JP3960656B2 - Fastening device with emergency release by a nut body that can be expanded - Google Patents
Fastening device with emergency release by a nut body that can be expanded Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3960656B2 JP3960656B2 JP15911697A JP15911697A JP3960656B2 JP 3960656 B2 JP3960656 B2 JP 3960656B2 JP 15911697 A JP15911697 A JP 15911697A JP 15911697 A JP15911697 A JP 15911697A JP 3960656 B2 JP3960656 B2 JP 3960656B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- nut
- fastener
- wheel
- nut body
- hole
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Footwear And Its Accessory, Manufacturing Method And Apparatuses (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
この発明は、締付具と、それと係合する拡開性ナット体と、そのナット体と係合可能な孔とを有する緊急解除と緊急取付が可能な締付装置に関し、特に、インラインスケートの車輪装置を迅速かつ容易に取り外し、取付および/または調整するのに用いられ、または、履き物等にすべり止めを迅速かつ容易に取り外しおよび取り付けるのに用いられる締付装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
現在、インラインローラスケートに車輪装置を取り付ける様々な締付装置が使用されており、それら従来の締付装置は、ヘッドと、軸部と、ヘッドの反対側の軸部に形成されたネジ部とで構成され、ネジ部は、対応するネジ付きナットと係合可能となっている。インラインスケートのシャーシまたはフレーム部は、構造上、複数の車輪部を略直線に整列させて保持するために、設けられている。それぞれの車輪装置は、フレームの一側を貫通して挿入され、フレームに形成された孔を通り、更に、車輪装置の中央スリーブ孔を通って、フレームの反対側の孔を貫通して延びる締付具でフレームに保持されている。ナットは、締付具のネジ部と係合し、それによって、車輪部がフレームに対して正しい位置に取り付けられる。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
従来の締付装置における課題の一つは、修理、交換の目的のため、または、車輪を調整してスケートの車輪を再構成または再位置決めさせるため、もしくは、例えば「揺動」効果を設けるために、車輪を取り外すのに時間がかかることである。普通のスケータは、一つ以上の車輪装置を取り替えるために時間を気にすることはないかもしれないが、インラインホッケー競技のように、迅速な修理および交換が重要である場合がたくさんあり、さらに、インラインスケートの最初の組立と、修理人によるインラインスケートの修理にとって重要なことは、容易で、能率的かつ確実な車輪の取り外しおよび交換である。
【0004】
このように、インラインスケートを使用する競技の人気が増大するのに伴なって、迅速で、能率的かつ確実な車輪装置の取り外しおよび交換の必要性が増大し、例えば、インラインスケートホッケーは、プロレベルとアマチュアレベルの両方で人気が増大しているスポーツであり、さらに、インラインスケータが距離と時間をめざして競争する多数のレースが、全土にわたって行われており、これらにおいて、迅速で、能率的かつ確実な車輪装置の取り外しおよび交換は重要なものである。レクリエーションのインラインスケータでさえ、修理の目的のために、またはスケートしようとする面に合わせて異なる組成物の車輪材料を使用するために、車輪材料を交換する必要がある可能性がある。速度および効率は、必要条件ではないかもしれないが、可能な限り迅速かつ容易に車輪の修理又は交換ができることは、レクリエーションのスケータにとっても望ましいことである。
【0005】
また、レクリエーションのアマチュアおよびプロの競争者が、「揺動」形状にする目的のために、インラインスケートを再構成することを望む場合には、レクリエーションのアマチュアおよびプロの競争者にとって、容易に使用可能で締付装置が確実であることが重要である。従来、インラインスケートは、車輪が共通面またはスケート面に対して略衝合しているか、または接している形状であるのに対して、「揺動」形状は、一つ以上の端部車輪を共通面から移動させて、略カーブした面が設けられる。揺動形状は、ホッケースケートに類似しており、スケートのブレードが、フィギュアスケートで使用されるような平らなブレードであるよりも、むしろわずかに凸状の弓形で接地している。このように使用するために、迅速かつ容易にインラインスケートの車輪装置を再構成することが望ましいことは明かであろう。
【0006】
先行技術のもう一つの課題は、従来、締付装置と連関するハードウェアには、少なくとも細長い締付具/軸と、係合ナットとで構成される多数の部材が設けられており、これらの締付装置が、車輪を取り外し、取付または調整するために分離しなければならない二つ以上の部材を有しているため、部材を紛失することとなり、さらに車輪装置の操作を行う時間が増大することとなる。ナットは、締付具/軸に捕捉的に保持されないため、ナットは外れ落ちて紛失し、車輪装置を交換する人が作業を進めるためにもう一つのナットを見つけることが必要となる。溝付きナットを有していることが望まれる結果、ナットに損傷を与えるのを防ぐためにナットを溝部に位置決めさせることを要することによって、問題はより深刻なものとなる。ナットに溝を設けることにより、締付具のネジ部を車輪のスリーブ孔を通して、フレームの反対側の部材の反対側開口部を貫通して整列させようするために、問題は複雑となる。
【0007】
インラインスケートに使用するための従来技術の締付装置の実施例が、下記のアメリカ特許、1990年3月20日にオルソン(Olson)に付与されたアメリカ特許第4,909,523号と、1991年7月2日にオルソン(Olson)に付与されたアメリカ特許第5,028,058号と、1991年9月17日にオルソン等(Olson et al.)に付与されたアメリカ特許第5,048,848号と、1991年12月3日にマレヴィックズ(Malewicz)に付与されたアメリカ特許第5,068,956号と、1992年3月3日にマレヴィックズ(Malewicz)に付与されたアメリカ特許第5,092,614号に開示されている。マレヴィックズ(Malewicz)’956に開示されている装置は、ナットをカバーするキャップを使用しており、ナットに溝を設ける必要がない。しかしながら、マレヴィックズ(Malewicz)’956の装置は、締付具をナットに確実に係合させるために、締付具を何回も回転させる必要がある。締付具をナットに確実に係合させるために、締付具を何回も回転させる必要があることは、上述したそれぞれの引用文献において開示されている。
【0008】
運動競技用の履き物のすべり止め装置は、迅速で、容易かつ確実な装置の取り外しおよび交換が必要とされるもう一つの用途である。運動競技用の履き物のすべり止めは、様々なスポーツ活動のために広く使用されている。例えば、すべり止めは、少数の例を挙げれば、サッカー、野球、フットボール、陸上競技、ラグビー等のプロおよびアマチュアのスポーツにおいて使用されている。すべり止めがすり減ったりまたは損傷を受けた時にすべり止めを交換すること、または競技場で使用される面のタイプに応じてすべり止めを替えることが、定期的に必要となる。
【0009】
従来、先行技術のすべり止め装置は、運動競技用の履き物の靴底に埋込成形されるナット体を使用している。ネジ付きすべり止めは、埋込成形されたナット体内に駆動される。これらのすべり止め装置により、すべり止めの履き物の靴底との確実な係合が確実に行われるが、このような係合には時間がかかる。
【0010】
インラインスケートの車輪装置の締付装置および運動競技用履き物のすべり止め装置の上述した実施例を念頭において、締付具の取り外しおよび交換の速度と効率と確実性を向上させる締付装置の恩恵を受けることとなる用途が他に沢山あることは明かであろう。
【0011】
本発明による主な目的は、保持される部材を、迅速で、能率的かつ確実な取付および取り外しを行うことができる締付装置を提供することにある。
【0012】
本発明によるもう一つの目的は、インラインスケートのフレームに対して回転位置で車輪装置を保持するために、インラインスケートの軸として使用可能な締付装置を提供することにある。
【0013】
さらに、本発明によるもう一つの目的は、履き物にすべり止めを、迅速に、能率的かつ確実に取付が可能な締付装置を提供することにある。
【0014】
またさらに、本発明による目的は、インラインスケートの車輪装置の緊急調整が可能な締付装置を提供することにある。
【0015】
【課題を解決するための手段】
簡単に説明すれば、本発明は、締付装置によって取り付けられる部材の能率的かつ確実な取付と、係合解除と、再取付とを行うための新規な緊急解除締付装置に関し、本発明による締付装置は、一端部に駆動構造と他端部にネジ部が設けられている軸部を有する細長い締付具部材を有し、また、その締付装置は、締付具のネジ部と係合し、円形または多角形の孔の車輪孔カバーに係合可能となっているナット部材を有している。ナット拡開構造が、ナットと締付具に設けられており、締付具が回転して係合すると、ナットが拡開また拡大するように設けられている。まず、ナットは、ナット拡開構造を係合解除させて、締付具のネジ部に保持される。ワークピースには、ナットを収容するための孔が設けられている。キーまたは同等の構造が、孔に形成されており、キー溝または同等の構造がナットに形成されている。キー溝は、キーを収容するように寸法決めされている。キー溝は、キーをキー溝に係合させて、ナットを拡張または拡開させることが可能であり、ナットが孔内で回転するのを防ぐ。ナットに対して、締付具を約90度または4分の1回転させることにより、締付具とナットのナット拡開構造に係合され、ナットの外面が孔の内面と強制的に接合されて係合される。車輪又はすべり止めは、締付具を4分の1回転させるだけで、取り外し又は取付が可能であるので、締付装置は、車輪装置のインラインスケートへの取り付けと、すべり止めの履き物への取り付けのために特に役立つ。特に、インラインスケート装置において、細長い締付具は、車輪装置を所定位置に保持するために、軸として機能する。このように、締付具を4分の1回転することにより、ナット部材と連関する孔との係合から開放される。拡開性ナットが取り付けられて、締付具/軸は取り外し可能であり、車輪が交換され、締付具/軸が再挿入され、それから締付具を4分の1回転させて取り付けられる。
【0016】
【実施例】
本発明は、異なる形状の実施例に影響を受けやすいが、本発明の説明は、本発明の原理を示すものと考えられ、ここで図示され説明された発明に限定されるものではないという了解のもとで、実施例を図示して、以下に詳細に説明する。
【0017】
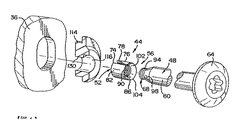
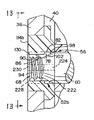
図1において、しばしば「インライン」ローラスケートと呼ばれている型のシングルローラスケート20は、ブーツ部24と、ブーツ部24に取り付けられた車輪フレーム28とを有し、その車輪フレーム28は、複数の車輪装置30を直線に整列させて保持し、さらに、図2及至図7について説明すれば、車輪フレーム28は、第一のサイドレール32と、第二のサイドレール36を有し、それらのサイドレール32,36は、離間して設けられ、それらの間に溝40を規定している。それぞれの車輪装置30は、締付具/軸装置44により溝40の所定位置に保持されている。
【0018】
締付装置44には、軸と、軸を第一および第二のサイドレール32,36と係合させて保持するための構造が設けられており、締付装置44は、締付具48と、拡開性ナット体52と、締付具48およびナット体52のナット拡開構造56とによって構成されている。その締付具48は、軸部60を有し、その一端部には駆動構造64と、その駆動構造64の反対側の他端部にはネジ部68が設けられている。
【0019】
拡開性ナット体52は、キー溝78を形成する二つの端部74,76を有する一つの壁構造72の形状で設けられており、その壁構造72は、外面82と内面86とを規定し、その内面86に設けたネジ山90は、締付具48のネジ部68のネジ山94と係合する。ナット体52は、外面82を孔の表面部に係合させて、孔内に配置可能となっている。
【0020】
ナット拡開構造56は、締付具の軸部60にテーパ面98と、ナットの先端104にナットテーパ面102を有し、それらのテーパ面98,102は、締付具48をナット体52にネジ係合させることにより、近い位置に導かれる。締付具48をナット体52内で継続して回転させるか、または係合させることにより、テーパ面98,102は係合して(図2及び5を参照)、ナット体52の拡張または拡開を引き起こすこととなる。
【0021】
ナット体52は、テーパ面98および102の接触後、締付具48がナット体52内で継続して回転すると大きくなる(図6の寸法108で示す)外径を有している。本発明の好適実施例は、テーパ面98,102が係合すると、締付具48がナット体に対して4分の1回転、約90度回転することにより、ナット体52が拡開および拡張することとなるように寸法決めされたネジ山90,94を有している。ナット拡開構造56の拡開機構と、それにより引き起こされる力によって、図1に示すインラインローラスケート20等の物品に使用される締付具/軸装置44の確実な取付が行われる。
【0022】
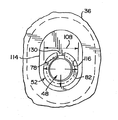
さらに、図2及至図7について説明すれば、まず、図2は、締付装置44により、第一および第二のサイドレール32,36間の溝40に保持される車輪装置30の部分的縦断側面図である。ブッシュ114は、図2及至図7に示す実施例に設けられており、より詳細に後述するように、ブッシュ114は、取り替えられても、除去されても良いが、車輪装置30の交換および調整の目的のために、インラインローラスケート20の沢山のモデルにおいて見られるものである。図2に示すように、締付具は、軸部60の一部分を第一の軸孔112に保持させて、ブッシュ114の孔により規定された第一の軸孔112を貫通して延びている。ナット体52は、第一の軸孔112を貫通して挿入され、受体または第二のブッシュ114の孔により規定された第二の軸孔116に配置される。軸部の一部分は、車輪装置の軸受け装置118の軸孔117に配置され、車輪装置30が取り付けられる軸を設けている。軸受け装置118の詳細に関しては、ここでは詳しく説明しないが、一般に公知の構造のものである。
【0023】
なお、軸部60の外径120と、拡開していないナット体52の外径108は略等しく、また軸孔117と軸孔112,116の内径122と等しいかまたは僅かに小さい。これらの寸法関係により、締付具48に取り付けられたナット体52を第一の軸孔112を通って、スリーブ孔126を通って、第二の軸孔116内に軸線方向に挿入することにより、締付装置44は、車輪装置30を貫通して第一および第二のサイドレール32,36に取り付け可能となっている。この装置により、複雑で、時間がかかる、信頼できないプロセスとなる可能性がある締付具48をナット体52にネジ係合させる必要性がなくなる。
【0024】
さらに、キー130が、第二の軸孔116に設けられており、そのキー130は、キー溝78に収容され、キー130をキー溝78に係合させることにより、締付具48をナット体52内で回転させる時に、第二のサイドレール36に対してナット体52が回転するのを防止する一方、ナット体52を拡開させて孔と係合させる。キー130は、キー溝78よりも小さく寸法決めされており、ナット体52がキー130と係合する時に、二つの構造間の結合を出来るだけ少なくしている。
【0025】
図2に示すように、締付装置44は、車輪装置30を貫通して延びて、第一のサイドレール32と第二のサイドレール36に取り付けられている。締付具48は、ナット体52に対して90度回転し、締付具のテーパ面98を付勢してナットのテーパ面102と拡開係合されている。ナットの拡開構造56が係合されているため、ナット体52の拡張および拡開により、ナット体52の外面82と第二の軸孔116の内面間で圧縮摩擦係合が行われることとなる。図において、ナット体52の外面82と軸孔116の内面間の摩擦係合が図示されている。機械的なインターロック等の他の形状の係合構造を、本発明の締付具/軸装置44のナット体52に用いる構成とすることができる。駆動構造64は、締付具を第一のサイドレール132の面138に対して保持する拡大ヘッド136を有している。図3は、テーパ面102および104と、キー130のキー溝78に対する関係をさらに示す分解斜視図である。
【0026】
図2から図4へ移って説明すれば、駆動構造64が係合されており、ナットの拡開構造56を係合解除させるために、締付具48を、所定量、例えば4分の1回転(約90度)回転させると、ナット体の外面82を軸孔116の内面に係合させていた外向きの力が開放され、力が開放されると、締付装置44は、軸孔116,112と、スリーブ孔126から軸線方向に引き抜き可能となる。締付装置44の引き抜きが、図4に図示されている。
【0027】
この締付装置44は、ナット体52が締付具48にネジ係合により保持されるため、部材の紛失を最小限にするかまたは紛失させない捕捉部材装置を設けるのに便利である。さらに、この締付装置44は、締付具48が車輪フレーム28内に挿入される度に、ネジ係合される必要がないため能率的である。先行技術の締付具を使用する場合、締付具を適当な孔を貫通して挿入しなければならず、それからナット体を反対側からネジ係合しなければならなくなる。本発明による新規な改良を考慮すると、これは時間がかかり、かつ無益である。
【0028】
図21は、締付具/軸装置44fが、後から取り付けられる装置として従来のスケート構造に使用可能な本発明の変形例を示す。図21に図示する実施例において、装置は、締付具48fと、ナット52と、ナット52を収容する受体139とによって構成され、その受体139は、内面にキー130を有する孔141を有する一方、ナット52は、上述したようにキー溝78をキー130に接合させて、孔141に係合され、受体139のフランジ143は、サイドレール36の外側面145に被さり、フランジ143は、受体139をサイドレール36に対して能動的に衝合させて、締付具44fと、受体139と、サイドレール36を貫通するブッシュ144が、軸線方向に取り外されるのを防ぐ。
【0029】
締付具48fの軸部60fは、軸部60fが、軸孔117を貫通して延び、サイドレール36の外側面145を越えて突出しなければならないため、図2及至図17に示す締付具48の軸部60よりも長い。軸部がサイドレール36を越えて突出しているため、締付装置44fは、従来のブッシュおよび車輪装置に使用できる。後から取り付けられる装置として使用される構成とすることができる。このような関係で、図21に示す実施例は、ブッシュにキーが形成されていることを要しない。図21の実施例のキーは、受体139の孔内にある。受体139の外面147には、レンチ構造が設けられており、レンチ工具を収容して係合させることができる。通常、締付装置44fは、上述した締付装置44の方法で操作する。締付具48fは、キー130をキー溝78に整列させた上で、ナット52を受体139内に挿入して、側壁33を通り、軸孔117を通り、側壁36を貫通して挿入される。締付具48fを回転させて、ナット52の外面を受体139の内面141と係合させて、ナット52を拡開させる。
【0030】
次に、図8は、本発明の締付装置44にバネ装置142を加えることによる付加的な改良が示されている。バネ装置または付勢装置142は様々な構造とすることができるが、バネ装置142の好適実施例として、螺旋状コイル圧縮バネを図8に示す。バネ装置142は、バネが圧縮されて公称の側面を呈すると、コイルをサイドレール32の溝143に収容可能な外向きに配置されたコイルを有している。バネ装置の第一端部144は、ヘッド64の下の軸部60に取り付けられて、締付装置44の捕捉片として、バネ装置142を保持し、バネ装置の第二端部146は、第一のサイドレール32に取り付けられる構造とすることができる。バネ装置を締付具とサイドレールに取り付けることにより、締付装置44は、車輪フレーム28のハードウェアの捕捉片となる。
【0031】
バネ装置142は、締付具の回転を解除する時に、締付装置44を第二の軸孔116と軸孔117から排出または取り外すバネ常数でデザインされており、このようなバネ常数により、締付装置44を移動させて、締付装置44を車輪フレーム28に保持したままで、車輪の溝からの取り外しが可能となる。この捕捉装置の利点は、通常の使用において、車輪フレーム28から部材が一つも取り外されないことである。このように、締付装置44とともにバネ装置142を使用することにより、車輪フレーム28の車輪の迅速かつ能率的な取り外しおよび交換が可能となる。
【0032】
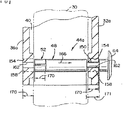
図9および10は変形例を図示し、図1及至図7において説明されているのと同一の構造は、同じ参照符号で示し、変形例の構造は、例えば締付装置44aのように英字の接尾辞を追加して、同じ参照符号で示す。図9及び10において、締付装置44aは、図1及至図7に示す締付装置44とほとんど同一のものである。図9および10において、環状溝150が、ヘッド64から離間した位置の軸部60aに設けられている。また、第一および第二の軸孔112a,116aは、上側の室154と下側の室158の二つの室で形成されている。上側および下側の室154,158は、第一のサイドレールおよび第二のサイドレール32a,36aの孔と実質的にオーバーラップしている。オーバーラップ部は、径方向の寸法の小さい通路162を形成している。第二の軸孔112aの上側および下側室154,158は、ナット52のキー溝78に係合するように寸法決めされたキー130を有している。
【0033】
図9および10に示された変形例は、車輪フレーム28に取り付けられる車輪を「揺動」可能にする。揺動することにより、ホッケー型のスケート面に類似させる等の様々な目的のために、または負荷を分散させるために、フレームに対して個々の車輪の調整が可能となる。先行技術に図示されている揺動構造の実施例は、1991年7月2日にオルソン(Olson)に付与されたアメリカ特許第5,028,058号に開示されている。オルソン(Olson)のアメリカ特許第5,028,058号に開示されている揺動装置は、偏心軸取付孔を有するプラグまたはブッシュを有している。プラグは、孔の位置を替えるために裏返され、フレーム内の車輪の位置を替えることができる。さらに、ブッシュ114は、サイドレール32aおよび36aに一体に成形されているが、上述したように室154および158は、図2及至図7に示するように取り外し可能なブッシュに形成する構成とすることができる。
【0034】
オルソン(Olson)のアメリカ特許第5,028,058号に開示されている装置は、車輪を調整するために有用であるが、時間がかかり、かつ幾分困難なプロセスである可能性がある。本発明により、車輪調整を迅速かつ能率的に変えることが可能となる。本発明において、締付装置44aは、第一の軸孔116aの所定の室154,158を貫通して挿入され、第二の軸孔112aの対応する室154,158にナット52を位置決めする。キー130は、キー溝78に係合される。
【0035】
例として、締付装置44aを下側の室158から上側の室154へ移動させて、車輪をフレームの上方へ調整することは、能率的でありかつ複雑ではないプロセスである。まず、締付具48aを、上述した方法に従って約4分の1回転させると、ナット拡開構造56が係合解除し、ナット52が取り付けられた締付具48aが(方向矢印166で示された)略軸線方向に引き抜かれ、環状溝150が、第一の軸孔116aの通路162と整列する地点まで引き抜かれる(図10を参照)。軸部60に沿った環状溝150の位置は、ナット52の長さ寸法170と、サイドレール36aの幅170と略同じ寸法168の位置にある。さらに、環状溝150の長さは、サイドレール32aの幅170よりも僅かに大きい。このように、環状溝150は、ナット52が通過する位置で通路162と整列し、第二の軸孔112aから完全に係合解除される。
【0036】
締付装置44aは、このように位置決めされて、通路162を通って上側の室154の位置へ移動して、キー溝78をキー130と整列させ、締付具48aおよびナット52を第二の軸孔112aの上側の室154に挿入させることができる。ナット52が、上側の室154に配置されると、締付具48aは、約4分の1回転してナット拡開構造56に再び係合し、ナット52を拡開させて上側の室154のナット52を保持する。
【0037】
下側の室158に対して上側の室154が略対角線方向であることは、軸孔112a,116aの締付装置44aを保持するのに都合がよい。例えば、軸孔112a,116aは、上向きおよび下向きの力に対して、締付装置44aと締付装置に保持される車輪を支持する。図6に示すように、上側および下側の室154,158には、上向きおよび下向きの力に対して、締付装置と締付装置に取り付けられる車輪を支持するための内面が設けられている。さらに、上側および下側の室154,158のそれぞれに対して少なくとも一方向に、横方向の力が明瞭かつ完全に支持される。さらに、上側および下側の室154および158のそれぞれから通路162に向う横方向の力でさえ、上側のリム174および下側のリム178がそれぞれの通路162と連関しているために、ほとんど完全に支持される。
【0038】
なお、上述したバネ装置142は、図6および7で説明した調整構造に使用される構成とすることができる。実際に、バネは、軸孔112a,116aからの締付具の伸び率を制限するための調整形状に非常に適用可能である。図6および7に図示した実施例においてバネを使用するために、所定の伸び率が達成されるように、バネのバネ常数および全体の寸法を選択しなければならない。本発明の方法を使用する同業者は、例えばナット52のみを第二の軸孔112aから係合解除するために、必要なバネ常数を決定することができると思われる。
【0039】
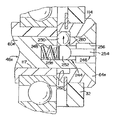
図11及至図13は、本発明によるナットの変形例を示し、前の図面に図示されかつ説明された構造と同一の構造は同じ参照符号を使用し、変えられた構造は、例えばナット52bのように英字の接尾辞を使用して示されている。
【0040】
本質的に、図11及至図13に示すナット52bと図1及至図7に示すナット52との違いは、ナット52bが複数のキー溝78,220,222,224を有していることである。同様に、複数のキー130,226,228,230が、ブッシュ114bの軸孔116bに設けられている。キー溝78と、対応するキー130は、図1及至図7に示すのと同じ係合が行われる。キー溝220,222,224は、キー溝78とは異なっており、ナット体52bの壁72を完全に貫通して延びていない。一般に、キー130,226,228,230は、同じ寸法であり、いづれのキー溝とも係合可能となっている。このように、図13に示されたキー溝78のキー130との係合は、図6に図示したものと同様のものであっても、ナット体52bは、例えばキー230をキー溝78と係合させるように、キーに対していづれの方向にもナット体52bを係合可能なように回転する構造とすることができる。
【0041】
複数のキー溝およびキーの目的は、ナットを挿入して、適切に位置させて、少しの努力で回転に対して保持可能なことである。図2及至図7に示すナット構造52は、回転に対してナット52を保持するが、キー130をキー溝78に配置させるために、回転させる必要がある可能性がある。このように、図11及至図13に示す実施例により、キー130,226,228,230の一つが、わずかに約90度だけ回転させれば、キー溝78,220,222,224の一つと係合可能となる。複数のキー溝を有するナット体52bは、ナットの軸孔116b内での配置をはかどらせるのに役立つ。
【0042】
次に、図14および15は、、本発明のもう一つの変形例を示し、この変形例では、ブッシュ234が設けられ、孔236を規定している。孔236は、孔116cを規定している。孔116c内で、ナット52は、側壁32,36と車輪装置30に係合させて締付装置44を保持するために、保持されて係合されている。さらに、円錐状コイルバネ238が、孔236の端部壁240と、ナット52および締付具48の端部間に配置されている。螺旋状コイルバネ38は、ナット52が孔116cに係合されると、それ自体内向きに螺旋状に巻かれる。締付具60を、ナット52に対して4分の1、約90度回転させると、ナット52と孔116c間で力が開放され、ナットが孔116cから係合解除される。螺旋状コイルバネ238には、開放された締付装置を軸孔117に沿ってかつ貫通して略軸線方向に押し進めるのに十分な力のバネ常数が設けられている。
【0043】
コイルバネ238により、スケート使用者は、締付具48がサイドレール32から突出しているため、フェイルセイフ機構が設けられていることに確実に気づく。さらに、コイルバネ238は、フレームおよび車輪装置30から係合解除されると、締付装置44のフレームおよび車輪装置30からの排出または取り外しに役立ち、締付装置44をより容易に取り外すことができる。
【0044】
図16および17は、本発明のもう一つの変形例を示し、この変形例には、駆動端部64eと、締付具48eの軸部60eの一部分に配置されているボール状突起装置244が設けられており、そのボール状突起装置は、押込構造246と、付勢バネ248と係合ボール250で構成され、その押込構造は、ボール移動部252とシャフト部254で構成され、そのシャフト部は、締付具48eの駆動端部64eに形成された駆動工具溝256に延びている。
【0045】
押込構造246は、シャフト部が押込孔258から駆動工具溝256に延びた状態で、押込孔258内に保持され、係合ボール250は、押込孔258と連通する第二の孔260に保持され、付勢バネ248は、押込孔258のボール移動部252の間で保持されている。
【0046】
なお、第二の孔260の壁は、内向きにテーパ処理されており、ここで係合ボールを保持し、係合ボールがここから取り除かれるのを防いでいる。係合ボール250は、第二の孔260から突出する時には、ブッシュ114に形成された溝262に係合している。図16に示すように、係合ボール250は、(図16または17には図示されていないが、図2及至15に図示されている)ナットが、対応するブッシュと係合されているかどうかに関係なく、溝262内に突出して締付具をブッシュ114に係合させて保持する。換言すれば、締付具を、ナットを拡開させるために回転させて、締付装置を車輪装置と軸線方向に整列させて保持しているかどうかに関係なく、ボール状突起装置246が、締付装置を保持する。このボール状突起装置には、締付具を保持して、車輪がフレームから取り外されるのを防ぐために、フェイルセイフ機構が設けられている。
【0047】
図17について説明すれば、ボール状突起装置が、係合解除されて、係合ボール250が、溝262から取り外され、第二の孔260を通って一部分が押込孔258内に移動可能となり、係合ボール250をシャフト部254を軸線方向に変位させることにより、溝262から係合解除される。(簡潔にするために図示されていない)工具を駆動工具溝256内に挿入すると、このシャフト部の軸線方向の変位が生じる。工具を挿入すると、シャフト部254とボール移動部252は、付勢バネ248を圧縮し、付勢バネを圧縮すると、ボール移動部252は、(図17に対して)左へ移動し、第二の孔260を貫通して移動するために係合ボール250を通過させる。
【0048】
係合ボールが係合解除されると、軸部60eを4分の1回転させるために使用される工具に対して僅かな傾き動作が働き、軸部60eを第二の軸孔117に対して保持する。さらに、図14および15に図示した螺旋状コイルバネ238を使用している本発明のバネ係合解除の実施例が、このボール突起装置に使用される構成とすることができる。係合ボール250が、溝262から係合解除されると、螺旋状コイルバネ238は、係合ボール250を(図17に示す)係合解除位置に維持するために十分な距離で、締付装置を軸線方向に変位させるために作動する。
【0049】
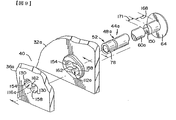
次に、本発明のもう一つの実施例について説明すれば、図18及至図20において、本発明の締付装置の基本的な構造および方法を使用しているすべり止め装置182が図示されている。図18において、ここでは、靴底の形状で示されているワークピース186に係合されている複数のすべり止め装置182が図示されている。すべり止め装置により、すべり止めの迅速で能率的かつ確実な係合と、取り外しと、交換が行われる。すなわち、図19に示すように、すべり止め装置は、すべり止め体190と、拡開性ナット部材52dで構成され、拡開性ナット部材52dは、円筒形外面82と、貫通キー溝78dを有し、すべり止め体190は、突出ヘッド部194と、ネジ付き部68dを有する軸部と、駆動構造64dとで構成されている。ナット拡開構造56dは、締付具のテーパ面98dと、ナットのテーパ面102dで構成され、靴底186は、孔198と、キー130dが設けられている内側面202で構成されている。すべり止めの操作は、上述した方法に従って行われる。ここで図示した駆動構造64dは、突出ヘッド部94の外面に形成された刻み目206と、環状フランジ214に形成された係合構造210を有し、環状フランジ214の係合構造210の一つの形は、テクストロン株式会社(Textron Inc.)のカムカー(Camcar)課の登録商標であるトルクス(TORX)である。どの形の駆動構造も受け入れ可能であるか、または付加的な駆動利点を設けるために組み合わされる構成とすることができる。環状フランジ214により、ワークピース186の底部218に、力の分散のための付加的な表面積が設けられている。
【0050】
このように、すべり止め装置182において、装置は、膨張ナット部材52dが回転するのを防ぐために、キー130dをキー溝78dに配置して孔198に係合されている。まず組み立てられると、すべり止めは4分の1回転し、これにより、テーパ面98dおよび102dが係合されることになる。さらに、ナット部材52dは回転できないため、ネジ部68dの前進と、テーパ面98dおよび102dの係合により、ナット部材52dを拡開させて、円筒形外面82を孔198の内側面202と摩擦係合させる。この係合により、4分の1回転ですべり止めを装置に維持し、すべり止め装置182の緊急解除部が、すべり止めの底部218への取付および取り外しに容易に使用するために設けられている。
【0051】
本発明の好適実施例が、図示され説明されているが、添付の請求項により規定されている本発明の精神および範囲から逸脱することなく、当業者により、様々な変更および変形が可能なことは明らかなことである。本発明は、上述した開示に限定されるものではない。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】ブーツ部と、フレームと、フレームに取り付けられた複数の車輪装置とを示す従来の典型的なインラインスケートの斜視図、
【図2】車輪装置をスケートのフレームで保持するために、締付具が拡開性ナットと係合している本発明による新規な締付装置を示す図1の2−2線に沿った一部拡大縦断側面図、
【図3】ナットのキー溝と、ブッシュのキーとの関係を示す本発明による新規な締付装置の一部断面を含む分解斜視図、
【図4】車輪装置とフレームから引き抜かれるために、締付具とナットのナット拡開構造がナットと締付具から係合解除されている状態を示す図2と同様の図、
【図5】ナットと係合する締付具のネジ部を示す図2の部分的断面拡大図、
【図6】締付具がナットとネジ係合した場合における、ナットのキーとの係合を示す図5の6−6線からみた側面図、
【図7】フレームの対応する部分と、挿入ブッシュと、締付装置との関係を図1の車輪装置で示す本発明による締付装置の一部拡大断面を含む分解斜視図、
【図8】インラインスケートのフレームに対して締付具およびナットを係合の解除および保持をするために使用される、補足的な螺旋状の填め込みバネの一部拡大断面の側面図、
【図9】インラインスケートの車輪を調整するための「揺動」の状態で使用される、本発明による実施例の一部拡大断面を含む斜視図、
【図10】関連する車輪(仮想線で示す)の位置を調整するために、締付具の環状溝が対応する孔に配置されている状態を示す、図9の「揺動」の状態で使用される締付装置の一部拡大断面の側面図、
【図11】締付装置が、外面に形成された四つのキー溝を有するナットを使用している、図7と同様の本発明による締付装置の一部拡大断面を含む分解斜視図、
【図12】ブッシュの孔に形成された対応するキーにより係合される三つのキー溝の位置を示す、図11のナットと係合された締付具のネジ部の一部拡大断面を含む側面図、
【図13】締付具がナットとネジ係合した時に、四つのキー溝が対応するキーと係合しているナットの配列を示す、図12の13−13線からみた側面図、
【図14】バネがブッシュ内で螺旋状に巻かれている係合形状の締付具とナットを示し、ナットをブッシュから係合解除するために、締付具とナットが係合解除される時に、締付具とナットに対して駆動するためにブッシュの一つに保持される填め込みバネの一部拡大縦断側面図、
【図15】ナットと締付具が係合解除して、バネがナットと締付具に対して拡開して、軸孔を貫通して、ナットと締付具を軸線方向に変位させている図14と同様の拡大図、
【図16】ボールがブッシュの溝と係合し、軸孔を通って係合して、締付具とナットを保持し、締付具がナットと係合されていない、またはナットに締め付けられていない場合に、締付装置が軸孔から係合解除されるのを防ぐ、本発明による締付装置のボール状突起装置の一部拡大縦断側面図、
【図17】ボール状突起装置が、溝からボールを係合解除するために作動し、締付装置が軸孔から引き抜き可能となる図16と同様の図、
【図18】履き物の靴底にすべり止めを取り付けた状態を示す斜視図、
【図19】ナットと、すべり止めのネジ部と、ナットおよびすべり止めを収容するためにキーが設けられている孔とを示す図18のすべり止めの拡大分解斜視図、
【図20】靴底の孔と係合するスタッドおよびナットを示す、本発明によるすべり止め装置の図18の20−20線に沿った部分的断面を含む側面図、
【図21】車輪装置をスケートのフレームに保持させるために、対応するサイドレールの外側に配置された受体を使用して、締付具を拡開性ナットと係合させる、本発明による新規な締付装置の変形示す、図2と同様の車輪装置とフレームの一部分の一部拡大断面の側面図である。
【符号の説明】
20 インラインローラースケート(シングルローラースケート)
24 ブーツ部
28 車輪フレーム
30 複数の車輪構造
32 第1のサイドフレーム
36 第2のサイドフレーム
40 溝
44 締付具/軸構造(締付装置)
48 締付具
52 拡開性ナット体
56 ナット拡開構造
60 軸部
64 駆動構造(ヘッド)
68 ネジ部
72 一つの壁構造
74,76 二つの端部
78 キー溝
82 外面
86 内面
90,94 ネジ山
88,102 テーパー面
104 ナットの先端
108 外径
112 第一の軸孔
114 ブッシュ
116 第二の軸孔
117 軸孔
118 軸受装置
120 外径
122 内径
126 スリーブ孔
130 キー
132 第一のサイドレール
136 拡大ヘッド
138 第一のサイドレールの面
139 受体
141 孔(内面)
142 バネ装置
143 フランジ(溝)
144 ブッシュ(バネ装置の第一端部)
145 外側面
146 バネ装置の第二端部
150 環状の溝
154 上側の室
158 下側の室
162 径方向の寸法の小さい通路
166 方向矢印
168 同じ寸法
170 サイドレール36aの幅
174 上側のリム
178 下側のリム
182 すべり止め装置
186 ワークピース
190 すべり止め体
194 突出ヘッド部
198 孔
202 内側面
206 刻み目
210 係合構造
214 環状フランジ
218 底部(靴底)
220,222 キー溝
226,228,230 複数のキー
234 ブッシュ
236 孔
238 円錐形螺旋状コイルバネ
244 ボール状突起装置
246 押込構造
248 付勢バネ
250 係合ボール
252 ボール移動部
254 シャフト部
256 駆動工具溝
258 押込孔
260 第二の孔
262 溝[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a fastening device capable of emergency release and emergency mounting, which has a fastening tool, an expandable nut body engaged therewith, and a hole engageable with the nut body. The present invention relates to a tightening device that is used to quickly and easily remove, attach and / or adjust a wheel device, or to quickly and easily remove and attach an anti-skid to footwear or the like.
[0002]
[Prior art]
Currently, various tightening devices for attaching a wheel device to an inline roller skate are used. These conventional tightening devices include a head, a shaft portion, and a screw portion formed on a shaft portion on the opposite side of the head. The threaded portion can be engaged with a corresponding threaded nut. The chassis or frame portion of the inline skate is provided in order to hold a plurality of wheel portions aligned in a substantially straight line. Each wheel device is inserted through one side of the frame, passes through a hole formed in the frame, and further passes through a central sleeve hole in the wheel device and extends through a hole on the opposite side of the frame. It is held on the frame with a tool. The nut engages the threaded portion of the fastener, thereby attaching the wheel portion in the correct position relative to the frame.
[0003]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
One of the challenges in conventional clamping devices is for the purpose of repair, replacement, or to adjust the wheels to reconfigure or reposition the skate wheels, or to provide, for example, a “swing” effect In addition, it takes time to remove the wheel. Ordinary skaters may not mind the time to replace one or more wheel devices, but there are many cases where quick repair and replacement is important, such as in-line hockey competitions, and The key to the initial assembly of the inline skate and the repair of the inline skate by the repairman is easy, efficient and reliable wheel removal and replacement.
[0004]
Thus, as the popularity of competition using inline skates increases, the need for quick, efficient and reliable wheel equipment removal and replacement has increased. For example, inline skate hockey is a professional It is a sport that is gaining popularity both at the level and at the amateur level, and there are numerous races throughout the country where inline skaters compete for distance and time, in which they are quick and efficient And reliable removal and replacement of the wheel device is important. Even recreational inline skater may need to change wheel material for repair purposes or to use wheel material of different composition for the surface to be skate. Speed and efficiency may not be a requirement, but it is also desirable for recreational skater to be able to repair or replace a wheel as quickly and easily as possible.
[0005]
It is also easy for recreational amateurs and professional competitors to use if they want to reconfigure the inline skates for the purpose of “rocking” shapes. It is important that the clamping device is possible and reliable. Traditionally, inline skates are shapes where the wheels are generally abutting or in contact with a common surface or skate surface, whereas a “swing” shape has one or more end wheels. A substantially curved surface is provided by moving from the common surface. The rocking shape is similar to hockey skates, with the skate blades grounding with a slightly convex bow rather than being a flat blade as used in figure skates. It will be apparent that it would be desirable to quickly and easily reconfigure an inline skate wheel system for use in this manner.
[0006]
Another problem of the prior art is that the hardware associated with the clamping device has conventionally been provided with a number of members composed of at least an elongated fastener / shaft and an engaging nut. Since the clamping device has two or more members that must be separated in order to remove, install or adjust the wheel, the member will be lost and the time for operating the wheel device will be increased. It will be. Since the nut is not captured and retained by the fastener / shaft, the nut will fall off and be lost, and the person replacing the wheel system will need to find another nut to proceed. As a result of the desire to have a grooved nut, the problem is exacerbated by requiring the nut to be positioned in the groove to prevent damage to the nut. Providing a groove in the nut complicates the problem because the threaded portion of the fastener is aligned through the wheel sleeve hole and through the opposite opening of the opposite member of the frame.
[0007]
An example of a prior art clamping device for use in inline skating is the following U.S. patent, U.S. Pat. No. 4,909,523 granted to Olson on March 20, 1990, and 1991. U.S. Pat. No. 5,028,058 granted to Olson on July 2, 1992 and U.S. Pat. No. 5,048 granted to Olson et al. On September 17, 1991. , 848, US Pat. No. 5,068,956 granted to Malevicz on December 3, 1991, and US Pat. No. 5 granted to Malevicz on March 3, 1992. , 092,614. The device disclosed in Malevicz '956 uses a cap that covers the nut and does not require a groove in the nut. However, the Malevicz '956 device requires that the fastener be rotated many times to ensure that the fastener is engaged with the nut. It has been disclosed in the above cited references that the fastener must be rotated many times in order to ensure that the fastener is engaged with the nut.
[0008]
An anti-skid device for athletic footwear is another application that requires quick, easy and reliable device removal and replacement. Non-skid footwear for athletics is widely used for various sports activities. For example, anti-skid is used in professional and amateur sports such as soccer, baseball, football, athletics, rugby, etc., to name a few examples. It is regularly necessary to replace the anti-skid when the anti-skid is worn or damaged, or to change the anti-skid depending on the type of surface used in the stadium.
[0009]
Conventionally, the anti-skid device of the prior art uses a nut body that is embedded in the sole of an athletic footwear. The threaded antiskid is driven into the embedded nut body. These anti-skid devices ensure positive engagement of the anti-skid footwear with the shoe sole, but such engagement takes time.
[0010]
With the above-described embodiments of the inline skate wheel device tightening device and the athletic footwear anti-skid device in mind, the benefits of the tightening device to improve the speed, efficiency and reliability of the removal and replacement of the fasteners. It will be clear that there are many other uses that you will receive.
[0011]
A main object of the present invention is to provide a tightening device capable of quickly and efficiently attaching and removing a member to be held.
[0012]
Another object of the present invention is to provide a clamping device that can be used as an inline skate shaft to hold the wheel device in a rotational position relative to the frame of the inline skate.
[0013]
Furthermore, another object of the present invention is to provide a tightening device capable of quickly, efficiently and reliably mounting a slip stopper on footwear.
[0014]
Still another object of the present invention is to provide a tightening device capable of emergency adjustment of an in-line skate wheel device.
[0015]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
Briefly described, the present invention relates to a novel emergency release tightening device for performing efficient and reliable attachment, disengagement and reattachment of members attached by a tightening device. The fastening device has an elongated fastening member having a shaft structure having a drive structure at one end and a threaded portion at the other end, and the fastening device includes a threaded portion of the fastening tool. The nut member engages and can engage with the wheel hole cover of a circular or polygonal hole. A nut expansion structure is provided in the nut and the fastening tool, and the nut is provided so as to expand and expand when the fastening tool rotates and engages. First, the nut is held on the screw portion of the fastener by disengaging the nut expansion structure. The workpiece is provided with a hole for receiving the nut. A key or equivalent structure is formed in the hole, and a keyway or equivalent structure is formed in the nut. The keyway is dimensioned to receive the key. The keyway allows the key to engage the keyway to expand or unfold the nut and prevent the nut from rotating within the hole. By rotating the fastener about 90 degrees or a quarter with respect to the nut, the nut is engaged with the nut expansion structure of the nut and the nut, and the outer surface of the nut is forcibly joined to the inner surface of the hole. Engaged. Since the wheel or anti-skid can be removed or attached by rotating the fastener only by a quarter turn, the fastening device is attached to the inline skate of the wheel device and attached to the footwear of the anti-skid. Especially useful for. In particular, in an inline skate device, the elongate fastener functions as a shaft to hold the wheel device in place. In this way, the nut is released from the engagement with the hole associated with the nut member by rotating the fastener by a quarter of a turn. With the expansible nut attached, the fastener / shaft is removable, the wheel is replaced, the fastener / shaft is reinserted, and then the fastener is attached with a quarter turn.
[0016]
【Example】
While the invention is susceptible to differently shaped embodiments, it is understood that the description of the invention is believed to be illustrative of the principles of the invention and is not limited to the invention shown and described herein. The embodiment will be illustrated and described in detail below.
[0017]
In FIG. 1, a
[0018]
The tightening
[0019]
The
[0020]
The
[0021]
The
[0022]
Further, FIG. 2 to FIG. 7 will be described. First, FIG. 2 shows a partial longitudinal section of the
[0023]
The
[0024]
Further, a key 130 is provided in the
[0025]
As shown in FIG. 2, the tightening
[0026]
Moving from FIG. 2 to FIG. 4, the
[0027]
This
[0028]
FIG. 21 shows a modification of the present invention in which the fastener / shaft device 44f can be used in a conventional skate structure as a device to be attached later. In the embodiment shown in FIG. 21, the apparatus is constituted by a fastener 48f, a
[0029]
The shaft portion 60f of the fastener 48f has a shaft portion 60f that extends through the
[0030]
Next, FIG. 8 shows an additional improvement by adding a
[0031]
The
[0032]
9 and 10 illustrate a modification, the same structure as described in FIGS. 1 to 7 is denoted by the same reference numeral, and the structure of the modification is an alphabetic character such as a fastening device 44a, for example. A suffix is added to indicate the same reference number. 9 and 10, the fastening device 44a is almost the same as the
[0033]
9 and 10 allows the wheels attached to the
[0034]
The device disclosed in Olson, US Pat. No. 5,028,058 is useful for adjusting the wheels, but can be a time consuming and somewhat difficult process. The invention makes it possible to change the wheel adjustment quickly and efficiently. In the present invention, the tightening device 44a is inserted through predetermined
[0035]
As an example, moving the clamping device 44a from the
[0036]
The clamping device 44a is thus positioned and moves through the
[0037]
The fact that the
[0038]
The
[0039]
11 to 13 show a variant of the nut according to the invention, wherein the same structure as shown and described in the previous drawings uses the same reference numerals and the modified structure is, for example, that of the
[0040]
Essentially, the difference between the
[0041]
The purpose of the multiple keyways and keys is that the nut can be inserted and properly positioned and held against rotation with little effort. The
[0042]
Next, FIGS. 14 and 15 show another variation of the present invention in which a
[0043]
The
[0044]
16 and 17 show another modification of the present invention, which includes a drive end 64e and a ball-
[0045]
The pushing
[0046]
Note that the wall of the
[0047]
Referring to FIG. 17, the ball-like projection device is disengaged, the
[0048]
When the engagement ball is disengaged, a slight tilting action is applied to the tool used to rotate the
[0049]
Next, another embodiment of the present invention will be described. In FIGS. 18 to 20, an anti-skid device 182 using the basic structure and method of the tightening device of the present invention is shown. . In FIG. 18, here are shown a plurality of anti-skid devices 182 engaged with a workpiece 186, shown in the shape of a sole. The anti-skid device allows quick, efficient and reliable engagement, removal and replacement of the anti-skid. That is, as shown in FIG. 19, the anti-slip device includes an
[0050]
Thus, in the anti-slip device 182, the device is engaged with the
[0051]
While the preferred embodiment of the invention has been illustrated and described, various changes and modifications can be made by one skilled in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention as defined by the appended claims. Is obvious. The present invention is not limited to the above disclosure.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a typical conventional inline skate showing a boot portion, a frame, and a plurality of wheel devices attached to the frame;
2 is taken along line 2-2 of FIG. 1 showing a novel clamping device according to the present invention in which a fastener is engaged with an expandable nut to hold the wheel device on the frame of the skate. Partially enlarged longitudinal side view,
FIG. 3 is an exploded perspective view including a partial cross-section of a novel tightening device according to the present invention showing the relationship between a keyway of a nut and a key of a bush;
4 is a view similar to FIG. 2 showing a state in which the nut expanding structure of the fastener and the nut is disengaged from the nut and the fastener so as to be pulled out from the wheel device and the frame;
5 is an enlarged partial cross-sectional view of FIG. 2 showing a threaded portion of a fastener that engages with a nut;
6 is a side view taken along line 6-6 of FIG. 5, showing engagement of the nut with the key when the fastener is screw-engaged with the nut;
7 is an exploded perspective view including a partially enlarged cross-section of the fastening device according to the present invention, showing the relationship between the corresponding part of the frame, the insertion bushing, and the fastening device as a wheel device of FIG. 1;
FIG. 8 is a side view of a partially enlarged cross-section of a supplemental helical fill spring used to disengage and retain the fasteners and nuts relative to the inline skate frame;
FIG. 9 is a perspective view including a partially enlarged cross-section of an embodiment according to the present invention used in a “swing” state for adjusting the wheels of an inline skate;
FIG. 10 shows the state of “swing” in FIG. 9, showing the state where the annular groove of the fastener is placed in the corresponding hole to adjust the position of the associated wheel (shown in phantom). Side view of a partially enlarged cross-section of the clamping device used,
11 is an exploded perspective view including a partially enlarged cross-section of the tightening device according to the present invention similar to FIG. 7, wherein the tightening device uses a nut having four key grooves formed on the outer surface;
12 includes a partially enlarged cross-section of the threaded portion of the fastener engaged with the nut of FIG. 11, showing the position of the three keyways engaged by corresponding keys formed in the bushing holes. Side view,
13 is a side view taken along line 13-13 of FIG. 12, showing an array of nuts in which four keyways are engaged with corresponding keys when the fastener is threadedly engaged with the nuts;
FIG. 14 shows an engagement shaped fastener and nut in which a spring is spirally wound in the bush, and the fastener and nut are disengaged to disengage the nut from the bush. Sometimes a partially enlarged longitudinal side view of a stuffing spring held in one of the bushes to drive against a fastener and nut,
FIG. 15 shows that the nut and the fastener are disengaged, the spring expands with respect to the nut and the fastener, passes through the shaft hole, and the nut and the fastener are displaced in the axial direction. An enlarged view similar to FIG.
FIG. 16 shows that the ball engages with the groove of the bush and engages through the shaft hole to hold the fastener and nut, and the fastener is not engaged with the nut or is tightened to the nut. A partially enlarged longitudinal side view of the ball projection device of the clamping device according to the present invention, which prevents the clamping device from being disengaged from the shaft hole if not
FIG. 17 is a view similar to FIG. 16 in which the ball-like projection device operates to disengage the ball from the groove, and the clamping device can be pulled out from the shaft hole;
FIG. 18 is a perspective view showing a state in which a slip stopper is attached to the shoe sole of footwear;
19 is an enlarged exploded perspective view of the anti-skid of FIG. 18 showing the nut, the screw part of the anti-skid, and the hole in which the key is provided to accommodate the nut and the anti-skid,
20 is a side view of the anti-skid device according to the invention, including a partial cross-section along line 20-20 of FIG. 18, showing the stud and nut engaging the hole in the sole;
FIG. 21 is a novel illustration of the present invention in which a catch disposed on the outside of a corresponding side rail is used to hold a wheel device to a frame of a skate to engage a fastener with an expandable nut. FIG. 3 is a side view of a partially enlarged cross section of a part of a wheel device and a frame similar to FIG.
[Explanation of symbols]
20 Inline roller skates (single roller skates)
24 Boots
28 Wheel frame
30 Multiple wheel structure
32 First side frame
36 Second side frame
40 grooves
44 Fastener / shaft structure (clamping device)
48 Fastener
52 Expandable nut body
56 Nut expansion structure
60 Shaft
64 Drive structure (head)
68 Screw part
72 One wall structure
74,76 Two ends
78 Keyway
82 Exterior
86 Inside
90,94 thread
88,102 Tapered surface
104 Tip of nut
108 Outer diameter
112 First shaft hole
114 bush
116 Second shaft hole
117 Shaft hole
118 Bearing device
120 outer diameter
122 inside diameter
126 Sleeve hole
130 keys
132 First side rail
136 Magnifying head
138 First side rail surface
139 Receiver
141 hole (inner surface)
142 Spring device
143 Flange (groove)
144 Bush (first end of spring device)
145 exterior
146 Second end of spring device
150 annular groove
154 Upper chamber
158 Lower chamber
162 Passage with small radial dimension
166 direction arrow
168 Same dimensions
170 Width of side rail 36a
174 Upper rim
178 Lower rim
182 Anti-slip device
186 Workpiece
190 Anti-slip body
194 Protruding head
198 hole
202 Inside surface
206 Notches
210 engagement structure
214 Annular flange
218 Bottom (shoe sole)
220, 222 Keyway
226, 228, 230 Multiple keys
234 bush
236 holes
238 Conical spiral coil spring
244 Ball projection device
246 Pushing structure
248 Biasing spring
250 engagement ball
252 Ball moving part
254 Shaft
256 Drive tool groove
258 Indentation hole
260 Second hole
262 groove
Claims (3)
車輪軸と、一側に駆動構造(64)と、該駆動構造の略反対側にネジ部(68)が設けられている軸部(60)を有する締付具(48)と、
内面(86)と外面(82)を規定する壁(72)と、少なくとも一つが、前記壁を貫通して完全に延びる前記ナット体の前記外面に形成される少なくとも一つのキー溝(78)と、先端を規定する一端部を有するナット体(52)と、
前記ナット体を拡開させるための、前記締付具と前記ナット体の前記先端のナット拡開構造(56)で構成され、
前記ナット体がネジ係合により保持された前記締付具が、前記第一のサイドレールの前記軸孔(112)を通り、前記車輪の前記軸孔を通って延び、前記第二のサイドレールの第二の軸孔(116)に少なくとも近接して配置され、前記ナット体が、前記第二の軸孔の内面に係合して取り付けられるために、前記第二のサイドレールの前記第二の軸孔に配置され、
前記締付具の前記軸部の外径(120)と、拡開していない前記ナット体の外径(108)は略等しく、また前記車輪軸孔(117)と前記軸孔(112,116)の内径(122)と等しいかまたは僅かに小さい、
ことを特徴とする車輪装置(30)をローラスケート(20)に取り付けるための締付装置(44)。A clamping device (44) for attaching a wheel device (30) to a roller skate (20), said roller skate having spaced first and second side rails defining a groove (40) therebetween 32, 36), at least one wheel device has a wheel shaft hole (117), and each of the side rails is substantially the same as one of the corresponding wheel shaft holes. Have matching axial holes (112, 116);
A fastener (48) having a wheel shaft, a drive structure (64) on one side, and a shaft part (60) provided with a screw part (68) on the substantially opposite side of the drive structure;
A wall (72) defining an inner surface (86) and an outer surface (82), and at least one keyway (78) formed in the outer surface of the nut body, at least one of which extends completely through the wall. A nut body (52) having one end defining the tip;
The nut for expanding the nut body is constituted by the fastener and the nut expansion structure (56) at the tip of the nut body,
The fastening tool in which the nut body is held by screw engagement passes through the shaft hole (112) of the first side rail and extends through the shaft hole of the wheel, and the second side rail. At least in close proximity to the second shaft hole (116) of the second side rail so that the nut body is engaged and attached to the inner surface of the second shaft hole. Arranged in the shaft hole of
The outer diameter (120) of the shaft portion of the fastener is substantially equal to the outer diameter (108) of the nut body that is not expanded, and the wheel shaft hole (117) and the shaft hole (112, 116). ) Equal to or slightly smaller than the inner diameter (122) of
A fastening device (44) for attaching the wheel device (30) to the roller skate (20).
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の締付装置(44)。When the screw portion (68) and the screw (90) of the nut body (52) rotate the fastener (48) about 90 degrees relative to the nut body, the nut expanding structure ( 56) and is dimensioned to engage
Fastening device (44) according to claim 1, characterized in that.
ことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の締付装置(44)。A key (130) is provided on the inner surface of the hole (116), and when the key is engaged with the nut expansion structure (56) by rotating the fastener (48), the nut body In order to prevent rotation of (52), it is accommodated in said keyway (78).
Fastening device (44) according to claim 1, characterized in that.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP15911697A JP3960656B2 (en) | 1997-05-12 | 1997-05-12 | Fastening device with emergency release by a nut body that can be expanded |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP15911697A JP3960656B2 (en) | 1997-05-12 | 1997-05-12 | Fastening device with emergency release by a nut body that can be expanded |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH10318236A JPH10318236A (en) | 1998-12-02 |
| JP3960656B2 true JP3960656B2 (en) | 2007-08-15 |
Family
ID=15686598
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP15911697A Expired - Fee Related JP3960656B2 (en) | 1997-05-12 | 1997-05-12 | Fastening device with emergency release by a nut body that can be expanded |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3960656B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4995529B2 (en) * | 2006-09-29 | 2012-08-08 | 株式会社三貴工業所 | Caster wheel mounting structure |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6259317U (en) * | 1985-10-01 | 1987-04-13 | ||
| JPH0225282U (en) * | 1988-08-03 | 1990-02-20 | ||
| JPH0424177Y2 (en) * | 1988-09-09 | 1992-06-08 | ||
| JPH02119515U (en) * | 1989-03-10 | 1990-09-26 | ||
| US5190301A (en) * | 1991-03-13 | 1993-03-02 | Rollerblade, Inc. | Fastening system for the wheels of an in-line roller skate |
| JPH0666307A (en) * | 1991-10-21 | 1994-03-08 | Mineichi Iwamoto | Nut-like member and ceiling skeleton material support tool applying it |
| JP3024498U (en) * | 1995-11-10 | 1996-05-21 | 作井 満 | Fixing means |
-
1997
- 1997-05-12 JP JP15911697A patent/JP3960656B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH10318236A (en) | 1998-12-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4666168A (en) | Roller skate apparatus | |
| JP4432393B2 (en) | Bicycle automatic pedal | |
| US4666169A (en) | Skate apparatus | |
| US5941539A (en) | Fastener system with expandable nut body | |
| US7559160B2 (en) | Studded footwear | |
| EP1045994B1 (en) | Bushing system | |
| EP0465224B1 (en) | Fastener head cover assembly for in-line roller skates | |
| US20150038258A1 (en) | Golf club head with repositionable weight | |
| JPS61191303A (en) | Sports shoes | |
| US5884923A (en) | Fastener system with expandable nut body | |
| US6301806B1 (en) | Detachable cleat system | |
| JP2000502272A (en) | Cane handle | |
| US6708428B2 (en) | Quick-release connector system for footwear with reliable engagement | |
| US20020152643A1 (en) | Spike for golf shoe | |
| US5025576A (en) | Sole for sports shoes | |
| JP3960656B2 (en) | Fastening device with emergency release by a nut body that can be expanded | |
| US6115947A (en) | Shoe system and method | |
| JP3824859B2 (en) | Non-slip for shoes | |
| US6173975B1 (en) | V-line skate with expandable axle | |
| US5887496A (en) | Wrench for use on golf shoes | |
| US5775707A (en) | Skate wheel fastening system | |
| US7874945B2 (en) | Head retaining mechanism for a lacrosse stick | |
| AU725967B2 (en) | Quick release fastener system with expandable nut body | |
| KR200238222Y1 (en) | a bottom structure of shoes | |
| JP3261570B2 (en) | Sports shoes spike mounting structure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040420 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040528 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20040528 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20040531 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20040528 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20060810 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20061003 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061207 |
|
| A524 | Written submission of copy of amendment under section 19 (pct) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A524 Effective date: 20061207 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070424 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070515 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20070727 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A711 Effective date: 20070727 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100525 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100525 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R360 | Written notification for declining of transfer of rights |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R360 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100525 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R371 | Transfer withdrawn |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R371 |
|
| A072 | Dismissal of procedure |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A072 Effective date: 20071120 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100525 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100525 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R360 | Written notification for declining of transfer of rights |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R360 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100525 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R370 | Written measure of declining of transfer procedure |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R370 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313113 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100525 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |