JP2015029461A - Imaging device - Google Patents
Imaging device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2015029461A JP2015029461A JP2013161165A JP2013161165A JP2015029461A JP 2015029461 A JP2015029461 A JP 2015029461A JP 2013161165 A JP2013161165 A JP 2013161165A JP 2013161165 A JP2013161165 A JP 2013161165A JP 2015029461 A JP2015029461 A JP 2015029461A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- imaging
- biological sample
- imaging device
- light source
- imaging apparatus
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Apparatus Associated With Microorganisms And Enzymes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、撮像装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an imaging apparatus.
近年の生物学研究、創薬研究、将来のES(Embryonic Stem)細胞やiPS細胞の臨床応用などの分野では、刻々と変化する細胞や生体組織を長時間継続して観察、記録することが重要になってきている。例えば、様々な薬剤に対する細胞の応答は、いつ、どのようにして起こるか予想できない。また、ES細胞やiPS細胞の分化の制御には、経時的に変化する細胞の状態に合わせて、細かく培養条件を変化させる必要がある。そのため、細胞や生体組織の経時的な観察が不可欠である。 In fields such as recent biological research, drug discovery research, and future clinical applications of ES (Embryonic Stem) cells and iPS cells, it is important to observe and record constantly changing cells and biological tissues for a long time. It is becoming. For example, it is unpredictable when and how cellular responses to various drugs occur. In addition, in order to control the differentiation of ES cells and iPS cells, it is necessary to finely change the culture conditions according to the state of the cells that change over time. Therefore, it is indispensable to observe cells and living tissues over time.
一般に、このような細胞や生体組織の経時観察には、光学顕微鏡が用いられる。しかし、通常の光学顕微鏡では、細胞の活性を保ちながら観察を行うことができない。そのため、細胞や生体組織の活性を保つため、光学顕微鏡に細胞や生体組織の培養条件を維持できる培養装置を組み合わせて観察する手法が用いられる。 In general, an optical microscope is used to observe such cells and biological tissues over time. However, an ordinary optical microscope cannot be observed while maintaining cell activity. Therefore, in order to maintain the activity of cells and biological tissues, a technique of observing in combination with an optical microscope and a culture apparatus capable of maintaining the culture conditions of the cells and biological tissues is used.
このような手法として、小型の培養インキュベーターを光学顕微鏡のステージに設置し、その内部に細胞培養皿を固定する手法が提案されている(特許文献1)。この手法では、ステージの細胞培養皿内の細胞や生体組織の活性を保ちつつ観察することができる。また、光学顕微鏡システム全体を細胞培養に適した場所(インキュベーター内)に設置する手法も提案されている(非特許文献1)。 As such a technique, a technique has been proposed in which a small culture incubator is installed on the stage of an optical microscope, and a cell culture dish is fixed therein (Patent Document 1). This technique allows observation while maintaining the activity of cells and living tissue in the stage cell culture dish. There has also been proposed a method of installing the entire optical microscope system in a place (in an incubator) suitable for cell culture (Non-patent Document 1).
他に、レンズアレイを用いて250倍〜450倍程度の高倍率観察を行う手法も提案されている(非特許文献2)。この手法では、レンズアレイの各レンズに対応するように複数の照明用発光ダイオードが設けられる。この手法では、レンズアレイの各レンズによる像が重複しないように照明のオン/オフを行い、かつ、像を最適に取得できるように結像光学系を最適化し、像を画像センサに導く。 In addition, a method of performing high-magnification observation of about 250 to 450 times using a lens array has been proposed (Non-Patent Document 2). In this method, a plurality of illumination light emitting diodes are provided so as to correspond to the respective lenses of the lens array. In this method, illumination is turned on / off so that images from the lenses of the lens array do not overlap, and the imaging optical system is optimized so as to obtain an image optimally, and the image is guided to the image sensor.
また、マイクロレンズアレイを用いて取得した像を一括して1個の画像センサで撮像する手法も提案されている(非特許文献3)。この手法では、ステージ上に設置した試料を移動させて、広範囲あるいは複数の試料を観察することが可能である。 In addition, a technique has been proposed in which images acquired using a microlens array are collectively captured by a single image sensor (Non-patent Document 3). In this method, it is possible to observe a wide range or a plurality of samples by moving the sample placed on the stage.
ところが、発明者は、上述の手法には以下に示す問題点が有ることを見出した。特許文献1の手法では、光学顕微鏡の観察ステージに培養インキュベーターを1個ずつ設置する必要が有る。そのため、観察の際には培養インキュベーターを培養に適した環境から取り出さねばならず、培養インキュベーター内の細胞などに悪影響を及ぼしてしまう。
However, the inventor has found that the above-described method has the following problems. In the method of
これに対し、非特許文献1の手法では、光学顕微鏡システム全体を培養に細胞培養に適した環境にいれるため、特許文献1が抱える問題は解消できる。しかし、光学顕微鏡システムを内包できる大きな恒温槽などを用意する必要が有り、観察できる試料の大きさに対してシステムが過大である。そのため、このシステムには、大きな運用コストが必要となってしまう。
On the other hand, the method of Non-Patent
本発明は、上記の事情に鑑みて成されたものであり、本発明の目的は、培養に適した環境において簡易な構成で生体試料を撮像することである。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to image a biological sample with a simple configuration in an environment suitable for culture.
本発明の第1の態様である撮像装置は、内部に生体試料が配置され、外部から前記生体試料の光学観察が可能に構成された試料保持手段と、前記試料保持手段を照明する光源と、前記試料保持手段を介して前記光源と対向して配置され、前記光源で照明された前記生体試料を3倍以下の倍率で撮像する撮像手段と、を備えるものである。これにより、簡易な構成で生体試料の培養環境を維持したまま、生体試料の撮像を行うことができる。 The imaging apparatus according to the first aspect of the present invention includes a sample holding unit configured to allow a biological sample to be disposed inside and optically observing the biological sample from the outside, a light source that illuminates the sample holding unit, An imaging unit that is arranged to face the light source via the sample holding unit and that images the biological sample illuminated by the light source at a magnification of 3 times or less. Thereby, imaging of a biological sample can be performed while maintaining the culture environment of the biological sample with a simple configuration.
本発明の第2の態様である撮像装置は、上記の撮像装置であって、複数の前記撮像手段が第1の面上に配置され、複数の前記光源が、前記複数の撮像手段のそれぞれに対応するように配置されるものである。これにより、構成で複数の生体試料の培養環境を維持したまま、複数の生体試料の撮像を一括して行うことができる。 An imaging apparatus according to a second aspect of the present invention is the above-described imaging apparatus, wherein the plurality of imaging units are arranged on the first surface, and the plurality of light sources are provided to each of the plurality of imaging units. It is arranged so as to correspond. Thereby, it is possible to collectively perform imaging of a plurality of biological samples while maintaining the culture environment of the plurality of biological samples with the configuration.
本発明の第3の態様である撮像装置は、上記の撮像装置であって、1又は2以上の試料保持手段は、前記生体試料が流動するフローセルとして構成されるマイクロ流路が形成され、前記マイクロ流路の複数箇所が観察できる位置に、前記複数の前記撮像手段の全部又は一部が配置される、これにより、生体試料の培養環境を維持したまま、フローセル中を流れる生体試料の撮像を連続的に行うことができる。 An imaging apparatus according to a third aspect of the present invention is the imaging apparatus described above, wherein the one or more sample holding means are formed with a microchannel configured as a flow cell through which the biological sample flows, All or a part of the plurality of the imaging means is arranged at a position where a plurality of locations of the microchannel can be observed, thereby imaging the biological sample flowing in the flow cell while maintaining the culture environment of the biological sample. Can be done continuously.
本発明の第4の態様である撮像装置は、上記の撮像装置であって、前記試料保持手段内の前記生体試料と前記撮像手段との間の距離は1mm以下であり、1つの前記撮像手段に対して前記光源である第1の光源及び第2の光源が設けられ、前記第1の光源で照明した場合に前記1つの撮像手段が取得する像が、前記第2の光源で照明した場合に前記1つの撮像手段が取得する像に対して、前記1つの撮像手段の画素の略半分だけ位置が異なるものである。これにより、生体試料の培養環境を維持したまま、生体試料の撮像をレンズレスで行うことができる。 An imaging apparatus according to a fourth aspect of the present invention is the imaging apparatus described above, wherein a distance between the biological sample in the sample holding unit and the imaging unit is 1 mm or less, and the one imaging unit When the first light source and the second light source, which are the light sources, are provided, and an image acquired by the one imaging unit when illuminated by the first light source is illuminated by the second light source In addition, the position of the image acquired by the one image pickup unit is different by about half of the pixels of the one image pickup unit. Thereby, the biological sample can be imaged without a lens while maintaining the culture environment of the biological sample.
本発明の第5の態様である撮像装置は、上記の撮像装置であって、前記試料保持手段と前記撮像手段との間に配置され、前記生体試料の像を前記撮像手段に結像させる光学系を更に備えるものである。これにより、生体試料の像を所定の倍率で撮像手段に結像させることができる。 An imaging apparatus according to a fifth aspect of the present invention is the imaging apparatus described above, wherein the optical apparatus is disposed between the sample holding unit and the imaging unit, and forms an image of the biological sample on the imaging unit. A system is further provided. Thereby, the image of the biological sample can be formed on the imaging means at a predetermined magnification.
本発明の第6の態様である撮像装置は、上記の撮像装置であって、前記撮像手段は、CCD又はCMOSイメージセンサである。これにより、生体試料の撮像を行うことができる。 An imaging apparatus according to a sixth aspect of the present invention is the imaging apparatus described above, wherein the imaging means is a CCD or CMOS image sensor. Thereby, imaging of a biological sample can be performed.
本発明によれば、培養に適した環境において簡易な構成で生体試料を撮像することができる。 According to the present invention, a biological sample can be imaged with a simple configuration in an environment suitable for culture.
本発明の上述及び他の目的、特徴、及び長所は以下の詳細な説明及び付随する図面からより完全に理解されるだろう。付随する図面は図解のためだけに示されたものであり、本発明を制限するためのものではない。 The above and other objects, features and advantages of the present invention will be more fully understood from the following detailed description and the accompanying drawings. The accompanying drawings are presented for purposes of illustration only and are not intended to limit the present invention.
以下、図面を参照して本発明の実施の形態について説明する。各図面においては、同一要素には同一の符号が付されており、必要に応じて重複説明は省略される。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. In the drawings, the same elements are denoted by the same reference numerals, and redundant description is omitted as necessary.
実施の形態1
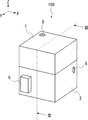
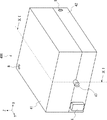
まず、実施の形態1にかかる撮像装置100について説明する。図1は、実施の形態1にかかる撮像装置100の外観の例を模式的に示す斜視図である。撮像装置100は、上部筐体1と下部筐体2とが成す箱の内部に、生体試料及び生体試料の撮像に必要な機器が内包されている。また、以降では、説明の都合上、撮像装置100の正面に平行な方向をX方向とする。撮像装置100の正面に垂直な方向(すなわち、X方向に垂直な方向)をY方向とする。撮像装置100の上面及び下面に垂直な方向(すなわち、X方向及びY方向に垂直な方向)をZ方向とする。
First, the
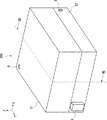
図2は、上部筐体1と下部筐体2とを分離した場合の撮像装置100の例を模式的に示す斜視図である。撮像装置100は、細胞や生体組織を内包する培養皿15を内部に格納可能に構成される。培養皿15は、内部の生体試料を保持し、生体試料を外部から光学的に観察することが可能な試料保持手段である。なお、試料保持手段は、内部に保持した生体試料を外部から光学的に観察することが可能であるならば、培養皿に限定されるものではない。
FIG. 2 is a perspective view schematically showing an example of the
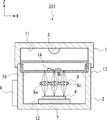
図3は、図1のIII−III線における撮像装置100の断面構成の例を模式的に示す断面図である。撮像装置100は、上部筐体1、下部筐体2、光源3、撮像素子4、レンズ5及び制御部6を有する。
FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing an example of a cross-sectional configuration of the
上部筐体1は、下部筐体2上に配置され、下部筐体2と一体となって内部が中空の箱を構成する。なお、上部筐体1と下部筐体2とは、着脱が可能である。上部筐体1及び下部筐体2は、樹脂や金属などの材料で作製することができる。なお、上部筐体1と下部筐体2とには、撮像装置100の内部に空気を供給するための通気口8が穿たれている。なお、通気口8の位置及び個数は例示にすぎず、この例に限られるものではない。
The
上部筐体1の内側の天井面11には、光源3が設けられる。光源3は、例えば発光ダイオードや小型のランプを用いることができる。光源3は、天井面11の中央に配置されることが望ましいが、配置場所はこれに限られない。
A
下部筐体2の上部には、例えば切欠き部13が設けられ、生体試料14を培養するための培養皿15を支持することができる。
For example, a
下部筐体2の内側の底面12上には、撮像素子4が撮像手段として設けられる。撮像素子4は、例えば高解像度のCMOS(Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor)イメージセンサ(例えば、ピクセルサイズ1μm程度、画素数1600万程度)などを用いることができる。生体試料14は、1又は複数の細胞を含むが、これらの細胞の大きさは10〜20μm程度である。したがって、ピクセルサイズ1μm程度の撮像素子4を用いることで、細胞の像を得ることができる。なお、ここでは、撮像手段としてCMOSイメージセンサを例示したが、例えばCCD(Charge Coupled Device)などの2次元平面に多数の画素が配置された他の撮像素子を用いることも可能である。
On the
レンズ5は、撮像素子4と培養皿15との間に位置するように、下部筐体2に固定される。レンズ5は、培養皿15内の生体試料14の像を、撮像素子4上に結像させる。レンズ5は、倍率が1〜3倍程度の低倍率レンズを用いる。
The
制御部6は、光源3及び撮像素子4を制御する。制御部6は、撮像素子4が撮像した画像や映像のデータを、有線通信又は無線通信により、撮像装置100の外部へ送信する。また、制御部6は、有線通信又は無線通信により受領した外部からの指令に応じて、撮像素子4を制御し、光源3をオン/オフすることができる。
The
なお、光源3、撮像素子4、制御部6には電源が必要であるが、撮像装置100にバッテリーを設けて電源としてもよいし、撮像装置100の外部に電源を設けてもよい。
Note that the
本構成では、撮像素子4を培養皿15に近接させ、かつ低倍率での撮像を行うので、通常の光学顕微鏡のような大型かつ複雑な光学系を用いる必要がない。したがって、本構成によれば、撮像装置の寸法を小型化することが可能となる。
In this configuration, since the
なお、撮像装置100の小型の観点からは、撮像素子4の撮像倍率は、3倍以下とすることが適している。これにより、数十倍〜数百倍の高倍率で観察するための光学顕微鏡に設けられる大型の結像光学系を用いる必要がなく、撮像装置の小型化を実現することができる。
From the viewpoint of the small size of the
以上説明したように、撮像装置100の小型化が可能なことより、撮像装置100は特有の態様で使用することができる。図4は、実施の形態1にかかる撮像装置100の使用態様例を模式的に示す図である。図4に示すように、撮像装置100は、細胞を含む生体試料の培養に適した環境を維持できる恒温槽1001内に安置することができる。また、恒温槽1001の内部に撮像装置100を置いたまま恒温槽1001を密閉したとしても、撮像装置100の制御部6は、例えば無線通信手段1003により、外部の制御コンピュータ1002と通信できる。よって、この場合でも、撮像装置100は、制御コンピュータ1002からの指令を受領し、又は、撮像データを制御コンピュータ1002へ送ることができる。
As described above, since the
このように、寸法を小型化できることを利用して、通常使用することができる恒温槽等の内部に撮像装置100を配置することが可能である。よって、観察のたびに生体試料を培養に適した環境外に取り出す必要はない。その結果、培養に適した環境を維持したまま、生体試料を観察することが可能となる。
In this manner, the
さらに、撮像装置100で取得した像は、例えば外部のコンピュータ(例えば図4の制御コンピュータ1002)によって、所望の画像処理を行うことができる。これにより、撮像した像に収差などの影響があったとしても、画像処理により収差を補正することができる。これは、撮像装置の小型化を追求するに当たり、画像処理により補正可能な収差な収差を許容できることを意味する。つまり、補正可能な範囲であれば、収差の影響を懸念することなく、撮像素子の小型化を行うことが可能である。
Furthermore, the image acquired by the
実施の形態2
次に、実施の形態2にかかる撮像装置200について説明する。撮像装置200の外観は、図1に示す撮像装置100の外観と同様であるので、説明を省略する。図5Aは、実施の形態2にかかる撮像装置200の断面構成の例を模式的に示す断面図である。図5Aは、図3の撮像装置100の断面と同様の位置における撮像装置200の断面を示している。撮像装置200は、実施の形態1にかかる撮像装置100にアクチュエータ7を追加した構成を有する。
Next, the
アクチュエータ7は、下部筐体2と撮像素子4との間に配置される。アクチュエータ7は、撮像素子4を駆動することで、撮像素子4と培養皿15との間の距離(Z方向の距離)を変化させることができる。
The
本構成によれば、撮像素子4での撮像時の焦点位置を深さ方向(Z方向)に変化させることができる。よって、焦点位置を変化させながら複数回の撮像を行い、像を制御部6又は外部の計算機で合成することにより、より明瞭な像を得ることができる。
According to this configuration, the focal position at the time of imaging with the
更に、撮像倍率を1倍にできれば、より有利な構成をとり得る。図5Bは、撮像装置200の変形例である撮像装置201の断面構成の例を模式的に示す断面図である。撮像装置201は、撮像装置200のレンズ5を、1倍のレンズアレイ9に置換した構成を有する。撮像装置201のその他の構成は、撮像装置200と同様であるので、説明を省略する。
Furthermore, if the imaging magnification can be made 1, the configuration can be more advantageous. FIG. 5B is a cross-sectional view schematically illustrating an example of a cross-sectional configuration of an
レンズアレイ9は、X方向及びY方向の一方又は双方に複数の1倍のレンズが配列された構成を有する。図5Bでは、X方向に3つの1倍レンズ9a、9b及び9cが配列されている例について示している。なお、配列されるレンズの個数は、この例に限られるものではない。このように、小さなレンズを複数個用いてレンズアレイを構成する場合、レンズ5(図5A)を用いる場合と比べて、広い視野角確保することができる。また、開口数の小さなレンズを用いてレンズアレイを構成できるので、撮像装置の小型の観点から、より有利である。
The
実施の形態3
次に、実施の形態3にかかる撮像装置300について説明する。撮像装置300は、複数の撮像ユニットが並列配置された構成を有する。図6は、実施の形態3にかかる撮像装置300の外観の例を模式的に示す斜視図である。撮像装置300は、上部筐体31と下部筐体32とが成す箱の内部に、生体試料及び生体試料の撮像に必要な機器が内包されている。
Next, the
図7は、実施の形態3にかかる撮像装置300の上部筐体31を除去した場合の例を示す例斜視図である。撮像装置300の下部筐体32には、細胞や生体組織を内包する、いわゆるウェルプレート16(または、マイクロプレートもしくはマイクロウェルプレートとも呼ばれる)が載置される。ウェルプレート16には、内部に仕切りが設けられ、試料を配置する領域がマトリックス上に配置されている。ここでは、一例として、ウェルプレート16に6行6列の合計36個を試料配置領域が形成されているものとする。
FIG. 7 is a perspective view illustrating an example in which the
図8は、図6のVIII−VIII線における撮像装置300の断面構成の例を模式的に示す断面図である。撮像装置300は、複数の撮像セル301がマトリックス状に形成されている。撮像セル301は、それぞれ実施の形態1にかかる撮像装置100と同様の構成を有する。つまり、複数の撮像セル301の上部筐体1が一体となって上部筐体31を形成する。複数の撮像セル301の下部筐体2が一体となって下部筐体32を形成する。撮像セル301のそれぞれには、マイクロプレートのウェルが1個ずつ配置される。換言すれば、撮像装置300は、複数の撮像装置100が一体化した構成を有するものとして理解できる。
FIG. 8 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing an example of a cross-sectional configuration of the
制御部6は、複数の撮像セル301で撮像した映像データを一括管理する。
The
本構成は小型の撮像装置100を束ねた構成であるので、用途に合わせて撮像セル301の個数を選択することで、撮像装置300を丸ごと恒温槽などの中に安置することができる。これにより、複数の生体試料を一括して同時に観察することが可能となる。
Since this configuration is a configuration in which
本実施の形態では、ウェルプレートを用いる例について説明したが、仕切がない大きな1つの培養皿を載置してもよい。 In the present embodiment, an example using a well plate has been described, but a large culture dish without a partition may be placed.
実施の形態4
次に、実施の形態4にかかる撮像装置400について説明する。撮像装置400は、実施の形態3にかかる撮像装置300の変形例である。図9は、実施の形態4にかかる撮像装置400の外観の例を模式的に示す斜視図である。撮像装置400は、撮像装置300の上部筐体31と下部筐体32とを、それぞれ上部筐体41と下部筐体42とに置換した構成を有する。また、撮像装置400には、後述する流入口47及び排出口48が設けられる。なお、排出口48は、図9では図示していない。
Next, an
図10は、実施の形態4にかかる撮像装置400の上部筐体41を除去した場合の例を示す斜視図である。また、撮像装置400の内部には、フローサイトメトリー等に用いられるマイクロ流路46(図10では不図示)が形成されたフローセル45が配置される。フローセル45は、試料保持手段の一例である。生体試料は、マイクロ流路46(図10では不図示)内を流動する。フローセル45には、撮像装置400の外部から流入口47を介して生体試料が導入される。また、排出口48を介して、フローセル45から撮像装置400の外部へ生体試料が排出される。撮像装置400のその他の構成は撮像装置300と同様であるので、説明を省略する。
FIG. 10 is a perspective view illustrating an example in which the
図11は、図9のXI−XI線における撮像装置400の断面構成の例を模式的に示す断面図である。図11に示すように、マイクロ流路46の延伸方向(X方向)に複数の撮像セル301が配置されることとなる。よって、マイクロ流路内を流れる生体試料49を、流速に同期して、連続的に観察することが可能である。
FIG. 11 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing an example of a cross-sectional configuration of the
実施の形態5
次に、実施の形態5にかかる撮像装置500について説明する。撮像装置500は、実施の形態1にかかる撮像装置100の変形例である。撮像装置500の外観は、撮像装置100の外観と同様であるので、説明を省略する。図12は、実施の形態5にかかる撮像装置500の断面構成の例を模式的に示す断面図である。図12は、図3の撮像装置100の断面と同様の位置における撮像装置500の断面を示している。
Next, an
撮像装置500では、撮像装置100に比べて切欠き部13が下方に設けられている。このため、培養皿15は、撮像素子4に近接して配置されることとなる。そのため、生体試料14と撮像素子4とが近接することとなる。例えば、生体試料14と撮像素子4との距離W2は、1mm以下である。一方、生体試料14と光源3は、撮像装置100と比べて離隔することとなる。
In the
本構成では、生体試料14と撮像素子4とを近接させることで、レンズ5がなくとも、生体試料14の像を撮像素子4に結像させることが可能である。これにより、いわゆるレンズレス撮像を実現することができる。その結果、レンズを除去することによる撮像装置の小型化、低コスト化の観点から有利である。
In this configuration, by bringing the
また、撮像装置500の光源を複数化することもできる。図13は、撮像装置500の光源を複数化した変形例である撮像装置501の断面構成の例を模式的に示す断面図である。複数の光源は、例えば紙面水平方向(図13のX方向)又は紙面に垂直な方向(図13のX方向及びZ方向に垂直な方向、すなわち、紙面手前側と紙面奥側を結ぶ方向であるY方向)に並んで配置される。また、複数の光源は、X方向及びY方向に、アレイ状に配置されてもよい。複数の光源には、例えば、LEDアレイや光ファイバアレイを用いることができる。図13では、光源3a及び3bがX方向に並んで配置される例を示している。
In addition, a plurality of light sources of the
光源3aと光源3bとは、択一的にオンとなる。そして、光源3bで照明した場合に撮像素子4が取得する像が、光源3aで照明した場合に撮像素子4が取得する像に対して、撮像素子4の画素の半分程度だけX方向に変位するように、光源3a及び光源3bが配置される。これにより、いわゆるサブピクセル結像光軸制御(非特許文献4及び5)のもとで、高解像のレンズレス撮像を行うことができる。
The
その他の実施の形態
なお、本発明は上記実施の形態に限られたものではなく、趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜変更することが可能である。
Other Embodiments The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments, and can be appropriately changed without departing from the spirit of the present invention.
上述の実施の形態3及び4にかかる撮像装置にも、実施の形態2にかかるアクチュエータ7を組み込むことが可能である。また、上述の実施の形態3及び4にかかる撮像装置についても、実施の形態5にかかる撮像装置と同様に、レンズレス撮像を行う構成とすることが可能である。
The
上述の実施の形態では、撮像装置が生体試料を撮像する例について説明したが、これは例示に過ぎない。すなわち、上述の実施の形態にかかる撮像装置の撮像対象物は、生体試料に限られず、他の試料の撮像を妨げるものではない。また、生体試料を含む各種試料の撮像は、静止画像及び動画の一方又は双方を取得することが可能である。また、生体試料を含む各種資料の観察方法としては、散乱像、反射像、明視野像、暗視野像、位相差観察及び蛍光観察など、光学観察で用いられる様々な観察方法を適用できる。さらに、これらの様々な観察方法を単一で、或いは複数個組み合わせて適用することができる。 In the above-described embodiment, the example in which the imaging apparatus images a biological sample has been described, but this is merely an example. That is, the imaging target of the imaging device according to the above-described embodiment is not limited to a biological sample, and does not hinder imaging of other samples. In addition, imaging of various samples including biological samples can acquire one or both of a still image and a moving image. As an observation method for various materials including a biological sample, various observation methods used in optical observation such as a scattered image, a reflected image, a bright field image, a dark field image, a phase difference observation, and a fluorescence observation can be applied. Furthermore, these various observation methods can be applied singly or in combination.
上述の実施の形態において、撮像装置を安置する恒温槽等や培養皿を含む試料保持手段内の培養環境(例えば、温度、湿度、二酸化炭素濃度、薬剤の種類や濃度、培養液の種類など)を変化させながら、生体試料の撮像を行うことも可能である。これにより、培養環境の変化に伴う生体試料の変化を連続的に観察することが可能となる。また、大量の試料を同一環境におきつつ、同時、また任意のタイミングで観察することができるようになる。 In the above-described embodiment, a culture environment (eg, temperature, humidity, carbon dioxide concentration, type and concentration of a drug, type of culture solution, etc.) in a sample holding means including a thermostat or a culture dish in which an imaging device is placed. It is also possible to perform imaging of a biological sample while changing. This makes it possible to continuously observe changes in the biological sample accompanying changes in the culture environment. In addition, a large number of samples can be observed at the same time or at any timing while being placed in the same environment.
1、31、41 上部筐体
2、32、42 下部筐体
3 光源
4 撮像素子
5、9a、9b、9c レンズ
6 制御部
7 アクチュエータ
8 通気口
9 レンズアレイ
11 天井面
12 底面
13 切欠き部
14、49 生体試料
15 培養皿
16 ウェルプレート
45 フローセル
46 マイクロ流路
47 流入口
48 排出口
100、200、300、400、500、501 撮像装置
301 撮像セル
1001 恒温槽
1002 制御コンピュータ
1003 無線通信手段
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
前記試料保持手段を照明する光源と、
前記試料保持手段を介して前記光源と対向して配置され、前記光源で照明された前記生体試料を3倍以下の倍率で撮像する撮像手段と、を備える、
撮像装置。 A sample holding means configured so that a biological sample is disposed inside and optical observation of the biological sample is possible from the outside;
A light source for illuminating the sample holding means;
An imaging unit that is arranged to face the light source via the sample holding unit and that images the biological sample illuminated by the light source at a magnification of 3 times or less,
Imaging device.
複数の前記光源が、前記複数の撮像手段のそれぞれに対応するように配置される、
請求項1に記載の撮像装置。 A plurality of the imaging means are disposed on the first surface;
The plurality of light sources are arranged to correspond to each of the plurality of imaging means.
The imaging device according to claim 1.
前記マイクロ流路の複数箇所が観察できる位置に、前記複数の前記撮像手段の全部又は一部が配置される、
請求項3に記載の撮像装置。 One or two or more sample holding means are formed with a microchannel configured as a flow cell through which the biological sample flows,
All or a part of the plurality of the imaging means is arranged at a position where a plurality of locations of the microchannel can be observed.
The imaging device according to claim 3.
1つの前記撮像手段に対して前記光源である第1の光源及び第2の光源が設けられ、
前記第1の光源で照明した場合に前記1つの撮像手段が取得する像が、前記第2の光源で照明した場合に前記1つの撮像手段が取得する像に対して、前記1つの撮像手段の画素の略半分だけ位置が異なり、
請求項1乃至3のいずれか一項に記載の撮像装置。 The distance between the biological sample in the sample holding means and the imaging means is 1 mm or less,
A first light source and a second light source, which are the light sources, are provided for one imaging means;
The image acquired by the one imaging unit when illuminated by the first light source is compared with the image acquired by the one imaging unit when illuminated by the second light source. The position is different by about half of the pixels,
The imaging device according to any one of claims 1 to 3.
請求項1乃至4のいずれか一項に記載の撮像装置。 An optical system that is disposed between the sample holding unit and the imaging unit and forms an image of the biological sample on the imaging unit;
The imaging device according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
請求項1乃至5のいずれか一項に記載の撮像装置。 The imaging means is a CCD or CMOS image sensor.
The imaging device according to any one of claims 1 to 5.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013161165A JP2015029461A (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2013-08-02 | Imaging device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013161165A JP2015029461A (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2013-08-02 | Imaging device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2015029461A true JP2015029461A (en) | 2015-02-16 |
| JP2015029461A5 JP2015029461A5 (en) | 2016-09-23 |
Family
ID=52515339
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013161165A Pending JP2015029461A (en) | 2013-08-02 | 2013-08-02 | Imaging device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2015029461A (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017023088A (en) * | 2015-07-24 | 2017-02-02 | Ckd株式会社 | Culture unit and culture apparatus comprising the same |
| JP2017166910A (en) * | 2016-03-15 | 2017-09-21 | 株式会社東芝 | Optical sensor, analyzer, and method of analysis |
| US10795142B2 (en) | 2017-05-12 | 2020-10-06 | Olympus Corporation | Cell-image acquisition device |
| CN112266846A (en) * | 2020-11-19 | 2021-01-26 | 北京麦科伦科技有限公司 | Culture dish frame fixed bolster, incubator and biological sample form imaging device |
| WO2021079522A1 (en) * | 2019-10-25 | 2021-04-29 | 株式会社 東芝 | Method, kit, and program for determining characteristic of tumor cell group |
| CN113801788A (en) * | 2021-08-30 | 2021-12-17 | 西安理工大学 | Cell culture device and method for monitoring cell growth state in real time |
| CN115144951A (en) * | 2022-06-09 | 2022-10-04 | 西安电子科技大学 | A Differential Phase Contrast Imaging Device Based on Optical Fiber Array Illumination |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000261629A (en) * | 1999-03-10 | 2000-09-22 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Image reader |
| JP2002191060A (en) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-05 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Three-dimensional imaging unit |
| JP2008096407A (en) * | 2006-10-16 | 2008-04-24 | Olympus Corp | Feeble light imaging device |
| JP2008237064A (en) * | 2007-03-26 | 2008-10-09 | Tsuru Gakuen | Cell observation apparatus and cell observation method |
| WO2011004568A1 (en) * | 2009-07-08 | 2011-01-13 | 株式会社ニコン | Image processing method for observation of fertilized eggs, image processing program, image processing device, and method for producing fertilized eggs |
| WO2011010449A1 (en) * | 2009-07-21 | 2011-01-27 | 国立大学法人京都大学 | Image processing device, culture observation apparatus, and image processing method |
| JP2012013888A (en) * | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-19 | Nikon Corp | Microscope and culture observation device |
| JP2012231764A (en) * | 2011-05-08 | 2012-11-29 | Kyokko Denki Kk | Apparatus and method for sorting and acquiring cell aggregate |
| JP2013516999A (en) * | 2010-01-20 | 2013-05-16 | イー・エム・デイー・ミリポア・コーポレイシヨン | Cell image acquisition and remote monitoring system |
-
2013
- 2013-08-02 JP JP2013161165A patent/JP2015029461A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000261629A (en) * | 1999-03-10 | 2000-09-22 | Ricoh Co Ltd | Image reader |
| JP2002191060A (en) * | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-05 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Three-dimensional imaging unit |
| JP2008096407A (en) * | 2006-10-16 | 2008-04-24 | Olympus Corp | Feeble light imaging device |
| JP2008237064A (en) * | 2007-03-26 | 2008-10-09 | Tsuru Gakuen | Cell observation apparatus and cell observation method |
| WO2011004568A1 (en) * | 2009-07-08 | 2011-01-13 | 株式会社ニコン | Image processing method for observation of fertilized eggs, image processing program, image processing device, and method for producing fertilized eggs |
| WO2011010449A1 (en) * | 2009-07-21 | 2011-01-27 | 国立大学法人京都大学 | Image processing device, culture observation apparatus, and image processing method |
| JP2013516999A (en) * | 2010-01-20 | 2013-05-16 | イー・エム・デイー・ミリポア・コーポレイシヨン | Cell image acquisition and remote monitoring system |
| JP2012013888A (en) * | 2010-06-30 | 2012-01-19 | Nikon Corp | Microscope and culture observation device |
| JP2012231764A (en) * | 2011-05-08 | 2012-11-29 | Kyokko Denki Kk | Apparatus and method for sorting and acquiring cell aggregate |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| OPTICS EXPRESS, vol. 18 (11), JPN6017025201, 2010, pages 11181 - 11191, ISSN: 0003594249 * |
| PNAS, vol. 108 (41), JPN6017025203, 2011, pages 16889 - 16894, ISSN: 0003594250 * |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017023088A (en) * | 2015-07-24 | 2017-02-02 | Ckd株式会社 | Culture unit and culture apparatus comprising the same |
| JP2017166910A (en) * | 2016-03-15 | 2017-09-21 | 株式会社東芝 | Optical sensor, analyzer, and method of analysis |
| US10156511B2 (en) | 2016-03-15 | 2018-12-18 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Optical sensor, analyzer and analysis method |
| US10795142B2 (en) | 2017-05-12 | 2020-10-06 | Olympus Corporation | Cell-image acquisition device |
| WO2021079522A1 (en) * | 2019-10-25 | 2021-04-29 | 株式会社 東芝 | Method, kit, and program for determining characteristic of tumor cell group |
| JPWO2021079522A1 (en) * | 2019-10-25 | 2021-04-29 | ||
| JP7273987B2 (en) | 2019-10-25 | 2023-05-15 | 株式会社東芝 | Methods, kits and programs for characterizing tumor cell populations |
| CN112266846A (en) * | 2020-11-19 | 2021-01-26 | 北京麦科伦科技有限公司 | Culture dish frame fixed bolster, incubator and biological sample form imaging device |
| CN113801788A (en) * | 2021-08-30 | 2021-12-17 | 西安理工大学 | Cell culture device and method for monitoring cell growth state in real time |
| CN115144951A (en) * | 2022-06-09 | 2022-10-04 | 西安电子科技大学 | A Differential Phase Contrast Imaging Device Based on Optical Fiber Array Illumination |
| CN115144951B (en) * | 2022-06-09 | 2024-06-04 | 陕西卓远众安网络科技有限公司 | Differential phase contrast imaging device based on fiber array illumination |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2015029461A (en) | Imaging device | |
| US10754140B2 (en) | Parallel imaging acquisition and restoration methods and systems | |
| Chan et al. | Parallel Fourier ptychographic microscopy for high-throughput screening with 96 cameras (96 Eyes) | |
| US8624967B2 (en) | Integrated portable in-situ microscope | |
| US9569664B2 (en) | Methods for rapid distinction between debris and growing cells | |
| JP5992456B2 (en) | Apparatus, system and method | |
| JP2019066861A (en) | Microscope module for imaging samples | |
| JP2018504628A (en) | Multiwell Fourier Tyography imaging and fluorescence imaging | |
| US20120223217A1 (en) | E-petri dishes, devices, and systems | |
| US20120133756A1 (en) | Compact, high-resolution fluorescence and brightfield microscope and methods of use | |
| EP2917719B1 (en) | Receptacle and system for optically analyzing a sample without optical lenses | |
| US20160152941A1 (en) | Device for analyzing cells and monitoring cell culturing and method for analyzing cells and monitoring cell culturing using same | |
| US20180164569A1 (en) | Microplate and microscope system | |
| CN107144516B (en) | shooting device | |
| Tristan-Landin et al. | Facile assembly of an affordable miniature multicolor fluorescence microscope made of 3D-printed parts enables detection of single cells | |
| JP2020507106A (en) | Low resolution slide imaging, slide label imaging and high resolution slide imaging using dual optical paths and a single imaging sensor | |
| Diederich et al. | Nanoscopy on the Chea (i) p | |
| Ashraf et al. | Random access parallel microscopy | |
| Wang et al. | The power in your pocket–uncover smartphones for use as cutting-edge microscopic instruments in science and research | |
| JP2023065612A (en) | System and method for managing plural scanning devices in high-throughput laboratory environment | |
| JP6952891B2 (en) | Carousel for 2x3 and 1x3 slides | |
| Fennell et al. | Design, development, and performance comparison of wide field lensless and lens-based optical systems for point-of-care biological applications | |
| TW201710736A (en) | Microscope monitoring device and system thereof | |
| Chan et al. | 96 eyes: parallel Fourier ptychographic microscopy for high-throughput screening | |
| KR102717991B1 (en) | Optical apparatus including a plurality of bright field light sources and method of operating thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160801 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20160801 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20170606 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20170711 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170911 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20180206 |