JP4835883B2 - Cylindrical container and manufacturing method thereof - Google Patents
Cylindrical container and manufacturing method thereof Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4835883B2 JP4835883B2 JP2009149497A JP2009149497A JP4835883B2 JP 4835883 B2 JP4835883 B2 JP 4835883B2 JP 2009149497 A JP2009149497 A JP 2009149497A JP 2009149497 A JP2009149497 A JP 2009149497A JP 4835883 B2 JP4835883 B2 JP 4835883B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- side wall
- sealing portion
- cylindrical container
- main body
- molding
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 24
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 142
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 claims description 71
- 238000010409 ironing Methods 0.000 claims description 63
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 55
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 26
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000013372 meat Nutrition 0.000 claims 1
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000543 intermediate Substances 0.000 description 23
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000010953 base metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000000078 claw Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012805 post-processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013585 weight reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D22/00—Shaping without cutting, by stamping, spinning, or deep-drawing
- B21D22/20—Deep-drawing
- B21D22/28—Deep-drawing of cylindrical articles using consecutive dies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/10—Primary casings; Jackets or wrappings
- H01M50/147—Lids or covers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B21—MECHANICAL METAL-WORKING WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D—WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL
- B21D51/00—Making hollow objects
- B21D51/16—Making hollow objects characterised by the use of the objects
- B21D51/26—Making hollow objects characterised by the use of the objects cans or tins; Closing same in a permanent manner
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M50/00—Constructional details or processes of manufacture of the non-active parts of electrochemical cells other than fuel cells, e.g. hybrid cells
- H01M50/10—Primary casings; Jackets or wrappings
- H01M50/102—Primary casings; Jackets or wrappings characterised by their shape or physical structure
- H01M50/107—Primary casings; Jackets or wrappings characterised by their shape or physical structure having curved cross-section, e.g. round or elliptic
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/052—Li-accumulators
- H01M10/0525—Rocking-chair batteries, i.e. batteries with lithium insertion or intercalation in both electrodes; Lithium-ion batteries
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Sealing Battery Cases Or Jackets (AREA)
- Shaping Metal By Deep-Drawing, Or The Like (AREA)
- Containers Having Bodies Formed In One Piece (AREA)
Description
本発明は、筒型容器とその製造方法、特に電池缶に好適な筒型容器とその製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a cylindrical container and a manufacturing method thereof, and more particularly to a cylindrical container suitable for a battery can and a manufacturing method thereof.
従来、電池の外層缶は、鉄を基材とする基板を絞り成形して得たカップをさらにダイスとパンチにより絞りしごき成形加工して側壁部が薄肉の缶体を得ているが、近年リチウムイオン電池等の高エネルギー密度・高密封性電池用の小型・軽量の電池缶が求められている。そのため、側壁部はより一層の薄肉化が求められているが、側壁部を薄肉にした場合、開口端部近傍の側壁(以下、封口部という)の強度が弱くなり、十分な密封強度が得られなくなるという問題点がある。その問題点を解決するために、絞りしごき加工に際してパンチの封口部成形面の外径を側壁本体部成形面の外径よりも小径にすることによって、胴部側壁の封口部を側壁本体部(本明細書では以下胴部側壁の前記封口部を除いた部分を側壁本体部と称する)よりも内側に向かって厚肉して、封口部の強度を確保した電池缶が提案されている(例えば特許文献1、2参照)。 Conventionally, the outer layer can of a battery has been obtained by drawing and squeezing and molding a cup obtained by drawing an iron-based substrate with a die and a punch. There is a need for a small and lightweight battery can for high energy density and high sealing batteries such as ion batteries. For this reason, the side wall is required to be thinner. However, when the side wall is made thinner, the strength of the side wall in the vicinity of the opening end (hereinafter referred to as the sealing portion) becomes weak, and sufficient sealing strength is obtained. There is a problem that it becomes impossible. In order to solve the problem, by making the outer diameter of the sealing part molding surface of the punch smaller than the outer diameter of the side wall main part molding surface during drawing ironing, the sealing part of the trunk side wall is made the side wall main part ( In the present specification, a battery can that is thicker inward than the portion of the body side wall excluding the sealing portion is referred to as a side wall main body portion to ensure the strength of the sealing portion is proposed (for example, (See Patent Documents 1 and 2).
しかしながら、上記提案されている電池缶は、胴部側壁の内径は、封口部は小さく側壁本体部で大きくなっているため、電池缶内に極板等を収納する際に封口部に接触して損傷をしやすいという問題と共に、缶内に収容する収容物の大きさは封口部の直径に拘束されるので、その分容積率を低下させる問題がある。そこで、その問題を解決するために、封口部の厚肉部を外側に向かって凸の板厚とし、内側は封口部から底壁に達するまで同径にして軸方向にストレートにした電池缶が提案されている(特許文献3参照)。 However, in the proposed battery can, the inner diameter of the side wall of the body portion is small in the sealing portion and large in the side wall main body portion, so that when the electrode plate or the like is stored in the battery can, it contacts the sealing portion. In addition to the problem of being easily damaged, the size of the contents to be accommodated in the can is restricted by the diameter of the sealing portion, and thus there is a problem of reducing the volume ratio. Therefore, in order to solve the problem, a battery can that has a thick wall portion of the sealing portion that is convex toward the outside and has the same inside diameter until reaching the bottom wall from the sealing portion and is straight in the axial direction. It has been proposed (see Patent Document 3).
前記特許文献3に提案されている電池缶の製造方法は、前記引用文献1、2に示すような方法で側壁の封口部が内側に向かって厚肉となっている缶体を得、該缶体をさらに、薄肉部となっている側壁本体部の内径と同径の凸部を有する拡管パンチによって封口部を拡管加工することによって、封口部の内側に向かって凸になっている厚肉部を外側に向かって凸の厚肉状態に変化させて、封口部から底壁にかけて内径が同寸法となるように加工する工程を経て製造している。そのため、その製造工程は、缶の絞りしごき工程のほかに、さらに拡管パンチによる拡管工程を必要とし、その分製造効率が低下すると共に付加設備を必要として設備コストが増大する等の問題点がある。さらに、拡管工程では外周部に凸部を有する拡管パンチを絞りしごき成形された缶体に挿入して軸荷重を付加することにより、缶体の内側に凸となっている部分を外側に向けて凸となるように成形するため、側壁本体部に強い軸荷重が作用し、薄肉となっている側壁本体部がそれに耐え得る強度を有しないと座屈を起こしてしまう恐れがある。そのため、側壁本体部の板厚を一定以上確保する必要があり、側壁本体部の板厚低減におのずから多大な制限を受けるという問題点もある。そのため、側壁本体部をより薄肉化して軽量化を図ると共に、低コストで且つ製造ラインの高速化を図るという要求に対して未だ満足するに至っていない。
The method for manufacturing a battery can proposed in
そこで、本発明は、上記問題点を解決しようとするものであり、絞りしごき加工により形成される缶体において、封口部の十分な封口強度を確保しながら、側壁本体部のより一層の薄肉化を可能にし、且つ封口部内周面が側壁本体部内周面と略同径の内周面を確保して内容物の収納を容易にすると共に容積率を高めることができ、しかも製造も容易で特別な工程や設備を必要とすることなく電池缶等に好適な缶を製造することができる筒型容器及びその製造方法を提供することを目的とするものである。 Therefore, the present invention is to solve the above problems, and in a can body formed by drawing and ironing, while ensuring sufficient sealing strength of the sealing portion, further reducing the thickness of the side wall main body portion. In addition, the inner peripheral surface of the sealing portion can secure an inner peripheral surface that is substantially the same diameter as the inner peripheral surface of the side wall body portion, making it easy to store contents and increasing the volume ratio. An object of the present invention is to provide a cylindrical container capable of producing a can suitable for a battery can and the like, and a method for producing the same without the need for any process or equipment.
本発明者は、側壁本体部の板厚をより薄肉化し且つ封口部の強度を高めるための手段として、絞りしごき加工により封口部を内側に向かって突出させて側壁本体部より板厚に成形したものを、封口強度を維持しつつ内容物の易収納性と収納効率の向上のために逆に外側に向かって突出させる加工方法として、従来の後工程での拡管パンチによる軸荷重付加による成形に代えて、軸荷重を付加しないで達成できれば側壁本体部が当該加工のために座屈を起こす恐れがなくなり、より薄肉化が可能となり、電池缶に対する近年特に要求が高まってきている小型化(薄肉軽量化)と封口強度の向上を共に満たすことができると着想して、鋭意研究と実験を繰り返した結果、次の事実が判明した。 As a means for further reducing the thickness of the side wall body part and increasing the strength of the sealing part, the inventor made the sealing part project inward by drawing and squeezing to form a thickness from the side wall body part. As a processing method for projecting outwards in order to improve the ease of storage and storage efficiency of the contents while maintaining the sealing strength, molding is performed by adding axial load with a tube expansion punch in the conventional post-process. Instead, if it can be achieved without adding an axial load, the side wall main body will not be buckled due to the processing, making it possible to make it thinner, and the miniaturization (thin wall thickness) that has become particularly demanding for battery cans in recent years. As a result of intensive research and experiments, the following facts were found out, with the idea that both the weight reduction and the improvement in sealing strength could be satisfied.
従来のパンチとダイスによる絞りしごき加工による封口部を内側に向かって凸の厚肉部を形成する場合、絞りしごき加工後のストリッピングにおいてパンチの径大部である側壁本体部成形面が成形後の胴壁の径小部である封口部から抜けることを可能にするために、封口部の弾性変形可能な範囲内で厚肉部を形成している。つまり、ストリッピング時には封口部に対しては拡管加工となるが、拡管率が大き過ぎるとひび割れ等の破胴が生じるため、弾性変形範囲で行なっている。しかしながら、本発明者の実験によれば側壁本体部の板厚と封口部の板厚の差がある一定条件の範囲内であれば、弾性域を超えての拡管加工が可能となり、その結果ストリッピング時に封口部が外側に塑性変形し、ストリッピング後も戻らずに外側に向かって板厚部となることが判明した。従って、その方法を利用することにより、特別な拡管パンチにより拡管成形工程を設けることなく、缶胴の絞りしごき加工後のストリッピングのみによって、外側に向かって凸の厚肉となっている封口部の成形が可能となることを見出し本発明に到達したものである。 When forming a thick part that protrudes inward from the sealing part by drawing ironing with a conventional punch and die, the side wall body part molding surface, which is the large diameter part of the punch, is formed after stripping after drawing ironing. In order to be able to come out from the sealing portion which is a small diameter portion of the body wall, the thick portion is formed within the elastically deformable range of the sealing portion. That is, at the time of stripping, tube expansion is applied to the sealing portion. However, if the tube expansion rate is too large, fractures such as cracks occur. However, according to the experiments by the present inventors, if the difference between the thickness of the side wall body portion and the thickness of the sealing portion is within a certain range, tube expansion processing exceeding the elastic range is possible. It was found that the sealing part plastically deformed outward during ripping, and became a thick part toward the outside without returning after stripping. Therefore, by using this method, a sealing portion that is convex toward the outside only by stripping after drawing and squeezing processing of the can body without providing a tube expansion molding process with a special tube expansion punch. The inventors have found that it is possible to mold the present invention and have reached the present invention.
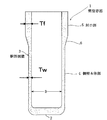
即ち、本発明の筒型容器は、絞りしごき加工法で成形された基材が金属の筒型容器であって、缶胴側壁が側壁本体部と封口部からなり、前記缶胴側壁の内周面は略均一半径で軸方向に略ストレートで、外周面は前記封口部が側壁本体部から外方に向かって段差面を介して厚肉になっている筒型容器において、前記側壁本体部の内径をD、前記封口部の拡管加工時の弾性限界伸び率をα、成形限界伸び率をβとすると、封口部の板厚Tfと側壁本体部の板厚Twとの差が、次式
α・D/{2(α+1)}≦ (Tf−Tw) ≦β・D/{2(β+1)}・・・(1)
を満たすような関係にあることを特徴とするものである。
That is, the cylindrical container of the present invention is a cylindrical container whose base material formed by the drawing ironing method, the can body side wall is composed of a side wall body part and a sealing part, and the inner periphery of the can body side wall In the cylindrical container in which the surface has a substantially uniform radius and is substantially straight in the axial direction, and the outer peripheral surface is thick from the side wall main body to the outside through the step surface, the side wall main body Assuming that the inner diameter is D, the elastic limit elongation during expansion of the sealing portion is α, and the molding limit elongation is β, the difference between the thickness Tf of the sealing portion and the thickness Tw of the side wall main body is expressed by the following equation: α D / {2 (α + 1)} ≦ (Tf−Tw) ≦ β · D / {2 (β + 1)} (1)
It is characterized by having a relationship that satisfies
封口部の板厚Tfと側壁本体部の板厚Twとの差が上記関係式を満たす場合にはじめて、後加工によらないで、絞りしごき加工後のストリッピング時のパンチによる拡管作用のみで封口部が割れを発生させることなく塑性変形し、最大Tf−Tw量だけ外側に凸状態に拡管状態を維持して、軽量化、容積率の向上、内径均一の筒型容器が得られる。本発明の筒型容器の基材は、鉄に限らず、アルミニウム、銅、又はそれらの合金、あるいはめっき等皮膜処理したもの等必要に応じて任意の金属材料が採用できる。例えば、電池缶としては、基材としてNiメッキ鋼板が好適に採用できる。また、本発明の筒型容器は、電池缶に限らず、飲料缶やその他の用途の容器にも適用可能である。 Only when the difference between the thickness Tf of the sealing portion and the thickness Tw of the side wall main body satisfies the above relational expression, the sealing is not performed by post-processing but only by the pipe expanding action by the punch at the time of stripping after drawing and ironing. The portion is plastically deformed without causing cracks, and the expanded state is maintained in a convex state outward by the maximum amount of Tf-Tw, thereby obtaining a cylindrical container having a light weight, an improved volume ratio, and a uniform inner diameter. The base material of the cylindrical container of the present invention is not limited to iron, and any metal material such as aluminum, copper, or an alloy thereof, or a film-treated one such as plating can be adopted as necessary. For example, as a battery can, a Ni-plated steel plate can be suitably employed as a base material. Moreover, the cylindrical container of this invention is applicable not only to a battery can but to a drink can and a container for other uses.
本発明の前記筒型容器は、基本的な形態として、側壁本体部の直径が13〜40mmで、たとえば直径が40mmの場合には、封口部の板厚Tfと側壁本体部の板厚Twとの差が、0.1mm≦Tf−Tw≦0.5mmであり、内径がほぼストレートで、前記封口部は外側に向かって板厚が厚くなっている電池缶として構成できる。 In the cylindrical container of the present invention, as a basic form, when the diameter of the side wall main body is 13 to 40 mm, for example, when the diameter is 40 mm, the plate thickness Tf of the sealing portion and the plate thickness Tw of the side wall main body The difference is 0.1 mm ≦ Tf−Tw ≦ 0.5 mm, the inner diameter is substantially straight, and the sealing portion can be configured as a battery can that increases in thickness toward the outside.
本発明の筒状容器は、(Tf−Tw)/Tf≦0.5の場合、前記封口部は外側に向かって1段段差であり、(Tf−Tw)/Tf>0.5の場合、前記封口部は外側に向かって2段段差であることが望ましい。(Tf−Tw)/Tf≦0.5の場合、1段段差でも良好に成形できるが、(Tf−Tw)/Tf>0.5の場合、1段段差であるとしごき率が限界しごき率を超えて破胴する恐れがあるので、2段段差にすることによって、最大しごき率を低減でき、より成形が容易で且つ側壁本体部のより薄肉化を図ることができる筒状容器を実現できる。 In the cylindrical container of the present invention, when (Tf−Tw) /Tf≦0.5, the sealing portion is a one-step step toward the outside, and when (Tf−Tw) / Tf> 0.5, The sealing portion is preferably a two-step step toward the outside. In the case of (Tf−Tw) /Tf≦0.5, it can be molded well even with a single step, but in the case of (Tf−Tw) / Tf> 0.5, the ironing rate is limited and the ironing rate is limited. Since there is a risk that the cylinder will be broken beyond the maximum, the maximum squeezing rate can be reduced by forming a two-step step, a cylindrical container that can be molded more easily and the side wall body can be made thinner can be realized. .
上記筒状容器を製造する本発明に係る筒状容器の製造方法は、基材が金属の絞り成形されたカップを絞りしごき加工により成形する筒型容器の成形方法であって、前記カップを絞りしごき加工するパンチの加工外周面が、側壁本体部成形面と封口部成形面とからなり、前記側壁本体部成形面の外径が前記封口部成形面の外径よりも径大で、且つ前記側壁本体部成形面と前記封口部成形面との連接部がテーパー状段差面に形成されており、該パンチとダイスにより前記カップを絞りしごき成形して、側壁本体部と該側壁本体部の上方内周面からテーパー段差面を介して内側に凸の厚肉になっている封口部を有する筒型容器中間体を形成し、ストリッピング時に該筒型容器中間体の前記封口部に前記パンチにより拡管率が弾性限界伸び率以上で且つ成形限界伸び率範囲内の拡管作用を与えることにより、前記封口部を外方に向かって塑性変形させ内周面が略ストレートで外周面は外側に向かって凸の板厚になっている封口部を有する筒型容器を得ることを特徴とするものである。 The method for manufacturing a cylindrical container according to the present invention for manufacturing the cylindrical container is a method for forming a cylindrical container in which a base metal is formed by drawing and squeezing a cup, and the cup is squeezed. The processing outer peripheral surface of the punch for ironing includes a side wall main body molding surface and a sealing portion molding surface, and the outer diameter of the side wall main body molding surface is larger than the outer diameter of the sealing portion molding surface, and A connecting portion between the side wall main body molding surface and the sealing portion molding surface is formed in a tapered step surface, and the cup is squeezed and ironed with the punch and the die, and the side wall main body and the side wall main body above Forming a cylindrical container intermediate body having a sealing portion that protrudes inwardly from the inner peripheral surface through a tapered step surface, and at the time of stripping, the sealing portion of the cylindrical container intermediate body is formed by the punch. The expansion rate is greater than the elastic limit elongation and By providing a pipe expansion action within the molding limit elongation range, the sealing portion is plastically deformed outward, the inner peripheral surface is substantially straight, and the outer peripheral surface has a convex plate thickness outward. It is characterized by obtaining the cylindrical container which has.
本発明の前記筒型容器の製造方法は、前記パンチの側壁本体部成形面の外径Daと封口部成形面の外径Dbとすると、封口部成形面の外径Dbは側壁本体部成形面の外径Daに対して次の関係にあることによって、より確実に達成できる。
{Da/(1+β)}≦Db≦{Da/(1+α)}
但し、αは前記筒型容器中間体の封口部の拡管加工時の弾性限界伸び率であり、βは成形限界伸び率であり、Daは成形する筒型容器の内径Dと等しい。
そして、本発明の製造方法は、前記筒型容器の前記側壁本体部の板厚をTw、前記封口部の板厚をTfとすると、(Tf−Tw)/Tf≦0.5の場合は前記パンチの封口部成形面は前記側壁本体部形成面より1段の段差で径小に形成し、(Tf−Tw)/Tf>0.5の場合は2段の段差で径小に形成し、前記カップ側壁のしごき工程においてしごき率が50%以内となるようにすることによって、絞りしごき成形加工時に胴部に破胴が生じることなく、より薄肉で且つ径小な筒状容器を製造することができる。
In the method for manufacturing the cylindrical container according to the present invention, when the outer diameter Da of the side wall body portion molding surface of the punch and the outer diameter Db of the sealing portion molding surface, the outer diameter Db of the sealing portion molding surface is the side wall body portion molding surface. It can achieve more reliably by having the following relationship with respect to the outer diameter Da.
{Da / (1 + β)} ≦ Db ≦ {Da / (1 + α)}
However, α is the elastic limit elongation rate at the time of tube expansion of the sealing portion of the cylindrical container intermediate body, β is the molding limit elongation rate, and Da is equal to the inner diameter D of the cylindrical container to be molded.
And when the thickness of the said side wall main-body part of the said cylindrical container is Tw and the board thickness of the said sealing part is set to Tf, the manufacturing method of this invention WHEREIN: When (Tf-Tw) / Tf <= 0.5, The punch sealing portion molding surface is formed with a small diameter by one step from the side wall main body forming surface, and when (Tf−Tw) / Tf> 0.5, it is formed with a small diameter by two steps. By making the squeezing rate within 50% in the squeezing process of the cup side wall, a cylindrical container having a thinner wall and a smaller diameter can be manufactured without causing the body part to be broken during the drawing and squeezing process. Can do.
本発明の筒型容器及びその製造方法によれば、絞りしごき加工により形成される筒型容器において、封口部の十分な封口強度を確保しながら、側壁本体部のより一層の薄肉化を可能にし、且つ封口部内周面が側壁本体部内周面と略同径の内周面を確保することができ、内容物の収納を容易にすると共に容積率を高めることができ、しかも製造も容易で特別な工程や設備を必要とすることなく電池缶等に好適な筒状容器を得ることができる。 According to the cylindrical container and the manufacturing method thereof of the present invention, in the cylindrical container formed by squeezing and ironing, it is possible to further reduce the thickness of the side wall main body portion while ensuring sufficient sealing strength of the sealing portion. In addition, the inner peripheral surface of the sealing portion can secure an inner peripheral surface that is substantially the same diameter as the inner peripheral surface of the side wall body portion, the contents can be easily stored and the volume ratio can be increased, and the manufacturing is also easy and special. A cylindrical container suitable for a battery can or the like can be obtained without requiring a simple process or equipment.
特に本発明の筒型容器及びその製造方法によれば、絞りしごき後のストリッピングの工程で、直接封口部を外側に凸状態に塑性変形させるので、従来のような封口部の拡管のために拡管パンチによる拡管工程を必要としない。そのため、余分な工程を必要とすることなく工程を単純化できると共に、拡管のために側壁本体部に圧縮荷重が作用することがないので、側壁本体のより薄肉化が可能となり、一段と薄肉で高容積率に優れた小型で密封性に優れた電池缶等の筒型容器を得ることができる。 In particular, according to the cylindrical container and the manufacturing method thereof of the present invention, since the sealing part is directly plastically deformed outward in the stripping step after squeezing and squeezing, for the conventional expansion of the sealing part. There is no need for a tube expansion process using a tube expansion punch. Therefore, the process can be simplified without requiring an extra process, and a compressive load does not act on the side wall main body for expanding the pipe, so that the side wall main body can be made thinner, and the thickness is further reduced. A cylindrical container such as a battery can having a small volume ratio and an excellent sealing property can be obtained.
以下、本発明の実施形態に係る筒型容器及びその製造方法を図面に基づき詳細に説明する。
図1は、本発明の実施形態に係る筒型容器1を示し、ニッケルめっき鋼板を基材として、後述する絞りしごき成形加工により得られたものであって、底壁2と胴部側壁3とからなり、上端が開口した円筒容器となっており、本実施形態では電池缶として形成されている。胴部側壁3は、板厚がTwの側壁本体部4と板厚がTfの封口部5とからなり、内周面は開口端から底壁2に達するまで略ストレートとなっているが、外周面は封口部5が外側に向けて突出して厚肉部となっており、薄肉の側壁本体部との間がテーパー面6となっている。本実施形態の筒型容器は、直径が13mm〜40mmの範囲であり、一次電池又は二次電池の外装缶として採用可能である。
Hereinafter, a cylindrical container and a manufacturing method thereof according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 shows a cylindrical container 1 according to an embodiment of the present invention, which is obtained by a drawing ironing process, which will be described later, using a nickel-plated steel plate as a base material. It is a cylindrical container having an upper end opened, and is formed as a battery can in this embodiment. The
本実施形態の筒型容器は、以上のような形状にすることによって、電池缶への極板等の内装品の挿入を容易にすると共に容積率を高めることができ、且つ側壁本体部を薄肉にしても封口部の強度を保つ缶が得られる。しかしながら、そのような封口部が外側に凸形状の缶体を直接カップから絞りしごき加工により得ることは困難であるが、本発明では、下記に示すような側壁本体部の板厚Twと封口部の板厚Tfとの関係が一定の条件を満たす封口部が内側に凸の筒型容器中間体を絞りしごき加工により得て、それをパンチのストリッピング時に封口部に塑性変形を与えることによって、簡単に得ることができたものである。 By making the cylindrical container of the present embodiment into the shape as described above, it is possible to facilitate the insertion of the interior parts such as the electrode plate into the battery can and increase the volume ratio, and the side wall main body portion is thin. Even so, a can that maintains the strength of the sealing portion can be obtained. However, although it is difficult to obtain such a sealed portion by directly squeezing and squeezing a can body having a convex shape outward from the cup, in the present invention, the thickness Tw and the sealed portion of the side wall main body as shown below A sealing portion satisfying a certain condition with respect to the plate thickness Tf is obtained by squeezing and squeezing a cylindrical container intermediate body that is convex inward, and applying plastic deformation to the sealing portion at the time of stripping the punch, It was easy to get.
即ち、側壁本体部の板厚Twと封口部側壁の板厚Tfとの関係は、後述する絞りしごき工程後のストリッピングによる封口部の拡管率が弾性変形域を超えて塑性変形を起こし、且つ封口部の成形限界伸び範囲内であることが重要である。拡管率が弾性限界範囲内であると、ストリッピング後にスプリングバックによって封口部が内側に戻り、内側方向に凸の状態を解消することができない。したがって、封口部のストリッピングによる拡管は弾性変形以上であり、塑性変形の比率が大きいことが望ましく、完全に塑性変形することによって内周面が軸方向に完全にストレートな缶が得られることが望ましいが、若干のスプリングバックはどうしても残留する。 That is, the relationship between the plate thickness Tw of the side wall body portion and the plate thickness Tf of the side wall of the sealing portion is such that the expansion ratio of the sealing portion by stripping after the drawing and squeezing step described later causes plastic deformation exceeding the elastic deformation range, and It is important to be within the molding limit elongation range of the sealing portion. If the expansion ratio is within the elastic limit range, the sealing portion returns to the inside by the spring back after stripping, and the convex state in the inward direction cannot be eliminated. Therefore, it is desirable that the expansion of the sealing portion by stripping is more than elastic deformation, and it is desirable that the ratio of plastic deformation is large, and by completely plastic deformation, a can whose inner peripheral surface is completely straight in the axial direction can be obtained. Although desirable, some springback will inevitably remain.
一方、ストリッピングによる封口部の拡管率が成形限界伸びの範囲を超えると、ストリッピング時に封口部周壁に割れが発生する不都合が生じ、良好な缶体を得ることはできない。したがって、上記条件を満たす筒状容器を得るためには、第1の条件として封口部のストリッピングによる拡管率が弾性変形域を超えること即ち弾性限界伸び率αを超えること、第2の条件として、拡管に際して拡管率が成形限界伸び率βを超えないことである。そこで、上記条件を満たすための側壁本体部板厚をTwとし、側壁本体部内径をD、封口部板厚をTfとした場合、Tf−Twは次式(1)を満たす範囲でなければならない。
α・D/{2(α+1)}≦ (Tf−Tw) ≦β・D/{2(β+1)}・・・(1)
上記式において、(Tf−Tw)の値が左辺値に近づく程、ストリッピング終了後の弾性変形による戻り率が多くなり、右辺値に近づく程塑性変形率が高くなる。
On the other hand, when the tube expansion rate of the sealing part by stripping exceeds the range of the limit of forming elongation, there arises a disadvantage that the peripheral wall of the sealing part is cracked at the time of stripping, and a good can body cannot be obtained. Therefore, in order to obtain a cylindrical container that satisfies the above conditions, the first condition is that the expansion rate by stripping of the sealing portion exceeds the elastic deformation region, that is, exceeds the elastic limit elongation rate α, and the second condition is The tube expansion rate does not exceed the molding limit elongation β during tube expansion. Therefore, when the side wall main body plate thickness for satisfying the above conditions is Tw, the side wall main body inner diameter is D, and the sealing portion plate thickness is Tf, Tf−Tw must be in a range satisfying the following expression (1). .
α · D / {2 (α + 1)} ≦ (Tf−Tw) ≦ β · D / {2 (β + 1)} (1)
In the above formula, the closer the value of (Tf−Tw) is to the left side value, the greater the return rate due to elastic deformation after the end of stripping, and the higher the value of (Tf−Tw) is, the higher the plastic deformation rate is.
上記弾性限界伸び率α及び成形限界伸び率βは、材質及び缶胴径等によって相違するが、本発明者が種々実験した結果、鉄系の缶の場合、塑性変形させると、約0.2%の弾性回復が起こる。従って明確な永久変形を得るには、最低でも加工率0.2%以上の歪みを与える必要がある。本件では、略0.5%程度の変形を与えることを前提とする。即ち弾性限界伸び率αを0.5%とする。さらに鉄系の缶の場合、絞りしごき加工後の缶胴は、加工硬化が激しく、高々2〜3%程度の伸び率しか得られない。従って本件では、安全をみて成形限界伸び率βを2.5%と定めた。成形限界伸び率βを2.5%とすると、缶胴径Dが40mmである場合、上記数式1により(Tf−Tw)≦0.5mmの範囲内であれば、成形限界伸びを超えないで封口部を塑性変形させることが可能ある。一方、封口部に塑性変形を与えるためには、0.1≦(Tf−Tw)でなければならない。よって、封口部が成形限界を超えないで、外側に凸状態に塑性変形させるためには、0.1mm≦(Tf−Tw)≦0.5mmでなければならない。 The elastic limit elongation rate α and the molding limit elongation rate β differ depending on the material, the diameter of the can body, and the like. As a result of various experiments conducted by the inventor, when an iron-based can is plastically deformed, it is about 0.2. % Elastic recovery occurs. Therefore, in order to obtain a clear permanent deformation, it is necessary to give a strain with a processing rate of 0.2% or more at a minimum. In this case, it is assumed that a deformation of about 0.5% is given. That is, the elastic limit elongation α is set to 0.5%. Furthermore, in the case of an iron-based can, the can body after the squeezing and ironing process is severely work-hardened, and only an elongation of about 2-3% can be obtained at most. Therefore, in this case, the molding limit elongation β was set to 2.5% for safety. When the forming limit elongation β is 2.5%, when the can body diameter D is 40 mm, the forming limit elongation is not exceeded as long as it is within the range of (Tf−Tw) ≦ 0.5 mm according to the above formula 1. It is possible to plastically deform the sealing portion. On the other hand, in order to give plastic deformation to the sealing portion, it is necessary that 0.1 ≦ (Tf−Tw). Therefore, in order for the sealing portion to be plastically deformed outwardly without exceeding the molding limit, 0.1 mm ≦ (Tf−Tw) ≦ 0.5 mm must be satisfied.
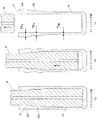
次に、以上のような本実施形態に係る筒型容器の製造方法を、図2〜図3により説明する。図2は絞りしごき工程の模式図、図3は絞りしごき工程後のストリッピング工程の模式図である。図2において、(a)パンチ20とカップ10の断面を示し、(b)は1回目のしごき工程を、(c)は2回目のしごき工程を(d)はしごき加工終了後の状態を、各工程ごとの断面として示している。
しごき加工するための本実施形態で使用するパンチ20は、径大の側壁本体部成形面21とそれよりも径小の封口部成形面22を有し、側壁本体部成形面21と封口部成形面22との間はテーパー面23の段差となっている。側壁本体部成形面21の直径Da、封口部成形面22の直径をDbとすると、Da−Db=2(Tf−Tw)となる関係に形成されている。Tfは図1に示す目的とする筒型容器の封口部5の板厚であり、Twは側壁本体部4の板厚である。つまりパンチの側壁本体部成形面21の半径は、封口部の板厚と側壁本体部の板厚との差に相当する量だけ、封口部形成面より大きくなっている。Tf−Twは、後述するように封口部の拡管量であり、該拡管量が弾性変形域を超えて塑性変形域に達し、且つ成形限界伸びを超えない範囲に設定されている。
Next, the manufacturing method of the cylindrical container which concerns on this embodiment as mentioned above is demonstrated with reference to FIGS. FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the drawing and ironing process, and FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of the stripping process after the drawing and ironing process. In FIG. 2, (a) shows a cross section of the
The
上記形状のパンチより、前工程で金属板の基材から絞り成形して得られたカップ10をダイス(図示してない)とパンチ20によりしごき成形するが、本実施形態では内径の相違するダイスを2段に配置し、2段階でしごき加工を行なっている。なお、以下の説明において、筒型容器の加工時の寸法を一次しごき加工で形成される部分には添え字1を付し、同様に2次しごき加工、3次しごき加工によって形成される部分には、それぞれ添え字2、3を付している。そして、最終的に得られた筒型容器の寸法には添え字は付していない。
From the punch of the above shape, the
絞りしごき工程では、周壁部12の板厚Td、底壁11の板厚Toのカップ10をまず1段目のダイスとパンチ20の側壁本体部成形面21により周壁部の板厚がTw1になるまで、第1次しごき加工を行なう。次いで2段目のダイスとパンチ20により最後までしごき加工を行なうことによって、側壁本体部成形面21により板厚Tw2の側壁本体部42を形成し、パンチの径小部である封口部成形面22に圧接する部分は板厚Tf2の封口部52が形成される。以上の2段しごきにより、側壁本体部42の板厚がTw=Tw2で拡管部が内側に(Tf2−Tw2)だけ凸の板厚Tf2(=Tf)の封口部52を有する筒型容器中間体15が形成された状態となり、絞りしごき加工が終了する。この状態を図2(d)に模式的に示している。
In the squeezing and squeezing step, the thickness of the
次いで、この状態から図3に示すように、パンチ20が復帰することによって、ストリッピングが行なわれるが、筒型容器中間体15は図示しないストリッパー爪によって上方への移動が拘束されて、パンチ20のみが上方(抜け方向)に移動することによって、筒型容器中間体15の拡管部52の内側の凸の部分がパンチのテーパー面23に圧接して拡管加工されて、図3(b)に示すように封口部52は次第に材料が外方に移動して、外方に(Tf2−Tw2)の厚さだけ凸になっている状態に変化する。前述したようにストリッピング時のパンチによる封口部の拡管は弾性限界伸び率を超えて且つ成形限界伸び率の範囲内で行なわれるので、ストリッピングが完全に終了しても理想的には封口部は塑性変形して完全に元の状態に戻らず、図3(c)に示すように、内周面は略ストレートで封口部は外側に向けて凸に板厚になっている胴部側壁板厚Tw(=Tw2)、封口部板厚Tf(=Tf2)の筒型容器1を得ることができる。したがって、本実施形態によれば、絞りしごき成形加工後に行うストリッピングだけで上記形状の筒型容器1を得ることができる。
Next, as shown in FIG. 3, when the
上記のストリッピング時における筒型容器中間体15の封口部52が塑性変形し且つ割れを発生することなく、良好に図1に示すような筒型容器を成形するためには、パンチ20の形状は次の条件を満たさなければならない。
即ち、図3の(a)の状態において、パンチが上昇することによって、筒型容器中間体の封口部52は内径がDになるまで拡管作用を受けるので、拡管率は2(Tf2−Tw2)/{D−2(Tf2−Tw2)}×100となる。そして、弾性限界率α以上で且つ成形限界伸び率βの範囲内でなければならないので、
α≦2(Tf2−Tw2)/{D−2(Tf2−Tw2)}≦βである。従って、パンチの封口部成形面の直径Dbは
{Da/(1+β)}≦Db≦{Da/(1+α)}を満足しなければならない。ここで、Daは得られる筒型容器の内径Dと等しいから、結局
{D/(1+β)}≦Db≦{D/(1+α)}によって規定される。
For sealing
That is, in the state of (a) 3, by the punch is increased, since the sealing
α ≦ 2 (Tf 2 −Tw 2 ) / {D−2 (Tf 2 −Tw 2 )} ≦ β. Accordingly, the diameter Db of the punch sealing part forming surface is
{Da / (1 + β)} ≦ Db ≦ {Da / (1 + α)} must be satisfied. Here, Da is equal to the inner diameter D of the obtained cylindrical container.
It is defined by {D / (1 + β)} ≦ Db ≦ {D / (1 + α)}.
図4は、本発明の他の実施形態に係る筒型容器30を示し、図1に示す実施形態の筒型容器1では、封口部5の板厚を外側に1段凸の段差で厚く形成しているが、本実施形態では封口部35を35a、35bと2段段差に形成することによって、最大しごき率を低減できて、胴部壁のより薄肉化を可能にしたものである。本発明者の実験によれば、鉄を基材とする筒型容器の場合、しごき工程でしごき率が52%を超えると破胴が発生しやすくなった。したがって、通常、封口部と側壁本体との段差は1段段差でよいが、(Tfb−Tw)/Tfb>0.5であると、2段段差が好ましい。2段段差の場合、最大しごき率を50%以下に軽減でき、良好な成形が可能となる。封口部を2段段差にすることによって、側壁本体を薄くできる。したがって、その場合パンチは、筒型容器の側壁本体部の板厚をTw、前記封口部の板厚をTfとすると、(Tf−Tw)/Tf≦0.5の場合はパンチの封口部成形面は側壁本体部形成面より1段の段差で径小に形成し、(Tf−Tw)/Tf>0.5の場合は2段の段差で径小に形成し、前記カップ側壁のしごき工程においてしごき率が50%以内となるようにする。
FIG. 4 shows a
図5は、封口部が2段段差に形成されている筒型容器30の製造工程におけるしごき加工により筒型容器中間体37を得る工程を示している。その場合のパンチ40は、外径Daの側壁本体部成形面41の上端に形成された封口部成形面42が2段に形成されている。即ち、側壁本体部成形面41の上端から第1テーパー面44を介して外径Db’の第1段目の封口部成形面42aが形成され、さらに内側に傾斜のテーパー面45を介して外径Dbの第2段目の封口部成形面42bが形成されている。
FIG. 5 shows a process of obtaining the cylindrical container
その場合、絞り成形されたカップの側壁のしごき加工は図5(a)〜図5(c)に示すように3回行ない、1次しごき加工は側壁本体部成形面の途中に達するまで行い、2次しごき加工は第1段目の封口部成形面42aの途中に達するまで行い、3次しごき加工は第2段目の封口部成形面42bに達する最後まで行なう。上記しごき工程において、絞り成形されたカップの側壁の板厚をTdとすると、1次しごきでは、側壁本体部成形面で板厚がTw1になるまで行い、ついで2次しごきで側壁本体部成形面で側壁本体部の板厚がTw2、第1段目の封口部成形面42aで封口部が板厚Tf2に達するまで行い、3次しごきで側壁本体部成形面で側壁本体部の板厚がTw3、第1段目の封口部成形面42aで一段目の封口部板厚Tf3’、第2段目封口部成形面42bで2段目封口部板厚がTf3となるまでしごき加工を行なう。したがって、各工程での最大しごき率は、1次しごきでは(Td−Tw1)/Td×100、2次しごきでは(Tw1−Tw2)/Tw1×100、3次しごきでは(Tw2−Tw3)/Tw2×100となるが、本実施形態では、それぞれの最大しごき率が50%以下となるように、前記パンチの側壁本体部成形面41、第1段目の封口部成形面42a、第2断面の封口部成形面42bの外径をそれぞれ採用している。図6は、図5に示すしごき加工後のストリッピングによって、図4に示す筒状容器30を得る工程を示すが、基本的には2段の段差を有する以外は図3と同様であるので、符号のみ付し、詳細な説明は省略する。
In that case, the ironing process of the side wall of the drawn cup is performed three times as shown in FIGS. 5 (a) to 5 (c), and the primary ironing process is performed until it reaches the middle of the side wall body portion molding surface, The secondary ironing process is performed until reaching the middle of the first-stage sealing
実施例1:
基材がNiメッキ鋼板からなる絞りカップより、外径18mm、高さ65mmの筒型電池容器を得る目標で、目標値が同寸法の筒型容器中間体を得るように、封口部成形面が2段段差となっているパンチを用いて、図5に示すようにして、封口部が2段段差となっていて、内側に向かって凸になっている筒型容器中間体を成形した。そのときの成形条件は表1に示す通りである。
Example 1:
In order to obtain a cylindrical battery container having an outer diameter of 18 mm and a height of 65 mm from a drawn cup made of a Ni-plated steel plate as a base material, As shown in FIG. 5, a cylindrical container intermediate body having a two-step sealing portion and projecting inward was formed using a punch having two steps. The molding conditions at that time are as shown in Table 1.
実施例2:
基材がNiメッキ鋼板からなる絞りカップより、外径32mm、高さ120mmの筒型電池容器を得る目標で、目標値が同寸法の筒型容器中間体を得るように、封口部成形面が1段段差となっているパンチを用いて、図2に示すようにして、封口部が2段段差となっていて、内側に向かって凸になっている筒型容器中間体を成形した。そのときの成形条件は表1に示す通りである。
Example 2:
In order to obtain a cylindrical battery container having an outer diameter of 32 mm and a height of 120 mm from a drawn cup whose base material is a Ni-plated steel plate, the sealing portion molding surface is formed so as to obtain a cylindrical container intermediate having the same target value. As shown in FIG. 2, a cylindrical container intermediate body having a two-step sealing portion and projecting inward was formed using a punch having a one-step step. The molding conditions at that time are as shown in Table 1.
比較例:
実施例と同様に基材がNiメッキ鋼板からなる絞りカップより、外径18mm、高さ65mmの筒型電池容器を得る目標で、封口部成形面が1段段差となっているパンチにより1回しごき加工して、封口部が外側に1段段差となっていて、内側に向かって凸になっている筒型容器中間体を成形した。そのときの成形条件を実施例1、2と共に表1に示す。
Comparative example:
In the same manner as in the example, the target is to obtain a cylindrical battery container having an outer diameter of 18 mm and a height of 65 mm from a drawn cup made of a Ni-plated steel plate. After the ironing process, a cylindrical container intermediate body was formed in which the sealing portion had one step on the outer side and was convex toward the inner side. The molding conditions at that time are shown in Table 1 together with Examples 1 and 2.
実施例1と比較例の目標封口部板厚は、同じ0.26mmであるが、比較例では封口部が1段段差に形成されて2段しごきによって行なわれ、実施例1では2段段差に形成されて3段しごきによって行なった。その結果、比較例では2回目のしごきでの最大しごき率が51.9%となり、限界しごき率を超えてしまい、破胴が生じ、良好なものが得られなかった。これに対して、実施例1では2段段差にして3回しごきを行なった結果、最大しごき率は38.1%に低減でき、破胴を生じることなく、良好にしごき加工ができた。また、実施例2は、筒型容器中間体のしごき加工では、拡管率が小さく最大しごき率も50%以下であるので、1段段差のパンチにより2回しごき加工で、破胴が発生することなく良好な筒状電池容器中間体が得られた。 The target sealing portion plate thickness of Example 1 and the comparative example is the same 0.26 mm, but in the comparative example, the sealing portion is formed in a one-step step and is performed by two-step ironing, and in Example 1, the two-step step is performed. This was done by three-stage ironing. As a result, in the comparative example, the maximum ironing rate in the second ironing was 51.9%, exceeding the limit ironing rate, causing a broken body, and a good product could not be obtained. On the other hand, in Example 1, ironing was performed three times with two steps, and as a result, the maximum ironing rate could be reduced to 38.1%, and ironing could be performed satisfactorily without causing breakage. Further, in Example 2, in the ironing process of the cylindrical container intermediate body, the tube expansion rate is small and the maximum ironing rate is 50% or less, so that the cylinder breakage occurs in the ironing process twice by the punch of one step. A good cylindrical battery container intermediate was obtained.
次に、前記実施例1、2で絞りしごきによって得られた絞りしごき加工が終わった状態の筒型容器中間体からストリッピングにより、パンチの側壁本体部成形面で直接封口部の拡管加工を行なって、実施例1、2の筒型電池容器を得た。そのときの加工データを表2に示す。
実施例1、2ともしごき加工後の筒型容器中間体から、ストリッピング工程でパンチを強制的に抜くことにより、前記内側に凸状態の封口部は外側に凸状態に変位した。そして、封口部の内径は、完全な拡管状態から直径に対して0.2%程度のスプリングバックがあり、実施例1では約0.04mm、実施例2では0.06mm、即ち、内段差が実施例1では0.02mm、実施例2では0.03mmがあったが、塑性変形を維持し、且つ割れ等も発生することなくほぼ目標とする電池缶を得ることができ、本発明の有用性が確認できた。 In both of Examples 1 and 2, the punching portion was forcibly removed from the tubular container intermediate body after ironing in the stripping step, whereby the sealing portion protruding inwardly was displaced outwardly. The inner diameter of the sealing portion has a spring back of about 0.2% with respect to the diameter from the fully expanded state, about 0.04 mm in Example 1, 0.06 mm in Example 2, that is, the inner step is Although it was 0.02 mm in Example 1 and 0.03 mm in Example 2, it is possible to obtain a battery can that is almost aimed without maintaining plastic deformation and without causing cracks, etc. The sex was confirmed.
本発明の筒型容器及びその製造方法によれば、十分な封口強度を確保しながら側壁本体部のより一層の薄肉化を可能にし、且つ封口部内周面が側壁本体部内周面と略同径の内周面を確保できる筒型容器を得ることができ、しかも特別な工程や設備を必要とすることなく容易に製造できるので、密封強度と小型・軽量化が要求される電池容器をはじめ種々の内容物の充填容器に好適に利用でき、産業上の利用可能性が高い。 According to the cylindrical container and the manufacturing method thereof of the present invention, it is possible to further reduce the thickness of the side wall main body while ensuring sufficient sealing strength, and the inner peripheral surface of the sealing main body is substantially the same diameter as the inner peripheral surface of the side wall main body. Can be obtained easily without the need for special processes and equipment, so that various battery containers such as battery containers that require sealing strength, small size, and light weight can be obtained. It can be suitably used for a container filled with the contents, and has high industrial applicability.
1、30 筒型容器
2、32 底壁
3 胴部側壁
4、34 側壁本体部
5、35 封口部
6 テーパー面
10 カップ
11 カップ底壁
12 側壁
15、37 筒型容器中間体
20、40 パンチ
21、41 側壁本体部成形面
22、42 封口部成形面
23、44、45 テーパー面
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
α・D/{2(α+1)}≦ (Tf−Tw) ≦β・D/{2(β+1)}・・・(1)
を満たすような関係にあり、
(Tf−Tw)/Tf≦0.5の場合、前記封口部は外側に向かって1段の段差であり、(Tf−Tw)/Tf>0.5の場合、前記封口部は外側に向かって2段の段差であることを特徴とする筒型容器。 The base material formed by the squeezing and ironing method is a metal cylindrical container, and the body side wall is composed of a side wall body part and a sealing part near the opening end, and the inner peripheral surface of the body side wall has a substantially uniform radius. It is substantially straight in the axial direction, and the outer peripheral surface is thicker through the step surface from the side wall body part to the outside, and the sealing part plate thickness Tf and the side wall body part plate thickness Tw When the difference between the inner diameter of the side wall body portion is D, the elastic limit elongation at the time of pipe expansion of the sealing portion is α, and the molding limit elongation is β, the following expression α · D / {2 (α + 1)} ≦ (Tf− Tw) ≦ β · D / {2 (β + 1)} (1)
There is a relationship, such as to satisfy the,
When (Tf−Tw) /Tf≦0.5, the sealing portion is one step toward the outside, and when (Tf−Tw) / Tf> 0.5, the sealing portion faces the outside. A cylindrical container having two steps .
{Da/(1+β)}≦Db≦{Da/(1+α)}
但し、αは前記筒型容器中間体の封口部の拡管加工時の弾性限界伸び率であり、βは成形限界伸び率であり、Daは成形する筒型容器の内径と等しい。 The manufacturing method of the cylindrical container according to claim 3 , wherein the outer diameter Db of the sealing portion molding surface of the punch has the following relationship with the outer diameter Da of the sidewall main body molding surface.
{Da / (1 + β)} ≦ Db ≦ {Da / (1 + α)}
However, (alpha) is an elastic limit elongation rate at the time of pipe expansion of the sealing part of the said cylindrical container intermediate body, (beta) is a shaping | molding limit elongation rate, and Da is equal to the internal diameter of the cylindrical container to shape | mold.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009149497A JP4835883B2 (en) | 2009-06-24 | 2009-06-24 | Cylindrical container and manufacturing method thereof |
| PCT/JP2010/059672 WO2010150649A1 (en) | 2009-06-24 | 2010-06-08 | Cylindrical container and production method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009149497A JP4835883B2 (en) | 2009-06-24 | 2009-06-24 | Cylindrical container and manufacturing method thereof |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011006087A JP2011006087A (en) | 2011-01-13 |
| JP2011006087A5 JP2011006087A5 (en) | 2011-07-28 |
| JP4835883B2 true JP4835883B2 (en) | 2011-12-14 |
Family
ID=43386420
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009149497A Active JP4835883B2 (en) | 2009-06-24 | 2009-06-24 | Cylindrical container and manufacturing method thereof |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4835883B2 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2010150649A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5551560B2 (en) * | 2010-10-07 | 2014-07-16 | Fdkトワイセル株式会社 | Cylindrical battery |
| FR3003190B1 (en) | 2013-03-14 | 2015-04-03 | Luxfer Gas Cylinders Ltd | PROCESS FOR MANUFACTURING LINERS FOR PRESSURE TANK |
| US11407022B2 (en) * | 2018-02-06 | 2022-08-09 | Tata Steel Ijmuiden B.V. | Process and apparatus for the production of a can body by wall ironing |
| CN112157175B (en) * | 2020-09-15 | 2024-10-01 | 苏州斯莱克精密设备股份有限公司 | Punch, die and stretching process for stretching battery can body |
| PL245172B1 (en) * | 2021-08-20 | 2024-05-27 | Canpack Spolka Akcyjna | Punch and semi-finished product and can produced using this punch |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FI55018C (en) * | 1975-02-21 | 1979-05-10 | Printal Oy | HOELJEAEMNE SAERSKILT FOER AEROSOLFOERPACKNINGAR OCH ANORDNING FOER AEMNETS FRAMSTAELLNING MEDELST KALLPRESSNING |
| JP2790072B2 (en) * | 1994-02-15 | 1998-08-27 | 東洋製罐株式会社 | Manufacturing method of seamless cans |
| JP3749127B2 (en) * | 2001-01-15 | 2006-02-22 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Sealed battery and method of manufacturing sealed battery |
| JP3694506B2 (en) * | 2003-02-04 | 2005-09-14 | 石崎プレス工業株式会社 | Method for producing negative electrode can for battery using press working |
| JP2007027046A (en) * | 2005-07-21 | 2007-02-01 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Battery can and method of manufacturing same |
| JP5108411B2 (en) * | 2007-08-03 | 2012-12-26 | パナソニック株式会社 | Battery can, manufacturing method and manufacturing apparatus |
-
2009
- 2009-06-24 JP JP2009149497A patent/JP4835883B2/en active Active
-
2010
- 2010-06-08 WO PCT/JP2010/059672 patent/WO2010150649A1/en active Application Filing
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2010150649A1 (en) | 2010-12-29 |
| JP2011006087A (en) | 2011-01-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6193794B2 (en) | Method for forming a rectangular battery case | |
| JP4835883B2 (en) | Cylindrical container and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5975573B2 (en) | Method for forming a rectangular battery case | |
| EP3124332B1 (en) | Method for manufacturing vehicle structural member | |
| US9808850B2 (en) | Process for forming hollow member with complicated cross-section | |
| KR101970423B1 (en) | Press-formed article, method of manufacturing the press-formed article, and manufacturing facility column | |
| JP6551523B2 (en) | Press processing method | |
| CN107249773B (en) | Press-processing method and press forming die | |
| CN101780507B (en) | Method for manufacturing deep square cylindrical metal shell | |
| CN108698105B (en) | Method for producing press-molded article | |
| JP6030178B2 (en) | Rectangular battery case for in-vehicle battery and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2018051609A (en) | Burring device, burring method, method for manufacturing metal component, product processed by burring method and metal component | |
| WO2018139000A1 (en) | Press forming method | |
| JP5613341B1 (en) | Ironing die and molding material manufacturing method | |
| JP5987942B1 (en) | Press mold | |
| CN105728527A (en) | Method and device for inward winding formation of end part of tail gas pipe | |
| JP2017109208A (en) | Manufacturing method of metal container | |
| JP2011006087A5 (en) | ||
| CN110404994B (en) | Multi-pass sequential back-extrusion forming method for combined punch of large-sized cylindrical part with bottom | |
| JP7310777B2 (en) | Press molding method, press molding die for intermediate molding and press molded product | |
| JP2016073987A (en) | Device and method for manufacturing end-thickened steel pipe | |
| JP7544109B2 (en) | Seamless can body and method for manufacturing seamless can body | |
| JPH0584524A (en) | Manufacture of draw-ironed can | |
| JP2023009798A (en) | Prismatic container having side wall different in plate thickness and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2008161923A (en) | Method of and apparatus for manufacturing bottomed-can |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110615 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110615 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20110615 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20110823 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110913 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20141007 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4835883 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20141007 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20141007 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20141007 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |