JP4394254B2 - Defective pixel correction device for solid-state imaging device in video camera - Google Patents
Defective pixel correction device for solid-state imaging device in video camera Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4394254B2 JP4394254B2 JP2000159567A JP2000159567A JP4394254B2 JP 4394254 B2 JP4394254 B2 JP 4394254B2 JP 2000159567 A JP2000159567 A JP 2000159567A JP 2000159567 A JP2000159567 A JP 2000159567A JP 4394254 B2 JP4394254 B2 JP 4394254B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- defective pixel
- correction
- solid
- circuit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 title claims description 68
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 title claims description 57
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 230000007274 generation of a signal involved in cell-cell signaling Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005070 sampling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000875 corresponding effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002596 correlated effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003252 repetitive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
- Picture Signal Circuits (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明はビデオカメラにおける固体撮像素子の欠陥画素からの撮像信号を補正する固体撮像素子の欠陥画素補正装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来の固体撮像素子の欠陥画素からの撮像信号に対する欠陥画素補正装置は、固体撮像素子の欠陥画素からの撮像信号と、撮像信号に同期しその極性が逆で実質同レベルの補正信号とを加算して、欠陥画素からの撮像信号レベルがなくなるよう補正された撮像信号を得ることで、欠陥画素を補正している。
【0003】
このような補正については、例えば、特開2000−23050号公報に記載されている。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
この加算による欠陥画素の補正は、通常の撮像モードにおいて、有効である。即ち、通常の撮像モードでは、CCD固体撮像素子における電荷の蓄積時間が一定の期間であるため、欠陥画素から得られる信号レベルは所定のレベル範囲となる。そのため、加算による補正信号のレベルもその所定のレベル範囲とすればよく、その所定レベルに応じたダイナミックレンジを有する補正信号発生回路によって、所定の精度となるような信号を、その所定レベル範囲に応じて発生することができる。そのため、通常の撮像モードにおいては、高精度な加算による補正信号によって、精度良く欠陥画素を補正することができる。
【0005】
しかしながら、長時間蓄積する高感度撮像モードにおいては、蓄積時間が可変され、欠陥画素から得られる信号レベルが、通常の撮像モードの上述の所定の動作レベル範囲に比べて極めて広範囲のレベル範囲の信号が出力される可能性があり、その高感度撮像モード時の広レベル範囲に合わせたダイナミックレンジを有する補正信号発生回路として上述の通常感度動作と同じ精度を有するものとするためには、分解能を高くするために、通常の撮像モードの場合に比べて極めて大規模な回路構成のものとしなければならない。
【0006】
また、回路規模を上述の通常の撮像モードの加算による補正信号発生回路と同程度のものとした場合には、分解能が極めて低くなってしまい、精度の悪い加算信号でしか発生することができず、その精度の悪い補正信号と欠陥画素からの映像信号とを加算したことでは、その精度の悪い分だけ欠陥画素からの映像信号をキャンセルしきれずに、そのキャンセル仕切れなかったレベルが、画像品質を悪化される場合がある。
【0007】
本発明の目的は、通常の撮像モードでの補正精度を確保しつつ、高感度モードでも良好な補正ができるビデオカメラにおける固体撮像素子の欠陥画素補正装置を提供することにある。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、固体撮像素子の欠陥画素からの撮像信号と前記撮像信号に同期しその極性が逆で実質同レベルの補正信号とを加算して前記欠陥画素を補正する加算による補正手段と、前記固体撮像素子の欠陥画素からの撮像信号を前記欠陥画素の周辺画素からの撮像信号で置換して前記欠陥画素を補正する置換による補正手段とを備えてなることを特徴とするビデオカメラにおける固体撮像素子の欠陥画素補正装置である。
【0009】
また、本発明は、前記加算による補正手段と前記置換による補正手段はビデオカメラの撮影モードに応じて切り替えられることを特徴とするビデオカメラにおける固体撮像素子の欠陥画素補正装置である。
【0010】
また、本発明は、前記加算による補正手段と前記置換による補正手段はビデオカメラの撮影モードに応じて切り替えられ、前記撮影モードが通常の撮影モード時には前記加算による補正手段に、高感度撮影モード時には前記置換による補正手段に切り替えられることを特徴とするビデオカメラにおける固体撮像素子の欠陥画素補正装置である。
【0011】
【発明の実施の形態】
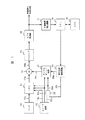
図1は、本発明のビデオカメラにおける固体撮像素子の欠陥画素補正装置の実施の形態の構成を示す図である。
【0012】
CCD(Charge Coupled Device)固体撮像素子11は、入射された撮像光を光電変換してCCD出力信号11aとして出力する。CCD出力信号11aはCDS(相関二重サンプル)回路12に入力される。CDS回路12はドライブ回路13からの制御信号で動作が制御され、ノイズ成分が除去され、CDS出力信号12aとして出力される。その後加算回路14を通り、プリアンプ15でアナログ処理された後、A/D変換器16でデジタル信号に変換され、一方は次段の映像信号処理回路へ入力され、もう一方は欠陥画素検出回路17に入力される。
【0013】
欠陥画素検出回路17で欠陥画素が検出され、検出された欠陥画素の情報はCPU18に入力され、メモリ19に格納されると共に補正信号発生回路20に入力される。補正信号発生回路20では検出された欠陥画素の情報から欠陥画素補正信号を発生する。
【0014】
ここで、CPU18は図示してない表示装置の表示画面と電気的に接続され、表示画面に表示するメニュー情報がメモリ19に予め格納されており、それによって、表示画面に、撮影モードを通常の撮像モードにするか高感度撮像モードにするかの選択メニューを表示し、どちらかの撮影モードにするのかを撮影者に選択させるようにし、さらに、その選択された撮影モードの情報がCPU18に入力され、メモリ19に格納されると共に補正信号発生回路20に入力される。
【0015】
補正信号発生回路20では、選択された撮影モードに応じて、加算用補正信号20aかまたは置換用補正信号20bを発生して出力する。ここで、加算用補正信号20aは、通常の撮像モード時に発生し、欠陥画素からの撮像信号とその極性が逆で実質同レベルの加算用補正信号であり、一方、置換用補正信号20bは、高感度撮像モード時に発生し、その極性が同じとされた置換用補正信号である。
【0016】
したがって、通常の撮像モード時には、加算用補正信号20aが出力されて、サンプルホールド回路21に入力され、サンプルホールド回路21で、欠陥画素の撮像信号期間に相当する期間の欠陥画素補正信号21aにして出力され、加算回路14で、CDS回路12からのCDS出力信号12aと加算されて、欠陥画素が補正される。
【0017】
高感度撮像モード時には、置換用補正信号20bがAND回路22に入力され、ドライブ回路13からの制御信号13bとのAND信号が、CDS回路12に入力され、CDS回路12で、欠陥画素からの撮像信号の出力を止めてその欠陥画素の1画素前の撮像信号を出力することで、欠陥画素が補正される。
【0018】
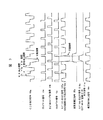
図2は、図1の一部についての詳細な構成を示す図である。図1と同一個所には同一符号が付けられている。図3は、加算による補正の動作を示す波形図である。また図4は、置換による補正の動作を示す波形図である。
【0019】
まず、撮影モードが通常の撮影モードである場合につき、図2の構成を、図3の加算による補正の動作を示す波形図を用いて説明する。
【0020】
CCD固体撮像素子11から出力されるCCD出力信号11aは、図3に図示のように、リセット期間、フィードスルー期間、信号出力期間を有する繰り返しの信号である。ここで、CCD固体撮像素子11の各画素に入射される撮影光が全て同一光量であると仮定した場合、その場合の信号期間における各画素の信号レベルは、欠陥画素を除いて同じレベルである。ここで、CCD固体撮像素子11に欠陥画素があると、例えば、格子歪みが多いために暗電流が増大するため、CCD固体撮像素子11から出力されるCCD出力信号11aのうち、その欠陥画素からの信号出力期間の撮像信号部分のレベルは、撮像光によらないで、その暗電流によって恒久的に大きく、他の期間の信号レベルよりも大きい。図1,図2において、ドライブ回路13は、CCD出力信号11aに同期して、制御信号であるクランプパルス信号13a,サンプルホールドパルス信号13b,リセットパルス信号13cを生成して出力する。
【0021】
また、図1,図2のAND回路22は、ドライブ回路13からのサンプルホールドパルス信号13bと補正信号発生回路20からの置換用補正信号20bとを入力としてAND出力信号22aを出力するが、この置換用補正信号20bは、撮影モードが通常の撮影モード時の場合には、H(ハイ)レベルに固定され、したがってサンプルホールドパルス信号13bがそのままスルーして出力信号22aとされる。CDS回路12において、CCD固体撮像素子11からのCCD出力信号11aは、そのフィードスルー期間に、クランプパルス信号13aにより、CDS回路12のスイッチ121がONされることで、そのフィードスルー期間のレベルがクランプされる。
【0022】
CCD出力信号11aはアンプ122を介してスイッチ123に入力される。そして、CCD出力信号11aの信号出力期間に、スイッチ123がサンプルホールドパルス信号13bによりONされ、その信号出力期間のCCD出力信号11aのレベルがサンプリングされ、コンデンサ124にそのサンプリングレベルの信号がホールドされる。そのホールドされたサンプリングレベルの信号が、アンプ125に入力され、アンプ125の出力に接続のスイッチ126が、リセットパルス信号13cによりONされて信号ラインが接地される前まで、アンプ127で増幅され、増幅された出力信号127aがCDS回路12の出力信号として出力され、この出力信号127aが加算回路14の抵抗141に入力される。
【0023】
一方、前述のように、補正信号発生回路20では、通常の撮像モード時に、欠陥画素からの撮像信号とその極性が逆で実質同レベルの加算用補正信号20a(図3に図示)を発生して出力し、その出力された加算用補正信号20は、サンプルホールド回路21に入力され、サンプルホールド回路21のアンプ211で増幅され、スイッチ212が信号出力期間にサンプルホールドパルス信号13bによりONされると、そのON期間の加算用補正信号20bのレベルがサンプリングされ、コンデンサ213にそのサンプリングレベルの信号がホールドされる。そのホールドされたサンプリングレベルの信号がアンプ214に入力され、アンプ214の出力に接続のスイッチ215が、リセットパルス信号13cによりONされて信号ラインが接地される前まで、アンプ216で増幅され、アンプ216から増幅された加算用補正制御信号216aがサンプルホールド回路21の出力信号として出力される。この加算用補正制御信号216aが加算回路14の抵抗142に入力される。
【0024】
そして、加算回路14で、抵抗141に入力されたCDS回路12の出力信号127aと、抵抗142に入力されたサンプルホールド回路21の出力信号216aとが加算され、補正後の出力信号14aとして、欠陥画素が実質補正された撮像信号を得ることができる。
【0025】
次に、撮影モードが高感度撮影モード時である場合につき、図2の構成を、図4の置換による補正の動作を示す図を用いて説明する。
【0026】
高感度撮影モード時である場合には、前述のように、補正信号発生回路20は、欠陥画素補正信号として、欠陥画素からの撮像信号が出力されるタイミングで、図4に図示のように、欠陥画素からの撮像信号の極性と同じ極性でL(ロウ)レベルの置換用補正信号20bを発生し出力する。この置換用補正信号20bがサンプルホールドパルス信号13bとともにAND回路22に入力されるので、置換用補正信号20bのL(ロウ)レベル中に、サンプルホールドパルス信号13bが入力されても、その出力信号22aは、欠陥画素の撮像信号部分だけサンプルホールドパルス信号13bが除去された形となる。
【0027】
このAND回路22の出力信号22aにより、CDS回路12のスイッチ123がONになると、CCD固体撮像素子11からの信号の信号出力期間のレベルがサンプリングされて、コンデンサ124にホールドされるが、サンプルホールドパルス13bが除去された部分ではサンプリングが行われず、1画素前のレベルがコンデンサ124に保持される。そして、スイッチ126がリセットパルスでONされて信号ラインが接地される前まで、増幅器127から出力信号127aが得られる。
【0028】
このようにして欠陥画素の出力信号はサンプリングされず欠陥画素の1画素前の出力信号が保持され、欠陥画素が1個前の画素で置換される形で欠陥画素が補正される。
【0029】
【発明の効果】
本発明によれば、通常の撮像時は加算方式で欠陥画素補正を行い、蓄積方式による高感度撮像時には置換方式で欠陥画素補正を行うことにより、通常の撮像モードでの補正精度を確保しつつ、高感度モードでも良好な補正ができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明のビデオカメラにおける固体撮像素子の欠陥画素補正装置の実施の形態の構成を示す図である。
【図2】図1の一部についての詳細な構成を示す図である。
【図3】加算による補正の動作を示す波形図である。
【図4】置換による補正の動作を示す波形図である。
【符号の説明】
11…CCD固体撮像素子、12…CDS回路、13…ドライブ回路、14…加算回路、15…プリアンプ、16…A/D変換器、17…欠陥画素検出回路、18…CPU、19…メモリ、20…補正信号発生回路、20a…加算用補正信号、20b…置換用補正信号、21…サンプルホールド回路、22…AND回路、122,125,127,211,214,216…アンプ、121,123,126,212,215…スイッチ、124,213…コンデンサ、141,142…抵抗。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a defective pixel correction device for a solid-state imaging device that corrects an imaging signal from a defective pixel of the solid-state imaging device in a video camera.
[0002]
[Prior art]
The conventional defective pixel correction device for the imaging signal from the defective pixel of the solid-state imaging device adds the imaging signal from the defective pixel of the solid-state imaging device and a correction signal that is synchronized with the imaging signal and has the opposite polarity and substantially the same level. Then, the defective pixel is corrected by obtaining an imaging signal corrected so that the imaging signal level from the defective pixel disappears.
[0003]
Such correction is described in, for example, Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2000-23250.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
The correction of defective pixels by this addition is effective in the normal imaging mode. That is, in the normal imaging mode, since the charge accumulation time in the CCD solid-state imaging device is a fixed period, the signal level obtained from the defective pixel is in a predetermined level range. For this reason, the level of the correction signal by addition may be set within the predetermined level range, and a signal having a predetermined accuracy is set within the predetermined level range by the correction signal generation circuit having a dynamic range corresponding to the predetermined level. Can be generated accordingly. Therefore, in the normal imaging mode, a defective pixel can be corrected with high accuracy by a correction signal obtained by high-precision addition.
[0005]
However, in the high-sensitivity imaging mode that accumulates for a long time, the accumulation time is variable, and the signal level obtained from the defective pixel is a signal in a very wide level range compared to the above-described predetermined operation level range in the normal imaging mode. In order to have the same accuracy as the normal sensitivity operation described above as a correction signal generation circuit having a dynamic range that matches the wide level range in the high-sensitivity imaging mode, the resolution must be reduced. In order to make it high, the circuit configuration must be extremely large compared to the normal imaging mode.
[0006]
In addition, when the circuit scale is the same as that of the correction signal generation circuit by the addition of the normal imaging mode described above, the resolution becomes extremely low, and it can be generated only with an addition signal with low accuracy. By adding the correction signal with poor accuracy and the video signal from the defective pixel, the video signal from the defective pixel cannot be canceled by the amount of the poor accuracy, and the level of the cancellation partition is not improved. May be exacerbated.
[0007]
An object of the present invention is to provide a defective pixel correction device for a solid-state image sensor in a video camera that can perform good correction even in a high sensitivity mode while ensuring correction accuracy in a normal imaging mode.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention provides a correction means by addition for correcting the defective pixel by adding an imaging signal from a defective pixel of a solid-state imaging device and a correction signal which is synchronized with the imaging signal and whose polarity is reversed and substantially the same level; Solid-state imaging in a video camera, comprising: replacement means for replacing an imaging signal from a defective pixel of a solid-state imaging device with an imaging signal from a peripheral pixel of the defective pixel to correct the defective pixel It is a defective pixel correction device for an element.
[0009]
According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a defective pixel correction apparatus for a solid-state imaging device in a video camera, wherein the correction means by addition and the correction means by replacement are switched according to a shooting mode of the video camera.
[0010]
Further, according to the present invention, the correction means by addition and the correction means by replacement are switched according to the shooting mode of the video camera, and when the shooting mode is a normal shooting mode, the correction means by addition is changed to a correction mode by the addition. A defective pixel correction apparatus for a solid-state imaging device in a video camera, wherein the correction means is switched to the correction means by the replacement.
[0011]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of an embodiment of a defective pixel correction device for a solid-state imaging device in a video camera of the present invention.
[0012]
A CCD (Charge Coupled Device) solid-
[0013]
A defective pixel is detected by the defective
[0014]
Here, the
[0015]
The correction
[0016]
Therefore, in the normal imaging mode, the
[0017]
In the high-sensitivity imaging mode, the
[0018]
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a detailed configuration of a part of FIG. The same parts as those in FIG. 1 are denoted by the same reference numerals. FIG. 3 is a waveform diagram showing a correction operation by addition. FIG. 4 is a waveform diagram showing a correction operation by replacement.
[0019]
First, when the shooting mode is the normal shooting mode, the configuration in FIG. 2 will be described with reference to the waveform diagram showing the correction operation by addition in FIG.
[0020]
The
[0021]
The AND
[0022]
The
[0023]
On the other hand, as described above, the correction
[0024]
Then, the
[0025]
Next, when the shooting mode is the high-sensitivity shooting mode, the configuration in FIG. 2 will be described with reference to the correction operation by replacement in FIG.
[0026]
In the case of the high-sensitivity shooting mode, as described above, the correction
[0027]
When the
[0028]
In this way, the output signal of the defective pixel is not sampled, the output signal of the previous pixel of the defective pixel is retained, and the defective pixel is corrected in such a manner that the defective pixel is replaced with the previous pixel.
[0029]
【The invention's effect】
According to the present invention, defect pixel correction is performed by the addition method during normal imaging, and defective pixel correction is performed by the replacement method during high-sensitivity imaging by the accumulation method, while ensuring correction accuracy in the normal imaging mode. Good correction is possible even in the high sensitivity mode.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of an embodiment of a defective pixel correction device for a solid-state imaging device in a video camera of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a detailed configuration of a part of FIG. 1;
FIG. 3 is a waveform diagram showing an operation of correction by addition.
FIG. 4 is a waveform diagram showing a correction operation by replacement.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000159567A JP4394254B2 (en) | 2000-05-25 | 2000-05-25 | Defective pixel correction device for solid-state imaging device in video camera |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000159567A JP4394254B2 (en) | 2000-05-25 | 2000-05-25 | Defective pixel correction device for solid-state imaging device in video camera |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001339642A JP2001339642A (en) | 2001-12-07 |
| JP2001339642A5 JP2001339642A5 (en) | 2007-05-17 |
| JP4394254B2 true JP4394254B2 (en) | 2010-01-06 |
Family
ID=18663868
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000159567A Expired - Lifetime JP4394254B2 (en) | 2000-05-25 | 2000-05-25 | Defective pixel correction device for solid-state imaging device in video camera |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4394254B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5147789B2 (en) * | 2009-07-13 | 2013-02-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and control method thereof |
-
2000
- 2000-05-25 JP JP2000159567A patent/JP4394254B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001339642A (en) | 2001-12-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2161919B1 (en) | Read out method for a CMOS imager with reduced dark current | |
| JP7353783B2 (en) | Imaging device and its control method; Imaging device and its control method | |
| JP2006005520A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| US7245318B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus that corrects an imbalance in output levels of image data | |
| US7990426B2 (en) | Phase adjusting device and digital camera | |
| JP5222068B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2008306565A (en) | Imaging apparatus and signal correcting method thereof | |
| JPH11112884A (en) | Method for correcting dark current of video camera device and video camera device using the method | |
| JPH11196335A (en) | Image pickup device | |
| JP4394254B2 (en) | Defective pixel correction device for solid-state imaging device in video camera | |
| JP2020115604A (en) | Imaging apparatus and control method of the same | |
| JP2008288723A (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and integrated circuit | |
| JP2007036457A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JPH0342750B2 (en) | ||
| JP2006121165A (en) | Imaging apparatus and image forming method | |
| JP5271201B2 (en) | Image signal processing apparatus and imaging apparatus | |
| JP2008053812A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| JP2003304453A (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2003153092A (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2007104222A (en) | Imaging apparatus and imaging method | |
| JP3705611B2 (en) | Image reading device | |
| JP2004297731A (en) | Image pickup device and electric charge detecting device | |
| JP3227809B2 (en) | Defect correction device for solid-state imaging device and solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2006157535A (en) | Imaging device | |
| JPH066685A (en) | Defect correcting device for solid image pickup element |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070326 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070326 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090708 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090714 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090910 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20090910 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20091006 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20091015 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4394254 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121023 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121023 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131023 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |