JP4615266B2 - Polymer electrolyte fuel cell - Google Patents
Polymer electrolyte fuel cell Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4615266B2 JP4615266B2 JP2004222671A JP2004222671A JP4615266B2 JP 4615266 B2 JP4615266 B2 JP 4615266B2 JP 2004222671 A JP2004222671 A JP 2004222671A JP 2004222671 A JP2004222671 A JP 2004222671A JP 4615266 B2 JP4615266 B2 JP 4615266B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electrode
- pair
- seal member
- rib
- electrolyte membrane
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/30—Hydrogen technology
- Y02E60/50—Fuel cells
Landscapes
- Gasket Seals (AREA)
- Fuel Cell (AREA)
Description
本発明は、ポータブル電源、携帯機器用電源、電気自動車用電源および家庭内コージェネレーションシステムなどに使用する高分子電解質型燃料電池に関する。 The present invention relates to a polymer electrolyte fuel cell used for a portable power source, a power source for portable devices, a power source for electric vehicles, a home cogeneration system, and the like.
高分子電解質膜を用いた燃料電池は、水素を含有する燃料ガスと、空気などの酸素を含有する酸化剤ガスとを、電気化学的に反応させることにより、電力と熱とを同時に発生させる。この燃料電池は、水素イオンを選択的に輸送する高分子電解質膜、および高分子電解質膜の両面に形成された一対の電極、すなわちアノードとカソードから構成される。これを電解質膜電極接合体(MEA)と呼ぶ。前記電極は、白金系の金属触媒を担持したカーボン粉末を主成分とし、高分子電解質膜の両面に形成される触媒層、および前記触媒層の外面に形成される、通気性と電子導電性とを併せ持つガス拡散層からなる。 A fuel cell using a polymer electrolyte membrane generates electric power and heat simultaneously by electrochemically reacting a fuel gas containing hydrogen and an oxidant gas containing oxygen such as air. This fuel cell includes a polymer electrolyte membrane that selectively transports hydrogen ions, and a pair of electrodes formed on both sides of the polymer electrolyte membrane, that is, an anode and a cathode. This is called an electrolyte membrane electrode assembly (MEA). The electrode is mainly composed of carbon powder carrying a platinum-based metal catalyst, and has a catalyst layer formed on both surfaces of the polymer electrolyte membrane, and an air permeability and electronic conductivity formed on the outer surface of the catalyst layer. It consists of a gas diffusion layer having both.
つぎに、供給する燃料ガスおよび酸化剤ガス(反応ガス)が外にリークしたり、これら二種類の反応ガスが互いに混合したりしないように、電極の周囲には、高分子電解質膜を挟んでガスケット等のシール材が配置される。このシール材は、電極および高分子電解質膜と一体化してあらかじめ組み立てられ、これを、電解質膜電極シール材接合体(MESA)と呼ぶ。 Next, a polymer electrolyte membrane is sandwiched around the electrodes so that the fuel gas and oxidant gas (reactive gas) to be supplied do not leak out or the two kinds of reactive gases are mixed with each other. A sealing material such as a gasket is disposed. This sealing material is integrated with an electrode and a polymer electrolyte membrane and assembled in advance, and this is called an electrolyte membrane electrode sealing material assembly (MESA).
MEAの外側には、これを機械的に固定するとともに、隣接したMEAを互いに電気的に直列に接続する導電性のセパレータ板が配置される。セパレータ板は、電極面に反応ガスを供給し、生成ガスや余剰ガスを運び去るためのガス流路を有する。ガス流路は、セパレータ板と別に設けることもできるが、セパレータ板の表面に溝を設けてガス流路とする方式が一般的である。 Outside the MEA, a conductive separator plate that mechanically fixes the MEA and electrically connects adjacent MEAs to each other in series is disposed. The separator plate has a gas flow path for supplying reaction gas to the electrode surface and carrying away generated gas and surplus gas. Although the gas flow path can be provided separately from the separator plate, a method of providing a gas flow path by providing a groove on the surface of the separator plate is generally used.
この溝に反応ガスを供給するためは、反応ガスを供給する配管を、使用するセパレータ板の枚数に分岐し、その分岐先を直接セパレータ板上の溝につなぎ込むための治具が必要となる。この治具をマニホールドと呼び、上記のような反応ガスの供給配管から直接つなぎ込むタイプを外部マニホールドと呼ぶ。また、このマニホールドには、構造をより簡単にした内部マニホールドと呼ぶ形式のものがある。内部マニホールドとは、ガス流路を形成したセパレータ板に、貫通した孔を設け、ガス流路の出入り口をこの孔まで通し、この孔から直接反応ガスを供給するものである。 In order to supply the reaction gas to the groove, a jig for branching the piping for supplying the reaction gas to the number of separator plates to be used and connecting the branch destination directly to the groove on the separator plate is required. . This jig is called a manifold, and the type that connects directly from the reaction gas supply pipe as described above is called an external manifold. In addition, there is a type of this manifold called an internal manifold with a simplified structure. The internal manifold is a separator plate in which a gas flow path is formed with a through-hole, through the gas flow path to the hole, and a reaction gas is directly supplied from the hole.
燃料電池は運転中に発熱するので、電池を良好な温度状態に維持するためには、冷却水などで冷却する必要がある。そこで通常、単電池1〜3個毎に冷却水用の流路を設ける。一般的には、セパレータ板の背面に冷却水用の流路を設けて冷却部とする場合が多い。これらのMEAとセパレータ板とを交互に重ねていき、単電池10〜200個積層してスタックを得た後、そのスタックを集電板および絶縁板を介して端板で挟み、締結ボルトで両端から固定する。このようにして一般的な構造を有する高分子電解質型燃料電池が得られる。 Since fuel cells generate heat during operation, it is necessary to cool them with cooling water or the like in order to maintain the cells in a favorable temperature state. Therefore, a flow path for cooling water is usually provided for every 1 to 3 cells. In general, a cooling water flow path is often provided on the back surface of the separator plate to form a cooling unit. These MEAs and separator plates are alternately stacked to obtain a stack by stacking 10 to 200 single cells. Then, the stack is sandwiched between end plates through current collector plates and insulating plates, and both ends are fastened with fastening bolts. Secure from. In this way, a polymer electrolyte fuel cell having a general structure is obtained.
ところで、上記のような高分子電解質型燃料電池に用いられるシール材には、セパレータ板と電極とを接触させつつ、反応ガスをシールするため、高い寸法精度、充分な弾性および充分な締め代を有することが必要である。このため、従来のシール材としては、樹脂もしくはゴムなどからなるシート状のガスケット、またはゴムからなるOリング形状のガスケットなどが用いられている。 By the way, the sealing material used in the polymer electrolyte fuel cell as described above has high dimensional accuracy, sufficient elasticity, and sufficient tightening allowance to seal the reaction gas while contacting the separator plate and the electrode. It is necessary to have. For this reason, as a conventional sealing material, a sheet-like gasket made of resin or rubber, an O-ring shaped gasket made of rubber, or the like is used.
また、最近では、例えば、特許文献1および2に開示されているように、スタックの締結荷重を低減することにより構造部材の軽量化、簡素化および低コスト化を行うため、ガスケットのシールに必要な荷重を低減することが試みられている。また、ガスケットの断面形状も、Oリング形状だけでなく、三角形状または半円形状などとすることが試みられている。 Recently, for example, as disclosed in Patent Documents 1 and 2, it is necessary to seal a gasket in order to reduce the weight of the structural member, reduce the cost, and reduce the cost by reducing the stack fastening load. Attempts have been made to reduce the load. In addition, attempts have been made to make the sectional shape of the gasket not only an O-ring shape but also a triangular shape or a semicircular shape.
Oリング形状の断面を有し、かつある程度の大きさの断面積を有するガスケットを用いる場合は、当該ガスケットをセパレータ板側に構成することが試みられている。しかし、スタックにおいては、多数の単電池が積層されて締結されているため、信頼性良くシール性を確保するためには、上記ガスケットでは不充分であるという問題がある。
Oリング形状のガスケットを用いる場合、当該ガスケットにより電解質膜をセパレータ板に押し付けることによりシールする。そのため、アノード(燃料極)と電解質膜との間、およびカソード(酸化剤極)と電解質膜との間の、2カ所においてシールが必要であり、すなわち燃料ガスシール用のガスケットおよび酸化剤ガスシール用のガスケットが必要であり、シールしなければならない部位が大型化するという問題がある。
When using a gasket having an O-ring-shaped cross section and a cross-sectional area of a certain size, it has been attempted to configure the gasket on the separator plate side. However, since a large number of single cells are stacked and fastened in the stack, there is a problem that the gasket is insufficient to ensure a reliable sealing property.
When using an O-ring shaped gasket, the gasket is sealed by pressing the electrolyte membrane against the separator plate. Therefore, two seals are required between the anode (fuel electrode) and the electrolyte membrane and between the cathode (oxidant electrode) and the electrolyte membrane, that is, a gasket for the fuel gas seal and an oxidant gas seal. For this reason, there is a problem in that the size of the part that must be sealed increases.
さらに、Oリング形状のガスケットが入る溝をセパレータ板の表面に設ける必要があり、その溝の寸法を確保するためセパレータ板を薄くすることができないなどの制約がある。これにより、スタックの体積の増大、コストの増大、およびセパレータ板形状の複雑化をもたらし、セパレータ板加工時における歩留まりが悪化する原因となっていた。このような問題点を解消するため、省スペースでシールすることが試みられている。 Furthermore, it is necessary to provide a groove for receiving an O-ring shaped gasket on the surface of the separator plate, and there is a restriction that the separator plate cannot be thinned in order to ensure the dimension of the groove. As a result, the volume of the stack is increased, the cost is increased, and the shape of the separator plate is complicated, which is a cause of deterioration of the yield when processing the separator plate. In order to solve such problems, attempts have been made to seal in a space-saving manner.
また、スタックを組み付ける際、セパレータ板上にMESAまたはMEAを配し、さらにそのMEAの上にセパレータ板、またはOリング形状ガスケットとセパレータ板とを配する。この工程を繰り返してスタックを得る。その際、MEAの上に配するOリング形状ガスケットまたはセパレータ板は、一般的に組み付け用治具であるガイドを用いて配している。しかし、各部材には寸法誤差があり、電極と、Oリング形状ガスケットまたはセパレータ板との組み付け易さの観点から、Oリング形状ガスケットと電極との間には、クリアランスが必要である。このクリアランスは、作業性または製造の歩留まり確保するためのものでもある。 Further, when assembling the stack, MESA or MEA is arranged on the separator plate, and further, the separator plate or the O-ring shaped gasket and the separator plate are arranged on the MEA. This process is repeated to obtain a stack. At that time, the O-ring shaped gasket or separator plate arranged on the MEA is generally arranged using a guide which is an assembling jig. However, each member has a dimensional error, and a clearance is required between the O-ring shaped gasket and the electrode from the viewpoint of easy assembly between the electrode and the O-ring shaped gasket or the separator plate. This clearance is also for ensuring workability or manufacturing yield.
このクリアランスが小さい場合、信頼性高くスタックを組み付けることが困難な傾向にある。例えば、Oリング形状ガスケットが電極の一部に乗り上げて噛み、シール不良が生じる。また、電極にOリング形状ガスケットが接触することにより、電極に対して過大な面圧がかかり、電解質膜の破損や耐久性の低下などにより電池性能が低下する可能性がある。
したがって、Oリング形状ガスケットと電極との間のクリアランスを小さくする場合には、部品寸法の精度を向上させなければ、歩留まりの低下および部品コストの上昇を招いてしまう。特に、成形セパレータ板を用いる場合には、組み付け時に用いるガイドなどの加工精度に限界があることから、Oリング形状ガスケットと電極との間のクリアランスを低減させることが困難である。このため、成形によりセパレータ板を得た後、ガイド部分を後加工で追加しており、コストを要していた。
If this clearance is small, it tends to be difficult to assemble the stack with high reliability. For example, an O-ring shaped gasket rides on a part of the electrode and bites it, resulting in poor sealing. Further, when the O-ring-shaped gasket comes into contact with the electrode, an excessive surface pressure is applied to the electrode, and the battery performance may be deteriorated due to damage to the electrolyte membrane or a decrease in durability.
Therefore, when the clearance between the O-ring shaped gasket and the electrode is reduced, unless the accuracy of the component dimensions is improved, the yield is reduced and the component cost is increased. In particular, when a molded separator plate is used, it is difficult to reduce the clearance between the O-ring shaped gasket and the electrode because there is a limit to the processing accuracy of a guide or the like used during assembly. For this reason, after obtaining a separator plate by molding, a guide portion is added by post-processing, which requires cost.
一方、組み付け性を確保するために、Oリング形状ガスケットと電極との間のクリアランスを大きくすると、反応ガスがそのクリアランスに流れ込み、セパレータ板のガス流路に反応ガスが流れなくなる可能性がある。また、MEAおよびOリング形状ガスケットの組み付け誤差等により各単電池毎のクリアランスにばらつきが生じると、各単電池間の圧力損失にばらつきが生じてしまう。このとき、スタックにおいて各単電池の圧力損失に見合う反応ガスがそれぞれの単電池に流れるため、反応ガスの流量にばらつきが生じる。このため、各単電池間の電池性能がばらつき、発電電圧の低下、耐久性の低下、および低出力運転時の安定性の低下などの弊害が生じてしまう。これらの症状は、反応ガスの利用率が比較的大きい燃料ガス側で顕著であった。 On the other hand, if the clearance between the O-ring-shaped gasket and the electrode is increased in order to ensure assemblability, the reaction gas may flow into the clearance and the reaction gas may not flow into the gas flow path of the separator plate. Further, if the clearance for each unit cell varies due to an assembly error of the MEA and the O-ring shaped gasket, the pressure loss between the unit cells varies. At this time, the reaction gas corresponding to the pressure loss of each unit cell in the stack flows through each unit cell, so that the flow rate of the reaction gas varies. For this reason, the battery performance varies between the individual cells, and adverse effects such as a decrease in generated voltage, a decrease in durability, and a decrease in stability during low output operation occur. These symptoms were remarkable on the fuel gas side where the utilization rate of the reaction gas was relatively large.
また、平形状ガスケットを用いる場合は、ガスケットの占める体積を低減することは可能であるものの、上記のスタックの組み付けに関する問題やクリアランスに関する問題は、Oリング形状ガスケットの場合と同様に存在する。さらに、シールに必要な面圧を確保するためには、過大な締結力が必要となる。したがって、スタック締結部材の軽量化、コンパクト化、低コスト化が困難である。
そこで、本発明は、スタック組み付け時には、信頼性高く単電池を積層することができ、かつスタック締結時には、シール材と電極との間のクリアランスを低減することができ、優れたシール性および安定した出力特性を有する高分子電解質型燃料電池を提供することを目的とする。 Therefore, the present invention can stack single cells with high reliability when the stack is assembled, and can reduce the clearance between the sealing material and the electrode when the stack is fastened. It is an object of the present invention to provide a polymer electrolyte fuel cell having output characteristics.
本発明に係る燃料電池は、高分子電解質膜と、前記電解質膜の両面に配置した一対の電極と、前記電極を挟み前記電極に反応ガスを供給するガス流路を有する一対の導電性のセパレータ板と、前記一対のセパレータ板間において前記電解質膜を挟み、かつ前記電極と前記一対のセパレータ板との間の気密を保つ一対のシール手段と、を具備し、
前記一対のシール手段が、面状に前記電解質膜と接する平面状部分を有する平面形状シール部材と、線状に前記電解質膜と接するリブを有する線形状シール部材と、の組み合わせにより構成され、
前記一対のシール手段は、前記一対の電極の周縁部に沿って配され、
前記電解質膜、前記一対の電極および前記一対のセパレータ板が積層されて締結されるとき、前記リブの少なくとも一部が、前記電極方向へ倒れ込むこと、を特徴とする。
A fuel cell according to the present invention includes a polymer electrolyte membrane, a pair of electrodes disposed on both sides of the electrolyte membrane, and a pair of conductive separators having a gas flow path that sandwiches the electrodes and supplies a reaction gas to the electrodes A pair of sealing means sandwiching the electrolyte membrane between the plate and the pair of separator plates, and maintaining airtightness between the electrode and the pair of separator plates,
The pair of sealing means is composed of a combination of a planar sealing member having a planar portion in contact with the electrolyte membrane in a planar shape and a linear sealing member having ribs in contact with the electrolyte membrane in a linear shape,
It said pair of sealing means is disposed along the periphery of the front Symbol pair of electrodes,
When the electrolyte membrane, the pair of electrodes, and the pair of separator plates are stacked and fastened, at least a part of the rib falls in the electrode direction.
上記燃料電池においては、前記リブが、前記電解質膜、前記一対の電極および前記一対のセパレータ板が積層されて締結されるとき、前記リブの全体が、前記電極方向へ倒れ込むことように構成されているのが好ましい。
また、前記リブの具体的な態様としては、前記リブが、前記積層方向において中央に向かうにつれて前記電極に近づくように、前記リブの前記積層方向における断面が、曲線形状を有しており、前記電解質膜、前記一対の電極および前記一対のセパレータ板が積層されて締結されるとき、前記リブが、前記電極側に撓んで湾曲することが好ましい。
In the fuel cell, the rib is configured such that when the electrolyte membrane, the pair of electrodes, and the pair of separator plates are stacked and fastened, the entire rib falls down in the electrode direction. It is preferable.
Further, as a specific aspect of the rib, a cross section of the rib in the stacking direction has a curved shape so that the rib approaches the electrode as it goes toward the center in the stacking direction, When the electrolyte membrane, the pair of electrodes, and the pair of separator plates are stacked and fastened, it is preferable that the rib bends and curves toward the electrode.
また、前記リブは、前記電極側に傾いており、前記電解質膜、前記一対の電極および前記一対のセパレータ板が積層されて締結されるとき、前記リブが、前記電極側に倒れ込むことも好ましい。
前記リブが、前記積層方向の断面において、前記電解質膜に接する先端に円形状部分を有し、前記円形状部分の直径が、実質的に前記電極の厚さの半分以上であること、が好ましい。
The rib is inclined to the electrode side, and when the electrolyte membrane, the pair of electrodes, and the pair of separator plates are stacked and fastened, the rib is preferably tilted to the electrode side.
It is preferable that the rib has a circular portion at a tip in contact with the electrolyte membrane in a cross section in the stacking direction, and the diameter of the circular portion is substantially more than half of the thickness of the electrode. .
前記リブの、前記積層方向における断面が、線形状であることが好ましい。
前記一対のシール手段が粘着層を有することが好ましい。
前記粘着層が耐酸性を有することが好ましい。
The cross section of the rib in the stacking direction is preferably linear .
Preferably before Symbol pair of sealing means has an adhesive layer.
It is preferable that the adhesive layer has acid resistance.
本発明によれば、シール性の確保、電池性能の低下の抑制、組付け性の容易化、締結力の低減によるスタック構成部材のコンパクト化、およびシールに必要なスペースのコンパクト化によるセパレータ板の薄型化が可能となる。また、セパレータ板に設けられるガイド部の寸法ラフ化が可能であり、セパレータ板成形後にガイド部を加工する必要がなくなる。これにより、得られる燃料電池の信頼性の向上、量産時における歩留まりの向上、コンパクト化、および大幅なコスト低減が可能となる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to secure a sealing property, suppress a decrease in battery performance, facilitate assembling, make a stack member compact by reducing a fastening force, and a separator plate by making a space necessary for sealing compact. Thinning is possible. Further, the guide portion provided on the separator plate can be roughened, and it is not necessary to process the guide portion after the separator plate is formed. This makes it possible to improve the reliability of the obtained fuel cell, improve the yield during mass production, make it compact, and significantly reduce costs.
本発明に係る燃料電池のポイントは、一対のシール手段が、平面形状シール部材と、線形状シール部材とで構成されている点にある。
平面形状シール部材は、主として、セパレータ板の面方向に略平行な平面部分で構成される。また、線形状シール部材は、主として、セパレータ板の面方向に交わる方向に延びたリブ(リップ状部分)で構成され、リブの先端部における線シール部位が、前記平面形状シール部材側に実質的に線状に接することによってシールを行う。
The point of the fuel cell according to the present invention is that the pair of sealing means is composed of a planar sealing member and a linear sealing member.
The planar sealing member is mainly composed of a planar portion substantially parallel to the surface direction of the separator plate. Further, the linear seal member is mainly composed of a rib (lip-shaped portion) extending in a direction intersecting with the surface direction of the separator plate, and the linear seal portion at the tip of the rib is substantially on the planar seal member side. Sealing is performed by contacting the wire linearly.
そして、前記リブは、前記線形状シール部材締結時に電極側へ倒れ込む形状を有している点に特徴を有する。このことから、一対のシール手段とセパレータ板と電極とを積層し、スタックを締結して燃料電池を作製する際、実質的に前記リブが、セパレータ板と電解質膜とに挟まれて締結されていく。このとき、前記リブが電極側へ倒れ込んでいきながらシール性を発現していき、締結完了時には線形状シール部材と電極との隙間(クリアランス)が、押しつけられて電極側に倒れ込んできたリブによりふさがれる。締結が開始されていない各部材の組み付け時には、セパレータ板、シール手段および電極の各部材同士が干渉しないようにクリアランスが確保され、各部材の干渉により引き起こされるシール不良などの組立不良が生じない。 And the said rib has the characteristic in the point which has the shape which falls to the electrode side at the time of the said linear seal member fastening. Therefore, when a fuel cell is manufactured by laminating a pair of sealing means, a separator plate, and an electrode and fastening a stack, the rib is substantially sandwiched between the separator plate and the electrolyte membrane and fastened. Go. At this time, the rib develops a sealing property while falling toward the electrode side, and when the fastening is completed, a gap (clearance) between the linear sealing member and the electrode is blocked by the rib that is pressed and falls toward the electrode side. It is. When assembling each member that has not yet been fastened, a clearance is secured so that the members of the separator plate, the sealing means, and the electrode do not interfere with each other, so that an assembly failure such as a seal failure caused by the interference of each member does not occur.
すなわち、本発明における線形状シール部材は、電極とセパレータ板との間に挟まれる前には、線シール部位と電極との間に充分なクリアランスを確保する形状を有し、電極とセパレータ板との間に挟まれて締結された後には、シール締代を有する状態で、線形状シール部材のリブの少なくとも一部が電極側に向かって倒れて、当該線形状シール部材と電極との隙間に進入し、前記クリアランスを低減させるのである。 That is, the linear sealing member in the present invention has a shape that ensures a sufficient clearance between the linear seal part and the electrode before being sandwiched between the electrode and the separator plate, After being sandwiched between and tightened, at least a part of the rib of the linear seal member falls toward the electrode side in a state having a seal tightening margin, and enters the gap between the linear seal member and the electrode. It enters and reduces the clearance.
このような一対のシール手段を用いることにより、安定したシール性が得られ、シールに必要なスペースを低減させ、スタック締結荷重を低減させることができる。また、スタック組み付け時には、特に線形状シール部材と電極との間のクリアランスを充分に確保でき、スタック締結時には、線形状シール部材のリブが電極側に湾曲したり、倒れ込むことにより、組み立て時よりもクリアランスを小さくすることができる。これにより、クリアランスへ反応ガスが流出することを抑えることができ、安定した発電性能が得られる。 By using such a pair of sealing means, a stable sealing property can be obtained, a space required for sealing can be reduced, and a stack fastening load can be reduced. Also, when assembling the stack, especially the clearance between the linear seal member and the electrode can be secured sufficiently, and when the stack is fastened, the rib of the linear seal member is bent toward the electrode side or falls down, so that it is more than that during assembly. Clearance can be reduced. Thereby, it is possible to suppress the reaction gas from flowing into the clearance, and stable power generation performance can be obtained.
すなわち、本発明によれば、信頼性の高い組み立て性の確保によるシール性の確保と、クリアランスの低減による反応ガスのクリアランスへの流出低減、およびそれに伴う電池性能の改善とが可能になる。また、組付け時におけるセパレータ板に必要なガイド部位の精度低減によるセパレータ板への後加工の廃止および製造時の歩留まりの向上、ならびにそれに伴うコストの低減、シール部材が占めるスペースの低減による電池積層体の体積の低減、スタック締結力の低減による軽量化、コンパクト化、および低コスト化が可能となる。 That is, according to the present invention, it is possible to ensure sealing performance by ensuring highly reliable assembly, reduce outflow of reaction gas to the clearance by reducing clearance, and improve battery performance associated therewith. Battery stacking by eliminating post-processing of separator plates by reducing the accuracy of guide parts required for separator plates during assembly and improving yield during manufacturing, as well as reducing costs and space occupied by seal members It is possible to reduce the body volume, reduce the stack fastening force, reduce the weight, reduce the size, and reduce the cost.
また、線形状シール部材においては、線シール部位を含むリブの、前記積層方向における断面が、電極側に凸形状であり、電極と反対側に凹形状を有することが好ましい。この場合、前記リブがこのような断面形状を有することで、スタック締結時に積層方向から前記リブに締結荷重が加わった場合、前記電解質膜に線状に接するとともに、かつ電極側に撓んで湾曲する。すなわち、前記リブが凸状に湾曲しながら、線形状シール部材がスタック間に締結される。 In the linear sealing member, it is preferable that the cross section of the rib including the linear sealing portion in the stacking direction has a convex shape on the electrode side and a concave shape on the side opposite to the electrode. In this case, since the rib has such a cross-sectional shape, when a fastening load is applied to the rib from the stacking direction at the time of stack fastening, the rib contacts the electrolyte membrane linearly and bends and curves toward the electrode side. . That is, the linear seal member is fastened between the stacks while the rib is curved in a convex shape.
そのため、前記線形状シール部材の弾性に基づく、セパレータ板および電解質膜への反力によって、シール性が確保される。また、線形状シール部材と電極とのクリアランスを充分に確保しても、湾曲したリブが電極方向に飛び出していくことで、線形状シール部材と電極との間の隙間を低減することができる。隙間が低減することで、隙間を通って電極で反応せずに流れていた燃料ガスまたは酸化剤ガスを、本来流れるべきセパレータ板の流路に流すことができる。 Therefore, the sealing performance is ensured by the reaction force to the separator plate and the electrolyte membrane based on the elasticity of the linear seal member. Moreover, even if a sufficient clearance between the linear seal member and the electrode is ensured, the gap between the linear seal member and the electrode can be reduced by the curved rib protruding in the electrode direction. By reducing the gap, the fuel gas or oxidant gas that has flowed without reacting with the electrode through the gap can be flowed into the flow path of the separator plate that should flow.
このことにより、上述した効果と同様の効果が得られる。すなわち、信頼性の高い組み立て性の確保によるシール性の確保と、クリアランスの低減による反応ガスのクリアランスへの流出低減、およびそれに伴う電池性能の改善とが可能になる。また、組付け時におけるセパレータ板に必要なガイド部位の精度低減によるセパレータ板への後加工の廃止および製造時の歩留まりの向上、ならびにそれに伴うコストの低減と、シール部材が占めるスペースの低減による電池積層体の体積の低減と、スタック締結力の低減による軽量化、コンパクト化、および低コスト化とが可能となる。 As a result, the same effect as described above can be obtained. That is, it is possible to ensure sealing performance by ensuring highly reliable assembly, reduce outflow of reaction gas to clearance by reducing clearance, and improve battery performance associated therewith. In addition, the battery is abolished by eliminating post-processing of the separator plate by reducing the accuracy of the guide part necessary for the separator plate during assembly, improving the yield during manufacturing, and reducing the cost associated with it, and reducing the space occupied by the seal member. It is possible to reduce the volume of the laminated body and to reduce the weight, the size, and the cost by reducing the stack fastening force.
さらに、線形状シール部材において締結時に電極側に倒れ込む前記リブは、前記積層方向の断面において、先端部に円形状部分を有し、前記円形状部分の直径が、実質的に前記電極の厚さの半分以上であることが好ましい。なお、前記先端部が前記電解質膜に線状に接する線シール部位に相当する。
これにより、スタックを締結した際、線形状シール部材がセパレータ板または電解質膜に対して発生する反力が大きくなり、より安定したシール性を確保することが可能である。すなわち、線形状シール部材がセパレータ板と電解質膜とに挟まれてスタックが締結されていく際、リブが電極側に湾曲して、または傾いて、または倒れ込んで、隙間を埋め、リブの先端の円形状部分は、セパレータ板と電解質膜とに挟まれて圧縮される。その際、円形状部分が電極厚さの半分以上の直径を持っているため、所定量圧縮されるとより大きな反力を発揮する。そのため、シール性が向上し、より安定したシールを得ることが可能となる。
Further, the rib that falls to the electrode side at the time of fastening in the linear seal member has a circular portion at the tip in the cross section in the stacking direction, and the diameter of the circular portion is substantially the thickness of the electrode. It is preferable that it is more than half. Note that the tip portion corresponds to a line seal portion in linear contact with the electrolyte membrane.
Thereby, when the stack is fastened, the reaction force generated by the linear sealing member against the separator plate or the electrolyte membrane is increased, and it is possible to secure a more stable sealing property. That is, when the stack is fastened with the linear seal member sandwiched between the separator plate and the electrolyte membrane, the rib is curved, tilted, or collapsed toward the electrode side, filling the gap, and The circular portion is compressed by being sandwiched between the separator plate and the electrolyte membrane. At that time, since the circular portion has a diameter of more than half of the electrode thickness, a larger reaction force is exerted when compressed by a predetermined amount. Therefore, the sealing performance is improved, and a more stable seal can be obtained.
前記平面形状シール部材および線形状シール部材を構成する材料としては、例えばフッ素ゴム、ポリイソブレン、ブチルゴム、エチレンプロピレンゴム、シリコーンゴム、ニトリルゴム、熱可塑性エラストマー、液晶ポリマー、ポリイミド樹脂、ポリエーテルエーテルケトン樹脂、ポリエーテルイミド樹脂、ポリフェニレンサルファイド樹脂、テレフタルアミド樹脂、ポリエーテルサルホン樹脂、ポリサルホン樹脂、シンジオタクチックポリスチレン樹脂、ポリメチルペンテン樹脂、変性ポリフェニレンエーテル樹脂、ポリアセタール樹脂、ポリプロピレン樹脂、フッ素樹脂、およびポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂などが上げられる。これらを単体、または2種以上の複合体として用いてもよい。 Examples of the material constituting the planar sealing member and the linear sealing member include fluorine rubber, polyisobrene, butyl rubber, ethylene propylene rubber, silicone rubber, nitrile rubber, thermoplastic elastomer, liquid crystal polymer, polyimide resin, and polyether ether ketone resin. , Polyetherimide resin, polyphenylene sulfide resin, terephthalamide resin, polyether sulfone resin, polysulfone resin, syndiotactic polystyrene resin, polymethylpentene resin, modified polyphenylene ether resin, polyacetal resin, polypropylene resin, fluorine resin, and polyethylene Examples include terephthalate resin. These may be used alone or as a composite of two or more.
前記平面形状シール部材および線形状シール部材の、電解質膜に接する部分および/またはセパレータ板に接する部分には、粘着層が形成されていることが好ましい。
例えば、上述した線形状シール部材におけるリブの先端部(線シール部位)は、電解質膜に圧接されてシール性を確保する。その際、電解質膜と接するリブの先端部に粘着層が形成されていることで、シール部材自体の反力が弱くても、粘着層の粘着力によって安定したシール性が得られる。
It is preferable that an adhesive layer is formed on a portion in contact with the electrolyte membrane and / or a portion in contact with the separator plate of the planar sealing member and the linear sealing member.
For example, the tip end portion (line seal portion) of the rib in the above-described linear seal member is pressed against the electrolyte membrane to ensure sealing performance. At this time, since the adhesive layer is formed at the tip of the rib in contact with the electrolyte membrane, a stable sealing property can be obtained by the adhesive force of the adhesive layer even if the reaction force of the seal member itself is weak.
前記粘着層を構成する材料としては、例えばスチレンとエチレンブチレンの共重合体、ポリイソブチレン、エチレンプロピレンゴム、およびブチルゴムなどが挙げられる。これらは、単体または2種以上の複合体として用いてもよい。
また、長時間におけるシール部材のシール性を確保するために、前記粘着層が耐酸性であることが好ましい。例えば水素イオン伝導性を有する電解質膜を用いる場合、粘着層と接する電解質膜部分はイオン伝導性が発現した状態で酸性を呈する。そのため、電解質膜と接している粘着層部分が長期に渡り安定したシール性を得るためには、当該粘着層は耐酸性を有していることが望ましい。
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面を参照しながら説明する。
Examples of the material constituting the adhesive layer include a copolymer of styrene and ethylene butylene, polyisobutylene, ethylene propylene rubber, and butyl rubber. These may be used alone or as a composite of two or more.
Moreover, in order to ensure the sealing performance of the sealing member for a long time, the adhesive layer is preferably acid resistant. For example, when an electrolyte membrane having hydrogen ion conductivity is used, the electrolyte membrane portion in contact with the adhesive layer exhibits acidity in a state where the ion conductivity is expressed. Therefore, in order for the adhesive layer portion in contact with the electrolyte membrane to obtain a stable sealing property over a long period of time, it is desirable that the adhesive layer has acid resistance.
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
実施の形態1
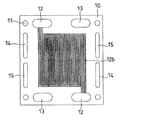
アノード側セパレータ板の正面図を図1に、その背面図を図2に示す。
導電性を有するアノード側セパレータ板10は、一対の燃料ガス用マニホールド孔12、一対の酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔13、一対の冷却水用マニホールド孔14、および一対の予備用マニホールド孔15、ならびに4個の締結用ボルト穴11を有する。
アノード側セパレータ板10のアノードに対向する面には、一対の燃料ガス用マニホールド孔12に連絡されてアノードに燃料ガスを供給するガス流路12bが設けられている。ガス流路12bは、4本の溝により構成されている。
Embodiment 1
A front view of the anode side separator plate is shown in FIG. 1, and a rear view thereof is shown in FIG.
The conductive anode-
A surface of the
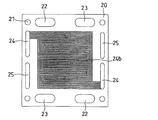
セパレータ板10の背面には、一対の冷却水用マニホールド孔14を連絡する冷却水用の流路14bが設けられている。流路14bは、並行する6本の溝により構成されている。各一対の燃料ガス用マニホールド孔12、酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔13の周りを囲むようにOリングを設置するためのOリング用溝12aおよび13aが設けられている。さらに、冷却水用マニホールド孔14、予備用マニホールド孔15、および冷却水用の流路14bの周りを囲むOリング用溝14aが設けられている。
On the back surface of the
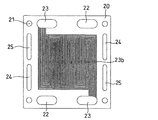
カソード側セパレータ板の正面図を図3に、その背面図を図4に示す。
導電性を有するカソード側セパレータ板20は、一対の燃料ガス用マニホールド孔22、一対の酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔23、一対の冷却水用マニホールド孔24、および一対の予備用マニホールド孔25、ならびに4個の締結用ボルト穴21を有する。
A front view of the cathode separator plate is shown in FIG. 3, and a rear view thereof is shown in FIG.
The
カソード側セパレータ板20のカソードに対向する面には、一対の酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔23に連絡されてカソードに酸化剤ガスを供給するガス流路23bが設けられている。ガス流路23bは、7本の溝により構成されている。
セパレータ板20の背面には、一対の冷却水用マニホールド孔24を連絡する冷却水用の流路24bが設けられている。流路24bは、並行する6本の溝により構成されている。
On the surface of the cathode-
On the back surface of the
ここで、図5に、アノード側シール部材として用いる線形状シール部材の正面図を示し、図6に、図5におけるX1−X2線断面図を示す。また、図7に、カソード側シール部材として用いる平面形状シール部材の正面図を示し、図8に、図7におけるY1−Y2線断面図を示す。この線形状シール部材および平面形状シール部材の組合せが、本発明の最大の特徴である一対のシール手段である。なお、X1−X2線断面およびY1−Y2線断面は、燃料電池の積層方向における断面である。 Here, FIG. 5 shows a front view of a linear seal member used as the anode side seal member, and FIG. 6 shows a cross-sectional view taken along line X 1 -X 2 in FIG. 7 shows a front view of a planar sealing member used as the cathode side sealing member, and FIG. 8 shows a cross-sectional view taken along line Y 1 -Y 2 in FIG. The combination of the linear sealing member and the planar sealing member is a pair of sealing means that is the greatest feature of the present invention. The X 1 -X 2 line cross section and the Y 1 -Y 2 line cross section are cross sections in the stacking direction of the fuel cells.
図6に示すように、アノード側セパレータ板10上に接着させる線形状シール部材30は、ポリイミドからなるフィルム4a、その一方の面にリブ(リップ状部分)36aを有する線状のベースシール部材36、および他方の面に形成されてアノード側セパレータ板10と接着する粘着層5aより構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 6, the
前記リブ36aは、高分子電解質膜と線状に接する先端部36bが実質的に円形状を有し、前記ベースシール部材36に沿って設けられている。リブ36aは、積層電池の圧接方向(積層方向)において、線形状を有し、電極側に曲がっている。そして、前記先端部36bが前記電解質膜を介して後述のカソード側の平面形状シール部材に線状に当接する。また、先端部36bの円の直径は、電極の厚さより大きい1mmとする。
The
図5に示すように、線形状シール部材30は、アノード側セパレータ板におけるガス流路12bおよび一対の燃料ガス用マニホールド孔12の外周を囲んで1つの閉ループを構成する第1のアノード側シール部と、酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔13、冷却水用マニホールド孔14、および予備用マニホールド孔15をそれぞれ独立に囲むマニホールド孔シール部33a、34aおよび35aと、を有する。また、ベースシール部材36は、上記のカソード側セパレータ板20における連絡用ガス流路23bの両側を囲むシール部38cおよび38dを有する。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
また、線形状シール部材30は、アノードを囲む電極シール部37と、燃料ガス用マニホールド孔32の外側半分を囲むマニホールド孔シール部32aと、前記電極シール部37と前記マニホールド孔シール部32aとを連絡し、ガス流路12bの両側を囲むシール部38aおよび38bとからなる。
The
さらに、線形状シール部材30は、燃料ガス用マニホールド孔シール部32aと酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔シール部33aとを結ぶシール部39a、燃料ガス用マニホールド孔シール部32aと冷却水用マニホールド孔シール部34aとを結ぶシール部39b、酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔シール部33aと予備用マニホールド孔シール部35aとを結ぶシール部39c、冷却水用マニホールド孔シール部34aと予備用マニホールド孔シール部35aとを結ぶシール部39dを有する。
前記フィルム4aおよび粘着層5aは、前記ベースシール部材36と同様の形状であり、これらが重ね合わせられてアノード側の線形状シール部材30が形成されている。
Further, the
The
一方、図8に示すように、上記カソード側セパレータ板20に接着されるカソード側の平面形状シール部材40は、ポリイミドからなるフィルム4b、その一方の面に形成された平板状のベースシール部材46、および他方の面に形成されてセパレータ板と接着する粘着層5bより構成されている。
On the other hand, as shown in FIG. 8, the cathode-side
前記フィルム4bおよび粘着層5bは、カソード側セパレータ板20における各マニホールド孔と対応する燃料ガス用マニホールド孔42、酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔43、冷却水用マニホールド孔44、および予備用マニホールド孔45、ならびにボルト穴41を有し、カソードと対応する部分(電極設置部)47は切り欠かれている。
前記カソード側のベースシール部材46は平板状であり、前記フィルム4bおよび粘着層5bと同形状である。
The
The cathode-side
上記のアノード側の線形状シール部材30における粘着層5a側の面をアノード側セパレータ板10のアノードと対向する側の面に接着させることにより、アノード側のベースシール部材36がアノード側セパレータ板10に固定される。
一方、カソード側の平面形状シール部材40における粘着層5b側の面をカソード側セパレータ板20のカソードと対向する側の面に接着させることにより、カソード側のベースシール部材46がカソード側セパレータ板20に固定される。
The anode-side
On the other hand, the cathode-side
そして、電解質膜を介して前記カソード側の平面形状シール部材40と前記アノード側の線形状シール部材30とを両セパレータ板で挟み、圧接することによりシールがなされる。
上記のアノード側の線形状シール部材30を備えたアノード側セパレータ板10およびカソード側の平面形状シール部材40を備えたカソード側セパレータ板20とで、一対の電極および電解質膜からなるMEAを挟むことにより単電池が構成される。この場合、それぞれの電極の面積は電解質膜の面積よりも小さく、電極が電解質膜の中央に位置する。そのため、MEAの周辺には電解質膜が露出している状態である。この露出部分が、前記線形状シール部材30および平面形状シール部材40によって挟まれる。
Then, the cathode-side
The MEA composed of a pair of electrodes and an electrolyte membrane is sandwiched between the anode-
一般的には、ガイドピンを立てた所定の組み立て用治具を用いて単電池を組み立てる。以下にその組み立ての手順の一例を示す。
まず、組み立て治具上に、上記のカソード側の平面形状シール部材40を備えたカソード側セパレータ板20を配置する。つぎに、MEAをガイドピンに沿ってカソード側セパレータ板20上に配置する。さらに、アノード側の線形状シール部材30を備えたアノード側セパレータ板10をMEA上に配する。
Generally, a unit cell is assembled using a predetermined assembly jig with a guide pin raised. An example of the assembly procedure is shown below.
First, the cathode-
上記のような手順で単電池を組み立てる場合、アノード側セパレータ板10を組み付ける際には、MEAとアノード側の線形状シール部材30との位置関係を目視で確認することができない。そのため、アノード側の線形状シール部材30が少しずれたりする場合がある。しかし、本実施の形態のアノード側の線形状シール部材30を用いれば、単電池の組み立て時において、MEAとアノード側の線形状シール部材30における電極シール部37との間に、充分なクリアランスを設けることができる。このため、アノード側の線形状シール部材30がMEAに乗り上げることがなく、安定してシール性を確保することができる。
When assembling the unit cell by the procedure as described above, when assembling the anode
また、単電池複数個を積層してスタックを構成する際、スタックを締結すると、アノード側の線形状シール部材30において電極側に曲がった形状のリブ36aが、MEAにおけるアノード側に湾曲し、アノードを囲む電極シール部37とMEAにおけるアノードとの間のクリアランスが小さくなる。このため、スタックを使用する際には、クリアランスへの反応ガスの流出を低減でき、安定した発電性能が得られる。
Further, when a stack is formed by stacking a plurality of single cells, when the stack is fastened, the
なお、上記構成のアノード側の線形状シール部材30においては、アノードと酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔33とが、マニホールド孔シール部33aおよび電極シール部37によりそれぞれ隔離されている。アノードとマニホールド孔33とは、マニホールド孔シール部33aまたは電極シール部37のみにより隔離されていてもよい。
また、上記構成のカソード側の平面上シール部材40は、カソード側セパレータ板20において、カソードおよび各マニホールド孔に対応する部分以外の主面全体を覆う形状を有するが、アノード側の線形状シール部材30に対応する部分のみで構成してもよい。
In the anode-side
The cathode-side
なお、上述の線形状シール部材および平面形状シール部材には、スタック締結時に相対応しない部分がある。例えば、図5に示す線形状シール部材30において、マニホールド孔シール部32aは、燃料ガス用マニホールド孔32の半分しか囲んでおらず、燃料ガス用マニホールド孔32とアノードとの間にはシール部材が存在しない。この存在しない部分においては、線形状シール部材は平面形状シール部材と相対応しない。しかし、スタックを構成する際には、弾性を有するシール部材が、両セパレータ板により適当な圧力で押さえつけられるため、前記両シール部材が相対応していなくても、シール部材の片方が直接セパレータ板に当接することによりシールできる。
また、前記存在しない部分にカバープレートなどの部材を設け、当該部材を平面形状シール部材と対応させてシールしてもよい。例えば、図5のシール部38aおよび38bの間におけるカソード側平面形状シール部材40と相対応する位置に、ガス流路12bの上方を覆うカバープレートを設けてもよい。
The linear seal member and the planar seal member described above have portions that do not correspond to each other when the stack is fastened. For example, in the
Further, a member such as a cover plate may be provided in the non-existing portion, and the member may be sealed in correspondence with the planar sealing member. For example, a cover plate that covers the upper side of the
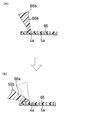
なお、実施の形態1のアノード側セパレータ板10における線形状シール部材30のリブの断面形状は、図6の形状には限定されない。図11および12に示すように、電解質膜と線状に接する先端部66b、76bを有するリブ66a、76aのような形状であってもよい。このリブ66a、76aは、スタックの積層方向(圧接方向)に対して電極側に傾いており、スタックの締結時に電極側(リブ66aおよび76aの左側)に倒れ込むような構成を有する。
このとき、リブ66a、76aの締結後における倒れ込み角度(図右側に示す倒れ込み前(点線)から倒れ込み後(実線)の間に傾いた分の角度)をθ、リブ66a、76aの長さをLとすると、Lsinθ分だけ電極とシール部材との間のクリアランスを減少させることが可能となる。
In addition, the cross-sectional shape of the rib of the linear sealing
At this time, the inclination angle after the fastening of the
また、リブの先端部36bの断面形状が実質的に円形状をなしており、本実施の形態ではその直径が電極の厚さ以上であることで、スタックを締結した際、シール部材によって大きな反力が得られ、安定したシールが確保できる。
リブの先端部36bの円断面形状の直径を変化させ、電極厚さの半分以上の直径を有した場合、安定したシール性を得やすいことがわかった。通常、電極をセパレータ板で圧接させていく場合、電極とセパレータ板との接触抵抗を低減し、得られた電池電圧を有効に出力するために10kgf/cm2程度の面圧で締結する。この際、電極は初期の厚さのほぼ半分の厚さまで圧縮されていることがわかった。そのため、リブの先端部36bの直径が電極初期厚さの半分以上あれば、締結時に反力が大きくなりシール性が向上することがわかった。
Further, the cross-sectional shape of the
It has been found that when the diameter of the circular cross-sectional shape of the
また、リブの先端部36bの直径が、電極の初期厚さの3倍以上あった場合は、シール性は得られたが、セパレータ板と電極との接触抵抗が増加するため、積層電池の出力電圧が低下する傾向にあった。そのため、リブの先端部36bの直径は、電極初期厚さの3倍未満であることが望ましいことがわかった。
Further, when the diameter of the
実施の形態2
つぎに、別の実施の形態に係るアノード側の線形状シール部材の正面図を図9に示し、図10に、図9におけるZ1−Z2線断面図を示す。
本実施の形態のアノード側の線形状シール部材56には、図5および6を用いて上述したアノード側の線形状シール部材30におけるリブ36aに相当するリブ状(リップ状)シール部材56aのみで構成される。
また、本実施の形態のアノード側の線形状シール部材56には、図5に示す線形状シール部材30の電極シール部37、ならびに各マニホールド孔シール部33a、34a、および35aに相当する位置に、リブ状シール部材56aが設けられている。そして、リブ状シール部材56aは、図9中のシール部52a、53a、54a、55a、57、58aおよび58bに設けられている。
Embodiment 2
Next, FIG. 9 shows a front view of a linear seal member on the anode side according to another embodiment, and FIG. 10 shows a sectional view taken along line Z 1 -Z 2 in FIG.
The anode-side
Further, the
リブ状シール部材56aは、スタックにおける積層方向(圧接方向)に対して電極側に曲がった形状を有し、セパレータ板および電解質膜と線状に接する先端部57a、57bをそれぞれ有している。そして、スタック締結時に、リブ状シール部材56aは電極方向に撓んで湾曲し、先端部57aはセパレータ板に固定され、先端部57bは、電池組み立て時に前記電解質膜を介して後述のカソード側の平面形状シール部材に線状に当接する。
The rib-shaped
また、本実施の形態のアノード側の線形状シール部材56では、上記実施の形態1における線形状シール部材30におけるシール部38c、38d、39a、39bおよび39cに相当する位置に薄い板状のシール部材56b、58c、58d、59a、59bおよび59cが設けられており、上記の各リブ状シール部材を連結して一体化している。
本実施の形態のさらにコンパクトなアノード側の線形状シール部材と、上記実施の形態1のカソード側シール部材とを組み合わせて用いることにより、実施の形態1と同様の効果が得られ、優れたシール性を確保することができる。
Further, in the
By using the more compact anode-side linear seal member of the present embodiment and the cathode-side seal member of the first embodiment in combination, the same effects as those of the first embodiment can be obtained and an excellent seal can be obtained. Sex can be secured.
なお、実施の形態2のアノード側セパレータ板上におけるリブ状シール部材の形状は、図13のような両先端部に電解質膜およびアノード側セパレータ板10とそれぞれ接する先端部87a、87bを有する直線状のリブ状シール部材87のような形状であってもよい。
この場合、先端部87bは、粘着剤によりアノード側セパレータ板10に固定され、先端部87aは先端部87bよりも電極側(リブ状シール部材87の左側)に位置する。すなわち、リブ状シール部材87は、アノード側セパレータ板10上において、電極側に傾いている。このため、リブ状シール部材87は、スタック締結時には、先端部87bを支点として電極側に倒れ込むことにより、電極とリブ状シール部材とのクリアランスを低減することができる。
The shape of the rib-like seal member on the anode side separator plate of the second embodiment is a linear shape having
In this case, the
なお、粘着剤には、例えば、スチレンとエチレンブチレンの共重合体を用いることができる。スチレンとエチレンブチレンの共重合体を含むトルエン溶液をシール部材の所定位置に塗布後、50℃の乾燥炉中で溶媒のトルエンを除去することにより、シール部材に粘着層が形成される。そして、この粘着層をセパレータ板に密着させることにより、シール部材をセパレータ板に固定することができる。
以下、本発明の実施例を詳細に説明する。
For the adhesive, for example, a copolymer of styrene and ethylene butylene can be used. After applying a toluene solution containing a copolymer of styrene and ethylene butylene to a predetermined position of the seal member, the solvent toluene is removed in a drying furnace at 50 ° C., thereby forming an adhesive layer on the seal member. And a sealing member can be fixed to a separator board by sticking this adhesion layer to a separator board.
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail.
《実施例1》
(i)セパレータ板の作製
等方性黒鉛板を用いて機械加工により実施の形態1の図1および図2に示すアノード側セパレータ板10ならびに図3および図4に示すカソード側セパレータ板20を作製した。このとき、セパレータ板の厚さは3mm、ガス流路および冷却水流路の溝は、3mmピッチで溝幅1.5mmとした。
Example 1
(I) Production of Separator Plate An anode-
(ii)シール部材の作製
図5〜図8に示す実施の形態1と同様の粘着層を備えた線形状シール部材30および平面形状シール部材40を作製した。
金型に厚さ100μmのポリイミドフィルム4a、4bを設置し、金型を締め、温度200℃、射出圧力150kgf/cm2の条件でフッ素ゴム(デュポン社製のフッ素ゴム、Viton)を射出成形することにより、ポリイミドフィルム4a、4b上に所定のベースシール部材36、46を形成した。二次架橋は200℃、10時間の条件で行った。その後、ブチルゴムからなる厚さ25μmの粘着層5a、5bをポリイミドフィルム4a、4b上に転写接合し、粘着層5a、5bの表面をポリプロピレン製の離型フィルムで覆った。
(Ii) Production of Seal Member A
このとき、フッ素ゴムからなるベースシール部材36の厚さは125μm、その幅は3mmとした。また、ベースシール部材36のアノードを囲む電極シール部37におけるリブ36aは、前記射出成形時に前記ベースシール部材36に一体的に形成し、電極側の先端部から0.7mmの位置に設けた。また、前記リブ36aは、ベースシール部材36に対して垂直方向に半径2.5mmの曲率で開き角度35°で設けた。電極シール部37以外のリブ36aについては、幅3mmのベースシール部材36の中央部に設けた。
一方、カソード側の平面形状シール部材40のベースシール部材46の厚さは、125μmとした。また、平面形状シール部材40における燃料ガス、酸化剤ガス、冷却水および予備用のマニホールド孔42〜45、締結用ボルト穴41、ならびに電極と対向する部分は抜き型で抜いた。
At this time, the
On the other hand, the thickness of the
上記で得られた粘着層5a、5bを備えた線形状シール部材30および平面形状シール部材40を、それぞれセパレータ板10および20上に設置し、ホットプレスによりそれぞれ圧着させた。ホットプレスの条件は、温度が100℃、プレス荷重が2000kgf、加圧時間が1分間とした。
The linear sealing
(iii)MEAの作製
アセチレンブラック系のカーボン粉末に、平均粒径約30Åの白金粒子を4:1の重量比で担持させ、電極用の触媒粉末を得た。この触媒粉末をイソプロパノール中に分散させたものと、パーフルオロカーボンスルホン酸の粉末をエチルアルコール中に分散させたものとを混合し、電極用ペーストを得た。スクリーン印刷法により、この電極用ペーストを原料として、厚さ250μmのカーボン不織布の一方の面に触媒層を形成し、電極を得た。このとき、触媒層形成後の触媒層中に含まれる白金量は0.5mg/cm2、パーフルオロカーボンスルホン酸の量は1.2mg/cm2とした。
(Iii) Preparation of MEA Platinum particles having an average particle diameter of about 30 mm were supported on an acetylene black carbon powder at a weight ratio of 4: 1 to obtain a catalyst powder for an electrode. The catalyst powder dispersed in isopropanol and the perfluorocarbon sulfonic acid powder dispersed in ethyl alcohol were mixed to obtain an electrode paste. Using this electrode paste as a raw material, a catalyst layer was formed on one surface of a 250 μm thick carbon non-woven fabric by screen printing to obtain an electrode. At this time, the amount of platinum contained in the catalyst layer after forming the catalyst layer 0.5 mg / cm 2, the amount of perfluorocarbon sulfonic acid was 1.2 mg / cm 2.
アノードおよびカソードとして、上記電極を用いた。すなわち、アノードとカソードの構成は同一とした。印刷した触媒層を内側にして、面積が100cm2の一対の電極で水素イオン伝導性高分子電解質膜(デュポン社製のNafion117)を挟み、ホットプレスすることにより、電解質膜電極接合体(MEA)を作製した。水素イオン伝導性高分子電解質膜には、パーフルオロカーボンスルホン酸を25μmの厚さに薄膜化したものを用いた。
前記電解質膜のサイズは、後述するセパレータ板のサイズと同様とし、電解質膜には、セパレータ板における一対の燃料ガス用マニホールド孔、冷却水用マニホールド孔、酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔に対応する穴を打ち抜き型により形成した。
The above electrodes were used as the anode and cathode. That is, the anode and cathode have the same configuration. An electrolyte membrane electrode assembly (MEA) is formed by sandwiching a hydrogen ion conductive polymer electrolyte membrane (Nafion 117 manufactured by DuPont) with a pair of electrodes having an area of 100 cm 2 with the printed catalyst layer inside and hot pressing. Was made. As the hydrogen ion conductive polymer electrolyte membrane, a perfluorocarbon sulfonic acid thinned to a thickness of 25 μm was used.
The size of the electrolyte membrane is the same as the size of the separator plate described later, and the electrolyte membrane has holes corresponding to a pair of fuel gas manifold holes, cooling water manifold holes, and oxidant gas manifold holes in the separator plate. It was formed by a punching die.
(iv)積層電池の組み立て
上記で得られたアノード側の線形状シール部材30を備えたアノード側のセパレータ板10、およびカソード側の平面形状シール部材40を備えたカソード側のセパレータ板20とで、電極面積100cm2のMEAを挟み、単電池を構成した。このとき、アノード側セパレータ板10のOリング溝12a〜14aにOリング3を設置した。そして、単電池を積層する際には、セパレータ板10の冷却水用の流路14bを有する面と、隣接する単電池のセパレータ板20の冷却水用の流路24bを有する面とが、向き合うように重ねることにより、冷却部を設けた。
(Iv) Assembling the laminated battery The anode-
単電池の組み立て手順を以下に説明する。
ガイドピンを立てた所定の組み立て用治具を置き、その上にカソード側の平面形状シール部材40を備えたカソード側セパレータ板20を配置した。つぎに、MEAをガイドピンに沿って設置した。その際、MEAにおけるカソードが平面形状シール部材40における電極設置部47の周縁部に乗り上げないよう、慎重にMEAをカソード側セパレータ板20に組み付けた。組み立て用治具に設置されたガイドピンと組み付けるこれらの部材との間にはクリアランスを要する。
The procedure for assembling the cell will be described below.
A predetermined assembling jig with a guide pin placed thereon was placed, and a cathode-
MEAにおけるカソードと、カソード側の平面形状シール部材40との間のクリアランスは、片側0.25mm確保した。このため、セパレータ板20とガイドピンとの間のクリアランスを0.2mmに設定することができた。なお、MEAは組み立て時の湿度により大きく寸法が変化するため、MEAとガイドピンとの間のクリアランスを大きく設ける必要がある。MEAを安定的に組み付けるには、ガイドピンとMEAとの間のクリアランスは1mm必要であった。
MEAを設置した後に、アノード側の線形状シール部材30を備えたアノード側セパレータ板10を組み付けた。このとき、アノードとベースシール部材36における電極シール部37とのクリアランスを、0.7mm確保した。セパレータ板10は不透明であり、MEAへのアノード側セパレータ板10の組み付け状態を目視できないため、ガイドピンに従ってアノード側セパレータ板10を組み付けた。
The clearance between the cathode in the MEA and the planar sealing
After installing the MEA, the anode-
上記の組み立て工程を繰り返して、単電池を50個積層し、得られたスタックの両端に集電板と絶縁板とを介してステンレス鋼製の端板を配し、締結ロッドにより600kgfの締結荷重でスタックを締結することにより燃料電池を作製した。この燃料電池を電池Aとした。締結後、電極シール部37のリブ36aがアノード側に湾曲することにより、アノードと電極シール部37とのクリアランスがほとんどない状態となった。このとき、感圧紙でMEAとセパレータ板の面圧を確認した結果、MEAにかかる面圧は10kgf/cm2であった。この結果、シール部材における反力は100kgfであり、充分に低い締結力で電池Aを構成することが可能であることがわかった。
By repeating the above assembly process, 50 unit cells are stacked, end plates made of stainless steel are arranged on both ends of the obtained stack via current collecting plates and insulating plates, and a fastening load of 600 kgf is applied by a fastening rod. A fuel cell was fabricated by fastening the stack at This fuel cell was designated as cell A. After the fastening, the
電池Aについてガスのリークチェックを行った。出口側マニホールド孔を締め切り、入口側マニホールド孔からHeガスを0.5kgf/cm2の圧力で流入させ、そのときの流入ガス流量を調べた。空気側、燃料ガス側、冷却水側共にガスリークはなく、電池Aは流体シール性に問題のないことが確認された。 The battery A was checked for gas leaks. The outlet side manifold hole was closed, and He gas was introduced from the inlet side manifold hole at a pressure of 0.5 kgf / cm 2 , and the inflow gas flow rate at that time was examined. There were no gas leaks on the air side, the fuel gas side, and the cooling water side, and it was confirmed that the battery A had no problem in fluid sealability.
《比較例1》
実施例1におけるアノード側の線形状シール部材およびカソード側の平面形状シール部材の代わりに、従来の平形状ガスケットを用いた以外は実施例1と同様の方法により積層電池Bを作製した。なお、平形状ガスケットとしては、厚さ100μmのPET製シートの両面に、厚さ75μmのシリコーンゴム製シートを貼り付けたものを用いた。部材の組み付けは実施例1と同様に組み立て用治具を用いて同様の手順で行なった。このとき、平形状ガスケットと電極とのクリアランスはアノード側およびカソード側でそれぞれ0.25mmとした。
<< Comparative Example 1 >>
A laminated battery B was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that a conventional flat gasket was used instead of the anode-side linear seal member and the cathode-side planar seal member in Example 1. In addition, as a flat gasket, the thing which affixed the 75-micrometer-thick silicone rubber sheet on both surfaces of the 100-micrometer-thick PET sheet | seat was used. The assembly of the members was performed in the same procedure using the assembly jig as in Example 1. At this time, the clearance between the flat gasket and the electrode was 0.25 mm on the anode side and the cathode side, respectively.
電池Bについて実施例1と同様の条件でガスのリークチェックを行った。締結荷重は4000kgfで、MEAにかかる面圧が10kgf/cm2であったため、締結は4000kgfとした。その結果、一部の単電池においてガスの外部リークまたは酸化剤ガス側から燃料ガス側へのクロスリーク、あるいはその両方が発生し、シール不良が生じた。 The battery B was checked for gas leakage under the same conditions as in Example 1. Since the fastening load was 4000 kgf and the surface pressure applied to the MEA was 10 kgf / cm 2 , the fastening was set to 4000 kgf. As a result, in some of the cells, an external leak of gas or a cross leak from the oxidant gas side to the fuel gas side, or both occurred, resulting in poor sealing.
《比較例2》
平形状ガスケットとアノードおよびカソードとのクリアランスをそれぞれ0.5mmとした以外は、比較例1と同様の方法により電池Cを作製した。部材の組み付けは実施例1と同様に組み立て用治具を用いて同様の手順で行なった。
電池Cについて実施例1と同様の条件でガスのリークチェックを行った。締結荷重は4000kgfで、MEAにかかる面圧が10kgf/cm2であったため、締結は4000kgfとした。その結果、酸化剤側、燃料ガス側、冷却水側共にガスリークはなく、積層電池としての流体シール性に問題のないことを確認した。
<< Comparative Example 2 >>
Battery C was produced in the same manner as in Comparative Example 1 except that the clearance between the flat gasket and the anode and cathode was 0.5 mm. The assembly of the members was performed in the same procedure using the assembly jig as in Example 1.
The battery C was subjected to a gas leak check under the same conditions as in Example 1. Since the fastening load was 4000 kgf and the surface pressure applied to the MEA was 10 kgf / cm 2 , the fastening was set to 4000 kgf. As a result, it was confirmed that there was no gas leak on the oxidant side, the fuel gas side, and the cooling water side, and there was no problem in the fluid sealability as a laminated battery.
リークチェックした後、実施例1および比較例1、2の電池A〜Cを分解し、組み付け具合を確認した。いずれの電池もMEAにおけるアノードが、アノード側の線形状シール部材の中心から多少ずれて組み付けられていたが、実施例1および比較例2の電池AおよびCでは、電極の周囲をシールする部位が電極よりも十分に余裕をもった外側にあるため、組み付け時にシール性を充分に確保することが可能であることがわかった。一方、比較例1の電池Bでは、同様に電極がずれていたが、電極が一部でもガスケットに乗り上げるとシール性が損なわれ、シール不良を生じることがわかった。 After performing a leak check, the batteries A to C of Example 1 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2 were disassembled and the assembly condition was confirmed. In any of the batteries, the anode in the MEA was assembled with a slight shift from the center of the linear seal member on the anode side. However, in the batteries A and C of Example 1 and Comparative Example 2, there was a portion that sealed the periphery of the electrode. It was found that it was possible to ensure a sufficient sealing property during assembly because it was outside the electrode with a sufficient margin. On the other hand, in the battery B of Comparative Example 1, the electrodes were similarly displaced. However, it was found that when even a part of the electrodes climbs onto the gasket, the sealing performance is impaired and a sealing failure occurs.
単電池を組み立てる際には、MEAを設置した後、アノード側セパレータ板を組み付ける。この際、MEAのアノードが、アノード側線形状シール部材の中心に設置されることが望ましいが、組み立て用治具のクリアランス、MEAの寸法誤差、セパレータ板の寸法誤差の集積により位置ずれが発生する。
アノードとアノード側の線形状シール部材との組み付け具合を目視できれば安定した組み付けが可能であるが、セパレータ板は不透明であるため目視ができず、ガイドピンに従って組み付ける。
When assembling the unit cell, after installing the MEA, the anode separator plate is assembled. At this time, it is desirable that the MEA anode is placed at the center of the anode-side linear seal member, but positional deviation occurs due to accumulation of assembly jig clearance, MEA dimensional error, and separator plate dimensional error.
If the degree of assembly between the anode and the linear seal member on the anode side can be visually confirmed, stable assembly is possible. However, the separator plate is opaque and cannot be visually observed, and is assembled according to the guide pins.
従来の平形状ガスケットであれば想定される位置ずれの上限付近では、電極がガスケットに乗り上げ、シール性を確保できない。組み付け性を向上するためにクリアランスを大きくとれば、反応ガスがそのクリアランスへ流出し、電極に供給されなくなるため、発電性能が低下した。 In the case of a conventional flat gasket, the electrode rides on the gasket in the vicinity of the upper limit of the positional deviation assumed, and the sealing performance cannot be secured. If the clearance is made large in order to improve the assemblability, the reaction gas flows out to the clearance and is not supplied to the electrode, so that the power generation performance is lowered.
一方、本発明のシール部材を用いた場合は、寸法ずれにより電極がずれても、ガスケットと電極とのクリアランスが十分にあるためシール性は確保可能となる。さらに、組み立て時においてスタックを締結すると、アノード側に撓んでいた線形状シール部材のリブが、両先端部を支点としてアノード側に飛び出すように湾曲する。このとき、シール部材の剛性から生じる反力によりシール部材にはシールに必要な面圧が生じる。さらに、電極側に湾曲し飛び出すことにより、電極とシール部材との間のクリアランスが減少する。
さらに、シール部材が積層方向に並んでいるため、スタックを締結した際に電解質膜やセパレータ板へせん断力や曲げモーメントが働かない。そのため、シール部材自体や、電解質膜、セパレータ板などへのストレスがなく、部材が破損する危険性がない。
On the other hand, when the seal member of the present invention is used, even if the electrode is displaced due to dimensional deviation, the sealability can be ensured because the clearance between the gasket and the electrode is sufficient. Further, when the stack is fastened at the time of assembly, the rib of the linear seal member that has been bent toward the anode side is curved so as to protrude toward the anode side with both end portions as fulcrums. At this time, a surface pressure necessary for sealing is generated in the sealing member due to a reaction force generated from the rigidity of the sealing member. Furthermore, the clearance between the electrode and the seal member is reduced by curving and projecting toward the electrode side.
Furthermore, since the sealing members are arranged in the stacking direction, no shear force or bending moment acts on the electrolyte membrane or the separator plate when the stack is fastened. Therefore, there is no stress on the seal member itself, the electrolyte membrane, the separator plate, etc., and there is no risk of the member being damaged.
実施例1の電池Aおよび比較例2の電池Cを75℃に保持し、アノード側に70℃の露点となるよう加湿・加温した水素ガスを、カソード側に60℃の露点となるように加湿・加温した空気をそれぞれ供給した。その結果、どちらの電池も電力を外部に供給しない無負荷時には、50Vの開放電圧を得た。また、ガスのクロスリークおよびショートなどの不具合がないことを確認した。 The battery A of Example 1 and the battery C of Comparative Example 2 were kept at 75 ° C., and the humidified and heated hydrogen gas was adjusted to a dew point of 70 ° C. on the anode side, and the dew point of 60 ° C. was set on the cathode side Humidified and warmed air was supplied. As a result, an open voltage of 50 V was obtained at the time of no load when neither battery supplies power to the outside. It was also confirmed that there were no problems such as gas cross leak and short circuit.
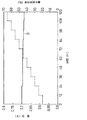
さらに、燃料利用率80%、電流密度0.3A/cm2、アノード側の露点70℃、酸化剤ガス側の露点65℃で、酸化剤利用率を20%から12時間毎に5%刻みで変更していく条件で発電を開始した。そして、この条件での発電の安定性を調べた。その評価結果を図14に示す。比較例2の電池Cでは、酸化剤利用率が40%以上で出力電圧が不安定となり、酸化剤利用率が50%では出力電圧が低下した。一方、実施例1の電池Aでは、酸化剤利用率が65%を超えるまで安定した出力電圧が得られた。 Furthermore, the fuel utilization rate is 80%, the current density is 0.3 A / cm 2 , the anode side dew point is 70 ° C., the oxidant gas side dew point is 65 ° C., and the oxidant utilization rate is from 20% in 5% increments every 12 hours. Power generation was started under changing conditions. Then, the stability of power generation under these conditions was investigated. The evaluation results are shown in FIG. In the battery C of Comparative Example 2, the output voltage became unstable when the oxidant utilization rate was 40% or more, and the output voltage decreased when the oxidant utilization rate was 50%. On the other hand, in the battery A of Example 1, a stable output voltage was obtained until the oxidant utilization rate exceeded 65%.
このことから、比較例2の電池Cにおける電極と平形状ガスケットとの間のクリアランスの大きさでは、クリアランスに反応ガスが流入しやすくなり、電池性能を維持するのに必要な量の反応ガスを電極へ供給できないことがわかった。これに対して、実施例1のシール部材を用いると組付け時には電極とシール部材との間のクリアランスは大きいが、電池積層体の締結時には電極とシール部材との間のクリアランスが低減するため、反応ガスのクリアランスへの流入を低減し、電池性能の低下を防止できることがわかった。 From this, in the size of the clearance between the electrode and the flat gasket in the battery C of Comparative Example 2, the reaction gas easily flows into the clearance, and the amount of the reaction gas necessary for maintaining the battery performance is increased. It was found that the electrode could not be supplied. On the other hand, when the seal member of Example 1 is used, the clearance between the electrode and the seal member is large at the time of assembly, but the clearance between the electrode and the seal member is reduced when the battery stack is fastened. It was found that the inflow of the reaction gas into the clearance can be reduced and the deterioration of the battery performance can be prevented.
さらに、実施例1の電池Aは比較例1および2の電池BおよびCよりも締結力が大幅に小さいため、燃料電池に用いる締結部材自体の簡素化、樹脂化等が可能であり、燃料電池のコンパクト化、低コスト化が可能である。
なお、Oリング型ガスケットを用いた場合と比較しても、実施例1ではセパレータ板にOリング用溝を設ける必要性がないため、その分セパレータ板の厚さを薄くすることができ、燃料電池をコンパクトにできることは言うまでもない。
Furthermore, since the battery A of Example 1 has a significantly smaller fastening force than the batteries B and C of Comparative Examples 1 and 2, the fastening member itself used for the fuel cell can be simplified, made into a resin, and the like. Can be reduced in size and cost.
Compared with the case where an O-ring type gasket is used, in Example 1, there is no need to provide an O-ring groove in the separator plate, so that the thickness of the separator plate can be reduced accordingly, and the fuel can be reduced. Needless to say, the battery can be made compact.
《実施例2》
フッ素ゴムを用いて所定の金型に射出成形することにより、実施の形態2と同様の図9および10に示すアノード側の線形状シール部材56を作製した。このとき、線形状シール部材56におけるリブ状シール部材56aは、厚さ0.25mmであり、アノード側セパレータ板に対して垂直方向に半径2.5mmの曲率で、開き角度35°で設けた。また、アノード側の線形状シール部材56における板状シール部材56bの厚さは0.15mm、幅は3mmとした。
実施例1の線形状シール部材30の代わりに、上記で得られた線形状シール部材56を用いた以外は、実施例1と同様の部材を用いて以下のように単電池を作製した。
Example 2
The anode-side
A unit cell was fabricated as follows using the same member as in Example 1 except that the
単電池の組み立て手順を以下に示す。
ガイドピンを立てた所定の組み立て用治具を置き、その上にカソード側の平面形状シール部材を備えたカソード側セパレータ板を配置した。つぎに、MEAをガイドピンに沿って設置した。その際、MEAのカソードがカソード側の平面形状シール部材における電極設置部47の周縁部に乗り上げないよう慎重に組み付けた。
MEAを設置した後に、上記のアノード側の線形状シール部材56を組み付けた。このとき、アノードとアノード側の線形状シール部材56における電極シール部57とのクリアランスを0.7mm確保した。その後、アノード側セパレータ板10を組み付けた。アノード側セパレータ板10は不透明であるため、セパレータ板とガスケットが接する状態を目視できないため、ガイドピンにしたがって組み付けを行った。
The procedure for assembling the cell is shown below.
A predetermined assembly jig with a guide pin placed thereon was placed, and a cathode side separator plate provided with a cathode-side planar shape sealing member was placed thereon. Next, MEA was installed along the guide pin. At that time, the MEA cathode was carefully assembled so as not to run over the peripheral edge portion of the
After installing the MEA, the anode-side
このようにして単電池を50個積層し、得られたスタックの両端に集電板と絶縁板とを介してステンレス鋼製の端板を配し、締結ロッドにより600kgfの締結荷重でスタックを締結することにより燃料電池を作製した。この燃料電池を電池Dとした。締結後では、リブ状シール部材56aがアノード側に湾曲することにより、アノードと電極シール部57とのクリアランスがほとんどない状態となった。このとき、感圧紙でMEAとセパレータ板の面圧を確認した結果、MEAにかかる面圧は10kgf/cm2であった。この結果、シール部材における反力は100kgfであり、充分に低い締結力で積層電池を構成することが可能であることがわかった。
In this way, 50 unit cells are stacked, stainless steel end plates are arranged on both ends of the obtained stack via current collector plates and insulating plates, and the stack is fastened with a fastening load of 600 kgf by a fastening rod. Thus, a fuel cell was produced. This fuel cell was designated as cell D. After the fastening, the rib-
電池Dについて実施例1と同様の方法によりガスのリークチェックを行った。その結果、空気側、燃料ガス側、冷却水側共にガスリークはなく、電池Dは流体シール性に問題のないことが確認された。
リークチェック後、実施例2の電池Dを分解し、構成部材の組み付け具合を調べた。MEAにおけるアノードがアノード側の線形状シール部材の中心から多少ずれて組み付けられていたが、本実施例の電池ではシールする部位が電極よりも十分な余裕をもった外側にあるため、組み付け時の電極のずれ範囲ではシール性を確保することができることがわかった。
The battery D was checked for gas leakage by the same method as in Example 1. As a result, there was no gas leak on the air side, the fuel gas side, and the cooling water side, and it was confirmed that the battery D had no problem in fluid sealability.
After the leak check, the battery D of Example 2 was disassembled and the assembling conditions of the constituent members were examined. The anode in the MEA was assembled with a slight deviation from the center of the linear seal member on the anode side. However, in the battery of this example, the portion to be sealed is on the outside with a sufficient margin than the electrode. It was found that sealability could be ensured in the electrode displacement range.
単電池を組み立てる際には、組み立て用治具にMEAを設置した後、アノード側セパレータ板を組み付ける。この際、MEAにおけるアノードがアノード側の線形状シール部材の中心に設置されることが好ましい。
本実施例のアノード側の線形状シール部材を用いた場合は、寸法ずれにより電極がずれても、シール部材と電極との間のクリアランスが充分であるため、シール性を確保できる。また、目視による組付けが可能になるため、電極の噛み込み等によるシール不良も低減できる。
When assembling the unit cell, the anode separator plate is assembled after installing the MEA on the assembly jig. At this time, it is preferable that the anode in the MEA is installed at the center of the linear seal member on the anode side.
When the linear seal member on the anode side of the present embodiment is used, even if the electrode is displaced due to a dimensional displacement, the clearance between the seal member and the electrode is sufficient, so that the sealing performance can be ensured. Further, since visual assembly is possible, it is possible to reduce a sealing failure due to the biting of the electrode.
また、実施例1の場合と同様に、組み立て時には大きなクリアランスも、スタックを締結する時には、実施例2のシール部材の形状の効果により、電解質膜とセパレータ板とのシール部を支点としてリブ状シール部材が電極側に湾曲する。これは、リブ状シール部材の重心位置がシール部位よりも電極側にあるためである。このとき、シール部材の剛性により生じる反力により、シール部位にはシールに必要な面圧が生じる。また、リブ状シール部材が電極側に湾曲し飛び出すことによりMEAとシール部材との間のクリアランスを減少させることができる。 Further, as in the case of the first embodiment, a large clearance at the time of assembling is obtained, and when the stack is fastened, a rib-shaped seal is used with the seal portion between the electrolyte membrane and the separator plate as a fulcrum due to the effect of the shape of the seal member of the second embodiment. The member curves to the electrode side. This is because the center of gravity of the rib-like seal member is on the electrode side with respect to the seal portion. At this time, a surface pressure necessary for sealing is generated at the seal portion due to a reaction force generated by the rigidity of the seal member. Moreover, the clearance between the MEA and the seal member can be reduced by the rib-like seal member being curved and protruding toward the electrode side.
さらに、シール部材が垂直方向(積層方向)に並んでいるため、スタックを締結する際に、電解質膜やセパレータ板へせん断力や曲げモーメントが働かない。そのため、電解質膜、シール部材、およびセパレータ板などへストレスがなく、部材が破損する危険性がない。 Furthermore, since the seal members are arranged in the vertical direction (stacking direction), no shearing force or bending moment acts on the electrolyte membrane or the separator plate when the stack is fastened. Therefore, there is no stress on the electrolyte membrane, the seal member, the separator plate, and the like, and there is no risk of the member being damaged.
実施例2の電池Dを75℃に保持し、アノード側に70℃の露点となるよう加湿・加温した水素ガスを、カソード側に60℃の露点となるように加湿・加温した空気をそれぞれ供給した。その結果、電力を外部に供給しない無負荷時には、50Vの開放電圧を得た。また、ガスのクロスリークおよびショートなどの不具合がないことを確認した。 The battery D of Example 2 was held at 75 ° C., hydrogen gas humidified and heated to a dew point of 70 ° C. on the anode side, and air humidified and heated to a dew point of 60 ° C. on the cathode side. Each was supplied. As a result, an open voltage of 50 V was obtained at no load when power was not supplied to the outside. It was also confirmed that there were no problems such as gas cross leak and short circuit.
この電池Dについて実施例1と同様の条件で発電を開始し、発電の安定性を調べた。その評価結果を図15に示す。実施例2の電池Dでは、酸化剤利用率が65%を超えるまで安定した出力電圧が得られた。このことから、実施例2の燃料電池では実施例1の場合と同様に、組付け時には電極とシール部材との間のクリアランスは大きいが、スタックの締結時にはシール部材の形状による効果により、電極とシール部材との間のクリアランスが低減し、反応ガスのクリアランスへの流入を低減し、電池性能の低下を防止できることがわかった。 With respect to this battery D, power generation was started under the same conditions as in Example 1, and the stability of power generation was examined. The evaluation results are shown in FIG. In the battery D of Example 2, a stable output voltage was obtained until the oxidant utilization rate exceeded 65%. Thus, in the fuel cell of Example 2, as in Example 1, the clearance between the electrode and the seal member is large when assembled, but the effect of the shape of the seal member when the stack is fastened, It has been found that the clearance with the seal member is reduced, the inflow of the reaction gas into the clearance can be reduced, and the deterioration of the battery performance can be prevented.
さらに、燃料電池の締結に必要な締結力が大幅に小さくて済むため、スタックの締結部材の簡素化、樹脂化等が可能となる。すなわち、燃料電池のコンパクト化、低コスト化が可能となる。 Furthermore, since the fastening force required for fastening the fuel cell can be significantly reduced, the stack fastening members can be simplified, made resin, and the like. That is, the fuel cell can be made compact and the cost can be reduced.
《実施例3》
実施例2のアノード側の線形状シール部材56におけるリブ状シール部材56aの厚みを0.15mmと薄くした以外は、実施例2と同様の方法により線形状シール部材56を作製した。
さらに、線形状シール部材56を粘着剤でコーティングした。粘着剤には、スチレンとエチレンブチレンの共重合体を用いた。スチレンとエチレンブチレンの共重合体のトルエン溶液を線形状シール部材に塗布した後、50℃の乾燥炉中で溶媒のトルエンを除去した。
Example 3
A
Further, the
上記線形状シール部材56をアノード側セパレータ板10上に設置し、さらにその上にテフロンシートを配した状態でホットプレスすることにより、線形状シール部材56をセパレータ板10に圧着した。このとき、温度は100℃、プレス荷重は2000kgf、加圧時間は1分間とした。
The linear sealing
上記で得られたアノード側の線形状シール部材56を備えたアノード側セパレータ板10を用いた以外は、実施例2と同様の方法により、単電池を作製した。この単電池を50個積層し、得られたスタックの両端に集電板と絶縁板とを介してステンレス鋼製の端板を配し、締結ロッドにより550kgfの締結荷重でスタックを締結することにより燃料電池を作製した。この燃料電池を電池Eとした。このとき、感圧紙でMEAとセパレータ板の面圧を確認した結果、MEAにかかる面圧は10kgf/cm2であった。この結果、シール部材における反力は50kgfであり、非常に低い締結力で燃料電池を構成することが可能であることがわかった。また、組み付け状態は実施例1および2と同様に良好であった。
A unit cell was produced in the same manner as in Example 2 except that the anode-
電池Eについて、実施例1と同様の方法によりリークチェックを行った。その結果、空気側、燃料ガス側、冷却水側共にガスリークはなく、燃料電池としての流体シール性に問題のないことを確認した。
積層電池の組み立ては、MEAを組み立て用治具に設置した後、アノード側セパレータ板を組み付けた。この際、MEAのアノードがアノード側の線形状シール部材の中心に設置されることが好ましい。
For the battery E, a leak check was performed in the same manner as in Example 1. As a result, it was confirmed that there were no gas leaks on the air side, the fuel gas side, and the cooling water side, and there was no problem in the fluid sealability as a fuel cell.
In assembling the laminated battery, the MEA was placed on an assembly jig, and then the anode separator plate was assembled. At this time, the MEA anode is preferably installed at the center of the linear seal member on the anode side.
リブ状シール部材56aを用いた場合は、寸法ずれにより電極がずれた場合でも、アノード側の線形状シール部材と電極との間のクリアランスが十分であるため、シール性を確保できる。また、目視による燃料電池の組付けが可能になるため、電極の噛み込み等によるシール不良も低減できる。
When the rib-shaped
《実施例4》
実施例3の粘着層を用いない以外は、実施例3と同様の方法により燃料電池を作製した。この燃料電池を電池Fとした。
比較例3の電池Fについて実施例1と同様の方法によりリークチェックを行った。その結果、一部の単電池においてガスの外部リークもしくは酸化剤ガス側から燃料ガス側へのクロスリーク、またはその両方が若干発生し、シール不良が生じ得る傾向にあった。
Example 4
A fuel cell was produced in the same manner as in Example 3 except that the adhesive layer of Example 3 was not used. This fuel cell was designated as cell F.
The battery F of Comparative Example 3 was checked for leaks by the same method as in Example 1. As a result, in some of the single cells, there is a tendency that a gas external leak or a cross leak from the oxidant gas side to the fuel gas side, or both, may occur slightly, resulting in poor sealing.
実施例3より、粘着層を用いることにより、本実施例のようなシール反力が比較的小さい線形状シール部材を用いた場合でもシール性を確保できることが確認された。このようにシールに必要な反力を小さくすることができるため、スタックの締結力を非常に低減することができる。したがって、スタックの締結部材の大幅な簡素化、樹脂化などが可能となる。すなわち、燃料電池のコンパクト化、低コスト化が可能となる。 From Example 3, it was confirmed that by using an adhesive layer, sealing performance can be ensured even when a linear sealing member having a relatively small sealing reaction force as in this example is used. Thus, the reaction force required for the seal can be reduced, so that the fastening force of the stack can be greatly reduced. Therefore, the stack fastening member can be greatly simplified and made into a resin. That is, the fuel cell can be made compact and the cost can be reduced.
また、シール反力が非常に小さいため、電解質膜やシール部材にかかるストレスを低減でき、電解質膜やシール部材の損傷を防ぐことができ、長時間のシール性の確保が可能となる。さらに、反応ガスのクロスリークを防止することができ、シール不良にともなうガスのクロスリークによる電解質膜の損傷を防止できるため、耐久性も向上する。 Further, since the seal reaction force is very small, stress applied to the electrolyte membrane and the seal member can be reduced, damage to the electrolyte membrane and the seal member can be prevented, and long-term sealing performance can be ensured. Furthermore, reaction gas cross-leakage can be prevented, and damage to the electrolyte membrane due to gas cross-leakage due to poor sealing can be prevented, thus improving durability.
実施例3の電池Eを75℃に保持し、アノード側に70℃の露点となるよう加湿・加温した水素ガスを、カソード側に60℃の露点となるように加湿・加温した空気をそれぞれ供給した。その結果、電力を外部に供給しない無負荷時には、50Vの開放電圧を得た。また、ガスのクロスリークおよびショートなどの不具合がないことを確認した。 The battery E of Example 3 was held at 75 ° C., hydrogen gas humidified and heated to a dew point of 70 ° C. on the anode side, and air humidified and heated to a dew point of 60 ° C. on the cathode side. Each was supplied. As a result, an open voltage of 50 V was obtained at no load when power was not supplied to the outside. It was also confirmed that there were no problems such as gas cross leak and short circuit.
この電池Eについて実施例1と同様の条件で発電を開始し、発電の安定性を調べた。その評価結果を図16に示す。実施例3の電池Eでは、酸化剤利用率が65%を超えるまで安定した出力電圧が得られた。このことから、実施例3の燃料電池では実施例2の場合と同様に、組み付け時には電極と線形状シール部材との間のクリアランスは大きいが、スタックの締結時には線形状シール部材の形状による効果により、電極と線形状シール部材との間のクリアランスが低減し、反応ガスのクリアランスへの流入を低減し、電池性能の低下を防止することができることがわかった。
なお、粘着層が耐酸性を有しない場合は、電解質膜とシール部材の間にPFAなどの保護シートを挿入することにより、本実施例と同様の効果が得られる。
With respect to this battery E, power generation was started under the same conditions as in Example 1, and the stability of power generation was examined. The evaluation results are shown in FIG. In the battery E of Example 3, a stable output voltage was obtained until the oxidant utilization rate exceeded 65%. From this, in the fuel cell of Example 3, as in Example 2, the clearance between the electrode and the linear seal member is large when assembled, but due to the effect of the shape of the linear seal member when the stack is fastened. It has been found that the clearance between the electrode and the linear seal member can be reduced, the inflow of the reaction gas into the clearance can be reduced, and the battery performance can be prevented from being lowered.
In addition, when an adhesion layer does not have acid resistance, the same effect as a present Example is acquired by inserting protective sheets, such as PFA, between an electrolyte membrane and a sealing member.
《実施例5》
所定の金型を用い、実施例1と同様の方法により、実施の形態1における図11および12と同様のアノード側の線形状シール部材を作製した。
実施例1で用いたアノード側線形状シール部材30の代わりに、この線形状シール部材を用いた以外は、実施例1と同様の方法によりそれぞれ燃料電池GおよびHを作製した。
また、所定の金型を用い、実施例2と同様の方法により、実施の形態2における図13と同様のアノード側の線形状シール部材を作製した。実施例2のアノード側線形状シール部材の代わりに、図13に示す線形状シール部材を用いた以外は、実施例2と同様の方法により燃料電池Iを作製した。
Example 5
Using a predetermined mold, a linear seal member on the anode side similar to that in FIGS. 11 and 12 in the first embodiment was produced by the same method as in the first embodiment.
Fuel cells G and H were produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that this linear seal member was used instead of the anode-side
Further, using a predetermined mold, an anode-side linear seal member similar to that in FIG. 13 in the second embodiment was produced by the same method as in the second embodiment. A fuel cell I was produced in the same manner as in Example 2 except that the linear seal member shown in FIG. 13 was used instead of the anode-side linear seal member in Example 2.
そして、電池G〜Iについて実施例1と同様の条件で発電を開始し、発電の安定性を調べた。その評価結果を図17に示す。いずれの場合も実施例1または2と同様に安定した出力特性が得られることが確認された。 Then, power generation for the batteries G to I was started under the same conditions as in Example 1, and the stability of power generation was examined. The evaluation results are shown in FIG. In any case, it was confirmed that stable output characteristics were obtained as in Example 1 or 2.
以上のように本発明の高分子電解質型燃料電池は、燃料電池組み立て時には、信頼性の高い組み立て性を有し、かつ燃料電池締結時には、シール部材と電極との間のクリアランスを低減することにより、優れたシール性および安定した出力特性を有し、ポータブル電源、携帯機器用電源、電気自動車用電源、および家庭内コージェネレーションシステムなどの用途に適用できる。 As described above, the polymer electrolyte fuel cell of the present invention has a highly reliable assembly property when assembling the fuel cell, and reduces the clearance between the seal member and the electrode when the fuel cell is fastened. It has excellent sealing properties and stable output characteristics, and can be applied to applications such as portable power supplies, portable device power supplies, electric vehicle power supplies, and home cogeneration systems.
4a、4b フィルム
5a、5b 粘着層
10 アノード側セパレータ板
11、21、41 締結用ボルト穴
12、22、32、42、52 燃料ガス用マニホールド孔
13、23、33、43、53 酸化剤ガス用マニホールド孔
14、24、34、44、54 冷却水用マニホールド孔
15、25、35、45、55 予備用マニホールド孔
12a、13a、14a Oリング用溝
12b、23b ガス流路
14b 24b 冷却水用の流路
20 カソード側セパレータ板
30、56 アノード側の線形状シール部材
36、66、76 アノード側のベースシール部材
36a、66a、76a リブ
36b、57a、57b、66b、76b 先端部
37、57、 電極シール部
40 カソード側の平面形状シール部材
46 カソード側のベースシール部材
56a リブ状シール部材
56b 板状シール部材
4a,
Claims (8)
前記一対のシール手段が、面状に前記電解質膜と接する平面状部分を有する平面形状シール部材と、線状に前記電解質膜と接するリブを有する線形状シール部材と、の組み合わせにより構成され、
前記一対のシール手段は、前記一対の電極の周縁部に沿って配され、
前記電解質膜、前記一対の電極および前記一対のセパレータ板が積層されて締結されるとき、前記リブの少なくとも一部が、前記電極方向へ倒れ込むこと、を特徴とする燃料電池。 A polymer electrolyte membrane; a pair of electrodes disposed on both surfaces of the electrolyte membrane; a pair of conductive separator plates having a gas flow path sandwiching the electrodes and supplying a reactive gas to the electrodes; and the pair of separator plates A fuel cell comprising a pair of sealing means sandwiching the electrolyte membrane therebetween and maintaining airtightness between the electrode and the pair of separator plates,
The pair of sealing means is composed of a combination of a planar sealing member having a planar portion in contact with the electrolyte membrane in a planar shape and a linear sealing member having ribs in contact with the electrolyte membrane in a linear shape,
It said pair of sealing means is disposed along the periphery of the front Symbol pair of electrodes,
The fuel cell, wherein when the electrolyte membrane, the pair of electrodes, and the pair of separator plates are stacked and fastened, at least a part of the rib falls in the electrode direction.
前記電解質膜、前記一対の電極および前記一対のセパレータ板が積層されて締結されるとき、前記リブが、前記電極側に撓んで湾曲することを特徴とする請求項1記載の燃料電池。 The cross section of the rib in the stacking direction has a curved shape so that the rib approaches the electrode as it goes toward the center in the stacking direction ,
2. The fuel cell according to claim 1, wherein when the electrolyte membrane, the pair of electrodes, and the pair of separator plates are stacked and fastened, the rib is bent and curved toward the electrode.
前記電解質膜、前記一対の電極および前記一対のセパレータ板が積層されて締結されるとき、前記リブが、前記電極側に倒れ込むことを特徴とする請求項1記載の燃料電池。 The rib is inclined toward the electrode;
2. The fuel cell according to claim 1, wherein when the electrolyte membrane, the pair of electrodes, and the pair of separator plates are stacked and fastened, the rib falls down to the electrode side.
前記円形状部分の直径が、実質的に前記電極の厚さの半分以上であること、を特徴とする請求項1〜4のいずれかに記載の燃料電池。 The rib has a circular portion at the tip in contact with the electrolyte membrane in the cross section in the stacking direction,
The fuel cell according to any one of claims 1 to 4, wherein a diameter of the circular portion is substantially half or more of a thickness of the electrode.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004222671A JP4615266B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2004-07-30 | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003285313 | 2003-08-01 | ||
| JP2004222671A JP4615266B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2004-07-30 | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005071989A JP2005071989A (en) | 2005-03-17 |
| JP2005071989A5 JP2005071989A5 (en) | 2007-09-06 |
| JP4615266B2 true JP4615266B2 (en) | 2011-01-19 |
Family
ID=34425121
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004222671A Expired - Fee Related JP4615266B2 (en) | 2003-08-01 | 2004-07-30 | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4615266B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5265273B2 (en) * | 2008-08-27 | 2013-08-14 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Fuel cell |
| GB201006403D0 (en) * | 2010-04-16 | 2010-06-02 | Itm Power | Laminated stack |
| JP6368995B2 (en) * | 2013-08-28 | 2018-08-08 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | Membrane electrode assembly and membrane electrode assembly laminate |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000133288A (en) * | 1998-10-28 | 2000-05-12 | Nok Corp | Carbon material for fuel cell |
| JP2002042837A (en) * | 2000-07-25 | 2002-02-08 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Sealing structure for fuel cell |
| JP2002042838A (en) * | 2000-07-31 | 2002-02-08 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Fuel cell and manufacturing method for porous conductor, seal structural body, and electrode film structural body |
| JP2002151108A (en) * | 2000-09-04 | 2002-05-24 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Fuel cell |
| JP2003017092A (en) * | 2001-06-29 | 2003-01-17 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Electrolyte membrane-electrode structure, and fuel cell |
| JP2003056704A (en) * | 2001-03-09 | 2003-02-26 | Nok Corp | Gasket |
| JP2003217616A (en) * | 2002-01-24 | 2003-07-31 | Uchiyama Mfg Corp | Gasket for fuel cell |
| JP2004039341A (en) * | 2002-07-01 | 2004-02-05 | Nok Corp | Gasket for fuel cell |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0765847A (en) * | 1993-08-24 | 1995-03-10 | Kansai Electric Power Co Inc:The | Solid high polymer electrolyte type fuel cell |
| JPH09167623A (en) * | 1995-12-18 | 1997-06-24 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | Solid polymer electrolyte type fuel cell |
| JPH10199551A (en) * | 1997-01-06 | 1998-07-31 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Fuel cell structural body and manufacture thereof |
-
2004
- 2004-07-30 JP JP2004222671A patent/JP4615266B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000133288A (en) * | 1998-10-28 | 2000-05-12 | Nok Corp | Carbon material for fuel cell |
| JP2002042837A (en) * | 2000-07-25 | 2002-02-08 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Sealing structure for fuel cell |
| JP2002042838A (en) * | 2000-07-31 | 2002-02-08 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Fuel cell and manufacturing method for porous conductor, seal structural body, and electrode film structural body |
| JP2002151108A (en) * | 2000-09-04 | 2002-05-24 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Fuel cell |
| JP2003056704A (en) * | 2001-03-09 | 2003-02-26 | Nok Corp | Gasket |
| JP2003017092A (en) * | 2001-06-29 | 2003-01-17 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Electrolyte membrane-electrode structure, and fuel cell |
| JP2003217616A (en) * | 2002-01-24 | 2003-07-31 | Uchiyama Mfg Corp | Gasket for fuel cell |
| JP2004039341A (en) * | 2002-07-01 | 2004-02-05 | Nok Corp | Gasket for fuel cell |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005071989A (en) | 2005-03-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4096027B2 (en) | Solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| JP5043923B2 (en) | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| KR101763662B1 (en) | Seal for solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| JP5079507B2 (en) | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell and fuel cell seal member used therefor | |
| JP4077509B2 (en) | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| US9034536B2 (en) | Fuel cell having voltage monitor terminal with exposed portion | |
| US20080280183A1 (en) | End plate for fuel cell stack and air breathing fuel cell stack using the same | |
| JP2017139218A (en) | Method of producing fuel cell stack and method of producing metal separator for fuel cell | |
| US9673458B2 (en) | Fuel cell | |
| JPWO2009072291A1 (en) | Method for producing electrode-membrane-frame assembly | |
| JP4772794B2 (en) | Sealed configuration for fuel cell stack | |
| US9196911B2 (en) | Fuel cell gas diffusion layer integrated gasket | |
| JP2003197224A (en) | High polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| US9780400B2 (en) | Fuel cell having an empty space gap between the separator and electrode | |
| KR100572087B1 (en) | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| JP4739685B2 (en) | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| JP2008300131A (en) | Fuel cell stack | |
| JP2002260693A (en) | High polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| US10826097B2 (en) | Fuel cell | |
| JP5143336B2 (en) | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| JP4615266B2 (en) | Polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| CN113675422B (en) | fuel cell stack | |
| JP5179093B2 (en) | Fuel cell stack | |
| JP2005174875A (en) | Fuel battery and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2001176519A (en) | Conductive separator, high molecular electrolyte-type fuel cell and method of manufacturing high molecular electrolyte-type fuel cell |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20061225 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070719 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070719 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100625 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100708 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100831 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100922 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20101020 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131029 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |