JP2018196656A - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2018196656A JP2018196656A JP2017103192A JP2017103192A JP2018196656A JP 2018196656 A JP2018196656 A JP 2018196656A JP 2017103192 A JP2017103192 A JP 2017103192A JP 2017103192 A JP2017103192 A JP 2017103192A JP 2018196656 A JP2018196656 A JP 2018196656A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- effect
- control
- display
- state
- game
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、パチンコ遊技機等の遊技機に関し、特に、遊技を行なうことが可能な遊技機に関する。 The present invention relates to a gaming machine such as a pachinko gaming machine, and more particularly to a gaming machine capable of playing a game.
このような遊技機としては、遊技枠に設けられた軸に対して回動可能に設けられた可動体(役物)を備えたものがあった(特許文献1)。 As such a gaming machine, there is one that includes a movable body (a combination) provided so as to be rotatable with respect to an axis provided in a gaming frame (Patent Document 1).
しかし、前述した特許文献1の遊技機では、可動体の回転角度を調整することが考慮されていないため、可動体の取付け位置によっては遊技機に隣接する別の遊技機の遊技枠や上部に配置されるデータランプ等の他の物体と当接する恐れがあった。
However, in the gaming machine of
本発明は、かかる実情に鑑み考え出されたものであり、その目的は、遊技枠に設けられた軸に対して回動可能に設けられた可動体が他の物体と当接することを防止することが可能な遊技機を提供することである。 The present invention has been conceived in view of such circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to prevent a movable body provided to be rotatable with respect to an axis provided in a game frame from coming into contact with another object. It is to provide a gaming machine capable of doing so.
(1) 遊技を行なうことが可能な遊技機(パチンコ遊技機1等)であって、
遊技枠に設けられた軸(軸290等)に対して回転することで当該遊技枠から突出可能な可動体(第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29R等)と、
前記可動体の回転角度を調整することで前記可動体の動作を制御可能な制御手段(図12のS752に示すように、設定された角度に応じて、第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rの回転角度・回転速度を設定する等)とを備える。
(1) A gaming machine capable of playing a game (such as a pachinko gaming machine 1),
A movable body (a first
Control means capable of controlling the operation of the movable body by adjusting the rotation angle of the movable body (as shown in S752 in FIG. 12, the first
このような構成によれば、遊技枠に設けられた軸に対して回転する可動体を動作させつつ、可動体が他の物体と当接することを防ぐことができる。 According to such a configuration, it is possible to prevent the movable body from coming into contact with other objects while operating the movable body that rotates with respect to the shaft provided in the game frame.
(2) 前記(1)の遊技機であって、
前記可動体の動作に関連した演出(図14に示す上部役物演出等)を実行する演出手段(演出表示装置9等)をさらに備え、
前記演出手段は、前記制御手段により前記可動体が前記遊技枠に対して突出しない回転角度に制御されているときには、前記可動体の動作に関連した演出の実行を制限する(図16のS901に示すように、上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされているときは、上部役物演出の実行を制限する等)。
(2) The gaming machine of (1),
Production means (
The effect means restricts execution of effects related to the operation of the movable body when the control means is controlled at a rotation angle at which the movable body does not protrude from the game frame (S901 in FIG. 16). As shown, when the upper feature effect restriction flag is set, execution of the upper feature effect is restricted).
このような構成によれば、可動体が遊技枠に対して突出しない回転角度に制御されているにも関わらず可動体の動作に関連した演出を実行してしまい、遊技者に違和感を与えることを防止できる。 According to such a configuration, although the movable body is controlled to a rotation angle that does not protrude with respect to the game frame, an effect related to the operation of the movable body is executed, and the player feels uncomfortable. Can be prevented.
(3) 前記(1)または(2)の遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、前記可動体の回転角度を段階的に調整可能である(図2に示すように
、上部役物の回転角度を段階的に調整可能等)。
(3) The gaming machine of (1) or (2),
The control means can adjust the rotation angle of the movable body stepwise (as shown in FIG. 2, the rotation angle of the upper accessory can be adjusted stepwise).
このような構成によれば、無段階で調整することによる制御の複雑化を防止することができる。 According to such a configuration, it is possible to prevent complication of control due to stepless adjustment.
(4) 前記(1)から(3)のいずれかの遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、初期状態において、前記可動体を前記遊技枠に対して最も突出する回転角度よりも突出しない回転角度となるように制御する(初期状態においては、90度よりも突出しない角度に制御する等)。
(4) The gaming machine according to any one of (1) to (3),
In the initial state, the control means controls the movable body to have a rotation angle that does not protrude more than a rotation angle that protrudes most with respect to the game frame (in the initial state, the angle that does not protrude more than 90 degrees). Control etc.).
このような構成によれば、調整をしていない場合であっても可動体が他の物体と当接することを防ぐことができる。 According to such a configuration, it is possible to prevent the movable body from coming into contact with another object even when the adjustment is not performed.
(5) 前記(1)から(4)のいずれかの遊技機であって、
前記制御手段は、前記可動体の回転角度によって前記可動体の動作速度を異ならせるように制御する(上部役物の回転角度によって回転速度を異ならせる等)。
(5) The gaming machine according to any one of (1) to (4),
The control means performs control so that the operation speed of the movable body varies depending on the rotation angle of the movable body (for example, the rotation speed varies depending on the rotation angle of the upper accessory).
このような構成によれば、可動体が動作するときに実行される演出の演出時間を共通化することができる。 According to such a configuration, it is possible to share the effect time of the effect executed when the movable body operates.
(6) 前記(1)から(5)のいずれかの遊技機であって、
前記可動体は、発光手段(第1上部LED29A,第2上部LED29B)を含み、
前記発光手段は、前記可動体の回転角度がいずれの角度であっても同一の輝度で発光する(第1上部LED29A,第2上部LED29Bは、上部役物の回転角度によらず同一の輝度で発光する等)。
(6) The gaming machine according to any one of (1) to (5),
The movable body includes light emitting means (first
The light emitting means emits light with the same luminance regardless of the rotation angle of the movable body (the first
このような構成によれば、発光手段の制御の複雑化を防止することができる。 According to such a configuration, it is possible to prevent complication of control of the light emitting means.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を、図面を参照して説明する。なお、遊技機の一例としてパチンコ遊技機を示すが、本発明はパチンコ遊技機に限られず、コイン遊技機、スロットマシン等のその他の遊技機であってもよく、遊技を行なうことが可能な遊技機であれば、どのような遊技機であってもよい。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Note that a pachinko gaming machine is shown as an example of a gaming machine, but the present invention is not limited to a pachinko gaming machine, and may be another gaming machine such as a coin gaming machine or a slot machine. Any game machine may be used as long as it is a machine.
[第1実施形態]
以下、本発明の実施の形態を、図面を参照して説明する。まず、遊技機の一例であるパチンコ遊技機1の全体の構成について説明する。図1はパチンコ遊技機1を正面からみた正面図である。
[First Embodiment]
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. First, the overall configuration of a
パチンコ遊技機1は、遊技媒体としての遊技球を遊技領域7に打込んで遊技が行なわれる遊技機である。パチンコ遊技機1は、縦長の方形状に形成された外枠(図示せず)と、外枠の内側に開閉可能に取付けられた遊技枠とで構成される。また、パチンコ遊技機1は、遊技枠に開閉可能に設けられている額縁状に形成されたガラス扉枠2を有する。遊技枠は、外枠に対して開閉自在に設置される前面枠(図示せず)と、機構部品等が取付けられる機構板(図示せず)と、それらに取付けられる種々の部品(後述する遊技盤6を除く)とを含む構造体である。パチンコ遊技機1では、遊技媒体としての遊技球を遊技領域に打込んで遊技が行なわれる。
The
ガラス扉枠2の下部表面には打球供給皿(上皿)3がある。打球供給皿3の下部には、打球供給皿3に収容しきれない遊技球を貯留する余剰球受皿4、および、打球を発射する打球操作ハンドル(操作ノブ)5等が設けられている。また、ガラス扉枠2の背面には、遊技盤6が着脱可能に取付けられている。遊技盤6は、それを構成する板状体と、その板状体に取付けられた種々の部品とを含む構造体である。また、遊技盤6の前面には、打込まれた遊技球が流下可能な遊技領域7が形成されている。
On the lower surface of the
余剰球受皿(下皿)4を形成する部材には、たとえば下皿本体の上面における手前側の所定位置(たとえば下皿の中央部分)等に、スティック形状(棒形状)に構成され、遊技者が把持して複数方向(前後左右)に傾倒する操作が可能なスティックコントローラ122が取付けられている。なお、スティックコントローラ122には、遊技者がスティックコントローラ122の操作桿を操作手(たとえば左手等)で把持した状態において、所定の操作指(たとえば人差し指等)で押引操作すること等により所定の指示操作が可能なトリガボタン125(図4参照)が設けられ、スティックコントローラ122の操作桿の内部には、トリガボタン125に対する押引操作等による所定の指示操作を検知するトリガセンサ121(図4参照)が内蔵されている。また、スティックコントローラ122の下部における下皿の本体内部等には、操作桿に対する傾倒操作を検知する傾倒方向センサユニット123(図4参照)が設けられている。また、スティックコントローラ122には、スティックコントローラ122を振動動作させるためのバイブレータ用モータ126(図4参照)が内蔵されている。
The member that forms the extra ball tray (lower tray) 4 is configured in a stick shape (bar shape), for example, at a predetermined position on the front side of the upper surface of the lower tray body (for example, the central portion of the lower tray). A
打球供給皿(上皿)3を形成する部材には、たとえば上皿本体の上面における手前側の所定位置(たとえばスティックコントローラ122の上方)等に、遊技者が押下操作等により所定の指示操作を可能なプッシュボタン120が設けられている。プッシュボタン120は、遊技者からの押下操作等による所定の指示操作を、機械的、電気的、あるいは、電磁的に、検出できるように構成されていればよい。プッシュボタン120の設置位置における上皿の本体内部等には、プッシュボタン120に対してなされた遊技者の操作行為を検知するプッシュセンサ124(図4参照)が設けられていればよい。図1に示す構成例では、プッシュボタン120とスティックコントローラ122の取付位置が、上皿及び
下皿の中央部分において上下の位置関係にある。これに対して、上下の位置関係を保ったまま、プッシュボタン120及びスティックコントローラ122の取付位置を、上皿及び下皿において左右のいずれかに寄せた位置としてもよい。あるいは、プッシュボタン120とスティックコントローラ122との取付位置が上下の位置関係にはなく、たとえば左右の位置関係にあるものとしてもよい。なお、操作手段としては、レバースイッチ、および、ジョグダイヤル等のその他の操作手段を設けてもよい。
A member that forms the hitting ball supply tray (upper plate) 3 is operated by a player to perform a predetermined instruction operation by a pressing operation or the like at a predetermined position on the upper surface of the upper plate body (for example, above the stick controller 122). A
遊技領域7の中央付近には、各々を識別可能な複数種類の識別情報としての演出図柄を変動表示(可変表示ともいう)可能な表示手段としての演出表示装置9が設けられている。遊技領域7における演出表示装置9の右側方には、各々を識別可能な複数種類の識別情報としての第1特別図柄を変動表示する第1特別図柄表示器(第1変動表示部)8aと、各々を識別可能な複数種類の識別情報としての第2特別図柄を変動表示する第2特別図柄表示器(第2変動表示部)8bとが設けられている。
In the vicinity of the center of the
第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bのそれぞれは、数字および文字を変動表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(たとえば7セグメントLED)で構成されている。演出表示装置9は、液晶表示装置(LCD)で構成されており、表示画面において、第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の変動表示に同期した演出図柄の変動表示を行なう演出図柄表示領域が設けられる。演出図柄表示領域には、たとえば左,中,右の3つの装飾用(演出用)の演出図柄を変動表示する図柄表示エリアが形成される。
Each of the first special
以下、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄とを特別図柄と総称することがあり、第1特別図柄表示器8aと第2特別図柄表示器8bとを特別図柄表示器(変動表示部)と総称することがある。
Hereinafter, the first special symbol and the second special symbol may be collectively referred to as a special symbol, and the first
なお、この実施の形態では、2つの特別図柄表示器8a,8bを備える場合を示しているが、遊技機は、特別図柄表示器を1つのみ備えるものであってもよい。
Although this embodiment shows a case where two
第1特別図柄表示器8aおよび第2特別図柄表示器8bのそれぞれは、主基板(遊技制御基板)に搭載されている遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。演出表示装置9は、演出制御基板に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータによって制御される。第1特別図柄表示器8aで第1特別図柄の変動表示が実行されているときに、その変動表示に伴なって演出表示装置9で演出表示が実行され、第2特別図柄表示器8bで第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行されているときに、その変動表示に伴なって演出表示装置9で演出表示が実行されるので、遊技の進行状況を把握しやすくすることができる。
Each of the first
より具体的には、第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄の変動表示は、変動表示の実行条件である第1始動条件または第2始動条件が成立(たとえば、遊技球が第1始動入賞口13または第2始動入賞口14を通過(入賞を含む)したこと)した後、変動表示の開始条件(たとえば、保留記憶数が0でない場合であって、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示が実行されていない状態であり、かつ、大当り遊技が実行されていない状態)が成立したことに基づいて開始され、変動表示時間(変動時間)が経過すると表示結果(停止図柄)を導出表示する。なお、遊技球が通過するとは、入賞口やゲート等の予め入賞領域として定められている領域を遊技球が通過したことであり、入賞口に遊技球が入った(入賞した)ことを含む概念である。また、表示結果を導出表示するとは、図柄(識別情報の例)を最終的に停止表示させることである。 More specifically, in the variation display of the first special symbol or the second special symbol, the first start condition or the second start condition which is the execution condition of the variation display is satisfied (for example, the game ball is in the first start winning opening 13). Or, after passing through the second start winning opening 14 (including winning), the start condition of the change display (for example, when the number of reserved memories is not 0 and the first special symbol and the second special symbol are changed) The display is not executed, and the big hit game is not executed) is started, and when the variable display time (variable time) elapses, the display result (stop symbol) is derived and displayed. To do. Note that the passing of a game ball means that the game ball has passed through a predetermined area such as a prize opening or a gate, and that includes a game ball entering (winning) a prize opening. It is. Deriving and displaying the display result is to finally stop and display a symbol (an example of identification information).
第1特別図柄表示器8aに特定表示結果としての大当り表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたとき、または、第2特別図柄表示器8bに特定表示結果としての大当り表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときには、演出表示装置9においても、特定表示結果
としての大当り表示結果(大当り図柄の組合せ)が導出表示される。このように変動表示の表示結果として特定表示結果が表示されたときには、遊技者にとって有利な価値(有利価値)が付与される有利状態としての特定遊技状態(大当り遊技状態)に制御される。
When the jackpot display result (bonus symbol) as the specific display result is derived and displayed on the first
また、演出表示装置9において、最終停止図柄(たとえば左右中図柄のうち中図柄)となる図柄以外の図柄が、所定時間継続して、大当り図柄(たとえば左中右の図柄が同じ図柄で揃った図柄の組合せ)と一致している状態で停止、揺動、拡大縮小もしくは変形している状態、または、複数の図柄が同一図柄で同期して変動表示したり、表示図柄の位置が入れ替わっていたりして、最終結果が表示される前で大当り発生の可能性が継続している状態(以下、これら状態をリーチ状態という。)で行なわれる演出をリーチ演出という。
Further, in the
ここで、リーチ状態は、演出表示装置9の表示領域において停止表示された演出図柄が大当り組合せの一部を構成しているときに未だ停止表示されていない演出図柄の変動表示が継続している表示状態、または、全部もしくは一部の演出図柄が大当り組合せの全部または一部を構成しながら同期して変動表示している表示状態である。言い換えると、リーチとは、複数の変動表示領域において識別情報が特定表示結果を構成しているが少なくとも一部の変動表示領域が変動表示中である状態をいう。この実施形態において、リーチ状態は、たとえば、左,右の図柄表示エリアで同じ図柄が停止し、中の図柄表示エリアで図柄が停止していない状態で形成される。リーチ状態が形成されるときの左,右の図柄表示エリアで停止された図柄は、リーチ形成図柄、または、リーチ図柄と呼ばれる。
Here, in the reach state, when the effect symbols that are stopped and displayed in the display area of the
そして、リーチ状態における表示演出が、リーチ演出表示(リーチ演出)である。また、リーチの際に、通常と異なる演出がランプや音で行なわれることがある。この演出をリーチ演出という。また、リーチの際に、キャラクタ(人物等を模した演出表示であり、図柄(演出図柄等)とは異なるもの)を表示させたり、演出表示装置9の背景画像の表示態様(たとえば、色等)を変化させたりすることがある。このキャラクタの表示や背景の表示態様の変化をリーチ演出表示という。また、リーチの中には、それが出現すると、通常のリーチに比べて、大当りが発生しやすいように設定されたものがある。このような特別のリーチをスーパーリーチという。
The display effect in the reach state is reach effect display (reach effect). In addition, during the reach, an unusual performance may be performed with a lamp or sound. This production is called reach production. Further, in the case of reach, a character (an effect display imitating a person or the like, which is different from a design (effect design etc.)) or a display mode (for example, a color etc.) of the background image of the
演出表示装置9の下方には、第1始動入賞口13を有する入賞装置が設けられている。第1始動入賞口13に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、第1始動口スイッチ13aによって検出される。
A winning device having a first
また、第1始動入賞口(第1始動口)13を有する入賞装置の下方には、遊技球が入賞可能な第2始動入賞口14を有する可変入賞球装置15が設けられている。第2始動入賞口(第2始動口)14に入賞した遊技球は、遊技盤6の背面に導かれ、第2始動口スイッチ14aによって検出される。可変入賞球装置15は、ソレノイド16によって開状態とされる。可変入賞球装置15が開状態になることによって、遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入賞可能になり(始動入賞し易くなり)、遊技者にとって有利な状態になる。可変入賞球装置15が開状態になっている状態では、第1始動入賞口13よりも、第2始動入賞口14に遊技球が入賞しやすい。また、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態では、遊技球は第2始動入賞口14に入賞しない。したがって、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態では、第2始動入賞口14よりも、第1始動入賞口13に遊技球が入賞しやすい。なお、可変入賞球装置15が閉状態になっている状態において、入賞はしづらいものの、入賞することは可能である(すなわち、遊技球が入賞しにくい)ように構成されていてもよい。以下、第1始動入賞口13と第2始動入賞口14とを総称して始動入賞口または始動口ということがある。
A variable winning
第2特別図柄表示器8bの上方には、第2始動入賞口14に入った有効入賞球数すなわ
ち第2保留記憶数を表示する4つの表示器からなる第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bが設けられている。第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bは、有効始動入賞がある毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1増やす。そして、第2特別図柄表示器8bでの変動表示が開始される毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1減らす。
Above the second
また、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bのさらに上方には、第1始動入賞口13に入った有効入賞球数すなわち第1保留記憶数(保留記憶を、始動記憶または始動入賞記憶ともいう。)を表示する4つの表示器からなる第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18aが設けられている。第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18aは、有効始動入賞がある毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1増やす。そして、第1特別図柄表示器8aでの変動表示が開始される毎に、点灯する表示器の数を1減らす。
Further, above the second special symbol
遊技機には、遊技者が打球操作ハンドル5を操作することに応じて駆動モータを駆動し、駆動モータの回転力を利用して遊技球を遊技領域7に発射する打球発射装置(図示せず)が設けられている。打球発射装置から発射された遊技球は、遊技領域7を囲むように円形状に形成された打球レールを通って遊技領域7に入り、その後、遊技領域7を下りてくる。遊技球が第1始動入賞口13に入り第1始動口スイッチ13aで検出されると、第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態であれば(たとえば、特別図柄の変動表示が終了し、第1の開始条件が成立したこと)、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおいて第1特別図柄の変動表示(変動)が開始されるとともに、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示が開始される。すなわち、第1特別図柄および演出図柄の変動表示は、第1始動入賞口13への入賞に対応する。第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態でなければ、第1保留記憶数が上限値に達していないことを条件として、第1保留記憶数を1増やす。
In the gaming machine, a ball striking device (not shown) that drives a driving motor in response to a player operating the batting operation handle 5 and uses the rotational force of the driving motor to launch a gaming ball to the gaming area 7. ) Is provided. A game ball launched from the ball striking device enters the
遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入り第2始動口スイッチ14aで検出されると、第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態であれば(たとえば、特別図柄の変動表示が終了し、第2の開始条件が成立したこと)、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて第2特別図柄の変動表示(変動)が開始されるとともに、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示が開始される。すなわち、第2特別図柄および演出図柄の変動表示は、第2始動入賞口14への入賞に対応する。第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始できる状態でなければ、第2保留記憶数が上限値に達していないことを条件として、第2保留記憶数を1増やす。
When the game ball enters the second
演出表示装置9は、第1特別図柄表示器8aによる第1特別図柄の変動表示時間中、および第2特別図柄表示器8bによる第2特別図柄の変動表示時間中に、装飾用(演出用)の図柄としての演出図柄の変動表示を行なう。第1特別図柄表示器8aにおける第1特別図柄の変動表示と、演出表示装置9における演出図柄の変動表示とは同期している。また、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける第2特別図柄の変動表示と、演出表示装置9における演出図柄の変動表示とは同期している。また、第1特別図柄表示器8aにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときと、第2特別図柄表示器8bにおいて大当り図柄が停止表示されるときには、演出表示装置9において大当りを想起させるような演出図柄の組合せが停止表示される。
The
また、演出表示装置9の表示画面における下部の位置には、第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数との合計数(合算保留記憶数)を表示する保留記憶表示部(合算保留記憶表示部、保留表示エリア、図示せず)が設けられる。合算保留記憶表示部では、保留記憶表示として保留記憶数をたとえば所定画像の表示個数により特定可能な保留記憶画像(保留記憶情報のそれぞれに対応して1つずつ保留記憶画像を表示することにより、保留記憶数を特定する。)が表示される。このように、合計数を表示する合算保留記憶表示部が設けられていることによって、変動表示の開始条件が成立していない実行条件の成立数の合計を把握しやすくすることができる。第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18a、第2特別図柄保留記憶
表示器18b、および、演出表示装置9のそれぞれにおいて、保留記憶数を示すための発光表示および画像表示は、保留表示、または、保留記憶表示と呼ばれる。
In addition, at the lower position on the display screen of the
また、図1に示すように、可変入賞球装置15の下方には、特別可変入賞球装置20が設けられている。特別可変入賞球装置20は開閉板を備え、第1特別図柄表示器8aに特定表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときと、第2特別図柄表示器8bに特定表示結果(大当り図柄)が導出表示されたときに生起する特定遊技状態(大当り遊技状態)においてソレノイド21によって開閉板が開放状態に制御されることによって、入賞領域となる大入賞口が開放状態になる。大入賞口に入賞した遊技球はカウントスイッチ23で検出される。
Further, as shown in FIG. 1, a special variable winning
大当り遊技状態においては、特別可変入賞球装置20が開放状態と閉鎖状態とを繰返す繰返し継続制御が行なわれる。繰返し継続制御において、特別可変入賞球装置20が開放されている状態が、ラウンドと呼ばれる。これにより、繰返し継続制御は、ラウンド制御とも呼ばれる。本実施の形態では、大当りの種別が複数設けられており、大当りとすることが決定されたときには、いずれかの大当り種別が選択される。
In the big hit gaming state, repeated continuous control is performed in which the special variable winning
演出表示装置9の左方には、各々を識別可能な普通図柄を変動表示する普通図柄表示器10が設けられている。この実施の形態では、普通図柄表示器10は、0〜9の数字を変動表示可能な簡易で小型の表示器(たとえば7セグメントLED)で実現されている。すなわち、普通図柄表示器10は、0〜9の数字(または、記号)を変動表示するように構成されている。また、小型の表示器は、たとえば方形状に形成されている。
On the left side of the
遊技球がゲート32を通過しゲートスイッチ32aで検出されると、普通図柄表示器10の表示の変動表示が開始される。そして、普通図柄表示器10における停止図柄が所定の図柄(当り図柄。たとえば、図柄「7」。)である場合に、可変入賞球装置15が所定回数、所定時間だけ遊技者にとって不利な閉状態から遊技者にとって有利な開状態に変化する。普通図柄表示器10の近傍には、ゲート32を通過した入賞球数を表示する4つのLEDによる表示部を有する普通図柄保留記憶表示器41が設けられている。ゲート32への遊技球の通過がある毎に、すなわちゲートスイッチ32aによって遊技球が検出される毎に、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41は点灯するLEDを1増やす。そして、普通図柄表示器10の変動表示が開始される毎に、点灯するLEDを1減らす。
When the game ball passes through the
また、演出表示装置9の上方には、役物12が設けられている。役物12は、遊技盤6と演出表示装置9との間に位置し、役物モータ17によって位置を変位することが可能である。役物12は、通常は遊技者から視認し難い場所に位置し、所定の演出が実行されるときに遊技者から視認可能な位置(たとえば、演出表示装置9の前方の位置)に移動する。
Further, an
遊技盤6の下部には、入賞しなかった打球が取込まれるアウト口26がある。また、遊技領域7の外側の左右上部および左右下部には、所定の音声出力として効果音や音声を発声する4つのスピーカ27が設けられている。遊技領域7の外周には、前面枠に設けられた枠LED28が設けられている。
At the lower part of the
また、遊技枠の上部には、遊技枠に設けられた軸290(図2参照)に対して回転することで当該遊技枠から突出可能な可動体としての第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rが設けられている。遊技者から向かって左側の第1上部役物29Lは、第1上部役物モータ30L(図4参照)によって回転動作することが可能であり、遊技者から向かって右側の第2上部役物29Rは、第2上部役物モータ30R(図4参照)によって回転動作することが可能である。以下では、第1上部役物29Lと第2上部役物29Rとを上部役物
と総称することがある。
Also, at the upper part of the game frame, a first
第1上部役物29Lと第2上部役物29Rとは、回転角度を段階的に調整可能である。また、第1上部役物29Lの内部には第1上部LED29Aが設けられており、第1上部役物29Lの回転角度によらず同一の輝度で発光する。また、第2上部役物29Rの内部には第2上部LED29Bが設けられており、第2上部役物29Rの回転角度によらず同一の輝度で発光する。このように、発光手段としての第1上部LED29A,第2上部LED29Bは、上部役物の回転角度によらず同一の輝度で発光するので、発光手段の制御の複雑化を防止することができる。
The rotation angle of the first
また、プリペイドカードが挿入されることによって球貸しを可能にするプリペイドカードユニット(以下、単に「カードユニット」ともいう。)が、パチンコ遊技機1に隣接して設置される(図示せず)。 In addition, a prepaid card unit (hereinafter also simply referred to as “card unit”) that enables lending a ball by inserting a prepaid card is installed adjacent to the pachinko gaming machine 1 (not shown).
図2は上部役物の動作を説明するための図である。図2においては、遊技者から向かって右側面におけるパチンコ遊技機1の様子を示している。第1上部役物29Lと第2上部役物29Rとは、遊技枠に設けられた軸290に対して回転角度を段階的に調整可能である。たとえば、図2(a)〜(d)に示すように、上部役物の回転角度は、0度、45度、60度、90度の4段階に調整可能である。上部役物の動作は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100によって制御される。たとえば、回転角度が45度に設定されている場合には、後述する上部役物演出の実行時に、0度から45度に向けて上部役物が動作し、上部役物演出が終了すると上部役物が最初の0度の位置に戻る。また、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bは、上部役物の回転角度によらず同一の輝度で発光するように、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100によって制御される。
FIG. 2 is a diagram for explaining the operation of the upper accessory. FIG. 2 shows the state of the
図2(a)は、遊技枠に対して上部役物が全く突出しない回転角度である0度に設定されているときの様子を示している。図2(a)では、上部役物の回転角度が0度に設定されているため、上部役物が動作することはなく、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bからの光が遊技者へ届くこともない。なお、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bからの光が遊技枠の隙間から漏れるような演出を実行してもよい。また、上部役物の回転角度がある0度の場合には、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bが発光しないように制御してもよい。
FIG. 2A shows a state when the upper angle is set to 0 degree, which is a rotation angle at which the upper accessory does not protrude at all with respect to the game frame. In FIG. 2A, since the rotation angle of the upper character is set to 0 degree, the upper character does not operate, and the light from the first
図2(b)は、遊技枠に対して上部役物が45度に設定されているときの様子を示している。このとき、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bからの光が遊技者に届くが、輝度が同じであっても発光面が少ないので遊技者に届く光は、60度や90度の場合と比べて少ない。図2(c)は、遊技枠に対して上部役物が60度に設定されているときの様子を示している。このとき、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bから遊技者に届く光は、45度の場合と比べて多い。
FIG. 2B shows a state in which the upper accessory is set to 45 degrees with respect to the game frame. At this time, the light from the first
図2(d)は、上部役物が遊技枠に対して最も突出する回転角度である90度に設定されているときの様子を示している。このとき、発光面が最も大きくなるので、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bからは最も多くの光が届く。
FIG. 2 (d) shows a state when the upper accessory is set to 90 degrees, which is the rotation angle at which it projects most with respect to the game frame. At this time, since the light emitting surface becomes the largest, most light reaches from the first
図2に示すように、上部役物の回転角度を段階的に調整可能であるので、上部役物の回転角度を無段階で調整することによる制御の複雑化を防止することができる。 As shown in FIG. 2, since the rotation angle of the upper accessory can be adjusted stepwise, it is possible to prevent the control from becoming complicated by adjusting the rotation angle of the upper accessory steplessly.
ここで、図2(b)〜(d)において、上部役物の回転角度によって上部役物の動作速度は異なるように制御される。具体的には、上部役物の回転動作は、45度<60度<90度の順に回転速度が速くなる。このように、上部役物の回転角度によって回転速度を異
ならせることにより上部役物が動作されるときに実行される演出の演出時間を共通化することができる。
Here, in FIGS. 2B to 2D, the operation speed of the upper accessory is controlled to be different depending on the rotation angle of the upper accessory. Specifically, the rotational speed of the upper action increases in the order of 45 degrees <60 degrees <90 degrees. In this way, by changing the rotation speed depending on the rotation angle of the upper character, it is possible to share the effect time of the effect executed when the upper character is operated.
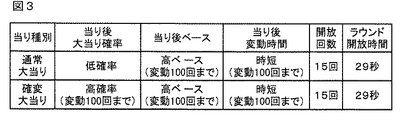
図3は当り種別表である。図3の当り種別表においては、大当りにおける当りの種別ごとに、大当り遊技状態の終了後の大当り確率、大当り遊技状態の終了後のベース、大当り遊技状態終了後の変動時間、大当りにおける開放回数(ラウンド数)、および、各ラウンドの開放時間が示されている。 FIG. 3 is a hit type table. In the hit type table of FIG. 3, for each hit type in the big hit, the big hit probability after the end of the big hit gaming state, the base after the end of the big hit gaming state, the variation time after the end of the big hit gaming state, the number of releases in the big hit ( The number of rounds) and the opening time of each round are shown.
具体的に、大当り遊技状態においては、特別可変入賞球装置20が、開放状態とされた後、所定の開放状態の終了条件(開放状態において所定期間(たとえば29秒間)が経過したこと、または、所定個数(たとえば10個)の入賞球が発生したという開放終了条件)が成立したことに応じて閉鎖状態とされる。そして、開放終了条件が成立すると、継続権が発生し、特別可変入賞球装置20の開放が再度行なわれる。継続権の発生は、大当り遊技状態における開放回数が予め定められた上限値となる15ラウンド(最終ラウンド)に達するまで繰返される。
Specifically, in the big hit gaming state, after the special variable winning
「大当り」のうち、大当り遊技状態に制御された後、特別遊技状態として、通常状態(確変状態でない通常の遊技状態)に比べて大当りとすることに決定される確率が高い状態である確変状態(確率変動状態の略語であり、高確率状態ともいう)に移行する大当りの種類(種別)は、「確変大当り」と呼ばれる。また、本実施の形態では、特別遊技状態としては、確変状態に付随して、特別図柄や演出図柄の変動時間(変動表示期間)が非時短状態よりも短縮される時短状態に制御される場合がある。なお、特別遊技状態としては、確変状態とは独立して時短状態に制御される場合があるようにしてもよい。 Among the “big hits”, after being controlled to the big hit gaming state, the probability change state in which the probability of being determined as a big hit is higher than the normal state (the normal gaming state that is not the probability change state) as the special gaming state. The type (type) of jackpot that shifts to (an abbreviation for probability variation state, also referred to as high probability state) is called “probability jackpot”. In the present embodiment, the special gaming state is controlled to a time-short state in which the variation time (variation display period) of the special symbol or the production symbol is shortened from the non-time-short state in association with the probability variation state. There is. Note that the special gaming state may be controlled to the short time state independently of the probability variation state.
このように、時短状態に移行することによって、特別図柄や演出図柄の変動時間が短縮されるので、時短状態となったときには、有効な始動入賞が発生しやすくなり大当り遊技が行なわれる可能性が高まる。なお、「大当り」のうち、15ラウンドの大当り遊技状態に制御された後、確変状態に移行しない大当りの種類(種別)は、「通常大当り」と呼ばれる。 In this way, the transition time to the short-time state reduces the variation time of the special symbol and the production symbol. Therefore, when the short-time state is reached, it is easy for an effective start winning to occur, and a big hit game may be performed. Rise. Note that the type of jackpot (type) that does not shift to the probability change state after being controlled to the 15-round jackpot gaming state among the “hits” is called “ordinary jackpot”.
また、特別遊技状態としては、確変状態または時短状態に付随して、可変入賞球装置15が開状態になる頻度を高くすることにより可変入賞球装置15に遊技球が進入する頻度を高くして可変入賞球装置15への入賞を容易化(高進入化、高頻度化)する電チューサポート制御状態に制御される場合がある。電チューサポート制御状態は、後述するように高ベース状態であるので、以下の説明においては、主として高ベース状態と呼ぶ。
Further, as the special game state, the frequency of the game ball entering the variable
ここで、電チューサポート制御について説明する。電チューサポート制御としては、普通図柄の変動時間(変動表示開始時から表示結果の導出表示時までの時間)を短縮して早期に表示結果を導出表示させる制御(普通図柄短縮制御)、普通図柄の停止図柄が当り図柄になる確率を高める制御(普通図柄確変制御)、可変入賞球装置15の開放時間を長くする制御(開放時間延長制御)、および、可変入賞球装置15の開放回数を増加させる制御(開放回数増加制御)が行なわれる。このような制御が行なわれると、当該制御が行なわれていないときと比べて、可変入賞球装置15が開状態となっている時間比率が高くなるので、第2始動入賞口14への入賞頻度が高まり、遊技球が始動入賞しやすくなる(特別図柄表示器8a,8bや演出表示装置9における変動表示の実行条件が成立しやすくなる)。この制御によって第2始動入賞口14への入賞頻度が高まることにより、第2始動条件の成立頻度および/または第2特別図柄の変動表示の実行頻度が高まる遊技状態となる。
Here, electric Chu support control will be described. As electric support control, normal symbol variation time (time from the start of variation display to display result derivation display time) is shortened and the display result is derived and displayed at an early stage (normal symbol shortening control), normal symbol The control to increase the probability that the stop symbol will be a winning symbol (ordinary symbol probability changing control), the control to increase the opening time of the variable winning ball device 15 (opening time extension control), and the number of opening of the variable winning
電チューサポート制御により第2始動入賞口14への入賞頻度が高められた状態(高頻
度状態)は、発射球数に対して入賞に応じて賞球として払出される遊技球数の割合である「ベース」が、当該制御が行なわれないときと比べて、高い状態であるので、「高ベース状態」と呼ばれる。また、このような制御が行なわれないときは、「低ベース状態」と呼ばれる。また、このような制御は、可変入賞球装置15、すなわち、電動チューリップにより入賞をサポートすることにより可変入賞球装置15への入賞を容易化する制御であり、「電チューサポート制御」と呼ばれる。
The state (high frequency state) in which the winning frequency at the second
この実施の形態においては、大当り確率の状態を示す用語として、「高確率状態(確変状態)」と、「低確率状態(非確変状態)」とを用い、ベースの状態の組合せを示す用語として、「高ベース状態(電チューサポート制御状態)」と、「低ベース状態(非電チューサポート制御状態)」とを用いる。 In this embodiment, “high probability state (probability variation state)” and “low probability state (non-probability variation state)” are used as terms indicating the state of jackpot probability, and terms indicating a combination of base states are used. , “High base state (electric Chu support control state)” and “low base state (non-electric Chu support control state)” are used.
また、この実施の形態においては、大当り確率の状態およびベースの状態の組合せを示す用語として、「低確低ベース状態」、「低確高ベース状態」、および、「高確高ベース状態」を用いる。「低確低ベース状態」とは、大当り確率の状態が低確率状態で、かつ、ベースの状態が低ベース状態であることを示す状態である。「低確高ベース状態」とは、大当り確率の状態が低確率状態で、かつ、ベースの状態が高ベース状態であることを示す状態である。「高確高ベース状態」とは、大当り確率の状態が高確率状態で、かつ、ベースの状態が高ベース状態であることを示す状態である。 Further, in this embodiment, as a term indicating a combination of the state of the big hit probability and the base state, “low accuracy low base state”, “low accuracy high base state”, and “high accuracy high base state” are used. Use. The “low probability low base state” is a state indicating that the state of the big hit probability is the low probability state and the base state is the low base state. The “low probability high base state” is a state indicating that the state of the big hit probability is the low probability state and the base state is the high base state. The “high probability high base state” is a state indicating that the state of the big hit probability is the high probability state and the base state is the high base state.
図3に示すように、15ラウンドの大当りとしては、通常大当りと確変大当りとの複数種類の大当りが設けられている。通常大当りは、15ラウンドの大当り遊技状態の終了後に、非確変状態、時短状態、および、高ベース状態(低確高ベース状態)に制御される大当りである。通常大当りにおいては、非確変状態が次回の大当りが発生するまでの期間継続し、時短状態、および、高ベース状態が、変動表示が100回という所定回数実行されるまでという条件と、次回の大当りが発生するまでという条件とのいずれか早い方の条件が成立するまでの期間継続する。なお、通常大当りは、非確変状態、非時短状態、および、非電チューサポート制御状態(低確低ベース状態)に制御される大当りとなるように制御するものであってもよい。 As shown in FIG. 3, as the big hit of 15 rounds, a plurality of types of big hits, a normal big hit and a probability variable big hit, are provided. The normal jackpot is a jackpot that is controlled to the non-probability changing state, the short time state, and the high base state (low probability high base state) after the end of the 15 rounds of the big hit gaming state. Normally, in the big hit, the non-probable change state continues for the period until the next big hit occurs, the condition that the short-time state and the high base state are executed a predetermined number of times, such as 100 fluctuation displays, and the next big hit It continues for a period until the earlier condition, which is the condition until the occurrence of, occurs. The normal big hit may be controlled so as to become a big hit controlled in a non-probability changing state, a non-time-short state, and a non-electricity chew support control state (low probability low base state).
確変大当りは、15ラウンドの大当り遊技状態の終了後に、確変状態、時短状態、および、高ベース状態(高確高ベース状態)に移行する制御が行なわれる大当りである。確変大当りにおいては、このような高確高ベース状態が、変動表示が100回という所定回数実行されるまでという条件と、次回の大当りが発生するまでという条件とのいずれか早い方の条件が成立するまでの期間継続する。 The probability variation jackpot is a jackpot in which control is performed to shift to the probability variation state, the time-short state, and the high base state (high probability high base state) after the end of the 15 rounds of the jackpot gaming state. In the probabilistic big hit, such a high-precise base state is satisfied, whichever is earlier, a condition that the fluctuation display is executed a predetermined number of times of 100 times or a condition that the next big hit occurs. It continues for a period until.
図4は、主基板(遊技制御基板)および演出制御基板における回路構成の一例を示すブロック図である。なお、図4には、払出制御基板37等も示されている。主基板31には、プログラムにしたがってパチンコ遊技機1を制御する遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ(遊技制御手段に相当)560が搭載されている。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ゲーム制御(遊技進行制御)用のプログラム等を記憶するROM54、ワークメモリとして使用される記憶手段としてのRAM55、プログラムにしたがって制御動作を行なうCPU56およびI/Oポート部57を含む。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、ROM54およびRAM55が内蔵された1チップマイクロコンピュータである。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560には、さらに、ハードウェア乱数(ハードウェア回路が発生する乱数)を発生する乱数回路503が内蔵されている。
FIG. 4 is a block diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the main board (game control board) and the effect control board. In FIG. 4, the
また、RAM55は、その一部または全部が電源基板(図示省略)において作成されるバックアップ電源によってバックアップされている不揮発性記憶手段としてのバックアップRAMである。すなわち、遊技機に対する電力供給が停止しても、所定期間(バックア
ップ電源としてのコンデンサが放電してバックアップ電源が電力供給不能になるまで)は、RAM55の一部または全部の内容は保存される。特に、少なくとも、遊技状態すなわち遊技制御手段の制御状態に応じたデータ(特別図柄プロセスフラグ等)と未払出賞球数を示すデータは、バックアップRAMに保存される。
The
なお、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560においてCPU56がROM54に格納されているプログラムにしたがって制御を実行するので、以下、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560(またはCPU56)が実行する(または、処理を行なう)ということは、具体的には、CPU56がプログラムにしたがって制御を実行することである。このことは、主基板31以外の他の基板に搭載されているマイクロコンピュータについても同様である。
In the
乱数回路503は、特別図柄の変動表示の表示結果により大当りとするか否か判定するための判定用の乱数を発生するために用いられるハードウェア回路である。乱数回路503は、初期値(たとえば、0)と上限値(たとえば、65535)とが設定された数値範囲内で、数値データを、設定された更新規則にしたがって更新し、ランダムなタイミングで発生する始動入賞時が数値データの読出(抽出)時であることに基づいて、読出される数値データが乱数値となる乱数発生機能を有する。また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、乱数回路503が更新する数値データの初期値を設定する機能を有している。
The
また、ゲートスイッチ32a、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14a、カウントスイッチ23からの検出信号を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560に与える入力ドライバ回路58も主基板31に搭載されている。また、可変入賞球装置15を開閉するソレノイド16、および大入賞口を形成する特別可変入賞球装置20を開閉するソレノイド21を遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560からの指令にしたがって駆動する出力回路59も主基板31に搭載されている。
Further, an
また、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、特別図柄を変動表示する第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8b、普通図柄を変動表示する普通図柄表示器10、第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18a、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18bおよび普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行なう。
Further, the
演出制御基板80は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100、ROM102、RAM103、VDP109、および、I/Oポート部105等を搭載している。ROM102は、表示制御等の演出制御用のプログラムおよびデータ等を記憶する。RAM103は、ワークメモリとして使用される。ROM102およびRAM103は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に内蔵されてもよい。VDP109は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100と共動して演出表示装置9の表示制御を行なう。
The
演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100は、主基板31から演出制御基板80の方向への一方向にのみ信号を通過させる中継基板77を介して、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から演出内容を指示する演出制御コマンドを受信し、演出表示装置9の変動表示制御を行なう他、ランプドライバ基板35を介して、枠側に設けられている枠LED28の表示制御を行なうとともに、音声出力基板70を介してスピーカ27からの音出力の制御を行なう等、各種の演出制御を行なう。なお、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100において演出制御用CPU101がROM102に格納されているプログラムにしたがって制御を実行するので、以下、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(または演出制御用CPU101)が実行する(または、処理を行なう)ということは、具体的には、演出制御用CPU101がプログラムにしたがって制御を実行することである。このことは、
演出制御基板80以外の他の基板に搭載されているマイクロコンピュータについても同様である。
The
The same applies to microcomputers mounted on boards other than the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、スティックコントローラ122のトリガボタン125に対する遊技者の操作行為を検出したことを示す情報信号としての操作検出信号を、トリガセンサ121から、I/Oポート部105の入力ポートを介して入力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、プッシュボタン120に対する遊技者の操作行為を検出したことを示す情報信号としての操作検出信号を、プッシュセンサ124から、I/Oポート部105の入力ポートを介して入力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、スティックコントローラ122の操作桿に対する遊技者の操作行為を検出したことを示す情報信号としての操作検出信号を、傾倒方向センサユニット123から、I/Oポート部105の入力ポートを介して入力する。また、演出制御用CPU101は、I/Oポート部105の出力ポートを介してバイブレータ用モータ126に駆動信号を出力することにより、スティックコントローラ122を振動動作させる。また、演出制御用CPU101は、モータ駆動回路(図示省略)を介して役物モータ17を駆動して役物12を動作させる。
Further, the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、モータ駆動回路(図示省略)を介して、第1上部役物モータ30Lを駆動して第1上部役物29Lを動作させる。また、演出制御用CPU101は、モータ駆動回路(図示省略)を介して、第2上部役物モータ30Rを駆動して第2上部役物29Rを動作させる。また、演出制御用CPU101は、ランプドライバ基板35を介して遊技枠の上部に設けられた第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bの表示制御を行なう。
Further, the
図5は、各乱数を示す説明図である。図5においては、乱数の種別、更新範囲、用途、および、加算条件が示されている。各乱数は、以下のように使用される。 FIG. 5 is an explanatory diagram showing each random number. FIG. 5 shows a random number type, an update range, a usage, and an addition condition. Each random number is used as follows.
(1)ランダムR:大当りにするか否かを判定する当り判定用のランダムカウンタである。ランダムRは、10MHzで1ずつ更新され、0から加算更新されてその上限である65535まで加算更新された後再度0から加算更新される。(2)ランダム1(MR1):大当りの種類(種別、通常大当り、および、確変大当りのいずれかの種別)および大当り図柄を決定する(大当り種別判定用、大当り図柄決定用)。(3)ランダム2(MR2):変動パターンの種類(種別)を決定する(変動パターン種別判定用)。(4)ランダム3(MR3):変動パターン(変動時間)を決定する(変動パターン判定用)。(5)ランダム4(MR4):普通図柄に基づく当りを発生させるか否か決定する(普通図柄当り判定用)。(6)ランダム5(MR5):ランダム4の初期値を決定する(ランダム4初期値決定用)。 (1) Random R: A random counter for hit determination for determining whether or not to make a big hit. Random R is updated one by one at 10 MHz, is added and updated from 0, and is added and updated to its upper limit of 65535, and then is added and updated again from 0. (2) Random 1 (MR1): Determines the type of jackpot (any type of type, normal jackpot or probability variation jackpot) and jackpot symbol (for jackpot type determination, jackpot symbol determination). (3) Random 2 (MR2): The type (type) of the variation pattern is determined (for variation pattern type determination). (4) Random 3 (MR3): A variation pattern (variation time) is determined (for variation pattern determination). (5) Random 4 (MR4): Determines whether or not to generate a hit based on the normal symbol (for normal symbol hit determination). (6) Random 5 (MR5): An initial value of random 4 is determined (for determining a random 4 initial value).
この実施の形態では、特定遊技状態である大当りとして、通常大当り、および、確変大当りという複数の種別が含まれている。したがって、大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値に基づいて、大当りとする決定がされたときには、大当り種別判定用乱数(ランダム1)の値に基づいて、大当りの種別が、これらいずれかの大当り種別に決定される。さらに、大当りの種別が決定されるときに、同時に大当り種別判定用乱数(ランダム1)の値に基づいて、大当り図柄も決定される。したがって、ランダム1は、大当り図柄決定用乱数でもある。 In this embodiment, the big hit that is the specific gaming state includes a plurality of types, that is, a normal big hit and a probable big hit. Therefore, when the big hit is determined based on the value of the big hit determination random number (random R), the big hit type is determined based on the value of the big hit type determination random number (random 1). Determined by type. Furthermore, when the type of jackpot is determined, the jackpot symbol is also determined based on the value of the jackpot type determination random number (random 1) at the same time. Therefore, random 1 is also a jackpot symbol determining random number.
また、変動パターンは、まず、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)を用いて変動パターン種別を決定し、変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)を用いて、決定した変動パターン種別に含まれるいずれかの変動パターンに決定する。そのように、この実施の形態では、2段階の抽選処理によって変動パターンが決定される。変動パターン種別とは、複数の変動パターンをその変動態様の特徴にしたがってグループ化したものである。変
動パターン種別には、1または複数の変動パターンが属している。変動パターン種別は、変動種別と呼ばれる場合もある。
In addition, the variation pattern is first determined using the variation pattern type determination random number (random 2), and is included in the determined variation pattern type using the variation pattern determination random number (random 3). To determine the variation pattern. Thus, in this embodiment, the variation pattern is determined by a two-stage lottery process. The variation pattern type is a group of a plurality of variation patterns according to the characteristics of the variation mode. One or more variation patterns belong to the variation pattern type. The variation pattern type may be referred to as a variation type.
この実施の形態では、変動パターンが、リーチを伴なわない変動パターン種別である通常変動パターン種別と、リーチを伴なう変動パターン種別であるリーチ変動パターン種別とに種別分けされている。 In this embodiment, the variation patterns are classified into a normal variation pattern type that is a variation pattern type that does not involve reach and a reach variation pattern type that is a variation pattern type that involves reach.
このような変動パターン種別は、表示結果がはずれとなる場合に、時短状態であるときと、時短状態でないときとで、変動パターン種別の選択割合が異なるように設定されていることにより、時短状態であるときには、時短状態でないときと比べて、変動時間が短縮される。たとえば、時短状態では、時短状態でないときと比べて、変動時間の平均時間を短くするために、所定の変動パターンの変動時間が時短でないときよりも短く設定されたり、変動パターン種別のうち最も変動時間が短い変動パターン種別が選択される割合が高くなり、リーチ種別が選択されるときでも変動パターン種別のうち最も変動時間が短いノーマルリーチの変動パターンが選択される割合が高くなるように設定されたりすることで、時短状態でないときと比べて、変動時間の平均時間が短くなる。 When the display result is out of order, such a variation pattern type is set so that the selection ratio of the variation pattern type is different depending on whether it is in the short-time state or not in the short-time state. When this is the case, the variation time is shortened compared to when the time is not short. For example, in the short-time state, in order to shorten the average time of the fluctuation time compared to when the time-short state is not, the fluctuation time of a predetermined fluctuation pattern is set shorter than when the time is not short, or the fluctuation pattern type is the most variable. The variation pattern type with the shortest time is selected more frequently, and even when the reach type is selected, the normal reach variation pattern with the shortest variation time is selected among the variation pattern types. By doing so, the average time of the fluctuation time is shorter than when not in the time-short state.
なお、このような変動パターン種別は、変動表示をする各特別図柄の保留記憶数が所定数以上であるときと、所定数未満であるときとで選択割合が異なるように設定されることにより、変動表示をする各特別図柄の保留記憶数が所定数以上であるときには、各特別図柄の保留記憶数が所定数未満であるときと比べて、変動表示時間が短縮される保留数短縮制御を実行するようにしてもよい。たとえば、保留数短縮制御状態では、保留数短縮制御状態でないときと比べて、通常変動パターン種別のような変動表示時間が短い変動パターン種別が選択される割合が高くなるように設定されることで、保留数短縮制御状態でないときと比べて、変動表示時間の平均時間が短くなるようにしてもよい。また、保留数短縮制御では、保留数短縮制御状態でないときと比べて、同じ変動パターン種別が選択される場合でも、その変動パターン種別の変動表示時間自体を短くしてもよい。 In addition, such a variation pattern type is set so that the selection ratio is different when the number of reserved memories of each special symbol that displays variation is greater than or equal to a predetermined number and when it is less than the predetermined number, When the number of reserved symbols for each special symbol for variable display is greater than or equal to a predetermined number, the number of reserved symbols for each special symbol is less than the predetermined number. You may make it do. For example, in the hold number shortening control state, the ratio of selecting a variation pattern type having a short variation display time, such as a normal variation pattern type, is set to be higher than in a case where the hold number shortening control state is not set. The average time of the variable display time may be shorter than that in the non-holding number shortening control state. In the hold number reduction control, the change display time itself of the change pattern type may be shortened even when the same change pattern type is selected as compared to the case where the hold number reduction control state is not set.
また、変動パターンは、変動パターン種別を決定してから変動パターンを決定する2段階の決定方法ではなく、1回の乱数抽選により変動パターンが決定される1段階の決定方法としてもよい。 The variation pattern may be a one-step determination method in which the variation pattern is determined by one random number lottery, instead of the two-step determination method of determining the variation pattern after determining the variation pattern type.
図6は、大当り判定テーブルおよび大当り種別判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図6(A)は、大当り判定テーブルを示す説明図である。大当り判定テーブルとは、ROM54に記憶されているデータの集まりであって、ランダムRと比較される大当り判定値が設定されているテーブルである。大当り判定テーブルには、通常状態(確変状態でない遊技状態、すなわち非確変状態)において用いられる通常時(非確変時)大当り判定テーブルと、確変状態において用いられる確変時大当り判定テーブルとがある。
FIG. 6 is an explanatory diagram showing a jackpot determination table and a jackpot type determination table. FIG. 6A is an explanatory diagram showing a jackpot determination table. The jackpot determination table is a collection of data stored in the
通常時大当り判定テーブルには、図6(A)の左欄に記載されている各数値が大当り判定値として設定され、確変時大当り判定テーブルには、図6(A)の右欄に記載されている各数値が大当り判定値として設定されている。確変時大当り判定テーブルに設定された大当り判定値は、通常時大当り判定テーブルに設定された大当り判定値と共通の大当り判定値(通常時大当り判定値または第1大当り判定値という)に、確変時固有の大当り判定値が加えられたことにより、確変時大当り判定テーブルよりも多い個数(10倍の個数)の大当り判定値(確変時大当り判定値または第2大当り判定値という)が設定されている。これにより、確変状態には、通常状態よりも高い確率で大当りとする判定がなされる。 Each numerical value described in the left column of FIG. 6 (A) is set as a big hit determination value in the normal jackpot determination table, and is described in the right column of FIG. 6 (A) in the probability change big hit determination table. Each value is set as a big hit judgment value. The jackpot judgment value set in the jackpot judgment table at the time of probability change is the jackpot judgment value common to the jackpot judgment value set in the normal jackpot judgment table (referred to as the normal jackpot judgment value or the first jackpot judgment value). Due to the addition of the unique jackpot judgment value, a larger number (10 times the number of jackpot judgment values) than the probability change jackpot judgment table (referred to as the jackpot judgment value or the second jackpot judgment value at the time of probability change) is set. . As a result, the probability variation state is determined to be a big hit with a higher probability than the normal state.
CPU56は、所定の時期に、乱数回路503のカウント値を抽出して抽出値を大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)の値と比較するのであるが、大当り判定用乱数値が図6(A)
に示すいずれかの大当り判定値に一致すると、特別図柄に関して大当り(通常大当り、または、確変大当り)にすることに決定する。なお、図6(A)に示す「確率」は、大当りになる確率(割合)を示す。
The
If it matches any of the jackpot determination values shown in (1), it is determined that the special symbol will be a jackpot (normal jackpot or probability variation jackpot). Note that “probability” shown in FIG. 6A indicates the probability (ratio) of a big hit.
図6(B),(C)は、ROM54に記憶されている大当り種別判定テーブルを示す説明図である。図6(B)は、遊技球が第1始動入賞口13に入賞したことに基づく保留記憶(第1保留記憶ともいう)を用いて大当り種別を決定する場合(第1特別図柄の変動表示が行なわれるとき)に用いる第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブル(第1特別図柄用)である。図6(C)は、遊技球が第2始動入賞口14に入賞したことに基づく保留記憶(第2保留記憶ともいう)を用いて大当り種別を決定する場合(第2特別図柄の変動表示が行なわれるとき)に用いる第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルである。
FIGS. 6B and 6C are explanatory diagrams showing a jackpot type determination table stored in the
図6(B)、および、図6(C)の第1,第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルのそれぞれは、変動表示結果を大当り図柄にする旨の判定がなされたときに、大当り種別判定用の乱数(ランダム1)に基づいて、大当りの種別を「通常大当り」と「確変大当り」とのうちのいずれかに決定するとともに、大当り図柄を決定するために参照される。 Each of the first and second special symbol jackpot type determination tables in FIG. 6B and FIG. 6C is used for determining the jackpot type when it is determined that the variable display result is a jackpot symbol. Based on the random number (random 1), the type of jackpot is determined to be either “normal jackpot” or “probable variation jackpot”, and is also referred to for determining the jackpot symbol.
図6(B)の第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルには、ランダム1の値と比較される数値であって、「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」のそれぞれに対応した判定値(大当り種別判定値)が設定されている。図6(C)の第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルには、ランダム1の値と比較される数値であって、「通常大当り」、「確変大当り」のそれぞれに対応した判定値(大当り種別判定値)が設定されている。 In the first special symbol jackpot type determination table of FIG. 6B, there are numerical values to be compared with random 1 values, which are judgment values corresponding to each of “normal jackpot” and “probability variation jackpot” (jackpot type judgment). Value) is set. The second special symbol jackpot type determination table of FIG. 6C is a numerical value to be compared with a random 1 value, and corresponding to each of “normal jackpot” and “probability big hit” (hit type determination) Value) is set.
また、図6(B),(C)に示すように、大当り種別判定値は、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の大当り図柄を決定する判定値(大当り図柄判定値)としても用いられる。「通常大当り」に対応した判定値は、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の大当り図柄の「3」に対応した判定値としても設定されている。「確変大当り」に対応した判定値は、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の大当り図柄の「7」に対応した判定値としても設定されている。 Further, as shown in FIGS. 6B and 6C, the big hit type determination value is also used as a determination value (big hit symbol determination value) for determining the big hit symbol of the first special symbol and the second special symbol. The determination value corresponding to “normal jackpot” is also set as the determination value corresponding to “3” of the jackpot symbol of the first special symbol and the second special symbol. The determination value corresponding to “probable big hit” is also set as the determination value corresponding to “7” of the big hit symbol of the first special symbol and the second special symbol.
大当り種別判定テーブルを用いて、CPU56は、大当り種別として、ランダム1の値が一致した大当り種別判定値に対応する種別を決定するともに、大当り図柄として、ランダム1の値が一致した大当り図柄を決定する。これにより、大当り種別と、大当り種別に対応する大当り図柄とが同時に決定される。
Using the jackpot type determination table, the
図6(B)の第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルと図6(C)の第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルとは、確変大当りに決定される割合が同じである。このような場合には、第1特別図柄と第2特別図柄とで大当り種別判定テーブルを分けなくてもよい。また、大当り種別として、大当り遊技状態での最大ラウンド数が異なる複数種類の大当りのうちから大当り種別を選択するときには、図6(C)の第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルの方が、図6(B)の第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルよりも、ラウンド数が多い大当り種別が選択される割合が高くなるように設定してもよい。このようにすれば、高ベース状態において、大当りの種別選択が遊技者にとって有利となり、遊技の興趣を向上させることができる。また、図6(C)の第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルの方が、図6(B)の第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルよりも、確変大当りに決定される割合を高くしてもよい。そうすることにより、第2特別図柄の変動表示の方が、第1特別図柄の変動表示よりも、確変大当りとなる割合を高くすることができる。また、第1特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルの方が、第2特別図柄大当り種別判定テーブルよりも、確変大当りに決定される割合が高くなるようにしてもよい。 The first special symbol jackpot type determination table in FIG. 6B and the second special symbol jackpot type determination table in FIG. 6C have the same ratio determined for probability variation jackpots. In such a case, the big hit type determination table may not be divided between the first special symbol and the second special symbol. When the big hit type is selected from a plurality of types of big hits having different maximum round numbers in the big hit gaming state as the big hit type, the second special symbol big hit type determination table of FIG. You may set so that the ratio by which the big hit type with many round numbers is selected becomes higher than the 1st special symbol big hit type determination table of (B). In this way, in the high base state, the big hit type selection is advantageous for the player, and the interest of the game can be improved. In addition, the second special symbol jackpot type determination table in FIG. 6C may have a higher ratio determined for the probability variation jackpot than the first special symbol jackpot type determination table in FIG. 6B. . By doing so, the variation display of the second special symbol can be more likely to be a big hit than the variation display of the first special symbol. In addition, the first special symbol jackpot type determination table may be set to have a higher ratio determined for the probability variation jackpot than the second special symbol jackpot type determination table.
次に、図7を用いて、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560において、特別図柄および演出図柄の変動パターンを選択決定するために用いる変動パターンテーブルについて説明する。図7は、変動パターンを決定するために用いる変動パターンテーブルを表形式で示す図である。
Next, a variation pattern table used to select and determine the variation pattern of the special symbol and the effect symbol in the
図7には、(a)に通常状態はずれ時判定テーブル、(b)に時短状態はずれ時判定テーブルが示されている。また、(c)に通常大当り時判定テーブル、(d)に確変大当り時判定テーブルが示されている。図7(a)〜(d)の各判定テーブルは、ROM54に記憶されており、遊技状態に応じて選択され、変動パターン種別および変動パターンを判定(決定)するために用いられる。
In FIG. 7, (a) shows a determination table for when the normal state is shifted, and (b) shows a determination table for when the short state is shifted. Further, (c) shows a normal big hit determination table, and (d) shows a probability variation big hit determination table. Each determination table in FIGS. 7A to 7D is stored in the
図7に示す判定テーブルは、ランダム2と変動パターン種別との関係を示す変動パターン種別判定テーブルと、各変動パターン種別についてランダム3と各種別に属する変動パターンとの関係を示す変動パターン判定テーブルとを含む。 The determination table shown in FIG. 7 includes a variation pattern type determination table that indicates the relationship between the random 2 and the variation pattern type, and a variation pattern determination table that indicates the relationship between the random 3 and the variation patterns belonging to various types for each variation pattern type. Including.
図7の各テーブルでの「変動パターン種別」または「変動パターン」の欄において、「通常」または「通常変動」は、リーチとならない通常変動パターンを示す。 In the column of “variation pattern type” or “variation pattern” in each table of FIG. 7, “normal” or “normal variation” indicates a normal variation pattern that does not reach.
また、図7の各テーブルでの「ノーマルリーチ」は、リーチ状態となったときに特に派手な演出を実行しないノーマルリーチの変動パターンを示している。「スーパーリーチ」は、リーチ状態となったときに特別な演出画像を表示するリーチ演出を行なう変動パターンを示している。 Further, “normal reach” in each table of FIG. 7 indicates a fluctuation pattern of normal reach that does not perform a particularly flashy effect when the reach state is reached. “Super Reach” indicates a variation pattern for performing a reach effect in which a special effect image is displayed when the reach state is reached.
また、前述したように、「スーパーリーチ」は、「ノーマルリーチ」と比べて大当りとなるときに選択される割合が高く、大当りとなる信頼度が高い変動パターンである。さらに、「スーパーリーチ」は、「ノーマルリーチ」と比べて変動時間が長い(たとえば、ノーマルリーチ10秒、スーパーリーチ50秒〜80秒)変動パターンである。なお、スーパーリーチには、4種類の変動パターンが設定されており、第1スーパーリーチ<第2スーパーリーチ<第3スーパーリーチ<第4スーパーリーチとなるような関係で大当り期待度(大当りとなる可能性)が高いことを示す。
Further, as described above, “super reach” is a variation pattern in which the ratio selected when a big hit is higher than that of “normal reach” is high, and the reliability of the big hit is high. Furthermore, “super reach” is a variation pattern in which the variation time is longer than that of “normal reach” (for example,
なお、“期待度”とは、大当りに対する期待度、確変に対する期待度等を含む概念である。具体的には、大当りに対する期待度(信頼度ともいう)とは、各リーチ変動パターンが選択された場合に大当りとなる期待度(大当りとなる割合)であり、たとえば、リーチ変動が100回行なわれた場合に60回大当りとなるのであれば、大当りに対する期待度が60%(大当りが出現する出現率(確率)が60%)となる。また、確変に対する期待度とは、確変状態に移行する期待度(確変となる割合)のことをいう。 The “expectation” is a concept including an expectation for jackpot, an expectation for probability change, and the like. Specifically, the degree of expectation (also referred to as reliability) for the big hit is an expectation degree (a ratio to be a big hit) when each reach fluctuation pattern is selected. For example, reach fluctuation is performed 100 times. If the number of hits is 60 times, the degree of expectation for the big hit is 60% (the appearance rate (probability) that the big hit appears is 60%). In addition, the degree of expectation for probability variation refers to the degree of expectation (proportion of probability variation) for shifting to the probability variation state.
なお、はずれ時判定テーブルに示される変動パターンは、変動表示の最終的な表示結果が「はずれ」の表示結果となる変動パターンである。通常大当り時判定テーブルに示される変動パターンは、変動表示の最終的な表示結果が「通常大当り」の表示結果となる変動パターンである。確変大当り時判定テーブルに示される変動パターンは、変動表示の最終的な表示結果が「確変大当り」の表示結果となる変動パターンである。 Note that the variation pattern shown in the loss determination table is a variation pattern in which the final display result of the variation display is a display result of “out”. The variation pattern shown in the normal jackpot determination table is a variation pattern in which the final display result of the variation display is a display result of “normal jackpot”. The variation pattern shown in the probability variation jackpot determination table is a variation pattern in which the final display result of the variation display is the display result of “probability variation jackpot”.
これらの情報に基づいて、たとえば、図7(a)の「変動パターン」の欄に示された「第4スーパーリーチ (80秒)」という変動パターンは、「はずれ表示結果となる変動時間が80秒で実行される第4スーパーリーチの変動パターン」であることが示される。 Based on this information, for example, the variation pattern “fourth super reach (80 seconds)” shown in the “variation pattern” column of FIG. It is shown that the variation pattern of the fourth super reach executed in seconds.
図7のテーブルで「ランダム2範囲」および「変動パターン種別」という記載がされた欄は、「ランダム2範囲」と「変動パターン種別」との関係を示す変動パターン種別判定
テーブル部としての機能を示す欄である。たとえば、図7(a)を例にとれば、「通常」、「ノーマルリーチ」、「スーパーリーチ」というような複数の変動パターン種別のそれぞれに、ランダム2(1〜251)のすべての値が複数の数値範囲に分けて割振られている。たとえば、図7(a)を例にとれば、所定のタイミングで抽出したランダム2の値が1〜251の乱数値のうち、140〜229に割振られた判定値のいずれかの数値と合致すると、変動パターン種別として「ノーマルリーチ」とすることが決定される。
In the table of “
また、図7のテーブルで「ランダム3範囲」および「変動パターン」という記載がされた欄は、「ランダム3範囲」と「変動パターン」との関係を示す変動パターン判定テーブル部としての機能を示す欄である。変動パターン種別判定テーブルの各種別に対応して示されている変動パターンが、各種別に属する変動パターンである。たとえば、図7(a)を例にとれば、「スーパーリーチ」の種別に属する変動パターンは、「第1スーパーリーチ」、「第2スーパーリーチ」、「第3スーパーリーチ」、および、「第4スーパーリーチ」である。
In the table of FIG. 7, “
各変動パターン種別に対応する複数の変動パターンのそれぞれに、ランダム3(1〜220)のすべての値が、複数の数値範囲に分けて割振られている。たとえば、図7(a)を例にとれば、「スーパーリーチ」の変動パターン種別とすることが決定されたときに、所定のタイミングで抽出したランダム3が1〜220の乱数値のうち、1〜70に割振られた判定値のいずれかの数値と合致すると、「第1スーパーリーチ(50秒)」の変動パターンとすることが決定される。 All values of random 3 (1-220) are assigned to a plurality of numerical ranges in each of a plurality of variation patterns corresponding to each variation pattern type. For example, taking FIG. 7A as an example, when it is determined that the variation pattern type of “super reach” is selected, random 3 extracted at a predetermined timing is 1 to 220 of random values of 1 to 220. If it matches any numerical value of the determination values assigned to ˜70, it is determined that the variation pattern of “first super reach (50 seconds)” is set.
第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄について変動表示結果がはずれとなるときには、変動パターンを決定するために、次のように判定テーブルを選択する。非時短状態において、変動表示結果がはずれとなるときには、図7(a)の通常状態はずれ時判定テーブルを選択する。一方、時短状態において、変動表示結果がはずれとなるときには、図7(b)の時短状態はずれ時判定テーブルを選択する。なお、図7(a),図7(b)の判定テーブルを用いることで、保留数に関わらず、通常状態はずれ時、時短状態はずれ時でのリーチ割合を一定にしている。 When the variation display result for the first special symbol or the second special symbol is off, the determination table is selected as follows to determine the variation pattern. In the non-short-time state, when the fluctuation display result is out of place, the normal state out-of-state determination table in FIG. 7A is selected. On the other hand, when the variable display result is out of time in the time reduction state, the time reduction state determination table in FIG. 7B is selected. It should be noted that by using the determination tables of FIGS. 7A and 7B, the reach ratio is constant when the normal state is deviated and when the short time state is deviated regardless of the number of holds.
時短状態か否かにかかわらず第1特別図柄または第2特別図柄について変動表示結果が大当りとなるときには、変動パターンを決定するために、次のように判定テーブルを選択する。変動表示結果が通常大当りとなるときには、図7(c)の通常大当り時判定テーブルを選択する。時短状態か否かにかかわらず変動表示結果が確変大当りとなるときには、図7(d)の確変大当り時判定テーブルを選択する。 When the variation display result is a big hit for the first special symbol or the second special symbol regardless of whether the time is short or not, the determination table is selected as follows in order to determine the variation pattern. When the fluctuation display result is a normal big hit, the normal big hit determination table of FIG. 7C is selected. When the variation display result is a probable big hit regardless of whether the time is short or not, the probable big hit judgment table of FIG. 7D is selected.
図7(b)の時短状態はずれ時判定テーブルでは、図7(a)の通常状態はずれ時判定テーブルと比べて、通常変動の変動時間が短く設定されている。そして、図7(b)の時短状態はずれ時判定テーブルでは、図7(a)の通常状態はずれ時判定テーブルと比べて、リーチ変動(ノーマルリーチ変動およびスーパーリーチ変動を含む)よりも変動時間が短い通常変動(非リーチはずれ変動(リーチとならずにはずれ表示結果となる変動))に決定される割合が高く、通常変動よりも変動時間が長いリーチ変動に決定される割合が低くなるように、データが設定されている。 In the time short state deviation determination table of FIG. 7B, the variation time of the normal fluctuation is set shorter than that in the normal state deviation time determination table of FIG. 7B, the fluctuation time is shorter than the reach fluctuation (including the normal reach fluctuation and the super reach fluctuation) compared to the normal state deviation determination table of FIG. 7A. So that the percentage determined for normal fluctuations (non-reach deviation fluctuations (variations resulting in deviation display results instead of reaching reach)) is low, and the percentage determined for reach fluctuations with longer fluctuation times than normal fluctuations is low. Data is set.
これにより、非時短状態(通常状態)のときと比べて、時短状態のときの方が、変動時間が短い変動パターンが選択される割合が高いので、時短状態のときの方が、非時短状態のときよりも平均的に短い変動時間で変動表示が行なわれることとなる。このように判定テーブルを選択することにより時短状態を実現することができる。また、通常変動を非時短状態よりも時短状態ときの方が変動時間が短くなるように設定することで、時短状態中の保留消化を短縮することができる。 As a result, compared to the non-time-short state (normal state), the rate of change in the short-time state is higher in the time-short state, so the time-short state is the non-time-short state. The change display is performed with a change time shorter than that in the mean time. By selecting the determination table in this way, the time saving state can be realized. In addition, by setting the normal fluctuation so that the fluctuation time is shorter in the time-short state than in the non-time-short state, it is possible to shorten the pending digestion during the time-short state.
はずれとなるときに選択される図7(a)および図7(b)の判定テーブルでは、リーチの種別の選択割合がノーマルリーチ>スーパーリーチとなるような高低関係で選択されるようにデータが設定されている。一方、大当りとなるときに選択される図7(c)および図7(d)の判定テーブルでは、リーチの種別の選択割合がノーマルリーチ<スーパーリーチというような割合の高低関係で選択されるようにデータが設定されている。これにより、大当りとなるときには、はずれとなるときと比べ、スーパーリーチのリーチ演出が行なわれる割合(リーチが選択されるときにおけるスーパーリーチのリーチ演出が占める割合)が高くなるので、スーパーリーチのリーチ演出がされることにより、遊技者の期待感を高めることができる。 In the determination tables shown in FIGS. 7A and 7B that are selected when there is a loss, the data is set so that the selection ratio of the reach type is selected in a height relationship such that normal reach> super reach. Has been. On the other hand, in the determination tables of FIG. 7C and FIG. 7D that are selected when a big hit is made, the selection ratio of the reach type is selected in a high / low relationship such that normal reach <super reach. Data is set. As a result, the ratio of super reach reach production (the ratio of super reach reach production when a reach is selected) is higher when a big hit is made than when it is out of reach. The performance can increase the player's expectation.
また、大当りのうち確変大当りとなるときに選択される図7(d)の判定テーブルでは、大当りのうち通常大当りとなるときに選択される図7(c)の判定テーブルと比べて、ノーマルリーチに対してスーパーリーチ演出の種別が選択される割合が高くなるようにデータが設定されている。これにより、確変大当りとなるときには、通常大当りとなるときと比べて、スーパーリーチのリーチ演出が行なわれる割合(リーチが選択されるときにおけるスーパーリーチのリーチ演出が占める割合)が高くなるので、スーパーリーチのリーチ演出が行なわれることにより、遊技者の確変大当りへの期待感を高めることができる。 In addition, the determination table shown in FIG. 7D selected when the big hit is a probable big hit has a normal reach compared to the determination table shown in FIG. 7C selected when the big hit is a normal big hit. On the other hand, the data is set so that the ratio of selecting the type of super reach production is high. As a result, when the probability is a big hit, the ratio of the reach reach of the super reach (the ratio of the reach reach of the super reach when the reach is selected) is higher than the case of the normal big win. By performing the reach of reach, it is possible to increase the player's expectation for a promising big hit.
なお、このような変動パターンは、変動表示をする第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の合算保留記憶数(合計値)が所定数以上であるとき(たとえば、合算保留記憶数が3以上)と、所定数未満であるときとで選択割合が異なるように設定されることにより、合算保留記憶数が所定数以上であるときには、合算保留記憶数が所定数未満であるときと比べて、変動時間が短縮される保留数短縮制御を実行するようにしてもよい。ただし、保留数短縮制御が実行される条件下でも(たとえば、合算保留記憶数が3以上)リーチ(ノーマルリーチ、スーパーリーチ含む)の割合を一定にすることで、リーチに対する期待感が保たれる。また、リーチの中でもスーパーリーチのみ変動時間が短縮されないようにして、保留数時短制御を実行するようにしてもよい。さらに、保留数時短制御は変動時間が短い通常変動が高い割合で選択されるようにすることで実行可能としてもよく、各変動パターン自体の変動時間を短くすることで実行可能としてもよいし、その組合せでもよい。 Note that such a variation pattern is obtained when the total number of reserved storage (total value) of the first special symbol and the second special symbol that display variation is greater than or equal to a predetermined number (for example, the total number of reserved storage is 3 or more). By setting the selection ratio to be different from when the number is less than the predetermined number, when the total number of pending storage is greater than or equal to the predetermined number, the variation time is longer than when the total number of pending storage is less than the predetermined number It is also possible to execute the hold number shortening control for shortening. However, the expectation for reach can be maintained by keeping the ratio of reach (including normal reach and super reach) constant even under the condition that the hold number shortening control is executed (for example, the total number of stored holds is 3 or more). In addition, only the super reach in the reach may not be shortened so as to execute the hold time reduction control. Furthermore, the short time control of the number of holdings may be executable by selecting a high rate of normal fluctuation with a short fluctuation time, or may be executable by shortening the fluctuation time of each fluctuation pattern itself, The combination may be used.
図8は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が送信する演出制御コマンドの内容の一例を示す説明図である。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560においては、図8に示すように、遊技制御状態に応じて、各種の演出制御コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100へ送信する。
FIG. 8 is an explanatory diagram showing an example of the contents of the effect control command transmitted by the
図8のうち、主なコマンドを説明する。コマンド80XX(H)は、特別図柄の変動表示に対応して演出表示装置9において変動表示される演出図柄の変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンド(変動パターンコマンド)である(それぞれ変動パターンXXに対応)。つまり、図7に示すような使用され得る変動パターンのそれぞれに対して一意な番号を付した場合に、その番号で特定される変動パターンのそれぞれに対応する変動パターンコマンドがある。「(H)」は16進数であることを示す。また、変動パターンを指定する演出制御コマンドは、変動開始を指定するためのコマンドでもある。したがって、演出制御用CPU101は、コマンド80XX(H)を受信すると、演出表示装置9において演出図柄の変動表示を開始するように制御する。
Main commands in FIG. 8 will be described. The command 80XX (H) is an effect control command (variation pattern command) for designating a variation pattern of the effect symbol that is variably displayed on the
コマンド8C01(H)〜8C03(H)は、大当りとするか否か、および大当り種別を示す表示結果指定コマンドである。 Commands 8C01 (H) to 8C03 (H) are display result designation commands indicating whether or not to make a big hit and the type of big hit.
コマンド8D01(H)は、第1特別図柄の変動表示を開始することを示す第1図柄変
動指定コマンドである。コマンド8D02(H)は、第2特別図柄の変動表示を開始することを示す第2図柄変動指定コマンドである。コマンド8F00(H)は、第1,第2特別図柄の変動を終了することを指定するコマンド(図柄確定指定コマンド)である。
The command 8D01 (H) is a first symbol variation designation command indicating that the variation display of the first special symbol is started. Command 8D02 (H) is a second symbol variation designation command indicating that the variation display of the second special symbol is started. The command 8F00 (H) is a command (design determination designation command) for designating to end the variation of the first and second special symbols.
コマンド9000(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたとき(RAMクリアによる初期設定のとき)に送信される演出制御コマンド(初期化指定コマンド:電源投入指定コマンド)である。コマンド9200(H)は、遊技機に対する電力供給が再開されたとき(RAMクリアではない停電等による再開時の初期設定のとき)に送信される演出制御コマンド(停電復旧指定コマンド)である。遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560は、遊技機に対する電力供給が開始されたときに、バックアップRAMにデータが保存されている場合には、停電復旧指定コマンドを送信し、そうでない場合には、初期化指定コマンドを送信する。コマンド9F00(H)は、客待ちデモンストレーションを指定する演出制御コマンド(客待ちデモ指定コマンド)である。
Command 9000 (H) is an effect control command (initialization designation command: power-on designation command) that is transmitted when power supply to the gaming machine is started (at the time of initialization by RAM clear). Command 9200 (H) is an effect control command (power failure recovery designation command) transmitted when power supply to the gaming machine is resumed (initial setting at the time of restart due to a power failure that is not RAM clear). When the power supply to the gaming machine is started, the
コマンドA001〜A002(H)は、大当りの種別(通常大当り、または、確変大当り)ごとに大当り遊技状態開始を指定する大当り開始指定コマンドである。 The commands A001 to A002 (H) are jackpot start designation commands that designate the jackpot gaming state start for each jackpot type (normal jackpot or probability variation jackpot).
コマンドA1XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口開放中の表示を示す大入賞口開放中指定コマンドである。A2XX(H)は、XXで示す回数目(ラウンド)の大入賞口開放後(閉鎖)を示す大入賞口開放後指定コマンドである。 The command A1XX (H) is a special winning opening open designation command that indicates a display during opening of the special winning opening for the number of times (round) indicated by XX. A2XX (H) is a designation command after opening the big prize opening indicating the opening (closing) of the big prize opening of the number of times (round) indicated by XX.
コマンドA301〜A302(H)は、大当りの種別(通常大当り、または、確変大当り)ごとに大当り遊技状態終了を指定する大当り終了指定コマンドである。 The commands A301 to A302 (H) are jackpot end designation commands for designating the jackpot gaming state end for each jackpot type (normal jackpot or probability variation jackpot).
コマンドA401(H)は、第1始動入賞があったことを指定する第1始動入賞指定コマンドである。コマンドA402(H)は、第2始動入賞があったことを指定する第2始動入賞指定コマンドである。 Command A 401 (H) is a first start winning designation command for designating that the first starting win has been received. Command A 402 (H) is a second start winning designation command for designating that there has been a second start winning.
コマンドB000(H)は、遊技状態が通常状態(低確率状態)であることを指定する通常状態指定コマンドである。コマンドB001(H)は、遊技状態が時短状態(高ベース状態)であることを指定する時短状態指定コマンドである。コマンドB002(H)は、遊技状態が確変状態(高確率状態)であることを指定する確変状態指定コマンドである。 Command B000 (H) is a normal state designation command for designating that the gaming state is a normal state (low probability state). Command B001 (H) is a short time state designation command for designating that the gaming state is the short time state (high base state). Command B002 (H) is a probability variation state designation command for designating that the gaming state is a probability variation state (high probability state).
コマンドC0XX(H)は、合算保留記憶数を示す合算保留記憶数指定コマンドである。コマンドC100(H)は、合算保留記憶数が1減算されることを示す合算保留記憶数減算指定コマンドである。この実施の形態では、合算保留記憶数指定コマンドは、第1始動入賞口13または第2始動入賞口14への遊技球の始動入賞時(たとえば、後述する始動口スイッチ通過処理の実行時)に、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送られる。また、合算保留記憶数減算指定コマンドは、変動表示開始時(たとえば、後述する特別図柄変動表示中処理の実行時)に演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送られる。なお、合算保留記憶指定コマンドおよび保留記憶数減算指定コマンドを兼用してもよい。たとえば、合算保留記憶数指定コマンドを、減算後の保留記憶数を特定可能なコマンドとして用いてもよい。なお、合算保留記憶数としてではなく、第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数とを特定可能なコマンドをそれぞれ送信し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が第1保留記憶数と第2保留記憶数との合計値を合算保留記憶数として特定してもよい。
Command C0XX (H) is a combined pending storage number designation command indicating the combined pending storage number. The command C100 (H) is a total pending storage number subtraction designation command indicating that the total pending storage number is decremented by one. In this embodiment, the total reserved memory number designation command is issued at the time of starting winning of a game ball to the first
コマンドC2XX(H)およびコマンドC3XX(H)は、第1始動入賞口13または第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞時における大当り判定、大当り種別判定、変動パターン種別判定等の入賞時判定結果の内容を示す演出制御コマンドである。このうち、コマンド
C2XX(H)は、入賞時判定結果のうち、大当りとなるか否か、および、大当りの種別の判定結果を示す図柄指定コマンドである。また、コマンドC3XX(H)は、入賞時判定結果のうち、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲となるかの判定結果(変動パターン種別の判定結果)を示す変動種別コマンドである。
The command C2XX (H) and the command C3XX (H) are the results of winning determination results such as jackpot determination, jackpot type determination, variation pattern type determination, etc. at the time of starting winning to the first
この実施の形態では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が、始動入賞時に、大当りとなるか否か、大当りの種別、変動パターン種別判定用乱数の値がいずれの判定値の範囲となるかを判定する。そして、図柄指定コマンドのEXTデータに、大当りとなることを指定する値、および、大当りの種別を指定する値を設定し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう。変動種別コマンドのEXTデータに変動パターン種別の判定結果としての判定値の範囲を指定する値を設定し、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御を行なう。この実施の形態では、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が、図柄指定コマンドに設定されている値に基づき、始動入賞時に、表示結果が大当りとなるか否か、および、大当りの種別を認識できるとともに、変動種別コマンドに基づき、変動パターン種別を認識できる。
In this embodiment, the
次に、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560側での保留記憶に対応する乱数等のデータ(保留記憶データ)を保存する領域(保留記憶バッファ)の構成例を説明する。保留記憶バッファは、RAM55に設けられる。
Next, a configuration example of an area (holding storage buffer) for storing data (holding storage data) such as random numbers corresponding to the holding storage on the
第1保留記憶バッファには、第1保留記憶数の上限値(この例では4)に対応した保存領域が確保されている。また、第2保留記憶バッファには、第2保留記憶数の上限値(この例では4)に対応した保存領域が確保されている。第1保留記憶バッファおよび第2保留記憶バッファには、ハードウェア乱数である大当り判定用乱数(ランダムR)、および、ソフトウェア乱数である大当り種別決定用乱数(ランダム1)、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)、および、変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)が記憶される。 In the first reserved memory buffer, a storage area corresponding to the upper limit value (4 in this example) of the first reserved memory number is secured. In addition, a storage area corresponding to the upper limit value of the second reserved storage number (4 in this example) is secured in the second reserved storage buffer. The first reserved storage buffer and the second reserved storage buffer include a jackpot determination random number (random R) that is a hardware random number, a jackpot type determination random number (random 1) that is a software random number, and a variation pattern type determination random number. (Random 2) and random number for variation pattern determination (Random 3) are stored.
第1始動入賞口13または第2始動入賞口14への入賞に基づいて、CPU56は、乱数回路503およびソフトウェア乱数を生成するためのランダムカウンタからこのような乱数値を抽出し、それらを、第1保留記憶バッファまたは第2保留記憶バッファにおける保存領域に保存(格納)する処理を実行する。具体的に、第1始動入賞口13への入賞に基づいて、これら乱数値が抽出されて第1保留記憶バッファに保存される。また、第2始動入賞口14への入賞に基づいて、これら乱数値が抽出されて第2保留記憶バッファに保存される。
Based on the winning at the first
第1保留記憶バッファまたは第2保留記憶バッファに前述のような始動入賞に関する情報が記憶されることを「保留記憶される」と示す場合がある。なお、変動パターン種別判定用乱数(ランダム2)および変動パターン判定用乱数(ランダム3)は、始動入賞時に抽出して保存領域に予め格納しておくのではなく、後述する変動パターン設定処理(特別図柄の変動開始時)に抽出するようにしてもよい。 In some cases, “holding stored” indicates that the information related to the start winning as described above is stored in the first holding storage buffer or the second holding storage buffer. Note that the random number for variation pattern type determination (random 2) and the random number for variation pattern determination (random 3) are not extracted at the time of starting winning and stored in the storage area in advance. It may be extracted at the time of the start of symbol variation.
このように保留記憶バッファに記憶されたデータは、後述するように、始動入賞時に読出されて先読み予告演出のために用いられるとともに、変動表示開始時に読出されて変動表示のために用いられる。 As described later, the data stored in the hold storage buffer is read out at the time of starting winning and used for the pre-reading notice effect, and is read out at the start of the variable display and used for the variable display.
第1始動入賞口13または第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞があったときには、図柄指定コマンド、変動種別コマンド、第1(第2)始動入賞指定コマンド、および、合算保留記憶数指定コマンドというような、始動入賞時判定処理の判定結果を示すコマンドが、主基板31から演出制御基板80へと送信される。演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100のRAM103に設けられた始動入賞時受信コマンドバッファには、受信した図柄指定コ
マンド、変動種別コマンド、第1(第2)始動入賞指定コマンド、および、合算保留記憶数指定コマンド等の各種コマンドを対応付けて格納できるように、受信したコマンドを特定可能なデータを記憶する記憶領域が確保されている。
When there is a start prize at the first
この実施の形態において、第1特別図柄および第2特別図柄の変動表示に対応して行なわれる演出図柄の演出制御パターンは、複数種類の変動パターンに対応して、演出図柄の変動表示動作、リーチ演出等における演出表示動作、あるいは、演出図柄の変動表示を伴わない各種の演出動作というような、様々な演出動作の制御内容を示すデータ等から構成されている。また、予告演出制御パターンは、予め複数パターンが用意された予告パターンに対応して実行される予告演出となる演出動作の制御内容を示すデータ等から構成されている。各種演出制御パターンは、パチンコ遊技機1における遊技の進行状況に応じて実行される各種の演出動作に対応して、その制御内容を示すデータ等から構成されている。
In this embodiment, the effect control pattern of the effect symbol performed in response to the variation display of the first special symbol and the second special symbol corresponds to a plurality of types of variation patterns, the variation display operation of the effect symbol, the reach It is composed of data indicating the contents of control of various effect operations, such as effect display operations in effects, etc., or various effect operations that are not accompanied by display changes of effect symbols. The notice effect control pattern includes data indicating the control content of the effect operation that becomes the notice effect executed corresponding to the notice pattern in which a plurality of patterns are prepared in advance. The various effect control patterns are composed of data indicating the control contents corresponding to various effect operations executed in accordance with the progress of the game in the
次に、パチンコ遊技機1の動作について説明する。パチンコ遊技機1においては、主基板31における遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560が予め定められたメイン処理を実行すると、所定時間(たとえば2ms)毎に定期的にタイマ割込がかかりタイマ割込処理が実行されることにより、各種の遊技制御が実行可能となる。
Next, the operation of the
メイン処理においては、たとえば、必要な初期設定処理、通常時の初期化処理、通常時以外の遊技状態復旧処理、乱数回路設定処理(乱数回路503を初期設定)、表示用乱数更新処理(変動パターンの種別決定、変動パターン決定等の各種乱数の更新処理)、および、初期値用乱数更新処理(普通図柄当り判定用乱数発生カウンタのカウント値の初期値の更新処理)等が実行される。
In the main processing, for example, necessary initial setting processing, normal time initialization processing, game state restoration processing other than normal time, random number circuit setting processing (
図9は、タイマ割込処理を示すフローチャートである。タイマ割込が発生すると、CPU56は、図9に示すステップS(以下、単に「S」と示す)20〜S34のタイマ割込処理を実行する。タイマ割込処理において、まず、電源断信号が出力されたか否か(オン状態になったか否か)を検出する電源断検出処理を実行する(S20)。次いで、入力ドライバ回路58を介して、ゲートスイッチ32a、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14aおよびカウントスイッチ23の検出信号を入力し、それらの状態判定を行なう(スイッチ処理:S21)。
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing the timer interrupt process. When the timer interrupt occurs, the
次に、CPU56は、第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8b、普通図柄表示器10、第1特別図柄保留記憶表示器18a、第2特別図柄保留記憶表示器18b、普通図柄保留記憶表示器41の表示制御を行なう表示制御処理を実行する(S22)。第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび普通図柄表示器10については、S32,S33で設定される出力バッファの内容に応じて各表示器に対して駆動信号を出力する制御を実行する。
Next, the
また、遊技制御に用いられる普通図柄当り判定用乱数および大当り種別判定用乱数等の各判定用乱数を生成するための各カウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行なう(判定用乱数更新処理:S23)。CPU56は、さらに、初期値用乱数および表示用乱数を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する処理を行なう(初期値用乱数更新処理,表示用乱数更新処理:S24,S25)。
In addition, a process of updating the count value of each counter for generating each determination random number such as a normal symbol determination random number and a big hit type determination random number used for game control is performed (determination random number update process: S23). . The
さらに、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセス処理を行なう(S26)。特別図柄プロセス処理では、第1特別図柄表示器8a、第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび大入賞口を所定の順序で制御するための特別図柄プロセスフラグにしたがって該当する処理を実行し、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Further, the
次いで、普通図柄プロセス処理を行なう(S27)。普通図柄プロセス処理では、CPU56は、普通図柄表示器10の表示状態を所定の順序で制御するための普通図柄プロセスフラグにしたがって該当する処理を実行し、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値を、遊技状態に応じて更新する。
Next, the normal symbol process is performed (S27). In the normal symbol process, the
また、CPU56は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に演出制御コマンドを送出する処理を行なう(演出制御コマンド制御処理:S28)。さらに、CPU56は、たとえばホール管理用コンピュータに供給される大当り情報、始動情報、確率変動情報等のデータを出力する情報出力処理を行なう(S29)。
Further, the
また、CPU56は、第1始動口スイッチ13a、第2始動口スイッチ14aおよびカウントスイッチ23の検出信号に基づく賞球個数の設定等を行なう賞球処理を実行する(S30)。
Further, the
この実施の形態では、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域(出力ポートバッファ)が設けられているのであるが、CPU56は、出力ポートの出力状態に対応したRAM領域におけるソレノイドのオン/オフに関する内容を出力ポートに出力する(S31:出力処理)。
In this embodiment, a RAM area (output port buffer) corresponding to the output state of the output port is provided. However, the
また、CPU56は、特別図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて特別図柄の演出表示を行なうための特別図柄表示制御データを特別図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する特別図柄表示制御処理を行なう(S32)。
Further, the
さらに、CPU56は、普通図柄プロセスフラグの値に応じて普通図柄の演出表示を行なうための普通図柄表示制御データを普通図柄表示制御データ設定用の出力バッファに設定する普通図柄表示制御処理を行なう(S33)。また、CPU56は、出力バッファに設定された表示制御データに応じて、S22において駆動信号を出力することによって、普通図柄表示器10における普通図柄の演出表示を実行する。
Further, the
その後、割込許可状態に設定し(S34)、処理を終了する。以上の制御によって、この実施の形態では、遊技制御処理は所定時間毎に起動されることになる。 Thereafter, the interrupt permission state is set (S34), and the process ends. With the above control, in this embodiment, the game control process is started every predetermined time.
図10は、特別図柄プロセス処理(S26)を示すフローチャートである。特別図柄プロセス処理では、第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bおよび大入賞口を制御するための処理が実行される。特別図柄プロセス処理においては、始動口スイッチ通過処理を実行する(S312)。そして、内部状態に応じて、S300〜S307のうちのいずれかの処理を行なう。
FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing the special symbol process (S26). In the special symbol process, a process for controlling the first
遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560において、RAM55には、前述したように、第1始動入賞口13への始動入賞に基づいて得られる大当り判定用乱数等の保留記憶データ(第1保留記憶データ)が記憶される第1保留記憶バッファと、第2始動入賞口14への始動入賞に基づいて得られる大当り判定用乱数等の保留記憶データ(第2保留記憶データ)が記憶される第2保留記憶バッファとが設けられている。これら各保留記憶バッファには、各保留記憶の記憶数の上限値(この例では4)に対応した保存領域が確保されている。
In the
始動口スイッチ通過処理では、第1始動口スイッチ13aがオンしていれば、第1保留記憶数が上限値(たとえば、4)に達していないことを条件として、第1保留記憶データの記憶数を計数する第1保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やし、乱数回路503やソフトウェア乱数を生成するためのカウンタから数値データ(たとえば、大当り判定用乱数、変動
パターン種別判定用乱数、および、変動パターン判定用乱数)を抽出し、それらを、第1保留記憶バッファにおける保存領域に保存(格納)する処理を実行する。さらに、合算保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やし、合算後の合算保留記憶数カウンタの値に対応した保留特定領域に「第1」を示すデータを保存(格納)する処理を実行する。一方、第2始動口スイッチ14aがオンしていれば、第2保留記憶数が上限値(たとえば、4)に達していないことを条件として、第2保留記憶データの記憶数を計数する第2保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やし、乱数回路503やソフトウェア乱数を生成するためのカウンタから数値データ(たとえば、大当り判定用乱数、変動パターン種別判定用乱数、および、変動パターン判定用乱数)を抽出し、それらを、第2保留記憶バッファにおける保存領域に保存(格納)する処理を実行する。さらに、合算保留記憶数カウンタの値を1増やし、合算後の合算保留記憶数カウンタの値に対応した保留特定領域に「第2」を示すデータを保存(格納)する処理を実行する。
In the start port switch passing process, if the first
S300〜S307の処理は、以下のような処理である。特別図柄通常処理(S300)は、変動表示の表示結果を大当りとするか否かの決定、および、大当りとする場合の大当り種別の決定等を行なう処理である。変動パターン設定処理(S301)は、変動パターンの決定(変動パターン種別判定用乱数および変動パターン判定用乱数を用いた変動パターンの決定)、および、決定された変動パターンに応じて変動時間を計時するための変動時間タイマの計時開始等の制御を行なう処理である。 The processing of S300 to S307 is as follows. The special symbol normal process (S300) is a process for determining whether or not the display result of the variable display is a big hit, and determining the big hit type in the case of the big hit. In the variation pattern setting process (S301), the variation pattern is determined (the variation pattern type determination random number and the variation pattern determination random number are determined), and the variation time is measured according to the determined variation pattern. This is a process for performing control such as the start of timing of the fluctuation time timer.
表示結果指定コマンド送信処理(S302)は、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に、表示結果指定コマンドを送信する制御を行なう処理である。特別図柄変動中処理(S303)は、変動パターン設定処理で選択された変動パターンの変動時間が経過すると特別図柄停止処理にプロセスを進める処理である。特別図柄停止処理(S304)は、決定された変動パターンに対応する変動時間の経過が変動時間タイマにより計時されたときに第1特別図柄表示器8aまたは第2特別図柄表示器8bにおける変動表示を停止して停止図柄を導出表示させる処理である。
The display result designation command transmission process (S302) is a process for performing control to transmit a display result designation command to the
大入賞口開放前処理(S305)は、大当りの種別に応じて、特別可変入賞球装置20において大入賞口を開放する制御等を行なう処理である。大入賞口開放中処理(S306)は、大当り遊技状態中のラウンド表示演出用の演出制御コマンドを演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に送信する制御、および、大入賞口の閉成条件の成立を確認する処理等を行なう処理である。大入賞口の閉成条件が成立し、かつ、まだ残りラウンドがある場合には、大入賞口開放前処理(S305)に移行する。また、全てのラウンドを終えた場合には、大当り終了処理(S307)に移行する。大当り終了処理(S307)は、大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100に行なわせるための制御等を行なう処理である。
The big winning opening opening pre-processing (S305) is a process of performing control for opening the big winning opening in the special variable winning
次に、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100の動作を説明する。図11は、演出制御基板80に搭載されている演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100(具体的には、演出制御用CPU101)が実行する演出制御メイン処理を示すフローチャートである。
Next, the operation of the
演出制御用CPU101は、電源が投入されると、演出制御メイン処理の実行を開始する。演出制御メイン処理では、まず、RAM領域のクリアや各種初期値の設定、また演出制御の起動間隔(たとえば、2ms)を決めるためのタイマの初期設定等を行なうための初期化処理を行なう(S701)。その後、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込フラグの監視(S702)を行なうループ処理に移行する。タイマ割込が発生すると、演出制御用CPU101は、タイマ割込処理においてタイマ割込フラグをセットする。演出制御メイン処理において、タイマ割込フラグがセットされていたら、演出制御用CPU101は、そのフラグをクリアし(S703)、以下の演出制御処理を実行する。
The
演出制御処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、まず、受信した演出制御コマンドを解析し、受信した演出制御コマンドがどのようなことを指示するコマンドであるかを特定可能なフラグ等のデータをセットする処理(たとえば、RAM103に設けられた各種コマンド格納領域に受信したコマンドを特定可能なデータを格納する処理等)等を行なう(コマンド解析処理:S704)。次いで、演出制御用CPU101は、演出制御プロセス処理を行なう(S705)。演出制御プロセス処理では、S704で解析した演出制御コマンドの内容にしたがって演出表示装置9での演出図柄の変動表示等の各種演出を行なうために、制御状態に応じた各プロセスのうち、現在の制御状態(演出制御プロセスフラグ)に対応した処理を選択して演出制御を実行する。
In the effect control process, the
次いで、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100が用いる乱数(演出図柄の左停止図柄決定用のSR1−1、演出図柄の中停止図柄決定用のSR1−2、演出図柄の右停止図柄決定用のSR1−3等)を生成するためのカウンタのカウント値を更新する乱数更新処理を実行する(S706)。このような乱数SR1−1〜SR1−3のそれぞれは、ソフトウェアによりカウント値を更新するランダムカウンタのカウントにより生成されるものであり、それぞれについて予め定められた範囲内でそれぞれ巡回更新され、それぞれについて定められたタイミングで抽出されることにより乱数として用いられる。
Next, random numbers (SR1-1 for determining the left stop symbol of the effect symbol, SR1-2 for determining the middle stop symbol of the effect symbol, SR1-3 for determining the right stop symbol of the effect symbol used by the
次いで、保留表示エリアにおける保留表示の表示状態の制御(保留表示の移動、消去等)を行なう保留記憶表示制御処理を実行する(S707)。その後、遊技枠の上部に取り付けられた上部役物の動作態様を設定する上部役物設定処理を実行する(S708)。そして、S702の処理へリターンする。上部役物設定処理については、図12により詳細に説明する。 Next, a hold storage display control process for controlling the display state of the hold display in the hold display area (moving or deleting the hold display, etc.) is executed (S707). Thereafter, an upper character setting process for setting an operation mode of the upper character attached to the upper part of the game frame is executed (S708). Then, the process returns to S702. The upper accessory setting process will be described in detail with reference to FIG.
このような演出制御メイン処理が実行されることにより、演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ100では、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ560から送信され、受信した演出制御コマンドに応じて、演出表示装置9、各種ランプ、第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29R、および、スピーカ27L,27R等の演出装置を制御することにより、遊技状態に応じた各種の演出制御が行なわれる。
By executing such effect control main processing, the
図12は、図11に示された演出制御メイン処理における上部役物設定処理(S708)を示すフローチャートである。上部役物設定処理は、電源投入後、図11に示されたS701からS707の処理後に、演出制御用CPU101によって実行される処理であり、遊技枠上部に取り付けられた第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rの回転角度(開閉角度)を設定する処理である。上部役物の回転角度は複数段階(たとえば、0度、45度、60度、90度など)設けられており、その中から任意に選択した一つの角度を設定できるようになっている。
FIG. 12 is a flowchart showing the upper accessory setting process (S708) in the effect control main process shown in FIG. The upper accessory setting process is a process executed by the
ここで、初期状態(最初に電源投入した場合やRAMクリアによる電源投入の場合)においては、上部役物の回転角度が遊技枠に対して最も突出する回転角度である90度よりも突出しない角度(たとえば、45度)になるように制御される。このようにすれば、調整をしていない場合であっても上部役物が他の物体と当接することを防ぐことができる。 Here, in the initial state (when power is turned on for the first time or when power is turned on by RAM clear), the angle at which the rotation angle of the upper accessory does not protrude more than 90 degrees, which is the rotation angle that most protrudes with respect to the game frame. It is controlled to be (for example, 45 degrees). In this way, even if the adjustment is not performed, it is possible to prevent the upper accessory from coming into contact with another object.
上部役物の角度を設定する設定画面は、RAM55をクリアしたときの電源投入が実行され、動作確認のための初期動作として各役物のイニシャル動作が実行された後に表示される。演出制御用CPU101は、イニシャル動作を実行する際に、各役物の近くに設けられた検出手段としての役物用センサからの検出信号に各役物が初期位置に存在するか否かを判定する。一方、RAM55をクリアせずに電源を投入した場合には、上部役物の設定はなされない。したがって、演出制御用CPU101は、図8に示された初期化指定コ
マンドを受信した場合には、上部役物設定期間であると判定し、初期化指定コマンドを受信していない場合(停電復旧指定コマンドを受信した場合)には、上部役物設定期間ではないと判定する。
The setting screen for setting the angle of the upper accessory is displayed after the power is turned on when the
S750では、演出制御用CPU101は、初期化指定コマンドを受信したか否かにより、上部役物設定期間であるか否かを判定する。演出制御用CPU101は、初期化指定コマンドを受信した場合、つまり、上部役物設定期間であると判定した場合(S750でY)には、S751へ移行し、初期化指定コマンドを受信していない場合、つまり、上部役物設定期間ではないと判定した場合(S750でN)には、処理を終了する。
In S750, the
S751では、演出制御用CPU101は、設定操作を検出したか否かを判定する。演出制御用CPU101は、店員等による設定操作を検出した場合(S751でY)には、設定された角度に応じて、上部役物の回転角度および上部役物の回転速度を設定し(S752)、S753へ移行する。一方、演出制御用CPU101は、設定操作を検出しなかった場合(S751でN)には、処理を終了する。
In S751, the
次いで、S753では、演出制御用CPU101は、設定角度が0度であるか否かを判定する。演出制御用CPU101は、設定角度が0度である場合には(S753でY)、上部役物演出制限フラグをセットし(S754)、処理を終了する。一方、演出制御用CPU101は、設定角度が0度ではない場合(S753でN)には、処理を終了する。
Next, in S753, the
S752に示すように、設定された角度に応じて、第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rの回転角度・回転速度を設定するので、遊技枠に設けられた軸290に対して回転する上部役物を動作させつつ、上部役物が遊技機に隣接する別の遊技機の遊技枠や上部に配置されるデータランプ等の他の物体と当接することを防ぐことができる。
As shown in S752, the rotation angle and the rotation speed of the first
図13は、図11に示された演出制御メイン処理における演出制御プロセス処理(S705)を示すフローチャートである。演出制御プロセス処理では、演出制御用CPU101は、先読み演出を実行するか否かの決定、および、先読み演出の種類の選択をする先読み演出処理(S700)を実行した後、演出制御プロセスフラグの値に応じてS800〜S807のうちのいずれかの処理を行なう。
FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing the effect control process (S705) in the effect control main process shown in FIG. In the effect control process, the
演出制御プロセス処理では、以下のような処理が実行される。演出制御プロセス処理では、演出表示装置9の表示状態が制御され、演出図柄の変動表示が実現されるが、第1特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の変動表示に関する制御も、第2特別図柄の変動に同期した演出図柄の変動表示に関する制御も、一つの演出制御プロセス処理において実行される。
In the effect control process, the following process is executed. In the effect control process, the display state of the
先読み演出処理(S700)は、先読み演出を実行するか否か等の先読み判定、および、先読み演出を実行するときの演出態様の決定等を行なう処理である。先読み演出とは、ある保留情報(保留記憶情報)に基づいた特別図柄の変動表示(図柄変動)の順番が到来する前に、その保留情報を先読みしてその保留情報に基づいた特別図柄の変動表示の内容を判定して、将来の特別図柄の変動表示がどのようになるかを、それよりも前の段階で予告をする等の演出技術である。たとえば、保留情報が大当りであるときに、当該保留情報による変動表示が実行される前に、当該保留情報に対応する保留表示の表示態様に基づいて、後に大当りが発生する可能性のあることを予告するといった類の演出が先読み演出として行なわれる。以下では、先読み演出の対象とした保留情報に基づいた変動表示を「ターゲットの変動表示」と称する。 The pre-reading effect process (S700) is a process of performing pre-reading determination such as whether or not to execute the pre-reading effect, and determining an effect mode when the pre-reading effect is executed. The pre-reading effect is a special symbol change based on the hold information by pre-reading the hold information before the order of the change display (symbol change) of the special symbol based on the hold information (holding storage information) comes. This is a production technique such as determining the contents of the display and giving a notice in advance of how the future special symbols will change. For example, when the hold information is a jackpot, before the variable display by the hold information is executed, the jackpot may occur later based on the display mode of the hold display corresponding to the hold information. An effect such as giving a notice is performed as a look-ahead effect. Hereinafter, the fluctuation display based on the hold information as the target of the pre-reading effect is referred to as “target fluctuation display”.
変動パターンコマンド受信待ち処理(S800)は、遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ
560から変動パターンコマンドを受信しているか否か確認する処理等を行なう処理である。変動パターンコマンドを受信していれば、演出図柄変動開始処理に移行する。
The variation pattern command reception waiting process (S800) is a process of performing a process of confirming whether or not a variation pattern command is received from the
演出図柄変動開始処理(S801)は、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動表示が開始されるように制御するための処理である。演出図柄変動中処理(S802)は、変動パターンを構成する各変動状態(変動速度)の切替えタイミングを制御する処理等を行なう処理である。演出図柄変動停止処理(S803)は、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動表示を停止し、変動表示の表示結果(最終停止図柄)を導出表示する制御を行なう処理である。 The effect symbol variation start process (S801) is a process for controlling the variation display of the effect symbol (decoration symbol) to be started. The effect symbol variation process (S802) is a process for performing processing for controlling the switching timing of each variation state (variation speed) constituting the variation pattern. The effect symbol fluctuation stop process (S803) is a process for performing control to stop the fluctuation display of the effect symbol (decoration symbol) and derive and display the display result of the fluctuation display (final stop symbol).
大当り表示処理(S804)は、変動時間の終了後、演出表示装置9に大当りの発生を報知するためのファンファーレ演出を表示する制御等の表示制御を行なう処理である。ラウンド中処理(S805)は、ラウンド中の表示制御を行なう処理である。ラウンド終了条件が成立したときに、最終ラウンドが終了していなければ、ラウンド後処理に移行し、最終ラウンドが終了していれば、大当り終了処理に移行する。ラウンド後処理(S806)は、ラウンド間の表示制御を行なう処理である。ラウンド開始条件が成立したら、ラウンド中処理に移行する。大当り終了演出処理(S807)は、演出表示装置9において、大当り遊技状態が終了したことを遊技者に報知する表示制御を行なう処理である。
The jackpot display process (S804) is a process for performing display control such as control for displaying a fanfare effect for notifying the
演出制御用CPU101は、変動表示の開始時から変動表示の停止時まで、および、大当り遊技状態開始時から大当り遊技状態終了時までの予め定められた演出制御期間中に、ROM102に格納されたプロセステーブルに設定されているプロセスデータに従って演出表示装置9等の演出装置(演出用部品)の制御を行なう。
The
プロセステーブルは、プロセスタイマ設定値と、表示制御実行データ、ランプ制御実行データおよび音番号データの組合せが複数集まったデータとで構成されている。表示制御実行データには、演出図柄(飾り図柄)の変動表示の変動時間(変動表示時間)中の変動態様を構成する各変動の態様を示すデータ等が記載されている。具体的には、演出表示装置9の表示画面の変更に関わるデータが記載されている。また、プロセスタイマ設定値には、その変動の態様での変動時間が設定されている。演出制御用CPU101は、プロセステーブルを参照し、プロセスタイマ設定値に設定されている時間だけ表示制御実行データに設定されている変動の態様で演出図柄を表示させる制御を行なう。このようなプロセステーブルは、各変動パターンに応じて用意されている。
The process table includes process timer set values and data obtained by collecting a plurality of combinations of display control execution data, lamp control execution data, and sound number data. The display control execution data includes data indicating each variation mode constituting the variation mode during the variation time (variation display time) of the variation display of the effect symbol (decoration symbol). Specifically, data relating to the change of the display screen of the
[上部役物演出]
次に、本実施の形態で実行される各種の演出について説明する。本実施の形態では、第1上部役物29Lおよび第2上部役物29Rが動作する上部役物演出が実行されることがある。上部役物演出では、上部役物が動作するとともに演出表示装置9の表示画面上で上部役物が動作することを報知する第1パターンによる演出と、上部役物は動作するが演出表示装置9の表示画面には上部役物が動作することが報知されない第2パターンによる演出が設けられている。
[Upper production]
Next, various effects performed in the present embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, there may be executed an upper accessory effect in which the first
図14は、上部役物演出の一例を示すための図である。図14(a)〜(c)では、第1パターンによる上部役物演出が実行されているときの演出表示装置9の表示画面を示している。図14(a)に示すように、変動表示中にチャンス画像95が表示されることで期待度が高い演出が実行されることが示される。その後、図14(b)に示すように、上部役物が可動することを示す報知画像96が演出表示装置9の画面上に表示される。たとえば、図14(b)では、第1上部役物29Lおよび第2上部役物29Rが遊技枠から上方に突出する映像が流れる。
FIG. 14 is a diagram for illustrating an example of the upper accessory effect. FIGS. 14A to 14C show display screens of the
さらに、図14(c)に示すように、上部役物が最も突出する90度の角度になること
が演出表示装置9の画面上で示される。図14(c)では、第1上部役物29Lに設けられた第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部役物29Rに設けられた第2上部LED29Bが発光する様子も示される。
Furthermore, as shown in FIG. 14C, it is indicated on the screen of the
図14に示すような上部役物演出の実行中に、上部役物が設定された角度によって回転動作を開始する。このように、演出表示装置9の画面において、上部役物が動作していることを示す報知画像96が表示されるので、上部役物が動作していることを確実に遊技者に報知することができる。なお、上部役物の実際の動作の開始時期は、演出表示装置9で上部役物が動作していることを示す映像が流れた後であってもよいし、映像が流れる前であってもよい。
During the execution of the upper accessory effect as shown in FIG. 14, the rotation operation is started at the angle at which the upper accessory is set. Thus, since the
ここで、上部役物が動作するときには、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29Bが発光する演出とともに、第1上部LED29Aおよび第2上部LED29B以外の枠LED28等が発光する演出も実行される。しかしながら、演出表示装置9の画面上には、上部役物が動作していることを示す報知画像96を表示する際に枠LED28による演出は表示しない。このようにすれば、枠LED28等による演出を含めずに上部役物演出が実行されるので、当該上部役物演出による上部役物の動作をより目立たせることができる。
Here, when the upper accessory operates, an effect that the first
なお、図14(b),(c)において、演出表示装置9の画面において表示される報知画像96に流れる映像内の液晶内において、所定の映像が流れるようにしてもよい。このような映像内の液晶における所定の映像としては、どのような映像を流すようにしてもよい。具体的には、上部役物の動作とは関連のない大当りを報知するようなプレミアム演出としてオリジナルキャラクタを表示してもよいし、枠LED28等が発光する映像を流すようにしてもよい。
14B and 14C, a predetermined video may flow in the liquid crystal in the video that flows in the
次に、上部役物演出の演出内容を決定するためのテーブルについて説明する。図15は、上部役物演出決定テーブルを示す図である。図15では、通常遊技中と高ベース中とで上部役物演出の決定に用いられるテーブルが異なっている。また、上部役物演出決定テーブルは、上部役物演出を実行するか否かを決定するとともに、上部役物演出を実行する場合には、第1パターン(動作と報知との両方を実行する場合)と第2パターン(動作のみを実行する場合)のうち、いずれの上部役物演出を実行するのかを決定するための抽選に用いるデータテーブルである。ここで、動作とは、上部役物が設定された角度によって動作する演出を示している。また、報知とは、図14で説明したように、演出表示装置9において、上部役物が動作していることを示す動画を再生する演出等である。
Next, a table for determining the contents of the effect of the upper accessory effect will be described. FIG. 15 is a diagram showing an upper accessory effect determination table. In FIG. 15, the table used for determining the upper feature effect differs between the normal game and the high base. Further, the upper accessory effect determination table determines whether or not to execute the upper accessory effect, and when executing the upper accessory effect, the first pattern (when both the operation and the notification are executed). ) And the second pattern (when only the operation is executed) is a data table used for a lottery to determine which upper accessory effect is to be executed. Here, the action indicates an effect in which the upper feature moves according to the set angle. In addition, as described with reference to FIG. 14, the notification is an effect or the like for reproducing a moving image indicating that the upper accessory is operating on the
図15(A),(B)は、通常遊技中における上部役物演出決定テーブルを示す図である。通常遊技中における上部役物演出決定テーブルには、図15(A)の通常遊技中大当り時上部役物演出決定テーブルと、図15(B)の通常遊技中はずれ時上部役物演出決定テーブルとが含まれている。これらの通常遊技中における上部役物演出決定テーブルは、演出制御基板80に設けられたROM102に記憶されている。
FIGS. 15A and 15B are diagrams showing an upper accessory effect determination table during a normal game. In the upper game effect determination table in the normal game, the upper game effect determination table in the normal game big hit in FIG. 15 (A) and the upper character effect determination table in the normal game in FIG. 15 (B). It is included. The upper accessory effect determination table during these normal games is stored in the
図15(A)の通常遊技中大当り時上部役物演出決定テーブルは、所定のタイミングで抽出したSR2の値によって、「第1パターン>第2パターン>実行なし」という大小関係となるようにデータが設定されている。図15(B)の通常遊技中はずれ時上部役物演出決定テーブルは、所定のタイミングで抽出したSR2の値によって、「第1パターン<第2パターン<実行なし」という大小関係となるようにデータが設定されている。 The upper game effect determination table for normal game mid-big hit in FIG. 15A is data so as to have a magnitude relationship of “first pattern> second pattern> no execution” according to the value of SR2 extracted at a predetermined timing. Is set. The upper-compartment effect determination table at the time of out of normal game in FIG. 15 (B) is data so as to have a magnitude relationship of “first pattern <second pattern <no execution” depending on the value of SR2 extracted at a predetermined timing. Is set.
図15(A),(B)でのデータの設定により、通常遊技中においては、変動表示の表示結果が大当り表示結果となるときには、はずれ表示結果となるときと比べ、上部役物演
出が実行される割合が高くなる。また、大当り表示結果となるときには、第1パターンの上部役物演出は、第2パターンの上部役物演出よりも高い割合で実行される。よって、上部役物演出が実行される場合には、上部役物演出が実行されない場合よりも、遊技者の大当りに対する期待度を高めることができる。さらに、第1パターンの上部役物演出が実行される場合には、第2パターンの上部役物演出が実行される場合よりも、遊技者の大当りに対する期待度を高めることができる。
15A and 15B, in the normal game, when the display result of the variable display becomes the jackpot display result, the upper feature effect is executed as compared with the case of the off-line display result. The rate of being increased. In addition, when the big hit display result is obtained, the upper character effect of the first pattern is executed at a higher rate than the upper character effect of the second pattern. Therefore, when the upper combination effect is executed, the player's expectation for the big hit can be increased as compared with the case where the upper combination effect is not executed. Furthermore, when the upper pattern effect of the first pattern is executed, the player's expectation for the big hit can be increased as compared with the case where the upper pattern effect of the second pattern is executed.
図15(A),(B)でのデータの設定により、通常遊技中においては、第1パターンまたは第2パターンのいずれで上部役物が動作されるかにより大当り期待度が異なるため、遊技枠に設けられた可動体を用いた演出の興趣を向上させることができる。より具体的には、通常遊技中においては、第1パターンが実行されたときの方が第2パターンが実行されたときよりも大当り期待度が高いので、第1パターンが実行されることに対する期待感を高めることができる。 Due to the data setting in FIGS. 15 (A) and 15 (B), in the normal game, the big hit expectation degree differs depending on whether the upper character is operated in the first pattern or the second pattern. The interest of the production using the movable body provided in can be improved. More specifically, during normal games, when the first pattern is executed, the expectation for jackpot is higher than when the second pattern is executed. A feeling can be heightened.
図15(C),(D)は、高ベース中における上部役物演出決定テーブルを示す図である。高ベース中における上部役物演出決定テーブルには、図15(C)の高ベース中大当り時上部役物演出決定テーブルと、図15(D)の高ベース中はずれ時上部役物演出決定テーブルとが含まれている。これらの高ベース中における上部役物演出決定テーブルは、演出制御基板80に設けられたROM102に記憶されている。
FIGS. 15C and 15D are diagrams showing an upper accessory effect determination table in the high base. In the upper base effect determination table in the high base, the upper base effect determination table at the time of high base medium hit in FIG. It is included. The upper accessory effect determination table in the high base is stored in the
図15(C)の高ベース中大当り時上部役物演出決定テーブルは、所定のタイミングで抽出したSR2の値によって、「第2パターン>実行なし」という大小関係となるようにデータが設定されており、第1パターンの上部役物演出に決定されることはない。図15(D)の高ベース中はずれ時上部役物演出決定テーブルは、所定のタイミングで抽出したSR2の値によることなく、100パーセントの割合で「実行なし」に決定されるようにデータが設定されている。つまり、高ベース中では、第2パターンによる上部役物演出が実行されることにより大当りが確定することになる。 In the upper base effect determination table at the time of high base middle and big hit in FIG. 15C, data is set so as to have a magnitude relationship of “second pattern> no execution” according to the value of SR2 extracted at a predetermined timing. Therefore, it is not determined to be the upper feature effect of the first pattern. The upper-compartment effect determination table at the time of high base deviation in FIG. 15D sets the data so that “no execution” is determined at a rate of 100% without depending on the value of SR2 extracted at a predetermined timing. Has been. In other words, during the high base, the big hit is determined by executing the upper feature effect by the second pattern.
図15(C),(D)でのデータの設定により、高ベース中においては、変動表示の表示結果が大当り表示結果となるときには、はずれ表示結果となるときと比べ、上部役物演出が実行される割合が高い。よって、高ベース中においても、通常遊技中と同様に、上部役物演出が実行される場合には、上部役物演出が実行されない場合よりも、遊技者の大当りに対する期待度を高めることができる。 15C and 15D, in the high base, when the display result of the variable display becomes the jackpot display result, the upper feature effect is executed compared to the case of the off-line display result. The rate that is done is high. Therefore, even during the high base, as in the normal game, when the upper role effect is executed, the player's expectation for the big hit can be increased as compared with the case where the upper role effect is not executed. .
また、図15(C),(D)でのデータの設定により、高ベース中においては、動作と報知との両方が実行される第1パターンの上部役物演出が実行されることはない。つまり、高ベース中において大当り遊技状態に制御されるときには、第2パターンにより上部役物を動作させる。よって、確変中や時短中等の大当りに制御されやすい高ベース状態では、報知を伴わない第2パターンによる上部役物演出を実行することによって、無駄な演出の実行を抑制することができる。 In addition, by setting the data in FIGS. 15C and 15D, the upper accessory effect of the first pattern in which both the operation and the notification are executed is not executed during the high base. That is, when the game is controlled to the big hit gaming state in the high base, the upper accessory is operated by the second pattern. Therefore, in a high base state that is easy to control for big hits such as during probability change and during a short time, it is possible to suppress the execution of useless effects by executing the upper accessory effect using the second pattern without notification.
このように、通常遊技状態における上部役物演出は、予告の1つとして可動体を動かす演出であり、高ベース状態中における上部役物演出は、予告というよりかは大当りの報知演出として可動体を動かす演出ということができる。つまり、高ベース状態中における上部役物演出は、大当り報知演出として大当り確定を示す期待度の高い演出である。このように、上部役物演出について予告と報知という関係で比較をすると、報知の方が期待度が高いということもできる。 As described above, the upper feature effect in the normal gaming state is an effect of moving the movable body as one of the notices, and the upper feature effect in the high base state is the movable object as a notification effect of the big hit rather than the notice. It can be said that the movement is moving. In other words, the upper feature effect in the high base state is a highly expected effect indicating the big hit notification as the big hit notification effect. As described above, when the upper feature effect is compared in the relationship of the notice and the notification, it can be said that the notification has a higher degree of expectation.
ここで、第1パターンによる上部役物演出と第2パターンによる上部役物演出とでは、設定された角度に対応する上部役物の動作態様は同じである。このようにすれば、上部役
物を動作させるときの制御の負担を軽減することができる。
Here, the operation mode of the upper feature corresponding to the set angle is the same in the upper feature effect by the first pattern and the upper feature effect by the second pattern. In this way, it is possible to reduce the control burden when operating the upper accessory.
なお、第1パターンによる上部役物演出と第2パターンによる上部役物演出とでは、上部役物の動作態様が全く同じものではなく動作が類似するようにしてもよい。ここで、類似とは一部が同じなど、共通点が多く存在することである。たとえば、類似として、動作速度、動作タイミング、動作の態様(動き方など)が多少違ってもよい。また、通常遊技状態と高ベース状態とで上部役物演出が実行されるときの上部役物の動作態様を異ならせてもよい。 It should be noted that the upper feature effect by the first pattern and the upper feature effect by the second pattern are not the same in the operation mode of the upper feature, and the operations may be similar. Here, “similar” means that there are many common points such as the same part. For example, similarly, the operation speed, the operation timing, and the operation mode (how to move, etc.) may be slightly different. In addition, the operation mode of the upper combination when the upper combination effect is executed in the normal gaming state and the high base state may be different.
次に、上部役物演出が実行されるときの演出の設定について説明する。図16は、演出設定処理を示すフローチャートである。図16においては、演出図柄変動開始処理(S801)における演出設定処理に含まれる各種の演出の設定に関する処理のうち、上部役物演出に関係する処理が示されている。演出設定処理において、演出制御用CPU101は、次のような処理を行なうことによって、上部役物演出で実行される各種演出を決定する。
Next, a description will be given of the setting of the effect when the upper accessory effect is executed. FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing the effect setting process. In FIG. 16, processing related to the upper feature effect among the processes related to the setting of various effects included in the effect setting process in the effect symbol variation start process (S801) is shown. In the effect setting process, the
演出制御用CPU101は、上部役物演出を制限するための上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされているか否かを判定する(S901)。演出制御用CPU101は、上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされていない場合(S901でN)には、S902へ移行する。一方、演出制御用CPU101は、上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされている場合(S901でY)には、その他の演出を決定し(S907)、処理を終了する。
The
S902では、演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動がスーパーリーチであるか否かを判定する。演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動がスーパーリーチである場合(S902でY)には、S903へ移行する。一方、演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動がスーパーリーチではない場合(S902でN)には、その他の演出を決定し(S907)、処理を終了する。
In S902, the
S903では、演出制御用CPU101は、現在の遊技状態が高ベース中であるか否かを判定する。演出制御用CPU101は、現在の遊技状態が高ベース中ではない場合(S903でN)には、S904へ移行する。一方、演出制御用CPU101は、現在の遊技状態が高ベース中である場合(S903でY)には、S908へ移行する。
In S903, the
S904では、演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動が大当りであるか否かを判定する。演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動が大当りである場合(S904でY)には、通常遊技中大当り時上部役物演出決定テーブルにより上部役物演出の内容を決定し(S905)、その他の演出を決定した後(S907)、処理を終了する。一方、演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動が大当りではない場合(S904でN)には、通常遊技中はずれ時上部役物演出決定テーブルにより上部役物演出の内容を決定し(S906)、その他の演出を決定した後(S907)、処理を終了する。
In S904, the
S908では、演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動が大当りであるか否かを判定する。演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動が大当りである場合(S908でY)には、高ベース中大当り時上部役物演出決定テーブルにより上部役物演出の内容を決定し(S909)、その他の演出を決定した後(S907)、処理を終了する。一方、演出制御用CPU101は、今回実行される変動が大当りではない場合(S908でN)には、高ベース中はずれ時上部役物演出決定テーブルにより上部役物演出の内容を決定し(S910)、その他の演出を決定した後(S907)、処理を終了する。
In S908, the
S901に示すように、上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされているときは、上部役物
演出の実行が制限される。このようにすれば、上部役物が遊技枠に対して突出しない回転角度に制御されているにも関わらず上部役物の動作に関連した演出(上部役物演出)を実行してしまい、遊技者に違和感を与えることを防止できる。
As shown in S901, when the upper feature effect restriction flag is set, execution of the upper feature effect is restricted. In this way, although the upper character is controlled at a rotation angle that does not protrude with respect to the game frame, the effect related to the operation of the upper character (upper character effect) is executed, and the game It can prevent a person from feeling uncomfortable.
[動作制御の変形例について]
次に上部役物における動作制御の変形例について説明する。原点検出を行なうことが必要な原点検出対象役物(動作対象役物)として第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rがある。第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rは、図示しない原点検出センサにより原点位置が検出可能である。なお、役物12を原点検出対象物として動作制御を行なってもよい。
[Modification of motion control]
Next, a modified example of the operation control in the upper accessory will be described. There are a first
ここで、動作エラー判定回数(たとえば3回)に達するまで繰返し動作対象役物を原点位置(初期位置)に移動させる動作を非検出時動作制御と称する。原点位置(初期位置)から一旦離れ、該原点位置(初期位置)から離れた位置から原点位置(初期位置)に戻るという動作を検出時動作プロセスデータに設定されている最低制御速度に基づく最低速度で行なう制御を検出時動作制御と称する。なお、原点位置から離れた位置とは、原点位置の近傍位置、つまり、各原点センサにより各上部役物の被検出部を検出できない位置であって各演出位置よりも原点位置に近い所定位置(検出時動作位置)として設定されている。実動作確認用プロセスデータに実動作確認用プロセスタイマのタイマカウント値に対応して設定されている制御速度にて動作対象役物を動作させることにより、動作対象役物の制御速度を、時系列的に順次変更して、上部役物による演出において当該上部役物を実際に動作させる際に設定する制御速度と同一の加速または減速を行なう制御を実動作確認用動作制御(ロング初期化動作制御)と称する。 Here, the operation of moving the subject to be repeatedly operated to the origin position (initial position) until reaching the operation error determination number (for example, 3 times) is referred to as non-detection operation control. The minimum speed based on the minimum control speed set in the operation process data at the time of detection of the operation of once returning from the origin position (initial position) and returning from the position away from the origin position (initial position) to the origin position (initial position) The control performed at is referred to as detection-time operation control. The position away from the origin position is a position in the vicinity of the origin position, that is, a position where the detected part of each upper accessory cannot be detected by each origin sensor, and is a predetermined position closer to the origin position than each effect position ( (Operating position at detection). By operating the target object at the control speed set in the actual operation confirmation process data corresponding to the timer count value of the actual operation confirmation process timer, the control speed of the target object is changed in time series. Control for actual operation confirmation (long initialization operation control) is performed in order to perform the same acceleration or deceleration as the control speed set when the upper accessory is actually operated in the production by the upper accessory. ).
上部役物の動作態様および制御内容について、図17、図18を用いて説明する。図17は、演出制御用CPU101が行なう非検出時動作制御、検出時動作制御および実動作確認用動作制御の動作態様を示す概略説明図である。図18は、(A)は実動作確認用動作制御における制御速度を示す説明図、(B)は検出時動作制御における制御速度を示す説明図、(C)は非検出時動作制御における制御速度を示す説明図である。
The operation mode and control contents of the upper accessory will be described with reference to FIGS. 17 and 18. FIG. 17 is a schematic explanatory diagram illustrating operation modes of non-detection operation control, detection operation control, and actual operation confirmation operation control performed by the
なお、図17および図18においては、原点検出対象役物である第1上部役物29Lおよび第2上部役物29Rにおける非検出時動作制御(ショート初期化動作制御)、検出時動作制御(ショート初期化動作制御)および実動作確認用動作制御(ロング初期化動作制御)についてのみ説明し、原点検出対象役物でない役物12についての説明は省略することとする。
In FIG. 17 and FIG. 18, non-detection operation control (short initialization operation control) and detection operation control (short) in the first
図17に示すように、第1上部役物29Lおよび第2上部役物29Rは、それぞれ原点位置(退避位置、初期位置)と演出位置との間で往復動作可能に設けられており、原点位置から演出位置への往動作や演出位置から原点位置への復動作は、上部役物演出等において実際に行なう実動作とされている。
As shown in FIG. 17, the first
演出制御用CPU101は、初期化処理を実行したときに上部役物の被検出部が原点検出センサにより検出されない場合、つまり、上部役物が何らかの理由(たとえば、搬送や遊技島への設置時に原点位置から動いてしまっている場合、前回の動作時に原点復帰できなかった場合(たとえば、演出の実行時において、モータの脱調、故障、引っ掛かりなどにより上部役物の原点復帰が確認できなかったり、動作できなくなるといった役物エラー(動作異常)が発生した場合など)、遊技機の振動により原点位置から動いてしまった場合など)により原点位置以外の位置(たとえば、図17における非検出時動作制御に対応する黒丸で示す位置など、原点位置と演出位置との間の所定位置)にある場合、原点復帰させるための非検出時動作制御を実行する。この非検出時動作制御を実行する場合、上部
役物は原点位置から離れた位置にあるため、動作としては上部役物を原点位置方向に移動させる動作のみとされている。
When the initialization control is executed, the
また、演出制御用CPU101は、初期化処理を実行したときに第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rの被検出部が原点検出センサにより検出された場合、検出時動作制御を実行する。
In addition, when the initialization processing is executed, the
たとえば、被検出部が原点検出センサにより確実に検出されるように、被検出部が原点検出センサにより検出されたときから上部役物の原点位置方向への動作が規制されるまでの間に所定の動作可能範囲(たとえば、遊び)が設定されている場合などにおいては、原点復帰して原点検出センサにより検出された位置よりもさらに奥側にずれた位置に停止することがある。よって、被検出部が原点検出センサにより検出されていても、上部役物をより正確な原点位置に復帰させるための検出時動作制御を行なう。 For example, in order to ensure that the detected part is detected by the origin detection sensor, a predetermined period between the time when the detected part is detected by the origin detection sensor and the operation of the upper accessory in the direction of the origin position is restricted. When an operable range (for example, play) is set, the origin may return and stop at a position shifted further to the back than the position detected by the origin detection sensor. Therefore, even when the detected part is detected by the origin detection sensor, the operation control during detection for returning the upper accessory to the more accurate origin position is performed.
この検出時動作制御は、原点検出センサによる被検出部の検出状態を一旦解除するために上部役物を原点位置から離れた位置へ移動させた後に原点位置に復帰させる必要があるが、演出位置まで移動させる必要はないので、上部役物を原点位置から該原点位置の近傍である検出時動作位置まで移動させた後、原点位置に復帰させる。つまり、実動作よりも短い距離で往復動作させる。 In this operation control at the time of detection, in order to temporarily cancel the detection state of the detected part by the origin detection sensor, it is necessary to move the upper accessory to a position away from the origin position and then return to the origin position. Therefore, the upper accessory is moved from the origin position to the operation position at the time of detection near the origin position, and then returned to the origin position. That is, the reciprocating operation is performed at a shorter distance than the actual operation.
また、演出制御用CPU101は、初期化処理において非検出時動作制御または検出時動作制御を実行した後、実動作確認用動作制御を実行する。実動作確認用動作制御は、上部役物が各種演出等において実際に行なう実動作と同一の動作とされている。
Further, the
次に、演出制御用CPU101が非検出時動作制御、検出時動作制御および実動作確認用動作制御を実行する際に設定する制御速度について比較する。なお、図18(A)、図18(B)、図18(C)にて示す速度は、演出制御用CPU101が各上部役物を動作させるために設定する制御速度であって、上部役物の実際の動作速度とは異なる。つまり、たとえば、所定の上部役物を動作させる場合において、原点位置と演出位置との間における一の移動区間と他の移動区間に同一の制御速度を設定した場合でも、一の移動区間と他の移動区間とで態様が異なる場合においては、上部役物を実際に動作させた場合の動作速度は制御速度とは異なることがある。また、上部役物に対し同一の制御速度を設定しても、各上部役物の大きさ、重量、動作態様、動作距離、駆動機構等の違いがある場合、各上部役物の実際の動作速度は必ずしも同一にはならない。複数の上部役物を同一性能のステッピングモータにて動作させる場合において、各上部役物に対し同一の制御速度を設定しても、各上部役物の大きさ、重量、動作態様、動作距離、駆動機構等の違いがある場合、各上部役物の実際の動作速度は必ずしも同一にはならない。
Next, the control speeds set when the
図18(A)に示すように、演出制御用CPU101は、実動作確認用動作制御を実行する場合、セットした実動作確認用プロセスデータにおいて実動作確認用プロセスタイマのタイマカウント値に対応して設定されている制御速度に基づいて確認対象役物を動作させる。具体的には、原点位置から加速した後に減速して演出位置に停止させるとともに、演出位置から加速した後に減速して原点位置に停止させる制御を行なう。すなわち、各上部役物が正常に動作可能であることを確認するための実動作確認用動作制御では、原点位置と演出位置との間において、上部役物の制御速度を低速→高速→低速の順に変化させる。つまり、演出制御用CPU101は、各上部役物の可動体演出を実行する場合、第1速度である最低速度(低速)と該最低速度よりも速い第2速度としての最高速度(高速)との範囲内の速度で各上部役物が動作するように制御するため、実動作確認用動作制御を実行する場合においても、第1速度である最低速度(低速)と該最低速度よりも速い第2速度としての最高速度(高速)との範囲内の速度で各上部役物が動作するように制御する。
As shown in FIG. 18A, when performing the actual operation check operation control, the
すなわち、上記第1速度としての最低速度や第2速度としての最高速度は、上部役物の実際の動作速度であって、該動作速度としての最低速度や最高速度となるように制御速度が設定されることになる。なお、以下においては、最低制御速度に基づいて上部役物を動作させた場合は最低速度にて動作し、最高制御速度に基づいて上部役物を動作させた場合は最高速度にて動作するものとして説明する。 That is, the minimum speed as the first speed and the maximum speed as the second speed are the actual operating speeds of the upper accessory, and the control speed is set to be the minimum speed and the maximum speed as the operating speed. Will be. In the following, when the upper character is operated based on the minimum control speed, it operates at the minimum speed, and when the upper character is operated based on the maximum control speed, it operates at the maximum speed. Will be described.
ここで、上部役物の加速時および減速時における動作速度が、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度となるように制御速度が設定されている。また、演出位置に移動した後に原点位置に復帰させる際においては、演出位置に停止させるときよりも長い時間にわたり実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度となるように制御することで、上部役物を確実に減速させてから原点検出センサにより被検出部が検出されるようにしている。 Here, the control speed is set so that the operation speed at the time of acceleration and deceleration of the upper accessory becomes the minimum speed in the action control for actual operation confirmation. In addition, when returning to the origin position after moving to the production position, by controlling so that it becomes the minimum speed in the operation control for actual operation confirmation over a longer time than when stopping at the production position, The detected portion is detected by the origin detection sensor after the vehicle is decelerated reliably.
図18(B)に示すように、演出制御用CPU101は、検出時動作制御を実行する場合、原点位置から演出位置まで移動させる期間および演出位置から原点位置まで移動させる期間において、常に実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度(第1速度)にて上部役物が動作するように制御する。つまり、演出制御用CPU101は、第1動作制御としての検出時動作制御における最高速度が、第2動作制御としての実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度以下の速度(実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度と同じ速度)となるように、常に実動作確認用動作制御において設定されている制御速度のうち最も低い最低制御速度に基づいて上部役物を動作させる制御を行なう。
As shown in FIG. 18B, when performing the motion control at the time of detection, the
また、検出時動作制御の場合、実動作確認用動作制御に比べて上部役物の動作距離が短いため、実動作確認用動作制御において加速したときの制御速度、つまり高速で動作させると、原点検出センサにて被検出部を確実に検出できなかったり、近距離から上部役物が原点位置に復帰して移動規制されたときの衝撃により上部役物等が破損したりする虞があるため、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度にて動作するように制御する。 In the case of detection-time operation control, the upper accessory has a shorter operating distance than the actual operation check operation control. There is a risk that the detected part cannot be reliably detected by the detection sensor, or the upper feature etc. may be damaged due to the impact when the upper feature returns to the origin position from a short distance and the movement is restricted, Control to operate at the minimum speed in the actual operation check operation control.
また、図18(C)に示すように、演出制御用CPU101は、非検出時動作制御を実行する場合、原点位置と演出位置との間の任意の位置から原点位置まで移動させる期間において、常に実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度(第1速度)にて動作するように制御する。つまり、演出制御用CPU101は、第1動作制御としての非検出時動作制御における最高速度(最大動作速度)が、第2動作制御としての実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度以下の速度(実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度と同じ速度)となるように、常に実動作確認用動作制御において設定されている制御速度のうち最も低い最低制御速度に基づいて上部役物を動作させる制御を行なう。
In addition, as shown in FIG. 18C, when performing the non-detection operation control, the
この場合、上部役物は原点位置からどの程度離れた位置にあるかが不明であるため、上部役物が原点位置の近傍に位置していた場合、実動作確認用動作制御において加速したときの制御速度、つまり高速で動作させると、上部役物が原点位置に復帰したときに原点検出センサにて被検出部を確実に検出できなかったり、近距離から上部役物が原点位置に復帰して移動規制されたときの衝撃により上部役物等が破損したりする虞があるため、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度にて動作するように制御する。 In this case, since it is unclear how far the upper character is located from the origin position, if the upper character is located in the vicinity of the origin position, When operating at a high speed, that is, when the upper feature returns to the origin position, the origin detection sensor cannot reliably detect the detected part, or the upper feature returns to the origin position from a short distance. Since there is a possibility that the upper accessory or the like may be damaged due to an impact when the movement is restricted, control is performed so as to operate at the minimum speed in the operation control for actual operation confirmation.
このように、演出制御用CPU101は、第1動作制御としての非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御を実行する場合、実動作確認用動作制御において設定されている最低制御速度に基づいて常に単一(一定)の動作速度で上部役物が動作するように制御を行なう。そしてこれら最低速度は、各上部役物に対応する実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度であり、各上部役物に共通する動作速度ではないので、各上部役物における最低速度は異なる場合がある。
As described above, when performing the non-detection operation control or the detection operation control as the first operation control, the
具体的には、第1上部役物29Lと第2上部役物29Rとは、大きさ、重量、動作態様、動作距離、駆動モータを含む駆動機構が各々異なるため、同一の制御速度を設定した場合でも上部役物の実際の動作速度は異なる。また、各上部役物に対し異なる制御速度を設定した場合においても上部役物の実際の動作速度は異なる。このように、最低速度は各上部役物に応じて設定された制御速度に基づく動作速度であり、上部役物に最適な最低速度にて動作するように制御するため、態様が異なる複数の上部役物を原点位置にて確実に検出させることが可能となる。
Specifically, since the first
以上説明したように、上部役物を動作させるための駆動手段としての第1上部役物モータ30L、第2上部役物モータ30Rによる上部役物の動作を制御する制御手段としての演出制御用CPU101と、を備え、演出制御用CPU101は、第1動作制御としての非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御と、上部役物が正常に動作可能であることを確認するための第2動作制御としての実動作確認用動作制御と、上部役物による上部役物演出を行なうための第3動作制御と、を実行可能であり、実動作確認用動作制御を実行する場合、第1速度である最低速度(低速)と該最低速度よりも速い第2速度としての最高速度(高速)との範囲内の速度で上部役物が動作するように制御し、非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御を実行する場合、第2動作制御としての実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度以下の速度で上部役物が動作するように制御する。
As described above, the
このようにすることで、第1動作制御において、上部役物はいかなるタイミングでも停止可能な速度で動作するため、安全に原点位置に位置させることができる。具体的には、非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御では、実動作確認用動作制御に比べて上部役物を原点位置まで移動させる距離が短い場合があるため、非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御における最高速度を、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度とすることで、被検出部を検出手段により確実に検出させることができるとともに、上部役物を高速で移動させたまま移動規制された衝撃で破損することを回避できる。 In this way, in the first operation control, the upper accessory operates at a speed that can be stopped at any timing, and thus can be safely positioned at the origin position. Specifically, in non-detection operation control and detection operation control, the distance to move the upper accessory to the origin position may be shorter than in actual operation confirmation operation control. By setting the maximum speed in hourly operation control to the minimum speed in action control for actual operation confirmation, the detected part can be reliably detected by the detection means and the movement restriction is performed while the upper accessory is moved at high speed. It is possible to avoid damage due to the impact applied.
なお、非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御を実行する際に、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度以下の速度で上部役物が動作するように制御する場合、非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御を実行する際に設定する制御速度と、実動作確認用動作制御において設定する最低制御速度とは同一の制御速度でもよいし異なる制御速度でもよい。 In addition, when performing non-detection operation control or detection operation control, if control is performed so that the upper actor operates at a speed equal to or lower than the minimum speed in the actual operation check operation control, non-detection operation control or detection The control speed set when executing the hourly operation control and the minimum control speed set in the action control for actual operation confirmation may be the same control speed or different control speeds.
また、演出制御用CPU101は、非検出時動作制御および検出時動作制御を実行する場合、常に予め設定された単一(一定)の動作速度、つまり、常に実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度にて第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rが動作するように制御してもよい。
Further, when executing the non-detection operation control and the detection operation control, the
このようにすることで、第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rを原点位置に位置させる際の速度を一定とすることができ、第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rの破損等を防ぐことができる。
By doing in this way, the speed at the time of positioning the 1st
また、演出制御用CPU101は、非検出時動作制御および検出時動作制御を実行する場合、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度(第1速度)にて第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rが動作するように制御してもよい。
Further, when performing the non-detection operation control and the detection operation control, the
このようにすることで、第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rの安全動作を確保しつつ、過度に速度を下げる(たとえば、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度よりも遅い速度とするなど)ことなく安全に動作できる最高速度(第1速度)を選択することで、非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御の期間を短縮することができる。
By doing so, the speed is excessively lowered while ensuring the safe operation of the first
また、第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rが原点位置に位置していることを検出可能な検出手段としての原点検出センサを備え、演出制御用CPU101は、原点検出センサが検出状態ではない場合は非検出時動作制御を実行し、原点検出センサが検出状態である場合は検出時動作制御を実行し、非検出時動作制御を実行する場合、検出時動作制御における最低速度で上部役物が動作するように制御してもよい。
In addition, an origin detection sensor is provided as a detecting means capable of detecting that the first
このようにすることで、非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御によって、原点検出センサの不具合の有無も把握することができる。また、非検出時動作制御を実行する場合は、上部役物が原点位置の近くにあるか否かが不明であるのに対し、検出時動作制御を実行する場合は、上部役物は原点位置にあることため、検出時動作制御においては、非検出時動作制御よりも速い速度であって、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度以下の速度で動作するようにしてもよい。 By doing in this way, the presence or absence of a defect of the origin detection sensor can be grasped by non-detection operation control or detection operation control. In addition, when performing non-detection operation control, it is unclear whether or not the upper accessory is near the origin position, whereas when performing detection operation control, the upper accessory is at the origin position. Therefore, the operation control at the time of detection may be performed at a speed faster than the operation control at the time of non-detection, which is lower than the minimum speed in the operation control for actual operation confirmation.
また、演出制御用CPU101は、特定の異常(たとえば、演出の実行時に発生した動作異常など)が発生している場合において、原点検出センサが検出状態でない場合、動作エラー判定回数が「3」に達するまで、実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度にて第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rが原点位置方向へ向けて移動するように制御してもよい。
Further, the
このようにすることで、特定の異常(たとえば、演出の実行時に発生した動作異常などのエラー)が発生している場合に実行される異常時動作においても、第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rを安全に動作させることができる。具体的には、たとえば、演出の実行時に動作異常が発生した場合、その後に初期化処理が行われるときは、上部役物は原点位置に復帰していないため、非検出時動作制御が実行されることになる。また、動作異常が発生した場合、初期化処理においても上部役物は動作しないことが考えられるため、異常時動作として実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度にて第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rが原点位置方向へ向けて動作するように制御する。
By doing in this way, even in the operation at the time of abnormality that is executed when a specific abnormality (for example, an error such as an operation abnormality that occurred during the performance) has occurred, the first
また、演出制御用CPU101は、当該対象役物の原点復帰エラーの記憶が有る場合、実動作確認用動作制御を行わないようにしてもよい。
Further, the
このようにすることで、異常によって第1上部役物29Lや第2上部役物29Rが実動作確認用動作制御中に原点位置以外で停止してしまうことを防ぐことができる。具体的には、たとえば、演出の実行時に動作異常が発生した場合、初期化処理においても上部役物は動作しないことが考えられるため、その場合は実動作確認用動作制御を実行しても駆動手段に負荷がかかるだけで無駄になるため、実動作確認用動作制御は実行しないことが好ましい。
By doing so, it is possible to prevent the first
また、上部役物として第1上部役物29Lおよび第2上部役物29Rを有し、演出制御用CPU101は、上部役物が原点検出を行なうことが必要な原点検出対象役物であると判定した場合、非検出時動作制御または検出時動作制御と実動作確認用動作制御とを実行する一方、上部役物が原点検出を行なうことが必要な原点検出対象役物でないと判定した場合、非検出時動作制御と検出時動作制御とを行わないようにしてもよい。
Moreover, it has the 1st
このようにすることで、必要な上部役物だけ実動作確認用動作制御を行なうことができ、実動作確認用動作制御による動作確認時間を短縮することができる。 By doing in this way, the operation control for actual operation confirmation can be performed only for the necessary upper accessory, and the operation confirmation time by the operation control for actual operation confirmation can be shortened.
また、演出制御用CPU101は、第1上部役物29Lと第2上部役物29Rの各々の第1動作としての非検出時動作制御や検出時動作制御を実行する場合、各々の実動作確認
用動作制御における最低速度にて上部役物が動作するように制御し、実動作確認用動作制御の動作速度は、第1上部役物29Lと第2上部役物29Rとで異なるようにしてもよい。
In addition, when performing the non-detection operation control or the detection operation control as the first operation of each of the first
このようにすることで、各々の上部役物に応じた動作速度によって各上部役物の安全動作を確保しつつ、非検出時動作制御および検出時動作制御の期間を短縮することができる。たとえば、第1上部役物29Lと第2上部役物29Rとにおいて、実動作確認用動作制御において同一の制御速度を設定しても、各上部役物の大きさ、重量、動作態様、動作距離、駆動機構等の違いがある場合、非検出時動作制御および検出時動作制御を実行した場合の各上部役物の実際の動作速度は異なることになる。
By doing in this way, the period of non-detection operation control and detection operation control can be shortened, ensuring the safe operation of each upper accessory by the operation speed according to each upper accessory. For example, even if the same control speed is set in the operation control for actual operation confirmation in the first
具体的には、非検出時動作制御および検出時動作制御において、同一の制御速度(実動作確認用動作制御において設定されている最低制御速度)を設定した場合でも、複数の上部役物のうち重量が大きい上部役物の実際の動作速度は、重量が小さい上部役物の実際の動作速度よりも遅くなる。また、上部役物を上昇させる場合、下降させる場合に比べて実際の動作速度は遅くなる。また、駆動機構として可動部を演出方向に付勢するバネ等が設けられている場合、バネが縮んでいる状態で付勢力に抗する方向に移動させる場合、バネが伸びている状態で付勢力に抗する方向に移動させる場合に比べて実際の動作速度は遅くなる。このように、非検出時動作制御および検出時動作制御において、上部役物を実動作確認用動作制御における最低速度以下の速度で上部役物が動作するように制御する場合、各上部役物の大きさ、重量、動作態様、動作距離、駆動機構等を考慮して、各々の実動作確認用動作制御において個別の最低制御速度を設定することが好ましい。 Specifically, in the non-detection operation control and the detection operation control, even when the same control speed (the minimum control speed set in the actual operation confirmation operation control) is set, The actual operation speed of the upper character having a large weight is slower than the actual operation speed of the upper character having a small weight. Further, when the upper accessory is raised, the actual operation speed is slower than when the upper accessory is lowered. In addition, when a spring or the like that biases the movable part in the effect direction is provided as the drive mechanism, when the spring is contracted and moved in a direction against the biasing force, the biasing force is in a state where the spring is extended. The actual operation speed is slower than when moving in a direction against the above. As described above, in the non-detection operation control and the detection operation control, when the upper accessory is controlled to operate at a speed lower than the minimum speed in the actual operation confirmation operation control, In consideration of size, weight, operation mode, operation distance, drive mechanism, etc., it is preferable to set an individual minimum control speed in each operation control for actual operation confirmation.
たとえば、第1可動部と第2可動部とが、原点位置に向けて移動する際に遊技者から見たときに第1可動部の手前側に第2可動部が重なるように前後に配置されるものにおいて、非検出時動作制御、検出時動作制御および実動作確認用動作制御のいずれかを実行する際に、第1可動部および第2可動部双方の動作制御を一緒に行なう場合、第1可動部と第2可動部の動作速度(最低速度)が異なるように制御することが好ましい。このようにすることで、仮に、第1可動部と第2可動部とが何らかの理由でそれぞれ原点位置から離れた位置まで移動した状態で電源がオン状態とされ、初期化処理において第1可動部および第2可動部双方の非検出時動作制御が一緒に実行される場合において、第1可動部および第2可動部双方の動作速度(最低速度)が同一になるように制御されると、第2可動部により第1可動部が隠れて原点位置へ移動する状況が見え難くなるが、第1可動部と第2可動部の最低速度が異なるように制御することで、第1可動部と第2可動部とが移動する際にずれていくので、第1可動部および第2可動部各々の原点復帰動作を確認しやすくなる。 For example, the first movable part and the second movable part are arranged at the front and back so that the second movable part overlaps the front side of the first movable part when viewed from the player when moving toward the origin position. When performing any one of the non-detection operation control, the detection operation control, and the actual operation confirmation operation control, when performing the operation control of both the first movable portion and the second movable portion together, It is preferable to control the operation speed (minimum speed) of the first movable part and the second movable part to be different. By doing in this way, if the first movable part and the second movable part are moved to a position away from the origin position for some reason, the power is turned on, and the first movable part in the initialization process When the non-detection operation control of both the second movable part and the second movable part is executed together, if the operation speed (minimum speed) of both the first movable part and the second movable part is controlled to be the same, Although it is difficult to see the situation where the first movable part is hidden by the two movable parts and moved to the origin position, the first movable part and the second movable part are controlled by controlling the minimum speeds of the first movable part and the second movable part to be different. Since the two movable parts shift when they move, it is easy to confirm the origin return operation of each of the first movable part and the second movable part.
また、第1可動部と、該第1可動部よりも大きい(あるいは長い)第2可動部とを有する場合においても、第1可動部と第2可動部の動作速度(最低速度)が異なるように制御することが好ましい。このようにすることで、たとえば、第2可動部よりも小さい(あるいは短い)ので目立たない第1可動部の非検出時動作制御、検出時動作制御および実動作確認用動作制御のいずれかにおける最低速度が、第1可動部よりも大きい(あるいは長い)ので目立つ第2可動部の非検出時動作制御、検出時動作制御および実動作確認用動作制御のいずれかにおける最低速度よりも遅くすることで、第1可動部および第2可動部それぞれの動作を確認しやすくなる。 Further, even when the first movable part and the second movable part larger (or longer) than the first movable part are included, the operation speed (minimum speed) of the first movable part and the second movable part is different. It is preferable to control. By doing so, for example, the minimum in any one of the non-detection operation control, the detection operation control, and the actual operation confirmation operation control of the first movable unit which is smaller (or shorter) than the second movable unit and is not noticeable. Since the speed is larger (or longer) than the first movable part, the speed is made slower than the minimum speed in any of the non-detection operation control, detection operation control and actual operation confirmation operation control of the second movable part. It becomes easy to confirm the operation of each of the first movable part and the second movable part.
このように、第1可動部と該第1可動部とは異なる第2可動部とを有する場合において、第1可動部と第2可動部それぞれの非検出時動作制御、検出時動作制御および実動作確認用動作制御における動作速度(最低速度)が異なるように制御することが好ましい。なお、このように第1可動部と第2可動部の動作速度(最低速度)が異なるように制御する
場合、第1可動部と第2可動部それぞれの非検出時動作制御、検出時動作制御および実動作確認用動作制御において設定する最低制御速度は異なっていてもよいし、同一でもよい。
As described above, when the first movable portion and the second movable portion different from the first movable portion are provided, the non-detection operation control, the detection operation control, and the actual operation of the first movable portion and the second movable portion, respectively. It is preferable to perform control so that the operation speed (minimum speed) in the operation control for operation confirmation is different. In addition, when controlling so that the operation speed (minimum speed) of the 1st movable part and the 2nd movable part differs in this way, operation control at the time of non-detection and operation control at the time of detection of the 1st movable part and the 2nd movable part, respectively And the minimum control speed set in the operation control for actual operation confirmation may be different or the same.
次に、前述した実施の形態により得られる主な効果を説明する。
(1) 図15に示すように、上部役物演出として第1パターンと第2パターンとでは、大当り遊技状態に制御される期待度が異なる。具体的に通常遊技中においては、上部役物演出として第1パターンが実行されたときの方が第2パターンが実行されたときよりも大当り期待度が高い。このようにすれば、第1パターンまたは第2パターンのいずれで上部役物が動作されるかにより大当り遊技状態に制御される期待度が異なるため、遊技枠に設けられた可動体を用いた演出の興趣を向上させることができる。また、第1パターンが実行されることに対する期待感を高めることができる。
Next, main effects obtained by the embodiment described above will be described.
(1) As shown in FIG. 15, the degree of expectation controlled to the big hit gaming state is different between the first pattern and the second pattern as the upper feature effect. Specifically, during the normal game, the big hit expectation is higher when the first pattern is executed as the upper feature effect than when the second pattern is executed. In this way, the degree of expectation that is controlled in the big hit game state differs depending on whether the upper character is operated in the first pattern or the second pattern, so the effect using the movable body provided in the game frame Can improve the interest of In addition, it is possible to increase expectation for the execution of the first pattern.
(2) 第1パターンと第2パターンとで上部役物を同じ動作とする。このようにすれば、可動体を動作させるときの制御の負担を軽減することができる。 (2) The upper feature is operated in the same manner in the first pattern and the second pattern. In this way, the control burden when operating the movable body can be reduced.
(3) 図14に示すように、演出表示装置9の画面において、上部役物が動作していることを示す報知画像96を表示する。このようにすれば、可動体を動作していることを確実に遊技者に報知することができる。
(3) As shown in FIG. 14, on the screen of the
(4) 図15に示すように、高ベース中において大当り遊技状態に制御されるときには、第2パターンにより上部役物を動作させる。このようにすれば、大当り遊技状態に制御されやすい高ベース状態では、第2パターンにより可動体の動作を制御することによって無駄な演出の実行を抑制することができる。 (4) As shown in FIG. 15, when the big hit gaming state is controlled in the high base, the upper accessory is operated by the second pattern. If it does in this way, in the high base state which is easy to be controlled to the big hit game state, execution of useless effects can be suppressed by controlling the operation of the movable body by the second pattern.
(5) 図14に示すように、演出表示装置9の画面において、上部役物が動作していることを示す報知画像96を表示する際に枠LED28による演出は表示しない。このようにすれば、枠LED28による演出を含めずに上部役物演出が実行されるので、当該上部役物演出による可動体の動作をより目立たせることができる。
(5) As shown in FIG. 14, the effect by the
(6) 図12のS752に示すように、設定された角度に応じて、第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rの回転角度・回転速度を設定する。このようにすれば、遊技枠に設けられた軸290に対して回転する可動体を動作させつつ、可動体が他の物体と当接することを防ぐことができる。
(6) As shown in S752 of FIG. 12, the rotation angle and rotation speed of the first
(7) 図16のS901に示すように、上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされているときは、上部役物演出の実行を制限する。このようにすれば、可動体が遊技枠に対して突出しない回転角度(0度)に制御されているにも関わらず可動体の動作に関連した演出を実行してしまい、遊技者に違和感を与えることを防止できる。 (7) As shown in S901 of FIG. 16, when the upper feature effect restriction flag is set, execution of the upper feature effect is restricted. In this way, although the movable body is controlled at a rotation angle (0 degree) that does not protrude with respect to the game frame, an effect related to the operation of the movable body is executed, and the player feels uncomfortable. It can prevent giving.
(8) 図2に示すように、上部役物の回転角度を段階的に調整可能である。このようにすれば、無段階で調整することによる制御の複雑化を防止することができる。 (8) As shown in FIG. 2, the rotation angle of the upper accessory can be adjusted stepwise. In this way, it is possible to prevent complication of control due to stepless adjustment.
(9) 初期状態においては、90度よりも突出しない角度に制御する。このようにすれば、調整をしていない場合であっても可動体が他の物体と当接することを防ぐことができる。 (9) In the initial state, the angle is controlled so as not to protrude more than 90 degrees. In this way, it is possible to prevent the movable body from coming into contact with other objects even when adjustment is not performed.
(10) 上部役物の回転角度によって回転速度を異ならせる。このようにすれば、可動体が動作するときに実行される演出の演出時間を共通化することができる。 (10) Vary the rotation speed depending on the rotation angle of the upper part. If it does in this way, the production time of the production performed when a movable body operates can be made common.
(11) 発光手段としての第1上部LED29A,第2上部LED29Bは、上部役物の回転角度によらず同一の輝度で発光する。このようにすれば、発光手段の制御の複雑化を防止することができる。
(11) The first
次に、以上に説明した実施の形態の変形例や特徴点等を以下に列挙する。
(1) 前述した実施の形態では、上部役物演出として動作+報知の第1パターンと動作のみの第2パターンとが設けられていた。第2パターンによる上部役物演出が実行されるときには、演出表示装置9の画面において、上部役物が動作していることを示す報知画像96を表示するのではなく、別の演出(上部役物の動作を示さないような別の画像による演出)が実行されるようにしてもよい。また、上部役物を遊技状態の切替り(大当りに制御されるとき)や演出の切替り(スーパーリーチへの発展時)等のタイミングに関連して動作するようにしてもよい。
Next, modifications, feature points, and the like of the embodiment described above are listed below.
(1) In the above-described embodiment, the first pattern of motion + notification and the second pattern of motion only are provided as the upper feature effect. When the upper character effect by the second pattern is executed, the screen of the
(2) 前述した実施の形態では、発光手段としての第1上部LED29A,第2上部LED29Bは、上部役物の回転角度(動作角度)によらず同一の輝度で発光する場合について説明した。しかしながら、回転角度と輝度とが対応しているようにしてもよい。たとえば、角度が45度のときは輝度が小、角度が60度のときは輝度が中、角度が90度のときは輝度が大となるようにしてもよい。また、逆に回転角度が狭い程、輝度を強めるようにしてもよい。このようにすれば、光が見え難くなることを防ぐことができる。
(2) In the above-described embodiment, the case where the first
(3) 前述した実施の形態では、役物の取付け位置として、遊技枠の上部について説明した。しかし、役物は、遊技枠の上部以外の位置に配置されるようにしてもよい。たとえば、遊技枠の側面、正面、下部等の位置に配置されるようにしてもよい。 (3) In embodiment mentioned above, the upper part of the game frame was demonstrated as an attachment position of an accessory. However, the accessory may be arranged at a position other than the upper part of the game frame. For example, you may make it arrange | position in positions, such as the side of a game frame, a front, and a lower part.
(4) 前述した実施の形態では、通常遊技状態において、動作+報知の第1パターンの方が動作のみの第2パターンよりも大当り期待度が高い場合について説明した。しかしながら、第2パターンの方が第1パターンよりも大当り期待度が高くなるようにしてもよい。また、高ベース状態において第1パターンにより上部役物演出が実行されるようにしてもよいし、第1パターンと第2パターンとで大当り期待度が異なるようにしてもよい。 (4) In the above-described embodiment, in the normal gaming state, the case where the first pattern of motion + notification has a higher jackpot expectation than the second pattern of only motion has been described. However, the second pattern may have a higher jackpot expectation than the first pattern. Further, the upper role effect may be executed by the first pattern in the high base state, or the big hit expectation may be different between the first pattern and the second pattern.
(5) 前述した実施の形態では、上部役物演出の第1パターンとして、上部役物が動作していることを示す動画を再生する報知について説明した。当該報知は、上部役物実物の動画や画像であってもよいし、実物を模した絵やCGなどであってもよい。 (5) In the above-described embodiment, the notification for reproducing the moving image indicating that the upper accessory is operating has been described as the first pattern of the upper accessory effect. The notification may be a moving picture or image of the real upper part, or a picture or CG imitating the real thing.
(6) 前述した実施の形態では、上部役物演出の実行時に上部役物以外の役物12やプッシュボタン120等の操作手段を動作させたり、発光させたりする演出を実行してもよい。このような場合であっても、上部役物が動作していることを示す報知画像96を表示する際に、役物12や操作手段による演出が実行されることを示す表示をしない方が望ましい。
(6) In the above-described embodiment, when executing the upper accessory effect, an effect may be executed in which operation means such as the
(7) 前述した実施の形態では、上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされているときは、上部役物演出の実行が制限されていた(実行されることがない禁止状態であった)。しかし、上部役物演出制限フラグがセットされているときは、上部役物演出に替えて代替演出が実行されるようにしてもよい。 (7) In the above-described embodiment, when the upper feature effect restriction flag is set, the execution of the upper feature effect is restricted (it is a prohibited state that is not executed). However, when the upper character effect restriction flag is set, an alternative effect may be executed instead of the upper character effect.
(8) 前述した実施の形態では、第1上部役物29L,第2上部役物29Rのように複数の可動体(役物)が設けられていた。このような可動体は、別々に動作の設定が実行できるようにしてもよい。
(8) In the above-described embodiment, a plurality of movable bodies (combinations) are provided, such as the first
(9) 前述した実施の形態では、初期状態(最初に電源投入した場合やRAMクリア
による電源投入の場合)においては、上部役物の回転角度が遊技枠に対して最も突出する回転角度である90度よりも突出しない角度(たとえば、45度)になるように制御される場合を説明した。しかしながら、90度まで全開放できる遊技店であるにも関わらず新たな設定をしない場合には、45度の角度に設定されていることに気付かずに使い続けてしまうことも想定される。そこで、パチンコ遊技機1の起動時に現在の回転角度を演出表示装置9の画面上で報知することが望ましい。このようにすれば、遊技場の店員は、現在の上部役物の回転角度を容易に把握することができる。
(9) In the above-described embodiment, in the initial state (when power is turned on for the first time or when power is turned on by RAM clear), the rotation angle of the upper accessory is the rotation angle that protrudes most with respect to the game frame. A case has been described in which the angle is controlled so as not to protrude more than 90 degrees (for example, 45 degrees). However, even though the game store can be fully opened up to 90 degrees, if it is not newly set, it may be assumed that it will continue to be used without noticing that the angle is set to 45 degrees. Therefore, it is desirable to notify the current rotation angle on the screen of the
(10) 前述した実施の形態に示した各種制御は、メダルが投入されて所定の賭け数が設定され、遊技者による操作レバーの操作に応じて複数種類の図柄を回転させ、遊技者によるストップボタンの操作に応じて表示手段における図柄を停止させたときに停止図柄の組合せが特定の図柄の組合せになると、所定数のメダルが遊技者に払出されるスロットマシン(スロット機)に適用することも可能である。スロットマシンにおいては、ビッグボーナス(BB)、レギュラーボーナス(RB)、といったボーナス、また内部抽選結果を報知する演出を実行するAT、通常遊技状態と比較して再遊技役の当選確率が異なるRT、ATとRTとに移行されたARTへの制御を示す演出として前述した上部役物演出を実行するようにしてもよい。たとえば、AT等に当選した契機(はずれの場合のガセ演出も含む)で上部役物演出を実行し、AT中においては、動作のみによる演出が実行されるようにしてもよい。 (10) In the various controls shown in the above-described embodiment, medals are inserted and a predetermined bet number is set, and a plurality of types of symbols are rotated in accordance with the operation of the operation lever by the player, and the stop by the player When the symbols on the display means are stopped according to the operation of the button, and the combination of the symbols to be stopped is a specific symbol combination, this is applied to a slot machine (slot machine) in which a predetermined number of medals are paid out to the player. Is also possible. In the slot machine, a bonus such as a big bonus (BB), a regular bonus (RB), an AT for performing an effect for notifying an internal lottery result, an RT in which the winning probability of the re-gamer is different from the normal gaming state, The above-described upper accessory effect may be executed as an effect indicating the control to the ART shifted to the AT and the RT. For example, an upper accessory effect may be executed at an opportunity won by an AT or the like (including a gasse effect in the case of a loss), and an effect based only on an operation may be executed during an AT.
(11) 前述した実施の形態では、遊技店員ではなく遊技者が上部役物の回転角度や輝度を調整できるようにしてもよい。このような場合には、変動表示中ではない状態で操作手段を操作することでメニュー画面を表示し、上部役物の回転角度等を設定できるようにすることが望ましい。なお、変動中に上部役物の回転角度や輝度が設定できるようにしてもよい。 (11) In the above-described embodiment, a player, not a game store clerk, may be able to adjust the rotation angle and brightness of the upper accessory. In such a case, it is desirable to display the menu screen by operating the operating means in a state where the variation display is not being performed so that the rotation angle of the upper accessory can be set. In addition, you may enable it to set the rotation angle and brightness | luminance of an upper accessory during a fluctuation | variation.
(12) 前述した実施の形態では、遊技者にとって有利な有利状態として、大当り遊技状態を代表例として説明した。しかし、これに限らず、遊技者にとって有利な有利状態としては、高確率状態(確変状態)、時短状態、および、高ベース状態等のその他の有利状態が含まれてもよい。 (12) In the embodiment described above, the big hit gaming state has been described as a representative example as an advantageous state advantageous to the player. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and advantageous states that are advantageous to the player may include other advantageous states such as a high probability state (probability variation state), a short time state, and a high base state.
(13) 本実施の形態として、入賞の発生に応じて遊技媒体を遊技者の手元に払い出す遊技機を説明したが、遊技媒体が封入され、入賞の発生に応じて遊技媒体を遊技者の手元に払い出すことなく遊技点(得点)を加算する封入式の遊技機を採用してもよい。封入式の遊技機には、遊技媒体の一例となる複数の玉を遊技機内で循環させる循環経路が形成されているとともに、遊技点を記憶する記憶部が設けられており、玉貸操作に応じて遊技点が記憶部に加算され、玉の発射操作に応じて遊技点が記憶部から減算され、入賞の発生に応じて遊技点が記憶部に加算されるものである。 (13) As the present embodiment, a gaming machine that pays out game media to the player's hand in response to the occurrence of a win has been described, but the game media is enclosed and the game media is You may employ | adopt the enclosure type game machine which adds a game point (score), without paying out at hand. The enclosed game machine has a circulation path for circulating a plurality of balls, which are examples of game media, in the game machine, and is provided with a storage unit for storing game points. The game points are added to the storage unit, the game points are subtracted from the storage unit according to the ball launching operation, and the game points are added to the storage unit according to the occurrence of the winning.
(14) 前述した実施の形態では、たとえば「1」〜「9」の複数種類の特別図柄や演出図柄を変動表示し表示結果を導出表示する場合を示したが、変動表示は、そのような態様にかぎられない。たとえば、変動表示される図柄と導出表示される図柄とが必ずしも同じである必要はなく、変動表示された図柄とは異なる図柄が導出表示されるものであってもよい。また、必ずしも複数種類の図柄を変動表示する必要はなく、1種類の図柄のみを用いて変動表示を実行するものであってもよい。この場合、たとえば、その1種類の図柄表示を交互に点灯および点滅を繰り返すことによって、変動表示を実行するものであってもよい。そして、この場合であっても、その変動表示に用いられる1種類の図柄が最後に導出表示されるものであってもよいし、その1種類の図柄とは異なる図柄が最後に導出表示されるものであってもよい。 (14) In the above-described embodiment, for example, a case where a plurality of types of special symbols and production symbols “1” to “9” are variably displayed and the display result is derived and displayed is shown. It is not limited to the embodiment. For example, the symbol that is variably displayed and the symbol that is derived and displayed are not necessarily the same, and a symbol that is different from the symbol that is variably displayed may be derived and displayed. Further, it is not always necessary to display a plurality of types of symbols in a variable manner, and the variable display may be executed using only one type of symbols. In this case, for example, the variable display may be performed by alternately lighting and blinking the one type of symbol display. Even in this case, one type of symbol used for the variation display may be derived and displayed last, or a symbol different from the one type of symbol may be derived and displayed last. It may be a thing.
(15) 前述した実施の形態では、「割合(比率、確率)」として、0%を越える所定の値を具体例に挙げて説明した。しかしながら、「割合(比率、確率)」としては、0%であってもよい。たとえば、所定の遊技期間における所定の遊技状態1の発生割合と他の遊技状態2との発生割合とを比較して、「一方の発生割合が他方の発生割合よりも高い」とした場合には、一方の遊技状態の発生割合が0%の場合も含んでいる。
(15) In the above-described embodiment, the “ratio (ratio, probability)” has been described using a specific value exceeding 0% as a specific example. However, the “ratio (ratio, probability)” may be 0%. For example, when the occurrence ratio of a
(16) 前述した実施の形態では、変動表示の表示結果を確変大当りとすることが決定されたときの変動表示結果が導出表示された後、大当り遊技状態の終了後に、無条件で確変状態に制御される確変状態制御例を示した。しかし、これに限らず、特別可変入賞球装置20における大入賞口内に設けられた特定領域を遊技球が通過したことが検出手段により検出されたときに、確変状態に制御される、確変判定装置タイプの確変状態制御が実行されるようにしてもよい。
(16) In the embodiment described above, after the variable display result when the display result of the variable display is determined to be a probable big hit is derived and displayed, after the big hit gaming state ends, the probable state is unconditionally changed. An example of controlled probability state control is shown. However, the present invention is not limited to this, and the probability variation determination device that is controlled to the probability variation state when the detection means detects that the game ball has passed through a specific area provided in the special winning opening in the special variable winning
(17) なお、今回開示された実施の形態はすべての点で例示であって制限的なものではないと考えられるべきである。本発明の範囲は上記した説明ではなく特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内でのすべての変更が含まれることが意図される。 (17) The embodiment disclosed this time should be considered as illustrative in all points and not restrictive. The scope of the present invention is defined by the terms of the claims, rather than the description above, and is intended to include any modifications within the scope and meaning equivalent to the terms of the claims.
1 パチンコ遊技機、9 演出表示装置、29L 第1上部役物、29R 第2上部役物、100 演出制御用マイクロコンピュータ、560 遊技制御用マイクロコンピュータ。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
遊技枠に設けられた軸に対して回転することで当該遊技枠から突出可能な可動体と、
前記可動体の回転角度を調整することで前記可動体の動作を制御可能な制御手段とを備える、遊技機。 A gaming machine capable of playing games,
A movable body capable of projecting from the game frame by rotating about an axis provided in the game frame;
A gaming machine comprising control means capable of controlling an operation of the movable body by adjusting a rotation angle of the movable body.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017103192A JP2018196656A (en) | 2017-05-25 | 2017-05-25 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017103192A JP2018196656A (en) | 2017-05-25 | 2017-05-25 | Game machine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018196656A true JP2018196656A (en) | 2018-12-13 |
| JP2018196656A5 JP2018196656A5 (en) | 2019-01-31 |
Family
ID=64663744
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017103192A Pending JP2018196656A (en) | 2017-05-25 | 2017-05-25 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2018196656A (en) |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009273905A (en) * | 2009-07-24 | 2009-11-26 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2011188909A (en) * | 2010-03-12 | 2011-09-29 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
| JP2011206182A (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2011-10-20 | Kyoraku Sangyo Kk | Button operation mechanism and game machine equipped with the same |
| JP2012223217A (en) * | 2011-04-15 | 2012-11-15 | Kyoraku Sangyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2013132533A (en) * | 2011-12-27 | 2013-07-08 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2013252213A (en) * | 2012-06-06 | 2013-12-19 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2014033707A (en) * | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-24 | Sophia Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2015089403A (en) * | 2013-11-05 | 2015-05-11 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
| JP2017000420A (en) * | 2015-06-10 | 2017-01-05 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2017055826A (en) * | 2015-09-14 | 2017-03-23 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
-
2017
- 2017-05-25 JP JP2017103192A patent/JP2018196656A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009273905A (en) * | 2009-07-24 | 2009-11-26 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2011188909A (en) * | 2010-03-12 | 2011-09-29 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
| JP2011206182A (en) * | 2010-03-29 | 2011-10-20 | Kyoraku Sangyo Kk | Button operation mechanism and game machine equipped with the same |
| JP2012223217A (en) * | 2011-04-15 | 2012-11-15 | Kyoraku Sangyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2013132533A (en) * | 2011-12-27 | 2013-07-08 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2013252213A (en) * | 2012-06-06 | 2013-12-19 | Sankyo Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2014033707A (en) * | 2012-08-07 | 2014-02-24 | Sophia Co Ltd | Game machine |
| JP2015089403A (en) * | 2013-11-05 | 2015-05-11 | 株式会社ソフイア | Game machine |
| JP2017000420A (en) * | 2015-06-10 | 2017-01-05 | 株式会社三共 | Game machine |
| JP2017055826A (en) * | 2015-09-14 | 2017-03-23 | 京楽産業.株式会社 | Game machine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6679533B2 (en) | Amusement machine | |
| JP2020068783A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6577445B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018068610A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019005128A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018149238A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018094306A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018099448A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6674919B2 (en) | Gaming machine | |
| JP2019022603A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018149240A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019013389A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6633582B2 (en) | Gaming machine | |
| JP6611270B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6839317B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019051180A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019051182A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019037432A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019037433A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018192189A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019022604A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018196655A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018068612A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2018196656A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2019037434A (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180620 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20181129 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190319 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20190328 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190520 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20191008 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20191206 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20200428 |