JP3828680B2 - Hydraulic circuit for work machine and hybrid work machine - Google Patents
Hydraulic circuit for work machine and hybrid work machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3828680B2 JP3828680B2 JP18117699A JP18117699A JP3828680B2 JP 3828680 B2 JP3828680 B2 JP 3828680B2 JP 18117699 A JP18117699 A JP 18117699A JP 18117699 A JP18117699 A JP 18117699A JP 3828680 B2 JP3828680 B2 JP 3828680B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- hydraulic
- flow rate
- pipe
- control valve
- work machine
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 24
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000009412 basement excavation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001172 regenerating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000004043 responsiveness Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004568 cement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010720 hydraulic oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005381 potential energy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008929 regeneration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011069 regeneration method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/62—Hybrid vehicles
Landscapes
- Operation Control Of Excavators (AREA)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (AREA)
- Fluid-Pressure Circuits (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、作業機械用液圧回路およびハイブリッド作業機械に関し、特に、動作部の微操作を良好に行うことができる作業機械用液圧回路およびハイブリッド作業機械に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、油圧ショベル、ホイールローダなどの建設機器やフォークリフトなどの油圧作業機を含む油圧駆動装置として、エンジンの負担や燃料消費率低減などのために動力源としてエンジンのほかに発電機およびバッテリをも備えるようにした、所謂ハイブリッド型のものの開発が進められている。
【0003】
かかるハイブリッド型の油圧駆動装置などでは、エンジンにより発生したトルクで油圧ポンプを駆動するのに代えて、バッテリに蓄えられた電気エネルギーを動力源とする電動機により発生したトルクで油圧ポンプを駆動し、これによって油圧シリンダを動作させることが可能である。
【0004】
このように、電動機で駆動される油圧ポンプに接続された油圧シリンダの速度を制御しようとする場合の技術としては、特開平9−174300号公報に記載されているように油圧シリンダの加圧圧力を検出し、検出された圧力に基づいてインバータを介して電動機の回転数を制御するという技術がある。このように油圧シリンダへの負荷変動に応じて電動機の回転数を制御することよって、油圧ポンプから吐出される圧油の流量が制御されて油圧シリンダの速度を変更することが可能である。
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
上記公報に記載された技術によって電動機で駆動される油圧ポンプに接続された油圧シリンダの位置決めをするための微操作を行う場合、電動機の回転数をきわめて低く保って油圧シリンダに供給される圧油量を少なくしなければならない。しかしながら、通常、電動機の回転数をきわめて低く保つのは、電動機の制御装置の精度上の問題、低回転域において油圧ポンプの効率が低下する問題や回転系の摩擦の問題などのために困難である。
【0006】
すなわち、操作レバーの操作量と油圧ポンプの吐出量との関係を示すグラフである図5に示すように、操作レバーの操作量が比較的大きい領域では両者は比例関係にあるが、レバー操作量が小さい微操作領域(図5において破線の円で囲んだ領域)ではレバー操作量をS1 以下としてもポンプ吐出量を所定量Q1 以下の微小な量にレバー操作に応じて制御することができない。そのために上述の公報に記載された技術では油圧シリンダに駆動される動作部の良好な微操作を行うことができないという問題がある。
【0007】
そこで、本発明の主な目的は、電動機で駆動される油圧ポンプに接続された液圧シリンダに駆動される動作部を良好に微操作することが可能な作業機械用液圧回路およびハイブリッド作業機械を提供することである。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記目的を達成するために、請求項1の作業機械用液圧回路は、電動機で駆動される液圧ポンプに接続された液圧シリンダを制御するための作業機械用液圧回路において、前記液圧ポンプと前記液圧シリンダとを液圧閉回路で接続する配管と、前記配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する流量制御弁と、該流量制御弁による圧液の流量の制限を操作レバーの微操作領域で機能させるコントローラとが設けられていることを特徴とするものである。
【0009】
また、請求項4のハイブリッド作業機械は、エンジンで駆動される発電機の電力により蓄電手段に蓄電可能であるとともに、これら発電機および蓄電手段の少なくとも一方の電力により電動機を作動させるハイブリッド作業機械において、前記電動機によって駆動される液圧ポンプと、前記液圧ポンプによって作動される液圧シリンダと、前記液圧ポンプと前記液圧シリンダとを液圧閉回路で接続する配管と、前記配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する流量制御弁と、該流量制御弁による圧液の流量の制限を操作レバーの微操作領域で機能させるコントローラとを備えていることを特徴とするものである。
【0010】
請求項1、4によると、液圧ポンプと液圧シリンダとの間に設けられ、液圧閉回路を形成する配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する流量制御弁及びこれを制御するコントローラを設けたことにより、電動機の回転数を同じにしたときに液圧シリンダに供給される圧液量を操作レバーの微操作領域において従来よりも少なくすることができるようになる。そのために、液圧シリンダを非常に小さい速度で移動させることが可能となり、その液圧シリンダで駆動される動作部の微操作性が改善される。
【0011】
また、請求項2の作業機械用液圧回路は、前記流量制御弁が、前記液圧ポンプから前記液圧シリンダに圧液を供給する配管に設けられていることを特徴とするものであり、請求項5のハイブリッド作業機械は、前記流量制御弁が、前記液圧ポンプから前記液圧シリンダに圧液を供給する配管に設けられていることを特徴とするである。
【0012】
請求項2、5では、液圧ポンプから液圧シリンダに圧液を供給する配管に流量制御弁が設けられているので、液圧シリンダから液圧ポンプに圧液が戻る配管に流量制御弁が設けられている場合よりも応答性の高い優れた微操作性を得ることができる。
【0013】
また、請求項3の作業機械用液圧回路は、前記流量制御弁が、前記配管内の圧力にかかわらず前記液圧シリンダに一定量の圧液を供給可能であることを特徴とするものであり、請求項6のハイブリッド作業機械は、前記流量制御弁が、前記配管内の圧力にかかわらず前記液圧シリンダに一定量の圧液を供給可能であることを特徴とするものである。
【0014】
請求項3、6によると、流量制御弁が配管内の圧力にかかわらず液圧シリンダに一定量の圧液を供給可能であるので、液圧シリンダの負荷が増減しても液圧シリンダに一定量の圧液を供給することができるようになって、常に一定の微操作性をオペレータに与えることができるようになる。
【0015】
また、請求項7の作業機械用液圧回路は、電動機と、前記電動機で駆動される液圧ポンプと、前記液圧ポンプから圧液が供給されて動作する液圧シリンダと、前記液圧ポンプと前記液圧シリンダとに接続されて液圧閉回路を形成する第1および第2の配管と、前記第1の配管が供給側配管となるときに前記第1の配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する第1の流量制御弁、および、前記第2の配管が供給側配管となるときに前記第2の配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する第2の流量制御弁と、前記第1および第2の流量制御弁を通過する圧液の流量が操作レバーの微操作領域で制限されるように制御するコントローラとを備えていることを特徴とするものである。
【0016】
請求項7によると、第1および第2の流量制御弁を通過する圧液の流量が操作レバーの微操作領域で制限されるようにコントローラが制御することにより、電動機の回転数を一定数よりも低くしなくとも液圧シリンダに供給される圧液量を非常に少なくすることができるようになる。そのために、液圧シリンダを非常に小さい速度で移動させることが可能となり、その液圧シリンダで駆動される動作部の微操作性が改善される。
【0017】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の好適な実施の形態について、図面を参照して説明する。
【0018】
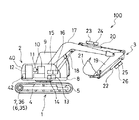
図1は、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係るハイブリッド作業機械であるショベルの概略構成を示す模式図である。図1において、ショベル100は、下部走行体1と、上部旋回体2と、掘削アタッチメント3とから構成されている。
【0019】
下部走行体1は、左右のクローラフレーム4およびクローラ5(いずれも片側のみ図示)と、クローラ5を回転駆動する左右の走行用電動機7(6)および走行減速機36(35)(図1には左側のみ示されている)とを有している。走行減速機36、35は、走行用電動機7、6の回転を減速して走行機構に伝える。
【0020】
上部旋回体2は、旋回フレーム8、キャビン9などから成っている。旋回フレーム8には、動力源としてのエンジン10と、エンジン10によって駆動される発電機11と、主バッテリ12と、補助バッテリ42と、上部旋回体3を回転させるための旋回用電動機13と、旋回用電動機13の回転を減速して旋回機構(旋回歯車)に伝える旋回減速機14と、ブーム用電動機15と、ブーム用油圧ポンプ(以下、「ブームポンプ」という)16が設置されている。このほか、上部旋回体3内には、インバータ37やコントローラ43(ともに図2参照)などを含む制御部(図示せず)が設けられている。
【0021】
掘削アタッチメント3は、ブーム17と、伸縮作動してブーム17を起伏させるブームシリンダ18と、アーム19と、アーム19を回動させるアームシリンダ20と、バケット21と、バケット21を回動させるバケットシリンダ22とを具備している。また、アームシリンダ20には、アーム用電動機23およびこれによって駆動されるアーム用油圧ポンプ(以下、「アームポンプ」という)24が取り付けられているとともに、バケットシリンダ22には、バケット用電動機25およびこれによって駆動されるバケット用油圧ポンプ(以下、「バケットポンプ」という)26が取り付けられている。本実施の形態において、アーム用電動機23とアームポンプ24とアームシリンダ20、および、バケット用電動機25とバケットポンプ26とバケットシリンダ22は、それぞれ一体化されたものが用いられている。
【0022】
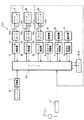
次に、ショベル100の駆動系について、図2に基づいて説明する。図2は、ショベル100の駆動系を概略的に示すブロック図である。図2に示すように、発電機11はエンジン10の出力軸に取り付けられている。また、発電機11は、エンジン10の出力トルクから交流電力を発生してインバータ37に供給する。発電機11に接続されたインバータ37は、発電機11で発生した交流電力を直流電力に変換してバッテリ12、42に蓄える通常充電作用、インバータ37に接続された電動機15、23、25、6、7、13の回生作用によって発生した交流電力を直流電力に変換してバッテリ32に蓄える回生充電作用の各作用を行なう。
【0023】
また、インバータ37は、バッテリ12、42に蓄えられた電気エネルギーを交流に変換して電動機15、23、25、6、7、13に供給する放電作用、発電機11からの交流電力を電動機15、23、25、6、7、13に供給する供給作用の各作用を行なう。これら2つの作用を行う際、インバータ37は交流電流の周波数をコントローラ43からの命令にしたがって任意の値に変更することが可能であり、これによって電動機15、23、25、6、7、13の回転数を制御することができるようになっている。
【0024】
インバータ37に接続された6つの電動機15、23、25、6、7、13のうち、ブーム用電動機15は、ブームポンプ16を作動させてブームシリンダ18を駆動し、アーム用電動機23は、アームポンプ24を作動させてアームシリンダ20を駆動し、バケット用電動機25は、バケットポンプ26を作動させてバケットシリンダ22を駆動する。旋回用電動機13および走行用電動機6、7はそれぞれ旋回減速機14および走行減速機35、36に連結されている。これら6つの電動機15、23、25、6、7、13は、オペレータによる操作レバー45の操作によって、それぞれのオンオフ、回転速度および回転方向が制御される。
【0025】
電動機15、23、25、6、7、13は、これらへの合計負荷が小さいときには発電機11からインバータ37経由で供給される交流電力によって駆動される。このとき、発電機11で発電された交流電力の余剰分は、インバータ37において直流電力に変換されてバッテリ12、42に蓄えられる。なお、例えばショベル100の走行時のようにアームシリンダ20およびブームシリンダ18を使用しておらず、主バッテリ12の蓄電力が十分であり且つ電動機15、23、25、6、7、13への合計負荷が小さいときには、エンジン10の出力を低下させ或いはエンジン10を停止して主バッテリ12だけから電動機15、23、25、6、7、13に電力を供給するようにしてもよい。これによって、エンジン10を無駄に動作させるのを防止して騒音および排ガスを削減し、さらに燃料消費率を低減することができる。
【0026】
一方、電動機15、23、25、6、7、13の合計負荷が所定値よりも大きくなると、発電機11で発電された交流電力のバッテリ12、42への蓄電は停止され、そして、電動機15、23、25、6、7、13の駆動エネルギーとして、発電機11から供給された電力だけではなく必要であれば主バッテリ12に蓄電された電力が併せて用いられる。
【0027】
このように、インバータ37は電動機15、23、25、6、7、13の合計負荷が所定値よりも大きいかどうかでその動作が切り換えられ、この切り換えは電動機15、23、25、6、7、13を流れる電流とその電圧の積に基づいて或いは手動により制御部の制御により行われる。
【0028】
また、運転中、電動機15、23、25、6、7、13をその位置エネルギーおよび運動エネルギーを利用して発電機として作用(回生作用)させ、これによって発生する回生電力をバッテリ12、42に蓄えることができる。特に、旋回用電動機13は旋回加速時に大きな運動エネルギーを蓄えることができるので減速時におけるエネルギーの回生効果が高い。
【0029】
本実施の形態によるショベル100においては、ブームポンプ16とブームシリンダ18とを結ぶ圧油配管に関連して2つの流量制御弁46a、46bが設けられている。また、同様の流量制御弁47a、47bおよび48a、48bは、アームポンプ24とアームシリンダ20とを結ぶ圧油配管、および、バケットポンプ26とバケットシリンダ22とを結ぶ圧油配管と関連しても設けられている。これら流量制御弁46a、46b;47a、47b;48a、48bは、操作レバー45の操作によりコントローラ43によって圧油通過流量を制御可能とされている。
【0030】
次に、本実施の形態のショベル100におけるブーム17の駆動系の詳細について図3に基づいて説明する。図3は、ブーム17に関連する駆動系を詳細に示した回路図であり、図1および図2と対応する部分には同じ符号が用いられている。なお、ここではブーム17について説明するがアーム19やバケット21についても同様の駆動系が構成されている。
【0031】
図3において、ブームシリンダ18のキャップ側の作動室18aおよびヘッド側の作動室18bには、それぞれ配管49a、49bが接続されている。そして、配管49a、49bが両回転型のブームポンプ16と接続されることにより油圧閉回路が形成されている。
【0032】
配管49a、49bとタンク53との間にはそれぞれチェック弁51a、51bが設けられており、配管49a、49b内が負圧になった場合にタンク53から配管49a、49b内に油が供給される。これにより、配管49a、49b内がキャビテーションを起こすのを防止している。また、配管49a、49bとタンク53との間にはリリーフ弁52a、52bが設けられている。これにより、配管49a、49b内の圧力が所定値を超えると油をタンク53に逃がすことができるので、配管49a、49b内の圧力上昇によって上記油圧閉回路が破損するのを防止している。
【0033】
また、本実施の形態においては、配管49a、49bの途中に上述した流量制御弁46a、46bが設けられているとともに流量制御弁46a、46bと並列にチェック弁50a、50bが接続されている。流量制御弁46a、46bはブームポンプ16からブームシリンダ18に供給される圧油を通過させ、チェック弁50a、50bはブームシリンダ18からブームポンプ16に戻る圧油を通過させる。流量制御弁46a、46bは、コントローラ43からの制御によって開口面積が可変であるオリフィスなど公知のものであってよく、流量制御弁46a、46bによって通過を制限された分量の圧油はタンク53に戻されるように構成されている。
【0034】
ブームシリンダ18が伸びる方向に操作レバー45が操作されると、コントローラ43およびインバータ37を介してブーム用電動機15が制御されて、配管49bがブームシリンダ18の作動室18aへの圧油の供給側配管となりかつ配管49aが作動室18bからの圧油の戻り側配管となるようにブームポンプ16が駆動され、ブームシリンダ18が図中右側に移動する。つまり、ブームポンプ16から供給される圧油は流量制御弁46bを経てブームシリンダ18に達し、さらにチェック弁50aを経てブームポンプ16に戻される。
【0035】
このとき、ブーム17を微操作するには、操作レバー45を微操作領域にまで移動させる。すると、操作レバー45の操作量に応じてコントローラ43およびインバータ7を介してブーム用電動機15が制御され、その回転数が減少する。それとともに、コントローラ43を介して流量制御弁46bが制御されることにより、ブームシリンダ18に供給される圧油の流量が制限される。
【0036】
そのため、図4に示すようにレバー操作量を流量制御可能な限界位置S1 にまで小さくしたときのブームポンプ16の吐出量(破線)がQ1 であるのに対して、流量制御弁46bの出口流量(実線)をQ2 にまで減少させることができる(つまり、Q1 −Q2 分が流量制御弁46bからタンク53に戻される)。従って、ブームシリンダ18に供給される圧油の流量もほぼQ2 程度にまで減少し、ブームシリンダ18への制御可能な最低流量をほぼQ1 −Q2 分だけ低下させることができるようになる。そのため、ブームシリンダ18を非常に小さい速度で移動させることが可能となり、ブームシリンダ18を伸ばす方向に関するブーム17の位置決めのための微操作性が改善される。
【0037】
一方、ブームシリンダ18が縮む方向に操作レバー45が操作されると、コントローラ43およびインバータ37を介してブーム用電動機15が制御されて、配管49aがブームシリンダ18の作動室18bへの圧油の供給側配管となりかつ配管49bが作動室18aからの圧油の戻り側配管となるようにブームポンプ16が駆動され、ブームシリンダ18が図中左側に移動する。つまり、ブームポンプ16から供給される圧油は流量制御弁46aを経てブームシリンダ18に達し、さらにチェック弁50bを経てブームポンプ16に戻される。
【0038】
このとき、ブーム17を微操作するには、操作レバー45を微操作領域にまで移動させる。すると、操作レバー45の操作量に応じてコントローラ43およびインバータ7を介してブーム用電動機15が制御され、その回転数が減少する。それとともに、コントローラ43を介して流量制御弁46aが制御されることにより、ブームシリンダ18に供給される圧油の流量が制限される。
【0039】
そのため、図4で説明したのと同様に、ブームシリンダ18への制御可能な最低流量をほぼQ1 −Q2 分だけ低下させることができるようになって、ブームシリンダ18を非常に小さい速度で移動させることが可能となり、ブームシリンダ18を縮める方向に関するブーム17の位置決めのための微操作性が改善される。
【0040】
このように、本実施の形態では、ブームポンプ16とブームシリンダ18とが配管49a、49bで接続された油圧閉回路において両方の配管49a、49bに流量制御弁46a、46bを設け、ブームシリンダ18に供給される圧油の流量を制限するようにしたので、ブームシリンダ18を伸ばす場合および縮める場合のいずれの場合についてもブームシリンダ18への制御可能な最低流量を低下させることができるようになり、良好なブーム17の微操作性が得られる。
【0041】
なお、本実施の形態では、ブームシリンダ18への圧油供給側に流量制御弁46a、46bを設けてブームシリンダ18に対する圧油供給量を制限するようにしたが、ブームシリンダ18からの圧油排出側に流量制御弁46a、46bと同様の流量制御弁を設けてブームシリンダ18からの圧油排出量を制限するようにしても、ブームシリンダ18を非常に小さい速度で移動させることが可能となってブーム17の微操作性が改善される。しかしながら、本実施の形態のようにブームシリンダ18への圧油供給側に流量制御弁46a、46bを設けたほうが、応答性の高いより優れた微操作性を得ることができる。
【0042】
また、本実施の形態で用いる流量制御弁46a、46bとしては、配管49a、49b内の圧力にかかわらずブームシリンダ18に一定量の圧液を供給可能である圧力補償付流量制御弁を用いることが好ましい。なぜなら、ブームシリンダ18の負荷が変動した場合に配管49a、49b内の圧力が変動することになるが、圧力補償付流量制御弁を用いれば配管49a、49b内の圧力変動にかかわらず一定の流量がブームシリンダ18に供給されるようになって、常に一定の微操作性をオペレータに与えることができるようになるからである。
【0043】
以上、本実施の形態の好適な実施の形態について説明したが、本発明は上述の実施の形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲に記載した限りにおいて様々な設計変更を行うことが可能である。例えば、上述の実施の形態では、液圧ポンプから液圧シリンダに圧液を供給する配管に流量制御弁を設けたが、液圧ポンプから液圧シリンダに圧液を供給する配管にコントロールバルブを接続し、コントロールバルブからタンクに連通する流路を設けてもよい。
【0044】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、請求項1、4によると、液圧シリンダを非常に小さい速度で移動させることが可能となり、その液圧シリンダで駆動される動作部の微操作性が改善される。
【0045】
請求項2、5によると、液圧シリンダから液圧ポンプに圧液が戻る配管に流量制御弁が設けられている場合よりも応答性の高い優れた微操作性を得ることができる。
【0046】
請求項3、6によると、液圧シリンダの負荷が増減しても液圧シリンダに一定量の圧液を供給することができるようになって、常に一定の微操作性をオペレータに与えることができるようになる。
【0047】
請求項7によると、第1および第2の流量制御弁を通過する圧液の流量が操作レバーの微操作領域で制限されるようにコントローラが制御することにより、電動機の回転数を一定数よりも低くしなくとも液圧シリンダに供給される圧液量を非常に少なくすることができるようになる。そのために、液圧シリンダを非常に小さい速度で移動させることが可能となり、その液圧シリンダで駆動される動作部の微操作性が改善される。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本発明の第1の実施の形態に係るハイブリッド作業機械であるショベルの概略構成を示す模式図である。
【図2】 図1に示したショベルの駆動系を概略的に示すブロック図である。
【図3】 図1に示したブームに関連する駆動系を詳細に示した回路図である。
【図4】 微操作領域におけるレバー操作量と流量との関係を示すグラフである。
【図5】 従来の技術において、レバー操作量とポンプ吐出量との関係を示すグラフである。
【符号の説明】
1 下部走行体
2 上部旋回体
3 掘削アタッチメント
6、7 走行用電動機
10 エンジン
11 発電機
12 主バッテリ
13 旋回用電動機
15 ブーム用電動機
16 ブームポンプ
17 ブーム
18 ブームシリンダ
19 アーム
20 アームシリンダ
21 バケット
22 バケットシリンダ
23 アーム用電動機
24 アームポンプ
25 バケット用電動機
26 バケットポンプ
37 インバータ
42 補助バッテリ
43 コントローラ
45 操作レバー
46a、46b;47a、47b;48a、48b 流量制御弁
49a、49b 配管
50a、50b チェック弁
51a、51b チェック弁
52a、52b リリーフ弁
53 タンク
100 ショベル[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a hydraulic circuit for a work machine and a hybrid work machine, and more particularly to a hydraulic circuit for a work machine and a hybrid work machine that can finely operate an operation unit.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, as a hydraulic drive device including construction equipment such as hydraulic excavators and wheel loaders and hydraulic working machines such as forklifts, in addition to the engine, a generator and a battery are also used as a power source to reduce engine burden and fuel consumption rate. The so-called hybrid type that is provided is being developed.
[0003]
In such a hybrid type hydraulic drive device, instead of driving the hydraulic pump with the torque generated by the engine, the hydraulic pump is driven with the torque generated by the electric motor that uses the electric energy stored in the battery as a power source, As a result, the hydraulic cylinder can be operated.
[0004]
As described above, as a technique for controlling the speed of the hydraulic cylinder connected to the hydraulic pump driven by the electric motor, as described in JP-A-9-174300, the pressurizing pressure of the hydraulic cylinder is described. There is a technique for detecting the motor and controlling the rotational speed of the electric motor via an inverter based on the detected pressure. In this way, by controlling the rotation speed of the electric motor according to the load fluctuation to the hydraulic cylinder, the flow rate of the pressure oil discharged from the hydraulic pump can be controlled to change the speed of the hydraulic cylinder.
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
When performing a fine operation for positioning a hydraulic cylinder connected to a hydraulic pump driven by an electric motor by the technique described in the above publication, the pressure oil supplied to the hydraulic cylinder while keeping the rotational speed of the electric motor extremely low The amount must be reduced. However, it is usually difficult to keep the rotational speed of the motor very low due to problems with the accuracy of the motor control device, problems with the lowering of the efficiency of the hydraulic pump at low speeds, and problems with friction of the rotating system. is there.
[0006]
That is, as shown in FIG. 5 which is a graph showing the relationship between the operation amount of the operation lever and the discharge amount of the hydraulic pump, the two are in a proportional relationship in a region where the operation amount of the operation lever is relatively large. In a fine operation region (region surrounded by a broken-line circle in FIG. 5), even if the lever operation amount is set to S1 or less, the pump discharge amount cannot be controlled to a minute amount less than the predetermined amount Q1 according to the lever operation. Therefore, there is a problem that the technique described in the above-mentioned publication cannot perform good fine operation of the operation unit driven by the hydraulic cylinder.
[0007]
Accordingly, a main object of the present invention is to provide a hydraulic circuit for a work machine and a hybrid work machine capable of finely manipulating an operation unit driven by a hydraulic cylinder connected to a hydraulic pump driven by an electric motor. Is to provide.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, a hydraulic circuit for a work machine according to claim 1 is the hydraulic circuit for a work machine for controlling a hydraulic cylinder connected to a hydraulic pump driven by an electric motor. A pipe connecting the pressure pump and the hydraulic cylinder with a hydraulic closed circuit, a flow control valve for limiting the flow rate of the pressure liquid passing through the pipe, and an operation lever for limiting the flow rate of the pressure liquid by the flow control valve And a controller that functions in the fine operation area .
[0009]
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a hybrid work machine capable of storing power in the power storage means with electric power of a generator driven by an engine and operating the electric motor with at least one power of the generator and power storage means. , passing a hydraulic pump, a hydraulic cylinder operated by the hydraulic pump, a pipe connected with the hydraulic pump and said hydraulic cylinder and a hydraulic pressure closing circuit, said pipes being driven by said electric motor The flow rate control valve for restricting the flow rate of the pressure fluid to be controlled, and the controller for causing the restriction of the flow rate of the pressure fluid by the flow rate control valve to function in the fine operation region of the operation lever are provided.
[0010]
According to Claims 1 and 4, a flow rate control valve that is provided between the hydraulic pump and the hydraulic cylinder and that restricts the flow rate of the hydraulic fluid that passes through the pipe forming the hydraulic pressure closed circuit, and a controller that controls the flow rate control valve. As a result, the amount of hydraulic fluid supplied to the hydraulic cylinder when the number of revolutions of the electric motor is the same can be reduced in the fine operation region of the operation lever as compared with the conventional case. Therefore, it is possible to move the hydraulic cylinders at a very small rate, improved if fine operability of the operation unit that is driven by the hydraulic cylinder.
[0011]
The hydraulic circuit for a work machine according to
[0012]
According to
[0013]
The hydraulic circuit for a work machine according to
[0014]
According to
[0015]
According to a seventh aspect of the present invention, there is provided a hydraulic circuit for a work machine comprising: an electric motor; a hydraulic pump driven by the electric motor; a hydraulic cylinder that operates by supplying pressurized liquid from the hydraulic pump; and the hydraulic pump And the first and second pipes connected to the hydraulic cylinder to form a hydraulic closed circuit, and the pressure fluid passing through the first pipe when the first pipe is a supply-side pipe A first flow rate control valve for limiting a flow rate, a second flow rate control valve for limiting a flow rate of pressurized liquid that passes through the second pipe when the second pipe is a supply-side pipe, and And a controller that controls the flow rate of the pressurized liquid that passes through the first and second flow rate control valves to be limited in the fine operation region of the operation lever .
[0016]
According to the seventh aspect, the controller controls the flow rate of the pressurized liquid passing through the first and second flow rate control valves to be limited in the fine operation region of the operation lever, so that the rotational speed of the electric motor can be controlled from a certain number. Even if the pressure is not lowered, the amount of hydraulic fluid supplied to the hydraulic cylinder can be greatly reduced. Therefore, the hydraulic cylinder can be moved at a very low speed, and the fine operability of the operating unit driven by the hydraulic cylinder is improved.
[0017]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
DESCRIPTION OF EXEMPLARY EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[0018]
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a schematic configuration of an excavator that is a hybrid work machine according to a first embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 1, an
[0019]
The lower traveling body 1 includes left and right crawler frames 4 and 5 (both shown only on one side), left and right traveling motors 7 (6) and a traveling speed reducer 36 (35) (see FIG. 1). Is shown on the left side only). The traveling speed reducers 36 and 35 decelerate the rotation of the traveling electric motors 7 and 6 and transmit it to the traveling mechanism.
[0020]
The
[0021]
The
[0022]
Next, the drive system of the
[0023]
Further, the
[0024]
Of the six
[0025]
The
[0026]
On the other hand, when the total load of the
[0027]
Thus, the operation of the
[0028]
Further, during operation, the
[0029]
In the
[0030]
Next, the details of the drive system of the
[0031]
In FIG. 3,
[0032]
Check
[0033]
In the present embodiment, the above-described
[0034]
When the
[0035]
At this time, in order to finely operate the
[0036]
Therefore, as shown in FIG. 4, the discharge amount (broken line) of the
[0037]
On the other hand, when the
[0038]
At this time, in order to finely operate the
[0039]
Therefore, as described with reference to FIG. 4, the controllable minimum flow rate to the
[0040]
Thus, in the present embodiment, in the hydraulic closed circuit in which the
[0041]
In this embodiment, the flow
[0042]
Further, as the
[0043]
The preferred embodiments of the present embodiment have been described above, but the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and various design changes can be made as long as they are described in the claims. Is possible. For example, in the above embodiment is provided with the flow control valve in the piping for supplying hydraulic fluid to the hydraulic cylinder from the hydraulic pump, co cement roll valve in a pipe for supplying pressurized liquid to the hydraulic cylinder from the hydraulic pump And a flow path communicating from the control valve to the tank may be provided.
[0044]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to claim 1, 4, it is possible to move the hydraulic cylinders at a very small rate, fine operation of the working unit is driven by the hydraulic cylinder is improved.
[0045]
According to the second and fifth aspects, it is possible to obtain fine operability with higher responsiveness than when the flow rate control valve is provided in the pipe from which the hydraulic fluid returns from the hydraulic cylinder to the hydraulic pump.
[0046]
According to the third and sixth aspects, even if the load on the hydraulic cylinder increases or decreases, a constant amount of pressurized fluid can be supplied to the hydraulic cylinder, and a constant fine operability can be always given to the operator. become able to.
[0047]
According to the seventh aspect, the controller controls the flow rate of the pressurized liquid passing through the first and second flow rate control valves to be limited in the fine operation region of the operation lever, so that the rotational speed of the electric motor can be controlled from a certain number. Even if the pressure is not lowered, the amount of hydraulic fluid supplied to the hydraulic cylinder can be greatly reduced. Therefore, the hydraulic cylinder can be moved at a very low speed, and the fine operability of the operating unit driven by the hydraulic cylinder is improved.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a schematic configuration of an excavator that is a hybrid work machine according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
2 is a block diagram schematically showing a drive system of the excavator shown in FIG. 1. FIG.
FIG. 3 is a circuit diagram showing in detail a drive system related to the boom shown in FIG. 1;
FIG. 4 is a graph showing a relationship between a lever operation amount and a flow rate in a fine operation region.
FIG. 5 is a graph showing a relationship between a lever operation amount and a pump discharge amount in the conventional technique.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (7)
前記液圧ポンプと前記液圧シリンダとを液圧閉回路で接続する配管と、前記配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する流量制御弁と、該流量制御弁による圧液の流量の制限を操作レバーの微操作領域で機能させるコントローラとが設けられていることを特徴とする作業機械用液圧回路。In a hydraulic circuit for a work machine for controlling a hydraulic cylinder connected to a hydraulic pump driven by an electric motor,
A pipe connecting the hydraulic pump and the hydraulic cylinder with a hydraulic closed circuit, a flow control valve for limiting the flow rate of the pressure liquid passing through the pipe, and limiting the flow rate of the pressure liquid by the flow control valve. A hydraulic circuit for a work machine, comprising a controller that functions in a fine operation region of an operation lever .
前記電動機によって駆動される液圧ポンプと、前記液圧ポンプによって作動される液圧シリンダと、前記液圧ポンプと前記液圧シリンダとを液圧閉回路で接続する配管と、前記配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する流量制御弁と、該流量制御弁による圧液の流量の制限を操作レバーの微操作領域で機能させるコントローラとを備えていることを特徴とするハイブリッド作業機械。In the hybrid work machine that can store power in the power storage means by the power of the generator driven by the engine and operates the electric motor by power of at least one of the generator and the power storage means,
Through a hydraulic pump driven by said electric motor, a hydraulic cylinder operated by the hydraulic pump, a pipe connected with the hydraulic pump and said hydraulic cylinder and a hydraulic closed circuit, the piping A hybrid work machine comprising: a flow control valve that restricts a flow rate of pressure fluid; and a controller that causes a restriction of the flow rate of pressure fluid by the flow rate control valve to function in a fine operation region of an operation lever .
前記電動機で駆動される液圧ポンプと、
前記液圧ポンプから圧液が供給されて動作する液圧シリンダと、
前記液圧ポンプと前記液圧シリンダとに接続されて液圧閉回路を形成する第1および第2の配管と、
前記第1の配管が供給側配管となるときに前記第1の配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する第1の流量制御弁、および、前記第2の配管が供給側配管となるときに前記第2の配管を通過する圧液の流量を制限する第2の流量制御弁と、
前記第1および第2の流量制御弁を通過する圧液の流量が操作レバーの微操作領域で制限されるように制御するコントローラとを備えていることを特徴とする作業機械用液圧回路。An electric motor,
A hydraulic pump driven by the electric motor;
A hydraulic cylinder that operates by being supplied with hydraulic fluid from the hydraulic pump ;
First and second pipes connected to the hydraulic pump and the hydraulic cylinder to form a hydraulic closed circuit;
When the first pipe becomes the supply side pipe, the first flow rate control valve for restricting the flow rate of the pressure liquid passing through the first pipe, and the second pipe becomes the supply side pipe A second flow rate control valve for restricting the flow rate of the pressure fluid passing through the second pipe;
A hydraulic circuit for a working machine, comprising: a controller that controls the flow rate of the pressurized fluid that passes through the first and second flow control valves to be limited in a fine operation region of the operation lever .
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP18117699A JP3828680B2 (en) | 1999-06-28 | 1999-06-28 | Hydraulic circuit for work machine and hybrid work machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP18117699A JP3828680B2 (en) | 1999-06-28 | 1999-06-28 | Hydraulic circuit for work machine and hybrid work machine |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2001011899A JP2001011899A (en) | 2001-01-16 |
| JP2001011899A5 JP2001011899A5 (en) | 2005-04-21 |
| JP3828680B2 true JP3828680B2 (en) | 2006-10-04 |
Family
ID=16096223
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP18117699A Expired - Fee Related JP3828680B2 (en) | 1999-06-28 | 1999-06-28 | Hydraulic circuit for work machine and hybrid work machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3828680B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022180997A1 (en) | 2021-02-25 | 2022-09-01 | 日立建機株式会社 | Work machine |
Families Citing this family (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4512283B2 (en) * | 2001-03-12 | 2010-07-28 | 株式会社小松製作所 | Hybrid construction machine |
| JP4632583B2 (en) * | 2001-07-10 | 2011-02-16 | 住友建機株式会社 | Electric closed circuit hydraulic cylinder drive |
| JP5309546B2 (en) * | 2007-04-10 | 2013-10-09 | 株式会社豊田自動織機 | Industrial vehicle control device |
| CN101990505B (en) * | 2008-04-11 | 2013-12-11 | 住友重机械工业株式会社 | Operating machine |
| JP5214365B2 (en) * | 2008-08-07 | 2013-06-19 | 新明和工業株式会社 | Actuator device and power assist device |
| JP5248271B2 (en) * | 2008-11-06 | 2013-07-31 | 日立建機株式会社 | Hydraulic drive device for work machine |
| GB2472004A (en) * | 2009-07-20 | 2011-01-26 | Ultronics Ltd | Control arrangement for controlling movement of a differential piston in a hydraulic circuit |
| WO2011077714A1 (en) * | 2009-12-25 | 2011-06-30 | 株式会社竹内製作所 | Device for driving/controlling ac motor |
| KR101123040B1 (en) * | 2010-04-29 | 2012-03-16 | 부산대학교 산학협력단 | Industrial electro hydraulic actuator system with single-rod double acting cylinder |
| CN208487010U (en) | 2014-02-28 | 2019-02-12 | 凤凰计划股份有限公司 | The integral pump of the prime mover independently driven with two |
| US10465721B2 (en) | 2014-03-25 | 2019-11-05 | Project Phoenix, LLC | System to pump fluid and control thereof |
| US10294936B2 (en) | 2014-04-22 | 2019-05-21 | Project Phoenix, Llc. | Fluid delivery system with a shaft having a through-passage |
| EP3149362B1 (en) | 2014-06-02 | 2019-04-10 | Project Phoenix LLC | Hydrostatic transmission assembly and system |
| EP3730793B1 (en) | 2014-06-02 | 2022-04-27 | Project Phoenix LLC | Linear actuator assembly and system |
| BR112017001234B1 (en) | 2014-07-22 | 2022-09-06 | Project Phoenix, LLC | PUMP WITH SELF-ALIGNMENT CASING AND METHOD OF TRANSFERRING FLUID FROM AN INLET PORT TO AN OUTLET PORT OF A PUMP INCLUDING A PUMP CASING |
| SG11201702336RA (en) * | 2014-09-23 | 2017-04-27 | Project Phoenix Llc | System to pump fluid and control thereof |
| US10072676B2 (en) | 2014-09-23 | 2018-09-11 | Project Phoenix, LLC | System to pump fluid and control thereof |
| WO2016057321A1 (en) | 2014-10-06 | 2016-04-14 | Afshari Thomas | Linear actuator assembly and system |
| US10677352B2 (en) | 2014-10-20 | 2020-06-09 | Project Phoenix, LLC | Hydrostatic transmission assembly and system |
| TWI777234B (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2022-09-11 | 美商鳳凰計劃股份有限公司 | System to pump fluid and control thereof |
| EP3344853B1 (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2020-11-04 | Project Phoenix LLC | System to pump fluid and control thereof |
| KR102568923B1 (en) * | 2021-06-03 | 2023-08-23 | 주식회사 엔디오에스 | Electric forklift using integrated controller |
-
1999
- 1999-06-28 JP JP18117699A patent/JP3828680B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2022180997A1 (en) | 2021-02-25 | 2022-09-01 | 日立建機株式会社 | Work machine |
| KR20230045078A (en) | 2021-02-25 | 2023-04-04 | 히다치 겡키 가부시키 가이샤 | work machine |
| EP4194621A4 (en) * | 2021-02-25 | 2024-08-21 | Hitachi Construction Mach Co | Work machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2001011899A (en) | 2001-01-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3828680B2 (en) | Hydraulic circuit for work machine and hybrid work machine | |
| JP5858818B2 (en) | Construction machinery | |
| JP3647319B2 (en) | Hydraulic drive | |
| JP3969068B2 (en) | Actuator drive device for hybrid work machine | |
| JP3862256B2 (en) | Hybrid machine with hydraulic drive | |
| JP5378061B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid construction machine | |
| CN104024659B (en) | The power regeneration device of Work machine and Work machine | |
| JP5334719B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid construction machine | |
| WO2012050028A1 (en) | Construction machine having rotary element | |
| WO2001000935A1 (en) | Drive device of working machine | |
| WO2007023584A1 (en) | Rotation drive device and working machine | |
| JP2013515883A (en) | Hybrid excavator boom drive system and control method thereof | |
| KR101121705B1 (en) | Apparatus And Method For Recovering Potential Energy Of Boom In A Construction Machinery | |
| JP2009052339A (en) | Operation control method of hybrid type working machine and working machine using the same method | |
| JP2006064071A (en) | Fluid pressure drive circuit | |
| JP6286282B2 (en) | Hydraulic regeneration device and construction machine equipped with the same | |
| JP2001002371A (en) | Actuator drive device for construction machine | |
| JP2001012418A (en) | Hybrid working machine | |
| JP6147153B2 (en) | Power control apparatus and construction machine equipped with the same | |
| JP2012097844A (en) | Hybrid hydraulic shovel | |
| JP4222995B2 (en) | Hydraulic cylinder drive device for construction machinery | |
| JP2011017426A (en) | Control device of hybrid construction machine | |
| JP2008275100A (en) | Construction vehicle | |
| JP2008275101A (en) | Hybrid type construction vehicle | |
| JP2002349505A (en) | Hydraulic actuator circuit |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040615 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040615 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20060131 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20060207 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060323 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20060704 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20060707 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090714 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100714 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110714 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110714 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120714 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120714 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130714 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |