JP2012183881A - Electric power steering device - Google Patents
Electric power steering device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012183881A JP2012183881A JP2011047415A JP2011047415A JP2012183881A JP 2012183881 A JP2012183881 A JP 2012183881A JP 2011047415 A JP2011047415 A JP 2011047415A JP 2011047415 A JP2011047415 A JP 2011047415A JP 2012183881 A JP2012183881 A JP 2012183881A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- steering
- torque
- assist
- basic
- vehicle speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Steering Control In Accordance With Driving Conditions (AREA)
- Power Steering Mechanism (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、電動パワーステアリング装置に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an electric power steering apparatus.
従来、電動パワーステアリング装置において、操舵トルクと車速から基本アシスト電流を演算し、その値に基づいてモータを回転させアシストトルク制御を行う。この方法は、車両のハンドル状況にかかわらず一般的である。 Conventionally, in an electric power steering apparatus, a basic assist current is calculated from the steering torque and the vehicle speed, and the motor is rotated based on the calculated value to perform assist torque control. This method is common regardless of the vehicle steering situation.
しかし、ハンドルが切り込み、保舵、切り戻し状態と変化するにもかかわらず、アシストトルクを操舵トルクと車速から一義的に決定してしまうと、操舵フィーリングに違和感があった。そのため、例えば、特許文献1に記載の電動パワーステアリング装置では、操舵速度によって基本シフト量を演算し、ハンドル切り込み、及びハンドル戻し時に応じて、基本アシストトルクを変えることが記載されている。
However, if the steering torque is uniquely determined from the steering torque and the vehicle speed in spite of the change of the steering wheel, the steering, and the switching back state, the steering feeling is uncomfortable. Therefore, for example, in the electric power steering apparatus described in
ところが、特許文献1の場合、操舵速度を操舵角センサから生成しているため、操舵角センサが付属しない場合には、上記基本シフト量が演算できず、操舵フィーリングを低下させるという虞があり、なお改善の余地を残すものとなっていた。
However, in the case of
本発明は、上記問題点を解決するためになされたものであって、その目的は、特に、操舵速度が検出できなくても、ハンドルの切り込み、切り戻し、及び保舵時に、快適な操舵フィーリングを得ることのできる電動パワーステアリング装置を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in order to solve the above-described problems, and its object is to provide a comfortable steering fee, particularly when the steering wheel is turned, turned back, and held even when the steering speed cannot be detected. An object of the present invention is to provide an electric power steering device capable of obtaining a ring.
上記課題を解決するために、請求項1に記載の発明は、車両の操舵系に操舵補助力を付与するモータ(12)と、操舵トルクを検出するトルクセンサ(15)と、車速を検出する車速センサ(16)と、上記操舵トルクと上記車速に対するモータ駆動目標値の基本特性である基本アシスト特性を設定する基本アシスト特性設定手段(23)と、ハンドルの操舵状態を判定する操舵状態判定手段(25)と、上記操舵トルクに基づいて、基本トルクシフト量を演算する基本トルクシフト量演算手段(26)と、上記車速に基づいて、車速ゲインを演算する車速ゲイン演算手段(27)と、を備え、前記操舵状態判定手段(25)から出力されたパラメータ(α)と、前記基本トルクシフト量演算手段(26)から出力された基本トルクシフト量(ΔTha)と、前記車速ゲイン演算手段(27)から出力された車速ゲイン(Gv)を乗算した値を、前記基本アシスト特性設定手段(23)により設定された基本アシスト特性に加算されたアシストトルク指令値設定手段(24)と、前記アシストトルク指令値設定手段(24)より出力されたアシストトルク指令値(Ta*)により前記モータ(12)を駆動する制御信号を生成するモータ制御信号出力手段(31)と、前記モータ制御信号出力手段(31)により生成されたモータ制御信号により前記モータ(12)を駆動するモータ駆動手段(40)とを含むこと、を要旨とする。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, the invention according to claim 1 detects a vehicle speed, a motor (12) for applying a steering assist force to a steering system of a vehicle, a torque sensor (15) for detecting a steering torque, and the like. A vehicle speed sensor (16), a basic assist characteristic setting means (23) for setting a basic assist characteristic that is a basic characteristic of the motor drive target value with respect to the steering torque and the vehicle speed, and a steering state determination means for determining the steering state of the steering wheel (25), a basic torque shift amount calculating means (26) for calculating a basic torque shift amount based on the steering torque, a vehicle speed gain calculating means (27) for calculating a vehicle speed gain based on the vehicle speed, And a parameter (α) output from the steering state determination means (25) and a basic torque shift amount output from the basic torque shift amount calculation means (26). ΔTha) multiplied by the vehicle speed gain (Gv) output from the vehicle speed gain calculation means (27) is added to the basic assist characteristic set by the basic assist characteristic setting means (23), and an assist torque command is added. Value setting means (24), and motor control signal output means for generating a control signal for driving the motor (12) by the assist torque command value (Ta *) output from the assist torque command value setting means (24). 31) and motor drive means (40) for driving the motor (12) by the motor control signal generated by the motor control signal output means (31).
上記構成によれば、操舵速度を検出することなく、操舵トルクに基づいて、操舵状態を判定することによって、基本アシスト特性にトルクシフト量の加算の有無を決定することができる。その結果、必要な場合のみ操舵トルクを増加/減少させることができるので、快適な操舵フィーリングを得ることができる。 According to the above configuration, it is possible to determine whether or not to add the torque shift amount to the basic assist characteristics by determining the steering state based on the steering torque without detecting the steering speed. As a result, the steering torque can be increased / decreased only when necessary, so that a comfortable steering feeling can be obtained.
請求項2に記載の発明は、前記操舵状態判定手段は、前記操舵トルクと前記操舵トルクの微分値の積が零より大きい場合には、切り込み状態と判定し、前記パラメータに「0」を書き込み、前記操舵トルクと前記操舵トルクの微分値の積が零より小さい場合には、切り戻し状態と判定し、前記パラメータに「1」を書き込み、前記操舵トルクと前記操舵トルクの微分値の積が零の場合には、保舵状態と判定し、前記パラメータに「1」を書き込むこと、を要旨とする。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, when the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is greater than zero, the steering state determination unit determines that the state is a cut state and writes “0” in the parameter. When the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is smaller than zero, it is determined that the switch-back state has occurred, and “1” is written in the parameter, and the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is In the case of zero, it is determined that the steering state is maintained and “1” is written in the parameter.
上記構成によれば、操舵トルクと操舵トルクの微分値の積が零より大きい場合には、切り込み状態と判定し、操舵トルクと操舵トルクの微分値の積が零より小さい場合には、切り戻し状態と判定する。そして、操舵トルクと操舵トルクの微分値の積が零の場合には、保舵状態と判定する。
その結果、切り込み状態か、切り戻し状態か保舵状態かを正確に判定できる。
According to the above configuration, when the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is larger than zero, it is determined as a cut-in state, and when the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is smaller than zero, the switchback is performed. Judged as a state. When the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is zero, it is determined that the steering is maintained.
As a result, it is possible to accurately determine whether the cutting state, the switching back state, or the steered state.
本発明によれば、切り込み状態と判定した場合には、基本トルクシフト量を無効となるようにして、操舵トルクを増加させることができ、切り戻し状態、又は保舵状態と判定した場合には、基本トルクシフト量を有効となるようにして、操舵トルクを減少させることができるので、快適な操舵フィーリングを得ることができる。 According to the present invention, the steering torque can be increased by invalidating the basic torque shift amount when it is determined that the cut-in state is established, and when it is determined that the switch-back state or the steered state is determined. Since the steering torque can be reduced by making the basic torque shift amount effective, a comfortable steering feeling can be obtained.
以下、コラム型の電動パワーステアリング装置1(以下、EPSという)に具体化した本発明の一実施形態を図面に従って説明する。
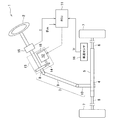
図1に示すように、本実施形態のEPS1において、ステアリング2が固定されたステアリングシャフト3は、ラックアンドピニオン機構4を介してラック軸5と連結されている。ステアリング操作に伴うステアリングシャフト3の回転は、ラックアンドピニオン機構4によりラック軸5の往復直線運動に変換される。
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention embodied in a column type electric power steering apparatus 1 (hereinafter referred to as EPS) will be described with reference to the drawings.
As shown in FIG. 1, in the
尚、本実施形態のステアリングシャフト3は、コラムシャフト8、インターミディエイトシャフト9、及びピニオンシャフト10を連結してなる。そして、このステアリングシャフト3の回転に伴うラック軸5の往復直線運動が、同ラック軸5の両端に連結されたタイロッド6を介して図示しないナックルに伝達されることにより、転舵輪7の舵角が変更される。
The
また、EPS1は、操舵系にステアリング操作を補助するためのアシスト力を付与するEPSアクチュエータ13と、EPSアクチュエータ13の作動を制御する制御手段としてのECU11とを備えている。
Further, the
本実施形態のEPSアクチュエータ13は、コラム型のEPSアクチュエータであり、その駆動源であるモータ12は、減速機構14を介してコラムシャフト8と駆動連結されている。EPSアクチュエータ13は、モータ12の回転を減速機構14により減速してコラムシャフト8に伝達することによって、そのモータトルクをアシスト力として操舵系に付与する。
The
ECU11には、車速センサ16、トルクセンサ15及びモータ回転角センサ18が接続されている。ECU11は、これら各センサの出力信号に基づいて、車速V、操舵トルクτ及びモータ回転角θmを検出する。例えば、本実施形態のトルクセンサ15は、一対のレゾルバが図示しないトーションバーの両端に設けられたツインレゾルバ型のトルクセンサである。また、ECU11は、これらの検出される各状態量に基づいて目標アシスト力を演算し、モータ12への駆動電力の供給を通じて、EPSアクチュエータ13の作動、即ち、操舵系に付与するアシスト力を制御する。
A
次に、本実施形態のEPSにおけるアシスト制御の態様について説明する。
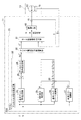
図2に示すように、ECU11は、モータ制御信号を出力するマイコン21と、そのモータ制御信号に基づいて、モータ12に駆動電力を供給する駆動回路40とを備えて構成されている。
Next, an aspect of assist control in the EPS of the present embodiment will be described.
As shown in FIG. 2, the ECU 11 includes a
本実施形態では、ECU11には、モータ12に通電される実電流値Imを検出するための電流センサ41、及びモータ12の回転角θmを検出するためのモータ回転角センサ18(図1参照)が接続されている。そして、マイコン21は、上記各車両状態量、並びにこれら電流センサ41及びモータ回転角センサ18の出力信号に基づき検出されたモータ12の実電流値Im及びモータ回転角θmに基づいて、駆動回路40に出力するモータ制御信号を生成する。
In the present embodiment, the
尚、以下に示す各制御ブロックは、マイコン21が実行するコンピュータプログラムにより実現されるものである。そして、同マイコン21は、所定のサンプリング周期で上記各状態量を検出し、所定周期毎に以下の各制御ブロックに示される各演算処理を実行することにより、モータ制御信号を生成する。
Each control block shown below is realized by a computer program executed by the
詳述すると、本実施形態のマイコン21は、上記操舵トルクτ及び車速Vに基づいて、モータ12に発生させるべきアシストトルク、即ち目標アシスト力に対応したアシストトルク指令値Ta*を演算するアシストトルク指令値演算部22と、同アシストトルク指令値Ta*に対応したアシスト電流指令値I*を演算するアシスト電流指令値演算部30とを備えている。
Specifically, the
そして、同マイコン21は、そのアシスト電流指令値I*にモータ12の電流センサ41により検出された実電流値Imを追従させるべく、モータ制御信号出力部31において、その電流偏差ΔIに基づく電流フィードバック制御を実行することにより、上記駆動回路40に出力するモータ制御信号を生成する。
Then, the
具体的には、本実施形態では、モータ12には、三相(U,V,W)の駆動電力の供給により回転するブラシレスモータが用いられている。そして、モータ制御信号出力部31は、実電流値Imとして検出されたモータ12の相電流値(Iu,Iv,Iw)をd/q座標系のd、q軸電流値に変換(d/q変換)することにより、上記電流フィードバック制御を行う。
Specifically, in the present embodiment, a brushless motor that rotates by supplying three-phase (U, V, W) driving power is used as the
即ち、アシスト電流指令値I*は、q軸電流指令値としてモータ制御信号出力部31に入力され、モータ制御信号出力部31は、回転角センサ18により検出されたモータ回転角回転角θmに基づいて相電流値(Iu,Iv,Iw)をd/q変換する。また、モータ制御信号出力部31は、そのd、q軸電流値及びq軸電流指令値に基づいてd、q軸電圧指令値を演算する。そして、そのd、q軸電圧指令値をd/q逆変換することにより相電圧指令値(Vu*,Vv*,Vw*)を演算し、当該相電圧指令値に基づいてモータ制御信号を生成する。
That is, the assist current command value I * is input to the motor control
このようにして生成されたモータ制御信号は、マイコン21から駆動回路40へと出力され、同駆動回路40により当該モータ制御信号に基づく三相の駆動電力がモータ12へと供給される。そして、その操舵トルクτに基づくアシスト力目標値としてのアシスト電流指令値I*に相当するモータトルクが発生することにより、当該アシスト力目標値に対応するアシスト力が操舵系に付与される構成となっている。
The motor control signal generated in this way is output from the
(アシストトルク指令値演算)
次に、本実施形態におけるアシストトルク指令値演算の態様について説明する。
本実施形態では、アシストトルク指令値演算部22には、操舵トルクτ及び操舵トルク変化量dτ/dtに基づいてハンドル切り込み、ハンドル切り戻し、及びハンドル保舵を判定する操舵状態判定部25が設けられている。そして、本実施形態の操舵状態判定部25は、ハンドルが切り込まれたと判定した場合には、操舵状態判定係数αを「0」(α=0)に、一方、ハンドルが切り戻された、又はハンドルが保舵状態にあると判定した場合には、操舵状態判定係数αを「1」(α=1)に設定する。
(Assist torque command value calculation)
Next, a mode of assist torque command value calculation in the present embodiment will be described.
In the present embodiment, the assist torque command
次に、上記のように構成されたアシストトルク指令値演算部22における操舵状態判定部25の処理手順について説明する。
図4のフローチャートに示すように、マイコン21は、操舵トルクτを取り込む(ステップS101)。次に、取り込んだ操舵トルクτを微分して、操舵トルクτの変化量dτ/dtを演算する(ステップS102)。そして、操舵トルクτと操舵トルクτの変化量dτ/dtの積が零より大きいか否かを判定する(ステップS103)。
Next, a processing procedure of the steering
As shown in the flowchart of FIG. 4, the
そして、操舵トルクτと操舵トルクτの変化量dτ/dtの積が零より大きい場合(τ・dτ/dt>0、ステップS103、YES)、ステップS104に移行する。
ステップS104では、操舵状態が切り込み状態であると判定し、操舵状態判定係数αを「0」(α=0)に設定し、処理を終わる。
When the product of the steering torque τ and the change amount dτ / dt of the steering torque τ is greater than zero (τ · dτ / dt> 0, step S103, YES), the process proceeds to step S104.
In step S104, it is determined that the steering state is the infeed state, the steering state determination coefficient α is set to “0” (α = 0), and the process ends.
また、操舵トルクτと操舵トルクτの変化量dτ/dtの積が零以下の場合(τ・dτ/dt≦0、ステップS103、NO)、ステップS105に移行する。
ステップS105では、操舵トルクτと操舵トルクτの変化量dτ/dtの積が零より小さいか否かを判定する。
If the product of the steering torque τ and the amount of change dτ / dt of the steering torque τ is less than zero (τ · dτ / dt ≦ 0, step S103, NO), the process proceeds to step S105.
In step S105, it is determined whether or not the product of the steering torque τ and the change amount dτ / dt of the steering torque τ is smaller than zero.
そして、操舵トルクτと操舵トルクτの変化量dτ/dtの積が零より小さい場合(τ・dτ/dt<0、ステップS105、YES)、ステップS106に移行する。
ステップS106では、操舵状態が切り戻し状態であると判定し、操舵状態判定係数αを「1」(α=1)に設定し、処理を終わる。
When the product of the steering torque τ and the change amount dτ / dt of the steering torque τ is smaller than zero (τ · dτ / dt <0, step S105, YES), the process proceeds to step S106.
In step S106, it is determined that the steering state is the switchback state, the steering state determination coefficient α is set to “1” (α = 1), and the process ends.
そして、操舵トルクτと操舵トルクτの変化量dτ/dtの積が零の場合(τ・dτ/dt=0、ステップS105、NO)、ステップS107に移行する。
ステップS107では、操舵状態が保舵状態であると判定し、操舵状態判定係数αを「1」(α=1)に設定し、処理を終わる。
When the product of the steering torque τ and the change amount dτ / dt of the steering torque τ is zero (τ · dτ / dt = 0, step S105, NO), the process proceeds to step S107.
In step S107, it is determined that the steering state is the holding state, the steering state determination coefficient α is set to “1” (α = 1), and the process ends.
また、本実施形態では、アシストトルク指令値演算部22には、操舵トルクτに基づいて基本トルクシフト量ΔThaを求めるトルクシフト演算部26が設けられている。
そして、本実施形態のトルクシフト演算部26は、図5で示されるように、操舵トルクτの正の値に対して、基本トルクシフト量ΔThaの正の値を対応付けている。一方、本実施形態のトルクシフト演算部26は、操舵トルクτの負の値に対して、基本トルクシフト量ΔThaの負の値を対応付けている。
In the present embodiment, the assist torque command
As shown in FIG. 5, the torque
また、本実施形態のトルクシフト演算部26は、操舵トルクτが零の近傍の不感帯内の値をとるときには、基本トルクシフト量ΔThaは零に保持される。そして、本実施形態のトルクシフト演算部26は、操舵トルクτが零の近傍の不感帯外の値をとるときには、所定の下限値及び上限値の間の範囲内で、操舵トルクの増加に対して単調に増加するように定められている。
Further, when the steering torque τ takes a value in the dead zone in the vicinity of zero, the torque
また、本実施形態では、アシストトルク指令値演算部22には、車速Vに基づいて車速ゲインGvを求める車速ゲイン演算部27が設けられている。そして、本実施形態の車速ゲイン演算部27は、図6で示されるように、車速Vが零から所定速度までの範囲において、車速Vの増加に伴って急増し、その後は穏やかに一定値に収束するように定められている。
In the present embodiment, the assist torque command
これによって、低速走行時におけるアシスト特性のシフト量が少なく抑えられるから、たとえば、Uターン操作を行なう場合のように、ステアリング2を同じ方向に切り込み続ける場合であっても、操舵負担が重くなり過ぎるなどということはない。
As a result, the shift amount of the assist characteristic during low-speed traveling can be suppressed to be small. For example, even when the
また、本実施形態では、アシストトルク指令値演算部22には、図2で示されるように、操舵トルクτ、車速Vに基づいて基本アシスト特性設定部23が設けられている。この基本アシスト特性は、操舵トルクτの正の値に対してアシストトルク指令値Ta*の正の値を対応付け、操舵トルクτの負の値に対してアシストトルク指令値Ta*の負の値を対応付けるように定められている。また、基本アシスト特性設定部23には、複数の車速域に対応した複数の基本アシストマップが記憶されている。
In the present embodiment, the assist torque command
そして、本実施形態では、アシストトルク指令値演算部22には、上記基本アシスト特性設定部23に、上記記載の操舵状態判定部25が出力する操舵状態判定係数α、トルクシフト演算部26が出力する基本トルクシフト量ΔTha、及び車速ゲイン演算部27が出力する車速ゲインGvが乗算器28で乗算されたトルクシフト量ΔTh(=α・ΔTha・Gv)が加算器29によって加算される。そして、基本アシスト特性設定部23から出力された基本アシスト特性に上記トルクシフト量ΔThが加算されアシストトルク指令値設定部24に入力される。
In this embodiment, the assist torque command
次に、本実施形態のアシストトルク指令値設定部24の機能を、図3に基づいて説明する。図3は、基本アシスト特性と、これを操舵トルク軸方向にシフトして得られる修正アシスト特性とを表している。トルクセンサ15によって検出される操舵トルクτは、ステアリング2に右方向操舵のためのトルクが加えられているときには正の値を取り、ステアリング2に左方向操舵のためのトルクが加えられているときには負の値を取る。
Next, the function of the assist torque command
基本アシスト特性は、図3において、曲線L10で示されている。この基本アシスト特性は、操舵トルクτの正の値に対して、アシストトルク指令値Ta*の正の値を対応付け、操舵トルクτの負の値に対して、アシストトルク指令値Ta*の負の値を対応付けるように定められている。 The basic assist characteristic is indicated by a curve L10 in FIG. In this basic assist characteristic, a positive value of the assist torque command value Ta * is associated with a positive value of the steering torque τ, and a negative value of the assist torque command value Ta * is associated with a negative value of the steering torque τ. It is determined to associate the values of.
上述のとおり、基本アシスト特性設定部23には、複数の車速域に対応した複数の基本アシストマップが記憶されているが、図3においては、或る車速域において、適用される1つの基本アシスト特性を示す。曲線L10に示された基本アシスト特性において、操舵トルクτ=0の近傍においては、操舵トルクτの値によらず、アシストトルク指令値Ta*=0とされる。このような操舵トルクの範囲が不感帯NSである。
As described above, the basic assist
本実施形態では、操舵トルクτに基づいて、トルクシフト演算部26によって演算されるトルクシフト量ΔThだけ、基本アシスト特性を操舵トルクτの軸方向(正方向または負方向)にシフトさせた仮想的な修正アシスト特性(たとえば、曲線L11、L12で示す特性)に基づいて、アシストトルク指令値Ta*が設定されることになる。
In the present embodiment, based on the steering torque τ, the virtual assist characteristic is shifted in the axial direction (positive direction or negative direction) of the steering torque τ by the torque shift amount ΔTh calculated by the torque
詳述すれば、本実施形態では、操舵トルクτが一定値以上の正の値をとるときには、基本アシスト特性を図3において、操舵トルク軸の正方向にシフトさせた仮想的な修正アシスト特性(たとえば、曲線L11で示すアシスト特性)に従って、操舵トルクτに対応したアシストトルク指令値Ta*が定められる。これに対して、操舵トルクτが一定値以下の負の値をとるときには、基本アシスト特性を図3において、操舵トルク軸の負方向にシフトさせた仮想的な修正アシスト特性(たとえば、曲線L12で示すアシスト特性)に従って、操舵トルクτに対応したアシストトルク指令値Ta*が定められる。 More specifically, in this embodiment, when the steering torque τ takes a positive value of a certain value or more, the virtual assist assist characteristic (in FIG. 3) is obtained by shifting the basic assist characteristic in the positive direction of the steering torque axis ( For example, the assist torque command value Ta * corresponding to the steering torque τ is determined according to the assist characteristic indicated by the curve L11. On the other hand, when the steering torque τ takes a negative value equal to or less than a certain value, the basic assist characteristic is shifted to the negative direction of the steering torque axis in FIG. The assist torque command value Ta * corresponding to the steering torque τ is determined according to the assist characteristics shown).
更に詳述すれば、本実施形態では、ステアリング2を中立位置から離れる方向へと切り込む操舵時においては、操舵トルクτは、正の値をとるので、仮想的な修正アシスト特性は、基本アシスト特性を操舵トルク軸方向に沿って、原点から離れる方向へとシフトされた特性となる。このときのトルクシフト量ΔThは、操舵トルクτの絶対値が大きいほど大きい。
More specifically, in the present embodiment, the steering torque τ takes a positive value during steering in which the
これにより、操舵トルクτが同じ場合に、アシストトルク指令値Ta*は、基本アシスト特性の場合に比較して、その絶対値が小さくなるので、操舵補助力は小さくなる。その結果、ステアリング2を切り込むときに、良好な手応え感を運転者に与えることができる。
As a result, when the steering torque τ is the same, the assist torque command value Ta * has a smaller absolute value than the basic assist characteristic, and thus the steering assist force is small. As a result, it is possible to give the driver a good feeling of response when turning the
一方、本実施形態では、ステアリング2を舵角中点に向かって操舵する切り込み戻し操舵時においては、操舵トルクτは、徐々に減少していき、微少な値となる。これに応じて、仮想的な修正アシスト特性は、基本アシスト特性を操舵トルク軸方向に沿って、原点に向かう方向へとシフトさせた特性となる。
On the other hand, in the present embodiment, at the time of turning-back steering in which the
これにより、操舵トルクτが同じ場合に、アシストトルク指令値Ta*は、基本アシスト特性の場合に比較して、その絶対値が大きくなるので、操舵補助力は大きくなる。その結果、ステアリング2を切り戻すときに、良好な手応え感を運転者に与えることができる。
As a result, when the steering torque τ is the same, the assist torque command value Ta * has a larger absolute value than the basic assist characteristic, and thus the steering assist force is increased. As a result, when the
また、保舵時の場合にも、操舵トルクτが同じ場合に、アシストトルク指令値Ta*は、基本アシスト特性の場合に比較して、その絶対値が大きくなるので、操舵補助力は大きくなる。その結果、ステアリング2を保舵するときにも、良好な手応え感を運転者に与えることができる。
In addition, when the steering torque is maintained, the assist torque command value Ta * has a larger absolute value than the basic assist characteristic when the steering torque τ is the same. Therefore, the steering assist force is increased. . As a result, it is possible to give the driver a good feeling of responsiveness when the
以上、本実施形態によれば、以下のような作用・効果を得ることができる。
操舵トルクと操舵トルクの微分値の積が零より大きい場合には、切り込み状態と判定し、操舵トルクと操舵トルクの微分値の積が零より小さい場合には、切り戻し状態と判定する。また、操舵トルクと操舵トルクの微分値の積が零の場合には、保舵状態と判定する。そして、切り戻し状態または保舵状態と判定した場合には、操舵トルクに基づいた基本トルクシフトを有効となるようにした。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the following operations and effects can be obtained.
When the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is larger than zero, it is determined as a cut-in state, and when the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is smaller than zero, it is determined as a switch-back state. When the product of the steering torque and the differential value of the steering torque is zero, it is determined that the steering is maintained. And when it determines with a switchback state or a steering hold state, the basic torque shift based on a steering torque was made effective.
その結果、切り込み状態か、切り戻し状態か保舵状態かを正確に判定できる。また、切り込み状態時には、操舵トルクに基づいた基本トルクシフトが無効になるため、操舵トルクτが同じ場合に、アシストトルク指令値Ta*は、基本アシスト特性の場合に比較して、その絶対値が小さくなるので、操舵補助力は小さくなり、ステアリング2を切り込むときに、良好な手応え感を運転者に与えることができる。
As a result, it is possible to accurately determine whether the cutting state, the switching back state, or the steered state. In addition, since the basic torque shift based on the steering torque becomes invalid in the cutting state, the absolute value of the assist torque command value Ta * is the same as that of the basic assist characteristic when the steering torque τ is the same. Since the steering assist force is reduced, the driver can feel good responsiveness when turning the
また、切り戻し状態か保舵状態時には、操舵トルクに基づいた基本トルクシフトが有効になるため、操舵トルクτが同じ場合に、アシストトルク指令値Ta*は、基本アシスト特性の場合に比較して、その絶対値が大きくなるので、操舵補助力は大きくなり、ステアリング2を切り戻すとき、または保舵時に、良好な手応え感を運転者に与えることができる。
In addition, since the basic torque shift based on the steering torque is effective in the switchback state or the steered state, the assist torque command value Ta * is compared with the basic assist characteristic when the steering torque τ is the same. Since the absolute value becomes large, the steering assist force becomes large, and a good feeling of response can be given to the driver when turning back the
尚、本実施形態は以下のように変更してもよい。
・上記各実施形態では、本発明を所謂コラム型のEPS1に具体化したが、本発明は、所謂ピニオン型やラックアシスト型のEPSに適用してもよい。
In addition, you may change this embodiment as follows.
In each of the above embodiments, the present invention is embodied in a so-called
・上記実施形態では、本発明を、ブラシレスモータを駆動源とするEPSに具体化したが、本発明は、ブラシ付の直流モータを駆動源とするEPSに適用してもよい。 In the above embodiment, the present invention is embodied in EPS using a brushless motor as a drive source. However, the present invention may be applied to EPS using a DC motor with a brush as a drive source.
1:電動パワーステアリング装置(EPS)、2:ステアリング、
3:ステアリングシャフト、4:ラックアンドピニオン機構、5:ラック軸、
6:タイロッド、7:転舵輪、8:コラムシャフト、
9:インターミディエイトシャフト、10:ピニオンシャフト、11:ECU、
12:モータ、13:EPSアクチュエータ、14:減速機構、
15:トルクセンサ、16:車速センサ、
18:モータ回転角センサ、21:マイコン、22:アシストトルク指令値演算部、
23:基本アシスト特性設定部、24:アシストトルク指令値設定部、
25:操舵状態判定部、26:トルクシフト演算部、27:車速ゲイン演算部、
28:乗算器、29:加算器、30:アシスト電流指令値演算部、
31:モータ制御信号出力部、40:駆動回路、41:電流センサ、
V:車速、τ:操舵トルク、dτ/dt:操舵トルク変化量、θm:モータ回転角、
Im:実電流値、I*:アシスト電流指令値、ΔI:電流偏差、
Iu,Iv,Iw:相電流値、Vu*,Vv*,Vw*:相電圧指令値、
Ta*:アシストトルク指令値、ΔTha:基本トルクシフト量、
ΔTh:トルクシフト量、α:操舵状態判定係数、Gv:車速ゲイン
1: Electric power steering device (EPS), 2: Steering,
3: Steering shaft, 4: Rack and pinion mechanism, 5: Rack shaft,
6: Tie rod, 7: Steering wheel, 8: Column shaft,
9: Intermediate shaft, 10: Pinion shaft, 11: ECU,
12: Motor, 13: EPS actuator, 14: Deceleration mechanism,
15: Torque sensor, 16: Vehicle speed sensor,
18: motor rotation angle sensor, 21: microcomputer, 22: assist torque command value calculation unit,
23: Basic assist characteristic setting unit, 24: Assist torque command value setting unit,
25: Steering state determination unit, 26: Torque shift calculation unit, 27: Vehicle speed gain calculation unit,
28: Multiplier, 29: Adder, 30: Assist current command value calculation unit,
31: Motor control signal output unit, 40: Drive circuit, 41: Current sensor,
V: vehicle speed, τ: steering torque, dτ / dt: steering torque change amount, θm: motor rotation angle,
Im: actual current value, I *: assist current command value, ΔI: current deviation,
Iu, Iv, Iw: Phase current value, Vu *, Vv *, Vw *: Phase voltage command value,
Ta *: assist torque command value, ΔTha: basic torque shift amount,
ΔTh: Torque shift amount, α: Steering state determination coefficient, Gv: Vehicle speed gain
Claims (2)
操舵トルクを検出するトルクセンサと、
車速を検出する車速センサと、
上記操舵トルクと上記車速に対するモータ駆動目標値の基本特性である基本アシスト特性を設定する基本アシスト特性設定手段と、
ハンドルの操舵状態を判定する操舵状態判定手段と、
上記操舵トルクに基づいて、基本トルクシフト量を演算する基本トルクシフト量演算手段と、
上記車速に基づいて、車速ゲインを演算する車速ゲイン演算手段と、を備え、
前記操舵状態判定手段から出力されたパラメータと、前記基本トルクシフト量演算手段から出力された基本トルクシフト量と、前記車速ゲイン演算手段から出力された車速ゲインを乗算した値を、前記基本アシスト特性設定手段により設定された基本アシスト特性に加算されたアシストトルク指令値設定手段と、
前記アシストトルク指令値設定手段より出力されたアシストトルク指令値により前記モータを駆動する制御信号を生成するモータ制御信号出力手段と、
前記モータ制御信号出力手段により生成されたモータ制御信号により前記モータを駆動するモータ駆動手段とを含むこと、
を特徴とする電動パワーステアリング装置。 A motor for applying a steering assist force to the vehicle steering system;
A torque sensor for detecting steering torque;
A vehicle speed sensor for detecting the vehicle speed;
Basic assist characteristic setting means for setting a basic assist characteristic that is a basic characteristic of a motor drive target value with respect to the steering torque and the vehicle speed;
Steering state determination means for determining the steering state of the steering wheel;
Basic torque shift amount calculating means for calculating a basic torque shift amount based on the steering torque;
Vehicle speed gain calculating means for calculating a vehicle speed gain based on the vehicle speed,
A value obtained by multiplying the parameter output from the steering state determining means, the basic torque shift amount output from the basic torque shift amount calculating means, and the vehicle speed gain output from the vehicle speed gain calculating means is the basic assist characteristic. Assist torque command value setting means added to the basic assist characteristics set by the setting means;
Motor control signal output means for generating a control signal for driving the motor according to the assist torque command value output from the assist torque command value setting means;
Motor driving means for driving the motor by a motor control signal generated by the motor control signal output means,
An electric power steering device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011047415A JP2012183881A (en) | 2011-03-04 | 2011-03-04 | Electric power steering device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011047415A JP2012183881A (en) | 2011-03-04 | 2011-03-04 | Electric power steering device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012183881A true JP2012183881A (en) | 2012-09-27 |
| JP2012183881A5 JP2012183881A5 (en) | 2014-04-24 |
Family
ID=47014355
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011047415A Pending JP2012183881A (en) | 2011-03-04 | 2011-03-04 | Electric power steering device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2012183881A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5983764B2 (en) * | 2012-12-07 | 2016-09-06 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Driving support device, operation detection device, and control device |
| JP2016532593A (en) * | 2013-10-08 | 2016-10-20 | ティーアールダブリュー・リミテッド | Electric power assisted steering system |
| JP2018008550A (en) * | 2016-07-11 | 2018-01-18 | 株式会社デンソー | Steering control device |
| JP2018008549A (en) * | 2016-07-11 | 2018-01-18 | 株式会社デンソー | Steering control device |
| WO2023139808A1 (en) * | 2022-01-19 | 2023-07-27 | 株式会社ジェイテクト | Motor control device |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005047376A (en) * | 2003-07-29 | 2005-02-24 | Hitachi Unisia Automotive Ltd | Steering control device |
| JP2006298300A (en) * | 2005-04-25 | 2006-11-02 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Electric power steering device |
| JP2007230259A (en) * | 2006-02-27 | 2007-09-13 | Toyota Motor Corp | Steering device of vehicle |
| JP2008149971A (en) * | 2006-12-20 | 2008-07-03 | Nsk Ltd | Electric power steering device |
| JP2009279994A (en) * | 2008-05-20 | 2009-12-03 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Device for suppressing vehicle body skidding |
| JP2010188825A (en) * | 2009-02-17 | 2010-09-02 | Denso Corp | Steering load estimating device and electric power steering device |
-
2011
- 2011-03-04 JP JP2011047415A patent/JP2012183881A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005047376A (en) * | 2003-07-29 | 2005-02-24 | Hitachi Unisia Automotive Ltd | Steering control device |
| JP2006298300A (en) * | 2005-04-25 | 2006-11-02 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Electric power steering device |
| JP2007230259A (en) * | 2006-02-27 | 2007-09-13 | Toyota Motor Corp | Steering device of vehicle |
| JP2008149971A (en) * | 2006-12-20 | 2008-07-03 | Nsk Ltd | Electric power steering device |
| JP2009279994A (en) * | 2008-05-20 | 2009-12-03 | Honda Motor Co Ltd | Device for suppressing vehicle body skidding |
| JP2010188825A (en) * | 2009-02-17 | 2010-09-02 | Denso Corp | Steering load estimating device and electric power steering device |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5983764B2 (en) * | 2012-12-07 | 2016-09-06 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Driving support device, operation detection device, and control device |
| JPWO2014087546A1 (en) * | 2012-12-07 | 2017-01-05 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Driving support device, operation detection device, and control device |
| JP2016532593A (en) * | 2013-10-08 | 2016-10-20 | ティーアールダブリュー・リミテッド | Electric power assisted steering system |
| JP2019104492A (en) * | 2013-10-08 | 2019-06-27 | ティーアールダブリュー・リミテッド | Electrical power assisted steering system |
| JP2018008550A (en) * | 2016-07-11 | 2018-01-18 | 株式会社デンソー | Steering control device |
| JP2018008549A (en) * | 2016-07-11 | 2018-01-18 | 株式会社デンソー | Steering control device |
| WO2023139808A1 (en) * | 2022-01-19 | 2023-07-27 | 株式会社ジェイテクト | Motor control device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5194716B2 (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP5575919B2 (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2012131471A (en) | Electric steering system | |
| JP2009269540A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2010162954A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2015020506A (en) | Steering device | |
| JP2017095076A (en) | Steering control device | |
| JP2012183881A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| CN111422244B (en) | Steering controller and steering control method | |
| JP2010274842A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2012171523A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2020069864A (en) | Steering control device | |
| JP2008006919A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2012166769A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2013159240A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP6446832B2 (en) | Steering device | |
| JP2013023002A (en) | Electric power steering system | |
| JP2017109581A (en) | Electric power steering apparatus | |
| JP5641189B2 (en) | Motor control device, electric power steering device, and motor impedance optimization method | |
| JP2017144845A (en) | Steering control device | |
| JP2012240440A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2013126822A (en) | Electric power steering apparatus | |
| JP2013189123A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2009184370A (en) | Electric power steering device | |
| JP2014051242A (en) | Electric power steering system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140218 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140307 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20141111 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20141202 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20150512 |