JP4545831B2 - データカード検証装置 - Google Patents
データカード検証装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4545831B2 JP4545831B2 JP53240498A JP53240498A JP4545831B2 JP 4545831 B2 JP4545831 B2 JP 4545831B2 JP 53240498 A JP53240498 A JP 53240498A JP 53240498 A JP53240498 A JP 53240498A JP 4545831 B2 JP4545831 B2 JP 4545831B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signature
- communication device
- signature scheme
- verification
- scheme
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 title claims description 45
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 claims 4
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 claims 2
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000013524 data verification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07F—COIN-FREED OR LIKE APPARATUS
- G07F7/00—Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus
- G07F7/08—Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus by coded identity card or credit card or other personal identification means
- G07F7/10—Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus by coded identity card or credit card or other personal identification means together with a coded signal, e.g. in the form of personal identification information, like personal identification number [PIN] or biometric data
- G07F7/1008—Active credit-cards provided with means to personalise their use, e.g. with PIN-introduction/comparison system
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/30—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks
- G06Q20/34—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks using cards, e.g. integrated circuit [IC] cards or magnetic cards
- G06Q20/341—Active cards, i.e. cards including their own processing means, e.g. including an IC or chip
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/30—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks
- G06Q20/36—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks using electronic wallets or electronic money safes
- G06Q20/367—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks using electronic wallets or electronic money safes involving electronic purses or money safes
- G06Q20/3674—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols characterised by the use of specific devices or networks using electronic wallets or electronic money safes involving electronic purses or money safes involving authentication
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/38—Payment protocols; Details thereof
- G06Q20/382—Payment protocols; Details thereof insuring higher security of transaction
- G06Q20/3825—Use of electronic signatures
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/38—Payment protocols; Details thereof
- G06Q20/40—Authorisation, e.g. identification of payer or payee, verification of customer or shop credentials; Review and approval of payers, e.g. check credit lines or negative lists
- G06Q20/401—Transaction verification
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q20/00—Payment architectures, schemes or protocols
- G06Q20/38—Payment protocols; Details thereof
- G06Q20/40—Authorisation, e.g. identification of payer or payee, verification of customer or shop credentials; Review and approval of payers, e.g. check credit lines or negative lists
- G06Q20/409—Device specific authentication in transaction processing
- G06Q20/4097—Device specific authentication in transaction processing using mutual authentication between devices and transaction partners
- G06Q20/40975—Device specific authentication in transaction processing using mutual authentication between devices and transaction partners using encryption therefor
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G07—CHECKING-DEVICES
- G07F—COIN-FREED OR LIKE APPARATUS
- G07F7/00—Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus
- G07F7/08—Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus by coded identity card or credit card or other personal identification means
- G07F7/10—Mechanisms actuated by objects other than coins to free or to actuate vending, hiring, coin or paper currency dispensing or refunding apparatus by coded identity card or credit card or other personal identification means together with a coded signal, e.g. in the form of personal identification information, like personal identification number [PIN] or biometric data
- G07F7/1016—Devices or methods for securing the PIN and other transaction-data, e.g. by encryption
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/30—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy
- H04L9/3066—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy involving algebraic varieties, e.g. elliptic or hyper-elliptic curves
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/32—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials
- H04L9/3247—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials involving digital signatures
- H04L9/3249—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials involving digital signatures using RSA or related signature schemes, e.g. Rabin scheme
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/32—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials
- H04L9/3247—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials involving digital signatures
- H04L9/3252—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials involving digital signatures using DSA or related signature schemes, e.g. elliptic based signatures, ElGamal or Schnorr schemes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q2220/00—Business processing using cryptography
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L2209/00—Additional information or applications relating to cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communication H04L9/00
- H04L2209/56—Financial cryptography, e.g. electronic payment or e-cash
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Accounting & Taxation (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Finance (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Algebra (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Financial Or Insurance-Related Operations Such As Payment And Settlement (AREA)
- Storage Device Security (AREA)
- Control Of Vending Devices And Auxiliary Devices For Vending Devices (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Description
本発明は、電子取引システムにおいてのデータ転送及び確認のための方法及び装置に、より詳しくは、スマートカードを用いた電子取引システムに関する。
[背景技術]
金融取引もしくは証券の交換のような取引を電子式に行うことは、広く受入れられている。自動化されたテラーマシン(ATM)及びクレジットカードは、個人の取引に広く使用されており、その使用が拡大されるのに伴って、かかる取引を検証する必要性も増大してきている。スマートカードは、多少クレジットカードに類似しており、いくらかの演算処理能力及び記憶能力を備えている。スマートカードは、例えば、疑いをもたないユーザーから情報を収集するためのダミー端局などによって不正使用され易い。そのため、端局とスマートカードとの間もしくは逆にスマートカードと端局との間の重要な情報の交換が行われる前に、端局並びにカードの真正さを検証することが必要となる。これらの検証の1つは、取引の真正さが後のセッションに加わる両当事者によって検証されうるように、最初の取引をデジタルに「署名」する形式を取り得る。この署名は、ランダムなメッセージ即ち取引と当事者に関連したシークレットキーとを使用したプロトコルに従って行われる。
署名は、当事者のシークレットキーを定めることができないように行われねばならない。シークレットキーの配分の複雑さをさけるために、署名の発生において公共キー暗号化スキーム(パブリックキー暗号方式)を利用することが好ましい。これらの能力は、比較的大きな計算リソースにアクセスする当事者間で行う場合に使用可能となるが、スマートカードの場合のように計算リソースがより限定されている個人レベルにおいてこれらの取引を容易化することも同様に大切である。
取引カード又はスマートカードは、現在は限られた計算能力と共に利用しうるが、これらは、商業的に存続し得る形で既存のデジタル署名プロトコルを実現するには十分ではない。前述したように、検証署名を作成するには、公共キー暗号化スキーム(パブリックキー暗号方式)を利用することが必要となる。現在、多くの公共キースキーム(パブリックキー方式)は、RSAに基づいているが、DSS(Digital Signature Standard)並びによりコンパクトなシステムに対する需要は、これを急速に変えつつある。ディフィー・ヘルマン(Diffie−Hellman)公共キープロトコル(パブリックキープロトコル)を具現したDSS(Digital Signature Standard)スキームは、整数ZPの集合を使用する。ここにpは大きな素数である。適切なセキュリティのためには、pは512ビットのオーダーとする必要がある。結果する署名は、減少mod q(ここにqは(p−1))を割算し、160ビットのオーダーとすることができる。
最初の十分に完成した公共キーアルゴリズム(パブリックキーアルゴリズム)の1つであり、暗号化にもデジタル署名にも役立つ、別の暗号化スキームは、RSAアルゴリズムである。RSAは、大きな数を因数分解することの困難さに、そのセキュリティを求めている。公共キー(パブリックキー)及びプライベートキーは、1対の(100−200桁又はそれ以上の)大きな素数の関数である。RSA暗号化の公共キー(パブリックキー)は、2つの素数p、q(p及びqは秘密に保つものとする)の積であるnと、(p−1)×(q−1)に対して比較的に素であるeとである。従って、暗号化キーdは、e-1(mod(p−1)×(q−1))である。ここにd、nは互いに素である。
メッセージmを暗号化するには、各々の数字ブロックがユニーク表示モジュラス(unique representation modulo)nであるような、複数の数字ブロックに割算する。その場合、暗号化メッセージブロックciは単純にmi e(mod n)である。メッセージを解号するには、各々の暗号化ブロックciを取り、
mi=ci d(mod n)を計算する。
比較的小さなモジュラス(modulus)で高いセキュリティを与える別の暗号化スキームは、有限なフィールド2mにおいて楕円曲線を利用するスキームである。155のオーダーのmの値は、512ビットモジュラスDSSと比較可能なセキュリティを与えるので、実施にとって大きな利点を提供する。
ディフィー・ヘルマン(Diffie−Hellman)公共キー暗号化(パブリックキー暗号化)は、ディスクリート・ログ(discrete logs)の性質を利用するので、ゼネレーターβ及びその指数化(exponentiation)βkが既知でも、kの値は定められない。任意の曲線上の2点の和が同じ曲線上の第3の点を生ずる楕円曲線の場合にも同様の性質が存在する。同様に、曲線上の点Pに整数kを掛算すれば、同じ曲線上に別の点を生ずる。楕円曲線の場合、点kPは、単に点Pのコピーk個を互いに加算することによって得られる。
しかし、開始点と終点とを知ることによっては、暗号化のためのセッションキーとして次に使用しうる整数kの値は明らかにされない。従って、値kP(Pは最初の既知の点)は、指数形βkと同様である。更に、楕円曲線の暗号化システムは、帯域効率、計算量の減少及び最小コードスペースがアプリケーションの目標である場合に、他のキー暗号化システムに比べて利点を提供する。
更に、スマートカード及び自動化テラーマシン取引の文脉においては、両当事者の確認(authentication)に、2つの主要なステップが含まれる。第1のステップは、スマートカードによる端局の確認であり、第2のステップは、端局によるスマートカードの確認である。一般に、確認には、端局によって生成されスマートカードによって受信される証明書の検証と、スマートカードによって署名され端局によって検証される証明書の検証が含まれる。2つの証明書が肯定的に検証されたら、スマートカードと端局との間の取引は、継続(続行)することができる。
スマートカードの処理能力は限定されているので、スマートカードによって実行される検証及び署名処理は、一般に、簡単な暗号化アルゴリズムに限定される。よりこみいった暗号化アルゴリズムは、一般に、スマートカードに含まれる処理能力の範囲を超えている。そのため、スマートカードにおいて実現され、比較的セキュリティの高い、署名検証及び発生方法に対する需要が存在する。
[発明の概要]
本発明は、一つの視点においてスマートカードと端局との間のデータの検証方法を提供することを目的としている。
この視点によれば、電子取引の1対の参加者を検証する方法が提供され、該方法は以下の各工程を含む:即ち第1の参加者から第2の参加者によって受信された情報を、第1の署名アルゴリズムに従って検証する工程と、第2の参加者から第1の参加者によって受信された情報を、第2の署名アルゴリズムに従って検証する工程と、を有し、どちらかの検証が失敗に終った場合には、取引は拒絶されるようにした検証方法が提供される。
第1の署名アルゴリズムは、検証よりも署名において計算上一層困難なアルゴリズムであることができ、また第2の署名アルゴリズムが署名よりも検証において計算上一層困難なアルゴリズムであるようにしてもよい。このような実施の形態においては、ハイレベルのセキュリティを保ちながら、第2の参加者が、比較的低い計算力をもって取引に参加することが可能となる。
別の実施の形態によれば、第1の署名アルゴリズムは、RSA型又はDSS(Digital Signature Standard)型アルゴリズムに基づいたものであり、第2の署名アルゴリズムは、楕円曲線アルゴリズムに基づいている。
【図面の簡単な説明】
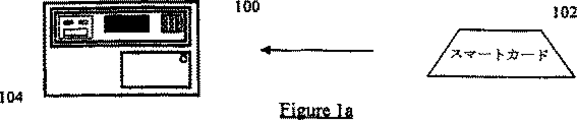
図1aは、スマートカードと端局とを示す概略図である。
図1bは、スマートカード取引システムにおいての検証プロセスの間に生起する一連の事象を示す概略図である。
図2は、特定のプロトコルを示す詳細な模式図である。
[発明を実施するための最良の形態]
図1aにおいて端局(ターミナル)100は、スマートカード102を受入れるようになされている。通常は、端局中にカード102を挿入することによって取引が開始される。次に、図1bに示すように、端局とカードとの間の相互の確認が行われる。非常に一般的には、この相互の確認は、「チャレンジ−レスポンス」(challenge−response)プロトコルに従って行われる。一般に、カードは、端局に情報を転送し、端局100は、RSAに基づいたアルゴリズム112によって、情報に署名し、次にカード102に送られ、カード102は、RSAに基づいたアルゴリズム114によって情報を確認する。カードと端局との間の情報交換(116)は、カードによって発生させた情報をも含み、この情報は、RSAアルゴリズムに従って端局によって署名されるべく端局に送られ、RSAアルゴリズムを用いて検証されるべくカードに返送される。関連する検証が行われる(118)と、別のステップが行われ、このステップでは、情報は、楕円曲線プロトコル120を用いて、カードによって署名され、楕円曲線に基づいたプロトコルを用いて端局により検証(124)されるべく端局に送られる。同様に、カードと端局との間の情報交換(122)は、端局によって発生される情報を含むことができ、この情報は、カードによって署名されるべくカードに送られ、検証されるべく端局に返送される。適正な情報が検証126されると、端局とカードとの間の以降の取引が進行可能(128)となる。
次に図2を参照すると、「チャレンジ−レスポンス」(challenged−response)プロトコルによる端局とカードとの相互の確認の詳細な実施形態が、全体として符号200によって示されている。端局100は、最初に、カード102によって検証され、次にカードが端局によって検証される。端局は、最初に、そのID、TIDを含む証明書Ci、20と、公共キー(パブリックキー)を含む公共情報(パブリック情報)とを、カードに送る。証明書20は、端局から受領した公共キー(パブリックキー)と端局ID TIDとの関連付けをカードが検証できるように、証明オーソリティないし官庁(CA)により署名されてもよい。端局とCAとによって用いられる、この実施の形態によるキーは、どちらも、RSAアルゴリズムに基づくことができる。
RSAアルゴリズムによれば、各々のメンバーないし当事者は、公共キー(パブリックキー)及びプライベートキーをもち、各々のキーは、2つの部分を有する。署名は、
S=md(mod n)
を形をもち、ここに、
mは署名されるべきメッセージであり、
nは公共キー(パブリックキー)であり、モジュラスであり、かつ2つの素数p、qの積、
eは、ランダムに選ばれたキーであり、公共キー(パブリックキー)でもあり、(p−1)×(q−1)に対して相対的に素であるように選ばれた数である。
dは、e-1(mod(p−1)×(q−1))に対して一致する(合同な)プライベートキーである。
RSAアルゴリズムに対して、対の整数(n、e)は、署名のために用いられる公共キー(パブリックキー)情報である。他方では、対の整数(d、n)は、公共キー(パブリックキー)情報(n、e)を用いて暗号化されたメッセージを解号するために使用しうる。
図2に戻って、数n、eは、CAの公共キー(パブリックキー)であり、システムパラメーターとして設定することができる。公共キー(パブリックキー)eは、スマートカード(以下「カード」とも略称)に格納しておいても、また別の実施の形態に従って、カードにおいて、ハード回路の論理回路にしておいてもよい。更に、eを比較的小さい値に選ぶことによって、指数化(exponentiation)が比較的すみやかに実行されることが保証される。
証明書20C1は、CAによって署名され、パラメーター(n、e)を有する。証明書は、端局ID TIdと端局公共キー(パブリックキー)情報Tn、Te(RSAアルゴリズムに基づく)を有する。証明書C1は、カード抽出TID、Tn、Teによって検証(24)される。この情報は、簡単に、C1 e mod nを実行することによって抽出される。カードは、次に、ランダムな数R1を発生(26)させることによって端局を確認する。これらの数は、カードによって端局に送られる。端局は、R1Te MODTnを実行することによって、そのシークレットキーTdを用いて、メッセージR1に署名し、値C2を発生させる(28)。なお、端局によって使用されるキーは、やはりRSAキーであり、このRSAキーは、公共キー(パブリックキー)Teがおそらくはシステムワイドであるような、値3を有する小さなパラメーターから成り、公共キー(パブリックキー)の他の部分は、端局に関連されるモジュラス(modulus)Tnであるように、オリジナルに作り出されたものである。端局プライベートキーTdは、小さな公共キー(パブリックキー)Teに対応するものであれば、小さくできない。端局の場合、端局は、指数化(exponentiation)を比較的すみやかに実行するための計算能力を備えているため、プライベートキーTdが大きく選ばれることは問題ではない。
端局は、値C2を計算する(28)と、ランダムなシークレットナンバーR2を発生させ(29)、端局は、R2、C2をカードに送る(32)。カードは次に端局のmodulus Tnを用いて、小さな指数Teによって、署名された値C2に対して、モジュールの指数化(modular exponentiation)を実行する(34)。これは、R1′=C2 Te mod Tnを計算することによって行う。R1′がR1に等しい(36)と、カードは、そのID TIDがモジュラスTnに関連(38)されている端局と取引していることを知る。カードは、一般に、前記の演算を実行するためのモジュール(modulo)算術プロセッサー(不図示)を備えている。
ランダムなシークレットナンバーR2は、カードによって署名(40)され、カードIDをその公共情報(パブリック情報)に関連付けるCAによって署名された証明書と共に、端局に返却される。カードによる署名は、楕円曲線署名アルゴリズムに従って実行される。
カードによる検証は、端局の検証と同様にして行われるが、カードによる署名は、楕円曲線暗号化システムを利用する。
典型的に、楕円曲線で実施の場合について、署名成分sは、次の形式を有する。
s=ae+k(mod n)
ここに、
Pは、システムの所定のパラメーターである曲線上の点、
kは、短い項(term)のプライベートキー又はセッションキーとして選ばれたランダムな整数であり、対応した短い項の公共キー(パブリックキー)R=kPを有する。
aは、送信側(カード)の長い項のプライベートキーであり、対応する公共キー(パブリックキー)aP=Qを有する。
eは、メッセージm(この場合R2)及び短い項の公共キー(パブリックキー)Rの確実なハッシュ、例えばSHAハッシュ関数である。
nは曲線の次数である。
単純化のために、この署名成分sは、前述したようにs=ae+kの形とするが、それ以外の署名プロトコルを用いても差支えない。
署名を検証するには、sP−eQを計算し、Rと比較しなければならない。カードは、例えばフィールド算術演算器(不図示)を用いて、Rを発生させる。カードは、図2のブロック(44)に示したm、sおよびRを含むメッセージを端局に送出し、kPに対応するべき値(sP−eQ)を計算(46)することによって、端局によって署名を検証する。計算された値が対応すれば(48)、署名は検証されるので、カードは、検証され、取引は継続(続行)することができる。
端局は、証明書をチェックし、次に、R2を含む取引データの署名をチェックし、端局に対してカードを確認する。本(第1の)実施形態によれば、カードによって発生させた署名は、楕円曲線署名であり、これは、カードが生成させるのは容易にできるが、端局による検証には、より多くの計算が必要とされる。
以上の式からわかるように、sの計算は比較的率直であり、大きな計算力を必要としない。しかし検証を行うには、sP、eQを得るために多数の点乗算を必要とし、その各々は計算が複雑である。他のプロトコル例えばMQVプロトコル(Menezes, Qu, Vanstone Protocol)は、楕円曲線に基づいて実施された場合、同様の計算を必要とし、計算能力が限られている場合、検証が遅くなる。しかし、一般に端局ではこのようにはならない。
端局及びカードの検証のための特定のプロトコルについて、本発明の実施の形態を以上に説明したが、これ以外のプロトコルも使用可能である。
Claims (10)
- 楕円曲線暗号を利用しない第1の署名スキームと楕円曲線暗号を利用し前記第1の署名スキームとは異なる第2の署名スキームとを有し、データ伝送システムを介して行われる電子取引の1対の通信装置間で交わされるメッセージの正当性の検証方法において、前記第1の署名スキームおよび前記第2の署名スキームの各々は、署名部分および検証部分を含み、前記第1の署名スキームの署名部分は、前記第1の署名スキームの検証部分よりも計算上より困難であり、前記第2の署名スキームの検証部分は、前記第2の署名スキームの署名部分よりも計算上より困難であり、
前記メッセージの正当性の検証方法は、以下の各工程:
第1の通信装置が、前記第1の署名スキームに従って、メッセージに署名し、第1の署名付きメッセージを第2の通信装置に送る工程、
前記第2の通信装置が、前記第1の署名スキームを用いて前記第1の通信装置から受信した前記第1の署名付きメッセージを検証する工程、
前記第2の通信装置が、前記第2の署名スキームに従って、メッセージに署名し、第2の署名付きメッセージを前記第1の通信装置に送る工程、
前記第1の通信装置が、前記第2の署名スキームを用いて前記第2の通信装置から受信した前記第2の署名付きメッセージを検証する工程、
どちらかの検証が失敗に終ったときは、前記各通信装置が前記電子取引を拒絶する工程、を有し、それにより、計算上より困難な部分が同一の通信装置で実行される、メッセージの正当性の検証方法。 - 前記通信装置は、異なった計算力を有し、より大きな計算力を有する通信装置で前記計算上より困難な部分が実行され、前記取引のセキュリティを保ちながら一方の前記通信装置が比較的低い計算力を持って参加することを可能とする請求の範囲第1項記載のメッセージの正当性の検証方法。
- 前記第1の署名スキームがRSA型アルゴリズムに基づく請求の範囲第1項記載のメッセージの正当性の検証方法。
- 前記第1の署名スキームがDSS(Digital Signature Standards)型スキームである請求の範囲第1項のメッセージの正当性の検証方法。
- 各通信装置が、第1の署名スキームと前記第1の署名スキームと異なる第2の署名スキームとを有し、データ伝送システムを介して行われる電子取引の1対の通信装置間で交わされるメッセージの正当性の検証方法において、前記第1の署名スキームおよび前記第2の署名スキームの各々は、署名部分および検証部分を含み、前記第1の署名スキームの署名部分は、前記第1の署名スキームの検証部分よりも計算上より困難であり、前記第2の署名スキームの検証部分は、前記第2の署名スキームの署名部分よりも計算上より困難であり、
前記メッセージの正当性の検証方法は、以下の各工程:
第1の通信装置が、公共キー(パブリックキー)及び該第1の通信装置の識別情報を含む第1の証明書C1を、第2の通信装置に送信する工程、
前記第2の通信装置が、該第1の証明書C1を検証し、それから前記公共キー(パブリックキー)及び識別情報を抽出する工程、
前記第2の通信装置が、第1のチャレンジR1を発生させ、該第1のチャレンジR1を、前記第1の通信装置に送信する工程、
該第1の通信装置が、前記公共キー(パブリックキー)に対応するプライベートキーを用いて、前記第1の署名スキームに従って、受信した該第1のチャレンジR1に署名し、第2の証明書C2を発生させる工程、
前記第1の通信装置が、第2のチャレンジR2を発生させ、該第2のチャレンジR2を、前記第2の証明書C2と共に、前記第2の通信装置に送信する工程、
前記第2の通信装置が、前記抽出した公共キー(パブリックキー)を用いて、前記第1の署名スキームに従って、前記第2の証明書C2を検証する工程、
前記第2の通信装置が、前記第2の署名スキームに従って、前記第2のチャレンジR2に署名し、この署名を前記第1の通信装置に送信する工程、及び、
前記第1の通信装置が、前記第2の署名スキームに従って、前記署名を検証し、前記各証明書又は署名が検証されなかったときは、前記各通信装置が前記電子取引を拒絶する工程、を有し、それにより、計算上より困難な部分が同一の通信装置で実行される、メッセージの正当性の検証方法。 - 通信装置との電子取引において使用するための、スマートカードであって、メモリを有し、該メモリは、
前記通信装置によって第1署名発生アルゴリズムにより行われた署名の検証を実行するための第1署名スキームによる検証アルゴリズムであって、前記第1署名スキームは、楕円曲線暗号を利用せず、前記第1署名スキームは、検証の場合よりも署名の場合が計算上より困難である、検証アルゴリズムと、
第2署名発生アルゴリズムに従って署名を実行するための、楕円曲線暗号を利用し前記第1署名スキームとは異なる第2署名スキームによる署名アルゴリズムであって、前記第2署名スキームは、署名の場合よりも検証の場合が計算上より困難である、署名アルゴリズムと、
前記各アルゴリズムを呼出すためのプログラムと、
前記検証アルゴリズムを作動させ、前記通信装置によって署名された第1のメッセージを検証し、更に、前記署名アルゴリズムを作動させ、第2のメッセージに署名し、前記通信装置に送信する演算手段と、
を含む、スマートカード。 - 前記検証アルゴリズムがRSA署名を検証する請求の範囲第6項記載のスマートカード。
- 前記検証アルゴリズムがDSS(Digital Signature Standards)署名を検証する請求の範囲第6項記載のスマートカード。
- 楕円曲線暗号を利用しない第1の署名スキームと楕円曲線暗号を利用し前記第1の署名スキームとは異なる第2の署名スキームとを有し、データ伝送システムを介して行われる電子取引の1対の通信装置間で交わされるメッセージの正当性の検証方法において、前記第1の署名スキームおよび前記第2の署名スキームの各々は、署名部分および検証部分を含み、前記第1の署名スキームの署名部分は、前記第1の署名スキームの検証部分よりも計算上より困難であり、前記第2の署名スキームの検証部分は、前記第2の署名スキームの署名部分よりも計算上より困難であり、
前記メッセージの正当性の検証方法は、第1の通信装置により実行され、以下の各工程:
前記第1の通信装置が、前記第1の署名スキームに従って、メッセージに署名し、第1の署名付きメッセージを第2の通信装置に送る工程、
前記第1の通信装置が、前記第2の署名スキームに従って署名された第2の署名付きメッセージを前記第2の通信装置から受信する工程、
前記第1の通信装置が、前記第2の署名スキームを用いて前記第2の通信装置から受信した前記第2の署名付きメッセージを検証する工程、
検証が失敗に終ったときは、前記第1の通信装置が前記電子取引を拒絶する工程、を有し、それにより、前記第1の署名スキームおよび前記第2の署名スキームの両スキームの計算上より困難な部分が前記第1の通信装置で実行される、メッセージの正当性の検証方法。 - 楕円曲線暗号を利用しない第1の署名スキームと楕円曲線暗号を利用し前記第1の署名スキームとは異なる第2の署名スキームとを有し、データ伝送システムを介して行われる電子取引の1対の通信装置間で交わされるメッセージの正当性の検証方法において、前記第1の署名スキームおよび前記第2の署名スキームの各々は、署名部分および検証部分を含み、前記第1の署名スキームの署名部分は、前記第1の署名スキームの検証部分よりも計算上より困難であり、前記第2の署名スキームの検証部分は、前記第2の署名スキームの署名部分よりも計算上より困難であり、
前記メッセージの正当性の検証方法は、第1の通信装置により実行され、以下の各工程:
前記第1の通信装置が、第2の通信装置から前記第1の署名スキームに従って署名されたメッセージを受信する工程、
前記第1の通信装置が、前記第1の署名スキームを用いて前記第2の通信装置から受信した第1の署名付きメッセージを検証する工程、
前記第1の通信装置が、前記第2の署名スキームに従ってメッセージに署名し、第2の署名付きメッセージを前記第2の通信装置に送る工程、
検証が失敗に終ったときは、前記第1の通信装置が前記電子取引を拒絶する工程、を有し、それにより、計算上より困難でない部分が前記第1の通信装置で実行される、メッセージの正当性の検証方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB9702152A GB2321741B (en) | 1997-02-03 | 1997-02-03 | Data card verification system |
| GB9702152.1 | 1997-03-02 | ||
| PCT/CA1998/000056 WO1998034202A2 (en) | 1997-02-03 | 1998-02-03 | Data card verification system |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001509926A JP2001509926A (ja) | 2001-07-24 |
| JP2001509926A5 JP2001509926A5 (ja) | 2005-12-02 |
| JP4545831B2 true JP4545831B2 (ja) | 2010-09-15 |
Family
ID=10806994
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP53240498A Expired - Lifetime JP4545831B2 (ja) | 1997-02-03 | 1998-02-03 | データカード検証装置 |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (6) | US6178507B1 (ja) |
| EP (3) | EP2323110A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4545831B2 (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU5849498A (ja) |
| CA (2) | CA2279462A1 (ja) |
| CH (1) | CH694601A5 (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE19804054B4 (ja) |
| FR (1) | FR2760583B1 (ja) |
| GB (1) | GB2321741B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO1998034202A2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (64)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB2321741B (en) * | 1997-02-03 | 2000-10-04 | Certicom Corp | Data card verification system |
| DE69930334T2 (de) | 1998-01-28 | 2006-11-09 | Hitachi, Ltd. | IC-Karte ausgerüstet mit einer Verarbeitungsanlage für Elliptische-Kurven-Verschlüsselung |
| EP1082836B1 (en) * | 1998-03-18 | 2005-11-23 | Kent Ridge Digital Labs | A method of exchanging digital data |
| FR2777371B1 (fr) * | 1998-04-09 | 2001-10-26 | Innovatron Electronique | Procede pour modifier de maniere indivisible une pluralite d'emplacements de la memoire non volatile d'une carte a microcircuit |
| JP2000049770A (ja) * | 1998-07-31 | 2000-02-18 | Hitachi Ltd | 暗号化通信方法、暗号アルゴリズム共有管理方法、暗号アルゴリズム変換方法、ネットワーク通信システム |
| EP1116358B1 (de) * | 1998-09-22 | 2003-09-03 | Infineon Technologies AG | Verfahren zur authentifikation zumindest eines teilnehmers bei einem datenaustausch |
| GB9824420D0 (en) * | 1998-11-07 | 1998-12-30 | Ncr Int Inc | Smart card and method of operating the smart card |
| US7404077B1 (en) | 1999-01-29 | 2008-07-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Extension of X.509 certificates to simultaneously support multiple cryptographic algorithms |
| FR2790177B1 (fr) * | 1999-02-22 | 2001-05-18 | Gemplus Card Int | Authentification dans un reseau de radiotelephonie |
| US7117369B1 (en) * | 1999-05-03 | 2006-10-03 | Microsoft Corporation | Portable smart card secured memory system for porting user profiles and documents |
| US7036738B1 (en) | 1999-05-03 | 2006-05-02 | Microsoft Corporation | PCMCIA-compliant smart card secured memory assembly for porting user profiles and documents |
| AU2001293598A1 (en) * | 2000-10-05 | 2002-04-15 | Certicom Corp. | A method for providing information security for wireless transmissions |
| US20020078352A1 (en) * | 2000-12-15 | 2002-06-20 | International Business Machines Corporation | Secure communication by modification of security codes |
| JP2002207427A (ja) * | 2001-01-10 | 2002-07-26 | Sony Corp | 公開鍵証明書発行システム、公開鍵証明書発行方法、および情報処理装置、情報記録媒体、並びにプログラム記憶媒体 |
| WO2003001734A1 (en) * | 2001-06-26 | 2003-01-03 | Valentin Kisimov | Secure digital communication protocols |
| DE10216396A1 (de) * | 2002-04-12 | 2003-10-23 | Scm Microsystems Gmbh | Verfahren zur Authentisierung |
| US7895443B2 (en) * | 2002-11-05 | 2011-02-22 | Safenet, Inc. | Secure authentication using hardware token and computer fingerprint |
| US7526555B2 (en) * | 2003-03-25 | 2009-04-28 | Toshiba Corporation | Smart card printing |
| DE10331733A1 (de) * | 2003-07-11 | 2005-01-27 | Rene Lehmann | Bezahlsystem |
| US7769995B2 (en) * | 2004-01-07 | 2010-08-03 | Microsoft Corporation | System and method for providing secure network access |
| US20050149732A1 (en) * | 2004-01-07 | 2005-07-07 | Microsoft Corporation | Use of static Diffie-Hellman key with IPSec for authentication |
| US20050198221A1 (en) * | 2004-01-07 | 2005-09-08 | Microsoft Corporation | Configuring an ad hoc wireless network using a portable media device |
| US7657612B2 (en) * | 2004-01-07 | 2010-02-02 | Microsoft Corporation | XML schema for network device configuration |
| US20050198233A1 (en) * | 2004-01-07 | 2005-09-08 | Microsoft Corporation | Configuring network settings of thin client devices using portable storage media |
| US7617390B2 (en) * | 2004-06-25 | 2009-11-10 | Sun Microsystems, Inc. | Server authentication in non-secure channel card pin reset methods and computer implemented processes |
| US7710587B2 (en) * | 2004-10-18 | 2010-05-04 | Microsoft Corporation | Method and system for configuring an electronic device |
| ATE533103T1 (de) * | 2005-01-18 | 2011-11-15 | Certicom Corp | Beschleunigte verifikation digitaler signaturen und öffentlicher schlüssel |
| US7826833B2 (en) * | 2005-02-17 | 2010-11-02 | Madhavan P G | Channel assay for thin client device wireless provisioning |
| US7616588B2 (en) * | 2005-03-31 | 2009-11-10 | Microsoft Corporation | Simplified creation and termination of an ad hoc wireless network with internet connection sharing |
| EP1752937A1 (en) * | 2005-07-29 | 2007-02-14 | Research In Motion Limited | System and method for encrypted smart card PIN entry |
| US20070124589A1 (en) * | 2005-11-30 | 2007-05-31 | Sutton Ronald D | Systems and methods for the protection of non-encrypted biometric data |
| US7992203B2 (en) | 2006-05-24 | 2011-08-02 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for secure shared smartcard access |
| US8098829B2 (en) * | 2006-06-06 | 2012-01-17 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for secure key delivery |
| US8495380B2 (en) * | 2006-06-06 | 2013-07-23 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for server-side key generation |
| US8332637B2 (en) | 2006-06-06 | 2012-12-11 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for nonce generation in a token |
| US7822209B2 (en) | 2006-06-06 | 2010-10-26 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for key recovery for a token |
| US8364952B2 (en) * | 2006-06-06 | 2013-01-29 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and system for a key recovery plan |
| US8180741B2 (en) | 2006-06-06 | 2012-05-15 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for providing data objects on a token |
| US9769158B2 (en) * | 2006-06-07 | 2017-09-19 | Red Hat, Inc. | Guided enrollment and login for token users |
| US8099765B2 (en) | 2006-06-07 | 2012-01-17 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for remote password reset using an authentication credential managed by a third party |
| US8412927B2 (en) | 2006-06-07 | 2013-04-02 | Red Hat, Inc. | Profile framework for token processing system |
| US8707024B2 (en) * | 2006-06-07 | 2014-04-22 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for managing identity management security domains |
| US8589695B2 (en) * | 2006-06-07 | 2013-11-19 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for entropy collection for server-side key generation |
| CN100511292C (zh) * | 2006-07-03 | 2009-07-08 | 上海交通大学 | 电子银行认证方法,及采用该方法的系统和智能卡 |
| US8806219B2 (en) | 2006-08-23 | 2014-08-12 | Red Hat, Inc. | Time-based function back-off |
| US8787566B2 (en) * | 2006-08-23 | 2014-07-22 | Red Hat, Inc. | Strong encryption |
| US9038154B2 (en) * | 2006-08-31 | 2015-05-19 | Red Hat, Inc. | Token Registration |
| US8356342B2 (en) * | 2006-08-31 | 2013-01-15 | Red Hat, Inc. | Method and system for issuing a kill sequence for a token |
| US8977844B2 (en) | 2006-08-31 | 2015-03-10 | Red Hat, Inc. | Smartcard formation with authentication keys |
| US8074265B2 (en) * | 2006-08-31 | 2011-12-06 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for verifying a location factor associated with a token |
| DE102006060760A1 (de) | 2006-09-29 | 2008-04-10 | Siemens Ag | Authentifikationsverfahren und Kommunikationssystem zur Authentifikation |
| US8693690B2 (en) * | 2006-12-04 | 2014-04-08 | Red Hat, Inc. | Organizing an extensible table for storing cryptographic objects |
| US8813243B2 (en) * | 2007-02-02 | 2014-08-19 | Red Hat, Inc. | Reducing a size of a security-related data object stored on a token |
| US8639940B2 (en) * | 2007-02-28 | 2014-01-28 | Red Hat, Inc. | Methods and systems for assigning roles on a token |
| US8832453B2 (en) | 2007-02-28 | 2014-09-09 | Red Hat, Inc. | Token recycling |
| US9081948B2 (en) * | 2007-03-13 | 2015-07-14 | Red Hat, Inc. | Configurable smartcard |
| CN101727712B (zh) * | 2008-10-16 | 2012-10-31 | 中国银联股份有限公司 | 一种电子现金的转账方法 |
| DE102013108713B8 (de) * | 2013-08-12 | 2016-10-13 | WebID Solutions GmbH | Verfahren zum Verifizieren der ldentität eines Nutzers |
| US10135621B2 (en) * | 2013-12-31 | 2018-11-20 | Nxp B.V. | Method to reduce the latency of ECDSA signature generation using precomputation |
| KR102266733B1 (ko) * | 2015-06-05 | 2021-06-22 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 데이터 스토리지 및 그것의 동작 방법 |
| EP3270344A1 (en) * | 2016-07-11 | 2018-01-17 | Gemalto Sa | Payment device adapted to establish a secure messaging channel with a remote server for a payment transaction and associated remote server |
| US9660978B1 (en) | 2016-08-08 | 2017-05-23 | ISARA Corporation | Using a digital certificate with multiple cryptosystems |
| JP6842090B2 (ja) * | 2018-01-18 | 2021-03-17 | 日本電信電話株式会社 | 通信装置、サーバ装置、秘匿通信システム、その方法、及びプログラム |
| CN108964916B (zh) * | 2018-08-03 | 2021-07-16 | 中思博安科技(北京)有限公司 | 签名生成方法、生成装置、签名验证方法和验证装置 |
Family Cites Families (40)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2536928B1 (fr) | 1982-11-30 | 1989-10-06 | France Etat | Systeme pour chiffrer et dechiffrer des informations, du type utilisant un systeme de dechiffrement a cle publique |
| EP0246823A3 (en) | 1986-05-22 | 1989-10-04 | Racal-Guardata Limited | Data communication systems and methods |
| US4748668A (en) | 1986-07-09 | 1988-05-31 | Yeda Research And Development Company Limited | Method, apparatus and article for identification and signature |
| FR2601795B1 (fr) * | 1986-07-17 | 1988-10-07 | Bull Cp8 | Procede pour diversifier une cle de base et pour authentifier une cle ainsi diversifiee comme ayant ete elaboree a partir d'une cle de base predeterminee, et systeme pour la mise en oeuvre |
| US5218637A (en) | 1987-09-07 | 1993-06-08 | L'etat Francais Represente Par Le Ministre Des Postes, Des Telecommunications Et De L'espace | Method of transferring a secret, by the exchange of two certificates between two microcomputers which establish reciprocal authorization |
| EP0383985A1 (de) * | 1989-02-24 | 1990-08-29 | Claus Peter Prof. Dr. Schnorr | Verfahren zur Identifikation von Teilnehmern sowie zur Generierung und Verifikation von elektronischen Unterschriften in einem Datenaustauschsystem |
| JP2731945B2 (ja) * | 1989-06-05 | 1998-03-25 | エヌ・ティ・ティ・データ通信株式会社 | 個別鍵による認証が可能なicカード |
| GB9008362D0 (en) | 1990-04-12 | 1990-06-13 | Hackremco No 574 Limited | Banking computer system |
| DE69113245D1 (de) * | 1991-03-14 | 1995-10-26 | Omnisec Ag Regensdorf | Verschlüsselungssystem mit öffentlichem Schlüssel unter Verwendung elliptischer Kurven über Ringe. |
| US5159632A (en) * | 1991-09-17 | 1992-10-27 | Next Computer, Inc. | Method and apparatus for public key exchange in a cryptographic system |
| US5271061A (en) * | 1991-09-17 | 1993-12-14 | Next Computer, Inc. | Method and apparatus for public key exchange in a cryptographic system |
| US5396558A (en) * | 1992-09-18 | 1995-03-07 | Nippon Telegraph And Telephone Corporation | Method and apparatus for settlement of accounts by IC cards |
| JPH06295154A (ja) * | 1993-04-09 | 1994-10-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 楕円曲線を用いた署名、認証及び秘密通信方式 |
| US5442707A (en) * | 1992-09-28 | 1995-08-15 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Method for generating and verifying electronic signatures and privacy communication using elliptic curves |
| JPH08504962A (ja) | 1992-12-22 | 1996-05-28 | テルストラ・コーポレイション・リミテッド | 暗号化方法 |
| US5299263A (en) * | 1993-03-04 | 1994-03-29 | Bell Communications Research, Inc. | Two-way public key authentication and key agreement for low-cost terminals |
| US5400403A (en) | 1993-08-16 | 1995-03-21 | Rsa Data Security, Inc. | Abuse-resistant object distribution system and method |
| US5825880A (en) | 1994-01-13 | 1998-10-20 | Sudia; Frank W. | Multi-step digital signature method and system |
| US5881038A (en) | 1994-04-18 | 1999-03-09 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Method and apparatus for preventing illegal copy or illegal installation of information of optical recording medium |
| US5515441A (en) * | 1994-05-12 | 1996-05-07 | At&T Corp. | Secure communication method and apparatus |
| JP2638525B2 (ja) | 1994-08-03 | 1997-08-06 | 日本電気株式会社 | 電子署名検証装置 |
| US5606617A (en) * | 1994-10-14 | 1997-02-25 | Brands; Stefanus A. | Secret-key certificates |
| US7127328B2 (en) * | 1994-12-30 | 2006-10-24 | Power Measurement Ltd. | System and method for federated security in an energy management system |
| US6157721A (en) * | 1996-08-12 | 2000-12-05 | Intertrust Technologies Corp. | Systems and methods using cryptography to protect secure computing environments |
| US5721781A (en) * | 1995-09-13 | 1998-02-24 | Microsoft Corporation | Authentication system and method for smart card transactions |
| US5748740A (en) * | 1995-09-29 | 1998-05-05 | Dallas Semiconductor Corporation | Method, apparatus, system and firmware for secure transactions |
| US5805702A (en) * | 1995-09-29 | 1998-09-08 | Dallas Semiconductor Corporation | Method, apparatus, and system for transferring units of value |
| US5793866A (en) | 1995-12-13 | 1998-08-11 | Motorola, Inc. | Communication method and device |
| GB9601924D0 (en) | 1996-01-31 | 1996-04-03 | Certicom Corp | Transaction verification protocol for smart cards |
| GB2309890A (en) | 1996-02-09 | 1997-08-13 | Peter Anthony Beasley | Reversible saddle rack |
| US5870470A (en) | 1996-02-20 | 1999-02-09 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for encrypting long blocks using a short-block encryption procedure |
| JPH10133576A (ja) * | 1996-10-31 | 1998-05-22 | Hitachi Ltd | 公開鍵暗号方法および装置 |
| US6041317A (en) * | 1996-11-19 | 2000-03-21 | Ascom Hasler Mailing Systems, Inc. | Postal security device incorporating periodic and automatic self implementation of public/private key pair |
| US5917913A (en) | 1996-12-04 | 1999-06-29 | Wang; Ynjiun Paul | Portable electronic authorization devices and methods therefor |
| US5960084A (en) | 1996-12-13 | 1999-09-28 | Compaq Computer Corporation | Secure method for enabling/disabling power to a computer system following two-piece user verification |
| US5907618A (en) | 1997-01-03 | 1999-05-25 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for verifiably providing key recovery information in a cryptographic system |
| GB2321741B (en) * | 1997-02-03 | 2000-10-04 | Certicom Corp | Data card verification system |
| US6424712B2 (en) * | 1997-10-17 | 2002-07-23 | Certicom Corp. | Accelerated signature verification on an elliptic curve |
| US6038549A (en) | 1997-12-22 | 2000-03-14 | Motorola Inc | Portable 1-way wireless financial messaging unit |
| US6041314A (en) | 1997-12-22 | 2000-03-21 | Davis; Walter Lee | Multiple account portable wireless financial messaging unit |
-
1997
- 1997-02-03 GB GB9702152A patent/GB2321741B/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1998
- 1998-02-02 US US09/016,926 patent/US6178507B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-02-03 EP EP10185101A patent/EP2323110A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1998-02-03 WO PCT/CA1998/000056 patent/WO1998034202A2/en not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1998-02-03 DE DE19804054A patent/DE19804054B4/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-02-03 FR FR9801204A patent/FR2760583B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-02-03 CA CA002279462A patent/CA2279462A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1998-02-03 JP JP53240498A patent/JP4545831B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-02-03 AU AU58494/98A patent/AU5849498A/en not_active Abandoned
- 1998-02-03 EP EP05075434A patent/EP1548665A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1998-02-03 CA CA2228958A patent/CA2228958C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-02-03 EP EP98901895A patent/EP0960405A2/en not_active Withdrawn
- 1998-02-03 CH CH00251/98A patent/CH694601A5/de not_active IP Right Cessation
-
2002
- 2002-07-01 US US10/185,042 patent/US7472276B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2008
- 2008-11-26 US US12/324,232 patent/US7822987B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2010
- 2010-09-28 US US12/892,719 patent/US8307211B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2012
- 2012-09-10 US US13/609,153 patent/US8966271B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2015
- 2015-02-23 US US14/629,395 patent/US9990796B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US7822987B2 (en) | 2010-10-26 |
| CA2228958C (en) | 2016-05-03 |
| CA2279462A1 (en) | 1998-08-06 |
| GB2321741A (en) | 1998-08-05 |
| CH694601A5 (de) | 2005-04-15 |
| US9990796B2 (en) | 2018-06-05 |
| US8966271B2 (en) | 2015-02-24 |
| GB2321741B (en) | 2000-10-04 |
| WO1998034202A2 (en) | 1998-08-06 |
| US8307211B2 (en) | 2012-11-06 |
| US20130067233A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 |
| US6178507B1 (en) | 2001-01-23 |
| EP2323110A1 (en) | 2011-05-18 |
| EP0960405A2 (en) | 1999-12-01 |
| US20150228144A1 (en) | 2015-08-13 |
| AU5849498A (en) | 1998-08-25 |
| US20020174339A1 (en) | 2002-11-21 |
| EP1548665A2 (en) | 2005-06-29 |
| WO1998034202A3 (en) | 1998-12-10 |
| US7472276B2 (en) | 2008-12-30 |
| GB9702152D0 (en) | 1997-03-26 |
| FR2760583B1 (fr) | 1999-10-08 |
| CA2228958A1 (en) | 1998-08-03 |
| DE19804054B4 (de) | 2010-04-01 |
| FR2760583A1 (fr) | 1998-09-11 |
| US20090164792A1 (en) | 2009-06-25 |
| JP2001509926A (ja) | 2001-07-24 |
| DE19804054A1 (de) | 1998-08-27 |
| EP1548665A3 (en) | 2006-06-21 |
| US20110016324A1 (en) | 2011-01-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4545831B2 (ja) | データカード検証装置 | |
| EP1847062B1 (en) | Challenge-response signatures and secure diffie-hellman protocols | |
| WO1998034202A9 (en) | Data card verification system | |
| US5955717A (en) | Transaction verification protocol for Smart Cards | |
| US6446207B1 (en) | Verification protocol | |
| EP1496644A2 (en) | Method for signature and session key generation | |
| US20050182936A1 (en) | Key agreement and transport protocol with implicit signatures | |
| EP0873617A1 (en) | Key agreement and transport protocol with implicit signatures | |
| JP2010093860A (ja) | 鍵認証方式 | |
| JP4307589B2 (ja) | 認証プロトコル | |
| EP2315389A2 (en) | Key agreement and transport protocol with implicit signatures | |
| CA2543094C (en) | Transaction verification protocol for smart cards | |
| Nyberg | Key Establishment Schemes |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050131 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050422 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20071002 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20080104 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20071227 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20080208 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080729 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20081024 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20081201 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20090317 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090716 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20090716 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20091112 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100210 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100507 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100609 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100701 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130709 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130709 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R3D04 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |