JP2023078703A - game machine - Google Patents
game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2023078703A JP2023078703A JP2021191957A JP2021191957A JP2023078703A JP 2023078703 A JP2023078703 A JP 2023078703A JP 2021191957 A JP2021191957 A JP 2021191957A JP 2021191957 A JP2021191957 A JP 2021191957A JP 2023078703 A JP2023078703 A JP 2023078703A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- game
- time
- pattern
- low
- state
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 abstract description 77
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 387
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 180
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 180
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 130
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 96
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 95
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 77
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 73
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 72
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 62
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 61
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 54
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 44
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 37
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 31
- 241000722921 Tulipa gesneriana Species 0.000 description 27
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 19
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 15
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 11
- 238000005034 decoration Methods 0.000 description 9
- 102220486681 Putative uncharacterized protein PRO1854_S10A_mutation Human genes 0.000 description 7
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000004397 blinking Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 238000012938 design process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003340 mental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008450 motivation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005236 sound signal Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000002784 stomach Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Abstract
Description
本発明は、特別遊技を実行するか否かを判定し、その判定結果に基づく演出を実行する遊技機に関する。 TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a gaming machine that determines whether or not to execute a special game, and executes an effect based on the determination result.
従来の遊技機では、始動口に遊技球が入賞して特別遊技を実行するか否かが判定されると、特別図柄表示器において、特別図柄が変動表示された後に判定結果を示す態様の特別図柄が停止表示される。特許文献1に記載の遊技機では、所定の画像表示装置において、特別図柄の変動表示の開始に伴って装飾図柄が変動表示され、特別図柄が停止表示されるのに伴って、判定結果を示す態様で装飾図柄が停止表示される。
In the conventional gaming machine, when it is determined whether or not a game ball is won in the starting hole and a special game is to be executed, the special symbol display device displays the determination result after the special symbol is variably displayed. The pattern is stopped and displayed. In the gaming machine described in
ところで、従来の遊技機では、遊技の興趣性を向上させるという点においては改善の余地があった。 By the way, conventional gaming machines have room for improvement in terms of enhancing the interest of games.
それ故に、本発明の目的は、遊技の興趣性を向上させることが可能な遊技機を提供することである。 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine capable of enhancing the interest of a game.
本発明は、上記の課題を解決するために以下の構成を採用した。
本発明に係る遊技機は、遊技球が入賞容易な開放状態と遊技球が入賞し難い閉鎖状態とに変化可能な入賞領域を備え、前記入賞領域に遊技球が入賞すると特別遊技を実行するか否かを判定する遊技機であって、第1遊技状態と、前記第1遊技状態よりも前記入賞領域に遊技球が入賞し易い第2遊技状態と、前記第2遊技状態よりも前記入賞領域に遊技球が入賞し易い第3遊技状態と、を含む複数の遊技状態のうちのいずれかの遊技状態に制御する遊技状態制御手段を備え、前記第2遊技状態のときに所定条件が成立すると、所定確率で前記第2遊技状態から前記第3遊技状態に移行し、前記第1遊技状態のときに所定条件が成立すると、前記所定確率よりも高確率で前記第1遊技状態から前記第3遊技状態に移行する。
The present invention employs the following configurations in order to solve the above problems.
The gaming machine according to the present invention includes a winning area that can be changed between an open state in which game balls can easily win and a closed state in which game balls cannot easily win, and whether a special game is executed when a game ball wins in the winning area. A gaming machine for determining whether or not a first game state, a second game state in which a game ball is more likely to enter the winning area than in the first gaming state, and the winning area rather than in the second gaming state and a third game state in which the game ball is likely to win a prize, and a game state control means for controlling the game state to any one of a plurality of game states including a third game state in which the game ball is likely to win, and when a predetermined condition is established in the second game state. , the second game state is shifted to the third game state with a predetermined probability, and when a predetermined condition is established in the first game state, the first game state is changed to the third game state with a higher probability than the predetermined probability. Move to game state.
この発明によれば、遊技性の興趣性を向上させることが可能である。 According to this invention, it is possible to improve the interest of the game.
以下、適宜図面を参照しつつ、本発明の一実施形態に係る遊技機1について説明する。
Hereinafter, a
[遊技機1の概略構成例]
まず、図1~図4を参照しつつ、遊技機1の概略構成について説明する。図1は、遊技機1の概略正面図である。図1に例示されるように、遊技機1は、入賞や判定に関する役物等が設けられた遊技盤2と、遊技盤2を支持固定する枠部材3とを備えている。枠部材3は、遊技盤2と所定の間隔を隔てて平行配置された透明なガラス板を支持しており、このガラス板と遊技盤2とによって、遊技球が流下可能な遊技領域10が形成されている。
[Example of schematic configuration of gaming machine 1]
First, the schematic configuration of the
遊技者がハンドル20を握ってレバー21を時計回りに回転させると、上皿28に溜められた遊技球が発射装置(不図示)へと案内され、ハンドル20の回転角度に応じた打球力で遊技領域10へと発射される。この遊技領域10には、不図示の遊技クギや風車等が設けられており、発射された遊技球は、遊技領域10における上部位置へと案内され、遊技クギや風車等に接触することでその移動方向を変化させながら遊技盤2に沿って落下する。なお、遊技球の発射は、遊技者が停止ボタン22を操作することによって一時的に停止される。
When the player grips the
上皿28は、発射装置へ供給される遊技球及び賞球を溜めるものである。この上皿28の下方には、賞球を溜める下皿29が設けられている。この下皿29と近接配置された取り出しボタン23を遊技者が操作すると、下皿29の下面の一部が開口されて、下皿29に溜まった遊技球が下皿29の下方に配置された不図示の箱に落下する。
The
遊技者がハンドル20を小さい回転角で回転させた状態を維持するいわゆる「左打ち」を行うと、遊技球が相対的に弱い打球力で打ち出される。この場合、遊技球は、矢印31に例示されるように遊技領域10における左側領域を流下する。一方、遊技者がハンドル20を大きい回転角で回転させた状態を維持するいわゆる「右打ち」を行うと、遊技球が相対的に強い打球力で打ち出される。この場合、遊技球は、矢印32に例示されるように遊技領域10における右側領域を流下する。
When the player performs so-called "left-handed hitting", in which the player rotates the
左打ちされた遊技球の通過経路には、入賞や判定に関する役物として、第1始動口11、3つの一般入賞口14が設けられている。また、右打ちされた遊技球の通過経路には、入賞や判定に関する役物として、第2始動口12、大入賞口13、一般入賞口14、ゲート16、電動チューリップ17、及び小入賞口19が設けられている。遊技者が左打ちを行った場合、基本的には第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞することはなく、遊技者が右打ちを行った場合、基本的には第1始動口11に遊技球が入賞することはない。
A first starting port 11 and three general winning
遊技球が遊技盤2に沿って流下する過程で第1始動口11、第2始動口12、大入賞口13、一般入賞口14、及び小入賞口19のいずれかに入球して入賞した場合、入賞した箇所に応じた所定数の賞球が上皿28又は下皿29に払い出される。上記入賞口のいずれにも入賞しなかった遊技球は、排出口18を介して遊技領域10から排出される。
A game ball enters any one of the first starting hole 11, the second starting
遊技機1では、遊技球が第1始動口11を通過して入賞した場合、又は遊技球が第2始動口12を通過して入賞した場合、遊技者に有利な大当たり遊技(特別遊技)を実行するか否かが判定される。大当たり遊技では大入賞口13に容易に遊技球を入賞できるので、遊技者は大入賞口13への遊技球の入賞に応じて多量の遊技球が得られる。
In the
以下の説明では、第1始動口11への遊技球の入賞を条件として実行される判定を「第1特別図柄判定」と呼び、第2始動口12への遊技球の入賞を条件として実行される判定を「第2特別図柄判定」と呼ぶ。また、これらの判定を総称して「特別図柄判定」と呼ぶ。第1特別図柄判定が行われると、第1特別図柄表示器41(図4参照)において第1特別図柄が変動表示されてから判定結果を示す第1特別図柄が停止表示される。第2特別図柄判定が行われると、第2特別図柄表示器42(図4参照)において第2特別図柄が変動表示されてから判定結果を示す第2特別図柄が停止表示される。第1特別図柄判定を条件に実行される大当たり遊技よりも第2特別図柄判定を条件に実行される大当たり遊技の方が、大当たり遊技で遊技者が得る賞球が多い。また、第1特別図柄判定よりも第2特別図柄判定の方が結果として大当たり遊技が実行される可能性が高い。これにより、第2始動口12に対して第1始動口11よりも遊技球を入賞させたいという遊技者の気持ちを高めることが可能となる。
In the following description, the judgment executed on the condition that the game ball enters the first start port 11 is called "first special symbol judgment", and the judgment executed on the condition that the game ball enters the
第1始動口11は、常時開放されている始動口である。第2始動口12は、普通電動役物としての電動チューリップ17が作動しているときだけ開放される始動口である。電動チューリップ17は、第2始動口12に近接配置されており、一対の羽根部材を有している。この電動チューリップ17は、一対の羽根部材が第2始動口12を閉塞する閉姿勢(図1の実線を参照)と、第2始動口12を開放する開姿勢(図1の破線を参照)とに姿勢変化可能に構成されている。電動チューリップ17は、開姿勢になることによって右打ちされた遊技球を第2始動口12に寄せ集める。
The first starting port 11 is a starting port that is always open. The
第2始動口12は、通常は閉姿勢の電動チューリップ17によって閉塞されている。遊技球がゲート16を通過すると、賞球の払い出しは行われないものの、第2始動口12を開放するか否かが判定される。以下の説明では、第2始動口12を開放するか否かの判定を「普通図柄判定」と呼ぶ。普通図柄判定が行われると、普通図柄表示器45(図4参照)において普通図柄が変動表示されてから普通図柄判定の判定結果を示す普通図柄が停止表示される。普通図柄判定の判定結果を示す普通図柄には、第2始動口12を開放することを示す当たり図柄と、第2始動口12を開放しないことを示すハズレ図柄とがある。当たり図柄にはショート開放図柄とロング開放図柄とがある。ショート開放図柄は電動チューリップ17の総開放時間が短く基本的に遊技球を第2始動口12に入賞できない図柄である(例えば、総開放時間0.2秒)。ロング開放図柄は電動チューリップの総開放時間が長く遊技者が右打ちさえしていれば遊技球を第2始動口12に入賞容易な図柄である(例えば、総開放時間5秒)。何れかの当たり図柄が停止表示された場合、普通図柄の種類に応じて予め定められた態様で電動チューリップ17の一対の羽根部材が規定時間開姿勢を維持した後に閉姿勢に戻る動作が規定回数行われる。ハズレ図柄が停止表示された場合、電動チューリップ17は開姿勢にならず閉姿勢のままであるため遊技球を第2始動口12に入賞できない。
The
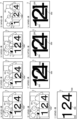
図2は、普通図柄判定について説明するための説明図である。図2(A)は、遊技機1における、普通図柄判定で第2始動口12を開放すると判定される確率について説明するための説明図である。普通図柄判定で第2始動口12を開放すると判定される確率には、時短状態(例えば、1/1)と、時短状態よりも確率が低い微時短状態(例えば、10/65536)と、微時短状態よりも確率が低い非時短状態(例えば、1/65536)とがある(図2(A))。なお、普通図柄判定で第2始動口12を開放すると判定される確率は微時短状態であるか非時短状態であるかに関わらず同じでもよい(例えば、1/65536)。
FIG. 2 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the normal symbol determination. FIG. 2(A) is an explanatory diagram for explaining the probability that the
図2(B)は、遊技機1における第2始動口12の開放時間群について説明するための説明図である。第2始動口12の開放時間(すなわち、電動チューリップ17が開姿勢に制御される時間)は、時短状態の方が微時短状態と非時短状態とよりも相対的に長い(図2(B))。具体的には、時短状態のときは、ロング開放図柄が停止表示されるのに対してショート開放図柄が停止表示されない。また、非時短状態と微時短状態とのときは、ショート開放図柄が停止表示されるのに対してロング開放図柄が停止表示されない。非時短状態と微時短状態とでは最も第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞し易い時短状態へと移行させることを目指して遊技者に第1始動口11を狙わせる遊技性を提供するために、基本的に遊技球を第2始動口12に入賞できないように予め構成されている。
FIG. 2B is an explanatory diagram for explaining the open time group of the
遊技機1では、左打ちされた遊技球の通過経路にはゲート16が設けられていない。このため、遊技機1では微時短状態において遊技球が一般入賞口14に入賞すると、賞球の払い出しが行われると共に普通図柄判定が実行される。なお、遊技機1には左打ちされた遊技球の通過経路にゲート16を設けてもよい。
In the
図2(C)は、遊技機1における普通図柄の変動時間群について説明するための説明図である。普通図柄の変動時間は、時短状態の場合よりも微時短状態の場合の方が相対的に長く、微時短状態の場合よりも非時短状態の場合の方が相対的に長い(図2(C))。例えば、時短状態の場合における普通図柄の変動時間は0.5秒間であり、微時短状態の場合における普通図柄の変動時間は59秒間であり、非時短状態の場合における普通図柄の変動時間は60秒間である。非時短状態における普通図柄の変動時間は、微時短状態における普通図柄の変動時間と差があまりなく、非時短状態と微時短状態とでは停止表示される普通図柄および電動チューリップ17の開放時間について同じである。これにより、非時短状態と微時短状態とが区別がつき難くできる。なお、普通図柄の変動時間は微時短状態であるか非時短状態であるかに関わらず同じでもよい(例えば60秒間)。
FIG. 2(C) is an explanatory diagram for explaining the variation time group of normal symbols in the
なお、下記3つのうち少なくとも1つに該当する状態を微時短状態としてもよい。
・普通図柄判定で第2始動口12を開放すると判定される確率が非時短状態に比べて高い。
・ロング開放図柄が停止される確率が非時短状態に比べて高い。
・普通図柄の変動時間が非時短状態に比べて短い。
In addition, it is good also considering the state applicable to at least one of the following three as a slightly short time state.
- The probability of being determined to open the
・ The probability that the long open pattern will be stopped is higher than in the non-time saving state.
・The fluctuation time of the normal pattern is shorter than the non-time saving state.
[遊技機1の演出手段の構成例]
図1に例示されるように、遊技機1には、各種の演出を行うものとして、液晶表示装置5、演出役物7、スピーカ24、盤用照明装置74、演出ボタン26、及び、枠用照明装置10が設けられている。
[Configuration example of effect means of gaming machine 1]
As illustrated in FIG. 1, the
液晶表示装置5(EL表示装置等でもよい)の表示画面(以下、「液晶画面5」と呼ぶ。)は、各種演出画像を表示する画像表示装置である。液晶表示装置5は遊技盤2よりも遊技機1の背面側(すなわち後方側)に設けられ、遊技盤2に形成された開口を通して視認できる。図1に示すように、液晶画面5は遊技者によって視認され易い位置に設けられている。液晶画面5には、装飾図柄55、小図柄56、第4図柄57及び59、CG又はアニメのキャラクタなどが表示される。
A display screen (hereinafter referred to as "
装飾図柄55、小図柄56、及び第4図柄57及び59は、特別図柄の変動表示に同期して変動表示される画像である。装飾図柄55は、1~9のうちの何れかの数字を表す図柄である。特別図柄の変動表示の開始に伴って3つの装飾図柄55(及び3つの小図柄56)が横並びで変動表示を開始し、特別図柄の停止表示の開始に伴って3つの装飾図柄55(及び3つの小図柄56)が横並びで停止表示する(「本停止」と呼ぶ。)。3つの数字の組み合わせによって、特別図柄判定の判定結果が報知される。停止表示する装飾図柄55の組み合わせは小図柄56の組み合わせと同じである。
The
第4図柄57及び59は色で表現されるものであり、装飾図柄55(及び特別図柄)と同期して変動表示した後、装飾図柄55(及び特別図柄)と同時に停止表示される。第4図柄57は第1特別図柄と同期しており、第4図柄59は第2特別図柄と同期している。第4図柄57及び59は、「赤」、「青」、「緑」、「黄」、及び「白」の第4図柄がこの順で同じ位置に一定の時間(例えば0.2秒間)ずつ繰り返し表示されることにより変動表示する。なお、第4図柄57及び59の変動表示は、所定色(例えば青)の第4図柄を一定の時間毎(例えば0.2秒毎)に表示と非表示とに切り替えて点滅させることにより実現されてもよい。
The fourth designs 57 and 59 are expressed in color, and after being variably displayed in synchronism with the decorative design 55 (and special design), they are stop-displayed at the same time as the decorative design 55 (and special design). The
停止表示される装飾図柄55(及び小図柄56)と、停止表示される第4図柄57の色との組み合わせは、特別図柄毎に異なるように予め定められている(図13参照)。装飾図柄55(及び小図柄56)と第4図柄57との組み合わせにより、停止表示された特別図柄が示す内容と同じ内容を報知できる。
The combination of the decorative pattern 55 (and the small pattern 56) to be stopped and the color of the
第4図柄57及び59は、液晶画面5の端の方に小さく表示される画像であり、装飾図柄55(及び小図柄56)に比べて目立たない画像である。このため、装飾図柄55と第4図柄57及び59との組み合わせによって特別図柄の種類を報知していても、遊技者に気付かれ難い。なお、第4図柄57及び59は、液晶画面5の右側近傍に設けられた発光素子(例えばフルカラーLED)で実現されてもよい。この発光素子を、装飾図柄55の停止表示と同時に予め定められた色で点灯させることにより第4図柄57及び59として用いて、特別図柄判定の判定結果を一義的に報知してもよい。
The
小図柄56および第4図柄57及び59は、大当たり遊技中以外は常に、演出役物7で隠れない位置において他の画像よりも手前側に表示される。このため、見えなくなることも視認性が低下することもない。これに対し、装飾図柄55は他の画像の後ろ側に重畳表示されて見えなくなったり、演出役物7で隠れたりする場合がある。また、装飾図柄55は、特別図柄が変動表示しているか否かに関わらず一部または全部が非表示となることがある。
The
演出役物7は、遊技盤2の前面とガラス板との間に設けられ、液晶画面5の上方中央に配置されている。演出役物7は、動作していないときは液晶画面5上方の初期位置に配される。演出役物7を動作させるタイミングとなると、演出役物7は、演出役物用モータ71の駆動力により初期位置から液晶画面5の中央に向かって回転しながら下方向に移動し、液晶画面5の前面に配される。演出役物7は、初期位置と進出位置との間で動作させることによって各種の演出に用いられる。
A
演出役物7は透光性のある合成樹脂材で形成される。演出役物7は、内蔵された複数の発光素子(盤用照明装置74の1種)を複数色または単色で発光させることによって各種の演出に用いられる。例えば、演出役物7に内蔵された各発光素子を7つの色(具体的には、赤色、橙色、黄色、緑色、水色、青色、及び紫色)で同時に発光させることにより全体として虹色で発光させる。演出役物7は、その位置に関わらず遊技者が視認可能である。このため、演出役物7に施された装飾および演出役物7の発光により、動作の有無に関わらず演出効果を高めることが可能である。
The
なお、演出役物7は、例えば遊技盤2と液晶画面5との間に設けられ、初期位置では遊技者が視認困難でもよい。また、演出役物7は、上下左右に移動可能でもよいし振動可能でもよい。
Note that the
スピーカ24は、液晶画面5で行われる画像を表示する演出と同期するように或いは非同期に、楽曲や音声、効果音等を出力して音による演出を行う。
The
盤用照明装置74は、遊技盤2に設けられた複数の発光素子(例えばフルカラーLED)の総称である。枠用照明装置10は、枠部材3に設けられた複数の発光素子(例えばフルカラーLED)の総称である。枠用照明装置10は、例えば、枠部材3の左側に設けられた左サイドランプと、枠部材3の右側に設けられた右サイドランプと、2つのスピーカ24の間に設けられたセンターランプと、遊技者によって操作可能な演出ボタン26(図2参照)に内蔵されたボタンランプとによって構成される。
The
図3は、演出ボタン26の一例について説明するための説明図である。演出ボタン26は枠部材3に設けられており、遊技者は操作(例えば押下)することによって操作情報を入力可能である。遊技機1では、演出ボタン26の操作に応じた演出が行われる場合がある。演出ボタン26は、その上面が枠部材3の上面と略同じ高さにある通常状態と、その上面が枠部材3の上面に対して所定の高さ(例えば10センチ)だけ上方に突出した突出状態との間でその高さを変更する制御が可能に構成されている。なお、演出ボタン26は、通常状態と突出状態との間におけるどの高さに制御されていても操作が可能である。
FIG. 3 is an explanatory diagram for explaining an example of the
また、枠部材3は、遊技者が選択操作またはカーソル移動を行うために演出キー27が設けられている(図3参照)。演出キー27はいわゆる十字キーであり、上キー、下キー、左キー、及び右キーを有して構成されている。演出キー27は、液晶画面5、盤用照明装置74、及び枠用照明装置10の光量調整に用いられたり、スピーカ24の音量調整に用いられたりする。
In addition, the
[表示器4の構成例]
図4は、図1における表示器4の拡大図である。表示器4は、主に特別図柄判定や普通図柄判定に関する情報を表示するものであり、図4に例示されるように、第1特別図柄表示器41、第2特別図柄表示器42、第1特別図柄保留表示器43、第2特別図柄保留表示器44、普通図柄表示器45、普通図柄保留表示器46、遊技状態表示器47、ラウンド表示器48、点灯により遊技者に右打ちを促す右打ちランプ49を有する。右打ちランプ49は低確非時短状態と低確微時短状態とでは継続して消灯しており(すなわち非報知態様であり)、大当たり遊技中と、小入賞口19を開放する小当たり遊技中と、低確時短状態中とでは継続して点灯している(すなわち報知態様である)。なお、右打ちランプ49に代えて(又は右打ちランプ49に加えて)、低確非時短状態と低確微時短状態とでは白丸となり(すなわち非報知態様であり)、大当たり遊技中と、小入賞口19を開放する小当たり遊技中と、低確時短状態中とでは継続して黒丸となる(すなわち報知態様である)ような画像を液晶画面5の端に表示し続けてもよい。また、右打ちランプ49に代えて(又は右打ちランプ49に加えて)、低確非時短状態と低確微時短状態とでは遊技者が視認し難いように倒れており(すなわち非報知態様であり)、大当たり遊技中と、小入賞口19を開放する小当たり遊技中と、低確時短状態中とでは遊技者が視認できるように継続して立っている(すなわち報知態様である)ような可動役物(例えば、旗を模した可動役物)を設けてもよい。
[Configuration example of display 4]
FIG. 4 is an enlarged view of the
第1特別図柄表示器41は、第1特別図柄判定が行われると、特別図柄を変動表示してから第1特別図柄判定の判定結果を示す特別図柄を停止表示することによって第1特別図柄判定の判定結果を報知する。第2特別図柄表示器42は、第2特別図柄判定が行われると、特別図柄を変動表示してから第2特別図柄判定の判定結果を示す特別図柄を停止表示することによって第2特別図柄判定の判定結果を報知する。
When the first special symbol determination is performed, the first special
第1特別図柄保留表示器43は、第1特別図柄判定の保留数(以下、「特1保留数」と呼ぶ。)を表示する。第2特別図柄保留表示器44は、第2特別図柄判定の保留数(以下、「特2保留数」と呼ぶ。)を表示する。液晶画面5には、第1特別図柄保留表示器43及び第2特別図柄保留表示器44の表示内容と同じ内容を報知する保留アイコン51及び保留数字52を表示することによって、遊技者が保留数を分かり易いようにしている。保留アイコン51は、保留の数(例えば最大4つ)だけ保留された順に並んで表示される。
The first special
ここで、青色、緑色、赤色、及び虹色が大当たり又は小当たりとなる可能性(以下、「信頼度」という)の高低を示唆する色として用いられる。各色は上述した順に、大当たりの場合に用いられ易くハズレの場合に用いられ難い。虹色は、信頼度が100%であり、大当たりである場合にのみ用いられ、ハズレである場合には用いられない。大当たりの場合やハズレであって特別図柄の変動時間が相対的に長い場合には、保留アイコン51は信頼度の高低を示唆する色のうちの何れかで表示され易い。以下の説明では、白色の保留アイコン51を通常態様の保留アイコン51と呼び、白色以外の上記の色の保留アイコン51を特別態様の保留アイコン51と呼ぶ。
Here, blue, green, red, and rainbow colors are used as colors that indicate the possibility of a big win or a small win (hereinafter referred to as "reliability"). Each color is more likely to be used in the case of a big win and less likely to be used in the case of a loss, in the order described above. The rainbow colors are 100% reliable and are used only for jackpots and not for losses. In the case of a big hit, or in the case of a loss and a relatively long variation time of the special symbol, the pending
保留数字52は、第1特別図柄判定の保留数および第2特別図柄判定の保留数に同期して、大当たりか否かに関わらず同じ態様で液晶画面5の左端に小さく表示される0~4の数字である。保留数字52には、第1特別図柄保留表示器43の表示と同期して保留数を0~4の数字で示す第1保留数字と、第2特別図柄保留表示器44の表示と同期して保留数を0~4の数字で示す第2保留数字とがある。例えば、第1特別図柄判定の保留が1つ増えると第1保留数字が1加算された数字で表示され、第2特別図柄判定の保留が1つ増えると第2保留数字が1加算された数字で表示される。ここで、保留アイコン51は装飾図柄55と同様に非表示にされたり他の画像で見えなくなったり表示されなかったりする。これに対して、保留数字52は小図柄56と同様に常に他の画像よりも手前側に表示されるので、他の画像によって見えなくなることも視認性が低下することもない。
The reserved
普通図柄表示器45は、普通図柄判定が行われると、普通図柄を変動表示してから普通図柄判定の判定結果を示す普通図柄を停止表示することによって普通図柄判定の判定結果を報知する。普通図柄保留表示器46は、普通図柄判定の保留数を表示する。遊技状態表示器47は、遊技機1の電源投入時点における遊技状態を表示する。ラウンド表示器48は、基本的には消灯しており、第1特別図柄表示器41又は第2特別図柄表示器42に大当たり図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて、大当たり遊技のラウンド数を表示する。ラウンド表示器48は、ハズレ図柄または小当たり図柄が停止表示されたことに応じては点灯せず消灯したままである。
When the normal symbol determination is performed, the
[遊技機1の制御装置の構成、及び、遊技機1で行われる各種判定の概要]
図5を参照しつつ、遊技機1が備える制御装置の構成例、及び、遊技機1で行われる各種判定の概要について説明する。図5は、遊技機1が備える制御装置の構成例を示すブロック図である。
[Configuration of Control Device of
With reference to FIG. 5, a configuration example of the control device provided in the
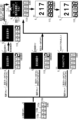
遊技盤2の裏面側には、上皿28又は下皿29へと送り出される遊技球を溜めておく球タンクの他に、遊技機1の動作を制御する制御装置が設けられている。図5に例示されるように、遊技機1の制御装置は、各種判定やコマンドの送信といった遊技の進行を制御する遊技制御基板100、遊技制御基板100から受信したコマンドに基づいて演出を統括的に制御する演出制御基板130、画像や音による演出を制御する画像音響制御基板140、各種ランプや演出役物7による演出を制御するランプ制御基板150等から構成されている。なお、制御装置の構成はこれに限定されるものではなく、例えば演出制御基板130、画像音響制御基板140、及びランプ制御基板150が1つの基板で構成されていてもよい。
On the back side of the
なお、遊技制御基板100と払出制御基板120との通信は、双方向にコマンドを送受信可能に構成されており、遊技制御基板100と演出制御装置130A(演出制御基板130)との通信は、遊技制御基板100から演出制御装置130A(演出制御基板130)への一方向のみにコマンドを送信可能に構成されている。
In addition, the communication between the
遊技制御基板100は、演算処理を行うメインCPU100a、遊技制御プログラム等が格納されたメインROM100b、演算処理時のワークエリアとなるメインRAM100c、及び、入出力ポートを備えている。
The
遊技制御基板100の入出力ポートには、一般入賞口検出スイッチ43a、ゲート検出スイッチ44a、第1始動口検出スイッチ45a、第2始動口検出スイッチ47a、第2始動口開閉ソレノイド48b、大入賞口検出スイッチ50a、大入賞口開閉ソレノイド51b、小入賞口検出スイッチ50c、小入賞口開閉ソレノイド51c、特定領域検出スイッチ52a、磁気検出センサ57a、電波検出センサ58a、アウト球検出スイッチ39a、表示器4、性能表示器113、RWMクリアスイッチ111a、設定キースイッチ112aが接続されている。特定領域検出スイッチ52aは小入賞口19の内部に設けられた特定領域を遊技球が通過(以下、「V入賞」と呼ぶ)したときに信号を入力する。RWMクリアスイッチ111aは、メインRAM100cに記憶された設定値以外の遊技の制御状態を初期化(すなわち、遊技機1を低確非時短状態に初期化)するための信号を入力する。RWMクリアスイッチ111aが操作されることによって初期化されることを「RWMクリア」と呼ぶ。
The input/output ports of the
設定キースイッチ112aは、設定キーを用いた操作によって設定値を変更または確認可能な状態に移行させるための信号を入力する。性能表示器113は、遊技機1の性能を示す性能情報および設定値を表示する。また、遊技制御基板100の入出力ポートには、遊技情報出力端子板90、払出制御基板120及び演出制御基板130が接続されている。
The setting
メインCPU100aはメインROM100bに記憶された遊技制御プログラムを読み出し、メインRAM100cをワークエリアとして活用しながら遊技に関する演算処理を行う。これにより、各種入力装置(検出スイッチや検出センサ等)からの検出信号に応じた制御処理、各種出力装置(ソレノイドや表示器等)を制御するための制御処理、各種制御コマンドを送受信するための制御処理、遊技情報出力端子板90を介して遊技機の外部(ホールコンピュータ等)に遊技情報を送信するための制御処理等を行う。
The
「遊技情報」には、第1始動口11又は第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞する毎に出力される始動口入賞信号、第1特別図柄又は第2特別図柄の変動表示が終了される毎に出力される図柄確定信号、大当たり遊技中に亘って出力される大当たり信号、小当り遊技中に亘って出力される小当り信号、ラウンド遊技(大入賞口の開放)中に亘って出力される開放中信号、時短状態に亘って出力される信号、遊技機1のセキュリティ上で問題となる(脅かす)状況(RWMクリアやエラー等)が発生したときに出力されるセキュリティ信号等が挙げられる。
In the "game information", the starting opening winning signal output each time the game ball wins in the first starting opening 11 or the second starting opening 12, and the variable display of the first special symbol or the second special symbol is terminated. A pattern confirmation signal output every time, a jackpot signal output during a jackpot game, a small hit signal output during a small win game, and an output during a round game (opening of the big winning opening) A signal that is being opened, a signal that is output over a time saving state, a security signal that is output when a situation (RWM clear, error, etc.) that poses a problem (threat) in terms of security of the
メインROM100bのメモリ領域には、遊技の進行に係るプログラムやデータが格納される遊技用ROM領域と、遊技機の性能表示に係るプログラムやデータが格納される情報用ROM領域とが順に配置されている。
In the memory area of the
遊技用ROM領域には、遊技の進行に係るプログラムが格納される遊技用プログラム領域と、遊技の進行に係るデータが格納される遊技用データ領域とが配置されている。情報用ROM領域には、遊技機の性能表示に係るプログラムが格納される情報用プログラム領域と、遊技機の性能表示に係るデータが格納される情報用データ領域とが配置されている。 In the game ROM area, a game program area for storing a program relating to the progress of the game and a game data area for storing data relating to the progress of the game are arranged. In the information ROM area, there are arranged an information program area in which a program relating to the performance display of the gaming machine is stored and an information data area in which data relating to the performance display of the gaming machine are stored.
メインRAM100cのメモリ領域には、遊技用プログラムの実行に際してワーク(作業領域)として用いられる遊技用RWM領域と、情報用プログラムの実行に際してワーク(作業領域)として用いられる情報用RWM領域とが配置されている。遊技用RWM領域には、遊技用プログラムがワークとして用いる遊技用ワーク領域と、遊技用プログラムが処理中のデータを一時的に退避させるための遊技用スタック領域とが配置されている。
In the memory area of the
遊技用ワーク領域には、設定値を格納するための設定値領域、RWM領域の異常を判定するための判定情報(チェックサム)を格納するための判定情報領域、遊技の進行によって変化する遊技データを格納するための遊技用データ領域が配置されている。 The game work area includes a set value area for storing set values, a judgment information area for storing judgment information (checksum) for judging an abnormality in the RWM area, and game data that changes as the game progresses. A game data area for storing is arranged.
情報用RWM領域には、情報用プログラムがワークとして用いる情報用ワーク領域と、情報用プログラムが処理中のデータを一時的に退避させるための情報用スタック領域とが配置されている。 The information RWM area includes an information work area used as a work by the information program and an information stack area for temporarily saving data being processed by the information program.
情報用ワーク領域には、遊技機1の性能に係る情報を格納するための性能情報領域、各種のエラー判定に係る情報を格納するためのエラー情報領域とが配置されている。
In the information work area, a performance information area for storing information relating to the performance of the
払出制御基板120は、払出装置95を駆動して遊技球の払い出しを制御する。また、払出制御基板120は、発射装置26を駆動して遊技球の発射を制御する。
The payout control board 120 drives the
払出制御基板120は、演算処理を行う払出CPU121a、払出用プログラム等が格納された払出ROM121b、演算処理時のワークエリアとなる払出RAM121c及び入出力ポート等を備えている。
The payout control board 120 includes a
払出制御基板120の入出力ポートには、開放検出スイッチ、満杯検出スイッチ、払出装置95から払い出される遊技球を検出するための払出球検出スイッチ、払出装置95から遊技球を払い出すための払出モータが接続されている。
The input/output ports of the payout control board 120 include an open detection switch, a full detection switch, a payout ball detection switch for detecting game balls paid out from the
払出CPU121aは、払出ROM121bに記憶された払出制御プログラムを読み出し、払出RAM121cをワークエリアとして活用しながら遊技球の払い出しに関する演算処理を行う。これにより、遊技制御基板100からの払出制御コマンドに応じて払出装置95から遊技球を払い出すための制御処理、演算処理の結果に基づくコマンドを遊技制御基板100に送信するための制御処理等を行う。
The
演出制御装置130Aは、遊技制御基板100からの演出制御コマンドの受信に基づき演出の進行を統括的に制御する演出制御基板130と、演出制御基板130からの演出制御コマンドの受信に基づき画像表示や音声出力の制御処理を行う画像音響制御基板140と、演出制御基板130からの演出制御コマンドの受信に基づき各種発光部材(LED等)や各種駆動源(モータ等)の制御処理を行うランプ制御基板150とを含む。
Effect control device 130A,
演出制御基板130は、演算処理を行うサブCPU130a、演出制御プログラムが格納されたサブROM130b、演算処理時のワークエリアとなるサブRAM130c、日時を計時するRTC130d、及び、入出力ポートを備えている。演出制御基板130の入出力ポートには、演出ボタン検出スイッチ17a、十字キー検出スイッチ19aが接続されている。
The
サブCPU130aは、サブROM130bに記憶された演出制御プログラムを読み出し、サブRAM130cをワークエリアとして活用しながら演出に関する演算処理を行う。これにより、特別図柄の変動表示に伴う演出の態様を決定するための制御処理、決定結果に基づく演出制御コマンドを画像音響制御基板140に送信するための制御処理、各種入力装置(検出スイッチ等)からの検出信号に応じた制御処理、各種出力装置(照明装置やモータ等)を制御するための制御処理等を行う。
The
画像音響制御基板140は、演出制御基板130からのコマンドを受けて、液晶画面5に所定の画像を表示させる制御を行ったり、スピーカ24から音やサウンドを出力させる制御を行ったりする。
The image
画像音響制御基板140は、演出制御基板130からの演出制御コマンドの受信に基づき画像表示や音声出力を統括的に制御する統括CPU141aと、統括制御プログラムが格納された統括ROM141bと、演算処理時のワークエリアとなる統括RAM141cと、統括CPU141aからの表示制御コマンド(ディスプレイリスト)の受信に基づき液晶画面5に出力する画像を生成するVDP145と、画像データ等が格納されたCGROM146と、統括CPU141aからの音声制御コマンドの受信に基づきスピーカ24を制御する音声制御部148(音声LSI)及び音声データ等が格納された音声ROMとを備えている。なお、VDP145が描画管理とサウンド管理との両方を担うような構成を採用してもよい。この場合、音声制御部148を別途設ける必要はない。
The image
統括CPU141aは、統括ROM141bに記憶された統括制御プログラムを読み出し、統括RAM141cをワークエリアとして活用しながら演出に関する演算処理を行う。これにより、液晶画面5に表示させる演出画像を指示する表示制御コマンド(ディスプレイリスト)を生成してVDP145に送信するための制御処理、スピーカ24から出力させる演出音を指示する音声制御コマンドを生成して音声制御部148(音声LSI)に送信するための制御処理等を行う。
The
また、画像音響制御基板140には、液晶画面5と、スピーカ24とが接続されている。画像音響制御基板140(のVDP145)は、所定のフレーム時間(例えば、1/30秒)間隔で画像を生成し、生成した画像を液晶画面5に出力する。これにより、液晶画面5に、例えば装飾図柄55等を含む画像が表示される。また、画像音響制御基板140(の音声制御部148)によって生成された音声信号がスピーカ24に出力されることで、音が出力される。
Also, the
また、演出制御装置130Aには、切替スイッチ22が接続されている。切替スイッチ22は、スピーカ24から出力される音(BGMや効果音等の演出音)の音量値を設定するためのスイッチである。例えば、切替スイッチ22に対する操作に応じて、音量値が「1」~「5」の5段階に設定される。また、切替スイッチ22は、液晶画面5、枠用照明装置10、及び、盤用照明装置74の光量値を設定するためのスイッチとしても用いられる。切替スイッチ22に対する操作に応じて、光量値が「1」~「5」の5段階に設定される。
Moreover, the
また、演出制御装置130Aには、演出ボタン検出スイッチ17a及び十字キー検出スイッチ19aが接続される。
Also, the effect
ランプ制御基板150は、演算処理を行うランプCPU150a、ランプ制御プログラムが格納されたランプROM150b、演算処理時のワークエリアとなるランプRAM150c、及び、入出力ポートを備えている。
The
ランプ制御基板150の入出力ポートには、枠用照明装置10(演出ボタン発光LED等)、演出役物7、盤用照明装置74、演出ボタン駆動装置17b(演出ボタン駆動モータ、演出ボタン振動モータ)が接続されている。
The input/output ports of the
ランプCPU150aは、ランプROM150bに記憶されたランプ制御プログラムを読み出し、ランプRAM150cをワークエリアとして活用しながら演出に関する演算処理を行う。これにより、枠用照明装置10、演出ボタン駆動装置17b、演出役物7及び盤用照明装置74の制御処理を行う。
The lamp CPU 150a reads the lamp control program stored in the
電源基板160は、遊技機の外部から供給される電源から遊技機の動作に必要なメイン電源(動作電源)を生成し、該メイン電源を遊技機1(遊技制御基板100、払出制御基板120、演出制御装置130Aや各種電子部品)に供給する(電源供給手段に相当)。
The
また、電源基板160は、遊技機1(遊技制御基板100、払出制御基板120、演出制御装置130Aや各種電子部品)へのメイン電源の供給を行うON状態と停止するOFF状態とに切り替えるための電源スイッチを遊技店の店員によって操作可能なように備えており、電源スイッチをON状態にするとメイン電源の供給が開始されて遊技機1の動作が開始する。なお、電源断(停電)時においては遊技制御基板100へのバックアップ電源の供給が維持される。これにより、電源断(停電)時においてもメインRAM100cの記憶内容が保持されることになり、電源断(停電)からの復旧後に遊技の制御状態を電源断(停電)前の状態に復旧させることができる。
In addition, the
遊技機1は、特別図柄判定の大当たり当選確率として「低確率状態」を有し、普通図柄判定の当たり当選確率として「非時短状態」と「微時短状態」と「時短状態」とを有する。遊技機1は、遊技が進行する際に下記3つの遊技状態で制御される。
・「低確率状態」且つ「非時短状態」である「低確非時短状態」
・「低確率状態」且つ「微時短状態」である「低確微時短状態」
・「低確率状態」且つ「時短状態」である「低確時短状態」
The
・"Low probability state" and "non-working time saving state"
・"Low probability state" and "low probability state"
・"Low probability state" and "short working time state"
遊技機1は初期的には低確非時短状態に制御される。設定値は「1」~「6」の6種類であり、特別図柄判定の大当たり当選確率は、設定値が「1」の場合は約1/300であり、設定値が「2」の場合約1/280であり、設定値が「3」の場合約1/260であり、設定値が「4」の場合約1/240であり、設定値が「5」の場合約1/220であり、設定値が「6」の場合約1/200である。非時短状態である場合と微時短状態である場合と時短状態である場合とは大当たり当選確率は同じである。
The
遊技機1では設定値が大きいほど特別図柄判定の大当たり当選確率が高い(すなわち、遊技者に有利となる)。なお、遊技機1では設定値が小さいほど特別図柄判定の大当たり当選確率が高くてもよい(すなわち、設定値が小さいほど遊技者に有利でもよい)。
In the
なお、特別図柄判定の大当たり当選確率として「低確率状態」に加えて「高確率状態」を有してもよい。「高確率状態」は、特別図柄判定の大当たり当選確率が低確率状態の10倍以下の予め定められた任意の確率である。低確率状態から高確率状態へは大当たり遊技終了後に移行する。 In addition to the "low probability state", it may have a "high probability state" as the jackpot winning probability of the special symbol determination. "High probability state" is a predetermined arbitrary probability that the jackpot winning probability of special symbol determination is 10 times or less than the low probability state. The low-probability state is shifted to the high-probability state after the jackpot game ends.
なお、払出制御基板120及び演出制御基板130にはバックアップ電源を供給していないが、電源断(停電)時においても払出RAM121c及びサブRAM130cの記憶内容が保持されるように、払出制御基板120及び演出制御基板130にバックアップ電源を供給してもよい。また、払出制御基板120及び演出制御基板130の何れか一方にのみバックアップ電源を供給してもよい。
In addition, although the backup power supply is not supplied to the payout control board 120 and the
次に、図6を参照して性能表示器113で表示される情報について説明する。図6は、性能表示器113で表示される情報について説明するための説明図である。性能表示器113は4個のセグメント表示器113a~113dを含んで構成される(図6(A)参照)。性能表示器113は低確非時短状態における「ベース値」を表示する。「ベース値」は低確非時短状態における特定の区間において、払い出された払出個数の総数を、遊技者が打ち出した遊技球の総数で除した値である(具体的には、(ベース算出用賞球カウンタの値/ベース算出用アウトカウンタの値)×100)。
Next, information displayed by the
性能表示器113の制御にはベース算出用賞球カウンタ、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ、及び総アウトカウンタが用いられる。各カウンタは、例えばメインRAM113に設けられる。ベース算出用賞球カウンタは、低確非時短状態における特定の区間において遊技球の入賞に応じて払い出された払出個数の総数を計数(例えば、加算または減算)する。例えば、遊技球が第1始動口11に入賞するとベース算出用賞球カウンタに「4」加算される。また、遊技球が第2始動口12に入賞するとベース算出用賞球カウンタに「1」加算される。また、遊技球が大入賞口13に入賞するとベース算出用賞球カウンタに「15」加算される。
A prize ball counter for base calculation, an out counter for base calculation, and a total out counter are used to control the
ベース算出用アウトカウンタは、低確非時短状態における特定の区間において遊技者が打ち出した遊技球の総数を計数(例えば、加算または減算)する。遊技機1では、アウト球検出スイッチ39aで遊技球が検出されるとベース算出用アウトカウンタに「1」加算される。
The base calculation out counter counts (for example, adds or subtracts) the total number of game balls launched by the player in a specific section in the low-probability short-time state. In the
ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタは低確非時短状態で計数される一方、低確非時短状態以外では計数されない。大当たり遊技中は遊技状態としては低確非時短状態であるものの、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数は停止している(なお、計数を継続してもよい)。低確非時短状態以外の遊技状態であるときは(すなわち、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が停止しているときは)、ベース値の算出が停止されていてもよいし、定期的(例えば、図19ステップS9Aの処理が行われる毎(例えば4ミリ秒毎))にベース値が算出され続けてもよい。 While the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation are counted in the low probability untime saving state, they are not counted except in the low probability untime saving state. During the jackpot game, although the game state is a low-probability short-time state, the counting by the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation is stopped (counting may be continued). Calculation of the base value may be stopped when the game state is other than the low-probability short-time state (that is, when the counting by the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation is stopped). However, the base value may continue to be calculated periodically (for example, every time the process of step S9A in FIG. 19 is performed (for example, every 4 milliseconds)).
総アウトカウンタは、遊技状態に関わらず遊技者が打ち出した遊技球の総数(「総アウト」と呼ぶ。)を計数(例えば、加算または減算)する。総アウトカウンタは低確非時短状態か否かに関わらず計数される。このため、例えば、低確非時短から低確微時短(又は低確時短)に移行したことによってベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計数が停止しているときにも総アウトカウンタでの計数は継続する。 The total out counter counts (for example, adds or subtracts) the total number of game balls launched by the player (referred to as "total out") regardless of the gaming state. The total out counter counts regardless of whether or not you are in a low-probability short-time condition. For this reason, for example, even when the counting at the base calculation out counter and the base calculation prize ball counter is stopped due to the transition from low probability short time to low probability short time (or low probability short time) Total out Counting in the counter continues.
メインCPU100aは、総アウトが6万個に達する前はリアルタイムベース値bLを算出している。そして、メインCPU100aは、総アウトが6万個になる毎にベース算出用賞球カウンタ及びベース算出用アウトカウンタの現在値からベース値を算出して保存し、総アウトカウンタ、ベース算出用賞球カウンタ、及びベース算出用アウトカウンタを初期化する。
The
総アウトが6万個に達することによって1回の区間が終了すると、この区間の最終ベース値が前回の区間の最終ベース値として保存される。性能表示器113では最大4つのベース値を一定間隔毎(例えば5秒毎)に切り替えて表示可能である(図6(B)参照)。具体的には、性能表示器113は、総アウトが6万個に達する前におけるリアルタイムベース値bL(現在の区間D)、3回前の区間Aにおける最終的なベース値b1、2回前の区間Bにおける最終的なベース値b2、1回前の区間Cにおける最終的なベース値b3の順で表示する。
When one interval ends with the total out reaching 60,000, the final base value of this interval is saved as the final base value of the previous interval. The
総アウトが予め定められた総数(例えば300)に達するまではリアルタイムベース値bL及びベース値b1~3として「--」が表示される。これにより、遊技機1の電源が投入された直後のリアルタイムベース値が実際のベース値と大きく異なるおそれが生じることを防止できる。
"--" is displayed as the real-time base value bL and the base values b1-3 until the total out reaches a predetermined total number (eg, 300). As a result, it is possible to prevent the possibility that the real-time base value immediately after the
総アウトが予め定められた総数より多いものの6万個に満たない場合、リアルタイムベース値bLだけが表示され、ベース値b1~3として「--」が表示される。また、保存された最終ベース値の数が3つに満たない場合、最終ベース値が記憶されていない区間のベース値b1~3として「--」が表示される。性能表示器113でのリアルタイムベース値bL及びベース値b1~3の巡回表示は、低確非時短から低確微時短(又は低確時短)に移行したことによってベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計数が停止しているときにも継続される。すなわち、性能表示器113でのリアルタイムベース値bL及びベース値b1~3の巡回表示は遊技状態に関わらず継続される。
When the total number of outs is greater than the predetermined total number but less than 60,000, only the real-time base value bL is displayed, and "--" is displayed as the base values b1-b3. Also, when the number of stored final base values is less than three, "--" is displayed as the base values b1 to b3 of the section in which the final base values are not stored. The cyclic display of the real-time base value bL and the base values b1 to 3 on the
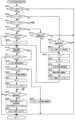
次に、図7を参照して設定変更モード、設定確認モード、及びRAMクリアモードについて説明する。遊技機1は、電源投入時の設定キースイッチ112aおよびRWMクリアスイッチ111aの状態に応じて、設定変更モード、設定確認モード、及びRAMクリアモードに移行する。設定変更モードは設定値を変更可能なモードである。設定確認モードは現在の設定値を性能表示器113に点灯表示させるモードである。RAMクリアモードはメインRAM100cに記憶された設定値以外の遊技の制御状態を初期化(すなわち、遊技機1は低確非時短状態に初期化)したときに移行するモードである。
Next, the setting change mode, setting confirmation mode, and RAM clear mode will be described with reference to FIG. The
なお、図7中の電源「ON」は電源スイッチがON状態にされたことを意味する。また、図10中の設定キーSW「ON」は、遊技店の店員による設定キーを用いた操作によって設定キースイッチ112aの回動部材がON姿勢となっていることを意味する。また、図10中の設定キーSW「OFF」は、設定キースイッチ112aの回動部材がOFF姿勢となっていることを意味する。また、図10中のRWMクリアSW「ON」は、RWMクリアスイッチ111aが操作されている状態であることを意味する。また、図10中のRWMクリアSW「OFF」は、RWMクリアスイッチ111aが操作されていない状態であることを意味する。
Note that the power "ON" in FIG. 7 means that the power switch is turned on. The setting key SW "ON" in FIG. 10 means that the turning member of the setting
遊技機1が電源「OFF」状態であるときに、設定キーSW「ON」状態かつRWMクリアSW「ON」状態で電源「ON」状態にされた場合、遊技機1が起動した直後に設定変更モードに移行する(図7(B)参照)。設定変更モードに移行した場合、遊技機1はメインRAM100cに記憶された設定値以外の遊技の制御状態が初期化されており、低確非時短状態に初期化されている(すなわちRWMクリアされている)。
When the
設定変更モードに移行すると、メインCPU100aは、記憶されている現在の設定値を性能表示器113に点灯表示させると共に、「設定変更中です」という音声をスピーカ24から出力する。設定変更モード中にRWMクリアスイッチ111aが操作されると、当該操作毎に設定値が変更される(図7(B)から(C)の流れ)。これに伴い、変更後の設定値が性能表示器113に点灯表示されると共に、設定値を報知する音声(例えば「3です」)がスピーカ24から出力する。なお、情報漏洩を防止するために設定値を報知する音声をスピーカ24から出力させなくてもよい。
When shifting to the setting change mode, the
変更後の設定値は、メインRAM100aに一時的に記憶されており、設定キーSW「OFF」状態にされた後に遊技機1の電源が再投入(具体的には、設定キーSW「OFF」状態かつRWMクリアSW「OFF」状態で電源「ON」状態)されることによって現在の設定値としてメインRAM100aに改めて記憶される(図7(C)から(D)の流れ)。このように設定値の変更後に遊技機1の電源が再投入(具体的には、設定キーSW「OFF」状態かつRWMクリアSW「OFF」状態で電源「ON」状態)されると、遊技機1は遊技店の店員が各種駆動源(モータ等)の動作を確認できる状態に移行する(図7(D)参照)。当該状態においては、各種駆動源(モータ等)が動作したり「ソレノイドの動作を確認して下さい」という音声がスピーカ24から出力したりすると共に、性能表示器113が消灯される。続いて、液晶画面5に対して装飾図柄55の表示が開始されると共に、性能表示器113が点滅表示された後にベース値の表示が開始される(図7(E)及び(F)参照)。
The setting values after the change are temporarily stored in the
なお、設定変更モード中に変更後の設定値としてメインRAM100aに一時的に記憶された設定値は、設定変更モード中に設定キーSW「OFF」状態にされることによって現在の設定値としてメインRAM100aに改めて記憶される構成でもよい。または、設定変更モード中にRWMクリアスイッチ111aが操作される毎に現在の設定値自体が更新される構成でもよい。これらの構成では、設定変更モード中に設定キーSW「OFF」状態にされたことに応じて、遊技機1は遊技店の店員が各種駆動源(モータ等)の動作を確認できる状態に移行する。
The set values temporarily stored in the
遊技機1が電源「OFF」状態であるときに、設定キーSW「ON」状態かつRWMクリアSW「OFF」状態で電源「ON」状態にされた場合、遊技機1が起動した直後に設定確認モードに移行する(図7(G)参照)。設定確認モードに移行した場合、遊技機1は遊技の制御状態が初期化されておらず、遊技機1は前回の遊技状態で制御される。
When the
設定確認モードに移行すると、メインCPU100aは、記憶されている現在の設定値を性能表示器113に点灯表示させると共に、「設定確認中です」という音声をスピーカ24から出力する。設定確認モード中に設定キーSW「OFF」状態にされると、遊技機1は遊技店の店員が各種駆動源(モータ等)の動作を確認できる状態に移行する(図7(D)参照)。以降の流れは設定キーSW「OFF」状態かつRWMクリアSW「OFF」状態で電源「ON」状態にされた場合の流れと同じである。
When shifting to the setting confirmation mode, the
遊技機1が電源「OFF」状態であるときに、設定キーSW「OFF」状態かつRWMクリアSW「ON」状態で電源「ON」状態にされた場合、遊技機1が起動した直後にRAMクリアモードに移行する(図7(H)参照)。RAMクリアモードに移行した場合、遊技機1は設定値以外の遊技の制御状態が初期化されており、低確非時短状態に初期化されている。
When the
RAMクリアモードに移行すると、メインCPU100aは、性能表示器113を消灯させると共に、「RAMクリアされました」という音声をスピーカ24から出力する。その後、予め定められた時間(例えば3秒)が経過すると遊技機1は遊技店の店員が各種駆動源(モータ等)の動作を確認できる状態に移行する(図7(D)参照)。以降の流れは設定キーSW「OFF」状態かつRWMクリアSW「OFF」状態で電源「ON」状態にされた場合の流れと同じである。
When shifting to the RAM clear mode, the
次に、図8を参照して装飾図柄55の表示優先度について説明する。低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態では、装飾図柄55が数字部分550とキャラクタ部分551とで構成される(図8(A)及び(B))。左列の装飾図柄(以下「左図柄」と呼ぶ)、中列の装飾図柄(以下「中図柄」と呼ぶ)、及び右列の装飾図柄(以下「右図柄」)は、数字部分550とキャラクタ部分551との表示優先度(具体的には、より手前側に表示される度合い)が変動表示中に変化する。なお、装飾図柄55は、数字部分550に代えてアルファベットで構成されてもよいし、キャラクタ部分551に代えて物体を表す画像で構成されてもよい。
Next, the display priority of the
低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態における装飾図柄55の表示優先度には表示パターンが5種類ある(HP1~5)。例えば、中図柄の数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、中図柄のキャラクタ部分551が優先度「2」であり、左図柄と右図柄との数字部分550が優先度「3」であり、左図柄と右図柄とのキャラクタ部分551が優先度「4」である場合(HP1)、図9(A)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重なっているときに中図柄を強調表示可能である。また、例えば、中図柄の数字部分550が優先度「3」であり、中図柄のキャラクタ部分551が優先度「4」であり、左図柄と右図柄との数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、左図柄と右図柄とのキャラクタ部分551が優先度「2」である場合(HP2)、図9(B)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重なっているときに中図柄の印象を薄くすることが可能である。また、例えば、中図柄の数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、中図柄のキャラクタ部分551が優先度「3」であり、左図柄と右図柄との数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、左図柄と右図柄とのキャラクタ部分551が優先度「2」である場合(HP3)、図9(C)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重なっているときに各装飾図柄の数字部分を強調表示可能である。また、例えば、各装飾図柄の数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、各装飾図柄のキャラクタ部分551が優先度「2」である場合(HP4)、図9(D)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重ならないように表示することで各装飾図柄を分かり易く表示可能である。また、例えば、中図柄の数字部分550が優先度「3」であり、中図柄のキャラクタ部分551が優先度「4」であり、左図柄の数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、左図柄のキャラクタ部分551が優先度「2」であり、右図柄の数字部分550が優先度「5」であり、右図柄のキャラクタ部分551が優先度「6」である場合(HP5)、図9(E)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重なることによって画面に奥行きがあるように見せることが可能である。
There are five types of display patterns in the display priority of the
低確時短状態では、装飾図柄55がキャラクタ部分551を有さず、数字部分550だけで構成される。低確時短状態における装飾図柄55の表示優先度には表示パターンが4種類ある(HP6~9)。例えば、中図柄の数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、左図柄と右図柄との数字部分550が優先度「2」である場合(HP6)、図9(F)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重なっているときに中図柄を強調表示可能である。また、例えば、中図柄の数字部分550が優先度「2」であり、左図柄と右図柄との数字部分550が優先度「1」である場合(HP7)、図9(G)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重なっているときに中図柄の印象を薄くすることが可能である。また、例えば、中図柄の数字部分550が優先度「2」であり、左図柄の数字部分550が優先度「1」であり、右図柄の数字部分550が優先度「3」である場合(HP8)、図9(H)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重なることによって画面に奥行きがあるように見せることが可能である。また、例えば、各装飾図柄の数字部分550が優先度「1」である場合(HP9)、図9(I)に例示するように3つの装飾図柄が重ならないように表示することで各装飾図柄を分かり易く表示可能である。
In the low probability time saving state, the
遊技機1では、停止表示時に装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1~9のうちの何れで表示されてもよい。遊技機1では装飾図柄55の停止表示時には数字部分550が互いに重ならないように表示される。これにより、遊技者に装飾図柄55の組み合わせが分かり易く報知できる。なお、遊技者に対しては装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示される小図柄56によって組み合わせを報知できるので、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1~9のうちの何れである場合においても、停止表示時に数字部分550が互いに重なるように表示されてもよい。
In the
[メインRAM100cの構成例]
図10は、遊技制御基板100におけるメインRAM100cの構成例及びメインRAM100cに格納される各種情報を説明するための説明図である。図10に例示されるように、メインRAM100cには、判定用記憶領域1030、第1保留記憶領域1031、第2保留記憶領域1032、第3保留記憶領域1033、第4保留記憶領域1034、第1保留記憶領域1035、第2保留記憶領域1036、第3保留記憶領域1037、及び第4保留記憶領域1038が設けられている。
[Configuration example of
FIG. 10 is an explanatory diagram for explaining a configuration example of the
判定用記憶領域1030は、特別図柄判定が実際に実行されるときにその特別図柄判定に使用される各種情報が記憶される記憶領域である。特別図柄判定に使用される各種情報には、大当たり乱数、図柄乱数、変動パターン乱数、及びリーチ乱数がある。大当たり乱数は、大当たりかハズレか小当たりかを判定するための乱数である。図柄乱数は、大当たりと判定した場合に大当たり図柄の種類を決定し、小当たりと判定した場合に小当たり図柄の種類を決定し、ハズレと判定した場合にハズレ図柄の種類を決定するための乱数である。 The determination storage area 1030 is a storage area for storing various information used for the special symbol determination when the special symbol determination is actually executed. Various types of information used for special symbol determination include jackpot random numbers, symbol random numbers, variation pattern random numbers, and reach random numbers. The jackpot random number is a random number for determining whether it is a jackpot, a loss, or a small hit. The symbol random number is a random number for determining the type of the big winning symbol when it is determined as a big win, determining the type of the small winning symbol when it is determined as a small winning, and determining the type of the losing symbol when it is determined as a losing. is.
遊技機1では、遊技状態と停止表示されたハズレ図柄とに応じて、遊技状態を変化可能になっている。これにより、大当たり及び小当たりを介さずに遊技状態を変化させることができ、現在の遊技状態および停止表示されたハズレ図柄に対して遊技者に興味を持たせることが可能である。また、遊技機1では、大当たり遊技のラウンド数と大当たり遊技終了直後の遊技状態との組み合わせが大当たり図柄(及び小当たり図柄)毎に異なる。このため、図柄乱数は遊技状態および大当たり遊技の種類を決定するための乱数といえる。
In the
変動パターン乱数は、特別図柄が変動表示を開始してから特別図柄判定の判定結果を示す態様で停止表示するまでの変動時間(変動パターン)を決定するための乱数である。リーチ乱数は、ハズレと判定した場合の変動パターンを決定する際に、特定秒数(例えば13.5秒)を超えるハズレ用変動パターン群と、当該変動パターン群以外(すなわち、特定秒数以下のハズレ用変動パターン群)とのうちの何れから変動パターンを決定するかを選択するための乱数である。 The variation pattern random number is a random number for determining the variation time (variation pattern) from when the special symbol starts to be displayed with variation until it is stopped and displayed in a manner indicating the determination result of the special symbol determination. Reach random number, when determining the variation pattern when it is determined to be lost, the variation pattern group for loss exceeding a specific number of seconds (for example, 13.5 seconds), and other than the variation pattern group (i.e., a specific number of seconds or less It is a random number for selecting which of the fluctuation pattern group for losing) to determine the fluctuation pattern.
第1保留記憶領域1031~第4保留記憶領域1034は、第1始動口11に遊技球が入賞する毎に第1保留記憶領域1031から順に第1特別図柄判定に係る各種情報が記憶される記憶領域である。第1保留記憶領域1035~第4保留記憶領域1038は、第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞する毎に第1保留記憶領域1035から順に第2特別図柄判定に係る各種情報が記憶される記憶領域である。
The first
例えば、特別図柄が変動表示されているときや大当たり遊技中(又は小当たり遊技中)に第1始動口11又は第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞しても、特別図柄判定や特別図柄の変動表示を直ちに行うことはできない。このような状況下では、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄判定に係る各種情報を、特別図柄判定の保留を示す情報として保留記憶領域1031~1038に格納する。一方、特別図柄が変動表示されておらず、特別図柄判定が保留されておらず、また、大当たり遊技中(又は小当たり遊技中)でもない場合には、メインCPU100aは、取得した各種乱数等を、遊技球が入賞した始動口に対応した第1保留記憶領域(1031又は1035)に記憶した直後、判定用記憶領域1030にシフトさせる。
For example, even if the game ball wins the first start port 11 or the
例えば、第1保留記憶領域1031~第4保留記憶領域1034のいずれにも情報が記憶されていない状態で第1始動口11に遊技球が入賞した場合、この入賞により取得された第1特別図柄判定に係る各種情報は、空きエントリの最上位である第1保留記憶領域1031に格納される。また、例えば、第1保留記憶領域1031及び第2保留記憶領域1032に情報が記憶された状態で第1始動口11に遊技球が入賞した場合、この入賞により取得された第1特別図柄判定に係る各種情報は、空きエントリの最上位である第3保留記憶領域1033に格納される。
For example, when the game ball wins the first start port 11 in a state in which information is not stored in any of the first
また、例えば、保留記憶領域1031~1038には「事前判定情報」も記憶される。始動口に遊技球が入賞した際に、大当たり乱数、図柄乱数、リーチ乱数、及び変動パターン乱数に基づいて、特別図柄判定に先立って大当たりか否か等を判定する事前判定が行われる。事前判定情報は、事前判定によって得られる情報であり、「入賞始動口情報」、大当たりであるか否かを示す情報、大当たりである場合には大当たり図柄の種類を示す情報、小当たりである場合には小当たり図柄の種類を示す情報、ハズレである場合にはハズレ図柄の種類を示す情報、特別図柄の変動パターンを示す情報、遊技状態を示す情報等を含んでいる。「入賞始動口情報」は、同じ保留記憶領域内に格納される各乱数が、第1始動口11及び第2始動口12のうちの何れの始動口に入賞したことを契機として取得されたのかを示す情報である。これらの情報を含む事前判定情報は、事前判定に使用された大当たり乱数等と同じ保留記憶領域内に格納される。
Further, for example, “pre-determination information” is also stored in the reserved
第1特別図柄判定の実行に際して第1保留記憶領域1031に記憶されている情報が判定用記憶領域1030にシフトされると、第1保留記憶領域1031より下位のエントリに記憶されている情報が1エントリずつ上位にシフトされる。例えば、第1保留記憶領域1031~第3保留記憶領域1033のそれぞれに情報が記憶された状態で第1保留記憶領域1031に記憶されている情報が判定用記憶領域1030にシフトされると、第2保留記憶領域1032に記憶されている情報が第1保留記憶領域1031にシフトされると共に、第3保留記憶領域1033に記憶されている情報が第2保留記憶領域1032にシフトされる。
When the information stored in the first
このような情報のシフト処理は、第2特別図柄判定に係る情報が記憶される第1保留記憶領域1035~第4保留記憶領域1038においても同様に行われる。遊技機1では、第1特別図柄判定及び第2特別図柄判定の両方が保留されている場合、すなわち第1保留記憶領域1031及び第1保留記憶領域1035の両方に情報が記憶されている場合、第1保留記憶領域1031~第4保留記憶領域1034におけるシフト処理に先立って、第1保留記憶領域1035~第4保留記憶領域1038におけるシフト処理が優先して行われる。よって、第2特別図柄判定が保留されている場合、判定用記憶領域1030には、第1保留記憶領域1035に記憶されている各種情報がシフトされる。また、第2特別図柄判定が保留されていない場合、すなわち第1特別図柄判定のみが保留されている場合には、第1保留記憶領域1031に記憶されている各種情報がシフトされる。なお、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄とを同時に変動表示可能な構成を採用してもよい。このような構成では、第1特別図柄判定用と第2特図判定用との2つの判定用記憶領域1030を備えてもよい。この場合、第1保留記憶領域1031~第4保留記憶領域1034におけるシフト処理は、第1保留記憶領域1035~第4保留記憶領域1038におけるシフト処理と独立して行われてもよい。
Such shift processing of information is similarly performed in the first
以下、一部の構成が異なる2つの実施形態について説明する。第1実施形態の特徴は低確微時短状態が遊技者に最も不利な状態であり、低確非時短状態の方が低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な点である。具体的には、第1実施形態では、低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて低確時短状態に移行可能な一方、低確微時短状態(及び低確時短状態)において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて低確時短状態に移行しない。第2実施形態の特徴は低確非時短状態が遊技者に最も不利な状態であり、低確非時短状態よりも低確微時短状態の方が遊技者に有利な点である。具体的には、第2実施形態では、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて低確時短状態に移行可能な一方、低確非時短状態(及び低確時短状態)において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて低確時短状態に移行しない。 Two embodiments with partially different configurations will be described below. The feature of the first embodiment is that the low-probability short working hours state is the most disadvantageous state for the player, and the low-probability non-shortening working hours state is more advantageous to the player than the low-probable short working hours state. Specifically, in the first embodiment, while it is possible to shift to the low probability short working hours state in response to the stop display of a specific losing pattern in the low certainty short working hours state, the low probability short working hours state (and state) does not shift to a low-probability short-time state in response to the stop display of a specific losing pattern. The feature of the second embodiment is that the low-probability short working hours state is the most disadvantageous state for the player, and the low-probability short working hours state is more advantageous to the player than the low-probable short working hours state. Specifically, in the second embodiment, while it is possible to shift to the low probability short working hours state in response to the stop display of a specific losing pattern in the low certainty short working hours state, state) does not shift to a low-probability short-time state in response to the stop display of a specific losing pattern.
[第1実施形態]
まず、第1実施形態について説明する。図11は、第1実施形態における遊技状態の移行について説明するための説明図である。ここで、遊技機1はRWMクリア(具体的には、設定変更を伴うRWMクリア又は設定変更を伴わないRWMクリア)が行われると低確非時短状態に制御される。このため、第1実施形態の遊技機1では、RWMクリアが行われたときは低確微時短状態よりも有利な低確非時短状態で遊技が開始できる。これにより、第1実施形態の遊技機1は遊技者に対して遊技店開店直後に遊技させる動機を与えることが可能である。
[First embodiment]
First, the first embodiment will be explained. FIG. 11 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the game state transition in the first embodiment. Here, when the
第1実施形態では、低確非時短状態において「通常のハズレ図柄」とは異なるハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されると低確時短状態に制御され、時短回数700回が設定される(図11(a)から(a3)を介して(b)に移行する流れ)。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が10回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が700回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が700回に設定される。なお、「通常のハズレ図柄」は、何れの遊技状態においても停止表示されたことに応じて遊技状態を変化させないハズレ図柄である。 In the first embodiment, when a losing (time saving A) pattern different from the "normal losing pattern" is stopped and displayed in the low probability non-time saving state, it is controlled to the low probability time saving state, and the time saving number of times is set to 700 times ( Flow from FIG. 11(a) to (b) via (a3)). Specifically, the time saving number J1 related to the first special design is set to 10 times, the time saving number J2 related to the second special design is set to 700 times, and the sum of the first special design and the second special design The time reduction frequency J3 is set to 700 times. It should be noted that the "normal losing symbol" is a losing symbol that does not change the game state in response to being stopped and displayed in any game state.
遊技機1において低確時短状態は第2始動口12を狙って大当たり(及び小当たり)を目指せる遊技状態なので、低確時短状態は第1始動口11を狙う低確非時短(及び低確微時短)よりも遊技者にとって有利な状態といえる。第1実施形態では、低確時短状態は、大当たりA又はDを示す大当たり図柄の停止表示を実行条件とする大当たり遊技が終了することに応じても制御される。例えば、大当たりA又はDに係る大当たり遊技が実行された場合には、時短回数として700回が設定される。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が10回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が700回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が700回に設定される。
In the
このように、第1実施形態では、低確非時短状態のときに所定条件(具体的にはハズレ又は大当たりとなったとき)が成立すると、ハズレ(時短A)図柄となる確率と大当たりA又はDとなる確率との合算確率で低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行する。第1実施形態では、低確微時短状態のときに所定条件(具体的にはハズレ又は大当たりとなったとき)が成立すると、大当たりA又はDとなる確率で低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行する。このため、低確時短状態への移行確率は低確非時短状態の方が低確微時短状態よりもハズレ(時短A)図柄となる確率の分だけ大きい。よって、低確微時短状態は低確非時短状態に比べて相対的に遊技者に不利な遊技状態である。 Thus, in the first embodiment, when a predetermined condition (specifically, when it becomes a loss or a jackpot) is established in a low-probability non-time-saving state, the probability of a loss (time-saving A) pattern and the jackpot A or With the combined probability with the probability of D, it shifts from the low-probability short-time state to the low-probability short-time state. In the first embodiment, when a predetermined condition (specifically, when it becomes a loss or a jackpot) is established in the low probability short working hours state, the low probability short working hours state from the low probability short working hours state with the probability of becoming a big hit A or D transition to state. For this reason, the probability of transition to the low-probability short working hours state is greater than the low-probability non-short working hours state by the probability of becoming a lost (shortening of working hours A) pattern than the low-probability small short working hours state. Therefore, the low-probability small time-saving state is a game state relatively disadvantageous to the player compared to the low-probability non-time-saving state.
また、低確時短状態には、設定変更後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、RWMクリア後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、又は大当たり遊技の終了から連続して750回ハズレたことで遊技状態に関わらず制御され、時短回数1000回が設定される。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が10回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が1000回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が1000回に設定される。この時短回数は大当たり(又は小当たり)を条件に設定される時短回数よりも多いため、遊技者にとってより有利な状態といえる。 In addition, in the low-probability time-saving state, the game state is that it has lost 750 times in succession after changing the setting, that it has lost 750 times in succession after clearing the RWM, or that it has lost 750 times in succession from the end of the jackpot game. Regardless, it is controlled, and the number of times of time saving is set to 1000 times. Specifically, the time saving number J1 related to the first special design is set to 10 times, the time saving number J2 related to the second special design is set to 1000 times, and the sum of the first special design and the second special design The time saving frequency J3 is set to 1000 times. Since the number of times of time saving is greater than the number of times of time saving set on the condition of a big win (or a small win), it can be said that the state is more advantageous for the player.
以下の説明では、設定変更後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、RWMクリア後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、又は大当たり遊技の終了から連続して750回ハズレたことを「連続ハズレ750回」と呼ぶ。遊技機1では連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすと、他の条件を満たすことによって低確時短に制御される時短回数よりも多い時短回数が設定される。このため、遊技機1において連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たしたことに応じて制御される低確時短状態は、他の条件を満たしたことに応じて制御される低確時短状態に比べて遊技者に有利な遊技状態である。なお、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たしたことによって設定される時短回数は、大当たり(又は小当たり)を条件に設定される時短回数よりも少なくてもよいし同じでもよい。また、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たしたことによって設定される時短回数は、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことを条件に設定される時短回数よりも少なくてもよいし同じでもよい。
In the following explanation, 750 consecutive losses after changing the setting, 750 consecutive losses after clearing the RWM, or 750 consecutive losses after the end of the jackpot game are referred to as "750 consecutive losses". call. In the
連続ハズレ750回の条件を1回満たした後、その後に大当たり遊技が行われることなく再び連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合、遊技状態は変化しない。連続ハズレ750回の条件を1回満たした後、その後に大当たり遊技が行われてから再び連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合、連続ハズレ750回の条件を1回目に満たしたときと同様に低確時短状態に制御される。 After the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied once, when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied again without performing a big win game after that, the game state does not change. After satisfying the condition of 750 consecutive losses once, when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied again after the jackpot game is played, it is the same as when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied for the first time. It is controlled in a low-probability short-time state.
低確微時短状態は、低確非時短状態において通常のハズレ図柄とは異なるハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示されることで制御される。ハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示された場合には、時短回数として500回が設定される。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が500回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が0回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が500回に設定される。なお、低確微時短状態および低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示されても時短回数は加算されず遊技状態は変化しない。 The low-probability small time-saving state is controlled by stop-displaying a losing (time-saving B) design different from the normal losing design in the low-probability non-time-saving state. When the lost (time saving B) symbol is stopped and displayed, 500 times are set as the number of times of time saving. Specifically, the time saving number J1 related to the first special design is set to 500 times, the time saving number J2 related to the second special design is set to 0 times, and the sum of the first special design and the second special design The time reduction frequency J3 is set to 500 times. In the low-probability small time-saving state and the low-probability time-saving state, even if the losing (time-saving B) symbol is stopped and displayed, the number of time-saving times is not added and the game state does not change.
以下の説明では、通常のハズレ図柄とは異なるハズレ図柄であって、少なくとも1以上の遊技状態において、停止表示されたことに応じて遊技状態を変化させるハズレ図柄を「特定のハズレ図柄」と呼ぶ。例えば、ハズレ(時短A)図柄およびハズレ(時短B)図柄は特定のハズレ図柄である。ハズレ(時短A)図柄は、ハズレ(時短B)図柄と違って低確時短に制御されるハズレ図柄であるためハズレ(時短B)図柄に比べて遊技者に有利なハズレ図柄である。 In the following description, a losing symbol that is different from normal losing symbols and that changes the game state in accordance with at least one or more game states in response to being stopped and displayed is referred to as a "specific losing symbol". . For example, the lost (time saving A) pattern and the losing (time saving B) pattern are specific losing patterns. Unlike the losing (time saving B) symbols, the losing (time saving A) symbols are controlled to have a low probability of working time saving, and are more advantageous to the player than the losing (time saving B) symbols.
また、低確微時短状態は、大当たりB又はCを示す大当たり図柄の停止表示を実行条件とする大当たり遊技が終了することで制御される。例えば、大当たりBに係る大当たり遊技が実行された場合には、時短回数として99回が設定される。また、例えば、大当たりCに係る大当たり遊技が実行された場合には、時短回数として500回が設定される。 In addition, the low-probability time-saving state is controlled by ending the jackpot game whose execution condition is the stop display of the jackpot symbol indicating the jackpot B or C. For example, when a jackpot game related to jackpot B is executed, 99 times is set as the number of times of time saving. Further, for example, when a jackpot game related to jackpot C is executed, 500 times are set as the number of times of time saving.
低確非時短状態は、初期状態(設定値の変更後の起動を含む)である場合の他、低確時短状態または低確微時短状態において時短回数が終了することで制御される。このように、低確時短状態が終了すると、低確時短状態よりは遊技者に有利ではないものの低確微時短状態よりは遊技者に有利な低確非時短状態に移行する。また、低確微時短状態が終了すると相対的に有利な低確非時短状態に移行する。 In addition to the initial state (including start-up after changing the setting value), the low-probability non-working time saving state is controlled by ending the number of times in the low-probability short-time state or low-probability short-time state. In this way, when the low-probability short working hours state ends, it shifts to a low-probable short working hours state that is not advantageous to the player than the low-probable short working hours state but is more advantageous to the player than the low-probable small short working hours state. Moreover, when the low-probability small time-saving state ends, it shifts to a relatively advantageous low-probability non-time-saving state.
また、低確非時短状態には、低確微時短状態において予め定められた回数(例えば2回)小当たりに当選したことで制御される。また、低確非時短状態は、大当たりEに係る大当たり遊技(遊技状態としては低確非時短状態)が終了することで制御される。また、低確非時短状態には、小当たりCに係る小当たり遊技中においてV入賞した場合は小当たり遊技に続いて実行される大当たり遊技が終了することで制御される。また、低確非時短状態には、小当たりCに係る小当たり遊技中においてV入賞しなかった場合は小当たり遊技が終了することで制御される。また、低確非時短状態には、小当たりBに係る小当たり遊技中においてV入賞しなかった場合に、小当たり遊技が終了することで制御される。 In addition, in the low-probability short working hours state, it is controlled by winning a small hit a predetermined number of times (for example, twice) in the low-probability small working hours state. In addition, the low-probability non-time-saving state is controlled by ending the jackpot game (low-probability non-time-saving state as a game state) related to the jackpot E. In addition, in the low-probability non-time-saving state, when the V prize is won during the small winning game related to the small winning C, the big winning game executed following the small winning game is finished. In addition, in the low-probability non-time-saving state, when the V prize is not won during the small winning game related to the small winning C, the small winning game is controlled by ending. In addition, in the low-probability non-time-saving state, when the V prize is not won during the small winning game related to the small winning B, the small winning game is finished.
なお、ハズレ(時短A)図柄は備える一方でハズレ(時短B)図柄は備えなくてもよい。 In addition, it is not necessary to provide the losing (time saving A) pattern while providing the losing (time saving B) pattern.
なお、ハズレ(時短B)図柄には、低確非時短状態において停止表示された場合に付与される時短回数が少ない第1ハズレ(時短B)図柄と、低確非時短状態において停止表示された場合に付与される時短回数が第1ハズレ(時短B)図柄よりも多い第2ハズレ(時短B)図柄と、があってもよい。例えば、第1ハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示された場合には、時短回数として99回に設定される(具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が99回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が0回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が99回に設定される)。第2ハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示された場合には、時短回数として500回が設定される(具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が500回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が0回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が500回に設定される)。第4図柄57はハズレ(時短B)図柄の種類に応じた図柄が停止表示されるのに対し、装飾図柄55はハズレ(時短B)図柄の種類に関らず「459」の組み合わせで停止表示される。これにより、装飾図柄55の組み合わせによっては第1ハズレ(時短B)図柄か第2ハズレ(時短B)図柄かを区別できないので、低確微時短状態において時短回数が99回であることを期待させながら遊技者に遊技させることが可能である。
In addition, in the losing (time saving B) pattern, the first losing (time saving B) pattern, which has a small number of time saving times given when it is stopped and displayed in a low time saving state, and a low time saving time state It was stopped and displayed. There may be a second losing (time saving B) pattern in which the number of times of time saving given in the case is larger than the first losing (time saving B) pattern. For example, when the first losing (time saving B) symbol is stopped and displayed, it is set to 99 times as the number of times of time saving (specifically, the number of times of time saving J1 related to the first special symbol is set to 99 times, The time saving frequency J2 related to the second special symbol is set to 0 times, and the time saving frequency J3 related to the sum of the first special symbol and the second special symbol is set to 99 times). When the second lost (time saving B) symbol is stopped and displayed, 500 times are set as the number of times of time saving (specifically, the number of times of time saving J1 related to the first special symbol is set to 500 times, and the second The time saving frequency J2 related to the special design is set to 0 times, and the time saving frequency J3 related to the addition of the first special design and the second special design is set to 500 times). The
図12は、第1実施形態における特別図柄判定の結果について説明するための説明図である。大当たりについては上述したため説明を省略する。第1実施形態では、第1特別図柄判定において設定値に関わらず約1/200の確率で小当たりに当選する。また、第1特別図柄判定において設定値に関わらず約1/10の確率で微時短状態または時短状態を発生させるハズレ(時短A又はB)となる。そして、大当たり、小当たり、又はハズレ(時短)と判定される以外の確率で遊技状態を変化させない通常のハズレとなる。 FIG. 12 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the result of the special symbol determination in the first embodiment. Since the jackpot has been described above, the explanation is omitted. In the first embodiment, a small hit is won with a probability of about 1/200 regardless of the set value in the first special symbol determination. Also, in the first special symbol determination, it becomes a loss (time saving A or B) that generates a slight time saving state or time saving state with a probability of about 1/10 regardless of the set value. Then, it becomes a normal loss that does not change the game state with a probability other than that it is determined as a big win, a small win, or a loss (time saving).
第1実施形態では、第2特別図柄判定において設定値に関わらず約1/7の確率で小当たりに当選する。また、第2特別図柄判定において設定値に関わらずハズレ(時短)とならない。大当たり又は小当たりと判定される以外は遊技状態を変化させない通常のハズレとなる。 In the first embodiment, a small hit is won with a probability of about 1/7 regardless of the set value in the second special symbol determination. In addition, it does not become a loss (time saving) regardless of the set value in the second special symbol determination. It becomes a normal loss that does not change the game state except that it is determined as a big win or a small win.
第1実施形態における特別図柄判定の結果についての特徴は、第1特別図柄判定と第2特別図柄判定とではハズレ(時短)と判定される確率が異なる点である。これにより、第1特別図柄判定では大当たり又はハズレ(時短)を引くことで遊技状態を変化させることを目指し、第2特別図柄判定では大当たり又は小当たりを引くことで遊技状態を変化させることを目指すという新たなゲーム性を提供できる。 The feature of the result of the special symbol determination in the first embodiment is that the probability of being determined to be lost (time saving) differs between the first special symbol determination and the second special symbol determination. As a result, the first special symbol determination aims to change the game state by pulling a big hit or a loss (time saving), and the second special symbol determination aims to change the game state by pulling a big hit or a small hit. It can provide a new game property.
図13は、第1実施形態における大当たり種別および小当たり種別について説明するための説明図である。図13(A)に例示するように、大当たりAは、大入賞口13を遊技球が容易に通過できるように開閉させるラウンド遊技を2回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確時短状態に移行する大当たりである。大当たりB及びCはラウンド遊技を2回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確微時短状態に移行する大当たりである。大当たりDはラウンド遊技を10回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確時短状態に移行する大当たりである。大当たりEはラウンド遊技を2回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確非時短状態に移行する大当たりである。
FIG. 13 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the jackpot type and the small hit type in the first embodiment. As illustrated in FIG. 13 (A), the jackpot A executes a round game twice to open and close the big winning
大当たりB及びCは小当たり上限回数を「2」に設定する大当たりであり、大当たりA、D、及びEは小当たり上限回数を設定しない大当たりである。小当たり上限回数が設定されると、低確微時短状態において小当たり上限回数となるまで小当たりを引くと低確非時短状態に移行する。なお、小当たり上限回数は予め定められた回数であれば「2」以外でもよく、例えば1又は5回でもよい。 Jackpots B and C are jackpots in which the upper limit number of small wins is set to "2", and jackpots A, D, and E are jackpots in which the upper limit number of small wins is not set. When the small hit upper limit number is set, when the small hit is pulled until the small hit upper limit number is reached in the low probability small time saving state, it shifts to the low probability non time saving state. It should be noted that the small hit upper limit number of times may be other than "2" as long as it is a predetermined number of times, and may be, for example, 1 or 5 times.
大当たりAの場合は3つの同じ装飾図柄55が停止表示されるのに対し、大当たりB及びCの場合は低確微時短状態に移行することを報知する特殊な装飾図柄(時短図柄)が停止表示される。大当たりB及びCは第4図柄の停止表示態様が異なるものの、装飾図柄55の停止表示態様からは大当たりB及びCのうち何れであるか遊技者は判別できない。このため、遊技に慣れていない遊技者は低確微時短状態に設定される時短回数が分からない状態で遊技を進めることが可能である。
In the case of the jackpot A, the same three
各大当たり遊技の有利度合いは、大当たりC<大当たりB<大当たりE<大当たりA<大当たりDの順に遊技者の有利度合いが高い。 The degree of advantage of each jackpot game is higher for the player in the order of jackpot C<jackpot B<jackpot E<jackpot A<jackpot D.
なお、第1特別図柄判定の結果として、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確非時短状態に移行する大当たりを有してもよい。 In addition, as a result of the first special symbol determination, there may be a big hit that shifts to a low-probability short-time state immediately after the end of the big-hit game.
図13(B)に例示するように、小当たりAは、基本的にV入賞しないように遊技球が小入賞口19を通過困難に開閉させる小当たり遊技を実行する小当たりである。小当たりAに係る小当たり遊技が実行されても基本的にV入賞しないので小当たり遊技の終了直後に大当たり遊技が実行されることはなく、遊技状態は変化しない。小当たりBは、V入賞容易に小入賞口19を開閉させる小当たり遊技を実行する小当たりである。小当たりBに係る小当たり遊技が実行されると基本的にV入賞し、小当たり遊技の終了直後に大当たり遊技が実行される。当該大当たり遊技ではラウンド遊技が10回実行され、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確時短状態に移行する。小当たりCは、V入賞容易に小入賞口19を開閉させる小当たり遊技を実行する小当たりである。小当たりCに係る小当たり遊技が実行されると基本的にV入賞し、小当たり遊技の終了直後に大当たり遊技が実行される。当該大当たり遊技ではラウンド遊技が2回実行され、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確非時短状態に移行する。
As exemplified in FIG. 13(B), the small hit A is basically a small hit to execute a small winning game that opens and closes the small winning
各小当たり遊技の有利度合いは、小当たりA<小当たりC<小当たりBの順に遊技者の有利度合いが高い。 The degree of advantage of each small winning game is higher for the player in the order of small winning A<small winning C<small winning B.
図14は、第1実施形態におけるハズレ(時短)種別について説明するための説明図である。ハズレ(時短A)は、変動開始時に低確非時短状態(すなわち、時短遊技フラグがOFF)であるときに停止表示されると大当たり遊技および小当たり遊技を実行せずに低確時短状態に移行させるハズレである。低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)が停止表示されると、総アウトカウンタでの計数は継続するもののベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計測は停止し、リアルタイムベース値bLの算出も停止される。これに伴い、特別図柄の変動回数の計測が継続したまま新たに時短回数の計測が開始される。すなわち、遊技制御基板100のメインCPU100aは、次に特別図柄判定を行ったことに応じて、今回の特別図柄の変動回数に対して1加算すると共に時短回数を1減算することになる。なお、特別図柄の変動回数は、設定変更、RWMクリア、又は大当たり遊技の実行に応じて0回に設定され、特別図柄判定が行われる毎に1加算される。
FIG. 14 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the failure (shortening of working hours) type in the first embodiment. Loss (time saving A) is stopped when it is in a low probability non-time saving state (that is, the time saving game flag is OFF) at the start of the fluctuation, and it shifts to a low probability time saving state without executing a big winning game and a small winning game. It is a mistake to let you. When the loss (time saving A) is stopped and displayed in the low-probability time-saving state, the total out counter continues counting, but the base calculation out counter and the base calculation prize ball counter stop counting, and the real-time base value The calculation of bL is also stopped. Along with this, while the measurement of the number of fluctuations in the special symbol continues, the measurement of the number of times of time reduction is newly started. That is, the
非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)が停止表示されたときは、液晶画面5上で時短残り回数の報知が開始されると共に、右打ちランプ49が点灯開始する。
When the failure (time saving A) is stopped and displayed in the non-time saving state, the number of remaining time saving starts on the
ハズレ(時短A)の停止表示に伴って装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせで停止表示される。「227」の組み合わせはハズレ(時短A)以外の特別図柄に伴って停止表示されないので、遊技者は装飾図柄55を見ることによってハズレ(時短A)であることを認識可能である。
The
ハズレ(時短B)は、変動開始時に低確非時短状態であるときに停止表示されると大当たり遊技および小当たり遊技を実行せずに低確微時短状態に移行させるハズレである。微時短回数は500回に設定される。低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短B)が停止表示されると、総アウトカウンタでの計数は継続するもののベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計測は停止し、リアルタイムベース値bLの算出も停止される。これに伴い、特別図柄の変動回数の計測が継続したまま新たに時短回数の計測が開始される。すなわち、遊技制御基板100のメインCPU100aは、次に特別図柄判定を行ったことに応じて、今回の特別図柄の変動回数に対して1加算すると共に時短回数を1減算することになる。
Loss (short working hours B) is a loss that shifts to a low-probable short-time state without executing a big winning game and a small winning game when it is stopped and displayed when it is in a low-probable short-time state at the start of fluctuation. The number of minute time reductions is set to 500 times. When the loss (time reduction B) is stopped in the low-probability time-saving state, the total out counter continues counting, but the base calculation out counter and the base calculation prize ball counter stop counting, and the real-time base value The calculation of bL is also stopped. Along with this, while the measurement of the number of fluctuations in the special symbol continues, the measurement of the number of times of time reduction is newly started. That is, the
低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短B)が停止表示されたときは非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)が停止表示されたときと異なり、液晶画面5上で時短残り回数の報知が開始されず右打ちランプ49の消灯が継続される。これにより、低確非時短状態と低確微時短状態とが区別がつき難くできる。
When the loss (time saving B) is stopped and displayed in the low probability non-time saving state, unlike when the loss (time saving A) is stopped and displayed in the non-time saving state, the notification of the remaining number of time saving is not started on the
ハズレ(時短B)の停止表示に伴って装飾図柄55は「459」の組み合わせで停止表示される。「459」の組み合わせはハズレ(時短B)以外の特別図柄に伴って停止表示されないので、遊技者は装飾図柄55を見ることによってハズレ(時短B)であることを認識可能である。
The
低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)が停止表示されると、次の普通図柄の変動表示からは低確時短用の変動時間で普通図柄が変動表示され、低確時短用の開放パターンで電動チューリップ17が開放される。低確時短用の普通図柄の変動時間は低確非時短用(及び低確微時短用)の普通図柄の変動時間よりも短い。また、低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)が停止表示されると、次の特別図柄の変動表示からは低確時短用の変動時間で特別図柄が変動表示される。低確時短用の特別図柄の変動時間は低確非時短用(及び低確微時短用)の特別図柄の変動時間よりも短い。
When the loss (shortening of working hours A) is stopped and displayed in the low-probability short-time state, the normal pattern is displayed fluctuating at the fluctuation time for low-probability short-time from the next normal pattern fluctuation display, and the open pattern for low-probability short working hours The
ハズレ(時短A)及びハズレ(時短B)は、変動開始時に低確微時短状態または低確時短状態(すなわち、時短遊技フラグがON)であるときに停止表示されると大当たり遊技および小当たり遊技を実行せず、且つ遊技状態も変化しないハズレとなる。すなわち、低確微時短状態である場合はハズレ(時短A)及びハズレ(時短B)が停止表示されると微時短回数が1減算されるだけで新たに時短回数が加算されることがない。そして、微時短回数が0でなければそのまま低確微時短状態が継続する。一方、微時短回数が0であるときは低確微時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行する。このため、例えば、低確微時短状態における微時短最終変動でハズレ(時短A)及びハズレ(時短B)が停止表示されると、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計測が再開し、リアルタイムベース値bLの算出も再開される。 Loss (time saving A) and loss (time saving B) are stopped when the low-probability small time-saving state or low-probability short-time state (that is, the time-saving game flag is ON) is displayed at the start of the fluctuation. is not executed, and the game state does not change, resulting in a loss. That is, in the case of a low-probability small time saving state, when the loss (time saving A) and the loss (time saving B) are stopped and displayed, the slight time saving number of times is only subtracted by 1, and the time saving number of times is not newly added. And if the number of times of minute time reduction is not 0, the low probability minute time reduction state continues as it is. On the other hand, when the minute number of times of working hours is 0, it shifts from the low-probable little working hours state to the low-probable non-working hours saving state. For this reason, for example, when the loss (time reduction A) and loss (time reduction B) are stopped and displayed due to the slight time reduction final fluctuation in the low probability small time reduction state, the measurement with the base calculation out counter and the base calculation prize ball counter is performed. Calculation of the real-time base value bL is also resumed.
また、低確時短状態である場合はハズレ(時短A)及びハズレ(時短B)が停止表示されると時短回数が1減算されるだけで新たに時短回数が加算されることがない。そして、時短回数が0でなければそのまま低確時短状態が継続する。一方、時短回数が0であるときは低確時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行する。このため、例えば、低確時短状態における時短最終変動でハズレ(時短A)及びハズレ(時短B)が停止表示されると、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計測が再開し、リアルタイムベース値bLの算出も再開される。 Further, in the low-probability time-saving state, if the failure (time-saving A) and the failure (time-saving B) are stopped and displayed, the number of times of time-saving is only subtracted by 1, and the number of times of time-saving is not newly added. If the number of times of shortening working hours is not 0, the low probability of shortening working hours continues as it is. On the other hand, when the number of times of time saving is 0, the state is shifted from the low-probability of working-time saving state to the low-probability of working-time saving state. For this reason, for example, when the loss (time reduction A) and loss (time reduction B) are stopped and displayed in the time saving final fluctuation in the low probability time saving state, the measurement with the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation restarts. , the calculation of the real-time base value bL is also resumed.
低確非時短状態では、遊技者は大当たりとハズレ(時短A)とによって低確時短状態へと移行することを目指せるのに対し、低確微時短状態では、遊技者は基本的には大当たりによって低確時短状態へと移行することを目指す。低確非時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率は大当たり当選確率とハズレ(時短A)となる確率との合算であるのに対し、低確微時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率は大当たり当選確率のみである。よって、低確非時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率は低確微時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率よりも高い。このため、低確非時短状態は低確微時短状態に比べて低確時短状態に移行し易く遊技者に有利である。これにより、第1実施形態では初期状態(例えば、設定変更後、又はRWMクリア後)において相対的に有利な遊技状態で遊技を開始できるという遊技性を提供できる。 In the low-probability short-time state, the player can aim to transition to the low-probability short-time state by a big hit and a loss (time-saving A), whereas in the low-probability short-time state, the player basically hits Aim to transition to a low-probability short-time state by The probability of transition to a low-probability short-time state in a low-probability short-time state is the sum of the probability of winning a jackpot and the probability of losing (short-time A), while the probability of transition to a low-probability short-time state in a low-probability short-time state is only the jackpot winning probability. Therefore, the transition probability to the low probability short working hours state in the low probability unprobable short working hours state is higher than the probability of transition to the low probability short working hours state in the low probability small short working hours state. For this reason, the low-probability short working hours state is advantageous to the player because it is easier to shift to the low-probable short working hours state than the low-probability small working hours state. As a result, in the first embodiment, it is possible to provide the game property that the game can be started in a relatively advantageous game state in the initial state (for example, after the setting is changed or after the RWM is cleared).
低確微時短状態に移行した場合、微時短回数が終了すると遊技者にとってより有利な低確非時短状態に移行する。なお、微時短回数を500回に設定するハズレ(時短B)に加えて、微時短回数を99回に設定するハズレを設けてもよい。低確微時短状態に移行してから連続して99回ハズレとなると、その後に微時短回数が0回になるまで連続してハズレた場合は必ず低確非時短状態に移行する。連続してハズレになっても低確非時短状態に移行できるので、遊技者に対して低確非時短状態を楽しみにしながら遊技を継続する動機を与えることが可能である。 In the case of shifting to the low-probability small time-saving state, when the number of times of small time-saving is completed, the game shifts to the low-probability non-working-time-saving state more advantageous for the player. In addition to the failure (time saving B) in which the number of times of slight time reduction is set to 500 times, a failure in which the number of times of slight time reduction is set to 99 times may be provided. When the player loses 99 times continuously after shifting to the low-probability small time-saving state, and when the number of times of small time-saving becomes 0 times after that, it always shifts to the low-probability non-time-saving state. Since it is possible to shift to the low-probability unreduced time-saving state even if there are consecutive losses, it is possible to give the player a motivation to continue the game while looking forward to the low-probability unreduced working-time state.
なお、図15に例示するように、第1実施形態において時短非遊技状態でハズレ(時短)となる確率は相対的に非常に高くてもよい。図15の例では約1/1の確率でハズレ(時短)となる。すなわち、図15に例示する構成では低確非時短状態において第1特別図柄判定が行われると基本的には低確時短状態または低確微時短状態に移行することになる。これにより、例えば低確時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行した直後(例えば1回目)の第1特別図柄判定によって相対的に高い確率で低確時短状態に移行できる。よって、一旦低確非時短状態を介しているものの低確時短状態が繋がって見えるので、結果として一旦低確非時短状態を介していても低確時短状態における大当たりが繋がって見えるという遊技性を提供できる。 In addition, as illustrated in FIG. 15, the probability of losing (time saving) in the time saving non-gaming state in the first embodiment may be relatively very high. In the example of FIG. 15, there is a probability of about 1/1 that it will be lost (time saving). That is, in the configuration illustrated in FIG. 15, when the first special symbol determination is performed in the low-probability non-time-saving state, it basically shifts to the low-probability small-time-saving state or the low-probability small-time-saving state. As a result, for example, it is possible to shift to the low-probability short working hours state with a relatively high probability by the first special symbol determination immediately after shifting from the low-probable short working hours state to the low-probable non-short working hours state (for example, the first time). Therefore, although the low-probability short working hours state is once passed through, the low-probable short-time working conditions appear to be connected. can provide.
図16は、第1実施形態における第1特別図柄の変動パターン(変動時間群)について説明するための説明図である。第1特別図柄の変動パターンにおいて特徴的な点は、低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)においてハズレ(時短A又はB)の変動時間の方が通常のハズレの変動時間よりも長いものが選択され易い点である。なお、ハズレ(時短A又はB)が停止表示される時間は通常のハズレが停止表示される時間と同じであるが、ハズレ(時短A又はB)の方が通常のハズレよりも停止表示される時間が長くてもよいし短くてもよい。 FIG. 16 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the variation pattern (variation time group) of the first special symbol in the first embodiment. The characteristic point in the variation pattern of the first special symbol is that the variation time of the loss (time reduction A or B) in the low probability non-time saving state (and the low probability small time saving state) is longer than the normal loss It is a point that things are easy to be selected. In addition, the time during which the loss (time saving A or B) is stopped and displayed is the same as the time during which the normal loss is stopped and displayed, but the loss (time saving A or B) is stopped and displayed more than the normal loss. The time can be long or short.
低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)においてハズレ(時短A)とハズレ(時短B)とは第1特別図柄の変動時間がほとんど変わらず、第1特別図柄の変動表示に伴って実行される演出も似通っている。これにより、第1特別図柄の変動時間および実行される演出によってハズレ(時短A)であるかハズレ(時短B)であるかを認識し難くできる。なお、第1特別図柄の変動時間としてハズレ(時短A)確定のもの、及びハズレ(時短B)確定のものがあってもよい。また、第1特別図柄の変動表示に伴って実行される演出にはハズレ(時短A)確定のもの、及びハズレ(時短B)確定のものがあってもよい。また、ハズレ(時短A)よりもハズレ(時短B)の方が第1特別図柄の変動時間が短くてもよいし長くてもよい。 In the low-probability non-time-saving state (and low-probability small time-saving state), the loss (time-saving A) and loss (time-saving B) are almost the same as the first special symbol's fluctuation time, and are executed along with the variable display of the first special symbol. The production is also similar. Thereby, it is possible to make it difficult to recognize whether it is a loss (time saving A) or a loss (time saving B) depending on the variation time of the first special symbol and the effect to be executed. It should be noted that, as the fluctuation time of the first special symbol, there may be a loss (time saving A) fixed one and a loss (time saving B) fixed one. In addition, the effect executed in conjunction with the variable display of the first special symbol may include a determination of loss (shortening of time A) and a determination of loss (shortening of time B). Further, the fluctuation time of the first special symbol may be shorter or longer in the loss (time saving B) than in the loss (time saving A).
低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示に伴って実行される演出は、装飾図柄55の組み合わせを除き大当たり及び通常のハズレの変動表示に伴って実行される演出と同じである。これにより、第1特別図柄の変動表示に伴って実行される演出によって大当たり、通常のハズレ、及びハズレ(時短A及びB)の何れであるかを認識し難くできる。
The effect that is executed with the variable display of the loss (time reduction A and B) in the low-probability non-time-saving state (and the low-probability small time-saving state) is accompanied by the variable display of the big hit and normal loss except for the combination of the
低確時短状態において、第1特別図柄の変動パターンにおいて特徴的な点は、ハズレ(時短A又はB)の変動時間は通常のハズレの変動時間と同じであるという点である。低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示に伴って実行される演出は、低確時短状態において通常のハズレの変動表示に伴って実行される演出と同様に単にハズレを報知する演出である。ここで、低確時短状態における第1特別図柄の変動パターンH113は、低確時短状態における第2特別図柄の変動パターンH201と同じ変動時間である。変動パターンH113の変動表示に伴って実行される演出は、変動パターンH201の変動表示に伴って実行される演出(具体的には、単にハズレを報知する演出)と同じである。 In the low probability time saving state, the characteristic point in the variation pattern of the first special symbol is that the variation time of losing (time saving A or B) is the same as the normal losing variation time. The performance executed with the variable display of failures (time saving A and B) in the low-probability short working hours state simply informs the failures in the same way as the performance performed with the normal variable display of failures in the low-probability short working hours state. It is a performance. Here, the variation pattern H113 of the first special symbol in the low probability time saving state is the same variation time as the second special symbol variation pattern H201 in the low probability time saving state. The effect that is executed with the variable display of the variable pattern H113 is the same as the effect that is executed with the variable display of the variable pattern H201 (specifically, the effect that merely notifies of a failure).
低確時短状態および低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55は、低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55の組み合わせと同じである。すなわち、低確時短状態および低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示で停止表示される装飾図柄55は、ハズレであって且つ遊技者に有利となることを示唆する組み合わせである。しかしながら、低確時短状態および低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)が停止表示されても遊技状態は変化しない。このため、低確時短状態および低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55は通常のハズレの変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55と同様に単にハズレを示す組み合わせであって且つ遊技者に有利となることを示唆しない組み合わせでもよい。すなわち、低確時短状態および低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55は、低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55の組み合わせと異なってもよい。
The
図17は、第1実施形態における第2特別図柄の変動パターン(変動時間群)について説明するための説明図である。第2特別図柄の変動パターンにおいて特徴的な点は、低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)の第1特別図柄の変動時間よりも相対的に短い点である。 FIG. 17 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the variation pattern (variation time group) of the second special symbol in the first embodiment. A characteristic point in the variation pattern of the second special symbol is that it is relatively shorter than the variation time of the first special symbol in the low-probability non-time-saving state (and low-probability small time-saving state).
[遊技制御基板100によるメイン処理]
図18は、遊技制御基板100において実行されるメイン処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図18に例示するように、メイン処理では、まず初期設定を行う(ステップMS1)。初期設定では、例えば割り込み時間の設定、メインCPU100aの設定、各種のフラグ及びカウンタ等のリセットを行う。フラグの初期値は「OFF」であり、カウンタの初期値は「0」である。また、初期設定では、設定変更に応じた処理、設定確認に応じた処理、及びRWMクリアに応じた処理を実行する。初期設定は、電源投入後に一度だけ実行され、以降は実行されない。
[Main processing by game control board 100]
FIG. 18 is a flowchart showing an example of main processing executed in the
初期設定(ステップMS2)に続いて、割込みを禁止し(ステップMS2)、普通図柄判定および特別図柄判定に用いる各種乱数を更新する乱数更新処理(ステップMS3))を実行する。この乱数更新処理では各種乱数を1加算して更新する。各種乱数は上限値に達すると「1」に戻って再び加算される。なお、各種乱数の周期初期値は「1」以外でもよいし、ランダムに変更されてもよい。 After initial setting (step MS2), interrupt is prohibited (step MS2), and random number update processing (step MS3) for updating various random numbers used for normal symbol determination and special symbol determination is executed. In this random number update process, 1 is added to each random number for update. When each random number reaches the upper limit, it returns to "1" and is added again. The period initial value of various random numbers may be other than "1", or may be changed randomly.
乱数更新処理(ステップMS3)に続いて、割込みを許可する(ステップMS4)。割込み許可中は、遊技制御基板100においてタイマ割込み処理(ステップMS5)の実行が可能となる。タイマ割込み処理については図19を参照して後に詳述する。
After the random number update process (step MS3), interrupts are permitted (step MS4). While the interrupt is enabled, the
[遊技制御基板100によるタイマ割込み処理]
次に、図19を参照しつつ、遊技制御基板100において実行されるタイマ割込み処理について説明する。ここで、図19は、遊技制御基板100において実行されるタイマ割込み処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。遊技制御基板100は、電源投入時や電源断時等の特殊な場合を除く通常の動作時において、一定時間(例えば4ミリ秒)毎に定期的にタイマ割込みがかかるように設定されている。タイマ割込みが発生すると、遊技制御基板100は、図19に例示されている一連の処理を実行する。なお、図19~図27に示す処理は、メインROM100bに記憶されているプログラムに基づいてメインCPU100aが発行する命令に従って行われる。
[Timer interrupt processing by game control board 100]
Next, with reference to FIG. 19, timer interrupt processing executed in the
まず、遊技制御基板100のメインCPU100aは、図柄乱数、リーチ乱数、変動パターン乱数、及び普通図柄乱数をソフトウェアにより更新するための乱数更新処理を実行する(ステップS1A)。
First, the
例えば、各乱数は、このステップS1Aの処理が行われる毎に「1」加算される。なお、このステップS1Aの処理を行うカウンタとしてはループカウンタが使用されており、各乱数は、予め設定された最大値に達した後は「1」に戻されて更新される。なお、大当たり乱数をソフトウェアにより更新したり、乱数回路104を用いて生成した値とソフトウェアにより生成した値との演算によって各乱数を生成したりするように予め設定されていてもよい。 For example, each random number is incremented by "1" each time the process of step S1A is performed. A loop counter is used as the counter for performing the processing of step S1A, and each random number is returned to "1" and updated after reaching a preset maximum value. In addition, it may be set in advance so that the jackpot random number is updated by software, or each random number is generated by calculating a value generated using the random number circuit 104 and a value generated by software.
ステップS1Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、第1始動口11に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための第1始動口検出スイッチ45a、第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞したことを検出するための第2始動口検出スイッチ47a等の各スイッチから入力される検知信号の状態を判定するスイッチ処理を実行する(ステップS2A)。このスイッチ処理については、図20に基づいて後に詳述する。
Following the processing of step S1A, the
ステップS2Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄判定を実行し、第1特別図柄表示器41又は第2特別図柄表示器42に特別図柄を変動表示させてから特別図柄判定の判定結果を示す特別図柄を停止表示させる処理等を含む特別図柄処理を実行する(ステップS3A)。特別図柄処理では、大当たりであるか否か、大当たり種別、小当たり種別、ハズレ種別、特別図柄の変動パターン等が決定される。この特別図柄処理については、図23に基づいて後に詳述する。
Following the processing of step S2A, the
ステップS3Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、普通図柄判定を実行し、普通図柄表示器45に普通図柄を変動表示させてから普通図柄判定の結果を示す普通図柄を停止表示させる処理等を含む普通図柄処理を実行する(ステップS4A)。この普通図柄処理については、図24に基づいて後に詳述する。
Following the process of step S3A, the
ステップS4Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、ステップS3Aの処理で小当たりであると判定した場合に、小入賞口開閉ソレノイド51cを制御して小入賞口19を開放する小入賞口開放制御処理を実行する(ステップS5A)。小入賞口開放制御処理は、小当たり遊技を制御する処理であり、小当たり遊技を実行すると判定されたことを示す特別図柄(小当たり図柄)が停止表示された場合に行われる。この小入賞口開放制御処理については、図37に基づいて後に詳述する。
Subsequent to the process of step S4A, the
ステップS5Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、ステップS3Aの処理で大当たりであると判定した場合に、大入賞口開閉ソレノイド51bを制御して大入賞口13を開放する大入賞口開放制御処理を実行する(ステップS6A)。この大入賞口開放制御処理については、図38に基づいて後に詳述する。
Subsequent to the processing of step S5A, the
ステップS6Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、遊技球の入賞に応じた賞球の払い出しを制御する賞球処理を実行する(ステップS7A)。ステップS7Aに続いて、メインCPU100aは、遊技球計数処理を実行する(ステップS8A)。具体的には、低確非時短状態中における各種入賞口(具体的には、一般入賞口、大入賞口、小入賞口、始動口)への遊技球の入賞に基づく賞球の払出数であるベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計測、低確非時短状態中にアウト球検出スイッチ39aで検出された遊技球数であるベース算出用アウトカウンタでの計測、遊技状態に関わらずアウト球検出スイッチ39aで検出された遊技球数である総アウトカウンタでの計測を行う。
Following the processing of step S6A, the
なお、総アウトカウンタの値、ベース算出用アウトカウンタの値、及びベース算出用賞球カウンタの値は設定値とは無関係な遊技情報であり、設定値を変更しても影響を受けない。これにより、設定値の影響を排除して性能表示(ベース値表示)を行うことが可能である。 The value of the total out counter, the value of the out counter for base calculation, and the value of the prize ball counter for base calculation are game information unrelated to the set values, and are not affected by changing the set values. As a result, it is possible to perform performance display (base value display) while eliminating the influence of set values.
ステップS8Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、性能情報算出・設定処理を実行する(ステップS9A)。具体的には、総アウトによって区切られる現在の区間におけるベース値bLを算出し記憶する。また、メインCPU110aは、ベース値bL及びベース値b1~b3を性能表示器113に表示させる。
Following the processing of step S8A, the
ステップS9Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、ステップS7A以前の処理ステップにおいてメインRAM100cにセット(格納)された各種コマンドや特別図柄の変動表示に伴う演出の内容を決定するために必要な情報を演出制御基板130に送信する送信処理を実行する(ステップS10A)。
Following the processing of step S9A, the
[遊技制御基板100によるスイッチ処理]
図20は、図19のステップS2Aにおけるスイッチ処理の詳細フローチャートである。ステップS1Aの処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、ゲート検出スイッチ44aからの検出信号があるか否かを判定する(ステップS2A1)。ゲート検出スイッチ44aからの検出信号がない場合(ステップS2A1:NO)、微時短状態であるか否かを判定する(ステップS2A2)。微時短状態である場合(ステップS2A2:YES)、一般入賞口検出スイッチ43aからの検出信号があるか否かを判定する(ステップS2A3)。
[Switch processing by game control board 100]
FIG. 20 is a detailed flowchart of the switch processing in step S2A of FIG. Following the processing of step S1A, the
ステップS2A3がYESである場合、又はステップS2A1がYESである場合、普通図柄の変動表示を待機中か否かを判定する(ステップS2A4)。普通図柄の変動表示を待機中とは、普通図柄の変動表示の実行中でも電動中に17の開放中でもない状態である。普通図柄の変動表示を待機中であれば(ステップS2A4:YES)、普通図柄乱数を取得してメインメインRAM100caに記憶する(ステップS2A5)。 When step S2A3 is YES, or when step S2A1 is YES, it is determined whether or not the variable display of normal symbols is on standby (step S2A4). Standby for variable display of normal symbols means a state in which variable display of normal symbols is not being executed and 17 is not being opened during electric operation. If the variable display of normal symbols is on standby (step S2A4: YES), a normal symbol random number is acquired and stored in the main RAM 100ca (step S2A5).
ステップS2A2がNOである場合、ステップS2A3がNOである場合、又はステップS2A4がNOである場合、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aからの検知信号の入力の有無を監視して、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aからの検知信号が入力された時点の特別図柄判定用の乱数(大当たり乱数、図柄乱数、リーチ乱数、及び変動パターン乱数)を取得する処理等を含む第1始動口スイッチ処理を実行する(ステップS2A6)。この第1始動口スイッチ処理については、図21に基づいて後に詳述する。
When step S2A2 is NO, when step S2A3 is NO, or when step S2A4 is NO, the presence or absence of the detection signal input from the first starting
次に、メインCPU100aは、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aからの検知信号の入力の有無を監視して、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aからの検知信号が入力された時点の特別図柄判定用の乱数を取得する処理等を含む第2始動口スイッチ処理を実行する(ステップS2A7)。この第2始動口スイッチ処理については、図22に基づいて後に詳述する。
Next, the
[遊技制御基板100による第1始動口スイッチ処理]
図21は、図20のステップS2A6における第1始動口スイッチ処理の詳細フローチャートである。図21に例示されるように、メインCPU100aは、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aからの検知信号が入力されたか否かに基づいて、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aが「ON」になったか否かを判定する(ステップS2101)。例えば、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aが「ON」になったことを示すON信号が入力された場合に、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aが「ON」になったと判定される。
[First start opening switch processing by game control board 100]
FIG. 21 is a detailed flowchart of the first start opening switch process in step S2A6 of FIG. As illustrated in FIG. 21, the
メインCPU100aは、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aが「ON」になったと判定した場合(ステップS2101:YES)、第1特別図柄判定に使用する取得情報として、大当たり乱数、図柄乱数、リーチ乱数、及び変動パターン乱数を取得する(ステップS2102~2105)。
When the
次に、メインCPU100aは、メインRAM100cに記憶されている第1特別図柄判定の保留数U1が、メインROM100bに記憶されている第1特別図柄判定の最大保留数Umax1(例えば「4」)未満であるか否かを判定する(ステップS2106)。
Next, the
メインCPU100aは、保留数U1が最大保留数Umax1未満であると判定した場合(ステップS2106:YES)、保留数U1の値を「1」加算した値に更新する(ステップS2107)。
When determining that the number of reservations U1 is less than the maximum number of reservations Umax1 (step S2106: YES), the
ステップS2107の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、低確時短状態であるか否かを判定する(ステップS2108)。メインCPU100aは、低確時短状態ではないと判定した場合(ステップS2108:NO)、事前判定処理を実行する(ステップS2109)。具体的には、メインCPU100aは、後述する大当たり判定処理(図25参照)や変動パターン決定処理(図26参照)に先立って、ステップS2102~2105の処理によって取得された取得情報に基づいて、大当たりと判定されるか否か及び変動パターンがどの種別に決定されることになるか等を事前判定する。
Following the processing of step S2107, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS2109の処理に続いて、ステップS2109の事前判定処理によって得られた事前判定情報と、ステップS2102~2105の処理で取得した各種乱数とをメインRAM100cにおける保留記憶領域に格納する(ステップS2110)。
Following the processing of step S2109, the
メインCPU100aは、低確時短状態であると判定した場合(ステップS2108:YES)、ステップS2102~2105の処理で取得した各種乱数をメインRAM100cにおける保留記憶領域に格納する(ステップS2111)。
When the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS2110又はステップS2111の処理を実行した場合、第1特別図柄判定に係る保留コマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS2112)。この保留コマンドは、第1特別図柄判定が保留されたことを通知するコマンドであって、ステップS2109の処理で得られた事前判定情報を含むものである。保留コマンドは、ステップS10Aの送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信される。
When the
ステップS2112の処理を実行した場合、第1始動口検出スイッチ45aが「ON」になっていないと判定した場合(ステップS2101:NO)、又は、保留数U1が最大保留数Umax1未満でないと判定した場合(ステップS2106:NO)、メインCPU100aは図21に示す処理を終了する。
When the process of step S2112 is executed, when it is determined that the first starting
[遊技制御基板100による第2始動口スイッチ処理]
図22は、図20のステップS2A7における第2始動口スイッチ処理の詳細フローチャートである。図22に例示されるように、メインCPU100aは、ステップS21の第1始動口スイッチ処理に続いて、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aからの検知信号が入力されたか否かに基づいて、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aが「ON」になったか否かを判定する(ステップS2201)。例えば、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aが「ON」になったことを示すON信号が入力された場合に、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aが「ON」になったと判定される。
[Second start opening switch processing by game control board 100]
FIG. 22 is a detailed flowchart of the second start opening switch process in step S2A7 of FIG. As exemplified in FIG. 22, the
メインCPU100aは、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aが「ON」になったと判定した場合(ステップS2201:YES)、第2特別図柄判定に使用する取得情報として、大当たり乱数、図柄乱数、リーチ乱数、及び変動パターン乱数を取得する(ステップS2202~2205)。
When the
次に、メインCPU100aは、メインRAM100cに記憶されている第2特別図柄判定の保留数U2が、メインROM100bに記憶されている第2特別図柄判定の最大保留数Umax2(例えば「4」)未満であるか否かを判定する(ステップS2206)。
Next, the
メインCPU100aは、保留数U2が最大保留数Umax2未満であると判定した場合(ステップS2206:YES)、保留数U2の値を「1」加算した値に更新する(ステップS2207)。
When determining that the number of reservations U2 is less than the maximum number of reservations Umax2 (step S2206: YES), the
ステップS2207の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは事前判定処理を実行する(ステップS2208)。なお、第2始動口12は低確時短状態(すなわち時短遊技フラグが「ON」である場合)にし入賞しないが、時短遊技フラグが「ON」である場合にのみ事前判定処理を実行してもよい。
Following the processing of step S2207, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS2208の処理に続いて、ステップS2208の事前判定処理によって得られた事前判定情報と、ステップS2202~2205の処理で取得した各種乱数とをメインRAM100cにおける保留記憶領域に格納する(ステップS2209)。
Following the process of step S2208, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS2209の処理に続いて、第2特別図柄判定に係る保留コマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS2110)。この保留コマンドは、第2特別図柄判定が保留されたことを通知するコマンドであって、ステップS2209の処理で得られた事前判定情報を含むものである。保留コマンドは、ステップS10Aの送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信される。
Following the processing of step S2209, the
ステップS2210の処理を実行した場合、第2始動口検出スイッチ47aが「ON」になっていないと判定した場合(ステップS2201:NO)、又は、保留数U2が最大保留数Umax2未満でないと判定した場合(ステップS2206:NO)、メインCPU100aは図22に示す処理を終了する。
If the process of step S2210 is executed, if it is determined that the second starting
[遊技制御基板100による特別図柄処理]
次に、図23を参照しつつ、遊技制御基板100によって実行される特別図柄処理の詳細について説明する。ここで、図23は、図19のステップS3Aにおける特別図柄処理の詳細フローチャートである。
[Special symbol processing by game control board 100]
Next, details of the special symbol processing executed by the
図23に例示されるように、メインCPU100aは、大当たり遊技中または小当たり遊技中であるか否かを判定する(ステップS301)。メインCPU100aは、例えば、メインRAM100cに記憶されている大当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されているか否かに基づいて、大当たり遊技中であるか否かを判定する。この大当たり遊技フラグは、大当たり遊技の実行中であるか否かを示すフラグであり、大当たり遊技の開始時に「ON」に設定され、大当たり遊技の終了時に「OFF」に設定される。また、メインCPU100aは、例えば、小当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されているか否かに基づいて、小当たり遊技中であるか否かを判定する。この小当たり遊技フラグは、メインRAM100cに記憶されている小当たり遊技の実行中であるか否かを示すフラグであり、小当たり遊技の開始時に「ON」に設定され、小当たり遊技の終了時に「OFF」に設定される。ここで、大当たり遊技中または小当たり遊技中であると判定された場合(ステップS301:YES)、ステップS4Aの普通図柄処理に処理が進められる。
As illustrated in FIG. 23, the
メインCPU100aは、大当たり遊技中ではないと判定した場合(ステップS301:NO)、特別図柄の変動表示中であるか否かを判定する(ステップS302)。ここで、特別図柄の変動表示中ではないと判定した場合(ステップS302:NO)、メインRAM100cに記憶されている第2特別図柄判定の保留数U2が「1」以上であるか否かを判定する(ステップS303)。ここで、保留数U2が「1」以上であると判定した場合(ステップS303:YES)、保留数U2を「1」減算した値に更新する(ステップS304)。
When the
メインCPU100aは、保留数U2が「1」以上ではないと判定した場合(ステップS303:NO)、メインRAM100cに記憶されている第1特別図柄判定の保留数U1が「1」以上であるか否かを判定する(ステップS305)。ここで、保留数U1が「1」以上ではないと判定された場合(ステップS305:NO)、ステップS4の普通図柄処理に処理が進められる。
When the
メインCPU100aは、保留数U1が「1」以上であると判定した場合(ステップS305:YES)、保留数U1を「1」減算した値に更新する(ステップS306)。
When the
ステップS304の処理又はステップS306の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、メインRAM100cの保留記憶領域に対するシフト処理を実行する(ステップS308)。具体的には、メインCPU100aは、ステップS304の処理に続いてシフト処理を実行する場合には、第2特別図柄判定用の保留記憶領域に記憶されている最先の取得情報を判定用記憶領域にシフトさせると共に、残りの取得情報を1エントリずつ上位にシフトさせる。判定用記憶領域は、特別図柄判定が実際に実行されるときにその特別図柄判定に使用される各種情報が記憶される記憶領域である。また、ステップS306の処理に続いてシフト処理を実行する場合には、第1特別図柄判定用の保留記憶領域に記憶されている最先の取得情報を判定用記憶領域にシフトさせると共に、残りの取得情報を1エントリずつ上位にシフトさせる。
Following the processing of step S304 or the processing of step S306, the
ステップS308の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、判定用記憶領域に記憶されている乱数に基づいて、大当たり判定処理を実行する(ステップS309)。この大当たり判定処理については、図25に基づいて後に詳述する。
Following the process of step S308, the
ステップS309の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄の変動パターンを選択する変動パターン決定処理を実行する(ステップS310)。この変動パターン決定処理については、図26に基づいて後に詳述する。
Following the process of step S309, the
ステップS310の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、ステップS309の処理で決定した特別図柄の設定情報、この特別図柄の設定情報が第1特別図柄判定に係るものであるか或いは第2特別図柄判定に係るものであるかを示す情報、ステップS310の処理で決定した変動パターンの設定情報、遊技機1の遊技状態に関する情報等を含む変動開始コマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS311)。
Following the process of step S310, the
この変動開始コマンドは、特別図柄の変動表示に伴う演出の開始を指示するコマンドであって、ステップS10Aの送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信される。これにより、液晶画面5における装飾図柄55の変動表示等が開始されることになる。
This variation start command is a command for instructing the start of the effect accompanying the variable display of the special symbol, and is transmitted to the
ステップS311の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、ステップS311の処理でセットした変動開始コマンドに含まれている変動パターンの設定情報に基づいて、特別図柄の変動表示を開始する(ステップS312)。その際、判定用記憶領域に第1特別図柄判定に係る取得情報(乱数)が記憶された状態でステップS309~311の処理が行われた場合には、第1特別図柄表示器41において特別図柄の変動表示を開始する。一方、第2特別図柄判定に係る取得情報(乱数)が記憶された状態でステップS309~311の処理が行われた場合には、第2特別図柄表示器42において特別図柄の変動表示を開始する。
Following the processing of step S311, the
次に、メインCPU100aは、ステップS312における変動表示を開始してからの経過時間である変動時間の計測を開始する(ステップS313)。そして、メインCPU100aは、客待ち状態フラグをクリアする(ステップS314)。
Next, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS314の処理を実行した場合、又は特別図柄の変動表示中であると判定した場合(ステップS302:YES)、ステップS313における変動時間の計測開始から、ステップS310の処理によって選択された変動パターンに対応する変動時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS315)。ここで、変動時間が経過していないと判定された場合(ステップS315:NO)、ステップS4の普通図柄処理に処理が進められる。
When the
メインCPU100aは、変動時間が経過したと判定した場合(ステップS315:YES)、第1特別図柄表示器41又は第2特別図柄表示器42に特別図柄判定の判定結果を示す特別図柄が停止表示されることを通知する図柄確定コマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS316)。この図柄確定コマンドは、ステップS9における送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信される。これにより、液晶画面5に変動表示されていた装飾図柄55を特別図柄判定の判定結果を示す態様で停止表示させる処理等が行われることになる。
When the
ステップS316の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、ステップS312の処理で開始した特別図柄の変動表示を終了させる(ステップS317)。具体的には、ステップS309の処理で決定した特別図柄(大当たり図柄又はハズレ図柄)を、変動表示させていた特別図柄表示器に停止表示させる。なお、この特別図柄の停止表示は、少なくとも所定の図柄確定時間(例えば1秒)が経過するまで継続される。
Following the process of step S316, the
このように、メインCPU100aは、第1特別図柄表示器41又は第2特別図柄表示器42に特別図柄を変動表示させてから大当たり判定処理の判定結果を示す特別図柄を第1特別図柄表示器41又は第2特別図柄表示器42に停止表示させる。
In this way, the
ステップS317の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、上記ステップS313の処理で計測を開始した変動時間をリセットし(ステップS318)、大当たりである場合に大当たり遊技を開始させ、小当たりである場合に小当たり遊技を開始させるためのオープニングコマンドをセットする処理等を含む停止中処理を実行する(ステップS319)。このオープニングコマンドがステップS9A(図19参照)の送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信されると、演出制御基板130のサブCPU130aは、例えば、大当たり(又は小当たり)の種類に対応したOP演出の開始を指示するOP演出開始コマンドをサブRAM130cにセットする。このOP演出開始コマンドがステップS30(図39参照)の送信処理によって画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150に送信されたことに応じてOP演出が開始される。停止中処理について、図27に基づいては後に詳述する。
Following the process of step S317, the
ステップS305でNOと判定された場合、客待ち状態であることを示す客待ち状態フラグがあるか否かを判定する(ステップS320)。客待ち状態フラグがない場合、客待ち状態フラグをセットする(ステップS321)。客待ち状態フラグがセットされるとステップS10Aの送信処理によって遊技制御基板100から演出制御基板130に対して客待ち状態指定コマンドが送信される。演出制御基板130は客待ち状態指定コマンドを受信したことに応じて客待ち状態であることを示す演出(例えば、音量操作可能であることを示す画像の表示)を開始する。
If NO in step S305, it is determined whether or not there is a customer waiting state flag indicating that the customer is in a waiting state (step S320). If there is no customer waiting flag, the customer waiting flag is set (step S321). When the customer waiting state flag is set, a customer waiting state designation command is transmitted from the
[遊技制御基板100による普通図柄判定処理]
図24は、図19のステップS4Aにおける普通図柄処理の詳細フローチャートである。メインCPU100aは、電動チューリップ17の作動中か否かを判定する(ステップS4A1)。電動チューリップ17の作動中でなければ(ステップS4A1:NO)、普通図柄の停止表示中(普通図柄の停止時間の開始から終了まで)か否かを判定する(ステップS4A2)。普通図柄の停止表示中でなければ(ステップS4A2:NO)、普通図柄の変動表示中か否かを判定する(ステップS4A3)。普通図柄の変動表示中でなければ(ステップS4A3:NO)、普通図柄乱数の記憶があるか否かを判定する(ステップS4A4)。普通図柄乱数の記憶がなければ(ステップS4A4:NO)、普通図柄判定処理を終了する。
[Normal symbol determination processing by game control board 100]
FIG. 24 is a detailed flowchart of normal symbol processing in step S4A of FIG. The
ステップS4A4でYESの場合、遊技状態に応じて当落と普通図柄と変動時間とを決定し(ステップS4A5)、普通図柄の変動表示を開始する(ステップS4A6)。なお、これに伴い、演出制御基板130に対して普通図柄の変動開始を知らせるために普通図柄変動開始コマンドをセットする。
In the case of YES in step S4A4, the winning, the normal design and the variation time are determined according to the game state (step S4A5), and the variable display of the normal design is started (step S4A6). Along with this, a normal symbol variation start command is set to inform the
普通図柄の変動表示中であれば(ステップS4A3:YES)、普通図柄の変動時間が経過したか否か判定し(ステップS4A7)、経過していなければ処理を終える。一方、ステップS4A7でNOの場合、普通図柄を、普通図柄判定の結果に応じた表示結果で停止させる(ステップS4A8)。なお、これに伴い、演出制御基板130に対して普通図柄の変動停止を知らせるために普通図柄変動停止コマンドをセットする。そして、メインCPU100aは普通図柄の停止時間(例えば0.5秒)をセットする(ステップS4A9)。
If the variable display of the normal symbols is in progress (step S4A3: YES), it is determined whether or not the variable time of the normal symbols has passed (step S4A7). On the other hand, in the case of NO in step S4A7, the normal design is stopped with the display result corresponding to the result of the normal design determination (step S4A8). Along with this, a normal symbol variation stop command is set to inform the
普通図柄の停止表示中であれば(ステップS4A2:YES)、普通図柄の停止時間が経過したか否か判定し(ステップS4A11)、経過していなければ処理を終える。一方、経過していれば(ステップS4A11:YES)、当たりか否かを判定し(ステップS4A12)、当たりでなければ本処理を終える(ステップS4A12:NO)。 If normal symbols are stopped and displayed (step S4A2: YES), it is determined whether or not the normal symbol stop time has elapsed (step S4A11), and if not, the process ends. On the other hand, if it has passed (step S4A11: YES), it is determined whether or not it is a hit (step S4A12), and if it is not a hit, the process ends (step S4A12: NO).
当たりであれば(ステップS4A12:NO)、電動チューリップ17の開放パターンをセットし(ステップS4A13)、セットした開放パターンに従って、電動チューリップ17を作動させる(ステップS4A14)。
If it is a hit (step S4A12: NO), the opening pattern of the
電動チューリップ17の作動中であれば(ステップS4A15)、電動チューリップ17の作動時間が経過したか否かを判定し(ステップS4A15)、経過していなければ処理を終える(ステップS4A15:NO)。一方、経過していれば(ステップS4A15:NO)、電動チューリップ17の作動を終了させる(ステップS4A16)。
If the
[遊技制御基板100による大当たり判定処理]
図25は、図23のステップS309における大当たり判定処理の詳細フローチャートである。メインCPU100aは、判定用記憶領域に記憶された大当たり乱数に基づいて大当たり判定を実行する(ステップS3091)。例えば、大当たり判定テーブルには、大当たり乱数と比較される判定値が大当たり、小当たり、又はハズレに予め割り当てられている。メインCPU100aは、図21のステップS2102の処理(又は図22のステップS2202の処理)で取得した大当たり乱数の値が、メインRAM100cにセットされた大当たり判定テーブルに定められた判定値の何れと一致するかに基づいて、大当たりであるか否かを判定する。
[Big hit determination processing by game control board 100]
FIG. 25 is a detailed flowchart of the big hit determination process in step S309 of FIG. The
ステップS3091の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、大当たり判定の判定結果が大当たりであるか否かを判定する(ステップS3092)。ここで、大当たりであると判定された場合(ステップS3092:YES)、メインCPU100aは、メインROM100bに予め記憶されている図柄決定テーブルを参照して、ステップS3091の大当たり判定に使用された大当たり乱数と一緒に判定用記憶領域に記憶されている図柄乱数に基づいて大当たり図柄の種類を決定し、その設定情報をメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3093)。大当たり図柄の種類が決定されることによって、大当たりの種類が決定されることになる。具体的には、例えば、図柄乱数が第1特別図柄判定に係るものである場合には、メインCPU100aは、その図柄乱数が、第1始動口用図柄決定テーブル(不図示)に規定されているどの判定値と一致するかに基づいて、大当たり図柄を決定する。また、図柄乱数が第2特別図柄判定に係るものである場合には、メインCPU100aは、その図柄乱数が、第2始動口用図柄決定テーブル(不図示)に規定されているどの判定値と一致するかに基づいて、大当たり図柄を決定する。
Following the process of step S3091, the
一方、メインCPU100aは、大当たりではないと判定した場合(ステップS3092:NO)、メインCPU100aは、小当たりであるか否かを判定する(ステップS3094)。ここで、小当たりであると判定された場合(ステップS3094:YES)、メインCPU100aは、メインROM100bに予め記憶されている図柄決定テーブルを参照して、図柄乱数に基づいて小当たり図柄の種類を決定し、その設定情報をメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3095)。
On the other hand, when the
一方、メインCPU100aは、小当たりではないと判定した場合(ステップS3094:NO)、大当たり遊技を実行せずに微時短状態または時短状態を発生させる特定のハズレ(時短)であるか否かを判定する(ステップS3096)。ステップS3096でNOの場合、通常の図柄の設定情報をメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3097)。これにより、ステップS317の処理において、第1特別図柄表示器41又は第2特別図柄表示器42に通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。この場合、大当たり遊技は行われず、微時短状態および時短状態は発生されない。
On the other hand, when the
ステップS3096でYESの場合、メインCPU100aは、図柄乱数に基づいてハズレ図柄の種類を決定し、その設定情報をメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3098)。これにより、ステップS317の処理において、第1特別図柄表示器41又は第2特別図柄表示器42に特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。この場合、大当たり遊技は行われず、遊技状態に応じて微時短状態または時短状態が発生される場合がある。
In the case of YES in step S3096, the
[遊技制御基板100による変動パターン決定処理]
図26は、図23のステップS310における変動パターン決定処理の詳細フローチャートである。メインCPU100aは、時短遊技フラグが「ON」であるか否かを判定する(ステップS3101)。
[Variation pattern determination processing by game control board 100]
FIG. 26 is a detailed flowchart of the variation pattern determination process in step S310 of FIG. The
ステップS3101の処理でNOと判定された場合、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄の種類に応じた時短遊技フラグOFF用の変動パターンテーブルをメインROM100bから読み出してメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3102)。なお、変動パターンテーブルは、特別図柄の種類と、特別図柄の変動パターンと、変動パターン乱数と比較するための判定値と、(ハズレの場合はさらに特別図柄判定の保留数)が対応付けられたテーブルであり、遊技状態毎にメインROM100bに予め記憶されているテーブルである。
When it is determined as NO in the process of step S3101, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS3102の処理でセットしたテーブルを参照して変動パターンを決定する(ステップS3103)。そして、特別図柄の変動回数に「1」加算する(ステップS3104)。
The
ステップS3101の処理でYESと判定された場合、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄の種類に応じた時短遊技フラグON用の変動パターンテーブルをメインROM100bから読み出してメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3105)。そして、メインCPU100aは、ステップS3105の処理でセットしたテーブルを参照して変動パターンを決定する(ステップS3106)。変動パターンの設定情報は、上述したステップS3091の大当たり判定処理によってメインRAM100cにセットされた特別図柄の設定情報と共に変動開始コマンドに含められて、ステップS10Aの送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信される。以上でメインCPU100aは図26に示す処理を終了する。
When it is determined as YES in the process of step S3101, the
[遊技制御基板100による停止中処理]
図27は、図23のステップS319における停止中処理の詳細フローチャートである。図27に例示されるように、メインCPU100aは、ステップS3091の大当たり判定処理の結果に基づいて、特別図柄判定の結果が大当たりか否かを判定する(ステップS3191A)。そして、メインCPU100aは、大当たりと判定した場合(ステップS3191A:YES)、メインRAM100cに記憶されている大当たり遊技フラグを「ON」に設定する(ステップS3192A)。
[Stopping process by game control board 100]
FIG. 27 is a detailed flowchart of the stop processing in step S319 of FIG. As illustrated in FIG. 27, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS3192Aの処理に続いて、メインRAM100cに記憶されている確変遊技フラグを「OFF」に設定すると共に各種時短回数をクリアする(ステップS3193A)。そして、メインCPU100aは、大当たり用のオープニングコマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3194A)。このオープニングコマンドは、大当たり遊技が開始されることを示すオープニング演出を演出制御基板130に行わせるためのコマンドであり、当該コマンドは、図10のステップS10Aの出力処理が実行されることによって演出制御基板130へ送信される。
Following the processing of step S3192A, the
一方、メインCPU100aは、大当たりでないと判定した場合(ステップS3191A:NO)、時短遊技フラグが「ON」か否かを判定する(ステップS3195A)。時短遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されていると判定した場合(ステップS3195A:YES)、第1特別図柄が停止表示されたか否かを判定する(ステップS3196A)。ステップS3196AでYESの場合、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1を「1」減算すると共に、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3を「1」減算する(ステップS3197A)。これらの時短回数はメインRAM100cに記憶されている。
On the other hand, when the
ステップS3196AでNOの場合、メインCPU100aは、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2を「1」減算すると共に、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3を「1」減算する(ステップS3198A)。時短回数J2はメインRAM100cに記憶されている。
In the case of NO in step S3196A, the
ステップS3195AでNOと判定された場合、ステップS3197Aの処理が実行された場合、及びステップS3198Aの処理が実行された場合、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄判定の結果が小当たりか否かを判定する(ステップS3199A)。小当たりである場合(ステップS3199A:YES)、メインCPU100aは、はメインRAM100cに小当たり上限回数の設定があるか否かを判定する(ステップS3191B)。
If it is determined NO in step S3195A, if the process of step S3197A is executed, and if the process of step S3198A is executed, the
ステップS3191BでYESの場合、メインCPU100aは、小当たり残り回数を「1」減算する(ステップS3192B)。そして、メインCPU100aは、小当たり残り回数が「0」か否かを判定する(ステップS3193B)。ステップS3193BでYESの場合、確変遊技フラグを「OFF」に設定すると共に各種時短回数をクリアする(ステップS3194B)。
In the case of YES in step S3191B, the
ステップS3194Bの処理が実行された場合、ステップS3191BでNOの場合、又はステップS3193BでNOの場合、メインCPU100aは、小当たり用のオープニングコマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS3195B)。このオープニングコマンドは、小当たり遊技が開始されることを示すオープニング演出を演出制御基板130に行わせるためのコマンドであり、当該コマンドは、図10のステップS10Aの出力処理が実行されることによって演出制御基板130へ送信される。
If the process of step S3194B is executed, if NO in step S3191B, or if NO in step S3193B, the
ステップS3199AでNOの場合、メインCPU100aは、特別図柄判定の結果がハズレ(時短)であるか否かを判定する(ステップS3197B)。ステップS3197BでYESの場合、メインCPU100aは、時短遊技フラグと特別図柄の種類とに応じて時短回数をセットする(ステップS3198B)。
In the case of NO in step S3199A, the
ステップS3198Bの処理を実行した場合、又はステップS3197BでNOの場合、特別図柄の変動回数が750に到達したか否かを判定する(ステップS3199B)。特別図柄の変動回数は、設定変更後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、RWMクリア後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、又は大当たり遊技の終了から連続して750回ハズレたことによって750に到達する。ステップS3199BでYESの場合、メインCPU100aは、時短回数(J1=10、J2=1000、J3=1000)をメインRAM103aにセットする(ステップS3191C)。
When the process of step S3198B is executed, or when NO in step S3197B, it is determined whether or not the number of fluctuations in the special symbol has reached 750 (step S3199B). The number of fluctuations of the special symbols reaches 750 by losing 750 times in succession after changing the setting, losing 750 times in succession after clearing the RWM, or losing 750 times in succession after the end of the jackpot game. . In the case of YES in step S3199B, the
ステップS3191Cの処理を実行した場合、ステップS3196Bの処理を実行した場合、又はステップS3199BでNOの場合、メインCPU100aは、時短回数J1~J3のうちの何れかが0であるか否かを判定する(ステップS3192C)。ステップS3192CでYESの場合、メインCPU100aは、時短遊技フラグをOFFに設定する(ステップS3193C)。時短遊技フラグがOFFに設定されると、次の普通図柄の変動表示からは低確非時短用の普通図柄の変動パターンが選択される。そして、この普通図柄判定が当たりの場合、低確非時短用の開放パターンで電動チューリップ17が開放される。また、時短遊技フラグがOFFに設定されると、次の特別図柄の変動表示からは低確非時短用の特別図柄の変動パターンが選択される。低確時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行した場合における低確非時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンは、低確時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンよりも相対的に短い(図17)。なお、低確時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行した場合における低確非時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンは、低確時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンよりも相対的に長くてもよい(又は同じ長さでもよい)。
If the process of step S3191C is executed, if the process of step S3196B is executed, or if NO in step S3199B, the
ステップS3193Cの処理を実行した場合、又はステップS3192CでNOの場合、メインCPU100aは、時短遊技フラグの状態から特定される現在の遊技状態に対応する遊技状態指定コマンドをメインRAM103aにセットする。この遊技状態指定コマンドは、演出制御基板130で遊技状態を更新するためのコマンドであり、当該コマンドは、図10のステップS10Aの出力処理が実行されることによって演出制御基板130へ送信される。
When the process of step S3193C is executed, or when NO in step S3192C, the
次に、図28を参照して第1実施形態における低確非時短状態の演出例について説明する。図28には、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される場合であって変動パターンH107が選択されたときの装飾図柄55の動きが表記されている。遊技機1では、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される場合、装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせ以外であって「459」の組み合わせ以外の組み合わせで停止表示する。なお、遊技機1において通常のハズレ図柄と他の特別図柄とで停止表示される装飾図柄55と停止表示される第4図柄57との組み合わせが異なれば、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される場合に装飾図柄55が「227」の組み合わせ又は「459」の組み合わせで停止表示してもよい。
Next, with reference to FIG. 28, the example of the production|presentation of the low-probability non-time-saving state in 1st Embodiment is demonstrated. FIG. 28 shows the movement of the
図28に例示するように、低確非時短状態であって特別図柄が変動表示可能であるとき、第1実施形態では天国モードで演出が制御される。天国モードでは天国モード用の背景画像が表示されると共に、演出モード名を表す「天国モード」との文字が液晶画面5の左下に常に表示される。図28(A)は、低確非時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留がある状態で第1特別図柄として通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたときの様子を例示している。このとき、3つの装飾図柄55がハズレ態様で本停止すると共に、装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせの小図柄56が本停止する。また、これに伴ってハズレを示す第4図柄57が停止表示する。遊技機1では通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP3である。なお、遊技機1において通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
As illustrated in FIG. 28, when the special symbol can be variably displayed in the low-probability short-time state, the production is controlled in the heaven mode in the first embodiment. In the heaven mode, the background image for the heaven mode is displayed, and the characters "heaven mode" representing the effect mode name are always displayed at the lower left of the
図28(A)の例では、保留数字52によって第1特別図柄判定の保留数が3であり、第2特別図柄判定の保留数が0であることが示されている。なお、特別図柄判定の保留数は図28の例では途中で増えないものとする。第1特別図柄が停止表示されてから所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、次の第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する。これに伴って、数字部分550及びキャラクタ部分551が動いたり装飾図柄55の大きさが大きくなったりする(図28(B)参照)。遊技機1では、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態において装飾図柄55が変動表示を開始するときには、図28(B)に例示するように装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP3からHP2に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態において装飾図柄55が変動表示を開始するときに装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンH2以外に変化してもよいし、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が変化しなくてもよい。
In the example of FIG. 28(A), the reserved
装飾図柄55が変動表示を開始すると、これに伴って小図柄56は高速変動を開始する。これと共に、最先の保留アイコン51が変動中アイコン53として表示されるように保留アイコン51が右側に移動されるアニメーションが表示される。また、第1特別図柄判定の保留数を示す数字保留52の値が1減少する。図28(C)~(H)に例示するように、変動表示を開始した装飾図柄55は高速変動した後に「仮停止表示」を介して本停止する。仮停止表示は、装飾図柄55(又は小図柄56)の表示位置をほとんど変化させずに上下方向に揺れるように微動させたり、わずかな拡大と縮小とを繰り返させたりする表示態様である。遊技機1では、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態において装飾図柄55が高速変動しているときから停止表示直前までの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP2である。なお、遊技機1において、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態において装飾図柄55が高速変動しているときから停止表示直前までの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
When the
図28の例では通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されるので装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせ以外であって「459」の組み合わせ以外の組み合わせで仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する。この本停止に応じて遊技状態は変化しない。よって、低確非時短状態のまま次の第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する(図28(I)参照)。
In the example of FIG. 28, normal losing symbols are stopped and displayed, so the
次に、図29を参照して第1実施形態において低確非時短から低確時短に移行するときに第1特別図柄判定が保留されている演出例について説明する。図29(A)~(D)には、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって特定のハズレ図柄(具体的にはハズレ(時短A)図柄)が停止表示されたことに応じて低確非時短から低確時短に移行したときの動きが表記されている。図29(A)は、低確非時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留だけがある状態で第1特別図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されたときの様子を例示している。図29(A)の例では、保留数字52によって第1特別図柄判定の保留数が3であり、第2特別図柄判定の保留数が0であることが示されている。
Next, with reference to FIG. 29, an effect example in which the first special symbol determination is suspended when shifting from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours in the first embodiment will be described. In FIG. 29 (A) to (D), in the case where the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, a specific losing pattern (specifically, a losing (time saving A) pattern) is stopped and displayed. The movement when moving from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours is shown. FIG. 29(A) illustrates the situation when the losing (time saving A) symbol is stop-displayed as the first special symbol in a state where only the first special symbol is reserved in the low-probability non-time-saving state. In the example of FIG. 29(A), the reserved
ハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されると、3つの装飾図柄55がハズレ態様で本停止すると共に、装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせの小図柄56が本停止する。また、これに伴ってハズレを示す第4図柄57が停止表示する。遊技機1では、ハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示される場合、装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせで停止表示する。なお、遊技機1においてハズレ(時短A)図柄と他の特別図柄とで停止表示される装飾図柄55と停止表示される第4図柄57との組み合わせが異なれば、ハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示される場合に装飾図柄55が「227」の組み合わせ以外で停止表示してもよい。
When the losing (time saving A) pattern is stop-displayed, the three
遊技機1では低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP3である。なお、遊技機1において、低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
In the
低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されてから所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。図29(A)では連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないので、時短回数は700回設定される。図29(B)の例では第1特別図柄判定の保留がある一方で第2特別図柄判定の保留がない。このため、低確時短状態移行後の1回目の変動表示として第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する(図29(B)参照)。当該変動表示中に第2特別図柄判定の保留が発生すると、図29(B)~(D)に例示するように次変動は第2特別図柄が変動表示を開始する。 When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses after the losing (time saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed in the low probability non working hours state, the low probability non working hours is shifted to the low probability short working hours. In FIG. 29(A), since the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, the number of times of time saving is set to 700 times. In the example of FIG. 29(B), there is no suspension of the second special symbol determination while there is suspension of the first special symbol determination. For this reason, the first special symbol starts the variable display as the first variable display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state (see FIG. 29(B)). When suspension of the second special symbol determination occurs during the variable display, the second special symbol starts variable display as shown in FIGS. 29(B) to (D).
図29(B)に例示するように、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて、遊技が再開することを強調する扉画像が表示開始される。扉画像としては、扉が閉鎖して画面全体を覆ってから扉が開放する動画像が表示される(図29(B)及び(C)参照)。扉画像は表示されてから所定時間(例えば2.5秒)経過したことに応じて表示が終了する。図29(C)に例示するように、仮に低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、当該ハズレ図柄の停止表示中に扉画像の表示が終了する。低確時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても時短回数は加算されず遊技状態は変化しない。ここで、遊技機1では、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51の方が扉画像よりも表示優先度が低い。よって、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51は扉画像が手前側に表示されることによって一旦見えなくなる。一方、遊技機1では、小図柄56並びに第4図柄57及び59の方が扉画像よりも表示優先度が高い。このため、遊技者は、扉画像の表示中は、高速変動後に停止表示された小図柄56及び第4図柄57を見ることによって低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第1特別図柄判定の判定結果を知ることが可能である。
As illustrated in FIG. 29(B), a door image emphasizing that the game is restarted is started to be displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the shift to the low-probability short working hours state. As the door image, a moving image is displayed in which the door closes, covers the entire screen, and then opens (see FIGS. 29B and 29C). The display of the door image ends when a predetermined time (for example, 2.5 seconds) has passed since it was displayed. As illustrated in FIG. 29 (C), if the determination result of the first special symbol determination after the transition to the low probability time saving state is a specific losing symbol, the door image during the stop display of the losing symbol display ends. Even if a specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed in the low-probability time-saving state, the number of times of time-saving is not added and the game state does not change. Here, in the
仮に低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が大当たり図柄であったとしても、扉画像が非表示となる時間は大当たりを期待させたり大当たり報知させたりするよりも前である。このため、低確時短状態移行後における扉画像の表示中は、大当たりを期待させる演出は実行不可能であり、演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出も実行不可能である。 Even if the judgment result of the first special pattern judgment after the transition to the low probability time saving state is a jackpot pattern, the time when the door image is hidden is before the jackpot is expected or the jackpot is notified. is. Therefore, during the display of the door image after shifting to the low-probability short-working-time state, it is impossible to execute the performance for expecting a big win, and it is also impossible to execute the performance for informing the big win, such as activating the performance accessory 7.例文帳に追加
なお、扉画像が表示される際の態様は、画面全体に黒い画像がオーバーラップする態様でもよいし、モザイク状に現れていく扉画像によって画面全体が覆われる態様でもよい。また、扉画像の表示終了態様は、画面全体を覆う扉画像の透明度が上がり最終的に扉画像が非表示になる態様でもよいし、扉画像がモザイク状に欠けていき最終的に扉画像が非表示になる態様でもよい。 Note that the manner in which the door image is displayed may be a manner in which a black image overlaps the entire screen, or a manner in which the entire screen is covered with the door image appearing in a mosaic pattern. In addition, the display of the door image may be ended in such a manner that the transparency of the door image covering the entire screen is increased and the door image is finally hidden, or the door image is missing in a mosaic pattern and the door image is finally displayed. A mode in which it is hidden may be used.
盤用照明装置74及び枠用照明装置10は、扉画像表示中は扉画像表示用の発光パターン(例えば、黄色で点滅する発光パターン)で発光する。なお、低確時短状態であるときに発光可能である一方で低確時短状態ではないときに発光しない発光手段(例えば右サイドランプ)を備えてもよく、低確時短状態移行後における扉画像の表示中は上記発光手段を扉画像表示用の発光パターンで発光させてもよい。
The
遊技機1では、低確時短状態移行後における1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて遊技者に右打ちを促す文字が表示開始される。右打ちを促す文字には、「右打ち→」との大文字および「右打ち」との小文字がある(例えば、図29(B)及び(C)並びに図51(B)及び(C))。「右打ち→」との大文字は遊技状態変化後の1回目の変動表示終了を条件に表示が終了する。一方、「右打ち」との小文字は低確時短から他の遊技状態への移行を条件に表示が終了する。右打ちを促す文字は扉画像と同様に遊技者に有利であることを示す画像である。遊技機1では、右打ちを促す文字よりも扉画像の方が表示優先度が低い。よって、右打ちを促す文字よりも後ろ側に扉画像が表示されるので、右打ちを促す文字は扉画像によって見えなくなることがない。なお、「右打ち→」との大文字は、遊技状態変化後の1回目の変動表示中に表示終了してもよいし、遊技状態変化後の1回目の変動表示から複数回(例えば2回)の変動表示に亘って表示されてもよい。
In the
遊技機1では、低確時短状態移行後における1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて遊技者にRUSHモードに移行したことを報知する「RUSHモード開始」との音声がスピーカ24から出力される。ここで、遊技機1では、大当たり遊技を介して低確時短状態に移行する場合は、大当たり遊技中に遊技者に遊技にのめり込まないように注意を促す第1注意喚起と、プリペイドカードを取り忘れないように注意を促す第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。これに対して、遊技機1では、特定のハズレ図柄の停止表示を介して低確時短状態に移行する場合は、上記注意喚起を表示することなく低確時短状態に移行する。なお、特定のハズレ図柄の停止表示を介して低確時短状態に移行する場合は、低確時短状態移行後における1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて第1注意喚起が所定時間(例えば2.5秒間)表示されてもよい。
In the
図29(D)に例示するように低確時短においてはRUSHモードで演出が制御される。RUSHモードではRUSHモード用の背景画像が表示されると共に、演出モード名を表す「RUSHモード」との文字が液晶画面5の左下に常に表示される。また、RUSHモードでは基本的には時短回数の残り回数を示す「時短残り回数」が液晶画面5の右上に表示される。遊技機1では、背景画像、演出モード名、及び時短残り回数の方が扉画像よりも表示優先度が低い。このため、遊技者には天国モードの画面構成が扉画像の表示を介してRUSHモードの画面構成に変化したように見える。
As illustrated in FIG. 29(D), the effect is controlled in the RUSH mode in the low probability of short working hours. In the RUSH mode, a background image for the RUSH mode is displayed, and the characters "RUSH MODE" representing the effect mode name are always displayed at the lower left of the liquid crystal screen 5.例文帳に追加In addition, in the RUSH mode, basically, the remaining number of times of time saving is displayed on the upper right of the
天国モードであるときは第1特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51及び第1特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53が表示される。これに対し、RUSHモードであるときは第2特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51及び第2特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53が表示される。RUSHモードであるときは第1特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51及び第1特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53は非表示にされる。RUSHモードは保留アイコン51及び当該アイコン53の態様(例えば形および表示位置)が天国モードと異なる。
When the heaven mode is selected, a
低確時短状態に移行すると、天国モードの画面構成であるときに表示パターンHP3であった装飾図柄55の表示優先度は、扉画像の表示を介して表示パターンHP9に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、低確時短状態移行直前における天国モードと、扉画像の表示を介してRUSHモードに変化したときとでは装飾図柄55の表示優先度が同じでもよい。
When shifting to the low probability time saving state, the display priority of the
扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の態様が異なってもよいし、同じでもよい。また、扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の表示領域が異なってもよいし、同じでもよい。また、扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは小図柄56の態様および表示領域が同じでもよいし、異なってもよい。
The patterns of the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be different or the same between the heaven mode immediately before displaying the door image and the RUSH mode immediately after displaying the door image. Further, the display areas of the left pattern, the middle pattern and the right pattern may be different or the same between the heaven mode immediately before displaying the door image and the RUSH mode immediately after displaying the door image. Further, the form and display area of the
図29(E)から図29(B)への流れ、及び、図29(F)から図29(B)への流れは、設定変更後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、RWMクリア後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、又は大当たり遊技の終了から連続して750回ハズレたことで低確非時短から低確時短に移行したときの動きが表記されている。低確非時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留だけがある状態で連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たす場合、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が停止表示された場合、時短回数1000回が設定される。 The flow from FIG. 29(E) to FIG. 29(B) and the flow from FIG. 29(F) to FIG. 750 times of losing or losing 750 times in succession from the end of the jackpot game, the movement when shifting from low probability short working hours to low probability short working hours is described. If the condition is 750 consecutive losses with only the first special pattern reserved in the low probability non-time saving state, even if the specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed, even if the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed, the low probability is not Transition from short working hours to low-accurate short working hours. When a losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses is stopped and displayed, the number of times of time saving is set to 1000 times.
図29(E)は連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が特定のハズレ図柄である場合の例である。図29(E)では特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示する場合の例を示しているが、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されてもよい。ハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示される場合、装飾図柄55は「459」の組み合わせで停止表示する。なお、遊技機1においてハズレ(時短B)図柄と他の特別図柄とで停止表示される装飾図柄55と停止表示される第4図柄57との組み合わせが異なれば、ハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示される場合に装飾図柄55が「459」の組み合わせ以外で停止表示してもよい。
FIG. 29(E) is an example of a case where the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings is a specific losing pattern. FIG. 29(E) shows an example in which a losing (time saving B) symbol is stopped and displayed as a specific losing symbol, but a losing (time saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed as a losing symbol that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings. may be When the lost (time saving B) pattern is stop-displayed, the
図29(F)は連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が通常のハズレ図柄である場合の例である。遊技機1では、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される場合、装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせ以外および「459」の組み合わせ以外で停止表示する。
FIG. 29(F) is an example of a case where the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings is a normal losing pattern. In the
遊技機1ではハズレ(時短B)図柄および通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP3である。なお、遊技機1においてハズレ(時短B)図柄および通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
In the
連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄の停止表示から所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。図29(B)以降の流れは、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されたときと基本的には同じである。異なる点は、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないときは時短残り回数の初期値は699回であるのに対し連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすときは時短残り回数の初期値は999回である点である。 When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses from the stop display of the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses, the game shifts from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours. The flow after FIG. 29B is basically the same as when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied and the losing (time saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed in the low probability non-time saving state. The difference is that when the condition of 750 consecutive failures is not satisfied, the initial value of the remaining time reduction is 699 times, whereas when the condition of 750 consecutive failures is satisfied, the initial value of the remaining time reduction is 999 times. It is a point.
連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした後に設定変更、RWMクリア、及び大当たり遊技のうちの何れも実行されずに連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たしてから連続して750回ハズレた場合、当該ハズレ図柄の停止表示に応じて遊技状態は変化しない。一方、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした後に大当たり遊技が実行され、当該大当たり遊技後に連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合、当該ハズレ図柄の停止表示に応じて低確時短に移行すると共に時短回数1000回が設定される。連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした後に大当たり遊技が実行され、その後RUSHモード中に連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合、RUSHモードのまま(すなわち低確時短状態のまま)時短回数が1000回に上書きされる(図29(G)参照)。今までに連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たしておらず、RUSHモード中に連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合も同様に、RUSHモードのまま(すなわち低確時短状態のまま)時短回数が1000回に上書きされる。 After satisfying the condition of 750 consecutive losses, when none of the setting change, RWM clear, and jackpot game is executed and the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied and then 750 consecutive losses occur, the corresponding losing pattern. The game state does not change according to the stop display of . On the other hand, when the jackpot game is executed after satisfying the condition of 750 consecutive losses, and when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied after the jackpot game, it shifts to a low-probability short-time according to the stop display of the losing pattern and shortens the time. 1000 times is set. After satisfying the condition of 750 consecutive losses, the jackpot game is executed, and if the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied during the RUSH mode, the number of times of time saving is 1000 times while remaining in RUSH mode (that is, remaining in a low-probability short-time state). is overwritten (see FIG. 29(G)). Even if the conditions for 750 consecutive losses have not been met so far, and the conditions for 750 consecutive losses are met during RUSH mode, the number of times of time saving remains 1000 while in RUSH mode (that is, in a low-probability short-time state). overwritten once.
なお、低確非時短から低確時短に移行する場合において、以下の構成でもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が中図柄全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が中図柄の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・低確非時短から低確時短に移行する場合において、扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・低確非時短から低確時短に移行する場合において、扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときは中図柄が左図柄(及び右図柄)よりも大きく、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときは左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の大きさは互いに同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における天国モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄相互間の大きさの比率が同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前は天国モード用の発光パターンで発光し、扉画像表示終了直後はRUSHモード用の発光パターンで発光する。
In addition, when shifting from low probability short working hours to low probability short working hours, the following configuration may be used.
The size of the entire middle pattern may be larger, smaller, or the same in the RUSH mode immediately after the door image is displayed than in the heaven mode immediately before the door image is displayed.
The size of the
・When shifting from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours, the overall size of the left pattern (and right pattern) is larger in RUSH mode immediately after displaying the door image than in heaven mode immediately before displaying the door image. It may be the same size, smaller, or the same size.
・When shifting from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours, the
・In heaven mode immediately before the door image is displayed, the middle pattern is larger than the left (and right) pattern, and in RUSH mode immediately after the door image is displayed, the left, middle, and right patterns are the same size. It's okay.
The size ratio between the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be the same between the heaven mode immediately before displaying the door image and the RUSH mode immediately after displaying the door image.
- Immediately before the door image is displayed, light is emitted in the light emission pattern for heaven mode, and immediately after the door image is displayed, light is emitted in the light emission pattern for RUSH mode.
次に、図30を参照して第1実施形態において低確非時短から低確時短に移行するときに第1特別図柄判定が保留されていない演出例について説明する。図30(A)~(D)には、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって特定のハズレ図柄(具体的にはハズレ(時短A)図柄)が停止表示されたことに応じて低確非時短から低確時短に移行したときの動きが表記されている。図30(A)は、低確非時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留がない状態で第1特別図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されたときの様子を例示している。図30(A)の例では、保留数字52によって第1特別図柄判定の保留数が0であり、第2特別図柄判定の保留数が0であることが示されている。
Next, with reference to FIG. 30, an effect example in which the first special symbol determination is not suspended when shifting from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours in the first embodiment will be described. In FIG. 30 (A) to (D), in the case where the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, a specific losing pattern (specifically, a losing (time saving A) pattern) is stopped and displayed. The movement when moving from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours is shown. FIG. 30(A) exemplifies the situation when the losing (time saving A) symbol is stop-displayed as the first special symbol in a state where the first special symbol is not reserved in the low-probability non-time-saving state. In the example of FIG. 30(A), the reserved
低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されてから所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。図30(A)では連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないので、時短回数は700回設定される。図30(B)の例では第1特別図柄判定の保留も第2特別図柄判定の保留も0である。このため、確定停止期間が経過したことに応じて客待ち状態になったことを通知する客待ちコマンドが遊技制御基板100から演出制御基板130に送信される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなく予め定められた時間(例えば10秒)が経過したことに応じて音量値および光量値を設定するための設定画像が表示開始される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなくさらに予め定められた時間(例えば20秒)が経過したことに応じて客待ち演出が開始される。客待ち演出では、遊技機1を宣伝するためのデモ動画の表示、遊技機1を製造する会社名の表示等が切り替わりながら繰り返し表示される。
When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses after the losing (time saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed in the low probability non working hours state, the low probability non working hours is shifted to the low probability short working hours. In FIG. 30(A), since the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, the number of times of time saving is set to 700 times. In the example of FIG. 30(B), both the suspension of the first special symbol determination and the suspension of the second special symbol determination are 0. For this reason, a customer waiting command for notifying that a customer waiting state has occurred is transmitted from the
遊技機1が客待ち状態であるときに遊技球がゲート16を通過すると普通図柄判定が行われる。遊技機1では低確時短状態では普通図柄判定が行われると100%の確率で第2始動口12がロング開放される(図2(A)参照)。遊技球が第2始動口12に入賞すると、低確時短状態移行後の1回目の変動表示として第2特別図柄が変動表示を開始する(図30(B)参照)。なお、図30(B)~(D)に例示するように仮に当該変動表示中に第1特別図柄判定の保留および第2特別図柄判定の保留がそれぞれ1発生すると、次変動では第2特別図柄が変動表示を開始する。
When a game ball passes through a
図30(B)に例示するように、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の第2特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて扉画像および右打ちを促す文字が表示開始される。図29及び図30に例示するように、扉画像および右打ちを促す文字は低確時短状態移行後において1回目に変動表示する特別図柄の種類に関わらず同じである。図30(B)では図29(B)と異なり第2特別図柄が変動表示しているので、扉画像の表示中には第2特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53が表示される。また、図30(C)では図29(C)と異なり第2特別図柄判定が保留しているので、扉画像の表示中には第2特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51が表示される。
As exemplified in FIG. 30(B), the display of the door image and the character prompting the right hand is started in response to the start of the second special symbol variation display for the first time after the shift to the low-probability short working hours state. As illustrated in FIGS. 29 and 30, the door image and the character prompting to hit to the right are the same regardless of the type of the special design that is variably displayed for the first time after the low probability short working hours state transition. In FIG. 30(B), unlike FIG. 29(B), the second special symbol is variably displayed, so the
図30(C)に例示するように、仮に低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第2特別図柄判定の判定結果が通常のハズレ図柄であった場合、当該ハズレ図柄の停止表示中に扉画像の表示が終了する。遊技者は、扉画像の表示中は、高速変動後に停止表示された小図柄56及び第4図柄57を見ることによって低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第2特別図柄判定の判定結果を知ることが可能である。
As illustrated in FIG. 30 (C), if the determination result of the first second special symbol determination after the transition to the low probability time saving state is a normal losing symbol, the door image during the stop display of the losing symbol display ends. During the display of the door image, the player sees the
仮に低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第2特別図柄判定の判定結果が大当たり図柄であったとしても、扉画像が非表示となる時間は大当たりを期待させたり大当たり報知させたりするよりも前である。このため、低確時短状態移行後における扉画像の表示中は、大当たりを期待させる演出は実行不可能であり、演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出も実行不可能である。 Even if the judgment result of the first second special design judgment after the transition to the low probability time saving state is a jackpot pattern, the time when the door image is hidden is before the jackpot is expected or the jackpot is notified. is. Therefore, during the display of the door image after shifting to the low-probability short-working-time state, it is impossible to execute the performance for expecting a big win, and it is also impossible to execute the performance for informing the big win, such as activating the performance accessory 7.例文帳に追加
図30(E)から図30(B)への流れ、及び、図30(F)から図30(B)への流れは、設定変更後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、RWMクリア後に連続して750回ハズレたこと、又は大当たり遊技の終了から連続して750回ハズレたことで低確非時短から低確時短に移行したときの動きが表記されている。低確非時短状態において特別図柄の保留がない状態で連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たす場合、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が停止表示された場合、時短回数1000回が設定される。 The flow from FIG. 30(E) to FIG. 30(B) and the flow from FIG. 30(F) to FIG. 750 times of losing or losing 750 times in succession from the end of the jackpot game, the movement when shifting from low probability short working hours to low probability short working hours is described. If the conditions for 750 consecutive losses are met in the low probability non-time saving state with no special pattern pending, even if the specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed, even if the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed, the low probability non-time saving to low Move in a short time. When a losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses is stopped and displayed, the number of times of time saving is set to 1000 times.
図30(E)は連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が特定のハズレ図柄である場合の例である。図30(E)では特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示する場合の例を示しているが、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されてもよい。図30(F)は連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が通常のハズレ図柄である場合の例である。 FIG. 30(E) is an example of a case where the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings is a specific losing pattern. FIG. 30(E) shows an example in which a losing (time saving B) symbol is stopped and displayed as a specific losing symbol, but a losing (time saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed as a losing symbol that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings. may be FIG. 30(F) is an example of a case where the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings is a normal losing pattern.
連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄の停止表示から所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。図30(E)及び(F)の例では第1特別図柄判定の保留も第2特別図柄判定の保留も0である。このため、確定停止期間が経過したことに応じて客待ちコマンドが遊技制御基板100から演出制御基板130に送信される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなく予め定められた時間(例えば10秒)が経過したことに応じて音量値および光量値を設定するための設定画像が表示開始される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなくさらに予め定められた時間(例えば20秒)が経過したことに応じて客待ち演出が開始される。
When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses from the stop display of the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses, the game shifts from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours. In the examples of FIGS. 30(E) and (F), both the suspension of the first special symbol determination and the suspension of the second special symbol determination are 0. Therefore, a customer waiting command is transmitted from the
遊技機1が客待ち状態であるときに遊技球がゲート16を通過すると普通図柄判定が行われる。普通図柄判定の結果、ロング開放された第2始動口12遊技球が入賞すると、低確時短状態移行後の1回目の変動表示として第2特別図柄が変動表示を開始する(図30(B)参照)。図30(B)以降の流れは、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されたときと基本的には同じである。異なる点は、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないときは時短残り回数の初期値は699回であるのに対し連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすときは時短残り回数の初期値は999回である点である。
When a game ball passes through a
次に、図31を参照して第1実施形態において低確非時短から低確微時短に移行する演出例について説明する。図31には、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって特定のハズレ図柄(具体的にはハズレ(時短B)図柄)が停止表示されたことに応じて低確非時短から低確微時短に移行したときの動きが表記されている。図31(A)は、低確非時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留だけがある状態で第1特別図柄としてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示されたときの様子を例示している。図31(A)の例では、保留数字52によって第1特別図柄判定の保留数が3であり、第2特別図柄判定の保留数が0であることが示されている。
Next, with reference to FIG. 31, the example of the production|presentation which transfers from low probability non-reduction of time to low probability reduction of time in 1st Embodiment is demonstrated. In FIG. 31, when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, a specific losing pattern (specifically, a losing (time saving B) pattern) is stopped and displayed. The movement when shifting to a short time is described. FIG. 31(A) exemplifies the situation when the losing (time saving B) symbol is stop-displayed as the first special symbol in a state where only the first special symbol is reserved in the low-probability non-time-saving state. In the example of FIG. 31(A), the
低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示されてから所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確非時短から低確微時短に移行する。図31(A)では連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないので、時短回数は500回設定される。また、小当たり上限回数は2回に設定される。 When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses after the losing (time saving B) symbol is stopped and displayed in the low-probability non-time-saving state, the low-probability short-time to low-probability shifts to the low-probability short-time. In FIG. 31(A), since the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, the number of times of time saving is set to 500 times. In addition, the small hit upper limit number of times is set to 2 times.
低確微時短状態移行後には、1回目の変動表示として第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する(図31(B)参照)。停止表示中に表示パターンHP3であった装飾図柄55の表示優先度は、図31(B)に例示するように変動表示開始時に表示パターンHP2に変化する。図31(B)の例では、保留数字52によって第1特別図柄判定の保留数が2であり、第2特別図柄判定の保留数が0であることが示されている。
After the transition to the low-probability short working hours state, the first special symbol starts the variable display as the first variable display (see FIG. 31(B)). The display priority of the
図31(B)に例示するように、第1実施形態では低確微時短においては地獄モードで演出が制御される。地獄モードでは地獄モード用の背景画像が表示されると共に、演出モード名を表す「地獄モード」との文字が液晶画面5の左下に常に表示される。地獄モードでは時短残り回数は表示されない。天国モードから地獄モードへ移行する際には、扉画像および右打ちを促す文字が表示されることはない。このため、遊技者には天国モードの画面構成が次変動開始に応じて地獄モードの画面構成に変化したように見える。なお、低確微時短状態移行後において1回目の第1特別図柄の変動表示開始に応じて扉画像を表示してもよい。なお、地獄モードにおける装飾図柄55は、天国モードにおける装飾図柄55と同じ態様でもよいし異なる態様でもよい。
As illustrated in FIG. 31(B), in the first embodiment, the performance is controlled in hell mode in the low-probability short working hours. In the hell mode, a background image for the hell mode is displayed, and the characters "hell mode" representing the effect mode name are always displayed at the lower left of the
その後、図31(C)及び(E)に例示するように低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示された場合、時短回数は加算されず遊技状態は変化しない。 After that, as shown in FIGS. 31(C) and (E), when a specific losing symbol is stopped and displayed in the low-probability time-saving state, the number of times of time-saving is not added and the game state does not change.
図31(F)に例示するように低確微時短状態において小当たりAが停止表示された場合、当該停止表示に応じて小当たりとなったことを示すハート画像が液晶画面5の右上隅に表示される。低確微時短状態では小当たりとなるたびにハート画像が1つ増えていく(図31(H)参照)。ハート画像の数が小当たり上限回数となると低確微時短から低確非時短に移行する(図31(I)参照)。
As illustrated in FIG. 31 (F), when the small hit A is stopped in the low-probability short-time state, a heart image indicating that the small hit has occurred in response to the stop display is displayed in the upper right corner of the
低確微時短状態における99回目の第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が通常のハズレ図柄または特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、図31(G)に例示するように次変動開始に応じて地獄モード用の特別な背景画像に変化する。上記特別な背景画像は、低確微時短から他の遊技状態に移行するまで表示される画像であって、その後に連続して400回ハズレると必ず天国モード(すなわち低確非時短)に移行することを示す画像である。第1実施形態では低確微時短よりも低確非時短の方が遊技者に有利なため、遊技者は上記特別な背景画像を見ることによってこのままハズレ続けると必ず低確非時短に移行できるということを心の支えに遊技を継続できる。 If the determination result of the 99th first special symbol determination in the low-probability short working hours state is a normal losing symbol or a specific losing symbol, Hell mode in response to the start of the next fluctuation as illustrated in FIG. 31 (G) It changes to a special background image for The above special background image is an image that is displayed until the transition from low-probability short working hours to another game state, and after that, if you lose 400 times in succession, it will always shift to heaven mode (i.e. low-probable short working hours) It is an image showing that In the first embodiment, since the low-probability short working hours is more advantageous to the player than the low-probability short working hours, the player can always shift to the low-probable short working hours if he continues to lose by looking at the special background image. You can continue playing with this as a mental support.
次に、図32を参照して第1実施形態において低確微時短から低確非時短に移行する演出例について説明する。図32には、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない変動表示であって、低確微時短の最終変動が行われたときの動きが表記されている。図32(A)の例では、保留数字52によって第1特別図柄判定の保留数が2であり、第2特別図柄判定の保留数が0であることが示されている。図32(A)に例示するように、低確微時短の最終変動開始に応じて地獄モード最終変動用の背景画像に変化する。なお、低確微時短の時短残り回数に関わらず同じ背景画像が表示されてもよい。また、地獄モード最終変動用の背景画像は、図31(G)に例示する、その後に連続して400回ハズレると必ず天国モード(すなわち低確非時短)に移行することを示す地獄モード用の特別な背景画像と同じ画像でもよい。
Next, with reference to FIG. 32, the example of the production|presentation which transfers to the low probability short working hours from the low probability small short working hours in 1st Embodiment is demonstrated. In FIG. 32, it is a variation display that does not satisfy the condition of 750 consecutive losses, and the movement when the final variation of the low-probability short working hours is performed is described. In the example of FIG. 32(A), the reserved
図32(B)に例示するように低確微時短の最終変動において通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されると、所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)経過に応じて低確微時短から低確非時短に移行する。ここで、遊技機1では、低確微時短の最終変動が停止表示されているときに時短遊技フラグがONのままハズレ図柄の種類に応じて時短回数が設定される。よって、図32(D)に例示するように低確微時短の最終変動において特定のハズレ図柄(図32(D)の例ではハズレ(時短A)図柄)が停止表示されたときは通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたときと同様に、所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)経過に応じて低確微時短から低確非時短に移行する。図32(D)の例では、時短残り回数に関わらず低確微時短において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じては右打ちを促す文字、扉画像、及び低確時短状態用の背景画像は表示されない。図32(B)及び(D)の例では連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないので時短回数はクリアされる。また、小当たり上限回数はクリアされる。低確非時短に移行するとベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が再開される。
As illustrated in FIG. 32 (B), when the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed in the final variation of the low-precision time-saving, a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) Transition in a non-time-saving manner. Here, in the
低確非短状態移行後には、1回目の変動表示として第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する(図32(C)参照)。これに伴って、地獄モード最終変動用の画面構成が天国モードの画面構成に変化する。なお、低確微時短の最終変動よりも所定回数前(例えば10変動前)の変動表示から低確微時短の最終変動までに亘って、第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する毎に時短残り回数を報知するカウントダウンを行ってもよい。上記カウントダウンは、図31(G)に例示する、その後に連続して400回ハズレると必ず天国モード(すなわち低確非時短)に移行することを示す地獄モード用の特別な背景画像が表示されていることを条件に行ってもよい。なお、カウントダウンに代えて(又は加えて)、低確微時短の最終変動よりも所定回数前(例えば10変動前)の変動表示から低確微時短の最終変動までに亘って、第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する毎に変化する演出画像(例えば、ゲージがたまっていくような演出画像)を表示してもよい。 After the transition to the low probability non-short state, the first special symbol starts variable display as the first variable display (see FIG. 32(C)). Along with this, the screen configuration for the hell mode final variation changes to the screen configuration for the heaven mode. In addition, from the final variation of the low-probability short working hours a predetermined number of times before (for example, 10 fluctuations before) to the final fluctuation of the low-probability short working hours, every time the first special symbol starts the variable display, the time saving remaining A countdown to notify the number of times may be performed. The above countdown is illustrated in FIG. 31 (G). After that, a special background image for hell mode is displayed, which indicates that if you lose 400 times in a row, you will definitely shift to heaven mode (that is, low probability and short working hours). You may go on the condition that you are Incidentally, instead of the countdown (or in addition), from the final variation of the low-probability short working hours a predetermined number of times before (for example, 10 fluctuations) from the fluctuation display to the final fluctuation of the low-probability short working hours, the first special symbol It is also possible to display an effect image that changes each time a variable display is started (for example, an effect image in which a gauge is filling up).
なお、低確微時短の最終変動が停止表示されているときに時短遊技フラグがOFFにされてからハズレ図柄の種類に応じて時短回数が設定されてもよい。このような場合、図32(E)に例示するように低確微時短の最終変動においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示されたときは、所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)経過に応じて低確微時短から低確時短に移行する。低確時短に移行するとベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が停止したままである。図32(E)の例では連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないので時短回数は700回設定される。また、小当たり上限回数はクリアされる。図32(E)に続く図32(F)は、低確時短状態移行後における1回目の変動表示として第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始し、これに伴って扉画像および右打ちを促す文字が表示されている様子を例示している。このように、図32(E)の例では低確微時短における最終変動においては、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちを促す文字、扉画像、及び低確時短状態用の背景画像が表示開始される。これに対して、図32(D)及び(E)の何れの例においても、低確微時短における最終変動よりも前の変動表示においては、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちを促す文字、扉画像、及び低確時短状態用の背景画像は表示されない。 In addition, after the time saving game flag is turned off when the final variation of the low-probability small time saving is stopped and displayed, the number of time saving times may be set according to the type of the losing pattern. In such a case, as illustrated in FIG. 32 (E), when the losing (time saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed in the final variation of the low probability time saving, a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) to shift from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours. Counting by the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation remains stopped when shifting to low probability time saving. In the example of FIG. 32(E), since the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, the number of times of time saving is set to 700 times. In addition, the small hit upper limit number of times is cleared. FIG. 32 (F) following FIG. 32 (E) shows that the first special symbol starts variable display as the first variable display after the transition to the low-probability time-saving state, and along with this the door image and characters that encourage right-handed hitting is displayed as an example. Thus, in the example of FIG. 32 (E) in the final variation in the low-probability short working hours, the character prompting to hit right in response to the stop display of a specific losing pattern, the door image, and the low-probable short working hours state for A background image starts to be displayed. On the other hand, in both examples of FIGS. 32 (D) and (E), in the fluctuation display before the final fluctuation in the low probability time saving, the right The text prompting to strike, the door image, and the background image for the low-probability time-saving state are not displayed.
次に、図33~図35を参照して、低確非時短においてリーチ演出が実行される演出例について説明する。図33は、第1実施形態において低確非時短状態のときにノーマルリーチ演出が実行される演出例について説明するための説明図である。図33の例では、白色の当該アイコン53が表示される図28及び図31の例とは異なり特別態様の当該アイコン53が表示されている。図34は、第1実施形態において低確非時短状態のときにSPリーチ演出が実行される演出例について説明するための説明図である。図35は、第1実施形態において低確非時短状態のときにSPリーチ演出でハズレ報知された直後の演出例について説明するための説明図である。なお、図33~図35の例では連続ハズレ750回の条件は満たさないものとする。
Next, with reference to FIGS. 33 to 35, an effect example in which the ready-to-win effect is executed in the low-probability short working hours will be described. FIG. 33 is an explanatory diagram for explaining an effect example in which a normal reach effect is executed in the low probability non-time saving state in the first embodiment. In the example of FIG. 33, unlike the examples of FIGS. 28 and 31 in which the
図33(A)及び(B)に例示するように、この例では「2」図柄でリーチが成立する。図33(C)に例示するように、リーチ成立から所定時間(例えば0.5秒)が経過したときに、リーチ成立状態の左右の装飾図柄55(以下、「リーチ図柄」と呼ぶ。)を強調するリーチラインが表示されたりリーチ成立を強調する「リーチ」との音声がスピーカ24から出力されたりする。リーチラインは、画面左端(又は左図柄の左端)から画面右端(又は右図柄の右端)までに亘るエフェクト画像であり、装飾図柄55よりも手前側に所定時間(例えば2秒間)表示される画像である。遊技機1では、リーチ成立を強調するためにリーチラインの表示に伴ってキャラクタ部分550(又は装飾図柄55全体)を発光させる。なお、リーチラインの表示に伴ってキャラクタ部分550(又は装飾図柄55全体)を発光させなくてもよい。図33(C)の例では小図柄56は高速変動を継続している。なお、リーチ成立に伴って、装飾図柄55と同じリーチ態様で小図柄56を表示してもよい。
As illustrated in FIGS. 33(A) and (B), in this example, reach is established with "2" symbols. As illustrated in FIG. 33(C), when a predetermined time (for example, 0.5 seconds) has passed since the establishment of ready-to-win, the left and right decorative patterns 55 (hereinafter referred to as "ready-to-win patterns") in the ready-to-win state are displayed. A reach line to be emphasized is displayed, or a voice saying "reach" is output from the
遊技機1では、変動表示開始時からリーチラインが非表示になるまで装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP2である。中図柄は変動表示開始時からリーチ成立時までは高速変動しており、リーチ成立に応じて開始される「ノーマルリーチ演出」中は低速変動する。リーチラインの表示中は中図柄が暗く表示される。「ノーマルリーチ演出」は、リーチ図柄を液晶画面5の中央に大きく表示した状態で、中図柄を相対的に遅いスピードでスクロールする演出態様である。ノーマルリーチ演出は、大当たりよりもハズレの場合に実行され易い。このため、ノーマルリーチ演出は、信頼度が相対的に低いリーチ演出であるといえる(例えば信頼度0.01%)。
In the
遊技機1では、ノーマルリーチ演出中は装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1である。すなわち、リーチ成立の前後で中図柄の表示優先度が高くなる。なお、ノーマルリーチ演出中は装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP2でもよい。
In the
遊技機1では、リーチ図柄として仮停止した装飾図柄以外の左図柄(及び右図柄)が非表示にされる。非表示にされた装飾図柄55は、当該変動表示が終了するまで再表示されない。なお、非表示にされた装飾図柄55は、当該変動表示が終了する直前に再表示されてもよい。
In the
遊技機1では、リーチ成立時よりもノーマルリーチ演出中の方が左図柄と右図柄との間隔が広くなる。また、リーチ成立時よりもノーマルリーチ演出中の方が中図柄が大きく表示される。このため、リーチ成立時とノーマルリーチ演出中とでは装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。一方、リーチ成立時とノーマルリーチ演出中とでは装飾図柄55の見た目は同じである。
In the
図33(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出でハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンH102に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果リーチハズレ目「272」で仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図33(E)及び(F)参照)。リーチハズレ目の仮停止表示開始時には、左図柄と右図柄との間隔が狭くなったり、中図柄が変動開始時と同じ大きさまで小さくなったりする。このため、ノーマルリーチ演出において中図柄が仮停止表示する前後で装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。また、リーチハズレ目の仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1からHP3に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、ノーマルリーチ演出においてハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。小図柄56はリーチハズレ目が本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、装飾図柄55の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。図33(F)に例示するようにハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示すると低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。
Following FIG. 33 (D), in the case of a variation pattern in which the losing (time saving A) pattern is stopped and displayed in the normal reach production (that is, when it corresponds to the variation pattern H102), the result of the normal reach production is a temporary stop at the reach losing eye "272". is displayed, and the main stop is performed as it is (see FIGS. 33(E) and (F)). At the start of the temporary stop display of the reach-losing eye, the interval between the left pattern and the right pattern is narrowed, or the middle pattern is reduced to the same size as at the start of fluctuation. Therefore, the display area of the
図33(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出で通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンH108に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果「272」以外のリーチハズレ目で仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図33(I)参照)。通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示すると低確非時短で次変動が開始する。 Following FIG. 33(D), in the case of a variation pattern in which the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed in the normal reach production (that is, in the case corresponding to the variation pattern H108), the result of the normal reach production is a temporary stop at the reach losing eyes other than "272". is displayed, and the main stop is performed as it is (see FIG. 33(I)). When the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed, the next fluctuation starts with a low probability and short time.
図33(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出で大当たりAが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO101に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果図柄揃い「222」で仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図33(G)参照)。図柄揃いの仮停止表示開始時には、左図柄と右図柄との間隔が狭くなったり、中図柄が変動開始時と同じ大きさまで小さくなったりする。このため、ノーマルリーチ演出において中図柄が仮停止表示する前後で装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。また、図柄揃いの仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1からHP4に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、ノーマルリーチ演出において大当たり図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。小図柄56は大当たり図柄が本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、大当たり図柄の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。図33(G)に例示するように大当たりAが停止表示すると大当たり遊技(遊技状態としては低確非時短)が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において遊技者に遊技にのめり込まないように注意を促す第1注意喚起と、プリペイドカードを取り忘れないように注意を促す第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。
Following FIG. 33(D), in the case of the variation pattern in which the jackpot A is stopped and displayed in the normal ready-to-win production (that is, in the case corresponding to the variation pattern O101), the result of the normal ready-to-win production is temporarily stopped and displayed with the pattern matching "222", and as it is. The motor is finally stopped (see FIG. 33(G)). At the start of the temporary stop display of matching patterns, the space between the left pattern and the right pattern is narrowed, or the middle pattern is reduced to the same size as at the start of fluctuation. Therefore, the display area of the
図33(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出で大当たりBが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO108に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果特殊な装飾図柄(時短図柄)が仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図33(H)参照)。時短図柄は、例えば低確微時短への移行を示唆する「地獄」との文字を含む装飾図柄である。なお、遊技機1において大当たりBと他の特別図柄とで停止表示される装飾図柄55と停止表示される第4図柄57との組み合わせが異なれば、大当たりBが停止表示される場合に装飾図柄55が図柄揃いで停止表示してもよい。
Following FIG. 33(D), in the case of a variation pattern in which the jackpot B is stopped and displayed in the normal reach production (that is, in the case corresponding to the variation pattern O108), a special decorative pattern (time saving pattern) is temporarily stopped and displayed as a result of the normal reach production. 33 (H)). The time-saving design is a decorative design including characters such as "hell" suggesting transition to low-probability time-saving, for example. In the
時短図柄の仮停止表示開始時には、左図柄と右図柄との間隔が狭くなったり、中図柄が変動開始時と同じ大きさまで小さくなったりする。このため、ノーマルリーチ演出において中図柄が仮停止表示する前後で装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。また、時短図柄の仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1からHP3に変化する。小図柄56は図柄揃いが本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、装飾図柄55の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。図33(H)に例示するように大当たりBが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確微時短に移行する。
When the temporary stop display of the time saving pattern is started, the interval between the left pattern and the right pattern is narrowed, or the middle pattern is reduced to the same size as when the fluctuation is started. Therefore, the display area of the
図33(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出から「SPリーチ演出」に発展する場合がある。SPリーチ演出は、キャラA~Dのうち何れか1人が敵と戦う演出である。SPリーチ演出中には、SPリーチ演出に対応するキャラクタを表す発光素子(不図示)が点灯し続ける一方でSPリーチ演出に対応しないキャラクタを表す発光素子(不図示)が消灯し続ける。SPリーチ演出中には新たなキャラクタが登場することがある。新たなキャラクタが登場したときから当該キャラクタを表す発光素子(不図示)が点灯し続ける。 Following FIG. 33(D), there is a case where the normal ready-to-win effect develops into the “SP ready-to-win effect”. The SP reach production is a production in which one of characters A to D fights an enemy. During the SP ready-to-win performance, light-emitting elements (not shown) representing characters corresponding to the SP ready-to-win performance continue to light up, while light emitting elements (not shown) representing characters not corresponding to the SP ready-to-win performance continue to go out. A new character may appear during the SP reach production. When a new character appears, a light-emitting element (not shown) representing that character continues to light up.
ノーマルリーチ演出からSPリーチ演出に発展する変動パターンの場合、ノーマルリーチ演出の終盤で中図柄が高速変動を開始する(図34(A)参照)。その後、中図柄が非表示にされると共にSPリーチ演出が開始される。これに伴って数字部分550とキャラクタ部分551とからなるリーチ図柄が、数字部分550のみからなるリーチ図柄に変化する。SPリーチ演出の開始前後には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP2からHP7に変化する。SPリーチ演出の開始に応じて当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51が非表示にされる。SPリーチ演出中は小図柄56が高速変動を継続する。なお、SPリーチ演出中は小図柄56がリーチ図柄と同じ組み合わせで仮停止表示してもよい。
In the case of the variation pattern that develops from the normal reach effect to the SP reach effect, the medium pattern starts to fluctuate at high speed at the end of the normal reach effect (see FIG. 34(A)). After that, the medium pattern is hidden and the SP ready-to-win effect is started. Along with this, the ready-to-win pattern consisting of the
SPリーチ演出でリーチハズレ目が仮停止表示することなく大当たりAが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO105に対応する場合)、図34(C)に続いてSPリーチ演出終盤で敵が敗北して図柄揃いが仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する。大当たりAが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。SPリーチ演出で大当たりBが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO115に対応する場合)、SPリーチ演出終盤で敵が敗北して時短図柄が仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する。図柄揃い又は時短図柄の仮停止表示中には、演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出を実行可能である一方、変動表示が続くことを示唆するチャレンジ演出は実行不可能である。
In the case of a variation pattern in which the reach-losing eye is not temporarily stopped and displayed in the SP reach production (that is, the case corresponding to the variation pattern O105), the enemy is displayed at the end of the SP reach production following FIG. After being defeated, the matching pattern is displayed as a temporary stop, and then it is stopped as it is. When the jackpot A is stopped and displayed, the jackpot game is executed. At the end of the jackpot game, the first alert and the second alert are displayed at the same time. After the end of the jackpot game, it shifts to a low-probability short-time. In the case of the variation pattern in which the big hit B is stopped and displayed in the SP ready-to-win performance (that is, the case corresponding to the variation pattern O115), the enemy is defeated at the end of the SP ready-to-win performance, the time-saving pattern is displayed to be temporarily stopped, and then the game is permanently stopped. During the temporary stop display of the matching pattern or the time-saving pattern, it is possible to execute the performance for notifying the jackpot such as operating the
図柄揃い又は時短図柄の仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP7からHP4に変化する。すなわち、数字部分550のみからなる装飾図柄55が数字部分550とキャラクタ部分551とからなる装飾図柄55に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、SPリーチ演出において大当たり図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。小図柄56は大当たり図柄が本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、大当たり図柄の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。なお、大当たり報知中は小図柄56が装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで仮停止表示してもよい。
The display priority of the
図34(D)に例示するようにSPリーチ演出終盤で敵が勝利してからリーチハズレ目が仮停止表示する変動パターンがある(すなわち、変動パターンO106、O107、H103、H106、H111、又はH112に対応する場合)。図34(E)及び(F)に例示するようにリーチハズレ目の仮停止表示中には遊技が再開することを強調する再開演出が実行される。すなわち、再開演出は、演出役物7が初期位置にある状態であって、演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出が行われないハズレ報知後に実行される。再開演出としては、画面右端から左端に向かって画面全体を覆うと共にオーバーラップしていく模様付きの黒い画像が表示される。再開演出は開始から所定時間(例えば2.5秒)経過したことに応じて終了する。再開演出中は装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP7からHP2に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、再開演出後に第1特別図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
As illustrated in FIG. 34 (D), there is a variation pattern in which the reach losing eye is temporarily stopped after the enemy wins at the end of the SP reach production (that is, the variation pattern O106, O107, H103, H106, H111, or H112 if applicable). As exemplified in FIGS. 34(E) and (F), a restart effect emphasizing that the game will be restarted is executed during the temporary stop display of the reach-losing eye. That is, the resuming effect is executed after the loss notification, in which the
図34(G)に例示するように、仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が通常のハズレ図柄であった場合、再開演出が終了してから当該ハズレ図柄が停止表示する。図34(I)に例示するように、仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が大当たりAであった場合、再開演出が終了してから図柄揃いが仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する。図34(H)及び(I)に例示するように、仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、再開演出が終了してから当該ハズレ図柄が停止表示する。図34(H)に例示するように、第1特別図柄判定の判定結果がハズレ(時短A)であった場合、「212」の組み合わせであった装飾図柄55が再開演出を介して「272」の組み合わせに変化する。これにより、再開演出によって気持ちを新たにした遊技者は低確時短で遊技を再開できる。また、図34(I)に例示するように、第1特別図柄判定の判定結果がハズレ(時短B)であった場合、「212」の組み合わせであった装飾図柄55が再開演出を介して「459」の組み合わせに変化する。これにより、再開演出によって気持ちを新たにした遊技者は低確微時短で遊技を再開することになる。なお、第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレである場合、再開演出の前後で装飾図柄55の組み合わせが変化することがなくてもよい。なお、ハズレ(時短A)である場合は再開演出を介して装飾図柄55が「272」の組み合わせに変化する一方、ハズレ(時短B)である場合は再開演出の前後で装飾図柄55の組み合わせが変化することがなくてもよい。
As exemplified in FIG. 34(G), if the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a normal lost symbol, the lost symbol is stopped and displayed after the restart effect is completed. As exemplified in FIG. 34(I), if the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a jackpot A, after the resuming effect is completed, the symbol alignment is temporarily stopped, and the game is permanently stopped. As illustrated in FIGS. 34(H) and (I), if the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a specific lost symbol, the lost symbol is stopped and displayed after the restart effect is completed. As exemplified in FIG. 34(H), when the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a loss (time saving A), the
第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、再開演出終了後には当該変動開始時と同じ天国モードの背景画像が表示される。なお、再開演出終了後であって当該変動終了までの間に背景画像が遊技状態変化確定用の天国モードの背景画像に変化してもよいし、変化先となる遊技状態用の背景画像が表示されてもよい。 When the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a specific lost symbol, the same heaven mode background image as at the start of the variation is displayed after the restart effect is finished. Note that the background image may change to the heaven mode background image for confirming the game state change until the end of the variation after the restart effect is finished, or the background image for the game state to be changed to is displayed. may be
ここで、SPリーチ演出の開始に応じて非表示にされた当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51は、SPリーチ演出開始直前と同じ見た目で再開演出中に再表示される。再表示された当該アイコン53は第1特別図柄の停止表示に応じて消去される。遊技機1では、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51の方が再開演出よりも表示優先度が低い。よって、再開演出中は、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51は再開演出が手前側に表示されることによって見えない。一方、遊技機1では、小図柄56並びに第4図柄57及び59の方が再開演出よりも表示優先度が高い。このため、遊技者は、再開演出の表示中であっても小図柄56及び第4図柄57を見ることができる。小図柄56及び第4図柄57の態様は再開演出の前後で同じ態様(具体的には高速変動)である。なお、小図柄56は再開演出中に装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで仮停止表示されてもよい。
Here, the
盤用照明装置74及び枠用照明装置10は、再開演出直前は天国モード用の発光パターンで発光し、再開演出中は再開演出用の発光パターン(例えば、白色で点滅する発光パターン)で発光し、再開演出終了直後は天国モード用の発光パターンで発光する。再開演出終了後には当該変動表示開始時と同じ天国モードに移行する。すなわち、再開演出中には、SPリーチ演出に対応する発光パターンとは異なる発光パターンで発光する。
The
ここで、仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が大当たり図柄であったとしても、再開演出が非表示となる時間は大当たり報知するよりも前である。このため、再開演出中は演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出も実行不可能であり、再開演出後に上記大当たり報知用の演出を実行可能である。なお、再開演出が実行された後に大当たりとなることがなくてもよい。この場合、再開演出中に加えて再開演出後も演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出を実行不可能である。
Here, even if the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a jackpot symbol, the time at which the restart effect is not displayed is before the jackpot is notified. Therefore, during the resuming effect, it is impossible to execute the effect for informing the big win such as activating the
再開演出中および再開演出後はチャレンジ演出を実行不可能である。なお、再開演出後にチャレンジ演出を実行可能でもよい。 The challenge presentation cannot be executed during and after the restart presentation. It should be noted that the challenge effect may be executed after the restart effect.
なお、再開演出が表示される際の態様は、画面全体に黒い画像がオーバーラップする態様でもよいし、モザイク状に現れていく画像によって画面全体が覆われる態様でもよい。また、再開演出の表示終了態様は、画面全体を覆う画像の透明度が上がり最終的に当該画像が非表示になる態様でもよいし、画面全体を覆う画像がモザイク状に欠けていき最終的に扉画像が非表示になる態様でもよい。 It should be noted that the form in which the restart effect is displayed may be a form in which the entire screen is overlapped with a black image, or a form in which the entire screen is covered with an image appearing in a mosaic pattern. In addition, the mode of ending the display of the resuming effect may be a mode in which the transparency of the image covering the entire screen is increased and the image is finally hidden, or the image covering the entire screen is missing in a mosaic pattern and finally the door is closed. The image may be hidden.
図34(D)に例示するようにSPリーチ演出終盤で敵が勝利してからリーチハズレ目が仮停止表示した後にチャレンジ演出が実行される変動パターンがある(すなわち、変動パターンO107又はH112に対応する場合)。図35(A)及び(B)に例示するように、チャレンジ演出中にはリーチ図柄が非表示にされると共に操作促進演出が実行される。操作促進演出は、ボタン画像90及びゲージ画像91を予め定められた有効期間(例えば3秒)に亘って表示することによって、遊技者に演出ボタン26の操作を促す演出である。チャレンジ演出中には中図柄として停止する装飾図柄の候補が表示されており、有効期間中の操作に応じて中図柄が仮停止表示する。なお、有効期間中に操作がなかった場合は、予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始時から3秒経過時)で中図柄が仮停止表示する。
As exemplified in FIG. 34(D), there is a variation pattern in which the challenge effect is executed after the enemy wins at the end of the SP reach effect and the reach losing eye is temporarily stopped (that is, the change pattern corresponds to O107 or H112 case). As illustrated in FIGS. 35A and 35B, during the challenge effect, the ready-to-win pattern is hidden and the operation promotion effect is executed. The operation promotion effect is an effect that prompts the player to operate the
チャレンジ演出が成功である場合はリーチ図柄と同じ中図柄が仮停止表示して大当たりAが報知される。大当たり報知中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP6、HP9、HP4の順に変化する。図35(G)に例示するように大当たりAが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。
When the challenge performance is successful, the medium symbol same as the ready-to-win symbol is temporarily stopped and a big hit A is announced. During the jackpot notification, the display priority of the
一方、チャレンジ演出が失敗である場合はリーチ図柄と異なる中図柄が仮停止表示して通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示することが示唆される。チャレンジ演出失敗に続いて再開演出が実行されてから通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示する。リーチ図柄は、チャレンジ演出失敗時から再開演出終了時まで非表示にされたままであり、再開演出終了時から再表示される。装飾図柄55の表示優先度は再開演出開始前は表示パターンHP7であり、再開演出中に表示パターンHP2に変化し、その後の停止表示時に表示パターンHP3に変化する。なお、再開演出の前後で装飾図柄55の表示優先度が変化しなくてもよい。
On the other hand, when the challenge effect is unsuccessful, it is suggested that the medium symbols different from the ready-to-win symbols are temporarily stopped and displayed and the normal losing symbols are stopped. After the restart performance is executed following the failure of the challenge performance, the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed. The ready-to-win pattern remains hidden from the failure of the challenge performance until the end of the restart performance, and is redisplayed after the end of the restart performance. The display priority of the
なお、再開演出を実行する場合において以下の構成でもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が中図柄全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が中図柄の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前は中図柄が左図柄(及び右図柄)よりも大きく、再開演出終了直後再開演出終了直後は左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の大きさは互いに同じでもよい。
・再開演出直前と再開演出終了直後とでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄相互間の大きさの比率が同じでもよい。
・再開演出直前と再開演出終了直後とでは装飾図柄55の見た目が同じでもよい。
・当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51はSPリーチ演出中に表示が継続されており、再開演出よりも当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51の方が表示優先度が高くてもよい。
・当該アイコン53は変動表示開始時またはSPリーチ演出開始時に消去され、その後に再表示されなくてもよい。
・停止表示される特別図柄の種類に関わらず、再開演出終了後にはSPリーチ演出に対応する演出モードであって当該変動表示開始時とは見た目が異なる特別な天国モードに移行してもよい。
・チャレンジ演出が実行されることを期待させる演出を実行した後、チャレンジ演出を実行することなく再開演出を実行してもよい。
・チャレンジ演出実行後のハズレ報知に応じて再開演出を実行してもよい。
Note that the following configuration may be used when executing the resuming effect.
- The size of the entire medium pattern may be larger, smaller, or the same immediately after the end of the resuming effect than immediately before the resuming effect.
The size of the
The size of the entire left pattern (and right pattern) may be larger, smaller, or the same immediately after the end of the resuming effect as compared to immediately before the resuming effect.
The size of the
・Just before the restart effect, the middle pattern is larger than the left pattern (and the right pattern), and immediately after the restart effect is finished.
- The size ratio between the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be the same immediately before the restart effect and immediately after the end of the restart effect.
- The appearance of the
The
- The
・Regardless of the type of the special symbol to be stopped and displayed, after the restart effect is completed, the game may shift to a special heaven mode which is a effect mode corresponding to the SP ready-to-win effect and looks different from when the variable display is started.
- After executing the effect to expect the challenge effect to be executed, the restart effect may be executed without executing the challenge effect.
- You may perform a restart production|presentation according to the loss alert|report after execution of a challenge production|presentation.
次に、図36を参照して第1実施形態における低確時短状態の演出例について説明する。図36(A)及び(B)に例示するように、大当たりDとなる変動パターンO201は、リーチ演出が実行されることなく図柄揃いとなる即当たりの変動パターンである。図36(B)に例示するように大当たりDが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。当該大当たり遊技では第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが表示されない。当該大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。なお、当該大当たり遊技では第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが表示されてもよい。遊技機1では、小当たりBとなる変動パターンK201である場合も変動パターンO201と同様の演出が実行される。
Next, with reference to FIG. 36, the example of the production|presentation of the low certainty short working hours state in 1st Embodiment is demonstrated. As exemplified in FIGS. 36A and 36B, the variation pattern O201 for the big win D is an immediate winning variation pattern in which the symbols are aligned without executing the ready-to-win effect. As shown in FIG. 36(B), when the jackpot D is stopped and displayed, the jackpot game is executed. In the jackpot game, the first alert and the second alert are not displayed. After the end of the jackpot game, it shifts to a low-probability reduction of working hours. In addition, in the jackpot game, the first alert and the second alert may be displayed. In the
図36(A)、(C)、および(B)に例示するように、大当たりDとなる変動パターンO202は、低確時短から低確非時短への移行(転落)を示唆してから即当たりとなる変動パターンである。転落示唆の開始時からは扉画像の表示が開始されると共に操作促進演出が実行される。扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像と同じである。なお、転落示唆の開始時から表示される扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像と異なってもよい。大当たりDとなる場合、有効期間中の操作の有無に関わらず予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始時から3秒経過時)で扉画像が開放して即当たりとなる。なお、大当たりDとなる場合、有効期間中の操作に応じて扉画像が開放して即当たりとなってもよい。 As illustrated in FIGS. 36 (A), (C), and (B), the variation pattern O202 that becomes a jackpot D suggests a transition (fall) from a low probability short working hour to a low probability short working hour and then immediately hits It is a fluctuation pattern that becomes From the start of the fall suggestion, the display of the door image is started and the operation prompting effect is executed. The door image is the same as the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state. In addition, the door image displayed from the start of the fall suggestion may be different from the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state. In the case of a jackpot D, the door image opens at a predetermined effective period end timing (for example, when 3 seconds elapse from the start of the operation promoting performance) regardless of whether or not there is an operation during the effective period, and the player wins immediately. Incidentally, when the jackpot D is won, the door image may be opened according to the operation during the validity period, and the win may be made immediately.
図36(A)、(C)、及び(D)に例示するように、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される変動パターンH202は、転落を示唆してからハズレ報知される変動パターンである。転落示唆の開始時から表示が開始された扉画像は、有効期間中の操作の有無に関わらず予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始時から3秒経過時)で扉画像が開放してハズレ報知される。なお、ハズレとなる場合、有効期間中の操作に応じて扉画像が開放してハズレ報知されてもよい。 As illustrated in FIGS. 36A, 36C, and 36D, the variation pattern H202 in which normal losing symbols are stopped and displayed is a variation pattern in which a failure is notified after suggesting a fall. The door image that started to be displayed from the start of the suggestion of falling is displayed at a predetermined effective period end timing (for example, when 3 seconds have passed since the start of the operation promotion effect) regardless of whether or not there is an operation during the effective period. is opened and a failure is notified. In addition, in the case of a failure, the door image may be opened according to the operation during the validity period to notify the failure.
図36(A)、(C)、及び(E)に例示するように、小当たりCとなる変動パターンK203は、転落を示唆してから小当たりCが小図柄56によって報知される変動パターンである。転落示唆の開始時から表示が開始された扉画像は、有効期間中の操作に関わらず予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始時から3秒経過時)で閉鎖する。図36(E)に例示するように小当たりCが停止表示すると小当たり遊技中のV入賞を条件に大当たり遊技が実行される。当該大当たり遊技では第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが表示されない。当該大当たり遊技終了後(遊技状態は低確非時短)は低確非時短に制御される。また、小当たり遊技中にV入賞しなかった場合は大当たり遊技が実行されることなく低確非時短に制御される。低確非時短へ移行するとベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が行われる。
As illustrated in FIGS. 36(A), (C), and (E), the variation pattern K203 that becomes the small hit C is a variation pattern in which the small hit C is reported by the
図36(F)は低確非時短に制御されているときに第2特別図柄判定の保留が消化されたときの演出例である。低確非時短における1回目の第2特別図柄の変動表示開始時から最先の第2特別図柄判定の保留に係る変動表示が終了する直前まで、遊技者が大当たり遊技によって得られた賞球数を示唆するリザルトが表示される。また、リザルトの開始時からは扉画像の表示が開始される。扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像、及び転落示唆の開始時から表示される扉画像と同じである。なお、リザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像、及び転落示唆の開始時から表示される扉画像と異なってもよい。なお、リザルト及びリザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像は、低確時短の時短回数が終了したときにも表示される(例えば、図36(D)から(F)への流れ)。低確時短の時短回数が終了する変動表示が連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合、当該変動表示が終了すると低確非時短に移行するので、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が行われるようになる。一方、低確時短の時短回数が終了する変動表示が連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たす場合、当該変動表示が終了すると低確時短に移行するので、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が停止したままである。 FIG. 36(F) is an example of an effect when the suspension of the second special symbol determination is digested while being controlled to the low probability and short working hours. From the start of the first variable display of the second special symbol in the low-probability short time period to immediately before the end of the variable display related to the suspension of the first second special symbol judgment, the number of prize balls obtained by the player through the jackpot game. A result suggesting is displayed. Moreover, the display of the door image starts from the start of the result. The door image is the same as the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state, and the door image displayed from the start of the fall suggestion. In addition, the door image displayed from the start of the result is the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol fluctuation display after the transition to the low probability time saving state, and the door image displayed from the start of the fall suggestion. may differ from In addition, the door image displayed from the start of the result and the result is also displayed when the number of times of reduced working hours of low probability ends (for example, the flow from FIG. 36 (D) to (F)). If the variable display at which the number of times of low-probability time-saving ends does not meet the condition of 750 consecutive losses, when the variable display ends, it will shift to low-probability non-time-saving, so the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation will be counted by On the other hand, if the variable display at which the number of times of low-probability time-saving ends ends in a continuous loss of 750 times, it will shift to low-probability of time-saving when the variable display ends, so the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation counting by remains stopped.
なお、低確時短の最終変動よりも所定回数前(例えば10変動前)の変動表示から低確時短の最終変動までに亘って、特別図柄が変動表示を開始する毎に時短残り回数を報知するカウントダウンを行ってもよい。遊技機1では、図36(D)に例示するように低確時短の最終変動よりも所定回数前(例えば3変動前)の変動表示から当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51が非表示にされる。なお、低確時短の最終変動が終わるまで当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51が表示された状態でもよい。
In addition, every time the special symbol starts the variable display, the remaining number of times of shortening is notified from the variable display of a predetermined number of times before the final variation of the low-probability short working hours (for example, 10 variations before) to the final variation of the low-probable short working hours. You can do a countdown. In the
仮にすべての第2特別図柄判定の保留がハズレであった場合、最先の第2特別図柄判定の保留に係る変動表示が終了する直前においてリザルトが非表示となると共に扉画像が開放する(図36(G)参照)。これに伴って装飾図柄55の表示優先度はリザルト表示中に表示パターンHP9からHP3に変化する。
If all the suspension of the second special symbol determination is lost, the result is hidden and the door image is opened immediately before the end of the variable display related to the suspension of the first special symbol determination (Fig. 36(G)). Along with this, the display priority of the
なお、リザルト表示に伴う扉画像を表示する場合において以下の構成でもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における天国モードのとき方が中図柄全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における天国モードのとき方が中図柄の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における天国モードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における天国モードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときは中図柄が左図柄(及び右図柄)よりも大きく、扉画像表示直後における天国モードのときは左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の大きさは互いに同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときと、扉画像表示直後における天国モードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄相互間の大きさの比率が同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示中は扉画像用の発光パターンで発光し、扉画像表示終了直後は天国モード用の発光パターンで発光する。
It should be noted that the following configuration may be used when displaying the door image accompanying the result display.
The size of the entire medium pattern may be larger, smaller, or the same size in the heaven mode immediately after the door image is displayed than in the RUSH mode before the door image is displayed.
The size of the
・The overall size of the left pattern (and the right pattern) may be larger, smaller, or the same size in heaven mode immediately after displaying the door image than in RUSH mode before displaying the door image. .
The size of the
・In the RUSH mode before the door image is displayed, the middle pattern is larger than the left (and right) pattern, and in the Heaven mode immediately after the door image is displayed, the left, middle, and right patterns are the same size. It's okay.
The size ratio between the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be the same between the RUSH mode before displaying the door image and the Heaven mode immediately after displaying the door image.
・While the door image is being displayed, light is emitted in the light emission pattern for the door image, and immediately after the door image is displayed, the light is emitted in the light emission pattern for heaven mode.
図36(H)に例示するように、低確非時短において消化された第2特別図柄判定の保留が大当たりDである場合、リザルトが消去されると共に及びリザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像が開放して即当たりとなる。図36(I)に例示するように、低確非時短において消化された第2特別図柄判定の保留が小当たりCである場合、リザルトが消去されると共に及びリザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像が開放して小当たりCが小図柄56によって報知される。 As exemplified in FIG. 36 (H), when the hold of the second special symbol judgment digested in the low probability and short working hours is a jackpot D, the result is erased and the door image displayed from the start of the result will open and hit immediately. As illustrated in FIG. 36 (I), when the hold of the second special symbol judgment digested in the low probability and short working hours is a small hit C, the result is erased and the door displayed from the start of the result The image is opened and a small winning C is notified by a small symbol 56.例文帳に追加
[遊技制御基板100による小入賞口開放制御処理]
以下、図37を参照しつつ、遊技制御基板100によって実行される小入賞口開放制御処理について説明する。この小入賞口制御処理は、メインROM100bに記憶されている小当たり時の図柄決定テーブルに基づいて選択した小当たり遊技を実行する処理である。ここで、図37は、図19のステップS5Aにおける小入賞口開放制御処理の詳細フローチャートである。メインCPU100aは、小当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されているか否かを判定する(ステップS641)。ここで、小当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されていないと判定された場合(ステップS641:NO)、ステップS7の大入賞口制御処理に処理が進められる。
[Small winning opening control processing by game control board 100]
Hereinafter, the small winning opening opening control process executed by the
メインCPU100aは、大当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されていると判定した場合(ステップS641:YES)、停止中処理によって小当たり遊技に係るオープニングコマンドをセットしてからの経過時間が所定のオープニング時間に達したか否かに基づいて、小当たり遊技のオープニング期間中であるか否かを判定する(ステップS642)。ここで、オープニング期間中であると判定した場合(ステップS642:YES)、同じく経過時間が所定のオープニング時間に達したか否かに基づいて、オープニング時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS643)。ここで、オープニング時間が経過していないと判定された場合(ステップS643:NO)、ステップS7の大入賞口制御処理に処理が進められる。
When the
メインCPU100aは、オープニング時間が経過したと判定した場合(ステップS643:YES)、小入賞口開閉ソレノイド51cの動作パターン等を設定して、その設定情報をメインRAM100cに格納する(ステップS644)。このステップS644の処理が実行されることによって、ラウンド終了後のエンディング時間等の小当たり遊技に関する各種時間も併せて設定される。
When determining that the opening time has elapsed (step S643: YES), the
ステップS644の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、メインRAM100cに記憶されている小入賞口19への遊技球の入賞数Xをリセットする(ステップS645)。
Following the process of step S644, the
ステップS645の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、小入賞口の開放制御を開始する(ステップS646)。次に、メインCPU100aは、この開放制御が開始されてからの経過時間である開放時間の計測を開始する(ステップS647)。
Following the process of step S645, the
メインCPU100aは、小当たり遊技におけるオープニング中ではないと判定した場合(ステップS642:NO)、例えばメインRAM100cに記憶されている現在の状態が小当たり遊技におけるどの時点であるかを示す情報に基づいて、エンディング期間中であるか否かを判定する(ステップS648)。ここで、エンディング期間中であると判定された場合(ステップS648:YES)、後述するステップS659に処理が進められる。
When the
メインCPU100aは、小当たり遊技におけるエンディング中ではないと判定した場合(ステップS648:NO)、小入賞口スイッチが「ON」になったか否かを判定する(ステップS649)。具体的には、小入賞口スイッチ116aからの検知信号の有無に基づいて、小入賞口スイッチ116aが「ON」になったか否かを判定する。
When the
ここで、メインCPU100aは、小入賞口スイッチ116aが「ON」になったと判定した場合(ステップS649:YES)、小入賞口19に1個の遊技球が入賞したと判断して、遊技球の入賞数Xを「1」加算した値に更新する(ステップS650)。
Here, when the
ステップS650の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、V入賞口スイッチ116bが「ON」になったか否かを判定する。V入賞口スイッチ116bが「ON」になったと判定した場合(ステップS651:YES)、V入賞コマンドをセットし(ステップS652)、大当たり遊技フラグを「ON」にする(ステップS653)。
Following the processing of step S650, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS653の処理を実行した場合、ステップS647の処理を実行した場合、又は小入賞口スイッチ116aが「ON」ではないと判定した場合(ステップS649:NO)、小入賞口19の開放開始から規定開放時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS654)。具体的には、上記ステップS647の処理によって計測が開始された開放時間が、メインROM100bに記憶されている規定開放時間に達したか否かを判定する。
When the
メインCPU100aは、規定開放時間が経過していないと判定した場合(ステップS654:NO)、メインRAM100cに記憶されている今回のラウンド遊技における遊技球の入賞数Xが、メインROM100bに記憶されている大入賞口13の閉塞タイミングを規定する遊技球数Xmax(例えば「9」)と一致するか否かを判定する(ステップS655)。ここで、入賞数Xが遊技球数Xmaxと一致しないと判定された場合(ステップS655:NO)、ステップS7の大入賞口制御処理に処理が進められる。
When the
一方、メインCPU100aは、入賞数Xが遊技球数Xmaxと一致すると判定した場合(ステップS655:YES)、小入賞口開閉ソレノイド51cにステップS646の処理で開始した小入賞口19の開放制御を終了させる(ステップS656)。
On the other hand, when the
ステップS656の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、エンディング時間の計測を開始し(ステップS657)、エンディングコマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS658)。このエンディングコマンドは、小当たり遊技のラウンド遊技が終了したことを通知するコマンドであり、ステップS9の送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信される。
Following the process of step S656, the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS658の処理を実行した場合、エンディング時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS659)。エンディング時間が経過していないと判定された場合(ステップS659:NO)、ステップS7の大入賞口制御処理に処理が進められる。
After executing the process of step S658, the
メインCPU100aは、エンディング時間が経過したと判定した場合(ステップS659:YES)、小当たり遊技を終了させるために、小当たり遊技フラグを「OFF」に設定する(ステップS660)。
When determining that the ending time has elapsed (step S659: YES), the
[遊技制御基板100による大入賞口開放制御処理]
以下、図38を参照しつつ、遊技制御基板100によって実行される大入賞口開放制御処理について説明する。この大入賞口制御処理は、メインROM100bに記憶されている大当たり時の図柄決定テーブルに基づいて選択した大当たり遊技を実行する処理である。ここで、図38は、図19のステップS6Aにおける大入賞口開放制御処理の詳細フローチャートである。メインCPU100aは、ステップS5Aの小入賞口開放制御処理に続いて、大当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されているか否かを判定する(ステップS601)。ここで、大当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されていないと判定された場合(ステップS601:NO)、ステップS8の賞球処理に処理が進められる。
[Big Winning Port Opening Control Processing by Game Control Board 100]
Hereinafter, with reference to FIG. 38, the big winning opening opening control process executed by the
メインCPU100aは、大当たり遊技フラグが「ON」に設定されていると判定した場合(ステップS601:YES)、停止中処理によって大当たり遊技に係るオープニングコマンドをセットしてからの経過時間が所定のオープニング時間に達したか否かに基づいて、大当たり遊技のオープニング中であるか否かを判定する(ステップS602)。ここで、オープニング中であると判定した場合(ステップS602:YES)、同じく経過時間が所定のオープニング時間に達したか否かに基づいて、オープニング時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS603)。ここで、オープニング時間が経過していないと判定された場合(ステップS603:NO)、ステップS8の賞球処理に処理が進められる。
When the
メインCPU100aは、オープニング時間が経過したと判定した場合(ステップS603:YES)、大当たり遊技のラウンド数Rmax、大入賞口開閉ソレノイド51bの動作パターン等を設定して、その設定情報をメインRAM100cに格納する(ステップS604)。このステップS604の処理が実行されることによって、ラウンドと次のラウンドとの間のインターバル時間、最終ラウンド終了後のエンディング時間等の大当たり遊技に関する各種時間も併せて設定される。
When determining that the opening time has elapsed (step S603: YES), the
ステップS604の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、メインRAM100cに記憶されている大入賞口13への遊技球の入賞数Yをリセットし(ステップS605)、同じくメインRAM100cに記憶されている大当たり中のラウンド数Rを「1」加算した値に更新する(ステップS606)。このラウンド数Rは、大当たり開始前は「0」に設定されており、ステップS606の処理が行われる毎に「1」加算される。
Following the process of step S604, the
ステップS606の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、大入賞口の開放制御を開始する(ステップS607)。次に、メインCPU100aは、この開放制御が開始されてからの経過時間である開放時間の計測を開始する(ステップS608)。そして、大入賞口13を開放するラウンド遊技が開始されたことを通知するラウンド開始コマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS609)。
Following the process of step S606, the
メインCPU100aは、大当たり遊技におけるオープニング中ではないと判定した場合(ステップS602:NO)、例えばメインRAM100cに記憶されている現在の状態が大当たり遊技におけるどの時点であるかを示す情報に基づいて、最終ラウンド終了直後のエンディング中であるか否かを判定する(ステップS611)。ここで、エンディング中であると判定された場合(ステップS611:YES)、後述するステップS625に処理が進められる。
When the
メインCPU100aは、大当たり遊技におけるエンディング中ではないと判定した場合(ステップS611:NO)、例えばメインRAM100cに記憶されている現在の状態が大当たり遊技におけるどの時点であるかを示す情報に基づいて、インターバル中(ラウンドと次のラウンドとの間)であるか否かを判定する(ステップS612)。ここで、インターバル中であると判定した場合(ステップS612:YES)、前回のラウンド遊技終了時に大入賞口13が閉塞してから、ステップS604の処理によって設定されたインターバル時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS613)。ここで、インターバル時間が経過したと判定された場合(ステップS613:YES)、次のラウンド遊技を開始するタイミングになっているため、上記ステップS605に処理が進められる。逆に、インターバル時間が経過していないと判定された場合(ステップS613:NO)、ステップS8の賞球処理に処理が進められる。
When the
一方、メインCPU100aは、インターバル中ではないと判定した場合(ステップS612:NO)、ラウンド遊技中であると判断して、大入賞口スイッチが「ON」になったか否かを判定する(ステップS614)。具体的には、大入賞口検出スイッチ50aからの検知信号の有無に基づいて、大入賞口検出スイッチ50aが「ON」になったか否かを判定する。
On the other hand, if the
ここで、メインCPU100aは、大入賞口検出スイッチ50aが「ON」になったと判定した場合(ステップS614:YES)、大入賞口13に1個の遊技球が入賞したと判断して、遊技球の入賞数Yを「1」加算した値に更新する(ステップS615)。
Here, when the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS615の処理を実行した場合、ステップS609の処理を実行した場合、又は大入賞口検出スイッチ50aが「ON」ではないと判定した場合(ステップS614:NO)、大入賞口13の開放開始から規定開放時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS616)。具体的には、上記ステップS608の処理によって計測が開始された開放時間が、メインROM100bに記憶されている規定開放時間に達したか否かを判定する。
When the
メインCPU100aは、規定開放時間が経過していないと判定した場合(ステップS616:NO)、メインRAM100cに記憶されている今回のラウンド遊技における遊技球の入賞数Yが、メインROM100bに記憶されている大入賞口13の閉塞タイミングを規定する遊技球数Ymax(例えば「9」)と一致するか否かを判定する(ステップS617)。ここで、入賞数Yが遊技球数Ymaxと一致しないと判定された場合(ステップS617:NO)、ステップS8の賞球処理に処理が進められる。
When the
一方、メインCPU100aは、入賞数Yが遊技球数Ymaxと一致すると判定した場合(ステップS617:YES)、又は規定開放時間が経過したと判定した場合(ステップS616:YES)、大入賞口開閉ソレノイド51bにステップS607の処理で開始した大入賞口13の開放制御を終了させる(ステップS618)。
On the other hand, if the
ステップS618の処理に続いて、メインCPU100aは、メインRAM100cに記憶されている大当たり遊技の現在のラウンド数Rが、上記ステップS604の処理によって設定されたラウンド数Rmaxと一致するか否かを判定する(ステップS619)。ここで、ラウンド数Rがラウンド数Rmaxと一致しないと判定した場合(ステップS619:NO)、次のラウンド遊技の開始タイミングを制御するために、大入賞口13が閉塞されてからの経過時間であるインターバル時間の計測を開始する(ステップS620)。このステップS620の処理によって計測が開始されたインターバル時間は、上記ステップS613の処理に使用される。
Following the process of step S618, the
一方、メインCPU100aは、ラウンド数Rがラウンド数Rmaxと一致すると判定した場合(ステップS619:YES)、エンディング時間の計測を開始し(ステップS622)、メインRAM100cに記憶されているラウンド数Rをリセットし(ステップS623)、エンディングコマンドをメインRAM100cにセットする(ステップS624)。このエンディングコマンドは、最後のラウンド遊技が終了したことを通知するコマンドであり、ステップS8の送信処理によって演出制御基板130に送信される。なお、このエンディングコマンドは、大当たり遊技終了後の遊技状態に関する情報(遊技情報)を含む。
On the other hand, if the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS624の処理を実行した場合、又はエンディング中であると判定した場合(ステップS611:YES)、設定エンディング時間が経過したか否かを判定する(ステップS625)。具体的には、上記ステップS622の処理によって計測を開始したエンディング時間が、上記ステップS604の処理によって設定された設定エンディング時間に達したか否かを判定する。ここで、エンディング時間が経過していないと判定された場合(ステップS625:NO)、ステップS8の賞球処理に処理が進められる。
When the
メインCPU100aは、設定エンディング時間が経過したと判定した場合(ステップS625:YES)、特別図柄の種類に応じて時短回数と遊技状態指定コマンドとをセットする(ステップS626)。
When determining that the set ending time has passed (step S625: YES), the
メインCPU100aは、ステップS626の処理の後、大当たり遊技を終了させるために、大当たり遊技フラグを「OFF」に設定する(ステップS627)。
After the processing of step S626, the
[演出制御基板130によるタイマ割込み処理]
以下、図39を参照しつつ、演出制御基板130において実行されるタイマ割込み処理について説明する。ここで、図39は、演出制御基板130において実行されるタイマ割込み処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。以下では、図39~図41に示す処理を演出制御基板130が行うものとして説明するが、これらの処理の一部または全部は、演出制御基板130、画像音響制御基板140、およびランプ制御基板150の何れにおいて実行されてもよい。
[Timer interrupt processing by production control board 130]
Hereinafter, timer interrupt processing executed in the
演出制御基板130におけるサブCPU130aは、遊技制御基板100で行われるタイマ割込み処理と同様に、図39に例示される一連の処理を一定時間(例えば4ミリ秒)毎に繰り返し実行する。なお、図39~図41に示す処理は、サブROM130bに記憶されているプログラムに基づいてサブCPU130aが発行する命令に従って行われる。
The
サブCPU130aは、まず、遊技制御基板100からのコマンドに応じた処理を行うコマンド受信処理を実行した後(ステップS10)、送信処理を実行する(ステップS30)。コマンド受信処理では、遊技制御基板100及びランプ制御基板150から各種コマンドを受信したことに応じた処理が行われる。具体的には、サブCPU130aは、例えば、遊技制御基板100から遊技情報としてのコマンドを受信し、受信したコマンドに応じた演出内容を設定する。例えば、サブCPU130aは、特別図柄の変動パターンに対応した変動演出パターンを決定し、決定した変動演出パターンにおいて実行可能な予告演出の実行の有無および内容を決定する。そして、サブCPU130aは、例えば、決定した演出の実行を指示するコマンドを生成し、画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150に送信する。これにより、演出制御基板130において決定された内容の演出が、画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150で実行されることになる。コマンド受信処理については、図40に基づいて後に詳述する。
The
ステップS30の処理に続いて、サブCPU130aは、データ転送処理を行う(ステップS50)。サブCPU130aは、例えば、各演出の開始に伴って枠用照明装置10等を発光制御させたり演出役物7等を制御(例えば動作)させたりするために、画像音響制御基板140から送信されたデータをランプ制御基板150に転送する。このデータ転送処理が行われることによって、例えば、液晶画面5に表示された演出画像やスピーカ24によって出力された演出音と連動して盤用照明装置74と枠用照明装置10とを発光させる発光制御が行われたり、演出役物7が動作されたりする。以上でサブCPU130aは、図39に示す処理を終了する。
Following the processing of step S30, the
[演出制御基板130によるコマンド受信処理]
図40は、図39のステップS10におけるコマンド受信処理の詳細フローチャートである。図40に例示されるように、サブCPU130aは、まず、遊技制御基板100又はランプ制御基板から送信されたコマンドを受信したか否かを判定する(ステップS11)。ここで、コマンドを受信していないと判定された場合(ステップS11:NO)、ステップS30に処理が進められる。
[Command reception processing by production control board 130]
FIG. 40 is a detailed flowchart of command reception processing in step S10 of FIG. As illustrated in FIG. 40, the
サブCPU130aは、コマンドを受信したと判定した場合(ステップS11:YES)、そのコマンドがステップS3194C(図27)又はステップS627(図38参照)の処理に応じて遊技制御基板100から送信された遊技状態指定コマンドであるか否かを判定する(ステップS12)。ここで、受信したコマンドが遊技状態指定コマンドではないと判定された場合(ステップS12:NO)、後述するステップS14に処理が進められる。
When the
サブCPU130aは、受信したコマンドが遊技状態指定コマンドであると判定した場合(ステップS12:YES)、遊技状態を更新する遊技状態更新処理を実行する(ステップS13)。
When the
サブCPU130aは、受信したコマンドが保留コマンドではないと判定した場合(ステップS12:NO)、そのコマンドがステップS311(図23参照)の処理に応じて遊技制御基板100から送信された変動開始コマンドであるか否かを判定する(ステップS14)。ここで、受信したコマンドが変動開始コマンドではないと判定された場合(ステップS14:NO)、後述するステップS16に処理が進められる。
When the
サブCPU130aは、受信したコマンドが変動開始コマンドであると判定した場合(ステップS14:YES)、変動開始コマンド受信処理を実行する(ステップS15)。変動開始コマンド受信処理では、サブCPU130aは、例えば、変動開始コマンドに含まれる特別図柄の変動パターンに対応した変動演出パターンを決定する。この変動開始コマンド受信処理については、図41に基づいて後に詳述する。
When the
サブCPU130aは、受信したコマンドが変動開始コマンドではないと判定した場合(ステップS14:NO)、そのコマンドがステップS316(図23参照)の処理に応じて遊技制御基板100から送信された図柄確定コマンドであるか否かを判定する(ステップS16)。サブCPU130aは、図柄確定コマンドであると判定した場合(ステップS16:YES)、変動演出終了コマンドをサブRAM130cにセットする(ステップS17)。この変動演出終了コマンドがステップS30の送信処理によって画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150に送信されることで、特別図柄の停止表示に伴って、装飾図柄55および小図柄56が液晶画面5に停止表示されることになる。
When the
サブCPU130aは、受信したコマンドが図柄確定コマンドではないと判定した場合(ステップS16:NO)、そのコマンドがランプ制御基板150から送信された操作コマンドであるか否かを判定する(ステップS18)。この操作コマンドは、ランプ制御基板150のランプCPU151が演出ボタン26や演出キー27の操作を検知した場合に、その情報を通知するためにランプ制御基板150から送信されるコマンドである。操作コマンドは、演出ボタン26及び演出キー27のうち何れが操作されたかを示す情報、演出キー27が操作された場合にはどのキーが操作されたかを示す情報等を含む。
When the
サブCPU130aは、操作コマンドを受信したと判定した場合(ステップS18:YES)、操作演出開始コマンドをサブRAM130cにセットする(ステップS19)。このコマンドは、ステップS30の送信処理によって画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150に送信される。画像音響制御基板140は、このコマンドを受信することで、例えば、有効期間中の操作に応じて液晶画面5やスピーカ24を用いて画像や音による演出を実行できる。また、ランプ制御基板150は、このコマンドを受信することで、有効期間中の操作に応じて各種ランプを発光させる演出を実行できる。
When the
一方、受信したコマンドが操作コマンドではないと判定された場合(ステップS18:NO)、そのコマンドに応じた処理を実行する(ステップS20)。一例として、サブCPU130aは、遊技制御基板100から送信されたオープニングコマンドを受信したと判定した場合は、大当たり(又は小当たり)の種類に対応した大当たり遊技(又は小当たり遊技)の演出の開始を指示するオープニングコマンドをセットする。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the received command is not an operation command (step S18: NO), a process corresponding to that command is executed (step S20). As an example, when the
[演出制御基板130による変動開始コマンド受信処理]
以下、図41を参照しつつ、遊技制御基板100から送信された変動開始コマンドを受信したことに応じて演出制御基板130において実行される変動開始コマンド受信処理について説明する。ここで、図41は、図40のステップS15における変動開始コマンド受信処理の詳細フローチャートである。
[Variation start command reception processing by production control board 130]
Hereinafter, with reference to FIG. 41, the variation start command reception processing executed in the
図40に例示されるように、サブCPU130aは、遊技制御基板100から受信したコマンドが変動開始コマンドであると判定した場合(ステップS14:YES)、変動演出パターン乱数を取得してサブRAM130cに格納する(ステップS1511)。変動演出パターン乱数等のサブCPU130aは、変動開始コマンドを受信した時点の値を変動演出パターン乱数として取得する。
As illustrated in FIG. 40, when the
ステップS1511の処理に続いて、サブCPU130aは、遊技制御基板100から受信した変動開始コマンドを解析する(ステップS1512)。変動開始コマンドには、上述したように、大当たり判定(図25参照)の判定結果を示す大当たりか否かの情報、特別図柄の種類、特別図柄の変動パターンの設定情報、遊技機1の遊技状態を示す情報等が含まれている。サブCPU130aは、この処理を行うことにより、変動演出パターンを決定するのに必要な情報を得ている。
Following the processing of step S1511, the
ステップS1512の処理に続いて、サブCPU130aは、時短遊技フラグON後の1回転目の特別図柄の変動表示であるか否かを判定する(ステップS1513)。ステップS1513の処理でYESと判定された場合、サブCPU130aは、低確時短用の変動パターンであるか否かを判定する(ステップS1514)。ステップS1514の処理でYESと判定された場合、サブCPU130aは、右打ちを促す文字および扉画像の表示を伴う右打ち報知態様の変動演出パターンを決定する(ステップS1515)。
Following the process of step S1512, the
ステップS1513又はステップS1514の処理でNOと判定された場合、サブCPU130aは、右打ち報知態様ではない変動演出パターンを決定する(ステップS1516)。
When it is determined as NO in the process of step S1513 or step S1514, the
ステップS1515の処理を実行した場合、又はステップS1516の処理を実行した場合、サブCPU130aは、これらの処理で決定した設定内容を含む変動演出開始コマンドをセットする(ステップS1517)。変動演出開始コマンドは、ステップS30の送信処理(図39参照)によって画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150に送信される。これにより、演出制御基板130において決定された態様の演出が、画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150によって実現されることになる。
When the process of step S1515 is executed, or when the process of step S1516 is executed, the
ステップS1517の処理に続いて、サブCPU130aは、サブRAM130cに格納されている保留数の値を「1」減算する(ステップS1518)。以上でサブCPU130aは、図41に示す処理を終了する。
Following the process of step S1517, the
[第1実施形態の効果]
第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確非時短状態は低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な遊技状態である。遊技機1が電源「OFF」状態であるときに、設定キーSW「OFF」状態かつRWMクリアSW「ON」状態で電源「ON」状態にされた場合、遊技機1が起動した直後にRAMクリアモードに移行する。RAMクリアモードに移行すると、遊技状態に関する情報が初期化されて遊技機1は確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な低確非時短状態で遊技を開始する。これにより、第1実施形態の遊技機1は遊技者に対して遊技店開店直後に遊技させる動機を与えることが可能である。
[Effect of the first embodiment]
The
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確非時短状態は低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な遊技状態である。遊技機1が電源「OFF」状態であるときに、設定キーSW「ON」状態かつRWMクリアSW「ON」状態で電源「ON」状態にされた場合、遊技機1が起動した直後に設定変更モードに移行する。設定変更モードに移行すると、遊技状態に関する情報が初期化されて遊技機1は確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な低確非時短状態で遊技を開始する。これにより、第1実施形態の遊技機1は遊技者に対して設定変更直後(すなわち、遊技店開店直後)に遊技させる動機を与えることが可能である。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において大当たりAとなった場合、大当たり遊技終了に応じて低確時短状態に移行する。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。一方、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、遊技状態が変化しない。このため、低確非時短状態である場合の方が低確微時短状態である場合よりも特定のハズレ図柄となる確率の分だけ低確時短状態への移行確率が高い。これにより、低確非時短状態を低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な遊技状態にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行すると判定される確率は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで同じである。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において大当たりAとなった場合、大当たり遊技終了に応じて低確時短状態に移行する。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。一方、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、遊技状態が変化しない。このため、低確非時短状態である場合の方が低確微時短状態である場合よりも特定のハズレ図柄となる確率の分だけ低確時短状態への移行確率が高い。これにより、大当たり遊技を実行すると判定される確率が同じである状況において、低確非時短状態を低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な遊技状態にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態(時短回数99回または500回)と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確微時短状態において特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数が99回または500回となることで低確微時短状態が終了する。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において大当たりAとなった場合、大当たり遊技終了に応じて低確時短状態(時短回数700回)に移行する。また、低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態(時短回数700回)に移行可能である。一方、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から遊技状態が変化しない。低確非時短状態である場合の方が低確微時短状態である場合よりも低確時短状態への移行確率が高い。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合、低確時短状態(時短回数1000回)に移行する。よって、第1実施形態の遊技機1において低確時短状態には、特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数が700回となることで低確時短状態が終了する状態と、特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数が1000回となることで低確時短状態が終了する状態とがある。低確微時短状態と低確時短状態(時短回数700回)と低確時短状態(時短回数1000回)とは互いに遊技者に対する有利度合いが異なる。これにより、特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数に対して遊技者に興味を持たせることが可能である。
In addition, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態(時短回数99回または500回)と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において大当たりAとなった場合、大当たり遊技終了に応じて低確時短状態(時短回数700回)に移行する。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。一方、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から遊技状態が変化しない。このため、低確微時短状態は低確非時短状態に比べて遊技者に不利な遊技状態である。低確微時短状態において時短回数の残り回数が0回になると低確非時短状態に移行する。これにより、低確微時短状態であるときに低確非時短状態に移行することを目指して遊技者に遊技をさせることが可能である。
In addition, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利である。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。これにより、低確非時短状態は、特定のハズレ図柄によって低確時短状態への移行を狙えるので遊技者はハズレても嬉しくなれる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利である。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確時短状態においては、時短最終変動よりも前の変動において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、遊技状態は変化しない。時短残り回数が0になることで低確時短状態が終了する。これにより、低確非時短状態であるときは低確時短状態であるときよりも特定のハズレ図柄となることを遊技者に期待させることができる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利である。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確微時短状態に移行可能である。低確時短状態においては、時短最終変動よりも前の変動において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、遊技状態は変化しない。時短回数が0回になることで低確時短状態が終了する。これにより、低確非時短状態であるときに特定のハズレ図柄となって低確時短状態へ移行するのか低確微時短状態に移行するのか遊技者にドキドキ感を与えることができる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利である。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。普通図柄は低確非時短状態においては低確非時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示され、低確時短状態においては低確時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示される。低確時短状態用の普通図柄の変動パターンの方が低確非時短状態用の普通図柄の変動パターンよりも短い。これにより、低確時短状態の方が低確非時短状態よりも頻繁に普通図柄を変動可能な状態にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利である。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。電動チューリップ17は低確非時短状態においては低確非時短状態用の開放パターンで開放され、低確時短状態においては低確時短状態用の開放パターンで開放される。電動チューリップ17の開放時間は低確時短状態の方が低確非時短状態よりも長い。これにより、低確時短状態の方が低確非時短状態よりも第2始動口12に遊技球を入賞容易にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態よりも遊技者に有利である。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。特別図柄は低確非時短状態においては低確非時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示され、低確時短状態においては低確時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示される。低確時短状態用の特別図柄の変動パターンの方が低確非時短状態用の特別図柄の変動パターンよりも短い。これにより、低確時短状態の方が低確非時短状態よりも頻繁に特別図柄を変動可能な状態にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態であるときは点灯により遊技者に右打ちを促す右打ちランプ49が点灯する。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態であるときは右打ちランプ49が消灯する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちランプ49が点灯する。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確微時短状態に移行可能である。低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短B)図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちランプ49が非点灯のままである。これにより、右打ちランプ49の状態によって第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞容易な状態か否かを遊技者に示唆可能である。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確非時短状態は低確微時短状態よりも低確時短状態への移行確率が高いため遊技者に有利である。低確微時短状態において時短回数が0回になると低確非時短状態に移行する。低確微時短状態において時短回数が0回になっていないときに小当たり図柄が所定の上限回数(例えば2回)停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行可能である。これにより、時短回数が0回となる前に小当たりとなることで低確微時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行可能なので、遊技者に対して変化のある遊技を提供可能である。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちを促す文字、扉画像、及び低確時短状態用の背景画像を表示する。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちを促す文字、扉画像、及び低確時短状態用の背景画像は表示されない。これにより、遊技状態を移行させる特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことを遊技者に対して分かり易く示唆できる。
Moreover, the
また、第1実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちを促す文字、扉画像、及び低確時短状態用の背景画像を表示する。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、単なるハズレであることを示す演出を実行する。これにより、遊技状態を移行させる特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたか、遊技状態を移行させることがない通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたかを遊技者に対して分かり易く示唆できる。
Moreover, the
[第2実施形態]
次に、図42~図52を参照して第2実施形態について説明する。第2実施形態の遊技機1は、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて低確時短状態に移行可能な一方、低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて低確時短状態に移行しない点で第1実施形態の遊技機1と主に異なる。
[Second embodiment]
Next, a second embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 42 to 52. FIG. The
なお、第2実施形態については第1実施形態と異なる部分について説明するが、説明のない部分については第1実施形態と一致するものとする。 In the second embodiment, parts different from the first embodiment will be explained, but parts without explanation shall be the same as those in the first embodiment.
図42は、第2実施形態における遊技状態の移行について説明するための説明図である。遊技機1はRWMクリアが行われた初期状態では低確非時短状態に制御されている。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄(具体的には、ハズレ(時短ア)図柄およびハズレ(時短イ)図柄)が停止表示されると低確微時短状態に制御され、時短回数20回または500回が設定される(図42(a)から(a6)を介して(c)に移行する流れ)。具体的には、ハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されると、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が20回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が0回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が20回に設定される。ハズレ(時短イ)図柄が停止表示されると、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が500回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が0回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が500回に設定される。ハズレ(時短イ)は、ハズレ(時短ア)図柄よりも低確微時短に制御される時短回数が多いためハズレ(時短ア)図柄に比べて遊技者に有利なハズレ図柄である。
FIG. 42 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the game state transition in the second embodiment. The
低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄(具体的には、ハズレ(時短ア)図柄およびハズレ(時短イ)図柄)が停止表示されると低確時短状態に制御され、時短回数700回が設定される(図42(c)から(c3)を介して(b)に移行する流れ)。具体的には、ハズレ(時短ア)図柄またはハズレ(時短イ)図柄が停止表示されると、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が10回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が700回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が700回に設定される。低確微時短状態に移行した場合、微時短回数が終了すると遊技者にとって不利な低確非時短状態に移行する。 When a specific losing pattern (specifically, a losing (time-saving A) pattern and a losing (time-saving I) pattern) is stopped and displayed in a low-probability small time-saving state, it is controlled to a low-probability time-saving state, and the number of times of time saving is set to 700 times. (flow from FIG. 42(c) to (b) via (c3)). Specifically, when the lost (time saving A) pattern or the losing (time saving I) pattern is stopped and displayed, the time saving frequency J1 relating to the first special pattern is set to 10 times, and the time saving frequency J2 relating to the second special pattern is set. is set to 700 times, and the time reduction frequency J3 related to the sum of the first special symbol and the second special symbol is set to 700 times. In the case of shifting to the low-probability short working hours state, when the number of times of short working hours is completed, the state is shifted to the low-probability non-shortening working hours state disadvantageous to the player.
低確時短状態は第2始動口12を狙って大当たり(及び小当たり)を目指せるので、第1始動口11を狙う低確非時短(及び低確微時短)よりも遊技者にとって有利な状態といえる。低確微時短状態は特定のハズレ図柄が停止したことに応じて低確時短状態に移行できるので、低確非時短よりも遊技者にとって有利な状態といえる。なお、低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)図柄およびハズレ(時短イ)図柄が停止表示されたことを条件には時短回数は加算されず遊技状態は低確時短状態のまま変化しない。
Since the low-probability short working hours state aims at the
また、低確時短状態は、大当たりアを示す大当たり図柄の停止表示を実行条件とする大当たり遊技が終了することで制御される。例えば、大当たりアに係る大当たり遊技が実行された場合には、時短回数として700回が設定される。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が10回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が700回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が700回に設定される。 In addition, the low-probability time-saving state is controlled by ending the jackpot game whose execution condition is the stop display of the jackpot symbol indicating the jackpot a. For example, when a jackpot game related to jackpot a is executed, 700 times are set as the number of times of time saving. Specifically, the time saving number J1 related to the first special design is set to 10 times, the time saving number J2 related to the second special design is set to 700 times, and the sum of the first special design and the second special design The time reduction frequency J3 is set to 700 times.
このように、第2実施形態では、低確微時短状態のときに所定条件(具体的にはハズレ又は大当たりとなったとき)が成立すると、特定のハズレ図柄となる確率と大当たりアとなる確率との合算確率で低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行する。第2実施形態では、低確非時短状態のときに所定条件(具体的にはハズレ又は大当たりとなったとき)が成立すると、大当たりアとなる確率で低確非時短状態から低確時短状態に移行する。このため、低確時短状態への移行確率は低確微時短状態の方が低確非時短状態よりも特定のハズレ図柄となる確率の分だけ大きい。よって、低確非時短状態は低確微時短状態に比べて相対的に遊技者に不利な遊技状態である。 Thus, in the second embodiment, when a predetermined condition (specifically, when a loss or a jackpot) is established in a low-probability small time-saving state, the probability of a specific losing pattern and the probability of a jackpot With the combined probability of moving from a low-probability short-time state to a low-probability short-time state. In the second embodiment, when a predetermined condition (specifically, when it becomes a loss or a big hit) is established in the low probability non-time-saving state, the low probability non-time-saving state from the low probability non-time-saving state with a probability of becoming a big hit Transition. For this reason, the probability of transition to the low-probability short working hours state is greater than the low-probability non-shortening working hours state by the probability of a specific losing pattern. Therefore, the low-probability short working hours state is a game state relatively disadvantageous to the player compared to the low-probability short working hours state.
また、低確時短状態には、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合に遊技状態に関わらず制御され、時短回数1000回が設定される。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が10回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が1000回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が1000回に設定される。この時短回数は大当たり(又は小当たり)を条件に設定される時短回数よりも多いため、遊技者にとってより有利な状態といえる。 In addition, in the low probability time saving state, when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied, it is controlled regardless of the game state, and the time saving number of times is set to 1000 times. Specifically, the time saving number J1 related to the first special design is set to 10 times, the time saving number J2 related to the second special design is set to 1000 times, and the sum of the first special design and the second special design The time saving frequency J3 is set to 1000 times. Since the number of times of time saving is greater than the number of times of time saving set on the condition of a big win (or a small win), it can be said that the state is more advantageous for the player.
低確微時短状態は、大当たりイ又はウを示す大当たり図柄の停止表示を実行条件とする大当たり遊技が終了することで制御される。例えば、大当たりイに係る大当たり遊技が実行された場合には、時短回数として20回が設定される。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が20回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が0回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が20回に設定される。また、例えば、大当たりウに係る大当たり遊技が実行された場合には、時短回数として500回が設定される。具体的には、第1特別図柄に係る時短回数J1が500回に設定され、第2特別図柄に係る時短回数J2が0回に設定され、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄との合算に係る時短回数J3が500回に設定される。 The low-probability short-time state is controlled by ending a jackpot game whose execution condition is a stop display of a jackpot symbol indicating jackpot b or c. For example, when a jackpot game related to jackpot B is executed, 20 times is set as the number of times of time saving. Specifically, the time reduction number J1 related to the first special design is set to 20 times, the time reduction number J2 related to the second special design is set to 0 times, and the sum of the first special design and the second special design The time saving frequency J3 is set to 20 times. Further, for example, when a jackpot game related to jackpot c is executed, 500 times is set as the number of times of time saving. Specifically, the time saving number J1 related to the first special design is set to 500 times, the time saving number J2 related to the second special design is set to 0 times, and the sum of the first special design and the second special design The time reduction frequency J3 is set to 500 times.
低確非時短状態は、初期状態である場合の他、低確時短状態または低確微時短状態において時短回数が終了することで制御される。また、大当たりオを示す大当たり図柄の停止表示を実行条件とする大当たり遊技が終了することで制御される。また、小当たりイを示す小当たり図柄の停止表示を実行条件とする小当たり遊技が実行されることで制御される。なお、小当たり遊技中においてV入賞した場合は小当たり遊技に続いて実行される大当たり遊技が終了することで低確非時短状態に制御され、小当たり遊技中においてV入賞しなかった場合は小当たり遊技が終了することで低確非時短状態に制御される。また、小当たりアを示す小当たり図柄の停止表示を実行条件とする小当たり遊技中においてV入賞しなかった場合に、小当たり遊技が終了することで低確非時短状態に制御される。 In addition to the initial state, the low-probability non-time saving state is controlled by ending the number of times in the low-probability short-time state or low-probability small time-saving state. In addition, it is controlled by ending the jackpot game whose execution condition is the stop display of the jackpot symbol indicating the jackpot E. In addition, it is controlled by executing a small winning game whose execution condition is the stop display of a small winning symbol indicating a small winning B. In addition, if V wins during the small winning game, the big winning game that is executed following the small winning game is ended, and is controlled to a low probability non-time-saving state, and if V does not win during the small winning game, it is small. It is controlled to a low-probability short-time state by the end of the winning game. In addition, when V prize is not won during a small winning game whose execution condition is the stop display of a small winning symbol indicating a small winning A, the small winning game is terminated, thereby being controlled to a low-probability non-time-saving state.
なお、低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄(具体的には、ハズレ(時短ア)図柄およびハズレ(時短イ)図柄)が停止表示されたことを条件に、時短回数は加算されず遊技状態が低確非時短状態のまま変化しなくてもよい。また、低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されたことを条件には時短回数は加算されず遊技状態は低確非時短状態のまま変化しない一方で、低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短イ)図柄が停止表示されると低確微時短状態に制御され、時短回数500回(20回でもよい)が設定されてもよい。 In addition, on the condition that a specific losing pattern (specifically, losing (time saving A) pattern and losing (time saving i) pattern) is stopped and displayed in a low probability non-time saving state, the number of time saving is not added and the game state does not have to change in a low-probability short-time state. In addition, on the condition that the loss (time saving a) pattern is stopped and displayed in the low probability non-time saving state, the number of time saving is not added and the game state does not change in the low probability non-time saving state, while the low probability non time saving state When the lost (time saving A) pattern is stopped and displayed, it is controlled to a low-probability small working time saving state, and the number of times of saving time may be set to 500 times (may be 20 times).
図43は、第2実施形態における特別図柄判定の結果について説明するための説明図である。第2実施形態では、第1特別図柄判定において設定値に関わらず約1/500の確率で微時短状態または時短状態を発生させる特定のハズレ(時短ア又はイ)となる。大当たり、小当たり、又は特定のハズレ(時短ア又はイ)と判定される以外の確率で遊技状態を変化させない通常のハズレとなる。 FIG. 43 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the result of the special symbol determination in the second embodiment. In the second embodiment, regardless of the setting value in the first special symbol determination, there is a probability of about 1/500 to generate a slight time saving state or a time saving state. It becomes a normal loss that does not change the game state with a probability other than being determined as a big win, a small win, or a specific loss (time saving A or B).
第2実施形態における特別図柄判定の結果についての特徴は、第1特別図柄判定と第2特別図柄判定とではハズレ(時短)と判定される確率が異なる点である。これにより、第1特別図柄判定では大当たり又はハズレ(時短)を引くことで遊技状態を変化させることを目指し、第2特別図柄判定では大当たり又は小当たりを引くことで遊技状態を変化させることを目指すという新たなゲーム性を提供できる。 The characteristic of the result of the special symbol determination in the second embodiment is that the probability of being determined to be lost (time saving) differs between the first special symbol determination and the second special symbol determination. As a result, the first special symbol determination aims to change the game state by pulling a big hit or a loss (time saving), and the second special symbol determination aims to change the game state by pulling a big hit or a small hit. It can provide a new game property.
図44は、第2実施形態における大当たり種別および小当たり種別について説明するための説明図である。図44(A)に例示するように、大当たりアは、大入賞口13を遊技球が容易に通過できるように開閉させるラウンド遊技を2回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確時短状態に移行する大当たりである。大当たりイ及びウはラウンド遊技を2回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確微時短状態に移行する大当たりである。大当たりエはラウンド遊技を10回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確時短状態に移行する大当たりである。大当たりオはラウンド遊技を2回実行し、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確非時短状態に移行する大当たりである。
FIG. 44 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the jackpot type and the small hit type in the second embodiment. As exemplified in FIG. 44 (A), the big hit a executes twice a round game that opens and closes the big winning
第2実施形態の大当たりは何れも小当たり上限回数を設定しない大当たりである点で、第1実施形態の大当たりと異なる。第2実施形態では低確非時短よりも低確微時短の方が遊技者に有利なため、低確微時短状態において小当たり上限回数となるまで小当たりを引くと低確非時短状態に移行するような構成を採用することは遊技者に不利となるためあまり好ましくない。そこで、第2実施形態では小当たり上限回数を設定しない構成を採用している。なお、第2実施形態において小当たり上限回数を設定すると共に大当たり遊技終了後に低確非時短に制御する大当たりを備え、低確非時短状態において小当たり上限回数となるまで小当たりを引くと低確微時短状態に移行してもよい。 The jackpots of the second embodiment are different from the jackpots of the first embodiment in that none of the jackpots set the upper limit number of small hits. In the second embodiment, the low probability short working hours is more advantageous to the player than the low probability short working hours, so if you draw a small hit until the upper limit number of small hits in the low probability short working hours state, the transition to the low low short working hours state Adopting such a configuration would be disadvantageous to the player, so it is not very preferable. Therefore, in the second embodiment, a configuration is adopted in which the upper limit number of small hits is not set. In addition, in the second embodiment, a small hit upper limit number is set and a jackpot controlled to a low probability short time after the end of the big hit game is provided. You may shift to a slight time reduction state.
大当たりアの場合は3つの同じ装飾図柄55が停止表示されるのに対し、大当たりイ及びウの場合は低確微時短状態に移行することを報知する特殊な装飾図柄(時短図柄)が停止表示される。大当たりイ及びウは第4図柄の停止表示態様が異なるものの、装飾図柄55の停止表示態様からは大当たりイ及びウのうち何れであるか遊技者は判別できない。このため、遊技に慣れていない遊技者は低確微時短状態に設定される時短回数が分からない状態で遊技を進めることが可能である。
In the case of a jackpot a, the same three
各大当たり遊技の有利度合いは、大当たりオ<大当たりイ<大当たりウ<大当たりア<大当たりエの順に遊技者の有利度合いが高い。 The degree of advantage of each jackpot game is higher in the order of jackpot O<jackpot B<jackpot C<jackpot A<jackpot D.
なお、第1特別図柄判定の結果として、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確非時短状態に移行する大当たりを有してもよい。 In addition, as a result of the first special symbol determination, there may be a big hit that shifts to a low-probability short-time state immediately after the end of the big-hit game.
図44(B)に例示するように、小当たりア及びイは、V入賞容易に小入賞口19を開閉させる小当たり遊技を実行する小当たりである。小当たりア及びイに係る小当たり遊技が実行されると基本的にV入賞し、小当たり遊技の終了直後に大当たり遊技が実行される。小当たりアに係る大当たり遊技ではラウンド遊技が10回実行され、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確時短状態に移行する。小当たりイに係る大当たり遊技ではラウンド遊技が2回実行され、大当たり遊技の終了直後に低確非時短状態に移行する。
As exemplified in FIG. 44(B), small wins A and B are small wins for executing a small winning game in which the small winning
各小当たり遊技の有利度合いは、小当たりイ<小当たりアの順に遊技者の有利度合いが高い。 The degree of advantage of each small winning game is higher for the player in the order of small winning A<small winning A.
図45は、第2実施形態におけるハズレ(時短)種別について説明するための説明図である。ハズレ(時短ア)及びハズレ(時短イ)は、変動開始時に低確非時短状態(すなわち、時短遊技フラグがOFF)であるときに停止表示されると大当たり遊技および小当たり遊技を実行せずに低確微時短状態に移行させるハズレである。低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短A)又はハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されると、総アウトカウンタでの計数は継続するもののベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計測は停止し、リアルタイムベース値bLの算出も停止される。これに伴い、特別図柄の変動回数の計測が継続したまま新たに時短回数の計測が開始される。すなわち、遊技制御基板100のメインCPU100aは、次に特別図柄判定を行ったことに応じて、今回の特別図柄の変動回数に対して1加算すると共に時短回数を1減算することになる。なお、特別図柄の変動回数は、設定変更、RWMクリア、又は大当たり遊技の実行に応じて0回に設定され、特別図柄判定が行われる毎に1加算される。
FIG. 45 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the failure (time saving) type in the second embodiment. Loss (time saving A) and loss (time saving I) are stopped when the low probability non-time saving state (that is, the time saving game flag is OFF) at the start of the fluctuation, without executing the jackpot game and the small hit game It is a loss to move to a low-probability short-time state. When the loss (time reduction A) or loss (time reduction I) is stopped and displayed in a low-probability time-saving state, the total out counter continues counting, but the base calculation out counter and the base calculation prize ball counter do not measure. stop, and the calculation of the real-time base value bL is also stopped. Along with this, while the measurement of the number of fluctuations in the special symbol continues, the measurement of the number of times of time reduction is newly started. That is, the
非時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)又はハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されたときは、液晶画面5上で時短残り回数が報知されず、右打ちランプ49は消灯したままである。これにより、低確非時短状態と低確微時短状態とが区別がつき難くできる。なお、非時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)又はハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されたときは、右打ちランプ49は消灯したまま液晶画面5上で時短残り回数を報知してもよい。これにより、低確非時短状態と低確微時短状態とが区別がつき易くできる。
When a failure (time saving A) or a failure (time saving B) is stop-displayed in the non-time saving state, the number of times of remaining time saving is not reported on the
特定のハズレ図柄(具体的には、ハズレ(時短ア)及びハズレ(時短イ))の停止表示に伴って装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせで停止表示される。「227」の組み合わせは特定のハズレ図柄以外の特別図柄に伴って停止表示されないので、遊技者は装飾図柄55を見ることによって低確微時短に移行するハズレであることを認識可能である。
The
低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)又はハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されると、次の普通図柄の変動表示からは低確微時短用の変動時間で普通図柄が変動表示され、低確微時短用の開放パターンで電動チューリップ17が開放される。図2に例示するように低確微時短用の普通図柄の変動時間は低確非時短用(及び低確微時短用)の普通図柄の変動時間よりも短い。また、低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)又はハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されると、次の特別図柄の変動表示からは低確微時短用の変動時間で特別図柄が変動表示される。低確微時短用の特別図柄の変動時間は低確非時短用(及び低確微時短用)の特別図柄の変動時間と同じである。なお、低確微時短用の特別図柄の変動時間は低確非時短用の特別図柄の変動時間よりも短くてもよい。
When the loss (time saving a) or loss (time saving i) is stopped and displayed in the low probability non-time saving state, from the next normal pattern fluctuation display, the normal pattern is displayed fluctuating at the low probability small time saving fluctuation time, low The
低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)又はハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されると、次の普通図柄の変動表示からは低確時短用の変動時間で普通図柄が変動表示され、低確時短用の開放パターンで電動チューリップ17が開放される。低確時短用の普通図柄の変動時間は低確微時短用(及び低確微時短用)の普通図柄の変動時間よりも短い。また、低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)又はハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されると、次の特別図柄の変動表示からは低確時短用の変動時間で特別図柄が変動表示される。低確時短用の特別図柄の変動時間は低確微時短用の特別図柄の変動時間よりも短い。
When the loss (time saving a) or loss (time saving i) is stopped and displayed in the low probability time saving state, from the next normal pattern fluctuation display, the normal pattern is displayed fluctuating at the low probability time saving fluctuation time, low probability The
ハズレ(時短A)及びハズレ(時短B)は、変動開始時に低確時短状態である場合、停止表示されると大当たり遊技および小当たり遊技を実行せず、且つ遊技状態も変化しないハズレとなる。すなわち、低確時短状態である場合はハズレ(時短ア)及びハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されると時短回数が1減算されるだけで新たに時短回数が加算されることがない。そして、時短回数が0でなければそのまま低確時短状態が継続する。一方、時短回数が0であるときは低確時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行する。このため、例えば、低確時短状態における時短最終変動でハズレ(時短ア)及びハズレ(時短イ)が停止表示されると、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタでの計測が再開し、リアルタイムベース値bLの算出も再開される。 Loss (time reduction A) and loss (time reduction B) are in a low-probability time-saving state at the start of fluctuation, and when stopped and displayed, the big winning game and the small winning game are not executed, and the game state does not change. That is, in the low-probability time-saving state, when the lost (time-saving A) and the losing (time-saving I) are stopped and displayed, the number of time-savings is only subtracted by 1, and the number of time-savings is not newly added. If the number of times of shortening working hours is not 0, the low probability of shortening working hours continues as it is. On the other hand, when the number of times of time saving is 0, the state is shifted from the low-probability of working-time saving state to the low-probability of working-time saving state. For this reason, for example, when the loss (time reduction A) and loss (time reduction B) are stopped and displayed in the time saving final fluctuation in the low probability time saving state, the measurement with the base calculation out counter and the base calculation prize ball counter restarts. , the calculation of the real-time base value bL is also resumed.
低確微時短状態では、遊技者は大当たりと特定のハズレ図柄とによって低確時短状態へと移行することを目指せるのに対し、低確非時短状態では、遊技者は基本的には大当たりによって低確時短状態へと移行することを目指す。低確微時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率は大当たり当選確率と特定のハズレ図柄となる確率との合算であるのに対し、低確非時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率は大当たり当選確率のみである。よって、低確微時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率は低確非時短状態における低確時短状態への移行確率よりも高い。このため、低確微時短状態は低確非時短状態に比べて低確時短状態に移行し易く遊技者に有利である。 In the low-probability small time-saving state, the player can aim to transition to the low-probability short-time state by hitting the jackpot and a specific losing pattern, whereas in the low-probability non-shorting state, the player basically depends on the jackpot. Aim to transition to a low-probability short-time state. The probability of transitioning to a low probability short working hours state in a low probability short working hours state is the sum of the probability of winning a jackpot and the probability of becoming a specific losing pattern, while the probability of transition to a low probability short working hours state in a low probability short working hours It is only the jackpot winning probability. Therefore, the transition probability to the low probability short working hours state in the low probability small working hours state is higher than the transition probability to the low probability short working hours state in the low probability non-short working hours state. For this reason, the low-probability small working hours state is more likely to shift to the low-probability short working hours state than the low-probability non-working hours state, which is advantageous for the player.
図46は、第2実施形態における第1特別図柄の変動パターン(変動時間群)について説明するための説明図である。第1特別図柄の変動パターンにおいて特徴的な点は、低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動時間の方が通常のハズレの変動時間よりも長いものが選択され易い点である。なお、ハズレ(時短ア又はイ)が停止表示される時間は通常のハズレが停止表示される時間と同じであるが、ハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の方が通常のハズレよりも停止表示される時間が長くてもよいし短くてもよい。 FIG. 46 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the variation pattern (variation time group) of the first special symbol in the second embodiment. The characteristic point in the fluctuation pattern of the first special symbol is that the fluctuation time of losing (time saving a or b) is longer than the fluctuation time of normal losing It is a point that things are easy to be selected. In addition, the time when the loss (time-saving A or B) is stopped and displayed is the same as the time when the normal loss is stopped and displayed, but the loss (time-saving A or B) is stopped and displayed more than the normal loss. The time can be long or short.
低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)においてハズレ(時短ア)とハズレ(時短イ)とは第1特別図柄の変動パターンが同じであり、第1特別図柄の変動表示に伴って実行される演出も同じである。これにより、第1特別図柄の変動時間および実行される演出によってハズレ(時短ア)であるかハズレ(時短イ)であるかを認識できなくできる。なお、第1特別図柄の変動時間としてハズレ(時短ア)確定のもの、及びハズレ(時短イ)確定のものがあってもよい。また、第1特別図柄の変動表示に伴って実行される演出にはハズレ(時短ア)確定のもの、及びハズレ(時短イ)確定のものがあってもよい。また、ハズレ(時短ア)よりもハズレ(時短イ)の方が第1特別図柄の変動時間が短くてもよいし長くてもよい。 In the low-probability non-time-saving state (and low-probability small time-saving state), the loss (time-saving A) and loss (time-saving I) have the same variation pattern of the first special symbol, and are executed along with the variation display of the first special symbol. The same is true of the production. Thereby, it is possible to make it impossible to recognize whether it is a loss (time saving A) or a loss (time saving B) depending on the variation time of the first special symbol and the effect to be executed. In addition, as the fluctuation time of the first special symbol, there may be a loss (time saving a) definite one and a loss (time saving ii) decision. In addition, the effect executed in conjunction with the variable display of the first special symbol may include a determination of loss (shortening of time a) and a determination of loss (shortening of time i). Also, the fluctuation time of the first special symbol may be shorter or longer in the case of loss (time saving a) than in the loss (time saving a).
低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動表示に伴って実行される演出は、装飾図柄55の組み合わせを除き大当たり及び通常のハズレの変動表示に伴って実行される演出と同じである。これにより、第1特別図柄の変動表示に伴って実行される演出によって大当たり、通常のハズレ、及びハズレ(時短ア及びイ)の何れであるかを認識し難くできる。
The effect that is executed with the variable display of the loss (time reduction a or b) in the low probability non-time saving state (and the low probability small time saving state) is accompanied by the fluctuation display of the big hit and normal loss except for the combination of the
低確時短状態において、第1特別図柄の変動パターンにおいて特徴的な点は、ハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動時間は通常のハズレの変動時間と同じであるという点である。低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動表示に伴って実行される演出は、低確時短状態において通常のハズレの変動表示に伴って実行される演出と同様に単にハズレを報知する演出である。ここで、低確時短状態における第1特別図柄の変動パターンH311は、低確時短状態における第2特別図柄の変動パターンH201と同じ変動時間である。変動パターンH311の変動表示に伴って実行される演出は、変動パターンH201の変動表示に伴って実行される演出(具体的には、単にハズレを報知する演出)と同じである。 In the low probability time saving state, the characteristic point in the fluctuation pattern of the first special symbol is that the fluctuation time of losing (time saving a or b) is the same as the normal losing fluctuation time. The effect executed with the variable display of the loss (time saving A or B) in the low probability time saving state simply informs the loss in the same way as the effect executed with the normal change display of the loss in the low probability time saving state. It is a performance. Here, the variation pattern H311 of the first special symbol in the low probability time saving state is the same variation time as the second special symbol variation pattern H201 in the low probability time saving state. The effect that is executed with the variable display of the variable pattern H311 is the same as the effect that is executed with the variable display of the variable pattern H201 (specifically, the effect that merely notifies of a failure).
低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55の組み合わせと同じである。すなわち、低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動表示で停止表示される装飾図柄55は、ハズレであって且つ遊技者に有利となることを示唆する組み合わせである。しかしながら、低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)が停止表示されても遊技状態は変化しない。このため、低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55は通常のハズレの変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55と同様に単にハズレを示す組み合わせであって且つ遊技者に有利となることを示唆しない組み合わせでもよい。すなわち、低確時短状態においてハズレ(時短A及びB)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55は、低確非時短状態および低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア又はイ)の変動表示によって停止表示される装飾図柄55の組み合わせと異なってもよい。
The
図47は、第2実施形態における第2特別図柄の変動パターン(変動時間群)について説明するための説明図である。第2特別図柄の変動パターンにおいて特徴的な点は、低確非時短状態(及び低確微時短状態)の第1特別図柄の変動時間よりも相対的に短い点である。 FIG. 47 is an explanatory diagram for explaining the variation pattern (variation time group) of the second special symbol in the second embodiment. A characteristic point in the variation pattern of the second special symbol is that it is relatively shorter than the variation time of the first special symbol in the low-probability non-time-saving state (and low-probability small time-saving state).
図47(A)及び(B)を比較すると、低確時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンよりも低確非時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンの方が短い。これにより、低確時短状態から低確非時短状態に移行したときの第2特別図柄の変動表示をあっさりと終えることが可能である。 When FIG. 47 (A) and (B) are compared, the variation pattern of the second special symbol for the low-probability short working hours state is shorter than the variation pattern of the second special symbols for the low-probability short working hours state. Thereby, it is possible to easily finish the variable display of the second special symbol when shifting from the low-probability short-time state to the low-probability non-short-time state.
なお、低確時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンよりも低確非時短状態用の第2特別図柄の変動パターンの方が長くてもよい。 In addition, the variation pattern of the second special symbol for the low-probability non-time-saving state may be longer than the variation pattern of the second special symbol for the low-probability short-time state.
次に、図48~図50を参照して、低確非時短においてリーチ演出が実行される演出例について説明する。図48は、第2実施形態において低確非時短状態のときにノーマルリーチ演出が実行される演出例について説明するための説明図である。図48の例では特別態様の当該アイコン53が表示されている。図49は、第2実施形態において低確非時短状態のときにSPリーチ演出が実行される演出例について説明するための説明図である。図50は、第2実施形態において低確非時短状態のときにSPリーチ演出でハズレ報知された直後の演出例について説明するための説明図である。なお、図48~図50の例では連続ハズレ750回の条件は満たさないものとする。第2実施形態では低確非時短のときに朝モードで演出が制御される。朝モードでは朝モード用の背景画像が表示されると共に、演出モード名を表す「朝モード」との文字が液晶画面5の左下に常に表示される。
Next, with reference to FIGS. 48 to 50, an effect example in which the ready-to-win effect is executed in the low-probability short working hours will be described. FIG. 48 is an explanatory diagram for explaining an effect example in which a normal reach effect is executed in the low probability non-time saving state in the second embodiment. In the example of FIG. 48, the
図48(A)及び(B)に例示するように、この例では「2」図柄でリーチが成立する。図48(C)に例示するように、リーチ成立から所定時間(例えば0.5秒)が経過したときにリーチラインが表示されたり「リーチ」との音声がスピーカ24から出力されたりする。図48(C)の例では小図柄56は高速変動を継続している。なお、リーチ成立に伴って、装飾図柄55と同じリーチ態様で小図柄56を表示してもよい。
As illustrated in FIGS. 48(A) and (B), in this example, reach is established with "2" symbols. As exemplified in FIG. 48(C), when a predetermined time (for example, 0.5 seconds) has passed since the establishment of the reach, the reach line is displayed or the voice "reach" is output from the
遊技機1では、変動表示開始時からリーチラインが非表示になるまで装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP2である。中図柄は変動表示開始時からリーチ成立時までは高速変動しており、リーチ成立に応じて開始されるノーマルリーチ演出中は低速変動する。
In the
遊技機1では、ノーマルリーチ演出中は装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1である。すなわち、リーチ成立の前後で中図柄の表示優先度が高くなる。なお、ノーマルリーチ演出中は装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP2でもよい。
In the
遊技機1では、リーチ図柄として仮停止した装飾図柄以外の左図柄(及び右図柄)が非表示にされる。非表示にされた装飾図柄55は、当該変動表示が終了するまで再表示されない。なお、非表示にされた装飾図柄55は、当該変動表示が終了する直前に再表示されてもよい。
In the
遊技機1では、リーチ成立時よりもノーマルリーチ演出中の方が左図柄と右図柄との間隔が広くなる。また、リーチ成立時よりもノーマルリーチ演出中の方が中図柄が大きく表示される。このため、リーチ成立時とノーマルリーチ演出中とでは装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。一方、リーチ成立時とノーマルリーチ演出中とでは装飾図柄55の見た目は同じである。
In the
図48(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出でハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンH301に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果リーチハズレ目「272」で仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図48(E)及び(F)参照)。リーチハズレ目の仮停止表示開始時には、左図柄と右図柄との間隔が狭くなったり、中図柄が変動開始時と同じ大きさまで小さくなったりする。このため、ノーマルリーチ演出において中図柄が仮停止表示する前後で装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。また、リーチハズレ目の仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1からHP3に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、ノーマルリーチ演出においてハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。小図柄56はリーチハズレ目が本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、装飾図柄55の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。図48(F)に例示するようにハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示すると低確非時短から低確微時短に移行する。
Following FIG. 48 (D), in the case of a variation pattern in which the losing (time saving a) pattern is displayed stopped in the normal reach production (that is, when it corresponds to the variation pattern H301), the result of the normal reach production is a temporary stop at the reach losing eye "272". is displayed, and the main stop is performed as it is (see FIGS. 48(E) and (F)). At the start of the temporary stop display of the reach-losing eye, the interval between the left pattern and the right pattern is narrowed, or the middle pattern is reduced to the same size as at the start of fluctuation. Therefore, the display area of the
図48(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出で通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンH306に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果「272」以外のリーチハズレ目で仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図48(I)参照)。通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示すると低確非時短で次変動が開始する。 Following FIG. 48 (D), in the case of a variation pattern in which the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed in the normal reach production (that is, when it corresponds to the variation pattern H306), the result of the normal reach production is a temporary stop at the reach losing eyes other than "272". is displayed, and the main stop is performed as it is (see FIG. 48(I)). When the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed, the next fluctuation starts with a low probability and short time.
図48(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出で大当たりアが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO301に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果図柄揃い「222」で仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図48(G)参照)。図柄揃いの仮停止表示開始時には、左図柄と右図柄との間隔が狭くなったり、中図柄が変動開始時と同じ大きさまで小さくなったりする。このため、ノーマルリーチ演出において中図柄が仮停止表示する前後で装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。また、図柄揃いの仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1からHP4に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、ノーマルリーチ演出において大当たり図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。小図柄56は大当たり図柄が本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、大当たり図柄の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。図48(G)に例示するように大当たりアが停止表示すると大当たり遊技(遊技状態としては低確非時短)が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。
Following FIG. 48(D), in the case of the variation pattern in which the big hit A is displayed stopped in the normal ready-to-win production (that is, the case corresponding to the variation pattern O301), the result of the normal ready-to-win production is temporarily stopped and displayed with the pattern matching "222", and as it is. Main stop (see FIG. 48(G)). At the start of the temporary stop display of matching patterns, the space between the left pattern and the right pattern is narrowed, or the middle pattern is reduced to the same size as at the start of fluctuation. Therefore, the display area of the
図48(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出で大当たりイが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO308に対応する場合)、ノーマルリーチ演出の結果特殊な装飾図柄(時短図柄)が仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する(図48(H)参照)。時短図柄は、例えば低確微時短への移行を示唆する「夜」との文字を含む装飾図柄である。ここで、第2実施形態では低確微時短のときに夜モードで演出が制御される。夜モードでは夜モード用の背景画像が表示されると共に、演出モード名を表す「夜モード」との文字が液晶画面5の左下に常に表示される。なお、遊技機1において大当たりイと他の特別図柄とで停止表示される装飾図柄55と停止表示される第4図柄57との組み合わせが異なれば、大当たりイが停止表示される場合に装飾図柄55が図柄揃いで停止表示してもよい。
Following FIG. 48(D), in the case of a variation pattern in which the jackpot B is stopped and displayed in the normal reach production (that is, in the case corresponding to the variation pattern O308), a special decorative pattern (time saving pattern) is temporarily stopped and displayed as a result of the normal reach production. 48 (H)). The time-saving design is a decoration design including characters of "night" suggesting a shift to low-probability time-saving, for example. Here, in 2nd Embodiment, production|presentation is controlled by night mode at the time of low probability short working hours. In the night mode, the background image for the night mode is displayed, and the characters "Night mode" representing the effect mode name are always displayed at the lower left of the
時短図柄の仮停止表示開始時には、左図柄と右図柄との間隔が狭くなったり、中図柄が変動開始時と同じ大きさまで小さくなったりする。このため、ノーマルリーチ演出において中図柄が仮停止表示する前後で装飾図柄55の表示領域が変わる。また、時短図柄の仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP1からHP3に変化する。小図柄56は図柄揃いが本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、装飾図柄55の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。図48(H)に例示するように大当たりイが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確微時短に移行する。
When the temporary stop display of the time saving pattern is started, the interval between the left pattern and the right pattern is narrowed, or the middle pattern is reduced to the same size as when the fluctuation is started. Therefore, the display area of the
図48(D)に続いて、ノーマルリーチ演出からSPリーチ演出に発展する場合がある。ノーマルリーチ演出からSPリーチ演出に発展する変動パターンの場合、ノーマルリーチ演出の終盤で中図柄が高速変動を開始する(図49(A)参照)。その後、中図柄が非表示にされると共にSPリーチ演出が開始される。これに伴って数字部分550とキャラクタ部分551とからなるリーチ図柄が、数字部分550のみからなるリーチ図柄に変化する。SPリーチ演出の開始前後には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP2からHP7に変化する。SPリーチ演出の開始に応じて当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51が非表示にされる。SPリーチ演出中は小図柄56が高速変動を継続する。なお、SPリーチ演出中は小図柄56がリーチ図柄と同じ組み合わせで仮停止表示してもよい。
Following FIG. 48(D), there is a case where the normal ready-to-win effect develops into the SP ready-to-win effect. In the case of the variation pattern that develops from the normal reach effect to the SP reach effect, the medium pattern starts to fluctuate at high speed at the end of the normal reach effect (see FIG. 49(A)). After that, the medium pattern is hidden and the SP ready-to-win effect is started. Along with this, the ready-to-win pattern consisting of the
SPリーチ演出でリーチハズレ目が仮停止表示することなく大当たりアが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO305に対応する場合)、図49(C)に続いてSPリーチ演出終盤で敵が敗北して図柄揃いが仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する。大当たりアが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。SPリーチ演出で大当たりイが停止表示する変動パターンの場合(すなわち、変動パターンO310に対応する場合)、SPリーチ演出終盤で敵が敗北して時短図柄が仮停止表示し、そのまま本停止する。図柄揃い又は時短図柄の仮停止表示中には、演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出を実行可能である一方、チャレンジ演出は実行不可能である。
In the case of a variation pattern in which the reach-losing eyes are not temporarily displayed in the SP reach production and the big hit is stopped and displayed (that is, the case corresponding to the variation pattern O305), following FIG. After being defeated, the matching pattern is displayed as a temporary stop, and then it is stopped as it is. When the jackpot A is stopped and displayed, the jackpot game is executed. At the end of the jackpot game, the first alert and the second alert are displayed at the same time. After the end of the jackpot game, it shifts to a low-probability short-time. In the case of the variation pattern in which the big hit B is stopped and displayed in the SP ready-to-win performance (that is, the case corresponding to the variation pattern O310), the enemy is defeated at the end of the SP ready-to-win performance, the time-saving pattern is displayed to be temporarily stopped, and then the game is permanently stopped. During the temporary stop display of the pattern alignment or the time-saving pattern, it is possible to execute the performance for informing the jackpot such as operating the
図柄揃い又は時短図柄の仮停止表示中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP7からHP4に変化する。すなわち、数字部分550のみからなる装飾図柄55が数字部分550とキャラクタ部分551とからなる装飾図柄55に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、SPリーチ演出において大当たり図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。小図柄56は大当たり図柄が本停止する直前まで高速変動しており、大当たり図柄の停止表示に応じて装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで停止表示する。なお、大当たり報知中は小図柄56が装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで仮停止表示してもよい。
The display priority of the
図49(D)に例示するようにSPリーチ演出終盤で敵が勝利してからリーチハズレ目が仮停止表示する変動パターンがある(すなわち、変動パターンO306、O307、H303、H304、H309、又はH310に対応する場合)。図49(E)及び(F)に例示するようにリーチハズレ目の仮停止表示中には再開演出が実行される。再開演出は、演出役物7が初期位置にある状態であって、演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出が行われないハズレ報知後に実行される。再開演出としては、画面右端から左端に向かって画面全体を覆うと共にオーバーラップしていく模様付きの黒い画像が表示される。再開演出は開始から所定時間(例えば2.5秒)経過したことに応じて終了する。再開演出中は装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP7からHP2に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、再開演出後に第1特別図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
As illustrated in FIG. 49(D), there is a variation pattern in which the reach losing eye is temporarily stopped after the enemy wins at the end of the SP reach production (that is, the variation pattern O306, O307, H303, H304, H309, or H310 if applicable). As illustrated in FIGS. 49(E) and (F), a restart effect is executed during the temporary stop display of the reach-losing eye. The resuming performance is executed after the loss notification is given when the
図49(G)~(I)に例示するように、仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、再開演出が終了してから当該ハズレ図柄が停止表示する。図49の例では、仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果がハズレ(時短ア)であった場合、「212」の組み合わせであった装飾図柄55が再開演出を介して「272」の組み合わせに変化する。これにより、再開演出によって気持ちを新たにした遊技者は低確微時短で遊技を再開できる。なお、第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレである場合、再開演出の前後で装飾図柄55の組み合わせが変化することがなくてもよい。
As illustrated in FIGS. 49(G) to (I), if the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a specific lost symbol, the lost symbol is stopped and displayed after the restart effect is completed. In the example of FIG. 49, if the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a failure (time saving A), the
第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、再開演出終了後であって当該変動終了までの間に背景画像が夜モード移行確定用の朝モードの背景画像に変化する。なお、第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、再開演出終了後には当該変動開始時と同じ朝モードの背景画像が表示されてもよいし、夜モード用の背景画像が表示されてもよい。 When the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a specific lost symbol, the background image changes to the morning mode background image for confirming the shift to the night mode during the period from the end of the restart performance to the end of the variation. In addition, when the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a specific losing symbol, after the restart effect is completed, the same morning mode background image as at the start of the variation may be displayed, or the background image for the night mode. may be displayed.
仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が通常のハズレ図柄であった場合、「212」の組み合わせであった装飾図柄55が再開演出を介してそのままの組み合わせで停止表示する。
If the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a normal losing symbol, the
ここで、SPリーチ演出の開始に応じて非表示にされた当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51は、SPリーチ演出開始直前と同じ見た目で再開演出中に再表示される。再表示された当該アイコン53は第1特別図柄の停止表示に応じて消去される。遊技機1では、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51の方が再開演出よりも表示優先度が低い。よって、再開演出中は、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51は再開演出が手前側に表示されることによって見えない。一方、遊技機1では、小図柄56並びに第4図柄57及び59の方が再開演出よりも表示優先度が高い。このため、遊技者は、再開演出の表示中であっても小図柄56及び第4図柄57を見ることができる。小図柄56及び第4図柄57の態様は再開演出の前後で同じ態様(具体的には高速変動)である。なお、小図柄56は再開演出中に装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせで仮停止表示されてもよい。
Here, the
盤用照明装置74及び枠用照明装置10は、再開演出直前は朝モード用の発光パターンで発光し、再開演出中は再開演出用の発光パターン(例えば、白色で点滅する発光パターン)で発光し、再開演出終了直後は朝モード用の発光パターンで発光する。すなわち、再開演出中には、SPリーチ演出に対応する発光パターンとは異なる発光パターンで発光する。なお、当該変動終了後に低確微時短に移行する場合、盤用照明装置74及び枠用照明装置10は再開演出終了直後に夜モード移行確定用の発光パターンで発光してもよい。
The
ここで、仮に第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が大当たり図柄であったとしても、再開演出が非表示となる時間は大当たり報知するよりも前である。このため、再開演出中は演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出も実行不可能であり、再開演出後に上記大当たり報知用の演出を実行可能である。なお、再開演出が実行された後に大当たりとなることがなくてもよい。この場合、再開演出中に加えて再開演出後も演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出を実行不可能である。
Here, even if the determination result of the first special symbol determination is a jackpot symbol, the time at which the restart effect is not displayed is before the jackpot is notified. Therefore, during the resuming effect, it is impossible to execute the effect for informing the big win such as activating the
再開演出中および再開演出後はチャレンジ演出を実行不可能である。なお、再開演出後にチャレンジ演出を実行可能でもよい。 The challenge presentation cannot be executed during and after the restart presentation. It should be noted that the challenge effect may be executed after the restart effect.
なお、再開演出が表示される際の態様は、画面全体に黒い画像がオーバーラップする態様でもよいし、モザイク状に現れていく画像によって画面全体が覆われる態様でもよい。また、再開演出の表示終了態様は、画面全体を覆う画像の透明度が上がり最終的に当該画像が非表示になる態様でもよいし、画面全体を覆う画像がモザイク状に欠けていき最終的に扉画像が非表示になる態様でもよい。 It should be noted that the form in which the restart effect is displayed may be a form in which the entire screen is overlapped with a black image, or a form in which the entire screen is covered with an image appearing in a mosaic pattern. In addition, the mode of ending the display of the resuming effect may be a mode in which the transparency of the image covering the entire screen is increased and the image is finally hidden, or the image covering the entire screen is missing in a mosaic pattern and finally the door is closed. The image may be hidden.
図49(D)に例示するようにSPリーチ演出終盤で敵が勝利してからリーチハズレ目が仮停止表示した後にチャレンジ演出が実行される変動パターンがある(すなわち、変動パターンO307、H304、又はH310に対応する場合)。図50(A)及び(B)に例示するように、チャレンジ演出の開始に応じてリーチ図柄が非表示にされる。チャレンジ演出中には中図柄として停止する装飾図柄の候補が表示された状態で操作促進演出が実行される。操作促進演出の有効期間中の操作に応じて中図柄が仮停止表示する。なお、有効期間中に操作がなかった場合は、予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始から3秒経過時)で中図柄が仮停止表示する。 As exemplified in FIG. 49(D), there is a variation pattern in which the challenge effect is executed after the enemy wins at the end of the SP reach effect and the reach losing eye is temporarily stopped (that is, the change pattern O307, H304, or H310 ). As illustrated in FIGS. 50A and 50B, the ready-to-win pattern is hidden according to the start of the challenge effect. During the challenge performance, the operation promotion performance is executed in a state in which candidates for decorative symbols to be stopped as medium symbols are displayed. The medium pattern is temporarily stopped and displayed according to the operation during the valid period of the operation promotion effect. If there is no operation during the valid period, the middle symbol is temporarily stopped and displayed at a predetermined valid period end timing (for example, when 3 seconds have passed since the start of the operation promotion effect).
チャレンジ演出が成功である場合はリーチ図柄と同じ中図柄が仮停止表示して大当たりアが報知される。大当たり報知中には、装飾図柄55の表示優先度が表示パターンHP6、HP9、HP4の順に変化する。図50(H)及び(I)に例示するように大当たりアが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。大当たり遊技の終盤において第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。
When the challenge effect is successful, the same medium symbol as the ready-to-win symbol is temporarily stopped and a big hit is announced. During the jackpot notification, the display priority of the
一方、チャレンジ演出が失敗である場合はリーチ図柄と異なる中図柄が仮停止表示して通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示することが示唆される。
チャレンジ演出失敗に続いては図49(E)及び(F)の場合と同じ再開演出が実行される。なお、チャレンジ演出失敗に続いて実行される再開演出として、図49(E)及び(F)の場合と異なる態様の再開演出が実行されてもよい。
On the other hand, when the challenge effect is unsuccessful, it is suggested that the medium symbols different from the ready-to-win symbols are temporarily stopped and displayed and the normal losing symbols are stopped.
Following the failure of the challenge effect, the same restart effect as in FIGS. 49(E) and (F) is executed. Incidentally, as the restart effect executed following the failure of the challenge effect, a restart effect different from the cases of FIGS. 49(E) and (F) may be executed.
チャレンジ演出失敗に続いて再開演出が実行されると、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示する場合と、特定のハズレ図柄(具体的には、ハズレ(時短ア又はイ))が停止表示する場合とがある。リーチ図柄は、チャレンジ演出失敗時から再開演出終了時まで非表示にされたままであり、再開演出終了時から再表示される。装飾図柄55の表示優先度は再開演出開始前は表示パターンHP7であり、再開演出中に表示パターンHP2に変化し、その後の停止表示時に表示パターンHP3に変化する。なお、再開演出の前後で装飾図柄55の表示優先度が変化しなくてもよい。
When the restart production is executed following the failure of the challenge production, there are cases where the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed, and when a specific losing pattern (specifically, losing (time saving A or B)) is stopped and displayed. be. The ready-to-win pattern remains hidden from the failure of the challenge performance until the end of the restart performance, and is redisplayed after the end of the restart performance. The display priority of the
なお、再開演出を実行する場合において以下の構成でもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が中図柄全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が中図柄の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前よりも再開演出終了直後のとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・再開演出直前は中図柄が左図柄(及び右図柄)よりも大きく、再開演出終了直後再開演出終了直後は左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の大きさは互いに同じでもよい。
・再開演出直前と再開演出終了直後とでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄相互間の大きさの比率が同じでもよい。
・再開演出直前と再開演出終了直後とでは装飾図柄55の見た目が同じでもよい。
・当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51はSPリーチ演出中に表示が継続されており、再開演出よりも当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51の方が表示優先度が高くてもよい。
・当該アイコン53は変動表示開始時またはSPリーチ演出開始時に消去され、その後に再表示されなくてもよい。
・停止表示される特別図柄の種類に関わらず、再開演出終了後にはSPリーチ演出に対応する演出モードであって当該変動表示開始時とは見た目が異なる特別な朝モードに移行してもよい。
・チャレンジ演出が実行されることを期待させる演出を実行した後、チャレンジ演出を実行することなく再開演出を実行してもよい。
・チャレンジ演出実行後のハズレ報知に応じて再開演出を実行してもよい。
Note that the following configuration may be used when executing the resuming effect.
- The size of the entire medium pattern may be larger, smaller, or the same immediately after the end of the resuming effect than immediately before the resuming effect.
The size of the
The size of the entire left pattern (and right pattern) may be larger, smaller, or the same immediately after the end of the resuming effect as compared to immediately before the resuming effect.
The size of the
・Just before the restart effect, the middle pattern is larger than the left pattern (and the right pattern), and immediately after the restart effect is finished.
- The size ratio between the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be the same immediately before the restart effect and immediately after the end of the restart effect.
- The appearance of the
The
- The
・Regardless of the type of special symbol to be stopped and displayed, after the end of the restart effect, the game may shift to a special morning mode which is a effect mode corresponding to the SP ready-to-win effect and is different in appearance from the start of the variable display.
- After executing the effect to expect the challenge effect to be executed, the restart effect may be executed without executing the challenge effect.
- You may perform a restart production|presentation according to the loss alert|report after execution of a challenge production|presentation.
次に、図51を参照して第2実施形態において低確微時短から低確時短に移行するときに第1特別図柄判定が保留されている演出例について説明する。図51(A)~(D)には、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって特定のハズレ図柄(具体的にはハズレ(時短ア)図柄)が停止表示されたことに応じて低確微時短から低確時短に移行したときの動きが表記されている。図51(A)は、低確微時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留だけがある状態で第1特別図柄としてハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されたときの様子を例示している。図51(A)の例では、保留数字52によって第1特別図柄判定の保留数が3であり、第2特別図柄判定の保留数が0であることが示されている。
Next, with reference to FIG. 51, an effect example in which the first special symbol determination is suspended when shifting from the low-probability short working hours to the low-probable short working hours in the second embodiment will be described. In FIG. 51 (A) to (D), when the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, a specific losing pattern (specifically, a losing (time-saving A) pattern) is stopped and displayed. The movement when moving from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours is shown. FIG. 51(A) exemplifies the situation when the losing (time saving A) symbol is stop-displayed as the first special symbol in a state where only the first special symbol is reserved in the low-probability time-saving state. In the example of FIG. 51(A), the
ハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されると、3つの装飾図柄55がハズレ態様で本停止すると共に、装飾図柄55と同じ組み合わせの小図柄56が本停止する。また、これに伴ってハズレを示す第4図柄57が停止表示する。遊技機1では、ハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示される場合、装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせで停止表示する。なお、遊技機1においてハズレ(時短A)図柄と他の特別図柄とで停止表示される装飾図柄55と停止表示される第4図柄57との組み合わせが異なれば、ハズレ(時短A)図柄が停止表示される場合に装飾図柄55が「227」の組み合わせ以外で停止表示してもよい。
When the losing (time-saving A) pattern is stop-displayed, the three
遊技機1では低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP3である。なお、遊技機1において、低確微時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
In the
低確非時短状態においてハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されてから所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確微非時短から低確時短に移行する。図51(A)では連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないので、時短回数は700回設定される。図51(B)の例では第1特別図柄判定の保留がある一方で第2特別図柄判定の保留がない。このため、低確時短状態移行後の1回目の変動表示として第1特別図柄が変動表示を開始する(図51(B)参照)。当該変動表示中に第2特別図柄判定の保留が発生すると、図29(B)~(D)に例示するように次変動は第2特別図柄が変動表示を開始する。 When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses after the losing (time saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed in the low probability non-working hours state, it shifts from the low probability non-working hours low to the low probability short working hours. In FIG. 51(A), since the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied, the number of times of time saving is set to 700 times. In the example of FIG. 51(B), while there is suspension of the first special symbol determination, there is no suspension of the second special symbol determination. For this reason, the first special symbol starts the variable display as the first variable display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state (see FIG. 51(B)). When suspension of the second special symbol determination occurs during the variable display, the second special symbol starts variable display as shown in FIGS. 29(B) to (D).
図51(B)に例示するように、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて扉画像が表示開始される。扉画像としては、扉が閉鎖して画面全体を覆ってから扉が開放する動画像が表示される(図51(B)及び(C)参照)。扉画像は表示されてから所定時間(例えば2.5秒)経過したことに応じて表示が終了する。仮に低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が特定のハズレ図柄であった場合、当該ハズレ図柄の停止表示中に扉画像の表示が終了する。低確時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても時短回数は加算されず遊技状態は変化しない。ここで、遊技機1では、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51の方が扉画像よりも表示優先度が低い。よって、装飾図柄55、当該アイコン53、及び保留アイコン51は扉画像が手前側に表示されることによって一旦見えなくなる。一方、遊技機1では、小図柄56並びに第4図柄57及び59の方が扉画像よりも表示優先度が高い。このため、遊技者は、扉画像の表示中は、高速変動後に停止表示された小図柄56及び第4図柄57を見ることによって低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第1特別図柄判定の判定結果を知ることが可能である。
As illustrated in FIG. 51(B), the display of the door image is started in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the shift to the low-probability short working hours state. As the door image, a moving image is displayed in which the door closes, covers the entire screen, and then opens (see FIGS. 51B and 51C). The display of the door image ends when a predetermined time (for example, 2.5 seconds) has passed since it was displayed. If the determination result of the first special symbol determination after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state is a specific lost symbol, the display of the door image ends during the stop display of the lost symbol. Even if a specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed in the low-probability time-saving state, the number of times of time-saving is not added and the game state does not change. Here, in the
仮に低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第1特別図柄判定の判定結果が大当たり図柄であったとしても、扉画像が非表示となる時間は大当たりを期待させたり大当たり報知させたりするよりも前である。このため、低確時短状態移行後における扉画像の表示中は、大当たりを期待させる演出は実行不可能であり、演出役物7を動作させるような大当たり報知用の演出も実行不可能である。 Even if the judgment result of the first special pattern judgment after the transition to the low probability time saving state is a jackpot pattern, the time when the door image is hidden is before the jackpot is expected or the jackpot is notified. is. Therefore, during the display of the door image after shifting to the low-probability short-working-time state, it is impossible to execute the performance for expecting a big win, and it is also impossible to execute the performance for informing the big win, such as activating the performance accessory 7.例文帳に追加
なお、扉画像が表示される際の態様は、画面全体に黒い画像がオーバーラップする態様でもよいし、モザイク状に現れていく扉画像によって画面全体が覆われる態様でもよい。また、扉画像の表示終了態様は、画面全体を覆う扉画像の透明度が上がり最終的に扉画像が非表示になる態様でもよいし、扉画像がモザイク状に欠けていき最終的に扉画像が非表示になる態様でもよい。 Note that the manner in which the door image is displayed may be a manner in which a black image overlaps the entire screen, or a manner in which the entire screen is covered with the door image appearing in a mosaic pattern. In addition, the display of the door image may be ended in such a manner that the transparency of the door image covering the entire screen is increased and the door image is finally hidden, or the door image is missing in a mosaic pattern and the door image is finally displayed. A mode in which it is hidden may be used.
盤用照明装置74及び枠用照明装置10は、扉画像表示中は扉画像表示用の発光パターン(例えば、黄色で点滅する発光パターン)で発光する。なお、低確時短状態であるときに発光可能である一方で低確時短状態ではないときに発光しない発光手段(例えば右サイドランプ)を備えてもよく、低確時短状態移行後における扉画像の表示中は上記発光手段を扉画像表示用の発光パターンで発光させてもよい。
The
遊技機1では、低確時短状態移行後における1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて遊技者に右打ちを促す文字が表示開始される(例えば、図29及び図51)。遊技機1では、右打ちを促す文字よりも扉画像の方が表示優先度が低い。よって、右打ちを促す文字は扉画像が後ろ側に表示されるので扉画像によって見えなくなることがない。
In the
遊技機1では、低確時短状態移行後における1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて遊技者にRUSHモードに移行したことを報知する「RUSHモード開始」との音声がスピーカ24から出力される。ここで、遊技機1では、大当たり遊技を介して低確時短状態に移行する場合は、大当たり遊技中に第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが同時に表示される。これに対して、遊技機1では、特定のハズレ図柄の停止表示を介して低確時短状態に移行する場合は、上記注意喚起を表示することなく低確時短状態に移行する。なお、特定のハズレ図柄の停止表示を介して低確時短状態に移行する場合は、低確時短状態移行後における1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて第1注意喚起が所定時間(例えば2.5秒間)表示されてもよい。
In the
図51(D)に例示するように低確時短においてはRUSHモードで演出が制御される。遊技機1では、背景画像、演出モード名、及び時短残り回数の方が扉画像よりも表示優先度が低い。このため、遊技者には夜モードの画面構成が扉画像の表示を介してRUSHモードの画面構成に変化したように見える。
As illustrated in FIG. 51(D), the effect is controlled in the RUSH mode in the low probability of short working hours. In the
夜モードであるときは第1特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51及び第1特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53が表示される。これに対し、RUSHモードであるときは第2特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51及び第2特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53が表示される。RUSHモードであるときは第1特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51及び第1特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53は非表示にされる。RUSHモードは保留アイコン51及び当該アイコン53の態様(例えば形および表示位置)が夜モードと異なる。
In the night mode, a pending
低確時短状態に移行すると、夜モードの画面構成であるときに表示パターンHP3であった装飾図柄55の表示優先度は、扉画像の表示を介して表示パターンHP9に変化する。なお、遊技機1において、低確時短状態移行直前における夜モードと、扉画像の表示を介してRUSHモードに変化したときとでは装飾図柄55の表示優先度が同じでもよい。
When shifting to the low probability time saving state, the display priority of the
扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の態様が異なってもよいし、同じでもよい。また、扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の表示領域が異なってもよいし、同じでもよい。また、扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは小図柄56の態様および表示領域が同じでもよいし、異なってもよい。
In the night mode immediately before displaying the door image and in the RUSH mode immediately after displaying the door image, the patterns of the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be different or the same. Further, the display areas of the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be different or the same in the night mode immediately before displaying the door image and in the RUSH mode immediately after displaying the door image. Further, the mode and display area of the
図51(E)から図51(B)への流れ、及び、図51(F)から図51(B)への流れは連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすことで低確非時短から低確時短に移行したときの動きが表記されている。低確非時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留だけがある状態で連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たす場合、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が停止表示された場合、時短回数1000回が設定される。 The flow from FIG. 51 (E) to FIG. 51 (B) and the flow from FIG. 51 (F) to FIG. The movement when moving to is described. If the condition is 750 consecutive losses with only the first special pattern reserved in the low probability non-time saving state, even if the specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed, even if the normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed, the low probability is not Transition from short working hours to low-accurate short working hours. When a losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses is stopped and displayed, the number of times of time saving is set to 1000 times.
図51(E)は連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が特定のハズレ図柄である場合の例である。図51(E)では特定のハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短イ)図柄が停止表示する場合の例を示しているが、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄としてハズレ(時短ア)図柄が停止表示されていてもよい。 FIG. 51(E) is an example of a case where the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings is a specific losing pattern. FIG. 51(E) shows an example in which a losing (time-saving I) symbol is stopped and displayed as a specific losing symbol, but a losing (time-saving A) symbol is stopped and displayed as a losing symbol that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings. may have been
図51(F)は連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が通常のハズレ図柄である場合の例である。遊技機1では、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される場合、装飾図柄55は「227」の組み合わせ以外で停止表示する。
FIG. 51(F) is an example of a case where the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losings is a normal losing pattern. In the
遊技機1では特定のハズレ図柄および通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP3である。なお、遊技機1において特定のハズレ図柄および通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されるときの装飾図柄55の表示優先度は表示パターンHP1~5のうちの何れでもよい。
In the
連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄の停止表示から所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確微時短から低確時短に移行する。図51(B)以降の流れは、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたときと基本的には同じである。異なる点は、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないときは時短残り回数の初期値は699回であるのに対し連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすときは時短残り回数の初期値は999回である点である。 When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses from the stop display of the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses, the game shifts from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours. The flow after FIG. 51(B) is basically the same as when the condition of 750 continuous losses is not satisfied and a specific losing pattern is stop-displayed in the low-probability/small-time-saving state. The difference is that when the condition of 750 consecutive failures is not satisfied, the initial value of the remaining time reduction is 699 times, whereas when the condition of 750 consecutive failures is satisfied, the initial value of the remaining time reduction is 999 times. It is a point.
なお、低確微時短から低確時短に移行する場合において、以下の構成でもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が中図柄全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が中図柄の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・低確非時短から低確時短に移行する場合において、扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・低確非時短から低確時短に移行する場合において、扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときよりも扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときは中図柄が左図柄(及び右図柄)よりも大きく、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときは左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の大きさは互いに同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前における夜モードのときと、扉画像表示直後におけるRUSHモードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄相互間の大きさの比率が同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示直前は夜モード用の発光パターンで発光し、扉画像表示終了直後はRUSHモード用の発光パターンで発光する。
In addition, when shifting from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours, the following configuration may be used.
The size of the entire middle pattern may be larger, smaller, or the same in the RUSH mode immediately after the door image is displayed than in the night mode immediately before the door image is displayed.
The size of the
・When transitioning from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours, the overall size of the left pattern (and right pattern) is larger in RUSH mode immediately after displaying the door image than in night mode immediately before displaying the door image. It may be the same size, smaller, or the same size.
・ When shifting from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours, the
・In the night mode immediately before the door image is displayed, the middle pattern is larger than the left pattern (and the right pattern), and in the RUSH mode immediately after the door image is displayed, the left, middle, and right patterns are the same size. It's okay.
In the night mode immediately before the door image is displayed and in the RUSH mode immediately after the door image is displayed, the size ratio between the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be the same.
- Immediately before the door image is displayed, light is emitted in the light emission pattern for the night mode, and immediately after the door image is displayed, light is emitted in the light emission pattern for the RUSH mode.
ここで、第2実施形態において低確微時短から低確時短に移行するときに第1特別図柄判定が保留されていない演出例について説明する。連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって低確微時短状態において第1特別図柄の保留がない状態で第1特別図柄として特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示された場合、停止表示されてから所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確微時短から低確時短に移行する。連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないので、時短回数は700回設定される。第1特別図柄判定の保留も第2特別図柄判定の保留も0であるときは、確定停止期間が経過したことに応じて客待ちコマンドが遊技制御基板100から演出制御基板130に送信される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなく予め定められた時間(例えば10秒)が経過したことに応じて音量値および光量値を設定するための設定画像が表示開始される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなくさらに予め定められた時間(例えば20秒)が経過したことに応じて客待ち演出が開始される。
Here, the production example in which the first special symbol determination is not suspended when shifting from the low-probability short working hours to the low-probable short working hours in the second embodiment will be described. When the condition of 750 consecutive losses is not satisfied and the specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed as the first special pattern in the state where the first special pattern is not reserved in the low-probability and minute time-saving state, it is stopped and displayed. When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses, it shifts from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours. Since the condition of 750 consecutive failures is not satisfied, the number of times of time saving is set to 700 times. When both the suspension of the first special symbol determination and the suspension of the second special symbol determination are 0, a customer waiting command is transmitted from the
遊技機1が客待ち状態であるときに遊技球がゲート16を通過すると普通図柄判定が行われる。遊技機1では低確時短状態では普通図柄判定が行われると100%の確率で第2始動口12がロング開放される(図2(A)参照)。遊技球が第2始動口12に入賞すると、低確時短状態移行後の1回目の変動表示として第2特別図柄が変動表示を開始する。
When a game ball passes through a
低確時短状態移行後において1回目の第2特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて扉画像および右打ちを促す文字が表示開始される。扉画像の表示中には第2特別図柄が変動表示していることを示す当該アイコン53が表示される。また、扉画像の表示中に第2特別図柄判定が保留されると、第2特別図柄判定の保留数を示す保留アイコン51が表示される。
After the transition to the low-probability short-working-time state, the display of the door image and the character prompting the right-handed strike is started according to the start of the second special symbol variation display for the first time. During the display of the door image, the
仮に低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第2特別図柄判定の判定結果が通常のハズレ図柄であった場合、当該ハズレ図柄の停止表示中に扉画像の表示が終了する。遊技者は、扉画像の表示中は、高速変動後に停止表示された小図柄56及び第4図柄57を見ることによって低確時短状態移行後における1回目の第2特別図柄判定の判定結果を知ることが可能である。
If the determination result of the first second special symbol determination after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state is a normal losing symbol, the display of the door image ends during the stop display of the losing symbol. During the display of the door image, the player sees the
なお、低確非時短状態において特別図柄の保留がない状態で連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たす場合、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されても低確非時短から低確時短に移行する。連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄が停止表示された場合、時短回数1000回が設定される。 In addition, if the conditions for 750 consecutive losses are met in a low probability non-time saving state with no special pattern reserved, even if a specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed, even if a normal losing pattern is stopped and displayed Low probability non-time saving Transition from low-accuracy short working hours. When a losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses is stopped and displayed, the number of times of time saving is set to 1000 times.
連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすハズレ図柄の停止表示から所定の確定停止期間(例えば1秒)が経過すると、低確微時短から低確時短に移行する。第1特別図柄判定の保留も第2特別図柄判定の保留も0である場合、確定停止期間が経過したことに応じて客待ちコマンドが遊技制御基板100から演出制御基板130に送信される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなく予め定められた時間(例えば10秒)が経過したことに応じて音量値および光量値を設定するための設定画像が表示開始される。その後、特別図柄の変動表示が行われることなくさらに予め定められた時間(例えば20秒)が経過したことに応じて客待ち演出が開始される。
When a predetermined fixed stop period (for example, 1 second) elapses from the stop display of the losing pattern that satisfies the condition of 750 consecutive losses, the game shifts from low-probability short working hours to low-probable short working hours. When both the suspension of the first special symbol determination and the suspension of the second special symbol determination are 0, a customer waiting command is transmitted from the
遊技機1が客待ち状態であるときに遊技球がゲート16を通過すると普通図柄判定が行われる。普通図柄判定の結果、ロング開放された第2始動口12遊技球が入賞すると、低確時短状態移行後の1回目の変動表示として第2特別図柄が変動表示を開始する。低確時短状態移行後の流れは、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合であって低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたときと基本的には同じである。異なる点は、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさないときは時短残り回数の初期値は699回であるのに対し連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすときは時短残り回数の初期値は999回である点である。
When a game ball passes through a
次に、図52を参照して第2実施形態における低確時短状態の演出例について説明する。図52(A)及び(B)に例示するように、大当たりエとなる変動パターンO201は即当たりの変動パターンである。図52(B)に例示するように大当たりエが停止表示すると大当たり遊技が実行される。当該大当たり遊技では第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが表示されない。当該大当たり遊技終了後は低確時短に移行する。なお、当該大当たり遊技では第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが表示されてもよい。遊技機1では、小当たりアとなる変動パターンK201である場合も変動パターンO201と同様の演出が実行される。
Next, with reference to FIG. 52, the production example of the low-probability short working hours state in the second embodiment will be described. As exemplified in FIGS. 52A and 52B, the variation pattern O201 that becomes a big hit is a variation pattern that is an instant hit. As shown in FIG. 52(B), when the big win D is stopped and displayed, the big win game is executed. In the jackpot game, the first alert and the second alert are not displayed. After the end of the jackpot game, it shifts to a low-probability reduction of working hours. In addition, in the jackpot game, the first alert and the second alert may be displayed. In the
図52(A)、(C)、および(B)に例示するように、大当たりエとなる変動パターンO202は転落を示唆してから即当たりとなる変動パターンである。転落示唆の開始時からは扉画像の表示が開始されると共に操作促進演出が実行される。扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像と同じである。なお、転落示唆の開始時から表示される扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像と異なってもよい。大当たりエとなる場合、有効期間中の操作の有無に関わらず予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始時から3秒経過時)で扉画像が開放して即当たりとなる。なお、大当たりエとなる場合、有効期間中の操作に応じて扉画像が開放して即当たりとなってもよい。 As illustrated in FIGS. 52A, 52C, and 52B, the variation pattern O202 that results in a big hit is a variation pattern that suggests a fall and then results in an immediate hit. From the start of the fall suggestion, the display of the door image is started and the operation prompting effect is executed. The door image is the same as the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state. In addition, the door image displayed from the start of the fall suggestion may be different from the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state. In the case of a big hit (d), the door image is opened at a predetermined valid period end timing (for example, when 3 seconds have elapsed from the start of operation promotion performance) regardless of whether or not there is an operation during the valid period, and the player wins immediately. In the case of a big win D, the door image may be opened according to the operation during the validity period, and the win may be made immediately.
図52(A)、(C)、及び(D)に例示するように、通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される変動パターンH202は、転落を示唆してからハズレ報知される変動パターンである。転落示唆の開始時から表示が開始された扉画像は、有効期間中の操作の有無に関わらず予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始時から3秒経過時)で扉画像が開放してハズレ報知される。なお、ハズレとなる場合、有効期間中の操作に応じて扉画像が開放してハズレ報知されてもよい。 As illustrated in FIGS. 52A, 52C, and 52D, the variation pattern H202 in which normal losing symbols are stopped and displayed is a variation pattern in which a failure is notified after suggesting a fall. The door image that started to be displayed from the start of the suggestion of falling is displayed at a predetermined effective period end timing (for example, when 3 seconds have passed since the start of the operation promotion effect) regardless of whether or not there is an operation during the effective period. is opened and a failure is notified. In addition, in the case of a failure, the door image may be opened according to the operation during the validity period to notify the failure.
図52(A)、(C)、及び(E)に例示するように、小当たりイとなる変動パターンK203は、転落を示唆してから小当たりイが小図柄56によって報知される変動パターンである。転落示唆の開始時から表示が開始された扉画像は、有効期間中の操作に関わらず予め定められた有効期間終了タイミング(例えば、操作促進演出開始時から3秒経過時)で閉鎖する。図52(E)に例示するように小当たりイが停止表示すると小当たり遊技中のV入賞を条件に大当たり遊技が実行される。当該大当たり遊技では第1注意喚起と第2注意喚起とが表示されない。当該大当たり遊技終了後(遊技状態は低確非時短)は低確非時短に制御される。また、小当たり遊技中にV入賞しなかった場合は大当たり遊技が実行されることなく低確非時短に制御される。低確非時短へ移行するとベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が行われるようになる。
As illustrated in FIGS. 52(A), (C), and (E), the variation pattern K203 that results in a small hit is a variation pattern in which a small hit is reported by the
図52(F)は低確非時短に制御されているときに第2特別図柄判定の保留が消化されたときの演出例である。低確非時短における1回目の第2特別図柄の変動表示開始時から最先の第2特別図柄判定の保留に係る変動表示が終了する直前まで、遊技者が大当たり遊技によって得られた賞球数を示唆するリザルトが表示される。また、リザルトの開始時からは扉画像の表示が開始される。扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像、及び転落示唆の開始時から表示される扉画像と同じである。なお、リザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像は、低確時短状態移行後において1回目の特別図柄変動表示開始に応じて表示される扉画像、及び転落示唆の開始時から表示される扉画像と異なってもよい。なお、リザルト及びリザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像は、低確時短の時短回数が終了したときにも表示される(例えば、図43(D)から(F)への流れ)。低確時短の時短回数が終了する変動表示が連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たさない場合、当該変動表示が終了すると低確非時短に移行するので、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が行われるようになる。一方、低確時短の時短回数が終了する変動表示が連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たす場合、当該変動表示が終了すると低確時短に移行するので、ベース算出用アウトカウンタ及びベース算出用賞球カウンタによる計数が停止したままである。 FIG. 52(F) is an example of an effect when the suspension of the second special symbol determination is digested while being controlled to the low probability and short working hours. From the start of the first variable display of the second special symbol in the low-probability short time period to immediately before the end of the variable display related to the suspension of the first second special symbol judgment, the number of prize balls obtained by the player through the jackpot game. A result suggesting is displayed. Moreover, the display of the door image starts from the start of the result. The door image is the same as the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol variation display after the transition to the low-probability short working hours state, and the door image displayed from the start of the fall suggestion. In addition, the door image displayed from the start of the result is the door image displayed in response to the start of the first special symbol fluctuation display after the transition to the low probability time saving state, and the door image displayed from the start of the fall suggestion. may differ from In addition, the door image displayed from the start of the result and the result is also displayed when the number of times of reduced working hours of low probability ends (for example, the flow from FIG. 43 (D) to (F)). If the variable display at which the number of times of low-probability time-saving ends does not meet the condition of 750 consecutive losses, when the variable display ends, it will shift to low-probability non-time-saving, so the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation will be counted by On the other hand, if the variable display at which the number of times of low-probability time-saving ends ends in a continuous loss of 750 times, it will shift to low-probability of time-saving when the variable display ends, so the out counter for base calculation and the prize ball counter for base calculation counting by remains stopped.
なお、低確時短の最終変動よりも所定回数前(例えば10変動前)の変動表示から低確時短の最終変動までに亘って、特別図柄が変動表示を開始する毎に時短残り回数を報知するカウントダウンを行ってもよい。遊技機1では、図52(D)に例示するように低確時短の最終変動よりも所定回数前(例えば3変動前)の変動表示から当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51が非表示にされる。なお、低確時短の最終変動が終わるまで当該アイコン53及び保留アイコン51が表示された状態でもよい。
In addition, every time the special symbol starts the variable display, the remaining number of times of shortening is notified from the variable display of a predetermined number of times before the final variation of the low-probability short working hours (for example, 10 variations before) to the final variation of the low-probable short working hours. You can do a countdown. In the
仮にすべての第2特別図柄判定の保留がハズレであった場合、最先の第2特別図柄判定の保留に係る変動表示が終了する直前においてリザルトが非表示となると共に扉画像が開放する(図52(G)参照)。これに伴って装飾図柄55の表示優先度はリザルト表示中に表示パターンHP9からHP3に変化する。
If all the suspension of the second special symbol determination is lost, the result is hidden and the door image is opened immediately before the end of the variable display related to the suspension of the first special symbol determination (Fig. 52(G)). Along with this, the display priority of the
なお、リザルト表示に伴う扉画像を表示する場合において以下の構成でもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における朝モードのとき方が中図柄全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における朝モードのとき方が中図柄の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における朝モードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)全体の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときよりも扉画像表示直後における朝モードのとき方が左図柄(及び右図柄)の数字部分550の大きさは大きくてもよいし小さくてもよいし同じ大きさでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときは中図柄が左図柄(及び右図柄)よりも大きく、扉画像表示直後における朝モードのときは左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄の大きさは互いに同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示前におけるRUSHモードのときと、扉画像表示直後における朝モードのときとでは、左図柄、中図柄、及び右図柄相互間の大きさの比率が同じでもよい。
・扉画像表示中は扉画像用の発光パターンで発光し、扉画像表示終了直後は朝モード用の発光パターンで発光する。
It should be noted that the following configuration may be used when displaying the door image accompanying the result display.
The size of the entire middle pattern may be larger, smaller, or the same in the morning mode immediately after the door image is displayed than in the RUSH mode before the door image is displayed.
The size of the
・The overall size of the left pattern (and the right pattern) may be larger, smaller, or the same size in the morning mode immediately after the door image is displayed than in the RUSH mode before the door image is displayed. .
The size of the
・In the RUSH mode before the door image is displayed, the middle pattern is larger than the left (and right) pattern, and in the morning mode immediately after the door image is displayed, the left, middle, and right patterns are the same size. It's okay.
In the RUSH mode before the door image is displayed and in the morning mode immediately after the door image is displayed, the size ratio between the left pattern, the middle pattern, and the right pattern may be the same.
・While the door image is displayed, light is emitted in the light emission pattern for the door image, and immediately after the door image is displayed, light is emitted in the light emission pattern for the morning mode.
図52(H)に例示するように、低確非時短において消化された第2特別図柄判定の保留が大当たりエである場合、リザルトが消去されると共に及びリザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像が開放して即当たりとなる。図52(I)に例示するように、低確非時短において消化された第2特別図柄判定の保留が小当たりイである場合、リザルトが消去されると共に及びリザルトの開始時から表示される扉画像が開放して小当たりイが小図柄56によって報知される。 As exemplified in FIG. 52 (H), when the hold of the second special symbol judgment digested in the low-probability short working hours is a big hit, the result is erased and the door image displayed from the start of the result will open and hit immediately. As exemplified in FIG. 52 (I), when the second special symbol judgment that has been digested in the low-probability short working hours is held for a small hit, the result is erased and the door displayed from the start of the result When the image is opened, a small winning A is notified by a small symbol 56.例文帳に追加
なお、第2実施形態において非時短状態では基本的に遊技球を第2始動口12に入賞できない一方で微時短状態では遊技球を第2始動口12に入賞できるように予め構成されてもよい。具体的には、微時短状態のときにショート開放図柄が停止表示される確率が例えば4999/5000であり、ロング開放図柄が停止表示される確率が例えば1/5000でもよい。これにより、非時短状態よりも微時短状態に制御させたいという遊技者の気持ちをより高める遊技性を提供可能である。
In addition, in the second embodiment, it may be configured in advance so that the game ball can not win the
[第1実施形態および第2実施形態の効果]
第1実施形態および第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態におけるベース値を算出する。ベース算出用賞球カウンタは、低確非時短状態における特定の区間において遊技球の入賞に応じて払い出された払出個数の総数を計数する。ベース算出用アウトカウンタは、低確非時短状態における特定の区間において遊技者が打ち出した遊技球の総数を計数する。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて低確時短状態に移行すると、ベース算出用賞球カウンタ及びベース算出用アウトカウンタでの計数を停止する。低確時短状態における時短最終変動において通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じてベース算出用賞球カウンタ及びベース算出用アウトカウンタでの計数を再開する。これにより、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて遊技状態が変化するときにベース算出用賞球カウンタ及びベース算出用アウトカウンタでの計数を停止できる。
[Effects of First Embodiment and Second Embodiment]
The
[第2実施形態の効果]
第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において大当たりアとなった場合、大当たり遊技終了に応じて低確時短状態に移行する。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から遊技状態が変化しない。一方、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。このため、低確非時短状態である場合よりも低確微時短状態である場合の方が特定のハズレ図柄となる確率の分だけ低確時短状態への移行確率が高い。これにより、低確微時短状態を低確非時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な遊技状態にできる。
[Effect of Second Embodiment]
The
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行すると判定される確率は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで同じである。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において大当たりアとなった場合、大当たり遊技終了に応じて低確時短状態に移行する。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から遊技状態が変化しない。一方、低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確非時短状態である場合よりも低確微時短状態である場合の方が低確時短状態への移行確率が高い。これにより、大当たり遊技を実行すると判定される確率が同じである状況において、低確微時短状態を低確非時短状態よりも遊技者に有利な遊技状態にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態(時短回数20回または500回)と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確微時短状態において特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数が20回または500回となることで低確微時短状態が終了する。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において大当たりアとなった場合、大当たり遊技終了に応じて低確時短状態(時短回数700回)に移行する。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確非時短状態である場合よりも低確微時短状態である場合の方が低確時短状態への移行確率が高い。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態において連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たした場合、低確時短状態(時短回数1000回)に移行する。よって、第2実施形態の遊技機1において低確時短状態には、特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数が700回となることで低確時短状態が終了する状態と、特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数が1000回となることで低確時短状態が終了する状態とがある。低確微時短状態と低確時短状態(時短回数700回)と低確時短状態(時短回数1000回)とは互いに遊技者に対する有利度合いが異なる。これにより、特別図柄判定の判定結果の報知回数に対して遊技者に興味を持たせることが可能である。
In addition, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確微時短状態に移行可能である。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。これにより、低確微時短状態は特定のハズレ図柄となる確率の分だけ低確非時短状態よりも低確時短状態への移行確率を高くできる。
Moreover, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確非時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確非時短状態から低確微時短状態に移行可能である。低確時短状態においては、時短最終変動よりも前の変動において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、遊技状態は変化しない。これにより、低確非時短状態であるときに低確時短状態に移行することを目指すのに加えて低確微時短状態に移行することを目指して遊技者に遊技をさせることが可能である。
Moreover, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。普通図柄は低確微時短状態においては低確微時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示され、低確時短状態においては低確時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示される。低確時短状態用の普通図柄の変動パターンの方が低確微時短状態用の普通図柄の変動パターンよりも短い。これにより、低確時短状態の方が低確微時短状態よりも頻繁に普通図柄を変動可能な状態にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。電動チューリップ17は低確微時短状態においては低確微時短状態用の開放パターンで開放され、低確時短状態においては低確時短状態用の開放パターンで開放される。電動チューリップ17の開放時間は低確時短状態の方が低確微時短状態よりも長い。これにより、低確時短状態の方が低確微時短状態よりも第2始動口12に遊技球を入賞容易にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。特別図柄は低確微時短状態においては低確微時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示され、低確時短状態においては低確時短状態用の変動パターンで変動表示される。低確時短状態用の特別図柄の変動パターンの方が低確微時短状態用の特別図柄の変動パターンよりも短い。これにより、低確時短状態の方が低確微時短状態よりも頻繁に特別図柄を変動可能な状態にできる。
Moreover, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。低確時短状態であるときは点灯により遊技者に右打ちを促す右打ちランプ49が点灯する。低確非時短状態または低確微時短状態であるときは右打ちランプ49が消灯する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちランプ49が点灯する。これにより、右打ちランプ49の状態によって第2始動口12に遊技球が入賞容易な状態か否かを遊技者に示唆可能である。
Moreover, the
また、第2実施形態の遊技機1は低確非時短状態と、低確微時短状態と、低確時短状態とで遊技を制御する。大当たり遊技を実行しないと判定された場合、特定のハズレ図柄または通常のハズレ図柄が停止表示される。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示した場合、低確微時短状態から低確時短状態に移行可能である。低確微時短状態において特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて右打ちを促す文字、扉画像、及び低確時短状態用の背景画像を表示する。これにより、遊技状態を移行させる特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことを遊技者に対して分かり易く示唆できる。
Moreover, the
[変形例]
本発明は、例えば、1種タイプの遊技機、回胴式遊技機、スロットマシン等の他の遊技機にも適用可能である。
[Modification]
The present invention can also be applied to other game machines such as, for example, single-type game machines, reel-type game machines, and slot machines.
第1実施形態および第2実施形態では、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすと他の条件を満たすことによって低確時短に制御される時短回数よりも多い時短回数が設定される。第1実施形態と第2実施形態との何れにおいても、低確時短に制御される時短回数は連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たす場合よりも特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示される場合の方が多くてもよい。このような構成では、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたことに応じて制御される低確時短状態は、他の条件を満たしたことに応じて制御される低確時短状態に比べて遊技者に有利な遊技状態である。 In 1st Embodiment and 2nd Embodiment, when the conditions of 750 times of continuation loss are satisfy|filled, the number of times of shortening of working hours more than the number of times of shortening of working hours controlled by low probability by satisfying other conditions is set. In both the first embodiment and the second embodiment, the number of times of reduced working hours controlled to be low-probability is more frequent when a specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed than when the condition of 750 consecutive losings is satisfied. may In such a configuration, the low-probability short working hours state controlled according to the stop display of a specific losing pattern is compared to the low-probable short working hours state controlled according to other conditions being satisfied. It is a game state that is advantageous to
第1実施形態と第2実施形態との何れにおいても、低確非時短状態であるか低確微時短状態であるかを遊技者が認識困難なようにしてもよい。例えば、低確非時短状態と低確微時短状態とでは同じ背景画像を表示すると共に同じ演出モード名を表示することによりどちらの遊技状態であるかを遊技者が認識困難なようにしてもよい。これにより、相対的に遊技者に不利な遊技状態(演出モード)であることを理由に遊技を行ってもらえないことを防止可能である。なお、低確非時短状態であるか低確微時短状態であるかを遊技者が認識困難な構成においても低確時短状態については遊技状態を遊技者が認識困難にする必要がないので、低確時短状態では演出モード名を表示することにより遊技者が遊技状態(演出モード)を認識できるようにする。 In any of the first embodiment and the second embodiment, it may be difficult for the player to recognize whether the low-probability short working hours state or the low-probability short working hours state. For example, the same background image is displayed in the low-probability non-time-saving state and the low-probability small time-saving state, and the same production mode name is displayed, thereby making it difficult for the player to recognize which game state it is. . As a result, it is possible to prevent the player from not playing the game because the game state (performance mode) is relatively disadvantageous to the player. In addition, even in a configuration where it is difficult for the player to recognize whether it is a low-probability short-time state or a low-probability short-time state, it is not necessary for the player to make it difficult to recognize the game state for the low-probability short-time state. A player can recognize the game state (performance mode) by displaying the name of the performance mode in the guaranteed time saving state.
第1実施形態と第2実施形態との何れにおいても、連続ハズレ750回の条件を満たすと時短回数が設定されるという構成を備えなくてもよい。すなわち、通常のハズレ図柄が何回連続して停止表示されても時短状態に制御されることがない。 Neither in the first embodiment nor in the second embodiment, there is no need to provide a configuration in which the number of times of time saving is set when the condition of 750 consecutive failures is satisfied. That is, no matter how many times normal losing symbols are stopped and displayed in succession, the game is not controlled to the time-saving state.
第1実施形態と第2実施形態とでは、連続ハズレ750回の条件と特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたという条件とを同時に満たした場合、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたという条件を非優先(無視)にして連続ハズレ750回の条件だけを満たしたときと同じ処理を行うものとして説明した。第1実施形態と第2実施形態との何れにおいても、連続ハズレ750回の条件と特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたという条件とを同時に満たした場合、連続ハズレ750回の条件を非優先(無視)にして特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示されたという条件だけを満たした場合と同じ処理を行ってもよい。 In the first embodiment and the second embodiment, when the condition of 750 consecutive losses and the condition that a specific losing pattern is stopped are satisfied at the same time, the condition that the specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed is non-existent. It has been explained that the same processing as when only the condition of 750 consecutive losses is satisfied with priority (ignorance) is performed. In both the first embodiment and the second embodiment, if the condition of 750 consecutive losses and the condition that a specific losing pattern is stopped are satisfied at the same time, the condition of 750 consecutive losses is given no priority ( ignoring), and the same processing as in the case of satisfying only the condition that a specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed may be performed.
第1実施形態と第2実施形態との何れにおいても、特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて低確時短状態に移行する場合、実際にはハズレであるものの特定のハズレ図柄が停止表示したことに応じて大当たりに見えるような演出を行ってもよい。 In both the first embodiment and the second embodiment, when the transition to the low-probability time-saving state occurs in response to the stop display of a specific losing pattern, the specific losing pattern is stopped and displayed although it is actually lost. Depending on what you have done, you may perform a production that looks like a big win.
なお、遊技者が操作することによって操作情報を入力するための操作手段はどのようなものでもよい。操作手段として、例えば、遊技者が指でタッチ操作を行うことによって操作情報を入力可能な表示画面であるタッチパネルを備えてもよい。また、遊技者がガラス板へのタッチ操作を行うことによって操作情報を入力可能なように、枠部材3に備えられた光センサ等を操作手段としてもよい。
It should be noted that any operation means may be used for inputting operation information by the player's operation. As the operation means, for example, a touch panel, which is a display screen on which operation information can be input by the player performing a touch operation with a finger, may be provided. Further, an optical sensor or the like provided on the
なお、画像音響制御基板140及びランプ制御基板150において実行される処理の一部を演出制御基板130に実行させたり、或いは、演出制御基板130において実行される処理の一部を画像音響制御基板140又はランプ制御基板150に実行させたりしてもよい。
In addition, the
また、上記実施形態において説明した遊技機1の構成や各部材の発光態様および動作態様は単なる一例に過ぎず、他の構成、発光態様、及び動作態様であっても本発明を実現できることは言うまでもない。また、上述したフローチャートにおける処理の順序、時短回数、割合、設定値、判定に用いられる閾値等は単なる一例に過ぎず、本発明の範囲を逸脱しなければ他の順序や値であっても、本発明を実現できることは言うまでもない。上記実施形態で例示した説明図等も単なる一例であって、他の態様であってもよい。
Further, the configuration of the
なお、上述した演出および数値は単なる一例であり、本発明は、上記実施形態に限定されず、様々な変形および応用が可能である。また、上記実施形態および変形例は互いに適用可能であり、様々な組み合わせで本発明が実現されてもよい。 Note that the effects and numerical values described above are merely examples, and the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and various modifications and applications are possible. Moreover, the above embodiments and modifications are mutually applicable, and the present invention may be implemented in various combinations.
1 遊技機
5 液晶表示装置の表示画面
7 演出役物
11 第1始動口
12 第2始動口
100 遊技制御基板
100a CPU
100b ROM
100c RAM
130 演出制御基板
130a CPU
130b ROM
130c RAM
140 画像音響制御基板
150 ランプ制御基板
1
100b ROM
100c RAM
130
130b ROM
130c RAM
140 image
Claims (1)
前記入賞領域に遊技球が入賞すると特別遊技を実行するか否かを判定する遊技機であって、
第1遊技状態と、前記第1遊技状態よりも前記入賞領域に遊技球が入賞し易い第2遊技状態と、前記第2遊技状態よりも前記入賞領域に遊技球が入賞し易い第3遊技状態と、を含む複数の遊技状態のうちのいずれかの遊技状態に制御する遊技状態制御手段を備え、
前記第2遊技状態のときに所定条件が成立すると、所定確率で前記第2遊技状態から前記第3遊技状態に移行し、
前記第1遊技状態のときに所定条件が成立すると、前記所定確率よりも高確率で前記第1遊技状態から前記第3遊技状態に移行する、遊技機。
Equipped with a winning area that can be changed between an open state in which game balls can easily win and a closed state in which game balls cannot easily win,
A gaming machine that determines whether or not to execute a special game when a game ball wins in the winning area,
A first game state, a second game state in which game balls are more likely to enter the winning area than in the first game state, and a third game state in which game balls are more likely to enter the winning area than in the second game state. and game state control means for controlling to any one of a plurality of game states including,
When a predetermined condition is established in the second game state, the game state is shifted from the second game state to the third game state with a predetermined probability,
A gaming machine, wherein when a predetermined condition is established in the first game state, the game state is shifted from the first game state to the third game state with a higher probability than the predetermined probability.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021191957A JP2023078703A (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2021-11-26 | game machine |
| JP2023209638A JP2024019518A (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2023-12-12 | gaming machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021191957A JP2023078703A (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2021-11-26 | game machine |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023209638A Division JP2024019518A (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2023-12-12 | gaming machine |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2023078703A true JP2023078703A (en) | 2023-06-07 |
Family
ID=86646368
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021191957A Pending JP2023078703A (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2021-11-26 | game machine |
| JP2023209638A Pending JP2024019518A (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2023-12-12 | gaming machine |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2023209638A Pending JP2024019518A (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2023-12-12 | gaming machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP2023078703A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7430405B2 (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2024-02-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | gaming machine |
| JP7430403B2 (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2024-02-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | gaming machine |
| JP7430404B2 (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2024-02-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | gaming machine |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022000080A (en) * | 2020-06-19 | 2022-01-04 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
-
2021
- 2021-11-26 JP JP2021191957A patent/JP2023078703A/en active Pending
-
2023
- 2023-12-12 JP JP2023209638A patent/JP2024019518A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022000080A (en) * | 2020-06-19 | 2022-01-04 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7430405B2 (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2024-02-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | gaming machine |
| JP7430403B2 (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2024-02-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | gaming machine |
| JP7430404B2 (en) | 2021-11-26 | 2024-02-13 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | gaming machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2024019518A (en) | 2024-02-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2023078703A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078832A (en) | game machine | |
| JP7430403B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7430404B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7430405B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP7460174B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP7460175B2 (en) | Gaming Machines | |
| JP2023078656A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078658A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078705A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078659A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078833A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078699A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078661A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078660A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078829A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078835A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078834A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078702A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078657A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078837A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078831A (en) | game machine | |
| JP2023078664A (en) | game machine | |
| JP7460173B2 (en) | gaming machine | |
| JP2023078830A (en) | game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20221201 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20230929 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20231013 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20240402 |