JP4686509B2 - Single crystal pulling crucible - Google Patents
Single crystal pulling crucible Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4686509B2 JP4686509B2 JP2007190416A JP2007190416A JP4686509B2 JP 4686509 B2 JP4686509 B2 JP 4686509B2 JP 2007190416 A JP2007190416 A JP 2007190416A JP 2007190416 A JP2007190416 A JP 2007190416A JP 4686509 B2 JP4686509 B2 JP 4686509B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- crucible
- reinforcing layer
- single crystal
- carbon fiber
- pulling
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2209/00—Vessel construction, in particular methods of manufacturing
- F17C2209/21—Shaping processes
- F17C2209/2154—Winding
Landscapes
- Crystals, And After-Treatments Of Crystals (AREA)
- Ceramic Products (AREA)
Description
本発明は、シリコン、ガリウム又はこれらの化合物の単結晶引き上げ装置に用いられるルツボに関わる。特に、炭素繊維強化炭素複合材製のルツボに関する。 The present invention relates to a crucible used in a single crystal pulling apparatus for silicon, gallium or a compound thereof. In particular, it relates to a crucible made of carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material.
本発明はチョクラルスキー法(CZ法)による半導体単結晶引き上げ装置等に用いられる単結晶引き上げ用ルツボに関する。CZ法によるシリコン単結晶の製造には、従来より、シリコンをその内部で溶融するための石英ルツボと、これを収容して外部から支持するための炭素製のルツボが用いられている。石英ルツボは使用中にシリコンの溶融熱を受けて軟化し、その外表面がルツボ内面に密着した状態となる。この状態のまま冷却すると、石英ルツボより熱膨張係数が大きな炭素製のルツボには大きな応力が発生する。 The present invention relates to a crucible for pulling a single crystal used in a semiconductor single crystal pulling apparatus or the like by the Czochralski method (CZ method). In the production of a silicon single crystal by the CZ method, conventionally, a quartz crucible for melting silicon inside thereof and a carbon crucible for containing and supporting this from the outside have been used. The quartz crucible is softened by receiving the heat of melting of silicon during use, and its outer surface is in close contact with the inner surface of the crucible. When cooled in this state, a large stress is generated in the carbon crucible having a larger thermal expansion coefficient than that of the quartz crucible.
そこで、このような応力に耐える機械的強度を有し、比較的石英ルツボに近い熱膨張係数を有し、大型化に対応しやすい炭素繊維強化炭素複合材(Carbon Fiber Reinforced Carbon Composite)或いはC/C複合材(C/C Composite) で単結晶引き上げ用ルツボを製造することが提案されている。下記文献は、胴部と底部からなるルツボのうち、胴部のみ又はその全体をC/C複合材で製造することを提案している。その製造方法としては、フィラメントワインディング法を用い、マトリックス前駆体が含浸された炭素繊維をヘリカル状にルツボ状のマンドレルに巻き付けて成形することを提案している。 Therefore, a carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite (C / C) that has mechanical strength that can withstand such stress, has a thermal expansion coefficient that is relatively close to that of a quartz crucible, and is easy to cope with upsizing. It has been proposed to produce crucibles for pulling single crystals with C / C Composite. The following document proposes that a crucible consisting of a body part and a bottom part is made of a C / C composite material only or entirely. As its manufacturing method, it has been proposed to use a filament winding method to wind a carbon fiber impregnated with a matrix precursor around a helical crucible-shaped mandrel.
しかしながら、ボウル状に湾曲した底部に滑りが生じないように、ヘリカル状に炭素繊維を巻き付けることは困難であるという問題があった。そのため、底部の巻き付けが不十分になって十分な強度を有する底部を形成することができなかった。 However, there is a problem that it is difficult to wind the carbon fiber in a helical shape so that the bottom curved in the bowl shape does not slip. For this reason, the bottom portion is not sufficiently wound and a bottom portion having sufficient strength cannot be formed.
また、経験的に最も応力が集中するのは、胴部から底部に至る部分であり、全体をフィラメントワインディング法によるC/C複合材で製造することの困難性に鑑み、胴部と底部の境界部分だけをC/C複合材で製造することも提案されている。しかし、この場合の製造方法も、フィラメントワインディング法を用い、マトリックス前駆体が含浸された炭素繊維をパラレル巻き又はヘリカル巻きでルツボ状のマンドレルに巻き付けて成形する方法である。胴部と底部の境界部分だけをC/C複合材で製造することは、胴部と底部の全体をC/C複合材で製造することより優しいが、胴部と底部の境界部分も湾曲しており、この湾曲した部分に滑りを生じないようにパラレル巻き又はヘリカル巻きを行うことは依然として困難であった。その結果、胴部のみならず、底部まで十分な強度を有するC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボを提案することができなかった。 In addition, it is empirically that the stress is concentrated most in the part from the body part to the bottom part, and considering the difficulty of manufacturing the whole with the C / C composite material by the filament winding method, the boundary between the body part and the bottom part It has also been proposed to produce only the part with a C / C composite. However, the manufacturing method in this case is also a method in which carbon fiber impregnated with a matrix precursor is wound around a crucible-shaped mandrel by parallel winding or helical winding using a filament winding method. Manufacturing only the boundary between the body and the bottom with a C / C composite material is easier than manufacturing the entire body and bottom with a C / C composite, but the boundary between the body and the bottom is also curved. Therefore, it is still difficult to perform parallel winding or helical winding so that the curved portion does not slip. As a result, it was not possible to propose a crucible for pulling a single crystal made of a C / C composite material having sufficient strength not only to the body but also to the bottom.
また、フィラメントワインディング法に用いられるルツボ状のマンドレルは底部の中心と胴部の中心の両端に軸が突設された形状をしている。そのため、胴部と底部の全体をC/C複合材で製造したとしても、底部の中心には孔が残り、この部分を別途のC/C複合材で栓をする必要があった。また、C/C複合材は黒鉛よりポーラスであるため、シリコンと反応するSiC化が生じやすいという問題点もあった。 A crucible-shaped mandrel used in the filament winding method has a shape in which shafts are projected from both ends of the center of the bottom and the center of the trunk. Therefore, even if the entire body and bottom are made of C / C composite material, a hole remains in the center of the bottom portion, and it is necessary to plug this portion with a separate C / C composite material. In addition, since the C / C composite material is more porous than graphite, there is also a problem that SiC reacts with silicon easily.
本発明は従来の技術のこのような問題点を解決するためになされたものであり、その第1の目的は、シリンダ状の胴部のみならずボウル状の底部もフィラメントワインディング法で強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボを提供することにある。また第2の目的は、フィラメントワインディング法の足らざる部分を炭素繊維シートで補いつつ全体として強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made to solve such problems of the prior art, and the first object thereof is to strengthen not only the cylindrical body but also the bowl-shaped bottom by the filament winding method. The object is to provide a crucible for pulling a single crystal made of a C / C composite material. A second object is to provide a crucible for pulling a single crystal made of a C / C composite material that is reinforced as a whole while supplementing a portion where the filament winding method is insufficient with a carbon fiber sheet.
また第3の目的は、ボウル状の底部に孔がなく、底部の全体が強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボを提供することにある。また第4の目的は、C/C複合材の表面性状を改善し、SiC化が生じにくいC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボを提供することにある。 A third object is to provide a crucible for pulling a single crystal made of a C / C composite material in which there is no hole in the bottom of the bowl shape and the entire bottom is reinforced. A fourth object of the present invention is to provide a crucible for pulling a single crystal made of a C / C composite material that improves the surface properties of the C / C composite material and hardly causes SiC.
(1) 上記目的を達成するために、本発明の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボは、シリンダ状の胴部とボウル状の底部とからなり、炭素繊維強化炭素複合材により形成された単結晶引き上げ用ルツボであって、前記炭素繊維を引き揃え、前記底部に掛けられ前記胴部に至るように巻きかけた第1強化層と、前記炭素繊維のシートの複数を、前記底部のうち前記胴部に隣接する部分に環状に張りつけた第2強化層と、前記炭素繊維を引き揃え、前記胴部の周方向に沿って巻き付けた第3強化層とを備え、前記第1強化層と前記第2強化層と前記第3強化層の組み合わせが、複数組重ねられてなるものである。 (1) In order to achieve the above object, a single crystal pulling crucible of the present invention comprises a cylindrical body and a bowl bottom and is formed of a carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material. The carbon fiber is aligned, and the first reinforcing layer wound around the bottom portion and wound to reach the body portion, and a plurality of the carbon fiber sheets are adjacent to the body portion of the bottom portion. A first reinforcing layer and a second reinforcing layer, the second reinforcing layer being annularly attached to a portion to be formed, and a third reinforcing layer in which the carbon fibers are aligned and wound along the circumferential direction of the body portion. And a plurality of combinations of the third reinforcing layers.
上記(1)の構成によれば、フィラメントワインディング法によって形成された第1及び第3強化層によってルツボの底部を押し下げようとする力及びルツボの胴部を押し広げようとする力に対抗し、更に、前記第1及び第3強化層によって足らざる部分を炭素繊維シートの張り付けによって形成された第2強化層で補っている。その結果、第2強化層によって、更に、円周方向が強化されると共に、全体の厚みが揃い、全体として強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボとなっている。また、胴部に隣接する部分は、ルツボ底部の曲率半径が小さい湾曲部分に相当し、この部分を炭素繊維のシートによって厚み調整することができる。更に、第1、第2、第3強化層が、複数組重ねられているので、全体として強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボとなっている。 According to the configuration of the above (1), the first and third reinforcing layers formed by the filament winding method counteract the force to push down the bottom of the crucible and the force to push the crucible body. Furthermore, the part which is not sufficient by the said 1st and 3rd reinforcement layer is supplemented with the 2nd reinforcement layer formed by sticking of the carbon fiber sheet. As a result, the circumferential direction is further strengthened by the second reinforcing layer, the entire thickness is uniform, and the C / C composite-made single crystal pulling crucible is strengthened as a whole. Moreover, the part adjacent to the trunk | drum corresponds to the curved part with a small curvature radius of a crucible bottom part, and thickness adjustment of this part can be carried out with the sheet | seat of carbon fiber. Furthermore, since a plurality of first, second, and third reinforcing layers are stacked, a single crystal pulling crucible made of C / C composite material that is reinforced as a whole.
(2)本発明の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボにおいては、前記第1強化層は前記底部の中心を覆って設けられ、前記底部は孔無しの一体で形成されたものであることが好ましい。 (2) In the crucible for pulling up a single crystal of the present invention, it is preferable that the first reinforcing layer is provided so as to cover the center of the bottom portion, and the bottom portion is formed integrally with no holes.
上記(2)の構成によれば、ボウル状の底部に孔がないので、上記(1)の発明による効果に加えて、更に、底部の全体が強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボとなっている。 According to the configuration of (2) above, since there is no hole in the bottom of the bowl shape, in addition to the effect of the invention of (1) above, a single crystal made of a C / C composite material whose entire bottom is further reinforced It is a crucible for lifting.
(4)本発明の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボにおいては、前記胴部と前記底部の最内層は、炭素繊維クロスの張りつけにより形成されていることが好ましい。 (4) In the crucible for pulling up a single crystal of the present invention, it is preferable that the innermost layer of the trunk portion and the bottom portion is formed by attaching a carbon fiber cloth.
上記(4)の構成によれば、上記(1)の発明による効果に加えて、ルツボの最内層が炭素繊維クロスの張りつけにより形成されているので、石英ルツボとの接触性が向上する。 According to the configuration of (4) above, in addition to the effect of the invention of (1) above, the innermost layer of the crucible is formed by attaching the carbon fiber cloth, so that the contact with the quartz crucible is improved.
(5)本発明の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボにおいては、前記炭素繊維強化炭素複合材の表面には、熱分解炭素が含浸されるとともに被覆されていることが好ましい。 (5) In the single crystal pulling crucible of the present invention, it is preferable that the surface of the carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material is impregnated with pyrolytic carbon and coated.
上記(5)の構成によれば、上記(1)の発明による効果に加えて、C/C複合材の表面に、熱分解炭素が含浸させられ被覆されているので、耐SiC化が向上する。 According to the configuration of (5) above, in addition to the effect of the invention of (1) above, the surface of the C / C composite material is impregnated with and covered with pyrolytic carbon, so that SiC resistance is improved. .
(6)別の観点として、本発明の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボは、シリンダ状の胴部とボウル状の底部とからなり、炭素繊維強化炭素複合材により形成された単結晶引き上げ用ルツボであって、前記炭素繊維を引き揃えて前記底部に掛けられた第1強化層と、前記底部のうち前記胴部に隣接する部分に炭素繊維シートを周方向に沿って環状に張りつけた第2強化層と、前記炭素繊維を引き揃えて前記胴部の周方向に沿って巻き付けた第3強化層との多層構造を備え、前記底部は孔無しの一体であってもよい。 (6) As another aspect, the single crystal pulling crucible of the present invention is a single crystal pulling crucible formed of a carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material, which includes a cylindrical body and a bowl-shaped bottom. A first reinforcing layer that is aligned with the carbon fiber and is hung on the bottom, and a second reinforcing layer in which a carbon fiber sheet is annularly attached to a portion of the bottom adjacent to the body portion along the circumferential direction. The multi-layer structure may be provided with a third reinforcing layer in which the carbon fibers are aligned and wound along the circumferential direction of the body portion, and the bottom portion may be integrated with no holes.
上記(6)の構成によれば、フィラメントワインディング法によって形成された第1及び第3強化層によってルツボの底部を押し下げようとする力及びルツボの胴部を押し広げようとする力に対抗し、更に、前記第1及び第3強化層によって足らざる部分を炭素繊維シートの張り付けによって形成された第2強化層で補える。更に、ボウル状の底部に孔がないので、底部の全体が、より強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボとなっている。また、胴部に隣接する部分は、ルツボ底部の曲率半径が小さい湾曲部分に相当し、この部分を炭素繊維のシートによって厚み調整することができる。更に、第1、第2、第3強化層が、複数組重ねられているので、全体として強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボとなっている。 According to the configuration of (6), the first and third reinforcing layers formed by the filament winding method counteract the force that pushes down the bottom of the crucible and the force that pushes out the crucible body. Furthermore, the part which is not sufficient by the said 1st and 3rd reinforcement layer can be supplemented with the 2nd reinforcement layer formed by sticking of the carbon fiber sheet. Furthermore, since there are no holes in the bowl-shaped bottom, the entire bottom is a reinforced C / C composite crucible for single crystal pulling. Moreover, the part adjacent to the trunk | drum corresponds to the curved part with a small curvature radius of a crucible bottom part, and thickness adjustment of this part can be carried out with the sheet | seat of carbon fiber. Furthermore, since a plurality of first, second, and third reinforcing layers are stacked, a single crystal pulling crucible made of C / C composite material that is reinforced as a whole.
(7)他の観点として、本発明の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボは、シリンダ状の胴部とボウル状の底部とからなり、炭素繊維強化炭素複合材により形成された単結晶引き上げ用ルツボであって、前記炭素繊維を引き揃えて前記底部に掛けられた第1強化層と、前記底部のうち前記胴部に隣接する部分に炭素繊維シートを周方向に沿って環状に張りつけた第2強化層と、前記炭素繊維を引き揃えて前記胴部の周方向に沿って巻き付けた第3強化層との多層構造を備え、前記炭素繊維強化炭素複合材の表面には、熱分解炭素が含浸されるとともに被覆されているものであってもよい。 (7) As another aspect, the single crystal pulling crucible of the present invention is a single crystal pulling crucible formed of a carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material, which includes a cylindrical body and a bowl-shaped bottom. A first reinforcing layer that is aligned with the carbon fiber and is hung on the bottom, and a second reinforcing layer in which a carbon fiber sheet is annularly attached to a portion of the bottom adjacent to the body portion along the circumferential direction. A multilayer structure with a third reinforcing layer in which the carbon fibers are aligned and wound along the circumferential direction of the trunk portion, and the surface of the carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material is impregnated with pyrolytic carbon It may be coated.
上記(7)の構成によれば、フィラメントワインディング法によって形成された第1及び第3強化層によってルツボの底部を押し下げようとする力及びルツボの胴部を押し広げようとする力に対抗し、更に、前記第1及び第3強化層によって足らざる部分を炭素繊維シートの張り付けによって形成された第2強化層で補っている。更に、C/C複合材の表面に、熱分解炭素が含浸させられ被覆されているので、耐SiC化が向上したC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボとなっている。また、胴部に隣接する部分は、ルツボ底部の曲率半径が小さい湾曲部分に相当し、この部分を炭素繊維のシートによって厚み調整することができる。更に、第1、第2、第3強化層が、複数組重ねられているので、全体として強化されたC/C複合材製の単結晶引き上げ用ルツボとなっている。 According to the configuration of (7), the first and third reinforcing layers formed by the filament winding method counteract the force that pushes down the bottom of the crucible and the force that pushes the crucible body, Furthermore, the part which is not sufficient by the said 1st and 3rd reinforcement layer is supplemented with the 2nd reinforcement layer formed by sticking of the carbon fiber sheet. Furthermore, since the surface of the C / C composite material is impregnated with and coated with pyrolytic carbon, it is a crucible for pulling a single crystal made of a C / C composite material with improved SiC resistance. Moreover, the part adjacent to the trunk | drum corresponds to the curved part with a small curvature radius of a crucible bottom part, and thickness adjustment of this part can be carried out with the sheet | seat of carbon fiber. Furthermore, since a plurality of first, second, and third reinforcing layers are stacked, a single crystal pulling crucible made of C / C composite material that is reinforced as a whole.
以下本発明の実施例を図面に基づいて説明する。図1において、マンドレル11は、円筒部12と、円筒部12の一端で膨出する膨出部13と、円筒部12の他端の中心から突設された軸部14とからなる金属製である。円筒部12はルツボ胴部の内径に相当する外径を有し、ルツボ胴部よりやや長くなっている。膨出部13はルツボ底部の内側の湾曲形状に沿う湾曲した外周面を有している。このマンドレル11を制御された回転が可能な軸部14によって支持し、マトリックス前駆体が含浸された炭素繊維を供給するデリバリアイ部15を図示のようにマンドレル11の外周に沿って移動させると、ポーラ巻き、パラレル巻き、レベル巻き等のフィラメントワインディングが自在に行える。このとき、円筒部12の他端側の側面に巻き付けられる炭素繊維は捨て巻きとなる。他端側円周部で炭素繊維がすべる事があるので、ピンを設置してズレ止めを行う事がある。
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. In FIG. 1, a
図2により図1のマンドレルを用いて成形体を得るまでの工程を説明する。マンドレル11の表面に、樹脂等のマトリックス前駆体が含浸された2Dクロス21の一層を織り目が中心軸16に交差するように張りつける(第1工程)。この2Dクロス21を最内層とすることにより、内表面がフラットになる。つぎに、フィラメントワインディング法により、樹脂等のマトリックス前駆体を含浸させた炭素繊維をマンドレル11の外周に巻き付ける。まず、膨出部13の頂点17を通るポーラ巻き22を行う(第2工程)。このポーラ巻き22は、中心軸16に対する巻き付け角度が0°となるように巻き付けられるものであって、頂点17の部分に密に集まる。このポーラ巻き22によって、最内層の2Dクロス21が締めつけられる。つぎに、円筒部12の周方向に沿って巻き付けるパラレル巻き23を行う(第3工程)。このパラレル巻き23は、中心軸16に対する巻き付け角度が90°近くとなるように巻き付けられるものであって、ルツボ胴部の周方向強化層を形成する。
With reference to FIG. 2, a process until a molded body is obtained using the mandrel of FIG. 1 will be described. A layer of
つぎに、膨出部13のうち円筒部12に隣接する部分に、樹脂等のマトリックス前駆体が含浸された1Dプリプレグ又は2Dクロスのシート25の複数を環状に張り合わせる(第4工程)。この隣接部分は、ルツボ底部の曲率半径が小さい湾曲部分に相当し、厚み調整の為に張られる。シート25の炭素繊維の並ぶ方向を周方向とすることが好ましい。つぎに、膨出部13に掛けられ円筒部12に至るレベル巻き26を行う(第5工程)。このレベル巻き26は、中心軸16に対する巻き付け角度が0°〜10°なるように巻き付けられるものであって、ルツボ底部からルツボ胴部に至る軸方向強化層を形成する。このとき、膨出部13におけるレベル巻き26が頂点17に集中しないように、頂点17からの距離を変えた巻きかけを行い、膨出部13の大きな曲率半径の湾曲部分の全体に炭素繊維が通るように分散する。上述したパラレル巻き(第3工程)とシート張りつけ(第4工程)とレベル巻き(第5工程)の組み合わせにより、マンドレル11の外周に略均一厚みの組み合わせ層が形成される。マンドレル11の外周の成形体が所定厚みになるまで、第3〜第5工程による組み合わせ層を複数層重ねる。
Next, a plurality of 1D prepregs or
図3により、以上の成形工程(S1)につづく工程を説明する。成形体が巻き付けられたマンドレルのまま乾燥させる。マンドレル外周の成形体に外圧を付与しながら加熱し、マトリックス前駆体の樹脂を熱硬化させる(S2)。そして、図2のA線で成形体をカットすることにより、ルツボ状の一次成形体を得る。ルツボ状一次成形体を不活性ガス中で加熱し、一次炭素化を行う(S3)。更に、ピッチ含浸(S4)と二次炭素化(S5)を必要数繰り返し、含浸による高密度化を行う。所定の密度が得られると、黒鉛化を行う(S6)。ルツボの長さ及びルツボ底部の外周に必要な機械加工を施して(S7)、所定形状となった二次成形体を得る。さらに、不純物を除去する高純度化処理を行い、更に、必要に応じて、CVI(Chemical Vapor Impregnation) により熱分解炭素(PyrolyticCarbon)を二次成形体表面の細孔に含浸させるとともに、二次成形体表面に被覆させ(S8)、最終製品を得る(S9)。 With reference to FIG. 3, the process following the above molding process (S1) will be described. The mandrel around which the molded body is wound is dried. Heating is performed while applying external pressure to the molded body on the outer periphery of the mandrel, and the resin of the matrix precursor is thermoset (S2). And a crucible-shaped primary molded object is obtained by cutting a molded object by the A line of FIG. The crucible-shaped primary molded body is heated in an inert gas to perform primary carbonization (S3). Furthermore, pitch impregnation (S4) and secondary carbonization (S5) are repeated as many times as necessary to increase the density by impregnation. When a predetermined density is obtained, graphitization is performed (S6). Necessary machining is performed on the length of the crucible and the outer periphery of the crucible bottom (S7) to obtain a secondary molded body having a predetermined shape. Furthermore, a high-purity treatment is performed to remove impurities, and if necessary, the pores on the surface of the secondary molded body are impregnated with pyrolytic carbon by CVI (Chemical Vapor Impregnation) and secondary molding is performed. The body surface is coated (S8) to obtain a final product (S9).
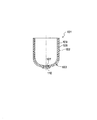
このようにして得られた単結晶引き上げ用ルツボの断面が図4に示される。ルツボ1は、シリンダ状の胴部2とボウル状の底部3の一体構造である。底部3は、胴部2に隣接する小さな曲率半径(R1)の湾曲部分4と、底部3の中心軸7の回りを形成する大きな曲率半径(R2)の湾曲部分5とからなっている。また底部3には孔がなく、機械加工による取付座6が形成されている。このようなルツボにあっては、底部3から胴部2にU字状に至る軸方向強化層8と胴部2の外周の周方向強化層9とを有している。このような単結晶引き上げ用ルツボ1に作用する応力の状態が図5に示される。ルツボ1の内部に石英ルツボ31が嵌められ、石英ルツボ31の中に少量のシリコン残渣32が残った状態で冷却される場合と、大きな応力がルツボ1に作用する。まず、シリコン残渣32の表面が固まり、次に底部に接する部分が固まり、やがて内部が固まっていく。ルツボ1は石英ルツボ31より熱膨張係数が大きく、また、シリコンは固体になる時に膨張するので、周方向に突っ張る力a1が発生し、つぎに下方向に突っ張る力a2が発生する。すなわち、胴部2には周方向の引っ張り応力b1以外に、底部3を胴部2から引き剥がそうとする軸方向の応力b2が発生する。周方向の引っ張り応力b1は、図4の周方向強化層9が受け持ち、軸方向の応力b2は、図4の軸方向強化層8が受け持つ。
A cross section of the single crystal pulling crucible thus obtained is shown in FIG. The
図6は、2個取りのマンドレル111を示す。マンドレル111は、右円筒部112Rと、右円筒部112Rの一端で膨出する右膨出部113Rと、左円筒部112Lと、左円筒部112Lの一端で膨出する左膨出部113Lと、右膨出部113Rの中心から突設された右軸部114Rと、左膨出部113Lの中心から突設された左軸部114Lとからなる金属製である。左右円筒部112R,112Lはルツボ胴部の内径に相当する外径を有し、ルツボ胴部の二倍よりやや長くなっている。左右膨出部113R,113Lはルツボ底部の内側の湾曲形状に沿う湾曲した外周面を有している。このマンドレル111を、制御された回転が可能な左右軸部114R,114Lによって支持し、マトリックス前駆体が含浸された炭素繊維を供給するデリバリアイ部115を図示のようにマンドレル111の外周に沿って移動させる。
FIG. 6 shows a two-
図7は、2個取りのマンドレル111で成形体を得る工程を示す。マンドレル111の表面に、樹脂等のマトリックス前駆体が含浸された2Dクロス121の一層を織り目が中心軸116に交差するように張りつける(第1工程)。つぎに、左右膨出部113R,113Lに掛けられ左右円筒部112R,112Lに至るレベル巻き122を行う(第2工程)。このレベル巻き122は、中心軸116に対する巻き付け角度が0°〜10°なるように巻き付けられるものであって、ルツボ底部からルツボ胴部に至る軸方向強化層を形成する。このとき、左右膨出部113R,113Lにおけるレベル巻き122が左右軸部114R,114Lの回りで散らばるような巻きかけを行い、左右膨出部113R,Lの全体に炭素繊維が通るようにする。つぎに、左右円筒部112R,112Lの周方向に沿って巻き付けるパラレル巻き123を行う(第3工程)。このパラレル巻き123は、中心軸116に対する巻き付け角度が90°近くとなるように巻き付けられるものであって、ルツボ胴部の周方向強化層を形成する。
FIG. 7 shows a process of obtaining a molded body with a two-
つぎに、左右膨出部113R,113Lのうち左右円筒部112R,112Lに隣接する部分に、樹脂等のマトリックス前駆体が含浸された1Dプリプレグ又は2Dクロスのシート125の複数を環状に張り合わせる(第4工程)。この隣接部分は、ルツボ底部の曲率半径が小さい湾曲部分に相当し、厚み調整の為に張られる。シート125の炭素繊維の並ぶ方向を周方向とすることが好ましい。上述したレベル巻き(第2工程)とパラレル巻き(第3工程)とシート張りつけ(第4工程)との組み合わせにより、マンドレル111の外周に略均一厚みの組み合わせ層が形成される。マンドレル111の外周の成形体が所定厚みになるまで、第2〜第4工程による組み合わせ層を複数層重ねる。
Next, a plurality of 1D prepreg or
このようにして得られたルツボの断面図が図8に示される。ルツボ101がシリンダ状の胴部102とボウル状の底部103の一体構造である点は図4と同様である。底部103の中心には、マンドレル111の左右軸部114R,114Lを通すための孔107が存在している。この孔107は、栓110が挿入されることによって塞がれる。その時、孔107を形成する面と、この面と接触する部分の栓の側面にそれぞれ雌ネジ、雄ネジを加工して栓110を取り付けてもよい。また、孔107を形成する面と、この面と接触する部分の栓の側面とを互いに係合するテーパ状としてもよいし、単にストレートな円筒状と円柱状の面としてもよい。したがって、軸方向強化層108は、孔107を迂回するようなU字状で掛け渡されている。周方向強化層109は図4と同様に胴部102の外周に沿うように配設されている。底部103特に孔107の回りの応力は、図4の孔無しに比較して大きくなるものの、マンドレル111の軸部の存在により、二個取りや効率的なワインディングが可能になる。
A cross-sectional view of the crucible thus obtained is shown in FIG. The
また、孔無しのルツボを二個同時に製作するためには、第1図に示した2個のマンドレル11を第9図(a)及び第9図(b)に示すように、駆動装置20を介して左右対称に連結するとよい。第9図(a)及び第9図(b)において、駆動装置20は左右両方に突き出した回転軸14a、14bを有する。この回転軸14a、14bによって2個のマンドレル11は支持されている。第9図(a)においては、マトリックス前駆体が含浸された炭素繊維を供給するための2個のデリバリアイ部15が、駆動装置20を介して点対称に配置されている。そして、それぞれのデリバリアイ部15をそれぞれのマンドレル11の外周に沿って移動させると、ポーラ巻き、パラレル巻き、レベル巻き等のフィラメントワインディングが自在に行える。第9図(b)においては、マトリックス前駆体が含浸された炭素繊維を供給するための2個のデリバリアイ部15が、駆動装置20を介して線対称に配置されている。そして、それぞれのデリバリアイ部15をそれぞれのマンドレル11の外周に沿って移動させると、ポーラ巻き、パラレル巻き、レベル巻き等のフィラメントワインディングが自在に行える。
In order to manufacture two crucibles without holes at the same time, the two
さらに、具体的実施例について説明する。 Further, specific examples will be described.
(実施例1)
図1のマンドレルを使用し、マンドレル表面にトレカT−300 6K 平織りクロス(東レ(株)製)にフェノール樹脂を含浸したものを1層張りつけ、その上にフィラメントワインディングを施した。フィラメントワインディングは、トレカT−300 12K(東レ(株)製)フィラメント6本にフェノール樹脂を含浸させながら、レベル巻き、中心軸に対する巻き付け角が85°〜90°のパラレル巻きを交互に3層づつ巻き付けた。胴部はパラレル巻きとレベル巻きの6層になるが、底部はレベル巻きだけになるので、パラレル巻きを行った後に、底部のうち胴部との隣接部分に、1Dプリプレグを扇状に裁断したものを一枚一枚張り合わせて環状にした。これらにより層厚み7mmの成形体が得られた。つぎに、オーブン中にて100°Cで揮発分調整を行ったのち、真空パックを被せて真空引きをしながら、オーブンの温度を200°Cまで上げて成形体を熱硬化させた。熱硬化後、マンドレルから取り外し、ルツボ状成形体を得た。つぎに、胴部の真円度を保つために、黒鉛製の変形防止用治具を取付け、電気炉で窒素注入しながら10°C/hrの昇温で1000°Cまで昇温し、C/C複合材を得た。
Example 1
The mandrel shown in FIG. 1 was used, and one layer of TORAYCA T-300 6K plain weave cloth (manufactured by Toray Industries, Inc.) impregnated with phenolic resin was applied to the mandrel surface, and filament winding was performed thereon. Filament winding consists of 6 layers of TORAYCA T-300 12K (manufactured by Toray Industries, Inc.), impregnated with phenol resin, level winding, and 3 layers of parallel winding with a winding angle of 85 ° to 90 ° with respect to the central axis. I wrapped it. The body part has 6 layers of parallel winding and level winding, but the bottom part is only level winding, so after performing parallel winding, 1D prepreg is cut into a fan shape on the bottom part adjacent to the body part Each piece was bonded to form a ring. As a result, a molded body having a layer thickness of 7 mm was obtained. Next, after adjusting the volatile content at 100 ° C. in an oven, the temperature of the oven was raised to 200 ° C. while vacuuming with a vacuum pack, and the molded body was thermally cured. After thermosetting, it was removed from the mandrel to obtain a crucible-like molded body. Next, in order to maintain the roundness of the body, a graphite deformation prevention jig is attached, and the temperature is raised to 1000 ° C. at a temperature of 10 ° C./hr while nitrogen is injected in an electric furnace. A / C composite material was obtained.
また、ピッチ含浸と焼成を4回繰り返して緻密化を行った。更に最終熱処理として黒鉛製の変形防止用治具を取付けたまま、窒素気流中で2000°Cの熱処理を行った。そののち、ルツボ底部の機械加工を施し、更に高純度化処理のために、真空炉にセットし、2000°Cまで加熱したのち、塩素ガスを供給し、炉内圧力10torrで20時間キープした。更に、熱分解炭素の含浸及び被覆のために、真空炉内にセットし、メタンガスを供給し、炉内圧力25torrで100時間キープし、CVI法の熱分解炭素によるC/C複合材の緻密化処理を行い最終製品を得た。このCVI処理によって、C/C複合材のかさ密度は1.6から1.7に上昇し、気孔率が20%から14.5%に下がった。このようにして得られたC/C複合材製のルツボを単結晶引き上げ装置に使用した。単結晶引き上げ操業毎に使い捨てされる石英ルツボ底部に割れが発生し、C/C複合材製ルツボの胴部及び底部共に強度があることが確認された。また、C/C複合材製ルツボの内面についても、熱分解炭素によりSiO2 との反応が抑制されており、30回の操業回数で底部のうち胴部に隣接する部分に多少の損耗が見られただけである。 Moreover, pitch impregnation and firing were repeated four times for densification. Further, as a final heat treatment, a heat treatment at 2000 ° C. was performed in a nitrogen stream while a graphite deformation preventing jig was attached. After that, the bottom of the crucible was machined, and further set in a vacuum furnace for high-purification treatment, heated to 2000 ° C., supplied with chlorine gas, and kept at a furnace pressure of 10 torr for 20 hours. Furthermore, for impregnation and coating of pyrolytic carbon, it is set in a vacuum furnace, methane gas is supplied, the pressure in the furnace is kept at 25 torr for 100 hours, and the C / C composite is densified by pyrolytic carbon of the CVI method. Processing was performed to obtain the final product. This CVI treatment increased the bulk density of the C / C composite from 1.6 to 1.7 and the porosity from 20% to 14.5%. The crucible made of C / C composite material thus obtained was used for a single crystal pulling apparatus. Cracks occurred at the bottom of the quartz crucible that was disposed of every single crystal pulling operation, and it was confirmed that both the body and bottom of the C / C composite crucible had strength. Also, the inner surface of the C / C composite material crucible also suppresses the reaction with SiO 2 due to pyrolytic carbon, and some wear is observed in the portion of the bottom adjacent to the trunk after 30 operations. It was only done.
(実施例2)
図7のようなマンドレルを使用し、ルツボ底部に孔が存在すること以外は実施例1と同様である。軽くて堅牢であるというハンドリング性に優れるという点と、SiO2 との反応の抑制という点は実施例1と同じである。ただし、実施例1と同じ30回の操業回数で底部の孔の周辺に亀裂の兆候が見られた。
(Example 2)
Example 1 is the same as Example 1 except that a mandrel as shown in FIG. 7 is used and a hole is present at the bottom of the crucible. It is the same as in Example 1 in that it is light and robust and has excellent handling properties and the suppression of reaction with SiO 2 . However, signs of cracks were observed around the hole at the bottom in the same 30 operations as in Example 1.
(比較例1)
図7に示すマンドレルを用い、ヘリカル巻きとパラレル巻きのみの組合せでルツボ形状の成形を行った。ヘリカル巻きは、炭素繊維糸がずれてしまい実施例2程に回転軸近傍まで巻き付けることが出来なかった。結果として実施例より底孔の大きなルツボとなった。パラレル巻きはヘリカル巻きと交互に行い、実施例1,2と同様に行った。また、CVI処理も同様に行い、同様な密度増加が得られた。しかし、実際の操業においては、底孔が大きいため毎回軟化した石英ルツボが底孔を塞いでいた栓を押し出す形で変形し、操業後は、必ずと言ってよいくらいルツボ自体が傾いていた。実施例1,2と同じ30回の操業回数では毎回の石英ルツボの変形による応力が大きかったためか亀裂が発生していた。
(Comparative Example 1)
Using the mandrel shown in FIG. 7, a crucible shape was formed by a combination of only helical winding and parallel winding. In helical winding, the carbon fiber yarn was displaced and could not be wound to the vicinity of the rotating shaft as in Example 2. As a result, a crucible having a larger bottom hole than that of the example was obtained. Parallel winding was performed alternately with helical winding, and was performed in the same manner as in Examples 1 and 2. Also, the CVI treatment was performed in the same manner, and a similar increase in density was obtained. However, in actual operation, since the bottom hole was large, the quartz crucible that was softened every time was deformed by pushing out the plug that had blocked the bottom hole, and after the operation, the crucible itself was tilted to the extent that it could be said. In the same number of operations as in Examples 1 and 2, cracks occurred because the stress due to deformation of the quartz crucible was large each time.
なお、本発明は、特許請求の範囲を逸脱しない範囲で設計変更できるものであり、上記実施形態や実施例に限定されるものではない。 The present invention can be changed in design without departing from the scope of the claims, and is not limited to the above-described embodiments and examples.
12 円筒部
13 膨出部
16 中心軸
17 頂点
21 クロス
22 ポーラ巻き
23 パラレル巻き
25 シート
26 レベル巻き
12
Claims (6)
前記第1強化層と前記第2強化層と前記第3強化層の組み合わせが、複数組重ねられてなる単結晶引き上げ用ルツボ。 A crucible for pulling a single crystal formed of a carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material, comprising a cylinder-shaped body and a bowl-shaped bottom, and aligns the carbon fibers and hangs on the bottom to reach the body The first reinforcing layer wound in the above manner, the second reinforcing layer in which a plurality of the carbon fiber sheets are annularly attached to the portion of the bottom adjacent to the body portion, and the carbon fibers are aligned, A third reinforcing layer wound around the circumferential direction of the trunk,
A crucible for pulling a single crystal, in which a plurality of combinations of the first reinforcing layer, the second reinforcing layer, and the third reinforcing layer are stacked.
前記底部が孔無しの一体であるとともに、
前記第1強化層と前記第2強化層と前記第3強化層の組み合わせが、複数組重ねられてなることを特徴とする単結晶引き上げ用ルツボ。 A crucible for pulling up a single crystal, which is formed of a carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material, and includes a cylinder-shaped body portion and a bowl-shaped bottom portion. The first reinforcing layer is formed by aligning the carbon fibers and hanging on the bottom portion. And a second reinforcing layer in which a carbon fiber sheet is annularly attached to a portion of the bottom adjacent to the body portion along the circumferential direction, and the carbon fibers are aligned and wound along the circumferential direction of the body portion. A multilayer structure with a third reinforcing layer,
The bottom is integral with no holes,
A crucible for pulling a single crystal, wherein a plurality of combinations of the first reinforcing layer, the second reinforcing layer, and the third reinforcing layer are stacked.
前記炭素繊維強化炭素複合材の表面には、熱分解炭素が含浸されるとともに被覆され、
前記第1強化層と前記第2強化層と前記第3強化層の組み合わせが、複数組重ねられてなることを特徴とする単結晶引き上げ用ルツボ。 A crucible for pulling up a single crystal, which is formed of a carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material, and includes a cylinder-shaped body portion and a bowl-shaped bottom portion. The first reinforcing layer is formed by aligning the carbon fibers and hanging on the bottom portion. And a second reinforcing layer in which a carbon fiber sheet is annularly attached to a portion of the bottom adjacent to the body portion along the circumferential direction, and the carbon fibers are aligned and wound along the circumferential direction of the body portion. A multilayer structure with a third reinforcing layer,
The surface of the carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite is impregnated with pyrolytic carbon and coated,
A crucible for pulling a single crystal, wherein a plurality of combinations of the first reinforcing layer, the second reinforcing layer, and the third reinforcing layer are stacked.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007190416A JP4686509B2 (en) | 1996-06-27 | 2007-07-23 | Single crystal pulling crucible |
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP18816096 | 1996-06-27 | ||
| JP1996188160 | 1996-06-27 | ||
| JP28013896 | 1996-09-30 | ||
| JP1996280138 | 1996-09-30 | ||
| JP2007190416A JP4686509B2 (en) | 1996-06-27 | 2007-07-23 | Single crystal pulling crucible |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP17136597A Division JP4029147B2 (en) | 1996-06-27 | 1997-06-27 | Single crystal pulling crucible and manufacturing method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007314421A JP2007314421A (en) | 2007-12-06 |
| JP4686509B2 true JP4686509B2 (en) | 2011-05-25 |
Family
ID=38848627
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007190416A Expired - Lifetime JP4686509B2 (en) | 1996-06-27 | 2007-07-23 | Single crystal pulling crucible |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4686509B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007314420A (en) * | 1996-06-27 | 2007-12-06 | Toyo Tanso Kk | Crucible for pulling single crystal |
| US20110124253A1 (en) * | 2009-11-23 | 2011-05-26 | Applied Nanostructured Solutions, Llc | Cnt-infused fibers in carbon-carbon composites |
| EP2531558B1 (en) | 2010-02-02 | 2018-08-22 | Applied NanoStructured Solutions, LLC | Carbon nanotube-infused fiber materials containing parallel-aligned carbon nanotubes, methods for production thereof, and composite materials derived therefrom |
| US9017854B2 (en) | 2010-08-30 | 2015-04-28 | Applied Nanostructured Solutions, Llc | Structural energy storage assemblies and methods for production thereof |
| CN114656271A (en) * | 2022-04-19 | 2022-06-24 | 浙江德鸿碳纤维复合材料有限公司 | Carbon-carbon crucible and preparation method thereof |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0312299A (en) * | 1989-06-12 | 1991-01-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Water purifying apparatus |
| JPH0429147A (en) * | 1990-05-24 | 1992-01-31 | Dainippon Ink & Chem Inc | Photosensitive composition |
| JPH0760859A (en) * | 1993-08-25 | 1995-03-07 | Nitto Denko Corp | Molding method for container |
| JPH0769777A (en) * | 1993-07-30 | 1995-03-14 | Schunk Kohlenstofftechnik Gmbh | Crucible, especially support crucible |
| JPH07206535A (en) * | 1993-12-29 | 1995-08-08 | Osaka Gas Co Ltd | Fiber-reinforced refractory structure and ts production |
| JPH09286689A (en) * | 1996-04-24 | 1997-11-04 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | Graphite crucible for pulling up single crystal and its manufacture |
| WO1998055238A1 (en) * | 1997-06-03 | 1998-12-10 | Hitco Carbon Composites, Inc. | High purity composite useful as a susceptor |
| JP2007314420A (en) * | 1996-06-27 | 2007-12-06 | Toyo Tanso Kk | Crucible for pulling single crystal |
-
2007
- 2007-07-23 JP JP2007190416A patent/JP4686509B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0312299A (en) * | 1989-06-12 | 1991-01-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Water purifying apparatus |
| JPH0429147A (en) * | 1990-05-24 | 1992-01-31 | Dainippon Ink & Chem Inc | Photosensitive composition |
| JPH0769777A (en) * | 1993-07-30 | 1995-03-14 | Schunk Kohlenstofftechnik Gmbh | Crucible, especially support crucible |
| JPH0760859A (en) * | 1993-08-25 | 1995-03-07 | Nitto Denko Corp | Molding method for container |
| JPH07206535A (en) * | 1993-12-29 | 1995-08-08 | Osaka Gas Co Ltd | Fiber-reinforced refractory structure and ts production |
| JPH09286689A (en) * | 1996-04-24 | 1997-11-04 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | Graphite crucible for pulling up single crystal and its manufacture |
| JP2007314420A (en) * | 1996-06-27 | 2007-12-06 | Toyo Tanso Kk | Crucible for pulling single crystal |
| WO1998055238A1 (en) * | 1997-06-03 | 1998-12-10 | Hitco Carbon Composites, Inc. | High purity composite useful as a susceptor |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2007314421A (en) | 2007-12-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0913504B1 (en) | Crucible for crystal pulling and method of manufacturing same | |
| JP4029147B2 (en) | Single crystal pulling crucible and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4686509B2 (en) | Single crystal pulling crucible | |
| JP4700218B2 (en) | A crucible made of carbon fiber reinforced carbon composite material for single crystal pulling | |
| CN113151893A (en) | Fiber bowl-shaped preform, carbon-carbon bowl body and crucible comprising same | |
| JP4634419B2 (en) | Single crystal pulling crucible | |
| JP2012254916A (en) | Carbon fiber-reinforced carbon composite cylindrical member, method of manufacturing carbon fiber-reinforced carbon composite cylindrical member, carbon fiber-reinforced carbon composite material crucible, and method of manufacturing carbon fiber-reinforced carbon composite material crucible | |
| JP4686508B2 (en) | Single crystal pulling crucible | |
| JP4634420B2 (en) | Method for producing crucible for pulling single crystal | |
| JP2007314420A (en) | Crucible for pulling single crystal | |
| JPH1160373A (en) | Crucible for pulling up single crystal | |
| JP4018503B2 (en) | Single crystal pulling crucible | |
| KR100694913B1 (en) | A method of manufacturing a thermostructural composite material bowl, in particular for an installation that produces silicon single crystals | |
| JPH11255587A (en) | Carbon-fiber reinforced carbonaceous material crucible for pulling single crystal and its production | |
| JPH09286689A (en) | Graphite crucible for pulling up single crystal and its manufacture | |
| US20100048073A1 (en) | Expanded graphite sheet, method of protecting carbonaceous crucible using the expanded graphite sheet, and single-crystal pulling apparatus | |
| CN214193511U (en) | Crucible with supporting structure | |
| JPH10167879A (en) | Crucible for pulling up single crystal | |
| JPH10245275A (en) | Production of carbon fiber-reinforced raw material using graphite mold | |
| JP2000086382A (en) | C/c crucible for pulling single crystal | |
| JP4170426B2 (en) | High temperature member for single crystal pulling apparatus and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2000185995A (en) | Crucible for pulling up single crystal made of carbon- fiber reinforced carbon composite material | |
| JPH10167878A (en) | Crucible for single crystal pulling | |
| JP2000290093A (en) | Carbon crucible for single crystal pulling-up | |
| JP4674887B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of large optical fiber preform |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20080128 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A132 Effective date: 20101116 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110117 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110208 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110214 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140218 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |