JP2005303807A - Photography-taking apparatus and method and program - Google Patents
Photography-taking apparatus and method and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005303807A JP2005303807A JP2004119110A JP2004119110A JP2005303807A JP 2005303807 A JP2005303807 A JP 2005303807A JP 2004119110 A JP2004119110 A JP 2004119110A JP 2004119110 A JP2004119110 A JP 2004119110A JP 2005303807 A JP2005303807 A JP 2005303807A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- change amount
- photographing
- time
- setting
- image
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Abandoned
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、特にインターバル撮影機能を備えたデジタルスチルカメラ等に好適な撮影装置、撮影方法及びプログラムに関する。 The present invention relates to a photographing apparatus, a photographing method, and a program suitable for a digital still camera having an interval photographing function.
従来より、デジタルスチルカメラで、インターバル時間を予め設定しておくことで、その設定した時間間隔で自動的に連続して撮影を実行するインターバル撮影機能を有したものが考えられている。(例えば、特許文献1)
このインターバル撮影機能では、カメラを三脚等に固定した上で、数[秒]乃至1時間程度のインターバル時間をユーザが任意に設定することにより、被写体となる花の開花や昆虫の羽化の様子、星の軌跡等を自動的に撮影することができるものである。
In this interval shooting function, the camera is fixed on a tripod, etc., and the user arbitrarily sets an interval time of several [seconds] to about 1 hour, so that the flower that becomes the subject blooms and the insect emerges, It is possible to automatically photograph the trajectory of stars.
上述した如く、インターバル時間はユーザが予め被写体の時間的な変化の度合いを想定して任意に設定しておくものであり、必ずしも実際の被写体が設定通りの時間的な変化を示すものではない。 As described above, the interval time is arbitrarily set by the user in advance assuming the degree of temporal change of the subject, and the actual subject does not necessarily indicate the temporal change as set.
そのため、例えば花の開花の様子を撮影しようとした結果、蕾のままの画像のみが多数撮影され、開花の途中の様子が全く撮影されない、というような事態も充分起こり得る。 For this reason, for example, as a result of trying to photograph the state of flowering, it is possible that a large number of only the images of the buds are photographed and the state during the flowering is not photographed at all.
本発明は上記のような実情に鑑みてなされたもので、その目的とするところは、インターバル撮影機能に代表される時間的に連続した複数の画像をユーザの意図に合わせて失敗することなく撮影することが可能な撮影装置、撮影方法及びプログラムを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and its purpose is to shoot a plurality of temporally continuous images represented by the interval shooting function without failure according to the user's intention. It is an object of the present invention to provide a photographing apparatus, a photographing method, and a program that can be used.
請求項1記載の発明は、撮影手段と、この撮影手段で撮影した画像を記録する記録手段と、上記撮影手段で時間的に連続して撮影する画像の変化量を設定する変化量設定手段と、上記撮影手段で時間的に連続して撮影される画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出手段と、この変化量算出手段で得た変化量と上記変化量設定手段で設定した変化量との比較結果により上記撮影手段で撮影された画像の上記記録手段への記録を制御する記録制御手段とを具備したことを特徴とする。
The invention described in
請求項2記載の発明は、上記請求項1記載の発明において、上記撮影手段が時間的に連続して画像を撮影する最低時間間隔を設定する時間間隔設定手段をさらに具備したことを特徴とする。
The invention described in
請求項3記載の発明は、時間的に連続して画像を撮影する時間間隔を設定する時間間隔設定手段と、この時間間隔設定手段で設定した時間間隔にしたがって画像を撮影する撮影手段と、この撮影手段で撮影した画像を記録する記録手段と、上記記録手段に記録された時間的に連続した画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出手段と、上記記録手段の空き容量を算出する残量検出手段と、この残量検出手段で上記記録手段が所定の空き容量となったことを検出すると、上記変化量算出手段で記録手段に記録された一連の画像中から最も変化量の少ないものを選択し、削除する削除制御手段とを具備したことを特徴とする。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, there is provided a time interval setting means for setting a time interval for taking images continuously in time, a photographing means for photographing images according to the time interval set by the time interval setting means, A recording unit that records an image captured by the imaging unit, a temporally continuous image recorded in the recording unit, a change amount calculating unit that calculates the amount of change, and a free space of the recording unit are calculated. When the remaining amount detecting means detects that the recording means has reached a predetermined free capacity, the change amount calculating means detects the largest amount of change from the series of images recorded on the recording means. A deletion control means for selecting and deleting a small number is provided.
請求項4記載の発明は、上記請求項3記載の発明において、上記撮影手段で時間的に連続する画像の撮影の終了を設定する終了設定手段をさらに具備したことを特徴とする。 According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, in the third aspect of the present invention, the image forming apparatus further includes an end setting unit configured to set an end of time-continuous image capturing by the image capturing unit.
請求項5記載の発明は、上記請求項4記載の発明において、上記終了設定手段は、上記撮影手段が撮影を開始してから終了するまでの総撮影時間を設定することを特徴とする。
The invention according to claim 5 is the invention according to
請求項6記載の発明は、上記請求項4記載の発明において、上記終了設定手段は、上記撮影手段が撮影を開始してから終了するまでの総撮影画像数を設定することを特徴とする。
The invention described in claim 6 is the invention described in
請求項7記載の発明は、画像を撮影して記録する撮影装置での撮影方法であって、時間的に連続して撮影する画像の変化量を設定する変化量設定工程と、時間的に連続して撮影される画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出工程と、この変化量算出工程で得た変化量と上記変化量設定工程で設定した変化量との比較結果により撮影された画像の記録を制御する記録制御工程とを有したことを特徴とする。 The invention according to claim 7 is a photographing method in a photographing apparatus for photographing and recording an image, and a change amount setting step for setting a change amount of an image photographed continuously in time, and a time continuous The change amount calculation step for comparing the images to be photographed and calculating the change amount, and the comparison result between the change amount obtained in the change amount calculation step and the change amount set in the change amount setting step. And a recording control step for controlling recording of the image.
請求項8記載の発明は、画像を撮影して媒体に記録する撮影装置での撮影方法であって、時間的に連続して画像を撮影する時間間隔を設定する時間間隔設定工程と、この時間間隔設定工程で設定した時間間隔で撮影され、上記媒体に記録された、時間的に連続した画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出工程と、上記媒体の空き容量を算出する残量検出工程と、この残量検出工程で上記媒体が所定の空き容量となったことを検出すると、上記変化量算出工程で媒体に記録された一連の画像中から最も変化量の少ないものを選択し、削除する削除制御工程とを有したことを特徴とする。 The invention according to claim 8 is a photographing method in a photographing apparatus for photographing an image and recording it on a medium, a time interval setting step for setting a time interval for photographing images continuously in time, and this time A change amount calculation step of comparing temporally continuous images shot at a time interval set in the interval setting step and recorded on the medium, and calculating a change amount thereof, and a remaining amount of calculation of the free space of the medium. When the amount detection step and the remaining amount detection step detect that the medium has a predetermined free space, the change amount calculation step selects the image with the smallest amount of change from the series of images recorded on the medium. And a deletion control step for deleting.
請求項9記載の発明は、画像を撮影して媒体に記録する撮影装置に内蔵されたコンピュータが実行するプログラムであって、時間的に連続して撮影する画像の変化量を設定する変化量設定ステップと、時間的に連続して撮影される画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出ステップと、この変化量算出ステップで得た変化量と上記変化量設定ステップで設定した変化量との比較結果により撮影された画像の記録を制御する記録制御ステップとをコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とする。 The invention according to claim 9 is a program executed by a computer incorporated in a photographing apparatus for photographing an image and recording it on a medium, and a change amount setting for setting a change amount of an image photographed continuously in time A change amount calculation step for comparing a step with an image photographed continuously in time, and calculating a change amount thereof, a change amount obtained in the change amount calculation step, and a change amount set in the change amount setting step And a recording control step for controlling recording of an image photographed based on the comparison result with the computer.
請求項10記載の発明は、画像を撮影して媒体に記録する撮影装置に内蔵されたコンピュータが実行するプログラムであって、時間的に連続して画像を撮影する時間間隔を設定する時間間隔設定ステップと、この時間間隔設定ステップで設定した時間間隔で撮影され、上記媒体に記録された、時間的に連続した画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出ステップと、上記媒体の空き容量を算出する残量検出ステップと、この残量検出ステップで上記媒体が所定の空き容量となったことを検出すると、上記変化量算出ステップで媒体に記録された一連の画像中から最も変化量の少ないものを選択し、削除する削除制御ステップとをコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とする。 A tenth aspect of the present invention is a program executed by a computer incorporated in a photographing apparatus for photographing an image and recording it on a medium, and sets a time interval for setting a time interval for photographing images continuously in time. A change amount calculating step for comparing the time-continuous images captured at the time interval set in the time interval setting step and recorded on the medium, and calculating a change amount thereof; The remaining amount detecting step for calculating the capacity, and when the remaining amount detecting step detects that the medium has reached a predetermined free space, the change amount is the largest in the series of images recorded on the medium in the change amount calculating step. It is characterized by having a computer execute a deletion control step that selects and deletes one with a small amount.
請求項1記載の発明によれば、時間ではなく被写体の変化の度合いを設定することで、その度合いに応じた間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するようにしたので、ユーザの意図に合わせて失敗することなく撮影することが可能となる。 According to the first aspect of the present invention, by setting the degree of change of the subject instead of the time, a plurality of continuous images are taken at intervals according to the degree, so that the user's intention is met. It becomes possible to shoot without failure.
請求項2記載の発明によれば、上記請求項1記載の発明の効果に加えて、時間的に連続して画像を撮影する最低時間間隔を併せて設定しておくことで、その間に装置の電源が無駄に消費してしまうのを防止し、容量が制限されている電源を効率的に使用することができる。
According to the invention described in
請求項3記載の発明によれば、所定の時間間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するインターバル撮影機能での撮影を実行した上で、画像を記録する媒体の空き容量に合わせて変化の度合いの小さい画像を自動的に削除するようにしたので、上記媒体の容量を充分有効に活用して被写体の変化を記録することができる。 According to the third aspect of the present invention, after performing photographing with the interval photographing function for photographing a plurality of continuous images at predetermined time intervals, the degree of change is adjusted in accordance with the free space of the medium on which the images are recorded. Since the small image is automatically deleted, the change of the subject can be recorded by making effective use of the capacity of the medium.
請求項4記載の発明によれば、上記請求項3記載の発明の効果に加えて、ユーザの任意設定により撮影を終了させることができるので、電源や画像を記録する媒体等の無駄な消費を回避することができる。 According to the fourth aspect of the invention, in addition to the effect of the third aspect of the invention, the photographing can be terminated by the user's arbitrary setting. It can be avoided.
請求項5記載の発明によれば、上記請求項4記載の発明の効果に加えて、設定した時間通りに撮影を終了し、装置を回収して撮影結果を確認することができる。 According to the fifth aspect of the present invention, in addition to the effect of the fourth aspect of the present invention, the photographing can be finished according to the set time, the apparatus can be recovered, and the photographing result can be confirmed.
請求項6記載の発明によれば、上記請求項4記載の発明の効果に加えて、画像を記録する媒体の残り容量や最低限必要な画像の数等を勘案した上でインターバル撮影を実行させることができる。
According to the invention described in claim 6, in addition to the effect of the invention described in
請求項7記載の発明によれば、時間ではなく被写体の変化の度合いを設定することで、その度合いに応じた間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するようにしたので、ユーザの意図に合わせて失敗することなく撮影することが可能となる。 According to the seventh aspect of the present invention, by setting the degree of change of the subject rather than the time, a plurality of continuous images are taken at intervals according to the degree, so that it is in accordance with the user's intention. It becomes possible to shoot without failure.
請求項8記載の発明によれば、所定の時間間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するインターバル撮影機能での撮影を実行した上で、画像を記録する媒体の空き容量に合わせて変化の度合いの小さい画像を自動的に削除するようにしたので、上記媒体の容量を充分有効に活用して被写体の変化を記録することができる。 According to the eighth aspect of the present invention, after performing photographing with the interval photographing function for photographing a plurality of continuous images at predetermined time intervals, the degree of change is adjusted in accordance with the free space of the medium on which the images are recorded. Since the small image is automatically deleted, the change of the subject can be recorded by making effective use of the capacity of the medium.
請求項9記載の発明によれば、時間ではなく被写体の変化の度合いを設定することで、その度合いに応じた間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するようにしたので、ユーザの意図に合わせて失敗することなく撮影することが可能となる。 According to the ninth aspect of the invention, by setting the degree of change of the subject instead of the time, a plurality of continuous images are taken at intervals according to the degree, so that it is in accordance with the user's intention. It becomes possible to shoot without failure.
請求項10記載の発明によれば、所定の時間間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するインターバル撮影機能での撮影を実行した上で、画像を記録する媒体の空き容量に合わせて変化の度合いの小さい画像を自動的に削除するようにしたので、上記媒体の容量を充分有効に活用して被写体の変化を記録することができる。 According to the tenth aspect of the present invention, after performing photographing with the interval photographing function for photographing a plurality of continuous images at predetermined time intervals, the degree of change is adjusted in accordance with the free space of the medium on which the images are recorded. Since the small image is automatically deleted, the change of the subject can be recorded by making effective use of the capacity of the medium.
(第1の実施の形態)
以下本発明を変化量検出撮影機能を有するデジタルカメラに適用した場合の第1の実施の形態について図面を参照して説明する。
(First embodiment)
A first embodiment when the present invention is applied to a digital camera having a change amount detection photographing function will be described below with reference to the drawings.
図1はその電子回路構成を示すものである。同図中、基本モードである撮影モードにおいては、モータ(M)11の駆動により合焦位置や絞り位置が移動される、撮影レンズを構成するレンズ光学系12の撮影光軸後方に配置された撮像素子であるCCD13が、タイミング発生器(TG)14、垂直ドライバ15によって走査駆動され、一定周期毎に結像した光像に対応する光電変換出力を1画面分出力する。
FIG. 1 shows the electronic circuit configuration. In the drawing, in the photographing mode which is the basic mode, the focusing position and the aperture position are moved by driving the motor (M) 11 and arranged behind the photographing optical axis of the lens optical system 12 constituting the photographing lens. A
この光電変換出力は、アナログ値の信号の状態でRGBの各原色成分毎に適宜ゲイン調整された後に、サンプルホールド回路(S/H)16でサンプルホールドされ、A/D変換器17でデジタルデータに変換され、カラープロセス回路18で画素補間処理及びγ補正処理を含むカラープロセス処理が行なわれて、デジタル値の輝度信号Y及び色差信号Cb,Crが生成され、DMA(Direct Memory Access)コントローラ19に出力される。
The photoelectric conversion output is appropriately gain-adjusted for each primary color component of RGB in the state of an analog value signal, sampled and held by a sample hold circuit (S / H) 16, and digital data by an A /
DMAコントローラ19は、カラープロセス回路18の出力する輝度信号Y及び色差信号Cb,Crを、同じくカラープロセス回路18からの複合同期信号、メモリ書込みイネーブル信号、及びクロック信号を用いて一度DMAコントローラ19内部のバッファに書込み、DRAMインタフェース(I/F)20を介してバッファメモリとして使用されるDRAM21にDMA転送を行なう。
The
制御部22は、CPUと、後述する変化量検出撮影機能時の処理を含む該CPUで実行される動作プログラムを固定的に記憶したROM、及びワークメモリとして使用されるRAM等により構成され、このデジタルカメラ全体の制御動作を司る。
The
しかして制御部22は、上記輝度及び色差信号のDRAM21へのDMA転送終了後に、この輝度及び色差信号をDRAMインタフェース20を介してDRAM21より読出し、VRAMコントローラ23を介してVRAM24に書込む。
Thus, after the DMA transfer of the luminance and color difference signals to the
デジタルビデオエンコーダ25は、上記輝度及び色差信号をVRAMコントローラ23を介してVRAM24より定期的に読出し、これらのデータを元にビデオ信号を発生して表示部26に出力する。
The
この表示部26は、デジタルカメラの背面側に設けられ、撮影モード時にはモニタ表示部(電子ファインダ)として機能し、デジタルビデオエンコーダ25からのビデオ信号に基づいた表示を行なうことで、その時点でVRAMコントローラ23から取込んでいる画像情報に基づく画像をリアルタイムに表示することとなる。
The
このように表示部26にその時点での画像がモニタ画像としてリアルタイムに表示されている、所謂スルー画像の表示状態で、静止画撮影を行ないたいタイミングでシャッタキーを操作すると、トリガ信号を発生する。
In this way, when the shutter key is operated at a timing at which still image shooting is desired in a so-called through-image display state in which the current image is displayed on the
制御部22は、このトリガ信号に応じてその時点でCCD13から取込んでいる1画面分の輝度及び色差信号のDRAM21へのDMA転送の終了後、直ちにCCD13からのDRAM21への経路を停止し、記録保存の状態に遷移する。
In response to this trigger signal, the
この記録保存の状態では、制御部22がDRAM21に書込まれている1フレーム分の輝度及び色差信号をDRAMインタフェース20を介してY,Cb,Crの各コンポーネント毎に縦8画素×横8画素の基本ブロックと呼称される単位で読出してJPEG(Joint Photograph coding Experts Group)回路27に書込み、このJPEG回路27でADCT(Adaptive Discrete Cosine Transform:適応離散コサイン変換)、エントロピ符号化方式であるハフマン符号化等の処理によりデータ圧縮する。
In this record storage state, the
そして、得た符号データを1画像のデータファイルとして該JPEG回路27から読出し、このデジタルカメラの記録媒体として着脱自在に装着される、フラッシュメモリを封入したメモリカード28に書込む。
The obtained code data is read out from the
そして、1フレーム分の輝度及び色差信号の圧縮処理及びメモリカード28への全圧縮データの書込み終了に伴なって、制御部22はCCD13からDRAM21への経路を再び起動する。
Then, along with the compression processing of the luminance and color difference signals for one frame and the completion of writing of all the compressed data to the
また、制御部22には、キー入力部29、音声処理部30、及びストロボ駆動部31が接続される。
In addition, a
キー入力部29は、電源キー、シャッタキーや、モードスイッチ、メニューキー、十字キー及びセットキー等から構成され、それらのキー操作に伴なう信号は直接制御部22へ送出される。
The
音声処理部30は、PCM音源等の音源回路を備え、音声の録音時にはマイクロホン部(MIC)32より入力された音声信号をデジタル化し、所定のデータファイル形式、例えばMP3(MPEG−1 audio layer 3)規格にしたがってデータ圧縮して音声データファイルを作成してメモリカード28へ送出する一方、音声の再生時にはメモリカード28から送られてきた音声データファイルの圧縮を解いてアナログ化し、デジタルカメラの背面側に設けられるスピーカ部(SP)33を駆動して、拡声放音させる。
The
ストロボ駆動部31は、静止画像撮影時に図示しないストロボ用の大容量コンデンサを充電した上で、制御部22からの制御に基づいてストロボ発光部34を閃光駆動する。
The
しかるに、静止画像ではなく動画像の撮影時においては、シャッタキーが操作され続けている間、上述した静止画データをJPEG回路27でデータ圧縮した静止画データファイルのメモリカード28への記録を時間的に連続して実行し、該シャッタキーの操作が終わるか、または所定の制限時間、例えば30秒が経過した時点でそれら一連の静止画データファイルを一括してモーションJPEGのデータファイル(AVIファイル)として設定し直す。
However, when shooting a moving image instead of a still image, the recording of the still image data file in which the above-described still image data is compressed by the
また、基本モードである再生モード時には、制御部22がメモリカード28に記録されている画像データを選択的に読出し、JPEG回路27で撮影モード時にデータ圧縮した手順と全く逆の手順で圧縮されている画像データを伸長し、伸長した画像データをDRAMインタフェース20を介してDRAM21に保持させた上で、このDRAM21の保持内容をVRAMコントローラ23を介してVRAM24に記憶させ、このVRAM24より定期的に画像データを読出してビデオ信号を発生し、上記表示部26で再生出力させる。
In the playback mode, which is the basic mode, the
選択した画像データが静止画像ではなく動画像であった場合、選択した動画像ファイルを構成する個々の静止画データの再生を時間的に連続して実行し、すべての静止画データの再生を終了した時点で、次に再生の指示がなされるまで先頭に位置する静止画データのみを用いて再生表示する。 If the selected image data is not a still image but a moving image, playback of the individual still image data constituting the selected moving image file is executed continuously in time, and playback of all the still image data is finished. At that time, the image is reproduced and displayed using only the still image data located at the head until the next reproduction instruction is given.
次に上記実施の形態の動作について説明する。
なお、以下に示す処理は、基本的に制御部22が予め固定記憶した動作プログラムに基づいて実行するもので、ここでは予めキー入力部29のメニューキー、十字キー及びセットキーの操作により変化量撮影機能が設定されたものとする。
Next, the operation of the above embodiment will be described.
The processing shown below is basically executed based on an operation program fixed and stored in advance by the
また、上記バッファメモリであるDRAM21は、スルー画像表示を行なうために常にCCD13での撮影で得た画像データを保持しておくカレントエリアと、後述する変化量検出のために比較対象となる画像データを保持しておく比較エリアとを有しているものとする。
In addition, the
図2は、変化量検出撮影機能時の処理内容を示すもので、その当初には、撮影枚数と変化量の数値[%]とをユーザが任意に入力するとこれを受付ける(ステップA01)。 FIG. 2 shows the contents of processing in the change amount detection photographing function. Initially, when the user arbitrarily inputs the number of shots and the numerical value [%] of the amount of change, this is accepted (step A01).
ここで変化量は、その直前に撮影し、メモリカード28に記録した画像に比して、新たに記録しようとする画像とを画素単位で比較し、画像全体でどの程度異なっているか否かを示すもので、被写体として例えば花の開花の様子や昆虫の羽化の様子等を撮影しようとする場合に、その被写体の変化の度合いに応じてユーザが任意に設定するものである。
Here, the amount of change is compared to the image recorded immediately before that and recorded on the
しかして、上記撮影枚数と変化量の設定を終えると、次にはキー入力部29のシャッタキーが操作されたか否かを繰返し判断することで、撮影の開始が指示されるのを待機する(ステップA02)。
When the setting of the number of shots and the amount of change is completed, next, it is determined whether or not the shutter key of the
ここでユーザは、カメラを三脚等に固定して被写体に対する構図を決定した上でシャッタキーを操作するもので、カメラ側では該シャッタキーの操作を上記ステップA02で判断すると、まず最初の1枚となる画像を撮影するべく撮影処理を実行する(ステップA03)。 Here, the user operates the shutter key after fixing the camera on a tripod or the like and determining the composition for the subject. When the camera determines the operation of the shutter key in step A02 above, the first one is selected. The photographing process is executed so as to photograph the image to become (step A03).
撮影により得た非圧縮の状態の画像データ(以下「RAWデータ」と称する)は、DRAM21の上述したカレントエリアに保持された後、JPEG回路27に読出されてJPEGの規格に基づいたデータ圧縮を受けた後にメモリカード28に記録される一方で、同DRAM21内のカレントエリアから比較エリアに移動されて上書きされる。
Uncompressed image data obtained by shooting (hereinafter referred to as “RAW data”) is held in the current area of the
その後、引き続きCCD13からの画像データを順次、例えば15[フレーム/秒]のフレームレートで順次取込んでDRAM21のカレントエリアに保持すると共に、同DRAM21の比較エリアに保持している、直前にメモリカード28に記録した画像のRAWデータと画素単位で比較し、その変化量を算出する(ステップA04)。
Thereafter, the image data from the
次いで、2度目のシャッタキーの操作がなされていないことを確認した上で(ステップA05)、上記ステップA04で算出した変化量が設定値以上であるか否かを判断する(ステップA06)、という処理を繰返し実行することにより、これらの状態となるのを待機する。 Next, after confirming that the second shutter key operation has not been performed (step A05), it is determined whether or not the amount of change calculated in step A04 is greater than or equal to a set value (step A06). By repeatedly executing the process, it waits for these states.
ここで、上記ステップA05での2度目のシャッタキーの操作の有無は、ユーザが一連の変化量検出撮影を強制的に終了させるべく操作した場合にこれを判断するためのもので、シャッタキーが操作された場合には即時この図2の処理を終了し、その時点でメモリカード28に記録されている一連の静止画データファイルを一括してモーションJPEGのデータファイル(AVIファイル)として設定し直す。
Here, the presence / absence of the second operation of the shutter key in step A05 is for determining this when the user operates to forcibly end the series of change amount detection photographing. When the operation is performed, the processing of FIG. 2 is immediately terminated, and a series of still image data files recorded on the
しかるに、ステップA06で設定した変化量以上の変化量を検出したと判断した場合には、その時点で新たに画像を撮影するべく撮影処理を実行する(ステップA07)。 However, if it is determined that a change amount equal to or greater than the change amount set in step A06 has been detected, a shooting process is executed to newly take a picture at that time (step A07).
撮影により得たRAWデータは、DRAM21の上述したカレントエリアに保持され、JPEG回路27に読出されてJPEGの規格に基づいたデータ圧縮を受けた後にメモリカード28に追加記録される一方で、同DRAM21内のカレントエリアから比較エリアに移動されて上書きされる。
RAW data obtained by shooting is held in the above-described current area of the
次いで、メモリカード28に記録した画像データの数が上記ステップA01で設定した撮影枚数となったか否かを判断し(ステップA08)、設定した撮影枚数になっていなければ再び上記ステップA04からの処理に戻って、次の撮影に備える。
Next, it is determined whether or not the number of image data recorded in the
こうしてステップA04〜A08の処理を繰返し実行することにより、設定した変化量以上の画像が得られる毎にこれを撮影してメモリカード28に記録する、という動作を設定した撮影枚数分だけ繰返す。
By repeatedly executing the processes in steps A04 to A08 in this manner, the operation of capturing and recording the image on the
そして、メモリカード28に記録した画像データの数が設定した撮影枚数となった時点でステップA08によりこれを判断し、この図2の処理を終了して、その時点でメモリカード28に記録されている一連の静止画データファイルを一括してモーションJPEGのデータファイル(AVIファイル)として設定し直す。
Then, when the number of image data recorded on the
このように、時間ではなく被写体の変化の度合いを変化量として設定することで、その度合いに応じた間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するようになるので、ユーザの意図に合わせて、失敗することなく時間的に連続した画像を撮影することが可能となる。 In this way, by setting the degree of change of the subject instead of time as the amount of change, a plurality of continuous images are photographed at intervals according to the degree of change, and thus fail according to the user's intention. It is possible to take images that are continuous in time without any problems.
なお、上記実施の形態では、その前に媒体であるメモリカード28に記録した画像に比して設定値以上の変化量のある新たな画像を撮影してこれもメモリカード28に記録した後、即時次の撮影に備えるような動作を行なうものとしたが、被写体によってはそんなに急激な変化を起こさないことも考えられるので、画像の撮影を実行してから次の撮影に備えるまでの間に最低時間間隔を併せて設定するものとしてもよく、その設定した時間間隔はカメラ内の少なくともCCD13を含む撮影系の回路の動作を一時的に休止させるものとして電源供給を停止してもよい。
In the above-described embodiment, a new image having a change amount equal to or larger than the set value compared to the image recorded on the
このように1回撮影を行なう毎に一部の回路の動作を設定時間だけ休止させることにより、不必要にカメラの電源である電池が無駄に消費してしまうのを防止し、容量が制限されている電池をより効率的に使用することができる。 In this way, by stopping the operation of some of the circuits for a set time each time one image is taken, it is possible to prevent the battery that is the power source of the camera from being consumed unnecessarily, and the capacity is limited. Can be used more efficiently.
(第2の実施の形態)
以下本発明をインターバル撮影機能を有するデジタルカメラに適用した場合の第2の実施の形態について図面を参照して説明する。
(Second Embodiment)
A second embodiment when the present invention is applied to a digital camera having an interval photographing function will be described below with reference to the drawings.
しかるにその電子回路構成については上記図1に示したものと基本的に同様であるものとし、同一部分には同一符号を用いるものとして、その図示及び説明は省略する。 However, the electronic circuit configuration is basically the same as that shown in FIG. 1, and the same reference numerals are used for the same parts, and illustration and description thereof are omitted.
次に上記実施の形態の動作について説明する。
なお、以下に示す処理は、基本的に制御部22が予め固定記憶した動作プログラムに基づいて実行するもので、ここでは予めキー入力部29のメニューキー、十字キー及びセットキーの操作によりインターバル撮影機能が設定されたものとする。
Next, the operation of the above embodiment will be described.
The processing shown below is basically executed based on an operation program fixedly stored in advance by the
また、上記バッファメモリであるDRAM21は、スルー画像表示を行なうために常にCCD13での撮影で得た画像データを保持しておくカレントエリアと、後述する新規撮影処理及び削除処理のために、比較対象となる画像データを保持しておく比較エリアとを有しているものとする。
In addition, the
加えて、画像データの記録媒体であるメモリカード28には、記録している一連のインターバル撮影で得た個々の画像データファイルの「ファイル名」「撮影時刻」及びその直前に記録した画像ファイルと比較した「変化量(%)」が管理テーブルとして記録されているものとする。
In addition, the
図3は、インターバル撮影機能時の処理内容を示すもので、その当初には、インターバル時間とトータルの撮影時間とをユーザが任意に入力するとこれを受付ける(ステップB01)。インターバル時間は、[秒]及び[分]を単位として設定するもので、ここでは例えば10[分]と選択した場合についてを以下に説明する。 FIG. 3 shows the processing contents during the interval shooting function. Initially, when the user arbitrarily inputs the interval time and the total shooting time, this is accepted (step B01). The interval time is set in units of [seconds] and [minutes], and a case where, for example, 10 [minutes] is selected will be described below.
インターバル時間とトータル撮影時間の設定を終えると、次にはキー入力部29のシャッタキーが操作されたか否かを繰返し判断することで、撮影の開始が指示されるのを待機する(ステップB02)。
When the setting of the interval time and the total shooting time is completed, next, it is determined whether or not the shutter key of the
ここでユーザは、カメラを三脚等に固定して被写体に対する構図を決定した上でシャッタキーを操作するもので、カメラ側では該シャッタキーの操作を上記ステップB02で判断すると、まず最初の1枚となる画像を撮影するべく撮影処理を実行する(ステップB03)。 Here, the user operates the shutter key after fixing the camera on a tripod or the like and determining the composition of the subject. When the camera side determines the operation of the shutter key in step B02, the first one The photographing process is executed to photograph the image to be (step B03).
撮影により得た非圧縮の状態の画像データ(以下「RAWデータ」と称する)は、DRAM21の上述したカレントエリアに保持された後、JPEG回路27に読出されてJPEGの規格に基づいたデータ圧縮を受けた後にメモリカード28に記録される一方で、DRAM21内のカレントエリアから比較エリアに移動されて上書きされ、併せてメモリカード28内の管理テーブルにその記録した画像データに関する各データを更新記録する。
Uncompressed image data obtained by shooting (hereinafter referred to as “RAW data”) is held in the current area of the
図6(A)は、この最初の1枚の画像データをメモリカード28に記録した状態での管理テーブルの内容を例示するもので、「Cimg0001.jpg」というファイル名のJPEGデータファイルのみがメモリカード28に記録されていることを示す。
FIG. 6A illustrates the contents of the management table in a state where the first piece of image data is recorded on the
ここで「変化量」が空欄であるのは、最初の1枚の画像データであり、比較対象となる画像データがないためである。 Here, the “change amount” is blank because it is the first piece of image data and there is no image data to be compared.
その後、2度目のシャッタキーの操作がなされていないことを確認した上で(ステップB04)、前回撮影を実行してから、設定したインターバル時間が経過したか否かを判断する(ステップB05)、という処理を繰返し実行することにより、これらの状態となるのを待機する。 Then, after confirming that the second shutter key operation has not been performed (step B04), it is determined whether or not the set interval time has elapsed since the previous shooting was performed (step B05). By repeatedly executing the process, it waits for these states.
ここで、上記ステップB04での2度目のシャッタキーの操作の有無は、ユーザが一連のインターバル撮影を強制的に終了させるべく操作した場合にこれを判断するためのもので、シャッタキーが操作された場合には即時この図3の処理を終了し、その時点でメモリカード28に記録されている一連の静止画データファイルを一括してモーションJPEGのデータファイル(AVIファイル)として設定し直す。
Here, the presence / absence of the second operation of the shutter key in step B04 is for determining when the user operates to forcibly end a series of interval shooting, and the shutter key is operated. 3 is immediately terminated, a series of still image data files recorded on the
しかるに、ステップB05で設定したインターバル時間となったと判断すると、次いでメモリカード28の残り容量をチェックし、新たな画像データの記録が充分できる程度の容量があるか否かを判断する(ステップB06)。
However, if it is determined that the interval time set in step B05 is reached, then the remaining capacity of the
ここで、充分な空き容量があると判断した場合、次いで設定したインターバル時間が経過したことによる新規の画像を撮影するべく撮影処理を実行する(ステップB08)。
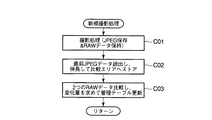
図4は、この新規撮影処理の詳細な処理内容を示すサブルーチンであり、新たに撮影を実行し、得たRAWデータをDRAM21のカレントエリアに保持し、JPEG回路27に読出してJPEGの規格に基づいたデータ圧縮を施した後にメモリカード28に追加記録させる(ステップC01)。
Here, if it is determined that there is sufficient free space, then a photographing process is executed to photograph a new image when the set interval time has elapsed (step B08).
FIG. 4 is a subroutine showing the detailed processing contents of this new shooting process. A new shooting is executed, the obtained RAW data is held in the current area of the
次いで、メモリカード28に既に記録されている直前の画像データ(JPEGデータ)を読出し、JPEG回路27でこれを伸長してRAWデータとした後にDRAM21の比較エリアに保持させる(ステップC02)。
Next, the immediately preceding image data (JPEG data) already recorded in the
そして、このDRAM21のカレントエリアに保持した今回の撮影により得たRAWデータと、比較エリアに保持した直前の撮影により得たRAWデータとを画素単位で比較し、変化量を求めてその数値をメモリカード28の管理テーブルの今回の撮影により得た画像データに対応するものとして更新記録する(ステップC03)。
Then, the RAW data obtained by the current photographing held in the current area of the
図6(B)は、この2枚目の画像データを上記新規撮影処理により撮影し、メモリカード28に記録した状態での管理テーブルの内容を例示するもので、新たに「Cimg0002.jpg」というファイル名のJPEGデータファイルがメモリカード28に追加記録され、且つその直前に記録された「Cimg0001.jpg」というファイル名のJPEGデータファイルとの変化量が「1(%)」であることを示す。
FIG. 6B illustrates the contents of the management table in a state where the second image data is shot by the above-described new shooting process and recorded in the
こうして図4の新規撮影処理を終了すると、図3のメインルーチンに戻り、続いて今回の新規撮影処理で予め設定したトータル撮影時間を経過したか否かを判断し(ステップB09)、まだ経過していないと判断すると、再び上記ステップB04からの処理に戻る。 When the new shooting process of FIG. 4 is completed in this manner, the process returns to the main routine of FIG. 3, and subsequently it is determined whether or not the total shooting time preset in this new shooting process has passed (step B09). If it is determined that it is not, the process returns to step B04.
こうしてステップB04〜B06,B08の処理を繰返し実行することにより、設定したインターバル時間にしたがって順次画像データをメモリカード28に記録していくと共に、同メモリカード28内の管理テーブルの内容も更新記録する。
By repeatedly executing the processes of steps B04 to B06 and B08 in this way, the image data is sequentially recorded on the
図6(C)〜図6(E)は、こうして合計9枚の画像データがインターバル時間10分毎にメモリカード28に順次記録される過程で管理テーブルが更新記録されていく状態の一部を例示するものである。
6C to 6E show a part of the state in which the management table is updated and recorded in the process in which a total of nine pieces of image data are sequentially recorded on the
このようにメモリカード28に時間的に連続した9枚の画像データが記録され、さらに次のインターバル時間となったとステップB05で判断し、続くステップB06でメモリカード28の空き容量が不足していると判断すると、そのままでは10枚目の画像データを撮影してもメモリカード28に記録する充分な容量がないため、ステップB08の新規撮影処理に進む前に、それまでにメモリカード28に記録した画像データの中から変化量の少ないもの及び変化量が極端に多いものを削除する削除処理を実行する(ステップB07)。
In this way, it is determined in step B05 that nine image data continuous in time are recorded in the
なお、変化量の少ないものを削除するのは変化を撮影するという目的にそぐわないためであり、変化量が極端に多いものを削除するのは、レンズが覆い隠された状態など、何らかの異常な撮影条件の場合が考えられ、これも本来の目的の画像とは異なるものであるからである。 It should be noted that deleting objects with small changes is not suitable for the purpose of shooting changes, and deleting objects with extremely large changes is due to some abnormal shooting such as when the lens is obscured. This is because a condition may be considered, which is also different from the original target image.
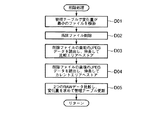
図5は、この削除処理の詳細な処理内容を示すサブルーチンであり、その当初には、まず管理テーブル中から最も変化量の少ないデータファイルを検索する(ステップD01)。 FIG. 5 is a subroutine showing the detailed processing contents of this deletion processing. At first, a data file with the smallest change amount is searched from the management table (step D01).
上記図6(E)の管理テーブルにおいては、最も変化量の少ない画像データは「Cimg0002.jpg」と「Cimg0009.jpg」の2つであり、その変化量は共に「1(%)」であるが、このように最小の変化量の画像データが複数存在する場合には、その撮影時刻がより古い方を優先して選択するものとすると、「Cimg0002.jpg」が選択されることとなる。 In the management table of FIG. 6E, the image data with the smallest change amount is “Cimg0002.jpg” and “Cimg0009.jpg”, and the change amounts thereof are both “1 (%)”. However, when there are a plurality of pieces of image data having the smallest change amount as described above, “Cimg0002.jpg” is selected if the shooting time of the older one is preferentially selected.
こうして変化量が最小である画像データを検索すると、次にその画像データをメモリカード28から削除(消去)し、併せて管理テーブルからの対応する内容を削除する(ステップD02)。
図7(A)はこうしてファイル名「Cimg0002.jpg」のデータを削除した管理テーブルの内容を例示するものである。
When the image data having the smallest change amount is searched in this way, the image data is then deleted (erased) from the
FIG. 7A illustrates the contents of the management table in which the data of the file name “Cimg0002.jpg” has been deleted in this way.
削除を実行した後、メモリカード28に既に記録されている削除した画像データの直前の「Cimg0001.jpg」の画像データ(JPEGデータ)を読出し、JPEG回路27でこれを伸長してRAWデータとした後にDRAM21の比較エリアに保持させる(ステップD03)。
After executing the deletion, the image data (JPEG data) of “Cimg0001.jpg” immediately before the deleted image data already recorded in the
次いで、メモリカード28に既に記録されている削除した画像データの直後の「Cimg0003.jpg」の画像データ(JPEGデータ)を読出し、JPEG回路27でこれも伸長してRAWデータとした後にDRAM21のカレントエリアに保持させる(ステップD04)。
Next, the image data (JPEG data) of “Cimg0003.jpg” immediately after the deleted image data already recorded in the
そして、このDRAM21のカレントエリアに保持した削除直後のRAWデータと、比較エリアに保持した削除直前のRAWデータとを画素単位で比較し、変化量を求めて、その数値をメモリカード28の管理テーブルの上記削除した直後の画像データに対応するものとして更新記録する(ステップD05)。
Then, the RAW data immediately after the deletion held in the current area of the
なお、上記図5は変化量が少ない例を示したが、変化量が極端に多いファイルを削除する際はステップD01で変化量が極端に多いファイルを抽出するが、その際、各ファイルの変化量の相対比較ではなく、予め設定された一定量を超える変化量をもったファイルが(あれば)選択される。したがって、必ずしも削除対象とされるファイルが抽出されるとは限らない。 Although FIG. 5 shows an example in which the amount of change is small, when deleting a file having an extremely large amount of change, a file having an extremely large amount of change is extracted in step D01. A file having a change amount exceeding a predetermined fixed amount is selected (if any) instead of the relative comparison of the amounts. Therefore, a file to be deleted is not necessarily extracted.
図7(B)はこうして更新記録した管理テーブルの内容を例示するもので、上記図7(A)で示した変化量の最小となる画像データを削除した状態から、その削除した画像データの直前のものと直後のもの相互間の変化量を新たに算出して更新記録することにより、次に同様の削除処理を行なう場合にも正確な変化量の検索を行なうことができるようになるものである。 FIG. 7B exemplifies the contents of the management table updated and recorded in this way. From the state in which the image data having the minimum change amount shown in FIG. 7A is deleted, immediately before the deleted image data. By calculating a new amount of change between the one immediately after and the one immediately after it, and updating and recording it, the same amount of change can be retrieved even when the same deletion process is performed next time. is there.
こうして図5の削除処理を終了すると、図3のメインルーチンに戻り、続いて充分な空き容量を設けたメモリカード28に新たな撮影による画像データを記録するべくステップB08に進み、新規撮影処理を実行する。
When the deletion process of FIG. 5 is completed in this way, the process returns to the main routine of FIG. 3, and then the process proceeds to step B08 to record new image data on the
図7(C)は、この新規撮影処理により10枚目の画像データがメモリカード28に記録され、併せて管理テーブルの内容が更新記録されたことを示すもので、ファイル名「Cimg0010.jpg」のデータが追加記録されていることがわかる。
FIG. 7C shows that the tenth image data is recorded in the
その後、ステップB09でまだトータル撮影時間が経過していないものと判断してステップB04からの処理に戻り、続くインターバル時間が経過してステップB05でこれを判断した後、続くステップB06でまたもメモリカード28の空き容量が不足していると判断すると、そのままでは11枚目の画像データを撮影してもメモリカード28に記録する充分な容量がないため、ステップB08の新規撮影処理に進む前に、ステップB07で上記と同様の削除処理を実行する。
Thereafter, it is determined in step B09 that the total shooting time has not yet elapsed, and the process returns to step B04. After the interval time has elapsed and this is determined in step B05, the memory is again stored in step B06. If it is determined that the free space of the
図5の削除処理においては、ステップD01で管理テーブル中から最も変化量の少ないデータファイルを検索する。 In the deletion process of FIG. 5, the data file with the smallest amount of change is searched from the management table in step D01.
上記図7(C)の管理テーブルにおいては、最も変化量の少ない画像データは「Cimg0009.jpg」と「Cimg0010.jpg」の2つであり、その変化量は共に「1(%)」であるので、上記と同様の撮影時刻がより古い方を優先して選択するものとして、「Cimg0009.jpg」を選択する。 In the management table of FIG. 7C, the image data with the smallest change amount is “Cimg0009.jpg” and “Cimg0010.jpg”, and the change amounts thereof are both “1 (%)”. Therefore, “Cimg0009.jpg” is selected as the one having the same shooting time as that described above to be selected with priority.
変化量が最小である画像データを検索すると、次にその画像データをメモリカード28から削除(消去)し、併せて管理テーブルからの対応する内容を削除する(ステップD02)。
図8(A)はこうしてファイル名「Cimg0009.jpg」のデータを削除した管理テーブルの内容を例示するものである。
When the image data having the smallest change amount is retrieved, the image data is then deleted (erased) from the
FIG. 8A illustrates the contents of the management table in which the data of the file name “Cimg0009.jpg” is deleted.
削除を実行した後、メモリカード28に既に記録されている削除した画像データの直前の「Cimg0008.jpg」の画像データ(JPEGデータ)を読出し、JPEG回路27でこれを伸長してRAWデータとした後にDRAM21の比較エリアに保持させる(ステップD03)。
After executing the deletion, the image data (JPEG data) of “Cimg0008.jpg” immediately before the deleted image data already recorded in the
次いで、メモリカード28に既に記録されている削除した画像データの直後の「Cimg0010.jpg」の画像データ(JPEGデータ)を読出し、JPEG回路27でこれも伸長してRAWデータとした後にDRAM21のカレントエリアに保持させる(ステップD04)。
Next, the image data (JPEG data) of “Cimg0010.jpg” immediately after the deleted image data already recorded in the
そして、このDRAM21のカレントエリアに保持した削除直後のRAWデータと、比較エリアに保持した削除直前のRAWデータとを画素単位で比較し、変化量を求めて、その数値をメモリカード28の管理テーブルの上記削除した直後の画像データに対応するものとして更新記録する(ステップD05)。
Then, the RAW data immediately after the deletion held in the current area of the
図8(B)はこうして更新記録した管理テーブルの内容を例示するもので、上記図8(A)で示した変化量の最小となる画像データを削除した状態から、その削除した画像データの直前のものと直後のもの相互間の変化量を新たに算出して更新記録することにより、次に同様の削除処理を行なう場合にも正確な変化量の検索を行なうことができるようになるものである。 FIG. 8B illustrates the contents of the management table updated and recorded in this manner. The image data having the minimum change amount shown in FIG. 8A is deleted and immediately before the deleted image data. By calculating a new amount of change between the one immediately after and the one immediately after it, and updating and recording it, the same amount of change can be retrieved even when the same deletion process is performed next time. is there.
こうして図5の削除処理を終了すると、図3のメインルーチンに戻り、続いて充分な空き容量を設けたメモリカード28に新たな撮影による画像データを記録するべくステップB08に進み、新規撮影処理を実行する。
When the deletion process of FIG. 5 is completed in this way, the process returns to the main routine of FIG. 3, and then the process proceeds to step B08 to record new image data on the
図8(C)は、この新規撮影処理により11枚目の画像データがメモリカード28に記録され、併せて管理テーブルの内容が更新記録されたことを示すもので、ファイル名「Cimg0011.jpg」のデータが追加記録されていることがわかる。
FIG. 8C shows that the eleventh image data is recorded in the
以上のように、メモリカード28から再度の画像データの削除と新規撮影、記録が実行され、同時に管理テーブルの更新記録も実行される。
As described above, the image data is again deleted from the
このように、記録されている画像データでその直前の画像データとの変化量が最小となるもの、さらにそれが複数ある場合には撮影時刻のより古い方を検索し、メモリカード28から削除して新規撮影を行なうという一連の動作を繰り返し実行していく。
As described above, the recorded image data having the smallest change amount from the immediately preceding image data, and if there are a plurality of the image data, the older one of the shooting times is searched and deleted from the
そして、上記ステップB09ではじめに設定したトータル撮影時間が経過したと判断した時点で、この図3の処理を終了して、その時点でメモリカード28に記録されている一連の静止画データファイルを一括してモーションJPEGのデータファイル(AVIファイル)として設定し直す。
When it is determined that the total shooting time set initially in step B09 has elapsed, the processing in FIG. 3 is terminated, and a series of still image data files recorded on the
このように、ユーザが任意に設定したインターバル時間の間隔で連続した複数の画像を撮影するインターバル撮影機能での撮影を実行した上で、画像を記録する媒体であるメモリカード28の空き容量に合わせて、最も変化の度合いの小さい画像を自動的に削除するようにしたので、メモリカード28の容量を充分有効に活用して、設定したトータル撮影時間となるまで被写体の変化を確実に記録することができる。
As described above, after performing shooting with the interval shooting function for shooting a plurality of continuous images at intervals of an interval time set arbitrarily by the user, it is matched with the free space of the
加えて、ユーザの任意設定により撮影を終了させるものとし、その要因をトータル撮影時間としたことにより、設定した時間一杯となるまで撮影を継続し、設定した時間となった時点で装置を回収して撮影結果を確認することができる。 In addition, the shooting is terminated according to the user's arbitrary settings, and the factor is the total shooting time, so the shooting is continued until the set time is full, and the device is recovered when the set time is reached. To check the shooting results.
(第2の実施の形態の他の動作例)
なお、上記第2の実施の形態では、インターバル撮影を終了させる要因をトータル撮影時間とする場合の処理内容について説明したが、インターバル撮影を終了させる要因としてはこれに限らず、他にも例えばトータル撮影枚数を設定することも考えられる。
(Another operation example of the second embodiment)
In the second embodiment, the processing content in the case where the factor for ending the interval shooting is set as the total shooting time has been described. However, the factor for ending the interval shooting is not limited to this. It is also possible to set the number of shots.
そのようにした場合のインターバル撮影機能の処理内容を本実施の形態の他の動作例として説明する。 The processing content of the interval shooting function in such a case will be described as another example of the operation of the present embodiment.
なお、以下に示す処理は、基本的に制御部22が予め固定記憶した動作プログラムに基づいて実行するもので、ここでは予めキー入力部29のメニューキー、十字キー及びセットキーの操作によりインターバル撮影機能が設定されたものとする。
The processing shown below is basically executed based on an operation program fixedly stored in advance by the
また、上記バッファメモリであるDRAM21は、スルー画像表示を行なうために常にCCD13での撮影で得た画像データを保持しておくカレントエリアと、後述する新規撮影処理及び削除処理のために、比較対象となる画像データを保持しておく比較エリアとを有しているものとする。
In addition, the
加えて、画像データの記録媒体であるメモリカード28には、記録している一連のインターバル撮影で得た個々の画像データファイルの「ファイル名」「撮影時刻」及びその直前に記録した画像ファイルと比較した「変化量(%)」が管理テーブルとして記録されているものとする。
In addition, the
図9は、インターバル撮影機能時の処理内容を示すもので、その当初には、インターバル時間とトータルの撮影枚数とをユーザが任意に入力するとこれを受付ける(ステップE01)。インターバル時間は、[秒]及び[分]を単位として設定する。 FIG. 9 shows the processing contents during the interval shooting function. Initially, when the user arbitrarily inputs the interval time and the total number of shots, this is accepted (step E01). The interval time is set in units of [seconds] and [minutes].
インターバル時間とトータル撮影枚数の設定を終えると、次にキー入力部29のシャッタキーが操作されたか否かを繰返し判断することで、撮影の開始が指示されるのを待機する(ステップE02)。
When the setting of the interval time and the total number of shots has been completed, it is determined whether or not the shutter key of the
ここでユーザは、カメラを三脚等に固定して被写体に対する構図を決定した上でシャッタキーを操作するもので、カメラ側では該シャッタキーの操作を上記ステップE02で判断すると、まず最初の1枚となる画像を撮影するべく撮影処理を実行する(ステップE03)。 Here, the user operates the shutter key after fixing the camera on a tripod or the like and determining the composition for the subject. When the operation of the shutter key is determined in step E02 on the camera side, the first one is first selected. The photographing process is executed to photograph the image to become (step E03).
撮影により得た非圧縮の状態の画像データ(以下「RAWデータ」と称する)は、DRAM21の上述したカレントエリアに保持された後、JPEG回路27に読出されてJPEGの規格に基づいたデータ圧縮を受けた後にメモリカード28に記録される一方で、DRAM21内のカレントエリアから比較エリアに移動されて上書きされ、併せてメモリカード28内の管理テーブルにその記録した画像データに関する各データを更新記録する。
Uncompressed image data obtained by shooting (hereinafter referred to as “RAW data”) is held in the current area of the
その後、2度目のシャッタキーの操作がなされていないことを確認した上で(ステップE04)、前回撮影を実行してから、設定したインターバル時間が経過したか否かを判断する(ステップE05)、という処理を繰返し実行することにより、これらの状態となるのを待機する。 Thereafter, after confirming that the second shutter key operation has not been performed (step E04), it is determined whether or not the set interval time has elapsed since the previous shooting was performed (step E05). By repeatedly executing the process, it waits for these states.
ここで、上記ステップE04での2度目のシャッタキーの操作の有無は、ユーザが一連のインターバル撮影を強制的に終了させるべく操作した場合にこれを判断するためのもので、シャッタキーが操作された場合には即時この図9の処理を終了し、その時点でメモリカード28に記録されている一連の静止画データファイルを一括してモーションJPEGのデータファイル(AVIファイル)として設定し直す。
Here, the presence / absence of the second operation of the shutter key in step E04 is for determining when the user operates to forcibly end a series of interval shooting, and the shutter key is operated. 9 immediately ends, the series of still image data files recorded on the
しかるに、ステップE05で設定したインターバル時間となったと判断すると、次いでメモリカード28の残り容量をチェックし、新たな画像データの記録が充分できる程度の容量があるか否かを判断する(ステップE06)。
However, if it is determined that the interval time set in step E05 is reached, then the remaining capacity of the
ここで、充分な空き容量があると判断した場合、次いで設定したインターバル時間が経過したことによる新規の画像を撮影するべく撮影処理を実行する(ステップE08)。
この新規撮影処理の詳細な処理内容は上記図4で説明した通りであるので、ここではその説明を省略する。
図4の新規撮影処理を終了すると、図9のメインルーチンに戻り、続いて今回の新規撮影処理で予め設定したトータル撮影枚数となったか否かを判断し(ステップE09)、まだなっていないと判断すると、再び上記ステップE04からの処理に戻る。
Here, when it is determined that there is sufficient free space, a shooting process is executed to capture a new image after the set interval time has elapsed (step E08).
Since the detailed processing contents of this new photographing processing are as described with reference to FIG. 4, the description thereof is omitted here.
When the new shooting process of FIG. 4 is completed, the process returns to the main routine of FIG. 9, and then it is determined whether or not the total number of shots set in advance in this new shooting process has been reached (step E09). If it judges, it will return to the process from said step E04 again.
こうしてステップE04〜B06,B08の処理を繰返し実行することにより、設定したインターバル時間にしたがって順次画像データをメモリカード28に記録していくと共に、同メモリカード28内の管理テーブルの内容も更新記録する。
By repeatedly executing the processes of steps E04 to B06 and B08 in this way, the image data is sequentially recorded on the
メモリカード28に時間的に連続した画像データが順次記録され、さらに次のインターバル時間となったとステップE05で判断し、続くステップE06でメモリカード28の空き容量が不足していると判断すると、そのままでは次の画像データを撮影してもメモリカード28に記録する充分な容量がないため、ステップE08の新規撮影処理に進む前に、それまでにメモリカード28に記録した画像データの中から変化量の少ないもの及び変化量が極端に多いものを削除する削除処理を実行する(ステップE07)。
In step E05, it is determined in step E05 that image data continuous in time is sequentially recorded on the
この削除処理の詳細な処理内容は上記図5で説明した通りであるので、ここではその説明を省略する。
図5の削除処理を終了すると、図9のメインルーチンに戻り、続いて充分な空き容量を設けたメモリカード28に新たな撮影による画像データを記録するべくステップE08に進み、新規撮影処理を実行する。
Since the detailed processing content of this deletion processing is as described with reference to FIG. 5, the description thereof is omitted here.
When the deletion process of FIG. 5 is completed, the process returns to the main routine of FIG. 9, and then the process proceeds to step E08 to record new image data on the
その後、ステップE09でまだトータル撮影枚数となっていないものと判断してステップE04からの処理に戻り、続くインターバル時間が経過してステップE05でこれを判断した後、続くステップE06でまたもメモリカード28の空き容量が不足していると判断すると、そのままでは次の画像データを撮影してもメモリカード28に記録する充分な容量がないため、ステップE08の新規撮影処理に進む前に、ステップE07で上記と同様の削除処理を実行する。
Thereafter, in step E09, it is determined that the total number of shots has not yet been reached, and the process returns to step E04. After the interval time has elapsed, this is determined in step E05, and then in step E06, the memory card is again returned. If it is determined that the free space of 28 is insufficient, there is not enough capacity to record the next image data in the
図5の削除処理を終了して図9のメインルーチンに戻り、続いて充分な空き容量を設けたメモリカード28に新たな撮影による画像データを記録するべくステップE08に進み、新規撮影処理を実行する。
5 is terminated and the process returns to the main routine of FIG. 9, and then the process proceeds to step E08 to record new image data on the
以上のように、メモリカード28から再度の画像データの削除と新規撮影、記録が実行され、同時に管理テーブルの更新記録も実行される。
As described above, the image data is again deleted from the
このように、記録されている画像データでその直前の画像データとの変化量が最小となるもの、さらにそれが複数ある場合には撮影時刻のより古い方を検索し、メモリカード28から削除して新規撮影を行なうという一連の動作を繰り返し実行していく。
As described above, the recorded image data having the smallest change amount from the immediately preceding image data, and if there are a plurality of the image data, the older one of the shooting times is searched and deleted from the
そして、上記ステップE09ではじめに設定したトータル撮影枚数となったと判断した時点で、この図9の処理を終了して、その時点でメモリカード28に記録されている一連の静止画データファイルを一括してモーションJPEGのデータファイル(AVIファイル)として設定し直す。
When it is determined that the total number of shots set at the beginning in step E09 is reached, the processing of FIG. 9 is terminated, and a series of still image data files recorded on the
このように、ユーザが任意に設定したトータルの撮影枚数に達した時点で撮影を終了させるものとしたことにより、画像を記録するメモリカード28の残り容量や最低限必要な画像の数等を勘案した上でインターバル撮影を実行させることができる。
As described above, the shooting is terminated when the total number of shots set arbitrarily by the user is reached, so that the remaining capacity of the
なお、上記第1及び第2の実施の形態は、いずれも本発明をデジタルカメラに適用した場合について説明したものであるが、本発明はこれに限らず、ビデオムービーカメラやカメラ機能を有するパーソナルコンピュータ、あるいは視覚センサとしてのカメラを備えた電子ペットロボット等にも容易に適用可能となる。 In the first and second embodiments described above, the present invention is applied to a digital camera. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and a video movie camera or a personal camera function is provided. It can be easily applied to a computer or an electronic pet robot equipped with a camera as a visual sensor.
その他、本発明は上記実施の形態に限らず、その要旨を逸脱しない範囲内で種々変形して実施することが可能であるものとする。 In addition, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made without departing from the scope of the invention.
さらに、上記実施の形態には種々の段階の発明が含まれており、開示される複数の構成要件における適宜な組合わせにより種々の発明が抽出され得る。例えば、実施の形態に示される全構成要件からいくつかの構成要件が削除されても、発明が解決しようとする課題の欄で述べた課題の少なくとも1つが解決でき、発明の効果の欄で述べられている効果の少なくとも1つが得られる場合には、この構成要件が削除された構成が発明として抽出され得る。 Further, the above embodiments include inventions at various stages, and various inventions can be extracted by appropriately combining a plurality of disclosed constituent elements. For example, even if some constituent elements are deleted from all the constituent elements shown in the embodiment, at least one of the problems described in the column of the problem to be solved by the invention can be solved, and described in the column of the effect of the invention. In a case where at least one of the obtained effects can be obtained, a configuration in which this configuration requirement is deleted can be extracted as an invention.
11…モータ(M)、12…レンズ光学系、13…CCD、14…タイミング発生器(TG)、15…垂直ドライバ、16…サンプルホールド回路(S/H)、17…A/D変換器、18…カラープロセス回路、19…DMAコントローラ、20…DRAMインタフェース(I/F)、21…DRAM、22…制御部、23…VRAMコントローラ、24…VRAM、25…デジタルビデオエンコーダ、26…表示部、27…JPEG回路、28…メモリカード、29…キー入力部、30…音声処理部、31…ストロボ駆動部、32…マイクロホン部(MIC)、33…スピーカ部(SP)、34…ストロボ発光部。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (10)
この撮影手段で撮影した画像を記録する記録手段と、
上記撮影手段で時間的に連続して撮影する画像の変化量を設定する変化量設定手段と、
上記撮影手段で時間的に連続して撮影される画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出手段と、
この変化量算出手段で得た変化量と上記変化量設定手段で設定した変化量との比較結果により上記撮影手段で撮影された画像の上記記録手段への記録を制御する記録制御手段と
を具備したことを特徴とする撮影装置。 Photographing means;
Recording means for recording an image photographed by the photographing means;
A change amount setting means for setting a change amount of an image photographed continuously in time by the photographing means;
A change amount calculating means for comparing images photographed continuously in time by the photographing means and calculating a change amount thereof;
A recording control means for controlling recording of the image photographed by the photographing means on the recording means based on a comparison result between the variation obtained by the variation calculating means and the variation set by the variation setting means; An imaging device characterized by that.
この時間間隔設定手段で設定した時間間隔にしたがって画像を撮影する撮影手段と、
この撮影手段で撮影した画像を記録する記録手段と、
上記記録手段に記録された時間的に連続した画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出手段と、
上記記録手段の空き容量を算出する残量検出手段と、
この残量検出手段で上記記録手段が所定の空き容量となったことを検出すると、上記変化量算出手段で記録手段に記録された一連の画像中から最も変化量の少ないものを選択し、削除する削除制御手段と
を具備したことを特徴とする撮影装置。 Time interval setting means for setting a time interval for capturing images continuously in time;
Photographing means for photographing images according to the time interval set by the time interval setting means;
Recording means for recording an image photographed by the photographing means;
A change amount calculating means for comparing temporally continuous images recorded in the recording means and calculating the change amount;
A remaining amount detecting means for calculating a free capacity of the recording means;
When the remaining amount detecting means detects that the recording means has reached a predetermined free space, the change amount calculating means selects the image with the smallest amount of change from the series of images recorded on the recording means and deletes it. And a deletion control means.
時間的に連続して撮影する画像の変化量を設定する変化量設定工程と、
時間的に連続して撮影される画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出工程と、
この変化量算出工程で得た変化量と上記変化量設定工程で設定した変化量との比較結果により撮影された画像の記録を制御する記録制御工程と
を有したことを特徴とする撮影方法。 A shooting method with a shooting device for shooting and recording images,
A change amount setting step for setting a change amount of an image taken continuously in time;
A change amount calculating step for comparing images taken continuously in time and calculating a change amount thereof,
An imaging method comprising: a recording control step for controlling recording of an image captured based on a comparison result between the variation obtained in the variation calculation step and the variation set in the variation setting step.
時間的に連続して画像を撮影する時間間隔を設定する時間間隔設定工程と、
この時間間隔設定工程で設定した時間間隔で撮影され、上記媒体に記録された、時間的に連続した画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出工程と、
上記媒体の空き容量を算出する残量検出工程と、
この残量検出工程で上記媒体が所定の空き容量となったことを検出すると、上記変化量算出工程で媒体に記録された一連の画像中から最も変化量の少ないものを選択し、削除する削除制御工程と
を有したことを特徴とする撮影方法。 A shooting method with a shooting device that takes an image and records it on a medium,
A time interval setting step for setting a time interval for capturing images continuously in time;
A change amount calculation step of comparing the temporally continuous images that are taken at the time interval set in this time interval setting step and recorded on the medium, and calculating the change amount;
A remaining amount detecting step for calculating the free space of the medium;
When it is detected in the remaining amount detection step that the medium has reached a predetermined free space, the change amount calculation step selects the image with the smallest change amount from the series of images recorded on the medium and deletes it for deletion And a control process.
時間的に連続して撮影する画像の変化量を設定する変化量設定ステップと、
時間的に連続して撮影される画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出ステップと、
この変化量算出ステップで得た変化量と上記変化量設定ステップで設定した変化量との比較結果により撮影された画像の記録を制御する記録制御ステップと
をコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とするプログラム。 A program executed by a computer incorporated in a photographing apparatus that captures an image and records it on a medium,
A change amount setting step for setting a change amount of an image taken continuously in time;
A change amount calculating step for comparing images taken continuously in time and calculating a change amount thereof,
A program for causing a computer to execute a recording control step for controlling recording of a photographed image based on a comparison result between a change amount obtained in the change amount calculation step and a change amount set in the change amount setting step. .
時間的に連続して画像を撮影する時間間隔を設定する時間間隔設定ステップと、
この時間間隔設定ステップで設定した時間間隔で撮影され、上記媒体に記録された、時間的に連続した画像を比較し、その変化量を算出する変化量算出ステップと、
上記媒体の空き容量を算出する残量検出ステップと、
この残量検出ステップで上記媒体が所定の空き容量となったことを検出すると、上記変化量算出ステップで媒体に記録された一連の画像中から最も変化量の少ないものを選択し、削除する削除制御ステップと
をコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とするプログラム。 A program executed by a computer incorporated in a photographing apparatus that captures an image and records it on a medium,
A time interval setting step for setting a time interval for capturing images continuously in time,
A change amount calculating step for comparing images that are taken in time intervals set in the time interval setting step and recorded on the medium, and that calculate a change amount;
A remaining amount detecting step for calculating the free space of the medium;
When it is detected in the remaining amount detection step that the medium has a predetermined free space, the change amount calculating step selects the image with the smallest amount of change from the series of images recorded on the medium and deletes it. A program for causing a computer to execute a control step.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004119110A JP2005303807A (en) | 2004-04-14 | 2004-04-14 | Photography-taking apparatus and method and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004119110A JP2005303807A (en) | 2004-04-14 | 2004-04-14 | Photography-taking apparatus and method and program |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005303807A true JP2005303807A (en) | 2005-10-27 |
| JP2005303807A5 JP2005303807A5 (en) | 2007-05-31 |
Family
ID=35334798
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004119110A Abandoned JP2005303807A (en) | 2004-04-14 | 2004-04-14 | Photography-taking apparatus and method and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005303807A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011014950A (en) * | 2009-06-30 | 2011-01-20 | Aiphone Co Ltd | Intercom device |
| KR101038695B1 (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2011-06-02 | 가시오게산키 가부시키가이샤 | Image processing device and recording medium |
| CN102710865A (en) * | 2012-06-18 | 2012-10-03 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | Mobile terminal with photography function and portrait self-timer method thereof |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04369979A (en) * | 1991-06-19 | 1992-12-22 | Canon Inc | Electronic camera |
| JP2002135724A (en) * | 2000-10-23 | 2002-05-10 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Methods for shooting and reproducing images and their device |
| JP2003189166A (en) * | 2001-12-20 | 2003-07-04 | Canon Inc | Image photographing apparatus, control method thereof, medium for providing control program, and the control program |
| JP2004096440A (en) * | 2002-08-30 | 2004-03-25 | Canon Inc | Image pickup device, image storing method, and program therefor |
-
2004
- 2004-04-14 JP JP2004119110A patent/JP2005303807A/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04369979A (en) * | 1991-06-19 | 1992-12-22 | Canon Inc | Electronic camera |
| JP2002135724A (en) * | 2000-10-23 | 2002-05-10 | Casio Comput Co Ltd | Methods for shooting and reproducing images and their device |
| JP2003189166A (en) * | 2001-12-20 | 2003-07-04 | Canon Inc | Image photographing apparatus, control method thereof, medium for providing control program, and the control program |
| JP2004096440A (en) * | 2002-08-30 | 2004-03-25 | Canon Inc | Image pickup device, image storing method, and program therefor |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101038695B1 (en) | 2008-08-05 | 2011-06-02 | 가시오게산키 가부시키가이샤 | Image processing device and recording medium |
| JP2011014950A (en) * | 2009-06-30 | 2011-01-20 | Aiphone Co Ltd | Intercom device |
| CN102710865A (en) * | 2012-06-18 | 2012-10-03 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | Mobile terminal with photography function and portrait self-timer method thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7417667B2 (en) | Imaging device with function to image still picture during moving picture imaging | |
| JP4730402B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging control method, and program | |
| US20130182166A1 (en) | Digital image processing apparatus and method of controlling the same | |
| JP2006215266A (en) | Imaging apparatus, image storage device, imaging method, storing method and program | |
| JP4639965B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP2010226702A (en) | Imaging apparatus | |
| KR100663390B1 (en) | Image sensing device, image edit method, and storage medium for recording image edit method | |
| JP2008193333A (en) | Image reproducing device, image display method and program | |
| US8538247B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method | |
| JP5332369B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer program | |
| JP4157228B2 (en) | Electronic camera and image printer apparatus | |
| JP4467232B2 (en) | Image recording apparatus and method | |
| JP2005303807A (en) | Photography-taking apparatus and method and program | |
| JP4872571B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program | |
| JP4535089B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| CN100585721C (en) | Image sensing apparatus, image edit method | |
| JP4735495B2 (en) | Voice processing apparatus and program | |
| JP5246106B2 (en) | Imaging device, program | |
| JP4784463B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program | |
| JP2011097525A (en) | Image data recording apparatus and image data recording program | |
| JP2006101373A (en) | Image pickup device, image pickup auxiliary method, and program | |
| JP5182405B2 (en) | Movie recording apparatus and program | |
| JP4872728B2 (en) | Movie recording apparatus and program | |
| JP4923722B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and program | |
| JP4968367B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, imaging assistance method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070411 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070411 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090108 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090120 |
|
| A762 | Written abandonment of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A762 Effective date: 20090319 |