JP4612281B2 - Position detection device - Google Patents
Position detection device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4612281B2 JP4612281B2 JP2003122709A JP2003122709A JP4612281B2 JP 4612281 B2 JP4612281 B2 JP 4612281B2 JP 2003122709 A JP2003122709 A JP 2003122709A JP 2003122709 A JP2003122709 A JP 2003122709A JP 4612281 B2 JP4612281 B2 JP 4612281B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- output
- magnetic sensors
- axis
- magnet
- signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 title claims description 41
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 13
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 11
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229920002050 silicone resin Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 210000001015 abdomen Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- KPLQYGBQNPPQGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt samarium Chemical compound [Co].[Sm] KPLQYGBQNPPQGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000003811 finger Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000000696 magnetic material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000938 samarium–cobalt magnet Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910000838 Al alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000861 Mg alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000014676 Phragmites communis Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005415 magnetization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004088 simulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000003813 thumb Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910000859 α-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of Length, Angles, Or The Like Using Electric Or Magnetic Means (AREA)
- Position Input By Displaying (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、物体の移動又は傾斜を検出する位置検出装置に関し、さらにはこの位置検出装置を用いて、パーソナルコンピュータや携帯電話等の入力手段として使用される位置検出装置に関する。より詳細には、マグネットの移動による周囲の磁界変化を検出することにより、座標検知を行う磁気検出方式の位置検出装置に関する。
【0002】
物体の移動又は傾斜あるいは移動角度を磁石や磁性体と磁気センサで検出する装置が知られている。また、パーソナルコンピュータ(アミューズメント用やシミュレーション用のコンピュータを含み)のポインティングデバイス(ジョイスティックやトラックボールなど)における座標検出の方式としては、光学式、感圧式、可変抵抗式、磁気検出式などが実用化されているが、近年、小型化が容易でしかも無接点で長寿命という特徴を有する磁気検出式が有力になってきている。
【0003】
【従来の技術】
図8は、従来の磁気検出式ポインティングデバイスの磁気検出回路を示すブロック図で、検出部31は、X軸及びY軸の沿って2個ずつ対称に配設された4個のホール素子41からなり、このホール素子41の上方に配設されたマグネットの移動によるX軸方向とY軸方向の各ホール素子41の出力信号をそれぞれ差動アンプ32が差動的に増幅し、その出力信号(アナログ値)をA/D変換器33がデジタル値に変換し、その出力信号(電圧)を検出制御部34がX座標値及びY座標値に変換し、これを出力制御部35を介して出力するように構成されている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
【0004】
前述したマグネットを移動可能にする支持機構の具体例としては、図9に示すように、コイルスプリング44の一端にマグネット42を支持し、コイルスプリング44を設置する基板に配設された磁気センサ41により、マグネット42の移動を磁気センサ41で検出するように構成されているものが提案されている。
【0005】
【特許文献1】
特開平10−20999号公報
【0006】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上述した位置検出装置や磁気検出式ポインティングデバイスは、以下に示すように3つの問題点がある。まず第1の問題点として、磁石の強さや磁気センサの感度のバラツキ、磁気センサの温度特性によるドリフトが、磁石の移動量や傾斜に対する出力信号に影響を及ぼすという問題がある。次に、第2の問題点として、同じ軸上の2つの磁気センサの間の距離が変わったり、磁気センサと磁石の間の距離がずれたりすると、同様に出力信号に影響を及ぼすという問題がある。さらに、第3の問題点として、磁石が磁気センサの間にある場合には、比較的、移動量と出力される信号とが単調増加するけれども、磁気センサの範囲を超えて大きく移動する場合には、差信号が徐々に暫減するため、磁気センサ間の距離を大きくできないという問題がある。
【0007】
本発明は、このような問題に鑑みてなされたもので、その目的とするところは、磁石や磁気センサの特性のバラツキや組立精度に対して影響を抑える位置検出装置を提供することにある。
【0008】
また、磁石の移動量に対して信号の単調増加の範囲が大きくなるような、小型化が可能な位置検出装置を提供することにある。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、このような目的を達成するために、請求項1に記載の発明は、X軸及びY軸に沿って2個ずつ配設された4つの磁気センサと、前記4つの磁気センサの中心付近に移動自在又は傾斜自在に配設される磁石とを備え、該磁石の移動量に対して出力信号の単調増加の範囲が大きくなるようにした位置検出装置であって、前記X軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの差信号を該X軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した出力値と、前記Y軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの差信号を該Y軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した出力値とをそれぞれ位置信号として出力し、前記磁石の移動距離に対して前記出力値が所定範囲以上で増加することを特徴とする。
【0010】
また、請求項2に記載の発明は、請求項1に記載の発明において、X軸及びY軸に沿って2個ずつ配設された4つの磁気センサと、前記4つの磁気センサの中心付近に移動自在又は傾斜自在に配設される磁石とを備え、X軸上の2つの磁気センサの差信号を前記4つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した値と、Y軸上の2つの磁気センサの差信号を前記4つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した値とをそれぞれ位置信号として出力することを特徴とする。
【0013】
なお、磁気センサとしては、ホール素子、ホールIC、磁気抵抗効果素子(MR素子)、磁気抵抗効果IC(MRIC)、リードスイッチなど様々な磁気センサの適用が可能であり、アナログ出力型のポインティングデバイスには、アナログ出力型の磁気センサが望ましく、デジタル出力型のポインティングデバイスには、デジタル出力型の磁気センサが望ましい。
【0014】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施例について説明する。
図1は、本発明に係るポインティングデバイスの一実施例を説明するための構成図で、図中符号1は磁気センサ、2はマグネット、3は弾性部材としてのシリコーン樹脂、4は実装基板、5は押圧部材、6はスイッチ、7は空間部、7aは切り欠き部である。磁気センサ1は、前述したようにX軸及びY軸に沿って2個ずつ対称に、実装基板4上に配置されている。マグネット2は、鉛直方向にNSの着磁がされている。
【0015】
シリコーン樹脂3を実装基板4に対して平行な面内においてずらすように動かすと、このシリコーン樹脂3は、切り欠き部7aの端部を支点として揺動し、これにともないマグネット2も同様に揺動する。
【0016】
このように、本発明のポインティングデバイスは、実装基板4上に設けられた複数の磁気センサ1と、実装基板4上に設けられて、任意の方向に揺動可能とする空間部7を有する弾性部材3と、この弾性部材3に設けられたマグネット2とを備え、弾性部材3の弾性変形によるマグネット2の摺動によって生じる磁気密度変化を複数の磁気センサ1で検出し、座標情報又はベクトル情報を入力するように構成されている。
【0017】
また、マグネット2は、上述したように水平方向に揺動自在であるとともに、実装基板4に対して垂直方向に変位可能であり、実装基板4に対して水平方向と垂直方向に動けるような自由度を有している。
【0018】
また、弾性部材3は屈曲部を有し、この屈曲部に切り欠き部7aを形成して、マグネット2の揺動自在を効果的なものにしている。
また、空間部7内で、実装基板4上にスイッチ6を配設し、ポインティングデバイスにスイッチ機能を持たせてある。
【0019】
また、スイッチとしては、特に種類の限定はないが、押しボタンスイッチなど、どのようなスイッチでもかまわないが、押したことが確認しやすく(クリック感のある)、スイッチを押し込んだ後に自動復帰するタクティール(tactile)スイッチ、タクト(tact)スイッチ、タッチ(touch)スイッチ、ストロークスイッチ等、対象物との物理的接触を利用して対象物を確認するスイッチが適している。
【0020】
また、マグネット2についても、特に種類の限定はないが、通常量産されているフェライト系、サマリウム−コバルト系、ネオジ系など様々なマグネットが適用可能である。ポインティングデバイスの小型化を進める上では、マグネットの小型化が必須であるので、小さくても強磁場を発生するサマリウム−コバルト系やネオジ系などのマグネットが好ましい。
【0021】
また、弾性部材についても、特に種類の限定はないが、現在様々な用途に使われているシリコーン樹脂が好ましい。
【0022】
また、押圧部材5は、指先で押したときにマグネット2がぶれたり、へこんで内側に位置がずれたりしないように、剛体的な性状を有する材料で形成するのがよい。特に、外部に漏れる磁場の強さを小さくするために非磁性体が好ましい。例えば、ポリカーボネートを切削加工したり、変性ポリフェリレンエーテル、ポリスチレンなどの樹脂、プレス加工などで成型したマグネシュウム合金、アルミニュウム合金などの金属などで作製される。
【0023】
このような構成により、押圧部材5を右側から左方向に向かって押すと、弾性部材3と実装基板4との結合端部を支点として、左方向に揺動変位し、逆に、押圧部材5を左側から右方向に向かって押すと、弾性部材3と実装基板4との結合端部を支点として、右方向に揺動変位する。このようにして、弾性部材3に設けられたマグネット2は左右に揺動自在となる。この操作は、人差し指の腹の部分、または親指の腹の部分によって可能である。この場合、指との密着性を考慮して、押圧部材5の表面を、粗面、凹状面、凸状面、凸状四角錐、凹状四角錐のいずれかにすることが望ましい。また、押圧部材5の形状を、円形、正方形、矩形、八角形、楕円形、歯車形のいずれかにすることも可能である。
【0024】
[実施例1]
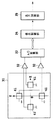
図2は、本発明に係る位置検出装置の実施例1を説明するための回路ブロックで、図中符号11は検出部、12(12x,12y)は差動アンプ、13はA/D変換器、14は検出制御部、15は座標変換部、16は座標切換部、17は出力方法記憶部、18は出力制御部、21(21a,21b,21c,21d)はホール素子、51は距離算出部、52は角度算出部、53は距離出力制限部を示している。
【0025】
検出部11は、4個の磁気センサ(例えば、ホール素子,半導体磁気抵抗素子,感磁性体磁気抵抗素子,GMR素子)21からなり、このホール素子21は、X軸及びY軸に沿って2個ずつ対称に配置されている。X軸及びY軸上に対称に配設された4個のホール素子21a,21b,21c,21dの中央付近にマグネットが配置されている。このマグネットの移動による磁界の変化によりホール素子21の出力電圧が変化する。差動アンプ12は、X軸方向とY軸方向の各ホール素子21の出力信号をそれぞれ差動的に増幅する。Z軸方向の磁界が原点Oについて対称、すなわち、マグネットの着磁方向が鉛直方向にあるとき、出力信号が0になるようにしてあり、マグネットが移動すると、これに応じて差動アンプ12x,12yに出力信号Xo,Yoがそれぞれ発生する。
【0026】
ここで、検出部11のX軸方向に配設されたホール素子21aからの信号をX1、ホール素子21bからの信号をX2とし、また、検出部11のY軸方向に配設されたホール素子21cからの信号をY1、ホール素子21dからの信号をY2とし、差動アンプ12xの出力をXo、差動アンプ12yの出力をYoとすると、
Xo=(X1−X2)/(X1+X2)
Yo=(Y1−Y2)/(Y1+Y2)
となるような出力を生成する。
【0027】
つまり、X軸方向に配設されたホール素子21a,21bの差信号(X1−X2)を、このホール素子21a,21bの和信号(X1+X2)で除算した信号(Xo=(X1−X2)/(X1+X2))を生成するとともに、Y軸方向に配設されたホール素子21c,21dの差信号(Y1−Y2)を、このホール素子21c,21dの和信号(Y1+Y2)で除算した信号(Yo=(Y1−Y2)/(Y1+Y2))を生成する。
【0028】
従来は、差動アンプ12xの出力Xoは、X1−X2であり、また、差動アンプ12yの出力YoはY1−Y2であった。磁石の移動距離が増加した場合の出力信号を図5及び図6に示す。図5は、従来の、2つの磁気センサの出力差と磁石の移動距離の関係を示す図であり、図6は、出力差/出力和と磁石の移動距離の関係を示す図である。ここで、磁石のサイズを3mm×3mm×0.8mm(縦×横×高さ)、軸上の2つのセンサのピッチを3.25mmとしている。図中に示すGapは、磁石表面とセンサ面までのZ軸方向の距離を示している。
【0029】
従来は、図5に示すように、2mmから暫減しているのに対し、本発明においては、図6に示すように(図中右側下段に示す3つの曲線)、2mm以上の範囲で差出力電圧は増加していることが分かる。
【0030】
A/D変換器13は、差動アンプ12の出力信号(アナログ値)をデジタル値に変換する。検出制御部14は、A/D変換器13からの出力信号(電圧)をX座標値及びY座標値に変換する。座標変換部15は、検出制御部14から出力されるXY座標の座標値(X,Y)を極座標の座標値(R,θ)に変換する。
【0031】
座標切換部16は、座標変換部15から出力される極座標の座標値と、検出制御部14から出力されるXY座標の座標値の双方の信号を受け、出力方法記憶部17の指示に従っていずれか一方を出力制御部18に出力する。出力方法記憶部17は、外部から指定された出力方法(XY座標/極座標)を記憶してこれを座標切換部16に指示する。出力制御部18は、外部に対する座標値出力を制御する。
【0032】
座標変換部15は、距離算出部51と角度算出部52と距離出力制限部53とからなり、距離算出部51で距離Rを、例えば、R=√(X2+Y2)の形で、また、角度算出部52を、例えば、θ=tan−1(Y/X)の形で、それぞれ算出する。距離出力制限部53は、距離算出部51が算出したRを予め定めた限界値Rmaxと比較し、R>Rmaxの場合には、RをRmaxに変換して出力する。これを図3により説明する。
【0033】
図3は、出力制限機能の説明図である。つまり、入力座標値(R,θ)におけるRがRmaxより大きい場合、出力座標値を常に(Rmax,θ)とする。
【0034】
なお、このRを制限する機能は、円形領域に表示を行うようなアプリケーションの場合に表示不能となることを防止するためのものであるが、機構的にRがRmaxを超えることがないようになっているなど、この機能を必要としない場合には、この距離出力制限部53を設けなくてよい。
【0035】
図4は、本発明に係る位置検出装置の他の実施例を説明するための回路ブロックで、図2と同じ機能を有する構成要素には同一の符号を付してある。この実施例において、検出制御部14と座標変換部15と出力制御部18とが直列に接続されており、図2における座標切換部16と出力方法記憶部17がなく、したがって、極座標の座標値のみを出力するように構成されている。
【0036】
[実施例2]
次に、本発明に係る位置検出装置の実施例2について説明する。この実施例2の回路ブロックは、上述した実施例1と同様である。実施例1との相違は、差動アンプ12xの出力Xoと差動アンプ12yの出力Yoの算出方法が異なる点である。
【0037】
検出部11のX軸方向に配設されたホール素子21aからの信号をX1、ホール素子21bからに信号をX2とし、また、検出部11のY軸方向に配設されたホール素子21cからの信号をY1、ホール素子21dからの信号をY2とし、差動アンプ12xの出力をXo、差動アンプ12yの出力をYoとすると、
Xo=(X1−X2)/(X1+X2+Y1+Y2)
Yo=(Y1−Y2)/(X1+X2+Y1+Y2)
となるような出力を生成する。
【0038】
つまり、X軸方向に配設されたホール素子21a,21bの差信号(X1−X2)を、このホール素子21a〜21dの和信号(X1+X2+Y1+Y2)で除算した信号(Xo=(X1−X2)/(X1+X2+Y1+Y2))を生成するとともに、Y軸方向に配設されたホール素子21c,21dの差信号(Y1−Y2)を、このホール素子21a〜21dの和信号(X1+X2+Y1+Y2)で除算した信号(Yo=(Y1−Y2)/(X1+X2+Y1+Y2))を生成する。この実施例2によれば、図6に示すように(図中右側上段に示す3つの曲線)、実施例1と比べて、さらに単調増加する範囲が広くなっていることが分かる。
【0039】
[実施例3]
図7は、本発明に係る位置検出装置のさらに他の実施例を説明するための図で、図中符号22は位置や移動量、傾斜度合いを検出する対象の被検出物体、23は磁石を示している。被検出物体22には磁石23が固定されていて、上述した図1に示した磁気センサ1上で磁石23を移動又は傾斜させることにより、被検出物体22の位置や移動量、傾斜度合いを検出できるように構成されている。なお、回路ブロックは、上述した実施例1,2と同じものである。
【0040】
本実施例3においては、このような構成により、温度変化や磁石のばらつきがあっても、被検出物体22の移動量を0.1mmレベルで検出することが可能となった。
【0041】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように本発明によれば、X軸及びY軸に沿って2個ずつ配設された4つの磁気センサと、前記4つの磁気センサの中心付近に移動自在又は傾斜自在に配設される磁石とを備え、該磁石の移動量に対して出力信号の単調増加の範囲が大きくなるようにした位置検出装置であって、前記X軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの差信号を該X軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した出力値と、前記Y軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの差信号を該Y軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した出力値とをそれぞれ位置信号として出力し、前記磁石の移動距離に対して前記出力値が所定範囲以上で増加するので、磁石や磁気センサの特性のバラツキやその温度特性によるドイフトに対して、全く影響を受けない出力を得ることができる。また、磁石と磁気センサの距離の影響が小さくなり、磁石の移動量に対して信号の単調増加の範囲が大きくなるので、設計、調整、組立てが容易になるという効果を奏する。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明に係るポインティングデバイスの一実施例を説明するための構成図である。
【図2】本発明に係る位置検出装置の実施例1を説明するための回路ブロックである。
【図3】出力制限機能の説明図である。
【図4】本発明に係る位置検出装置の他の実施例を説明するための回路ブロックである。
【図5】従来の、2つの磁気センサの出力差と磁石の移動距離の関係を示す図である。
【図6】出力差/出力和と磁石の移動距離の関係で、2つの和と4つの和で割った場合を示す図である。
【図7】本発明に係る位置検出装置のさらに他の実施例を説明するための図である。
【図8】従来の磁気検出式ポインティングデバイスの磁気検出回路を示すブロック図である。
【図9】従来のポインティングデバイスで使用されているマグネット支持機構の例を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1 磁気センサ
2 マグネット
3 弾性部材としてのシリコーン樹脂
4 実装基板
5 押圧部材
6 スイッチ
7 空間部
7a 切り欠き部
11 検出部
12(12x,12y) 差動アンプ
13 A/D変換器
14 検出制御部
15 座標変換部
16 座標切換部
17 出力方法記憶部
18 出力制御部
21(21a,21b,21c,21d) ホール素子
22 被検出物体
23 磁石
31 検出部
32 差動アンプ
33 A/D変換器
34 検出制御部
35 出力制御部
41 ホール素子
51 距離算出部
52 角度算出部
53 距離出力制限部[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a position detection device that detects the movement or inclination of an object, and more particularly to a position detection device that uses the position detection device and is used as input means for a personal computer, a mobile phone, or the like. More specifically, the present invention relates to a magnetic detection type position detection device that performs coordinate detection by detecting a change in the surrounding magnetic field due to movement of a magnet.
[0002]
Devices that detect the movement, tilt, or movement angle of an object with a magnet, a magnetic material, and a magnetic sensor are known. In addition, optical, pressure-sensitive, variable resistance, and magnetic detection methods have been put to practical use as pointing detection methods (joysticks, trackballs, etc.) for personal computers (including amusement and simulation computers). However, in recent years, magnetic detection methods that are easy to miniaturize, have no contact, and have a long life have become prominent.
[0003]
[Prior art]
FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing a magnetic detection circuit of a conventional magnetic detection type pointing device. The
[0004]
As a specific example of the above-described support mechanism that enables the magnet to move, as shown in FIG. 9, a
[0005]
[Patent Document 1]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 10-20999 [0006]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, the position detection device and the magnetic detection type pointing device described above have three problems as described below. First, there is a problem that the magnet strength, the variation in the sensitivity of the magnetic sensor, and the drift due to the temperature characteristics of the magnetic sensor affect the output signal with respect to the moving amount and inclination of the magnet. Next, as a second problem, if the distance between two magnetic sensors on the same axis changes or the distance between the magnetic sensor and the magnet shifts, the output signal is similarly affected. is there. Furthermore, as a third problem, when the magnet is located between the magnetic sensors, the movement amount and the output signal increase relatively monotonously, but when the magnet moves greatly beyond the range of the magnetic sensor. Has a problem that the distance between the magnetic sensors cannot be increased because the difference signal gradually decreases for a while.
[0007]
The present invention has been made in view of such problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a position detection device that suppresses the influence on variation in characteristics of magnets and magnetic sensors and assembly accuracy.
[0008]
It is another object of the present invention to provide a position detecting device that can be miniaturized so that the range of monotonous increase in signal with respect to the amount of movement of the magnet becomes large.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, the present invention is characterized in that the invention according to
[0010]
According to a second aspect of the present invention, there is provided the magnetic sensor according to the first aspect of the present invention, wherein four magnetic sensors are disposed along the X-axis and the Y-axis, and two magnetic sensors are disposed near the center of the four magnetic sensors. A magnet that is arranged so as to be movable or tiltable. A value obtained by dividing a difference signal of two magnetic sensors on the X axis by a sum signal of the four magnetic sensors, and two magnetic sensors on the Y axis. A value obtained by dividing the difference signal by the sum signal of the four magnetic sensors is output as a position signal .
[0013]
As the magnetic sensor, various magnetic sensors such as a Hall element, Hall IC, magnetoresistive effect element (MR element), magnetoresistive effect IC (MRIC), and reed switch can be applied, and an analog output type pointing device. For this, an analog output type magnetic sensor is desirable, and a digital output type magnetic sensor is desirable for a digital output type pointing device.
[0014]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a block diagram for explaining an embodiment of a pointing device according to the present invention. In the figure,
[0015]
When the silicone resin 3 is moved so as to be shifted in a plane parallel to the
[0016]
As described above, the pointing device of the present invention includes a plurality of
[0017]
Further, the
[0018]
Further, the elastic member 3 has a bent portion, and a
Further, a switch 6 is disposed on the
[0019]
There is no particular limitation on the type of switch, but any switch such as a push button switch may be used. However, it is easy to confirm that the switch has been pressed (it has a feeling of clicking), and it automatically returns after the switch is pressed. A switch for confirming an object using physical contact with the object such as a tactile switch, a tact switch, a touch switch, or a stroke switch is suitable.
[0020]
Also, the
[0021]
Further, the elastic member is not particularly limited in kind, but a silicone resin currently used for various applications is preferable.
[0022]
Further, the pressing
[0023]
With this configuration, when the
[0024]
[Example 1]
FIG. 2 is a circuit block for explaining the first embodiment of the position detection apparatus according to the present invention, in which
[0025]
The
[0026]
Here, the signal from the
Xo = (X1-X2) / (X1 + X2)
Yo = (Y1-Y2) / (Y1 + Y2)
Produces output such that
[0027]
That is, a signal (Xo = (X1−X2) /) obtained by dividing the difference signal (X1−X2) between the
[0028]
Conventionally, the output Xo of the
[0029]
Conventionally, as shown in FIG. 5, the distance is gradually reduced from 2 mm, but in the present invention, as shown in FIG. 6 (three curves shown on the lower right side in the figure), the difference is within a range of 2 mm or more. It can be seen that the output voltage has increased.
[0030]
The A /
[0031]
The coordinate switching
[0032]
The coordinate
[0033]
FIG. 3 is an explanatory diagram of the output restriction function. That is, when R in the input coordinate value (R, θ) is larger than Rmax, the output coordinate value is always (Rmax, θ).
[0034]
The function for limiting R is to prevent the display from being disabled in the case of an application that displays in a circular area. However, R does not exceed Rmax mechanically. In the case where this function is not required, for example, the distance
[0035]
FIG. 4 is a circuit block for explaining another embodiment of the position detecting apparatus according to the present invention. Components having the same functions as those in FIG. 2 are denoted by the same reference numerals. In this embodiment, the
[0036]
[Example 2]
Next, a second embodiment of the position detection apparatus according to the present invention will be described. The circuit block of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment described above. The difference from the first embodiment is that the calculation method of the output Xo of the
[0037]
The signal from the
Xo = (X1-X2) / (X1 + X2 + Y1 + Y2)
Yo = (Y1-Y2) / (X1 + X2 + Y1 + Y2)
Produces output such that
[0038]
That is, a signal (Xo = (X1−X2) /) obtained by dividing the difference signal (X1−X2) between the
[0039]
[Example 3]
FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining still another embodiment of the position detection apparatus according to the present invention. In the figure, reference numeral 22 denotes a detected object to be detected for position, amount of movement, and inclination, and 23 denotes a magnet. Show. A
[0040]
In the third embodiment, such a configuration makes it possible to detect the amount of movement of the detected object 22 at the 0.1 mm level even when there is a temperature change or magnet variation.
[0041]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, four magnetic sensors arranged two by two along the X-axis and the Y-axis, and movable or tilted are arranged near the centers of the four magnetic sensors. that a magnet, a position detecting device range of monotonous increase was larger in the output signal with respect to the moving amount of the magnet, the difference signal the X of the two magnetic sensors on the X axis the output value divided by the sum signal of the two magnetic sensors on the axis, the Y-axis on the two output values divided by the sum signal of the two magnetic sensors on the Y-axis the difference signal of the magnetic sensor Are output as position signals, and the output value increases beyond a predetermined range with respect to the moving distance of the magnet. You can get output that doesn't receive In addition, the influence of the distance between the magnet and the magnetic sensor is reduced, and the range of the monotonous increase of the signal with respect to the amount of movement of the magnet is increased, so that the design, adjustment, and assembly are facilitated.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram for explaining an embodiment of a pointing device according to the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a circuit block for explaining Example 1 of the position detecting apparatus according to the present invention.
FIG. 3 is an explanatory diagram of an output restriction function.
FIG. 4 is a circuit block for explaining another embodiment of the position detecting apparatus according to the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a relationship between an output difference between two conventional magnetic sensors and a moving distance of a magnet.
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a case of dividing by two sums and four sums in relation to an output difference / output sum and a moving distance of a magnet.
FIG. 7 is a diagram for explaining still another embodiment of the position detection apparatus according to the present invention.
FIG. 8 is a block diagram showing a magnetic detection circuit of a conventional magnetic detection type pointing device.
FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating an example of a magnet support mechanism used in a conventional pointing device.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (2)
前記X軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの差信号を該X軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した出力値と、前記Y軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの差信号を該Y軸上の前記2つの磁気センサの和信号で除算した出力値とをそれぞれ位置信号として出力し、前記磁石の移動距離に対して前記出力値が所定範囲以上で増加することを特徴とする位置検出装置。Four magnetic sensors arranged two each along the X-axis and the Y-axis, and a magnet arranged so as to be movable or tiltable near the center of the four magnetic sensors, and the amount of movement of the magnets A position detection device in which the range of the monotonic increase of the output signal is increased,
The output value divided by the sum signal of the two magnetic sensors on the X-axis the difference signal of the two magnetic sensors on the X axis, a difference signal of the two magnetic sensors on the Y axis the Y wherein on the shaft two the output value divided by the sum signal of the magnetic sensor output as each position signal, the position detection in which the output value to the movement distance of the magnet is characterized in that to increase above the predetermined range apparatus.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003122709A JP4612281B2 (en) | 2003-03-25 | 2003-04-25 | Position detection device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003083787 | 2003-03-25 | ||
| JP2003122709A JP4612281B2 (en) | 2003-03-25 | 2003-04-25 | Position detection device |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004348173A JP2004348173A (en) | 2004-12-09 |
| JP2004348173A5 JP2004348173A5 (en) | 2006-09-21 |
| JP4612281B2 true JP4612281B2 (en) | 2011-01-12 |
Family
ID=33543009
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003122709A Expired - Lifetime JP4612281B2 (en) | 2003-03-25 | 2003-04-25 | Position detection device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4612281B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4697656B2 (en) * | 2005-03-11 | 2011-06-08 | 日本電気株式会社 | Mobile phone pointing device, method, and computer program |
| JP4400500B2 (en) | 2005-04-06 | 2010-01-20 | コニカミノルタオプト株式会社 | Position detector and positioning device |
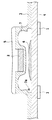
| JP4931552B2 (en) * | 2005-10-31 | 2012-05-16 | 旭化成ホームズ株式会社 | Locking structure of the opening |
| CN101331385B (en) | 2005-12-16 | 2011-11-30 | 旭化成电子材料元件株式会社 | Position detector |
| JP5483516B2 (en) * | 2006-09-20 | 2014-05-07 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | POSITION DETECTION DEVICE, OPTICAL SYSTEM HAVING POSITION DETECTION DEVICE, AND IMAGING DEVICE |
| JP4926626B2 (en) * | 2006-09-20 | 2012-05-09 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | POSITION DETECTION SYSTEM, OPTICAL SYSTEM USING POSITION DETECTION SYSTEM, AND IMAGING DEVICE |
| JP5513718B2 (en) * | 2008-05-23 | 2014-06-04 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP5124879B2 (en) * | 2008-10-31 | 2013-01-23 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | POSITION DETECTING DEVICE AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE USING THE POSITION DETECTING DEVICE |
| JP5275829B2 (en) * | 2009-01-19 | 2013-08-28 | アルプス電気株式会社 | Motion detection apparatus and motion detection method |
| JP5155966B2 (en) * | 2009-08-12 | 2013-03-06 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | Position detection device |
| JP5352861B2 (en) * | 2009-10-09 | 2013-11-27 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | pointing device |
| JP5144694B2 (en) * | 2010-02-17 | 2013-02-13 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | Magnetic sensor unit |
| JP5715023B2 (en) * | 2011-10-12 | 2015-05-07 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | POSITION DETECTION DEVICE, POSITION DETECTION METHOD, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE USING THE SAME |
| JP6621253B2 (en) | 2015-06-23 | 2019-12-18 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, control method, and program |
| JP6798853B2 (en) * | 2016-10-21 | 2020-12-09 | 旭化成エレクトロニクス株式会社 | Signal detector |
| KR102246679B1 (en) * | 2018-12-21 | 2021-04-30 | 주식회사 지니틱스 | Method for making a displacement curve of an auto focus driver unit into a linear form |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07134613A (en) * | 1993-11-10 | 1995-05-23 | Daifuku Co Ltd | Guide sensor device and vehicle using the same |
| JPH09189509A (en) * | 1996-01-06 | 1997-07-22 | Unisia Jecs Corp | Device for detecting rotation angle |
| JPH1020999A (en) * | 1996-07-03 | 1998-01-23 | Fujitsu Takamizawa Component Kk | Pointing device |
-
2003
- 2003-04-25 JP JP2003122709A patent/JP4612281B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07134613A (en) * | 1993-11-10 | 1995-05-23 | Daifuku Co Ltd | Guide sensor device and vehicle using the same |
| JPH09189509A (en) * | 1996-01-06 | 1997-07-22 | Unisia Jecs Corp | Device for detecting rotation angle |
| JPH1020999A (en) * | 1996-07-03 | 1998-01-23 | Fujitsu Takamizawa Component Kk | Pointing device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004348173A (en) | 2004-12-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4612281B2 (en) | Position detection device | |
| JP4559706B2 (en) | pointing device | |
| JP4408862B2 (en) | pointing device | |
| US6606085B1 (en) | Coordinate input device | |
| US6762748B2 (en) | Compact low profile magnetic input device | |
| US10840041B1 (en) | Multifunctional control element | |
| KR100827621B1 (en) | Input device | |
| US6670946B2 (en) | Coordinates input apparatus | |
| US8698738B2 (en) | Position detection device | |
| EP0477098A2 (en) | Cursor displacement control device for a computer display | |
| US20110134029A1 (en) | Electronic device and a pointer motion control method thereof | |
| JP5131777B2 (en) | Input device and electronic device using the same | |
| JPH04125723A (en) | Pointing controller | |
| JP5434542B2 (en) | Input device | |
| JP2011210078A (en) | Input device | |
| JP2003196019A (en) | Magnetic sensor array and pointing device | |
| JP2003196018A (en) | Operating adaptor for pointing device | |
| JP5352861B2 (en) | pointing device | |
| JP5098774B2 (en) | Input device | |
| JP4721915B2 (en) | Operation member for slide input device and slide input device | |
| WO2008063021A1 (en) | Pointing device and electronic device having the same | |
| JP2002182846A (en) | Pointing device | |
| JPH06309094A (en) | Coordinate input device | |
| JPH04282718A (en) | Pointing device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060316 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060808 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080826 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080905 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20081104 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20091204 |
|
| RD13 | Notification of appointment of power of sub attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7433 Effective date: 20100210 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100224 |
|
| RD13 | Notification of appointment of power of sub attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7433 Effective date: 20100226 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20100210 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20100226 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20100325 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20101008 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20101015 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131022 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4612281 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |