JP4392947B2 - Image reading apparatus, control method of image reading apparatus, and storage medium - Google Patents
Image reading apparatus, control method of image reading apparatus, and storage medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4392947B2 JP4392947B2 JP2000066995A JP2000066995A JP4392947B2 JP 4392947 B2 JP4392947 B2 JP 4392947B2 JP 2000066995 A JP2000066995 A JP 2000066995A JP 2000066995 A JP2000066995 A JP 2000066995A JP 4392947 B2 JP4392947 B2 JP 4392947B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- dimming
- time
- output level
- light source
- level
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 15
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 16
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003705 background correction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Exposure In Printing And Copying (AREA)
- Image Input (AREA)
- Facsimile Scanning Arrangements (AREA)
- Studio Devices (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は画像読み取り装置、画像読み取り装置の制御方法及び記憶媒体に関し、特に、原稿台上に載せられた原稿の反射光又は透過光を読み取るための画像読み取り装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来、画像読み取り装置としてCCDリニアイメージセンサ(以下CCD)を用いたイメージスキャナが知られている。図6(a)、(b)はフラットベッド型スキャナと呼ばれる装置の構成を簡単に示したものであり、図6(a)は上面図、図6(b)は側面図である。
【0003】
図6において、Dは原稿台ガラス100上に置かれた読取原稿で、これを光源101によって照射した反射光をミラー102,103,104によって折り返し、レンズ105によってCCD106に結像するようにしている。
【0004】
光源101及びミラー102,103,104、レンズ105,CCD106を固定載置した読み取りユニット107を原稿台ガラス100に平行に、図6中の左方向から右方向に走査することにより原稿Dの全体を読み取り、CCD106から1ぺ一ジ分の画像信号を得る。上記CCD106を載置したCCDボード113と画像読み取り装置に固定されたメインボード112は、ケーブル111によって接続されている。
【0005】
図6(a)に示すように、上から下に向かう方向が主走査方向、右から左に向かう方向が副走査方向となる。外部光からの影響を避けるべく、外装カバー1、原稿抑え110によって内部は遮光されている。
【0006】
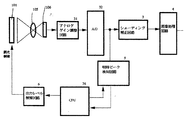
図7に、出力レベル調整手段を構成する回路ブロック例を示す。調光制御可能な光源101から照射されて原稿に当たった反射光、あるいは原稿を透過した光信号は、レンズ105を介してCCD106に結像される。
【0007】
CCD106に結像された光信号は、アナログゲイン調整回路31によって信号処理された後、A/D変換器32にてデジタル化される。そして、シエーディング補正回路3、画像処理回路4に順次供給される。
【0008】
また、A/D変換器32の出力は明時ピーク検知回路5に与えられ、上記明時ピーク検知回路5でCPU36によって指定された領域における、ピーク出力を8bitで検出して記憶される。また、CPU36からの制御信号が出力レベル制御回路6に与えられ、上記制御信号が出力レベル制御回路6を通じて出力レベルの制御を行うことが可能と成されている。
【0009】
なお、図7においては、出力レベル制御手段としてランプ101の調光制御手段として説明しているが、CCD106の蓄積時間制御、電子シャッタレベル制御手段、アナログゲイン調整回路31、及び図示しないA/D変換器のref制御によるゲイン調整手段、さらに画像処理回路4においてレベル調整手段等のレベル制御手段等、公知の種々の手段を用いることができる。
【0010】
しかしながら、よりS/Nの良い画像を得るためには、図7のような調光制御によることが最も効果的である。ところで、調光制御を行う上で、ランプの温度特性は無視できない要素である。図8にランプの温度による相対照度変化の違いを示す。
【0011】
この場合の相対照度とは、常温時(25℃)の安定時の照度を100%としている。実際に、スキャナで使うランプ照度は、図8でいうと、約50〜55%の辺りであり、低温時においても必要なレベルには達するが、それまでには約50秒かかる。
【0012】
常温時(25℃)及び高温時(35℃)の場合は、約10秒足らずでそのレベルに達する。また、出力レベルが飽和した後のグラフを見ると、低温時は出力が下がり続け、なかなか安定しにくい。常温時及び高温時のように、温度が高くなってくると、早く安定しやすいという特性がある。
【0013】
つまり、低温時では必要なレベルに達するまでの時間及び安定化のための時間が長いので、常温時、高温時に比べて調光制御の時間が圧倒的に長くかかることになる。
【0014】
調光制御による光信号によって出力レベルを制御する例として、図9に調光制御に関するフローチャートを示す。図9において、ステップS101は画像読み取り装置の電源投入時から処理を行う例をしているため、光源101の点灯開始という意味でランプONから説明している。
【0015】
通常、光源101としては、冷陰極ランプ、ハロゲンランプ等があり、調光制御も電圧制御、電流制御及び間欠点灯制御などがある出力レベル制御回路6内にてPWM制御によるのが通例である。
【0016】
ステップS101では、通常ランプONのため、ランプPWM100%となる。ステップS102では、10秒間のwait時間を設けて、光源101の光量が安定点灯するのを待つが、このwait時間は、ランプの性能や画像読み取り装置の構成にも依存するため一定ではない。
【0017】
ステップS103は、光源101の安定度を測るために明時ピーク検知回路5によって、明時出力レベルPnを検出する。次に、ステップS104では、目標とするターゲット出力レベルPt付近に到達するまで調光制御を行う。次に、ステップS105において、明時出力レベルPnがターゲット出力レベルPtに達しているか否かを判断する。この判断の結果、明時出力レベルPnがターゲット出力レベルPtに達していない場合は、言うまでもなくランプのPWMは100%を維持する。
【0018】
次に、ステップS106の0.75秒ごとに明時出力レベルPnの検出を繰り返し、明時出力レベルPnがレベルターゲット出力レベルPtの±1%以内に達したらステップS107以降の安定化制御に移る。
【0019】
ステップS108の安定性チェックでは、出力レベルの変動が一定時間(この場合は1.5秒)の間に1レベル以下の変動に維持されていたら、安定したと判断して調光制御を終了する。
【0020】
図10に、低温時(10℃)と常温時(25℃)のランプの出力レベルの変化を示す。常温時では、ステップS102の10秒のwait時間(T1)を経た後、既に出力レベルがターゲット出力レベルPt付近に達しているので、ステップS107のwait時間とステップS108の安定性チェック(T2)後、調光制御が終了する。
【0021】
一方、低温時では10秒のwait時間では、明時出力レベルPnがターゲット出力レベルPt近辺に達しないので、ステップS104〜106をターゲット出力レベルPt付近に達するまで行う(T3)。そして、その後のステップS107とステップS108の安定性チェック(T4)を行うが、上記の通り低温時には、常温及び高温時に比べてランプが安定するために時間がかかるので、安定性チェック時間T4は長くなる。
【0022】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
上記図9のフローチャートに従うと、上記図10のように環境温度が常温時の場合、調光制御時間(T1+T2)が約30秒であるのに対して、低温時は調光制御時間(T3+T4)が約100秒と常温時に比べて約3,3倍の時間がかかってしまうことになる。すなわち、従来はトータルの調光制御時間が長くなる問題点があった。
【0023】
本発明は上述の問題点にかんがみ、低温時において必要なレベルに達するまでの時間及び安定化するまでの時間を短くできるようにすることを目的とする。
【0024】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明の画像読み取り装置は、光源と、上記光源により照明された原稿の反射光が結像されるイメージセンサと、上記イメージセンサの出力を検出する検知手段と、上記検知手段の出力レベルを所定のしきい値と比較する比較手段と、上記検知手段の出力が目標レベルになるように上記光源を調光する調光手段とを有する画像読み取り装置であって、上記目標レベルよりも低く、上記光源の点灯開始から第1の時間経過後の上記検知手段の出力レベルが常温では上回り低温では下回るレベルに、第1のしきい値が設定されていて、上記光源の点灯開始から上記第1の時間経過後に上記比較手段で、上記第1のしきい値よりも上記出力レベルが上回る時には、上記調光手段により上記光源の調光を開始し、上記第1のしきい値よりも上記出力レベルが下回る時には、上記目標レベルよりも高い第2のしきい値を上回るまで待った後に上記調光手段により上記光源の調光を開始することを特徴とする。
また、本発明の画像読み取り装置の他の特徴とするところは、上記調光手段はPWM制御を行ない、上記調光の開始までは上記PWMを100%に保つことを特徴とする。
また、本発明の画像読み取り装置のその他の特徴とするところは、上記目標レベルよりも高い第2のしきい値を上回るまで待った後に、さらに第2の時間経過後に上記調光手段により上記光源の調光を開始することを特徴とする。
ことを特徴とする。
【0025】
本発明の画像読み取り装置の制御方法は、光源と、上記光源により照明された原稿の反射光が結像されるイメージセンサと、上記イメージセンサの出力を検出する検知手段と、上記検知手段の出力レベルが目標レベルになるように前記光源を調光する調光手段とを有する画像読み取り装置の制御方法であって、上記光源の点灯を開始する点灯工程と、
上記点灯を開始した後に第1の時間の経過を待つ第1時間待工程と、上記目標レベルよりも低く、上記光源の点灯開始から上記第1の時間経過後の上記検知手段の出力レベルが常温では上回り低温では下回るレベルに、第1のしきい値が設定されていて、上記第1時間待工程の後に、上記検知手段の出力レベルと上記第1のしきい値とを比較する第1比較工程と、上記第1比較工程の後、上記検知手段の出力レベルが上記目標レベルよりも高い第2のしきい値を上回るまで待つ第2比較工程と、上記調光手段で調光を行なう調光工程とを有し、上記第1比較工程で前記出力レベルが上記第1のしきい値を上回るときには上記調光工程を開始し、上記第1比較工程で前記出力レベルが上記第1のしきい値を下回るときには上記第2比較工程を経た後に上記調光工程を開始することを特徴とする。
また、本発明の画像読み取り装置の制御方法の他の特徴とするところは、第2の時間を待つ第2時間待工程を有し、上記第1比較工程で前記出力レベルが上記第1のしきい値を下回るときには上記第2比較工程の後に上記第2時間待工程を経た後に上記調光工程を開始することを特徴とする。
【0026】
本発明の記憶媒体は、上記に記載の画像読み取り装置の制御方法を実行する各工程をコンピュータに実行させるプログラムを記憶したことを特徴とする。
【0027】
【作用】
本発明は上記技術手段を有するので、環境温度が低温であると判断した場合には、目標とするレベルよりも上のレベルまで出力レベルが上げられることにより、ランプが安定化制御に入っって出力が安定するまでの時間を短くすることが可能となる。
【0028】
【発明の実施の形態】
(第1の実施形態)
図1に、本発明の画像読み取り装置、画像読み取り装置の制御方法及び記憶媒体の第1の実施形態の処理手順を説明するフローチャートを示す。
【0029】
最初のステップS201は、画像読み取り装置の電源投入時からを例にしているため、光源101の点灯開始という意味でランプONから説明している。通常光源101としては、冷陰極ランプ、ハロゲンランプ等があり、調光制御も電圧制御、電流制御及び間欠点灯制御などがある。
【0030】
また、実際の制御は、図7に示した出力レベル制御回路6内にてPWM制御によるのが通例である。ステップS201では通常ランプONのため、ランプPWM100%となる。
次のステップS202では、10秒間のwait時間を設けて、光源101の光量が安定点灯するのを待つが、このwait時間は、光源101の性能や画像読取装置の構成にも依存するため一定ではない。
【0031】
本実施形態では、予めランプ出力のしきい値Psを、図3における第1の時間T1’(この場合は10秒)経過後に常温では上回り、低温では下回るレベルに設定しておき、第1の時間T1’が経過後のステップS203で検出した明時ピーク出力レベルPnと、しきい値PsとをステップS204で比較して、明時出力レベルPn≦Psのときにはスキャナ本体が低温環境であると判定するようにしている。
【0032】
図2に、ランプのPWMの変化による安定時のランプの管壁温度の変化の様子を示す。この図2から、安定時のランプの管壁温度とランプのPWMにはほぼ比例関係があることがわかる。
【0033】
上述した図8より、ランプの管壁温度が高いほど安定化のための時間が短い。よって、図2及び図8より、ランプの安定化の時間である第4の時間T4’を短くするためには、ランプ管壁温度を高くすること、つまり、ランプの出力が高い状態で安定化を図ることが重要となる。
【0034】
ランプの出力レベルがしきい値Psまで行っていない低温状態のときに、ステップS205でランプのPWMが100%の状態で一定時間の待ち時間を入れる。この待ち時間の設定は、これを入れることによって第3の時間T3’は長くなるが、長くなった分よりも安定化に要する時間である。第4の時間T4’がより短くなるようにすることによって、結果的に「第3の時間T3’」と「第4の時間T4’」との合計時間が短くなるような時間に設定する。
【0035】
そして、明時出力レベルPnがターゲット出力レベルPtに達した後は、光源101が安定するのを待つために、ステップS209とステップS210の明時出力レベルPnの安定性チェックで1.5秒の間に出力レベルの変化が「1」以下に収まるまで繰り返し、安定したと判断すると調光制御を終了する。
【0036】
図3に、本実施形態を用いたときのランプの出力レベルの時間経過を示す。
本実施形態では、ランプのPWM100%の状態で一定の待ち時間を入れることによって調光制御時間である第3の時間T3’に,従来例よりも長い時間を取るようにしている。すると、ステップS204で明時出力レベルPnがしきい値Psに達したときに、図3の第3の時間T3’終了時のように、出力レベルがターゲット出力レベルPtよりも高い状態になる。
【0037】
そして、ステップS206でターゲット出力レベルPt±1%になるようにPWMを調節してレベルを抑えることになるが、このときは既にランプの管壁温度は高くなっているので、その後の安定化制御時間ではランプ管壁の温度が高いために安定しやすくなり、安定化の時間である第4の時間T4’を従来例より短くすることが可能である。
【0038】
調光制御の時間が長くなる分よりも、安定化のための時間が短くなるように、つまり、(T3’−T3)≦(T4−T4’)となるように、ステップS205の待ち時間を設定することによって、トータルの調光制御時間を短くすることが可能である。
【0039】
本実施形態で入れるステップS205の一定の待ち時間はランプの特性などにより変動するが、同じランプを使うのであれば、この待ち時間の設定を変更するだけで、最適なランプの調光制御時間を設定することが可能となる。
【0040】
(第2の実施形態)
図4に本発明の第2の実施形態を示す。図4において、最初のステップS301は、画像読み取り装置の電源投入時からを例にしているため、光源101の点灯開始という意味でランプONから説明している。通常光源101としては、冷陰極ランプ、ハロゲンランプ等があり、調光制御も電圧制御、電流制御及び間欠点灯制御などがある。出力レベル制御回路6内にてPWM制御によるのが通例である。
【0041】
最初のステップS301では通常ランプONのため、ランプPWM100%となる。次のステップS302では、10秒間のwait時間を設けて、光源101の光量が安定点灯するのを待つが、このwait時間は、ランプの性能や画像読み取り装置の構成にも依存するため一定ではない。
【0042】
本実施形態では、予めランプ出力のしきい値Psを、図5における第1の時間T1”(この場合は10秒)経過後に常温では上回り、低温では下回るレベルに設定しておき、第1の時間T1”経過後のステップS303で検出した明時出力レベルPnと、しきい値PsをステップS304で比較して、明時出力レベルPn≦Ps、の時にはスキャナ本体が低温環境であると判定する。
【0043】
ステップS304において、低温環境であると判定された場合はステップS306において明時出力レベルPnを検出し、ステップS307で明時出力レベルPnがターゲット出力レベルPtよりも高く設定されたPvtに達したか否かを判定する。この判定の結果、達していない場合はステップS308の待ち時間を行った後再びステップS306,ステップS307の処理を行う。
【0044】
明時出力レベルPnがPvtに達したら、ステップS309の5秒間の待ち時間を行った後、ステップS305の調光制御を行う。なお、ステップS304において明時出力レベルPnがしきい値Psに達している場合は常温以上の環境にあると判断して、ステップS305を行う。
【0045】
次に、ステップS310で明時出力レベルPnがターゲット出力レベルPtに到達するまでステップS305を繰り返し、到達したらステップS311,ステップS312の安定化制御に移り、ステップS312の安定化制御では1.5secの間に出力レベルの変動が1レベルに抑えられると安定化されたと判定して全ての調光制御を終了する。
【0046】
図5に、本実施形態を用いたときのランプの出力レベルの時間経過を示す。
ステップS304で低温状態と判定された場合、ランプのPWMを100%に保った状態で明時出力レベルPnをターゲット出力レベルPtよりも高いターゲットPvtまで上げていく。ターゲット出力レベルPtよりも上のレベルに必ず一度上げることにより、ランプ管壁温度を従来例よりも高い状態に持っていくことができる。
【0047】
ターゲットPvtに達したら、特定の待ち時間(この場合は5秒間)を入れて、さらにランプ管壁の温度を高くするとともに、ステップS305の調光制御に入る前におけるランプの出力レベルのばらつきをある程度の範囲に抑えることができる。
【0048】
そして、ステップS310でターゲット出力レベルPt±1%になるようにPWMを調節してレベルを抑えることになるが、このとき、既にランプの管壁温度は高くなっているので、その後の安定化制御時間では、図8にもある通り、安定しやすくなり安定化の時間T4”を従来の安定化時間T4よりも短くすることが可能である。
【0049】
本実施形態における第3の時間T3”は、上述した第3の時間T3よりも長くなるが、本実施形態における第3の時間T3”が長くなる分よりも、安定化のための時間が短くなるようにすることができる。つまり、(T3”−T3)≦(T4−T4”)となるように、ステップS307のレベルPvt、及びステップS309の待ち時間を設定することにより、トータルの調光時間を短くすることが可能である。
【0050】
図11に、本発明の画像読み取り装置を構成するコンピュータシステムの一例を示す。
図11は、一般的な画像読み取り装置の制御装置の構成を示す図である。図11において、1200はコンピュータPCである。上記PC1200は、CPU1201を備え、ROM1202またはハードディスク(HD)1211に記憶された、あるいはフロッピーディスクドライブ(FD)1212より供給されるネットワーク印刷デバイス制御ソフトウェアを実行し、システムバス1204に接続される各デバイスを制御する。
【0051】
1203はRAMで、CPU1201の主メモリ、ワークエリア等として機能する。1207はディスクコントローラ(DKC)で、ブートプログラム(起動プログラム:パソコンのハードやソフトの実行(動作)を開始するプログラム)、複数のアプリケーション、編集ファイル、ユーザファイルそしてネットワーク管理プログラム等を記憶するハードディスク(HD)1211、及びフロッピーディスク(FD)1212とのアクセスを制御する。
【0052】
1208はネットワークインタフエースカード(NIC)で、実施形態の画像読み取り装置を、LAN1220を介してネットワークに接続する場合に使用するものである。
【0053】
上記PC1200のCPU1201、ROM1202またはハードディスク(HD)1211に記憶されたプログラムにより、本実施形態の画像読み取り装置における環境判定手段、調光手段、レベル検出手段、制御手段等が構成されている。
【0054】
(本発明の他の実施形態)
本発明は複数の機器(例えば、ホストコンピュータ、インタフェース機器、リーダ、プリンタ等)から構成されるシステムに適用しても1つの機器からなる装置に適用しても良い。
【0055】
また、上述した実施の形態の機能を実現するように各種のデバイスを動作させるように、上記各種デバイスと接続された装置あるいはシステム内のコンピュータに対し、上記実施の形態の機能を実現するためのソフトウェアのプログラムコードを供給し、そのシステムあるいは装置のコンピュータ(CPUあるいはMPU)に格納されたプログラムに従って上記各種デバイスを動作させることによって実施したものも、本発明の範疇に含まれる。
【0056】
また、この場合、上記ソフトウェアのプログラムコード自体が上述した実施の形態の機能を実現することになり、そのプログラムコード自体、及びそのプログラムコードをコンピュータに供給するための手段、例えばかかるプログラムコードを格納した記憶媒体は本発明を構成する。かかるプログラムコードを記憶する記憶媒体としては、例えばフロッピーディスク、ハードディスク、光ディスク、光磁気ディスク、CD−ROM、磁気テープ、不揮発性のメモリカード、ROM等を用いることができる。
【0057】
また、コンピュータが供給されたプログラムコードを実行することにより、上述の実施形態で説明した機能が実現されるだけでなく、そのプログラムコードがコンピュータにおいて稼働しているOS(オペレーティングシステム)あるいは他のアプリケーションソフト等の共同して上述の実施の形態で示した機能が実現される場合にもかかるプログラムコードは本発明の実施の形態に含まれることは言うまでもない。
【0058】
さらに、供給されたプログラムコードがコンピュータの機能拡張ボードやコンピュータに接続された機能拡張ユニットに備わるメモリに格納された後、そのプログラムコードの指示に基いてその機能拡張ボードや機能拡張ユニットに備わるCPU等が実際の処理の一部または全部を行い、その処理によって上述した実施の形態の機能が実現される場合にも本発明に含まれる。
【0059】
【発明の効果】
上述したように、本発明によれば、簡単な構成で使用環境を判定することができる。また、使用環境にかかわらず、出力が安定するまでの時間を短くすることが可能となり、トータルのスキャン時間を短縮することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施形態を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図2】実施形態のランプのPWMの変化による安定時のランプの管壁温度の変化の様子を示す図である。
【図3】実施形態を用いたときのランプの出力レベルの時間経過を示す特性図である。
【図4】本発明の第2の実施形態を説明するためのフローチャートである。
【図5】第2の実施形態におけるランプの出力レベルの時間経過を示す特性図である。
【図6】画像読み取り装置の概略構成を示す上面図である。
【図7】出力レベル調整を行う回路の一例を示すブロック図である。
【図8】点灯後の経時変化の一例を示す特性図である。
【図9】調光制御の手順を説明するフローチャートである。
【図10】低温時(10℃)と常温時(25℃)のランプの出力レベルの変化を説明する動作出力特性図である。
【図11】本実施形態の画像読み取り装置の制御装置を構成するコンピュータシステムの一例を示すブロック図である。
【符号の説明】
3 シエーディング補正回路
4 画像処理回路
5 明時ピーク検知回路
6 出力レベル制御回路
31 アナログゲイン調整回路
32 A/D変換器
36 CPU
101 光源
105 レンズ
106 CCD[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an image reading apparatus, a method for controlling the image reading apparatus, and a storage medium, and more particularly to an image reading apparatus for reading reflected light or transmitted light of a document placed on a document table.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Conventionally, an image scanner using a CCD linear image sensor (hereinafter referred to as a CCD) is known as an image reading device. FIGS. 6A and 6B simply show the configuration of an apparatus called a flatbed scanner. FIG. 6A is a top view and FIG. 6B is a side view.
[0003]
In FIG. 6, D is a read original placed on the
[0004]
The entire original D is scanned by scanning the
[0005]
As shown in FIG. 6A, the direction from top to bottom is the main scanning direction, and the direction from right to left is the sub-scanning direction. In order to avoid the influence from external light, the inside is shielded by the exterior cover 1 and the
[0006]
FIG. 7 shows an example of a circuit block constituting the output level adjusting means. Reflected light irradiated from the
[0007]
The optical signal imaged on the
[0008]
The output of the A /
[0009]
In FIG. 7, the dimming control means of the
[0010]
However, in order to obtain an image with a better S / N, it is most effective to use light control as shown in FIG. By the way, when performing dimming control, the temperature characteristic of the lamp is an element that cannot be ignored. FIG. 8 shows the difference in relative illuminance change depending on the lamp temperature.
[0011]
The relative illuminance in this case is defined as 100% of the illuminance at the normal temperature (25 ° C.). Actually, the illuminance of the lamp used in the scanner is about 50 to 55% in FIG. 8 and reaches a required level even at low temperatures, but it takes about 50 seconds.
[0012]
At normal temperature (25 ° C.) and high temperature (35 ° C.), the level is reached in less than about 10 seconds. Also, looking at the graph after the output level is saturated, the output continues to decrease at low temperatures, making it difficult to stabilize. As at normal temperature and high temperature, when temperature rises, there is a characteristic that it is easy to stabilize quickly.
[0013]
In other words, since the time required to reach the required level and the stabilization time are long at low temperatures, the light control time is overwhelmingly longer than at normal temperatures and high temperatures.
[0014]
As an example of controlling the output level by an optical signal by dimming control, FIG. 9 shows a flowchart relating to dimming control. In FIG. 9, step S101 is an example in which processing is performed from when the image reading apparatus is turned on.
[0015]
Usually, the
[0016]
In step S101, the lamp PWM is 100% because the normal lamp is ON. In step S102, a wait time of 10 seconds is provided to wait for the light quantity of the
[0017]
In
[0018]
Next, detection of the light output level Pn is repeated every 0.75 seconds in step S106. When the light output level Pn reaches within ± 1% of the level target output level Pt, the control proceeds to stabilization control in step S107 and thereafter.
[0019]
In the stability check of step S108, if the fluctuation of the output level is maintained at a fluctuation of 1 level or less for a certain time (in this case, 1.5 seconds), it is determined that the output is stable and the dimming control is terminated. .
[0020]
FIG. 10 shows a change in the output level of the lamp at a low temperature (10 ° C.) and at a normal temperature (25 ° C.). At room temperature, after the wait time (T1) of 10 seconds of step S102, the output level has already reached the target output level Pt. Therefore, after the wait time of step S107 and the stability check (T2) of step S108 Then, the light control is finished.
[0021]
On the other hand, since the light output level Pn does not reach the target output level Pt in the wait time of 10 seconds at the low temperature, steps S104 to S106 are performed until the target output level Pt is reached (T3). Then, the stability check (T4) in subsequent steps S107 and S108 is performed. As described above, at low temperatures, it takes time for the lamp to stabilize compared to normal temperatures and high temperatures, so the stability check time T4 is long. Become.
[0022]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
According to the flowchart of FIG. 9, when the ambient temperature is normal as shown in FIG. 10, the dimming control time (T1 + T2) is about 30 seconds, while the dimming control time (T3 + T4) is low. Is about 100 seconds, which is about 3 to 3 times as long as that at room temperature. In other words, there has been a problem that the total light control time is long.
[0023]
The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object of the present invention is to shorten the time required to reach a necessary level and the time required for stabilization at a low temperature.
[0024]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The image reading apparatus of the present invention includes a light source, an image sensor on which reflected light of an original illuminated by the light source is imaged, a detection unit that detects an output of the image sensor, and an output level of the detection unit. An image reading apparatus having a comparing means for comparing with a threshold value and a dimming means for dimming the light source so that an output of the detecting means becomes a target level, which is lower than the target level, and The first threshold value is set so that the output level of the detection means after the first time has elapsed from the start of lighting of the light source is above the normal temperature and below the low temperature, and the first threshold is set from the start of lighting of the light source. When the output level exceeds the first threshold value by the comparing means after a lapse of time, the light control means starts dimming of the light source, and the output level exceeds the first threshold value. When Le is below is characterized in that to start the dimming of the light source by the light control means after waiting until above a second threshold higher than the target level.
Another feature of the image reading apparatus according to the present invention is that the dimming means performs PWM control and maintains the PWM at 100% until the dimming starts.
According to another feature of the image reading apparatus of the present invention, after waiting until the second threshold value higher than the target level is exceeded, and further after the second time has elapsed, the light control means controls the light source. The dimming is started.
It is characterized by that.
[0025]
The control method of the image reading apparatus according to the present invention includes a light source, an image sensor on which reflected light of a document illuminated by the light source is imaged, a detection unit that detects an output of the image sensor, and an output of the detection unit. A method of controlling an image reading apparatus having a dimming unit for dimming the light source so that a level becomes a target level, and a lighting step for starting lighting of the light source,
A first time waiting step of waiting for the elapse of a first time after starting the lighting, and an output level of the detecting means lower than the target level and after the first time elapses from the start of lighting of the light source. In the first comparison, the first threshold value is set at a level lower than the upper temperature and lower, and the output level of the detection means is compared with the first threshold value after the first waiting time step. A second comparison step that waits until the output level of the detection means exceeds a second threshold value that is higher than the target level after the first comparison step, and a dimming operation that performs dimming by the dimming device. And when the output level exceeds the first threshold value in the first comparison step, the dimming step is started. In the first comparison step, the output level is set to the first level. When the value falls below the threshold, the second comparison step is performed. Characterized in that to start the dimming process later.
Another feature of the control method for an image reading apparatus according to the present invention is that it includes a second time waiting step for waiting for a second time, and the output level is set to the first level in the first comparison step. When the value falls below the threshold value, the dimming step is started after the second comparison step and after the second waiting time step.
[0026]
The storage medium of the present invention stores a program for causing a computer to execute each step of executing the control method for the image reading apparatus described above.
[0027]
[Action]
Since the present invention has the above technical means, when it is determined that the environmental temperature is low, the output level is raised to a level above the target level, so that the lamp enters the stabilization control. It is possible to shorten the time until the output is stabilized.
[0028]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
(First embodiment)
FIG. 1 is a flowchart for explaining an image reading apparatus, a control method for the image reading apparatus, and a processing procedure of a storage medium according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0029]
Since the first step S201 is taken from the time when the image reading apparatus is turned on as an example, the explanation starts from the lamp ON in the sense that the lighting of the
[0030]
Further, the actual control is usually based on PWM control in the output
In the next step S202, a wait time of 10 seconds is provided to wait for the light quantity of the
[0031]
In this embodiment, the threshold value Ps of the lamp output is set in advance to a level that exceeds the normal temperature and decreases below the low temperature after the first time T1 ′ (in this case, 10 seconds) in FIG. 3 has elapsed. In step S204, the bright peak output level Pn detected in step S203 after the elapse of time T1 ′ is compared with the threshold value Ps. Judgment is made.
[0032]
FIG. 2 shows a change in lamp tube wall temperature at the time of stabilization due to a change in lamp PWM. From FIG. 2, it can be seen that the lamp tube wall temperature at the time of stability and the PWM of the lamp have a substantially proportional relationship.
[0033]
From FIG. 8 described above, the higher the tube wall temperature of the lamp, the shorter the time for stabilization. Therefore, from FIGS. 2 and 8, in order to shorten the fourth time T4 ′, which is the lamp stabilization time, the lamp tube wall temperature is increased, that is, the lamp is stabilized in a high output state. It is important to plan.
[0034]
When the lamp output level is a low temperature state not reaching the threshold value Ps, a waiting time of a predetermined time is put in step S205 with the lamp PWM being 100%. The setting of this waiting time is the time required for stabilization rather than the increased amount of time, although the third time T3 ′ becomes longer by inserting this. By setting the fourth time T4 ′ to be shorter, as a result, the total time of the “third time T3 ′” and the “fourth time T4 ′” is set to be short.
[0035]
Then, after the light output level Pn reaches the target output level Pt, in order to wait for the
[0036]
FIG. 3 shows the time course of the output level of the lamp when this embodiment is used.
In the present embodiment, a fixed waiting time is set in the state of 100% PWM of the lamp so that the third time T3 ′ that is the dimming control time is longer than the conventional example. Then, when the light output level Pn reaches the threshold value Ps in step S204, the output level becomes higher than the target output level Pt as in the end of the third time T3 ′ in FIG.
[0037]
Then, in step S206, the level is suppressed by adjusting the PWM so that the target output level Pt ± 1% is obtained. At this time, the tube wall temperature of the lamp is already high. Since the temperature of the lamp tube wall is high in time, it becomes easy to stabilize, and the fourth time T4 ′, which is the stabilization time, can be made shorter than in the conventional example.
[0038]
The waiting time in step S205 is set so that the time for stabilization is shorter than the amount of time for the dimming control, that is, (T3′−T3) ≦ (T4−T4 ′). By setting, the total dimming control time can be shortened.
[0039]
The constant waiting time of step S205 to be entered in this embodiment varies depending on the characteristics of the lamp, etc. If the same lamp is used, the optimum lamp dimming control time can be set by simply changing the setting of this waiting time. It becomes possible to set.
[0040]
(Second Embodiment)
FIG. 4 shows a second embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 4, since the first step S301 is taken from the time when the image reading apparatus is turned on as an example, the explanation starts from the lamp ON in the sense that the lighting of the
[0041]
In the first step S301, since the normal lamp is ON, the lamp PWM is 100%. In the next step S302, a wait time of 10 seconds is provided to wait for the light amount of the
[0042]
In this embodiment, the threshold value Ps of the lamp output is set in advance to a level that exceeds the normal temperature after the first time T1 ″ (in this case, 10 seconds) in FIG. The bright output level Pn detected in step S303 after the elapse of time T1 ″ and the threshold value Ps are compared in step S304, and when the bright output level Pn ≦ Ps, it is determined that the scanner body is in a low temperature environment. .
[0043]
If it is determined in step S304 that the environment is a low temperature environment, the light output level Pn is detected in step S306, and whether the light output level Pn has reached Pvt set higher than the target output level Pt in step S307. Determine whether or not. If the result of this determination is that it has not reached, after waiting for step S308, the processing of step S306 and step S307 is performed again.
[0044]
When the light output level Pn reaches Pvt, after the waiting time of 5 seconds in step S309, the dimming control in step S305 is performed. If the light output level Pn has reached the threshold value Ps in step S304, it is determined that the environment is at room temperature or higher, and step S305 is performed.
[0045]
Next, in step S310, step S305 is repeated until the light output level Pn reaches the target output level Pt. When the output level Pn reaches the target output level Pt, the process proceeds to the stabilization control in step S311 and step S312. If the fluctuation of the output level is suppressed to 1 level in the meantime, it is determined that the output has been stabilized, and all the light control is finished.
[0046]
FIG. 5 shows the time course of the output level of the lamp when this embodiment is used.
If it is determined in step S304 that the temperature is low, the light output level Pn is raised to a target Pvt higher than the target output level Pt with the lamp PWM maintained at 100%. The lamp tube wall temperature can be brought to a higher state than in the conventional example by always raising the target output level to a level higher than the target output level Pt.
[0047]
When the target Pvt is reached, a specific waiting time (in this case, 5 seconds) is inserted to further increase the temperature of the lamp tube wall, and to some extent cause variations in the lamp output level before entering the dimming control in step S305. Can be kept within the range.
[0048]
In step S310, the level is suppressed by adjusting the PWM so that the target output level Pt ± 1%. However, since the lamp tube wall temperature is already high at this time, the subsequent stabilization control is performed. In time, as shown in FIG. 8, it becomes easy to stabilize, and the stabilization time T4 ″ can be made shorter than the conventional stabilization time T4.
[0049]
The third time T3 ″ in the present embodiment is longer than the above-described third time T3, but the stabilization time is shorter than the amount of increase in the third time T3 ″ in the present embodiment. Can be. That is, the total light control time can be shortened by setting the level Pvt in step S307 and the waiting time in step S309 so that (T3 ″ −T3) ≦ (T4−T4 ″). is there.
[0050]
FIG. 11 shows an example of a computer system constituting the image reading apparatus of the present invention.
FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating a configuration of a control device of a general image reading device. In FIG. 11,
[0051]
A
[0052]
A network interface card (NIC) 1208 is used when the image reading apparatus according to the embodiment is connected to a network via the
[0053]
The program stored in the
[0054]
(Other embodiments of the present invention)
The present invention may be applied to a system composed of a plurality of devices (for example, a host computer, an interface device, a reader, a printer, etc.) or an apparatus composed of a single device.
[0055]
In addition, for operating various devices so as to realize the functions of the above-described embodiments, for realizing the functions of the above-described embodiments for an apparatus or a computer in the system connected to the various devices. Implementations by supplying software program codes and operating the various devices in accordance with programs stored in a computer (CPU or MPU) of the system or apparatus are also included in the scope of the present invention.
[0056]
In this case, the program code itself of the software realizes the functions of the above-described embodiment, and the program code itself and means for supplying the program code to the computer, for example, the program code are stored. This storage medium constitutes the present invention. As a storage medium for storing the program code, for example, a floppy disk, a hard disk, an optical disk, a magneto-optical disk, a CD-ROM, a magnetic tape, a nonvolatile memory card, a ROM, or the like can be used.
[0057]
In addition, by executing the program code supplied by the computer, not only the functions described in the above embodiments are realized, but also the OS (Operating System) or other application in which the program code is running on the computer. It goes without saying that the program code is also included in the embodiment of the present invention even when the functions described in the above-described embodiment are realized in cooperation with software or the like.
[0058]
Further, after the supplied program code is stored in the memory provided in the function expansion board of the computer or the function expansion unit connected to the computer, the CPU provided in the function expansion board or function expansion unit based on the instruction of the program code The present invention also includes a case where the functions of the above-described embodiment are realized by performing part or all of the actual processing.
[0059]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, the use environment can be determined with a simple configuration. In addition, regardless of the use environment, the time until the output is stabilized can be shortened, and the total scan time can be shortened.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a flowchart for explaining a first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a state of a change in lamp tube wall temperature at the time of stabilization due to a change in PWM of the lamp according to the embodiment.
FIG. 3 is a characteristic diagram showing a lapse of time of the output level of the lamp when the embodiment is used.
FIG. 4 is a flowchart for explaining a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a characteristic diagram showing a lapse of time of the output level of the lamp in the second embodiment.
FIG. 6 is a top view illustrating a schematic configuration of the image reading apparatus.
FIG. 7 is a block diagram illustrating an example of a circuit that performs output level adjustment.
FIG. 8 is a characteristic diagram showing an example of a change over time after lighting.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart for explaining a procedure of dimming control.
FIG. 10 is an operation output characteristic diagram illustrating a change in the output level of the lamp at a low temperature (10 ° C.) and at a normal temperature (25 ° C.).
FIG. 11 is a block diagram illustrating an example of a computer system that constitutes a control device of the image reading apparatus according to the present exemplary embodiment.
[Explanation of symbols]
3
101
Claims (6)
上記光源により照明された原稿の反射光が結像されるイメージセンサと、
上記イメージセンサの出力を検出する検知手段と、
上記検知手段の出力レベルを所定のしきい値と比較する比較手段と、
上記検知手段の出力が目標レベルになるように上記光源を調光する調光手段とを有する画像読み取り装置であって、
上記目標レベルよりも低く、上記光源の点灯開始から第1の時間経過後の上記検知手段の出力レベルが常温では上回り低温では下回るレベルに、第1のしきい値が設定されていて、上記光源の点灯開始から上記第1の時間経過後に上記比較手段で、上記第1のしきい値よりも上記出力レベルが上回る時には、上記調光手段により上記光源の調光を開始し、上記第1のしきい値よりも上記出力レベルが下回る時には、上記目標レベルよりも高い第2のしきい値を上回るまで待った後に上記調光手段により上記光源の調光を開始することを特徴とする画像読み取り装置。A light source;
An image sensor on which reflected light of an original illuminated by the light source is imaged;
Detection means for detecting the output of the image sensor;
Comparing means for comparing the output level of the detecting means with a predetermined threshold;
An image reading device having dimming means for dimming the light source so that the output of the detecting means reaches a target level,
The first threshold value is set to a level lower than the target level, and the output level of the detection means after the first time has elapsed from the start of lighting of the light source is higher than normal and lower than low. after the lamp starts lighting by the comparing means after the lapse of the first time, the when the output level is above than the first threshold value, by the light control means starts the dimming of the light source, the first When the output level is lower than a threshold value, the image reading apparatus is configured to start dimming of the light source by the dimming unit after waiting until the second threshold value higher than the target level is exceeded. .
上記光源の点灯を開始する点灯工程と、
上記点灯を開始した後に第1の時間の経過を待つ第1時間待工程と、
上記目標レベルよりも低く、上記光源の点灯開始から上記第1の時間経過後の上記検知手段の出力レベルが常温では上回り低温では下回るレベルに、第1のしきい値が設定されていて、上記第1時間待工程の後に、上記検知手段の出力レベルと上記第1のしきい値とを比較する第1比較工程と、
上記第1比較工程の後、上記検知手段の出力レベルが上記目標レベルよりも高い第2のしきい値を上回るまで待つ第2比較工程と、
上記調光手段で調光を行なう調光工程とを有し、
上記第1比較工程で前記出力レベルが上記第1のしきい値を上回るときには上記調光工程を開始し、上記第1比較工程で前記出力レベルが上記第1のしきい値を下回るときには上記第2比較工程を経た後に上記調光工程を開始することを特徴とする画像読み取り装置の制御方法。A light source, an image sensor light reflected document illuminated by the light source is imaged, detection means for detecting an output of the image sensor, the light source so that the output level of the detecting means becomes a target level A method for controlling an image reading apparatus having a light control means for adjusting light,
A lighting process for starting lighting of the light source;
A first time waiting step of waiting for the passage of a first time after starting the lighting;
The first threshold value is set to a level lower than the target level, and the output level of the detection means after the first time has elapsed from the start of lighting of the light source is higher than normal and lower than low. after the first hour waiting step, a first comparison step for comparing the output level and the first threshold value of the detection means,
A second comparison step of waiting after the first comparison step until the output level of the detection means exceeds a second threshold value higher than the target level;
A dimming step of performing dimming with the dimming means,
The output level in the first comparison step starts the dimming step when exceeding the first threshold value, when said said output level in the first comparing step is lower than said first threshold said first A control method for an image reading apparatus, wherein the dimming step is started after two comparison steps.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000066995A JP4392947B2 (en) | 2000-03-10 | 2000-03-10 | Image reading apparatus, control method of image reading apparatus, and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000066995A JP4392947B2 (en) | 2000-03-10 | 2000-03-10 | Image reading apparatus, control method of image reading apparatus, and storage medium |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001257843A JP2001257843A (en) | 2001-09-21 |
| JP2001257843A5 JP2001257843A5 (en) | 2007-04-26 |
| JP4392947B2 true JP4392947B2 (en) | 2010-01-06 |
Family
ID=18586261
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000066995A Expired - Fee Related JP4392947B2 (en) | 2000-03-10 | 2000-03-10 | Image reading apparatus, control method of image reading apparatus, and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4392947B2 (en) |
-
2000
- 2000-03-10 JP JP2000066995A patent/JP4392947B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001257843A (en) | 2001-09-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4777178B2 (en) | Image processing method | |
| JP3340451B2 (en) | Compensation method for illumination fluctuation of lamp of scanning device | |
| JP4392947B2 (en) | Image reading apparatus, control method of image reading apparatus, and storage medium | |
| US7209265B2 (en) | Method, apparatus and computer program product for initializing image processing apparatus | |
| JPH04309064A (en) | Picture reader | |
| US20080231916A1 (en) | Image reading device and image forming apparatus | |
| US6989917B2 (en) | Image reading apparatus and its control method | |
| JP2005045309A (en) | Control method of image scanner | |
| JP4001218B2 (en) | Image reading apparatus, image processing apparatus, and image signal processing characteristic adjusting method | |
| JP2008263292A (en) | Image reader | |
| JP2001257848A (en) | Image scanning apparatus and method and storage medium | |
| JP3625419B2 (en) | Image reading device | |
| US7342687B2 (en) | Image reading apparatus and light source stability determination method | |
| JP4246409B2 (en) | Image reading device | |
| JP2002101278A (en) | Original reader | |
| JP2002084400A (en) | Scanner device and method for removing clouding | |
| JP2005045310A (en) | Control method of image scanner | |
| JPH1028199A (en) | Picture read device | |
| JP2000165624A (en) | Picture reader, shading correcting method and storage medium | |
| US7312905B2 (en) | Method for scanner lamp warm-up optimization | |
| JP2006211526A (en) | Image reading device | |
| JP2007267031A (en) | Image forming apparatus | |
| JP2008271130A (en) | Image reader | |
| JP2008067324A (en) | Image reader and image forming apparatus | |
| JP2009272860A (en) | Image reading device, and control method of image reading device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070309 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070309 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090424 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090512 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090710 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20091006 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20091013 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121023 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131023 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |