JP4635665B2 - Liquid concentration control method - Google Patents
Liquid concentration control method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4635665B2 JP4635665B2 JP2005076198A JP2005076198A JP4635665B2 JP 4635665 B2 JP4635665 B2 JP 4635665B2 JP 2005076198 A JP2005076198 A JP 2005076198A JP 2005076198 A JP2005076198 A JP 2005076198A JP 4635665 B2 JP4635665 B2 JP 4635665B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- concentration
- control method
- replenishment
- liquid
- water
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Cleaning And De-Greasing Of Metallic Materials By Chemical Methods (AREA)
Description
本発明は、タンク内の液濃度を制御する液濃度制御方法に関し、特に濃度計の監視機能を備えた液濃度制御方法に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a liquid concentration control method for controlling the liquid concentration in a tank, and particularly to a liquid concentration control method having a monitoring function of a concentration meter.
一般に、濃度計で濃度を検出して水と薬剤を補給する濃度制御においては、濃度が濃い場合は、濃度計の濃度測定値が所定の濃度になるまで水を補給し、濃度が薄い場合は、濃度計の濃度測定値が所定の濃度になるまで薬剤を補給する方法が行われている。また、濃度計の濃度測定値が正常がどうかの判断は、上下限チェックで行われている。 In general, in concentration control where the concentration is detected by a concentration meter and water and chemicals are replenished, if the concentration is high, water is replenished until the concentration measurement value of the concentration meter reaches a predetermined concentration, and if the concentration is low A method of replenishing medicine until the concentration measurement value of the densitometer reaches a predetermined concentration is performed. Further, whether or not the concentration measurement value of the densitometer is normal is determined by an upper and lower limit check.
例えば、特許文献1ないし特許文献3には、冷延鋼鈑や熱延鋼鈑といった処理鋼鈑の酸洗処理における連続酸洗槽の酸洗液の液濃度制御方法が開示されている。酸洗液濃度が濃い場合は、濃度計の濃度測定値が所定の濃度になるまで純水を補給し、濃度が薄い場合は、濃度計の濃度測定値が所定の濃度になるまで塩酸、硫酸などの酸液を補給するものである。
しかしながら、上下限チェックによる濃度測定値の正常判定と、特許文献1ないし特許文献3で開示された濃度制御の組み合わせでは、何らかの原因(例えば、電磁濃度計の測定コイルの穴が不純物によって詰まった)により、濃度測定値が上下限チェック内で変化しなくなった場合は、水または薬剤を投入しつづけることになってしまうという問題がある。従来のこの場合の検出方法は、レベルが異常に高くなって初めてレベル異常として解るものであった。 However, in the combination of the normal determination of the concentration measurement value by the upper and lower limit check and the concentration control disclosed in Patent Documents 1 to 3, for some reason (for example, the hole of the measuring coil of the electromagnetic densitometer is clogged with impurities) Thus, when the concentration measurement value does not change within the upper and lower limit checks, there is a problem that water or a medicine is continuously added. The conventional detection method in this case is understood as a level abnormality only when the level becomes abnormally high.
本発明は、上記事情に鑑みてなされたもので、上記課題を解決して、濃度計の監視機能を備えた液濃度制御方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to solve the above problems and provide a liquid concentration control method having a monitoring function of a concentration meter.
本発明の請求項1に係る発明は、濃度計による濃度測定値に基づいて水と薬剤を補給することにより、タンク内の液濃度を制御する液濃度制御方法において、前記濃度測定値と予め定められた濃度目標値との差である濃度偏差を求め、該濃度偏差に基づいて水または薬剤の必要補給量を求め、該必要補給量を複数回に分割補給するとともに、それぞれの分割補給後に前記濃度計の異常判定を行うことを特徴とする液濃度制御方法である。
また本発明の請求項2に係る発明は、請求項1に記載の液濃度制御方法において、前記異常判定は、分割補給する前後の濃度測定値に基づいて行うことを特徴とする液濃度制御方法である。
さらに本発明の請求項3に係る発明は、請求項1または請求項2に記載の液濃度制御方法において、前記タンクは酸洗処理用のタンクであり、前記薬剤は酸液であることを特徴とする液濃度制御方法である。
The invention according to claim 1 of the present invention is a liquid concentration control method for controlling a liquid concentration in a tank by replenishing water and chemicals based on a concentration measurement value obtained by a densitometer. A concentration deviation that is a difference from the obtained concentration target value is obtained, a necessary replenishment amount of water or medicine is obtained based on the concentration deviation, and the necessary replenishment amount is divided and replenished a plurality of times, and after each divided replenishment, A liquid concentration control method is characterized in that abnormality determination of a concentration meter is performed.
According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the liquid concentration control method according to the first aspect, the abnormality determination is performed based on a concentration measurement value before and after divided replenishment. It is.
Furthermore, the invention according to claim 3 of the present invention is the liquid concentration control method according to claim 1 or 2, wherein the tank is a tank for pickling treatment and the chemical is an acid solution. This is a liquid concentration control method.
本発明によれば、液濃度を所定の濃度にするために必要な水または薬剤の補給量を計算し、その補給量と予め決めた分割補給比率から分割補給量を計算するようにしたので、濃度計が正常な場合は液濃度を高精度で制御でき、濃度計が異常になった場合は水または薬剤の過剰補給を最小限に抑え異常の早期発見・対策ができる。また、濃度計の異常監視として分割補給前と補給後の濃度変化を監視するようにしたので、濃度測定値が上下限外れにはなっていないケースにおいても対応できる。 According to the present invention, the replenishment amount of water or chemicals necessary for setting the liquid concentration to a predetermined concentration is calculated, and the divided replenishment amount is calculated from the replenishment amount and a predetermined divided replenishment ratio. When the densitometer is normal, the liquid concentration can be controlled with high accuracy, and when the densitometer becomes abnormal, it is possible to detect and take countermeasures early by minimizing excessive supply of water or chemicals. Further, since the concentration change is monitored before and after the replenishment as an abnormality monitoring of the densitometer, it is possible to cope with a case where the concentration measurement value does not deviate from the upper and lower limits.
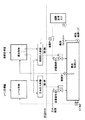
以下、本発明を実施するための最良の形態について、図面を参照して説明する。図1は、本発明を実施するための酸洗液の制御構成の一例を示した図である。酸洗循環タンクへの工水および塩酸投入量を制御するために、工水配管および塩酸原液タンクからの配管に操作端として流量調整弁がそれぞれに設けられている。そして、それぞれの流量調整弁を調整すべく、計装DCSに工水投入制御および塩酸投入制御の機能を持たせている。さらに、この上位には本発明に係る濃度制御、およびレベル制御の機能があり、工水投入制御および塩酸投入制御を統括する構成となっている。 The best mode for carrying out the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an example of a control configuration of pickling liquid for carrying out the present invention. In order to control the amount of industrial water and hydrochloric acid input to the pickling circulation tank, flow control valves are provided as operation ends in the industrial water piping and the piping from the hydrochloric acid stock solution tank, respectively. And in order to adjust each flow regulating valve, the instrumentation DCS is provided with functions of industrial water charging control and hydrochloric acid charging control. Further, the upper level has functions of concentration control and level control according to the present invention, and is configured to supervise industrial water charging control and hydrochloric acid charging control.
レベル制御と濃度制御の関係は、レベル制御ではレベル設定値と下限レベル値の範囲を大きく取るようにし、レベルがこの下限レベル値を下回った場合のみレベル制御が働く。本発明の濃度制御は、レベル制御が働いていない場合、すなわちレベル制御の下限レベル値以上で働くようにしている。ただし、レベルが上限値超えの場合にも濃度制御は行わない。 As for the relationship between level control and density control, the level control takes a large range between the level setting value and the lower limit level value, and the level control works only when the level falls below the lower limit level value. The density control according to the present invention works when the level control is not working, that is, when the level control is above the lower limit level value. However, density control is not performed even when the level exceeds the upper limit.
計測器としては、レベル制御では酸洗循環タンクに設けたレベル計を、濃度制御では酸洗循環タンクに設けた濃度計、および塩酸原液タンクからの配管に設けた流量計を使用している。なお、図示していないが工水用の流量計を設けるようにしてもよい。 As the measuring device, a level meter provided in the pickling circulation tank is used for level control, and a concentration meter provided in the pickling circulation tank and a flow meter provided in piping from the hydrochloric acid stock solution tank are used for concentration control. Although not shown, a flow meter for industrial water may be provided.
濃度制御が自動、かつ、濃度制御インターロック条件(後述する)で無い、かつ、濃度偏差(濃度測定値−濃度目標値)が濃度制御開始偏差を超えた時に以下の処理を行う。なお、図1の工水および塩酸を、以下では水および薬剤にそれぞれ読み替えて説明する。 The following processing is performed when the density control is automatic, the density control interlock condition (described later) is not satisfied, and the density deviation (density measurement value−density target value) exceeds the density control start deviation. In the following description, the construction water and hydrochloric acid in FIG. 1 are replaced with water and chemicals, respectively.
Step1:濃度偏差から水または薬剤の必要補給量を求める((1)および(2)式)。
水の計算条件:濃度測定値>濃度目標値+α(水補給不感帯)の時
水必要補給量=レベル測定値×(濃度測定値−濃度目標値)/濃度目標値×タンク底面積・・・・・・・・(1)
薬剤の計算条件:濃度測定値<濃度目標値−β(薬剤補給不感帯)の時
薬剤必要補給量=レベル測定値×(濃度測定値−濃度目標値)/(濃度目標値−薬剤原液濃度)×タンク底面積・・・・・・・・・(2)
なお、上記α(水補給不感帯)およびβ(薬剤補給不感帯)は、濃度測定値の変化に制御系が余り敏感に反応しないように、対象プラント毎に予め決めておくものであり、具体的には、濃度管理範囲以内であり、かつ濃度のふらつき以上の濃度に設定するようにする。
Step1: Calculate the required replenishment amount of water or medicine from the concentration deviation (Equations (1) and (2)).
Water calculation conditions: Concentration measurement value> Concentration target value + α (Water replenishment dead zone) Required water replenishment amount = Level measurement value × (Concentration measurement value-Concentration target value) / Concentration target value × Tank bottom area (1)
Drug calculation condition: concentration measurement value <concentration target value−β (drug supply dead zone) required drug supply amount = level measurement value × (concentration measurement value−concentration target value) / (concentration target value−drug stock solution concentration) × Tank bottom area ... (2)
Note that α (water replenishment dead zone) and β (drug replenishment dead zone) are determined in advance for each target plant so that the control system does not react very sensitively to changes in concentration measurement values. Is set within a density control range and a density greater than the fluctuation of density.
Step2:水または薬剤の必要補給量と、予め決めておいた初回補給比率と分割補給比率によって、例えば以下の(3)および(4)式で、初回補給量と2回目以降の分割補給量を求める。なお、(3)および(4)式は例示であり、初回補給比率と分割補給比率は適宜変更可能であるとともに、最初の数回と残りの回数分に分けて、それぞれを等分割して補給するなど様々な分割方法が考えられ、いかなる分割補給の決め方であっても構わない。この例のように、分割補給比率は初回と2回目以降で別に持つようすれば、初回の補給量を多めにすることによって、濃度制御の完了を早めることができる効果がある。
初回の水または薬剤補給量=水または薬剤必要補給量×1/2・・・・・・・・(3)
2回目以降の水または薬剤補給量=(水または薬剤必要補給量−初回の水または薬剤補給量)×1/分割回数・・・・・・・・(4)
Step3:初回補給前の濃度測定値を記憶する。
Step2: Depending on the required replenishment amount of water or medicine, and the predetermined initial replenishment ratio and divided replenishment ratio, for example, the initial replenishment amount and the second and subsequent divided replenishment amounts are calculated by the following formulas (3) and (4). Ask. The formulas (3) and (4) are examples, and the initial supply ratio and the divided supply ratio can be changed as appropriate, and the supply is divided into equal parts in the first several times and the remaining number of times. Various division methods, such as, can be considered, and any division supply method may be determined. If the divided replenishment ratio is separately provided for the first time and the second and subsequent times as in this example, the completion of density control can be accelerated by increasing the initial replenishment amount.
Initial water or drug supply amount = Water or drug required supply amount x 1/2 (3)
Second or subsequent water or drug replenishment amount = (Necessary water or drug replenishment amount-First water or drug replenishment amount) × 1 / Number of divisions (4)
Step3: Store the concentration measurement value before the first replenishment.
Step4:水または薬剤を、Step2で計算した初回補給量分補給する。 Step4: Supply water or medicine for the initial replenishment amount calculated in Step2.
Step5:予め決めておいた時間待つ。(攪拌され濃度が安定するまでの時間)
Step6:判定する。
a.以下の場合は正常終了する。
水補給の場合:濃度測定値≦濃度目標値+α(水補給不感帯)
薬剤補給の場合:濃度測定値≧濃度目標値−β(薬剤補給不感帯)
b.以下の場合は、異常終了する(オペレーターヘの外部通知処理などを行う)。
Step3で記憶した濃度測定値と補給後の濃度測定値に変化が無い時
c.上記(a&b)以外は、以下のStep7以降を実行する。
Step5: Wait for a predetermined time. (Time until stirring and concentration stabilizes)
Step6: Judge.
a. Terminate normally if:
For water replenishment: measured concentration value ≤ concentration target value + α (water replenishment dead zone)
In the case of drug supply: measured concentration value ≥ target concentration value-β (drug supply dead zone)
b. Terminate abnormally in the following cases (external notification processing to the operator, etc.).
When there is no change in the concentration measurement value stored in Step 3 and the concentration measurement value after replenishment
c. Except for the above (a & b), the following Step 7 and subsequent steps are executed.
Step7:分割補給前の濃度測定値を記憶する。 Step7: Memorize the concentration measurement value before divided supply.
Step8:水または薬剤を、Step2で計算した分割補給量分補給する。 Step8: Supply water or medicine for the divided replenishment amount calculated in Step2.
Step9:予め決めておいた時間待つ。(撹拝され濃度が安定するまでの時間)
Step10:判定する。
a.以下の場合は正常終了する。
水補給の場合:濃度測定値≦濃度目標値+α
薬剤補給の場合:濃度測定値≧濃度目標値−β
b.以下の場合は、異常終了する(オペレーターヘの外部通知処理などを行う)。
・Step3で記憶した濃度測定値と補給後の濃度測定値に変化が無い時
・予め決めておいた分割補給回数を超えた時
c.上記(a&b)以外はStep7以降を繰り返す。
Step9: Wait for a predetermined time. (Time to stir and stabilize concentration)
Step10: Determine.
a. Terminate normally if:
For water replenishment: measured concentration value ≤ target concentration value + α
For drug replenishment: measured concentration value ≥ target concentration value-β
b. Terminate abnormally in the following cases (external notification processing to the operator, etc.).
・ When there is no change in the concentration measurement value memorized in Step 3 and the concentration measurement value after replenishment.
c. Repeat Step 7 and subsequent steps except for the above (a & b).
なお、濃度制御インターロック条件は設備によって異なるものの、例えば一般的な例として以下のいずれかで濃度制御インターロックとして濃度制御は実行しないこととするとよい。
(1)タンクの液面レベルが濃度計の測定可能レベル以下の時
(2)タンク内の液を攪拌していない時
(3)濃度計が異常(濃度測定値が上下限外れ)の時
(4)流量計が異常(流量測定値の振り下がり)の時
(5)温度測定値が、濃度計の温度補償範囲外の時
It should be noted that although the density control interlock condition varies depending on the facility, for example, as a general example, the density control may not be executed as the density control interlock in any of the following.
(1) When the liquid level in the tank is below the measurable level of the densitometer (2) When the liquid in the tank is not agitated (3) When the densitometer is abnormal (concentration measurement value is out of the upper and lower limits) ( 4) When the flow meter is abnormal (flow measurement drop) (5) When the temperature measurement value is outside the temperature compensation range of the densitometer
Claims (3)
前記濃度測定値と予め定められた濃度目標値との差である濃度偏差を求め、該濃度偏差に基づいて水または薬剤の必要補給量を求め、該必要補給量を複数回に分割補給するとともに、それぞれの分割補給後に前記濃度計の異常判定を行うことを特徴とする液濃度制御方法。 In the liquid concentration control method for controlling the liquid concentration in the tank by replenishing water and chemicals based on the concentration measurement value by the densitometer,
Obtaining a concentration deviation that is a difference between the measured concentration value and a predetermined concentration target value, obtaining a necessary replenishment amount of water or medicine based on the concentration deviation, and dividing the replenishment amount into a plurality of times A liquid concentration control method, wherein abnormality determination of the concentration meter is performed after each divided replenishment.
前記異常判定は、分割補給する前後の濃度測定値に基づいて行うことを特徴とする液濃度制御方法。 In the liquid concentration control method according to claim 1,
The liquid concentration control method according to claim 1, wherein the abnormality determination is performed based on concentration measurement values before and after divided replenishment.
前記タンクは酸洗処理用のタンクであり、
前記薬剤は酸液であることを特徴とする液濃度制御方法。 In the liquid concentration control method according to claim 1 or 2,
The tank is a tank for pickling treatment,
The liquid concentration control method, wherein the chemical is an acid liquid.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005076198A JP4635665B2 (en) | 2005-03-17 | 2005-03-17 | Liquid concentration control method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005076198A JP4635665B2 (en) | 2005-03-17 | 2005-03-17 | Liquid concentration control method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006257487A JP2006257487A (en) | 2006-09-28 |
| JP4635665B2 true JP4635665B2 (en) | 2011-02-23 |
Family
ID=37097068
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005076198A Expired - Fee Related JP4635665B2 (en) | 2005-03-17 | 2005-03-17 | Liquid concentration control method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4635665B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101834370B1 (en) * | 2016-11-04 | 2018-03-05 | 한호산업(주) | Detecting apparatus and method of quenching water density for high-frequency heat treatment |
| JP7072453B2 (en) * | 2018-06-29 | 2022-05-20 | 東京エレクトロン株式会社 | Board processing equipment and board processing method |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6130686A (en) * | 1984-07-19 | 1986-02-12 | Sumitomo Special Metals Co Ltd | Method for controlling automatically concentration of pickling solution |
| JP2763967B2 (en) * | 1991-04-17 | 1998-06-11 | 株式会社神戸製鋼所 | Method and apparatus for controlling acid concentration in jet pickling equipment |
| JPH06190389A (en) * | 1992-12-25 | 1994-07-12 | Meidensha Corp | Abnormality detectorof water treatment system |
| JPH09173903A (en) * | 1995-12-25 | 1997-07-08 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Dust concentration controller for electrostatic precipitator |
| JP3651407B2 (en) * | 2001-03-29 | 2005-05-25 | トヨタ車体株式会社 | Ozone water concentration meter abnormality judgment method |
| JP3885743B2 (en) * | 2003-02-24 | 2007-02-28 | 松下電工株式会社 | smoke detector |
-
2005
- 2005-03-17 JP JP2005076198A patent/JP4635665B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006257487A (en) | 2006-09-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5855791A (en) | Performance-based control system | |
| US8489240B2 (en) | Control system for industrial water system and method for its use | |
| CN101776258B (en) | For controlling the system and method for the liquid level in container | |
| EP2641027B1 (en) | Device and method for controlling opening of a valve in an hvac system | |
| EP2175224A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for controlling chemical feeding in cooling water system | |
| CA2308777C (en) | Method and apparatus for measurement and automatic control of acid concentration | |
| EP2453172A1 (en) | Liquid level control system | |
| WO2000039652A1 (en) | Performance-based control system | |
| US20090107921A1 (en) | Chemical treatment system and method | |
| JP4635665B2 (en) | Liquid concentration control method | |
| KR20220115624A (en) | A decarburization end point determination method, a decarburization end point determination apparatus, a steelmaking secondary refining operation method, and a manufacturing method of molten steel | |
| US20040238417A1 (en) | Machining fluid treating device for wire-cut electric discharge machine | |
| KR20150106831A (en) | Heat source device controller and air conditioning system | |
| GB1564648A (en) | Temperature contrl system for liquid plant | |
| JP5115145B2 (en) | Cogeneration system | |
| JP5714355B2 (en) | Activated sludge treatment apparatus and treatment method thereof | |
| EP4562359A1 (en) | Methods and systems for evaluating heat exchangers | |
| JP2020157327A (en) | Control method for outlet side temperature of finished steel sheet, control device therefor and production method for steel sheet | |
| JP2596831B2 (en) | Nutrient control system for hydroponics | |
| CN112083704A (en) | Chemical plant control loop performance quantitative evaluation method and machine readable storage medium | |
| JP6098601B2 (en) | Acid concentration control method, acid concentration control device, and metal plate manufacturing method | |
| KR100851221B1 (en) | Blast body temperature control device | |
| KR100476546B1 (en) | An Apparatus for Controlling Concentration of Releasing Solution by Using Load-cell | |
| CN110088559B (en) | Cooling tower adjusting method and system | |
| JP5050410B2 (en) | Acid concentration control method / apparatus for pickling process, and steel plate manufacturing method using them |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20060921 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080125 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20101018 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20101026 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20101108 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131203 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4635665 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |