JP3968262B2 - Information processing apparatus for mobile object, information processing system for mobile object, and transmission station, server, method, recording medium and program used therefor - Google Patents
Information processing apparatus for mobile object, information processing system for mobile object, and transmission station, server, method, recording medium and program used therefor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3968262B2 JP3968262B2 JP2002094539A JP2002094539A JP3968262B2 JP 3968262 B2 JP3968262 B2 JP 3968262B2 JP 2002094539 A JP2002094539 A JP 2002094539A JP 2002094539 A JP2002094539 A JP 2002094539A JP 3968262 B2 JP3968262 B2 JP 3968262B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- narrow area
- map
- current position
- area information
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、移動体用の情報処理装置に関し、より特定的には、現在位置の特定を行い経路案内機能を有する移動体用の情報処理装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来より、GPS(Global Positioning System:全地球測位システム)によって現在位置を検出して経路案内(ナビゲーション)を行うナビゲーション装置が存在する。ところが、GPSによる測量結果には、10〜100m程度の誤差が生じるため、正確に経路案内するためには、その誤差を補正する必要がある。そのため、様々なシステムが提案されている。
【0003】
たとえば、特開平08−136638号公報などに記載のディファレンシャルGPSシステムを用いれば、誤差を数m程度にまで軽減させることができる。ディファレンシャルGPSシステムでは、位置が正確に分かっている定点に基準局を設置し、そこから各GPS衛星までの距離を正確に計算しておく。その基準局では、GPS衛星からの電波で測距を行い、計算結果と測距結果との差異をもとに補正値を求める。当該補正値は、FM多重放送などによって利用者のナビゲーション装置に通知される。ナビゲーション装置は、当該補正値に基づいて、GPSで検出した位置情報を補正し、より正確な位置を求めることができる。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかし、検出した位置情報をディファレンシャルGPSシステムによって補正し、現在位置の緯度経度を高精度に特定したとしても、未だ、従来のナビゲーション装置では、十分に経路案内できない場合が生じる。たとえば、高速道路が高い所にあり、その下を一般道路が走っているような場合、両者とも緯度経度は同一であるので、従来のナビゲーション装置では、どちらの道路を走っているかを区別するのは困難である。すなわち、GPSを用いれば、緯度経度といったグローバルな位置情報を得ることはできるものの、どういった道路を走っているのかなどのローカルな位置情報を得ることはできなかった。
【0005】
また、従来のナビゲーション装置では、工事などにより道路の車線が制限されていたりする場合など、十分に経路案内ができない場合が多々存在し、柔軟に道路状況の変化などに対応して経路案内をすることが困難であった。
【0006】
それゆえ、本発明の目的は、GPSによる位置検出と並行してローカルな情報に基づいて現在位置を特定し、さらに、柔軟に経路案内を行うことができる移動体用情報処理装置を提供することである。
【0007】
【課題を解決するための手段および発明の効果】
第1の発明は、移動体に備え付けられ、現在位置の特定を行う移動体用情報処理装置であって、
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出する広域位置情報検出手段と、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得する狭域情報取得手段と、
狭域情報に基づいて、広域位置情報検出手段が検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定する現在位置特定手段と、
地図データを格納する地図記憶手段と、
前記現在位置特定手段が特定した現在位置に対応する前記地図データを前記地図記憶手段から読み出し、当該地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示する地図表示手段とを含む。
【0008】
第1の発明によれば、狭域情報を用いて広域情報から検出した位置情報を修正し、現在位置を特定するので、より正確に移動体の現在位置を特定し、地図記憶手段に格納されている地図データには含まれない詳細な地図を補って表示することができる移動体用情報処理装置を提供することが可能となる。
【0009】
第2の発明は、第1の発明に従属する発明であって、狭域情報には、狭域情報を無線で送信する送信局が配置されている配置場所に関する情報が含まれており、
現在位置特定手段は、配置場所に関する情報に基づいて現在位置を特定することを特徴とする。
【0010】
第2の発明によれば、送信局の配置場所に関する情報を得ることができるので、現在移動体がどの道路に位置しているかなど緯度経度だけでは認識できない情報を入手することができ、現在位置をより正確に特定することが可能となる。
【0011】
第3の発明は、第1または第2の発明に従属する発明であって、狭域情報には、狭域情報を無線で送信する送信局が位置する正確な緯度経度が含まれており、
現在位置特定手段は、正確な緯度経度に基づいて広域位置情報検出手段が検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定することを特徴とする。
【0012】
第3の発明によれば、移動体の近傍に存在する送信局の正確な緯度経度に基づいて広域情報から得られる位置情報を修正するので、移動体の現在の緯度経度をより正確なものにすることができ、より正確に現在位置を特定することが可能となる。
【0013】
第4の発明は、第1の発明に従属する発明であって、さらに、
地図表示手段の地図表示に基づいて経路案内を行う経路案内手段とを含む。
【0014】
第4の発明によれば、現在位置の地図を表示して経路案内を行うことが可能となる。
【0015】
第5の発明は、第4の発明に従属する発明であって、狭域情報には、現在位置の周辺情報が含まれており、
地図表示手段は、現在位置の地図と共に、周辺情報も併せて表示することを特徴とする。
【0016】
第5の発明によれば、地図と共に周辺情報も併せて表示されるので、ユーザは、最新の周辺の状況に応じて移動することができ、より柔軟に経路上を移動することが可能となる。
【0017】
第6の発明は、第5の発明に従属する発明であって、経路案内手段は、周辺情報に基づいて経路案内することを特徴とする。
【0018】
第6の発明によれば、周辺情報に基づいて経路案内するので、周辺状況に応じたより柔軟な経路案内をユーザに提供することが可能となる。
【0021】
第7の発明は、第1の発明に従属する発明であって、さらに、狭域情報を無線で送信する送信局に対し、ユーザが所望する狭域情報の送信を要求する狭域情報要求手段と、
所望する狭域情報を送信局から取得する所望狭域情報取得手段と、
所望狭域情報取得手段が取得した狭域情報を表示する所望狭域情報表示手段とを含む。
【0022】
第7の発明によれば、ユーザが所望する狭域情報を入手することができるので、様々な情報を利用しながら移動することが可能となる。
【0023】
第8の発明は、第1の発明に従属する発明であって、さらに、ユーザが所望する狭域情報を受け付ける受付部と、
受付部で受け付けた所望の狭域情報を送信局から取得する所望狭域情報取得手段と、
所望狭域情報取得手段が取得した狭域情報を表示する所望狭域情報表示手段とを含む。
【0024】
第8の発明によれば、ユーザが所望する狭域情報を受け付けて表示することができので、様々な情報を利用しながら移動することが可能となる。
【0025】
第9の発明は、移動体の現在位置を特定するためのシステムであって、
現在位置の特定を行う移動体用情報処理装置と、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を無線で送信する狭域情報送信局とを備え、
移動体用情報処理装置は、
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出する広域位置情報検出手段と、
狭域情報送信局から送信される狭域情報を取得する狭域情報取得手段と、
狭域位置情報に基づいて、広域位置情報検出手段が検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定する現在位置特定手段と、
地図データを格納する地図記憶手段と、
前記現在位置特定手段が特定した現在位置に対応する前記地図データを前記地図記憶手段から読み出し、現在位置の地図と前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示する地図表示手段とを含む。
【0026】
第9の発明によれば、道路上などに設置された狭域情報送信局から送信され、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を移動体情報処理装置が利用できるので、移動体は、より正確な現在位置を特定し、地図記憶手段に格納されている地図データには含まれない詳細な地図を補って表示しながら移動することができるシステムが提供される。
【0027】
第10の発明は、第9の発明に従属する発明であって、さらに、ネットワークを介して狭域情報送信局と接続されており、移動体用情報処理装置からの要求に応じて、所望の狭域情報を、狭域情報送信局を介して、移動体用情報処理装置に送信する狭域情報送信サーバとを備える。
【0028】
第10の発明によれば、所望の狭域情報を移動体用情報処理装置に送信することができるシステムが提供される。
【0029】
第11の発明は、広域で用いられる広域情報および狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報に基づいて移動体の現在位置を特定して、特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを読み出し、当該地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するためのシステムに用いられる狭域情報を無線で送信するための送信局であって、
自己が位置する正確な緯度経度および/または自己が配置されている配置場所に関する情報を狭域情報に含めて送信する狭域情報送信手段を含む。
【0030】
第12の発明は、広域で用いられる広域情報および狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報に基づいて移動体の現在位置を特定して、特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを読み出し、当該地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するためのシステムに用いられるサーバであって、
ネットワークを介して接続されている狭域情報を無線で送信するための送信局からの要求に応じて、所望の狭域情報を、送信局に送信する狭域情報送信手段を含む。
【0031】
第13の発明は、第12の発明に従属する発明であって、狭域情報送信手段は、予め登録されている移動体宛にのみ狭域情報を送信することを特徴とする。
【0032】
第13の発明によれば、狭域情報を提供するサービスを行うビジネスを展開するためのサーバが提供できる。したがって、狭域情報サービス普及への貢献が期待される。
【0033】
第14の発明は、現在位置の特定を行う方法であって、
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップと、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得するステップと、
狭域位置情報に基づいて、広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップで検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定するステップと、
特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを地図記憶媒体から読み出すステップと、
読み出した前記地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するステップとを含む。
【0034】
第15の発明は、現在位置の特定を行うプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読みとり可能な記録媒体であって、
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップと、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得するステップと、
狭域位置情報に基づいて、広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップで検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定するステップと、
特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを地図記憶媒体から読み出すステップと、
読み出した前記地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するステップとを含むプログラムが格納されている。
【0035】
第16の発明は、現在位置の特定を行うコンピュータで実行されるプログラムであって、
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップと、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得するステップと、
狭域位置情報に基づいて、広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップで検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定するステップと、
特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを地図記憶媒体から読み出すステップと、
読み出した前記地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するステップとを含む。
【0036】
【発明の実施の形態】
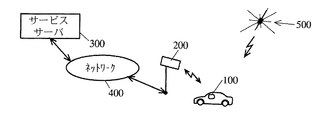
図1は、本発明の第1の実施形態に係る移動体用情報システムの全体構成を示す図である。図1において、移動体用情報システムは、車両に設置されている移動体用情報処理装置100と、DSRC(Dedicated Short Range Communications:狭域通信)方式による無線信号を送受信するDSRC局200と、サービスサーバ300と、ネットワーク400とを備える。
【0037】
移動体用情報処理装置100とDSRC局200とは、DSRC方式によって、双方向高速通信を行う。
【0038】
移動体用情報処理装置100は、GPS衛星500(図1では、一つしか示していないが実際は複数である)からの電波を受信して現在位置の緯度経度(以下、GPS位置情報という)を検出し、地図と共に表示して、ユーザを経路案内する。また、移動体用情報処理装置100は、DSRC局200のアンテナから出力されるDSRC方式による無線信号を受信し、無線信号に含まれている情報(以下、DSRC情報という)に基づき、GPS位置情報を修正しながら地図および周辺情報(たとえば、交通情報、渋滞情報、工事情報や近隣の店情報など)を表示する。さらに、移動体用情報処理装置100は、ユーザの入力に応じて、DSRC局200に所望するDSRC情報を得るための要求を行う。DSRC情報は、約30m範囲内の狭域で使用される情報である。一方、GPS位置情報は、全地球のように広域で使用される情報である。
【0039】
DSRC局200は、道路上や店舗の駐車場に設置されており、移動体用情報処理装置100に対し、画一的なDSRC情報を一方的に送信すると共に、移動体用情報処理装置100の要求に応じて必要な情報をネットワーク400を介してサービスサーバ300から取得し、移動体用情報処理装置100に送信する。DSRC局200が一方的に送信する画一的なDSRC情報(以下、画一的DSRC情報という)は、定期的にサービスサーバ300からネットワーク400を介してDSRC局200に送信される。画一的DSRC情報には、位置情報(GPS位置情報と区別するため、DSRC位置情報ということにする)の他、交通情報、工事情報、渋滞情報、近隣の店情報などの周辺情報が含まれている。DSRC位置情報には、DSRC局200の正確な緯度経度および自己の配置場所に関する情報(たとえば、国道何号、○○高速道路など道路の名称)が含まれている。また、DSRC位置情報には、地図情報として例えば店舗、サービスエリア等の駐車場の地図が含まれていても良い。DSRC位置情報の地図は、一旦移動体用情報処理装置100内に記憶され、次回以降も活用することが出来る。なお、図1においては、DSRC局200を一つしか示さなかったが、実際は、道路上などに複数存在する。
【0040】
ネットワーク400は、専用線などで構成される交換網である。
【0041】
サービスサーバ300は、定期的に画一的DSRC情報をDSRC局200に送信すると共に、DSRC局200からの要求に応じて必要なDSRC情報をDSRC局200に送信する。
【0042】
図2は、移動体用情報処理装置100の構成を示すブロック図である。図2において、移動体用情報処理装置100は、制御部101と、地図情報記憶部102と、車両ID記憶部103と、操作部104と、DSRC情報送受信部105と、GPS位置検出部106と、表示部107と、一時記憶部108とを含む。
【0043】
操作部104は、ユーザの入力に応じて、制御部101の動作を制御する操作ボタンなどである。操作部104は、ユーザがDSRC情報を入手したいと所望する場合、それを受け付けて制御部101に所望のDSRC情報を取得させる。
【0044】
表示部107は、制御部101からの指示に応じて、地図およびDSRC情報を表示する液晶画面装置などである。車両ID記憶部103は、移動体用情報処理装置100が設置されている車両に割り当てられているIDナンバー(以下、車両IDという)を格納するためのメモリである。車両IDは、DSRC局200にDSRC情報の送信を要求する際に利用される。地図情報記憶部102は、地図のデータを格納しているCD−ROMなどの記録媒体である。一時記憶部108は、DSRC情報を一時的に格納しておくためのメモリである。
【0045】
DSRC情報送受信部105は、DSRC局200から無線で送信されるDSRC情報を受信して制御部101に与えると共に、制御部101からの要求をDSRC局200に無線で送信する。GPS位置検出部106は、GPS衛星500からの電波に基づいて、GPS位置情報を検出し、制御部101に送る。
【0046】
制御部101は、GPS位置検出部106からのGPS位置情報およびDSRC情報送受信部105からのDSRC情報に基づいて、地図情報記憶部102から地図データを取り出し、表示部107に地図を表示させ経路案内を行うと共に、DSRC情報に含まれる周辺情報を表示させる。また、制御部101は、操作部104からの指示に応じて、ユーザが所望するDSRC情報の送信を、DSRC情報送受信部105を介して、DSRC局200に要求し、所望のDSRC情報を取得する。この際、制御部101は、車両ID記憶部103に格納されている車両IDを共に送信する。さらに、制御部101は、取得したDSRC情報を一時記憶部108に格納しておく。DSRC情報に地図情報などが含まれた場合には、地図情報を一時格納部108に格納し、次回以降も再利用する。またCD−ROMに入った地図データと、DSRC情報に含まれた地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やすことが出来る。例えばDSRC情報に店舗、サービスエリア等の駐車場の地図を入れておけば、ドライバーは、具体的な駐車場の地図により、駐車時の操作をスムーズに行うことが出来る。
【0047】
図3は、DSRC局200の構成を示すブロック図である。図3において、DSRC局200は、第1のDSRC情報送受信部201と、制御部202と、DSRC情報記憶部203と、第2のDSRC情報送受信部204とを含む。
【0048】
DSRC情報記憶部203は、DSRC情報を格納する記録媒体である。第1のDSRC情報送受信部201は、DSRC方式によって、移動体用情報処理装置100と制御部202との間でDSRC情報の送受信を行う。第2のDSRC情報送受信部204は、ネットワーク400を介して、サービスサーバ300と制御部202との間でDSRC情報の送受信を行う。
【0049】
制御部202は、第2のDSRC情報送受信部204から送られてくる画一的DSRC情報をDSRC情報記憶部203に格納しておいて、画一的DSRC情報を第1のDSRC情報送受信部201に送る。また、制御部202は、移動体用情報処理装置100からの要求に基づき、必要なDSRC情報を第2のDSRC情報送受信部204を介してサービスサーバ300から取得し、移動体用情報処理装置100宛に送信する。
【0050】
図4は、サービスサーバ300の構成を示すブロック図である。図4において、サービスサーバ300は、DSRC情報送受信部301と、制御部302と、DSRC情報記憶部303とを含む。
【0051】
DSRC情報記憶部303は、DSRC情報を格納する記録媒体である。DSRC情報送受信部301は、ネットワーク400を介して、DSRC局200と制御部302との間でDSRC情報の送受信を行う。制御部302は、定期的に画一的DSRC情報をDSRC情報記憶部303から取り出し、DSRC局200に送信する。また、制御部302は、DSRC局200から要求があった場合、必要なDSRC情報をDSRC情報記憶部303から取り出し、送信要求に含まれる車両ID宛に送信する。
【0052】
図5は、移動体用情報処理装置100における制御部101の動作を示すフローチャートである。以下、図5を参照しながら、制御部101の動作について説明する。まず、制御部101は、GPS位置検出部106が検出したGPS位置情報を取得する(ステップS101)。次に、制御部101は、現在、DSRC情報送受信部105が画一的DSRC情報を受信中であるか否か判断する(ステップS102)。
【0053】
画一的DSRC情報を受信中でない場合、制御部101は、GPS位置情報に基づいて地図情報記憶部102から対応する地図データを取得し、表示部107に地図を表示させ経路案内を行う(ステップS112)。次に、制御部101は、地図表示と併せて、一時記憶部108に格納されているDSRC情報に基づいて、DSRC情報に含まれる周辺情報を表示部107に表示させ、より現状に即した経路案内を行い(ステップS113)、ステップS108の動作に進む。
【0054】
一方、画一的DSRC情報を受信中である場合、制御部101は、画一的DSRC情報からDSRC位置情報を取り出す(ステップS103)。次に、制御部101は、DSRC位置情報に含まれる正確な緯度経度によってGPS位置情報の緯度経度を修正し(ステップS104)、さらに、DSRC位置情報に含まれる配置場所に関する情報(道路の名称など)によって現在位置している道路を特定する(ステップS105)。
【0055】
次に、制御部101は、修正したGPS位置情報に基づいて、地図情報記憶部102から対応する地図データを取得し、さらに特定された道路に基づいて現在位置を特定し、表示部107に現在位置と共に地図を表示させて経路案内を行う(ステップS106)。次に、制御部101は、受信中のDSRC情報に基づいて、周辺情報を表示部107に表示させ、より現状に即した経路案内を行い(ステップS107)、ステップS108の動作に進む。
【0056】
ステップS108の動作において、制御部101は、操作部104からDSRC情報(現在表示中のDSRC情報にリンクされている情報を含む)を表示するための指示が与えられているか否かを判断する。指示が与えられていない場合、制御部101は、ステップS101の動作に戻る。
【0057】
一方、指示が与えられている場合、制御部101は、近隣の交信可能なDSRC局200に対して、DSRC情報送受信部105を介して、所望のDSRC情報を送信するよう要求する(ステップS109)。当該送信要求には、車両IDが含まれる。次に、制御部101は、DSRC情報送受信部105が受信した所望のDSRC情報を受け取り(ステップS110)、取得したDSRC情報を地図表示と共に表示し(ステップS111)、ステップS101の動作に戻る。
【0058】
図6は、移動体用情報処理装置100からDSRC情報の送信要求がある場合の移動体用情報処理装置100、DSRC局200およびサービスサーバ300の動作を示すフローチャートである。図6において、図5に示したステップと同一の動作については、同一のステップ番号を付す。
【0059】
まず、移動体用情報処理装置100は、交信可能なDSRC局200に対し、DSRC情報の送信を要求する(ステップS109)。次に、DSRC局200の制御部202は、移動体用情報処理装置100からの送信要求を受信し(ステップS201)、サービスサーバ300に対して、DSRC情報の送信を要求する(ステップS202)。
【0060】
次に、サービスサーバ300の制御部302は、DSRC局200からの送信要求を受信し、送信要求に含まれている車両IDを確認する(ステップS301)。次に、サービスサーバ300の制御部302は、DSRC情報記憶部303から必要なDSRC情報を取得し(ステップS302)、車両IDに対応する移動体用情報処理装置100宛に、当該DSRC情報をDSRC局200に送信し(ステップS303)、処理を終了する。
【0061】
次に、DSRC局200の制御部202は、サービスサーバ300から送信されてくるDSRC情報を受信して(ステップS203)、車両IDに対応する移動体用情報処理装置100に当該DSRC情報を送信し(ステップS204)、処理を終了する。その後、移動体用情報処理装置100は、送信されてくるDSRC情報を受信する(ステップS110)。
【0062】
このように、DSRC位置情報には、DSRC局200の正確な緯度経度と共に、道路の名称などのローカルな情報が含まれているので、移動体用情報処理装置100は、DSRC位置情報に基づいてGPS位置情報を修正してさらに現在位置を特定することが可能となる。したがって、より正確な地図表示および経路案内を行うことが可能となる。たとえば、高速道路の下を一般道路が走っている場合、移動体用情報処理装置100では、DSRC情報に基づいてどちらの道路に位置しているのかを認識することが可能となる。
【0063】
また、DSRC情報に含まれる周辺情報(交通情報、渋滞情報、工事情報、店情報など)を地図と共に表示できるので、移動体用情報処理装置100は、より柔軟に経路案内を行うことができる。
【0064】
さらに、移動体用情報処理装置100はユーザが所望するDSRC情報を取得することができるので、ユーザは、有益な情報を入手することが可能となる。
【0065】
なお、ここでは、DSRC位置情報に道路の名称を含むこととしたが、それに代わって住所や店の名前などを使用するようにしてもよい。
【0066】
また、DSRC位置情報として、DSRC局200の正確な緯度経度と配置場所に関する情報とを用いたが、ディファレンシャルGPSで用いるような補正値と配置場所に関する情報とを用いるようにしてもよい。
【0067】
なお、サービスサーバ300では、予め登録してある車両IDの車両にのみ、所望するDSRC情報を送信するようにしてもよい。これにより、DSRC情報を送信するビジネスが展開できる。
【0068】
なお、上記実施形態では、DSRC方式による双方向通信を利用することとしたが、双方向通信を行えるのであれば、これに限られるものではない。
【0069】
なお、制御部101をCPUとし、プログラムを実行することによって、制御部101を動作させるようにしてもよい。また、当該プログラムは、コンピュータ装置に利用可能な記録媒体に格納しておいてもよい。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施形態に係る移動体用情報システムの全体構成を示す図である。
【図2】移動体用情報処理装置100の構成を示すブロック図である。
【図3】DSRC局200の構成を示すブロック図である。
【図4】サービスサーバ300の構成を示すブロック図である。
【図5】移動体用情報処理装置100における制御部101の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【図6】移動体用情報処理装置100からDSRC情報の送信要求がある場合の移動体用情報処理装置100、DSRC局200およびサービスサーバ300の動作を示すフローチャートである。
【符号の説明】
100 移動体用情報処理装置
200 DSRC局
300 サービスサーバ
400 ネットワーク
500 GPS衛星
101,202,302 制御部
102 地図情報記憶部
103 車両ID記憶部
104 操作部
105,301 DSRC情報送受信部
106 GPS位置検出部
107 表示部
108 一時記憶部
201 第1のDSRC情報送受信部
203,303 DSRC情報記憶部
204 第2のDSRC情報送受信部[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an information processing apparatus for a mobile object, and more particularly to an information processing apparatus for a mobile object that specifies a current position and has a route guidance function.
[0002]
[Prior art]
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, there are navigation devices that perform route guidance (navigation) by detecting a current position by using a GPS (Global Positioning System). However, since an error of about 10 to 100 m occurs in the survey result by GPS, it is necessary to correct the error in order to guide the route accurately. For this reason, various systems have been proposed.
[0003]
For example, if a differential GPS system described in Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 08-136638 is used, the error can be reduced to about several meters. In the differential GPS system, a reference station is installed at a fixed point whose position is accurately known, and the distance to each GPS satellite is accurately calculated. The reference station performs distance measurement using radio waves from a GPS satellite, and obtains a correction value based on the difference between the calculation result and the distance measurement result. The correction value is notified to the user's navigation device by FM multiplex broadcasting or the like. The navigation device can correct the position information detected by the GPS based on the correction value and obtain a more accurate position.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, even if the detected position information is corrected by the differential GPS system and the latitude and longitude of the current position are specified with high accuracy, there are still cases where the conventional navigation apparatus cannot sufficiently provide route guidance. For example, when a highway is high and a general road is running underneath, the latitude and longitude are the same for both, so the conventional navigation device distinguishes which road is running. It is difficult. That is, if GPS is used, global position information such as latitude and longitude can be obtained, but local position information such as which road is running cannot be obtained.
[0005]
Also, with conventional navigation devices, there are many cases where route guidance is not possible, such as when road lanes are restricted due to construction, etc., and route guidance is flexibly dealt with in response to changes in road conditions. It was difficult.
[0006]
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an information processing apparatus for a mobile body that can specify a current position based on local information in parallel with position detection by GPS and can perform route guidance flexibly. It is.
[0007]
[Means for Solving the Problems and Effects of the Invention]
A first invention is an information processing apparatus for a moving body that is provided in a moving body and identifies a current position,
Wide-area position information detecting means for detecting position information from wide-area information used in a wide area;
Used in narrow areas, Including narrow location information and map informationNarrow area information acquisition means for acquiring narrow area information;
Current position specifying means for correcting the position information detected by the wide area position information detecting means based on the narrow area information and specifying the current position;,
Map storage means for storing map data;
The current position where the map data corresponding to the current position specified by the current position specifying means is read from the map storage means and the amount of information on the map used for route guidance is increased using the map data and the map information Map display means for displaying the map ofincluding.
[0008]
According to the first invention, the position information detected from the wide area information is corrected using the narrow area information, and the current position is specified, so the current position of the moving object is specified more accuratelyThe detailed map that is not included in the map data stored in the map storage means is displayed.It is possible to provide an information processing apparatus for a moving body that can be used.
[0009]
The second invention is an invention subordinate to the first invention, and the narrow area information includes information on an arrangement location where a transmitting station for transmitting the narrow area information wirelessly is arranged,
The current position specifying means specifies the current position on the basis of information on the arrangement location.
[0010]
According to the second invention, since information on the location of the transmitting station can be obtained, it is possible to obtain information that cannot be recognized only by latitude and longitude, such as on which road the moving body is currently located. Can be specified more accurately.
[0011]
The third invention is an invention subordinate to the first or second invention, and the narrow area information includes an accurate latitude and longitude where a transmitting station that wirelessly transmits the narrow area information is located,
The current position specifying means is characterized in that the current position is specified by correcting the position information detected by the wide area position information detecting means based on accurate latitude and longitude.
[0012]
According to the third invention, since the position information obtained from the wide area information is corrected based on the accurate latitude and longitude of the transmitting station existing in the vicinity of the mobile body, the current latitude and longitude of the mobile body is made more accurate. And the current position can be specified more accurately.
[0013]
The fourth invention is an invention subordinate to the first invention, and further,
Route guidance means for performing route guidance based on the map display of the map display means.
[0014]
According to the fourth invention, it is possible to perform route guidance by displaying a map of the current position.
[0015]
The fifth invention is an invention subordinate to the fourth invention, and the narrow area information includes peripheral information of the current position,
The map display means displays the surrounding information together with the map of the current position.
[0016]
According to the fifth aspect, since the surrounding information is also displayed together with the map, the user can move according to the latest surrounding situation, and can move on the route more flexibly. .
[0017]
A sixth invention is an invention subordinate to the fifth invention, wherein the route guidance means performs route guidance based on peripheral information.
[0018]
According to the sixth aspect of the invention, route guidance is performed based on the surrounding information, so that more flexible route guidance according to the surrounding situation can be provided to the user.
[0021]
First7The invention of the invention is an invention subordinate to the first invention, and further, narrow area information requesting means for requesting transmission of narrow area information desired by a user to a transmitting station that wirelessly transmits narrow area information,
Desired narrow area information obtaining means for obtaining desired narrow area information from the transmitting station;
Desired narrow area information display means for displaying the narrow area information acquired by the desired narrow area information acquisition means.
[0022]
First7According to this invention, it is possible to obtain narrow area information desired by the user, and thus it is possible to move while utilizing various information.
[0023]
First8The invention is an invention subordinate to the first invention, and further includes a reception unit that receives narrow area information desired by the user;
Desired narrow area information acquisition means for acquiring desired narrow area information received by the reception unit from the transmitting station;
Desired narrow area information display means for displaying the narrow area information acquired by the desired narrow area information acquisition means.
[0024]
First8According to this invention, since it is possible to receive and display narrow area information desired by the user, it is possible to move while utilizing various information.
[0025]
First9The present invention is a system for specifying the current position of a mobile object,
A mobile information processing device for identifying the current position;
Used in narrow areas, Including narrow location information and map informationWith a narrow area information transmitting station that transmits narrow area information wirelessly,
The mobile information processing device
Wide-area position information detecting means for detecting position information from wide-area information used in a wide area;
Narrow area information obtaining means for obtaining narrow area information transmitted from the narrow area information transmitting station;
Narrow areapositionCurrent position specifying means for correcting the position information detected by the wide area position information detecting means and specifying the current position based on the information;,
Map storage means for storing map data;
The map data corresponding to the current position specified by the current position specifying means is read from the map storage means, and the current amount of information on the map used for route guidance is increased using the map of the current position and the map information. A map display means for displaying a map of the position;including.
[0026]
First9According to this invention, it is transmitted from a narrow area information transmitting station installed on a road or the like., Including narrow location information and map informationSince the mobile information processing device can use the narrow area information, the mobile object specifies the current position more accurately.A detailed map that is not included in the map data stored in the map storage means is displayed.A system that can move while is provided.
[0027]
First10The invention of the9And is connected to a narrow area information transmitting station via a network, and in response to a request from the mobile information processing device, the desired narrow area information is converted into the narrow area information. A narrow area information transmission server that transmits the information to the mobile information processing apparatus via the transmission station.
[0028]
First10According to this invention, the system which can transmit desired narrow area information to the information processing apparatus for mobile bodies is provided.
[0029]
First11The invention is used in wide area information used in wide area and in narrow area, Including narrow location information and map informationIdentifying the current position of a moving object based on narrow area informationThen, the map data corresponding to the specified current position is read out, and the map of the current position with the increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance is displayed using the map data and the map information.A transmitting station for wirelessly transmitting narrow area information used in a system for
Narrow area information transmitting means is included for transmitting information on the exact latitude and longitude where the self is located and / or the location where the self is located in the narrow area information.
[0030]
First12The invention is used in wide area information used in wide area and in narrow area, Including narrow location information and map informationIdentifying the current position of a moving object based on narrow area informationThen, the map data corresponding to the specified current position is read out, and the map of the current position with the increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance is displayed using the map data and the map information.A server used in a system for
Narrow area information transmitting means for transmitting desired narrow area information to the transmitting station in response to a request from the transmitting station for wirelessly transmitting the narrow area information connected via the network.
[0031]
First13The invention of the12The narrow area information transmitting means transmits the narrow area information only to a mobile body registered in advance.
[0032]
First13According to the invention, it is possible to provide a server for developing a business that provides a service for providing narrow area information. Therefore, contribution to the spread of narrow area information services is expected.
[0033]
First14The present invention is a method for specifying the current position,
Detecting position information from wide area information used in a wide area;
Used in narrow areas, Including narrow location information and map informationObtaining narrow area information;
Narrow areapositionCorrecting the position information detected in the step of detecting position information from the wide area information based on the information and identifying the current position; and,
Reading map data corresponding to the identified current position from the map storage medium;
Using the read map data and the map information, displaying a map of the current position with an increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance; andincluding.
[0034]
First15The present invention is a computer-readable recording medium recording a program for specifying the current position,
Detecting position information from wide area information used in a wide area;
Used in narrow areas, Including narrow location information and map informationObtaining narrow area information;
Narrow areapositionCorrecting the position information detected in the step of detecting position information from the wide area information based on the information and identifying the current position; and,
Reading map data corresponding to the identified current position from the map storage medium;
Using the read map data and the map information, displaying a map of the current position with an increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance; andA program containing is stored.
[0035]
First16The present invention is a program executed by a computer for specifying the current position,
Detecting position information from wide area information used in a wide area;
Used in narrow areas, Including narrow location information and map informationObtaining narrow area information;
Narrow areapositionCorrecting the position information detected in the step of detecting position information from the wide area information based on the information and identifying the current position; and,
Reading map data corresponding to the identified current position from the map storage medium;
Using the read map data and the map information, displaying a map of the current position with an increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance; andincluding.
[0036]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an overall configuration of a mobile information system according to a first embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 1, a mobile information system includes a mobile
[0037]
The mobile
[0038]
The mobile
[0039]
The
[0040]
The
[0041]
The
[0042]
FIG. 2 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the mobile
[0043]
The
[0044]
The
[0045]
The DSRC information transmission /
[0046]
Based on the GPS position information from the GPS
[0047]
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing the configuration of the
[0048]
The DSRC
[0049]
The
[0050]
FIG. 4 is a block diagram illustrating a configuration of the
[0051]
The DSRC
[0052]
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing the operation of the
[0053]
When the uniform DSRC information is not being received, the
[0054]
On the other hand, when the uniform DSRC information is being received, the
[0055]
Next, the
[0056]
In the operation of step S108, the
[0057]
On the other hand, when the instruction is given, the
[0058]
FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing the operations of mobile
[0059]
First, the mobile
[0060]
Next, the
[0061]
Next, the
[0062]
As described above, since the DSRC position information includes local information such as the name of the road along with the exact latitude and longitude of the
[0063]
In addition, since peripheral information (traffic information, traffic jam information, construction information, store information, etc.) included in the DSRC information can be displayed together with a map, the mobile
[0064]
Furthermore, since the mobile
[0065]
Here, the name of the road is included in the DSRC position information, but an address, a store name, or the like may be used instead.
[0066]
Further, as the DSRC position information, the exact latitude and longitude of the
[0067]
The
[0068]
In the above-described embodiment, bidirectional communication using the DSRC method is used. However, the present invention is not limited to this as long as bidirectional communication can be performed.
[0069]
The
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an overall configuration of a mobile information system according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a mobile
3 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a
4 is a block diagram showing a configuration of a
FIG. 5 is a flowchart showing the operation of the
FIG. 6 is a flowchart showing operations of mobile
[Explanation of symbols]
100 Information processing apparatus for moving body
200 DSRC station
300 Service server
400 network
500 GPS satellite
101, 202, 302 Control unit
102 Map information storage unit
103 Vehicle ID storage unit
104 Operation unit
105,301 DSRC information transmitter / receiver
106 GPS position detector
107 Display
108 Temporary storage
201 First DSRC information transmitting / receiving unit
203,303 DSRC information storage unit
204 Second DSRC information transceiver
Claims (16)
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出する広域位置情報検出手段と、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得する狭域情報取得手段と、
前記狭域位置情報に基づいて、前記広域位置情報検出手段が検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定する現在位置特定手段と、
地図データを格納する地図記憶手段と、
前記現在位置特定手段が特定した現在位置に対応する前記地図データを前記地図記憶手段から読み出し、当該地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示する地図表示手段とを含む、移動体用情報処理装置。An information processing apparatus for a moving body that is provided in a moving body and identifies a current position,
Wide-area position information detecting means for detecting position information from wide-area information used in a wide area;
Narrow area information acquisition means for acquiring narrow area information including narrow area position information and map information, which is used in a narrow area ;
Based on the narrow area position information, current position specifying means for correcting the position information detected by the wide area position information detecting means and specifying the current position ;
Map storage means for storing map data;
The current position where the map data corresponding to the current position specified by the current position specifying means is read from the map storage means and the amount of information on the map used for route guidance is increased using the map data and the map information And a map display means for displaying the map of the mobile object.
前記現在位置特定手段は、前記配置場所に関する情報に基づいて現在位置を特定することを特徴とする、請求項1に記載の移動体用情報処理装置。The narrow area information includes information on an arrangement location where a transmitting station that wirelessly transmits the narrow area information is arranged,
The information processing apparatus for a moving body according to claim 1, wherein the current position specifying unit specifies a current position based on information on the arrangement location.
前記現在位置特定手段は、前記緯度経度に基づいて前記広域位置情報検出手段が検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定することを特徴とする、請求項1または2に記載の移動体用情報処理装置。The narrow area information includes latitude and longitude where a transmitting station that wirelessly transmits the narrow area information is located,
3. The mobile object according to claim 1, wherein the current position specifying unit specifies the current position by correcting the position information detected by the wide area position information detecting unit based on the latitude and longitude. Information processing device.
前記地図表示手段は、現在位置の地図と共に、前記周辺情報も併せて表示することを特徴とする、請求項4に記載の移動体用情報処理装置。The narrow area information includes surrounding information of the current position,
The mobile information processing apparatus according to claim 4, wherein the map display unit displays the peripheral information together with a map of a current position.
前記所望する狭域情報を前記送信局から取得する所望狭域情報取得手段と、
前記所望狭域情報取得手段が取得した狭域情報を表示する所望狭域情報表示手段とを含む、請求項1に記載の移動体用情報処理装置。Furthermore, narrow area information requesting means for requesting transmission of the narrow area information desired by the user to a transmitting station that wirelessly transmits the narrow area information,
Desired narrow area information acquisition means for acquiring the desired narrow area information from the transmitting station;
The information processing apparatus for a moving body according to claim 1, further comprising desired narrow area information display means for displaying the narrow area information acquired by the desired narrow area information acquisition means.
前記受付部で受け付けた所望の狭域情報を前記送信局から取得する所望狭域情報取得手段と、
前記所望狭域情報取得手段が取得した狭域情報を表示する所望狭域情報表示手段とを含む、請求項1に記載の移動体用情報処理装置。Furthermore, the reception part which receives the narrow area information which a user desires,
Desired narrow area information acquisition means for acquiring desired narrow area information received by the reception unit from the transmitting station;
The information processing apparatus for a moving body according to claim 1, further comprising desired narrow area information display means for displaying the narrow area information acquired by the desired narrow area information acquisition means.
現在位置の特定を行う移動体用情報処理装置と、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を無線で送信する狭域情報送信局とを備え、
前記移動体用情報処理装置は、
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出する広域位置情報検出手段と、
前記狭域情報送信局から送信される前記狭域情報を取得する狭域情報取得手段と、
前記狭域位置情報に基づいて、前記広域位置情報検出手段が検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定する現在位置特定手段と、
地図データを格納する地図記憶手段と、
前記現在位置特定手段が特定した現在位置に対応する前記地図データを前記地図記憶 手段から読み出し、当該地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示する地図表示手段とを含む、移動体用情報システム。A system for identifying the current position of a moving object,
A mobile information processing device for identifying the current position;
A narrow area information transmitting station that is used in a narrow area and wirelessly transmits narrow area information including narrow area position information and map information ,
The mobile object information processing apparatus comprises:
Wide-area position information detecting means for detecting position information from wide-area information used in a wide area;
Narrow area information obtaining means for obtaining the narrow area information transmitted from the narrow area information transmitting station;
Based on the narrow area position information, current position specifying means for correcting the position information detected by the wide area position information detecting means and specifying the current position ;
Map storage means for storing map data;
The current position where the map data corresponding to the current position specified by the current position specifying means is read from the map storage means and the amount of information on the map used for route guidance is increased using the map data and the map information And a map display means for displaying the map of the mobile object.
自己が位置する正確な緯度経度および/または自己が配置されている配置場所に関する情報を前記狭域情報に含めて送信する狭域情報送信手段を含む、狭域情報送信局。Wide area information used in a wide area and narrow area, the current position of the mobile body is identified based on the narrow area information including the narrow area position information and map information, and the map data corresponding to the identified current position is read, A transmitting station for wirelessly transmitting the narrow area information used in a system for displaying a map of the current position with an increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance using the map data and the map information Because
A narrow area information transmitting station, including narrow area information transmitting means for transmitting information on the exact latitude and longitude where the self is located and / or the location where the self is located in the narrow area information.
ネットワークを介して接続されている前記狭域情報を無線で送信するための送信局からの要求に応じて、所望の狭域情報を、前記送信局に送信する狭域情報送信手段を含む、狭域情報送信サーバ。Wide area information used in a wide area and narrow area, the current position of the mobile body is identified based on the narrow area information including the narrow area position information and map information, and the map data corresponding to the identified current position is read, Using the map data and the map information, a server used in a system for displaying a map of the current position with an increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance ,
Narrow area information transmitting means for transmitting desired narrow area information to the transmitting station in response to a request from a transmitting station for wirelessly transmitting the narrow area information connected via a network. Area information transmission server.
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップと、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得するステップと、
前記狭域位置情報に基づいて、前記広域情報から前記位置情報を検出するステップで検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定するステップと、
特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを地図記憶媒体から読み出すステップと、
読み出した前記地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するステップとを含む、現在位置特定方法。A method for identifying the current position,
Detecting position information from wide area information used in a wide area;
Obtaining narrow area information including narrow area position information and map information used in a narrow area ;
Correcting the position information detected in the step of detecting the position information from the wide area information based on the narrow area position information, and specifying the current position ;
Reading map data corresponding to the identified current position from the map storage medium;
A method of specifying a current position, comprising: using the read map data and the map information to display a map of a current position with an increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance .
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップと、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得するステップと、
前記狭域位置情報に基づいて、前記広域情報から前記位置情報を検出するステップで検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定するステップと、
特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを地図記憶媒体から読み出すステップと、
読み出した前記地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するステップとを含むプログラムが格納された、記録媒体。A computer-readable recording medium that records a program for identifying the current position,
Detecting position information from wide area information used in a wide area;
Obtaining narrow area information including narrow area position information and map information used in a narrow area ;
Correcting the position information detected in the step of detecting the position information from the wide area information based on the narrow area position information, and specifying the current position ;
Reading map data corresponding to the identified current position from the map storage medium;
A recording medium storing a program including a step of displaying a map of a current position obtained by increasing the amount of information on a map used for route guidance using the read map data and the map information .
広域で用いられる広域情報から位置情報を検出するステップと、
狭域で用いられ、狭域位置情報および地図情報を含む狭域情報を取得するステップと、
前記狭域位置情報に基づいて、前記広域情報から前記位置情報を検出するステップで検出した位置情報を修正して現在位置を特定するステップと、
特定した現在位置に対応する地図データを地図記憶媒体から読み出すステップと、
読み出した前記地図データと前記地図情報とを用いて、経路案内に用いる地図上の情報 量を増やした現在位置の地図を表示するステップとを含む、現在位置特定プログラム。A program that is executed on a computer that identifies the current position,
Detecting position information from wide area information used in a wide area;
Obtaining narrow area information including narrow area position information and map information used in a narrow area ;
Correcting the position information detected in the step of detecting the position information from the wide area information based on the narrow area position information, and specifying the current position ;
Reading map data corresponding to the identified current position from the map storage medium;
A current position specifying program, comprising: using the read map data and the map information to display a map of the current position with an increased amount of information on the map used for route guidance .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002094539A JP3968262B2 (en) | 2002-03-29 | 2002-03-29 | Information processing apparatus for mobile object, information processing system for mobile object, and transmission station, server, method, recording medium and program used therefor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002094539A JP3968262B2 (en) | 2002-03-29 | 2002-03-29 | Information processing apparatus for mobile object, information processing system for mobile object, and transmission station, server, method, recording medium and program used therefor |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003294467A JP2003294467A (en) | 2003-10-15 |
| JP2003294467A5 JP2003294467A5 (en) | 2005-07-21 |
| JP3968262B2 true JP3968262B2 (en) | 2007-08-29 |
Family
ID=29238479
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002094539A Expired - Fee Related JP3968262B2 (en) | 2002-03-29 | 2002-03-29 | Information processing apparatus for mobile object, information processing system for mobile object, and transmission station, server, method, recording medium and program used therefor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3968262B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005241258A (en) * | 2004-02-24 | 2005-09-08 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Information providing system, roadside device, on-vehicle information terminal device and information providing method |
| JP2006292689A (en) * | 2005-04-14 | 2006-10-26 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Traffic system |
-
2002
- 2002-03-29 JP JP2002094539A patent/JP3968262B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003294467A (en) | 2003-10-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5689252A (en) | Navigation system for an automotive vehicle | |
| EP1986170B1 (en) | Traffic situation determination system | |
| JP4695983B2 (en) | Traffic information processing equipment | |
| US8244450B2 (en) | Vehicle position information providing devices, methods, and programs | |
| US6859720B2 (en) | Traffic-information distribution method on-vehicle navigation apparatus | |
| US9127954B2 (en) | Navigation system, navigation apparatus, and data center | |
| JP4013630B2 (en) | Accident frequent location notification device, accident frequent location notification system, and accident frequent location notification method | |
| JP2007205872A (en) | Information communication system and information communication method | |
| JP2009139125A (en) | Relative inter-vehicle position calculation apparatus, transmission apparatus and program for same, program for transmission apparatus | |
| JP3407920B2 (en) | Mobile information processing system | |
| JP3269229B2 (en) | Mobile station location management system | |
| JP2009289223A (en) | Traffic situation prediction system, navigator, and server | |
| JP3895183B2 (en) | Map information updating apparatus and system | |
| EP0840094A2 (en) | Navigation system | |
| JP3968262B2 (en) | Information processing apparatus for mobile object, information processing system for mobile object, and transmission station, server, method, recording medium and program used therefor | |
| JP2005156246A (en) | Vehicle-mounted positioning system and present location positioning system | |
| JP3780895B2 (en) | Navigation device, program, and recording medium | |
| JP2012098077A (en) | Positional information service device, positional information service system and positional information service method | |
| JP2005016955A (en) | Navigation system for vehicle and positioning method of the same | |
| JP5237163B2 (en) | Traffic information management device, traffic information management method, and traffic information management program | |
| JP3900962B2 (en) | Navigation system, information center and in-vehicle device | |
| JP4007164B2 (en) | Navigation system | |
| JP3314490B2 (en) | Mobile location management system | |
| JP4730414B2 (en) | Mobile terminal device | |
| JP2005291732A (en) | Navigation device, method, and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041203 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20041203 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20061031 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20061109 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061227 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070510 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070604 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 3968262 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100608 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110608 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120608 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120608 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130608 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |