JP4188095B2 - refrigerator - Google Patents
refrigerator Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4188095B2 JP4188095B2 JP2003008856A JP2003008856A JP4188095B2 JP 4188095 B2 JP4188095 B2 JP 4188095B2 JP 2003008856 A JP2003008856 A JP 2003008856A JP 2003008856 A JP2003008856 A JP 2003008856A JP 4188095 B2 JP4188095 B2 JP 4188095B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- cooling chamber
- heat exchanger
- indoor heat
- air
- cooling
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Defrosting Systems (AREA)
- Removal Of Water From Condensation And Defrosting (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
この発明は、冷凍機に係り、特に室内熱交換器に付着した霜を除霜運転によって溶解させた溶解水の排水に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
図4及び図5は、従来の冷凍機を示す。
図4は、冷凍倉庫1を冷却する冷却運転時の冷凍機を示し、冷凍倉庫1から吸入ダクト3を介して空気を冷凍機本体2の冷却室4へ取り入れて冷やし、冷気を送出ダクト5を介して冷凍倉庫1へ戻す。即ち、空気は図4に矢印で示した順路で循環して冷凍倉庫1内を冷却する。
ここで、冷凍機本体2は、冷凍倉庫1の空気を吸入ダクト3を介して吸入口11から吸入する。この吸入口11にはダンパ12が取り付けられていて冷却運転時は開放されている。冷却室4内には、室内熱交換器13が取り付けられており、冷凍倉庫1からの空気は、室内熱交換器13を通過することにより冷やされる。送出口14にはダンパ15が取り付けられていて冷却運転時は開放されている。送出口14に取り付けられたダクト16内にはファン17が取り付けられている。このファン17は冷却運転時に作動して冷却室4の冷気を送出口14から送り出すと共に、吸入口11から空気を吸入して冷却室4内へ取り込む。
【0003】
なお、冷凍サイクルは、圧縮機21、室外熱交換器23、絞り機構22及び室内熱交換器13によって構成される。即ち、冷媒は図4に矢印で示した方向へ流れ、圧縮機21で圧縮された冷媒は高温高圧の蒸気となって室外熱交換器23へ送られる。室外熱交換器23で冷却ファン24によって冷されて冷媒は常温高圧の液体となる。絞り機構22を通過すると冷媒の圧力は低下すると共に蒸発して低温状態となる。この低温の冷媒が室内熱交換器13を通過するときに冷却室4内の熱を吸収する。
【0004】
上記冷却運転を継続すると、室内熱交換器13の表面に霜や氷が付着して熱交換率が低下する。そこで、冷却運転を停止して除霜運転に切り替えて霜を溶解させ、溶解した溶解水を冷却室4外へ排出するようになっている。
図5は、冷凍機の除霜運転を示し、図4と同符号は同一部分を示す。
除霜運転時は、ファン17は停止し、ダンパ12及び15は閉じて冷凍倉庫1と冷凍機本体2とは遮断される。冷媒は図5に矢印で示したとおり、冷却運転時とは逆の方向へ流れ、室内熱交換器13は高温になる。このため、室内熱交換器13に付着した霜又は氷は溶解して水滴31となって落下してドレンパン32に溜まる。
【0005】
ドレンパン32の底には排水口が設けられており、この排水口はドレンパン32の底面に取り付けられたエアカットバルブ34に通じている。このエアカットバルブ34は先端部34aが軟質ゴムで構成されており、冷却運転時にファン17が作動して冷却室4が負圧になることにより先端部34aの開口が閉じ、外気が排水口から侵入するのを阻止するようになっている。つまり逆止弁として機能する。更に、エアカットバルブ34はドレントラップ35に包囲されて保護されており、上記逆止弁の機能維持が図られている。
【0006】
除霜運転では、ファン17は停止しているので、エアカットバルブ34は開放状態になる。このため、ドレンパン32に溜まった溶解水33はエアカットバルブ34及びドレントラップ35を介して排出される。
上記除霜運転が所定時間行われた後、乾燥運転を数分間行う。乾燥運転はダンパ12及び15を閉じたまま圧縮機21を停止させるもので、室内熱交換器13に付着している溶解水を蒸発させると共に温度上昇した室内熱交換器13を冷やす。乾燥運転が終了すると冷却運転を再開して冷凍倉庫1を冷却する。
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
従来の冷凍機は上記のとおり、乾燥運転ではダンパ12及び15を閉じた状態で圧縮機21を停止させるのみであり、除霜運転で暖められた室内熱交換器13は自然冷却に頼っていた。このため、室内熱交換器13の余熱が排除されるまでに長時間を要し、十分温度が低下しないまま冷却運転を再開して圧縮機21に大きな負担をかける、という問題があった。
また、溶解水33には塵埃が混入しており、特にエアカットバルブ34における溶解水33の流路は狭小であるため、塵埃が堆積し易い、という問題もあった。
更に、溶解水33が流路に残留したまま冷却運転が再開されると、結氷して流路が塞がれ、次の除霜運転では結氷したままとなり、溶解水33は排出されないことも考えられる。このような状態を避けるため、ドレンパン32、エアカットバルブ34及びドレントラップ35を頻繁に清掃しなければならず、保守に手間がかかる、という問題もあった。
【0008】
この発明は、上記問題点を解決するためになされたものであり、室内熱交換器に付着した霜を溶解させた溶解水を円滑に排出させることができる冷凍機を提供することを目的とする。
また、除霜運転で暖められた室内熱交換器の温度を短時間で低下させることができる冷凍機を提供することを目的とする。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
請求項1に記載の冷凍機は、冷却室と、冷却室に設けられた室内熱交換器と、冷却運転時、冷却室に形成された送出口から、室内熱交換器を通過して冷却された冷気を冷却対象の区画室に送り込むと共に、冷却室に形成された吸入口から、区画室の空気を冷却室内に取り入れるための第1ファンと、室内熱交換器を境とする冷却室の一方の側に設けられ、室内熱交換器に付着した霜又は氷が溶解した水滴を溜めるドレンパンと、ドレンパンの底面から下方に設けられ、冷却室が外気圧以上の場合に、ドレンパンから溶解水を排出させるエアカットバルブと、冷却室の他方の側に形成された開口から、外気を冷却室内に取り入れるための第2ファンと、を備え、乾燥運転時、吸入口及び送出口を閉じ、且つ開口を開くと共に、第2ファンを動作させて開口から冷却室内に外気を送り込むことにより、冷却室を加圧して、ドレンパン内の溶解水及び冷却室内の空気をエアカットバルブから強制排出させるようにしたものである。
【0010】
請求項2に記載の冷凍機は、冷却室と、冷却室に設けられた室内熱交換器と、冷却運転時、室内熱交換器を境とする冷却室の一方の側に形成された送出口から、室内熱交換器を通過して冷却された冷気を冷却対象の区画室に送り込むと共に、冷却室の他方の側に形成された吸入口から、区画室の空気を冷却室内に取り入れるためのファンと、冷却室の他方の側に設けられ、室内熱交換器に付着した霜又は氷が溶解した水滴を溜めるドレンパンと、ドレンパンの底面から下方に設けられ、冷却室が外気圧以上の場合に、ドレンパンから溶解水を排出させるエアカットバルブと、吸入口を開閉する第1ダンパと、ファンよりも出側において送出口を開閉する第2ダンパと、ファン及び第2ダンパ間に形成された開口を開閉する第3ダンパと、を備え、乾燥運転時、第1ダンパ及び第2ダンパによって吸入口及び送出口を閉じ、且つ第3ダンパによって開口を開くと共に、ファンを冷却運転時とは逆回転させて開口から冷却内に外気を送り込むことにより、冷却室を加圧して、ドレンパン内の溶解水及び冷却室内の空気をエアカットバルブから強制排出させるようにしたものである。
【0011】
請求項3に記載の冷凍機は、室内熱交換器は、吸入口側に傾斜されて冷却室に取り付けられ、ドレンパンは、室内熱交換器の下方に配置されたものである。
【0013】
【発明の実施の形態】
実施の形態1.
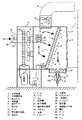
図1及び図2は、この発明の実施の形態1における冷凍機を示す。
図において、1は冷凍対象の区画室である冷凍倉庫、2は冷凍機本体、3は冷凍倉庫1内の空気を冷凍機本体2へ導く吸入ダクト、4は冷凍機本体2の冷却室、5は冷気を冷凍機本体2から冷凍倉庫1へ導く送出ダクトである。
11は冷凍機本体2の吸入口、12は吸入口11を開閉するダンパ、13は冷却室4に取り付けられた室内熱交換器、14は室内熱交換器13で冷却された冷気を送り出す送出口、15は送出口14を開閉するダンパで、冷却運転時は開放される。16は送出口14に取り付けられたダクト、17はダクト16内に取り付けられたファンで、冷却運転時に作動して冷却室4の冷気を送出口14から送り出す。
なお、室内熱交換器13は、吸入口11と送出口14とを隔てる位置に設置され、かつ、吸入口11側へ傾斜させて冷却室4に取り付けられる。
【0014】
21は圧縮機、23は室外熱交換器、22は絞り機構、13は室内熱交換器で、圧縮機21は室外熱交換器23及び室内熱交換器13に管路で接続され、絞り機構22は室外熱交換器23及び室内熱交換器13を介して圧縮機21に接続されて冷凍サイクルを構成している。24は室外熱交換器23を冷やす冷却ファン24である。
【0015】
31は室内熱交換器13に付着した霜又は氷が溶解した水滴、32は水滴31を溜めるドレンパンで、底面に排水口が設けられている。33はドレンパン32内の溶解水、34はドレンパン32の排水口部位の底面から下方へ垂設されたエアカットバルブで、先端部34aは軟質ゴムで構成されて先細化され、開口は狭小になっている。このため、冷却室4が外気圧の場合、溶解水33はドレンパン32から滴下するが、冷却室4が負圧になると外気によって押圧されるので、先端部34aの開口は閉鎖されて溶解水33の滴下は阻止されると共に外気の流入も阻止される。従って、エアカットバルブ34は逆止弁として機能する。35はエアカットバルブ34を包囲して保護するドレントラップである。
なお、ドレンパン32とエアカットバルブ34とドレントラップ35は排水器36を構成し、室内熱交換器13を境として吸入口11側の冷却室4の底面に取り付けられる。また、水滴31は室内熱交換器13が傾斜取付されているので、排水器36側へ滴下又は伝って下降する。
【0016】
41は外気を取り入れて冷却室4を加圧し、溶解水33を強制的に排出させる強制排出手段で、冷凍機本体2の側壁に設けられた開口42と、この開口42を開閉するダンパ43と、外気を開口42へ導くダクト44と、外気を冷却室4内へ送り込むファン45とからなる。
なお、強制排出手段41は、室内熱交換器13を境として送出口14側の冷却室4の側面に取り付けられる。
【0017】
次に、動作を説明する。動作は、冷却運転、除霜運転及び乾燥運転からなる。1.冷却運転
冷却運転では、図1に示す開口42はダンパ43によって閉じられており、強制排出手段41による外気の取入れはない。従って、冷却運転は従来例と同じであり、図4に従って説明する。
即ち、冷媒は圧縮機21で圧縮され、高温高圧の蒸気となって図4に矢印で示した方向へ流れ、室外熱交換器23へ送られる。室外熱交換器23で冷却ファン24によって冷されて冷媒は高圧の液体となる。絞り機構22を通過すると冷媒の圧力は低下すると共に蒸発して低温状態となる。室内熱交換器13は低温の冷媒によって冷却される。
【0018】
ファン17の作動により冷却室4の空気が送出口14から送り出される。この送出しにより冷却室4内は負圧になるため、ダンパ12が開いて吸入口11から冷凍倉庫1内の空気が冷却室4へ取り込まれる。取り込まれた空気は室内熱交換器13を通過することにより冷却されて送出ダクト5を介して冷凍倉庫1へ送り戻される。上記空気の循環により冷凍倉庫1は冷却される。
なお、冷却運転では冷却室4は負圧になるため、エアカットバルブ34は閉じて外気の流入は阻止される。
【0019】
2.除霜運転
上記冷却運転を継続すると室内熱交換器13の表面に霜や氷が付着して熱交換率が低下する。そこで、冷却運転を停止して除霜運転に切り替えて霜を溶解させる。
除霜運転も、図1において開口42はダンパ43によって閉じられており、強制排出手段41による外気の取入れはない。従って、除霜運転も従来例と同様である。即ち、図2において、ファン17は停止し、ダンパ15は閉じる。このため、ダンパ12は吸入口11を閉じて冷凍倉庫1と冷凍機本体2とは遮断される。冷媒は図2に矢印で示したとおり、冷却運転時とは逆の方向へ流れ、室内熱交換器13は高温になる。このため、室内熱交換器13に付着した霜又は氷は溶解し、室内熱交換器13の傾斜により水滴31となって落下して除去され、ドレンパン32に溜まる。
除霜運転では、ファン17は停止しているので、エアカットバルブ34は開放状態になる。このため、ドレンパン32に溜まった溶解水33はエアカットバルブ34及びドレントラップ35を介して排出される。
【0020】
3.乾燥運転
除霜運転では室内熱交換器13の温度が上昇しており、また、溶解水も付着している。そこで、室内熱交換器13を冷やすと共に、溶解水を蒸発させるため、上記除霜運転の終了後、乾燥運転を行う。
乾燥運転は、図2に示したとおり、ダンパ12及び15を閉じ圧縮機21を停止させる。また、強制排出手段41はダンパ43を開くと共に、ファン45を作動させて開口42から外気を冷却室4内へ送り込む。
【0021】
開口42は室内熱交換器13を境として送出口14側に設けられているから、外気は送出口14側から室内熱交換器13を通過して吸入口11側へ流れる。これによって、室内熱交換器13は外気によって冷やされると共に、付着した溶解水は蒸発する。更に、冷却室4内は正圧になっているから、空気はエアカットバルブ34の開口から溶解水33と共に排出される。
乾燥運転が終了すると冷却運転に戻る。
【0022】
上記実施の形態1によれば、吸入口11及び送出口14を閉じると共に、冷却室4内へ外気を送り込んで加圧して溶解水33を排水器36から排出させる強制排出手段41を設けたので、乾燥運転時に空気はエアカットバルブ34の開口から溶解水33と共に円滑に排出される。仮に塵埃がエアカットバルブ34に堆積して開口が塞がれていたとしても、冷却室4内へ送り込まれた外気によって押し出されるので、冷却室4から外気に通じる流路は確保される。この流路の確保によって乾燥運転時も溶解水33は円滑に排出される。
また、排水器36は、室内熱交換器13を境とする冷却室4の一方の側から溶解水33を排出し、強制排出手段41は、冷却室4の他方の側から外気を送り込んで室内熱交換器13を通過させるようにしたので、短時間で室内熱交換器13を冷却させることができる。
更に、室内熱交換器13は、吸入口11と送出口14とを隔てる位置に設置され、かつ、吸入口11側へ傾斜させて冷却室4に取り付けられ、強制排出手段41は、送出口14側から冷却室4内へ外気を送り込むようにしたので、溶解水は室内熱交換器13の傾斜により水滴31となって落下して短時間で除去される。
【0023】
実施の形態2.
図3は、この発明の実施の形態2における冷凍機を示す。図中、図1及び図2と同符号は同一部分を示す。
58は送出口14と送出ダクト5の間に設けられたダクト、59はダクト58の送出口14側の端部に設けられた可逆回転可能なファン、60はダクト58の送出ダクト5側の端部に設けられてダクト58を開閉するダンパである。
61はファン59とダンパ60との間に設けられた強制排出手段で、外気に通じる開口62と、常時閉鎖し乾燥運転時のみ開口62を開くダンパ63と、逆回転して外気を開口62から取り込むファン59とからなる。
【0024】
次に、動作を説明する。
ダンパ63は常時閉鎖しているので、冷却運転及び除霜運転は上記実施の形態1と同様であり、説明を省略する。
乾燥運転では、ダンパ60はダクト58を閉鎖し、ダンパ63は開く。ファン59は冷却運転の時の回転方向とは逆の方向へ回転して外気を開口62から冷却室4内へ取り込む。実施の形態1と同様に、取り込まれた外気によって室内熱交換器13は乾燥され、溶解水33は排水器36から排出される。
【0025】
上記実施の形態2によっても、強制排出手段61を設けたので、溶解水33はエアカットバルブ34の開口から円滑に排出される。仮に塵埃が堆積して開口が塞がれたとしても、冷却室4内へ送り込まれた外気によって押し出されるので、冷却室4から外気に通じる流路は確保される。また、短時間で室内熱交換器13を冷却させることができる。
特に、冷却運転時に冷気を送出するファン59及びダクト58を、強制排出手段61に兼用したので、ダクト工事が簡単になる。
たものである。
【0026】
【発明の効果】
この発明は上記のとおり構成されているので、以下の効果を奏する。
請求項1に記載の冷凍機は、冷却室と、冷却室に設けられた室内熱交換器と、冷却運転時、冷却室に形成された送出口から、室内熱交換器を通過して冷却された冷気を冷却対象の区画室に送り込むと共に、冷却室に形成された吸入口から、区画室の空気を冷却室内に取り入れるための第1ファンと、室内熱交換器を境とする冷却室の一方の側に設けられ、室内熱交換器に付着した霜又は氷が溶解した水滴を溜めるドレンパンと、ドレンパンの底面から下方に設けられ、冷却室が外気圧以上の場合に、ドレンパンから溶解水を排出させるエアカットバルブと、冷却室の他方の側に形成された開口から、外気を冷却室内に取り入れるための第2ファンと、を備え、乾燥運転時、吸入口及び送出口を閉じ、且つ開口を開くと共に、第2ファンを動作させて開口から冷却室内に外気を送り込むことにより、冷却室を加圧して、ドレンパン内の溶解水及び冷却室内の空気をエアカットバルブから強制排出させるようにしたものである。
このため、溶解水は排水器から円滑に排出されると共に、仮に塵埃が堆積して排水器が塞がれていたとしても、冷却室内へ送り込まれた外気によって押し出されるので、冷却室から外気に通じる流路は確保される、という効果を奏する。
また、外気が室内熱交換器を通過するので、除霜運転で温度上昇した室内熱交換器を短時間で冷却させることができる、という効果を奏する。
【0027】
請求項2に記載の冷凍機は、冷却室と、冷却室に設けられた室内熱交換器と、冷却運転時、室内熱交換器を境とする冷却室の一方の側に形成された送出口から、室内熱交換器を通過して冷却された冷気を冷却対象の区画室に送り込むと共に、冷却室の他方の側に形成された吸入口から、区画室の空気を冷却室内に取り入れるためのファンと、冷却室の他方の側に設けられ、室内熱交換器に付着した霜又は氷が溶解した水滴を溜めるドレンパンと、ドレンパンの底面から下方に設けられ、冷却室が外気圧以上の場合に、ドレンパンから溶解水を排出させるエアカットバルブと、吸入口を開閉する第1ダンパと、ファンよりも出側において送出口を開閉する第2ダンパと、ファン及び第2ダンパ間に形成された開口を開閉する第3ダンパと、を備え、乾燥運転時、第1ダンパ及び第2ダンパによって吸入口及び送出口を閉じ、且つ第3ダンパによって開口を開くと共に、ファンを冷却運転時とは逆回転させて開口から冷却内に外気を送り込むことにより、冷却室を加圧して、ドレンパン内の溶解水及び冷却室内の空気をエアカットバルブから強制排出させるようにしたものである。
このものにあっても冷却室から外気に通じる溶解水の流路は確保されると共に、短時間で室内熱交換器を冷却させることができる、という効果を奏する。
特に、冷却運転時に冷気を送出するファン及びダクトを、強制排出手段に兼用したので、ダクト工事が簡単になる、という効果も併せて奏する。
【0028】
請求項3に記載の冷凍機は、室内熱交換器は、吸入口側に傾斜されて冷却室に取り付けられ、ドレンパンは、室内熱交換器の下方に配置されたものである。
このため、除霜運転時、溶解水は室内熱交換器の傾斜により水滴となって落下して短時間で除去される、という効果を奏する。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 この発明の実施の形態1における冷凍機の外観を示す斜視図。
【図2】 この発明の実施の形態1における冷凍機の除霜運転時及び乾燥運転時を示す縦断面図。
【図3】 この発明の実施の形態2における冷凍機の除霜運転時及び乾燥運転時を示す縦断面図。
【図4】 従来の冷凍機の冷房運転時を示す縦断面図。
【図5】 従来の冷凍機の除霜運転時及び乾燥運転時を示す縦断面図。
【符号の説明】
1 冷凍倉庫、 2 冷凍機本体、 3 吸入ダクト、 4 冷却室、 5 送出ダクト、 11 吸入口、 12 ダンパ、 13 室内熱交換器、 14送出口、 15 ダンパ、 16 ダクト、 17 ファン、 21 圧縮機、 22 絞り機構、 23 室外熱交換器、 24 冷却ファン、 31 水滴、 32 ドレンパン、 33 溶解水、 34 エアカットバルブ、 34a 先端部、 35 ドレントラップ、 41 強制排出手段、 42 開口、43 ダンパ、 44 ダクト、 45 ファン、 58 ダクト、 59 ファン、 60 ダンパ、 61 強制排出手段、 62 開口、 63 ダンパ。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a refrigerator, and particularly to drainage of dissolved water in which frost attached to an indoor heat exchanger is dissolved by a defrosting operation.
[0002]
[Prior art]
4 and 5 show a conventional refrigerator.
FIG. 4 shows a refrigerator during a cooling operation for cooling the freezer warehouse 1, air is taken into the cooling chamber 4 of the refrigerator
Here, the refrigerator
[0003]
The refrigeration cycle includes the
[0004]
If the cooling operation is continued, frost or ice adheres to the surface of the
FIG. 5 shows the defrosting operation of the refrigerator, and the same reference numerals as those in FIG. 4 denote the same parts.
During the defrosting operation, the
[0005]
A drain port is provided at the bottom of the
[0006]
In the defrosting operation, since the
After the defrosting operation is performed for a predetermined time, the drying operation is performed for several minutes. In the drying operation, the
[0007]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
As described above, the conventional refrigerator only stops the
Further, there is a problem that dust is easily accumulated because dust is mixed in the dissolved
Furthermore, if the cooling operation is resumed with the dissolved
[0008]
This invention was made in order to solve the said problem, and it aims at providing the refrigerator which can discharge | emit the dissolved water which melt | dissolved the frost adhering to an indoor heat exchanger smoothly. .
Moreover, it aims at providing the refrigerator which can reduce the temperature of the indoor heat exchanger heated by the defrost operation in a short time.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The refrigerator according to claim 1 is cooled through the indoor heat exchanger from the cooling chamber, the indoor heat exchanger provided in the cooling chamber, and the outlet formed in the cooling chamber during the cooling operation. One of the first fan for taking the air in the compartment into the cooling chamber from the suction port formed in the cooling chamber and the cooling chamber bordering on the indoor heat exchanger A drain pan that collects frost or ice dissolved water droplets attached to the indoor heat exchanger, and is provided below the drain pan from the bottom of the drain pan. When the cooling chamber is at or above the atmospheric pressure, the dissolved water is discharged from the drain pan. A second fan for taking outside air into the cooling chamber from an opening formed on the other side of the cooling chamber, and closing the inlet and the outlet during the drying operation. Open and operate second fan Allowed by feeding the outside air from the opening to the cooling chamber, it pressurizes the cooling chamber is obtained by the dissolved water and cooling indoor air in the drain pan so as to forcibly discharged from the air cut valve.
[0010]
The refrigerator according to
[0011]
In the refrigerator according to
[0013]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Embodiment 1 FIG.
1 and 2 show a refrigerator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
In the figure, 1 is a freezing warehouse which is a compartment to be frozen, 2 is a refrigerator main body, 3 is a suction duct for guiding the air in the freezer warehouse 1 to the refrigerator
11 is a suction port of the
The
[0014]
[0015]
31 is a water droplet in which frost or ice adhering to the
The
[0016]
41 is a forced discharge means that takes in the outside air to pressurize the cooling chamber 4 and forcibly discharge the dissolved
The forced discharge means 41 is attached to the side surface of the cooling chamber 4 on the
[0017]
Next, the operation will be described. The operation includes a cooling operation, a defrosting operation, and a drying operation. 1. Cooling Operation In the cooling operation, the
That is, the refrigerant is compressed by the
[0018]
The air in the cooling chamber 4 is sent out from the
In the cooling operation, since the cooling chamber 4 has a negative pressure, the air cut
[0019]
2. Defrosting operation If the cooling operation is continued, frost or ice adheres to the surface of the
Also in the defrosting operation, the
In the defrosting operation, since the
[0020]
3. In the drying operation defrosting operation, the temperature of the
In the drying operation, as shown in FIG. 2, the
[0021]
Since the
When the drying operation is completed, the operation returns to the cooling operation.
[0022]
According to the first embodiment, since the
The
Further, the
[0023]
FIG. 3 shows a refrigerator according to
58 is a duct provided between the
61 is a forced discharge means provided between the
[0024]
Next, the operation will be described.
Since the
In the drying operation, the
[0025]
Also in the second embodiment, since the forced discharge means 61 is provided, the dissolved
In particular, since the
It is a thing.
[0026]
【The invention's effect】
Since this invention is comprised as mentioned above, there exist the following effects.
The refrigerator according to claim 1 is cooled through the indoor heat exchanger from the cooling chamber, the indoor heat exchanger provided in the cooling chamber, and the outlet formed in the cooling chamber during the cooling operation. One of the first fan for taking the air in the compartment into the cooling chamber from the suction port formed in the cooling chamber and the cooling chamber bordering on the indoor heat exchanger A drain pan that collects frost or ice dissolved water droplets attached to the indoor heat exchanger, and is provided below the drain pan from the bottom of the drain pan. When the cooling chamber is at or above the atmospheric pressure, the dissolved water is discharged from the drain pan. A second fan for taking outside air into the cooling chamber from an opening formed on the other side of the cooling chamber, and closing the inlet and the outlet during the drying operation. Open and operate second fan Allowed by feeding the outside air from the opening to the cooling chamber, it pressurizes the cooling chamber is obtained by the dissolved water and cooling indoor air in the drain pan so as to forcibly discharged from the air cut valve.
Therefore, the dissolved water is smoothly discharged from the drainage device, and even if dust accumulates and the drainage device is blocked, it is pushed out by the outside air sent into the cooling chamber. There is an effect that the flow path leading to is secured.
Moreover, since outside air passes an indoor heat exchanger, there exists an effect that the indoor heat exchanger which raised the temperature by the defrost operation can be cooled in a short time.
[0027]
Refrigerator according to
Even if it exists in this thing, while the flow path of the melted water which leads to external air from a cooling chamber is ensured, there exists an effect that an indoor heat exchanger can be cooled in a short time.
In particular, since the fan and the duct that send out the cold air during the cooling operation are also used as the forced discharge means, there is also an effect that the duct work is simplified.
[0028]
In the refrigerator according to
For this reason, at the time of a defrost operation, there exists an effect that dissolved water falls as a water droplet by the inclination of an indoor heat exchanger, and is removed in a short time.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing an appearance of a refrigerator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a vertical cross-sectional view showing a defrosting operation and a drying operation of the refrigerator in Embodiment 1 of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a defrosting operation and a drying operation of a refrigerator according to
FIG. 4 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a conventional refrigerator during cooling operation.
FIG. 5 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a conventional refrigerator in a defrosting operation and a drying operation.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1 Refrigeration warehouse, 2 Refrigerator main body, 3 Suction duct, 4 Cooling chamber, 5 Delivery duct, 11 Suction inlet, 12 Damper, 13 Indoor heat exchanger, 14 Outlet, 15 Damper, 16 Duct, 17 Fan, 21 Compressor , 22 throttle mechanism, 23 outdoor heat exchanger, 24 cooling fan, 31 water droplet, 32 drain pan, 33 dissolved water, 34 air cut valve, 34a tip, 35 drain trap, 41 forced discharge means, 42 opening, 43 damper, 44 Duct, 45 fan, 58 duct, 59 fan, 60 damper, 61 forced discharge means, 62 opening, 63 damper.
Claims (3)
上記冷却室に設けられた室内熱交換器と、
冷却運転時、上記冷却室に形成された送出口から、上記室内熱交換器を通過して冷却された冷気を冷却対象の区画室に送り込むと共に、上記冷却室に形成された吸入口から、上記区画室の空気を上記冷却室内に取り入れるための第1ファンと、
上記室内熱交換器を境とする上記冷却室の一方の側に設けられ、上記室内熱交換器に付着した霜又は氷が溶解した水滴を溜めるドレンパンと、
上記ドレンパンの底面から下方に設けられ、上記冷却室が外気圧以上の場合に、上記ドレンパンから溶解水を排出させるエアカットバルブと、
上記冷却室の他方の側に形成された開口から、外気を上記冷却室内に取り入れるための第2ファンと、
を備え、
乾燥運転時、上記吸入口及び上記送出口を閉じ、且つ上記開口を開くと共に、上記第2ファンを動作させて上記開口から上記冷却室内に外気を送り込むことにより、上記冷却室を加圧して、上記ドレンパン内の溶解水及び上記冷却室内の空気を上記エアカットバルブから強制排出させることを特徴とする冷凍機。 A cooling chamber;
An indoor heat exchanger provided in the cooling chamber;
During the cooling operation, from the outlet formed in the cooling chamber, the cooled air passing through the indoor heat exchanger is sent to the compartment to be cooled, and from the suction port formed in the cooling chamber, A first fan for taking the air in the compartment into the cooling chamber;
A drain pan that is provided on one side of the cooling chamber with the indoor heat exchanger as a boundary, and stores water droplets in which frost or ice adhering to the indoor heat exchanger is dissolved;
An air cut valve provided below the bottom surface of the drain pan and for discharging dissolved water from the drain pan when the cooling chamber is at or above the atmospheric pressure;
A second fan for taking outside air into the cooling chamber from an opening formed on the other side of the cooling chamber;
With
During the drying operation, the inlet and the outlet are closed and the opening is opened, and the second fan is operated to send outside air into the cooling chamber from the opening, thereby pressurizing the cooling chamber, A refrigerator that forcibly discharges dissolved water in the drain pan and air in the cooling chamber from the air cut valve .
上記冷却室に設けられた室内熱交換器と、
冷却運転時、上記室内熱交換器を境とする上記冷却室の一方の側に形成された送出口から、上記室内熱交換器を通過して冷却された冷気を冷却対象の区画室に送り込むと共に、上記冷却室の他方の側に形成された吸入口から、上記区画室の空気を上記冷却室内に取り入れるためのファンと、
上記冷却室の他方の側に設けられ、上記室内熱交換器に付着した霜又は氷が溶解した水滴を溜めるドレンパンと、
上記ドレンパンの底面から下方に設けられ、上記冷却室が外気圧以上の場合に、上記ドレンパンから溶解水を排出させるエアカットバルブと、
上記吸入口を開閉する第1ダンパと、
上記ファンよりも出側において上記送出口を開閉する第2ダンパと、
上記ファン及び上記第2ダンパ間に形成された開口を開閉する第3ダンパと、
を備え、
乾燥運転時、上記第1ダンパ及び上記第2ダンパによって上記吸入口及び上記送出口を閉じ、且つ上記第3ダンパによって上記開口を開くと共に、上記ファンを冷却運転時とは逆回転させて上記開口から上記冷却内に外気を送り込むことにより、上記冷却室を加圧して、上記ドレンパン内の溶解水及び上記冷却室内の空気を上記エアカットバルブから強制排出させることを特徴とする冷凍機。 A cooling chamber;
An indoor heat exchanger provided in the cooling chamber;
During the cooling operation, from the outlet formed on one side of the cooling chamber with the indoor heat exchanger as a boundary, the cooled air passing through the indoor heat exchanger is sent to the compartment to be cooled. A fan for taking air in the compartment into the cooling chamber from an inlet formed on the other side of the cooling chamber;
A drain pan that is provided on the other side of the cooling chamber and stores water droplets in which frost or ice adhering to the indoor heat exchanger is dissolved;
An air cut valve that is provided below the bottom surface of the drain pan, and discharges dissolved water from the drain pan when the cooling chamber is at or above the atmospheric pressure;
A first damper that opens and closes the inlet;
A second damper that opens and closes the outlet on the outlet side of the fan;
A third damper that opens and closes an opening formed between the fan and the second damper;
With
During the drying operation, the inlet and the outlet are closed by the first damper and the second damper, the opening is opened by the third damper, and the fan is rotated in the reverse direction from the cooling operation to open the opening. A refrigerating machine that pressurizes the cooling chamber by forcing outside air into the cooling and forcibly discharges the dissolved water in the drain pan and the air in the cooling chamber from the air cut valve .
上記ドレンパンは、上記室内熱交換器の下方に配置された
ことを特徴とする請求項1又は請求項2に記載の冷凍機。 The indoor heat exchanger is inclined to the inlet side and attached to the cooling chamber,
The drain pan is disposed below the indoor heat exchanger.
The refrigerator according to claim 1 or 2, characterized in that .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003008856A JP4188095B2 (en) | 2003-01-16 | 2003-01-16 | refrigerator |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003008856A JP4188095B2 (en) | 2003-01-16 | 2003-01-16 | refrigerator |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004218986A JP2004218986A (en) | 2004-08-05 |
| JP2004218986A5 JP2004218986A5 (en) | 2005-09-08 |
| JP4188095B2 true JP4188095B2 (en) | 2008-11-26 |
Family
ID=32898521
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003008856A Expired - Fee Related JP4188095B2 (en) | 2003-01-16 | 2003-01-16 | refrigerator |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4188095B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6641752B2 (en) * | 2015-07-16 | 2020-02-05 | 富士電機株式会社 | Cooling system |
| JP6698490B2 (en) * | 2016-09-28 | 2020-05-27 | 株式会社不二工機 | Cooling unit |
-
2003
- 2003-01-16 JP JP2003008856A patent/JP4188095B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004218986A (en) | 2004-08-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| RU2008133223A (en) | ICE GENERATOR FOR REFRIGERATING DEVICE | |
| JP3688892B2 (en) | Freezer refrigerator | |
| JPH08327208A (en) | Refrigerator and circulating method of cold air in refrigerator | |
| CN104567192A (en) | Refrigerator | |
| KR100531298B1 (en) | refrigerator having freezer in lower part | |
| JP3611447B2 (en) | refrigerator | |
| JP2009109110A (en) | Refrigeration system | |
| JP4188095B2 (en) | refrigerator | |
| KR101330936B1 (en) | Refrigerator | |
| KR200416645Y1 (en) | Structure of ice guidance device for icehouse ice discharge of ice machine | |
| KR20020043852A (en) | Vacuum refrigerator | |
| KR20050104129A (en) | Transparent ice maker | |
| JPH11148759A (en) | Refrigerator equipped with two sets of evaporators | |
| KR100621237B1 (en) | Duct structure for cooled air in refrigerator | |
| JP4248726B2 (en) | Hot gas defrosting type refrigerator-freezer | |
| JP2005241139A (en) | Refrigerator | |
| KR200226090Y1 (en) | Pressure regulator for opening the door of the refrigerator | |
| KR200416642Y1 (en) | Accumulation prevention device of ice machine | |
| WO2023284589A1 (en) | Refrigerator | |
| CN218544942U (en) | Refrigerator with a door | |
| KR102297757B1 (en) | refrigerator | |
| JP2000230768A (en) | Refrigerator | |
| JPH1047837A (en) | Freezing container | |
| KR20180121139A (en) | Show case | |
| KR100254466B1 (en) | Apparatus for cycling of cooling air in a refrigerator |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050314 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050314 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080401 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080415 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080522 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20080522 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080909 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080910 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4188095 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110919 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120919 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130919 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |