JP2013047525A - Turbocharger - Google Patents
Turbocharger Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2013047525A JP2013047525A JP2012257474A JP2012257474A JP2013047525A JP 2013047525 A JP2013047525 A JP 2013047525A JP 2012257474 A JP2012257474 A JP 2012257474A JP 2012257474 A JP2012257474 A JP 2012257474A JP 2013047525 A JP2013047525 A JP 2013047525A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- heat shield
- shield plate
- housing
- bearing housing
- turbine
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、ターボチャージャに関し、特に、内燃機関から排出される排気ガスの熱を遮熱する遮熱板を有するターボチャージャに関する。 The present invention relates to a turbocharger, and more particularly to a turbocharger having a heat shield plate that shields heat of exhaust gas discharged from an internal combustion engine.
一般に、ターボチャージャは、内燃機関の排気系に設けられたタービンと内燃機関の吸気系に設けられたコンプレッサとを備えており、このタービンおよびコンプレッサのそれぞれに設けられたタービンホイールおよびコンプレッサホイールが一体回転可能に1つのシャフトによって連結されている。すなわち、内燃機関の排気によりタービンホイールが回転駆動されると、この回転駆動力が前述のシャフトを介してコンプレッサホイールに伝達されるようになっている。このように、コンプレッサホイールが回転されることによって、内燃機関へ吸入される空気が圧縮されて、内燃機関の燃焼室に強制的に圧送されるようになっている。上述のように構成されたターボチャージャは、排気によるエネルギを利用して過給を行うことにより、内燃機関の出力向上を図ることができる。 Generally, a turbocharger includes a turbine provided in an exhaust system of an internal combustion engine and a compressor provided in an intake system of the internal combustion engine. The turbine wheel and the compressor wheel provided in each of the turbine and the compressor are integrated. A single shaft is rotatably connected. That is, when the turbine wheel is rotationally driven by the exhaust of the internal combustion engine, this rotational driving force is transmitted to the compressor wheel via the above-described shaft. As described above, when the compressor wheel is rotated, the air sucked into the internal combustion engine is compressed and forcibly pumped to the combustion chamber of the internal combustion engine. The turbocharger configured as described above can improve the output of the internal combustion engine by performing supercharging using the energy from the exhaust.
従来、この種のターボチャージャとして、図8(a)に示すようなターボチャージャが知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。
図8(a)に示すように、従来の特許文献1に記載されたターボチャージャは、タービン131を回転自在に支持するタービンハウジング132とタービンホイールおよびコンプレッサホイールを連結するシャフト133を回転可能に支持するベアリングハウジング134との間に、ベアリングハウジング134のタービン側端面134aに対し断熱空間135を保有するよう遮熱板136を配設し、ベアリングハウジング134に形成された取付フランジ137とタービンハウジング132に形成されたシール面138との境界部の内周側の部分に形成された溝部139に前述の遮熱板136の外縁部(外周部)136aを挿入配置し前述の取付フランジ137とシール面138を互いに当接して両ハウジングをボルトにより締結するとともに、前述の遮熱板136の外縁部136aに屈曲部136bを形成し、両ハウジングの締結により遮熱板136を両ハウジング間に弾性変形状態で保持するようになっている。
Conventionally, a turbocharger as shown in FIG. 8A is known as this type of turbocharger (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
As shown in FIG. 8A, the conventional turbocharger described in
これにより、上述の特許文献1に記載されたターボチャージャは、遮熱板136が、タービンハウジング132内部に入りタービン131を回転させる高温の排ガスが直接ベアリングハウジング134へ接触するのを防止するとともに、断熱空間135によって排ガスからの熱伝達を抑え、ベアリングハウジング134の温度上昇を抑制することができる。
Accordingly, the turbocharger described in
また、遮熱板136の外縁部136aに屈曲部136bを形成し、この屈曲部136bが溝部139に弾性変形状態で支持されることにより、遮熱板136のガタツキが防止される。そのため、ターボチャージャが取付けられた内燃機関からの振動やこの内燃機関から間欠的に送られてくる排ガスの脈動などが作用した場合でも、遮熱板136の摩耗が防止される。
Further, the
しかしながら、上述のような従来のターボチャージャにあっては、遮熱板136の外縁部136aに屈曲部136bが形成されることで遮熱板136自体のガタツキは防止することができるものの、この屈曲部136bが断続的に遮熱板136の外縁部136aに形成されているため、遮熱板136を溝部139に保持することによってタービンハウジング132とベアリングハウジング134との間のシール性を確保することは困難であるという問題があった。
However, in the conventional turbocharger as described above, the
すなわち、図8(b)に示すように、上述の遮熱板136の屈曲部136bは、遮熱板136の外縁部136aのうち所定箇所(図8(b)では、3箇所)に設けられているだけであり、遮熱板136の外縁部136aにおいて屈曲部136bが形成されていない箇所が存在する。そのため、屈曲部136bの形成されていない箇所を介して、タービンハウジング132側からの高温の排ガスがベアリングハウジング134の遮熱板対向面と遮熱板136との間の断熱空間135に流入して、ベアリングハウジング134に高温の排ガスが接触することを防止することができないという問題があった。
That is, as shown in FIG. 8B, the
また、通常、ベアリングハウジングは、冷却液などにより冷却されているため、冷却された状態のベアリングハウジングに水蒸気を含んだ高温の排ガスが接すると凝縮水が付着することとなる。したがって、上述のような従来のターボチャージャにあっては、遮熱板136によるシール性の確保ができないという上述の問題に起因して、前述のような凝縮水がベアリングハウジング134に付着することにより、この凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジング134の腐食を抑制することができないという問題があった。
In addition, since the bearing housing is usually cooled by a cooling liquid or the like, condensed water adheres when high-temperature exhaust gas containing water vapor comes into contact with the cooled bearing housing. Therefore, in the conventional turbocharger as described above, due to the above-described problem that the sealing performance by the
本発明は、上述のような従来の問題を解決するためになされたもので、遮熱板によるタービンハウジングとベアリングハウジングとの間のシール性を確保することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジングの腐食を防止することができるターボチャージャを提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in order to solve the above-described conventional problems, and can ensure the sealing performance between the turbine housing and the bearing housing by the heat shield plate, and the bearing housing by adhesion of condensed water. An object of the present invention is to provide a turbocharger that can prevent corrosion of the steel.
本発明に係るターボチャージャは、上記目的達成のため、(1)内燃機関の吸気通路上にコンプレッサホイールが配設されるとともに、前記コンプレッサホイールに回転軸を介して連結されるタービンホイールが前記内燃機関の排気通路上に配設されたターボチャージャであって、前記回転軸を回転自在に支持するとともに外周部に周方向全周に亘って形成されたフランジ部を有し、前記回転軸を収容するベアリングハウジングと、前記排気通路に連通する排気ガス導入通路を有するとともに、内周端面が前記フランジ部に取付けられ、内部に前記タービンホイールを収容するタービンハウジングと、前記ベアリングハウジングと前記タービンハウジングの間に介装された円板状の遮熱板とを備え、前記フランジ部の前記タービンハウジング側端面と前記タービンハウジングの前記フランジ部側内周面との間に、前記フランジ部の周方向全周に亘って間隙部が形成されたターボチャージャにおいて、前記遮熱板が、前記遮熱板の放射方向外端部に周方向全周に亘って形成されるとともに、前記間隙部に屈曲された状態で圧入される屈曲部を有し、前記屈曲部の弾性力によって前記遮熱板が前記タービンハウジングまたは前記ベアリングハウジングの前記遮熱板対向面に密着するよう構成する。 In order to achieve the above object, the turbocharger according to the present invention includes: (1) a compressor wheel is disposed on an intake passage of an internal combustion engine, and a turbine wheel coupled to the compressor wheel via a rotating shaft is provided in the internal combustion engine. A turbocharger disposed on an exhaust passage of an engine, which rotatably supports the rotating shaft and has a flange portion formed on the outer peripheral portion over the entire circumference, and accommodates the rotating shaft A bearing housing, an exhaust gas introduction passage communicating with the exhaust passage, an inner peripheral end face attached to the flange portion, and housing the turbine wheel therein, and the bearing housing and the turbine housing. A disc-shaped heat shield plate interposed therebetween, and the turbine housing of the flange portion In the turbocharger in which a gap portion is formed over the entire circumference in the circumferential direction of the flange portion between the end surface and the flange portion side inner peripheral surface of the turbine housing, the heat shield plate is formed of the heat shield plate. A radially outer end is formed over the entire circumference, and has a bent portion that is press-fitted into the gap portion in a bent state, and the heat shield plate is formed by the elastic force of the bent portion. The housing or the bearing housing is configured to be in close contact with the heat shield plate facing surface.
この構成により、遮熱板の放射方向外端部に周方向全周に亘って形成された屈曲部が間隙部に屈曲された状態で圧入されるので、遮熱板のガタツキを防止でき、このガタツキに起因した遮熱板の摩耗を防止できるとともに、遮熱板の放射方向外端部の周方向全周に亘ってタービンハウジングとベアリングハウジングとの間のシール性を向上させることができる。 With this configuration, the bent portion formed over the entire circumference in the radial direction of the heat shield plate is press-fitted in a state bent to the gap portion, so that the heat shield plate can be prevented from rattling. Wear of the heat shield plate due to rattling can be prevented, and the sealing performance between the turbine housing and the bearing housing can be improved over the entire circumference in the radial outer end of the heat shield plate.
さらに、屈曲部の弾性力によって遮熱板をタービンハウジングまたはベアリングハウジングの遮熱板対向面に密着させることができるので、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスにベアリングハウジングが晒されるのを防止して、凝縮水の発生を抑制することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジングの腐食を防止することができる。 Furthermore, since the heat shield plate can be brought into close contact with the heat shield plate facing surface of the turbine housing or the bearing housing by the elastic force of the bent portion, it is possible to prevent the bearing housing from being exposed to high-temperature exhaust gas containing water vapor, Generation | occurrence | production of condensed water can be suppressed and corrosion of the bearing housing by adhesion of condensed water can be prevented.
なお、上述の屈曲部は、ベアリングハウジングの外周面に対向して開口する略断面U字状に形成されるよう構成してもよい。 In addition, you may comprise the above-mentioned bending part so that it may be formed in the substantially cross-sectional U shape opened facing the outer peripheral surface of a bearing housing.
この場合、屈曲部がベアリングハウジングの外周面に対向して開口する略断面U字状に形成されているので、例えば、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスが排気ガス導入通路から間隙部側に流入した際には、流入した排気ガスの内圧により略断面U字状に開口した屈曲部が間隙部に圧入された状態で押し広げられる。そのため、屈曲部の弾性力に加えて排気ガスの内圧により、間隙部を形成するタービンハウジング側端面およびフランジ部側内周面に屈曲部が密着した状態となるので、遮熱板のガタツキを確実に防止して、このガタツキに起因した遮熱板の摩耗をより確実に防止するとともに、間隙部において遮熱板の放射外端部の周方向全周に亘って、タービンハウジングとベアリングハウジングとの間のシール性を確保することができる。さらに、屈曲部の弾性力に加えて排気ガスの内圧によって、遮熱板をタービンハウジングまたはベアリングハウジングの遮熱板対向面に密着させることができるので、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスにベアリングハウジングが晒されるのを防止して、凝縮水の発生を抑制することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジングの腐食を防止することができる。 In this case, since the bent portion is formed in a substantially cross-sectional U shape that opens to face the outer peripheral surface of the bearing housing, for example, high-temperature exhaust gas containing water vapor flows from the exhaust gas introduction passage to the gap portion side. At this time, the bent portion opened in a substantially U-shaped cross section is pushed and expanded by being pressed into the gap portion by the internal pressure of the inflowing exhaust gas. Therefore, in addition to the elastic force of the bent part, the bent part is in close contact with the turbine housing side end face and the flange side inner peripheral surface that form the gap due to the internal pressure of the exhaust gas. In addition, the wear of the heat shield plate due to the rattling is prevented more reliably, and the turbine housing and the bearing housing are disposed over the entire circumference of the radial outer end of the heat shield plate in the gap. A sealing property between them can be secured. Further, since the heat shield plate can be brought into close contact with the heat shield plate facing surface of the turbine housing or the bearing housing by the internal pressure of the exhaust gas in addition to the elastic force of the bent portion, the bearing housing is attached to the high-temperature exhaust gas containing water vapor. It can be prevented from being exposed, the generation of condensed water can be suppressed, and corrosion of the bearing housing due to the adhesion of condensed water can be prevented.
本発明によれば、遮熱板によるタービンハウジングとベアリングハウジングとの間のシール性を確保することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジングの腐食を防止することができるターボチャージャを提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the turbocharger which can ensure the sealing performance between the turbine housing and bearing housing by a heat shield, and can prevent the corrosion of a bearing housing by adhesion of condensed water is provided. it can.
以下、本発明の実施の形態について、図面を参照して説明する。
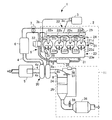
図1は、本発明の実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャ20が適用されるディーゼルエンジン1の構成図である。
Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a
まず、構成について説明する。
過給機としての可変容量型ターボチャージャ20は、車両に搭載され、内燃機関としてのディーゼルエンジン1の一部を構成している。この内燃機関は、ディーゼルエンジン以外のものでもよく、例えば、ガソリンやエタノールなどの液体を燃料とする内燃機関であってもよい。
First, the configuration will be described.
A variable capacity turbocharger 20 as a supercharger is mounted on a vehicle and constitutes a part of a
図1に示すように、ディーゼルエンジン1は、その種類、型式などのエンジン仕様は任意に選択され、例えば、直列4気筒などの公知のディーゼルエンジンで構成されている。具体的には、ディーゼルエンジン1は、エンジン本体2と、エンジン本体2に燃料を供給する燃料供給装置3と、吸気管4と、吸気管4に設けられたエアクリーナ5と、インタークーラ6およびスロットルバルブ7と、排気管8と、エンジン本体2から排出される排気ガスの一部を吸気管4内に還流させるEGR(Exhaust Gas Recirculation)装置9と、排気管8に設けられた排気ガス後処理装置11と、可変容量型ターボチャージャ20とを含んで構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
エンジン本体2は、シリンダ21と、吸気装置22と、排気装置23と、インジェクタ24と、コモンレール25と、排気装置23内に燃料を噴射する排気用インジェクタ26とを含んで構成されている。
The engine
シリンダ21は、4個のシリンダ21a、21b、21c、21dから構成されており、シリンダ21a〜21dには、それぞれ図示しない吸気ポートを介して吸気装置22が接続されるとともに、それぞれ図示しない排気ポートを介して排気装置23が接続されている。
The
吸気装置22は、吸気通路を有するとともに、一端部で4個に分岐された分岐部22a、22b、22c、22dを有している。吸気装置22は、他方端部で吸気管4に連結され、分岐部22a〜22dの各端部でエンジン本体2の各吸気ポートに連結されている。
The
吸気装置22においては、吸気管4から供給された空気が分岐部22a〜22dから各吸気ポートを介してシリンダ21a〜21dに供給されるようになっている。
In the
排気装置23は、一方端部で4個に分岐された分岐部23a、23b、23c、23dを有するとともに、分岐部23a〜23dの一端がエンジン本体2の各排気ポートに連結され、他方端部で分岐部23a〜23dが集合するとともに可変容量型ターボチャージャ20に連結される集合管23eを有している。集合管23eには、EGR装置9が接続されており、シリンダ21a〜21dから排出される排気ガスの一部がEGR装置9に流入するようになっている。
The
インジェクタ24は、4個のインジェクタ24a、24b、24c、24dから構成され、それぞれ燃料噴射ノズルを有しシリンダ21a〜21dに設けられており、燃料噴射ノズルからシリンダ21a〜21d内に燃料を噴射して霧状にするようになっている。
The
コモンレール25は、燃料供給装置3から供給された高圧の燃料を蓄圧する図示しない蓄圧部を有し、インジェクタ24a〜24dに連結されており、インジェクタ24a〜24dに高圧燃料を配給するようになっている。
The
排気用インジェクタ26は、インジェクタ24と同様に燃料噴射ノズルを有し、集合管23e内に設けられており、集合管23eの排気通路内に燃料をポスト噴射して排気ガスに燃料を添加するようになっている。このポスト噴射により、排気ガス後処理装置11を昇温させて処理効率を高めるとともに、排気ガス後処理装置11に堆積したPM(Paticulate Matter:粒子状物質)などの堆積物の酸化を促進させ、目詰まりを防止するようにしている。
Similarly to the
燃料供給装置3は、図示しない燃料タンクおよび燃料ポンプと、燃料供給管3a、3bとを含んで構成されており、燃料タンク内の燃料を燃料ポンプにより高圧にしてコモンレール25および排気用インジェクタ26に供給するようになっている。
The fuel supply device 3 includes a fuel tank and a fuel pump (not shown), and
吸気管4は、図示しない吸気口から吸入した新気を吸気装置22に導入する配管からなり、吸気通路4aを有しており、可変容量型ターボチャージャ20に連結され吸気通路4a内の新気が可変容量型ターボチャージャ20を経由して吸気装置22に導入されるようになっている。また、吸気通路4a内の新気は、吸気管4に設けられたエアクリーナ5により浄化され、さらに吸気管4に設けられたインタークーラ6により冷却されて密度が高められるようになっている。
The intake pipe 4 is composed of a pipe for introducing fresh air drawn from an intake port (not shown) into the
スロットルバルブ7は、例えば、バタフライバルブなどの絞り弁からなり、インタークーラ6を通過した新気のエンジン内部への流入量を調整するようになっている。
The
排気管8は、排気装置23の集合管23eから排出される排気ガスを大気に放出させる配管からなり、排気通路8aを有し、一端が集合管23eに連結されている。この排気管8には、排気ガス後処理装置11が設けられており、排気ガス中の有害物質が除去されるようになっている。また、排気管8には、排気ガス後処理装置11の下流側に図示しないマフラーなどの消音装置が設けられている。
The
EGR装置9は、EGR管31と、EGRバルブ32と、EGRクーラ33とを含んで構成されており、排気装置23の排気通路8a内の排気ガスを吸気装置22の吸気通路4a内に還流させるようになっている。
The EGR device 9 includes an
EGR管31は、EGR通路を有しており、EGR管31の吸気装置22側には、EGRバルブ32が設けられ、EGR管31の排気装置23側には、EGRクーラ33が設けられている。
The
EGRバルブ32は、その開度が図示しない電子制御ユニット(ECU:Electronic Control Unit)により制御され、吸気通路内に還流される排気ガスの量が調整されるようになっている。また、EGRクーラ33により、還流される排気ガスの温度が下げられ、その密度が高められるようになっている。
The opening degree of the
排気ガス後処理装置11は、NSR触媒(NOx Storage−reduction Catalyst)34と、DPNR触媒(Diesel Paticulate−NOx Reduction catalyst)35と、酸化触媒36と、排気温センサ37、差圧センサ38と、空燃比センサ39とを含んで構成されている。
The exhaust
NSR触媒34は、NOx吸蔵物質を含んで構成されており、排気空燃比がリーンのときに排気ガス中のNOxを吸蔵し、排気空燃比がリッチになったときに吸蔵していたNOxを還元させて排気ガス中のNOxを低減するようになっている。
The
DPNR触媒35は、PMを酸化させる性能を有するNOx吸蔵還元触媒が塗布された多孔質セラミックからなり、排気ガス中のPMを捕集し、これを排気ガス中のNOxと同時に浄化させるようになっている。これらの浄化の際には、PMが酸化されるとともに、CO(一酸化炭素)やHC(炭化水素)も酸化され、NOxが還元される。
The
酸化触媒36は、各種ガスに対して酸化活性のある白金、パラジウムなどの触媒金属からなり、排気ガス中の有害物質、例えば、HCを酸化させ、CO2(二酸化炭素)およびH2O(水蒸気)に分解処理するようになっている。
The
排気温センサ37は、サーミスタなどの検出素子からなり、温度変化を抵抗値変化として検出するようになっている。
差圧センサ38は、圧力センサからなり、NSR触媒34の上流側の排気ガスの圧力とDPNR触媒35の下流側の排気ガスの圧力との差圧を検出することにより、DPNR触媒35のPMによる目詰まりを検出するようになっている。
The
The
空燃比センサ39は、ジルコニア素子などの検出素子からなり、酸素濃度差に応じた電力を検出することにより排気ガス中の酸素濃度を検出するようになっている。
排気温センサ37、差圧センサ38および空燃比センサ39から検出された情報は、図示しない電子制御ユニットに送られるようになっている。
The air-
Information detected from the
次いで、本実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャ20の構成について、図面を参照し説明する。
図2は、本発明の実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャ20の断面図である。図3は、本発明の実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャ20の可変ノズル機構を示す側面図であり、(a)は、図2中左方より可変ノズル機構を見た側面図を示し、(b)は、図2中右方より可変ノズル機構を見た側面図を示す。
Next, the configuration of the
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of the
図2に示すように、可変容量型ターボチャージャ20は、ベアリングハウジング41と、タービン42と、コンプレッサ43と、アクチュエータ44と、可変ノズル機構45と、遮熱板50とを含んで構成されており、排気装置23(図1参照)から排出される排気ガスのエネルギを利用してタービン42を回転させ、その動力でコンプレッサ43を駆動させて大気圧よりも高い圧力の新気を吸気装置22(図1参照)内に供給するようになっている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
ベアリングハウジング41は、外周部に周方向全周に亘って形成され、タービン42に連結するフランジ部41aと、コンプレッサ43に連結するフランジ部41bと、一対のベアリング部41cとを含んで構成されている。
The bearing
一対のベアリング部41cは、例えばフルフロートタイプのベアリングで構成されており、回転軸62を回転自在に支持するようになっている。すなわち、ベアリングハウジング41は、一対のベアリング部41cを介して回転軸62を回転自在に支持するとともに、回転軸62を収容するようになっている。
The pair of bearing
また、回転軸62の一方端部には、後述するタービンホイール73が連結され、他方端部には後述するコンプレッサホイール83が連結されており、回転軸62とともにタービンホイール73およびコンプレッサホイール83が回転するようになっている。
A
また、ベアリングハウジング41には、ウォータジャケット41dがベアリング部41cの近傍に設けられており、ベアリング部41cの近傍が冷却され、回転軸62の焼き付きが防止されるようになっている。
Further, the bearing
タービン42は、タービンハウジング71と、タービンホイール73とを含んで構成されており、タービンホイール73は、回転軸62に連結されるようになっている。
The
タービンハウジング71には、排気ガスを旋回させるスクロール通路71aと、スクロール通路71a内の排気ガスを、タービンホイール73に向けて流通させる環状のガス流路71bと、タービンホイール73を介して排出される排気ガスを通す排気ガス通路71cとが形成されている。
The
タービンハウジング71の一方端部は、図1に示す上流側の排気管8と連結されており、上流側の排気管8内の排気通路8aとスクロール通路71aとが連通し、排気通路8a内の排気ガスがスクロール通路71a内に流入するようになっている。一方、タービンハウジング71の他方端部は、図1に示す下流側の排気管8と連結されており、下流側の排気管8内の排気通路8aと排気ガス通路71cとが連通し、排気ガス通路71c内の排気ガスが下流側の排気管8内の排気通路8aに排出されるようになっている。また、ガス流路71bは、排気通路8aと連通するスクロール通路71a内に流入した排気ガスをタービンホイール73に導入するようになっている。なお、本実施の形態におけるガス流路71bは、本発明における排気ガス導入通路を構成している。
One end of the
また、タービンハウジング71は、回転軸62の軸方向であってコンプレッサ43側の内周端面71dにおいて、前述のベアリングハウジング41のフランジ部41aに取付けられ、タービンホイール73を内部に収容するようになっている。
The
タービン42においては、上流側の排気管8内の排気通路8aからスクロール通路71a内に流入した排気ガスがガス流路71bを通ってタービンホイール73に導入され、排気ガスの流動圧力によりタービンホイール73が回転するようになっている。
In the
コンプレッサ43は、コンプレッサハウジング81と、コンプレッサホイール83とを含んで構成されており、コンプレッサホイール83は、回転軸62に連結されるようになっている。
The
コンプレッサハウジング81には、図1に示すエアクリーナ5を通過し浄化された吸入空気を、コンプレッサホイール83に向けて導入させる導入通路81aと、コンプレッサホイール83の回転により圧力が高められた吸入空気を吸気管4の吸気通路4aに排出させる排出通路81bと、コンプレッサホイール83で圧縮された吸入空気を排出通路81b内に流入させる流入通路81cとが形成されている。
In the
コンプレッサハウジング81の一方端部は、図1に示す上流側の吸気管4と連結されており、上流側の吸気管4内の吸気通路4aと導入通路81aとが連通し、吸気通路4a内の吸入空気が導入通路81a内に流入するようになっている。一方、コンプレッサハウジング81の他方端部は、下流側の吸気管4と連結されており、下流側の吸気管4内の吸気通路4aと排出通路81bとが連通し、排出通路81b内の吸入空気が下流側の吸気管4内の吸気通路4aに排出されるようになっている。
One end of the
コンプレッサ43においては、上流側の吸気管4内の吸気通路4aから導入通路81a内に導入された吸入空気は、コンプレッサホイール83に導入され、コンプレッサホイール83の回転により圧力が高められて、流入通路81cを介して排出通路81b内に排出されるようになっている。
In the
アクチュエータ44は、図示しない駆動部に連結されるとともに、後述する可変ノズル機構45に連結されており、前述の電子制御ユニットにより車両の運転状態に応じて制御されることによって、可変ノズル機構45を作動させるようになっている。
The
可変ノズル機構45は、図2ないし図3(a)、(b)に示すように、タービンハウジング71のガス流路71b内に配置された複数のベーン91と、ベーン91を軸92を介して回動可能に支持するノズルプレート93と、各軸92の端部に固定されたアーム94を介して軸92を回動させるユニゾンリング95と、一端部でユニゾンリング95に回動可能に係合し、他端部でリンクシャフト96に固定された従動リンク97と、ベアリングハウジング41に設けられリンクシャフト96を回動可能に支持するブッシュ98と、一端部でリンクシャフト96に固定され、他端部でアクチュエータ44に固定された駆動リンク101とを含んで構成されている。
As shown in FIGS. 2 to 3A and 3B, the
この可変ノズル機構45においては、複数のベーン91により、排気ガスの流入容量を可変にする複数のベーンノズル45aが画成されており、この複数のベーンノズル45aを通って排気ガスがタービン42のスクロール通路71aからタービンホイール73に向けて流入するようになっている。
In the
また、可変ノズル機構45においては、ユニゾンリング95を回動させ、ユニゾンリング95と係合しているアーム94を軸92を中心にして回動させることにより、ベーン91の開度が変わるよう構成されている。このユニゾンリング95は、従動リンク97、リンクシャフト96および駆動リンク101を介してアクチュエータ44に連結されており、このアクチュエータ44の作動によりベーン91の開度が変わるようになっている。ベーン91の開度が変わることにより、タービンハウジング71のガス流路71bに流入し各ベーン91の間を流通して、タービンホイール73に流入する排気ガスの流速を可変できるようになっている。これによりタービンホイール73の回転速度を可変することができるので、コンプレッサホイール83の回転速度を可変することができ、コンプレッサ43により圧縮される吸入空気の過給圧を可変できるようになっている。
The
遮熱板50は、ベアリングハウジング41とタービンハウジング71との間に介装され、ガス流路71bから流入される高温の排気ガスがベアリングハウジング41に接するのを防止するとともに、排気ガスの熱を遮蔽するようになっている。なお、遮熱板50の詳細については、後述する。
The
次に、遮熱板50の構成について、図4を参照して詳しく説明する。
図4は、図2の一部を拡大した部分拡大断面図である。また、図5は、本発明の実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャ20の遮熱板50の構成を示す図であり、(a)は、遮熱板50を図2中、右方向から見た正面図を示し、(b)は、(a)のA−A断面を示す断面図である。
Next, the configuration of the
FIG. 4 is a partially enlarged cross-sectional view in which a part of FIG. 2 is enlarged. 5 is a diagram showing the configuration of the
図4に示すように、可変容量型ターボチャージャ20のタービン42側には、フランジ部41aを含むベアリングハウジング41の外周面とタービンハウジング71の内周面とノズルプレート93のコンプレッサ43(図2参照)側の側面とによりリンク室102が画成されている。
As shown in FIG. 4, on the
ここで、リンク室102を画成するタービンハウジング71の内周面とノズルプレート93の外周端面との間には、少なからず隙間が存在する。そのため、スクロール通路71a内の排気圧力が上昇し、リンク室102内の排気圧力よりも高くなると、スクロール通路71a内を流通する水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスがガス流路71bを介してタービンホイール73に導入される際に、前述のタービンハウジング71の内周面とノズルプレート93の外周端面との間の隙間を介してリンク室102内に流入することがある。
Here, there is not a little gap between the inner peripheral surface of the
このように、リンク室102内に水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスが流入するおそれがあるため、リンク室102を画成するベアリングハウジング41の外周面に直接、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスが接することを避けるべく、このベアリングハウジング41のリンク室102に対向する面に密着するよう遮熱板50が設けられている。
As described above, since there is a possibility that the high-temperature exhaust gas containing water vapor flows into the
また、ベアリングハウジング41のフランジ部41aのタービンハウジング側端面41eとタービンハウジング71のフランジ部側内周面71eとの間には、フランジ部41aの周方向全周に亘って間隙部104が形成されている。
Further, a
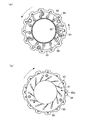
図5(a)、(b)に示すように、遮熱板50は、円板状の例えばステンレス鋼板などの熱伝導率の低い部材によって構成されており、リンク室102を画成するベアリングハウジング41のフランジ部41aを覆う環状の底面部51と、リンク室102を画成するベアリングハウジング41の外周面を覆う円筒状の側面部52とを含んで構成されている。
As shown in FIGS. 5 (a) and 5 (b), the
遮熱板50の底面部51の放射方向外端部には、周方向全周に亘ってタービンハウジング71側に屈曲する屈曲部51aが形成さている。この屈曲部51aは、ベアリングハウジング41の外周面に対向して開口する略断面U字状に形成されており、間隙部104に屈曲された状態で圧入されるようになっている。すなわち、遮熱板50は、この屈曲部51aの弾性力によって、放射方向外端部において、間隙部104を形成するタービンハウジング側端面41eとフランジ部側内周面71eとに密着するよう間隙部104に保持されるとともに、間隙部104におけるシール性が遮熱板50の放射方向外端部の周方向全周に亘って確保されるようになっている(図4参照)。
また、屈曲部51aの弾性力によって、遮熱板50がベアリングハウジング41の遮熱板対向面に密着するようになっている(図4参照)。
また、底面部51には、可変ノズル機構45におけるリンクシャフト96を通すためのリンクシャフト孔51bが形成されている。
A
Further, the
In addition, a
一方、側面部52は、上述の底面部51の放射方向内端部から鉛直方向(回転軸62の軸方向)に延在する円筒状に形成されており、ベアリングハウジング41の外周面を覆うようになっている。また、側面部52の先端部近傍には、放射内方に向けて突出した環状凸部52aが周方向全周に亘って形成されており、この環状凸部52aがベアリングハウジング41の外周面に押圧されることにより、遮熱板50をベアリングハウジング41に対して保持するようになっている。さらに、環状凸部52aは、遮熱板50の側面部52の先端部において、遮熱板50とベアリングハウジング41の外周面との間のシール性を確保するようになっている。
On the other hand, the
次いで、遮熱板50の底面部51の放射方向外端部に形成された屈曲部51aの作用について、図6を参照して説明する。
図6は、本発明の実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャ20の遮熱板50の作用を説明する一部拡大断面図である。
Next, the action of the
FIG. 6 is a partially enlarged sectional view for explaining the operation of the
図6に示すように、間隙部104に屈曲部51aが屈曲された状態で圧入された際、遮熱板50は、この屈曲部51aの弾性力によって、放射方向外端部において、間隙部104を形成するタービンハウジング側端面41eとフランジ部側内周面71eとに密着するよう間隙部104に保持されるとともに、間隙部104におけるシール性が遮熱板50の放射方向外端部の周方向全周に亘って確保される。これにより、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスがリンク室102に流入した場合であっても、間隙部104におけるシール性を向上させることができる。
As shown in FIG. 6, when the
さらに、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスがリンク室102に流入した場合においては、屈曲部51aの内周面には、図中矢印で示されるような排気ガスの内圧がかかる。屈曲部51aは、この排気ガスの内圧がかかることにより、放射外方に押し広げられる。これにより、遮熱板50は、放射方向外端部の周方向全周に亘って形成された屈曲部51aにおいて、略断面U字状に形成された屈曲部51aの弾性力に加えて、排気ガスの内圧によって、より確実に間隙部104を形成するタービンハウジング側端面41eとフランジ部側内周面71eとに密着する。このため、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスがリンク室102に流入した場合であっても、間隙部104におけるシール性を確保することができる。
Further, when a high-temperature exhaust gas containing water vapor flows into the
以上のように、本発明の実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャは、遮熱板50の放射方向外端部に周方向全周に亘って形成された屈曲部51aが間隙部104に屈曲された状態で圧入されるので、遮熱板50のガタツキを防止でき、このガタツキに起因した遮熱板50の摩耗を防止できるとともに、遮熱板50の放射方向外端部の周方向全周に亘ってタービンハウジング71とベアリングハウジング41との間のシール性を向上させることができる。
As described above, in the variable capacity turbocharger according to the embodiment of the present invention, the
また、屈曲部51aの弾性力によって遮熱板50がタービンハウジング71またはベアリングハウジング41の遮熱板対向面に密着させることができるので、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスにベアリングハウジング41が晒されるのを防止して、凝縮水の発生を抑制することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジング41の腐食を防止することができる。
Further, since the
また、屈曲部51aがベアリングハウジング41の外周面に対向して開口する略断面U字状に形成されているので、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスがリンク室102に流入した際には、この排気ガスの内圧により略断面U字状に開口した屈曲部51aが間隙部104に圧入された状態で押し広げられる。そのため、屈曲部51aの弾性力に加えて排気ガスの内圧により、間隙部104を形成するタービンハウジング側端面41eおよびフランジ部側内周面71eに屈曲部51aが密着した状態となるので、遮熱板50のガタツキを確実に防止して、このガタツキに起因した遮熱板50の摩耗をより確実に防止するとともに、間隙部104において遮熱板50の放射外端部の周方向全周に亘って、タービンハウジング71とベアリングハウジング41との間のシール性を確保することができる。さらに、屈曲部51aの弾性力に加えて排気ガスの内圧によって、遮熱板50をタービンハウジング71またはベアリングハウジング41の遮熱板対向面に密着させることができるので、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスにベアリングハウジング41が晒されるのを防止して、凝縮水の発生を抑制することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジング41の腐食を防止することができる。
In addition, since the
なお、本実施の形態においては、屈曲部51aの弾性力によって、遮熱板50がベアリングハウジング41の遮熱板対向面に密着するよう構成したが、これに限らず、例えば、遮熱板50をリンク室102を画成するノズルプレート93の遮熱板対向面を含むタービンハウジング71の遮熱板対向面に密着するよう構成してもよい。この場合、スクロール通路71a内を流通する水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスがガス流路71bを介してタービンホイール73に導入される際に、タービンハウジング71の内周面とノズルプレート93の外周端面との間の隙間を介してリンク室102内に流入することを防止することができる。これにより、リンク室102を画成するベアリングハウジング41の外周面に直接、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスが接触することを防止することができる。
In the present embodiment, the
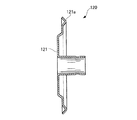
また、本実施の形態に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャ20においては、屈曲部51aの形状を略断面U字状に形成したものを適用したが、これに限らず、間隙部104におけるシール性を確保することができるものであれば何れの形状でもよく、例えば、図7に示すような略断面くの字状のビード構造を採用してもよい。
In addition, in the
すなわち、図7に示すように、遮熱板120の底面部121の放射方向外端部に、周方向全周に亘って略断面くの字状の屈曲部121aを形成してもよい。この屈曲部121aは、タービンハウジング71側に向けて略断面くの字状に屈曲した形状をしており、上述の遮熱板50と同様、間隙部104に屈曲した状態で圧入されるようになっている(図4参照)。
That is, as shown in FIG. 7, a
このように、遮熱板120は、放射方向外端部に周方向全周に亘って形成された屈曲部121aが間隙部104に屈曲された状態で圧入されるので、遮熱板120のガタツキを防止でき、このガタツキに起因した遮熱板120の摩耗を防止できるとともに、遮熱板120の放射方向外端部の周方向全周に亘ってタービンハウジング71とベアリングハウジング41との間のシール性を向上させることができる。
Thus, the
また、屈曲部121aの弾性力によって遮熱板120がタービンハウジング71またはベアリングハウジング41の遮熱板対向面に密着させることができるので、水蒸気を含む高温の排気ガスにベアリングハウジング41が晒されるのを防止して、凝縮水の発生を抑制することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジング41の腐食を防止することができる。
Further, since the
また、本実施の形態においては、可変ノズル機構45を採用する可変容量型ターボチャージャ20に本発明を適用する例について説明したが、これに限らず、例えば可変ノズル機構を採用していないターボチャージャに本発明を適用するようにしてもよい。
In the present embodiment, the example in which the present invention is applied to the
また、今回開示された実施の形態は、すべての点で例示であって、この実施の形態に制限されるものではない。本発明の範囲は、上記した実施の形態のみの説明ではなくて特許請求の範囲によって示され、特許請求の範囲と均等の意味および範囲内での全ての変更が含まれることが意図される。 In addition, the embodiment disclosed this time is illustrative in all respects, and is not limited to this embodiment. The scope of the present invention is shown not by the above description of the embodiments but by the scope of the claims, and is intended to include all modifications within the meaning and scope equivalent to the scope of the claims.
以上説明したように、本発明に係る可変容量型ターボチャージャは、遮熱板によるタービンハウジングとベアリングハウジングとの間のシール性を確保することができ、凝縮水の付着によるベアリングハウジングの腐食を防止することができるという効果を有し、内燃機関から排出される排気ガスの熱を遮熱する遮熱板を有するターボチャージャ全般に有用である。 As described above, the variable capacity turbocharger according to the present invention can ensure the sealing performance between the turbine housing and the bearing housing by the heat shield and prevent the corrosion of the bearing housing due to the adhering condensed water. The present invention is useful for all turbochargers having a heat shield plate that shields the heat of exhaust gas discharged from an internal combustion engine.
1…ディーゼルエンジン(内燃機関)、4a…吸気通路、8a…排気通路、20…可変容量型ターボチャージャ(ターボチャージャ)、41…ベアリングハウジング、41a、41b…フランジ部、41e…タービンハウジング側端面、50、120…遮熱板、51、121…底面部、51a、121a…屈曲部、52…側面部、62…回転軸、71…タービンハウジング、71b…ガス流路(排気ガス導入通路)、71d…内周端面、71e…フランジ部側内周面、73…タービンホイール、83…コンプレッサホイール、102…リンク室、104…間隙部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (1)
前記回転軸を回転自在に支持するとともに外周部に周方向全周に亘って形成されたフランジ部を有し、前記回転軸を収容するベアリングハウジングと、
前記排気通路に連通する排気ガス導入通路を有するとともに、内周端面が前記フランジ部に取付けられ、内部に前記タービンホイールを収容するタービンハウジングと、
前記ベアリングハウジングと前記タービンハウジングの間に介装された円板状の遮熱板とを備え、
前記フランジ部の前記タービンハウジング側端面と前記タービンハウジングの前記フランジ部側内周面との間に、前記フランジ部の周方向全周に亘って間隙部が形成されたターボチャージャにおいて、
前記遮熱板が、前記遮熱板の放射方向外端部に周方向全周に亘って形成されるとともに、前記間隙部に屈曲された状態で圧入される屈曲部を有し、前記屈曲部の弾性力によって前記遮熱板が前記タービンハウジングまたは前記ベアリングハウジングの前記遮熱板対向面に密着することを特徴とするターボチャージャ。 A compressor wheel is disposed on an intake passage of the internal combustion engine, and a turbine wheel connected to the compressor wheel via a rotation shaft is a turbocharger disposed on the exhaust passage of the internal combustion engine,
A bearing housing that rotatably supports the rotating shaft and has a flange portion formed on the outer peripheral portion over the entire circumference, and accommodates the rotating shaft;
A turbine housing having an exhaust gas introduction passage communicating with the exhaust passage, an inner peripheral end face attached to the flange portion, and housing the turbine wheel therein;
A disk-shaped heat shield disposed between the bearing housing and the turbine housing;
In the turbocharger in which a gap portion is formed over the entire circumference in the circumferential direction of the flange portion between the turbine housing side end surface of the flange portion and the flange portion side inner peripheral surface of the turbine housing.
The heat shield plate has a bent portion that is formed in the radially outer end of the heat shield plate over the entire circumference and is press-fitted in a bent state in the gap portion, and the bent portion The turbocharger is characterized in that the heat shield plate comes into close contact with the heat shield plate facing surface of the turbine housing or the bearing housing by the elastic force of the turbocharger.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012257474A JP2013047525A (en) | 2012-11-26 | 2012-11-26 | Turbocharger |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012257474A JP2013047525A (en) | 2012-11-26 | 2012-11-26 | Turbocharger |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008318680A Division JP2010138885A (en) | 2008-12-15 | 2008-12-15 | Turbocharger |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013047525A true JP2013047525A (en) | 2013-03-07 |
| JP2013047525A5 JP2013047525A5 (en) | 2013-05-02 |
Family
ID=48010613
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012257474A Pending JP2013047525A (en) | 2012-11-26 | 2012-11-26 | Turbocharger |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2013047525A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018179328A1 (en) * | 2017-03-31 | 2018-10-04 | 三菱重工エンジン&ターボチャージャ株式会社 | Turbine housing and turbo charger provided with same |
| CN110520607A (en) * | 2017-10-31 | 2019-11-29 | 三菱重工发动机和增压器株式会社 | Turbine and turbocharger with the turbine |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63150424A (en) * | 1986-12-15 | 1988-06-23 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Housing structure for turbocharger |
| JPS63158546U (en) * | 1987-04-04 | 1988-10-18 | ||
| JPH11229886A (en) * | 1998-02-13 | 1999-08-24 | Taiho Kogyo Co Ltd | Turbocharger sealing unit |
| JP2001173450A (en) * | 1999-12-20 | 2001-06-26 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Variable turbocharger |
| JP2007231934A (en) * | 2006-02-02 | 2007-09-13 | Ihi Corp | Turbocharger with variable nozzle |
-
2012
- 2012-11-26 JP JP2012257474A patent/JP2013047525A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS63150424A (en) * | 1986-12-15 | 1988-06-23 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Housing structure for turbocharger |
| JPS63158546U (en) * | 1987-04-04 | 1988-10-18 | ||
| JPH11229886A (en) * | 1998-02-13 | 1999-08-24 | Taiho Kogyo Co Ltd | Turbocharger sealing unit |
| JP2001173450A (en) * | 1999-12-20 | 2001-06-26 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | Variable turbocharger |
| JP2007231934A (en) * | 2006-02-02 | 2007-09-13 | Ihi Corp | Turbocharger with variable nozzle |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018179328A1 (en) * | 2017-03-31 | 2018-10-04 | 三菱重工エンジン&ターボチャージャ株式会社 | Turbine housing and turbo charger provided with same |
| US11506086B2 (en) | 2017-03-31 | 2022-11-22 | Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Engine & Turbocharger, Ltd. | Turbine housing and turbo charger provided with same |
| CN110520607A (en) * | 2017-10-31 | 2019-11-29 | 三菱重工发动机和增压器株式会社 | Turbine and turbocharger with the turbine |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2010138885A (en) | Turbocharger | |
| US8596063B2 (en) | Exhaust treatment system for an internal combustion engine | |
| CN107339168B (en) | Engine system | |
| US8196394B2 (en) | Exhaust purification apparatus for engine | |
| JP5763294B2 (en) | Exhaust purification equipment | |
| JP2010180863A (en) | Exhaust pipe liquid injection system, exhaust emission control system, exhaust pipe liquid injection method and exhaust emission control method | |
| JP2013142363A (en) | Exhaust emission control device of diesel engine | |
| JP2016148259A (en) | Exhaust emission control device | |
| JP5471650B2 (en) | Turbocharger compressor housing | |
| JP2009091984A (en) | Exhaust emission control device | |
| JP2010031769A (en) | Exhaust emission control device | |
| JP5020185B2 (en) | Exhaust purification device | |
| US11008982B2 (en) | Exhaust-gas turbocharger | |
| JP2009257090A (en) | Variable capacity turbocharger | |
| JP2013047525A (en) | Turbocharger | |
| JP2011236874A (en) | Emission control device | |
| US9982590B2 (en) | Internal-combustion-engine supercharger | |
| JP2008240552A (en) | Exhaust emission control device for internal combustion engine | |
| JP5032409B2 (en) | Exhaust purification device | |
| JP2016211486A (en) | Exhaust emission control system | |
| JP2010031719A (en) | Exhaust emission control device | |
| JP2010090875A (en) | Exhaust gas control device for internal combustion engine | |
| US8800267B2 (en) | Control system for modulating an air mass | |
| JP2012092746A (en) | Exhaust emission control device | |
| US20170074149A1 (en) | Thermal management system for aftertreatment system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20121126 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130313 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131112 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140108 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140401 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140528 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20140701 |