外であれば異常として判定する。なお、判定に使用する判定基準値(上限値と下限値)は、予め第1信号判定基準記憶部に記憶を行っておく。 In this comparison process, if it is within the range between the upper limit value and the lower limit value, it is determined as normal, and if it is out of the range, it is determined as abnormal. Note that the determination reference values (upper limit value and lower limit value) used for the determination are stored in advance in the first signal determination reference storage unit.
なお、パルス信号の欠落を検知した場合には、パルスが入力されるまで第1信号周期情報信号210には反映されない。このため、第1信号周期検出部101でカウントアップを行っているカウンタ出力である第1信号周期カウント信号218と上限値との比較を行い、第1信号周期カウント信号218の異常の判定を行う。
In addition, when the lack of a pulse signal is detected, it is not reflected in the 1st signal period information signal 210 until a pulse is input. For this reason, the first signal cycle count signal 218, which is a counter output counted up by the first signal
第1信号周期カウント信号218について判定した結果、異常の場合には第1信号周期補正部104にて第1信号周期補正記憶部105に記憶されている補正値に置き換える。この補正値により信号の補完を行う。
If the result of determination on the first signal cycle count signal 218 is abnormal, the first signal cycle correction unit 104 replaces the correction value stored in the first signal cycle
図12は上で説明した第1信号補正部153のタイミングチャートで、立ち上がり信号とは第1信号周期検出部101内において、移動パルス信号の立ち上がりを示す信号である。図12においてパルス1からパルス5までの5つのパルスの中で、パルス#3のみパルス幅が上限値を超えた場合の例である。正常なパルス#1の先頭の立ち上がりから内部のカウンタにて0からカウントを始める。このカウンタ値は第1信号周期カウント信号である。パルス#2の立ち上がったときのカウンタ値 “t1”をラッチし、第1信号周期情報信号210にパルス#2の期間、出力するのと同時にカウンタは0に戻してパルス#2の周期のカウントを始める。パルス#2の期間は、第1信号周期情報210が上限値と下限値の範囲内であり、かつ第1周期カウント信号218のカウント中の値が上限値を越えていないため、パルス#1の周期情報は正常と判断し、正常であることを第1周期判定結果信号212に出力する。本実施形態では正常である場合は“Low”レベルの信号を出力する。
FIG. 12 is a timing chart of the first
この判定結果を受け取った第1信号周期補正部104では判定結果が正常であるため、第1信号周期情報信号210の周期情報“t1”を補正後第1信号周期情報信号214にそのまま出力する。パルス#3の立ち上がりでも同様にラッチされたパルス#2の周期“t2”が正常であるため補正後第1信号周期情報信号214に“t2”が出力される。
The first signal period correction unit 104 that has received the determination result outputs the normal period information “t1” of the first signal period information signal 210 to the corrected first signal period information signal 214 because the determination result is normal. Similarly, since the period “t2” of the latched
しかし、パルス#3の期間は、パルス#3の周期をカウントしているカウンタの値である第1信号周期カウント信号が上限値を越えた時点で異常と判定し、異常であることを第1周期判定結果信号212に出力する。本実施形態では異常である時は“High”レベルの信号を出力する。
However, during the period of
この判定結果を受け取った第1信号周期補正部104では判定結果が異常であるため、第1信号周期補正値記憶部105に記憶されている第1信号周期補正値信号213“tc”を補正後第1信号周期情報信号214に出力する。
Since the determination result is abnormal in the first signal cycle correction unit 104 that has received this determination result, the first signal cycle correction value signal 213 “tc” stored in the first signal cycle correction
パルス#4の立ち上がりにてラッチされたパルス#3の周期情報“t3”が第1信号周期情報信号210が上限値を超えているためパルス#4の期間も異常として処理される。パルス#5の立ち上がりでパルス#4の周期情報“t4”がラッチされると正常であるため、正常として処理が行われる。このようにして移動パルス信号203のパルス周期が規定範囲を超えた場合の補正処理を行う。
The period information “t3” of the
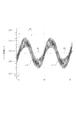
<移動パルス信号の説明(図13)>
図13は移動パルス信号203の波形と異常を検知するための上限値及び下限値を説明する図である。移動パルス信号203の波形は長周期な変動と短周期の変動が合わさった波形である。図13(A)に示すように、長周期の変動は搬送ローラ1回転と同じ周期である。
<Description of moving pulse signal (FIG. 13)>
FIG. 13 is a diagram for explaining the waveform of the moving
この移動パルス信号203の波形は24.9μSを中心に変動し、最大値は25.5μS、最小値は、24.3μSである。このような波形の値に基づき、上限値及び下限値を求めている。最大値に基づき上限値を定め、例えば25.9μSに設定する。同様に、最小値に基づき下限値を定め、24.1μSに設定する。このような上限値と下限値を設定した後、この設定値を用いてパルス周期の判定を行う。
The waveform of the moving
なお、図13(B)に示すように、時間が経過すると、移動パルス信号203の波形は変化する。例えば、時刻t1〜t3の期間では、移動パルス信号203の波形の中心値は24.9μSであった。しかし、時刻t4〜t6の期間では、移動パルス信号203の波形の中心値は25.1μSであった。
As shown in FIG. 13B, the waveform of the moving pulse signal 203 changes with time. For example, during the period from time t1 to time t3, the center value of the waveform of the moving
このため、定期的に、移動パルス信号203の波形を調べる制御を行っても構わない。
For this reason, you may perform control which investigates the waveform of
なお、予め設定する上限値、下限値および補正値は設計値より決めても良いし、予め動作させたときの測定値より決めても良い。 Note that the preset upper limit value, lower limit value, and correction value may be determined from design values, or may be determined from measured values when operating in advance.
(第2の実施形態)
<タイミング生成手段11の第1信号補正部の説明(図15))>
図15について説明する。第2の実施形態のタイミング生成手段11の第1信号補正部153は、図10の第1信号補正部と一部を除いて同じである。異なる点は、第1信号周期判定基準記憶部103と第1信号周期補正値記憶部105に対して、第1信号周期情報信号210が入力されていることである。記録装置の初期化処理(電源を投入した時)を行い、予め定めた搬送動作を行い、第1信号周期判定基準記憶部103と第1信号周期補正値記憶部105にデータを格納する。
(Second Embodiment)
<Description of First Signal Correction Unit of Timing Generation Unit 11 (FIG. 15)>
FIG. 15 will be described. The first
具体的には、第1信号周期情報信号210の平均値を算出し、第1信号周期情報信号210の平均値に一定の割合(例えば5%)を加算した値を判定のための上限値(閾値)とする。第1信号周期情報信号210の平均値に一定の割合(例えば5%)を差し引いた値を下限値(閾値)とする。また、第1信号周期情報信号210の平均値を補正値として記憶を行う。 Specifically, an average value of the first signal period information signal 210 is calculated, and a value obtained by adding a certain ratio (for example, 5%) to the average value of the first signal period information signal 210 is an upper limit value for determination ( Threshold). A value obtained by subtracting a certain ratio (for example, 5%) from the average value of the first signal period information signal 210 is defined as a lower limit value (threshold value). Further, the average value of the first signal cycle information signal 210 is stored as a correction value.
なお、割合の値は一例であり、他の値でも構わない。また、上限値と下限値を求める際、割合を異ならせても構わない。例えば、平均値に7%を加算したものを上限値とし、平均値から3%を減算したものを下限値とするのである。 The ratio value is an example, and other values may be used. Moreover, when calculating | requiring an upper limit and a lower limit, you may change a ratio. For example, the upper limit value is obtained by adding 7% to the average value, and the lower limit value is obtained by subtracting 3% from the average value.
なお、第2の実施形態に適用する記録装置は、第1の実施形態で説明した図1に示す記録装置である。 Note that the recording apparatus applied to the second embodiment is the recording apparatus shown in FIG. 1 described in the first embodiment.
(第3の実施形態)
<タイミング生成手段11の第1信号補正部の説明(図16)>
図16について説明する。第1信号補正部は、図10の第1信号補正部と一部を除いて同じである。異なる点は、第1信号周期判定基準記憶部103と第1信号周期補正値記憶部105に対して、補正後の第1信号周期情報信号214が入力されていることである。図15と異なる点は、記憶を行うための信号として第1信号周期情報信号210の換わりに補正後第1信号周期情報信号214を用いた場合のブロック図である。
(Third embodiment)
<Description of First Signal Correction Unit of Timing Generation Unit 11 (FIG. 16)>
FIG. 16 will be described. The first signal correction unit is the same as the first signal correction unit in FIG. The difference is that the corrected first signal cycle information signal 214 is input to the first signal cycle determination
図15の場合では異常時の情報も含んだ平均値から判定基準値や補正値を生成するのに対し、図16のブロック図では既に記憶されている判定基準値や補正値により異常時の情報が補正されているため、より精度の高い判定基準値と補正値が得られる。 In the case of FIG. 15, the determination reference value and the correction value are generated from the average value including the information at the time of abnormality, whereas in the block diagram of FIG. 16, the information at the time of abnormality is determined by the already stored determination reference value and correction value. Is corrected, a more accurate determination reference value and correction value can be obtained.
なお、第3の実施形態に適用する記録装置は、第1の実施形態で説明した図1に示す記録装置である。 Note that the recording apparatus applied to the third embodiment is the recording apparatus shown in FIG. 1 described in the first embodiment.
(第4の実施形態)
<タイミング生成手段11の第1信号補正部の説明(図17)>
図10と同じ部分は説明を省略する。図17において、第1の実施形態や第2の実施形態と異なる点は2つある。1つは、第1信号周期判定基準記憶部103と第1信号周期補正値記憶部105にローラ原点信号215が入力されていることである。もう1つ異なる点は、信号生成部113に第1信号周期変動情報信号220しか入力されないことである。つまり、図16には第2信号周期検出部がないのである。
(Fourth embodiment)
<Description of First Signal Correction Unit of Timing Generation Unit 11 (FIG. 17)>
Description of the same parts as those in FIG. 10 is omitted. In FIG. 17, there are two points different from the first embodiment and the second embodiment. One is that the roller origin signal 215 is input to the first signal cycle determination
<第1信号変動検出部の説明(図17)>
次に図18において、第1信号変動検出部154の説明を行う。
<Description of First Signal Fluctuation Detection Unit (FIG. 17)>
Next, the first signal fluctuation detection unit 154 will be described with reference to FIG.
第1信号変動検出部154では移動パルス信号203が正常か否かの判定処理や補正処理については、上述した実施形態と同じである。
In the first signal fluctuation detection unit 154, the determination process and the correction process for determining whether the moving
異なる点は、判定に用いる判定基準値(上限値と下限値)および補正値は、一定期間経過すると更新される点である。例えば、搬送ローラが1回転毎に、判定基準値(上限値と下限値)および補正値は更新される。 The difference is that the determination reference value (upper limit value and lower limit value) and correction value used for determination are updated after a certain period of time. For example, the determination reference value (upper limit value and lower limit value) and the correction value are updated every rotation of the transport roller.
更新に使用する値は、更新するタイミングの前(例えば直前)の搬送ローラ1回転の期間において測定した移動パルス信号203から取得する。例えば移動パルス信号203のパルス周期の平均値から求める。
The value used for the update is acquired from the
更新タイミングとして、ローラ原点信号215が入力される毎に行われる。図18はそのタイミングを示す図である。例えば、t1,t9,t17のタイミングで更新される。ローラ原点信号215が入力されるt9のタイミングでは、t1からt8の間の第1信号周期情報信号210の平均値を用いて上限値や下限値を求める。そして、上限値や下限値、平均値を補正値として記憶を行う。なお、上限値や下限値の算出については、既に説明しているので説明を省く。 This is performed every time the roller origin signal 215 is input as the update timing. FIG. 18 shows the timing. For example, it is updated at timings t1, t9, and t17. At the timing of t9 when the roller origin signal 215 is input, the upper limit value and the lower limit value are obtained using the average value of the first signal period information signal 210 between t1 and t8. Then, the upper limit value, lower limit value, and average value are stored as correction values. Since the calculation of the upper limit value and the lower limit value has already been described, the description thereof will be omitted.
なお、第4の実施形態に適用する記録装置は、第1の実施形態で説明した図1に示す記録装置である。 Note that the recording apparatus applied to the fourth embodiment is the recording apparatus shown in FIG. 1 described in the first embodiment.
(第5の実施形態)
<第1信号補正部の説明(図19)>
図19について説明する。図19の第1信号補正部は、図17の第1信号補正部と一部を除いて同じである。異なる点は、第1信号周期判定基準記憶部103と第1信号周期補正値記憶部105に対して、補正後の第1信号周期情報信号214が入力されていることである。
(Fifth embodiment)
<Description of First Signal Correction Unit (FIG. 19)>
FIG. 19 will be described. The first signal correction unit in FIG. 19 is the same as the first signal correction unit in FIG. The difference is that the corrected first signal cycle information signal 214 is input to the first signal cycle determination
図17の場合では異常時の情報も含んだ平均値から判定基準値や補正値を生成するのに対し、図19のブロック図では既に記憶されている判定基準値や補正値により異常時の情報が補正されているため、より精度の高い判定基準値と補正値が得られる。 In the case of FIG. 17, the determination reference value and the correction value are generated from the average value including the information at the time of abnormality, whereas in the block diagram of FIG. 19, information at the time of abnormality is determined by the already stored determination reference value and correction value. Is corrected, a more accurate determination reference value and correction value can be obtained.
なお、第5の実施形態に適用する記録装置は、第1の実施形態で説明した図1に示す記録装置である。 Note that the recording apparatus applied to the fifth embodiment is the recording apparatus shown in FIG. 1 described in the first embodiment.
(第6の実施形態)
回転パルス信号201より更新する期間を生成する場合のタイミング生成手段11のブロック図が図20である。図10と共通に機能する記号については説明を省略する。
(Sixth embodiment)
FIG. 20 is a block diagram of the timing generation means 11 in the case of generating a period for updating from the
図20において114は第1信号周期補正値記憶制御部で、判定基準値および補正値を記憶する周期を回転パルス信号201から生成を行う。222は生成された第1信号記憶更新信号である。108は第1信号周期平均値算出制御部で、搬送変動を抽出するための第1信号周期情報の平均値を更新する周期を回転パルス信号201から生成を行う。216は生成された第1信号平均値更新信号である。第1信号周期平均値算出部106では連続する複数の更新期間の補正後第1信号周期情報信号214の値から第1信号周期平均値算出信号217の生成を行う。
In FIG. 20,
例えば搬送ローラ1回転の回転パルス信号201のパルス数が600パルスで、その間に30回更新を行う場合、600パルスを30回で割った20パルス毎に更新するような第1信号記憶更新信号222を生成する。
For example, when the number of pulses of the
図21に示すように上限値及び下限値は、時間とともに変化する。これにより、例えば時間t3やt4のような異常値を検出することができる。 As shown in FIG. 21, the upper limit value and the lower limit value change with time. Thereby, for example, an abnormal value such as time t3 or t4 can be detected.
(図20の第1信号変動検出部の処理説明)
図22は搬送ローラ1回転を8つの区間に分割し、各区間の境界時間t1〜t17において過去8区分の平均値を更新する場合のタイミングチャートである。例えば時間t12で更新される平均値は時間t4〜t12の8区間の平均値、時間t13で更新される平均値は時間t5〜t13の8区間の平均値となる。時間taで周期変動の抽出に使用される平均値は、時間t4〜t12の8区間の平均値が用いられる。時間tbで周期変動の抽出に使用される平均値は、時間t5〜t13の8区間の平均値が用いられる。このように1回転に要する時間より短い期間の数を設けて、搬送ローラ1回転中に更新される回数を増やすことにより、より最新の搬送ローラ1回転の平均値を用いることができる。
(Description of processing of first signal fluctuation detection unit in FIG. 20)
FIG. 22 is a timing chart in the case where one rotation of the conveying roller is divided into eight sections and the average value of the past eight sections is updated at the boundary times t1 to t17 of each section. For example, the average value updated at time t12 is the average value of 8 sections from time t4 to t12, and the average value updated at time t13 is the average value of 8 sections from time t5 to t13. The average value used for extraction of the period variation at time ta is the average value of eight sections from time t4 to t12. The average value used for extracting the period fluctuation at time tb is the average value of 8 sections from time t5 to time t13. Thus, by providing the number of periods shorter than the time required for one rotation and increasing the number of times of updating during one rotation of the conveying roller, the latest average value of one rotation of the conveying roller can be used.
本実施例では、各区間の境界を示す更新信号の生成を回転パルス信号201から行う。この更新信号の生成は、図20のブロック図の第1信号周期平均値算出制御部108にて行われ、生成された更新信号が第1信号平均値更新信号216である。例えば搬送ローラ1回転で回転パルス信号201が600パルスで、1回転で8回更新したい時は、回転パルス信号201が75パルス毎に第1信号平均値更新信号216を出力する。
In the present embodiment, an update signal indicating the boundary of each section is generated from the
このようにして得られた移動パルス信号203の周期の平均値を用いて移動パルス信号203の周期変動の取り出しを行う。この処理は第1周期変動検出部111にて行われるが、第1の実施形態の図10と同じであるため説明は省略する。
The period fluctuation of the moving
なお、第6の実施形態に適用する記録装置は、第1の実施形態で説明した図1に示す記録装置である。 Note that the recording apparatus applied to the sixth embodiment is the recording apparatus shown in FIG. 1 described in the first embodiment.
なお、図20の変形例として、第1信号周期補正値記憶制御部114や第1信号周期平均値算出制御部108が入力する信号を、回転パルス信号201の代わりに、内部で生成されるクロック信号としても構わない。
As a modification of FIG. 20, a signal input by the first signal period correction value
(第7の実施形態)
図23のブロック図は、図20のブロック図に対して、記憶を行うための信号として第1信号周期情報信号210の換わりに補正後第1信号周期情報信号214を用いた場合のブロック図である。図20の場合では異常時の情報も含んだ平均値から判定基準値や補正値を生成するのに対し、図23では既に記憶されている判定基準値や補正値により異常時の情報が補正されているため、より精度の高い判定基準値と補正値が得られる。
(Seventh embodiment)
The block diagram of FIG. 23 is a block diagram in the case where the corrected first signal period information signal 214 is used instead of the first signal period information signal 210 as a signal for performing storage in comparison with the block diagram of FIG. is there. In the case of FIG. 20, the determination reference value and the correction value are generated from the average value including the information at the time of abnormality, whereas in FIG. 23, the information at the time of abnormality is corrected by the already stored determination reference value and correction value. Therefore, more accurate determination reference values and correction values can be obtained.
なお、第7の実施形態に適用する記録装置は、第1の実施形態で説明した図1に示す記録装置である。 Note that the recording apparatus applied to the seventh embodiment is the recording apparatus shown in FIG. 1 described in the first embodiment.
なお、図23の変形例として、第1信号周期補正値記憶制御部114や第1信号周期平均値算出制御部108が入力する信号を、回転パルス信号201の代わりに、内部で生成されるクロック信号としても構わない。
As a modification of FIG. 23, a signal input by the first signal cycle correction value
(記録装置についての共通の実施形態)
以上、図1に適用する補正制御手段について、第1の実施形態から第7の実施形態について説明したが、記録装置に適用する形態について補足説明する。
(Common Embodiment for Recording Apparatus)
As described above, the correction control means applied to FIG. 1 has been described from the first embodiment to the seventh embodiment.
補正制御手段は、図1に示すようにヘッド駆動制御部へ信号を出力していたが、図23に示すように、更にモータ制御部102へ出力する形態でも構わない。
The correction control means outputs a signal to the head drive control unit as shown in FIG. 1, but it may be further output to the
即ち、補正制御手段からの信号に基づき、ヘッドの駆動制御と搬送手段の制御を行う。 That is, based on the signal from the correction control means, the head drive control and the transport means control are performed.
なお、別の形態として、補正制御手段からの信号に基づき、搬送手段の制御のみを行う構成であっても構わない。 As another form, a configuration in which only the transport unit is controlled based on a signal from the correction control unit may be used.
また、記録装置の実施形態の例として、搬送ベルトにて記録媒体を搬送する記録装置を用いて説明したが、他の形態でも構わない。 In addition, as an example of the embodiment of the recording apparatus, the recording apparatus that transports the recording medium by the transport belt has been described. However, other forms may be used.
例えば、図25に示すようにロール状の記録媒体を搬送する記録装置に適用しても構わない。図1では、記録媒体を搬送する搬送ベルトの移動速度をレーザードップラー式速度センサを用いて測定していたが、図25では、ロール状の記録媒体の搬送速度を測定している。 For example, the present invention may be applied to a recording apparatus that conveys a roll-shaped recording medium as shown in FIG. In FIG. 1, the moving speed of the conveying belt that conveys the recording medium is measured using a laser Doppler speed sensor, but in FIG. 25, the conveying speed of the roll-shaped recording medium is measured.
図25に示す記録装置では、2はロール状の記録媒体でロール状から引き出しながら記録を行われる。4は2つの搬送ローラ、5は2つの従送ローラで、本図では右側の搬送ローラ4によって搬送制御できるように右側の搬送ローラ4と従送ローラ5間の圧力が左側より強い。また左側の搬送ローラは記録媒体が2つの搬送ローラ間で弛まないように張力が掛かるように右側より少し速い速度で回転するように制御を行う。8の回転検出センサーは記録媒体の速度に影響が大きい右側の搬送ローラ軸6に取り付けてある。尚、3つ上の搬送ローラで構成される場合には、記録媒体の搬送速度に一番影響のある搬送ローラ軸に取り付ける。
In the recording apparatus shown in FIG. 25, 2 is a roll-shaped recording medium, and recording is performed while being pulled out from the roll shape. Reference numeral 4 denotes two transport rollers, and 5 denotes two follower rollers. In this figure, the pressure between the right transport roller 4 and the
このようにロール状記録媒体の搬送に一番支配力のある搬送ローラの回転を基準に、この搬送ローラの偏心を補正することにより搬送ローラ偏心の影響の無い画像形成が可能となる。 As described above, by correcting the eccentricity of the conveying roller based on the rotation of the conveying roller having the most dominant power for conveying the roll-shaped recording medium, it is possible to form an image without the influence of the eccentricity of the conveying roller.
あるいは、図26に示すように感光ドラムに形成したトナー画像を、転写ベルトに転写した後に、記録媒体に記録を行う記録装置に適用しても構わない。 Alternatively, the toner image formed on the photosensitive drum as shown in FIG. 26 may be applied to a recording apparatus that records on a recording medium after being transferred to a transfer belt.
25は像担持体としての感光ドラムである。26は感光ドラムの表面に均一な帯電量の電荷を与える一次帯電器である。27は記録画像信号に応じて変調した例えばレーザービームなどの光線を生成する光学系である。28は光学系からの光線を感光ドラムに照射して感光ドラム上に静電潜像を形成するための折り返しミラーである。29は収納された現像財であるトナーを上記静電潜像を顕像化する現像装置である。30は転写されずに感光ドラム上に残っているトナーを掻き落としてドラム表面の清掃を行うクリーニング装置である。20は複数の感光ドラムに形成されたトナー画像を1つの画像として形成した後、記録媒体に画像に転写を行うための中間転写ベルトである。11は感光ドラム上に形成されたトナー画像を中間転写ベルトに1次転写を行うための1次転写用帯電器である。24は本図に示さない記録媒体供給手段から記録媒体を供給するためのレジストローラーである。21は中間転写体に対して適度な圧力で加圧し、中間転写ベルト上に形成されたトナー画像を記録媒体に転写する二次転写ローラである。22は二次転写対向ローラである。24は転写された記録媒体を定着させるために本図に示さない定着ユニットまで導くためのガイドである。106は搬送基準信号は4つの光学系にて形成された画像が中間転写ベルト上に形成されるように制御を行う露光制御部である。本構成での露光制御部は、搬送基準信号202に従って各光学系27のスキャン開始のタイミング制御を行う。
なお、図25、図26に示す記録装置についても、補正制御手段で生成した信号を、モータ駆動部に出力する形態であっても構わない。 Note that the recording apparatus shown in FIGS. 25 and 26 may also be configured to output the signal generated by the correction control means to the motor drive unit.
101 ヘッド駆動制御部
102 モーター駆動部
201 回転パルス信号
202 搬送基準信号
103 搬送補正制御手段
151 画像形成手段
152 処理回路部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (10)
ローラーを含み記録媒体を搬送するための搬送手段と、
記録媒体の表面を検出することで、記録媒体の移動速度に応じてパルス周期が変化するパルス信号である第1信号を生成するレーザードップラー式センサと、
前記ローラーの回転に応じてパルス信号である第2信号を生成するエンコーダと、
前記レーザードップラー式センサで生成される前記第1信号の前記パルス周期が所定の範囲を越えた場合は前記第1信号を補正する補正手段と、
前記補正手段を経た前記第1信号のパルス周期の成分であって、前記ローラーの1回転を1周期とする周期的な変動情報を取得する取得手段と、
前記エンコーダで生成される前記第2信号により前記記録媒体に対する記録の制御を行う際に、前記ローラーの偏心による前記記録媒体の移動速度むらの影響を抑制するように前記変動情報を前記記録の制御に反映させる制御手段と
を備えることを特徴とする記録装置。 An ink jet recording head;
Conveying means for conveying a recording medium including a roller;
By detecting the surface of the recording medium, a laser Doppler sensor that generates a first signal which is a pulse signal whose pulse cycle varies according to the moving speed of the recording medium,
An encoder that generates a second signal which is a pulse signal in accordance with rotation of the roller,
Correction means for correcting the first signal when the pulse period of the first signal generated by the laser Doppler sensor exceeds a predetermined range;
An acquisition means for acquiring periodic fluctuation information that is a component of a pulse period of the first signal that has passed through the correction means and that makes one rotation of the roller as one period ;
When controlling the recording with respect to the recording medium by the second signal generated by the encoder, the control of the recording is performed on the variation information so as to suppress the influence of the moving speed variation of the recording medium due to the eccentricity of the roller. And a control means for reflecting the recording apparatus.
前記エンコーダは前記第1ローラーの回転に応じた前記第2信号を生成し、前記制御手段は前記第1ローラーの偏心の影響を抑制するように制御を行うことを特徴とする請求項1乃至6のいずれかに記載の記録装置。 Said conveying means, conveying a recording medium is disposed upstream of the pre-type recording head and the first roller for conveying the transport direction, the recording medium is disposed downstream from said plurality of recording heads in the conveyance direction And a second roller having an influence on the moving speed of the recording medium to be smaller than the first roller,
The encoder generates the second signal corresponding to the rotation of the first roller, according to claim 1 to 6 and the control means performing control so as to suppress the influence of the eccentricity of the first roller A recording apparatus according to any one of the above.
前記複数の記録ヘッドよりも上流に配置され記録媒体を前記搬送方向に搬送するための第1ローラーと、
前記複数の記録ヘッドよりも下流に配置され記録媒体を前記搬送方向に搬送するための、前記第1ローラーよりも記録媒体を保持する圧力が小さく且つ前記第1ローラーよりも回転の速度が大きい第2ローラーと、
記録媒体の表面を検出することで記録媒体の移動に応じた第1信号を生成するためのレーザードップラー式センサと、
前記第1ローラーの回転に応じた第2信号を生成するためのエンコーダと、
前記第1信号と前記第2信号に基づいて前記第1ローラーの偏心の影響を抑制するように前記記録媒体に対する記録の制御を行う制御手段と
を備えることを特徴とする記録装置。 A plurality of inkjet recording heads arranged from upstream to downstream in the conveying direction of the roll-shaped recording medium; and
A first roller disposed upstream of the plurality of recording heads for conveying a recording medium in the conveying direction;
A pressure which holds the recording medium smaller than the first roller and is higher in rotation speed than the first roller, which is arranged downstream of the plurality of recording heads and conveys the recording medium in the conveying direction. Two rollers,
A laser Doppler sensor for generating a first signal corresponding to the movement of the recording medium by detecting the surface of the recording medium;
An encoder for generating a second signal according to the rotation of the first roller;
A recording apparatus comprising: control means for controlling recording on the recording medium so as to suppress the influence of eccentricity of the first roller based on the first signal and the second signal.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007172286A JP4974787B2 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2007-06-29 | Recording device |
| US12/163,604 US7959248B2 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2008-06-27 | Recording apparatus and method for controlling the recording apparatus |
| US13/095,682 US8608274B2 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2011-04-27 | Recording apparatus and method for controlling the recording apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007172286A JP4974787B2 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2007-06-29 | Recording device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009006655A JP2009006655A (en) | 2009-01-15 |
| JP2009006655A5 JP2009006655A5 (en) | 2010-08-12 |
| JP4974787B2 true JP4974787B2 (en) | 2012-07-11 |
Family
ID=40322240
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007172286A Expired - Fee Related JP4974787B2 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2007-06-29 | Recording device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4974787B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5251609B2 (en) * | 2009-03-03 | 2013-07-31 | 株式会社リコー | Recording apparatus, control method, and program |
| JP5463926B2 (en) * | 2010-01-15 | 2014-04-09 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Rotating body abnormality detection device and image forming apparatus |
| JP5054139B2 (en) | 2010-02-26 | 2012-10-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | Printing apparatus and sheet processing apparatus |
| JP5014462B2 (en) | 2010-05-11 | 2012-08-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | Printing apparatus and sheet processing apparatus |
| JP5754957B2 (en) | 2011-01-27 | 2015-07-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | Printing device |
| JP6128734B2 (en) * | 2011-02-10 | 2017-05-17 | キヤノン株式会社 | Recording device |
| JP6024380B2 (en) * | 2012-10-22 | 2016-11-16 | 富士ゼロックス株式会社 | Image forming apparatus and program |
| JP6710997B2 (en) | 2016-02-09 | 2020-06-17 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | Printing device and printing method |
| NL2016518B1 (en) * | 2016-03-31 | 2017-10-17 | Spgprints B V | Control of printing operation of printing heads in a digital printing apparatus. |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH08101618A (en) * | 1994-09-30 | 1996-04-16 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Color image recorder |
| JPH08292264A (en) * | 1995-04-20 | 1996-11-05 | Fuji Xerox Co Ltd | Laser doppler speed measuring equipment and color image forming equipment using the same |
| JPH1086350A (en) * | 1996-09-13 | 1998-04-07 | Canon Inc | Image forming apparatus |
| JP3518432B2 (en) * | 1999-07-23 | 2004-04-12 | 住友金属工業株式会社 | Hot-rolled steel sheet passing speed measuring device and measuring method |
| JP2003211770A (en) * | 2002-01-18 | 2003-07-29 | Hitachi Printing Solutions Ltd | Color image recorder |
| JP2004317538A (en) * | 2003-04-11 | 2004-11-11 | Canon Inc | Image forming apparatus |
| JP4616777B2 (en) * | 2005-03-04 | 2011-01-19 | 株式会社リコー | Conveyance control device and image forming apparatus |
| JP4950859B2 (en) * | 2006-12-08 | 2012-06-13 | キヤノン株式会社 | Inkjet recording device |
-
2007
- 2007-06-29 JP JP2007172286A patent/JP4974787B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2009006655A (en) | 2009-01-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4974787B2 (en) | Recording device | |
| US7959248B2 (en) | Recording apparatus and method for controlling the recording apparatus | |
| JP5303337B2 (en) | Image control device | |
| JP4923714B2 (en) | Image recording device | |
| JP2008162274A (en) | Inkjet printing apparatus and inkjet printing method | |
| JP2009249166A (en) | Pulse signal generating device, transport device, image forming apparatus and pulse generating method | |
| US9022500B2 (en) | System and method for adjusting the registration of an image applied to recording media in a printing system | |
| JP2008114547A (en) | Droplet discharge device | |
| JP5463926B2 (en) | Rotating body abnormality detection device and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2009107310A (en) | Image forming device | |
| JP5580015B2 (en) | Image control device | |
| EP2251201B1 (en) | Printing machine and ejection control method for the same | |
| JP5040576B2 (en) | Detection device and recording device | |
| JP5022977B2 (en) | Recording apparatus and recording control method | |
| JP2009214397A (en) | Image formation device | |
| JP5396110B2 (en) | Printing apparatus and discharge control method thereof | |
| JP2006240251A (en) | Liquid droplet discharge type recorder | |
| JP4876747B2 (en) | Image recording apparatus and program | |
| JP2009220346A (en) | Image forming apparatus and program | |
| JP4300084B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP6238769B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| KR100340158B1 (en) | Image forming apparatus and method | |
| JP5390893B2 (en) | Printing apparatus and discharge control method thereof | |
| JP5286722B2 (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2005238706A (en) | Imaging device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20100201 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100624 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100624 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20100713 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20111130 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20111213 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120213 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120313 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120410 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 4974787 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150420 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |