JP4860028B2 - Broadcast receiver - Google Patents
Broadcast receiver Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4860028B2 JP4860028B2 JP2000183978A JP2000183978A JP4860028B2 JP 4860028 B2 JP4860028 B2 JP 4860028B2 JP 2000183978 A JP2000183978 A JP 2000183978A JP 2000183978 A JP2000183978 A JP 2000183978A JP 4860028 B2 JP4860028 B2 JP 4860028B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- program
- epg
- same
- displayed
- display
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は放送受信装置に関し、特に、BS(Broadcasting Satellite)デジタル放送などにおいて電子番組ガイドに基づき作成される電子番組表がより見易くなるように改良された放送受信装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来から、CS(communications satellite)放送では、電子番組ガイド(Electric Program Guide 以下、「EPG」という)のサービスが提供されている。このEPGサービスにより、たとえば、放送局名、放送される番組の開始時刻、番組タイトル、その他、必要とされる各チャンネル(放送局)の情報がユーザのもとへ提供される。ユーザはこれを利用して、新聞のテレビ欄等を見なくても現在どのような番組が放送されているかを確認することができる。そして、所望の番組を選択し、選局や録画/視聴予約をすることができる。
【0003】
現行の地上波、BSアナログ放送、CS放送では、同時刻においては、複数のチャンネルそれぞれが異なった番組を放送している。つまり、ある1つの番組が同時刻に複数のチャンネルにまたがって放送されるということはない。したがって、各々のチャンネルが独立したものとなっているため、提供されるEPGは、次のようなものとして表示されることになる。
【0004】
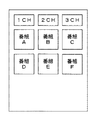
図8は、このような従来の状況におけるEPGの表示例を示した図である。ここでは、テレビなどの受信装置においてEPGが表示されているものとする。横軸にはチャンネルがとられており、縦軸には時間がとられている。
【0005】
異なるチャンネル1CH,2CH,3CHでは、同時刻においては、異なる番組A、番組B、番組Cまたは番組D、番組E、番組Fがそれぞれ放送されている。このため、EPGの構成としては、本図に示すように、各々のチャンネルがそれぞれ独立したものとなって表示されることになる。
【0006】
これは、1つの放送局が複数のチャンネルを所有していたとしても同様である。すなわち、たとえ同じ放送局のチャンネルであっても各チャンネルごとに独立しており本図に示すようにそれぞれ異なる番組が表示されることになる。
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
上述したEPGサービスは、今後もBSデジタル放送や地上波デジタル放送の実現などで、さらに普及が進んでくると思われる。こういった状況において、従来のEPGの表示方法では、以下に示すような問題が発生してくる。
【0008】
たとえば、BSデジタル放送には、HDTV(High Definition TV)とSDTV(Standard Definition TV)という2つの放送方式がある。SDTVは現行で放送されている方式であり、HDTVはさらに高精細の画質で放送する方式である。このように2つの放送方式が存在することにより、BSデジタル放送では、1つの放送局が所有する複数のSDTVチャンネルを用いて、1つのHDTVの番組を放送するといったことが可能となる。
【0009】
たとえば、ある放送局では、SDTVを3番組同時に放送できる帯域幅を所有しているとする。すると、今日の夜7時からは番組A、番組B、番組Cの3つの番組をそれぞれ3つのSDTVのチャンネルで同時に放送し、夜8時からはSDTVチャンネル3つ分の帯域を用いて1つのHDTVの番組Dを放送するといった状況が発生し得る。
【0010】
このような場合、従来の表示方法にしたがってEPGを表示すると図9のようになる。図9を参照して、ここでも横軸にはチャンネルが、縦軸には時間がそれぞれとられている。ある時間帯には各SDTVチャンネルにそれぞれ異なる番組A、番組B、番組Cの情報が表示され、また、ある時間帯には各SDTVチャンネルにそれぞれ同じ番組Dの情報が表示される。つまり、たとえ同一のHDTVの番組Dがチャンネル1、2、3にまたがって放送されていても、それぞれ独立に、チャンネル1では番組D、チャンネル2では番組D、チャンネル3では番組Dという表示がされることになる。
【0011】
このような表示がされると、ユーザがその表示を見て放送形態を理解する上で、以下に示す2つの問題がある。
【0012】
まず第1には、チャンネル1、2、3で放送されている番組Dが全く同一の番組であるかどうかの判断を一見して行なうことが困難ということである。すなわち、ユーザは、チャンネル1、2、3に表示されている番組Dの表示内容をそれぞれ確認し、相互に比較して初めて、これらが同一の番組であることを知ることができる。
【0013】
第2には、HDTVという高精細な画質で放送されているということが、一見して判断し難いということである。ユーザは、上述したように相互比較して、チャンネル1、2、3で同一番組Dが放送されていることを知った後、同じ放送局が所有するチャンネル1、2、3で同じ番組Dが放送されているため、この番組はHDTVで放送されるものであるという思考で判断せざるを得ない。
【0014】
今後、BSデジタル放送が開始されたときは、1つの放送局が複数のチャンネルにまたがってHDTVの番組を放送したり、あるいは通常通りのSDTVの番組を複数放送したり、これらSDTVとHDTVとが時間によって混在するような放送状況が発生すると考えられる。こういった中、従来のEPG表示方法では、上述した問題が生じる機会がさらに増加し、決してユーザにとって満足のいくものとは言えない。
【0015】
本発明はかかる実状に鑑み考え出されたものであり、その目的は、より容易に放送形態を認識することのできるEPGテーブルが得られる放送受信装置を提供することである。
【0016】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するため、本発明のある局面に従うと、放送受信装置は、電子番組ガイドのデータを受信する受信手段と、電子番組ガイドのデータが受信された場合に、電子番組ガイドのデータから同じ時刻に複数のチャンネルを用いて放送される同一番組があるか否かを判断する第1の判断手段と、第1の判断手段により同一番組があると判断された場合、同一番組の内容が、対応する複数のチャンネルに渡った同一領域に表示されるように、電子番組ガイドのデータに基づいて、各チャンネルに対応する番組の内容を表示する電子番組表を作成する作成手段と、作成手段により作成された電子番組表を保存するための保存手段と、ユーザより電子番組表の表示要求を受付けた場合に、保存手段に保存された電子番組表を表示する表示手段とを備える。
【0017】
この発明に従うと、同じ時刻に複数のチャンネルを用いて放送される同一番組がある場合は、その同一番組の内容が、対応する複数のチャンネルに渡った同一領域に表示されるように電子番組表(EPGテーブル)が作成される。
【0018】
このため、ユーザは、複数のチャンネル毎に表示内容を確認し相互に一致するかどうかを確認せずとも、一目で同一番組が放送されることを理解できる。また、HDTV放送であるなど、高精細の画質でもって放送される番組であることも一見して知ることができる。
【0019】
したがって、より容易に放送形態を認識することのできるEPGテーブルが得られる放送受信装置を提供することが可能となる。
【0020】
好ましくは、放送受信装置は、表示対象となっている電子番組表に、同一番組があるか否かを判断する第2の判断手段と、第2の判断手段により同一番組があると判断された場合に、表示可能な幅に合わせて同一番組のデータを加工する加工手段とをさらに備え、表示手段には、第2の判断手段により同一番組があると判断された場合、対応する複数のチャンネルに渡った同一領域に、加工手段によって加工された内容が表示されることを特徴とする。
【0021】
この発明に従うと、表示対象となっている電子番組表に複数のチャンネルに渡った同一領域に表示される同一番組がある場合、表示手段には、対応する複数のチャンネルに渡った同一領域に、加工手段によって加工された内容が表示される。このため、同一領域に表示される同一番組の内容が途切れるなどといった不都合が回避され、ユーザによりその内容が適切に認識される。
【0022】
さらに好ましくは、加工手段は、同一番組のデータを圧縮するように加工することを特徴とする。
【0023】
この発明に従うと、表示領域に、同一番組の一部が表示されるときは、その同一番組のデータが圧縮される。したがって、スクロールさせたとしても、その番組についての情報量が確保されることになる。
【0024】
【発明の実施の形態】
次に、本発明の実施の形態を、図面に基づいて説明する。
【0025】
図1は、本発明の実施の形態における放送受信装置1の全体構成を示すブロック図である。図1を参照して、放送受信装置1は、EPGデータを受信するEPG受信部101と、受信されたEPGデータを一旦保存する受信EPG保存部103と、受信されたEPGデータの解析、EPGテーブル(電子番組表)の作成等を行なうEPG処理部105と、作成されたEPGテーブルを保存する整形後EPG保存部115と、EPGテーブルの表示およびユーザからの入力指示を受け付ける表示/入力部117(表示部117、入力部117と別々に示す場合もある)とを備えている。
【0026】
EPG受信部101は、放送系10、メモリカードやCD−ROM等の外部メモリ11、またはネットワーク12からEPGデータを受信する。受信されたEPGデータは、順次受信EPG保存部103に格納されていく。
【0027】
ここで、EPGデータについて説明する。図2は、EPG受信部101において受信するEPGデータのフォーマット例を示した図である。本図を参照して、EPGデータは、チャンネル数Nを表わすチャンネルヘッダを先頭に、以下、チャンネルごとのデータがチャンネル1からチャンネルNまでチャンネル数分続いている。
【0028】
チャンネルごとのデータは、そのチャンネルで放送される番組数Mとチャンネル名とを含む番組ヘッダと、個々の番組の詳細なデータを含むM個の番組情報とで構成されている。番組情報には、その番組の開始時刻、放送時間、番組名、番組内容が含まれている。
【0029】
図1に戻って、EPG処理部105は、EPGデータ全部の内容を解析する全EPGチェック部107と、EPGテーブルを作成するEPG作成部109と、HTDV番組を検出するHDTV番組検出部113と、EPGデータを圧縮するEPGデータ圧縮部111とを含む。
【0030】
全EPGチェック部107は、EPG保存部103に格納されたEPGデータの内容を解析する。すなわち、EPGテーブルの作成のために、図2に示したフォーマットのEPGデータを解析する。この際、同一の番組が同じ時間帯に複数存在するか否かも確認する。
【0031】
全EPGチェック部107の解析結果を受けたEPG作成部109は、所定の形式に従ってEPGテーブルを作成する。すなわち、同じ時間帯に同一番組が複数存在しない場合は、図8で示したような通常通りのEPGテーブル(以下「通常のEPGテーブル」という)を作成する。一方、同一番組が複数存在する場合は、該当する複数のチャンネルに渡って同一内容の番組1つが表示されるような形式のEPGテーブル(以下「本形式のEPGテーブル」という)を作成する。詳細は後述する。
【0032】
作成されたEPGテーブルは、整形後EPG保存部115に保存される。そして、ユーザからの表示要求があると、保存されているEPGテーブルが読み出されて、表示部117へと送られる。
【0033】
HDTV番組検出部113は、入力部117から送られてくるユーザのスクロール要求を受けて、表示対象となっているEPGテーブルの中からHDTV番組を検出する。EPGデータ圧縮部111は、HDTV番組検出部113によりHDTV番組が検出された場合に、スクロール後に表示される範囲のEPGテーブルのデータを圧縮する。圧縮されたEPGテーブルは、表示部117に送られる。
【0034】
なお、HDTV番組が検出されない場合は、非圧縮のEPGデータを用いたテーブルがスクロール後に表示される。
【0035】
表示部117は、整形後EPG保存部115から送られてくるEPGテーブルまたは、EPGデータ圧縮部111から送られてくる圧縮されたEPGテーブルの一部あるいは全部を表示する。また、入力部117は、ユーザからの表示やスクロール等の指示がある場合、その指示を検知し、HDTV番組検出部113または整形後EPG保存部115に送信する。
【0036】
続いて、放送受信装置1の処理の流れについて説明する。
図3は、放送受信装置1におけるEPGデータの受信からEPGテーブルの保存までの処理の流れを示したフローチャートである。本図を参照して、EPG受信部101によるEPGデータの受信があれば(ステップS301で“あり”)、ステップS303において、受信EPG保存部103にEPGデータが保存される。
【0037】
ステップS305において、全EPGチェック部107により、受信されたEPGデータ全てのチェック(解析)が行なわれる。EPGテーブル作成のためである。そして、ステップS307において、解析の結果、同一番組が同じ時間帯に複数存在するか否かが判断される。
【0038】
複数存在しない場合は、ステップS309において、通常のEPGテーブの作成が行なわれる。すなわち、図8で示したように、各チャンネルごとに、該当する番組の内容が表示されるという形式のテーブルが作成される。
【0039】
一方、ステップS307において、同一番組が複数存在すると判断された場合は、ステップS311において、複数のチャンネルに渡って同一の番組内容を1つ表示するという本形式のEPGテーブルが作成される。
【0040】
図4は、このような形式のEPGテーブルの一部を取り出して示した図である。番組Dは、SDTVのチャンネルである1CH、2CHおよび3CHを用いて放送されるHDTV番組である。図8に示したように各チャンネル毎に同じ内容が繰り返し表示されるのではなく、1CH〜3CHの3チャンネル分の幅を用いて一つの番組Dの内容が表示される。このため、ユーザは一見して1〜3CHでは同じ番組Dが放送されることが分かる。また、同時に、番組Dが高精細画質のHDTV番組として放送されるものであることも分かる。
【0041】
ステップS309において作成された通常のEPGテーブル、あるいはステップS311において作成された本形式のEPGテーブルは、ステップS313において、整形後EPG保存部115に保存される。そして、再びステップS301の処理に戻り、EPGデータの受信待ち状態となる。
【0042】
以上の処理によると、受信されたEPGデータに、同一時間帯に同一番組が複数存在する場合は、HDTV番組であると判断され、該当するSDTVの複数のチャンネルに渡って1つの番組の内容が表示されるようなEPGテーブルが作成される。このため、EPGテーブルを見たユーザは直ぐに、複数のチャンネルにおいて同一の番組が放送されることを知り、また、その番組がHDTV番組であることを知ることができる。
【0043】
図5は、入力部117からのユーザ入力に応じて行なわれる処理の流れを示したフローチャートである。本図を参照して、まず、ステップS501において、入力部117からのユーザの入力待ちが行なわれる。入力があると、ステップS503において、その入力の内容が表示要求なのかスクロールなのか、あるいは、番組選択なのかが判断される。
【0044】
番組選択の場合は、ステップS513に進み、番組選択に応じた処理が実行される。番組選択に応じた処理とは、たとえば、番組選局、番組の録画/視聴予約等である。
【0045】
ユーザ入力が表示要求である場合は、ステップS505の処理へと進み、表示部117に対象となるEPGテーブルの一部または全部が表示される。表示後は、再び、ステップS501に戻りユーザ入力待ち状態となる。
【0046】
一方、ユーザ入力がスクロールの場合は、ステップS507へと進む。ステップS507では、HDTV番組検出部113により、対象となるEPGテーブルにHDTV番組が存在するか否かが判断される。
【0047】
HDTV番組が存在すると判断された場合は、ステップS509において、対象となる部分のデータ圧縮が行なわれる。すなわち、次に表示されるEPGテーブルにおいて表示可能な幅に合わせてHDTV番組の表示内容が圧縮される。
【0048】
そして、ステップS511において、少々データの圧縮された部分を含むEPGテーブルが表示部117に表示される。図6に、スクロールに際してEPGテーブルが圧縮されて表示される例を示す。ここでは、図4で示したようなEPGテーブルが表示部117に表示されている場合に、右方向にスクロール要求が出された場合を考えている。
【0049】
図4では、番組Dの内容が1CHから3CHの3チャンネル分の幅に表示されているため、これを右方向にスクロールすることにより、その表示幅が2チャンネル分に狭まることになる。したがって、図6に示すように、番組Dの内容は、2CHと3CHの幅に収まるようにD’に圧縮されて表示される。このように圧縮表示されることにより、番組内容が切断されるという不都合が生じず、ユーザは、スクロール後も番組Dの内容を理解することができる。
【0050】
なお、ステップS507において、HDTV番組が存在しないと判断された場合は、ステップS509の圧縮処理はスキップされて、ステップS511において、スクロール後にも通常通りのEPGテーブルが表示される。スクロール表示がされた後は、ステップS501の処理に戻り、ユーザ入力待ち状態になる。
【0051】
以上の処理に従うと、スクロール要求があった場合、その対象となるEPGテーブルにHDTV番組があれば、スクロール後に表示可能な幅にHDTV番組の内容が圧縮されて表示されることになる。このため、スクロール後も番組の内容が途切れることなく表示される。
【0052】
なお、図5のステップS509の圧縮処理は、どのような処理方法を用いてもよい。たとえば、単にスクロール後に表示可能な幅に合わせて、番組内容の最後の方の文字列を削除するだけでもよいし、別途番組名の圧縮形が図2で示した番組データと共に提供されるようにし、それを利用するようにしてもよい。
<変形例>
次に、本発明の実施の形態の変形例について説明する。図3等で説明したように、今回示した実施の形態では、ステップS305における全EPGのチェックの際に、同一の時間帯に複数のチャンネルにおいて同一の番組が放送されるか否かのチェックも行なわれた。そして、その後、EPGテーブルが作成された。しかし、このような処理手順に限られず、EPGテーブルを作成してから同一番組のチェックを行なうようにしてもよい。
【0053】
図7は、作成されたEPGテーブルをもとに複数の同一番組の存在を判断する場合の処理の流れを示したフローチャートである。本図を参照して、まず、ステップS301でEPGデータの受信を待ち、ステップS303で受信されたEPGデータを保存するまでは、図3の処理と同様である。
【0054】
ステップS705において、この保存された全EPGがチェックされる。ただし、ここでは、図3のステップS305の処理内容とは異なり、同一番組が複数存在するか否かのチェックは行なわれない。通常のEPGテーブルを作成するために必要なデータ解析のみが行なわれる。
【0055】
したがって、ステップS707においては、通常のEPGテーブルが一旦作成される。そして、ステップS709において、この作成されたEPGテーブルを基にして、同一番組が複数存在するか否かが判断される。
【0056】
同一番組が複数存在すると判断されると(ステップS709で“Yes”)、ステップS711において、EPGテーブルの書き換え処理が行なわれる。すなわち、ステップS707において、一旦作成された通常のEPGテーブルの該当する個所を書きかえることにより、本形式のEPGテーブルが作成される。
【0057】
一方、同一番組が複数存在しないと判断されると(ステップS709で“No”)、ステップS711の処理がスキップされる。すなわち、EPGテーブルの書き換えは行なわれない。
【0058】
そして、ステップS313において、通常のEPGテーブル、あるいは、本形式のEPGテーブルが、一旦保存される。
【0059】
このように、一度通常のEPGテーブルが作成されてから、必要に応じてEPGテーブルの書き換えを行なうようにしてもよい。
【0060】
今回開示された実施の形態はすべての点で例示であって、制限的なものではないと考えるべきである。本発明の範囲は、上記した説明ではなく特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味及び範囲内ですべての変更が含まれることが意図される。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明の実施の形態における放送受信装置1の全体構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】 EPG受信部101において受信するEPGデータのフォーマット例を示した図である。
【図3】 放送受信装置1におけるEPGデータの受信からEPGテーブルの保存までの処理の流れを示したフローチャートである。
【図4】 本形式のEPGテーブルの一部を取り出して示した図である。
【図5】 入力部117からのユーザ入力に応じて行なわれる処理の流れを示したフローチャートである。
【図6】 スクロールに際してEPGテーブルが圧縮されて表示される例を示した図である。
【図7】 作成されたEPGテーブルをもとに複数の同一番組の存在を判断する場合の処理の流れを示したフローチャートである。
【図8】 従来の状況におけるEPGの表示例を示した図である。
【図9】 従来の表示方法にしたがってEPGが表示される例を示した図である。
【符号の説明】
1 放送受信装置、101 EPG受信部、103 受信EPG保存部、105 EPG処理部、107 全EPGチェック部、109 EPG作成部、111 EPGデータ圧縮部、113 HDTV番組検出部、115 整形後EPG保存部、117 表示/入力部。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a broadcast receiving apparatus, and more particularly to a broadcast receiving apparatus improved so that an electronic program guide created based on an electronic program guide in BS (Broadcasting Satellite) digital broadcasting or the like is easier to see.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, in CS (communications satellite) broadcasting, an electronic program guide (hereinafter referred to as “EPG”) service has been provided. With this EPG service, for example, the broadcast station name, the start time of the broadcast program, the program title, and other information on each required channel (broadcast station) are provided to the user. The user can use this to check what program is currently being broadcast without looking at the television column of the newspaper. Then, a desired program can be selected to select a channel and make a recording / viewing reservation.
[0003]
In the current terrestrial wave, BS analog broadcast, and CS broadcast, a plurality of channels broadcast different programs at the same time. In other words, a single program is not broadcast over a plurality of channels at the same time. Therefore, since each channel is independent, the provided EPG is displayed as follows.
[0004]
FIG. 8 is a diagram showing an EPG display example in such a conventional situation. Here, it is assumed that an EPG is displayed on a receiving apparatus such as a television. Channels are taken on the horizontal axis, and time is taken on the vertical axis.
[0005]
In different channels 1CH, 2CH, and 3CH, different programs A, B, C, or D, E, and F are broadcast at the same time. Therefore, as a configuration of the EPG, as shown in the figure, each channel is displayed as being independent.
[0006]
This is the same even if one broadcasting station has a plurality of channels. That is, even if the channel is the same broadcast station, each channel is independent and different programs are displayed as shown in FIG.
[0007]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
The above EPG service is expected to become more popular in the future due to the realization of BS digital broadcasting and terrestrial digital broadcasting. Under such circumstances, the following problems occur in the conventional EPG display method.
[0008]
For example, in BS digital broadcasting, there are two broadcasting systems, HDTV (High Definition TV) and SDTV (Standard Definition TV). SDTV is a system that is currently broadcast, and HDTV is a system that broadcasts with higher definition image quality. Since there are two broadcasting systems in this manner, in BS digital broadcasting, it is possible to broadcast one HDTV program using a plurality of SDTV channels owned by one broadcasting station.
[0009]
For example, it is assumed that a certain broadcasting station has a bandwidth capable of simultaneously broadcasting three SDTV programs. Then, from today 7:00 pm, three programs, Program A, Program B, and Program C, will be broadcast simultaneously on three SDTV channels, and from 8:00 pm, one program will be used using three SDTV channels. A situation may occur in which an HDTV program D is broadcast.
[0010]
In such a case, when the EPG is displayed according to the conventional display method, the result is as shown in FIG. Referring to FIG. 9, the horizontal axis represents the channel and the vertical axis represents the time. Information on different programs A, B, and C is displayed on each SDTV channel in a certain time zone, and information on the same program D is displayed on each SDTV channel in a certain time zone. In other words, even if the same HDTV program D is broadcast over
[0011]
When such a display is made, there are the following two problems when the user sees the display and understands the broadcasting form.
[0012]
First of all, it is difficult to determine at a glance whether or not the program D broadcast on the
[0013]
Second, it is difficult to judge at a glance that a high-definition image quality called HDTV is being broadcast. As described above, the user compares each other and knows that the same program D is broadcast on
[0014]
When BS digital broadcasting is started in the future, one broadcasting station broadcasts HDTV programs across multiple channels, or broadcasts multiple normal SDTV programs, and these SDTV and HDTV It is thought that the broadcasting situation that mixes with time occurs. Under such circumstances, the conventional EPG display method further increases the chances of the above-mentioned problems, and is not satisfactory for the user.
[0015]
The present invention has been conceived in view of such a situation, and an object of the present invention is to provide a broadcast receiving apparatus from which an EPG table capable of easily recognizing a broadcast form can be obtained.
[0016]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, according to one aspect of the present invention, a broadcast receiving device receives a receiving means for receiving electronic program guide data, and receives electronic program guide data from the electronic program guide data. The first determination means for determining whether or not there is the same program broadcast using a plurality of channels at the same time, and when the first determination means determines that there is the same program, the contents of the same program are , to appear in the same area over a corresponding plurality of channels, and generating means for generating, based on the electronic program guide data, an electronic program guide to display the contents of a program corresponding to each channel, creating a storage means for storing an electronic program guide created by means, when accepting the display request of an electronic program guide from a user, display means for displaying an electronic program guide stored in the storage means Ru equipped with.
[0017]
According to the present invention, when there is the same program that is broadcast using a plurality of channels at the same time, the contents of the same program are displayed in the same area across the corresponding channels. (EPG table) is created.
[0018]
For this reason, the user can understand that the same program is broadcast at a glance without checking the display contents for each of a plurality of channels and checking whether or not they match each other. It can also be seen at a glance that the program is broadcast with high definition image quality such as HDTV broadcasting.
[0019]
Therefore, it is possible to provide a broadcast receiving apparatus that can obtain an EPG table that can more easily recognize a broadcast form.
[0020]
Preferably, the broadcast receiving apparatus determines that the same program is present by the second determining means for determining whether or not the same program exists in the electronic program guide to be displayed, and the second determining means. A processing means for processing data of the same program in accordance with the displayable width, and when the second judging means determines that there is the same program, the display means has a plurality of corresponding channels. The content processed by the processing means is displayed in the same area extending over.
[0021]
According to the present invention, if there is the same program that is displayed in the same area over a plurality of channels in an electronic program guide that is a display target, the display unit, in the same area over a corresponding plurality of channels, The content processed by the processing means is displayed. For this reason, the inconvenience that the content of the same program displayed in the same area is interrupted is avoided, and the content is appropriately recognized by the user.
[0022]
More preferably, the processing means processes the data of the same program so as to be compressed.
[0023]
According to the present invention, the table display region, when a part of the same program is displayed, the data of the same program is compressed. Therefore, even if is scrolled, so that the amount of information about the program is secured.
[0024]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Next, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0025]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an overall configuration of a
[0026]
The
[0027]
Here, the EPG data will be described. FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a format example of EPG data received by the
[0028]
The data for each channel includes a program header including the number M of programs broadcast on the channel and a channel name, and M program information including detailed data of each program. The program information includes the start time, broadcast time, program name, and program content of the program.
[0029]
Returning to FIG. 1, the
[0030]
The all
[0031]
Receiving the analysis result of all
[0032]
The created EPG table is stored in the post-shaping
[0033]
The HDTV
[0034]
If an HDTV program is not detected, a table using uncompressed EPG data is displayed after scrolling.
[0035]
The
[0036]
Next, the process flow of the
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing the flow of processing from reception of EPG data to storage of the EPG table in the
[0037]
In step S305, all
[0038]
If there are not more than one, a normal EPG table is created in step S309. That is, as shown in FIG. 8, a table is created in which the contents of the corresponding program are displayed for each channel.
[0039]
On the other hand, if it is determined in step S307 that there are a plurality of the same programs, an EPG table of this format is created in step S311 to display one identical program content across a plurality of channels.
[0040]
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a part of the EPG table in such a format. Program D is an HDTV program that is broadcast using SDCH channels 1CH, 2CH, and 3CH. As shown in FIG. 8, the same content is not repeatedly displayed for each channel, but the content of one program D is displayed using the width of three channels from 1CH to 3CH. For this reason, the user can see at a glance that the same program D is broadcast on 1 to 3 channels. At the same time, it can also be seen that the program D is broadcast as a high-definition image quality HDTV program.
[0041]
The normal EPG table created in step S309 or the EPG table of this format created in step S311 is stored in the post-formatting
[0042]
According to the above processing, when there are a plurality of the same programs in the same time zone in the received EPG data, it is determined that the program is an HDTV program, and the contents of one program over a plurality of channels of the corresponding SDTV are determined. An EPG table as displayed is created. Therefore, the user who sees the EPG table can immediately know that the same program is broadcast on a plurality of channels, and can know that the program is an HDTV program.
[0043]
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing a flow of processing performed in response to a user input from the
[0044]
In the case of program selection, the process proceeds to step S513, and processing according to program selection is executed. The process according to program selection includes, for example, program selection, program recording / viewing reservation, and the like.
[0045]
If the user input is a display request, the process proceeds to step S505, and a part or all of the target EPG table is displayed on the
[0046]
On the other hand, if the user input is scrolling, the process proceeds to step S507. In step S507, the HDTV
[0047]
If it is determined that there is an HDTV program, data compression is performed on the target portion in step S509. That is, the display content of the HDTV program is compressed in accordance with the displayable width in the EPG table displayed next.
[0048]
In step S511, an EPG table including a slightly compressed portion of data is displayed on the
[0049]
In FIG. 4, since the contents of the program D are displayed in the width of 3 channels from 1CH to 3CH, by scrolling this to the right, the display width is narrowed to 2 channels. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 6, the content of the program D is displayed by being compressed to D ′ so as to be within the width of 2CH and 3CH. By compressing and displaying in this way, there is no inconvenience that the program content is disconnected, and the user can understand the content of the program D even after scrolling.
[0050]
If it is determined in step S507 that there is no HDTV program, the compression process in step S509 is skipped, and a normal EPG table is displayed after scrolling in step S511. After the scroll display, the process returns to step S501 and waits for user input.
[0051]
According to the above processing, when there is a scroll request, if there is an HDTV program in the target EPG table, the content of the HDTV program is compressed and displayed in a width that can be displayed after scrolling. For this reason, the content of the program is displayed without interruption even after scrolling.
[0052]
In addition, what kind of processing method may be used for the compression process of step S509 of FIG. For example, the character string at the end of the program content may be simply deleted according to the width that can be displayed after scrolling, or a compressed form of the program name may be provided together with the program data shown in FIG. You may make it utilize it.
<Modification>
Next, a modification of the embodiment of the present invention will be described. As described with reference to FIG. 3 and the like, in the embodiment shown this time, when checking all EPGs in step S305, it is also checked whether or not the same program is broadcast on a plurality of channels in the same time zone. It was done. After that, an EPG table was created. However, the processing procedure is not limited to this, and the same program may be checked after the EPG table is created.
[0053]
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the flow of processing when determining the presence of a plurality of identical programs based on the created EPG table. Referring to this figure, first, the process waits for reception of EPG data in step S301 and until the EPG data received in step S303 is stored, is the same as the process of FIG.
[0054]
In step S705, all the stored EPGs are checked. However, here, unlike the processing contents of step S305 in FIG. 3, it is not checked whether there are a plurality of the same programs. Only data analysis necessary to create a normal EPG table is performed.
[0055]
Therefore, in step S707, a normal EPG table is once created. In step S709, it is determined whether or not a plurality of identical programs exist based on the created EPG table.
[0056]
If it is determined that there are a plurality of the same programs (“Yes” in step S709), the EPG table is rewritten in step S711. That is, in step S707, the EPG table of this format is created by rewriting the corresponding part of the normal EPG table once created.
[0057]
On the other hand, if it is determined that there are not a plurality of the same programs (“No” in step S709), the process of step S711 is skipped. That is, the EPG table is not rewritten.
[0058]
In step S313, a normal EPG table or an EPG table of this format is temporarily stored.
[0059]
As described above, once the normal EPG table is created, the EPG table may be rewritten as necessary.
[0060]
The embodiment disclosed this time should be considered as illustrative in all points and not restrictive. The scope of the present invention is defined by the terms of the claims, rather than the description above, and is intended to include any modifications within the scope and meaning equivalent to the terms of the claims.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing an overall configuration of a
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a format example of EPG data received by an
FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a flow of processing from reception of EPG data to storage of an EPG table in the
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing a part of an EPG table in this format.
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing a flow of processing performed in response to a user input from an
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing an example in which an EPG table is compressed and displayed when scrolling.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the flow of processing when determining the presence of a plurality of identical programs based on the created EPG table.
FIG. 8 is a diagram showing a display example of an EPG in a conventional situation.
FIG. 9 is a diagram showing an example in which an EPG is displayed according to a conventional display method.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
前記電子番組ガイドのデータが受信された場合に、前記電子番組ガイドのデータから同じ時刻に複数のチャンネルを用いて放送される同一番組があるか否かを判断する第1の判断手段と、
前記第1の判断手段により前記同一番組があると判断された場合、前記同一番組の内容が、対応する複数のチャンネルに渡った同一領域に表示されるように、前記電子番組ガイドのデータに基づいて、各チャンネルに対応する番組の内容を表示する電子番組表を作成する作成手段と、
前記作成手段により作成された前記電子番組表を保存するための保存手段と、
ユーザから前記電子番組表の表示要求を受付けた場合に、前記保存手段に保存された前記電子番組表を表示する表示手段と、
表示対象となっている前記電子番組表に、前記同一番組があるか否かを判断する第2の判断手段と、
前記第2の判断手段により前記同一番組があると判断された場合に、表示可能な幅に合わせて前記同一番組の内容を統合し、前記同一番組に対応する統合された前記同一領域の前記表示対象の領域内へと収まるように、最後の方の文字列を削除することによって前記同一番組の内容を圧縮する加工手段とを備え、
前記表示手段は、前記第2の判断手段により前記同一番組があると判断された場合に、前記対応する複数のチャンネルに渡った前記同一番組に対応する統合された前記同一領域の前記表示対象の領域内に、前記加工手段によって統合されて圧縮された前記同一番組の内容を表示する、請求項1に記載の放送受信装置。Receiving means for receiving electronic program guide data;
First determination means for determining whether or not there is an identical program broadcast using a plurality of channels at the same time from the electronic program guide data when the electronic program guide data is received;
Based on the data of the electronic program guide so that the content of the same program is displayed in the same area across a plurality of corresponding channels when the first determining means determines that the same program exists. Creating means for creating an electronic program guide for displaying the contents of the program corresponding to each channel;
Storage means for storing the electronic program guide created by the creation means;
Display means for displaying the electronic program guide stored in the storage means when a display request for the electronic program guide is received from a user ;
Second determination means for determining whether or not the same program is present in the electronic program guide to be displayed;
When the second determining means determines that there is the same program, the contents of the same program are integrated in accordance with the displayable width, and the integrated display of the same area corresponding to the same program is performed. Processing means for compressing the content of the same program by deleting the last character string so as to fit in the target area ,
The display means, when it is determined that the there is the same program by the second determination means, of the displayed integrated the same regions corresponding to the same program, across a plurality of channels the corresponding in the area, to display the contents of the same program, which is compressed are integrated by the processing means, the broadcast receiving apparatus according to claim 1.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000183978A JP4860028B2 (en) | 2000-06-20 | 2000-06-20 | Broadcast receiver |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000183978A JP4860028B2 (en) | 2000-06-20 | 2000-06-20 | Broadcast receiver |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009163017A Division JP2009225486A (en) | 2009-07-09 | 2009-07-09 | Broadcast receiver |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002010162A JP2002010162A (en) | 2002-01-11 |
| JP2002010162A5 JP2002010162A5 (en) | 2009-08-27 |
| JP4860028B2 true JP4860028B2 (en) | 2012-01-25 |
Family
ID=18684477
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000183978A Expired - Fee Related JP4860028B2 (en) | 2000-06-20 | 2000-06-20 | Broadcast receiver |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4860028B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006080656A (en) * | 2004-09-07 | 2006-03-23 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Receiver |
| JP6309393B2 (en) * | 2014-08-22 | 2018-04-11 | シャープ株式会社 | Program guide generator |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3447207B2 (en) * | 1997-12-05 | 2003-09-16 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Program information creation transmission apparatus and method |
| JP2000152114A (en) * | 1998-11-11 | 2000-05-30 | Toshiba Corp | Display device for contents of mixed broadcast and its display method |
-
2000
- 2000-06-20 JP JP2000183978A patent/JP4860028B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002010162A (en) | 2002-01-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11812094B2 (en) | Systems and methods for determining subscription data | |
| US6732371B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for guiding broadcasting information of TV | |
| US7571455B2 (en) | TV having language selection function and control method of the same | |
| EP0889645B1 (en) | Broadcasting reception apparatus and data broadcasting | |
| KR100246792B1 (en) | Pnognoum pnocessing time guide method amd apparatus | |
| US6924848B2 (en) | Digital/analog television signal receiving set | |
| JP4525760B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus and information providing method | |
| US20100281498A1 (en) | Information providing device, information display device, information providing system, control method, control program and storage medium | |
| JPH08251122A (en) | Information selection device/method | |
| JP4802425B2 (en) | Video display device | |
| US20050076389A1 (en) | Apparatus for displaying program information for a video display appliance and method thereof | |
| KR100565035B1 (en) | Program guide method and program guide apparatus for the same | |
| JP4860028B2 (en) | Broadcast receiver | |
| US20090265732A1 (en) | Contents providing system, and contents providing method | |
| US20080295026A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for displaying application program and menu | |
| JP3439326B2 (en) | Broadcast receiver | |
| JP2009225486A (en) | Broadcast receiver | |
| KR20100053300A (en) | Broadcast receiving device for providing broadcast supplement information and method thereof | |
| JP3694582B2 (en) | Receiver | |
| KR20080079045A (en) | Broadcast signal processing apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP3611513B2 (en) | Digital broadcasting system | |
| JPH11220704A (en) | Transmitter and receiver for data broadcast system | |
| EP0854649A2 (en) | Television broadcasting system and receiver | |
| JP4701649B2 (en) | Television broadcast receiver | |
| EP1998479A2 (en) | User interface for the image processing apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070327 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090709 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090818 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20091002 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20100119 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100311 |
|
| A911 | Transfer of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20100427 |
|
| A912 | Removal of reconsideration by examiner before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20100611 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20111102 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20141111 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |