JP4968769B2 - Laminated film and multiple packaging bag comprising the same - Google Patents
Laminated film and multiple packaging bag comprising the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4968769B2 JP4968769B2 JP2006113325A JP2006113325A JP4968769B2 JP 4968769 B2 JP4968769 B2 JP 4968769B2 JP 2006113325 A JP2006113325 A JP 2006113325A JP 2006113325 A JP2006113325 A JP 2006113325A JP 4968769 B2 JP4968769 B2 JP 4968769B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- film
- laminated
- laminated film
- density polyethylene
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 title claims description 52
- 239000000565 sealant Substances 0.000 claims description 54
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 36
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 32
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 31
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 claims description 31
- 229920000092 linear low density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000004707 linear low-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 claims description 30
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000003925 fat Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000003475 lamination Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000001125 extrusion Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 229920006284 nylon film Polymers 0.000 claims description 9
- 235000014593 oils and fats Nutrition 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- 229920006267 polyester film Polymers 0.000 claims description 7
- 229920005672 polyolefin resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 229920001684 low density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004702 low-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920001903 high density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000004700 high-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 200
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 107
- -1 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 16
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 description 15
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 14
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 13
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 13
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 13
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000005022 packaging material Substances 0.000 description 10
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 9
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 9
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000001954 sterilising effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000004659 sterilization and disinfection Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000009820 dry lamination Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 229920013716 polyethylene resin Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000004677 Nylon Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920001778 nylon Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 238000003851 corona treatment Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910003460 diamond Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000010432 diamond Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000008157 edible vegetable oil Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 4
- 235000021056 liquid food Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 4
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002292 Nylon 6 Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000032798 delamination Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000005001 laminate film Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 3
- FATBGEAMYMYZAF-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleamide Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(N)=O FATBGEAMYMYZAF-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 3
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BAPJBEWLBFYGME-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl acrylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C=C BAPJBEWLBFYGME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ozone Chemical compound [O-][O+]=O CBENFWSGALASAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241000282320 Panthera leo Species 0.000 description 2
- 229920001328 Polyvinylidene chloride Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 2
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910001882 dioxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N dodecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O POULHZVOKOAJMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229920006242 ethylene acrylic acid copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920005648 ethylene methacrylic acid copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- FPYJFEHAWHCUMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N maleic anhydride Chemical compound O=C1OC(=O)C=C1 FPYJFEHAWHCUMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 2
- FTQWRYSLUYAIRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[(octadecanoylamino)methyl]octadecanamide Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NCNC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC FTQWRYSLUYAIRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012188 paraffin wax Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005678 polyethylene based resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000005033 polyvinylidene chloride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 235000015067 sauces Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000344 soap Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000005846 sugar alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000004381 surface treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 description 2
- WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N (E)-8-Octadecenoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCC(O)=O WRIDQFICGBMAFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CFVWNXQPGQOHRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound CC(C)COC(=O)C=C CFVWNXQPGQOHRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 20:1omega9c fatty acid Natural products CCCCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O LQJBNNIYVWPHFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HNNQYHFROJDYHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(4-ethylcyclohexyl)propanoic acid 3-(3-ethylcyclopentyl)propanoic acid Chemical compound CCC1CCC(CCC(O)=O)C1.CCC1CCC(CCC(O)=O)CC1 HNNQYHFROJDYHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-Heptadecensaeure Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O QSBYPNXLFMSGKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000251468 Actinopterygii Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 description 1
- IEPRKVQEAMIZSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Di-Et ester-Fumaric acid Natural products CCOC(=O)C=CC(=O)OCC IEPRKVQEAMIZSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IEPRKVQEAMIZSS-WAYWQWQTSA-N Diethyl maleate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)\C=C/C(=O)OCC IEPRKVQEAMIZSS-WAYWQWQTSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000219 Ethylene vinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 244000017020 Ipomoea batatas Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000002678 Ipomoea batatas Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000005639 Lauric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- JHWNWJKBPDFINM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Laurolactam Chemical compound O=C1CCCCCCCCCCCN1 JHWNWJKBPDFINM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000294411 Mirabilis expansa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000015429 Mirabilis expansa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000571 Nylon 11 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000299 Nylon 12 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003189 Nylon 4,6 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002302 Nylon 6,6 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000572 Nylon 6/12 Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005642 Oleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 240000004808 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Species 0.000 description 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002125 Sokalan® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 101150043385 Tpm3 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000005299 abrasion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000003973 alkyl amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052788 barium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001400 block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052793 cadmium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 description 1
- 150000001733 carboxylic acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000008280 chlorinated hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000021438 curry Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004205 dimethyl polysiloxane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013870 dimethyl polysiloxane Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000002845 discoloration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000015071 dressings Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- UAUDZVJPLUQNMU-KTKRTIGZSA-N erucamide Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCCCCC(N)=O UAUDZVJPLUQNMU-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004715 ethylene vinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006225 ethylene-methyl acrylate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005680 ethylene-methyl methacrylate copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005674 ethylene-propylene random copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000019688 fish Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000005021 flexible packaging material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002457 flexible plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- NBVXSUQYWXRMNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluoromethane Chemical compound FC NBVXSUQYWXRMNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012041 food component Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003205 fragrance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001530 fumaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000578 graft copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000012447 hatching Effects 0.000 description 1
- RZXDTJIXPSCHCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexa-1,5-diene-2,5-diol Chemical compound OC(=C)CCC(O)=C RZXDTJIXPSCHCI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000012943 hotmelt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N isooleic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC=CCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QXJSBBXBKPUZAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000015094 jam Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 235000008960 ketchup Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052745 lead Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229940057995 liquid paraffin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000010746 mayonnaise Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008268 mayonnaise Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013372 meat Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 244000005700 microbiome Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004200 microcrystalline wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013536 miso Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003097 mucus Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000435 poly(dimethylsiloxane) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004584 polyacrylic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920006122 polyamide resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001707 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001225 polyester resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004645 polyester resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000223 polyglycerol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000010695 polyglycol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000151 polyglycol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001522 polyglycol ester Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 1
- WBHHMMIMDMUBKC-XLNAKTSKSA-N ricinelaidic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC[C@@H](O)C\C=C\CCCCCCCC(O)=O WBHHMMIMDMUBKC-XLNAKTSKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003656 ricinoleic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- FEUQNCSVHBHROZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ricinoleic acid Natural products CCCCCCC(O[Si](C)(C)C)CC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OC FEUQNCSVHBHROZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000014347 soups Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000013555 soy sauce Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013547 stew Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052712 strontium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010998 test method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013585 weight reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Bag Frames (AREA)
- Wrappers (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Description
本発明は、食品や医薬品等のごとき、油脂類を含有する液体、粘体状の流動体である内容物を充填包装し、その品質を保持するための包装袋に関し、特に主に業務用に使用される油脂類を含有する液体食品等を自動的に製袋充填包装し、さらに殺菌等の目的から比較的高温で熱処理するために使用され、熱処理した後の包装袋が耐屈曲疲労性、耐ピンホール性、耐落下衝撃性等の機械特性に優れたフレキシブルな積層フィルム、またはそれからなる多重包装袋に関する。 The present invention relates to a packaging bag for filling and packaging the content of a liquid or viscous fluid containing oils and fats such as foods and pharmaceuticals, etc., and mainly used for business use. It is used for automatically filling and packaging liquid foods containing fats and oils, and heat-treating at relatively high temperatures for purposes such as sterilization. The present invention relates to a flexible laminated film excellent in mechanical characteristics such as pinhole property and drop impact resistance, or a multiple packaging bag made of the same.
従来、業務用に使用される液体または粘体の食品等は、金属やプラスチック等の硬質容器に充填して輸送、保管、販売等の流通に供されていた。しかしながら、金属等の硬質容器は使用後の容器が嵩張ること、内容物を取出し難いこと、容器の再利用が困難なことなどの欠点があった。近時、取り扱い性の良さや、軽量化、廃棄物の減量などの点から、柔軟なプラスチック包装袋に充填されることが多い。これら軟包装材料は、酸素ガス、および水蒸気等に対するバリアー性、柔軟性、耐衝撃性、耐ピンホール性、耐突き刺し性、透明性、耐熱性、ヒートシール性、品質保持性、印刷適正、開口性、充填包装適正等、様々な特性が要求される。特に内容物が流動性であったり、粘稠性流体であったり、低温保存用であったりする場合に、包装袋の耐ピンホール性は、内容物の保護や漏洩等に対する基本的な問題であり、様々なフィルム素材や構成による包装材料の提案がなされてきた。 Conventionally, liquid or viscous foods used for business have been packed in hard containers such as metals and plastics for transportation, storage and sales. However, a hard container such as metal has drawbacks such as a bulky container after use, difficulty in taking out the contents, and difficulty in reusing the container. Recently, flexible plastic packaging bags are often filled from the standpoints of ease of handling, weight reduction, and reduction of waste. These flexible packaging materials have barrier properties against oxygen gas, water vapor, etc., flexibility, impact resistance, pinhole resistance, puncture resistance, transparency, heat resistance, heat sealability, quality retention, printability, opening Various properties are required, such as properties and suitability for filling and packaging. In particular, when the contents are fluid, viscous fluid, or for low-temperature storage, the pinhole resistance of the packaging bag is a fundamental problem with respect to content protection and leakage. There have been proposals for packaging materials with various film materials and configurations.
包装袋の材料として単層フィルムが用いられる場合も多いが、上記の要求特性を満たす必要性から、フィルムの強度、熱シール性、ガスバリアー性などの機能を持たせたラミネートフィルムを用いることが好ましい。ラミネートフィルムの構成としては、機械的強度を保持するための基材フィルムとして、強度の大きい二軸延伸ポリエステルフィルムや、低温疲労、衝撃性など衝撃特性に優れた二軸延伸ナイロンフィルムなどが主として単独または組み合わせて用いられ、また熱シール可能なシーラントフィルムとしては、一般的にはポリエチレンフィルム、中でも特にヒートシール強度、耐ストレスクラック性、耐衝撃性、低温特性など多くの特性に優れた線状低密度ポリエチレンフィルムが好ましく用いられている。 Although a single layer film is often used as a packaging bag material, it is necessary to use a laminated film having functions such as film strength, heat sealing property, gas barrier property, etc., because it is necessary to satisfy the above required characteristics. preferable. The laminate film is composed mainly of a biaxially stretched polyester film with high strength and a biaxially stretched nylon film with excellent impact properties such as low-temperature fatigue and impact as the base film for maintaining the mechanical strength. Or as a sealant film that can be used in combination and can be heat-sealed, it is generally a polyethylene film, and in particular, linear low with excellent properties such as heat seal strength, stress crack resistance, impact resistance, and low-temperature characteristics. A density polyethylene film is preferably used.
さて、主に輸送過程での振動による包装袋の屈曲、磨耗の繰り返しによるピンホールの発生に対する解決手段として、基材フィルム層とシーラント層との間に、部分的に未接着部位を持つ構成とした耐ピンホール性包装材料が提案されている。即ち、シーラント層になり得るポリオレフィン系樹脂フィルムとガスバリアー性を有するガスバリアー層とが、この2層と接着性を有する材料と接着性を有さない材料とが任意の割合で混合分散された接着層を介して積層され、前記接着性を有する材料が、被着体表面上を50%以上占有していることを特徴とする包装材料が開示されている(特許文献1参照)。 Now, as a solution to the generation of pinholes due to repeated bending and bending of packaging bags due to vibration during the transportation process, there is a structure with a partially unbonded part between the base film layer and the sealant layer. Proposed pinhole-resistant packaging materials have been proposed. That is, a polyolefin-based resin film that can be a sealant layer and a gas barrier layer having gas barrier properties were mixed and dispersed at an arbitrary ratio between the two layers, a material having adhesive properties, and a material having no adhesive properties. A packaging material is disclosed in which a material laminated with an adhesive layer and having adhesive properties occupies 50% or more of the surface of an adherend (see Patent Document 1).
また、他の解決手段として、ラミネートフィルムを二重またはそれ以上重ねた多重袋とし、液体を直接包装する最内側の袋と外容器(段ボール)間に外側の袋を介在させることにより、輸送時の振動等により最内側の袋と段ボールが直接擦れること及び袋が屈曲した時にラミネートフィルムに加わる曲げ応力の増大を防止して、耐ピンホール性や耐落袋性を向上させた技術が開示されている。具体的には、二軸延伸ナイロンフィルムと二軸延伸ポリエステルフィルムよりなる群から選ばれた少なくとも一種のフィルムと、線状低密度ポリエチレンフィルムが、相互にブロッキング接着した2層以上のフィルムからなることを特徴とする包装材である。この多重袋は1枚のフィルムにピンホールが生じても他の1枚は無傷であり、また屈曲応力に対しても、個々の独立したフィルム1枚がその応力を受け、他の1枚は滑って逃げることができるため極度の屈曲応力が加わるおそれもなく、優れた機械的強度を有している(特許文献2参照)。 In addition, as another solution, a multi-layer bag in which laminate films are doubled or stacked is used, and an outer bag is interposed between an innermost bag for directly packaging liquid and an outer container (corrugated cardboard), so that it can be transported. Technology that improves pinhole resistance and drop bag resistance by preventing the innermost bag and corrugated cardboard from rubbing directly due to vibration, etc., and preventing an increase in bending stress applied to the laminate film when the bag is bent is disclosed. ing. Specifically, at least one film selected from the group consisting of a biaxially stretched nylon film and a biaxially stretched polyester film, and a linear low density polyethylene film are composed of two or more layers of films bonded to each other by blocking. Is a packaging material characterized by Even if a pinhole occurs in one film, this multiple bag is intact, and the other sheet is not damaged. Also, with respect to bending stress, one individual independent film receives the stress, and the other sheet Since it can slip and escape, there is no fear of applying an extreme bending stress, and it has excellent mechanical strength (see Patent Document 2).
昨今、食品に対する衛生上の要請、そしてこの対応効率の観点から、加熱殺菌された液体食品等を高温のまま充填包装したり、或いは充填包装した状態で加熱殺菌等の目的で比較的高温で熱処理できることが求められている。特許文献2に記載の技術は、ラミネート工程、製袋、包装作業時の機械適正を損なわない程度の相互にブロッキング接着した2層以上のフィルムを得るために、使用する線状低密度ポリエチレンの密度を選択する必要があったため、加熱殺菌等の高温処理により、最内層と外層との間で強固な熱ブロッキングが形成し、あたかも単層としての挙動を呈し、当該多重袋の特徴であった耐屈曲疲労性、耐ピンホール性、耐落下衝撃性が著しく低下することが判り、大きな問題となっている。
本発明の課題は、積層フィルムを用いて油脂類を含有する流動体の包装体とした場合に、包装体が耐屈曲疲労性、耐ピンホール性、耐落下衝撃性等の性能において優れた性能を有する積層フィルム等を提供する。 The problem of the present invention is that when a laminated film is used to make a fluid packaging containing oils and fats, the packaging has excellent performance in bending fatigue resistance, pinhole resistance, drop impact resistance, etc. Provided are laminated films and the like.
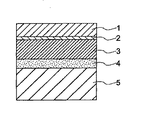
本発明の第1は、基材層(1)、第1の接合層(2)、中間層(3)、第2の接合層(4)、シーラント層(5)が順次積層された積層フィルムであって、前記中間層(3)がポリオレフィン系樹脂フィルムであり、前記シーラント層(5)が線状低密度ポリエチレン樹脂フィルムであり、前記第2の接合層(4)が押出ラミネーション法により形成された厚み3〜13μmのポリエチレン系樹脂層である、油脂類を含有する流動体の包装用積層フィルムである。ここで、前記基材層(1)が2軸延伸ナイロンフィルムと2軸延伸ポリエステルフィルムとからなる群から選ばれた少なくとも1種のフィルムであり、前記基材層(1)と前記中間層(3)との間にガスバリアー層(7)がさらに積層されたことは好ましい。 The first of the present invention is a laminated film in which a base material layer (1), a first bonding layer (2), an intermediate layer (3), a second bonding layer (4), and a sealant layer (5) are sequentially laminated. The intermediate layer (3) is a polyolefin resin film, the sealant layer (5) is a linear low density polyethylene resin film, and the second bonding layer (4) is formed by an extrusion lamination method. It is the laminated film for packaging of the fluid containing the fats and oils which is the made polyethylene-type resin layer of thickness 3-13 micrometers. Here, the base material layer (1) is at least one film selected from the group consisting of a biaxially stretched nylon film and a biaxially stretched polyester film, and the base material layer (1) and the intermediate layer ( It is preferable that a gas barrier layer (7) is further laminated between the layer 3).
発明の第2は、上記の積層フィルムを用い、前記シーラント層(5)を内側にしてヒートシールにより製袋された、油脂類を含有する流動体包装用の多重包装袋である。 A second aspect of the invention is a multiple packaging bag for fluid packaging containing fats and oils, which is produced by heat sealing with the above-mentioned laminated film and with the sealant layer (5) on the inside.
発明の第3は、上記の多重包装袋に、油脂類を含有する流動体を充填密封し、70℃以上で、かつ前記シーラント層(5)を形成する線状低密度ポリエチレン樹脂の示差走査熱量計によって測定される結晶融解ピーク温度Tpmより5℃低い温度以下の温度に加熱処理する、油脂類を含有する流動体の包装方法である。 A third aspect of the invention is the differential scanning calorific value of the linear low density polyethylene resin in which the fluid containing oils and fats is filled and sealed in the multiple packaging bag, and the sealant layer (5) is formed at 70 ° C. or higher. It is a packaging method for a fluid containing fats and oils, which is heat-treated at a temperature not higher than 5 ° C. lower than the crystal melting peak temperature Tpm measured by a meter.
発明の第4は、上記の多重包装袋に、油脂類を含有する液体・粘体状食品が密封充填されており、かつ、前記積層フィルムの中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)間の剥離強度が、5〜100g/15mmの範囲である多重包装体である。 A fourth aspect of the invention is that the above-described multiple packaging bag is hermetically filled with a liquid / viscous food containing fats and oils, and peeling between the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) of the laminated film. It is a multiple package body whose strength is in the range of 5 to 100 g / 15 mm.
積層フィルムを用いて油脂類を含有する流動体の包装体とした場合に、流動体の密封性等には何ら問題なく、包装体の耐屈曲疲労性、耐ピンホール性、耐落下衝撃性等の性能において優れた耐性を示す。 When using a laminated film to make a fluid package containing oils and fats, there is no problem with the fluid's sealing properties, etc., and the package's bending fatigue resistance, pinhole resistance, drop impact resistance, etc. Excellent resistance in performance.
以下、本発明の積層フィルム、およびそれからなる多重包装袋等の実施の形態例について図面も用いて詳しく説明する。図1は本発明にかかる積層フィルムの積層構造の一例を示す断面図である。図1において、基材層(1)は、第1の接合層(2)を介してポリオレフィン系樹脂からなる中間層(3)に接着されている。中間層(3)は、厚み3〜13μmのポリエチレン系樹脂の押出ラミネーションで形成される第2の接合層(4)を介して、シーラント層(5)に接着されている。また、図2は、積層フィルムに関する他の実施の形態例であり、上記構成の積層構成に加えて、第1の接合層(2)と基材層(1)との間にガスバリアー層(7)を第3の接合層(2a)を介して積層ラミネートしたものである。このように、積層フィルムは、基材層(1)と第1の接合層(2)とに関して必要により様々な変型を行うことが可能である。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the laminated film of the present invention and a multi-packaging bag comprising the same will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view showing an example of a laminated structure of a laminated film according to the present invention. In FIG. 1, the base material layer (1) is bonded to the intermediate layer (3) made of a polyolefin resin via the first bonding layer (2). The intermediate layer (3) is bonded to the sealant layer (5) via a second bonding layer (4) formed by extrusion lamination of a polyethylene resin having a thickness of 3 to 13 μm. FIG. 2 shows another embodiment relating to the laminated film. In addition to the laminated structure of the above structure, a gas barrier layer (between the first bonding layer (2) and the base material layer (1) is shown. 7) is laminated and laminated through the third bonding layer (2a). As described above, the laminated film can be variously modified as necessary with respect to the base material layer (1) and the first bonding layer (2).
ところで、一般にポリエチレン系樹脂を用いた押出ラミネーションにおいては、当該業務に精通した者の熟知するところであるが、十分なラミネート強度を発現させるためには、押し出されるポリエチレン系樹脂の厚みは15μm以上とすることが行われている。しかし、本発明においては、従来概念とは異なり、この厚みを3〜13μmと生産上可能な限り薄い層厚みとした第2の接合層(4)を設けることに特徴の1つがある。 By the way, in general, in the extrusion lamination using a polyethylene-based resin, those who are familiar with the work are familiar, but in order to develop a sufficient laminate strength, the thickness of the extruded polyethylene-based resin is 15 μm or more. Things have been done. However, unlike the conventional concept, the present invention is characterized in that the second bonding layer (4) having a thickness of 3 to 13 μm, which is as thin as possible in production, is provided.
本発明者は、鋭意研究の結果、基材層(1)以外に中間層(3)を設け、この中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)との間の第2の接合層(4)を上記の厚みの薄い層とし、さらにこのような積層フィルムをシーラント層(5)が油脂類を含有する液体・粘体状の食品の内容物と接触した状態で、適度に加熱処理することで、第2の接合層(4)とシーラント層(5)間、または中間層(3)と第2の接合層(4)間のラミネート強度が低下し、易剥離性の界面が形成されて包装材料の耐ピンホール性、耐衝撃破壊性を向上させることを見出した。即ち、包装体が振動による屈曲や落下衝撃を受けた際に、包装材に発生する局部的な応力が、包装袋を構成する積層フィルムの層間剥離を誘発し、応力分散、或いは緩和されて、包装材料の破壊を未然に防ぐことができることを見出し、本発明をなすに至った。 As a result of earnest research, the inventor provided an intermediate layer (3) in addition to the base material layer (1), and a second bonding layer (4) between the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5). In the state where the above-mentioned thin film is in contact with the contents of the liquid / viscous food containing the fats and oils, the laminated film is further heat-treated. The laminate strength between the second bonding layer (4) and the sealant layer (5), or between the intermediate layer (3) and the second bonding layer (4) is reduced, and an easily peelable interface is formed to form a packaging material. Has been found to improve the resistance to pinholes and impact fracture. That is, when the package is subjected to bending or a drop impact due to vibration, local stress generated in the packaging material induces delamination of the laminated film constituting the packaging bag, and is dispersed or relaxed. The present inventors have found that the destruction of the packaging material can be prevented in advance.
ここに、適度な加熱処理とは、70℃以上で、かつシーラント層(5)を形成する線状低密度ポリエチレン樹脂の示差走査熱量計(DSC)によって測定される結晶融解ピーク温度Tpmより5℃低い温度以下の温度に加熱処理することである。即ち、上記積層フィルムから袋を製袋し、これに充填された内容物の温度として、液状食品であれば、殺菌のために加熱されるために少なくとも70℃以上であり、また、シーラント層(5)と第2の接合層(4)、及び中間層(3)とが強固な溶融接着を起こさずに、易剥離性の界面を発現できる上限の温度として、シーラント層(5)の結晶融解温度Tpm−5℃の範囲において加熱処理することである。このようにすることにより、内容物の密封包装には何ら問題無く、かつ包装体が振動による屈曲や落下衝撃を受けた際に、包装材に発生する局部的な応力が、包装袋を構成する積層フィルムの層間剥離を誘発する。 Here, the appropriate heat treatment is 70 ° C. or higher and 5 ° C. from the crystal melting peak temperature Tpm measured by a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) of the linear low density polyethylene resin forming the sealant layer (5). Heat treatment to a temperature below a low temperature. That is, a bag is made from the laminated film, and the temperature of the contents filled in the bag is at least 70 ° C. or higher because it is heated for sterilization if it is a liquid food. 5), the second bonding layer (4), and the intermediate layer (3) do not cause strong melt adhesion, and the crystal melting of the sealant layer (5) is the upper limit temperature at which an easily peelable interface can be expressed. Heat treatment is performed in a temperature range of Tpm-5 ° C. By doing so, there is no problem with the sealed packaging of the contents, and the local stress generated in the packaging material when the packaging body is subjected to bending or dropping impact due to vibration constitutes the packaging bag. Induces delamination of laminated films.
図3は、本発明の積層フィルムから製造した2重包装袋の一例であるピロー包装袋9である(ヒートシール部分を斜線で表示)。このピロー包装袋9は、シーラント層を内側にして、横シール部分8a、及び背貼り縦シール部分8bでヒートシールされている。包装袋の形状はピロー包装袋に限定されるものではなく、油脂類を含有する流動体の包装に用いられる公知の様々な形状とすることができる。
FIG. 3 shows a pillow packaging bag 9 which is an example of a double packaging bag manufactured from the laminated film of the present invention (the heat seal portion is indicated by hatching). The pillow packaging bag 9 is heat-sealed with a
図4は、図1の構造を有する積層フィルムを折り畳んで製袋した多重袋に、油脂類を含有する流動体である内容物11を充填包装した時の、シール部の拡大断面図である。図中の10は、シーラント層(5)の線状低密度ポリエチレンフィルムどうしを内側にして重ね合わせてヒートシール、インパルスシール、超音波シール、高周波シールなどの方法で熱シールすることによって密封されたシール部10である。シール部10においては、線状低密度ポリエチレンのシーラント層(5)、押出ラミネート法により形成されるポリエチレン系樹脂の第2の接合層(4)、及びポリオレフィン系樹脂の中間層(3)が溶融圧着して互いに接着されており、合計6層が強固に接着一体化されている。即ち、シール部10では、包装材料を構成するすべての積層ラミネート層が強固に接着一体化して内容物の液体の漏れを防ぐことができる。
FIG. 4 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of the seal portion when the
シール部10以外では、内容物11がシーラント層(5)に直接接触しており、シーラント層(5)が第2の接合層(4)を介して中間層(3)に積層され、さらに中間層(3)には第1の接合層(2)を介して基材層(1)が積層されている。内容物が、油脂類を含有する流動体、具体的には、流動性の食品または医薬品等の、油脂類を含有する液体や粘体である場合に、殺菌のために上述のような温度範囲で加熱処理を行うことにより、該積層フィルムは、中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)間の剥離強度が、5〜100g/15mmと低下する。なお、内容物が油脂類を含有しない水のような場合には、剥離強度が低下せず、高いままとなる。
Except for the
このような現象が生じる原因は明らかではないが、包装袋の内容物である油脂類を含有する流動体が、包装袋の積層フィルムと高温で接触することによって、内容物中に含有される油脂類がシーラント層の線状低密度ポリエチレン中に浸透し、当該層と接合層との間の接着性を低下させ、そこに易剥離性の界面を形成させるのではないかと考えられる。このようにして得られた包装体がダンボール等に集合包装され、運搬・輸送に供され、振動や落下衝撃を受けた場合、屈曲や衝撃等による瞬時的な局部応力を受けても、中間層とシーラント層間での剥離現象が起こり、瞬時的な応力分散が達成されることによって耐ピンホール性や耐落袋性が向上されるものと推定される。なお、中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)間の剥離強度は、5〜70g/15mmの範囲内となるのがより好ましい。 The cause of such a phenomenon is not clear, but the fluid containing the fats and oils that are the contents of the packaging bag comes into contact with the laminated film of the packaging bag at a high temperature, so that the fats and oils contained in the contents It is thought that the kind penetrates into the linear low density polyethylene of the sealant layer, reduces the adhesion between the layer and the bonding layer, and forms an easily peelable interface there. If the package obtained in this way is packed in cardboard, etc., used for transportation and transportation, and subjected to vibration or drop impact, even if it receives instantaneous local stress due to bending or impact, the intermediate layer It is presumed that pinhole resistance and drop bag resistance are improved by the occurrence of a peeling phenomenon between the sealant layer and the instantaneous stress distribution. The peel strength between the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) is more preferably in the range of 5 to 70 g / 15 mm.
以下、少なくとも5層からなる積層フィルムの構成について述べる。まず、基材層(1)は積層フィルムへの強靭性の付与を主たる目的とする。基材層(1)は、包装袋に必要とされる性能が複数ある場合、例えば、強靭性とガスバリア性の双方が必要な場合には、それに応じた性能を有する層を積層した複合基材層とすることが出来る。基材層(1)の厚みは、包装袋の目的に応じ適宜選択することができるが、突き刺しや耐磨耗性等の機械的強度の点から、10〜50μmの厚みであることが好ましい。 Hereinafter, the structure of the laminated film consisting of at least five layers will be described. First, the main purpose of the base material layer (1) is to impart toughness to the laminated film. When the base material layer (1) has a plurality of performances required for the packaging bag, for example, when both toughness and gas barrier properties are required, a composite base material in which layers having performances corresponding thereto are laminated. It can be a layer. The thickness of the base material layer (1) can be appropriately selected according to the purpose of the packaging bag, but is preferably 10 to 50 μm from the viewpoint of mechanical strength such as piercing and abrasion resistance.
基材層(1)を構成する基材は、ポリアミド系樹脂やポリエステル系樹脂、及びポリプロピレン系樹脂の延伸フィルムないしシートであればよい。基材層(1)は、フィルム強度、強靭性、酸素ガスや水蒸気等に対するガスバリアー性、耐衝撃性、耐屈曲ピンホール性、耐突き刺し性等の必要な性能を適宜有するようにする。延伸フィルムとしては、例えば2軸延伸ナイロン(商標)フィルム、2軸延伸ポリエステルフィルム、2軸延伸ポリプロピレンフィルムを代表例としてあげることができる。 The base material constituting the base material layer (1) may be a stretched film or sheet of polyamide resin, polyester resin, or polypropylene resin. The base material layer (1) appropriately has necessary properties such as film strength, toughness, gas barrier properties against oxygen gas, water vapor, etc., impact resistance, flex pinhole resistance, puncture resistance, and the like. Typical examples of the stretched film include a biaxially stretched nylon (trademark) film, a biaxially stretched polyester film, and a biaxially stretched polypropylene film.
2軸延伸ナイロンフィルムの例としては、MXDナイロン6フィルム、MXDナイロン樹脂とナイロン46、ナイロン6、ナイロン66、ナイロン612、ナイロン11、ナイロン12等の商品名で示される各種のポリアミド系樹脂の、Tダイ法やインフレーション法による単独または共押出の、同時または逐次2軸延伸フィルムが挙げられる。特にナイロン6フィルムがコスト、製膜のし易さから最も好ましい。また、2軸延伸ポリエステルフィルムの例としては、例えば、ポリエチレンテレフタレート、ポリブチレンテレフタレート等の単独または共重合体のTダイ法による2軸延伸フィルムを用いることができるが、このうちポリエチレンテレフタレートの単独または共重合体が、コストの面から最も好ましい。
Examples of the biaxially stretched nylon film include MXD nylon 6 film, MXD nylon resin and nylon 46, nylon 6, nylon 66, nylon 612,
ところで、内容物が酸素と反応して変褪色、褐変、味・香りの変化、栄養成分の減少、有害成分の発生などを伴う変質が生じる場合や、内容物に酸素存在下で細菌、カビ、酵母などの微生物が発育し易い場合は、これを防止するために、上述の2軸延伸ナイロンフィルム、2軸延伸ポリエステルフィルム、2軸延伸ポリプロピレンフィルム等の基材層と、後述の中間層(3)との間に、ガスバリアー層(7)を設けて酸素を遮断するのが好ましい。ガスバリアー層としては、ポリ塩化ビニリデン系樹脂フィルム、エチレン−ビニルアルコール系樹脂フィルム、ポリビニルアルコール系樹脂フィルム、ポリ塩化ピニリデンコート系薄膜、架橋ポリアクリル酸系コート薄膜、アルミニウムなどの金属蒸着薄膜、酸化珪素や酸化アルミニウムなどの金属酸化物蒸着薄膜、またはアルミニウム箔の一種または2種以上をラミネートすることができる。 By the way, when the contents react with oxygen, discoloration, browning, changes in taste and fragrance, decrease in nutritional components, generation of harmful components, etc., or in the presence of oxygen, bacteria, mold, When microorganisms such as yeast are likely to grow, in order to prevent this, a base layer such as the above-described biaxially stretched nylon film, biaxially stretched polyester film, biaxially stretched polypropylene film, and an intermediate layer (3 described later) ) Is preferably provided with a gas barrier layer (7) to block oxygen. As the gas barrier layer, polyvinylidene chloride resin film, ethylene-vinyl alcohol resin film, polyvinyl alcohol resin film, polyvinylidene chloride coating thin film, crosslinked polyacrylic acid coating thin film, metal vapor deposition thin film such as aluminum, A metal oxide vapor-deposited thin film such as silicon oxide or aluminum oxide, or one or more of aluminum foil can be laminated.
次に、第1の接合層(2)は、基材層(1)と中間層(3)、及び必要に応じて設けられるガスバリアー層(7)とを接合する為の層であり、第1の接合層(2)を形成するラミネーション法としては、例えば接着剤を介して接着するドライラミネーション法、無溶剤ラミネーション法、ホットメルトラミネーション法、押出ラミネーション法などを用いればよい。 Next, the first bonding layer (2) is a layer for bonding the base material layer (1), the intermediate layer (3), and the gas barrier layer (7) provided as necessary, As a lamination method for forming one bonding layer (2), for example, a dry lamination method, a solvent-free lamination method, a hot melt lamination method, an extrusion lamination method, or the like, which are bonded via an adhesive, may be used.
ドライラミネーション法による場合、接着剤の種類は内容物の種類、包装形態などを考慮して選択されるが、一液性または二液性のポリウレタン接着剤を用いるのが好ましい。より好ましくは、二液性のポリエステル系ポリウレタン接着剤である。 In the case of the dry lamination method, the type of adhesive is selected in consideration of the type of contents, the packaging form, etc., but it is preferable to use a one-component or two-component polyurethane adhesive. More preferably, it is a two-component polyester polyurethane adhesive.
ラミネートするフィルム間の貼り合わせ接着力を向上するために、ラミネーションに先立ってまたはラミネーションと同時に、ラミネートする層のいずれか一方または両方の貼り合わせ接着面に、コロナ放電処理、オゾン処理、アンカーコート剤塗布などの方法による表面処理をすることが好ましい。 Corona discharge treatment, ozone treatment, anchor coating agent on the bonding surface of one or both of the layers to be laminated prior to or at the same time as the lamination to improve the adhesion between the films to be laminated It is preferable to perform surface treatment by a method such as coating.
中間層(3)は、基材層(1)と強固に接着することで基材層(1)を補完すると共に、内容物を充填した包装袋とされたあとに、ヒートシール部分を除き、屈曲や瞬時的な衝撃応力を受けた際に、シーラント層(5)に対して移動可能な界面を形成して応力分散させるという多重袋としての機能を発現させるために必須の構成要素である。中間層の材質はポリオレフィン系重合体を用いることが好ましい。具体的には、線状低密度ポリエチレン、高圧法低密度ポリエチレン、低圧法高密度ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン、エチレン−プロピレンブロック共重合体、エチレン−プロピレンランダム共重合体、或いはこれらの混合物等を用いるのが好ましい。なかでも、線状低密度ポリエチレンが、ヒートシール強度の観点から特に好ましい。これら中間層(3)を形成する樹脂には、滑剤等の添加剤が配合されても良い。当該中間層の厚みは、自動充填特性の観点から好ましくは20〜80μmであり、さらに好ましくは25〜60μmである。 The intermediate layer (3) complements the base material layer (1) by firmly adhering to the base material layer (1), and after being a packaging bag filled with the contents, excluding the heat seal portion, It is an essential component for expressing the function as a multiple bag that forms a movable interface with the sealant layer (5) and disperses the stress when subjected to bending or instantaneous impact stress. The intermediate layer is preferably made of a polyolefin polymer. Specifically, linear low density polyethylene, high pressure method low density polyethylene, low pressure method high density polyethylene, polypropylene, ethylene-propylene block copolymer, ethylene-propylene random copolymer, or a mixture thereof may be used. preferable. Among these, linear low density polyethylene is particularly preferable from the viewpoint of heat seal strength. Additives such as a lubricant may be blended in the resin forming these intermediate layers (3). The thickness of the intermediate layer is preferably 20 to 80 μm, more preferably 25 to 60 μm, from the viewpoint of automatic filling characteristics.
次に、第2の接合層(4)は、製袋時には中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)とを接合する機能を担うと共に、屈曲や瞬時的な衝撃応力を受けた際には部分的に剥がれることで中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)とを相互移動可能とするための層である。 Next, the second bonding layer (4) has a function of bonding the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) at the time of bag making and is partly subjected to bending or instantaneous impact stress. It is a layer for enabling the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) to move relative to each other by being peeled off.
第2の接合層(4)の材質は、エチレン系重合体とするのが好ましく、具体的には線状低密度ポリエチレン、高圧法低密度ポリエチレン、高密度ポリエチレンが好ましい。なかでも線状低密度ポリエチレンがさらに好ましい。殊にホットパックを目的とする場合は、線状低密度ポリエチレンが好ましい。線状低密度ポリエチレンの密度は好ましくは0.905〜0.930g/cm3であり、さらに好ましくは0.915〜0.925g/cm3である。また、メルトインデックス(190℃、2.16kg)は、好ましくは2〜12g/10分、さらに好ましくは5〜10g/10分である。 The material of the second bonding layer (4) is preferably an ethylene polymer, and specifically, linear low density polyethylene, high pressure method low density polyethylene, and high density polyethylene are preferred. Of these, linear low density polyethylene is more preferable. Particularly for the purpose of hot pack, linear low density polyethylene is preferred. The density of the linear low density polyethylene is preferably 0.905 to 0.930 g / cm 3 , more preferably 0.915 to 0.925 g / cm 3 . The melt index (190 ° C., 2.16 kg) is preferably 2 to 12 g / 10 minutes, more preferably 5 to 10 g / 10 minutes.
第2の接合層(4)には、他の樹脂を配合しても良い。他の樹脂としては、エチレン−不飽和カルボン酸共重合体があげられる。不飽和カルボン酸は特に限定しないが、エチレンと共重合可能な不飽和カルボン酸であれば良い。エチレン−不飽和カルボン酸共重合体の具体例として、エチレン−アクリル酸共重合体、エチレン−メタクリル酸共重合体、エチレン−エタクリル酸共重合体、エチレン−マレイン酸共重合体、エチレン−フマール酸共重合体、エチレン−無水マレイン酸共重合体等を挙げることができる。 You may mix | blend another resin with a 2nd joining layer (4). Examples of other resins include ethylene-unsaturated carboxylic acid copolymers. The unsaturated carboxylic acid is not particularly limited as long as it is an unsaturated carboxylic acid copolymerizable with ethylene. Specific examples of the ethylene-unsaturated carboxylic acid copolymer include ethylene-acrylic acid copolymer, ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymer, ethylene-ethacrylic acid copolymer, ethylene-maleic acid copolymer, ethylene-fumaric acid. Examples thereof include a copolymer and an ethylene-maleic anhydride copolymer.
なかでもエチレン−アクリル酸共重合体、エチレン−メタクリル酸共重合体が好ましい。また、エチレンや不飽和カルボン酸と共重合可能な他の単量体を用いてもよい。そのような他の単量体としては、アクリル酸メチル、アクリル酸イソブチル、マレイン酸ジエチル等の不飽和カルボン酸エステル等を挙げることができるが、他の単量体の配合量は、第2の接合層(4)の樹脂量に対して40重量%以下、好ましくは30重量%以下である。 Of these, ethylene-acrylic acid copolymers and ethylene-methacrylic acid copolymers are preferred. Moreover, you may use the other monomer copolymerizable with ethylene and unsaturated carboxylic acid. Examples of such other monomers include unsaturated carboxylic acid esters such as methyl acrylate, isobutyl acrylate, diethyl maleate, and the like. The amount is 40% by weight or less, preferably 30% by weight or less, based on the resin amount of the bonding layer (4).
なお、ここで云うエチレン−不飽和カルボン酸共重合体には、エチレンと不飽和カルボン酸との共重合体の他に、例えばポリエチレンに無水マレイン酸をグラフト反応させて得られた無水マレイン酸グラフトポリエチレン共重合体のような、グラフト共重合体も包含する。 The ethylene-unsaturated carboxylic acid copolymer referred to here includes, for example, a maleic anhydride graft obtained by grafting maleic anhydride onto polyethylene in addition to a copolymer of ethylene and unsaturated carboxylic acid. Also included are graft copolymers, such as polyethylene copolymers.
また、配合しても良い他の樹脂として、上記したエチレン−不飽和カルボン酸共重合体に加え、エチレン−アクリル酸メチル共重合体、エチレン−メタクリル酸メチル共重合体、エチレン−メタクリル酸エチル共重合体等のエチレン−不飽和カルボン酸エステル共重合体を挙げることができる。なお、第2の接合層(4)に使用されるポリエチレン系樹脂には、滑剤等の添加剤は使用しないことが好ましい。 Further, as other resins that may be blended, in addition to the above-mentioned ethylene-unsaturated carboxylic acid copolymer, ethylene-methyl acrylate copolymer, ethylene-methyl methacrylate copolymer, ethylene-ethyl methacrylate copolymer Mention may be made of ethylene-unsaturated carboxylic acid ester copolymers such as polymers. In addition, it is preferable not to use additives, such as a lubricant, for the polyethylene-type resin used for a 2nd joining layer (4).
第2の接合層(4)の形成法としては、押出ラミネーション法を用いる。ラミネートに先立ち、ラミネートする中間層(3)、及びシーラント層(5)のいずれか一方または両方の貼り合わせ接着する面にコロナ放電処理、オゾン処理、アンカーコート剤塗布などの方法による表面処理をすることが好ましい。層の厚みは、押し出しラミネーション加工特性、界面接着性、さらには本発明の特徴である加熱処理による界面剥離性を発現させる為に3〜13μmであり、好ましくは5〜12μm、さらに好ましくは8〜10μmである。 As a method for forming the second bonding layer (4), an extrusion lamination method is used. Prior to laminating, the surface to be bonded and bonded to either or both of the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) to be laminated is subjected to surface treatment by a method such as corona discharge treatment, ozone treatment or anchor coating agent application. It is preferable. The thickness of the layer is from 3 to 13 μm, preferably from 5 to 12 μm, more preferably from 8 to 8 in order to develop extrusion lamination processing characteristics, interfacial adhesiveness, and interfacial peelability by heat treatment, which is a feature of the present invention. 10 μm.
次に、シーラント層(5)は、製袋に必要なヒートシールの機能を担った層である。ここに用いられる樹脂は、線状低密度ポリエチレンが好ましい。線状低密度ポリエチレンの密度は好ましくは0.905〜0.925g/cm3である。また、メルトインデックス(190℃、2.16kg)は、好ましくは1〜10g/10分である。シーラント層(5)の層の厚みは、好ましくは30〜100μmである。 Next, the sealant layer (5) is a layer having a heat sealing function necessary for bag making. The resin used here is preferably linear low density polyethylene. The density of the linear low density polyethylene is preferably 0.905 to 0.925 g / cm 3 . The melt index (190 ° C., 2.16 kg) is preferably 1 to 10 g / 10 minutes. The thickness of the layer of the sealant layer (5) is preferably 30 to 100 μm.
上記の少なくとも5層が積層された積層フィルムは、それを用いて包装袋を製袋し、油脂類を含んだ流動体を密封包装して適度な加熱処理を加えた場合に、密封性能には何ら問題ないにも係わらず、積層フィルムのシール部以外の剥離強度が上記の一定範囲に低下し、そのため、包装体が運搬時等に受ける局部的な応力が積層フィルムの層間剥離を誘発し、応力分散や応力緩和が生じることで包装体の破壊を防ぐことが可能になる。 A laminated film in which at least five layers are laminated is used to make a packaging bag, and when a fluid containing oils and fats is hermetically packaged and subjected to appropriate heat treatment, the sealing performance is Despite no problem, the peel strength of the laminated film other than the seal portion is reduced to the above-mentioned fixed range, and therefore, the local stress that the package receives during transportation induces delamination of the laminated film, It becomes possible to prevent the package from being destroyed by causing stress dispersion and stress relaxation.
包装体に対して加えるべき適度な加熱処理についてはすでに上記したが、加熱処理の温度範囲において用いられる示差走査熱量計(DSC)による測定は、JIS K7121に準じて行えばよい。具体的には、試験片をDSC装置の容器に入れ、昇温速度10℃/minにて融解ピーク終了時より約30℃高い温度まで加熱溶融させ、その温度に10分間保持した後、10℃/minで室温まで冷却した試験片を当該測定に供する。上記した結晶融解ピーク温度Tpmは、融解ピークが2以上存在する樹脂の場合は、最も低温側のピーク温度をTpmとする。 The appropriate heat treatment to be applied to the package has already been described above, but the measurement with a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) used in the temperature range of the heat treatment may be performed according to JIS K7121. Specifically, the test piece is put into a container of a DSC apparatus, heated and melted to a temperature about 30 ° C. higher than the end of the melting peak at a temperature rising rate of 10 ° C./min, held at that temperature for 10 minutes, and then 10 ° C. A test piece cooled to room temperature at / min is subjected to the measurement. The above-described crystal melting peak temperature Tpm is the lowest temperature peak temperature Tpm in the case of a resin having two or more melting peaks.
上記した、70℃以上でかつ結晶融解ピーク温度Tpmより5℃低い温度以下の温度に加熱処理後、該積層フィルムの中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)間の剥離強度を測定するに際しては、積層フィルムを製袋し、油脂を含有する液状食品を充填して、ヒートシールして包装体とした後、該包装体を上記温度範囲に少なくとも10分以上加熱処理した後、室温に冷却して測定に供する。剥離強度の測定は、JIS Z0237に準じて行えばよく、180度引き剥がし法により、毎分50mmの速さで試験片を引き剥がす。 When the peel strength between the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) of the laminated film is measured after the heat treatment at a temperature of 70 ° C. or higher and 5 ° C. or lower than the crystal melting peak temperature Tpm. Then, after making a laminated film into a bag, filling a liquid food containing fats and oils, and heat-sealing to make a package, the package is heated to the above temperature range for at least 10 minutes and then cooled to room temperature. For measurement. The peel strength may be measured according to JIS Z0237, and the test piece is peeled off at a speed of 50 mm per minute by a 180-degree peeling method.
上記した適度な加熱処理の温度範囲は、積層フィルムからなる多重包装袋に充填される内容物、つまり油脂を含有する流動体を殺菌等の目的で加熱する時の温度に対応する。そのため、内容物の充填後に加熱殺菌処理を行うことで、積層フィルムが実質的に2つ以上のフィルムからなる多重フィルムとなる。なお、積層フィルムを実質的に3重に機能するようにするには、図1において接合層4とシーラント層5との間に、さらに二つ目の中間層3と二つ目の接合層4とを設けて、合計7層とすればよい。
The above-mentioned temperature range of the appropriate heat treatment corresponds to the temperature when the contents filled in the multi-packaging bag made of the laminated film, that is, the fluid containing the oil and fat is heated for the purpose of sterilization or the like. For this reason, by performing a heat sterilization treatment after filling the contents, the laminated film becomes a multi-film consisting essentially of two or more films. In order to make the laminated film function substantially triple, in FIG. 1, a second
このシーラント層(5)を形成する樹脂には、滑剤が配合されていることが好ましい。またシーラント層(5)のラミネートされる側の表面は、あらかじめコロナ放電処理等で、カルボニル基を生成させておくことが有効である。コロナ放電処理により得られる表面張力は38〜50dyn/cmが望ましい。 The resin forming the sealant layer (5) preferably contains a lubricant. In addition, it is effective to generate a carbonyl group in advance on the surface on the side of the sealant layer (5) to be laminated by corona discharge treatment or the like. The surface tension obtained by the corona discharge treatment is desirably 38 to 50 dyn / cm.
中間層(3)及びシーラント層(5)の樹脂に配合できる滑剤を以下に例示する。なお、参考までに、各滑剤の代表的な商品名と製造メーカー名または滑剤の内容を一緒に例示する。
(イ)オレイン酸アミド系滑剤;アーモスリップCP(ライオン・アクゾ)、ニュートロン(日本精化)、ニュートロンE−18(日本精化)、アマイドO(日東化学)、アルフロE−10(日本油脂)、ダイヤミッドO−200(日本化成)、ダイヤミッドG−200(日本化成)等
(ロ)エルカ酸アミド系滑剤;アルフロ−P−10(日本油脂)等
(ハ)ステアリン酸アミド系滑剤;アルフロ−S−10(日本油脂)、ニュートロン2(日本精化)、ダイヤミッド200ビス(日本化成)等
(ニ)ビス脂肪酸アミド系滑剤;ビスアマイド(日本化成)、ダイヤミッド200ビス(日本化成)、アーモワックスEBS(ライオン・アクゾ)等
(ホ)アルキルアミン系滑剤;エレクトロストリッパ−TS−2(花王石鹸)等
(ヘ)炭化水素系滑剤;流動パラフィン、天然パラフィン、マイクロワックス、合成パラフィン、ポリエチレンワックス、ポリプロピレンワックス、塩素化炭化水素、フルオロカルボン等
(ト)脂肪酸系滑剤;高級脂肪酸(C12以上が好ましい)、オキシ脂肪酸等
(チ)エステル系滑剤;脂肪酸の低級アルコールエステル、脂肪酸の多価アルコールエステル、脂肪酸のポリグリコールエステル、脂肪酸の脂肪アルコールエステル等
(リ)アルコール系滑剤;多価アルコール、ポリグリコール、ポリグリセロール等
(ヌ)金属石けん;ラウリン酸、ステアリン酸、リシノール酸、ナフテン酸、オレイン酸等の高級脂肪酸とLi、Mg、Ca、Sr、Ba、Zn、Cd、Al、Sn、Pb等の金属との化合物等
(ル)シリコーン系滑剤;各種グレードのジメチルポリシロキサン及びその変性物(信越シリコーン、東レシリコーン)等
Examples of the lubricant that can be blended in the resin of the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) are shown below. For reference, a representative trade name of each lubricant and a manufacturer name or the contents of the lubricant are illustrated together.
(I) Oleic acid amide lubricant: Armoslip CP (Lion Akzo), Neutron (Nippon Seika), Neutron E-18 (Nippon Seika), Amide O (Nitto Chemical), Alfro E-10 (Japan) (Oil), Diamond O-200 (Nippon Kasei), Diamond G-200 (Nippon Kasei), etc. (b) Erucic acid amide lubricants; Alfro-P-10 (Nippon Fats and oils), etc. Alfro-S-10 (Nippon Yushi), Neutron 2 (Nippon Seika), Diamond 200 bis (Nippon Kasei) etc. (d) Bis fatty acid amide lubricants; Bisamide (Nippon Kasei), Diamond 200 bis (Japan) Kasei), Armo wax EBS (Lion Akzo) etc. (e) Alkylamine lubricants; Electro stripper TS-2 (Kao soap) etc. (f) Hydrocarbons Agents: liquid paraffin, natural paraffin, micro wax, synthetic paraffin, polyethylene wax, polypropylene wax, chlorinated hydrocarbon, fluorocarbon, etc. (g) Fatty acid type lubricants; higher fatty acids (preferably C12 or more), oxy fatty acids, etc. Ester lubricants: lower alcohol esters of fatty acids, polyhydric alcohol esters of fatty acids, polyglycol esters of fatty acids, fatty alcohol esters of fatty acids, etc. (Li) alcohol lubricants; (nu) metals such as polyhydric alcohols, polyglycols, polyglycerols Soap: Compounds of higher fatty acids such as lauric acid, stearic acid, ricinoleic acid, naphthenic acid, oleic acid and metals such as Li, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Zn, Cd, Al, Sn, Pb, etc. Silicone lubricants; various grades of dimethyl Polysiloxane and modified products thereof (manufactured by Shin-Etsu Silicone, Toray Silicone), etc.
滑剤の中間層(3)、及びシーラント層(5)を形成する樹脂への配合量は50乃至1000ppmが好ましく、100乃至600ppmがさらに好ましく、150乃至400ppmがさらに好ましい。 The blending amount of the lubricant in the resin forming the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) is preferably 50 to 1000 ppm, more preferably 100 to 600 ppm, and further preferably 150 to 400 ppm.
次に、これら各層からなる積層フィルムの製法について述べる。あらかじめ製膜された基材層(1)と中間層(3)とを接合するラミネーション法として、例えば接着剤を介して接着するドライラミネーション法、押出しラミネーション法などを用いられることができるが、得られる包装材料の性能からドライラミネーション法が好ましい。これらのラミネーション法を用いることにより、基材層(1)と中間層(3)との間に第1の接合層(2)が形成される。 Next, the manufacturing method of the laminated film which consists of each of these layers is described. As a lamination method for joining the base material layer (1) and the intermediate layer (3) formed in advance, for example, a dry lamination method, an extrusion lamination method, etc., which are bonded via an adhesive, can be used. The dry lamination method is preferred from the performance of the packaging material to be produced. By using these lamination methods, the first bonding layer (2) is formed between the base material layer (1) and the intermediate layer (3).
次いで、この基材層(1)、第1の接合層(2)、中間層(3)からなる積層フィルムの原反を捲出し、一方からシーラント層(5)の原反フィルムを捲出し、両原反フィルムを貼合せる。その際、両フィルムの貼り合わせ面に対し、第2の接合層(4)を形成するポリエチレン系樹脂の溶融物を、Tダイを備えた押出機からフィルム状に押し出し、これらが積層されたものをニップロール等で挟み込み、圧接することにより両原反フィルムを貼合せる。これで、基材層(1)、第1の接合層(2)、中間層(3)、第2の接合層(4)、シーラント層(5)が順次積層された積層フィルムが得られる。 Next, the raw film of the laminated film composed of the base material layer (1), the first bonding layer (2), and the intermediate layer (3) is crushed, and the raw film of the sealant layer (5) is crushed from one side, Paste both original films. At that time, a polyethylene resin melt forming the second bonding layer (4) is extruded into a film form from an extruder equipped with a T-die on the bonding surfaces of both films, and these are laminated. Is sandwiched between nip rolls and the like, and the two raw films are bonded together by pressing. Thus, a laminated film in which the base material layer (1), the first bonding layer (2), the intermediate layer (3), the second bonding layer (4), and the sealant layer (5) are sequentially laminated is obtained.
このようにして得られた少なくとも5層からなる積層フィルムは、シーラント層が油脂類を含有する流動体、例えば、液体・粘体状の食品や医薬品に接した状態で加熱処理(例えば、85℃×30分)することで、シーラント層と中間層の間の剥離強度が低下し、5〜100g/15mmの範囲となる。さらに好ましくは5〜70g/15mmの範囲となる。 The laminated film consisting of at least 5 layers thus obtained is heat-treated in a state where the sealant layer is in contact with a fluid containing oils and fats, for example, a liquid / viscous food or medicine (for example, 85 ° C. × 30 minutes), the peel strength between the sealant layer and the intermediate layer decreases, and the range is 5 to 100 g / 15 mm. More preferably, it is the range of 5-70 g / 15mm.
油脂類を含む食品の例としては、例えば液体スープ、たれ、ソース、醤油、ケチャップ、カレー、味噌、シチュー、ジャム、マヨネーズ、ドレッシング、あん類、魚肉練りなどの液体及び流動性の食品が挙げられるがこれらに限定されるものではなく、これらの食品以外の液体及び流動性物質の充填包装も可能である。 Examples of foods containing fats and oils include liquid and fluid foods such as liquid soup, sauce, sauce, soy sauce, ketchup, curry, miso, stew, jam, mayonnaise, dressing, sweet potato, fish meat paste, etc. However, the present invention is not limited thereto, and filling and packaging of liquid and fluid substances other than these foods is also possible.
以下、本発明を実施例によって具体的に説明するが、本発明は以下の具体的態様に限定されるものではない。 EXAMPLES Hereinafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention concretely, this invention is not limited to the following specific aspects.
図1に記載の層構成を有する積層フィルムを作成した。基材層(1)としては厚み15μmの2軸延伸ナイロンフィルムを使用し、中間層(3)として厚み25μmの線状低密度ポリエチレン樹脂(密度:0.925g/cm3、MI:7g/10分)より製膜した未延伸フィルムを用い、基材層(1)の一面に第1の接合層(2)として3g/m2のポリエステル系ポリウレタン接着剤を塗布し、この塗布面に中間層(3)を積層することで、ドライラミネーション法によりラミネートした。 A laminated film having the layer structure shown in FIG. 1 was prepared. A biaxially stretched nylon film having a thickness of 15 μm is used as the base layer (1), and a linear low density polyethylene resin having a thickness of 25 μm (density: 0.925 g / cm 3 , MI: 7 g / 10) as the intermediate layer (3). 3) Polyester adhesive of 3 g / m 2 as a first bonding layer (2) is applied to one surface of the base material layer (1) using an unstretched film formed from (1), and an intermediate layer is applied to the coated surface. By laminating (3), lamination was performed by a dry lamination method.
次に、シーラント層(5)として厚み50μmの線状低密度ポリエチレン樹脂(密度:0.920g/cm3、MI:7g/10分)より製膜した未延伸フィルムを準備し、この片面にコロナ処理を施し、このコロナ処理面と、上記でラミネートしたフィルムの中間層(3)側の面とを対向させて、両者の間に厚み12μm又は9μmの線状低密度ポリエチレン樹脂(密度:0.920g/cm3、MI:7g/10分、Tpm:105℃)を用いた溶融押出し樹脂層を第2の接合層(4)として積層し、2種の積層フィルムを得た。その結果、層構成として、2軸延伸ナイロンによる基材層(1)/ポリウレタン系接着剤による第1の接合層(2)/線状低密度ポリエチレン未延伸フィルムによる中間層(3)/溶融押出しポリエチレン樹脂による第2の接合層(4)/線状低密度ポリエチレン未延伸フィルムによるシーラント層(5)からなる、総厚みが105μm(表1のa)、及び102μm(表1のb)の2種の積層フィルムを得た。得られた積層フィルムの機械強度、及びシール部の強度をヒートシール強度として表1に示した。 Next, an unstretched film formed from a linear low density polyethylene resin (density: 0.920 g / cm 3 , MI: 7 g / 10 min) having a thickness of 50 μm was prepared as a sealant layer (5), and a corona was formed on one side thereof. The corona-treated surface and the surface on the intermediate layer (3) side of the laminated film described above are opposed to each other, and a linear low-density polyethylene resin having a thickness of 12 μm or 9 μm (density: 0.00). A melt-extruded resin layer using 920 g / cm 3 , MI: 7 g / 10 min, Tpm: 105 ° C.) was laminated as the second bonding layer (4) to obtain two kinds of laminated films . As a result, as a layer structure, a base layer (1) made of biaxially stretched nylon / a first bonding layer made of polyurethane adhesive (2) / an intermediate layer made of a linear low density polyethylene unstretched film (3) / melt extruded 2 having a total thickness of 105 μm (Table 1 a) and 102 μm (Table 1 b), comprising a second bonding layer (4) made of polyethylene resin / a sealant layer (5) made of a linear low density polyethylene unstretched film. A seeded laminated film was obtained. The mechanical strength of the obtained laminated film and the strength of the seal part are shown in Table 1 as heat seal strength.
なお、上記で用いた材料の種類を以下に示す。
・2軸延伸ナイロンフィルム: 商品名「NH#15」(ユニチカ(株)製)
・未延伸の線状低密度ポリエチレンフィルム: 商品名「XHT」(二村化学(株)製)
・溶融押出しポリエチレン樹脂: 商品名「021GT」(宇部興産(株)製)
・未延伸の線状低密度ポリエチレンフィルム: 商品名「MTN」(二村化学(株)製)
In addition, the kind of material used above is shown below.
-Biaxially stretched nylon film: Product name “NH # 15” (manufactured by Unitika Ltd.)
・ Unstretched linear low-density polyethylene film: Trade name “XHT” (manufactured by Futamura Chemical Co., Ltd.)
Melt extruded polyethylene resin: Trade name “021GT” (manufactured by Ube Industries)
・ Unstretched linear low-density polyethylene film: Trade name “MTN” (manufactured by Nimura Chemical Co., Ltd.)
得られた2種の積層フィルムをそれぞれ420mmの幅にスリットして、縦型ピロー自動充填製袋機にて図3に記載のものと同様の包装袋を作成した。具体的には図3の縦シール部8bを、次いで下側の横シール部8a形成を形成した後、食用油を0.5、または4重量%を含有する90℃の熱水をノズルより1kgを加熱状態のまま充填して(ホットパック)、上側の横シール部8cを設けて、図3に示すピロー包装袋(寸法:縦260mm、横200mm)に内容物が充填された包装体(サンプル1〜4)を得た。次いで、各包装体を90℃に30分間保持してボイル処理(加熱処理)を行った。ボイル処理前後における包装体のヒートシール部分のシール強度、及び充填された内容物と接していた積層フィルム部分のラミネート強度を中間層(3)とシーラント層間の剥離強度として測定し、その結果をn数8の平均値として表2に示した。
The obtained two kinds of laminated films were each slitted to a width of 420 mm, and a packaging bag similar to that shown in FIG. 3 was prepared using a vertical pillow automatic filling bag making machine. Specifically, after forming the
表2から明らかなように、ヒートシール部のシール強度は、加熱処理で変化することなく、大きな値を維持している。一方、ヒートシールされていない積層フィルムの部分では、90℃に30分間の加熱処理後の剥離強度がホットパック後の強度に比べて大幅に低い値となっていることが分かる。即ち、加熱処理により、中間層(3)とシーラント層(5)間の剥離強度が低下して、易剥離性の界面が形成されていることがわかる。 As is clear from Table 2, the seal strength of the heat seal part maintains a large value without being changed by the heat treatment. On the other hand, in the part of the laminated film that is not heat-sealed, it can be seen that the peel strength after the heat treatment at 90 ° C. for 30 minutes is significantly lower than the strength after the hot pack. That is, it can be seen that the peel strength between the intermediate layer (3) and the sealant layer (5) is reduced by the heat treatment, and an easily peelable interface is formed.
包装袋に充填する内容物として、食用油を含まない90℃の熱水を用いた以外は、実施例1と同様にして包装体を得て、実施例1と同様にして各部の剥離強度を測定した。結果をn数8の平均値として表2に示す。内容物が熱水だけの場合は、ホットパック後のラミネート強度(剥離強度)が、ホットパック前の値に対して大幅に増加していることがわかる。 As the contents to be filled in the packaging bag, except that hot water of 90 ° C. not containing edible oil was used, a package was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, and the peel strength of each part was determined in the same manner as in Example 1. It was measured. The results are shown in Table 2 as an average value of n number 8. When the content is only hot water, it can be seen that the laminate strength (peel strength) after hot pack is greatly increased with respect to the value before hot pack.
溶融押出し樹脂による第2の接合層(4)の厚みを10μm、及びシーラント層(5)の厚みを80μmとした以外は、実施例1と同様にして積層フィルムを作成し、層構成として、2軸延伸ナイロンの基材層(1)/ポリウレタン系接着剤の第1の接合層(2)/線状低密度ポリエチレン未延伸フィルムの中間層(3)/溶融押出しポリエチレン樹脂の第2の接合層(4)/線状低密度ポリエチレン未延伸フィルムのシーラント層(5)からなる、総厚みが133μmの積層フィルムを得た。該積層フィルムを420mm幅にスリットして、実施例1と同様にして、食用油を4重量%となるように添加した90℃の熱水1kgが充填されたピロー包装体を得た。当該充填ピロー袋を以下に示す方法で落下試験、及び振盪試験に供し、破袋に至るまでの落下回数、及びピンホール発生に至るまでの振盪時間(分)を測定した。その結果を表3に示す。表3から、積層フィルムによる多重袋が耐衝撃性や耐屈曲疲労性、耐ピンホール性に優れることがわかった。
(落下試験)
・試験方式: 上記ピロー包装体をJIS Z0201の重包装袋の呼称に準じて、天面、底面、下端、上端の順番で、JIS Z0238に準じて水平・鉛直の交互落下試験を行った。
・落下距離: 80cm
・測定温度: 5℃(大型冷蔵庫内にて試験した)
・判定 : 落下後の破袋の有無、ピンホールの有無を調べ、破袋またはピンホールの発生にいたる落下回数を記録した。
(振盪試験)
・試験方式 : 上記ピロー包装体2個を、内寸が410×210×170mmの段ボール箱に底板を敷いた上に中仕切り板(段ボール製)で隔絶して配置して、開封状態で試験に供した。
・振盪試験機 : 振盪台が、その振れ幅が30mmとなるように水平移動するものを使用し、毎分300往復の条件で試験を行った。
・測定温度 : 5℃(大型冷蔵庫内にて試験した)
・判定 : 所定時間の振盪試験後、破袋の有無、ピンホールの有無を調べ、破袋またはピンホールの発生にいたる時間を記録した。
A laminated film was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the thickness of the second bonding layer (4) made of the melt-extruded resin was 10 μm and the thickness of the sealant layer (5) was 80 μm. Axis-stretched nylon substrate layer (1) / polyurethane adhesive first bonding layer (2) / linear low density polyethylene unstretched film intermediate layer (3) / melt-extruded polyethylene resin second bonding layer (4) A laminated film having a total thickness of 133 μm, comprising a sealant layer (5) of a linear low density polyethylene unstretched film was obtained. The laminated film was slit to a width of 420 mm, and a pillow package filled with 1 kg of 90 ° C. hot water to which edible oil was added to 4 wt% was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1. The filled pillow bag was subjected to a drop test and a shake test by the following method, and the number of drops until the bag was broken and the shaking time (min) until the pinhole was generated were measured. The results are shown in Table 3. From Table 3, it was found that a multilayer bag made of a laminated film is excellent in impact resistance, flex fatigue resistance, and pinhole resistance.
(Drop test)
Test method: The pillow package was subjected to horizontal and vertical alternating drop tests in accordance with JIS Z0238 in the order of the top, bottom, bottom and top in accordance with the name of the heavy packaging bag of JIS Z0201.
・ Falling distance: 80cm
Measurement temperature: 5 ° C. (tested in a large refrigerator)
-Judgment: The presence or absence of a broken bag after dropping and the presence or absence of a pinhole were examined, and the number of drops that resulted in the broken bag or the occurrence of a pinhole was recorded.
(Shaking test)
・ Testing method: Two pillow packaging bodies are placed on a cardboard box with inner dimensions of 410 x 210 x 170 mm, placed on a bottom plate, separated by a partition plate (made of cardboard), and tested in an unsealed state. Provided.
-Shaking test machine: The shaking table used the thing which moved horizontally so that the swing width might be set to 30 mm, and tested on the conditions of 300 reciprocations per minute.
Measurement temperature: 5 ° C (tested in a large refrigerator)
-Judgment: After a shaking test for a predetermined time, the presence or absence of a broken bag and the presence or absence of a pinhole were examined, and the time until the occurrence of broken bag or pinhole was recorded.
基材層(1)として厚み15μmの2軸延伸ナイロンフィルムを使用し、その裏面に第1の接合層(2)として3g/m2でポリエステル系ポリウレタン接着剤を塗布し、シーラント層(5)として、厚み120μmの線状低密度ポリエチレン樹脂(密度:0.925g/cm3、MI:7g/10分)より製膜した未延伸フィルムをドライラミネーション法によりラミネートして3層のフィルムを作成した。層構成としては、中間層(3)と第2の接合層(4)が無く、2軸延伸ナイロンの基材層(1)/ポリウレタン系接着剤の第1の接合層(2)/線状低密度ポリエチレン未延伸フィルムのシーラント層(5)からなる総厚みが138μmの3層のフィルムを得た。該フィルムを420mm幅にスリットして、実施例1と同様にして、食用油を4重量%となるように添加した90℃の熱水1kgが充填されたピロー包装体を得た。当該ピロー包装体を用いて実施例2と同様の試験評価を行った。その結果を表3に示す。実施例2とほぼ同一の厚みの積層フィルムであるにも拘わらず、強固に一体化された積層フィルムでは、落下衝撃、及び振動による屈曲疲労による破袋が、試験の初期に発生することがわかる。 A biaxially stretched nylon film having a thickness of 15 μm is used as the base material layer (1), a polyester polyurethane adhesive is applied to the back surface thereof at 3 g / m 2 as the first bonding layer (2), and the sealant layer (5). As a film, a non-stretched film formed from a linear low density polyethylene resin having a thickness of 120 μm (density: 0.925 g / cm 3 , MI: 7 g / 10 min) was laminated by a dry lamination method to form a three-layer film. . As a layer structure, there are no intermediate layer (3) and second bonding layer (4), biaxially stretched nylon base material layer (1) / first bonding layer of polyurethane adhesive (2) / linear A three-layer film having a total thickness of 138 μm consisting of a sealant layer (5) of a low-density polyethylene unstretched film was obtained. The film was slit to a width of 420 mm, and a pillow package filled with 1 kg of 90 ° C. hot water to which edible oil was added to 4 wt% was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1. The same test evaluation as in Example 2 was performed using the pillow package. The results are shown in Table 3. Although it is a laminated film having almost the same thickness as that of Example 2, it can be seen that, in the laminated film that is firmly integrated, breakage due to drop impact and bending fatigue due to vibration occurs at the initial stage of the test. .
1 基材層
2 接合層
2a 接合層
3 中間層
4 接合層
5 シーラント層
7 ガスバリアー層
8a〜c ヒートシール部
9 ピロー包装袋
10 シール部
11 内容物
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006113325A JP4968769B2 (en) | 2006-04-17 | 2006-04-17 | Laminated film and multiple packaging bag comprising the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006113325A JP4968769B2 (en) | 2006-04-17 | 2006-04-17 | Laminated film and multiple packaging bag comprising the same |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007284105A JP2007284105A (en) | 2007-11-01 |
| JP2007284105A5 JP2007284105A5 (en) | 2009-05-28 |
| JP4968769B2 true JP4968769B2 (en) | 2012-07-04 |
Family
ID=38756250
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006113325A Active JP4968769B2 (en) | 2006-04-17 | 2006-04-17 | Laminated film and multiple packaging bag comprising the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4968769B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5251417B2 (en) * | 2008-10-17 | 2013-07-31 | 東ソー株式会社 | Laminate film |
| JP5481969B2 (en) * | 2009-06-29 | 2014-04-23 | 東ソー株式会社 | Laminate film for liquid packaging |
| JP2012030866A (en) * | 2010-07-30 | 2012-02-16 | Kyoraku Co Ltd | Method of manufacturing cooking oil contained in packaging bag |
| JP6425369B2 (en) * | 2012-09-20 | 2018-11-21 | 四国化工株式会社 | Method of producing multilayer stretched film |
| JP2020121725A (en) * | 2019-01-29 | 2020-08-13 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Packaging bag and manufacturing method of laminated film |
| JP2020131519A (en) * | 2019-02-18 | 2020-08-31 | 株式会社プライムポリマー | Method of producing packing bag |
| WO2021033533A1 (en) * | 2019-08-21 | 2021-02-25 | 株式会社悠心 | Laminated plastic film, filling and packaging method for item to be packaged in packaging bag comprising laminated plastic film, and package |
| JP6818261B2 (en) * | 2020-06-15 | 2021-01-20 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Laminated body with a resin layer derived from biomass |
| JP2021049784A (en) * | 2020-12-15 | 2021-04-01 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | Laminate having resin layer derived from biomass |
| KR102442819B1 (en) * | 2022-05-09 | 2022-09-16 | (주) 해시즈 | Manufacturing method of wrapping paper using recycled paper |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3317003B2 (en) * | 1994-03-18 | 2002-08-19 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Packaging material with content resistance |
| JPH10202807A (en) * | 1997-01-27 | 1998-08-04 | Meiwa Packs:Kk | Laminated film and packaging bag |
| JP2001130598A (en) * | 1999-08-26 | 2001-05-15 | Daiwa Gravure Co Ltd | Storage bag |
| JP4321042B2 (en) * | 2002-10-30 | 2009-08-26 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Packaging material with pinhole resistance |
-
2006
- 2006-04-17 JP JP2006113325A patent/JP4968769B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2007284105A (en) | 2007-11-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4968769B2 (en) | Laminated film and multiple packaging bag comprising the same | |
| US7288316B2 (en) | Cycloolefin copolymer heat sealable films | |
| JP6109038B2 (en) | Strippable sealing structure | |
| JP5466636B2 (en) | Heat-sealable multilayer film | |
| EP1541335A3 (en) | Frangible heat-sealable films for cook-in applications and packages made thereof | |
| KR20100114928A (en) | Peelable composite thermoplastic sealants in packaging films | |
| JP2004538189A (en) | Heat-shrinkable laminate useful for packaging | |
| JP2008080543A (en) | Multilayer coextrusion film, laminated film and packaging material using the coextrusion film | |
| JPWO2012144536A1 (en) | Film and packaging bag | |
| JP2017177579A (en) | Easily-peelable sealant film | |
| US20020160135A1 (en) | Polylmeric films and packages produced therefrom | |
| JP2020078942A (en) | Multilayer film, and package | |
| JP2020045473A (en) | Resin composition for water-repellent layer formation, and water-repellent film, water-repellent laminate, package and container using the same | |
| JP6797353B2 (en) | Multilayer film and packaging material | |
| JP4344997B2 (en) | Easy-open coextruded multilayer film and easy-open laminate film | |
| JP3515194B2 (en) | Packaging material for bag-in-box | |
| JP2018053104A (en) | Sealant film having resealing properties and dead hold properties | |
| JP6103302B2 (en) | Easy-open coextruded multilayer film | |
| JP4383847B2 (en) | Easy-open composite film | |
| WO2005028201A1 (en) | Multilayer heat sealant structures, packages and methods of making the same | |
| JP6805685B2 (en) | Resealable sealant film | |
| JP2019177692A (en) | Multilayer film and package | |
| JP2005103904A (en) | Coextrusion multilayered film and laminated film | |
| JPH11221887A (en) | Sealant film | |
| JP7326909B2 (en) | Liquid-repellent laminate and packaging material |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090410 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090410 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110808 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110815 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111013 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120328 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120329 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150413 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4968769 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |