JP4270105B2 - Solid-state image sensor - Google Patents
Solid-state image sensor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4270105B2 JP4270105B2 JP2004317088A JP2004317088A JP4270105B2 JP 4270105 B2 JP4270105 B2 JP 4270105B2 JP 2004317088 A JP2004317088 A JP 2004317088A JP 2004317088 A JP2004317088 A JP 2004317088A JP 4270105 B2 JP4270105 B2 JP 4270105B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- region
- imaging device
- state imaging
- solid
- semiconductor substrate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 56
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 55
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims description 54
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 54
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 13
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 7
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000002161 passivation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052681 coesite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052906 cristobalite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009416 shuttering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052682 stishovite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052905 tridymite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Transforming Light Signals Into Electric Signals (AREA)
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
Description
本発明は、固体撮像素子に関する。 The present invention relates to a solid-state imaging device .
固体撮像素子としては、X−Yアドレスを指定して読み出すCMOS固体撮像素子と、電荷転送型であるCCD固体撮像素子が代表的である。これらいずれの固体撮像素子も2次元に配置された光電変換素子となるフォトダイオードに入射した光を光電変換し、そのうちの一方の電荷(例えば電子)を信号電荷としている。 Typical examples of the solid-state imaging device include a CMOS solid-state imaging device that reads by specifying an XY address, and a CCD solid-state imaging device that is a charge transfer type. Any of these solid-state imaging devices photoelectrically converts light incident on a photodiode that is a two-dimensionally arranged photoelectric conversion device, and one of the charges (for example, electrons) is used as a signal charge.
CCD固体撮像素子としては、受光部でオーバーフローした電荷を基板側に掃き捨てるようにした縦型オーバーフロー構造のインターライン転送方式のCCD固体撮像素子が代表的である。このCCD固体撮像素子は、画素となる受光部と、垂直転送レジスタと、水平転送レジスタと、水平転送レジスタに接続された出力部とを有し、例えばn型半導体基板にオーバーフローコントロールゲート領域となるp型半導体ウェル領域が形成され、このp型半導体ウェル領域に受光部となるフォトダイオードが形成され、受光部でオーバーフローした電荷がp型半導体ウェル領域からなるオーバーフローコントロールゲート領域を通じてn型半導体基板に掃き捨てるように構成される(非特許文献1のp36,103参照)。 A typical CCD solid-state image sensor is an interline transfer type CCD solid-state image sensor having a vertical overflow structure in which charges overflowed in the light receiving section are swept away to the substrate side. This CCD solid-state imaging device has a light receiving portion that becomes a pixel, a vertical transfer register, a horizontal transfer register, and an output portion connected to the horizontal transfer register, and serves as an overflow control gate region in an n-type semiconductor substrate, for example. A p-type semiconductor well region is formed, a photodiode serving as a light receiving portion is formed in the p-type semiconductor well region, and the charge overflowed in the light receiving portion is transferred to the n-type semiconductor substrate through the overflow control gate region formed of the p-type semiconductor well region. It is configured to sweep away (see p36, 103 of Non-Patent Document 1).
CMOS固体撮像素子としては、図10A,Bに示すように、例えば、n型半導体基板111にp型半導体ウェル領域112を形成し、画素分離領域113で区画された各領域のp型半導体ウェル領域112にフォトダイオードPDと複数のMOSトランジスタTrからなる単位画素114を形成し、基板表面側に多層配線層115を介してカラーフィルタ116及びオンチップレンズ117を形成した表面照射型に構成される。フォトダイオードPDは、n型半導体領域121と表面のアキュミュレーション層となるp+半導体領域122とを有して形成される。画素を構成するMOSトランジスタTrとしては、例えば4つのMOSトランジスタで構成する場合には、読み出しトランジスタTr1,リセットトランジスタTr2,垂直選択トランジスタ(図示しない)、増幅トランジスタ(図示しない)を有している。読み出しトランジスタTr1は、フローティングディフュージョン(FD)となるn型ソース・ドレイン領域124とフォトダイオードPDとその間にゲート絶縁膜を介して形成したゲート電極125とにより形成される。リセットトランジスタTr2は、一対のn型ソース・ドレイン領域124及び126とその間にゲート絶縁膜を介して形成したゲート電極127とにより形成される。多層配線層115は、層間絶縁膜128を介して形成した多層配線129により形成される。この多層配線層115上にパシベーション膜130を介してカラーフィルタ116、オンチップレンズ117が形成される(特許文献1の図9参照)。このCMOS固体撮像素子110は、図10Aに示すように、1つの半導体チップ141の表面側に複数の画素114がマトリックス状に配列された撮像領域、すなわちフォトダイオードPDとMOSトランジスタによるセンサ回路とを有するいわゆるフォトダイオードPD・センサ回路領域142が形成されて成る。このCMOS固体撮像素子110は、光を基板表面側から入射する表面照射型に構成される。
The CMOS solid-state imaging device, as shown in FIG. 10 A, B, for example, a p-type
一方、CMOS固体撮像素子では、光を基板の裏面側から入射させるようにした、いわゆる裏面照射型のCMOS固体撮像素子も提案されている(特許文献1参照)。 On the other hand, as a CMOS solid-state image sensor, a so-called back-illuminated CMOS solid-state image sensor in which light is incident from the back side of the substrate has also been proposed (see Patent Document 1).
ところで、CMOS固体撮像素子は、その構造からフォーカルプレーンシャッタとなり、完全同時シャッタの実現は困難とされていた。すなわち、シャッタを切っても順次画素から読み出す順番でシャッタが切れる(非特許文献1のp179参照)。CCD固体撮像素子の場合は、半導体基板側に電荷(電子)を掃き捨ててリセットすること、各受光部の電荷を同時に垂直転送レジスタに転送し、垂直転送レジスタを通じて電荷を保持する構成であるため、同時電子シャッタ化が可能である(非特許文献1のp139,179参照)。しかし、CMOS固体撮像素子の場合は、リセットトランジスタでフローティングディフュージョン(FD)の電荷をリッセトし、次いで画素のフォトダイオードの電荷を読み出しトランジスタのフローティングディフュージョン(PD)に読み出し、この動作を各画素の配列順に行うようにしている。CMOS固体撮像素子では、フローティングディフュージョン(FD)へ例えば1/30秒間映像電荷を保持させた場合、光電変換を行うフォトダイオードPDと比較して多大なノイズ(漏れ電流など)が発生する。結果として、CMOS固体撮像素子においては、微細画素でかつ高画質状態で完全同時シャッタを実現させる方法は現在のところ存在していない。 By the way, the CMOS solid-state imaging device has a focal plane shutter due to its structure, and it has been difficult to realize a complete simultaneous shutter. That is, even if the shutter is released, the shutter is released in the order of reading from the pixels in sequence (see p179 of Non-Patent Document 1). In the case of a CCD solid-state imaging device, the charge (electrons) is swept away and reset on the semiconductor substrate side, and the charge of each light receiving unit is transferred to the vertical transfer register at the same time, and the charge is held through the vertical transfer register. Simultaneous electronic shuttering is possible (see p139, 179 of Non-Patent Document 1). However, in the case of a CMOS solid-state imaging device, the charge of the floating diffusion (FD) is reset by the reset transistor, the charge of the photodiode of the pixel is then read out to the floating diffusion (PD) of the transistor, and this operation is performed for each pixel array. I do it in order. In a CMOS solid-state imaging device, when a video charge is held in a floating diffusion (FD) for 1/30 seconds, for example, much noise (leakage current or the like) is generated compared to a photodiode PD that performs photoelectric conversion. As a result, in a CMOS solid-state imaging device, there is currently no method for realizing a complete simultaneous shutter with fine pixels and high image quality.
一方、CMOS固体撮像素子において、完全同時シャッタを実現する方法として、図8及び図9の比較例に示す構成が考えられる。このCMOS固体撮像素子151は、各微細画素に応じてそれぞれアナログ/デジタル変換手段及びメモリ手段を搭載し、光電変換後に直ちに全画素一斉にアナログ/デジタル変換させ、メモリ手段にデータとして保持し、その後メモリ手段から各画素の信号順次読み出す方式である。すなわち、この方式のCMOS固体撮像素子151は、図8に示すように、1つの半導体チップ152の表面側の一部、すなわち撮像領域にフォトダイオードPDと複数のMOSトランジスタ(センサトランジスタ)からなる画素を複数配列した、いわゆるフォトダイオードPD・センサ回路領域154を形成し、上記表面側の他部に各画素に対応したアナログ/デジタル変換手段(ADC)及びメモリ手段を形成した、いわゆるADC・メモリ領域155を形成して構成される。
On the other hand, in the CMOS solid-state imaging device, a configuration shown in the comparative example of FIGS. 8 and 9 is conceivable as a method for realizing a complete simultaneous shutter. This CMOS solid-
図9は、上記比較例のCMOS固体撮像素子151の概略断面構造を示す。フォトダイオードPD・センサ回路領域154には、前述の図10Bと同様の表面照射型の複数の画素114が配列され、ADC・メモリ領域155には一対のn+ソース・ドレイン領域131とその間にゲート絶縁膜を介して形成したゲート電極132からなるMOSトランジスタTr11等を有して形成されたアナログ/デジタル変換手段、メモリ手段が形成されてなる。なお、同図において図10Bと対応する部分には同一符号を付して重複説明を省略する。
FIG. 9 shows a schematic cross-sectional structure of the CMOS solid-
図8及び図9の構成においては、全画素同時シャッタを実現できるが、チップ面積が増大し、コスト高となる欠点を有する。 8 and 9, the all-pixel simultaneous shutter can be realized. However, there is a disadvantage that the chip area is increased and the cost is increased.
本発明は、上述の点に鑑み、裏面照射型の固体撮像素子を利用して、チップ面積の増大を抑制しつつ、完全同時電子シャッタの実現を可能にした固体撮像素子を提供するものである。 In view of the above points, by using a back-illuminated solid-state imaging device, while suppressing an increase in chip area, there is provided a solid-state imaging device that enables realization of full simultaneous electronic shutter .
本発明に係る固体撮像素子は、半導体基板に、この半導体基板の裏面側に臨む光電変換素子とこの半導体基板の表面側に形成したセンサトランジスタとからなる画素を複数備え、各画素毎に接続されたアナログ/デジタル変換手段及びメモリ手段が半導体基板の表面側に形成され、半導体基板の表面上に、層間絶縁膜を介して多層配線を形成した多層配線層が形成され、全画素の光電変換素子の信号を同時にアナログ/デジタル変換手段にてアナログ/デジタル変換した後、メモリ手段にデータとして保持するようにして成ることを特徴とする。 Solid-state imaging device according to the present invention, the semiconductor substrate, a plurality of pixels composed of a photoelectric conversion element which faces the back surface side of the semiconductor substrate and the sensor transistor formed on the surface side of the semiconductor substrate, is connected to each pixel The analog / digital conversion means and the memory means are formed on the surface side of the semiconductor substrate, and a multilayer wiring layer is formed on the surface of the semiconductor substrate with an interlayer insulating film interposed therebetween. These signals are simultaneously subjected to analog / digital conversion by the analog / digital conversion means, and then stored as data in the memory means.
本発明に係る固体撮像素子の好ましい形態としては、半導体基板の裏面側に臨んで光電変換素子領域が形成され、半導体基板の表面側にセンサトランジスタ領域と、各画素毎に接続されたアナログ/デジタル変換回路領域と、メモリ素子もしくは容量素子からなるメモリ回路領域が形成され、入射光を半導体基板の裏面側から光電変換素子に入射するようにした構成とする。 As a preferred form of the solid-state imaging device according to the present invention, a photoelectric conversion element region is formed facing the back side of the semiconductor substrate, a sensor transistor region is formed on the front side of the semiconductor substrate, and analog / digital connected for each pixel. A conversion circuit region and a memory circuit region including a memory element or a capacitor element are formed, and incident light is incident on the photoelectric conversion element from the back surface side of the semiconductor substrate.
本発明に係る固体撮像素子の好ましい形態としては、光電変換素子領域がセンサトランジスタ領域下まで延長して形成された構成とする。
本発明に係る固体撮像素子の好ましい形態としては、光電変換素子領域がセンサトランジスタ領域とアナログ/デジタル変換回路領域とメモリ回路の下まで延長して形成された構成とする。
さらに本発明に係る固体撮像素子の好ましい形態は、半導体基板の裏面に電極パッドが形成された構成とする。
As a preferred embodiment of the solid-state imaging device according to the present invention, the photoelectric conversion element region is formed so as to extend below the sensor transistor region.
As a preferred embodiment of the solid-state imaging device according to the present invention, the photoelectric conversion element region is formed to extend to the sensor transistor region, the analog / digital conversion circuit region, and the memory circuit.
Furthermore, the preferable form of the solid-state imaging device according to the present invention is configured such that an electrode pad is formed on the back surface of the semiconductor substrate.
本発明に係る固体撮像素子によれば、各画素にそれぞれアナログ/デジタル変換手段及びメモリ手段を接続し、全画素の信号をアナログ/デジタル変換手段にて同時にアナログ/デジタル変換した後、一旦メモリ手段6に保持するように構成されるので、全画素の完全同時電子チャッタが可能になる。また、裏面照射型の固体撮像素子を利用するので、基板裏面側に臨むように光電変換素子を形成し、基板表面側に光電変換素子の電荷を読み出すセンサトランジスタ、アナログ/デジタル変換手段及びメモリ手段を形成することができ、半導体チップ面積の増大を抑制して完全同時電子シャッタを行うことができる。微細画素でかつ高画質状態で完全同時電子シャッタを実現できる。また、表面照射型に比べて光電変換素子の開口率が上がり感度の向上が図れる。 According to the solid-state imaging device according to the present invention, the analog / digital conversion means and the memory means are connected to each pixel, and the analog / digital conversion is performed simultaneously on the signals of all the pixels by the analog / digital conversion means. 6, it is possible to perform complete simultaneous electronic chatter of all pixels. In addition, since a back-illuminated solid-state image sensor is used, a photoelectric conversion element is formed so as to face the back side of the substrate, and a sensor transistor, an analog / digital conversion unit, and a memory unit that read the charge of the photoelectric conversion device on the front side of the substrate Thus, a complete simultaneous electronic shutter can be performed while suppressing an increase in the area of the semiconductor chip. A completely simultaneous electronic shutter can be realized with fine pixels and high image quality. Further, the aperture ratio of the photoelectric conversion element is increased and sensitivity can be improved as compared with the surface irradiation type.
光電変換素子をセンサトランジスタの領域下まで延長して形成することにより、光電変換素子の開口率が上がり感度の向上を図ることができる。
光電変換素子をセンサトランジスタの領域とアナログ/デジタル変換回路領域とメモリ回路領域の下まで延長して形成することにより、さらに光電変換素子の開口率が向上し、ハンドの大幅な向上を図ることがでる。
By forming the photoelectric conversion element to extend below the region of the sensor transistor, the aperture ratio of the photoelectric conversion element can be increased and the sensitivity can be improved.
By forming the photoelectric conversion element extending below the sensor transistor area, the analog / digital conversion circuit area, and the memory circuit area, the aperture ratio of the photoelectric conversion element can be further improved, and the hand can be greatly improved. Out.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施の形態を詳述する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
図1及び図2に、本発明に係る固体撮像素子の実施の形態の一例を示す。本実施の形態に係る固体撮像素子1は、裏面照射型のCMOS固体撮像素子を用いて構成するものであり、図1に示すように、光電変換素子となるフォトダイオードPDと複数のMOSトランジスタ2〔21、22、23、24〕からなる単位画素3がマトリクス状に2次元配列され、各画素3の出力線4にそれぞれアナログ/デジタル変換手段、すなわちアナログ/デジタル変換回路5が接続され、さらに各画素に対応するように各アナログ/デジタル変換回路5にそれぞれメモリ手段6が接続されて成る。
1 and 2 show an example of an embodiment of a solid-state imaging device according to the present invention. The solid-state imaging device 1 according to the present embodiment is configured using a back-illuminated CMOS solid-state imaging device. As shown in FIG. 1, a photodiode PD and a plurality of MOS transistors 2 serving as photoelectric conversion devices.
本例の画素3は、1つのフォトダイオードPDと、電荷読み出しトランジスタ21とリセットトランジスタ22と増幅トランジスタ23と負荷トランジスタの4つのMOSトランジスタで構成される。すなわち、フォトダイオードPDが電荷読み出しトランジスタ21のソースに接続され、そのゲートが読出しパルスを供給する読出し配線7に接続される。電荷読み出しトランジスタのドレインはリセットトランジスタ22のソースに接続されると共に、電荷読み出しトランジスタ21のドレインとリセットトランジスタ22のソース間のいわゆるフローティングディフュージョン(FD)が増幅トランジスタ23のゲートに接続される。リセットトランジスタ22のドレインは電源電圧Vddが供給される電源配線8に接続され、リセットトランジスタ22のゲートにはリセットパルスφRが供給されるリセット配線9が接続される。増幅トランジスタ23のドレインは電源配線8に接続される。増幅トランジスタ23のソースには負荷トランジスタ24が接続される。負荷トランジスタ24のソースはグランド(GND)に接続され、そのゲートは負荷配線10に接続される。そして、増幅トランジスタ23と負荷トランジスタ24との接続中点が出力線4に接続される。
The
なお、上例では画素のMOSトランジスタを、電荷読出しトランジスタとリセットトランジスタと増幅トランジスタと負荷トランジスタの4つのトランジスタで構成したが、その他の複数トランジスタで構成することも可能である。画素を構成するMOSトランジスタの数は目的に応じて適宜選択することができる。 In the above example, the MOS transistor of the pixel is composed of four transistors, that is, a charge readout transistor, a reset transistor, an amplifying transistor, and a load transistor, but may be composed of other plural transistors. The number of MOS transistors constituting the pixel can be appropriately selected according to the purpose.
メモリ手段6としては、例えばDRAM,SRAM,フラシュメモリ等のデジタルメモリ、あるいは容量素子で形成されるアナログメモリで構成することができる。 The memory means 6 can be constituted by, for example, a digital memory such as a DRAM, SRAM, flash memory, or an analog memory formed by a capacitive element.
この裏面照射型のCMOS固体撮像素子1では、各画素3のフォトダイオードPDで光電変換され蓄積された信号電荷がそれぞれの電荷読出しトランジスタ21を通じてフローティングディフュージョン(FD)に読み出され、信号電荷に応じた信号出力がそれぞれ出力線4を通じて、全画素一斉に対応するアナログ/デジタル変換回路5に供給され、アナログ/デジタル変換された信号がメモリ手段6に一旦データとして保持される。この動作は、全画素同一期間で実行される。その後、各メモリ手段6から保持された画像データを順次読み出すようになされる。
In this back-illuminated type CMOS solid-state imaging device 1, the signal charge photoelectrically converted and accumulated by the photodiode PD of each
このCMOS固体撮像素子1において、フォトダイオードPDが受光する受光期間は全画素同じである。電子シャッタ動作させるときは、各画素同時にリセットトランジスタ22を通じて受光開始から所要時間までの光電変換された電荷を掃き捨て、残りの受光期間に光電変換して得た信号電荷のみを読み出すようになす。
In this CMOS solid-state imaging device 1, the light receiving period in which the photodiode PD receives light is the same for all pixels. When the electronic shutter is operated, the photoelectrically converted charges from the start of light reception to the required time are simultaneously swept away from each pixel through the
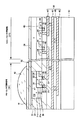
図2は、本実施の形態のCMOS固体撮像素子1の概略断面構造の一例を示す。この断面構造は、薄膜化された半導体基板、例えばn型のシリコン基板31の撮像領域26に画素分離領域32が形成され、画素分離領域32にて区画された各画素領域のp型半導体ウェル領域33にn型ソース・ドレイン領域34、ゲート絶縁膜35及びゲート電極36からなる前述の複数のMOSトランジスタ2〔21〜24〕が形成される。この複数のMOSトランジスタ2〔21〜24〕からなる所謂センサトランジスタは基板表面側に形成される。また、基板裏面側から表面に至るように且つセンサトランジスタ2〔21〜24〕が形成されたp型半導体ウェル領域33の下まで延長するように、フォトダイオードPDが形成される。フォトダイオードPDはn+電荷蓄積領域31a及びn半導体領域31bと、基板の表裏両面に形成した暗電流を抑制するためのアキュミュレーション層となるp+半導体領域38とにより形成される。そして、基板裏面側にパシベーション膜39を介してカラーフィルタ41が形成され、さらにカラーフィルタ41上に各画素に対応したオンチップレンズ42が形成される。この撮像領域26は、いわゆるフォトダイオードPD・センサ回路領域となる。
FIG. 2 shows an example of a schematic cross-sectional structure of the CMOS solid-state imaging device 1 of the present embodiment. This cross-sectional structure is such that a
このn型半導体基板31のフォトダイオードPD・センサ回路領域26に隣接する領域27の基板表面側にp型半導体ウェル領域43が形成され、このp型半導体ウェル領域43に各画素に対応したアナログ/デジタル変換回路5、メモリ手段6が形成される。すなわち、p型半導体ウェル領域43に、n+ソース・ドレイン領域44、ゲート絶縁膜45及びゲート電極46からなるMOSトランジスタ27等を有して形成したアナログ/デジタル変換回路5と、デジタルメモリあるいはアナログメモリなどによるメモリ手段6とが形成される。この領域27は、いわゆるADC・メモリ領域となる。
A p-type
そして、基板表面側には、それぞれの領域26、27に対応して層間絶縁膜48を介して多層配線49を形成した多層配線層50が形成される。さらに多層配線層50上に例えばシリコン基板等による補強用の支持基板51が接合される。
On the substrate surface side, a
上述の本実施の形態のCMOS固体撮像素子1によれば、各画素3にそれぞれアナログ/デジタル変換回路5及びメモリ手段6を接続し、全画素の信号を同時に読出してアナログ/デジタル変換後に一旦メモリ手段6に保持する構成であるので、全画素の完全同時電子チャッタが可能になる。また、裏面照射型のCMOS固体撮像素子を利用するので、基板裏面側に臨むようにフォトダイオードPDを形成し、基板表面側にフォトダイオードPDの電荷を読み出すセンサトランジスタ2〔21〜24〕、アナログ/デジタル変換回路5及びメモリ手段6を形成することができ、半導体チップ面積の増大を抑制して完全同時電子シャッタを行うことができる。微細画素でかつ高画質状態で完全同時電子シャッタを実現できる。また、表面照射型に比べてフォトダイオードPDの開口率が上がり感度の向上が図れる。
According to the above-described CMOS solid-state imaging device 1 of the present embodiment, the analog / digital conversion circuit 5 and the memory means 6 are connected to each
図3及び図4は、それぞれ本発明のCMOS固体撮像素子を1つの半導体チップに構成した実施の形態の例を示す。図3の実施の形態では、1つの半導体チップ61の基板裏面側の一部(撮像領域に対応する)に複数画素のフォトダイオードを配列した、いわゆるフォトダイオードPD領域62が形成され、基板表面側のフォトダイオードPD領域62に対応する領域に複数画素を構成するMOSトランジスタによるセンサトランジスタを形成した、いわゆるセンサ回路領域63が形成され、このセンサ回路領域63に隣接して各画素に接続した複数のアナログ/デジタル変換回路5及びメモリ手段6を配置したADC・メモリ領域64が形成される。
この実施の形態によれば、裏面照射型で、かつフォトダイオードPDがセンサトランジスタに対応する領域まで形成されているので、光電変換素子であるフォトダイオードPDの開口率が上がり感度の向上が図れる。
3 and 4 each show an example of an embodiment in which the CMOS solid-state imaging device of the present invention is configured on one semiconductor chip. In the embodiment of FIG. 3, a so-called
According to this embodiment, since the backside illumination type and the photodiode PD are formed up to the region corresponding to the sensor transistor, the aperture ratio of the photodiode PD which is a photoelectric conversion element is increased, and the sensitivity can be improved.
図4の実施の形態では、1つの半導体チップ61の基板表面側に図3と同様にセンサ回路領域63とADC・メモリ領域64が形成され、基板裏面側にセンサ回路領域63及びADC・メモリ領域64に対応する全領域にわたってフォトダイオードPD領域62を形成して成る。この場合、表面側のセンサ回路及びADC・メモリ回路に配線を張り巡らせて、裏面側の拡張したフォトダイオードPDとコンタクトする。表面側のレイアウトとしては、図4に示すように、チップの中心にセンサ回路領域63を配置し、周辺にADC・メモリ領域64を配置することが好ましい。なお、センサ回路領域63とADC・メモリ領域64とをチップを例えば図3のように上下二分するように配置することも考えられる。
この実施の形態では、裏面照射型でフォトレジストPD領域62がセンサ回路領域63とADC・メモリ領域に対応する領域にわたって形成されるので、フォトダイオードPDの開口率がさらに改善され、感度も大幅に向上することができる。
In the embodiment of FIG. 4, a
In this embodiment, the back-illuminated
次に、図5〜図7を用いて図2に示すCMOS固体撮像素子1の製造方法の一例を説明する。
先ず、図5Aに示すように、シリコン基板66上にシリコン酸化膜(SiO2 膜)67を介して薄膜のn型シリコン層(図2の半導体基板に相当する)31が形成されたSOI(Silicon On Insulator)基板68を用意する。このSOI基板68のシリコン層31の所要位置にアライメントマーク69を形成する。
Next, an example of a method for manufacturing the CMOS solid-state imaging device 1 shown in FIG. 2 will be described with reference to FIGS.
First, as shown in FIG. 5A, an SOI (Silicon On) in which a thin n-type silicon layer (corresponding to the semiconductor substrate of FIG. 2) 31 is formed on a
次に、図5Bに示すように、n型シリコン層31のフォトダイオードPD・センサ回路領域(撮像領域に相当)26に表面側よりアライメントマーク69を基準にして、撮像領域の画素分離領域32を形成する。n型シリコン層31のフォトダイオードPD・センサ回路領域26及びADC・メモリ領域27に、p型半導体ウェル領域33及び43を形成する。次いで、p型半導体ウェル領域33に画素を構成する複数のMOSトランジスタ2〔21〜24〕を形成し、p型半導体ウェル領域43にMOSトランジスタ等を含むアナログ/デジタル変換回路、及びメモリ手段を形成する。これらMOSトランジスタ2〔21〜24〕、アナログ/デジタル変換回路を構成するMOSトランジスタについては、図2と同様であるので、同一符号を付して重複説明を省略する。さらに、n型シリコン層31の表面上に層間絶縁膜48を介して多層配線49を積層した多層配線層50を形成する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 5B, the
次に、図6Cに示すように、多層配線層50上に例えばシリコン基板などによる支持基板51を貼り合わせる等して接合する。
次に、図6Dに示すように、SOI基板68を反転して、シリコン酸化膜67をストッパ膜としてシリコン基板66をバックグラインド(機械的な粗削り)及びウェットエッチングにより研磨除去する。さらにシリコン酸化膜67をウェットエッチングで除去する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 6C, a
Next, as shown in FIG. 6D, the
次に、図7Eに示すように、シリコン層31の裏面にパシベーション膜となる例えばシリコン窒化膜71を形成し、シリコン窒化膜71と共にシリコン層31の一部、すなわち配線層49aから電極を導出すべき部分に選択エッチングにより、配線層49aに達する開口72を形成する。さらに開口72の内側壁からシリコン窒化膜71の表面を覆うように、例えばシリコン酸化膜等の絶縁膜73を形成する。この開口72内に配線層49aと接続する導電体層75を形成すると共に、導電体層75に接続して裏面に臨む電極パッド76を形成して、いわゆる裏面電極77を形成する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 7E, for example, a
次に、図7Fに示すように、基板裏面上の各画素のフォトレジストPDに対応した位置にカラーフィルタ41及びオンチップレンズ42を形成して、目的のCMOS固体撮像素子1を得る。
Next, as shown in FIG. 7F, the
1・・裏面照射型のCMOS固体撮像素子、PD・・フォトダイオード、2〔21、22、23、24〕・・MOSトランジスタ、21・・電荷読出しトランジスタ、22・・リセットトランジスタ、23・・増幅トランジスタ、24・・負荷トランジスタ、3・・単位画素、4・・出力線、5・・アナログ/デジタル変換回路、6・・メモリ手段、26・・フォトダイオードPD・センサ領域、27・・ADC・メモリ領域、28・・MOSトランジスタ、31・・n型半導体基板、32・・画素分離領域、33、43・・p型半導体ウェル領域、34・・n+ソース・ドレイン領域、35・・ゲート絶縁膜、36・・ゲート電極、44・・n+ソース・ドレイン領域、45・・ゲート絶縁膜、46・・ゲート電極、48・・層間絶縁膜、49・・多層配線、50・・多層配線層、51・・支持基板、61・・半導体チップ、62・・フォトダイオードPD領域、63・・センサ回路領域、64・・ADC・メモリ領域
1..Back-illuminated CMOS solid-state imaging device, PD..Photodiode, 2 [21, 22, 23, 24] .. MOS transistor, 21..Charge read transistor, 22..Reset transistor, 23..Amplification Transistor, 24 ... Load transistor, 3 ... Unit pixel, 4 ... Output line, 5 ... Analog / digital conversion circuit, 6 ... Memory means, 26 ... Photodiode PD, Sensor area, 27 ... ADC Memory region, 28 ... MOS transistor, 31 ... n-type semiconductor substrate, 32 ... Pixel isolation region, 33, 43 ... p-type semiconductor well region, 34 ... n + source / drain region, 35 ...
Claims (5)
各画素毎に接続されたアナログ/デジタル変換手段及びメモリ手段が、前記半導体基板の表面側に形成され、
前記半導体基板の表面上に、層間絶縁膜を介して多層配線を形成した多層配線層が形成され、
全画素の光電変換素子の信号を同時に前記アナログ/デジタル変換手段にてアナログ/デジタル変換した後、前記メモリ手段にデータとして保持するようにして成る
ことを特徴とする固体撮像素子。 A semiconductor substrate is provided with a plurality of pixels composed of photoelectric conversion elements facing the back side of the semiconductor substrate and sensor transistors formed on the front side of the semiconductor substrate ,
An analog / digital conversion means and a memory means connected to each pixel are formed on the surface side of the semiconductor substrate,
On the surface of the semiconductor substrate is formed a multilayer wiring layer in which a multilayer wiring is formed via an interlayer insulating film,
A solid-state imaging device, wherein signals of photoelectric conversion elements of all the pixels are simultaneously subjected to analog / digital conversion by the analog / digital conversion means and then held as data in the memory means.
前記半導体基板の表面側にセンサトランジスタ領域と、各画素毎に接続されたアナログ/デジタル変換回路領域と、メモリ素子もしくは容量素子からなるメモリ回路領域が形成され、
入射光を前記半導体基板の裏面側から光電変換素子に入射するようにして成る
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載の固体撮像素子。 A photoelectric conversion element region is formed facing the back side of the semiconductor substrate,
A sensor transistor region, an analog / digital conversion circuit region connected to each pixel, and a memory circuit region including a memory element or a capacitor element are formed on the surface side of the semiconductor substrate.
2. The solid-state imaging device according to claim 1, wherein incident light is incident on the photoelectric conversion element from the back side of the semiconductor substrate.
ことを特徴とする請求項2記載の固体撮像素子。 The solid-state imaging device according to claim 2, wherein the photoelectric conversion element region is formed to extend below the sensor transistor region.
ことを特徴とする請求項2記載の固体撮像素子。 3. The solid-state imaging device according to claim 2, wherein the photoelectric conversion element region is formed to extend below the sensor transistor region, the analog / digital conversion circuit region, and the memory circuit region.
ことを特徴とする請求項1、2、3又は4記載の固体撮像素子。The solid-state imaging device according to claim 1, 2, 3, or 4.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004317088A JP4270105B2 (en) | 2004-10-29 | 2004-10-29 | Solid-state image sensor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004317088A JP4270105B2 (en) | 2004-10-29 | 2004-10-29 | Solid-state image sensor |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006129298A JP2006129298A (en) | 2006-05-18 |
| JP2006129298A5 JP2006129298A5 (en) | 2007-08-23 |
| JP4270105B2 true JP4270105B2 (en) | 2009-05-27 |
Family
ID=36723461
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004317088A Expired - Lifetime JP4270105B2 (en) | 2004-10-29 | 2004-10-29 | Solid-state image sensor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4270105B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008172580A (en) * | 2007-01-12 | 2008-07-24 | Toshiba Corp | Solid-state imaging element, and solid-state imaging apparatus |
| JP2009068863A (en) * | 2007-09-10 | 2009-04-02 | Toshiba Corp | Infrared detecting element and infrared image sensor using it |
| JP4609497B2 (en) * | 2008-01-21 | 2011-01-12 | ソニー株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and camera |
| US8101978B2 (en) * | 2008-02-08 | 2012-01-24 | Omnivision Technologies, Inc. | Circuit and photo sensor overlap for backside illumination image sensor |
| JP4886721B2 (en) * | 2008-03-18 | 2012-02-29 | 日本放送協会 | Stereo imaging device and stereoscopic display device |
| US9142586B2 (en) * | 2009-02-24 | 2015-09-22 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Pad design for backside illuminated image sensor |
| JP5836581B2 (en) * | 2010-10-04 | 2015-12-24 | キヤノン株式会社 | Manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device |
| JP6053333B2 (en) | 2012-05-31 | 2016-12-27 | キヤノン株式会社 | Imaging device, imaging system, and driving method of imaging device |
| DE102013206404B3 (en) | 2013-04-11 | 2014-03-06 | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft | Sensor chip, computer tomographic detector having this, as well as a manufacturing method and an operating method therefor |
| JP2018011304A (en) * | 2017-07-31 | 2018-01-18 | 株式会社ニコン | Imaging device |
| JP6611779B2 (en) * | 2017-11-08 | 2019-11-27 | キヤノン株式会社 | Solid-state imaging device and imaging system |
| JP6929337B2 (en) * | 2017-11-08 | 2021-09-01 | キヤノン株式会社 | Solid-state image sensor and imaging system |
| JP7358300B2 (en) * | 2019-08-15 | 2023-10-10 | 株式会社ニコン | Image sensor |
-
2004
- 2004-10-29 JP JP2004317088A patent/JP4270105B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2006129298A (en) | 2006-05-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101679864B1 (en) | Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method therefor, and electronic device | |
| JP4752447B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and camera | |
| JP3571909B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP4835710B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device, method for manufacturing solid-state imaging device, driving method for solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP5552768B2 (en) | SOLID-STATE IMAGING DEVICE, ITS MANUFACTURING METHOD, AND ELECTRONIC DEVICE | |
| JP5489705B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and imaging system | |
| CN103247648B (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacture method thereof and electronic equipment | |
| KR100506440B1 (en) | Image pickup apparatus | |
| JP4534634B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device | |
| US20080170149A1 (en) | Solid-state imager and solid-state imaging device | |
| JP4792821B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP4935838B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2011204797A (en) | Solid-state imaging apparatus, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic equipment | |
| JP2012199489A (en) | Solid state image pickup device, solid state image pickup device manufacturing method and electronic apparatus | |
| JP2013098446A (en) | Solid-state imaging element, method for manufacturing solid-state imaging element, and electronic device | |
| JP2003142674A (en) | Mos type solid-state image pickup device | |
| JP4972924B2 (en) | Solid-state imaging device, manufacturing method thereof, and camera | |
| US8440954B2 (en) | Solid-state image pickup device with a wiring becoming a light receiving surface, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic apparatus | |
| US20120104523A1 (en) | Solid-state imaging device manufacturing method of solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus | |
| JP4270105B2 (en) | Solid-state image sensor | |
| JP2007194488A (en) | Solid photographing device | |
| JP2005353994A (en) | Solid-state imaging element and its driving method | |
| JP4967291B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing solid-state imaging device | |
| JP2006108497A (en) | Solid state imaging apparatus | |
| JP2012009697A (en) | Solid-state imaging element |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070706 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070706 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20081021 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20081222 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20090203 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20090216 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120306 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 4270105 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120306 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120306 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130306 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130306 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140306 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |