JP4157228B2 - Electronic camera and image printer apparatus - Google Patents
Electronic camera and image printer apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4157228B2 JP4157228B2 JP17408599A JP17408599A JP4157228B2 JP 4157228 B2 JP4157228 B2 JP 4157228B2 JP 17408599 A JP17408599 A JP 17408599A JP 17408599 A JP17408599 A JP 17408599A JP 4157228 B2 JP4157228 B2 JP 4157228B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- continuous
- still image
- still
- images
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、連写機能を有する電子カメラ及びこの電子カメラで撮影した連写画像をプリントする画像プリンタ装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近時、記録媒体(メモリ)の容量の増大と撮影した画像の処理速度の向上に伴ない、静止画像のみならず、時間的に連続した静止画像からなる連写画像を撮影する連写機能を有する電子スチルカメラが種々製品化されている。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかして、上記連写機能により、時間的に連続した多数の静止画像からなる連写画像ファイルを得た場合、この連写画像ファイル全体を一つの動画像ファイルとして扱う分には問題ないが、所望するシャッタチャンスを逃さないために連写機能を用いた場合、あるいは1回のみの静止画撮影が失敗するのをおそれて連写機能を利用した場合であれば、その連写画像ファイル中からシャッタタイミングの適したもの、あるいは最も写りの良いものを選択する必要がある。
【0004】
しかしながら、一般に連写画像中から任意の静止画像を選択するためには、再生モードでコマ送りを指示して、連写画像を構成する個々の静止画像を1コマずつ表示させる必要があり、その操作が大変煩雑であった。
【0005】
本発明は上記のような実情に鑑みてなされたもので、その目的とするところは、煩雑な操作を必要とすることなく、撮影した連写画像中から最も写りの良い静止画像を選択して表示し、あるいはプリントに供することが可能な電子カメラ及び画像プリンタ装置を提供することにある。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
請求項1記載の発明は、時間的に連続した静止画像からなる連写画像の撮影を指示する第1の指示手段と、上記第1の指示手段の指示により連写画像を撮影する撮影手段と、上記撮影手段により撮影される連写画像を構成する個々の静止画像に対し、その撮影条件から評価値を算出する算出手段と、上記算出手段により算出した評価値を対応する静止画像に付加して記録媒体に記録する記録手段と、上記記録媒体に記録された連写画像の出力を指示する第2の指示手段と、上記第2の指示手段で指示された連写画像を構成する各静止画像に付加されている評価値に応じて静止画像を選択する選択手段と、上記選択手段で選択した静止画像を上記記録媒体から読出して出力する出力手段とを具備したことを特徴とする。
【0007】
このような構成とすれば、連写画像中で最も撮影条件が良いと思われる静止画像を特別の操作を必要とせずに選択的に読出して表示出力またはプリント出力させることができるために、連写画像から所望の静止画像を選択するための手間を大幅に簡略化することができる。
【0008】
請求項2記載の発明は、上記請求項1記載の発明において、上記算出手段は、撮影条件としてコントラスト値、自動合焦値、及び自動露出値の少なくとも一つを用いることを特徴とする。
【0009】
このような構成とすれば、上記請求項1記載の発明の作用に加えて、通常の静止画像撮影に際して用いている値から評価値の算出を行なうので、特別な計算を必要とせず、また評価の信頼性を高くすることができる。
【0010】
請求項3記載の発明は、上記請求項1記載の発明において、上記撮影手段により撮影される連写画像を構成する個々の静止画像から構成画素を間引いたプレビュー画像を作成するプレビュー画像作成手段をさらに具備し、上記記録手段は、上記算出手段で得た評価値と上記プレビュー画像作成手段が作成したプレビュー画像とを対応する静止画像に付加して上記記録媒体に記録し、上記選択手段は、上記第2の指示手段により選択された連写画像を構成する各静止画像に付加されているプレビュー画像の相関演算を行なうことで同一の構図を有する静止画像の静止画像の範囲を特定し、特定した範囲内の静止画像中からその評価値に応じて静止画像を選択することを特徴とする。
【0011】
このような構成とすれば、上記請求項1記載の発明の作用に加えて、例えば、連写画像中に、ねらった構図以外の静止画像が入っており、且つその静止画像の評価値が本来の構図の静止画像の評価値より高かった場合でも、その影響を除去して、ねらった構図を有する静止画像の中から、評価値の高いものを選択することができる。また、プレビュー(サムネイル)画像はデータ量が本画像より大幅に少ないため、大まかな構図を判断する程度の相関演算が負担となることはなく、短時間のうちに処理できる。
【0014】
請求項4記載の発明は、時間的に連続した静止画像にそれぞれその撮影条件が付加されて連写画像として記録されている記録媒体を装着する記録媒体装着手段と、上記記録媒体に記録された連写画像の出力を指示する指示手段と、上記指示手段で指示された連写画像を構成する各静止画像に付加されている撮影条件からそれぞれ評価値を算出する算出手段と、上記算出手段で得た評価値に応じて静止画像を選択する選択手段と、上記選択手段で選択した静止画像を上記記録媒体から読出してプリント出力するプリント手段とを具備したことを特徴とする。
【0015】
このような構成とすれば、連写記録中で最も撮影条件が良いと思われる静止画像を特別の操作を必要とせずに選択的に読出してプリント出力させることができるため、連写画像から所望の静止画像を選択するための手間を大幅に簡略化することができる。また、プリンタ側で各静止画像の撮影条件から評価値を算出するために、画像に撮影条件のデータを付加するのは多くの電子カメラで通常に行なっていることであるから、電子カメラのより多くの機種に対応することができる。
【0016】
【発明の実施の形態】
(第1の実施の形態)
以下本発明を連写機能を有する電子スチルカメラに適用した場合の第1の実施の形態について図面を参照して説明する。
【0017】
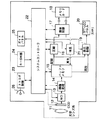
まず、図1によりこの電子カメラの具体的な回路構成を例示する。同図で、記録モード時に、光学レンズ系11により被写体の光学像が撮像素子であるCCD12上に結像され、このCCD12の出力がA/D変換器13で各画素単位でデジタル化された後に画像処理回路14に送られる。
【0018】
この画像処理回路14は、A/D変換器13から送られてきたデジタル値の画像データを後述するシステムコントローラ22からの制御に基づいて適宜画素間引き処理等を施した後にバッファメモリ15に送出する。
【0019】
このバッファメモリ15は、ビットマップ形式の画像データを複数枚分蓄えておくもので、ここに蓄えられた個々の画像データは随時、圧縮回路16で所定のファイル形式、例えばJPEGによりデータ圧縮が施されてファイル化され、その後に媒体制御回路17に送られて、この電子カメラ1の記録媒体である、着脱自在に装着されるメモリカード18に書込まれる。
【0020】
また、この記録モード時に撮影内容をモニタリングしたい場合には、EVF(電子ビューファインダ)としても機能するTFT−LCDパネル20を使用するべく、バッファメモリ15から表示制御回路19へも画素数を大幅に減少した画像データが読出され、表示制御回路19はこの画像データに基づいてバックライト付のカラーTFT−LCDパネル20を表示駆動することで、CCD12で撮像されている内容をリアルタイムで表示させる。
【0021】
一方、再生モード時には、メモリカード18に記録されている画像データのファイルが媒体制御回路17により選択的に読出され、伸長回路21で上記圧縮回路16での処理とは反対の手順で伸長されてビットマップ形式に展開された後にバッファメモリ15に蓄えられる。
【0022】
このバッファメモリ15に蓄えられた画像データが表示制御回路19に読出され、表示制御回路19はこの画像データに基づいてTFT−LCDパネル20を表示駆動することで、記録した画像の再生表示を行なわせる。
【0023】
しかして、上記CCD12、A/D変換器13、画像処理回路14、バッファメモリ15、圧縮回路16、媒体制御回路17、表示制御回路19、及び伸長回路21の動作をすべてシステムコントローラ22が統括制御する。
【0024】
このシステムコントローラ22は、電子カメラの全回路の動作制御を行なうもので、またストロボ制御回路23、キースイッチ(SW)部24、及びガイドパネル25とも接続され、これらを制御する。
【0025】
ストロボ制御回路23は、システムコントローラ22の制御の下に静止画撮影時にストロボ26を閃光駆動させる。
【0026】
キースイッチ部24は、上記静止画像と連写画像の撮影のためのレリーズスイッチ、記録モードと再生モード、記録モード時の静止画像モードと連写画像モード、画質設定モード等の各種モード設定を行なうモード設定スイッチ、電源スイッチ、カーソルキースイッチ、及び上記TFT−LCDパネル20での表示のオン/オフを切換えるLCD表示スイッチ等を有し、その操作信号を直接上記システムコントローラ22へ送出する。
【0027】
ガイドパネル25は、システムコントローラ22からの駆動制御信号に基づいて上述した如くこの電子カメラの各種動作状態を表示出力する。
【0028】
次に上記実施の形態の動作について説明する。
【0029】
ここでは、電子カメラの動作モードとして、記録(REC)モードと再生(PLAY)モードとがあり、さらに記録モード時には、静止画像と時間的に連続した連写画像のいずれかをモード設定により切換えて撮影できるものとする。連写画像は、例えば1秒当たり4枚×最大5秒間で計最大20枚分の画像を得ることができるものとする。
【0030】
静止画像のファイルはJPEG形式(拡張子.jpg)で、連写画像のファイルはモーションJPEG形式(拡張子.mjp)で、それぞれ媒体としての上記メモリカード18にその時点での日付時刻情報をファイル名として記録するものとする。
【0031】
まず、記録モード時の処理について説明する。
【0032】
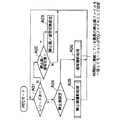
図2は記録モード時の主としてシステムコントローラ22による処理内容を示すもので、その当初にはキースイッチ部24のレリーズスイッチが操作されたか否かにより撮影の指示がなされたかどうかを判断し(ステップA01)、操作がない場合には、静止画像の撮影と連写画像の撮影とを切換えるためのモード設定スイッチの操作があったか否かを判断する(ステップA02)、という動作を繰返し実行することで、これらの入力を待機する。
【0033】
しかして、ステップA02で静止画像の撮影と連写画像の撮影とを切換えるためのモード設定スイッチの操作があったと判断した場合には、その操作に対応して静止画像モードと連写画像モードとを切換え設定し(ステップA03)、その後に再び上記ステップA01からの待機処理に戻る。
【0034】
また、ステップA01でレリーズスイッチが操作されたと判断すると、次いでその時点で静止画像モードが設定されているか否かを判断し(ステップA04)、静止画像モードが設定されている場合には、上記レリーズスイッチの操作に対応して静止画像の撮影処理を実行し(ステップA05)、その後に上記ステップA01に戻る。
【0035】
図3はこの静止画像の撮影処理のサブルーチンを示すもので、直ちにこのスイッチ操作に基づいてその時点での被写体像までの距離を測定し(ステップB01)、適性露出を計測し(ステップB02)、併せて適性ホワイトバランスを調整した上で(ステップB03)、適宜必要によりストロボ制御回路23でストロボ26を発光させて静止画像の撮影を実施する(ステップB04)。
【0036】
この場合、撮影によりCCD12から得られた画像データは各構成画素毎にA/D変換器13でデジタル化され、画像処理回路14でその時点で設定されている画質に合わせて適宜画素間引き等が行なわれた後にバッファメモリ15に蓄えられ、それから圧縮回路16でJPEGに基づいたADCT、ハフマン符号化等のデータ圧縮が施されてファイル化される(ステップB05)。
【0037】
このとき、併せて画像データのコントラスト値と上記ステップB01,B02で得られた自動合焦値(距離値)、及び自動露出値により予め用意された演算式を用いて演算を行なうことで、撮影した静止画像の評価値を算出し(ステップB06)、その後に上記画像データから構成画素を大幅に間引いたプレビュー画像としてのサムネイル画像を作成する(ステップB07)。
【0038】
そして、上記データ圧縮した静止画像の画像データファイルに上記評価値とサムネイル画像とを付加し、媒体制御回路17によりメモリカード18にその時点での日付時刻情報をファイル名として、例えば「19990309101030.jpg(1999年3月9日10時10分30秒に記録したJPEGファイルの意)」のように記録させて(ステップB08)、以上でこのサブルーチンを終了して上記図2の処理に戻る。
【0039】
また、図2の上記ステップA04でレリーズスイッチの操作が静止画像モードではなく連写画像モードの設定されている状態でなされたと判断した場合には、そのレリーズスイッチの操作に対応して連写画像の撮影処理を実行し(ステップA06)、その後に上記ステップA01に戻る。
【0040】
図4はこの連写画像の撮影処理のサブルーチンを示すもので、直ちにこのスイッチ操作に基づいてその時点での被写体像までの距離を測定し(ステップC01)、適性露出を計測し(ステップC02)、併せて適性ホワイトバランスを調整した上で(ステップC03)、適宜必要によりストロボ制御回路23でストロボ26を発光させて静止画像の撮影を実施する(ステップC04)。
【0041】
この場合、撮影によりCCD12から得られた画像データは各構成画素毎にA/D変換器13でデジタル化され、画像処理回路14でその時点で設定されている画質に合わせて適宜画素間引き等が行なわれた後にバッファメモリ15に蓄えられ、それから圧縮回路16でJPEGに基づいたADCT、ハフマン符号化等のデータ圧縮が施されてファイル化される(ステップC05)。
【0042】
このとき、併せて画像データのコントラスト値と上記ステップC01,C02で得られた自動合焦値(距離値)、及び自動露出値により予め用意された演算式を用いて演算を行なうことで、撮影した静止画像の評価値を算出し(ステップC06)、その後に上記画像データから構成画素を大幅に間引いたプレビュー画像としてのサムネイル画像を作成する(ステップC07)。
【0043】
そして、上記データ圧縮した静止画像の画像データファイルに上記評価値とサムネイル画像とを付加し、媒体制御回路17によりメモリカード18にその時点での日付時刻情報をファイル名として記録させる(ステップC08)。
【0044】
その後、上記レリーズスイッチがまだ操作されていることを確認し(ステップC09)、さらに連写撮影を開始してからの経過時間が予め制限された5秒に達していないことを確認しながら(ステップC10)、上記連写速度(4枚/秒)に基づく次の撮影タイミング、すなわちその前の撮影から0.25秒後となるのを待機し(ステップC11)、次の撮影タイミングとなったと判断した時点で、再び上記ステップC01からの処理を繰返す。
【0045】
こうして、ステップC09でレリーズスイッチの操作が解除されたと判断するか、あるいはステップC10で連写撮影を開始してからの経過時間が予め制限された5秒に達したと判断するまでの間、上記ステップC01〜C11の処理を繰返し実行し、時間的に連続した複数の静止画像のJPEGファイルをメモリカード18に記録していく。
【0046】
しかして、ステップC09でレリーズスイッチの操作が解除されたと判断するか、あるいはステップC10で連写撮影を開始してからの経過時間が予め制限された5秒に達したと判断すると、その時点で連写画像の撮影を終了し、後処理としてメモリカード18に記録した時間的に連続した複数の静止画像のJPEGファイルをモーションJPEGファイルとしてその時点での日付時刻情報をファイル名に、例えば「19990309101035.mjp(1999年3月9日10時10分35秒に記録したモーションJPEGファイルの意)」のように一括設定し(ステップC12)、以上でこのサブルーチンを終了して上記図2の処理に戻る。
【0047】
次に、上記のようにしてメモリカード18に記録された画像ファイルを再生モード時に表示出力させる際の動作について説明する。
【0048】
図5はキースイッチ部24のモード設定スイッチで再生モードを設定した状態からの処理内容を示すものである。同図に示すように、そのモード設定当初には、メモリカード18に記録されている複数の画像データのファイルの中でそのファイル名から最新のものを設定する(ステップD01)。
【0049】
次いで、その選択した最新の画像データのファイルが連写画像であるか否かを、そのファイル名の拡張子が「.mjp」であるか否かにより判断する(ステップD02)。
【0050】
ここで、選択された画像データのファイルが連写画像であると判断すると、この連写画像のファイルを構成する複数の静止画像ファイルそれぞれのサムネイル画像により、時間的に隣接する画像間での相関を得るための演算を実施し、その相関値が予め設定した閾値以内である画像の連続範囲を同一の構図を有する範囲として求める(ステップD03)。
【0051】
この場合、本来の静止画像の画像ファイルそのものではなく、大幅にデータ量の少ないサムネイル画像を用いて相関演算を実施するため、大まかな構図を判断する程度の相関演算がシステムコントローラ22にとって負担となることはなく、ごく短時間のうちに処理することができる。
【0052】
次いで、この同一の構図を有する範囲内の各静止画像データのファイルで、付加されている評価値が最も高いものを同連写画像を代表する静止画像として選択する(ステップD04)。
【0053】
そして、この選択した静止画像データのファイルを媒体制御回路17によりメモリカード18から読出させ、伸長回路21で伸長してビットマップ形式に展開した後にバッファメモリ15に記憶させる。
【0054】
このバッファメモリ15に記憶させた画像データを表示制御回路19に読出させ、表示制御回路19によりTFT−LCDパネル20で再生表示させる(ステップD05)。
【0055】
なお、上記ステップD02で、選択した画像データのファイルが連写画像ではなく静止画像であり、そのファイル名の拡張子が「.jpg」であると判断した場合には、上記ステップD03,D04の処理は省略して直接ステップD05においてその選択した静止画像のデータをメモリカード18から読出してTFT−LCDパネル20で表示させる。
【0056】
この再生表示を行なっている状態で、キースイッチ部24の「→」キーまたは「←」キーの操作があるか否かにより、その時点で表示させている画像を他のものに切換えるための操作を待機する(ステップD06,D07)。
【0057】
しかして、ステップD06で「→」キーが操作されたと判断すると、これはより新しい画像ファイルへの表示切換えを指示するための操作であるとして、メモリカード18に記録されている画像データのファイル名で現在表示している画像データより1つ新しい日付時刻情報が付されているものを選択した上で(ステップD08)、再び上記ステップD02からの処理を実行する。
【0058】
同様に、「←」キーが操作されたと判断すると、これはより古い画像ファイルへの表示切換えを指示するための操作であるとして、メモリカード18に記録されている画像データのファイル名で現在表示している画像データより1つ古い日付時刻情報が付されているものを選択した上で(ステップD09)、再び上記ステップD02からの処理を実行する。
【0059】
このように、連写記録中で最も撮影条件が良いと思われる静止画像を特別の操作を必要とせずに選択的に読出して表示再生させることができるため、連写画像から所望の静止画像を選択するための手間を大幅に簡略化することができる。
【0060】
さらに、上記撮影条件としてコントラスト値、自動合焦値、及び自動露出値を用いており、通常の静止画像撮影に際して用いている一般的な値から評価値の算出を行なうので、特別な計算を必要とせず、また評価の信頼性を高くすることができる。
【0061】
また、連写画像中に、ねらった構図以外の静止画像が入っており、且つその静止画像の評価値が本来の構図の静止画像の評価値より高かった場合でも、その影響を除去して、サムネイル画像による画像相関演算により時間的に連続した同一の構図と思われる範囲内から評価値の高いものを選択することができる。
【0062】
なお、上記実施の形態は、メモリカード18に記録した連写画像中から評価値の高い静止画像を選択して再生表示させる場合について説明したが、この電子カメラをプリンタ装置とライン接続して任意の静止画像をプリント出力させる場合であっても、プリント出力させる静止画像は電子カメラの側で選択することとなるので、同様の操作性を得ることができる。
【0063】
(第2の実施の形態)
次いで本発明を画像プリンタ装置に適用した場合の第2の実施の形態について図面を参照して説明する。
【0064】
まず、図6により画像プリンタ装置の具体的な回路構成を例示する。同図で、電子カメラでの撮影により画像データを記録したメモリカード18はこの画像プリンタ装置のメモリカードスロットに挿入されることでメモリ読出制御回路31に接続される。
【0065】
このメモリ読出制御回路31は、メモリカード18から任意の画像データのファイルを読出してデータ伸長などの処理を施してビットマップ形式に展開し、フレームメモリ32に記憶させる。
【0066】
このフレームメモリ32は、1画面分の静止画像データを記憶するもので、その記憶内容は熱転写プリント部33及び表示回路34に読出される。
【0067】
熱転写プリント部33は、例えば昇華型の熱転写プリンタでなり、フレームメモリ32から送られてくる画像データを専用紙に印刷して排出する。
【0068】
表示回路34は、フレームメモリ32から読出されてくる画像データに基づいてバックライト付のカラーTFT−LCDパネル35を表示駆動することで、メモリカード18から選択的に読出している内容を表示させる。
【0069】
しかるに、上記メモリ読出制御回路31、フレームメモリ32、及び熱転写プリント部33の動作をすべて制御部36が統括制御する。
【0070】
この制御部36は、画像を選択するための「←/→」キー37及びプリントの実行を指示する「プリント」キー38の操作を受けてこの画像プリンタ装置の全回路の動作制御を行なう。
【0071】
次に上記実施の形態の動作について説明する。
【0072】
ここでは、メモリカードスロットに挿入されたメモリカード18にJPEG形式(拡張子.jpg)の静止画像のデータファイルとモーションJPEG形式(拡張子.mjp)の連写画像のデータファイルとが各データファイル毎に撮影時の日付時刻情報をファイル名として混在して記録されており、且つ静止画像のデータのみならず連写画像を構成する個々の静止画像にもそれぞれサムネイル画像と評価値とが予め付加されているものとする。
【0073】
図7はメモリカードスロットにメモリカード18を挿入してこの画像プリンタ装置の電源が自動的に投入された状態からの処理内容を示すものである。同図に示すように、その動作当初には、メモリカード18に記録されている複数の画像データのファイルの中でそのファイル名から最新のものを設定する(ステップE01)。
【0074】
次いで、その選択した最新の画像データのファイルが連写画像であるか否かを、そのファイル名の拡張子が「.mjp」であるか否かにより判断する(ステップE02)。
【0075】
ここで、選択された画像データのファイルが連写画像であると判断すると、この連写画像のファイルを構成する複数の静止画像ファイルそれぞれのサムネイル画像により、時間的に隣接する画像間での相関を得るための演算を実施し、その相関値が予め設定した閾値以内である画像の連続範囲を同一の構図を有する範囲として求める(ステップE03)。
【0076】
この場合、本来の静止画像の画像ファイルそのものではなく、大幅にデータ量の少ないサムネイル画像を用いて相関演算を実施するため、大まかな構図を判断する程度の相関演算が制御部36にとって負担となることはなく、ごく短時間のうちに処理することができる。
【0077】
次いで、この同一の構図を有する範囲内の各静止画像データのファイルで、付加されている評価値が最も高いものを同連写画像を代表する静止画像として選択する(ステップE04)。
【0078】
そして、この選択した静止画像のデータファイルをメモリ読出制御回路31によりメモリカード18から読出し、伸長してビットマップ形式に展開した後にフレームメモリ32に記憶させる。
【0079】
このフレームメモリ32に記憶した画像データを適宜画素間引きを行ないながら表示回路34に読出させ、表示回路349によりTFT−LCDパネル35で再生表示させる(ステップE05)。
【0080】
また、上記ステップE02で、選択した画像データのファイルが連写画像ではなく静止画像であり、そのファイル名の拡張子が「.jpg」であると判断した場合には、上記ステップE03,E04の処理は省略して直接ステップE05においてその選択した静止画像データをメモリカード18から読出してTFT−LCDパネル35で表示させる。
【0081】
この再生表示を行なっている状態で、「←/→」キー37で「→」キーまたは「←」キーの操作があるか否かにより、その時点で表示させている画像を他のものに切換えるための操作があったか否かを判断し(ステップE06,E07)、さらに「プリント」キー38により表示している静止画像のプリント出力を指示するキー操作がなされた否かを判断する(ステップE08)、という処理を繰返し実行することで、これらのキー入力を待機する。
【0082】
しかして、ステップE06で「←/→」キー37の「→」キーが操作されたと判断すると、これはより新しい画像ファイルへの表示切換えを指示するための操作であるとして、メモリカード18に記録されている画像データのファイル名で現在表示している画像データより1つ新しい日付時刻情報が付されているものを選択した上で(ステップE09)、再び上記ステップE02からの処理を実行する。
【0083】
同様に、ステップE07で「←/→」キー37の「←」キーが操作されたと判断すると、これはより古い画像ファイルへの表示切換えを指示するための操作であるとして、メモリカード18に記録されている画像データのファイル名で現在表示している画像データより1つ古い日付時刻情報が付されているものを選択した上で(ステップE10)、再び上記ステップE02からの処理を実行する。
【0084】
そして、ステップE08で「プリント」キー38が操作されたと判断した場合には、その時点でフレームメモリ32に記憶されているビットマップ状の静止画像をフルに活用して熱転写プリント部33で専用紙に印刷出力させ(ステップE11)、その後に上記ステップE02からの処理に戻る。
【0085】
このように、時間的に連続した静止画像からなる連写画像中で最も撮影条件が良いと思われる静止画像を特別の操作を必要とせずに選択的に読出してプリント出力させることができるため、連写画像から所望の静止画像を選択するための手間を大幅に簡略化することができる。
【0086】
なお、上記実施の形態では、メモリカード18に記録されている静止画像及び連写画像を構成する個々の静止画像は、それぞれその評価値を予め付加しているものとして説明したが、該評価値に代えて、コントラスト値、自動合焦値、自動露出値等の撮影条件を付加し、特に連写画像が選択された場合にはその連写画像を構成する個々の静止画像毎に撮影条件から評価値を算出して、最も高い評価値を有する静止画像をその連写画像を代表するものとして選択して表示させるようにしてもよい。
【0087】
このようにすると、画像データにその撮影条件等をデータとして付加するのは多くの電子カメラで一般的に行なっていることであるので、画像を撮影した電子カメラの機種等を限定することなしに、画像の評価の高いものを選択してプリントさせることができる。
【0088】
また、この際、通常の静止画像撮影に際して用いている一般的な値から評価値の算出を行なうので、特別な計算を必要とせず、また評価の信頼性を高くすることができる。
【0089】
なお、上記第1及び第2の実施の形態は本発明を限定するためのものではなく、本発明はその要旨を逸脱しない範囲内で種々限定して実施することが可能であるものとする。
【0090】
【発明の効果】
請求項1記載の発明によれば、連写画像中で最も撮影条件が良いと思われる静止画像を特別の操作を必要とせずに選択的に読出して表示出力またはプリント出力させることができるために、連写画像から所望の静止画像を選択するための手間を大幅に簡略化することができる。
【0091】
請求項2記載の発明によれば、上記請求項1記載の発明の効果に加えて、通常の静止画像撮影に際して用いている値から評価値の算出を行なうので、特別な計算を必要とせず、また評価の信頼性を高くすることができる。
【0092】
請求項3記載の発明によれば、上記請求項1記載の発明の効果に加えて、例えば、連写画像中に、ねらった構図以外の静止画像が入っており、且つその静止画像の評価値が本来の構図の静止画像の評価値より高かった場合でも、その影響を除去して、ねらった構図を有する静止画像の中から、評価値の高いものを選択することができる。また、プレビュー(サムネイル)画像はデータ量が本画像より大幅に少ないため、大まかな構図を判断する程度の相関演算が負担となることはなく、短時間のうちに処理できる。
【0094】
請求項4記載の発明によれば、連写記録中で最も撮影条件が良いと思われる静止画像を特別の操作を必要とせずに選択的に読出してプリント出力させることができるため、連写画像から所望の静止画像を選択するための手間を大幅に簡略化することができる。また、プリンタ側で各静止画像の撮影条件から評価値を算出するために、画像に撮影条件のデータを付加するのは多くの電子カメラで通常に行なっていることであるから、電子カメラのより多くの機種に対応することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る電子カメラの回路構成を示すブロック図。
【図2】同実施の形態に係る記録モード時の処理内容を示すフローチャート。
【図3】図2の静止画像の撮影処理のサブルーチンの内容を示すフローチャート。
【図4】図2の連写画像の撮影処理のサブルーチンの内容を示すフローチャート。
【図5】同実施の形態に係る再生モード時の処理内容を示すフローチャート。
【図6】本発明の第2の実施の形態に係る画像プリンタ装置の回路構成を示すブロック図。
【図7】同実施の形態に係るプリント出力の処理内容を示すフローチャート。
【符号の説明】
11…光学レンズ系
12…CCD
13…A/D変換器
14…画像処理回路
15…バッファメモリ
16…圧縮回路
17…媒体制御回路
18…メモリカード
19…表示制御回路
20…TFT−LCDパネル
21…伸長回路
22…システムコントローラ
23…ストロボ制御回路
24…キースイッチ部
25…ガイドパネル
26…ストロボ
31…メモリ読出制御回路
32…フレームメモリ
33…熱転写プリント部
34…表示回路
35…TFT−LCDパネル
36…制御部
37…「←/→」キー
38…「プリント」キー[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an electronic camera having a continuous shooting function and an image printer apparatus for printing a continuous shooting image taken by the electronic camera.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Recently, as the capacity of recording media (memory) has increased and the processing speed of captured images has increased, not only still images but also continuous shooting functions that capture continuous images consisting of temporally continuous still images have been developed. Various electronic still cameras have been commercialized.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
Thus, when the continuous shooting function obtains a continuous image file consisting of a large number of still images continuous in time, there is no problem in handling the entire continuous image file as one moving image file. If the continuous shooting function is used to avoid missing the desired shutter chance, or if the continuous shooting function is used because there is a fear that only one still image shooting will fail, from among the continuous shooting image file It is necessary to select an appropriate shutter timing or the best image.
[0004]
However, in general, in order to select an arbitrary still image from among continuous shot images, it is necessary to instruct frame advance in the playback mode and display individual still images constituting the continuous shot image one by one. The operation was very complicated.
[0005]
The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and the purpose of the present invention is to select a still image with the best image from among continuously shot images taken without requiring a complicated operation. It is an object to provide an electronic camera and an image printer apparatus that can be displayed or used for printing.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The invention according to claim 1 is a first instruction means for instructing photographing of continuous shot images composed of still images that are temporally continuous; the above First instruction means Instructions Photographing means for photographing continuous shot images by, the above Calculation means for calculating an evaluation value from the shooting conditions for each still image constituting a continuous shot image shot by the shooting means; the above Add the evaluation value calculated by the calculation means to the corresponding still image Record Recording means for recording on a medium; and Record Second instruction means for instructing output of a continuous shot image recorded on the medium; the above Selecting means for selecting a still image according to an evaluation value added to each still image constituting the continuous image instructed by the second instruction means; the above The still image selected by the selection means Record Output means for reading out from the medium and outputting the medium.
[0007]
With such a configuration, a still image that seems to have the best shooting conditions among continuous shot images can be selectively read out without requiring any special operation, and can be displayed or printed out. The effort for selecting a desired still image from the captured image can be greatly simplified.
[0008]
According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the first aspect of the present invention, the calculation means uses at least one of a contrast value, an automatic focus value, and an automatic exposure value as a photographing condition.
[0009]
With such a configuration, in addition to the operation of the first aspect of the invention, the evaluation value is calculated from the value used in normal still image shooting, so that no special calculation is required and the evaluation is performed. The reliability of can be increased.
[0010]
According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the first aspect of the present invention, each of the still images constituting the continuous shot image photographed by the photographing means is configured. Thinned out pixels A preview image creating means for creating a preview image is further provided, and the recording means creates the evaluation value obtained by the calculating means and the preview image creating means. preview Append the image to the corresponding still image Above record The still image recorded in the medium and having the same composition is obtained by performing correlation calculation of the preview image added to each still image constituting the continuous shot image selected by the second instruction unit. A still image range is specified, and a still image is selected according to the evaluation value from among the still images within the specified range.
[0011]
With such a configuration, in addition to the operation of the invention described in claim 1, for example, a still image other than the intended composition is included in the continuous shot image, and the evaluation value of the still image is originally Even when the evaluation value is higher than the evaluation value of the still image with the composition, it is possible to remove the influence and select the still image with the higher evaluation value from the still images having the intended composition. In addition, since the preview (thumbnail) image has a data amount much smaller than that of the main image, the correlation calculation to determine the rough composition is not burdened and can be processed in a short time.
[0014]
Claim 4 In the described invention, continuous shooting images are recorded with their shooting conditions added to temporally continuous still images. Record Load media Record Medium mounting means, and Record Instruction means for instructing output of continuous shot images recorded on the medium; the above Calculating means for calculating an evaluation value from each shooting condition added to each still image constituting the continuous shot image instructed by the instruction means; the above Selection means for selecting a still image according to the evaluation value obtained by the calculation means; the above The still image selected by the selection means Record And printing means for reading out from the medium and printing out.
[0015]
With such a configuration, it is possible to selectively read out and print out a still image that seems to have the best shooting conditions during continuous shooting recording without requiring a special operation. It is possible to greatly simplify the effort for selecting a still image. Also, in order to calculate the evaluation value from the shooting conditions of each still image on the printer side, it is normal for many electronic cameras to add shooting condition data to the image. It can support many models.
[0016]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
(First embodiment)
A first embodiment when the present invention is applied to an electronic still camera having a continuous shooting function will be described below with reference to the drawings.
[0017]
First, FIG. 1 illustrates a specific circuit configuration of the electronic camera. In the figure, in the recording mode, the optical lens system 11 forms an optical image of the subject on the
[0018]
The
[0019]
The
[0020]
In addition, when it is desired to monitor the photographing contents in this recording mode, the number of pixels is greatly increased from the
[0021]
On the other hand, in the reproduction mode, the image data file recorded on the
[0022]
The image data stored in the
[0023]
Thus, the
[0024]
This
[0025]
The
[0026]
The
[0027]
The
[0028]
Next, the operation of the above embodiment will be described.
[0029]
Here, the operation mode of the electronic camera includes a recording (REC) mode and a playback (PLAY) mode. In the recording mode, either a still image or a continuous continuous image is switched by mode setting. It shall be possible to shoot. For example, it is assumed that continuous shot images can obtain images of a maximum of 20 images in a total of 4 images per second × maximum 5 seconds.
[0030]
The still image file is in JPEG format (extension .jpg), the continuous shot image file is in motion JPEG format (extension .mjp), and the date and time information at that time is filed in the
[0031]
First, processing in the recording mode will be described.
[0032]
FIG. 2 mainly shows the contents of processing by the
[0033]
If it is determined in step A02 that there has been an operation of a mode setting switch for switching between still image shooting and continuous shooting image shooting, the still image mode and the continuous shooting image mode are set in response to the operation. Is switched (step A03), and then the process returns to the standby process from step A01.
[0034]
If it is determined in step A01 that the release switch has been operated, it is then determined whether or not the still image mode is set at that time (step A04). If the still image mode is set, the release is performed. In response to the switch operation, a still image shooting process is executed (step A05), and then the process returns to step A01.
[0035]
FIG. 3 shows a sub-routine of the still image shooting process. Immediately based on this switch operation, the distance to the subject image at that time is measured (step B01), and the appropriate exposure is measured (step B02). At the same time, after adjusting the appropriate white balance (step B03), the
[0036]
In this case, image data obtained from the
[0037]
At this time, the calculation is performed by using an arithmetic expression prepared in advance based on the contrast value of the image data, the automatic focus value (distance value) obtained in steps B01 and B02, and the automatic exposure value. The evaluation value of the still image is calculated (step B06), and then a thumbnail image is created as a preview image in which the constituent pixels are substantially thinned out from the image data (step B07).
[0038]
Then, the evaluation value and the thumbnail image are added to the image data file of the compressed still image, and the date and time information at that time is added to the
[0039]
If it is determined in step A04 of FIG. 2 that the release switch is operated not in the still image mode but in the continuous image mode, the continuous image corresponding to the release switch is operated. Is executed (step A06), and then the process returns to step A01.
[0040]
FIG. 4 shows a sub-routine of the continuous image photographing process. Immediately based on this switch operation, the distance to the subject image at that time is measured (step C01), and the appropriate exposure is measured (step C02). In addition, after adjusting the appropriate white balance (step C03), if necessary, the
[0041]
In this case, image data obtained from the
[0042]
At this time, the calculation is performed by using an arithmetic expression prepared in advance based on the contrast value of the image data, the automatic focus value (distance value) obtained in steps C01 and C02, and the automatic exposure value. The evaluation value of the still image thus calculated is calculated (step C06), and then a thumbnail image is created as a preview image obtained by thinning out the constituent pixels from the image data (step C07).
[0043]
Then, the evaluation value and the thumbnail image are added to the image data file of the compressed still image, and the date and time information at that time is recorded as a file name in the
[0044]
Thereafter, it is confirmed that the release switch is still operated (step C09), and further, while confirming that the elapsed time from the start of continuous shooting has not reached the previously limited 5 seconds (step S09). C10) Waits for the next shooting timing based on the continuous shooting speed (4 frames / second), that is, 0.25 seconds after the previous shooting (step C11), and determines that the next shooting timing has come. At this point, the processing from step C01 is repeated.
[0045]
Thus, until it is determined in step C09 that the operation of the release switch has been released, or until it is determined in step C10 that the elapsed time from the start of continuous shooting has reached the previously limited 5 seconds, The processes in steps C01 to C11 are repeatedly executed, and a plurality of still image JPEG files that are temporally continuous are recorded in the
[0046]
If it is determined in step C09 that the release switch operation has been released, or if it is determined in step C10 that the elapsed time from the start of continuous shooting has reached 5 seconds, which is limited in advance, at that time. The continuous shooting image shooting is finished, and a plurality of temporally continuous still image JPEG files recorded in the
[0047]
Next, an operation for displaying and outputting the image file recorded on the
[0048]
FIG. 5 shows the processing contents from the state in which the playback mode is set by the mode setting switch of the
[0049]
Next, it is determined whether or not the selected latest image data file is a continuous shot image based on whether or not the extension of the file name is “.mjp” (step D02).
[0050]
If it is determined that the selected image data file is a continuous shot image, the correlation between the temporally adjacent images is determined by the thumbnail images of each of the plurality of still image files constituting the continuous shot image file. And a continuous range of images whose correlation value is within a preset threshold is determined as a range having the same composition (step D03).
[0051]
In this case, since the correlation calculation is performed using the thumbnail image having a significantly small amount of data, not the original still image file itself, the correlation calculation to the extent that the rough composition is determined becomes a burden on the
[0052]
Next, among the still image data files in the range having the same composition, the one with the highest evaluation value added is selected as a still image representing the continuous shot image (step D04).
[0053]
Then, the selected still image data file is read from the
[0054]
The image data stored in the
[0055]
If it is determined in step D02 that the selected image data file is not a continuous image but a still image and the file name extension is “.jpg”, the above-described steps D03 and D04 are performed. The processing is omitted, and the selected still image data is directly read from the
[0056]
An operation for switching the image displayed at that time to another image depending on whether or not the “→” key or the “←” key of the
[0057]
If it is determined in step D06 that the “→” key has been operated, the file name of the image data recorded on the
[0058]
Similarly, if it is determined that the “←” key has been operated, it is assumed that this is an operation for instructing to switch the display to an older image file, and the file name of the image data recorded in the
[0059]
In this way, since a still image that seems to have the best shooting conditions during continuous shooting recording can be selectively read out and displayed without requiring any special operation, a desired still image can be reproduced from the continuous shooting image. The labor for selection can be greatly simplified.
[0060]
Furthermore, contrast values, autofocus values, and autoexposure values are used as the above shooting conditions, and evaluation values are calculated from general values used for normal still image shooting, requiring special calculations. In addition, the reliability of the evaluation can be increased.
[0061]
In addition, even if still images other than the intended composition are included in the continuous shot image, and the evaluation value of the still image is higher than the evaluation value of the still image of the original composition, the influence is removed, An image having a high evaluation value can be selected from a range considered to be the same composition in time sequence by image correlation calculation using thumbnail images.
[0062]
In the above embodiment, a case has been described in which a still image with a high evaluation value is selected from the continuously shot images recorded on the
[0063]
(Second Embodiment)
Next, a second embodiment when the present invention is applied to an image printer apparatus will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0064]
First, FIG. 6 illustrates a specific circuit configuration of the image printer apparatus. In the figure, a
[0065]
The memory read
[0066]
The
[0067]
The thermal
[0068]
The
[0069]
However, the
[0070]
In response to the operation of the “← / →” key 37 for selecting an image and the “print”
[0071]
Next, the operation of the above embodiment will be described.
[0072]
Here, a data file of still image data in JPEG format (extension .jpg) and a data file of continuous shot images in motion JPEG format (extension .mjp) are stored in the
[0073]
FIG. 7 shows the processing contents from the state in which the
[0074]
Next, it is determined whether or not the selected latest image data file is a continuous image based on whether or not the extension of the file name is “.mjp” (step E02).
[0075]
If it is determined that the selected image data file is a continuous shot image, the correlation between the temporally adjacent images is determined by the thumbnail images of each of the plurality of still image files constituting the continuous shot image file. A continuous range of images whose correlation value is within a preset threshold value is obtained as a range having the same composition (step E03).
[0076]
In this case, since the correlation calculation is performed using the thumbnail image having a significantly small data amount, not the original still image file itself, the correlation calculation to the extent that the rough composition is determined becomes a burden on the
[0077]
Next, among the still image data files within the range having the same composition, the one with the highest evaluation value added is selected as a still image representing the continuous shot image (step E04).
[0078]
The selected still image data file is read from the
[0079]
The image data stored in the
[0080]
If it is determined in step E02 that the selected image data file is not a continuous shot image but a still image and the file name extension is “.jpg”, the above steps E03 and E04 are performed. The processing is omitted, and the selected still image data is directly read from the
[0081]
While this playback display is being performed, the image displayed at that time is switched to another depending on whether the “→” key or the “←” key is operated with the “← / →”
[0082]
If it is determined in step E06 that the “→” key of the “← / →” key 37 has been operated, it is recorded on the
[0083]
Similarly, when it is determined in step E07 that the “←” key of the “← / →” key 37 has been operated, this is recorded in the
[0084]
If it is determined in step E08 that the “print”
[0085]
In this way, it is possible to selectively read out and print out a still image that seems to have the best shooting conditions among continuous shot images consisting of still images continuous in time, without requiring a special operation. The effort for selecting a desired still image from the continuous shot images can be greatly simplified.
[0086]
In the above-described embodiment, the still image recorded on the
[0087]
In this way, since it is common for many electronic cameras to add the shooting conditions and the like to the image data as data, without limiting the model of the electronic camera that shot the image. It is possible to select and print an image with a high image evaluation.
[0088]
At this time, since the evaluation value is calculated from the general value used for normal still image shooting, no special calculation is required and the reliability of the evaluation can be increased.
[0089]
The first and second embodiments are not intended to limit the present invention, and the present invention can be implemented in various ways without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
[0090]
【The invention's effect】
According to the first aspect of the present invention, it is possible to selectively read out and display or print out a still image that seems to have the best shooting conditions among continuous shot images without requiring any special operation. Thus, the effort for selecting a desired still image from the continuous shot images can be greatly simplified.
[0091]
According to the invention described in claim 2, in addition to the effect of the invention described in claim 1 above, the evaluation value is calculated from the value used in normal still image shooting, so no special calculation is required. Moreover, the reliability of evaluation can be increased.
[0092]
According to the invention described in claim 3, in addition to the effect of the invention described in claim 1, for example, a still image other than the intended composition is included in the continuous shot image, and the evaluation value of the still image Even if the evaluation value is higher than the evaluation value of the still image of the original composition, it is possible to select the one having a high evaluation value from among the still images having the aimed composition by removing the influence. In addition, since the preview (thumbnail) image has a data amount much smaller than that of the main image, the correlation calculation to determine the rough composition is not burdened and can be processed in a short time.
[0094]
Claim 4 According to the described invention, a still image that seems to have the best shooting conditions during continuous shooting recording can be selectively read out and printed out without requiring any special operation. The effort for selecting a still image can be greatly simplified. Also, in order to calculate the evaluation value from the shooting conditions of each still image on the printer side, it is normal for many electronic cameras to add shooting condition data to the image. It can support many models.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a circuit configuration of an electronic camera according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing processing contents in a recording mode according to the embodiment.
3 is a flowchart showing the contents of a still image shooting processing subroutine of FIG. 2;
4 is a flowchart showing the contents of a subroutine for continuous image shooting processing in FIG. 2;
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing processing contents in a playback mode according to the embodiment;
FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a circuit configuration of an image printer apparatus according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing processing contents of print output according to the embodiment;
[Explanation of symbols]
11 ... Optical lens system
12 ... CCD
13 ... A / D converter
14 Image processing circuit
15 ... Buffer memory
16: Compression circuit
17 ... Medium control circuit
18 ... Memory card
19 ... Display control circuit
20 ... TFT-LCD panel
21 ... Extension circuit
22 ... System controller
23. Strobe control circuit
24 ... Key switch
25 ... Guide panel
26 Strobe
31. Memory read control circuit
32 ... Frame memory
33 ... Thermal transfer print section
34. Display circuit
35 ... TFT-LCD panel
36 ... Control unit
37 ... "← / →" key
38 ... "Print" key
Claims (4)
上記第1の指示手段の指示により連写画像を撮影する撮影手段と、
上記撮影手段により撮影される連写画像を構成する個々の静止画像に対し、その撮影条件から評価値を算出する算出手段と、
上記算出手段により算出した評価値を対応する静止画像に付加して記録媒体に記録する記録手段と、
上記記録媒体に記録された連写画像の出力を指示する第2の指示手段と、
上記第2の指示手段で指示された連写画像を構成する各静止画像に付加されている評価値に応じて静止画像を選択する選択手段と、
上記選択手段で選択した静止画像を上記記録媒体から読出して出力する出力手段と
を具備したことを特徴とする電子カメラ。First instruction means for instructing to shoot continuous images composed of still images that are temporally continuous;
A photographing means for photographing a continuous image by an instruction of said first instruction means,
To each still image constituting the continuous image captured by the imaging means, and calculating means for calculating an evaluation value from the imaging conditions,
Recording means for recording on a recording medium in addition to the still image corresponding evaluation value calculated by the calculating means,
Second instruction means for instructing output of continuous shot images recorded on the recording medium;
Selection means for selecting a still image according to the evaluation value that is added to each still image constituting the continuous image instructed by the second instructing means,
An electronic camera, characterized in that the still image selected by the selection means to and an output means for outputting reads from the recording medium.
上記記録手段は、上記算出手段で得た評価値と上記プレビュー画像作成手段が作成したプレビュー画像とを対応する静止画像に付加して上記記録媒体に記録し、
上記選択手段は、上記第2の指示手段により選択された連写画像を構成する各静止画像に付加されているプレビュー画像の相関演算を行なうことで同一の構図を有する静止画像の静止画像の範囲を特定し、特定した範囲内の静止画像中からその評価値に応じて静止画像を選択する
ことを特徴とする請求項1記載の電子カメラ。A preview image creating means for creating a preview image obtained by thinning out constituent pixels from individual still images constituting a continuous shot image photographed by the photographing means;
It said recording means adds the preview image evaluation value obtained by the calculating means and the preview image creating device creates the corresponding still image recorded on the recording medium,
The selection means performs a correlation operation of the preview images added to the still images constituting the continuous shot image selected by the second instruction means, thereby causing a still image range of still images having the same composition. The electronic camera according to claim 1, wherein a still image is selected according to an evaluation value from among still images within the specified range.
上記記録媒体に記録された連写画像の出力を指示する指示手段と、
上記指示手段で指示された連写画像を構成する各静止画像に付加されている撮影条件からそれぞれ評価値を算出する算出手段と、
上記算出手段で得た評価値に応じて静止画像を選択する選択手段と、
上記選択手段で選択した静止画像を上記記録媒体から読出してプリント出力するプリント手段と
を具備したことを特徴とする画像プリンタ装置。A recording medium mounting unit for mounting the recording medium are recorded as continuous images temporally continuous respectively to the still image that photographing condition is appended to,
Instruction means for instructing output of continuous shot images recorded on the recording medium;
Calculation means for calculating the respective evaluation values from the imaging condition that is added to each still image constituting the continuous image instructed by the instruction means,
Selection means for selecting a still image according to the evaluation value obtained by the calculating means,
Image printing apparatus, characterized in that the still image selected by the selection means to and a printing means for printing out by reading from the recording medium.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP17408599A JP4157228B2 (en) | 1999-06-21 | 1999-06-21 | Electronic camera and image printer apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP17408599A JP4157228B2 (en) | 1999-06-21 | 1999-06-21 | Electronic camera and image printer apparatus |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001008135A JP2001008135A (en) | 2001-01-12 |
| JP2001008135A5 JP2001008135A5 (en) | 2006-04-06 |
| JP4157228B2 true JP4157228B2 (en) | 2008-10-01 |
Family
ID=15972400
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP17408599A Expired - Fee Related JP4157228B2 (en) | 1999-06-21 | 1999-06-21 | Electronic camera and image printer apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4157228B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4695785B2 (en) * | 2001-07-27 | 2011-06-08 | キヤノン株式会社 | IMAGING DEVICE, IMAGING DEVICE CONTROL METHOD, COMPUTER-READABLE STORAGE MEDIUM, AND PROGRAM |
| JP4654552B2 (en) * | 2001-09-06 | 2011-03-23 | ソニー株式会社 | Image recording / reproducing apparatus, reproducing apparatus, recording / reproducing method, and reproducing method |
| JP2003304492A (en) | 2002-02-08 | 2003-10-24 | Canon Inc | Image processing device |
| JP3984175B2 (en) | 2003-01-31 | 2007-10-03 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Photo image sorting apparatus and program |
| US7602836B2 (en) | 2003-12-01 | 2009-10-13 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd | Receiver |
| JP5324152B2 (en) * | 2008-07-31 | 2013-10-23 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program |
| JP4661964B2 (en) | 2009-02-09 | 2011-03-30 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | Imaging apparatus and program |
-
1999
- 1999-06-21 JP JP17408599A patent/JP4157228B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001008135A (en) | 2001-01-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7417667B2 (en) | Imaging device with function to image still picture during moving picture imaging | |
| JPH1118044A (en) | Digital still camera | |
| JP4140231B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP2001169167A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP2008085689A (en) | Image pickup device, image pickup control program and image pickup control method | |
| JP3747914B2 (en) | Image recording apparatus, image recording method, and program | |
| JP4157228B2 (en) | Electronic camera and image printer apparatus | |
| JP4349873B2 (en) | Digital camera and image data recording method | |
| JP4905017B2 (en) | Image display apparatus and program | |
| JP5539078B2 (en) | Display control apparatus, method, program, and recording medium | |
| JP3880489B2 (en) | IMAGING DEVICE, DATA PROCESSING METHOD IN IMAGING DEVICE, STORAGE MEDIUM, AND PROGRAM | |
| JP2000352759A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP2001186397A (en) | Electronic camera | |
| JP2004186866A (en) | Image recording apparatus | |
| JP4211764B2 (en) | Electronic camera, image recording apparatus, image recording method and program | |
| JP3064948B2 (en) | An electronic camera that can change the compression ratio of image information | |
| JP4276763B2 (en) | Electronic camera device | |
| JP4735495B2 (en) | Voice processing apparatus and program | |
| JP2005236483A (en) | Image processing apparatus and program thereof | |
| JP2001111965A (en) | Image reproducing device, electronic camera and printer device | |
| JP2006279303A (en) | Digital camera | |
| JP4872728B2 (en) | Movie recording apparatus and program | |
| JP4147935B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, image reproducing apparatus, and program | |
| JP2005303807A (en) | Photography-taking apparatus and method and program | |
| JP3885271B2 (en) | CAMERA DEVICE, CAMERA DEVICE EXPOSURE CONTROL METHOD, AND RECORDING MEDIUM |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060216 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060216 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080507 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080604 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080708 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080711 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110718 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110718 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120718 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130718 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |