JP2013150740A - Game machine - Google Patents
Game machine Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2013150740A JP2013150740A JP2012013766A JP2012013766A JP2013150740A JP 2013150740 A JP2013150740 A JP 2013150740A JP 2012013766 A JP2012013766 A JP 2012013766A JP 2012013766 A JP2012013766 A JP 2012013766A JP 2013150740 A JP2013150740 A JP 2013150740A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- signal
- lamp
- board
- control
- circuit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Pinball Game Machines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、遊技動作に起因する抽選処理によって大当り状態を発生させる遊技機に関し、特に、迫力ある各種の演出を安定して実行できる遊技機に関する。 The present invention relates to a gaming machine that generates a big hit state by a lottery process caused by a gaming operation, and more particularly to a gaming machine that can stably execute various powerful effects.
パチンコ機などの弾球遊技機は、遊技盤に設けた図柄始動口と、複数の表示図柄による一連の図柄変動態様を表示する図柄表示部と、開閉板が開閉される大入賞口などを備えて構成されている。そして、図柄始動口に設けられた検出スイッチが遊技球の通過を検出すると入賞状態となり、遊技球が賞球として払出された後、図柄表示部では表示図柄が所定時間変動される。その後、7・7・7などの所定の態様で図柄が停止すると大当り状態となり、大入賞口が繰返し開放されて、遊技者に有利な遊技状態を発生させている。 A ball game machine such as a pachinko machine has a symbol start opening provided on the game board, a symbol display section for displaying a series of symbol variation patterns by a plurality of display symbols, and a big winning opening for opening and closing the opening and closing plate. Configured. When the detection switch provided at the symbol start port detects the passage of the game ball, the winning state is entered, and after the game ball is paid out as a prize ball, the display symbol is changed for a predetermined time in the symbol display section. Thereafter, when the symbol is stopped in a predetermined manner such as 7, 7, 7, etc., a big hit state is established, and the big winning opening is repeatedly opened to generate a gaming state advantageous to the player.
このような遊技状態を発生させるか否かは、図柄始動口に遊技球が入賞したことを条件に実行される大当り抽選で決定されており、上記の図柄変動動作は、この抽選結果を踏まえたものとなっている。例えば、抽選結果が当選状態である場合には、リーチアクションなどと称される演出動作を20秒前後実行し、その後、特別図柄を整列させている。一方、ハズレ状態の場合にも、同様のリーチアクションが実行されることがあり、この場合には、遊技者は、大当り状態になることを強く念じつつ演出動作の推移を注視することになる。そして、図柄変動動作の終了時に、停止ラインに所定図柄が揃えば、大当り状態であることが遊技者に保証されたことになる。 Whether or not to generate such a game state is determined by a jackpot lottery executed on the condition that a game ball has won at the symbol start opening, and the above symbol variation operation is based on this lottery result. It has become a thing. For example, when the lottery result is in a winning state, an effect operation called reach action or the like is executed for about 20 seconds, and then the special symbols are aligned. On the other hand, a similar reach action may be executed even in the case of a lost state. In this case, the player pays close attention to the big hit state and pays close attention to the transition of the performance operation. When the predetermined symbols are aligned on the stop line at the end of the symbol variation operation, the player is guaranteed to be in the big hit state.
上記した演出動作は、液晶表示装置での画像演出が中心となるが、この画像演出に連動して、各種のランプを点滅させるランプ演出や、遊技者を盛り上げる音声を出力する音声演出や、可動物が移動する可動演出などが実行される。そして、これらの遊技演出を豊富化すればするほど、配線が煩雑化すると共に、消費電力が増加するので、可能な限り、配線数や消費電力を抑制できる回路構成が必要となる。 The above-mentioned performance operation is centered on the image production on the liquid crystal display device. In conjunction with this image production, a lamp production that blinks various lamps, an audio production that outputs a sound that excites the player, Movable effects such as moving animals are executed. As the game effects are enriched, the wiring becomes more complicated and the power consumption increases. Therefore, a circuit configuration capable of suppressing the number of wirings and power consumption as much as possible is required.
また、この種の遊技機では、機種毎の個性が重視されるが、機種毎にバリエーションに富んだ個性を有する一方で、極力、回路基板を統一化できる機器構成が望まれる。例えば、ランプ個数を大幅に増やしてランプ演出をアピールする機種と、ランプ個数を抑制して、余裕が生じた消費電力を他の演出動作に振り分ける機種とで、回路基板を共通化できれば、製作コストを抑制することができる。 In addition, in this type of gaming machine, individuality for each model is emphasized, but there is a demand for a device configuration that can unify circuit boards as much as possible while having individuality rich in variations for each model. For example, if the circuit board can be shared between a model that greatly increases the number of lamps and appeals the lamp effect, and a model that suppresses the number of lamps and distributes the power consumption with room for other effects, the production cost Can be suppressed.
本発明は、上記の問題点に鑑みてなされたものであって、配線数や消費電力を抑制できると共に、回路基板の多くを共通化できる遊技機を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a gaming machine that can suppress the number of wires and power consumption and can share many circuit boards.
上記の目的を達成するため、本発明は、所定のスイッチ信号に基づいて遊技者に有利な遊技状態を発生させるか否かを抽選決定して遊技動作を中心的に制御する主制御部と、前記主制御部が出力する制御コマンドに基づいて、多数のランプを発光させるランプ演出を実行する演出制御部と、を有して構成された遊技機であって、前記演出制御部は、前記ランプ演出を制御する制御回路基板と、ランプを駆動して前記ランプ演出を実行する同一構成の駆動回路を各々搭載した複数個のランプ駆動基板と、前記制御回路基板からランプ駆動信号をシリアル信号として受けて、これを全てのランプ駆動基板に転送する中継基板と、を有して構成され、前記ランプ駆動基板に搭載された駆動回路のアドレス番号の少なくとも一部は、中継基板から受けるアドレス信号に基づいて各々規定され、前記ランプ駆動信号は、これを受信すべき駆動回路を特定して伝送されている。 In order to achieve the above object, the present invention comprises a main control unit that centrally controls a game operation by lottery determination as to whether or not to generate a gaming state advantageous to a player based on a predetermined switch signal; An effect control unit that executes a lamp effect for causing a plurality of lamps to emit light based on a control command output by the main control unit, wherein the effect control unit includes the lamp A control circuit board for controlling the presentation, a plurality of lamp driving boards each equipped with a drive circuit having the same configuration for driving the lamp to execute the lamp presentation, and receiving the lamp driving signal from the control circuit board as a serial signal And a relay board that transfers this to all the lamp drive boards, and at least part of the address numbers of the drive circuits mounted on the lamp drive board is received from the relay board. Each is defined on the basis of the address signal, the lamp driving signal is transmitted to identify the driver circuit to receive it.
本発明では、ランプ駆動信号は、シリアル信号として伝送されるので、ランプ演出を如何に豊富化しても、これに対応して、配線数が増加するということがない。また、ランプを駆動してランプ演出を実行する同一構成の駆動回路を各々搭載した複数個のランプ駆動基板と、制御回路基板からランプ駆動信号をシリアル信号として受けて、これを全てのランプ駆動基板に転送する中継基板とを有して構成されるので、ランプ駆動基板を共通化することができ、中継基板を変更するだけで、多数の機種に対応することができる。 In the present invention, since the lamp driving signal is transmitted as a serial signal, the number of wirings does not increase correspondingly, no matter how much the lamp effect is enriched. In addition, a plurality of lamp drive boards each equipped with a drive circuit having the same configuration for driving a lamp to execute a lamp effect, and a lamp drive signal received as a serial signal from the control circuit board, all of the lamp drive boards are received. Therefore, it is possible to use a common lamp driving board, and it is possible to deal with a large number of models simply by changing the relay board.
好ましくは、前記アドレス信号は、中継基板又はその上流側の回路基板のハードウェア構成に基づいて、予め固定的に設定され、前記アドレス番号は、複数ビット長で規定され、その全ビット又は一部ビットが前記アドレス信号で規定され、残りのビットがランプ駆動基板において規定される。 Preferably, the address signal is fixedly set in advance based on a hardware configuration of the relay board or an upstream circuit board, and the address number is defined by a plurality of bits, and all or a part of the address number is defined. Bits are defined by the address signal and the remaining bits are defined in the lamp driving board.
また、前記駆動回路は、前記ランプ駆動信号を含んだシリアル信号と、シリアル信号の伝送中であることを示す制御信号と、シリアル信号の伝送クロック信号と、を受けて動作しているのが好適である。また、前記シリアル信号には、前記ランプ駆動信号と、前記ランプ駆動信号を受信すべき駆動回路を特定するアドレス番号とが、含まれているのが好適であり、この場合には、配線数を更に抑制することができる。 Preferably, the drive circuit operates in response to a serial signal including the lamp drive signal, a control signal indicating that the serial signal is being transmitted, and a serial signal transmission clock signal. It is. The serial signal preferably includes the lamp driving signal and an address number for specifying a driving circuit to receive the lamp driving signal. In this case, the number of wirings is determined. Further suppression can be achieved.
前記シリアル信号は、前記制御回路基板の汎用コンピュータ回路において生成される構成を採ると、回路構成を簡素化することができる。また、前記駆動回路は、駆動態様を決定する制御レジスタを含んで構成され、前記ランプ駆動信号に基づいて、所定の制御レジスタに、所望の制御データが設定されるのが好適である。 If the serial signal is generated in a general-purpose computer circuit of the control circuit board, the circuit configuration can be simplified. Preferably, the drive circuit includes a control register that determines a drive mode, and desired control data is set in a predetermined control register based on the lamp drive signal.
駆動態様には、ランプの点灯/消灯状態の他に、点灯/消灯状態に至るまでのフェード動作の有無、及び/又は、PWM制御による発光duty比率が含まれているのが好適であり、この場合には、ランプ演出を更に豊富化することができる。 It is preferable that the driving mode includes, in addition to the lighting / extinguishing state of the lamp, the presence / absence of a fade operation until the lighting / extinguishing state and / or the light emission duty ratio by PWM control. In this case, the lamp effect can be further enriched.
汎用コンピュータ回路は、好ましくは、3.5V以下の電源電圧で動作するべきであり、制御回路基板には、3.5V以下の電源電圧で動作して音声演出用の音声信号を生成する専用コンピュータ回路が搭載されているのが好適である。 The general-purpose computer circuit should preferably operate with a power supply voltage of 3.5 V or less, and the control circuit board operates with a power supply voltage of 3.5 V or less and generates a sound signal for sound production. It is preferable that a circuit is mounted.
上記した通り、本発明の遊技機によれば、配線数や消費電力を抑制できると共に、回路基板の多くを共通化できる遊技機を実現することができる。 As described above, according to the gaming machine of the present invention, it is possible to realize a gaming machine that can suppress the number of wires and power consumption and can share many circuit boards.
以下、実施例に基づいて本発明を詳細に説明する。図1は、本実施例のパチンコ機GMを示す斜視図である。このパチンコ機GMは、島構造体に着脱可能に装着される矩形枠状の木製外枠1と、外枠1に固着されたヒンジ2を介して開閉可能に枢着される前枠3とで構成されている。この前枠3には、遊技盤5が、裏側からではなく、表側から着脱自在に装着され、その前側には、ガラス扉6と前面板7とが夫々開閉自在に枢着されている。
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail based on examples. FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a pachinko machine GM of the present embodiment. This pachinko machine GM includes a rectangular frame-shaped wooden
ガラス扉6の外周には、LEDランプなどによる電飾ランプが、略C字状に配置されている。一方、ガラス扉6の上部左右位置と下側には、全3個のスピーカが配置されている。上部に配置された2個のスピーカは、各々、左右チャネルR,Lの音声を出力し、下側のスピーカは重低音を出力するよう構成されている。
On the outer periphery of the
前面板7には、発射用の遊技球を貯留する上皿8が装着され、前枠3の下部には、上皿8から溢れ出し又は抜き取った遊技球を貯留する下皿9と、発射ハンドル10とが設けられている。発射ハンドル10は発射モータと連動しており、発射ハンドル10の回動角度に応じて動作する打撃槌によって遊技球が発射される。
The
上皿8の外周面には、チャンスボタン11が設けられている。このチャンスボタン11は、遊技者の左手で操作できる位置に設けられており、遊技者は、発射ハンドル10から右手を離すことなくチャンスボタン11を操作できる。このチャンスボタン11は、通常時には機能していないが、ゲーム状態がボタンチャンス状態となると内蔵ランプが点灯されて操作可能となる。なお、ボタンチャンス状態は、必要に応じて設けられるゲーム状態である。
A chance button 11 is provided on the outer peripheral surface of the upper plate 8. The chance button 11 is provided at a position where it can be operated with the left hand of the player, and the player can operate the chance button 11 without releasing the right hand from the
上皿8の右部には、カード式球貸し機に対する球貸し操作用の操作パネル12が設けられ、カード残額を3桁の数字で表示する度数表示部と、所定金額分の遊技球の球貸しを指示する球貸しスイッチと、ゲーム終了時にカードの返却を指令する返却スイッチとが設けられている。
On the right side of the upper plate 8, an
図2に示すように、遊技盤5の表面には、金属製の外レールと内レールとからなるガイドレール13が環状に設けられ、その略中央には、中央開口HOが設けられている。そして、中央開口HOの下方には、不図示の可動演出体が隠蔽状態で収納されており、可動予告演出時には、その可動演出体が上昇して露出状態となることで、所定の信頼度の予告演出を実現している。ここで、予告演出とは、遊技者に有利な大当り状態が招来することを不確定に報知する演出であり、予告演出の信頼度とは、大当り状態が招来する確率を意味している。
As shown in FIG. 2, a
中央開口HOには、大型の液晶カラーディスプレイ(LCD)で構成されたメイン表示装置DS1が配置され、メイン表示装置DS1の右側には、小型の液晶カラーディスプレイで構成された可動式のサブ表示装置DS2が配置されている。 A main display device DS1 composed of a large liquid crystal color display (LCD) is disposed in the central opening HO, and a movable sub display device composed of a small liquid crystal color display is disposed on the right side of the main display device DS1. DS2 is arranged.
メイン表示装置DS1は、大当り状態に係わる特定図柄を変動表示すると共に背景画像や各種のキャラクタなどをアニメーション的に表示する装置である。この表示装置DS1は、中央部に特別図柄表示部Da〜Dcと右上部に普通図柄表示部19とを有している。そして、特別図柄表示部Da〜Dcでは、大当り状態の招来を期待させるリーチ演出が実行されることがあり、特別図柄表示部Da〜Dc及びその周りでは、適宜な予告演出などが実行される。
The main display device DS1 is a device that variably displays a specific symbol related to the big hit state and displays a background image and various characters in an animated manner. The display device DS1 has special symbol display portions Da to Dc in the center portion and a normal
サブ表示装置DS2は、通常時には、その表示画面が遊技者に見やすい角度に傾斜した静止状態で画像情報を表示している。但し、所定の予告演出時には、遊技者に見やすい角度に傾斜角度を変えながら、図示の左側に移動する共に、所定の予告画像を表示するようになっている。 The sub display device DS2 normally displays the image information in a stationary state in which the display screen is inclined at an angle that is easy for the player to see. However, at the time of a predetermined notice effect, while moving to the left side of the figure while changing the inclination angle to an angle that is easy for the player to see, a predetermined notice image is displayed.
すなわち、実施例のサブ表示装置DS2は、単なる表示装置ではなく、予告演出を実行する可動演出体としても機能している。ここで、サブ表示装置DS2による予告演出は、その信頼度が高く設定されており、遊技者は、大きな期待感をもってサブ表示装置DS2の移動動作に注目することになる。 That is, the sub display device DS2 of the embodiment functions not only as a display device but also as a movable effect body that executes a notice effect. Here, the announcement effect by the sub display device DS2 is set with high reliability, and the player pays attention to the moving operation of the sub display device DS2 with a great sense of expectation.
遊技球が落下移動する遊技領域には、第1図柄始動口15a、第2図柄始動口15b、第1大入賞口16a、第2大入賞口16b、普通入賞口17、及び、ゲート18が配設されている。これらの入賞口15〜18は、それぞれ内部に検出スイッチを有しており、遊技球の通過を検出できるようになっている。
In the game area in which the game ball falls and moves, the first
第1図柄始動口15aの上部には、導入口INから進入した遊技球がシーソー状又はルーレット状に移動した後に、第1図柄始動口15に入賞可能に構成された演出ステージ14が配置されている。そして、第1図柄始動口15に遊技球が入賞すると、特別図柄表示部Da〜Dcの変動動作が開始されるよう構成されている。
On the upper part of the first
第2図柄始動口15bは、左右一対の開閉爪を備えた電動式チューリップで開閉されるように構成され、普通図柄表示部19の変動後の停止図柄が当り図柄を表示した場合には、所定時間だけ、若しくは、所定個数の遊技球を検出するまで、開閉爪が開放されるようになっている。
The second symbol start port 15b is configured to be opened and closed by an electric tulip having a pair of left and right opening and closing claws. When the stop symbol after fluctuation of the normal
なお、普通図柄表示部19は、普通図柄を表示するものであり、ゲート18を通過した遊技球が検出されると、普通図柄が所定時間だけ変動し、遊技球のゲート18の通過時点において抽出された抽選用乱数値により決定される停止図柄を表示して停止する。
The normal
第1大入賞口16aは、前後方向に進退するスライド盤を有して構成され、第2大入賞口16bは、下端が軸支されて前方に開放する開閉板を有して構成されている。第1大入賞口16aや第2大入賞口16bの動作は、特に限定されないが、この実施例では、第1大入賞口16aは、第1図柄始動口15aに対応し、第2大入賞口16bは、第1図柄始動口15bに対応するよう構成されている。
The first
すなわち、第1図柄始動口15aに遊技球が入賞すると、特別図柄表示部Da〜Dcの変動動作が開始され、その後、所定の大当り図柄が特別図柄表示部Da〜Dcに整列すると、第1大当りたる特別遊技が開始され、第1大入賞口16aのスライド盤が、前方に開放されて遊技球の入賞が容易化される。
That is, when a game ball is won at the first symbol start opening 15a, the changing operation of the special symbol display portions Da to Dc is started. After that, when the predetermined big hit symbol is aligned with the special symbol display portions Da to Dc, the first big hit A special game is started, and the slide board of the first big winning
一方、第2図柄始動口15bへの遊技球の入賞によって開始された変動動作の結果、所定の大当り図柄が特別図柄表示部Da〜Dcに整列すると、第2大当りたる特別遊技が開始され、第2大入賞口16bの開閉板が開放されて遊技球の入賞が容易化される。なお、特別遊技(大当り状態)の遊技価値は、整列する大当り図柄などに対応して種々相違するが、何れの遊技価値が付与されるかは、遊技球の入賞タイミングに応じた抽選結果に基づいて予め決定される。 On the other hand, when a predetermined big hit symbol is aligned with the special symbol display portions Da to Dc as a result of the fluctuating motion started by winning the game ball in the second symbol start opening 15b, a special game corresponding to the second big hit is started, The open / close plate of the two major winning openings 16b is opened to facilitate the winning of game balls. The game value of a special game (hit state) varies according to the jackpot symbols to be arranged, but which game value is given depends on the lottery result according to the winning timing of the game ball. Determined in advance.
典型的な大当り状態では、大入賞口16の開閉板が開放された後、所定時間が経過し、又は所定数(例えば10個)の遊技球が入賞すると開閉板が閉じる。このような動作は、最大で例えば15回まで継続され、遊技者に有利な状態に制御される。なお、特別図柄表示部Da〜Dcの変動後の停止図柄が特別図柄のうちの特定図柄であった場合には、特別遊技の終了後のゲームが高確率状態(確変状態)となるという特典が付与される。
In a typical big hit state, the opening / closing plate closes when a predetermined time elapses after the opening / closing plate of the big winning
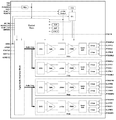
図3は、上記した各動作を実現するパチンコ機GMの全体回路構成を示すブロック図であり、図4〜図8はその一部を詳細に図示したものである。図3に示す通り、このパチンコ機GMは、AC24Vを受けて各種の直流電圧や、電源異常信号ABN1、ABN2やシステムリセット信号(電源リセット信号)SYSなどを出力する電源基板20と、遊技制御動作を中心統括的に担う主制御基板21と、主制御基板21から受けた制御コマンドCMDに基づいてランプ演出及び音声演出を実行する演出制御基板22と、演出制御基板22から受けた制御コマンドCMD’に基づいて表示装置DS1,DS2を駆動する画像制御基板23と、主制御基板21から受けた制御コマンドCMD”に基づいて払出モータMを制御して遊技球を払い出す払出制御基板24と、遊技者の操作に応答して遊技球を発射させる発射制御基板25と、を中心に構成されている。
FIG. 3 is a block diagram showing an overall circuit configuration of the pachinko machine GM that realizes the above-described operations, and FIGS. 4 to 8 show a part of the details in detail. As shown in FIG. 3, the pachinko machine GM receives 24V AC and outputs various DC voltages, power supply abnormality signals ABN1, ABN2, a system reset signal (power reset signal) SYS, and the like, and a game control operation.
但し、この実施例では、主制御基板21が出力する制御コマンドCMDは、コマンド中継基板26と演出インタフェイス基板27を経由して、演出制御基板22に伝送される。また、演出制御基板22が出力する制御コマンドCMD’は、演出インタフェイス基板27と画像インタフェイス基板28を経由して、画像制御基板23に伝送され、主制御基板21が出力する制御コマンドCMD”は、主基板中継基板32を経由して、払出制御基板24に伝送される。制御コマンドCMD,CMD’,CMD”は、何れも16ビット長であるが、主制御基板21や払出制御基板24が関係する制御コマンドは、8ビット長毎に2回に分けてパラレル送信されている。一方、演出制御基板22から画像制御基板23に伝送される制御コマンドCMD’は、16ビット長をまとめてパラレル伝送されている。そのため、可動予告演出を含む予告演出を、多様化して多数の制御コマンドを連続的に送受信するような場合でも、迅速にその処理を終えることができ、他の制御動作に支障を与えない。
However, in this embodiment, the control command CMD output from the
ところで、本実施例では、演出インタフェイス基板27と演出制御基板22とは、配線ケーブルを経由することなく、雄型コネクタと雌型コネクタとを直結されて二枚の回路基板が積層されている。同様に、画像インタフェイス基板28と画像制御基板23についても、配線ケーブルを経由することなく、雄型コネクタと雌型コネクタとを直結されて二枚の回路基板が積層されている。そのため、各電子回路の回路構成を複雑高度化しても基板全体の収納空間を最小化できると共に、接続ラインを最短化することで耐ノイズ性を高めることができる。
By the way, in the present embodiment, the
これら主制御基板21、演出制御基板22、画像制御基板23、及び払出制御基板24には、ワンチップマイコンを備えるコンピュータ回路がそれぞれ搭載されている。そこで、これらの制御基板21〜24とインタフェイス基板27〜28に搭載された回路、及びその回路によって実現される動作を機能的に総称して、本明細書では、主制御部21、演出制御部22’、画像制御部23’、及び払出制御部24と言うことがある。すなわち、この実施例では、演出制御基板22と演出インタフェイス基板27とで演出制御部22’を構成し、画像制御基板23と画像インタフェイス基板28とで画像制御部23’を構成している。なお、演出制御部22’、画像制御部23’、及び払出制御部24の全部又は一部がサブ制御部である。
The
また、このパチンコ機GMは、図3の破線で囲む枠側部材GM1と、遊技盤5の背面に固定された盤側部材GM2とに大別されている。枠側部材GM1には、ガラス扉6や前面板7が枢着された前枠3と、その外側の木製外枠1とが含まれており、機種の変更に拘わらず、長期間にわたって遊技ホールに固定的に設置される。一方、盤側部材GM2は、機種変更に対応して交換され、新たな盤側部材GM2が、元の盤側部材の代わりに枠側部材GM1に取り付けられる。なお、枠側部材1を除く全てが、盤側部材GM2である。
The pachinko machine GM is roughly divided into a frame side member GM1 surrounded by a broken line in FIG. 3 and a board side member GM2 fixed to the back of the
図3の破線枠に示す通り、枠側部材GM1には、電源基板20と、払出制御基板24と、発射制御基板25と、枠中継基板35とが含まれており、これらの回路基板が、前枠3の適所に各々固定されている。一方、遊技盤5の背面には、主制御基板21、演出制御基板22、画像制御基板23が、表示装置DS1,DS2やその他の回路基板と共に固定されている。そして、枠側部材GM1と盤側部材GM2とは、一箇所に集中配置された接続コネクタC1〜C4によって電気的に接続されている。
As shown in the broken line frame in FIG. 3, the frame-side member GM1 includes a
電源基板20は、接続コネクタC2を通して、主基板中継基板32に接続され、接続コネクタC3を通して、電源中継基板33に接続されている。電源基板20には、交流電源の投入と遮断とを監視する電源監視部MNTが設けられている。電源監視部MNTは、交流電源が投入されたことを検知すると、所定時間だけシステムリセット信号SYSをLレベルに維持した後に、これをHレベルに遷移させる。
The
また、電源監視部MNTは、交流電源の遮断を検知すると、電源異常信号ABN1,ABN2を、直ちにLレベルに遷移させる。なお、電源異常信号ABN1,ABN2は、電源投入後に速やかにHレベルとなる。 Further, when power supply monitoring unit MNT detects the interruption of the AC power supply, power supply abnormality signals ABN1 and ABN2 are immediately shifted to the L level. The power supply abnormality signals ABN1 and ABN2 quickly become H level after the power is turned on.
ところで、本実施例のシステムリセット信号は、交流電源に基づく直流電源によって生成されている。そのため、交流電源の投入(通常は電源スイッチのON)を検知してHレベルに増加した後は、直流電源電圧が異常レベルまで低下しない限り、Hレベルを維持する。したがって、直流電源電圧が維持された状態で、交流電源が瞬停状態となっても、システムリセット信号SYSがCPUをリセットすることはない。なお、電源異常信号ABN1,ABN2は、交流電源の瞬停状態でも出力される。 Incidentally, the system reset signal of this embodiment is generated by a DC power supply based on an AC power supply. For this reason, after detecting the turning-on of the AC power supply (usually turning on the power switch) and increasing it to the H level, the H level is maintained unless the DC power supply voltage drops to an abnormal level. Therefore, even if the AC power supply is in an instantaneous power interruption state while the DC power supply voltage is maintained, the system reset signal SYS does not reset the CPU. The power supply abnormality signals ABN1 and ABN2 are also output even when the AC power supply is instantaneously stopped.
主基板中継基板32は、電源基板20から出力される電源異常信号ABN1、バックアップ電源BAK、及びDC5V,DC12V,DC32Vを、そのまま主制御部21に出力している。一方、電源中継基板33は、電源基板20から受けたシステムリセット信号SYSや、交流及び直流の電源電圧を、そのまま演出インタフェイス基板27に出力している。演出インタフェイス基板27は、受けたシステムリセット信号SYSを、そのまま演出制御部22’と画像制御部23’に出力している。
The main
一方、払出制御基板24は、中継基板を介することなく、電源基板20に直結されており、主制御部21が受けると同様の電源異常信号ABN2や、バックアップ電源BAKを、その他の電源電圧と共に直接的に受けている。
On the other hand, the
電源基板20が出力するシステムリセット信号SYSは、電源基板20に交流電源24Vが投入されたことを示す電源リセット信号であり、この電源リセット信号によって演出制御部22’と画像制御部23’のワンチップマイコンは、その他のIC素子と共に電源リセットされるようになっている。
The system reset signal SYS output from the
但し、このシステムリセット信号SYSは、主制御部21と払出制御部24には、供給されておらず、各々の回路基板21,24のリセット回路RSTにおいて電源リセット信号(CPUリセット信号)が生成されている。そのため、例えば、接続コネクタC2がガタついたり、或いは、配線ケーブルにノイズが重畳しても、主制御部21や払出制御部24のCPUが異常リセットされるおそれはない。演出制御部22’と画像制御部23’は、主制御部21からの制御コマンドに基づいて、従属的に演出動作を実行することから、回路構成の複雑化を回避するために、電源基板20から出力されるシステムリセット信号SYSを利用している。
However, the system reset signal SYS is not supplied to the
ところで、主制御部21や払出制御部24に設けられたリセット回路RSTは、各々ウォッチドッグタイマを内蔵しており、各制御部21,24のCPUから、定時的なクリアパルスを受けない限り、各CPUは強制的にリセットされる。
By the way, the reset circuits RST provided in the
また、この実施例では、RAMクリア信号CLRは、主制御部21で生成されて主制御部21と払出制御部24のワンチップマイコンに伝送されている。ここで、RAMクリア信号CLRは、各制御部21,24のワンチップマイコンの内蔵RAMの全領域を初期設定するか否かを決定する信号であって、係員が操作する初期化スイッチSWのON/OFF状態に対応した値を有している。
In this embodiment, the RAM clear signal CLR is generated by the
主制御部21及び払出制御部24は、電源基板20から電源異常信号ABN1,ABN2を受けることによって、停電や営業終了に先立って、必要な終了処理を開始するようになっている。また、バックアップ電源BAKは、営業終了や停電により交流電源24Vが遮断された後も、主制御部21と払出制御部24のワンチップマイコンの内蔵RAMのデータを保持するDC5Vの直流電源である。したがって、主制御部21と払出制御部24は、電源遮断前の遊技動作を電源投入後に再開できることになる(電源バックアップ機能)。このパチンコ機では少なくとも数日は、各ワンチップマイコンのRAMの記憶内容が保持されるよう設計されている。
The
図3に示す通り、主制御部21は、主基板中継基板32を経由して、払出制御部24に制御コマンドCMD”を送信する一方、払出制御部24からは、遊技球の払出動作を示す賞球計数信号や、払出動作の異常に係わるステイタス信号CONや、動作開始信号BGNを受信している。ステイタス信号CONには、例えば、補給切れ信号、払出不足エラー信号、下皿満杯信号が含まれる。動作開始信号BGNは、電源投入後、払出制御部24の初期動作が完了したことを主制御部21に通知する信号である。
As shown in FIG. 3, the
また、主制御部21は、遊技盤中継基板31を経由して、遊技盤5の各遊技部品に接続されている。そして、遊技盤上の各入賞口16〜18に内蔵された検出スイッチのスイッチ信号を受ける一方、電動式チューリップなどのソレノイド類を駆動している。ソレノイド類や検出スイッチは、主制御部21から配電された電源電圧VB(12V)で動作するよう構成されている。また、図柄始動口15への入賞状態などを示す各スイッチ信号は、電源電圧VB(12V)と電源電圧Vcc(5V)とで動作するインタフェイスICで、TTLレベル又はCMOSレベルのスイッチ信号に変換された上で、主制御部21に伝送される。
The
先に説明した通り、演出制御基板22と演出インタフェイス基板27とはコネクタ連結によって一体化されており、演出制御部22’は、電源中継基板33を経由して、電源基板20から各レベルの直流電圧(5V,12V,32V)と、システムリセット信号SYSを受けている(図3及び図5参照)。また、演出制御部22’は、コマンド中継基板26を経由して、主制御部21から制御コマンドCMDとストローブ信号STBとを受けている(図3及び図5参照)。
As described above, the
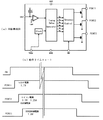
そして、演出制御部22’は、ランプ接続基板29を経由して、複数個(実施例では4個)のランプ駆動基板37・・・に対して、ランプ駆動信号を含んだシリアル信号DATAを出力することで、多数のLEDランプや装飾ランプ(ランプ群)を駆動している(図3〜図5参照)。図4に示す通り、4個のランプ駆動基板37・・・は、全て同一回路構成であり、遊技機の機種毎に、その個数が適宜に増減変更される。
Then, the
一方、ランプ接続基板29は、ランプ駆動基板37・・・の個数に対応して、遊技機の機種毎に用意されており、図4の実施例では、4個のランプ駆動基板37・・・に対応した内部構成を有している。すなわち、実施例のランプ接続基板29は、4個のランプ駆動基板37・・・に対応して4個のバッファ回路BUFを有して構成され、演出制御部22’(ワンチップマイコン40)から受ける3種類の信号(EN,DATA,CK)を、バッファ回路BUFを経由して各ランプ駆動基板37に転送している。3種類の信号は、具体的には、動作制御信号EN、ランプ駆動信号を含んだシリアル信号DATA、及び、転送クロック信号CKである。
On the other hand, the
また、ランプ接続基板29は、各ランプ駆動基板37(具体的には駆動回路DRi)を特定する2ビット長のアドレス信号と、演出インタフェイス基板20から受ける直流13V及び5Vと、リセット信号RSTとを、グランド信号GNDと共に、各ランプ駆動基板37に伝送している。なお、直流13Vは、ランプ群に供給される駆動電源であり、直流5Vは、ランプ群を駆動する駆動回路DR1〜DR4の電源電圧である。また、リセット信号RSTは、電源基板20から受けるシステムリセット信号SYSに基づいて生成され、電源投入時に各駆動回路DR1〜DR4を電源リセットしている。
Further, the
図4に示す通り、各ランプ駆動基板37には、アドレス端子A0−A4の5ビットデータ(アドレス番号)で付番される同一内部構成の駆動回路DR1〜DR4が1個ずつ搭載されている。図示の通り、全ての駆動回路DR1〜DR4において、アドレス端子の下位3ビットは、予め0に設定され、上位2ビットは、ランプ接続基板29から受けるアドレス信号によって固定的に設定される。
As shown in FIG. 4, each lamp driving substrate 37 is mounted with one driving circuit DR1 to DR4 having the same internal configuration numbered by the 5-bit data (address number) of the address terminals A0 to A4. As shown in the figure, in all the drive circuits DR1 to DR4, the lower 3 bits of the address terminal are set to 0 in advance, and the upper 2 bits are fixedly set by an address signal received from the
したがって、この実施例では、駆動回路DR1〜DR4のアドレス番号は、ランプ接続基板29から伝送される2ビット長のアドレス信号に基づいて、固定的に00000、01000、10000、11000に付番されることになる。本実施例は、このような構成を採るので、遊技機の機種に応じてランプ個数を変更する場合には、ランプ接続基板29を交換すると共に、ランプ駆動基板37・・・の個数を適宜に変更すれば足り、それ以外の回路構成を変更する必要が無いので、ランプ接続基板29以外の回路基板を共通化することができる。
Therefore, in this embodiment, the address numbers of the drive circuits DR1 to DR4 are fixedly assigned 00000, 01000, 10000, and 11000 based on the 2-bit length address signal transmitted from the
駆動回路DRは、動作制御信号ENと転送クロック信号CKとに基づいて、ランプ駆動信号を含んだシリアル信号DATAを受信し、受信したランプ駆動信号をパラレル変換して出力する回路である。具体的な回路構成は、特に限定されないが、実施例の駆動回路DRは、多数の制御レジスタR1〜Rmを内蔵し、各制御レジスタR1〜Rmに制御データDi(8ビット長)を設定する(書込む)ことで、16ビット長の出力端子の各出力が適宜に制御される駆動ICを使用している。 The drive circuit DR is a circuit that receives the serial signal DATA including the lamp drive signal based on the operation control signal EN and the transfer clock signal CK, converts the received lamp drive signal into parallel, and outputs it. Although a specific circuit configuration is not particularly limited, the drive circuit DR of the embodiment includes a large number of control registers R1 to Rm, and sets control data Di (8-bit length) in each of the control registers R1 to Rm ( By using the driver IC, the outputs of the 16-bit output terminals are appropriately controlled.
ここで、制御レジスタR1〜Rmのレジスタ番号は、8ビット長である。なお、先に説明した通り、5ビット長のアドレス端子(A0−A4)は、ランプ接続基板29からの2ビット長も含め、予め、H/Lレベルに設定されており、各駆動回路DR1〜DR4のアドレス番号は、この実施例では00H、08H、10H、18Hである。
Here, the register numbers of the control registers R1 to Rm are 8 bits long. As described above, the 5-bit address terminals (A0 to A4) including the 2-bit length from the
各制御レジスタR1〜Rmに制御データDiを設定することで実現される動作内容としては、各出力端子のON/OFF状態だけでなく、ON/OFF状態に至るまでのフェード動作(fade in/out)の有無、ON状態の出力端子のPWM制御におけるduty比(0〜99.6%)などが可能である。そのため、輝度制御時やfade in/out演出時に、ワンチップマイコン40は、ランプ駆動信号(シリアルデータ)を、わざわざPWM制御用に変更する必要がなく、単に、該当レジスタRiの制御データを設定変更するだけでよいので、制御負担が大幅に軽減される。
The operation contents realized by setting the control data Di in each control register R1 to Rm include not only the ON / OFF state of each output terminal but also the fade operation (fade in / out) until reaching the ON / OFF state. ) And the duty ratio (0 to 99.6%) in the PWM control of the output terminal in the ON state. Therefore, the one-
もっとも、ランプ駆動信号をPWM制御することで、固定的なフェード動作とは異なる個性的なfade in/out演出時を実施できるのは勿論であり、要するに、本実施例によれば、多様なランプ演出が可能となる。 Of course, by controlling the lamp driving signal by PWM, it is possible to implement a unique fade in / out effect different from the fixed fade operation. In short, according to this embodiment, various lamps can be used. Production is possible.
図4(b)は、ワンチップマイコン40と、複数の駆動回路DR1〜DR4との間の通信プロトコルを示すタイムチャートである。図示の通り、ワンチップマイコン40は、先ず、動作制御信号ENをON状態(Hレベル)に設定した状態で、(1)制御データDiを書込むべき駆動回路DR1〜DR4のアドレス番号ADRi(8ビット長に拡張)、(2)その駆動回路DRiにおける制御データDiを書込むべき制御レジスタR1〜Rmの番号(8ビット長)、(3)その制御レジスタRiに書込むべき制御データDi(8ビット長の設定値)を、転送クロック信号CKに同期させてシリアル信号DATAとして出力する。
FIG. 4B is a time chart showing a communication protocol between the one-
なお、一連の制御レジスタR1〜Rmについて、その先頭レジスタ番号Riを指定すれば、その後に連続する制御データ(設定値)D1,D2,R3・・・は、Ri,Ri+1,Ri+2・・・の制御データであると駆動回路DRiに認識されて自動的に取得される。したがって、必ずしも、全ての制御レジスタRiに設定値を設定する必要は無く、例えば、一連M個の制御レジスタRi〜Ri+M−1への書込み処理であれば、制御データM個と、アドレスデータ2個とで、合計8×(M+2)ビット長の出力処理で足りる。 If the first register number Ri is designated for a series of control registers R1 to Rm, the subsequent control data (set values) D1, D2, R3... Are represented by Ri, Ri + 1, Ri + 2. The control data is recognized by the drive circuit DRi and automatically acquired. Therefore, it is not always necessary to set a set value in all the control registers Ri. For example, in the case of a write process to a series of M control registers Ri to Ri + M−1, M pieces of control data and two pieces of address data Therefore, a total output process of 8 × (M + 2) bits is sufficient.
そして、全てのデータの出力を終えると、ワンチップマイコン40は、動作制御信号ENをON状態からOFF状態に戻せばよく、この動作に対応して、アドレス番号ADRiで特定された駆動回路DRでは、一連の制御レジスタRi・・・Ri+M−1に取得した制御データD1・・・に対応する動作を開始する。
When the output of all data is completed, the one-
図3や図5に示す通り、演出制御部22’は、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30にも、ランプ駆動信号及びモータ駆動信号を出力することで、ランプ群を駆動すると共に、複数のステッピングモータで構成された演出モータ群M1〜Mnを駆動している。ここで、ランプ駆動信号とモータ駆動信号は、図4のシリアル信号DATAと同一構成のシリアル信号として出力されるので、演出内容を豊富化するべくランプ個数や演出モータ個数を如何に増やしても、配線ケーブルが増加することがなく、機器構成が簡素化される。なお、ランプ群は、ほぼ定常的にランプ演出を実現する一方、演出モータ群は、突然動作を開始して、可動演出体による可動予告演出を実現している。
As shown in FIG. 3 and FIG. 5, the
また、演出制御部22’は、画像制御部23’に対して、制御コマンドCMD’及びストローブ信号STB’と、電源基板20から受けたシステムリセット信号SYSと、2種類の直流電圧(12V,5V)とを出力している(図3及び図5参照)。
In addition, the
そして、画像制御部23’では、制御コマンドCMD’に基づいてメイン表示装置DS1を駆動して各種の画像演出を実行している。図5に示す通り、メイン表示装置DS1は、LEDバックライトによって発光しており、画像インタフェイス基板28から5対のLVDS(低電圧差動伝送Low voltage differential signaling)信号と、バックライト電源電圧(12V)とを受けて駆動されている。メイン表示装置DS1のバックライト光は、PWM制御による輝度が制御可能に構成されている。
The image controller 23 'drives the main display device DS1 based on the control command CMD' to execute various image effects. As shown in FIG. 5, the main display device DS1 emits light by the LED backlight, and five pairs of LVDS (Low voltage differential signaling) signals from the
また、画像制御部23’は、制御コマンドCMD’に基づく予告演出として、サブ表示装置DS2において適宜な予告演出を実行している。サブ表示装置DS2も、バックライト光によって発光しており、そのON/OFF状態が制御可能に構成されている。
Further, the
サブ表示装置DS2は、画像インタフェイス基板28からバックライト電源電圧(5V)と、V−by−One(登録商標)信号とを受ける中継基板36によって駆動されており、予告演出時には、演出制御部22’に制御される演出モータMiが同期して駆動されて可動演出が実行される。
The sub display device DS2 is driven by the
続いて、図5に基づいて、上記した演出制御部22’と画像制御部23’の構成を更に詳細に説明する。図5に示す通り、演出インタフェイス基板27は、電源中継基板33を経由して、電源基板20から3種類の直流電圧(5V,12V,32V)を受けている。ここで、直流電圧5Vは、デジタル論理回路の電源電圧として、演出インタフェイス基板27と、ランプ接続基板29及びランプ駆動基板37と、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30と、画像インタフェイス基板28と、画像制御基板23とに配電されて各デジタル回路を動作させている。
Next, the configuration of the above-described effect control unit 22 'and image control unit 23' will be described in more detail with reference to FIG. As shown in FIG. 5, the
但し、演出制御基板22には、直流電圧5Vが配電されておらず、12VからDC/DCコンバータで降圧された直流電圧3.3Vと、3.3VからDC/DCコンバータで更に降圧された直流電圧1.8Vだけが、演出インタフェイス基板27から演出制御基板22に配電されている。このように、本実施例の演出制御基板22は、全ての回路が電源電圧3.3Vで駆動されているので、電源電圧を5Vで動作する場合と比較して大幅に低電力化することができ、例えば、演出制御基板22の直上に演出インタフェイス基板27を配置して積層しても放熱上の問題が生じない。
However, the direct
また、演出インタフェイス基板27が、電源基板20から受けた直流電圧12Vは、そのままデジタルアンプ46の電源電圧として使用されると共に、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30に配電されている。一方、電源基板20から受けた直流電圧32Vは、演出インタフェイス基板のDC/DCコンバータにおいて直流電圧13Vに降圧されて、ランプ接続基板29及びランプ駆動基板37と、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30とに配電されている。
The direct
図5に示すように、演出制御部22’は、音声演出・ランプ演出・演出可動体による予告演出・データ転送などの処理を実行するワンチップマイコン40と、ワンチップマイコン40の制御プログラムなどを記憶するフラッシュメモリ(flash memory)41と、ワンチップマイコン40からの指示に基づいて音声信号を再生して出力する音声合成回路42と、再生される音声信号の元データである圧縮音声データを記憶する音声用メモリ43とを備えて構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 5, the
ここで、ワンチップマイコン40、フラッシュメモリ41、及び音声用メモリ43は、電源電圧3.3Vで動作しており、また、音声合成回路42は、電源電圧3.3V及び電源電圧1.8Vで動作しており大幅な省電力化が実現されている。1.8Vは、音声合成回路のコンピュータ・コア部の電源電圧であり、3.3Vは、I/O部の電源電圧である。
Here, the one-
ワンチップマイコン40には、複数のパラレル入出力ポートPIOが内蔵されている。そして、第1入力ポートPO1には、主制御部21からの制御コマンドCMD及びストローブ信号STBが入力され、第2入力ポートPO2からは、制御コマンドCMD’及びストローブ信号STB’が出力されるよう構成されている。
The one-
具体的には、第1入力ポートPO1には、主制御基板21から出力された制御コマンドCMDとストローブ信号(割込み信号)STBとが、演出インタフェイス基板27のバッファ44において、電源電圧3.3Vに対応する論理レベルに変換されて8ビット単位で供給される。割込み信号STBは、ワンチップマイコンの割込み端子に供給され、受信割込み処理によって、演出制御部22’は、制御コマンドCMDを取得するよう構成されている。
Specifically, the control command CMD and the strobe signal (interrupt signal) STB output from the
演出制御部22’が取得する制御コマンドCMDには、(1)異常報知その他の報知用制御コマンドなどの他に、(2)図柄始動口への入賞に起因する各種演出動作の概要特定する制御コマンド(変動パターンコマンド)や、図柄種別を指定する制御コマンド(図柄指定コマンド)が含まれている。ここで、変動パターンコマンドで特定される演出動作の概要には、演出開始から演出終了までの演出総時間と、大当たり抽選における当否結果とが含まれている。
The control command CMD acquired by the
また、図柄指定コマンドには、大当たり抽選の結果に応じて、大当たりの場合には、大当たり種別に関する情報(15R確変、2R確変、15R通常、2R通常など)を特定する情報が含まれ、ハズレの場合には、ハズレを特定する情報が含まれている。変動パターンコマンドで特定される演出動作の概要には、演出開始から演出終了までの演出総時間と、大当り抽選における当否結果とが含まれている。なお、これらに加えて、リーチ演出や予告演出の有無などを含めて変動パターンコマンドで特定しても良いが、この場合でも、演出内容の具体的な内容は特定されていない。 In addition, the symbol designating command includes information for identifying information on the jackpot type (15R probability variation, 2R probability variation, 15R normal, 2R normal, etc.) in the case of a jackpot according to the result of the jackpot lottery. In some cases, information for identifying a loss is included. The outline of the production operation specified by the variation pattern command includes the production total time from the production start to the production end, and the result of success or failure in the big hit lottery. In addition to these, the change pattern command including the presence or absence of the reach effect or the notice effect may be specified, but even in this case, the specific content of the effect content is not specified.
そのため、演出制御部22’では、変動パターンコマンドを取得すると、これに続いて演出抽選を行い、取得した変動パターンコマンドで特定される演出概要を更に具体化している。例えば、リーチ演出や予告演出について、その具体的な内容が決定される。そして、決定された具体的な遊技内容にしたがい、LED群などの点滅によるランプ演出や、スピーカによる音声演出の準備動作を行うと共に、画像制御部23’に対して、ランプやスピーカによる演出動作に同期した画像演出に関する制御コマンドCMD’を出力する。
Therefore, when the change pattern command is acquired, the
このような演出動作に同期した画像演出を実現するため、演出制御部22’は、第2入力ポートPO2を通して、画像制御部23’に対するストローブ信号(割込み信号)STB’と共に、16ビット長の制御コマンドCMD’を演出インタフェイス基板27に向けて出力している。なお、演出制御部22’は、図柄指定コマンドや、表示装置DS1に関連する報知用制御コマンドや、その他の制御コマンドを受信した場合は、その制御コマンドを、16ビット長に纏めた状態で、割込み信号STB’と共に演出インタフェイス基板27に向けて出力している。
In order to realize such an image effect synchronized with the effect operation, the
上記した演出制御基板22の構成に対応して、演出インタフェイス基板27には出力バッファ45が設けられており、16ビット長の制御コマンドCMD’と1ビット長の割込み信号STB’を画像インタフェイス基板28に出力している。そして、これらのデータCMD’,STB’は、画像インタフェイス基板28を経由して、画像制御基板23に伝送される。
Corresponding to the configuration of the
また、演出インタフェイス基板27には、音声合成回路42から出力される音声信号を受けるデジタルアンプ46が配置されている。先に説明した通り、音声合成回路42は、3.3Vと1.8Vの電源電圧で動作しており、また、デジタルアンプ46は、電源電圧12VでD級増幅動作しており、消費電力を抑制しつつ大音量の音声演出を可能にしている。
The
そして、デジタルアンプ46の出力によって、遊技機上部の左右スピーカと、遊技機下部のスピーカとを駆動している。そのため、音声合成回路42は、3チャネルの音声信号を生成する必要があり、これをパラレル伝送すると、音声合成回路42とデジタルアンプ46との配線が複雑化する。
The left and right speakers at the upper part of the gaming machine and the speakers at the lower part of the gaming machine are driven by the output of the digital amplifier 46. Therefore, the
そこで、本実施例では、音質の劣化を防止すると共に、配線の複雑化を回避するため、音声合成回路42とデジタルアンプ46との間は、4本の信号線で接続されており、具体的には、転送クロック信号SCLKと、チャネル制御信号LRCLKと、2ビット長のシリアル信号SDATA1,SDATA2との合計4ビットの信号線に抑制されている。なお、何れの信号も、その振幅レベルは3.3Vである。
Therefore, in this embodiment, the
ここで、SDATA1は、遊技機上部に配置された左右スピーカのステレオ信号R,Lを特定するPCMデータについてのシリアル信号であり、SDATA2は、遊技機下部に配置された重低音スピーカのモノラル信号を特定するPCMデータについてのシリアル信号である。そして、音声合成回路342は、チャネル制御信号LRCLKをLレベルに維持した状態で、左チャネルの音声信号Lを伝送し、チャネル制御信号LRCLKをHレベルに維持した状態で、右チャネルの音声信号Rを伝送する。なお、重低音スピーカは本実施例では1個であるので、モノラル音声信号が伝送されているが、ステレオ音声信号として伝送できるのは勿論である。 Here, SDATA1 is a serial signal for PCM data specifying the stereo signals R and L of the left and right speakers arranged at the upper part of the gaming machine, and SDATA2 is a monaural signal of the heavy bass speaker arranged at the lower part of the gaming machine. This is a serial signal for the PCM data to be specified. The voice synthesis circuit 342 transmits the left channel audio signal L while maintaining the channel control signal LRCLK at the L level, and maintains the channel control signal LRCLK at H level while maintaining the channel control signal LRCLK at the L level. Is transmitted. Note that since there is only one heavy bass speaker in this embodiment, a monaural audio signal is transmitted, but it is of course possible to transmit it as a stereo audio signal.
何れにしても本実施例では、4種類の音声信号を4本のケーブルで伝送可能であるので、最小のケーブル本数によってノイズによる音声劣化のない信号伝達が可能となる。すなわち、シリアル伝送であるのでパラレル伝送より圧倒的にケーブル本数が少な。なお、アナログ伝送を採る場合には、ケーブル本数は同数であるが、3.3V振幅のアナログ信号に、少なからずノイズが重畳して、音質が大幅に劣化する。一方、振幅レベルを上げると、電源配線が複雑化する上に消費電力が増加する。 In any case, in this embodiment, four types of audio signals can be transmitted with four cables, and therefore, signal transmission without audio deterioration due to noise can be performed with the minimum number of cables. That is, since it is serial transmission, the number of cables is far smaller than that of parallel transmission. Note that when analog transmission is employed, the number of cables is the same, but noise is superimposed on an analog signal having an amplitude of 3.3 V, and the sound quality is greatly deteriorated. On the other hand, when the amplitude level is increased, the power supply wiring becomes complicated and the power consumption increases.
このようなシリアル信号SDATA1,SDATA2は、クロック信号SCLKの立上りエッジに同期して、デジタルアンプ46に取得される。そして、デジタルアンプ46内部で、所定ビット長毎にパラレル変換され、DA変換後にD級増幅されて各スピーカに供給されている。 Such serial signals SDATA1 and SDATA2 are acquired by the digital amplifier 46 in synchronization with the rising edge of the clock signal SCLK. In the digital amplifier 46, parallel conversion is performed for each predetermined bit length, and after D / A conversion, D-class amplification is performed and supplied to each speaker.
デジタルアンプ46の内部構成は適宜であるが、図7は、デジタルアンプとしてYDA171(YAMAHA)を使用した場合の内部構成図を示している。このような内部構成に限定されないが、何れにしても、本実施例では、音声合成回路42とデジタルアンプ46とをシリアル回線で接続するので、PCMデータ(音声データ)のビット長を如何に増やして高音質化を実現しても配線ケーブルその他を変更する必要がなく、回路構成の簡素化を維持することができる。
Although the internal configuration of the digital amplifier 46 is appropriate, FIG. 7 shows an internal configuration diagram when YDA171 (YAMAHA) is used as the digital amplifier. Although it is not limited to such an internal configuration, in any case, in this embodiment, since the
また、演出インタフェイス基板27には、ワンチップマイコン40から出力されるシリアルデータを出力するバッファ回路47,48が設けられている。ここで、出力バッファ47は、ワンチップマイコン40から伝送された3種類の信号(EN,DATA,CK)を、ランプ接続基板29を経由して4個のランプ駆動基板37に転送しており、この点は、図4に関して説明した通りである。そして、ランプ駆動基板37の駆動回路DR1〜DR4では、動作制御信号ENと転送クロック信号CKとに基づいて、シリアル信号DATAからランプ駆動信号を抽出し、ランプ駆動信号をパラレル信号に変換してLEDランプ群を駆動していることも前述した通りである。
In addition, the
もう一方のバッファ回路48は、入出力バッファとして機能しており、ワンチップマイコン40から伝送されたシリアル信号をモータ/ランプ駆動基板30に、そのまま転送する一方、一群の演出モータM1〜Mnの原点位置を示す原点センサ信号(シリアル信号)をワンチップマイコン40に転送している。
The
本実施例の場合、ワンチップマイコン40からバッファ回路48に伝送されたシリアル信号は、ランプ群を点灯させるためのランプ駆動信号(シリアル信号)と、演出モータを回転させるためのモータ駆動信号(シリアル信号)とが連続するよう構成されている。そして、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30では、これら一連のシリアル信号を16ビット長毎に分断すると共に、各16ビット長をパラレル信号に変換して、ランプ演出と可動予告演出を実行している。具体的には、制御コマンドCMDに対応して抽選決定された演出動作として、一連のランプ演出を実行すると共に、モータ駆動信号を受信した場合には、演出モータM1〜Mnを回転させて適宜な可動予告演出を実行している。
In the case of the present embodiment, the serial signal transmitted from the one-
図6(a)は、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30の回路構成を、具体的に示すブロック図である。図示の通り、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30は、演出モータM1〜Mnの原点センサ信号をシリアル変換するPS変換部50と、PS変換部50への制御信号をワンチップマイコン40から受ける入力バッファ51と、直流電圧13Vを12Vに降圧する降圧部52と、ランプ駆動信号やモータ駆動信号をワンチップマイコン40から受ける入力バッファ53と、ランプ群や演出モータ群を駆動制御する駆動制御部54,55と、各演出モータの駆動電流を受けるシンクドライバ56とを有して構成されている。
FIG. 6A is a block diagram specifically showing the circuit configuration of the motor /
なお、PS変換部50、入力バッファ51,53、駆動制御部54、及び、シンクドライバ56は、直流電圧5Vを電源電圧として動作している。
Note that the
原点センサ信号は、演出モータM1〜Mnが原点に位置するか否かを検出する原点センサの出力であり、各原点センサは、直流電圧12V又は5Vを電源電圧としている。これら各1ビットで全nビットの原点センサ信号は、ワンチップマイコン40が出力する保持信号LOADに同期して、PS変換部51に取得され、PS変換部51は、ワンチップマイコン40から受ける転送クロックCKに同期して、原点センサ信号をシリアル信号に変換してワンチップマイコン40に伝送している。
The origin sensor signal is an output of an origin sensor that detects whether or not the production motors M1 to Mn are located at the origin, and each origin sensor uses a DC voltage of 12V or 5V as a power supply voltage. These 1-bit and n-bit origin sensor signals are acquired by the PS converter 51 in synchronization with the hold signal LOAD output from the one-
このように、本実施例では、各演出モータM1〜Mnが原点に位置しているか否かを、ワンチップマイコン40が適宜に把握できるよう構成されている。なお、各原点センサの電源電圧として、電磁ノイズが重畳する可能性のある電源ライン(13V)とは別系統の直流電圧(12V,5V)を使用することで誤判定の可能性を大幅に低減させている。
As described above, in this embodiment, the one-
次に、降圧部52は、その入力側13Vが各ランプの駆動電源として使用され、出力側12Vが演出モータM1〜Mnの駆動電源として使用され、電源ラインが互いに分離されている。また、先に説明した通り、入力バッファ53や、駆動制御部54,55は、直流電圧13Vとは全く別系統に生成された直流電圧5Vを電源電圧としている。
Next, in the step-down
そのため、大型の演出モータ群M1〜Mnが突発的に動作を開始しても、各ランプのランプ駆動信号に電源ノイズなどの影響が及ぶ可能性が極めて低い。同様に、各ランプを高輝度で激しく点滅させても、各演出モータM1〜Mnのモータ駆動信号に電源ノイズなどの影響が及ぶ可能性の極めて低い。 Therefore, even if the large production motor groups M1 to Mn suddenly start operation, there is a very low possibility that the lamp drive signal of each lamp is affected by power supply noise or the like. Similarly, even if the lamps are flashed violently with high luminance, the possibility that the motor drive signals of the effect motors M1 to Mn are affected by power supply noise or the like is extremely low.
ところで、演出モータ用の駆動制御部54と、ランプ用の駆動制御部55は、何れも、図4に示す駆動回路DRiと同一構成であり、ワンチップマイコン40から、動作制御信号ENと、シリアル信号DATAと、転送クロック信号CKとを共通に受けて動作している。なお、シリアル信号DATAには、ランプ駆動信号とモータ駆動信号とが含まれている。
By the way, both the
図4の駆動回路DRiと同様に、駆動制御部54,55も、5ビット長のアドレス端子(A0−A4)を有して、適宜にアドレスが付番可能に構成されている。5ビット長のアドレス端子(A0−A4)は、ハードウェア構成として、モータ/ランプ駆動基板30において、予めHレベル又はLレベルに固定的に付番されている。但し、図4の回路構成の場合と同様に、アドレス端子(A0−A4)の全部又は一部について、これを上流側の回路基板から伝送を受ける構成を採っても良い。
Similarly to the drive circuit DRi in FIG. 4, the
先に説明した通り、各制御レジスタR1〜Rmに制御データDiを設定することで、各出力端子のON/OFF状態だけでなく、ON/OFF状態に至るまでのフェード動作(fade in/out)の有無、ON状態の出力端子のPWM制御におけるduty比(0〜99.6%)などが可能となる。また、図6(b)は、ワンチップマイコン40と、複数の駆動制御部54,55・・・55との間の通信プロトコルを示すタイムチャートであり、動作内容は、図4(b)に関して説明した通りである。
As described above, by setting the control data Di in each of the control registers R1 to Rm, not only the ON / OFF state of each output terminal but also the fade operation up to the ON / OFF state (fade in / out) The duty ratio (0 to 99.6%) in the PWM control of the output terminal in the ON state can be made. 6B is a time chart showing a communication protocol between the one-
演出モータM1〜Mnは、可動予告演出として稼働されるので、通常は隠蔽状態で原点位置に待機している。したがって、駆動制御部54は、OFF状態の制御データを保持したままであり、通常は、ワンチップマイコン40から、制御データの転送を受ける必要がない。しかし、この本実施例の制御駆動部は、アドレス番号ADRiを特定して制御データDiを受けるので、繰り返しシリアル信号が転送されても、アドレス番号で指定されない駆動制御部54には何の影響も与えない。
Since the production motors M1 to Mn are operated as a movable notice production, the production motors M1 to Mn are normally waiting at the origin position in a concealed state. Accordingly, the
したがって、本発明の構成によれば、動的なランプ演出を継続的に繰り返すランプ制御用の駆動制御部55・・55と、稀にしか予告動作を開始しない可動予告演出用の駆動制御部54とを同一構成とすることができる。しかも、ワンチップマイコン40は、モータ駆動信号をランプ駆動信号に付加するか否かを判定する以外は、モータ駆動信号とランプ駆動信号とを同列に扱うことができるので、ワンチップマイコン40の制御負担を軽減することができる。
Therefore, according to the configuration of the present invention, the
また、ランプ制御用の駆動制御部55・・55の全部又は一部を、同一アドレス番号に設定することで、多数のランプに関する点灯データ(制御データ)の転送処理を纏めることができ、演出制御部22の制御負担が軽減される。例えば、遊技機の右側と左側のランプ群を、常に、同一態様で発光させる場合には、右側のランプ群を駆動する駆動制御部55Rと、左側のランプ群を駆動する駆動制御部55Lとを、同一アドレス番号に設定するだけで、点灯データの転送処理を一回で終えることができる。
In addition, by setting all or part of the
図8は、画像制御部23’(画像インタフェイス基板28と画像制御基板23)について、その周りの基板も含めて詳細に図示した回路ブロック図である。先に説明した通り、画像制御部23’は、演出制御部22’から制御コマンドCMD’とストローブ信号STB’とシステムリセット信号SYSとを受けて動作している。また、演出制御部を経由して2種類の直流電圧5V,12Vを受けている。
FIG. 8 is a circuit block diagram illustrating in detail the
図示の通り、画像制御部23’は、演出インタフェイス基板27を経由して制御コマンドを受信して画像制御動作を実行するワンチップマイコン60と、ワンチップマイコン60の制御プログラムなどを記憶するフラッシュメモリ61と、ワンチップマイコン60の指示に基づき表示装置DS1,DS2を駆動するVDP(Video Display Processor)62と、画像演出用の画像圧縮データを記憶するグラフィックROM(CGROM)63と、VDP62の作業領域(Video RAM)として機能するSDRAM(Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory)64と、ワンチップマイコン60を強制リセットさせるウォッチドッグタイマWDTなどを有して構成されている。
As shown in the figure, the
図示の通り、ウォッチドッグタイマWDTの出力は、システムリセット信号SYSと共にOR回路の供給されており、OR回路への入力信号の何れかがアクティブレベルになると、ワンチップマイコン60とVDP62とが同期してリセットされるようになっている。したがって、ワンチップマイコン60のプログラム暴走などに起因して制御動作が初期化されると、これに対応して、VDP62の動作を初期化されることになり、矛盾した不自然な画像演出が実行されることがない。
As shown in the figure, the output of the watchdog timer WDT is supplied to the OR circuit together with the system reset signal SYS. When one of the input signals to the OR circuit becomes an active level, the one-chip microcomputer 60 and the
また、本実施例では、消費電力を可能な限り抑制するべく、各素子の電源電圧を最小化しており、各素子の電源電圧は、(1)ワンチップマイコン60が3.3Vと1.25V、(2)フラッシュメモリ61が1.25V、(3)VDP62が3.3Vと1.8Vと1.1V、(4)CGROM63が3.3V、(5)SDRAM64が1.8Vとなっている。
In this embodiment, the power supply voltage of each element is minimized in order to suppress the power consumption as much as possible. The power supply voltage of each element is (1) the one-chip microcomputer 60 is 3.3V and 1.25V. (2)
このように本実施例では、省電力化のために多数の直流電圧が必要となり、しかも、複数の電源電圧を有する回路素子については、その供給タイミングを最適化する必要がある。一方、演出制御部22’と画像制御部23’との間の配線ケーブル数を抑制する趣旨から2種類の直流電圧しか配電されていない。 As described above, in this embodiment, a large number of DC voltages are required to save power, and the supply timings of circuit elements having a plurality of power supply voltages need to be optimized. On the other hand, only two types of direct current voltages are distributed for the purpose of suppressing the number of wiring cables between the effect control unit 22 'and the image control unit 23'.
そこで、制御端子を有する複数のDC/DCコンバータを配置すると共に、電源シーケンサ65を設けることで、多数の直流電圧を最適なタイミングで各素子に供給している。図9は、電源シーケンサ65の一例としてLM3881(national semiconductor)の内部構成(a)と、電源シーケンサ65を使用した場合にも実行される動作タイムチャート(b)を図示したものである。
Therefore, by arranging a plurality of DC / DC converters having control terminals and providing a
図9(a)の電源シーケンサ65の場合には、INV端子がLレベルであると、Hレベルの動作開始指令ENを受けて動作を開始し、TADJ端子に接続されるキャパシタンスで規定されるクロック信号Clockの9周期後に第一制御信号PCNT1が立上り、クロック信号の8周期後に第二制御信号PCNT2が立上り、クロック信号の更に8周期後に第三制御信号PCNT3が立上がる。
In the case of the
一方、動作開始指令ENがLレベルに遷移すると、クロック信号の9周期後に第三制御信号PCNT3が立下り、クロック信号の8周期後に第二制御信号PCNT2が立下り、クロック信号の更に8周期後に第三制御信号PCNT3が立下がる。 On the other hand, when the operation start command EN transitions to the L level, the third control signal PCNT3 falls after 9 cycles of the clock signal, the second control signal PCNT2 falls after 8 cycles of the clock signal, and further 8 cycles after the clock signal. The third control signal PCNT3 falls.
本実施例では、図8に示す通り、動作開始指令ENは、演出制御部22’(演出インタフェイス基板27)から供給される2種類の直流電圧のAND論理出力となっている。そして、第一制御信号PCNT1は、1.1V生成用のDC/DCコンバータV1の動作イネーブル端子ENに供給され、第二制御信号PCNT2は、3.3V生成用のDC/DCコンバータV2の動作イネーブル端子ENに供給されている。 In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 8, the operation start command EN is an AND logic output of two types of DC voltages supplied from the effect control unit 22 '(effect interface board 27). The first control signal PCNT1 is supplied to the operation enable terminal EN of the DC / DC converter V1 for generating 1.1V, and the second control signal PCNT2 is an operation enable for the DC / DC converter V2 for generating 3.3V. It is supplied to the terminal EN.
また、第三制御信号PCNT3は、3.3VとのAND論理出力に変換されて、1.8V生成用のDC/DCコンバータV3の動作イネーブル端子ENに供給されている。上記した各DC/DCコンバータは、動作イネーブル端子ENがHレベルとなることを条件に電圧変換動作を開始する。 The third control signal PCNT3 is converted into an AND logic output with 3.3V and supplied to the operation enable terminal EN of the DC / DC converter V3 for generating 1.8V. Each DC / DC converter described above starts the voltage conversion operation on condition that the operation enable terminal EN becomes H level.
そのため、図9(b)に示す通り、演出制御部22’から配電される5Vに基づいてDC/DCコンバータV1が最初に機能して、直流電圧1.1Vが生成される。この直流電圧1.1Vは、VDP62に内蔵されたデジタル回路及び内蔵VRAM用の電源電圧であり、他の内蔵回路より先に動作を開始することで、電源投入後のVDP62の正常な動作開始シーケンスが担保される。
Therefore, as shown in FIG. 9B, the DC / DC converter V1 first functions based on 5V distributed from the effect control unit 22 'to generate the DC voltage 1.1V. This DC voltage 1.1V is a power supply voltage for the digital circuit and the built-in VRAM built in the
上記の動作の後に、第二制御信号PCNT2がHレベルになるので、演出制御部22’から配電される12Vを受けるDC/DCコンバータV2が機能して直流電圧3.3Vが生成される。直流電圧3.3Vは、1.25V用のDC/DCコンバータV4に供給されているが、このコンバータV4には、動作イネーブル端子が存在しないので、直ちに、動作を開始して、直流電圧1.25Vが生成される。 After the above operation, since the second control signal PCNT2 becomes H level, the DC / DC converter V2 that receives 12V distributed from the effect control unit 22 'functions to generate the DC voltage 3.3V. The DC voltage 3.3V is supplied to the DC / DC converter V4 for 1.25V. Since this converter V4 does not have an operation enable terminal, the DC voltage 1.V is started immediately. 25V is generated.
これら第二制御信号PCNT2に制御されて生成される2種類の直流電圧3.3V,1.25Vは、ワンチップマイコン60、フラッシュメモリ61、及びCGROM63に、ほぼ同タイミングで供給されるので、前記の各回路素子は、電源投入後に遅滞なく動作開始の準備が完了することになる。なお、このタイミングでは、システムリセット信号SYSがLレベルであり、このレベルがしばらく維持された後に、Hレベルに変化するよう電源基板の電源回路が動作しているので、ワンチップマイコン60は、正しく電源リセットされることになる。
The two types of DC voltages 3.3V and 1.25V generated by being controlled by the second control signal PCNT2 are supplied to the one-chip microcomputer 60, the
最後に第三制御信号PCNT3がHレベルに変化すると、第三制御信号PCNT3と3.3VのAND論理出力が、DC/DCコンバータV3に供給されて直流電圧1.8Vが生成される。この直流電圧1.8Vは、VDP62と、DDRSRAM64と、DDRSRAM用の電源回路68とに、ほぼ同タイミングで供給されるので、DDRSRAM64と、VDP62内部のDDRSRAMインタフェイス回路が同期して動作可能状態となる。したがって、システムリセット信号SYSがHレベルに変化すると、VDP62は、円滑に初期設定動作を開始することができる。
Finally, when the third control signal PCNT3 changes to H level, the AND logic output of the third control signal PCNT3 and 3.3V is supplied to the DC / DC converter V3 to generate a DC voltage of 1.8V. The DC voltage 1.8V is supplied to the
以上、本発明の実施例について詳細に説明したが、具体的な記載内容は、特に本発明を限定するものではない。例えば、実施例のランプ駆動基板37では、各駆動回路DRi毎に異なるアドレス番号を付番したが、モータランプ駆動基板30の場合と同様に、駆動回路DRiの全部又は一部に共通アドレス番号を付番しても良い。同一のアドレス番号に付番された駆動回路は、複数のLEDランプを同期して点滅させるので、ランプ演出に迫力が増すだけでなく、ランプ駆動信号(実施例では、制御データ)の転送処理を一回に纏めることができ、演出制御部22の制御負担が軽減される。
As mentioned above, although the Example of this invention was described in detail, the concrete description content does not specifically limit this invention. For example, in the lamp drive board 37 of the embodiment, different address numbers are assigned to the respective drive circuits DRi. However, as in the case of the motor
また、実施例のランプ接続基板29は、駆動回路DRiのアドレス番号を規定する5ビットのうち、2ビットだけを伝送したが、伝送するアドレス番号のビット長は、1〜5ビット長の範囲で適宜に変更可能である。また、任意ビット長のアドレス番号は、必ずしも、ランプ接続基板29から伝送する必要は無く、ランプ駆動基板37より上流側に位置する回路基板から伝送したので良い。
The
なお、本発明の適用は、必ずしも、弾球遊技機に限定されないのは勿論である。 Of course, the application of the present invention is not necessarily limited to a ball game machine.
GM 遊技機
22’ 演出制御部
37 ランプ駆動基板
29 中継基板
DR 駆動回路
GM gaming machine 22 'presentation control unit 37
Claims (10)
前記演出制御部は、前記ランプ演出を制御する制御回路基板と、ランプを駆動して前記ランプ演出を実行する同一構成の駆動回路を各々搭載した複数個のランプ駆動基板と、前記制御回路基板からランプ駆動信号をシリアル信号として受けて、これを全てのランプ駆動基板に転送する中継基板と、を有して構成され、
前記ランプ駆動基板に搭載された駆動回路のアドレス番号の少なくとも一部は、中継基板から受けるアドレス信号に基づいて各々規定され、前記ランプ駆動信号は、これを受信すべき駆動回路を特定して伝送されていることを特徴とする遊技機。 Based on a control command output by the main control unit, the main control unit for randomly controlling whether or not to generate a gaming state advantageous to the player based on a predetermined switch signal, and controlling the game operation centrally An effect control unit that executes a lamp effect for causing a number of lamps to emit light, and a gaming machine configured to include:
The effect control unit includes a control circuit board for controlling the lamp effect, a plurality of lamp drive boards each having a drive circuit having the same configuration for driving the lamp and executing the lamp effect, and the control circuit board. A relay board that receives the lamp drive signal as a serial signal and transfers it to all the lamp drive boards,
At least a part of the address number of the driving circuit mounted on the lamp driving board is defined based on an address signal received from the relay board, and the lamp driving signal is transmitted by specifying the driving circuit that should receive it. A gaming machine characterized by being made.
前記ランプ駆動信号に基づいて、所定の制御レジスタに、所望の制御データが設定されるよう構成されている請求項1〜6の何れかに記載の遊技機。 The drive circuit includes a control register that determines a drive mode,
The gaming machine according to any one of claims 1 to 6, wherein desired control data is set in a predetermined control register based on the lamp driving signal.
The gaming machine according to any one of claims 1 to 9, wherein a dedicated computer circuit that operates with a power supply voltage of 3.5 V or less to generate an audio signal for audio production is mounted on the control circuit board.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012013766A JP2013150740A (en) | 2012-01-26 | 2012-01-26 | Game machine |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012013766A JP2013150740A (en) | 2012-01-26 | 2012-01-26 | Game machine |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015227587A Division JP6047647B2 (en) | 2015-11-20 | 2015-11-20 | Game machine |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013150740A true JP2013150740A (en) | 2013-08-08 |
| JP2013150740A5 JP2013150740A5 (en) | 2014-12-11 |
Family
ID=49047660
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012013766A Pending JP2013150740A (en) | 2012-01-26 | 2012-01-26 | Game machine |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2013150740A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016140609A (en) * | 2015-02-03 | 2016-08-08 | 株式会社藤商事 | Game machine |
| JP2019000390A (en) * | 2017-06-15 | 2019-01-10 | 株式会社大一商会 | Game machine |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000126429A (en) * | 1998-10-29 | 2000-05-09 | Sankyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2006141682A (en) * | 2004-11-19 | 2006-06-08 | Heiwa Corp | Game machine |
| JP2008093218A (en) * | 2006-10-13 | 2008-04-24 | Daiman:Kk | Control device and game machine equipped with the control device |
| JP2008212271A (en) * | 2007-03-01 | 2008-09-18 | Heiwa Corp | Game machine |
| JP2010240091A (en) * | 2009-04-03 | 2010-10-28 | Renesas Electronics Corp | Drive control system and semiconductor device |
| JP2011160996A (en) * | 2010-02-10 | 2011-08-25 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
-
2012
- 2012-01-26 JP JP2012013766A patent/JP2013150740A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000126429A (en) * | 1998-10-29 | 2000-05-09 | Sankyo Kk | Game machine |
| JP2006141682A (en) * | 2004-11-19 | 2006-06-08 | Heiwa Corp | Game machine |
| JP2008093218A (en) * | 2006-10-13 | 2008-04-24 | Daiman:Kk | Control device and game machine equipped with the control device |
| JP2008212271A (en) * | 2007-03-01 | 2008-09-18 | Heiwa Corp | Game machine |
| JP2010240091A (en) * | 2009-04-03 | 2010-10-28 | Renesas Electronics Corp | Drive control system and semiconductor device |
| JP2011160996A (en) * | 2010-02-10 | 2011-08-25 | Daito Giken:Kk | Game machine |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016140609A (en) * | 2015-02-03 | 2016-08-08 | 株式会社藤商事 | Game machine |
| JP2019000390A (en) * | 2017-06-15 | 2019-01-10 | 株式会社大一商会 | Game machine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5706462B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5833430B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5250690B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5676422B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5536745B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2013128576A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5536750B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6320493B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6047647B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP2013150740A (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5968950B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5961658B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5944449B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5624016B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5384713B1 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6121031B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6279659B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6038204B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5944435B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5961654B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5443582B1 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5961655B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP5400214B1 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6132742B2 (en) | Game machine | |
| JP6132741B2 (en) | Game machine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141023 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20141023 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150924 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20151120 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20160426 |