JP3717064B2 - Photonic node, photonic network, route selection method and program - Google Patents
Photonic node, photonic network, route selection method and program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3717064B2 JP3717064B2 JP2002140544A JP2002140544A JP3717064B2 JP 3717064 B2 JP3717064 B2 JP 3717064B2 JP 2002140544 A JP2002140544 A JP 2002140544A JP 2002140544 A JP2002140544 A JP 2002140544A JP 3717064 B2 JP3717064 B2 JP 3717064B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- node
- path
- repeaters
- cost
- photonic
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は光信号を交換接続するフォトニックネットワークに利用する。特に、3R(Reshaping,Retiming,Regenerating)中継を行うフォトニックノードを含むフォトニックネットワークに関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
フォトニックネットワークでは、ファイバの損失やロス、クロストークを考慮して光伝送路の途中で3R処理を施す必要がある。従来のフォトニックネットワーク構成を図5に示す。3R処理を施すためには光伝送路途中のノードに3R中継器を挿入する。3R処理を行わなくてもある程度の距離までは伝送可能であるが、その距離を決定するためには複雑な計算を必要とするため、図5に示すように、1〜2段毎に3R中継器を挿入し、如何なるルートにパスが設定されても光信号の劣化を補うことができるようにする。
【0003】
あるいは、フォトニックネットワークの特定ルートに3R中継器を挿入しておき、これを多数のパスが共通のルートとしてパス設定を行い、3R中継器を共用するという利用形態もある。ただし、この利用形態では、3R処理が必要なデータ転送の場合に経由するルートが限定される。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
3R中継器は高価でありこの3R中継器をできるだけ使用しないとフォトニックネットワークはきわめて経済的に実現できる。しかし、従来のパス設定では、3R中継器の利用状況をノードが把握してパス設定を行うといった配慮は無く、各ノードは、あらかじめ定められた3R中継器の配置箇所を把握しているだけであり、少数の3R中継器を多数のパスが共用することになると、一部の3R中継器に多数の負荷が集中するといった不都合が生じる可能性がある。また、少数の3R中継器を多数のパスが共用すると3R中継器の挿入箇所をパスが必ず経由することが必要になり、パス設定のフレキシビリティが低下する。
【0005】
例えば、3R負荷が集中している特定のルートに対する新規パスの追加要求があっても、他のルートが空いているにも係わらず、そのルートにパスが設定できない事態が発生する。
【0006】
本発明は、このような背景に行われたものであって、少数の3R中継器を用いてネットワークリソースの有効利用を図りながらフォトニックネットワークを構成してもフレキシビリティの高いフォトニックネットワークを実現でき、新規パスの追加に柔軟に対応することができるフォトニックノードおよびフォトニックネットワークおよびルート選択方法を提供することを目的とする。
【0007】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、パス設定の際に、3R中継コストを考慮してパス設定を行うことにより、3R処理負荷が低いルートにパス設定を行うことができることを特徴とする。これにより、少数の3R中継器を用いてネットワークリソースの有効利用を図りながらフォトニックネットワークを構成した場合でも3R処理負荷が特定の箇所に集中してしまう事態を回避することができる。したがって、フレキシビリティの高いフォトニックネットワークを実現でき、空きルートを有効に利用して新規パスの追加に柔軟に対応することができる。
【0008】
すなわち、本発明の第一の観点は、光信号を交換接続するフォトニックネットワークに適用され、光信号を交換接続する手段と、自ノードがソースノードであるときには自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間のパスを検索する手段と、この検索結果に基づき自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間にパスを設定する手段とを含み、3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードである。
【0009】
ここで、本発明の特徴とするところは、自ノードとディスティネーションノード間の通過ノード数が最小となるショーテストパスを求める手段と、前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストを算出する手段とを備え、前記パスを設定する手段は、前記ショーテストパスが一つのときはそれをショーテストパスとして設定し、ショーテストパスが複数存在するときには前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストが最小となるショーテストパスを選択して設定する手段を備えたところにある。
【0010】
これにより、複数のパスの選択を3R中継コストも含めて検討し、最も3R中継コストが低いパスを選択することができる。ここで、3R中継コストが低いパスとは、すなわち、3R処理負荷が低いパスである。
【0011】
前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストとして前記ショーテストパス上に存在する全てのノードにおける未使用の前記3R中継器の数の逆数を計算する手段を備えることができる。すなわち、未使用の3R中継器が多いか少ないかによって、3R処理負荷が高いか低いかを表現することができる。
【0012】
あるいは、前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストとして前記ショーテストパス上に存在する全てのノードに含まれる全ての前記3R中継器の数を未使用の前記3R中継器の数から1を減じた値により除した値を当該3R中継コストとして計算する手段を備えることができる。
【0013】
すなわち、ノード内の3R中継器の使用率が高いか低いかによって、3R処理負荷が高いか低いかを表現することができる。ここで、自ノードに含まれる全ての3R中継器の数を未使用の3R中継器の数から1を減じた値により除する理由を説明すると、例えば、初めから100個の3R中継器を有するノードと、初めから1個の3R中継器しかないノードとがある場合に、もし、未使用の3R中継器の数から1を減じた値を用いないと、全3R中継器が未使用な場合に、前者の3R中継コストは100/100=1となるが、後者の3R中継コストも1/1=1となり、同じ3R中継コストとなってしまい、いずれも等しく選択対象となる。しかし、このような場合には、当然のことながら、3R中継器の数が100個のノードの方が選択されることが望ましい。このような不都合を解消するために未使用の3R中継器の数から1を減じた値を用いる。また、未使用の3R中継器の数が1個の場合には、演算式がn/(1−1)=n/0(nは全3R中継器数)となり、演算式として成立しないが、このような場合には、3R中継コストが無限大あるいはきわめて大きな値となることとして定義を行えばよい。また、未使用の3R中継器の数が0の場合には、演算式がn/(0−1)=−nとなり、3R中継コストがマイナスの値をとるが、このような場合にも3R中継コストが無限大あるいはきわめて大きな値となることとして定義を行えばよい。
【0014】
また、前記選択する手段は、前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えない他ノードのコストをxとし、前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えた他ノードの3R中継コストを含むコストをyとし、当該コストyの重み付け係数をαとし、ショーテストパス全体のコストをCostとするときに、Cost=Σx+αΣyとして計算する手段と、当該計算する手段の計算結果が最小となるショーテストパスを選択する手段とを備えることができる。このようにして、ショーテストパスのコストを3Rコストを含めて総合的に評価することにより、最適なパスを選択することができる。
【0015】
あるいは、本発明の特徴とするところは、前記パスを設定する手段は、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合に、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、有する3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定する手段を備えたところにある。
【0016】
あるいは、本発明の特徴とするところは、前記パスを設定する手段は、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定するところにある。
【0017】
あるいは、本発明の特徴とするところは、前記パスを設定する手段は、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、前記検索されたパスの各々について、パス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する未使用の3R中継器の合計から1を引いた値をパス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する3R中継器の合計で割った値を計算し、前記割った値が最大となるパスを設定するところにある。
【0018】
本発明の第二の観点は、本発明のフォトニックノードを備えたことを特徴とするフォトニックネットワークである。
【0019】
本発明の第三の観点は、光信号を交換接続する手段と、自ノードがソースノードであるときには自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間のパスを検索する手段と、この検索結果に基づき自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間にパスを設定する手段とを含み、3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードを備えたフォトニックネットワークに適用されるルート選択方法である。
【0020】
ここで、本発明の特徴とするところは、自ノードとディスティネーションノード間の通過ノード数が最小となるショーテストパスを求め、前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストを算出し、前記パスを設定する際には、前記ショーテストパスが一つのときはそれをショーテストパスとして設定し、ショーテストパスが複数存在するときには前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストが最小となるショーテストパスを選択して設定するところにある。
【0021】
前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストとして前記ショーテストパス上に存在する全てのノードにおける未使用の前記3R中継器の数の逆数を計算することができる。
【0022】
あるいは、前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストとして前記ショーテストパス上に存在する全てのノードに含まれる全ての前記3R中継器の数を未使用の前記3R中継器の数から1を減じた値により除した値を当該3R中継コストとして計算することもできる。
【0023】
また、前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えない他ノードのコストをxとし、前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えた他ノードの3R中継コストを含むコストをyとし、当該コストyの重み付け係数をαとし、ショーテストパス全体のコストをCostとするときに、Cost=Σx+αΣyとして計算し、当該計算結果が最小となるショーテストパスを選択することができる。
【0024】
あるいは、本発明の特徴とするところは、前記パスを設定する際に、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合に、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、有する3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定するところにある。
【0025】
あるいは、本発明の特徴とするところは、前記パスを設定する際に、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定するところにある。
【0026】
あるいは、本発明の特徴とするところは、前記パスを設定する際に、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、前記検索されたパスの各々について、パス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する未使用の3R中継器の合計から1を引いた値をパス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する3R中継器の合計で割った値を計算し、前記割った値が最大となるパスを設定するところにある。
【0027】
【発明の実施の形態】
本発明実施例のフォトニックノードおよびフォトニックネットワークを図1ないし図4を参照して説明する。図1は本実施例のフォトニックネットワークの一例を示す図である。図2は本実施例のフォトニックノードのブロック構成図である。図3は本実施例の公告パケットの構成図である。図4は第三実施例を説明するためのフォトニックネットワークの一例を示す図である。
【0028】
(第一実施例)
第一実施例では、3R中継コスト計算部5は、自ノードの3R中継コストとして自ノードにおける未使用の3R中継器7i(iは1〜nのいずれか)の数の逆数を当該3R中継コストとして計算する。すなわち、未使用の3R中継器が多いか少ないかによって、3R処理負荷が高いか低いかを表現することができる。例えば、自ノードの未使用の3R中継器7iの数が全3R中継器71〜7nと等しければ、3R中継コストは(1/n)となり小さな値となるので、3R中継能力に十分な余裕があることがわかる。また、自ノードの未使用の3R中継器7iの数が“0”であれば(1/0)となって演算式が成立しないがこれを無限大あるいはきわめて大きな値として定義することにより、3R中継能力に全く余裕がないことを表現することができる。この場合の3R中継コストの取り得る範囲は、例えば、0<3R中継コスト<∞である。
【0029】
(第二実施例)
第二実施例では、3R中継コスト計算部5は、自ノードの3R中継コストとして自ノードに含まれる全ての3R中継器71〜7nの数を未使用の3R中継器7iの数から1を減じた値により除した値を当該3R中継コストとして計算する。すなわち、ノード内の3R中継器の使用率が高いか低いかによって、3R処理負荷が高いか低いかを表現することができる。例えば、自ノードの全3R中継器71〜7nの数が100個である場合に、自ノードの未使用の3R中継器7iの数が全3R中継器71〜7nと等しければ、3R中継コストは(100/99)となり、また、自ノードの未使用の3R中継器7iの数が“1”であれば(100/0)となって演算式が成立しないがこれを無限大あるいはきわめて大きな値として定義することにより、3R中継能力に全く余裕がないことがわかる。また、未使用の3R中継器7iの数が“0”の場合には、演算式が100/(0−1)=−100となり、3R中継コストがマイナスの値をとるが、このような場合にも3R中継コストが無限大あるいはきわめて大きな値となることとして定義を行えばよい。
【0030】
この場合の3R中継コストの取り得る範囲は、例えば、1<3R中継コスト<∞である。なお、未使用の3R中継器7iの数から1を減じる理由は前述したとおりである。
【0031】
(第三実施例)
第三実施例では、パス設定部3は、ネットワークトポロジに基づきショーテストパスに含まれる3R中継器を備えない他ノードのコストをxとし、3R中継コスト集計部4の集計結果に基づきショーテストパスに含まれる3R中継器を備えた他ノードの3R中継コストを含むコストをyとし、当該コストyの重み付け係数をαとし、ショーテストパス全体のコストをCostとするときに、Cost=Σx+αΣyとして計算し、当該計算結果が最小となるショーテストパスを選択する。
【0032】
なお、重み付け係数αは、3R中継器を備えない他ノードのコストに対する3R中継器を備えた他ノードの3R中継コストを含むコストの重み付けを行うための係数であり、例えば、二つのフォトニックネットワークがあり、その一方のフォトニックネットワーク全体の3R中継器数が他方のフォトニックネットワーク全体の3R中継器数よりも多い場合には、比較的3R中継器数の多いフォトニックネットワークにおける係数αの値は他方のフォトニックネットワークにおける係数αの値よりも小さくてよい。
【0033】
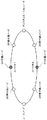
すなわち、図4に示すように、ショーテストパスとしてルート#1および#2があり、各ルート上の白丸が3R中継器を備えない3R無中継ノードであり、黒丸が3R中継器を備えた3R中継を行うノードである。ここでは、ルート#1の3R無中継ノードのコストを5とし、3R中継を行うノードのコストを7および9とする。また、ルート#2の3R無中継ノードのコストを5とし、3R中継を行うノードのコストを7とする。また、重み付け係数αは2とする。
【0034】
このときに、ルート#1のCostは、Cost=5+2(7+9)=37である。ルート#2のCostは、Cost=(5+5+5)+2(7)=29である。これにより、ルート#2の方がホップ数は多いがショーテストパス全体としての3R中継コストも含めたコストが小さいことがわかるので、パス設定部3はルート#2を選択し、ルート#2上の各ノードに対してパス設定要求を送出する。
【0035】
(第四実施例)
本実施例のフォトニックノードを制御する機能は、情報処理装置であるコンピュータ装置を用いて実現することができる。すなわち、コンピュータ装置にインストールすることにより、そのコンピュータ装置に、光信号を交換接続するフォトニックネットワークに適用され、光信号を交換接続する光クロスコネクト1と、自ノードがソースノードであるときには自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間の通過ノード数が最小となるショーテストパスを計算するルート計算部2と、このルート計算部2の計算結果に基づき自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間にパスを設定するパス設定部3とを含み、3R中継器71〜7nを1以上備えるかもしくは備えないフォトニックノードを制御する機能を実現させるプログラムであって、自ノードの3R中継コストを計算する3R中継コスト計算部5に相応する機能と、この3R中継コスト計算部5の計算結果を他ノードに公告する3R中継コスト公告部6に相応する機能と、他ノードから公告された3R中継コストを当該他ノードのアドレスに対応させてそれぞれ集計する3R中継コスト集計部4に相応する機能とを実現させ、パス設定部3に相応する機能として、ルート計算部2の計算結果が複数存在するときには3R中継コスト集計部4の集計結果に基づき3R中継コストが最小となるショーテストパスを選択する機能を実現させるプログラムをコンピュータ装置にインストールすることにより、そのコンピュータ装置に、本実施例のフォトニックノードを制御する機能を実現させることができる。
【0036】
さらに、3R中継コスト計算部5に相応する機能として、自ノードの3R中継コストとして自ノードにおける未使用の3R中継器7iの数の逆数を当該3R中継コストとして計算する機能を実現させるプログラムをコンピュータ装置にインストールすることにより、そのコンピュータ装置に、前述した第一実施例のフォトニックノードを制御する機能を実現させることができる。
【0037】
あるいは、3R中継コスト計算部5に相応する機能として、自ノードの3R中継コストとして自ノードに含まれる全ての3R中継器71〜7nの数を未使用の3R中継器7iの数から1を減じた値により除した値を当該3R中継コストとして計算する機能を実現させるプログラムをコンピュータ装置にインストールすることにより、そのコンピュータ装置に、前述した第二実施例のフォトニックノードを制御する機能を実現させることができる。
【0038】
あるいは、パス制御部3に相応する機能として、ネットワークトポロジに基づきショーテストパスに含まれる3R中継器を備えない他ノードのコストをxとし、3R中継コスト集計部5の集計結果に基づきショーテストパスに含まれる3R中継器を備えた他ノードの3R中継コストを含むコストをyとし、当該コストyの重み付け係数をαとし、ショーテストパス全体のコストをCostとするときに、Cost=Σx+αΣyとして計算する機能と、当該計算する機能の計算結果が最小となるショーテストパスを選択する機能とを実現させるプログラムをコンピュータ装置にインストールすることにより、そのコンピュータ装置に、前述した第三実施例のフォトニックノードを制御する機能を実現させることができる。
【0039】
本実施例のプログラムは本実施例の記録媒体に記録されることにより、コンピュータ装置は、この記録媒体を用いて本実施例のプログラムをインストールすることができる。あるいは、本実施例のプログラムを保持するサーバからネットワークを介して直接コンピュータ装置に本実施例のプログラムをインストールすることもできる。
【0040】
これにより、コンピュータ装置を用いて、少数の3R中継器を用いてネットワークリソースの有効利用を図りながらフォトニックネットワークを構成してもフレキシビリティの高いフォトニックネットワークを実現でき、新規パスの追加に柔軟に対応することができるフォトニックノードおよびフォトニックネットワークを実現することができる。
【0041】
(第五実施例)
なお、フォトニックノードとして、自ノードがソースノードであるときに、自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間のパスを検索し、この検索結果に基づき自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間にパスを設定する際に、検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、検索されたすべてのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、有する3R中継器の台数が最も多いノードを検索し、その3R中継器の台数が最も多いノードを含むパスを設定する。あるいは、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、未使用の3R中継器の最も多いノードを検索し、未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も多いノードを含むパスを設定する。あるいは、検索されたパスの各々について、パス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する3R中継器の合計から1を引いた値をパス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する3R中継器の合計で割った値を計算し、その割った値が最大となるパスを設定する。
【0042】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、少数の3R中継器を用いてネットワークリソースの有効利用を図りながらフォトニックネットワークを構成してもフレキシビリティの高いフォトニックネットワークを実現でき、新規パスの追加に柔軟に対応することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 本実施例のフォトニックネットワークの一例を示す図。
【図2】 本実施例のフォトニックノードのブロック構成図。
【図3】 本実施例の公告パケットの構成図。
【図4】 第三実施例を説明するためのフォトニックネットワークの一例を示す図。
【図5】 従来のフォトニックネットワーク構成を示す図。
【符号の説明】
1 光クロスコネクト
2 ルート計算部
3 パス設定部
4 3R中継コスト集計部
5 3R中継コスト計算部
6 3R中継コスト公告部
71〜7n 3R中継器[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention is used for a photonic network for switching and connecting optical signals. In particular, the present invention relates to a photonic network including a photonic node that performs 3R (Reshaping, Retiming, Regenerating) relay.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In a photonic network, it is necessary to perform 3R processing in the middle of an optical transmission line in consideration of fiber loss, loss, and crosstalk. A conventional photonic network configuration is shown in FIG. In order to perform 3R processing, a 3R repeater is inserted into a node in the middle of the optical transmission path. Although transmission is possible up to a certain distance without performing 3R processing, since complicated calculation is required to determine the distance, 3R relay is performed every one or two stages as shown in FIG. So as to compensate for the deterioration of the optical signal regardless of the route set.
[0003]
Alternatively, there is a usage form in which a 3R repeater is inserted into a specific route of a photonic network, a path is set by using a common route for many paths, and the 3R repeater is shared. However, in this usage mode, the route through which data transfer requires 3R processing is limited.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
A 3R repeater is expensive, and if this 3R repeater is not used as much as possible, a photonic network can be realized extremely economically. However, in the conventional path setting, there is no consideration that the node grasps the usage status of the 3R repeater and sets the path, and each node only knows a predetermined location of the 3R repeater. When a large number of paths share a small number of 3R repeaters, there is a possibility that a large number of loads are concentrated on some 3R repeaters. In addition, if a large number of paths share a small number of 3R repeaters, it is necessary for the paths to always pass through the insertion location of the 3R repeater, which reduces the flexibility of path setting.
[0005]
For example, even when there is a request to add a new path to a specific route where the 3R load is concentrated, there is a situation where a path cannot be set for that route even though another route is available.
[0006]
The present invention has been implemented against this background, and realizes a highly flexible photonic network even if a photonic network is configured while effectively using network resources using a small number of 3R repeaters. An object of the present invention is to provide a photonic node, a photonic network, and a route selection method that can flexibly cope with addition of a new path.
[0007]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The present invention is characterized in that a path can be set for a route with a low 3R processing load by setting the path in consideration of the 3R relay cost when setting the path. As a result, even when a photonic network is configured while effectively using network resources using a small number of 3R repeaters, it is possible to avoid a situation where the 3R processing load is concentrated at a specific location. Therefore, a highly flexible photonic network can be realized, and it is possible to flexibly cope with the addition of a new path by effectively using a free route.
[0008]
That is, the first aspect of the present invention is applied to a photonic network for exchanging and connecting optical signals, and between the means for exchanging and connecting optical signals and the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node. And a means for setting a path between the own node and the destination node based on the search result, and the 3R repeater is used with or without one or more 3R repeaters. Either a photonic node or an unused state is selected.
[0009]
Here, the feature of the present invention is that it includes means for obtaining a shortest test path that minimizes the number of passing nodes between the self node and the destination node, and means for calculating the 3R relay cost of the shortest path. The path setting means sets the show test path when there is one show test path, and sets the show test path to minimize the 3R relay cost of the show test path when there are a plurality of show test paths. It is in the place with the means to select and set.
[0010]
Thereby, selection of a plurality of paths including the 3R relay cost can be considered, and the path with the lowest 3R relay cost can be selected. Here, the path with a low 3R relay cost is a path with a low 3R processing load.
[0011]
Means may be provided for calculating the reciprocal of the number of unused 3R repeaters in all nodes existing on the Shortest path as the 3R relay cost of the Shortest path. That is, whether the 3R processing load is high or low can be expressed by whether there are many or few unused 3R repeaters.
[0012]
Alternatively, the 3R relay cost of the Shortest path is a value obtained by subtracting 1 from the number of unused 3R repeaters in the number of all 3R repeaters included in all nodes existing on the Shortest path. Means for calculating the divided value as the 3R relay cost can be provided.
[0013]
That is, whether the 3R processing load is high or low can be expressed by whether the usage rate of the 3R repeater in the node is high or low. Here, the reason why the number of all 3R repeaters included in the own node is divided by a value obtained by subtracting 1 from the number of unused 3R repeaters will be described. For example, from the beginning, there are 100 3R repeaters. When there is a node and a node that has only one 3R repeater from the beginning, if the value obtained by subtracting 1 from the number of unused 3R repeaters is not used, all 3R repeaters are unused In addition, the former 3R relay cost is 100/100 = 1, but the latter 3R relay cost is also 1/1 = 1, which is the same 3R relay cost. However, in such a case, as a matter of course, it is desirable to select a node having 100 3R repeaters. In order to eliminate such inconvenience, a value obtained by subtracting 1 from the number of unused 3R repeaters is used. In addition, when the number of unused 3R repeaters is one, the calculation formula is n / (1-1) = n / 0 (n is the total number of 3R repeaters), and the calculation formula does not hold. In such a case, the 3R relay cost may be defined as being infinite or extremely large. Further, when the number of unused 3R repeaters is 0, the arithmetic expression is n / (0-1) = − n, and the 3R relay cost takes a negative value. It may be defined that the relay cost is infinite or extremely large.
[0014]
Further, the means for selecting sets the cost of another node not including the 3R repeater included in the shortest path as x, and the 3R relay cost of another node including the 3R repeater included in the shortest path. When the cost including Y is y, the weighting factor of the cost y is α, and the cost of the entire show test path is Cost, the calculation result of Cost = Σx + αΣy and the calculation result of the calculation means are minimized. Means for selecting a show test pass. In this way, the optimum path can be selected by comprehensively evaluating the cost of the show test path including the 3R cost.
[0015]
Alternatively, the present invention is characterized in that, when there are a plurality of searched paths, the means for setting the path includes a 3R repeater having all the nodes included in all the searched paths. There is provided means for searching for a node having the largest number of nodes and setting a path including a node having the largest number of 3R repeaters.
[0016]
Alternatively, the feature of the present invention is that, when there are a plurality of searched paths, the means for setting the path is an unused 3R among all nodes included in all the searched paths. The node having the largest number of repeaters is searched, and a path including the node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters is set.
[0017]
Alternatively, the feature of the present invention is that, when there are a plurality of searched paths, the means for setting the path includes, for each of the searched paths, all nodes included in the path. A value obtained by subtracting 1 from the total of 3R repeaters in use and dividing the sum by the sum of 3R repeaters of all nodes included in the path, and setting a path that maximizes the divided value. It is in.
[0018]
A second aspect of the present invention is a photonic network comprising the photonic node of the present invention.
[0019]
According to a third aspect of the present invention, there are provided means for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and the own node based on the search result. And a means for setting a path between the destination node and one or more 3R repeaters, wherein the 3R repeater is selected to be used or unused. This is a route selection method applied to a photonic network having nodes.
[0020]
Here, the present invention is characterized in that a shortest path that minimizes the number of passing nodes between the self node and the destination node is obtained, the 3R relay cost of the shortest path is calculated, and the path is set. When there is one show test path, it is set as a show test path, and when there are a plurality of show test paths, a show test path that minimizes the 3R relay cost of the show test path is selected and set. There is a place to do.
[0021]
As the 3R relay cost of the Shortest path, the reciprocal of the number of unused 3R relays in all nodes existing on the Shortest path can be calculated.
[0022]
Alternatively, the 3R relay cost of the Shortest path is a value obtained by subtracting 1 from the number of unused 3R repeaters in the number of all 3R repeaters included in all nodes existing on the Shortest path. The divided value can also be calculated as the 3R relay cost.
[0023]
In addition, the cost of another node that does not include the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path is x, and the cost that includes the 3R relay cost of another node that includes the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path is y. Then, when the weighting coefficient of the cost y is α and the cost of the entire show test path is Cost, it is calculated as Cost = Σx + αΣy, and the show test path that minimizes the calculation result can be selected.
[0024]
Alternatively, a feature of the present invention is that, when the path is set, when there are a plurality of searched paths, the 3R repeater having all of the nodes included in all the searched paths The node having the largest number of nodes is searched and a path including the node having the largest number of 3R repeaters is set.
[0025]
Alternatively, the present invention is characterized in that, when the path is set, if there are a plurality of searched paths, an unused 3R is selected from all the nodes included in all the searched paths. The node having the largest number of repeaters is searched, and a path including the node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters is set.
[0026]
Alternatively, the present invention is characterized in that when there are a plurality of searched paths when the path is set, for each of the searched paths, all the nodes included in the path have no search. A value obtained by subtracting 1 from the total of 3R repeaters in use and dividing the sum by the sum of 3R repeaters of all nodes included in the path, and setting a path that maximizes the divided value. It is in.
[0027]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
A photonic node and a photonic network according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an example of a photonic network according to the present embodiment. FIG. 2 is a block diagram of the photonic node of this embodiment. FIG. 3 is a configuration diagram of the announcement packet of this embodiment. FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example of a photonic network for explaining the third embodiment.
[0028]
(First Example)
In the first embodiment, the 3R relay
[0029]
(Second embodiment)
In the second embodiment, the 3R relay
[0030]
In this case, the possible range of the 3R relay cost is, for example, 1 <3R relay cost <∞. The reason why 1 is subtracted from the number of unused 3R repeaters 7i is as described above.
[0031]
(Third embodiment)
In the third embodiment, the
[0032]
The weighting coefficient α is a coefficient for weighting the cost including the 3R relay cost of the other node having the 3R repeater with respect to the cost of the other node not having the 3R repeater, for example, two photonic networks If the number of 3R repeaters in one photonic network is larger than the number of 3R repeaters in the other photonic network, the value of the coefficient α in the photonic network having a relatively large number of 3R repeaters May be smaller than the value of the coefficient α in the other photonic network.
[0033]
That is, as shown in FIG. 4, there are routes # 1 and # 2 as show test paths, white circles on each route are 3R non-relay nodes without 3R repeaters, and black circles are 3R with 3R repeaters A node that performs relay. Here, the cost of the 3R non-relay node of route # 1 is 5, and the costs of the nodes that perform 3R relay are 7 and 9. The cost of the 3R non-relay node of
[0034]
At this time, the cost of route # 1 is Cost = 5 + 2 (7 + 9) = 37. The cost of
[0035]
(Fourth embodiment)
The function of controlling the photonic node of this embodiment can be realized by using a computer device that is an information processing device. That is, by installing in a computer device, the optical device is applied to a photonic network for exchanging and connecting optical signals to the computer device. When the own node is a source node, the own node is used.
[0036]
Further, as a function corresponding to the 3R relay
[0037]
Alternatively, as a function corresponding to the 3R relay
[0038]
Alternatively, as a function corresponding to the
[0039]
By recording the program of the present embodiment on the recording medium of the present embodiment, the computer apparatus can install the program of the present embodiment using this recording medium. Alternatively, the program of this embodiment can be directly installed on the computer device from the server holding the program of this embodiment via the network.
[0040]
As a result, a highly flexible photonic network can be realized even if a photonic network is configured using a small number of 3R repeaters while effectively using network resources using a computer device, and it is flexible to add new paths. It is possible to realize a photonic node and a photonic network that can cope with the above.
[0041]
(Fifth embodiment)
As a photonic node, when the local node is the source node, search the path between the local node and the destination node, and set the path between the local node and the destination node based on the search result When there are a plurality of searched paths, the node having the largest number of 3R repeaters is searched from all the nodes included in all the searched paths, and the number of the 3R repeaters is determined. Set the path that contains the node with the most. Alternatively, the node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters is searched from all the nodes included in all the searched paths, and the path including the node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters is set. . Alternatively, for each of the searched paths, the value obtained by subtracting 1 from the sum of the 3R repeaters of all the nodes included in the path is divided by the sum of the 3R repeaters of all the nodes included in the path. Calculate the value and set the path that maximizes the divided value.
[0042]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, a highly flexible photonic network can be realized even if a photonic network is configured using a small number of 3R repeaters while effectively using network resources. It can respond flexibly to the addition.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating an example of a photonic network according to an embodiment.
FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a photonic node according to the present embodiment.
FIG. 3 is a configuration diagram of a notification packet according to the present embodiment.
FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example of a photonic network for explaining a third embodiment.
FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a conventional photonic network configuration.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF SYMBOLS 1
Claims (19)
3R(Reshaping,Retiming,Regenerating)中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードにおいて、
自ノードとディスティネーションノード間の通過ノード数が最小となるショーテストパスを求める手段と、
前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストを算出する手段と
を備え、
前記パスを設定する手段は、前記ショーテストパスが一つのときはそれをパスとして設定し、ショーテストパスが複数存在するときには前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストが最小となるショーテストパスを選択して設定する手段を備えた
ことを特徴とするフォトニックノード。Applied to a photonic network for switching and connecting optical signals, means for switching and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and the search result And a means for setting a path between the own node and the destination node based on
In a photonic node with or without one or more 3R (Reshaping, Retiming, Regenerating) repeaters, the 3R repeater being used or unused
Means for obtaining a show test path that minimizes the number of passing nodes between the self node and the destination node;
Means for calculating the 3R relay cost of the show test pass,
The means for setting the path sets the shortest test path as a path when there is one shortest test path, and selects the shortest test path that minimizes the 3R relay cost of the shortest test path when there are a plurality of shortest test paths. A photonic node characterized by having a means for setting.
前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えない他ノードのコストをxとし、前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えた他ノードの3R中継コストを含むコストをyとし、当該コストyの重み付け係数をαとし、ショーテストパス全体のコストをCostとするときに、
Cost=Σx+αΣy
として計算する手段と、
当該計算する手段の計算結果が最小となるパスを選択する手段と
を備えた請求項1記載のフォトニックノード。The means for selecting is
The cost of another node that does not include the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path is x, and the cost that includes the 3R relay cost of another node that includes the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path is y, When the weighting coefficient of the cost y is α and the cost of the entire show test pass is Cost,
Cost = Σx + αΣy
As a means to calculate as
The photonic node according to claim 1, further comprising: a path that selects a path that minimizes a calculation result of the calculating means.
光信号を交換接続する手段と、自ノードがソースノードであるときには自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間のパスを検索する手段と、この検索結果に基づき自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間にパスを設定する手段とを含み、
3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードにおいて、
前記パスを設定する手段は、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合に、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、有する3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定する手段を備えた
ことを特徴とするフォトニックノード。Applied to photonic networks that exchange and connect optical signals,
Means for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and a path between the own node and the destination node based on the search result And means for setting
In a photonic node with or without one or more 3R repeaters, where the 3R repeater is selected to be either used or unused,
The means for setting the path searches for a node having the largest number of 3R repeaters from among all nodes included in all the searched paths when there are a plurality of searched paths. A photonic node comprising means for setting a path including a node having the largest number of 3R repeaters.
3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードにおいて、
前記パスを設定する手段は、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定する
ことを特徴とするフォトニックノード。Applied to a photonic network for switching and connecting optical signals, means for switching and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and the search result And a means for setting a path between the own node and the destination node based on
In a photonic node with or without one or more 3R repeaters, where the 3R repeater is selected to be either used or unused,
When there are a plurality of searched paths, the means for setting the path searches for a node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters from all nodes included in all the searched paths. A path including a node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters is set.
3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードにおいて、
前記パスを設定する手段は、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、前記検索されたパスの各々について、パス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する未使用の3R中継器の合計から1を引いた値をパス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する3R中継器の合計で割った値を計算し、前記割った値が最大となるパスを設定する
ことを特徴とするフォトニックノード。Applied to a photonic network for switching and connecting optical signals, means for switching and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and the search result And a means for setting a path between the own node and the destination node based on
In a photonic node with or without one or more 3R repeaters, where the 3R repeater is selected to be either used or unused,
When there are a plurality of searched paths, the means for setting the path subtracts 1 from the total of unused 3R repeaters of all nodes included in the path for each of the searched paths. A value obtained by dividing the obtained value by the sum of the 3R repeaters of all nodes included in the path is calculated, and a path that maximizes the divided value is set.
3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードを備えたフォトニックネットワークに適用されるルート選択方法において、
自ノードとディスティネーションノード間の通過ノード数が最小となるショーテストパスを求め、前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストを算出し、前記パスを設定する際には、前記ショーテストパスが一つのときはそれをパスとして設定し、ショーテストパスが複数存在するときには前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストが最小となるショーテストパスを選択して設定する
ことを特徴とするルート選択方法。Means for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and a path between the own node and the destination node based on the search result And means for setting
In a route selection method applied to a photonic network comprising a photonic node with or without one or more 3R repeaters, wherein the 3R repeaters are selected to be used or unused.
When a shortest path that minimizes the number of passing nodes between its own node and the destination node is obtained, the 3R relay cost of the shortest path is calculated, and when the shortest path is set, A route selection method characterized by: setting a path as a path, and selecting and setting a shortest path that minimizes the 3R relay cost of the shortest path when there are a plurality of shortest paths.
Cost=Σx+αΣy
として計算し、当該計算結果が最小となるショーテストパスを選択する請求項8記載のルート選択方法。The cost of the other node that does not include the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path is x, and the cost that includes the 3R relay cost of the other node that includes the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path is y, When the weighting coefficient of the cost y is α and the cost of the entire show test pass is Cost,
Cost = Σx + αΣy
9. The route selection method according to claim 8, wherein a shortest test path that minimizes the calculation result is selected.
3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードを備えたフォトニックネットワークに適用されるルート選択方法において、
前記パスを設定する際に、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合に、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、有する3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定する
ことを特徴とするルート選択方法。Means for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and a path between the own node and the destination node based on the search result And means for setting
In a route selection method applied to a photonic network comprising a photonic node with or without one or more 3R repeaters, wherein the 3R repeaters are selected to be used or unused.
When setting the path, if there are a plurality of searched paths, search for a node having the largest number of 3R repeaters from all nodes included in all the searched paths, A route selection method comprising setting a path including a node having the largest number of 3R repeaters.
3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードを備えたフォトニックネットワークに適用されるルート選択方法において、
前記パスを設定する際に、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、検索された全てのパスに含まれる全てのノードの中から、未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを検索し、前記未使用の3R中継器の台数が最も大きいノードを含むパスを設定する
ことを特徴とするルート選択方法。Means for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and a path between the own node and the destination node based on the search result And means for setting
In a route selection method applied to a photonic network comprising a photonic node with or without one or more 3R repeaters, wherein the 3R repeaters are selected to be used or unused.
When setting the path, if there are a plurality of searched paths, the node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters is searched from all the nodes included in all the searched paths. A route selection method including setting a path including a node having the largest number of unused 3R repeaters.
3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードを備えたフォトニックネットワークに適用されるルート選択方法において、
前記パスを設定する際に、前記検索されたパスが複数ある場合は、前記検索されたパスの各々について、パス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する未使用の3R中継器の合計から1を引いた値をパス上に含まれる全てのノードが有する3R中継器の合計で割った値を計算し、前記割った値が最大となるパスを設定する
ことを特徴とするルート選択方法。Means for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for searching for a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and a path between the own node and the destination node based on the search result And means for setting
In a route selection method applied to a photonic network comprising a photonic node with or without one or more 3R repeaters, wherein the 3R repeaters are selected to be used or unused.
When setting the path, if there are a plurality of searched paths, subtract 1 from the total of unused 3R repeaters of all nodes included in the path for each of the searched paths. A route selection method comprising: calculating a value obtained by dividing the obtained value by the sum of the 3R repeaters of all nodes included in the path, and setting a path that maximizes the divided value.
光信号を交換接続するフォトニックネットワークに適用され、光信号を交換接続する手段と、自ノードがソースノードであるときには自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間のパスを検索する手段と、この検索結果に基づき自ノードとディスティネーションノードとの間にパスを設定する手段とを含み、3R中継器を1以上備えるかもしくは備えず、前記3R中継器は使用または未使用の状態のどちらかが選択されているフォトニックノードを制御する機能を実現させるプログラムであって、Applied to a photonic network for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for exchanging and connecting optical signals, means for retrieving a path between the own node and the destination node when the own node is a source node, and the search result And a means for setting a path between the own node and the destination node based on the above, the 3R repeater is provided with one or more 3R repeaters, and the 3R repeater is selected to be used or unused. A program for realizing a function for controlling a photonic node,
自ノードとディスティネーションノード間の通過ノード数が最小となるショーテストパスを求める機能と、A function for obtaining a shortest test path that minimizes the number of passing nodes between the own node and the destination node;
前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストを算出する機能とA function for calculating the 3R relay cost of the show test pass;
を実現させ、Realized,
前記パスを設定する機能として、前記ショーテストパスが一つのときはそれをパスとして設定し、ショーテストパスが複数存在するときには前記ショーテストパスの3R中継コストが最小となるショーテストパスを選択して設定する機能を実現させるAs a function of setting the path, when there is one show test path, it is set as a path, and when there are a plurality of show test paths, a show test path that minimizes the 3R relay cost of the show test path is selected. To realize the function to be set
ことを特徴とするプログラム。A program characterized by that.
前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えない他ノードのコストをxとし、前記ショーテストパスに含まれる前記3R中継器を備えた他ノードの3R中継コストをLet x be the cost of another node that does not include the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path, and 3R relay cost of the other node that includes the 3R repeater included in the Shortest path. 含むコストをyとし、当該コストyの重み付け係数をαとし、ショーテストパス全体のコストをCostとするときに、When the cost to include is y, the weighting coefficient of the cost y is α, and the cost of the entire show test path is Cost,
Cost=Σx+αΣyCost = Σx + αΣy
として計算する機能と、With the ability to calculate as
当該計算する機能の計算結果が最小となるパスを選択する機能とA function for selecting a path with the smallest calculation result of the function to be calculated;
を実現する請求項16記載のプログラム。The program of Claim 16 which implement | achieves.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002140544A JP3717064B2 (en) | 2002-05-15 | 2002-05-15 | Photonic node, photonic network, route selection method and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002140544A JP3717064B2 (en) | 2002-05-15 | 2002-05-15 | Photonic node, photonic network, route selection method and program |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003333078A JP2003333078A (en) | 2003-11-21 |
| JP2003333078A5 JP2003333078A5 (en) | 2005-05-26 |
| JP3717064B2 true JP3717064B2 (en) | 2005-11-16 |
Family
ID=29701401
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002140544A Expired - Fee Related JP3717064B2 (en) | 2002-05-15 | 2002-05-15 | Photonic node, photonic network, route selection method and program |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3717064B2 (en) |
-
2002
- 2002-05-15 JP JP2002140544A patent/JP3717064B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2003333078A (en) | 2003-11-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7852836B2 (en) | Reduced arbitration routing system and method | |
| JP3996455B2 (en) | Data transfer method for information processing system and information processing system | |
| US6904462B1 (en) | Method and system for allocating protection path resources | |
| US8892772B1 (en) | Limiting candidate routing backup paths based on policy considerations | |
| US6574669B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for routing traffic within a network utilizing linear optimization | |
| JP4015628B2 (en) | Distributed structure router and method for dynamically managing forwarding information | |
| JP5534481B2 (en) | Communication quality monitoring system, communication quality monitoring method, and storage medium | |
| US8004984B2 (en) | Routing control technique in MPLS | |
| US20030147645A1 (en) | Optical network, optical cross-connect apparatus, photonic-IP network, and node | |
| CA2141354C (en) | Method of routing multiple virtual circuits | |
| JPH0831876B2 (en) | Routing control method in packet switching network | |
| US20090034972A1 (en) | Optical Path Routing in an Optical Communications Network | |
| EP0448049B1 (en) | Packet transfer regulating apparatus | |
| JP2012216078A (en) | Information processor, parallel computer system, and method for controlling parallel computer system | |
| CN113542099B (en) | Data transmission method, device, electronic equipment, medium and product | |
| US20140010077A1 (en) | Method and Apparatus for Enhanced Routing within a Shortest Path Based Routed Network Containing Local and Long Distance Links | |
| CN104168194A (en) | Cluster network path control method equipment and cluster network system | |
| US20040233850A1 (en) | Device and a method for determining routing paths in a communication network in the presence of selection attributes | |
| JP3717064B2 (en) | Photonic node, photonic network, route selection method and program | |
| EP3104561A1 (en) | Communication control system, communication control method, and communication control program | |
| JP3717866B2 (en) | Photonic nodes and photonic networks and programs | |
| US6067573A (en) | Technique for reducing the flow of topology information in a computer network to only nodes that require the information | |
| CN106233680A (en) | A kind of routing resource, optical-fiber network controller and optical transport network | |
| US20090086734A1 (en) | Method and Apparatus for Providing a Distributed Forwarding Plane for a Mobility Home Agent | |
| JP3690671B2 (en) | Photonic node |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040804 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040804 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20050420 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20050607 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20050801 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20050824 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20050825 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20080909 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090909 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20090909 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100909 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20100909 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110909 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120909 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |