JP3617455B2 - Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium - Google Patents
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3617455B2 JP3617455B2 JP2001002373A JP2001002373A JP3617455B2 JP 3617455 B2 JP3617455 B2 JP 3617455B2 JP 2001002373 A JP2001002373 A JP 2001002373A JP 2001002373 A JP2001002373 A JP 2001002373A JP 3617455 B2 JP3617455 B2 JP 3617455B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- line segment
- image
- component
- image processing
- pixel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 title claims description 13
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 claims description 53
- 230000001629 suppression Effects 0.000 claims description 51
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 16
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 19
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 101100115215 Caenorhabditis elegans cul-2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001454 recorded image Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Color Television Image Signal Generators (AREA)
- Processing Of Color Television Signals (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、デジタルカメラ等に用いられる画像処理装置の構成および画像処理方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
デジタルカメラやデジタルビデオカメラ等においては、従来から画像撮像装置としてCCD(Charge Coupled Device)が利用されている。CCDは光電変換をつかさどる多数のフォトダイオードがマトリクス状に配列されて構成されている。
【0003】
撮像レンズを含む光学系を介してCCDに入射した被写体の光学像は、フォトダイオードで光電変換されたのち電荷蓄積される。マトリクス配置されたフォトダイオードに蓄積された電荷は、CCDから順次取り出された後、画像処理回路に転送されて画像信号として検出されるのである。
【0004】
このようにCCDは光学像の明暗に応じた電荷の蓄積を行い、電気信号として出力する役割を果たすが、カラー画像を取得するためには、3原色成分(R、G、B)に対応した電気信号が得られる必要がある。
【0005】
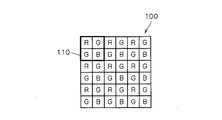
図5を用いて、単板式のカラー撮像装置に用いられるベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイ100について説明する。
【0006】
ベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイ100は、市松状に輝度信号に寄与するGのフィルタを配置し、残りの部分にR、Bのフィルタをさらに市松状に配置している。このように配置された各色のフィルタが、各画素(フォトダイオード)に対応しており、各画素にはR,G,Bいずれかの原色成分に対応した電荷が蓄積されることとなる。
【0007】
ベイヤー方式によると、各画素からは、いずれかの原色成分に対する電気信号が出力されることになるため、各画素に対しては、欠落している色の情報を補う必要がある。
【0008】
たとえば、Rのフィルタに覆われた画素では、Rの情報しか持っていないため、GとBを周辺の画素の値を基に推測する補間処理を行うのである。このようにして、1個のCCDを利用してカラー画像を撮像するようにしている。
【0009】
このように、近傍画素の情報を利用して補間処理を行うベイヤー方式においては、補間処理を行う領域内で同じ被写体が結像する必要がある。たとえば、図5に太線で示した領域110内で、画素の補間を相互に行う場合には、領域110内には同じ被写体が結像する必要がある。
【0010】
しかし、被写体のもつコントラスパターンによっては、領域110よりも狭い領域内で高周波成分を持つ場合があり、このような場合には、いわゆる偽色が発生することとなる。偽色は高周波部分で発生し、被写体の輪郭部、ライン、細かな模様などで発生し、光学LPF(low−pass filter)、補間処理等では完全に除去することができない。
【0011】
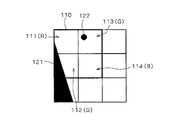
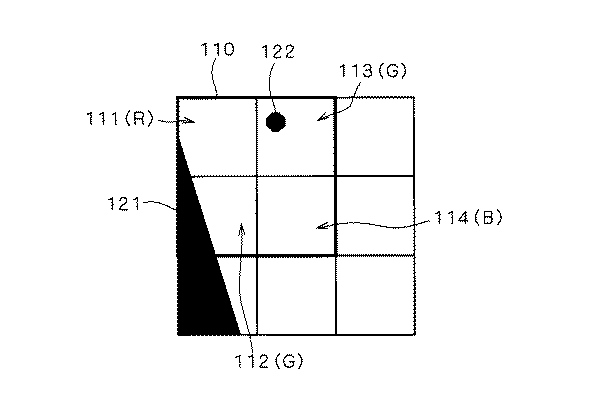
たとえば、図6に示すように、領域110内に境界121やドット122の被写体が結像している場合を想定する。この場合、領域110内の右下の画素114については、Bの情報しか持っていないため、画素111,112,113からRやGの情報を補間することとなる。このため、画素114には本来存在しない被写体についての情報で補間処理が行われることになり、偽色が発生するのである。
【0012】
そこで、偽色の発生する部分に対して彩度の抑圧を行い、発生した偽色を目立たなくする処理が行われている。
【0013】
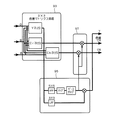
図7は、偽色の抑圧を行う処理装置の従来構成図を示す。CCDから出力されたRGBの原色成分の電気信号は、色差マトリクス回路93に入力される。色差マトリクス回路93において、RGBの原色成分をもつ色空間が、輝度成分(Y)と、色差成分(Cr,Cb)とをもつ色空間に変換される。
【0014】
変換された電気信号のうち、輝度成分Yは、輪郭強調フィルタ95に入力される。輪郭強調フィルタ95において、輝度成分Yは、HPF(high−pass filter)、アンプ、ベースクリップを経て、所定値以上の高周波成分が検出される。
【0015】
検出された高周波成分は、LPFを通過した輝度成分Yに加算される。これによって、輝度成分Yに対して輪郭強調処理が施されることとなる。
【0016】
一方、検出された高周波部分については、前述の如く、偽色が発生している確率が高い。そこで、色差抑圧回路97には輪郭強調フィルタ95において高周波成分として検出された領域(画素)の情報が入力され、当該画素の色差成分Cr,Cbに対して色差の抑圧制御が行われるのである。このようにして、ベイヤー方式の画像形成により生ずる偽色を目立たなくするようにしているのである。
【0017】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところが、上述した偽色抑圧制御では、被写体のエッジを強調する輪郭強調フィルタ95の出力から抑圧対象となる画素を決定するため、被写体の高周波成分をすべて抑圧することになる。つまり、被写体の画像パターンに関わらず、エッジ成分の強い部分はすべて抑圧されることになる。
【0018】
このため、輪郭等の線として表現される部分に対しては、偽色を有効に抑圧することができるが、ドット状のパターンに対しては、ドット状の抑圧がかかり、穴のような色抜けが発生し、見栄えの悪い描写となる。
【0019】
図6で示した例を用いると、高周波成分の検出された画素113においては、色差の抑圧制御が行われ、画素113においてドット状の色抜けが発生するのである。これに対して、境界121に対しては、境界に沿って連続的に偽色が発生するため、色差の抑圧制御を行うことが望ましい。
【0020】
そこで、本発明は前記問題点に鑑み、色抜けなどを発生させることなく、偽色成分を効果的に抑圧することを可能とした処理装置を提供することを目的とする。
【0021】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記課題を解決するため、請求項1の発明は、撮像素子から入力した画像信号に所定の画像処理を施す画像処理装置であって、前記撮像素子は、3原色成分のうち、いずれかの原色成分の画像信号をそれぞれ出力する3種の光電変換素子が、画素ごとに所定の配列規則に従って配置されたものであり、前記撮像素子から入力した各画素の画像信号に対して近傍の画素の画像信号を用いて補間処理を行い、各画素について3原色成分の画像信号を出力する補間手段と、3原色成分をもつ色空間の画像信号を、輝度成分と色差成分とをもつ色空間の画像信号に変換する色空間変換手段と、前記輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出する線分抽出手段と、前記線分抽出手段により線分成分と判別された画素については、前記色差成分の信号値を抑圧する抑圧手段とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0022】
請求項2の発明は、請求項1に記載の画像処理装置において、前記抑圧手段は、前記線分成分の検出レベルに応じて、抑圧制御の程度を変更する手段を含むことを特徴とする。
【0023】
請求項3の発明は、請求項1に記載の画像処理装置において、前記撮像素子は、ベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイを備えたCCDとしたことを特徴とする。
【0024】
請求項4の発明は、撮像素子から入力した画像信号に所定の画像処理を施す画像処理方法であって、前記撮像素子は、3原色成分のうち、いずれかの原色成分の画像信号をそれぞれ出力する3種の光電変換素子が、画素ごとに所定の配列規則に従って配置されたものであり、前記撮像素子から入力した各画素の画像信号に対して近傍の画素の画像信号を用いて補間処理を行い、各画素について3原色成分の画像信号を出力する補間工程と、3原色成分をもつ色空間の画像信号を、輝度成分と色差成分とをもつ色空間の画像信号に変換する色空間変換工程と、前記輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出する線分抽出工程と、前記線分抽出工程により線分成分と判別された画素については、前記色差成分の信号値を抑圧する抑圧工程とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0025】
請求項5の発明は、請求項4に記載の画像処理方法において、前記抑圧工程は、前記線分成分の検出レベルに応じて、抑圧制御の程度を変更する工程を含むことを特徴とする。
【0026】
請求項6の発明は、撮像素子からの出力である画像信号に所定の画像処理を施すプログラムを記録した処理装置読み取り可能な記録媒体であって、前記撮像素子は、3原色成分のうち、いずれかの原色成分の画像信号をそれぞれ出力する3種の光電変換素子が、画素ごとに所定の配列規則に従って配置されたものであり、前記プログラムは前記処理装置に、前記撮像素子の出力である各画素の画像信号に対して近傍の画素の画像信号を用いて補間処理を行い、各画素について3原色成分の画像信号を出力する補間工程と、3原色成分をもつ色空間の画像信号を、輝度成分と色差成分とをもつ色空間の画像信号に変換する色空間変換工程と、前記輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出する線分抽出工程と、前記線分抽出工程により線分成分と判別された画素については、前記色差成分の信号値を抑圧する抑圧工程とを実行させることを特徴とする。
請求項7の発明は、請求項1に記載の画像処理装置において、前記線分抽出手段は、線分抽出フィルタを用いて前記線分成分を抽出することを特徴とする。
請求項8の発明は、請求項7に記載の画像処理装置において、前記線分抽出フィルタはソーベル線分抽出フィルタであることを特徴とする。
請求項9の発明は、請求項4に記載の画像処理方法において、前記線分抽出工程では、線分抽出フィルタを用いて前記線分成分が抽出されることを特徴とする。
請求項10の発明は、請求項9に記載の画像処理方法において、前記線分抽出フィルタはソーベル線分抽出フィルタであることを特徴とする。
請求項11の発明は、請求項6に記載の記録媒体において、前記線分抽出工程では、線分抽出フィルタを用いて前記線分成分が抽出されることを特徴とする。
請求項12の発明は、請求項11に記載の記録媒体において、前記線分抽出フィルタはソーベル線分抽出フィルタであることを特徴とする。
【0027】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、図面を参照しつつ本発明の実施の形態について説明する。まず、本実施の形態にかかる画像処理装置を搭載したデジタルカメラ31の概略構成について説明する。
【0028】
{1.デジタルカメラの概略構成}
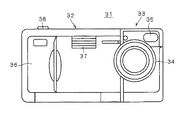
図2は、デジタルカメラ31の正面図である。デジタルカメラ31は、箱型のカメラ本体部32と直方体状の撮像部33とから構成されている。撮像部33の前面側には、撮像レンズであるズームレンズ34が設けられるとともに、光学ファインダ35が設けられている。
【0029】
カメラ本体部32の一端部はグリップ部36としており、前面側の中央上部に内蔵フラッシュ37が設けられ、上面側にはシャッタボタン38が設けられている。
【0030】
図示を省略するが、カメラ本体部32の背面側には、撮像画像のモニタ表示、記録画像の再生表示等を行うための液晶ディスプレイ(LCD)が設けられている。その他、カメラ本体部32の背面側には、電源スイッチや、各種操作ボタン等が設けられている。
【0031】
{2.画像処理装置の構成}
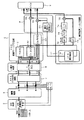
図1は、デジタルカメラ31が内部に搭載する本実施形態にかかる画像処理装置のブロック構成図である。
【0032】
<2−1 ベイヤー式CCDおよび補間処理>
CCD1はベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイを備えた単板式CCDである。CCD1には、光電変換をつかさどる多数のフォトダイオードがマトリクス状に2次元配列されて各画素に対応しており、各画素は原色成分(R,G,B)のうちいずれかの色フィルタに覆われている。
【0033】
本実施の形態では図5で示した色フィルタアレイ100と同様に、市松状に輝度信号に寄与するGのフィルタを配置し、残りの部分にR、Bのフィルタをさらに市松状に配置している。このようにして、各画素にはR,G,Bいずれかの原色成分に対応した電荷が蓄積されることとなる。
【0034】
なお、ベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイとしては、図5で示したタイプの他に、Gを上下方向に並べたタイプ等、いくつかの方式が存在するが、本実施形態の画像処理装置に適用できる色フィルタアレイのタイプは特に限定されるものではない。ただし、後述する補間処理においては、色フィルタアレイのタイプに応じた処理が行われる必要がある。
【0035】
CCD1において蓄積された電荷は、1ラインずつ順次取り出され、1次元の電気信号として出力される。さらに、各画素の電気信号は、A/D変換回路(図示せぬ)において12bitのデジタル電気信号に変換された後、WB(ホワイトバランス)回路2に入力され、RGBのレベル変換が行われることでホワイトバランスが調整される。
【0036】
ホワイトバランスの調整が行われた後、各画素の電気信号は補間回路3に入力され、各画素について補間処理が行われる。
【0037】
つまり、各画素は、R,G,Bいずれか1つの原色成分に関する情報しか持っていないため、他の原色成分の情報を周辺の画素の値を基に推測する補間処理を行うのである。この補間処理により、各画素に対して、R,G,Bそれぞれ12bitの情報が与えられることになる。
【0038】
補間処理が行われた後、各画素の電気信号(R,G,B)は、リニアマトリクス回路4において、所定の補正処理が行われた後、γ補正回路5に入力される。γ補正回路5において、電気信号(R,G,B)はγ補正テーブル(RGBガンマLUT)51によって、表示ディスプレイの再現特性に応じた補正が行われる。さらに、γ補正回路5においては、12bitの電気信号が8bitに圧縮される。
【0039】
<2−2 色空間の変換処理>
8bitに圧縮された電気信号(R,G,B)は、次に、色差マトリクス回路6に入力される。色差マトリクス回路6は、変換用のマトリクスであるYマトリクス61、Crマトリクス62、Cbマトリクス63を備えており、RGBの原色成分をもつ色空間が、輝度成分(Y)と、色差成分(Cr,Cb)とをもつ色空間に変換される。
【0040】
数1式は、Yマトリクス61、Crマトリクス62、Cbマトリクス63を、3行3列の色差マトリクスで表現したものである。従って、RGB色空間が、色差マトリクスによって、輝度成分と色差成分とをもつ色空間に変換されると表現することができる。
【0041】
【数1】
【0042】
<2−3 輪郭強調フィルタ処理>
色差マトリクス回路6において出力された輝度成分Y(以下の説明においては、適宜、輝度成分の電気信号を輝度信号Yと表現する。)は、次に、輪郭強調フィルタ回路7に入力される。輪郭強調フィルタ回路7において、輝度信号Yは3つに分岐される。分岐された輝度信号Yのうち1つは、HPF72を通過し、1つは、LPF71を通過する。他の1つは、後述するが線分抽出回路77に入力される。
【0043】
HPF72を通過した輝度信号Yからは、高周波成分が検出され、この検出された高周波成分をアンプ73に入力して増幅させた後、さらにベースクリップ74において所定値以上の高周波成分のみが検出され、出力される。
【0044】
そして、加算器75において、LPF71を通過した輝度信号Yに、ベースクリップ74から出力された所定値以上の高周波成分を加算することによって、輝度信号Yは輪郭強調されたうえで出力されるのである。
【0045】
<2−4 線分抽出処理>
輪郭強調フィルタ回路7内で分岐された輝度信号Yのうち、残る1つは線分抽出回路77に入力される。線分抽出回路77においては、ソーベル線分抽出フィルタA1〜A4を用いることによって、輝度信号Yから線分成分が抽出されるのである。ソーベル線分抽出フィルタA1〜A4を数2式に示す。
【0046】
【数2】
【0047】
数2式において、フィルタA1は、右上がりの斜線の境界を検出する空間フィルタであり、フィルタA2は、縦線の境界を検出する空間フィルタであり、フィルタA3は、右下がりの斜線の境界を検出する空間フィルタであり、フィルタA4は、横線の境界を検出する空間フィルタである。
【0048】
線分抽出回路77に入力された輝度信号Yは、バッファ(図示せず)に蓄積されており、このバッファに蓄積された輝度信号Yをもとに対象画素の線分抽出処理が行われる。たとえば、本実施の形態においては、線分抽出フィルタA1〜A4は3行3列の行列形式で表されており、対象画素の輝度信号Y、および、対象画素の8近傍の画素の輝度信号Yを使って線分抽出処理が行われることになる。したがって、バッファには少なくともこれら9画素の輝度信号Yが蓄積されている必要がある。
【0049】
そして、3行3列の9画素の輝度信号Yについて、線分抽出フィルタA1〜A4とそれぞれパターンマッチングを行う。そして、マッチングした場合には、注目画素(パターンマッチングした際に中央に位置する画素、つまり、2行2列名に相当する画素)を線分成分として判断するのである。
【0050】
具体的には、注目画素について線分抽出フィルタA1を施した場合を例にとると、注目画素および8近傍画素の輝度信号Yの値に、フィルタA1の対応する各成分を係数として乗算し、これらの演算値の合計値を得る。そして、この合計値の絶対値が所定の値よりも大きくなる場合には、注目画素はフィルタA1により線分成分として判断されることになるのである。
【0051】
そして、上記の演算値(合計値)は注目画素における線分の検出レベルを表すことになる。つまり、各線分フィルタA1〜A4のいずれか空間フィルタを用いた演算値(合計値)は、その値が大きい程、線分としての検出度合が大きいことを意味するのである。
【0052】
<2−5 線分クロマキラー処理>
線分抽出回路77が線分成分を抽出すると、線分クロマキラー回路8には、線分成分として判別された画素の位置情報と、当該画素における線分成分の検出レベルとが入力される。
【0053】
線分クロマキラー回路8では、入力した線分成分の検出レベルを基に、Cr,Cbの両色差成分に対して色差信号(以下の説明においては、適宜、色差成分の電気信号を色差信号Cr,Cbと表す。)の抑圧処理を行う。つまり、線分クロマキラー回路8においては、入力した線分成分の検出レベルをもとに、線分クロマキラー設定LUT(Lookup Table)81を参照して色差信号Cr,Cbの抑圧度を求め、乗算器82,83によって抑圧度に応じた色差信号Cr,Cbの抑圧処理を行うのである。
【0054】
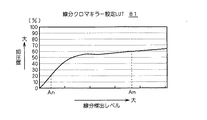
図3は、線分クロマキラーの設定LUT81を示す。図中、横軸は、線分成分の検出レベルを示し、縦軸は、抑圧度を示している。つまり、線分成分の検出レベルが高い画素程、高い抑圧をかけるような抑圧制御を行うのである。
【0055】
ただし、線分成分の検出レベルがある程度大きくなると、抑圧度の上昇率を小さくし、抑圧度が過度に大きくならないようにしている。
【0056】
たとえば、画素nにおける線分成分の検出レベルがAnである場合には、画素nにおける色差成分には20%程度の抑圧を行うのである。また、画素mにおける線分成分の検出レベルがAmである場合には、画素mにおける色差成分には60%程度の抑圧を行うのである。このように、より線分成分の検出レベルの高い画素mについては、検出レベルの低い画素nよりも大きな抑圧を行うようにしているのである。
【0057】
このように、線分成分の検出レベルに応じて、抑圧制御の程度を変更しているので、出力画像に不自然さが残らないような抑圧制御が可能となる。
【0058】
以上の処理により、本実施の形態にかかる画像処理装置は、輪郭強調処理が施された輝度信号Yと、抑圧制御が行われた色差信号Cr,Cbが出力されることになる。出力された輝度信号Y、色差信号Cr,Cbはバッファ9に記録された後、たとえば、JPEG等の圧縮規格に従った処理が行われ、画像ファイルとしてメモリカード等に保存されるのである。
【0059】
このように、本実施形態においては、線分成分として抽出された画素に対してのみ、抑圧制御を行うようにしているので、全てのエッジ成分に対して抑圧制御を行うことによる問題を解消することができる。
【0060】
従来は、全てのエッジ成分を抑圧していたため、発生した偽色の抑圧には効果が得られるが、その一方で、細かなエッジに対しても色の抑圧がかかり不自然なドット状の色抜けが発生してしまうという問題があった。本実施形態によれば、線分のみに色の抑圧がかけられるため細かな色抜けが無く自然な描写が得られるのである。
【0061】
図6で示した被写体を例とすれば、境界121に対しては、偽色の抑圧を行なわれる。従って、境界に沿って広い領域で発生する偽色が抑えられ、違和感のある偽色を効果的に抑圧することができる。これに対して、ドット122には偽色の抑圧が行われない。従って、ドット状のパターンに対して穴のような色抜けが発生することはない。
【0062】
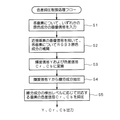
図4は、以上説明した色差抑圧制御処理のフローチャートである。色差抑圧制御処理は、図に示すように大きく5つの工程から成り立っている。まず、第1の工程は、CCD1から出力されたRGBの画像信号を入力する工程である(ステップS1)。この画像信号は、各画素におけるRGB原色成分のうち、いずれか1つの原色成分の画像信号である。
【0063】
第2の工程は、入力した画素について、近傍の画素を用いて補間処理を行う工程である。この工程により、各画素においてそれぞれ3原色成分の画像信号が得られることになる(ステップS2)。
【0064】
第3の工程は、RGB3原色成分の画像信号を、輝度信号Yおよび色差信号Cr,Cbに変換する工程である(ステップS3)。
【0065】
第4の工程は、ステップS3で得られた輝度信号Yをもとに、ソーベルの線分抽出フィルタを用いて線分抽出を行う工程である(ステップS4)。この線分抽出工程においては、注目画素についての線分検出レベルも出力される。
【0066】
そして、第5の工程は、線分成分と検出された画素に対して、線分検出レベルに応じた色差信号の抑圧を行う工程である(ステップS5)。
【0067】
以上説明した本実施の形態にかかる画像処理装置は、デジタルカメラ、デジタルビデオなど、ベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイを備えたCCDから画像信号を入力するあらゆる機器に適応可能である。
【0068】
また、デジタルカメラによっては、線画を複写する動作モード(文字モードなどと呼ばれている)を備えたものがある。文字モードは、線画をはっきりと撮像することを目的としたモードであり、文字モード設定状態で、ホワイトボードに描写された文字等を撮影することで、議事の記録を残すことができるなどの効果がある。
【0069】
従って、文字モードを備えたデジタルカメラにおいて、本実施の形態にかかる画像処理装置を搭載し、文字モード動作時に、上述した色差成分の抑圧制御を行うようにすれば、本発明の効果が顕著に現れることとなる。
【0070】
{3.変形例}
上述した実施の形態においては、線分成分として抽出された領域(画素)のみ色差成分の抑圧制御を行うこととした。これは、ドット状の色抜けなど不自然な画像の仕上がりを回避するためであった。つまり、ドット状の偽色に対しては、抑圧制御を行って色抜けを発生させるよりも、抑圧制御を行わずに微小な偽色として残す方が、不自然さを小さく抑えることができるからである。
【0071】
そこで、本発明の変形例として次のような構成が考えられる。色差成分の抑圧制御回路は、全ての輪郭部(エッジ部)に対して抑圧処理を行うものとする。ただし、線分成分の抑圧量に比して、他の輪郭部に対しては、その抑圧量を小さくするような抑圧制御するのである。
【0072】
たとえば、ドット状の高周波成分に対しては、色抜けが発生しない程度の色差成分の抑圧を行うのである。このような処理を行うことにより、線分成分以外の輪郭部には自然な色再現処理を行い、線分成分に対しては、偽色の発生を抑えることが可能となるのである。
【0073】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、請求項1、7及び8の発明では、色補間処理が行われた画像信号に対する画像処理であって、輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出し、線分成分が抽出された画素についてのみ、色差成分の信号値を抑圧するので、不自然な色抜け等を発生させることなく、線分成分の偽色の発生を抑えることが可能である。
【0074】
請求項2の発明では、線分成分の検出レベルに応じた抑圧制御を行うので、出力画像の不自然さを低減させることが可能となる。
【0075】
請求項3の発明では、ベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイを備えたCCDを撮像素子とする構成であり、本発明をデジタルカメラ等、広く適用可能となる。
【0076】
請求項4、9及び10の発明は、輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出し、線分成分が抽出された画素についてのみ、色差成分の信号値を抑圧する方法であり、不自然な色抜け等を発生させることなく、線分成分の偽色の発生を抑えることが可能な方法である。
【0077】
請求項5の発明では、線分成分の検出レベルに応じた抑圧制御を行うので、出力画像の不自然さを低減させることが可能となる。
【0078】
請求項6、11及び12の発明では、線分成分の偽色の発生を抑えるプログラムを記録媒体に記録することにより、上記プログラムを記録媒体読み取り可能なコンピュータにおいて実行可能となる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本実施形態にかかる画像処理装置のブロック構成図である。
【図2】本実施形態にかかる画像処理装置を搭載したデジタルカメラの概観図である。
【図3】線分クロマキラーの設定LUTを示す図である。
【図4】本実施形態にかかる画像処理のフローチャートである。
【図5】ベイヤー方式CCDにおける色フィルタアレイの一例を示す図である。
【図6】高周波成分をもつ被写体の光学像がベイヤー方式のCCDに結像した状態を示す図である。
【図7】従来の画像処理装置のブロック図である。
【符号の説明】
1 CCD
3 補間回路
6 色差マトリクス回路
7 輪郭強調フィルタ回路
8 線分クロマキラー回路
77 線分抽出回路
78 ソーベル線分抽出フィルタ
81 線分クロマキラー設定LUT[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a configuration of an image processing apparatus used in a digital camera or the like and an image processing method.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In a digital camera, a digital video camera, and the like, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) has been conventionally used as an image capturing device. A CCD is configured by arranging a large number of photodiodes that control photoelectric conversion in a matrix.
[0003]
An optical image of a subject incident on the CCD through an optical system including an imaging lens is photoelectrically converted by a photodiode and then accumulated. The charges accumulated in the photodiodes arranged in a matrix are sequentially taken out from the CCD and then transferred to the image processing circuit to be detected as an image signal.
[0004]
In this way, the CCD plays a role of accumulating charges according to the contrast of the optical image and outputting it as an electrical signal. In order to obtain a color image, it corresponds to the three primary color components (R, G, B). An electrical signal needs to be obtained.
[0005]
A Bayer
[0006]
In the Bayer
[0007]
According to the Bayer method, each pixel outputs an electrical signal for one of the primary color components, and therefore it is necessary to compensate for the missing color information for each pixel.
[0008]
For example, since the pixel covered with the R filter has only R information, interpolation processing for estimating G and B based on the values of the surrounding pixels is performed. In this way, a color image is picked up using one CCD.
[0009]
As described above, in the Bayer method in which interpolation processing is performed using information on neighboring pixels, it is necessary to form an image on the same subject within the region in which interpolation processing is performed. For example, in the case where the pixels are mutually interpolated in the
[0010]
However, depending on the contrast pattern of the subject, there may be a case where a high frequency component is present in a region narrower than the
[0011]
For example, as illustrated in FIG. 6, a case is assumed in which a subject having a
[0012]
In view of this, the saturation is suppressed for the portion where the false color is generated, and the generated false color is made inconspicuous.
[0013]
FIG. 7 shows a conventional block diagram of a processing apparatus that suppresses false colors. The RGB primary color component electrical signals output from the CCD are input to the color
[0014]
Of the converted electrical signal, the luminance component Y is input to the
[0015]
The detected high frequency component is added to the luminance component Y that has passed through the LPF. As a result, the edge enhancement process is performed on the luminance component Y.
[0016]
On the other hand, the detected high frequency portion has a high probability that a false color is generated as described above. Therefore, the color
[0017]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the false color suppression control described above, since the pixel to be suppressed is determined from the output of the
[0018]
For this reason, false colors can be effectively suppressed for portions expressed as lines such as contours, but dot-like suppression is applied to dot-like patterns, and colors such as holes Omissions occur and the picture looks bad.
[0019]
Using the example shown in FIG. 6, color difference suppression control is performed in the
[0020]
In view of the above problems, an object of the present invention is to provide a processing apparatus that can effectively suppress false color components without causing color loss.
[0021]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to solve the above-described problem, the invention of
[0022]
According to a second aspect of the present invention, in the image processing apparatus according to the first aspect, the suppression means includes means for changing a degree of suppression control in accordance with a detection level of the line segment component.
[0023]
According to a third aspect of the present invention, in the image processing apparatus according to the first aspect, the image pickup device is a CCD having a Bayer color filter array.
[0024]
According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, there is provided an image processing method for performing predetermined image processing on an image signal input from an image pickup device, wherein the image pickup device outputs an image signal of any one of the three primary color components. The three types of photoelectric conversion elements are arranged according to a predetermined arrangement rule for each pixel, and interpolation processing is performed using image signals of neighboring pixels with respect to image signals of pixels input from the imaging element. And an interpolation step for outputting an image signal of three primary color components for each pixel, and a color space conversion step of converting an image signal of a color space having the three primary color components into an image signal of a color space having a luminance component and a color difference component A line segment extraction step for extracting a line segment component from the signal value of the luminance component, and a suppression step for suppressing the signal value of the color difference component for the pixel determined as the line segment component by the line segment extraction step; Equipped with The features.
[0025]
According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, in the image processing method according to the fourth aspect, the suppression step includes a step of changing a degree of suppression control according to a detection level of the line segment component.
[0026]
The invention according to claim 6 is a processing apparatus-readable recording medium that records a program for performing predetermined image processing on an image signal that is output from the image sensor, and the image sensor is one of the three primary color components. The three types of photoelectric conversion elements that respectively output image signals of the primary color components are arranged in accordance with a predetermined arrangement rule for each pixel, and the program outputs the output of the imaging element to the processing device. Interpolation processing is performed on the image signal of the pixel using the image signal of the neighboring pixel, and the image signal of the three primary color components is output for each pixel, and the image signal of the color space having the three primary color components is converted into luminance. A color space conversion step for converting into an image signal in a color space having a component and a color difference component, a line segment extraction step for extracting a line segment component from the signal value of the luminance component, and a line segment component by the line segment extraction step. Size For the pixels which are characterized in that to execute a suppression step of suppressing the signal value of the color difference component.
A seventh aspect of the present invention is the image processing apparatus according to the first aspect, wherein the line segment extraction unit extracts the line segment component using a line segment extraction filter.
According to an eighth aspect of the present invention, in the image processing apparatus according to the seventh aspect, the line segment extraction filter is a Sobel line segment extraction filter.
The invention according to claim 9 is the image processing method according to
According to a tenth aspect of the present invention, in the image processing method according to the ninth aspect, the line segment extraction filter is a Sobel line segment extraction filter.
According to an eleventh aspect of the present invention, in the recording medium according to the sixth aspect, in the line segment extraction step, the line segment component is extracted using a line segment extraction filter.
According to a twelfth aspect of the present invention, in the recording medium according to the eleventh aspect, the line segment extraction filter is a Sobel line segment extraction filter.
[0027]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. First, a schematic configuration of the
[0028]
{1. Schematic configuration of digital camera}
FIG. 2 is a front view of the
[0029]
One end of the
[0030]
Although not shown, a liquid crystal display (LCD) for performing monitor display of a captured image, reproduction display of a recorded image, and the like is provided on the back side of the
[0031]
{2. Configuration of image processing apparatus}
FIG. 1 is a block configuration diagram of an image processing apparatus according to the present embodiment that is mounted inside a
[0032]
<2-1 Bayer CCD and interpolation processing>
The
[0033]
In the present embodiment, like the
[0034]
In addition to the type shown in FIG. 5, there are several types of Bayer-type color filter arrays, such as a type in which G is arranged in the vertical direction, but it can be applied to the image processing apparatus of this embodiment. The type of the color filter array is not particularly limited. However, in the interpolation processing described later, it is necessary to perform processing according to the type of the color filter array.
[0035]
The charges accumulated in the
[0036]
After the white balance is adjusted, the electric signal of each pixel is input to the
[0037]
That is, since each pixel has only information on one of the primary color components of R, G, and B, an interpolation process for estimating information on other primary color components based on the values of surrounding pixels is performed. By this interpolation processing, 12-bit information for each of R, G, and B is given to each pixel.
[0038]
After the interpolation processing is performed, the electrical signals (R, G, B) of each pixel are input to the
[0039]
<2-2 Color space conversion processing>
The electrical signals (R, G, B) compressed to 8 bits are then input to the color difference matrix circuit 6. The color difference matrix circuit 6 includes a
[0040]
[0041]
[Expression 1]
[0042]
<2-3 Outline enhancement filter processing>
The luminance component Y output in the color difference matrix circuit 6 (in the following description, the electric signal of the luminance component is appropriately expressed as the luminance signal Y) is then input to the contour enhancement filter circuit 7. In the edge enhancement filter circuit 7, the luminance signal Y is branched into three. One of the branched luminance signals Y passes through the
[0043]
A high-frequency component is detected from the luminance signal Y that has passed through the
[0044]
Then, the
[0045]
<2-4 Line segment extraction processing>
The remaining one of the luminance signals Y branched in the contour enhancement filter circuit 7 is input to the line segment extraction circuit 77. In the line segment extraction circuit 77, line segment components are extracted from the luminance signal Y by using the Sobel line segment extraction filters A1 to A4. The Sobel line segment extraction filters A1 to A4 are shown in
[0046]
[Expression 2]
[0047]
In
[0048]
The luminance signal Y input to the line segment extraction circuit 77 is stored in a buffer (not shown), and line segment extraction processing of the target pixel is performed based on the luminance signal Y stored in the buffer. For example, in the present embodiment, the line segment extraction filters A1 to A4 are represented in a 3 × 3 matrix format, and the luminance signal Y of the target pixel and the luminance signal Y of the pixels in the vicinity of the target pixel are eight. Line segment extraction processing is performed using. Therefore, it is necessary that the luminance signal Y of at least these nine pixels is accumulated in the buffer.
[0049]
Then, pattern matching is performed with the line segment extraction filters A1 to A4 for the luminance signal Y of 9 pixels in 3 rows and 3 columns. In the case of matching, the target pixel (the pixel located at the center when pattern matching is performed, that is, the pixel corresponding to the name of 2 rows and 2 columns) is determined as a line segment component.
[0050]
Specifically, taking the case where the line segment extraction filter A1 is applied to the target pixel as an example, the value of the luminance signal Y of the target pixel and eight neighboring pixels is multiplied by the corresponding component of the filter A1 as a coefficient, The total value of these calculated values is obtained. When the absolute value of the total value is larger than a predetermined value, the target pixel is determined as a line segment component by the filter A1.
[0051]
The above calculated value (total value) represents the detection level of the line segment in the target pixel. That is, the calculated value (total value) using any one of the line segment filters A1 to A4 means that the greater the value, the greater the degree of detection as a line segment.
[0052]
<2-5 line segment chroma killer processing>
When the line segment extraction circuit 77 extracts the line segment component, the position information of the pixel determined as the line segment component and the detection level of the line segment component in the pixel are input to the line segment chroma killer circuit 8.
[0053]
In the line segment chroma killer circuit 8, based on the detection level of the input line segment component, the color difference signal (in the following description, the electrical signal of the color difference component is appropriately converted to the color difference signal Cr, Cb)) is performed. In other words, the line chroma killer circuit 8 obtains the degree of suppression of the color difference signals Cr and Cb by referring to the line chroma killer setting LUT (Lookup Table) 81 based on the input detection level of the line segment component, and a multiplier. The color difference signals Cr and Cb corresponding to the degree of suppression are performed by 82 and 83, respectively.
[0054]
FIG. 3 shows a line segment chroma
[0055]
However, when the detection level of the line segment component increases to some extent, the rate of increase of the suppression degree is reduced so that the suppression degree does not become excessively large.
[0056]
For example, when the detection level of the line segment component in the pixel n is An, the color difference component in the pixel n is suppressed by about 20%. Further, when the detection level of the line segment component in the pixel m is Am, the color difference component in the pixel m is suppressed by about 60%. In this way, the pixel m having a higher detection level of the line segment component is subjected to greater suppression than the pixel n having a lower detection level.
[0057]
In this way, since the degree of suppression control is changed according to the detection level of the line segment component, it is possible to perform suppression control that does not leave unnaturalness in the output image.
[0058]
Through the above processing, the image processing apparatus according to the present embodiment outputs the luminance signal Y subjected to the contour enhancement processing and the color difference signals Cr and Cb subjected to the suppression control. The output luminance signal Y and color difference signals Cr and Cb are recorded in the buffer 9 and then processed according to a compression standard such as JPEG, and stored as an image file in a memory card or the like.
[0059]
As described above, in this embodiment, since suppression control is performed only on pixels extracted as line segment components, the problem caused by performing suppression control on all edge components is solved. be able to.
[0060]
In the past, all edge components were suppressed, so it was effective to suppress the generated false color. On the other hand, color suppression was also applied to fine edges, resulting in an unnatural dot-like color. There was a problem that omissions occurred. According to this embodiment, since color suppression is applied only to the line segment, there is no fine color loss and a natural depiction can be obtained.
[0061]
Taking the subject shown in FIG. 6 as an example, false color suppression is performed on the
[0062]
FIG. 4 is a flowchart of the color difference suppression control process described above. The color difference suppression control process mainly includes five steps as shown in the figure. First, the first step is a step of inputting RGB image signals output from the CCD 1 (step S1). This image signal is an image signal of any one primary color component among the RGB primary color components in each pixel.
[0063]
The second step is a step of performing interpolation processing on the input pixel using neighboring pixels. With this process, an image signal of three primary color components is obtained in each pixel (step S2).
[0064]
The third step is a step of converting the RGB three primary color component image signals into luminance signal Y and color difference signals Cr and Cb (step S3).
[0065]
The fourth step is a step of performing line segment extraction using a Sobel line segment extraction filter based on the luminance signal Y obtained in step S3 (step S4). In this line segment extraction step, the line segment detection level for the target pixel is also output.
[0066]
And a 5th process is a process of suppressing the color difference signal according to a line segment detection level with respect to the pixel detected as a line segment component (step S5).
[0067]
The image processing apparatus according to the present embodiment described above can be applied to any device that inputs an image signal from a CCD having a Bayer color filter array, such as a digital camera or digital video.
[0068]
Some digital cameras have an operation mode (referred to as a character mode) for copying a line drawing. Character mode is a mode that aims to capture line drawings clearly. Effects such as recording the proceedings by shooting characters drawn on the whiteboard in the character mode setting state. There is.
[0069]
Therefore, if the image processing apparatus according to the present embodiment is installed in a digital camera equipped with a character mode and the above-described color difference component suppression control is performed during the character mode operation, the effect of the present invention becomes remarkable. Will appear.
[0070]
{3. Modification}
In the embodiment described above, suppression control of the color difference component is performed only for the region (pixel) extracted as the line segment component. This is to avoid unnatural image finish such as dot-like color loss. In other words, for dot-like false colors, it is possible to reduce the unnaturalness by leaving a fine false color without performing suppression control, rather than performing color loss by performing suppression control. It is.
[0071]
Therefore, the following configuration can be considered as a modification of the present invention. It is assumed that the color difference component suppression control circuit performs suppression processing on all contour portions (edge portions). However, the suppression control is performed so as to reduce the amount of suppression for the other contour portions as compared with the amount of suppression of the line segment component.
[0072]
For example, with respect to dot-like high-frequency components, the color difference components are suppressed to such an extent that no color loss occurs. By performing such processing, it is possible to perform natural color reproduction processing on the contour portion other than the line segment component, and to suppress the generation of false colors for the line segment component.
[0073]
【The invention's effect】
As explained above,
[0074]
According to the second aspect of the present invention, since suppression control is performed in accordance with the detection level of the line segment component, it is possible to reduce the unnaturalness of the output image.
[0075]
According to the invention of
[0076]
[0077]
In the invention of
[0078]
Claim 6, 11 and 12In this invention, by recording a program that suppresses the generation of false color of line segment components on a recording medium, the program can be executed on a computer that can read the recording medium.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram of an image processing apparatus according to an embodiment.
FIG. 2 is an overview of a digital camera equipped with the image processing apparatus according to the present embodiment.
FIG. 3 is a diagram showing a line segment chroma killer setting LUT;
FIG. 4 is a flowchart of image processing according to the present embodiment.
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of a color filter array in a Bayer CCD.
FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating a state in which an optical image of a subject having a high frequency component is formed on a Bayer type CCD.
FIG. 7 is a block diagram of a conventional image processing apparatus.
[Explanation of symbols]
1 CCD
3 Interpolation circuit
6 Color difference matrix circuit
7 Outline enhancement filter circuit
8-segment chroma killer circuit
77 Line segment extraction circuit
78 Sobel line extraction filter
81 line segment chroma killer setting LUT
Claims (12)
前記撮像素子は、3原色成分のうち、いずれかの原色成分の画像信号をそれぞれ出力する3種の光電変換素子が、画素ごとに所定の配列規則に従って配置されたものであり、
前記撮像素子から入力した各画素の画像信号に対して近傍の画素の画像信号を用いて補間処理を行い、各画素について3原色成分の画像信号を出力する補間手段と、
3原色成分をもつ色空間の画像信号を、輝度成分と色差成分とをもつ色空間の画像信号に変換する色空間変換手段と、
前記輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出する線分抽出手段と、
前記線分抽出手段により線分成分と判別された画素については、前記色差成分の信号値を抑圧する抑圧手段と、
を備えることを特徴とする画像処理装置。An image processing apparatus that performs predetermined image processing on an image signal input from an image sensor,
The image sensor is one in which three types of photoelectric conversion elements that respectively output image signals of any one of the three primary color components are arranged according to a predetermined arrangement rule for each pixel,
Interpolation means for performing an interpolation process on an image signal of each pixel input from the image sensor using an image signal of a neighboring pixel, and outputting an image signal of three primary color components for each pixel;
Color space conversion means for converting an image signal in a color space having three primary color components into an image signal in a color space having a luminance component and a color difference component;
Line segment extraction means for extracting a line segment component from the signal value of the luminance component;
For pixels determined as line segment components by the line segment extraction means, suppression means for suppressing the signal value of the color difference component;
An image processing apparatus comprising:
前記抑圧手段は、
前記線分成分の検出レベルに応じて、抑圧制御の程度を変更する手段、
を含むことを特徴とする画像処理装置。The image processing apparatus according to claim 1.
The suppression means includes
Means for changing the degree of suppression control according to the detection level of the line segment component;
An image processing apparatus comprising:
前記撮像素子は、ベイヤー方式の色フィルタアレイを備えたCCDとしたことを特徴とする画像処理装置。The image processing apparatus according to claim 1.
An image processing apparatus, wherein the image pickup device is a CCD having a Bayer color filter array.
前記撮像素子は、3原色成分のうち、いずれかの原色成分の画像信号をそれぞれ出力する3種の光電変換素子が、画素ごとに所定の配列規則に従って配置されたものであり、
前記撮像素子から入力した各画素の画像信号に対して近傍の画素の画像信号を用いて補間処理を行い、各画素について3原色成分の画像信号を出力する補間工程と、
3原色成分をもつ色空間の画像信号を、輝度成分と色差成分とをもつ色空間の画像信号に変換する色空間変換工程と、
前記輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出する線分抽出工程と、
前記線分抽出工程により線分成分と判別された画素については、前記色差成分の信号値を抑圧する抑圧工程と、
を備えることを特徴とする画像処理方法。An image processing method for performing predetermined image processing on an image signal input from an image sensor,
The image sensor is one in which three types of photoelectric conversion elements that respectively output image signals of any one of the three primary color components are arranged according to a predetermined arrangement rule for each pixel,
An interpolation process for performing an interpolation process on an image signal of each pixel input from the image sensor using an image signal of a neighboring pixel, and outputting an image signal of three primary color components for each pixel;
A color space conversion step of converting an image signal of a color space having three primary color components into an image signal of a color space having a luminance component and a color difference component;
A line segment extraction step of extracting a line segment component from the signal value of the luminance component;
For a pixel determined as a line segment component by the line segment extraction step, a suppression step of suppressing the signal value of the color difference component;
An image processing method comprising:
前記抑圧工程は、
前記線分成分の検出レベルに応じて、抑圧制御の程度を変更する工程、
を含むことを特徴とする画像処理方法。The image processing method according to claim 4,
The suppression step includes
Changing the degree of suppression control according to the detection level of the line segment component;
An image processing method comprising:
前記撮像素子は、3原色成分のうち、いずれかの原色成分の画像信号をそれぞれ出力する3種の光電変換素子が、画素ごとに所定の配列規則に従って配置されたものであり、
前記プログラムは前記処理装置に、
前記撮像素子の出力である各画素の画像信号に対して近傍の画素の画像信号を用いて補間処理を行い、各画素について3原色成分の画像信号を出力する補間工程と、
3原色成分をもつ色空間の画像信号を、輝度成分と色差成分とをもつ色空間の画像信号に変換する色空間変換工程と、
前記輝度成分の信号値から線分成分を抽出する線分抽出工程と、
前記線分抽出工程により線分成分と判別された画素については、前記色差成分の信号値を抑圧する抑圧工程と、
を実行させることを特徴とする記録媒体。A processing apparatus-readable recording medium that records a program for performing predetermined image processing on an image signal that is an output from an image sensor,
The image sensor is one in which three types of photoelectric conversion elements that respectively output image signals of any one of the three primary color components are arranged according to a predetermined arrangement rule for each pixel,
The program is stored in the processor.
An interpolation process for performing an interpolation process on an image signal of each pixel, which is an output of the image sensor, using an image signal of a neighboring pixel, and outputting an image signal of three primary color components for each pixel;
A color space conversion step of converting an image signal of a color space having three primary color components into an image signal of a color space having a luminance component and a color difference component;
A line segment extraction step of extracting a line segment component from the signal value of the luminance component;
For a pixel determined as a line segment component by the line segment extraction step, a suppression step of suppressing the signal value of the color difference component;
The recording medium characterized by performing this.
前記線分抽出手段は、線分抽出フィルタを用いて前記線分成分を抽出することを特徴とする画像処理装置。The image processing apparatus, wherein the line segment extraction unit extracts the line segment component using a line segment extraction filter.
前記線分抽出フィルタはソーベル線分抽出フィルタであることを特徴とする画像処理装置。The image processing apparatus, wherein the line segment extraction filter is a Sobel line segment extraction filter.
前記線分抽出工程では、線分抽出フィルタを用いて前記線分成分が抽出されることを特徴とする画像処理方法。In the line segment extraction step, the line segment component is extracted using a line segment extraction filter.
前記線分抽出フィルタはソーベル線分抽出フィルタであることを特徴とする画像処理方法。An image processing method, wherein the line segment extraction filter is a Sobel line segment extraction filter.
前記線分抽出工程では、線分抽出フィルタを用いて前記線分成分が抽出されることを特徴とする記録媒体。In the line segment extraction step, the line segment component is extracted using a line segment extraction filter.
前記線分抽出フィルタはソーベル線分抽出フィルタであることを特徴とする記録媒体。The recording medium, wherein the line segment extraction filter is a Sobel line segment extraction filter.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001002373A JP3617455B2 (en) | 2001-01-10 | 2001-01-10 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001002373A JP3617455B2 (en) | 2001-01-10 | 2001-01-10 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002209224A JP2002209224A (en) | 2002-07-26 |
| JP3617455B2 true JP3617455B2 (en) | 2005-02-02 |
Family
ID=18870893
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001002373A Expired - Fee Related JP3617455B2 (en) | 2001-01-10 | 2001-01-10 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3617455B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004241991A (en) | 2003-02-05 | 2004-08-26 | Minolta Co Ltd | Imaging apparatus, image processor, and image processing program |
| JP4770154B2 (en) * | 2004-11-08 | 2011-09-14 | ソニー株式会社 | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer program |
| KR100647402B1 (en) | 2005-11-01 | 2006-11-23 | 매그나칩 반도체 유한회사 | Image quality improvement device and method of image sensor |
| DE102005058415A1 (en) * | 2005-12-07 | 2007-06-14 | Olympus Soft Imaging Solutions Gmbh | Method for color correction calculation |
-
2001
- 2001-01-10 JP JP2001002373A patent/JP3617455B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2002209224A (en) | 2002-07-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5108172B2 (en) | Image data size conversion processing apparatus, electronic still camera, and image data size conversion processing recording medium | |
| JP5045421B2 (en) | Imaging apparatus, color noise reduction method, and color noise reduction program | |
| CN101322416B (en) | Image signal processing device and image signal processing method | |
| JP3510037B2 (en) | Adaptive color interpolation single-sensor color electronic camera | |
| US7065246B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus | |
| CN102256140A (en) | Image processing device, image processing method, and imaging device | |
| US8189066B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer-readable medium | |
| JP5268321B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program | |
| JP4182566B2 (en) | Digital camera and computer-readable recording medium | |
| JP3633561B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP4941219B2 (en) | Noise suppression device, noise suppression method, noise suppression program, and imaging device | |
| JP5291788B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP2009044676A (en) | Image processor, image processing method, and program | |
| JP3617455B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and recording medium | |
| JP5948167B2 (en) | Imaging device | |
| JP3863808B2 (en) | Outline enhancement circuit | |
| JP3543766B2 (en) | Image processing device | |
| US20110142331A1 (en) | System and method of color interpolation | |
| JP3660504B2 (en) | Color solid-state imaging device | |
| JP4687454B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and imaging apparatus | |
| JP4478981B2 (en) | Color noise reduction method and color imaging apparatus | |
| JP3974988B2 (en) | Image restoration device | |
| JP4687750B2 (en) | Digital camera and image signal processing storage medium | |
| JP2012227869A (en) | Image processing device, image processing method and digital camera | |
| JP2000253411A (en) | Imaging device and image processing method in the imaging device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20041019 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20041101 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20071119 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081119 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20081119 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091119 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20091119 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101119 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111119 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121119 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121119 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131119 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |