JP2013200944A - Light source device - Google Patents
Light source device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2013200944A JP2013200944A JP2012066778A JP2012066778A JP2013200944A JP 2013200944 A JP2013200944 A JP 2013200944A JP 2012066778 A JP2012066778 A JP 2012066778A JP 2012066778 A JP2012066778 A JP 2012066778A JP 2013200944 A JP2013200944 A JP 2013200944A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- cooling
- light source
- unit
- source device
- detection electrode
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02B—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO BUILDINGS, e.g. HOUSING, HOUSE APPLIANCES OR RELATED END-USER APPLICATIONS
- Y02B20/00—Energy efficient lighting technologies, e.g. halogen lamps or gas discharge lamps
- Y02B20/40—Control techniques providing energy savings, e.g. smart controller or presence detection
Abstract
Description
本発明の実施形態は、光源装置に関する。 Embodiments described herein relate generally to a light source device.
例えば、液晶や半導体等の製造プロセス、流体の殺菌や光反応処理、照明、
光化学反応等に用いる光源装置は、大光量化が要求されている。大光量を得るには、大電力を投入し光源を点灯する必要があるが、光源や電源から発生する熱の影響により、光源装置の変換効率が低下したり、寿命が短くなる課題がある。
For example, liquid crystal and semiconductor manufacturing processes, fluid sterilization and photoreaction processing, lighting,
A light source device used for a photochemical reaction or the like is required to increase the amount of light. In order to obtain a large amount of light, it is necessary to turn on the light source by turning on a large amount of power. However, there is a problem that the conversion efficiency of the light source device is lowered or the life is shortened due to the influence of heat generated from the light source or the power source.
この種の光源装置では、冷却液を使用した液冷式の冷却システムを使用して、光源や電源からの発熱を低減し、高効率化及び長寿命化を図っている。しかし、光源装置の製造不具合や部品の劣化により、冷却システムから冷却液が液漏れすると、例えば、光源または電源に冷却液が付着して電気的短絡を起こし、光源や電源を破損させる恐れがあり、安全性確保のため、液漏れを的確に検出する必要がある。 In this type of light source device, a liquid cooling type cooling system using a cooling liquid is used to reduce heat generation from the light source and the power source, thereby achieving higher efficiency and longer life. However, if the coolant leaks from the cooling system due to a manufacturing failure of the light source device or deterioration of parts, for example, the coolant may adhere to the light source or the power source, causing an electrical short circuit, which may damage the light source or the power source. In order to ensure safety, it is necessary to accurately detect liquid leakage.
本発明が解決しようとする課題は、光源装置を冷却する冷却システムからの冷却液の液漏れを検出し、冷却液の付着に伴う光源や電源の破損を防止することができる光源装置を提供することにある。 The problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a light source device that can detect a leakage of coolant from a cooling system that cools the light source device and prevent damage to the light source and power supply accompanying the attachment of the coolant. There is.
本実施形態の光源装置は、内部に冷却液を流通可能な導電性の冷却部と、前記冷却液によって冷却可能なように前記冷却部の外部に接続された照射部と、前記冷却部に対して電気的に絶縁される位置、かつ、前記冷却部からの前記冷却液の液漏れ時に、前記冷却液が前記冷却部との間で架橋可能な位置に設けられた検出電極と、前記検出電極と前記冷却部との間の電気特性を検出し、その電気特性の変化から前記液漏れを検出する検出部と、を具備する。 The light source device according to the present embodiment includes a conductive cooling unit capable of circulating a cooling liquid therein, an irradiation unit connected to the outside of the cooling unit so as to be cooled by the cooling liquid, and the cooling unit. And a detection electrode provided at a position where the cooling liquid can be bridged with the cooling section when the cooling liquid leaks from the cooling section. And a detecting unit for detecting the liquid leakage from a change in the electric characteristic.
以下、発明を実施するための実施形態について説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments for carrying out the invention will be described.
(第1の実施形態)
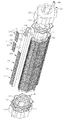
第1の実施形態の光源装置を、図面を参照して説明する。図1は、光源装置の分解斜視図で、図2は図1に示す光源装置の組み立て状態を説明するための外観斜視図、図3は図2に示す光源装置の断面構造を説明するための断面図である。図4は、光源装置の冷却系及びシステム構成を説明するための概略図である。尚、図4では、説明を簡略化するため光源装置を平面的に模式化している。
(First embodiment)
A light source device according to a first embodiment will be described with reference to the drawings. 1 is an exploded perspective view of the light source device, FIG. 2 is an external perspective view for explaining an assembled state of the light source device shown in FIG. 1, and FIG. 3 is a sectional view for explaining the cross-sectional structure of the light source device shown in FIG. It is sectional drawing. FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram for explaining a cooling system and a system configuration of the light source device. In FIG. 4, the light source device is schematically illustrated in a plane in order to simplify the description.
第1の実施形態の光源装置100は、液晶や半導体等の製造プロセス、流体の殺菌や光反応処理、照明等に用いる光源装置であり、主要部として冷却部1を備えている。
The
冷却部1は、その外周面に複数の照射部21a、21bを載置するとともに、照射部21a、21bから発生する熱を液冷式で冷却する構成である。
The
冷却部1は、例えば、図1に示すように、互いに同一形状を成す4つの冷却基体111を環状に配置した集合体の開口した両端を、液漏れを防止する接合部材131、132を介して、それぞれ、蓋部141、151で固定した構造で、外周形状が略八角星形状で、内周形状が8角形をなす柱状体である。
For example, as shown in FIG. 1, the
冷却基体111の外装面112と内装面113との間の内部には、長手方向に貫通した冷却水路121〜128が、例えば、押し出し成形または、掘削により形成されている。冷却水路121〜128は、後述する冷却液が循環する経路で、例えば、2つの外装面112毎に設けられている。
Inside the space between the
冷却基体111の長手方向の一端側を塞ぐ蓋部141には、図4に示すように、冷却水路121と122、123と124、125と126、及び、127と128を、それぞれ、連結する連結路142、143、144、及び145が設けられている。また、冷却基体111の長手方向の他端側を塞ぐ蓋部151には、冷却水路122と123、124と125、及び、126と127、をそれぞれ連結する連結路152、153及び154と、冷却水路121に接続される取水口155と、冷却水路128に接続される排水口156が設けられている。連結路142〜145、152〜154は、断面形状が例えば、U字状である。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
これにより、冷却部1内の、取水口155と排水口156との間に、冷却液を流す一連の流路が形成されている。
As a result, a series of flow paths through which the cooling liquid flows are formed between the
冷却基体111、及び、蓋部141、151は、ステンレス、アルミ合金、銅等の導電性の金属で作成される。
The
接合部材131、132は、接合面において気密性、水密性を持たせるために用いる固定用シール材である。接合部材131、132は、ガスケットで、ゴム、樹脂等の絶縁体、金属体、または、絶縁体と金属体の複合体等を、接合形状に合わせてシート状に加工した構成である。
The joining
冷却基体111の集合体の外周部には、例えば、16面の矩形形状の外装面112が備えられており、連続した山折部と谷折部を備えたつづら折り状に形成されている。外装面112には、照射部21aと21bとが載置されている。
ここで、谷折部分の外装面112間の角度αは、例えば、135度で設定され、谷部の一方の外装面112に載置される照射部21a、21bからの出射光が、他方の外装面112に載置される照射部21a、21bに入射して光損失となることを低減するように調整される。このように、複数の外装面112を形成することにより、冷却部1の大型化を招くことなく、複数の照射部21a、21bを効率的に配置することができ、光源装置の大光量化が実現できる。
For example, a 16-sided rectangular
Here, the angle α between the
照射部21a、21bは、例えば、矩形形状の基板211の片面に所定数量の発光ダイオード(LED)212をマトリクス状に配列した構成である。
The
基板211は、窒化アルミやアルミナ等のセラミックス基板等が使用される。
As the
発光ダイオード212は、紫外線、可視光、または赤外線を放射する発光ダイオードで、光源装置100の用途で必要とされる光放射の波長を有する種類が選定される。発光ダイオード212は、例えば、3mm〜4mm角の略矩形形状をなす平面実装型の発光ダイオードで、出射面に設けられたレンズ部材により配光特性が調整される。発光ダイオード212は、例えば、0.5mm〜1mmの間隔で、基板211上に実装される。発光ダイオード212は、基板211に設けられた配線パターン(図示無)により、電気的に接続され、図4に示すように、電源部22から電力を供給することで発光する。
The light-
照射部21a、21bの点灯に際し発生する熱は、図4に示すように、冷却部1内の、冷却水路121〜128、連結路142〜145、152〜154に冷却液を充填し、循環させることで液冷することが出来る。冷却液は、水、油等が使用される。
As shown in FIG. 4, the heat generated when the
例えば、照射部21a、21bからの発熱を受熱した冷却液は、排水口156から排出された後、送液管31を介して、冷液部32に送り込まれ、冷却される。冷液部32は、冷却タンクや熱交換器等から構成される。
For example, the coolant that has received the heat generated from the
冷却された冷却液は、例えば、送液管33、冷却液を循環させるポンプ34、送液管35、冷却液の供給量を電子的に制御する電磁バルブ36、及び、送液管37を介して、冷却部1の取水口155に供給される。
The cooled coolant is, for example, via a
冷却液は、再び、冷却部1の冷却水路121〜128、連結路142〜145、152〜154を循環し、照射部21a、21bからの排熱に利用され、この繰り返しによって、照射部21a、21bを冷却する。照射部21a、21bを冷却することにより、発光ダイオード212の温度を低減し、熱による発光効率の低下や部材の熱劣化を抑制することが出来る。
The coolant again circulates in the
ところで、冷却基体111と蓋部141、151は、接合部材131、132を介して気密に接合されるが、製造の不具合や、接合部材131、132等の熱的または経時的な劣化により、気密性が失われ、これらの接合部分から冷却液Wの漏れが発生する可能性がある。
By the way, the
これらの接合面からの液漏れを検出するため、冷却部1の冷却基体111の外装面112に対して電気的に絶縁されている位置(第1の位置条件)と、冷却部1からの液漏れ時に外装面112との間に冷却液Wが架橋可能な位置(第2の位置条件)の両方を満足する位置に、検出電極41を配置する。
In order to detect liquid leakage from these joint surfaces, a position (first position condition) that is electrically insulated from the
例えば、冷却部1の長手方向を重力方向に沿うように配置する場合は、液漏れした冷却液は、重力により、下側に移動する性質を有する。この場合、例えば、図5に示すように、最上部に配置される照射部21aの基板211の発光ダイオード212を実装する面側(第1の位置条件)で、基板211の上側(第2の位置条件)の位置に直線状の検出電極41を配置することで、上部の蓋部151及び冷却基体111と、接合部材132との接合面からの液漏れを検出することができる。検出電極41は導電性で、銀ペーストや、半田、金メッキパターン等を基板211上に印刷や、蒸着等により形成したものである。
For example, when arrange | positioning so that the longitudinal direction of the
検出電極41を用いて、冷却部1からの冷却液Wの液漏れを検出する方法の概略図を図6に示す。液漏れがない場合は、図6(a)に示すように、検出電極41と、冷却基体111の外装面112との間は、絶縁層である空気層及び基板211が介在した状態であり、両者間は電気的に絶縁状態である。ここで、冷却基体111は、例えば、電源部22や外部に設けられた接地端子にハーネスを介して接続され、接地処理Gが施こされている。
A schematic diagram of a method for detecting the leakage of the coolant W from the
一方、冷却液Wの液漏れが発生した際は、例えば、図6(b)に示すように、冷却液Wは、重力または表面張力により、冷却基体111の外装面112に沿って下側に移動し、照射部21aの基板211上に達する。基板211上の検出電極41と、冷却基体111との間に、冷却液Wが架橋する、すなわち、連続的につながるようになると、冷却液Wは導電性で電気を通電するため、検出電極41と冷却基体111との間の電気的特性、例えば、抵抗、静電容量等が変化する。検出電極41と冷却基体111との間の電気的特性の変化を、検出部51で検出することにより、冷却液Wの液漏れの有無を判定できる。検出部51は、例えば、図6に示すように、出力端子Voが設けられており、液漏れが無い場合は低電圧(low)を出力し、液漏れを検出した場合は高電圧(high)で出力する。
On the other hand, when the coolant W leaks, for example, as shown in FIG. 6B, the coolant W is lowered along the
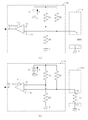
図7に、検出部51の回路構成の一例を示す。検出部51は、比較器(コンパレータ)511を用いて判定を行う。比較器511は、入力電圧Viと基準電圧Vrを入力し、入力電圧Viと基準電圧Vrの大小により、異なる出力電圧Voを出力する構成である。例えば、比較器511は、入力電圧Viが基準電圧Vrに対して大きい場合に、出力電圧Voとして低電圧(low)信号を出力し、逆に、入力電圧Viが基準電圧Vrに対して小さい場合には、出力電圧Voとして高電圧(high)信号を出力する。
FIG. 7 shows an example of the circuit configuration of the
電源Vcと、抵抗R1と、抵抗R2とは直列に接続されており、電源Vcと抵抗R2は、接地処理Gされている。ここで、抵抗R2間の電位が、比較器511に基準電圧Vrとして入力される。電源Vcの電位をE、抵抗R1の抵抗値をr1、抵抗R2の抵抗値をr2と置くと、基準電圧VrはVr=r2×E/(r1+r2)で与えられる。
The power source Vc, the resistor R1, and the resistor R2 are connected in series, and the power source Vc and the resistor R2 are grounded. Here, the potential between the resistors R2 is input to the
一方、検出電極41からの出力は、抵抗R3を介して、電源Vcと直列に接続されている。ここで、電源Vcと冷却基体111は接地処理Gされており、冷却基体111の外装面112に対する検出電極41の電位が、比較器511に入力電圧Viとして入力される。
On the other hand, the output from the
図6(a)に示すように、検出電極41と冷却基体111との間に冷却液Wが存在しない場合は、両者間は絶縁体となるため、入力電圧Viは、電源Vcの電位Eと等しくなり、上述した基準電圧Vrより大きくなり、比較器511の出力Voは、低電圧(low)信号を出力する。
As shown in FIG. 6A, when the coolant W does not exist between the
図6(b)に示すように、検出電極41と冷却基体111との間に冷却液Wが介在すると、冷却液Wが導電性を有するため、両者間で電流が流れる。すなわち、冷却液Wは、等価回路的に抵抗Rwとなる。ここで、冷却液の抵抗Rwの抵抗値をrw、抵抗R3の抵抗値をr3と置くと、入力電圧Viは、Vi=rw×E/(r3+rw)で与えられる。ここで、抵抗r3は、入力電圧Viが、基準電圧Vrより小さくなるように調整されており、これにより、比較器511は、高電圧(high)信号を出力する。比較器511は、冷却液Wの液漏れの有無に応じて、異なる信号を出力することができる。
As shown in FIG. 6B, when the coolant W is interposed between the
検出部51からの出力信号Voは、例えば、図4に示すように制御部61に導かれる。液漏れ異常を検出した制御部61は、例えば、電源部22を自動停止させて、照射部21a、21bへの電力供給を遮断する。その結果、照射部21a、21bの冷却液Wによる電気的短絡を防止し、照射部21a、21bの破損を事前に防止できる。また、通電された冷却液Wによる漏電も防止でき、作業者の安全性も確保できる。
The output signal Vo from the
その他、制御部61に接続された電磁バルブ36を制御して、冷却部1への冷却液の供給を自動停止させ、冷却液の液漏れの拡大を抑制することや、警報装置63を動作させて、作業者に警報音や光の点滅で異常を知らせることも可能である。異常を察知した作業者は、操作パネル62等で、光源装置の停止や、異常からの復旧操作を行うことが可能であり、異常発生時の光源装置の安全性を向上させることが出来る。
(第2の実施形態)
図8及び図9は、光源装置に関する第2の実施形態について説明するためのもので、光源装置の断面図である。この第2の実施形態の各部について、第1の実施形態の光源装置の各部と同一部分は同一符号で示す。
In addition, the
(Second Embodiment)
8 and 9 are cross-sectional views of the light source device for explaining a second embodiment related to the light source device. About each part of this 2nd Embodiment, the same part as each part of the light source device of 1st Embodiment is shown with the same code | symbol.
第2の実施形態では、電源部22は、冷却部1の冷却基体111の内装面113上に設置されている。これにより電源部22も、照射部21bと同様に、冷却液によって効率的に冷却できる。
In the second embodiment, the
照射部21bを設置する外装面112の面積は、電源部22を設置する内装面113の面積より広い構成とすることにより、冷却部1の大型化を招くことなく、複数の照射部21bを効率的に配置することができ、光源装置の大光量化が実現できる。
The area of the
電源部22は、例えば、基板221に回路部品222を実装した構成であるが、回路部品の抵抗やトランジスタ等の発熱部品から発熱する。照射部21bからの発熱量に対して、電源部22からの発熱量は小さいものの、電源部22の回路部品222が温度上昇すると、回路の誤動作や、回路損失の低下、回路寿命の低下を生じる。電源部22を、第1の実施形態と同様な原理で、冷却することで、回路部品222に対する熱の影響を抑制し、安定した回路動作が確保できると共に、回路効率及び回路寿命の向上を図ることができる。
The
電源部22は、例えば、冷却液の向きが異なる2つの冷却水路121と122、123と124、125と126、及び、127と128を跨るようにして、内装面113に配置される。電源部22を、2つの冷却水路を介して、液冷させることで、冷却効率を向上させることができる。
For example, the
第2の実施形態では、図9に示すように、冷却部1の長手方向が重力方向に沿うように配置した状態であり、電源部22の基板221の回路部品222が実装される面側(第1の位置条件)で、かつ、重力の上側となる蓋部151側(第2の位置条件)の位置に、冷却液Wの液漏れを検出する検出電極41を形成している。検出電極41と冷却部1の冷却基体111との間の電気的変化を、第1の実施形態と同様に検出部51で検出することで、冷却液Wの液漏れの有無を検出することができる。
(第3の実施形態)
図10は、光源装置に関する第3の実施形態について説明するためのもので、光源装置の断面図である。この第3の実施形態の各部について、第1の実施形態の光源装置の各部と同一部分は同一符号で示す。
In the second embodiment, as shown in FIG. 9, the
(Third embodiment)
FIG. 10 is a cross-sectional view of a light source device for explaining a third embodiment related to the light source device. About each part of this 3rd Embodiment, the same part as each part of the light source device of 1st Embodiment is shown with the same code | symbol.
第3の実施形態では、冷却部1の冷却基体111と、蓋部151との間に介在する接合部材132内に、冷却部1からの液漏れを検出する検出電極41を配置した構成である。
In 3rd Embodiment, it is the structure which has arrange | positioned the
検出電極41は、冷却基体111及び蓋部151との間に、絶縁性の接合部材132を介在させることで、検出電極41と、冷却基体111及び蓋部151との間の絶縁性を確保している。検出電極41の、冷却通路121〜128と対向する側は、空気層に対して露出している。検出電極41と、冷却基体111及び蓋部151との間は、接合部材132及び空気層を介して離間しており、絶縁状態にある(第1の位置条件)。一方、検出電極41の、冷却通路121〜128側は、接合部材132で被覆し、冷却通路121〜128を循環する冷却液を介して、検出電極41と、冷却基体111及びは蓋部151とが、通電しないようにしている。
The
冷却液Wの液漏れが発生する際は、検出電極41と冷却基体111、または、検出電極41と蓋部151との間に冷却液が架橋する(第2の位置条件)ように、接合部材132の厚みを調整している。
When liquid leakage of the cooling liquid W occurs, the joining member is configured so that the cooling liquid bridges between the
検出電極41は、検出部51に接続される。ここで、検出電極41と出力線との接続を容易にするため、例えば、検出電極41を部分的に大きくして、冷却部1から突出させ、この突出部分(図示無)で端子を接続する構成を採る。
The
検出電極41を用いて、冷却部1からの冷却液Wの液漏れを検出する方法を、図10にて説明する。液漏れがない場合は、図10(a)に示すように、検出電極41と、冷却基体111及び蓋部151との間は、絶縁性の接合部材132及び空気層が介在した状態であり、両者間は電気を導通しない状態である。ここで、冷却基体111または蓋部151は、例えば、接地処理Gが施こされている。
A method of detecting the leakage of the coolant W from the
一方、冷却液Wの液漏れが発生した際は、例えば、図10(b)に示すように、冷却液Wは、冷却基体111、検出電極41、接合部材132、蓋部151の一部表面を覆う。検出電極41と冷却基体111、または、検出電極41と蓋部151との間に、冷却液Wが架橋するようになると、冷却液Wは導電性で電気を通電するため、検出電極41と冷却基体111、または、検出電極41と蓋部151との間の電気的特性、例えば、抵抗、静電容量等が変化する。検出電極41と冷却基体111、または、検出電極41と蓋部151との間の電気的特性の変化を、第1の実施形態と同様に、検出部51で検出することで、冷却液Wの液漏れの有無を検出することができる。
On the other hand, when the leakage of the coolant W occurs, for example, as shown in FIG. 10B, the coolant W is a part of the surface of the
第1の実施形態および第2の実施形態では、冷却部1の重力の上から下方向に移動する冷却液Wの液漏れを検出できるのに対し、第3の実施形態では、検出電極41を、液漏れが発生する冷却基体111の蓋部141側の接合面に配置することで、重力による冷却液の漏れ方向を考慮しなくても、冷却液Wの液漏れを検出することが可能である。その結果、冷却部1の長手方向を重力方向に沿わせる以外の構成での検出や、冷却基体111の蓋部141側に加えて、蓋部151側での検出も可能となり、液漏れの検出精度を向上できる。
In the first embodiment and the second embodiment, it is possible to detect the leakage of the coolant W that moves downward from above the gravity of the
本発明は上記実施形態に限定されるものではなく、種々の変形が可能である。 The present invention is not limited to the above embodiment, and various modifications are possible.
例えば、照射部21a、21bの光源は、用途に応じた光源であればよいので、発光ダイオード以外に、メタルハライドランプ、低圧水銀ランプ、HIDランプ、または、レーザーダイオード等に置き換えが可能である。電源部22は、夫々の光源に適した構成とすることができる。
For example, since the light sources of the
光源装置の使用形態は、長尺状の冷却部1の長手方向を重力方向に沿う方向で配置した構成を示したが、重力方向に対して傾斜させた構成や、水平方向に配置する構成でも良い。この場合、冷却液は重力の下側に移動すると共に、冷却液の表面張力により、冷却部1の一部表面に沿って広がる性質があるため、液漏れの際に冷却液が広がる範囲を実験的・経験的に求め、その部分に検出電極41を配置する構成でも良い。
Although the usage form of the light source device showed the structure which has arrange | positioned the longitudinal direction of the
冷却部1及び照射部21a、21bは、その周囲を、例えば、石英ガラスを覆い、処理液の内部に浸透させる構成で、使用しても良い。また、この場合、石英ガラスの割れに伴う処理液の漏れを、検出電極41で検出する構成としても良い。
The
また、冷却部1による冷却に伴い、空気中の水分が結露し、照射部21a、21bや、電源部22に付着するため、結露の水分を検出電極41で検出する構成としても良い。
In addition, the moisture in the air condenses with the cooling by the
検出電極41は、照射部21a、21bの一部または電源部22の一部に設けた構成を示したが、例えば、図2に示す重力下側の蓋部141に、検出電極41を設けた独立基板を配置し、冷却基体111の蓋部141側の接合面から下方向に漏れる冷却液を検出する構成でも良い。
The configuration of the
検出部51は、比較器を用いた回路構成を示したが、例えばマイコンを用いてもよい。
Although the
本発明のいくつかの実施形態を説明したが、これらの実施形態は、例として提示したものであり、発明の範囲を限定することは意図していない。これら新規な実施形態は、その他の様々な形態で実施されることが可能であり、発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲で、種々の省略、置き換え、変更を行うことができる。これら実施形態やその変形は、発明の範囲や要旨に含まれるとともに、特許請求の範囲に記載された発明とその均等の範囲に含まれる。 Although several embodiments of the present invention have been described, these embodiments are presented by way of example and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. These novel embodiments can be implemented in various other forms, and various omissions, replacements, and changes can be made without departing from the scope of the invention. These embodiments and modifications thereof are included in the scope and gist of the invention, and are included in the invention described in the claims and the equivalents thereof.
100 光源装置
1 冷却部
21a、21b 照射部
211 基板
212 発光ダイオード(LED)
22 電源部
41 検出電極
51 検出部
61 制御部
W 冷却液
100
21a,
22
Claims (3)
前記冷却液によって冷却可能なように前記冷却部の外部に接続された照射部と、
前記冷却部に対して電気的に絶縁される位置、かつ、前記冷却部からの前記冷却液の液漏れ時に、前記冷却液が前記冷却部との間で架橋可能な位置に設けられた検出電極と、
前記検出電極と前記冷却部との間の電気特性を検出し、その電気特性の変化から前記液漏れを検出する検出部と、
を具備する光源装置。 A conductive cooling section capable of circulating a coolant inside;
An irradiation unit connected to the outside of the cooling unit so as to be cooled by the cooling liquid;
A detection electrode provided at a position that is electrically insulated from the cooling section and at a position where the cooling liquid can be bridged with the cooling section when the cooling liquid leaks from the cooling section. When,
A detection unit that detects an electrical characteristic between the detection electrode and the cooling unit, and detects the liquid leakage from a change in the electrical characteristic;
A light source device comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012066778A JP2013200944A (en) | 2012-03-23 | 2012-03-23 | Light source device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012066778A JP2013200944A (en) | 2012-03-23 | 2012-03-23 | Light source device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013200944A true JP2013200944A (en) | 2013-10-03 |
Family
ID=49521062
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012066778A Pending JP2013200944A (en) | 2012-03-23 | 2012-03-23 | Light source device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2013200944A (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015216017A (en) * | 2014-05-09 | 2015-12-03 | 東芝ライテック株式会社 | Lighting device |
| WO2016171447A1 (en) * | 2015-04-21 | 2016-10-27 | 주식회사 필룩스 | Lighting device and lighting module |
| KR20160125299A (en) * | 2015-04-21 | 2016-10-31 | 주식회사 필룩스 | Lighting device and lighting module |
| JP2016194992A (en) * | 2015-03-31 | 2016-11-17 | 東芝ライテック株式会社 | Irradiation lamp and irradiation device |
| JPWO2016056371A1 (en) * | 2014-10-09 | 2017-04-27 | 東レ株式会社 | Photochemical reaction apparatus, photochemical reaction method using the same, and lactam production method using the same |
| US10448537B2 (en) | 2015-06-11 | 2019-10-15 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Power supply device, photochemical reaction device and method in which same is used, and lactam production method |
| KR20200123915A (en) * | 2019-04-23 | 2020-11-02 | (주) 제이엔엠 메카텍 | Cooling Device |
| WO2021149367A1 (en) * | 2020-01-24 | 2021-07-29 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | Light irradiation device |
-
2012
- 2012-03-23 JP JP2012066778A patent/JP2013200944A/en active Pending
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015216017A (en) * | 2014-05-09 | 2015-12-03 | 東芝ライテック株式会社 | Lighting device |
| JPWO2016056371A1 (en) * | 2014-10-09 | 2017-04-27 | 東レ株式会社 | Photochemical reaction apparatus, photochemical reaction method using the same, and lactam production method using the same |
| US10414724B2 (en) | 2014-10-09 | 2019-09-17 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Photochemical reaction device, photochemical reaction method using same, and lactam production method using said method |
| JP2016194992A (en) * | 2015-03-31 | 2016-11-17 | 東芝ライテック株式会社 | Irradiation lamp and irradiation device |
| WO2016171447A1 (en) * | 2015-04-21 | 2016-10-27 | 주식회사 필룩스 | Lighting device and lighting module |
| KR20160125299A (en) * | 2015-04-21 | 2016-10-31 | 주식회사 필룩스 | Lighting device and lighting module |
| KR101882938B1 (en) | 2015-04-21 | 2018-07-27 | 주식회사 필룩스 | Lighting device and lighting module |
| US10448537B2 (en) | 2015-06-11 | 2019-10-15 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Power supply device, photochemical reaction device and method in which same is used, and lactam production method |
| KR20200123915A (en) * | 2019-04-23 | 2020-11-02 | (주) 제이엔엠 메카텍 | Cooling Device |
| KR102247484B1 (en) * | 2019-04-23 | 2021-05-03 | (주) 제이엔엠 메카텍 | Evaporator for Cooling Device for Cooling Semiconductor elements and Cooling Device Including the Same |
| WO2021149367A1 (en) * | 2020-01-24 | 2021-07-29 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | Light irradiation device |
| JP7331713B2 (en) | 2020-01-24 | 2023-08-23 | ウシオ電機株式会社 | Light irradiation device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2013200944A (en) | Light source device | |
| RU2475675C2 (en) | Lighting device and method of cooling lighting device | |
| KR101819024B1 (en) | Thermal trim for a luminaire | |
| JP6140672B2 (en) | Insulated LED device | |
| US20100253226A1 (en) | Energy-saving lighting fixture | |
| TWI445897B (en) | Semiconductor light module | |
| RU2559808C2 (en) | Lighting fixture (versions) | |
| US20100177519A1 (en) | Electro-hydrodynamic gas flow led cooling system | |
| JP2010182796A (en) | Led lamp | |
| JP5725278B2 (en) | Light source device | |
| US20130063946A1 (en) | Lighting apparatus | |
| JP2012243393A (en) | Lighting fixture | |
| JP2008235118A (en) | Lighting system and method of manufacturing same | |
| FI116116B (en) | hybrid fittings | |
| US8917011B2 (en) | LED heat dissipation structure | |
| US10480770B2 (en) | Lamp | |
| US8936378B2 (en) | LED light source | |
| US9523494B2 (en) | LED lighting unit | |
| KR101262661B1 (en) | Airfield light module for waterproof | |
| JP6192586B2 (en) | Lighting device | |
| JP2009194008A (en) | Light-emitting diode module, lighting system, and wiring pattern setting method of light-emitting diode module | |
| JP6544002B2 (en) | Irradiator | |
| EP2834559B1 (en) | Led light structure | |
| JP2012089417A (en) | Light source device | |
| KR101105006B1 (en) | LED heat emission assembly and method of manufacturing the same |