JP2020164342A - Concrete of high strength and high fluidity, and method of producing the same - Google Patents
Concrete of high strength and high fluidity, and method of producing the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2020164342A JP2020164342A JP2019063585A JP2019063585A JP2020164342A JP 2020164342 A JP2020164342 A JP 2020164342A JP 2019063585 A JP2019063585 A JP 2019063585A JP 2019063585 A JP2019063585 A JP 2019063585A JP 2020164342 A JP2020164342 A JP 2020164342A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- cement
- mass
- strength
- concrete
- water
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02W—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO WASTEWATER TREATMENT OR WASTE MANAGEMENT
- Y02W30/00—Technologies for solid waste management
- Y02W30/50—Reuse, recycling or recovery technologies
- Y02W30/91—Use of waste materials as fillers for mortars or concrete
Landscapes
- Curing Cements, Concrete, And Artificial Stone (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、低水セメント比においても高い流動性を保有し、かつ高強度を発現する高強度高流動コンクリートについて、その流動性の予測方法に基づいた製造方法とその高強度高流動コンクリートに関する。 The present invention relates to a high-strength, high-fluidity concrete that retains high fluidity even at a low water cement ratio and exhibits high strength, a manufacturing method based on a method for predicting the fluidity, and the high-strength, high-fluidity concrete.
日本建築学会のコンクリート工事標準仕様(JASS5)では、Fc36を超えるコンクリートを高強度コンクリートと定義しており、高強度コンクリート用のセメントについて、水セメント比(W/C)30%を基準にして評価している。しかし、これは主に圧縮強度の評価方法であり、流動性に対する評価方法ではない。また、水セメント比(W/C)30質量%の基準は、超高強度コンクリートとしては水セメント比が高く、例えば、極低水セメント比(水セメント比20質量%以下)において高流動性のコンクリートが知られている(特許文献1)。このような極低水セメント比のコンクリートの流動性の測定方法として上記試験方法は適切ではない。 The Architectural Institute of Japan's Standard Specifications for Concrete Construction (JASS5) defines concrete that exceeds Fc36 as high-strength concrete, and evaluates cement for high-strength concrete based on a water-cement ratio (W / C) of 30%. are doing. However, this is mainly an evaluation method for compressive strength, not an evaluation method for fluidity. Further, the standard of water-cement ratio (W / C) of 30% by mass is that the water-cement ratio is high for ultra-high-strength concrete, for example, high fluidity at an extremely low water-cement ratio (water-cement ratio of 20% by mass or less). Concrete is known (Patent Document 1). The above test method is not suitable as a method for measuring the fluidity of concrete having such an extremely low water cement ratio.
一般にコンクリートの流動性はスランプ値やスランプフロー値によって測定されるが、この試験は練り混ぜたコンクリートをスランプコーンに入れて測定しており、コンクリートの流動性を測定するには試験用のコンクリートを調製する必要がある。 Generally, the fluidity of concrete is measured by the slump value or slump flow value, but this test is measured by putting mixed concrete in a slump cone, and to measure the fluidity of concrete, use concrete for testing. Need to be prepared.
高流動性コンクリートについて、流動性の測定は試験体としてコンクリートを用いており、モルタルでコンクリートの流動性を判断することは行われていない。しかし、コンクリートを調製して試験を行うのは手間と時間がかると云う問題がある。また、従来の試験方法はコンクリートの水セメント比が高く、低水セメント比のコンクリートについては適切に評価できないと云う問題もある。 For high-fluidity concrete, concrete is used as a test piece for measuring the fluidity, and the fluidity of concrete is not judged by mortar. However, there is a problem that it takes time and effort to prepare concrete and perform a test. In addition, the conventional test method has a problem that the water-cement ratio of concrete is high and concrete with a low water-cement ratio cannot be evaluated appropriately.
本発明は、高強度高流動コンクリートについて、従来の試験方法における上記問題を解決したものであり、水セメント比15質量%以下の低水セメント比のコンクリートについても予め流動性を適切に予測することができ、しかも試験体としてコンクリートを調製することなく、モルタルを用いてコンクリートの流動性を予測できる製造方法を提供する。また、本発明は、モルタルを用いた流動性の予測に基づいて製造された高強度高流動性のコンクリートを提供する。 The present invention solves the above-mentioned problems in the conventional test method for high-strength and high-fluidity concrete, and appropriately predicts the fluidity in advance for concrete having a low-water cement ratio of 15% by mass or less. Provided is a manufacturing method capable of predicting the fluidity of concrete using mortar without preparing concrete as a test piece. The present invention also provides high-strength, high-fluidity concrete produced based on the prediction of fluidity using mortar.
本発明は、以下の構成を有する高強度高流動コンクリートとその製造方法に関する。
〔1〕高強度用セメントにJIS R 5201に規定された標準砂が配合され、砂セメント比(S/C)50〜70質量%、水セメント比(W/C)12〜15質量%、および高性能減水剤の添加量が上記セメントの1〜5質量%であるモルタルについて、JIS R 5201に規定された静置フローが260mm以上および該静置フローが250mmに到達する時間が30〜60秒の範囲になる高強度用セメントを用いて製造されたことを特徴とする高強度高流動コンクリート。
〔2〕コンクリートの水セメント比(W/C)12〜15質量%、単位水量150〜170kg/m3、単位セメント量1000〜1400kg/m3、および単位粗骨材かさ容積0.50〜0.60m3/m3である上記[1]に記載した高強度高流動コンクリート。
〔3〕スランプフロー55〜70cm、および標準養生での材齢91日の圧縮強度が130N/mm2以上である上記[1]または上記[2]に記載した高強度高流動コンクリート。
〔4〕高強度用セメントが、ポルトランドセメント100質量部に対して、シリカフュームが5〜20質量部配合されたものである上記[1]〜上記[3]の何れかに記載する高強度高流動コンクリート。
〔5〕ポルトランドセメントが、低熱ポルトランドセメントであり、そのクリンカー中のC3A量が3.9質量%以下であって、全アルカリ量(Na2O+0.656K2O)が0.4質量%以下である上記[1]〜上記[4]の何れかに記載する高強度高流動コンクリート。
〔6〕JIS R 5201に規定された標準砂とセメントの砂セメント比(S/C)が50〜70質量%、水セメント比(W/C)が12〜15質量%、および高性能減水剤の添加量が上記セメントの1〜5質量%であるモルタルについて、JIS R 5201に規定された静置フローが260mm以上および該静置フローが250mmに到達する時間が30〜60秒の範囲になる高強度用セメントを用い、コンクリートの配合比が、水セメント比(W/C)12〜15質量%、単位水量150〜170kg/m3、単位セメント量1000〜1400kg/m3、および単位粗骨材かさ容積0.50〜0.60m3/m3になるように上記高強度用セメント、細骨材、粗骨材、および高性能減水剤を配合することを特徴とする高強度高流動コンクリートの製造方法。
The present invention relates to high-strength, high-fluidity concrete having the following configurations and a method for producing the same.
[1] Standard sand specified in JIS R 5201 is blended with high-strength cement, sand cement ratio (S / C) 50 to 70% by mass, water cement ratio (W / C) 12 to 15% by mass, and For mortar in which the amount of high-performance water reducing agent added is 1 to 5% by mass of the above cement, the standing flow specified in JIS R 5201 is 260 mm or more and the time required for the standing flow to reach 250 mm is 30 to 60 seconds. High-strength, high-fluidity concrete characterized by being manufactured using high-strength cement that falls within the range of.
[2] Concrete water-cement ratio (W / C) 12 to 15% by mass, unit water amount 150 to 170 kg / m 3 , unit cement amount 1000 to 1400 kg / m 3 , and unit coarse aggregate bulk volume 0.50 to 0 The high-strength, high-fluidity concrete according to [1] above, which is .60 m 3 / m 3 .
[3] The high-strength, high-fluidity concrete according to the above [1] or the above [2], which has a slump flow of 55 to 70 cm and a compressive strength of 130 N / mm 2 or more at a material age of 91 days under standard curing.
[4] The high-strength, high-fluidity according to any one of the above [1] to [3], wherein the high-strength cement is a mixture of 5 to 20 parts by mass of silica fume with respect to 100 parts by mass of Portland cement. concrete.
[5] Portland cement is a low heat Portland cement, there is C 3 A content of the in clinker or less 3.9 wt%, the total amount of alkali (Na 2 O + 0.656K 2 O ) is 0.4 wt% The high-strength, high-fluidity concrete according to any one of the above [1] to [4] below.
[6] The sand-cement ratio (S / C) of standard sand and cement specified in JIS R 5201 is 50 to 70% by mass, the water-cement ratio (W / C) is 12 to 15% by mass, and a high-performance water reducing agent. For mortar in which the amount of the cement added is 1 to 5% by mass of the cement, the standing flow specified in JIS R 5201 is 260 mm or more, and the time for the standing flow to reach 250 mm is in the range of 30 to 60 seconds. Using high-strength cement, the concrete compounding ratio is 12 to 15% by mass of water cement ratio (W / C), unit water amount 150 to 170 kg / m 3 , unit cement amount 1000 to 1400 kg / m 3 , and unit coarse bone. High-strength, high-fluidity concrete characterized by blending the above-mentioned high-strength cement, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate, and high-performance water reducing agent so as to have a bulk volume of 0.50 to 0.60 m 3 / m 3. Manufacturing method.
〔具体的な説明〕
以下、本発明を具体的に説明する。
本発明の高強度高流動コンクリートは、高強度用セメントにJIS R 5201に規定された標準砂が配合され、砂セメント比(S/C) 50〜70質量%、水セメント比(W/C)12〜15質量%、および高性能減水剤の添加量が上記セメントの1〜5質量%であるモルタルについて、JIS R 5201に規定された静置フローが260mm以上および該静置フローが250mmに到達する時間が30〜60秒の範囲になる高強度用セメントを用いて製造されたことを特徴とする高強度高流動コンクリートである。
[Specific explanation]
Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described.
In the high-strength, high-fluidity concrete of the present invention, standard sand specified in JIS R 5201 is mixed with high-strength cement, sand-cement ratio (S / C) is 50 to 70% by mass, and water-cement ratio (W / C). For mortars in which 12 to 15% by mass and the amount of high-performance water reducing agent added is 1 to 5% by mass of the above cement, the static flow specified in JIS R 5201 reaches 260 mm or more and the static flow reaches 250 mm. It is a high-strength, high-fluidity concrete manufactured by using a high-strength cement having a time of 30 to 60 seconds.
<流動性の予測>
本発明において、高強度高流動コンクリートの流動性は、水セメント比(W/C)が同じ範囲のモルタルの流動性によって予測できることが見出された。本発明の高強度高流動コンクリートは、このモルタルの流動性の予測に基づいたものである。
<Forecast of liquidity>
In the present invention, it has been found that the fluidity of high-strength, high-fluidity concrete can be predicted by the fluidity of mortar having the same water-cement ratio (W / C). The high-strength, high-fluidity concrete of the present invention is based on the prediction of the fluidity of this mortar.
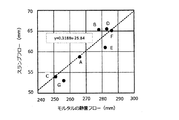
具体的には、高強度用セメントにJIS R 5201に規定された標準砂を配合したモルタルについて、砂セメント比(S/C) 50〜70質量%、水セメント比(W/C)12〜15質量%、および高性能減水剤の添加量が上記セメントの1〜5質量%の配合比で調製し、JIS R 5201に規定された静置フローを測定し、また、上記モルタルと同じセメントを用い、上記モルタルと同じ水セメント比(W/C)にし、その他の配合条件を調整したコンクリートを製造して、そのスランプフローを測定すると、図1に示す結果が得られる。 Specifically, for mortars in which standard sand specified in JIS R 5201 is mixed with high-strength cement, the sand cement ratio (S / C) is 50 to 70% by mass and the water cement ratio (W / C) is 12 to 15. Prepare by mass% and the amount of high-performance water reducing agent added in a blending ratio of 1 to 5% by mass of the above cement, measure the static flow specified in JIS R 5201, and use the same cement as the above mortar. , The water-cement ratio (W / C) is the same as that of the above mortar, and concrete is manufactured by adjusting other compounding conditions, and the slump flow is measured. The results shown in FIG. 1 are obtained.
図1に示すように、モルタルの静置フロー250mm〜290mmの範囲において、コンクリートのスランプフローとモルタルの静置フローは直線状に良く対応した関係を有しており、モルタルの静置フローによって、コンクリートの流動性が予測できることが分かる。 As shown in FIG. 1, in the range of the static flow of mortar from 250 mm to 290 mm, the slump flow of concrete and the static flow of mortar have a linear and well-corresponding relationship. It can be seen that the fluidity of concrete can be predicted.
上記モルタルの砂セメント比(S/C)は50〜70質量%に調整される。S/Cが70質量%を超えると、練り混ぜ量が多くなるので、モルタルミキサでの練混ぜが困難になる。一方、S/Cが50質量%を下回ると、結合材が多くなるため混和剤の添加率が高くなり適切な評価ができない。 The sand-cement ratio (S / C) of the mortar is adjusted to 50 to 70% by mass. If the S / C exceeds 70% by mass, the amount of kneading increases, which makes kneading with a mortar mixer difficult. On the other hand, when the S / C is less than 50% by mass, the amount of binder increases and the addition rate of the admixture increases, so that an appropriate evaluation cannot be performed.
上記モルタルないしコンクリートの水セメント比(W/C)は12〜15質量%である。水セメント比(W/C)が12質量%より小さいとモルタルおよびコンクリートの練り混ぜが困難になる。また、この水セメント比(W/C)が15質量%より高いと超低水セメント比とは云えなくなる。 The water-cement ratio (W / C) of the mortar or concrete is 12 to 15% by mass. If the water-cement ratio (W / C) is less than 12% by mass, it becomes difficult to mix mortar and concrete. Further, if this water-cement ratio (W / C) is higher than 15% by mass, it cannot be said to be an ultra-low water-cement ratio.
また、一般にJIS R 5201に規定された静置フローが250mmに到達する時間が60秒を超えるものは流動性が高いとは云えず、一方、上記静置フローが250mmに到達する時間が30秒より短いと、過剰な流動性のために材料分離が生じる虞があるので好ましくない。従って、静置フローが250mmに到達する時間が30〜60秒の範囲になるセメントが用いられる。 In general, if the static flow specified in JIS R 5201 reaches 250 mm for more than 60 seconds, it cannot be said that the fluidity is high, while the static flow reaches 250 mm for 30 seconds. If it is shorter, material separation may occur due to excessive fluidity, which is not preferable. Therefore, cement is used in which the time it takes for the static flow to reach 250 mm is in the range of 30 to 60 seconds.
<高強度高流動コンクリート>
本発明の高強度高流動コンクリートは、上記セメント、およびJIS R 5201に規定された標準砂を用い、コンクリートの水セメント比(W/C)は流動性の予測に用いたモルタルと同じ範囲の水セメント比(W/C)であって、その他の配合条件は、例えば、単位水量150〜170kg/m3、単位セメント量1000〜1400kg/m3、および単位粗骨材かさ容積0.50〜0.60m3/m3のコンクリートである。
<High-strength, high-fluidity concrete>
The high-strength, high-fluidity concrete of the present invention uses the above cement and standard sand specified in JIS R 5201, and the water-cement ratio (W / C) of the concrete is in the same range as the mortar used for predicting fluidity. The cement ratio (W / C) and other compounding conditions are, for example, a unit water amount of 150 to 170 kg / m 3 , a unit cement amount of 1000 to 1400 kg / m 3 , and a unit coarse aggregate bulk volume of 0.50 to 0. It is .60 m 3 / m 3 concrete.
単位水量150〜170kg/m3、および単位セメント量1000〜1400kg/m3の範囲を外れると、水セメント比(W/C)を12〜15質量%の範囲に保つのが難しくなる。また、単位粗骨材かさ容積が0.50m3/m3より小さいと、コンクリート中のモルタル分が過剰に多くなり、コンクリートの収縮(乾燥収縮、自己収縮)によるひび割れが発生しやすくなる。一方、単位粗骨材嵩容積が0.60m3/m3を上回ると、コンクリートの粘性が過剰に高くなり、施工性が低下する。 Unit water 150~170kg / m 3, and is outside the scope of the unit cement content 1000~1400kg / m 3, water-cement ratio (W / C) to keep a range of 12 to 15 mass% becomes difficult. Further, when the unit coarse aggregate bulk volume is smaller than 0.50 m 3 / m 3 , the mortar content in the concrete becomes excessively large, and cracks due to shrinkage of the concrete (dry shrinkage, self-shrinkage) are likely to occur. On the other hand, when the unit coarse aggregate bulk volume exceeds 0.60 m 3 / m 3 , the viscosity of the concrete becomes excessively high and the workability deteriorates.
本発明のコンクリートは、好ましくは、スランプフローが55〜70cm、および標準養生での材齢91日の圧縮強度が130N/mm2以上の高流動性コンクリートである。 The concrete of the present invention is preferably a highly fluid concrete having a slump flow of 55 to 70 cm and a compressive strength of 130 N / mm 2 or more at a material age of 91 days under standard curing.
本発明のコンクリートに用いる高強度用セメントは、好ましくは、ポルトランドセメント100質量部に対して、シリカフュームを5〜20質量部含むセメントである。セメント中のシリカフューム量が5質量部未満であり、または20質量部を超えると目的の高強度を発現するのは難しい。 The high-strength cement used for the concrete of the present invention is preferably a cement containing 5 to 20 parts by mass of silica fume with respect to 100 parts by mass of Portland cement. If the amount of silica fume in the cement is less than 5 parts by mass or exceeds 20 parts by mass, it is difficult to achieve the desired high strength.
上記高強度用セメントは、好ましくは、上記ポルトランドセメントが低熱ポルトランドセメントであり、そのクリンカー中のC3A量が3.9質量%以下であって、かつ全アルカリ量(Na2O+0.656K2O)が0.4%質量以下のセメントである。 The high strength cement is preferable that the Portland cement is a low heat Portland cement, C 3 A content of the in clinker is not more than 3.9 mass%, and the total amount of alkali (Na 2 O + 0.656K 2 O) is a cement having a mass of 0.4% or less.
低熱ポルトランドセメント以外のセメントは、流動性を阻害するC3A(アルミン酸三カルシウム、3CaO・Al2O3)を多く含み、流動性が低下するので好ましくない。例えば、普通ポルトランドセメントおよび早強ポルトランドセメントのC3Aは8〜12%、中庸熱ポルトランドセメントのC3Aは6〜8%であり、何れも低熱ポルトランドセメントよりも多い。 Cement other than the low heat Portland cement, C 3 A (tricalcium aluminate, 3CaO · Al 2 O 3) to inhibit the fluidity rich in, unfavorably flowability is decreased. For example, C 3 A is 8% to 12% of ordinary Portland cement and high-early-strength Portland cement, C 3 A of moderate heat Portland cement is 6% to 8%, both higher than the low heat Portland cement.
上記低熱ポルトランドセメントは、そのクリンカー中のC3A量が3.9質量%以下であって、かつ全アルカリ量(Na2O+0.656K2O)が0.4質量%以下であるものが好ましい。クリンカー中のC3A量が3.9質量%を超える場合、または全アルカリ量(Na2O+0.656K2O)が0.4質量%を超える場合の何れにおいても、所要の流動性を得るための高性能減水剤量が多量に必要となり、しかも高性能減水剤量を標準添加量の上限まで増加させても所要の流動性が得られないことがある。 The low heat Portland cement, a is the C 3 A content in the clinker is less 3.9 wt%, and those total alkali content (Na 2 O + 0.656K 2 O ) is less than 0.4% by mass .. If C 3 A content in the clinker is more than 3.9 mass%, or in any of the cases where the total amount of alkali (Na 2 O + 0.656K 2 O ) is more than 0.4 mass%, to obtain the required fluidity Therefore, a large amount of high-performance water reducing agent is required, and even if the amount of high-performance water reducing agent is increased to the upper limit of the standard addition amount, the required fluidity may not be obtained.
<製造方法>
本発明の高強度高流動コンクリートは、以下のようにして製造することができる。
まず、JIS R 5201に規定された標準砂とセメントの砂セメント比(S/C)が50〜70質量%、水セメント比(W/C)が12〜15質量%、および高性能減水剤の添加量が上記セメントの1〜5質量%であるモルタルを調製し、このモルタルについて、JIS R 5201に規定された静置フローを測定し、該静置フローが260mm以上および該静置フローが250mmに到達する時間が30〜60秒の範囲になる高強度用セメントを用いる。
<Manufacturing method>
The high-strength, high-fluidity concrete of the present invention can be produced as follows.
First, the sand-cement ratio (S / C) of standard sand and cement specified in JIS R 5201 is 50 to 70% by mass, the water-cement ratio (W / C) is 12 to 15% by mass, and high-performance water reducing agents. A mortar having an addition amount of 1 to 5% by mass of the above cement was prepared, and the static flow specified in JIS R 5201 was measured for this mortar, and the static flow was 260 mm or more and the static flow was 250 mm. Use high-strength cement that takes 30 to 60 seconds to reach.
上記セメントを用い、コンクリートの配合比が、水セメント比(W/C)12〜15質量%、単位水量150〜170kg/m3、単位セメント量1000〜1400kg/m3、および単位粗骨材かさ容積0.50〜0.60m3/m3になるように上記高強度用セメント、細骨材、粗骨材、および高性能減水剤を配合する。なお、水セメント比(W/C)は12〜15質量%の範囲で先に静置フローを測定したモルタルと同一の水セメント比(W/C)になるように配合される。 Using the above cement, the concrete compounding ratio is 12 to 15% by mass of water cement ratio (W / C), unit water amount 150 to 170 kg / m 3 , unit cement amount 1000 to 1400 kg / m 3 , and unit coarse aggregate bulk. The above-mentioned high-strength cement, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate, and high-performance water reducing agent are blended so as to have a volume of 0.50 to 0.60 m 3 / m 3 . The water-cement ratio (W / C) is in the range of 12 to 15% by mass so that the water-cement ratio (W / C) is the same as that of the mortar whose static flow was measured earlier.
上記配合後、通常のコンクリート製造に従って混錬、養生を経て本発明の高強度高流動コンクリートが得られる。 After the above blending, the high-strength, high-fluidity concrete of the present invention is obtained through kneading and curing according to ordinary concrete production.
本発明の高強度高流動コンクリートは、コンクリートの試験練りをすることなく、コンクリートの流動性(スランプフロー)を予測することができる。従って、簡便および迅速にコンクリートの流動性を把握することができるので、コンクリート調製の作業労力を各段に削減することができる。
また、本発明の製造方法によれば、流動性(スランプフロー)を予測することができる高強度高流動性のコンクリートを容易に製造することができる。
The high-strength, high-fluidity concrete of the present invention can predict the fluidity (slump flow) of concrete without test-kneading the concrete. Therefore, since the fluidity of concrete can be grasped easily and quickly, the work labor for preparing concrete can be reduced to each stage.
Further, according to the production method of the present invention, it is possible to easily produce high-strength and high-fluidity concrete whose fluidity (slump flow) can be predicted.
以下、本発明の実施例を示す。
〔実施例1〕
表1に示すセメント(A〜G)および、表2に示す標準砂と混和剤(高性能減水剤)を用い、砂セメント比(S/C)60質量%、水セメント比(W/C)13質量%、高性能減水剤の添加量が上記セメントの1〜5質量%のモルタルを調製し、JIS R 5201に規定された静置フローと、静置フローが250mmに到達する時間を測定した。また、表1に示すセメント(A〜G)について、表2の材料を用い、表3の配合比〔水セメント比(W/C)13質量%〕に従ってコンクリートを調製し、そのスランプフローおよび圧縮強度を測定した。この結果を表4および図1に示す。
Hereinafter, examples of the present invention will be shown.
[Example 1]
Using the cements (A to G) shown in Table 1 and the standard sand and admixture (high-performance water reducing agent) shown in Table 2, the sand cement ratio (S / C) is 60% by mass and the water cement ratio (W / C). A mortar having an amount of 13% by mass and a high-performance water reducing agent added of 1 to 5% by mass of the above cement was prepared, and the static flow specified in JIS R 5201 and the time required for the static flow to reach 250 mm were measured. .. For the cements (A to G) shown in Table 1, using the materials in Table 2, concrete was prepared according to the compounding ratio in Table 3 [water cement ratio (W / C) 13% by mass], and its slump flow and compression were performed. The intensity was measured. The results are shown in Table 4 and FIG.
図1のグラフに示すように、モルタルの静置フローとコンクリートのスランプフローは直線状の対応関係を有しており、モルタルの静置フローによってコンクリートの流動性(スランプフロー)を予測できることが分かる。具体的には、例えば、モルタルの静置フローが約270mmであるときには、モルタルと同一の水セメント比のコンクリートのスランプフローは約60cmになることが分かる。 As shown in the graph of FIG. 1, the static flow of mortar and the slump flow of concrete have a linear correspondence relationship, and it can be seen that the fluidity of concrete (slump flow) can be predicted by the static flow of mortar. .. Specifically, for example, when the static flow of mortar is about 270 mm, it can be seen that the slump flow of concrete having the same water-cement ratio as mortar is about 60 cm.
表4に示すように、セメントA、B、D、E、Fを用いた本発明の試料は、何れも、モルタルの静置フローは260mm以上であって、該静置フローが250mmに到達する時間は35〜52秒であり、コンクリートのスランプフローは58.8〜65.5cm、材齢91日圧縮強度は171N/mm2以上である。一方、C3A量が4.0質量%のセメントCと全アルカリ量が0.44質量%のセメントGは何れもモルタルの静置フローが260mmに達せず、またコンクリートのスランプフローも55cmに達しない。 As shown in Table 4, in each of the samples of the present invention using cements A, B, D, E, and F, the static flow of the mortar is 260 mm or more, and the static flow reaches 250 mm. The time is 35 to 52 seconds, the slump flow of concrete is 58.8 to 65.5 cm, and the material age is 91 days, and the compressive strength is 171 N / mm 2 or more. On the other hand, C 3 A content of 4.0% by weight of the cement C and standing flow total alkali amount is 0.44 mass% of cement G Any mortar not reach 260 mm, The slump flow of concrete to 55cm Not reached.
〔実施例2〕
表1に示すセメント(A〜G)を用い、表2に示す材料を用い、表5に示す配合比(水セメント比15質量%)に従って、モルタルとコンクリートを調製し、モルタルの静置フローおよび静置フローが250mmに達する時間、コンクリートのスランプフロー、圧縮強度を測定した。この結果を表6に示した。
セメントA、B、D、E、Fを用いた本発明の試料は、何れも、モルタルの静置フローは260mm以上であって、該静置フローが250mmに到達する時間は35〜52秒であり、コンクリートのスランプフローは59.6〜65.0cm、材齢91日圧縮強度は136.5N/mm2以上である。
一方、C3A量が4.0質量%のセメントCと全アルカリ量が0.44質量%のセメントGは何れもモルタルの静置フローが260mmに達せず、またセメントGのコンクリートのスランプフローは55cmに達せず、材齢91日の圧縮強度は130N/mm2に達しない。
[Example 2]
Using the cements (A to G) shown in Table 1, using the materials shown in Table 2, prepare mortar and concrete according to the compounding ratio shown in Table 5 (water cement ratio 15% by mass), and set the mortar stationary flow and The slump flow and compressive strength of concrete were measured for the time when the static flow reached 250 mm. The results are shown in Table 6.
In each of the samples of the present invention using cements A, B, D, E, and F, the static flow of the mortar was 260 mm or more, and the time for the static flow to reach 250 mm was 35 to 52 seconds. Yes, the slump flow of concrete is 59.6 to 65.0 cm, and the material age is 91 days, and the compressive strength is 136.5 N / mm 2 or more.
On the other hand, C 3 A content of 4.0% by weight of the cement C and standing flow total alkali amount is 0.44 mass% of cement G Any mortar not reach 260 mm, The concrete slump flow of cement G Does not reach 55 cm, and the compressive strength at 91 days of age does not reach 130 N / mm 2 .
Claims (6)
The sand-cement ratio (S / C) of standard sand and cement specified in JIS R 5201 is 50 to 70% by mass, the water-cement ratio (W / C) is 12 to 15% by mass, and the amount of high-performance water reducing agent added. For high-strength mortar, which is 1 to 5% by mass of the above cement, the static flow specified in JIS R 5201 is 260 mm or more and the time required for the static flow to reach 250 mm is in the range of 30 to 60 seconds. Using cement, the concrete compounding ratio is water-cement ratio (W / C) 12 to 15% by mass, unit water amount 150 to 170 kg / m 3 , unit cement amount 1000 to 1400 kg / m 3 , and unit coarse aggregate bulk volume. A method for producing high-strength, high-fluidity concrete, which comprises blending the above-mentioned high-strength cement, fine aggregate, coarse aggregate, and high-performance water reducing agent so as to be 0.50 to 0.60 m 3 / m 3. ..
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019063585A JP2020164342A (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2019-03-28 | Concrete of high strength and high fluidity, and method of producing the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019063585A JP2020164342A (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2019-03-28 | Concrete of high strength and high fluidity, and method of producing the same |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020164342A true JP2020164342A (en) | 2020-10-08 |
| JP2020164342A5 JP2020164342A5 (en) | 2021-11-04 |
Family
ID=72714838
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019063585A Pending JP2020164342A (en) | 2019-03-28 | 2019-03-28 | Concrete of high strength and high fluidity, and method of producing the same |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2020164342A (en) |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018168004A (en) * | 2017-03-29 | 2018-11-01 | 三菱マテリアル株式会社 | Silica fume-containing high fluidity cement composition and production method thereof |
-
2019
- 2019-03-28 JP JP2019063585A patent/JP2020164342A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018168004A (en) * | 2017-03-29 | 2018-11-01 | 三菱マテリアル株式会社 | Silica fume-containing high fluidity cement composition and production method thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Leung et al. | Sorptivity of self-compacting concrete containing fly ash and silica fume | |
| Nepomuceno et al. | Mechanical performance evaluation of concrete made with recycled ceramic coarse aggregates from industrial brick waste | |
| Mardani-Aghabaglou et al. | Effect of cement fineness on properties of cementitious materials containing high range water reducing admixture | |
| Abdur Rashid et al. | Effect of replacing natural coarse aggregate by brick aggregate on the properties of concrete | |
| JP5165873B2 (en) | Reinforcement joint filling method using filler for reinforcing steel joints | |
| RU2649996C1 (en) | Fine-grained concrete mixture | |
| JP6338855B2 (en) | Concrete composition having initial and long-term high strength development and high crack resistance and concrete body using the composition | |
| Kismi et al. | Minimizing water dosage of superplasticized mortars and concretes for a given consistency | |
| JPH10152359A (en) | High-fluidity cement composition | |
| JPH0680456A (en) | Fluid hydraulic composition | |
| JP2020164342A (en) | Concrete of high strength and high fluidity, and method of producing the same | |
| Bradu et al. | Modulus of elasticity of self compacting concrete with diferents levels of limestone powder | |
| JP2019065638A (en) | Concrete, tunnel lining body and concrete mixing design method | |
| JP6320878B2 (en) | Cement composition for low temperature environment | |
| JP2017165625A (en) | Grout composition | |
| Abed et al. | Characteristics of cement pastes incorporating different amounts of waste cellular concrete powder | |
| JP2007176742A (en) | Shearing strength-reinforced type lightweight concrete | |
| Abed et al. | Mechanical behavior of self-compacting concrete containing nano-metakaolin | |
| JP2020164342A5 (en) | ||
| Dubey et al. | An empirical approach to design optimized self-compacting concrete mixes | |
| Ravindrarajah et al. | Properties of high-strength high-performance concrete for marine environment | |
| JP7120866B2 (en) | cement composition | |
| JP7120865B2 (en) | cement composition | |
| JP2018168004A (en) | Silica fume-containing high fluidity cement composition and production method thereof | |
| Redondo-Soto et al. | Processing and hydration activation of limestone calcined clay belite rich cements. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210922 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20210930 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20220616 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20220628 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220802 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20220929 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20221122 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20230118 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20230516 |