JP4453174B2 - Electric double layer capacitor - Google Patents
Electric double layer capacitor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4453174B2 JP4453174B2 JP2000253455A JP2000253455A JP4453174B2 JP 4453174 B2 JP4453174 B2 JP 4453174B2 JP 2000253455 A JP2000253455 A JP 2000253455A JP 2000253455 A JP2000253455 A JP 2000253455A JP 4453174 B2 JP4453174 B2 JP 4453174B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electric double
- double layer
- layer capacitor
- salt
- quaternary ammonium
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/13—Energy storage using capacitors
Landscapes
- Electric Double-Layer Capacitors Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は電気二重層キャパシタに関する。さらに詳しくは、高容量を示す電気二重層キャパシタに関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
電気二重層キャパシタは、セパレータを介して対向配置した正極および負極からなる電極素子において、正極及び負極の両方を活性炭繊維、活性炭粒子の成形体、活性炭粒子の塗布膜等を用いて構成される分極性電極とし、該電極素子に電解質を含ませたものである。前記構成の電気二重層キャパシタでは、前記分極性電極と前記電解液との界面に生成する電気二重層に電荷が蓄えられる。
【0003】
前記電解質には、その性状から液体電解質(電解液)と固体電解質とに大別され、さらに前記電解液は使用される溶媒や塩の種類から、水系電解液と非水系電解液とに分けられる。前記水系電解液としては硫酸水溶液、水酸化カリウム水溶液等が用いられる(宇恵誠、電気化学、66,904(1998))が、水系電解液は非水系電解液に比べ耐電圧が低いため、一定電流Iで、電圧ViからVfまで放電させたときの下記式(1)で表される電気二重層キャパシタの単セル当たりのエネルギーWが低く、近年、注目を集めている電気自動車、ハイブリッド車や電力貯蔵などパワー用途には、非水系電解液を使用したものが適している。
【0004】
【数1】
W=1/2・C・(Vi2 −Vf2)・・・・・・・(1)
(ここでCは静電容量(F)である。)
前記非水系電解液としてはプロピレンカーボネート等の有機溶媒に過塩素酸の四級アンモニウム塩を溶解した電解液(特公昭54−9704号公報)、四級アンモニウムのBF4塩やPF6塩を溶解した電解液(特公昭52−40025号公報、特開昭63−173312号公報)、四級ホスホニウム塩を溶解した電解液(特公平6−66233号公報)、アミジン基を有する化合物の塩を溶解した電解液(WO95/15572号公報)、イミダゾリウム化合物をカチオン成分とする塩を溶質とした電解液(WO99/08299号公報、特開平8−321439号公報)や、有機溶媒を使用しない常温溶融塩を電解液とするもの(特開平5−74656号公報、WO97/02252号公報)等が知られている。また、特開平5−74656号公報中では、常温溶融塩として無機塩と有機塩の混合物を使用することが開示されている。有機塩としては四級アンモニウムまたは四級ホスホニウム塩の塩化物または臭化物が、無機塩としてはAlCl3、TiCl3、TiCl4、及びBeCl2からなる群から選ばれた塩化物が好ましいと記述されている。しかしながら、四級アンモニウム塩の塩化物とAlCl3の混合物として実施例に記載されている1−エチル−3−メチルイミダゾリウム(EMI)AlCl4は空気中の酸素や湿気に不安定で、取り扱いが制限され、電解液としては満足できるものではなかった。
【0005】
その改良として、空気中でも安定なフッ素系常温溶融塩がいくつか報告されている。J. Chem. Soc.,Chem. Commun., 965 (1992)ではWilkesらがEMIBF4を発表し、WO97/02252号公報では環状四級アンモニウムカチオンと100Å3以上のファンデルワールス体積を有するアニオンの組み合わせによる常温溶融塩とその電解液、並びにその電解液を用いた電気化学セルが示されている。
【0006】
また、WO95/15572号公報中ではイミダゾリウム等の環状アミジン化合物の4級塩をカチオンとする塩を有機溶媒に溶解した電解液およびそれを用いた電気化学素子が示されている。また、WO99/08299号公報では環状四級アンモニウムカチオンとPF6 -、BF4 -、AsF6 -およびCF3SO3 -といった100Å3以下のファンデルワールス体積を有するアニオンを組み合わせた塩を有機溶媒に溶解した電解液並びにその電解液を使用した電気化学キャパシタが示されている。
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
前記の有機溶媒を使用した非水系電解液は静電容量が高いのに対し、可燃性であるため、衝撃や劣化に伴う内圧上昇による破損で電解液が漏洩した場合に発火の危険性が伴うことが危惧された。一方、有機溶媒を使用しない従来の常温溶融塩の場合、不燃性なので安全性は高いが、有機溶媒を使用した非水系電解液に比べ静電容量が低いという難点があった。
【0008】
そこで本発明は、安全で且つ静電容量の大きい電気二重層キャパシタを提供することを目的とする。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明者らは、上記の目的を達成すべく鋭意検討した結果、4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩を電解液に用いると高容量な電気二重層キャパシタが得られることを見いだし、本発明を完成するに至った。
すなわち本発明の要旨は、主構成材料として、セパレータを介して対向配置した正極と負極の両極に分極性電極を用いる電気二重層キャパシタにおいて、4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩を電解液中に含有することを特徴とする電気二重層キャパシタに関する。
【0010】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明を詳細に説明する。
本発明の電気二重層キャパシタは、主構成材料として、セパレータを介して対向配置した正極と負極の両極に分極性電極を用い、該電極に含浸させる電解液中に4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩を含有するものである。
【0011】
4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩の4級アンモニウムカチオンの具体例としては、テトラメチルアンモニウム、メチルトリエチルアンモニウム、ジメチルジエチルアンモニウム、トリメチルエチルアンモニウム、テトラエチルアンモニウム、テトラブチルアンモニウム、ベンジルトリメチルアンモニウム、1,1−ジメチルピロリジニウム、1−メチル−1−エチルピロリジニウム、1,1−ジメチルピペリジニウム、1−エチルピリジニウム、1,3−ジメチルイミダゾリウム、1−エチル−3−メチルイミダゾリウム、1,3−ジメチルベンズイミダゾリウム、1,3−ジメチルイミダゾリニウム、1−エチル−3−メチルイミダゾリニウム、1−エチル−2,3−ジメチルイミダゾリニウム、1,2,3,4−テトラメチルイミダゾリニウム等が挙げられるが、これに限定されるものではない。
【0012】
4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩として好ましいものは、環状4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩であり、さらに好ましいのは
上記4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩の中でも、好ましいのは下記(1)式で表されるイミダゾリウム塩である。
【0013】
【化2】
【0014】
(式中、R1及びR3は、それぞれ独立して炭素数1〜4のアルキル基を表し、R2,R4,及びR5は、それぞれ独立して水素原子又は炭素数1〜4のアルキル基を示す。またR1〜R5の一部又は全てが相互に結合して環を形成してもよい。nは1〜4の数値を表す。)
炭素数1〜4のアルキル基としては、メチル基、エチル基、n−プロピル基、i−プロピル基、n−ブチル基等が挙げられ、高い電気伝導率を示すことから、メチル基又はエチル基を示すことが好ましい。本発明においては、R1及びR3を非対称性とすると粘度が低粘度になり、より好ましい。R2,R4,及びR5は、水素原子、メチル基、又はエチル基を表すことが好ましく、より好ましくは水素原子である。
【0015】
かかる(1)式で表される化合物の具体例としては、1,3−ジメチルイミダゾリウム塩、1,3,4−トリメチルイミダゾリウム塩、1−エチル−3−メチルイミダゾリウム塩等が挙げられ、最も好適なのは常温溶融塩である1−エチル−3−メチルイミダゾリウム塩である。
またR1〜R5の一部または全ては相互に結合して環を形成していてもよい。具体例としては1,3−ジメチルベンズイミダゾリウム塩、1−エチル−3−メチルベンズイミダゾリウム塩等が挙げられる。
【0016】
nは1〜4の数値であり、必ずしも整数でなくてもいい。nの値は化合物の元素分析値から算出するものである。
上記(1)式で表される4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩の製造方法としては、その一例として常温溶融塩である1−エチル−3−メチルイミダゾリウムフルオリドHF塩について、本発明者らの著作によるJ.Fluorine Chemistry, 99 ,1-3 (1999)に記載した方法を挙げることができるが、製造方法はこれに限定されるものではない。
【0017】
また、上記4級アンモニウムフルオリドHF塩同士あるいは他のアニオンからなる4級アンモニウム塩と混合して用いてもよい。他のアニオンの具体例としては、PF6 -、BF4 -、AsF6 -およびトリフレートアニオン等が挙げられる。
電解液中の混入水分は耐電圧の低下を引き起こすので、含水量は300ppm以下、好ましくは100ppm以下、特に好ましくは30ppm以下にする必要がある。
【0018】
含浸性向上等の目的で、本発明の特性を損なわない範囲でプロピレンカーボネート、エチレンカーボネート、γ−ブチロラクトン等の有機溶媒を加えても良い。ただし、電解液中の有機溶媒の含有量は少なければ少ないほど不燃性になり安全性が向上して好ましく、最も好ましいのは有機溶媒を含まない場合である。
本発明における電気二重層キャパシタの正極、負極として用いられる分極性電極の主成分は、電解液に対して電気化学的に不活性で、かつ、適度な電気導電性を有することから炭素質物質が好ましく、特に、電荷が蓄積する電極界面が大きい点から、活性炭を用いることが好ましい。
【0019】
以下、炭素質物質として活性炭を用いた場合について、詳細に説明するが、本発明はこれに限定されるものではない。
活性炭の比表面積は、炭素質種による単位面積あたりの静電容量(F/m2)、高比表面積化に伴う嵩密度の低下等の理由から一概には言えないが、窒素吸着法によるBET法により求めた比表面積は500〜2500m2/gが好ましく、特に、比表面積が1000〜2000m2/gの活性炭は、体積あたりの静電容量が大きく好ましい。
【0020】
本発明に使用する活性炭の製造方法は特に問わないが、一般的には、植物系の木材、のこくず、ヤシ殻、パルプ廃液、化石燃料系の石炭、石油重質油、或いはそれらを熱分解した石炭及び石油系ピッチ、石油コークス、カーボンアエロゲル、タールピッチを紡糸した繊維、合成高分子、フェノール樹脂、フラン樹脂、ポリ塩化ビニル樹脂、ポリ塩化ビニリデン樹脂、ポリイミド樹脂、ポリアミド樹脂、液晶高分子、プラスチック廃棄物、廃タイヤ等多種多用の原料を炭化した後、賦活して製造される。賦活法としては、炭化された原料を高温で水蒸気、炭酸ガス、酸素、その他の酸化ガス等と接触反応させるガス賦活法と炭化された原料に塩化亜鉛、りん酸、りん酸ナトリウム、塩化カルシウム、硫化カリウム、水酸化カリウム、水酸化ナトリウム、炭酸カリウム、炭酸ナトリウム、硫酸ナトリウム、硫酸カリウム、炭酸カルシウム等を均等に含侵させて、不活性ガス雰囲気中で加熱し、薬品の脱水及び酸化反応により活性炭を得る薬品賦活法があり、いずれも用いることが出来る。
【0021】
賦活処理後の活性炭を、窒素、アルゴン、ヘリウム、キセノン等の不活性雰囲気下で、500〜2500℃、好ましくは700〜1500℃で熱処理し、不要な表面官能基を除去したり、炭素の結晶性を発達させて電子伝導性を増加させても良い。
活性炭の形状は、破砕、造粒、顆粒、繊維、フェルト、織物、シート状等各種の形状等特に限定されず利用できるが、粒状の場合、電極の嵩密度の向上、内部抵抗の低減という点で、平均粒子径は30μm以下が好ましい。
【0022】
正極、負極は、通常、炭素質物質、導電剤とバインダー物質から構成され、薄い塗布膜、シート状または板状の成形体として使用する。導電剤としては、アセチレンブラック、ケッチェンブラック等のカーボンブラック、天然黒鉛、熱膨張黒鉛、炭素繊維、酸化ルテニウム、酸化チタン、アルミニウム、ニッケル等の金属ファイバーからなる群より選ばれる少なくとも一種の導電剤が好ましい。少量で効果的に導電性が向上する点で、アセチレンブラック及びケッチェンブラックが特に好ましく、活性炭との配合量は、活性炭の嵩密度により異なるが多すぎると活性炭の割合が減り容量が減少するため、活性炭の重量の5〜50%、特には10〜30%程度が好ましい。また、バインダー物質としては、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン、ポリフッ化ビニリデン、カルボキシメチルセルロース、フルオロオレフィン共重合体架橋ポリマー、ポリビニルアルコール、ポリアクリル酸、ポリイミド、石油ピッチ、石炭ピッチ、フェノール樹脂のうち少なくとも1種類以上用いるのが好ましい。
【0023】
電極中のバインダー物質の配合量は、炭素質物質の種類と形状によっても異なるが、例えば炭素質物質が活性炭の場合、多すぎると活性炭の割合が減り容量が減少し、少なすぎると結着性が悪くなり強度が低下するため、活性炭の重量の0.5〜30%が好ましく、2〜30%が特に好ましい。
正極、負極は、従来から知られている方法により成形することが可能である。例えば、活性炭とアセチレンブラックの混合物に、ポリテトラフルオロエチレンを添加混合した後、プレス成形して得られる。また、活性炭とピッチ、タール、フェノール樹脂等のバインダー物質を混合、成型した後、不活性雰囲気下で熱処理して焼結体が得られる。さらに、活性炭とバインダー或いは活性炭のみを焼結して分極性電極とすることも可能である。
【0024】
また本実施例には、正極及び負極に同一の活性炭および成形方法を用いているが、正極と負極の活性炭及び成形方法は必ずしも同一である必要はなく、負極と正極とが同程度の比表面積を備えるものであればよい。
セパレータの種類は、紙、セルロース繊維、ポリプロピレンまたはポリエチレン等の耐フッ化水素性の高い材料によって構成されたものが好適である。反対にガラス繊維製のセパレータは腐食して溶解するため適していない。
【0025】
集電体も耐フッ化水素性の材料を用いることが好ましく、ブチルゴムにカーボンを分散させた導電性ゴムシートやステンレスが使用可能であるが、前者の方がより好ましい。
ガスケットは耐熱・耐酸性のあるABS樹脂やポリプロピレン製が好ましい。
気密性を高めることから、ガスケットと集電体およびケースは耐酸性の高いエポキシ接着剤で接着して、周囲をボルト・ナットで固定するのも好適である。
【0026】
本発明の電気二重層キャパシタの使用電圧は特に制限されるものではないが、2.5V以下である用途に好適に用いられる。
該電気二重層キャパシタの安全性の評価法として、電解液を含浸したマニラ紙の燃焼速度を採用した。
【0027】
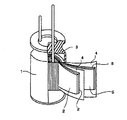
図1〜3に一般的なコイン型、巻回型、角型の電気二重層キャパシタを示したが、本発明はいずれのタイプの電気二重層キャパシタにも使用でき、またこれら形状に限定されるものではない。
【0028】
【実施例】
以下に、実施例を挙げて、本発明を更に詳細に説明するが、本発明はその要旨を超えない限り、これらの実施例に限定される物ではない。
(実施例1)
J.Fluorine Chemistry, 99 , 1-3(1999)の中で示した方法により、構造式(2)を有する化合物(EMIF・(HF)2.3)を合成し、電解液とした。該電解液への水分混入を防ぐため、該電解液の取り扱いは乾燥アルゴン雰囲気下で行った。
構造式(2)
【0029】
【化3】
【0030】
電気二重層キャパシタとしての性能を評価するため、次のように作製した。炭素質物質を水蒸気賦活処理して得られたやしがら系活性炭粉末(比表面積1700m2/g、平均粒子径10μm)80重量%、アセチレンブラック10重量%、ポリテトラフルオロエチレン10重量%からなる混合物を混練した後、50kgf/cm2 の圧力で加圧成型して直径10mm,厚さ0.5mm の円盤状の成型体を得、これを分極性電極とした。この成型操作を繰り返して、同一の組成及び形状を有する分極性電極をさらに一枚得た。得られた2枚の成型体を0.1torr 以下の真空中、300 ℃で3 時間乾燥した後、これらをアルゴン雰囲気のグローブボックス中へ移動した。放冷後の2枚の分極性電極体(活性炭成型体)へ、上記の電解液を減圧下で含浸させた。該電解液を含浸させた2枚の分極性電極の間にポリプロピレン製セパレータを挟み、これらを、ステンレス製ケース内にポリプロピレン製ガスケットを介してかしめ封じることにより、図1に示すような電気二重層キャパシタを得た。
【0031】
得られた電気二重層キャパシタに、70℃で、5mAの定電流充電後、所定の電圧で充電開始から50分定電圧充電を行い、その後5mAの定電流放電を行って性能の指標として静電容量密度を測定した。前記所定電圧は、0.8Vから0.1V刻みで4.7Vまで試験した。前記静電容量密度は放電時の総エネルギーから求めた静電容量を正極及び負極の合計体積で除して算出し、静電容量密度の最大値を表1に示した。
【0032】
一方、得られた電気二重層キャパシタの安全性を評価するため、使用した電解液に幅15mm、長さ320mm、厚さ40μ、密度0.6g/cm3のマニラ紙を1分間浸し、3分間、垂直に吊下げ余分な電解液を除いた後、25mm間隔で支持針を有するサンプル保持台に水平に固定し、その一端にマッチで着火し、燃焼した長さと時間を測定し、燃焼速度を求め表1に示した。
(実施例2)
本実施例では電解液として、炭酸プロピレン(PC)溶媒に、溶質として1.0モル濃度のEMIF・(HF)2.3を溶解した溶液を用いた以外は、実施例1と全く同一にして、図1に示した構造を備える電気二重層キャパシタを作製し、静電容量密度を測定し、その最大値を表1に示した。
【0033】
安全性評価も実施例1と同様に行い、燃焼速度を表1に示した。
(比較例1)
本比較例では、電解液として、常温溶融塩である1−エチル−3−メチルイミダゾリウムテトラフルオロボレート(EMIBF4)を用いた以外は、実施例1と全く同一にして、図1に示した構造を備える電気二重層キャパシタを作製し、静電容量密度を測定し、その最大値を表1に示した。
【0034】
安全性評価も実施例1と同様に行い、燃焼速度を表1に示した。
(比較例2)
本比較例では、電解液として、炭酸プロピレン(PC)溶媒に、溶質として1.0モル濃度のホウフッ化トリエチルメチルアンモニウム(TEMABF4)を溶解した溶液を用いた以外は、実施例1と全く同一にして、図1に示した構造を備える電気二重層キャパシタを作製し、静電容量密度を測定し、その最大値を表1に示した。
【0035】
安全性評価も実施例1と同様に行い、燃焼速度を表1に示した。
【0036】
【表1】
【0037】
【発明の効果】
本発明の電気二重層キャパシタは静電容量が大きく安全性にも優れるため、各種電子機器のメモリーバックアップ用や衝突による漏洩の危険性のある電気自動車用として好適である。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】代表的なコイン型電気二重層キャパシタのセル構造を示す図である。
【図2】代表的な巻回型電気二重層キャパシタのセル構造を示す図である。
【図3】代表的な角型電気二重層キャパシタのセル構造を示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1.ケース
2.正極
3.ガスケット
4.セパレータ
5.負極
6.上蓋[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an electric double layer capacitor. More specifically, the present invention relates to an electric double layer capacitor exhibiting a high capacity.
[0002]
[Prior art]
An electric double layer capacitor is an electrode element composed of a positive electrode and a negative electrode arranged opposite to each other with a separator interposed between the positive electrode and the negative electrode using activated carbon fibers, a molded product of activated carbon particles, a coating film of activated carbon particles, and the like. A polar electrode is used, and an electrolyte is included in the electrode element. In the electric double layer capacitor configured as described above, electric charges are stored in the electric double layer generated at the interface between the polarizable electrode and the electrolyte.
[0003]
The electrolytes are roughly classified into liquid electrolytes (electrolyte solutions) and solid electrolytes according to their properties, and the electrolyte solutions are classified into aqueous electrolyte solutions and non-aqueous electrolyte solutions depending on the type of solvent and salt used. . As the aqueous electrolyte, an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid, an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide, or the like is used (Ue, Makoto, Electrochemistry, 66, 904 (1998)), but the aqueous electrolyte has a lower withstand voltage than the non-aqueous electrolyte, and is constant. When the electric current I is discharged from the voltage Vi to Vf, the energy W per unit cell of the electric double layer capacitor represented by the following formula (1) is low. For power applications such as power storage, those using non-aqueous electrolytes are suitable.
[0004]
[Expression 1]
W = 1/2 · C · (Vi 2- Vf 2 ) ··· (1)
(Where C is the capacitance (F))
As the non-aqueous electrolyte, an electrolyte obtained by dissolving a quaternary ammonium salt of perchloric acid in an organic solvent such as propylene carbonate (Japanese Patent Publication No. 54-9704), a BF 4 salt or a PF 6 salt of quaternary ammonium is dissolved. Electrolytic solution (Japanese Patent Publication No. Sho 52-40025, Japanese Patent Publication No. Sho 63-17312), an electrolytic solution in which a quaternary phosphonium salt is dissolved (Japanese Patent Publication No. 6-66233), and a salt of a compound having an amidine group. Electrolyte solution (WO95 / 15572), electrolyte solution containing salt containing imidazolium compound as a cation component (WO99 / 08299, JP-A-8-32439), and melting at room temperature without using an organic solvent Those using a salt as an electrolytic solution (Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 5-74656, WO97 / 02252) are known. JP-A-5-74656 discloses that a mixture of an inorganic salt and an organic salt is used as a room temperature molten salt. The organic salt is preferably a chloride or bromide of a quaternary ammonium or quaternary phosphonium salt, and the inorganic salt is preferably a chloride selected from the group consisting of AlCl 3 , TiCl 3 , TiCl 4 , and BeCl 2. Yes. However, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (EMI) AlCl 4 described in the examples as a mixture of chloride of quaternary ammonium salt and AlCl 3 is unstable to oxygen and moisture in the air, and is difficult to handle. It was limited and the electrolyte solution was not satisfactory.
[0005]
As improvements, several fluorine-based room temperature molten salts that are stable even in air have been reported. Wilkes et al. Published EMIBF 4 in J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 965 (1992). In WO 97/02252, an anion having a cyclic quaternary ammonium cation and an anion having a van der Waals volume of 100 3 or more is disclosed. A combination of a room temperature molten salt and an electrolytic solution thereof, and an electrochemical cell using the electrolytic solution are shown.
[0006]
Also, WO95 / 15572 discloses an electrolytic solution in which a salt having a quaternary salt of a cyclic amidine compound such as imidazolium as a cation is dissolved in an organic solvent, and an electrochemical device using the electrolytic solution. In addition, WO99 / 08299 discloses an organic solvent that is a combination of a cyclic quaternary ammonium cation and an anion having a van der Waals volume of 100 3 or less, such as PF 6 − , BF 4 − , AsF 6 −, and CF 3 SO 3 −. 1 shows an electrolytic solution dissolved in 1 and an electrochemical capacitor using the electrolytic solution.
[0007]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
Non-aqueous electrolytes using the above organic solvents have high electrostatic capacity, but are flammable, so there is a risk of ignition if the electrolyte leaks due to damage due to internal pressure increase due to impact or deterioration. I was worried. On the other hand, in the case of a conventional room temperature molten salt that does not use an organic solvent, the safety is high because it is nonflammable, but there is a problem that the capacitance is lower than that of a non-aqueous electrolyte using an organic solvent.
[0008]
Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an electric double layer capacitor that is safe and has a large capacitance.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
As a result of intensive studies to achieve the above object, the present inventors have found that when a quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt is used as an electrolyte, a high-capacity electric double layer capacitor can be obtained, thereby completing the present invention. It came to.
That is, the gist of the present invention is that, in the electric double layer capacitor using a polarizable electrode for both the positive electrode and the negative electrode arranged opposite to each other with a separator as a main constituent material, the quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt is contained in the electrolyte. The present invention relates to an electric double layer capacitor.
[0010]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
The electric double layer capacitor of the present invention uses, as a main constituent material, polarizable electrodes on both the positive electrode and the negative electrode arranged opposite to each other with a separator interposed therebetween, and quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt is contained in the electrolyte solution impregnated in the electrode. It contains.
[0011]
Specific examples of the quaternary ammonium cation of the quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt include tetramethylammonium, methyltriethylammonium, dimethyldiethylammonium, trimethylethylammonium, tetraethylammonium, tetrabutylammonium, benzyltrimethylammonium, 1,1-dimethyl. Pyrrolidinium, 1-methyl-1-ethylpyrrolidinium, 1,1-dimethylpiperidinium, 1-ethylpyridinium, 1,3-dimethylimidazolium, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1,3 -Dimethylbenzimidazolium, 1,3-dimethylimidazolinium, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolinium, 1-ethyl-2,3-dimethylimidazolinium, 1,2,3,4-tetramethylimidazole Hexafluorophosphate and the like, but not limited thereto.
[0012]
A preferable quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt is a cyclic quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt, and a more preferable quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt is represented by the following formula (1). It is an imidazolium salt.
[0013]
[Chemical formula 2]
[0014]
(In the formula, R 1 and R 3 each independently represent an alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms, and R 2 , R 4 , and R 5 are each independently a hydrogen atom or a carbon atom having 1 to 4 carbon atoms. Represents an alkyl group, and some or all of R 1 to R 5 may be bonded to each other to form a ring, and n represents a numerical value of 1 to 4.)
Examples of the alkyl group having 1 to 4 carbon atoms include a methyl group, an ethyl group, an n-propyl group, an i-propyl group, an n-butyl group, and the like. It is preferable to show. In the present invention, when R 1 and R 3 are asymmetric, the viscosity becomes lower, which is more preferable. R 2 , R 4 , and R 5 preferably represent a hydrogen atom, a methyl group, or an ethyl group, and more preferably a hydrogen atom.
[0015]
Specific examples of the compound represented by the formula (1) include 1,3-dimethylimidazolium salt, 1,3,4-trimethylimidazolium salt, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium salt and the like. Most preferred is 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium salt which is a room temperature molten salt.
A part or all of R 1 to R 5 may be bonded to each other to form a ring. Specific examples include 1,3-dimethylbenzimidazolium salt, 1-ethyl-3-methylbenzimidazolium salt, and the like.
[0016]
n is a numerical value of 1 to 4, and is not necessarily an integer. The value of n is calculated from the elemental analysis value of the compound.
As a method for producing a quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salt represented by the above formula (1), as an example, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium fluoride HF salt which is a room temperature molten salt is obtained by the present inventors. J. Although the method described in Fluorine Chemistry, 99, 1-3 (1999) can be mentioned, a manufacturing method is not limited to this.
[0017]
Further, the quaternary ammonium fluoride HF salts may be mixed with quaternary ammonium salts composed of other anions. Specific examples of other anions include PF 6 − , BF 4 − , AsF 6 − and triflate anions.
Since mixed water in the electrolyte causes a decrease in withstand voltage, the water content needs to be 300 ppm or less, preferably 100 ppm or less, particularly preferably 30 ppm or less.
[0018]
For the purpose of improving the impregnation property, an organic solvent such as propylene carbonate, ethylene carbonate, and γ-butyrolactone may be added as long as the characteristics of the present invention are not impaired. However, the smaller the content of the organic solvent in the electrolytic solution, the better the nonflammability and the improved safety, and the most preferable is the case where no organic solvent is contained.
The main component of the polarizable electrode used as the positive electrode and negative electrode of the electric double layer capacitor in the present invention is electrochemically inactive with respect to the electrolytic solution and has an appropriate electric conductivity. In particular, it is preferable to use activated carbon because the electrode interface where charges are accumulated is large.
[0019]
Hereinafter, although the case where activated carbon is used as a carbonaceous substance is demonstrated in detail, this invention is not limited to this.
The specific surface area of the activated carbon cannot be unequivocally stated due to the capacitance per unit area (F / m 2 ) due to the carbonaceous species and the decrease in bulk density associated with the increase in the specific surface area. the specific surface area is preferably 500~2500m 2 / g as determined by the law, especially, a specific surface area of activated carbon 1000 to 2000 2 / g, the capacitance per volume greater preferred.
[0020]
The method for producing the activated carbon used in the present invention is not particularly limited, but in general, plant wood, sawdust, coconut husk, pulp waste liquid, fossil fuel coal, heavy petroleum oil, or heat them. Decomposed coal and petroleum pitch, petroleum coke, carbon aerogel, tar pitched fiber, synthetic polymer, phenol resin, furan resin, polyvinyl chloride resin, polyvinylidene chloride resin, polyimide resin, polyamide resin, liquid crystal high It is manufactured by carbonizing a wide variety of raw materials such as molecules, plastic waste, and waste tires, and then activating them. The activation method includes a gas activation method in which the carbonized raw material is brought into contact with water vapor, carbon dioxide gas, oxygen, and other oxidizing gases at a high temperature, and the carbonized raw material is zinc chloride, phosphoric acid, sodium phosphate, calcium chloride, Impregnate potassium sulfide, potassium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide, potassium carbonate, sodium carbonate, sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, calcium carbonate, etc., and heat in an inert gas atmosphere. There are chemical activation methods for obtaining activated carbon, and any of them can be used.
[0021]
The activated carbon after the activation treatment is heat-treated at 500 to 2500 ° C., preferably 700 to 1500 ° C. in an inert atmosphere such as nitrogen, argon, helium, xenon, etc. to remove unnecessary surface functional groups, The electronic conductivity may be increased by developing the sex.
The shape of the activated carbon can be used without any particular limitation such as crushing, granulation, granule, fiber, felt, woven fabric, sheet shape, etc., but in the case of granular, the point is that the bulk density of the electrode is improved and the internal resistance is reduced. The average particle size is preferably 30 μm or less.
[0022]
The positive electrode and the negative electrode are usually composed of a carbonaceous material, a conductive agent, and a binder material, and are used as a thin coating film, a sheet-shaped or plate-shaped molded body. The conductive agent is at least one conductive agent selected from the group consisting of carbon fibers such as acetylene black and ketjen black, natural graphite, thermally expanded graphite, carbon fiber, ruthenium oxide, titanium oxide, aluminum, nickel, and the like. Is preferred. Acetylene black and ketjen black are particularly preferable in that the conductivity is effectively improved in a small amount, and the blending amount with activated carbon varies depending on the bulk density of the activated carbon, but if the amount is too large, the proportion of activated carbon decreases and the capacity decreases. The weight of activated carbon is preferably 5 to 50%, particularly about 10 to 30%. In addition, as the binder material, at least one of polytetrafluoroethylene, polyvinylidene fluoride, carboxymethylcellulose, fluoroolefin copolymer cross-linked polymer, polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylic acid, polyimide, petroleum pitch, coal pitch, and phenol resin. It is preferable to use it.
[0023]
The amount of binder material in the electrode varies depending on the type and shape of the carbonaceous material.For example, when the carbonaceous material is activated carbon, if the amount is too large, the proportion of activated carbon decreases and the capacity decreases. Is reduced, and the strength is reduced, so 0.5 to 30% of the weight of the activated carbon is preferable, and 2 to 30% is particularly preferable.
The positive electrode and the negative electrode can be formed by a conventionally known method. For example, it is obtained by adding polytetrafluoroethylene to a mixture of activated carbon and acetylene black and then press-molding. Moreover, after mixing and shaping | molding binder materials, such as activated carbon and pitch, tar, and a phenol resin, it heat-processes in inert atmosphere and a sintered compact is obtained. Furthermore, it is also possible to sinter only activated carbon and a binder or activated carbon into a polarizable electrode.
[0024]
In this example, the same activated carbon and forming method are used for the positive electrode and the negative electrode, but the activated carbon and forming method of the positive electrode and the negative electrode are not necessarily the same, and the specific surface area of the negative electrode and the positive electrode is the same. What is necessary is just to have.
The separator is preferably made of a material having high hydrogen fluoride resistance such as paper, cellulose fiber, polypropylene or polyethylene. Conversely, glass fiber separators are not suitable because they corrode and dissolve.
[0025]
The current collector is also preferably made of a hydrogen fluoride-resistant material, and a conductive rubber sheet in which carbon is dispersed in butyl rubber or stainless steel can be used, but the former is more preferable.
The gasket is preferably made of heat- and acid-resistant ABS resin or polypropylene.
In order to enhance the airtightness, it is also preferable that the gasket, the current collector and the case are bonded with a highly acid-resistant epoxy adhesive and the periphery is fixed with bolts and nuts.
[0026]
The working voltage of the electric double layer capacitor of the present invention is not particularly limited, but is suitably used for applications of 2.5 V or less.
As a method for evaluating the safety of the electric double layer capacitor, the burning rate of Manila paper impregnated with an electrolytic solution was employed.
[0027]
1 to 3 show general coin-type, wound-type, and square-type electric double layer capacitors, but the present invention can be used for any type of electric double layer capacitors and is limited to these shapes. It is not a thing.
[0028]
【Example】
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail with reference to examples. However, the present invention is not limited to these examples as long as the gist thereof is not exceeded.
Example 1
J. et al. A compound having the structural formula (2) (EMIF · (HF) 2.3 ) was synthesized by the method shown in Fluorine Chemistry, 99, 1-3 (1999), and used as an electrolytic solution. In order to prevent water from being mixed into the electrolytic solution, the electrolytic solution was handled in a dry argon atmosphere.
Structural formula (2)
[0029]
[Chemical 3]
[0030]
In order to evaluate the performance as an electric double layer capacitor, it was produced as follows. It consists of 80% by weight of activated carbon powder (specific surface area 1700m 2 / g, average particle size 10μm) obtained by steam activation of carbonaceous material, 10% by weight of acetylene black, and 10% by weight of polytetrafluoroethylene. After the mixture was kneaded, it was pressure-molded at a pressure of 50 kgf / cm 2 to obtain a disk-shaped molded body having a diameter of 10 mm and a thickness of 0.5 mm, which was used as a polarizable electrode. This molding operation was repeated to obtain one more polarizable electrode having the same composition and shape. The obtained two molded bodies were dried at 300 ° C. for 3 hours in a vacuum of 0.1 torr or less, and then moved into a glove box in an argon atmosphere. The above-mentioned electrolytic solution was impregnated under reduced pressure into two polarizable electrode bodies (activated carbon molded body) after being allowed to cool. An electric double layer as shown in FIG. 1 is obtained by sandwiching a polypropylene separator between two polarizable electrodes impregnated with the electrolytic solution and caulking them in a stainless steel case with a polypropylene gasket. A capacitor was obtained.
[0031]
The obtained electric double layer capacitor was charged at a constant current of 5 mA at 70 ° C., and then charged at a predetermined voltage for 50 minutes from the start of charging, and then discharged at a constant current of 5 mA to provide an electrostatic performance index. The capacity density was measured. The predetermined voltage was tested from 0.8V to 4.7V in increments of 0.1V. The capacitance density was calculated by dividing the capacitance obtained from the total energy during discharge by the total volume of the positive electrode and the negative electrode, and the maximum value of the capacitance density is shown in Table 1.
[0032]
On the other hand, in order to evaluate the safety of the obtained electric double layer capacitor, Manila paper with a width of 15mm, a length of 320mm, a thickness of 40μ, and a density of 0.6g / cm3 was immersed in the used electrolyte for 1 minute, and then vertically for 3 minutes. After removing the excess electrolyte, the sample is fixed horizontally on a sample holder with support needles at intervals of 25 mm, one end of the sample is ignited with a match, the length and time of combustion are measured, and the combustion rate is obtained. It was shown in 1.
(Example 2)
In this example, the electrolyte solution was exactly the same as Example 1, except that a solution of 1.0 mol EMIF · (HF) 2.3 dissolved in propylene carbonate (PC) solvent was used as the solute. An electric double layer capacitor having the structure shown in FIG. 1 was produced, the capacitance density was measured, and the maximum value is shown in Table 1.
[0033]
Safety evaluation was also performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
(Comparative Example 1)
This comparative example is exactly the same as Example 1 except that 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate (EMIBF 4 ), which is a room temperature molten salt, was used as the electrolyte, and is shown in FIG. An electric double layer capacitor having the structure was prepared, and the capacitance density was measured. The maximum value is shown in Table 1.
[0034]
Safety evaluation was also performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
(Comparative Example 2)
In this comparative example, exactly the same as Example 1 except that a solution in which 1.0 mol concentration of triethylmethylammonium borofluoride (TEMABF 4 ) was dissolved as a solute in a propylene carbonate (PC) solvent was used as an electrolytic solution. Thus, an electric double layer capacitor having the structure shown in FIG. 1 was produced, the capacitance density was measured, and the maximum value is shown in Table 1.
[0035]
Safety evaluation was also performed in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0036]
[Table 1]
[0037]
【The invention's effect】
Since the electric double layer capacitor of the present invention has a large capacitance and is excellent in safety, it is suitable for use as a memory backup for various electronic devices or an electric vehicle having a risk of leakage due to a collision.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a cell structure of a typical coin-type electric double layer capacitor.
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a cell structure of a typical wound type electric double layer capacitor.
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a cell structure of a typical square electric double layer capacitor.
[Explanation of symbols]
1.
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000253455A JP4453174B2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2000-08-24 | Electric double layer capacitor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000253455A JP4453174B2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2000-08-24 | Electric double layer capacitor |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002075797A JP2002075797A (en) | 2002-03-15 |
| JP2002075797A5 JP2002075797A5 (en) | 2007-10-04 |
| JP4453174B2 true JP4453174B2 (en) | 2010-04-21 |
Family
ID=18742549
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000253455A Expired - Fee Related JP4453174B2 (en) | 2000-08-24 | 2000-08-24 | Electric double layer capacitor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4453174B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1646054A4 (en) | 2003-07-11 | 2010-05-19 | Ube Industries | Acid-base mixture and ion conductor composed of such mixture |
| JP5053504B2 (en) * | 2004-03-02 | 2012-10-17 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Fuel cell electrolyte and fuel cell |
| US7955738B2 (en) * | 2004-03-05 | 2011-06-07 | Honeywell International, Inc. | Polymer ionic electrolytes |
-
2000
- 2000-08-24 JP JP2000253455A patent/JP4453174B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002075797A (en) | 2002-03-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI430304B (en) | Storage element | |
| US6414837B1 (en) | Electrochemical capacitor | |
| US11270850B2 (en) | Ultracapacitors with high frequency response | |
| JP5931326B2 (en) | Activated carbon for electric double layer capacitors | |
| WO2012056050A2 (en) | An electrical double layer capacitor with enhanced working voltage | |
| JP5041977B2 (en) | Method for producing electrode sheet for electric double layer capacitor and electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP4527821B2 (en) | Electrochemical capacitor | |
| JP4453174B2 (en) | Electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP2006024611A (en) | Electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP3812098B2 (en) | Electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP2002151364A (en) | Electric double-layer capacitor and its manufacturing method | |
| JP5178031B2 (en) | Electrolyte for electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP5184013B2 (en) | Electrolyte for electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP2005327785A (en) | Electric double layer capacitor and electrolyte therefor | |
| JP3837866B2 (en) | Electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP3800810B2 (en) | Electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP2003082533A (en) | Carbon fiber of vapor phase and use thereof | |
| WO2007077906A1 (en) | Nonaqueous capacitor and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP3792528B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of electric double layer capacitor | |
| JP2003324038A (en) | Electrolyte for electrochemical capacitor and electrochemical capacitor using it | |
| Jha et al. | Electrolytes for Electrochemical Energy Storage Supercapacitors | |
| JP2007281382A (en) | Nonaqueous electrolyte for electric double layer capacitor | |
| JPH11297580A (en) | Electric double-layer capacitor | |
| JP2003173935A (en) | Electrolyte solution for electrochemical capacitor and electrochemical capacitor using the same | |
| JP2005217008A (en) | Electric double layer capacitor and electrolyte therefor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070820 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070820 |
|
| RD05 | Notification of revocation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7425 Effective date: 20090609 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20091222 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20100112 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20100125 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130212 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |