JP2011124293A - Plasma processing apparatus - Google Patents
Plasma processing apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2011124293A JP2011124293A JP2009279035A JP2009279035A JP2011124293A JP 2011124293 A JP2011124293 A JP 2011124293A JP 2009279035 A JP2009279035 A JP 2009279035A JP 2009279035 A JP2009279035 A JP 2009279035A JP 2011124293 A JP2011124293 A JP 2011124293A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- faraday shield
- bell jar
- plasma
- processing apparatus
- plasma processing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67005—Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67011—Apparatus for manufacture or treatment
- H01L21/67017—Apparatus for fluid treatment
- H01L21/67063—Apparatus for fluid treatment for etching
- H01L21/67069—Apparatus for fluid treatment for etching for drying etching
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01J—ELECTRIC DISCHARGE TUBES OR DISCHARGE LAMPS
- H01J37/00—Discharge tubes with provision for introducing objects or material to be exposed to the discharge, e.g. for the purpose of examination or processing thereof
- H01J37/32—Gas-filled discharge tubes
- H01J37/32009—Arrangements for generation of plasma specially adapted for examination or treatment of objects, e.g. plasma sources
- H01J37/32082—Radio frequency generated discharge
- H01J37/321—Radio frequency generated discharge the radio frequency energy being inductively coupled to the plasma
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Plasma Technology (AREA)
- Drying Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明はプラズマ処理装置に係り、特に、処理容器の外周に巻かれたコイル状のアンテナに高周波を供給して処理室内に形成したプラズマを用いて試料をエッチング等処理するプラズマ処理装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a plasma processing apparatus, and more particularly to a plasma processing apparatus that performs processing such as etching on a sample using plasma formed in a processing chamber by supplying a high frequency to a coiled antenna wound around the outer periphery of a processing container.
上記のようなエッチング装置では、一般的に、エッチング対象の半導体ウエハ等基板状の試料の表面に配置された膜を構成する材料や処理ガスの種類によって、これから形成される反応生成物が処理容器の内部に配置された処理室の内壁面に付着する。このような不着物が上記内壁面の表面に堆積した量が大きくなると壁面上から剥がれたり解離したりして試料の表面に再付着してこれを汚染する異物の原因となってしまうことが知られている。 In the etching apparatus as described above, in general, a reaction product formed from the material constituting the film disposed on the surface of the substrate-like sample such as a semiconductor wafer to be etched and the kind of the processing gas is processed in the processing container. It adheres to the inner wall surface of the processing chamber disposed inside the chamber. It is known that when the amount of such non-adhering material deposited on the surface of the inner wall becomes large, it will peel off or dissociate from the surface of the wall and re-adhere to the surface of the sample, causing foreign matter to contaminate it. It has been.
また、このような生成物の堆積は、例えばAl2O3をCl2でエッチングする場合やSiO2をCF等でエッチングする場合に処理の安定性を低下させてしまうことが知られている。そこで、従来より、処理室内壁面上への生成物の付着を低減する構成を備えた技術が知られていた。 In addition, it is known that the deposition of such a product lowers the stability of the process when, for example, Al 2 O 3 is etched with Cl 2 or SiO 2 is etched with CF or the like. Therefore, conventionally, there has been known a technique having a configuration for reducing the adhesion of a product on the wall surface of the processing chamber.
例えば、真空容器の外部で周囲を巻くように配置されたコイル状のアンテナとプラズマとの間にファラデーシールドを設置し、これに高周波電力を供給することで、真空容器内壁のデポジションを抑制、あるいは除去することができるものが知られている。このような従来技術の例としては、特開2000−323298号公報(特許文献1)に開示されたものが知られている。この特許文献1では、コイル状のアンテナに供給される高周波電力によって絶縁体製の処理容器の内側に誘導電界または磁場によるプラズマが形成されるが、このプラズマを構成する荷電粒子をファラデーシールドに供給された電力によって処理容器内壁面上に維持される所定の大きさの電位との電位差により引き込んで内壁面の生成物と衝突させてこれを取り除くものが開示されている。
For example, by setting a Faraday shield between the coiled antenna and the plasma arranged so as to wrap around the outside of the vacuum vessel and supplying high frequency power to this, the deposition of the inner wall of the vacuum vessel is suppressed, Or what can be removed is known. As an example of such a prior art, what was disclosed by Unexamined-Japanese-Patent No. 2000-323298 (patent document 1) is known. In
さらにまた、このようなファラデーシールドを構成する一つの手法として、処理容器の外壁面上に特定の金属の皮膜を配置してこれをファラデーシールドとして機能させるものが知られている。例えば、特開2004−235545号公報(特許文献2)には、絶縁体製の処理容器の外壁面上にタングステンの皮膜を溶射して形成する技術が開示されている。 Furthermore, as one method for constructing such a Faraday shield, there is known a method in which a specific metal film is disposed on the outer wall surface of a processing vessel and functions as a Faraday shield. For example, Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2004-235545 (Patent Document 2) discloses a technique of spraying a tungsten film on the outer wall surface of an insulating processing container.
上記の従来技術では、次のような点について考慮が不十分であったため問題が生じていた。 In the above-described prior art, problems have arisen because the following points are not sufficiently considered.
すなわち、特許文献2に開示のように、真空容器外面に皮膜を形成するものでは、皮膜のファラデーシールドと真空容器間の外壁面との間の隙間がなくなり、これによってファラデーシールドとプラズマ間の静電容量をできるだけ小さくすることができる。そして、このため従来のものに比べデポジションを抑制、又は除去する効果を向上させることができる一方で、形成されるファラデーシールドの面方向についての形状は、板状の部材により構成されていた従来のものと同様に、縦方向(上下方向)に延びるスリットを有する形状であるため、このスリット部の直下(スリットの内部の空間に対応する処理容器内側の内壁面には、ファラデーシードに供給される電力によって形成される静電界は働かない。
That is, as disclosed in
つまり、このスリット部には荷電粒子が真空容器内壁面に引き込まれないか、左右の非スリット部(板状または膜状の部材に外周側が覆われている内壁面)と比較して荷電粒子の引き込み量が大きく減少する、言い替えればイオンスパッタリングが小さくなる。このため、スリット部と非スリット部に対応する真空容器内壁面のそれぞれの表面での生成物の付着の量,堆積の量に大きな差が生じてしまい付着物を均一に除去することは困難となっていた。これは、試料の周方向(円筒あるいは円錐(台)形状を有する処理容器の周方向)について処理が負均一,不安定となることであり、上記ファラデーシールドの構成により均一な処理の実現を損なってしまうという問題が生じていた。 In other words, charged particles are not drawn into the inner wall surface of the vacuum vessel in this slit portion, or charged particles are compared to the left and right non-slit portions (inner wall surface covered with a plate-like or film-like member). The amount of entrainment is greatly reduced, in other words, ion sputtering is reduced. For this reason, there is a large difference in the amount of product adhesion and the amount of deposition on the inner surface of the vacuum vessel inner wall corresponding to the slit portion and the non-slit portion, and it is difficult to remove the deposit uniformly. It was. This is because the processing is negatively uniform and unstable in the circumferential direction of the sample (circumferential direction of a processing vessel having a cylindrical shape or a cone (trapezoid) shape), and the above-described Faraday shield configuration impairs the realization of uniform processing. There was a problem that it would end up.
本発明の目的は、より均一な処理を実現することができるプラズマ処理装置を提供することにある。また、本発明の目的は、異物の発生を抑制して歩留まりを向上させたプラズマ処理装置を提供することにある。 The objective of this invention is providing the plasma processing apparatus which can implement | achieve a more uniform process. Another object of the present invention is to provide a plasma processing apparatus that improves the yield by suppressing the generation of foreign matter.
上記課題は、真空容器内部の処理室に配置された試料台上に載せられたウエハをこの処理室内で形成をしたプラズマを用いて処理するプラズマ処理装置であって、前記真空容器の上部を構成し前記処理室を囲む誘電体性のベルジャと、このベルジャの外周に巻かれて配置され前記プラズマを形成するための高周波電力が供給されるコイル状のアンテナと、このアンテナと前記ベルジャとの間で内側と外側とで隙間をあけて二重に配置され各々が複数のスリットを有して所定の電位にされる導電体製のファラデーシールドとを備え、前記外側のファラデーシールドと前記内側ファラデーシールドとが各々のスリットが互い違いに覆う位置に配置されたプラズマ処理装置により達成される。 An object of the present invention is a plasma processing apparatus for processing a wafer placed on a sample stage disposed in a processing chamber inside a vacuum chamber using plasma formed in the processing chamber, and constituting an upper portion of the vacuum chamber. A dielectric bell jar surrounding the processing chamber, a coiled antenna wound around the bell jar and supplied with high-frequency power to form the plasma, and between the antenna and the bell jar And a Faraday shield made of a conductor which is arranged in a double manner with a gap between the inner side and the outer side, each having a plurality of slits and being set to a predetermined potential, and the outer Faraday shield and the inner Faraday shield. Is achieved by a plasma processing apparatus disposed at a position where each slit alternately covers.
さらに、前記ファラデーシールドが前記ベルジャの外周壁面上に配置された複数の膜層から構成されたことにより達成される。 Further, this is achieved by the Faraday shield being composed of a plurality of film layers disposed on the outer peripheral wall surface of the bell jar.
さらにまた、前記ファラデーシールドに高周波電力が供給されることにより達成される。 Furthermore, this is achieved by supplying high-frequency power to the Faraday shield.
さらにまた、前記外側のファラデーシールドの前記隣り合うスリット間の部材が前記内側のファラデーシールドのスリットの前記ウエハの周方向の隙間の全体を覆って配置されたことにより達成される。 Furthermore, this is achieved by arranging the member between the adjacent slits of the outer Faraday shield so as to cover the entire gap in the circumferential direction of the wafer of the slits of the inner Faraday shield.
さらにまた、前記内側および外側のファラデーシールドの間に絶縁体製の膜が配置されたことにより達成される。 Furthermore, this is achieved by disposing an insulating film between the inner and outer Faraday shields.
さらにまた、前記内側または外側のファラデーシールドが溶射により形成されたことにより達成される。 Furthermore, this is achieved by forming the inner or outer Faraday shield by thermal spraying.
以下、図面を用いて本発明に係るプラズマ処理装置の実施の形態を説明する。 Embodiments of a plasma processing apparatus according to the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings.
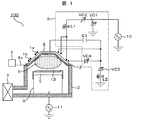
図1は、本発明の実施例に係るプラズマ処理装置の構成の概略を説明する図である。本実施例のプラズマ処理装置100では、真空処理室を囲んで構成する真空容器2を有する容器とこの容器外部に配置されて真空処理室内に供給される電界または磁界を供給する電波源または磁場源と容器内部を排気して減圧する排気手段とを備えている。
FIG. 1 is a diagram for explaining the outline of the configuration of a plasma processing apparatus according to an embodiment of the present invention. In the
容器は、円筒状の真空容器2とこの上方に配置されて真空容器2と連結されて内部の円筒形状の空間を閉塞する絶縁材料(例えば、石英,セラミック等の非導電性材料)製のベルジャ12を備えている。このベルジャ12は縦断面が台形状を有しており、横断面の円形中心を通る上下方向の中心軸周りに軸対象の形状を備えた円錐台形状を有している。これらの内部に配置された空間である真空処理室は、真空容器2とベルジャ12の内壁面により囲まれて構成され、これらの連結はプラズマ処理装置100の外部の大気圧の雰囲気に対して気密に内部を封止可能にされている。
The container is a bell jar made of a
容器の内部の空間である真空処理室内部には、ベルジャ12の頂部の平面部分の内壁面に対して平行となるように、基板状の試料13を載置するための載置台5を備えている。載置台5の上方の真空処理室内の空間は、後述のように所定の真空度まで減圧されてプラズマ6が形成されこれを用いて試料13が処理される領域となっている。また、載置台5はこれを含む円筒形状を有する試料保持部9の上部を構成している。試料保持部9の外周と真空容器2の円筒形の内壁との間の空間は、真空処理室を構成する空間であって、試料13上方で形成されたプラズマ6、供給された処理ガスや試料13の処理に伴って生成された生成物等の粒子を含むガスが下方に流れて排気される通路となっている。
The vacuum processing chamber, which is the space inside the container, includes a mounting table 5 on which a substrate-
ベルジャ12の傾斜面の外壁面外周には、コイル状のアンテナ1がその外壁に沿って複数回巻かれて配置されている。本実施例のアンテナ1は複数の高さの位置に分けられて上部アンテナ1a及び下部アンテナ1bが配置されている。さらに、ベルジャ12の上記傾斜面の外壁面の外側にはこれに沿って膜状のファラデーシールド8が傾斜面を覆うように配置されている。
On the outer peripheral surface of the inclined surface of the
本実施例のベルジャ12は、真空容器2上方に取り付けられて気密に連結された状態で、その下端が載置台5の上面の試料載置面より上方に位置し、円形の下端部が載せられた試料13の上方でこれを円周方向に囲むように配置されている。ベルジャ12の外周側でこれを覆って配置されるファラデーシールド8及びこの外側で巻かれて配置されるコイル状のアンテナ1は、載置台5または載せられた試料13の上方のプラズマ6が形成される真空処理室の外周側からこれを囲んで配置されている。
The
本実施例のファラデーシールド8は、ベルジャ12の傾斜面および頂部の平面部を含んでその外壁面を覆って配置されている。整合器(マッチングボックス)3を介して高周波電源(第1の高周波電源)10に直列に接続されており、試料13の処理中に全体が所定の電位を有し、誘電体として特定の電位を有するプラズマ6と静電容量的に結合する。前記上部アンテナ1a及び下部アンテナ1b及びファラデーシールド8は、また、ファラデーシールド8とアース間に並列にインピーダンスの大きさが可変可能な直列共振回路(可変コンデンサVC3及びリアクトルL2)が接続されている。
The Faraday shield 8 of the present embodiment is disposed so as to cover the outer wall surface including the inclined surface of the
直列共振回路を含む整合器3により、ファラデーシールド8の電位は所期のものとなるように調節される。特に、本実施例のファラデーシールド8の電位は、接地電位のみならず正負の任意の値に調節可能であり、この値は例えば真空処理室内のプラズマ中の荷電粒子をファラデーシールド8の方向に引き込んでベルジャ12の表面に衝突させるものに設定可能である。この荷電粒子の衝突により付着した生成物が物理的,化学的に真空処理室内の空間に再度遊離させられて付着物の低減が可能となる。
The potential of the Faraday shield 8 is adjusted so as to become the desired value by the matching unit 3 including the series resonance circuit. In particular, the potential of the Faraday shield 8 of this embodiment can be adjusted to an arbitrary positive or negative value as well as the ground potential. This value draws charged particles in the plasma in the vacuum processing chamber in the direction of the Faraday shield 8, for example. Can be set to collide with the surface of the
真空容器2と真空処理室内に供給される処理ガスのガス源4との間を連結するガス供給管4aが真空容器2の上端部に連結されている。このガス供給管4a内部を通流するガス源4からの処理ガスが真空処理室に面した開口部から内部に供給される。また、真空処理室内のガスは真空容器2下方でこれと連結されて配置された排気装置7の動作によってこれに連通した真空処理室下部の開口から排気されて、真空処理室内部が所定の圧力に減圧される。
A
排気装置7はターボ分子ポンプ等本発明の技術分野で一般的に用いられる排気ポンプを備え、これと真空処理室内部とを連通する開口は真空容器2下部の載置台5の中心軸から設計上定められた水平方向の距離だけ離されて設置されている。この開口と排気ポンプの入口との間を連通する通路上には水平方向に配置された軸周りに回転して通路の開放された面積を増減する複数の排気バルブが配置され、これらを回転させて通路の流路の面積を調節し排気量速度を調節することにより圧力の調節が行われる。
The exhaust device 7 includes an exhaust pump that is generally used in the technical field of the present invention, such as a turbo molecular pump. The opening that communicates this with the inside of the vacuum processing chamber is designed from the central axis of the mounting table 5 below the
ガス供給管4aを介して真空処理室内に供給された処理ガスを前記上部アンテナ1a及び下部アンテナ1bに供給された電力によって発生する電界または磁界の作用によってプラズマ化する。載置台5内部に配置された電極には基板バイアス電源(第2の高周波電源)11が接続されており、この基板バイアス電源11から電極に供給された電力によって載置台5およびこれに載せられた試料13上方にバイアス電位が形成される。このバイアス電位とプラズマ6の電位との電位差に応じてプラズマ6中に存在するイオン等荷電粒子を試料13上に引き込んで所望の試料13の処理を高速に実施することができる。
The processing gas supplied into the vacuum processing chamber through the
なお、高周波電源10から供給される電力は、周波数として例えば13.56MHzや更に周波数が高いVHF帯等の高周波の電力を用いる。このような高周波の電力をアンテナ1あるいはファラデーシールド8に供給することにより、真空処理室内にプラズマ6を生成するための誘導電界または磁界を形成する。このとき、整合器(マッチングボックス)3を用いて、アンテナ1のインピーダンスを高周波電源10の出力インピーダンスに一致させて、電力の反射を抑えるように調節することができる。本実施例では、整合器3として、例えば図に示すように可変容量コンデンサVC1,VC2を逆L字型に接続したものを使用する。
Note that the power supplied from the high-
このような実施例では、真空容器2の外側側壁に連結されその内部が減圧された容器内の搬送室を(図示しない真空用ロボットアームに保持されて)搬送されて来た半導体ウエハ等の試料13が真空処理室内の載置台5上で複数のピン上に受け渡された後載置台5の円形の上面に載せられて吸着され保持される。試料13裏面と載置台5との間に熱伝達ガスが供給された状態で、試料13上方の真空処理室内に供給された処理ガスの粒子がアンテナ1から供給された誘導電界または磁界により解離されて、誘導結合によるプラズマ、所謂誘導型のプラズマ6が形成されるとともに、載置台5内の電極に供給された電力によって試料13上方に基板バイアスを形成してその処理が実施される。
In such an embodiment, a sample such as a semiconductor wafer that has been transported (held by a vacuum robot arm (not shown)) in a transport chamber in a container connected to the outer side wall of the
処理が開始されて試料13の所定の処理が終了したことが検出された後、吸着を解除して前記の搬入の手順を逆に試料13が搬出される。
After the processing is started and it is detected that the predetermined processing of the
本実施例では、プラズマ6を生成する上でファラデーシールド8は重要な効果を発揮する。ファラデーシールド8がない場合、アンテナ1供給された高周波の電力によって電圧が印加されたアンテナ1のコイルの各部は任意に定まる電位を有し、このためアンテナ1のコイルおよび真空処理室内で電位を有するプラズマ6との間での静電的結合が生じて、これによって傾斜面部の外周に巻かれたアンテナ1の近傍のベルジャ12内壁面が局所的にプラズマ6からの荷電粒子の衝突により削られることになって真空処理室の内壁面が不均一に消耗する。
In the present embodiment, the Faraday shield 8 exhibits an important effect in generating the
さらには、このような壁面の状態の変化によって、アンテナ1とベルジャ12内プラズマ6との結合状態が変化し、試料13表面でのエッチングの特性、例えば速度やその均一性、処理の垂直性等が変動するという悪影響を受けてしまう。このような問題を低減するためにプラズマ6とファラデーシールド8が設置され、ベルジャ12の内壁面とプラズマとの間の電位差を低減するようにファラデーシールド8に所定の電位を与える。さらには、本発明のように、ファラデーシールド8に供給してこれに形成する電位を、プラズマ6からの荷電粒子の衝突によってベルジャ12内壁面に付着して堆積する付着物が取り除かれるように調節することで、ベルジャ12内壁面の消耗を抑えつつ処理の均一性や経時の変化を抑制して歩留まりを向上することができる。
Furthermore, the coupling state between the
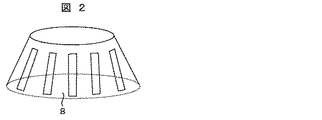
図2は、従来技術によるファラデーシールドの構成について模式的に示す斜視図である。この図において、図上上方がベルジャ12の上方であり、金属等導電体製のファラデーシールド8はベルジャ12の上面および傾斜面を覆うように所定の隙間を介してこれに被せられる。そして、ファラデーシールド8の傾斜面を覆う部分には、このファラデーシールド8の外周側で絶縁されて配置されているアンテナ1のコイルの巻き方向を横切るように上下方向に延びる複数のスリットが円形の上面の中心の軸周りに放射状に配置されている。これらのスリットはアンテナ1により形成される電界または磁界を全て遮蔽するのではなくプラズマ6の点火を用意にするために一部を真空処理室内部に導入する目的で配置されている。
FIG. 2 is a perspective view schematically showing the configuration of the Faraday shield according to the prior art. In this figure, the upper side of the figure is the upper side of the
このような従来技術に係るファラデーシールド8を用いた処理装置では、以下に示すように、スリット部直下のベルジャ12内壁面とファラデーシールド8のスリット間の部材との間で付着物の量に差異が大きく生じてしまう。つまり、スリットの直内側のベルジャ12内壁面上では付着物の量が大きく、スリット間の直内側では量が少なくなって、真空処理室内壁面上の付着物の量が試料13または真空処理室の円筒形状の周方向について不均一となってしまい、ひいては試料13の処理が周方向に不均一となってしまう。
In such a processing apparatus using the Faraday shield 8 according to the prior art, the amount of deposits differs between the inner wall surface of the
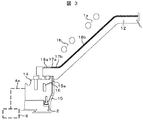
図3は、図1に示す実施例の主要部を拡大したものを示す縦断面図である。本図に示すように、ベルジャ12は絶縁材料(例えば、石英,酸化アルミニウムといったセラミック等の非導電性材料)製で縦断面が台形の形状をしており、ベルジャ12傾斜部の外周に巻かれるように前記アンテナ1(上部アンテナ1a,下部アンテナ1b)が配置されている。これら上部アンテナ1a及び下部1bとベルジャ1bの外周壁面との間にファラデーシールド8が位置している。
FIG. 3 is a longitudinal sectional view showing an enlarged main part of the embodiment shown in FIG. As shown in the figure, the
ガスリング14は、ベルジャ12の円形状の下端の下方に配置されたリング状の部材であって、真空処理室の外周側を囲んで配置される。このガスリング14は、上記供給される処理ガスが真空処理室内に導入される少なくとも1つの開口が真空処理室に面した箇所に配置された部材である。ガスリング14の内部には、ガス供給管4aから供給された処理ガス(例えばCl2,BCl3,C4F8,C5F8,CO,CF4等の弗化炭素)が通流する図示しないガス通路が配置されている。このガス通路と通った処理ガスは、ガスリング14の真空処理室内側に面した設置されているガス吹き出し口16から真空処理室内に流出する。
The
本実施例では、ガスリング14の真空処理室に面した内壁面の内側には、隙間を介してこれを覆うリング状の防着板15が配置され、ガスリング14特にガス吹き出し口16の表面に生成物等付着物が堆積することを抑制している。ガス吹き出し口16から真空処理室内に導入された処理ガスは、防着板15上に形成されている吹き出し開口15aを通過して試料13上方の空間に流入,拡散する。なお、防着板15はその上端部が本実施例はベルジャ12の下端でその下面とガスリング14上端面との間に挟まれて配置されているが、上端部をベルジャ12の下端部の内壁面を覆うように延在させて配置されていても良い。
In the present embodiment, a ring-shaped
本実施例では、ファラデーシールド8はベルジャ12外周壁面を覆う導電性薄膜17により構成されている。特に、図3に示すように複数の膜層から構成されており、下方の膜である導電性薄膜17a及び上方の膜である導電性薄膜17b(例えばW)とこれらの層間およびベルジャ12との間を絶縁する例えばAl2O3製の絶縁材層18が配置されている。絶縁材層18も複数の導電性薄膜17a,17bを絶縁するために複数の層から構成されており下方の絶縁材層18a及び上方の絶縁材層18bが導電性薄膜17a,17bと交互に積層されて配置されている。
In this embodiment, the Faraday shield 8 is composed of a conductive thin film 17 covering the outer peripheral wall surface of the
これらの膜層は、ベルジャ12の外側表面上に特定の製膜の方法によって形成される。特に、本実施例では溶射によって配置されている。ファラデーシールド8および絶縁材層18を溶射によって薄膜として形成したことにより、その厚さを周方向および上下の方向について精度良く構成することができる。このため、ファラデーシールド8とプラズマ6間の距離を精度良く管理することができ、ベルジャ12内壁面の付着物の量の均一性が向上して、ベルジャ12内壁面に対するデポジション除去が均一化される。
These film layers are formed on the outer surface of the
さらには、ファラデーシールド8が所定の距離を開けて配置された複数の膜層として構成されたことにより、ファラデーシールド8にかかる電圧(Faraday Shield Voltage;FSV)を低い電圧でデポを除去することが可能となる。これにより、スリットを有したファラデーシールド8によるベルジャ内壁面の消耗を緩和することができる。なお、ファラデーシールドのベルジャ内壁面クリーニング原理とFSVを最適化する方法については、前記特許文献4に詳細が記載されている。
Furthermore, since the Faraday shield 8 is configured as a plurality of film layers arranged at a predetermined distance, the depot can be removed with a low voltage (Faraday Shield Voltage; FSV) applied to the Faraday shield 8. It becomes possible. Thereby, the consumption of the inner wall surface of the bell jar by the Faraday shield 8 having the slit can be reduced. Details of the Faraday shield bell jar inner wall cleaning principle and the method of optimizing the FSV are described in detail in the
図4は、図1に示す実施例に係るファラデーシールドおよび真空容器の構成の概略を模式的に示す断面図である。本図のように、本実施例ではファラデーシールド8を構成する複数層の導電性薄膜17a,17bは絶縁材層18a,18bを挟んで交互に配置されてファラデーシールド8のスリット部を3次元的に構成されている。
FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view schematically showing an outline of the configuration of the Faraday shield and the vacuum vessel according to the embodiment shown in FIG. As shown in this figure, in this embodiment, the plurality of layers of conductive
すなわち、ベルジャ12外周表面から上方(外側)に順にタングステン製の導電性薄膜17a,アルミナ製の薄膜である絶縁材層18a,同様にタングステン製の導電性薄膜17b,アルミナ製の絶縁材層18bが設置されている。上方の導電性薄膜17bおよび下方の導電性薄膜17aは、それぞれベルジャ12の傾斜面部および頭頂部の全体を覆って配置されていると共に、アンテナ1が巻かれた方向(本実施例では左右方向)を横切るような方向に、つまり上下方向に延在する複数のスリット部を有している。
That is, the conductive
これらのスリット部は、ファラデーシールド8にアンテナ1またはプラズマ6の誘導電界または磁界によって生起される逆起電流が上記電界または磁界の形成を妨げる方向に流れることを抑制するために配置され、上記電界または磁界の及ぶ範囲でできるだけ広い範囲で多くの箇所に配置されている。つまり、図2の構成を備えている。
These slit portions are arranged to suppress a back electromotive force generated in the Faraday shield 8 by the induction electric field or magnetic field of the
また、上方の導電性薄膜17bのスリット間の膜部は下方の導電性薄膜17aをスリット部の外側(上方)を覆うように配置されている。つまり、導電性薄膜17a,17bは上下で各スリット部が一方のスリット部を他方のスリット間の部材が覆い合う構成を備えている。言い替えれば、多重に配置されたファラデーシールド8の導電性薄膜17a,17bはその複数のスリット部またはスリット間の部材の部分が互い違いとなるように配置されている。
The film portion between the slits of the upper conductive
導電性薄膜17a及び17bのスリット間の膜部の左右方向の端部の相対位置は、図4に示すように、外側の方向(上記放射状の方向)について見た場合に隙間が空いても良いし、端部から内側に入り込んで膜部が重なってオーバーラップされていてもよい。本実施例では、スリット間の膜部同士の端点が直線上の位置に重なっているか、作用・効果が著しく損なわれない程度に重ねられている。
As shown in FIG. 4, the relative positions of the end portions in the left-right direction of the film portion between the slits of the conductive
一方、本図に示すαのように上下の導電性薄膜17a,17bのスリット間の膜部の端点同士に隙間が大きく空いてしまうと、この隙間部分αの直内側のベルジャ12内壁面上にはその周囲と比べて大きく生成物が堆積されることになる。また、βのようにタングステン薄膜を大きくオーバーラップした場合、オーバーラップした領域が大きいほど、導電性薄膜17a,17bの間で浮遊容量を介し周回電流が発生しやすくなる。この際、アンテナ1から発生される誘導磁場が周回電流によって打ち消され形成されるプラズマ6の密度や分布を所期のものにすることが困難となる場合があることから、仕様を実現するためにオーバーラップの量を適切なものとすることが望ましい。
On the other hand, when a large gap is formed between the end points of the film portions between the slits of the upper and lower conductive
本実施例のファラデーシールド8の膜層構造を実現する各膜の厚さは、導電性薄膜17a,17bは各々100μm、絶縁材層18a,18bは各々150μmとなるように形成される。本発明において、これらの厚さの値は、本実施例の値に限られるものではなく、導電性薄膜17a,17b全体に周回電流が発生しない適切な膜厚に設定される。さらには、これらのスリットの幅,スリット間膜部の幅についても、供給される電力の大きさ,周波数,ベルジャ12の材料,厚さ等仕様に応じて適切に選択される。
The thickness of each film that realizes the film layer structure of the Faraday shield 8 of this embodiment is formed such that the conductive
また、本実施例では、下方の膜層とともに絶縁材層18bがベルジャ12の頭頂部および傾斜面部の全体を覆って配置されベルジャ12を被覆し、導電体性薄膜17a及び17bはその外側の外気に露出がなくなっている。このため、ベルジャ12をプラズマ処理装置100本体から取り外してこれを洗浄する際に、導電性薄膜17a,17bが大気や洗浄用の材料に触れて腐食することが低減され、取り扱いも容易となり洗浄の効率が向上する。
Further, in this embodiment, the insulating
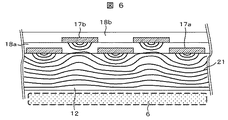
次に、本実施例の静電界または磁界の作用について、図5、および図6を用いて説明する。図5は、従来技術に係るファラデーシールドを用いたプラズマ処理装置における処理容器及びその内部の静電界または磁界の分布を模式的に示す図である。図6は、図1に示す実施例における処理容器及びその内部の静電界または磁界の分布を模式的に示す図である。これらの図において太実線で示される等高線は、ファラデーシールド8または導電性薄膜17a,17bから供給される静電界または磁界の等強度を結ぶものであり、この等高線がより平坦であるほど、プラズマ6中の荷電粒子を引き込む作用の大きさがより平坦となる、つまり、荷電粒子のベルジャ12の内壁面への衝突の程度がより均一となることになる。
Next, the action of the electrostatic field or magnetic field of this embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 5 is a view schematically showing a processing container and a distribution of an electrostatic field or a magnetic field therein in a plasma processing apparatus using a Faraday shield according to the prior art. FIG. 6 is a diagram schematically showing the distribution of the processing container and the electrostatic or magnetic field therein in the embodiment shown in FIG. In these drawings, the contour lines indicated by thick solid lines connect the equal strengths of the electrostatic field or magnetic field supplied from the Faraday shield 8 or the conductive
従来技術に係る図5に示すファラデーシールド8の構成では、供給される電力によってこれから発生する静電界20は、前記の通り、スリット部において静電界20の強度が低下する箇所が生じてしまいその等高線に不均一な箇所が生じるため、プラズマ6に対してベルジャ12の内壁面上において不均一な状態で静電界20が到達する。このため、ベルジャ内壁面上に到達するイオンの密度,量ひいては付着量が面上での周方向について不均一さが著しかった。
In the configuration of the Faraday shield 8 shown in FIG. 5 according to the prior art, the
一方、本実施例においては、図6に示すように、ファラデーシールド8を構成する多重層の導電性薄膜17a,17bの各スリットは絶縁材層18aを挟んで互い違いに配置されている。この構成において、絶縁材層18aの下方の膜である導電性薄膜17aのスリット部およびその上部には上方の導電性薄膜17bのスリット間の膜部から静電界または磁界が供給されることになり、この電界または磁界によって上記スリット部(下方の導電性薄膜17aの膜部端部同士の間)での導電性薄膜17aの静電界または磁界の強度は増加され、導電性薄膜17bから発生する静電界または磁界21と結合を起こし、下方の導電性薄膜17aのスリット部での静電界または磁界21の低下が抑制されてベルジャ12の内側壁面に到達した静電界または磁界21がより平坦な状態でプラズマ6と面することができる。そのため、従来の技術に比べて均一性よくデポを除去することが可能となる。
On the other hand, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 6, the slits of the multi-layered conductive
一方、上下の導電性薄膜17a,17bのスリット同士が相互に膜部で覆われることになるが、アンテナ1からの誘導電場または磁場は上下方向に積層された導電性薄膜17a,17bの間に配置された絶縁材層18a,18bを通り、導電性薄膜17aのスリット部からベルジャ12を介して、真空処理室内部に電界,磁界を形成することができる。このため、プラズマ6を着火して維持するに要する電界,磁界は、従来技術と比らべて本実施例の構成のファラデーシールド8は著しく損なわれることが抑制されている。
On the other hand, the slits of the upper and lower conductive
以上の通り、本実施例によれば、ファラデーシールド8に外周壁面が覆われた真空処理室の内側壁面の付着物の量あるいは消耗の量が試料13または真空処理室の周方向について均等化され、信頼性と寿命を向上させたプラズマ処理装置が実現できる。また、周方向についての試料の処理が均等化され、あるいは異物の発生が抑制され異物の分布が均等化されて、処理の効率,歩留まりが向上される。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the amount of deposits or the amount of wear on the inner wall surface of the vacuum processing chamber whose outer wall surface is covered with the Faraday shield 8 is equalized in the circumferential direction of the
上記の本発明の構成は、本実施例に限定されるものではなく、付着および処理の均等化、あるいは信頼性と効率の向上の作用・効果を損なわない範囲で要求される仕様に応じて適切なものを選択できる。例えば、本実施例では高周波電力をファラデーシールド8に供給しバイアス電位をベルジャ12の内壁面上に形成して荷電粒子を引き込んでいるが、従来技術のように接地電位としてもよく、付着物を適切に付着させて均等な量に維持させる電位となるように供給電力を調節しても良い。
The above-described configuration of the present invention is not limited to this embodiment, and is appropriate according to specifications required within a range that does not impair the operation and effect of equalization of adhesion and treatment, or improvement of reliability and efficiency. You can choose anything. For example, in the present embodiment, high-frequency power is supplied to the Faraday shield 8 and a bias potential is formed on the inner wall surface of the
1 アンテナ
2 真空容器
3 整合器
4 ガス源
5 載置台
6 プラズマ
7 排気装置
8 ファラデーシールド
9 試料保持部
10 高周波電源
11 基板バイアス電源
12 ベルジャ
13 試料
14 ガスリング
15 防着板
16 ガス吹き出し口
17 導電性薄膜
18 絶縁材層
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (7)
前記真空容器の上部を構成し前記処理室を囲む絶縁体製のベルジャと、このベルジャの外周に巻かれて配置され前記プラズマを形成するための高周波電力が供給されるコイル状のアンテナと、このアンテナと前記ベルジャとの間で内側と外側とで隙間をあけて二重に配置され各々が複数のスリットを有して所定の電位にされる導電体製のファラデーシールドとを備え、
前記外側のファラデーシールドと前記内側ファラデーシールドとが各々のスリットが互い違いに覆う位置に配置されたプラズマ処理装置。 A plasma processing apparatus for processing a wafer placed on a sample stage disposed in a processing chamber inside a vacuum vessel using plasma formed in the processing chamber,
An insulator bell jar that forms an upper part of the vacuum vessel and surrounds the processing chamber; a coiled antenna that is wound around the bell jar and supplied with high-frequency power to form the plasma; and A Faraday shield made of a conductor that is arranged in a double manner with a gap between the antenna and the bell jar between the inside and the outside and each of which has a plurality of slits and has a predetermined potential,
The plasma processing apparatus, wherein the outer Faraday shield and the inner Faraday shield are arranged at positions where respective slits alternately cover.
前記ファラデーシールドが隙間をあけて二重に配置され各々が複数のスリットを有した内側及び外側ファラデーシールドを有し、これら内側及び外側ファラデーシールドの前記複数のスリット間の部材が他方のスリットを互いに覆い合う位置に配置されたプラズマ処理装置。 A sample stage disposed in a processing chamber disposed inside a processing container whose inside is depressurized and on which a circular wafer is placed, and an upper part of the processing container are formed above the sample stage, and an outer periphery of the sample stage is formed. A surrounding insulator bell jar, a coiled antenna wound around the sample stage outside the outer wall surface of the bell jar, a power source for supplying high frequency power to the antenna, and between the bell jar and the antenna A membrane-like Faraday shield disposed at a predetermined potential, and an exhaust means coupled to the lower part of the processing vessel and disposed in communication with the processing chamber,
The Faraday shield is doubled with a gap and each has inner and outer Faraday shields having a plurality of slits, and a member between the plurality of slits of the inner and outer Faraday shields connects the other slit to each other. A plasma processing apparatus disposed in a covering position.
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009279035A JP2011124293A (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2009-12-09 | Plasma processing apparatus |
| KR1020100013164A KR101142411B1 (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2010-02-12 | Plasma processing apparatus |
| US12/712,795 US20110132540A1 (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2010-02-25 | Plasma processing apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009279035A JP2011124293A (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2009-12-09 | Plasma processing apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011124293A true JP2011124293A (en) | 2011-06-23 |
| JP2011124293A5 JP2011124293A5 (en) | 2013-07-25 |
Family
ID=44080850
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009279035A Pending JP2011124293A (en) | 2009-12-09 | 2009-12-09 | Plasma processing apparatus |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20110132540A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2011124293A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR101142411B1 (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013080643A (en) * | 2011-10-05 | 2013-05-02 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Plasma processing device |
| KR20140145621A (en) * | 2012-04-19 | 2014-12-23 | 로트 운트 라우 악치엔게젤샤프트 | Microwave plasma generating device and method for operating same |
| JP2019179749A (en) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | 株式会社ダイヘン | Plasma generator |
| JP2019179750A (en) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | 株式会社ダイヘン | Plasma generator |
| JP2022523969A (en) * | 2019-03-05 | 2022-04-27 | エーイーエス グローバル ホールディングス, プライベート リミテッド | Single-turn and laminated wall inductively coupled plasma sources |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5711953B2 (en) * | 2010-12-13 | 2015-05-07 | 株式会社日立ハイテクノロジーズ | Plasma processing equipment |
| WO2013099372A1 (en) * | 2011-12-27 | 2013-07-04 | キヤノンアネルバ株式会社 | Discharge vessel and plasma treatment device |
| JP6620078B2 (en) * | 2016-09-05 | 2019-12-11 | 株式会社日立ハイテクノロジーズ | Plasma processing equipment |
| JP7139181B2 (en) * | 2018-07-26 | 2022-09-20 | ワイエイシイテクノロジーズ株式会社 | Plasma processing equipment |
| KR102540773B1 (en) * | 2021-01-19 | 2023-06-12 | 피에스케이 주식회사 | Faraday shield and apparatus for treating substrate |
| CN114864367A (en) * | 2022-03-25 | 2022-08-05 | 上海谙邦半导体设备有限公司 | Medium tube with shielding effect and plasma reaction cavity |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0888220A (en) * | 1994-06-23 | 1996-04-02 | Applied Materials Inc | Inductive coupling type high density plasma reactor for plasma promotion material processing |
| JP2001085195A (en) * | 1999-09-13 | 2001-03-30 | Hitachi Ltd | High frequency discharge device and plasma treatment method |
| JP2007158373A (en) * | 2007-02-13 | 2007-06-21 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Apparatus for plasma processing |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6063233A (en) * | 1991-06-27 | 2000-05-16 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Thermal control apparatus for inductively coupled RF plasma reactor having an overhead solenoidal antenna |
| US6024826A (en) * | 1996-05-13 | 2000-02-15 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Plasma reactor with heated source of a polymer-hardening precursor material |
| US5650032A (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 1997-07-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Apparatus for producing an inductive plasma for plasma processes |
| US6132551A (en) * | 1997-09-20 | 2000-10-17 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Inductive RF plasma reactor with overhead coil and conductive laminated RF window beneath the overhead coil |
| US6149760A (en) * | 1997-10-20 | 2000-11-21 | Tokyo Electron Yamanashi Limited | Plasma processing apparatus |
| US6280563B1 (en) * | 1997-12-31 | 2001-08-28 | Lam Research Corporation | Plasma device including a powered non-magnetic metal member between a plasma AC excitation source and the plasma |
| US6388382B1 (en) * | 1999-03-09 | 2002-05-14 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Plasma processing apparatus and method |
| US6447636B1 (en) * | 2000-02-16 | 2002-09-10 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Plasma reactor with dynamic RF inductive and capacitive coupling control |
| US6685799B2 (en) * | 2001-03-14 | 2004-02-03 | Applied Materials Inc. | Variable efficiency faraday shield |
| KR100452920B1 (en) | 2002-07-19 | 2004-10-14 | 한국디엔에스 주식회사 | Inductive coupled plasma etching apparatus |
| WO2004012221A2 (en) | 2002-07-31 | 2004-02-05 | Lam Research Corporation | Method for adjusting voltage on a powered faraday shield |
| KR20040077019A (en) * | 2003-02-27 | 2004-09-04 | 가부시키가이샤 히다치 하이테크놀로지즈 | Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method |
| US20070170867A1 (en) * | 2006-01-24 | 2007-07-26 | Varian Semiconductor Equipment Associates, Inc. | Plasma Immersion Ion Source With Low Effective Antenna Voltage |
| KR100783071B1 (en) | 2006-12-22 | 2007-12-07 | 세메스 주식회사 | Faraday shield unit and substrate processing apparatus having the same |
-
2009
- 2009-12-09 JP JP2009279035A patent/JP2011124293A/en active Pending
-
2010
- 2010-02-12 KR KR1020100013164A patent/KR101142411B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2010-02-25 US US12/712,795 patent/US20110132540A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0888220A (en) * | 1994-06-23 | 1996-04-02 | Applied Materials Inc | Inductive coupling type high density plasma reactor for plasma promotion material processing |
| JP2001085195A (en) * | 1999-09-13 | 2001-03-30 | Hitachi Ltd | High frequency discharge device and plasma treatment method |
| JP2007158373A (en) * | 2007-02-13 | 2007-06-21 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Apparatus for plasma processing |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013080643A (en) * | 2011-10-05 | 2013-05-02 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Plasma processing device |
| KR20140145621A (en) * | 2012-04-19 | 2014-12-23 | 로트 운트 라우 악치엔게젤샤프트 | Microwave plasma generating device and method for operating same |
| JP2015520478A (en) * | 2012-04-19 | 2015-07-16 | ロス・ウント・ラウ・アーゲー | Microwave plasma generator and method of operating the same |
| KR101880702B1 (en) * | 2012-04-19 | 2018-07-20 | 마이어 버거 (저머니) 게엠베하 | Microwave plasma generating device and method for operating same |
| JP2019179749A (en) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | 株式会社ダイヘン | Plasma generator |
| JP2019179750A (en) * | 2018-03-30 | 2019-10-17 | 株式会社ダイヘン | Plasma generator |
| JP7042143B2 (en) | 2018-03-30 | 2022-03-25 | 株式会社ダイヘン | Plasma generator |
| JP7042142B2 (en) | 2018-03-30 | 2022-03-25 | 株式会社ダイヘン | Plasma generator |
| JP2022523969A (en) * | 2019-03-05 | 2022-04-27 | エーイーエス グローバル ホールディングス, プライベート リミテッド | Single-turn and laminated wall inductively coupled plasma sources |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101142411B1 (en) | 2012-05-07 |
| US20110132540A1 (en) | 2011-06-09 |
| KR20110065252A (en) | 2011-06-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2011124293A (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP7527928B2 (en) | Substrate processing apparatus and substrate processing method | |
| JP7364288B2 (en) | Inductively coupled plasma processing system | |
| KR101456810B1 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP5606821B2 (en) | Plasma processing equipment | |
| TW201814407A (en) | Chamber with flow-through source | |
| TWI576889B (en) | Plasma processing device | |
| KR20170022902A (en) | Application of powered electrostatic faraday shield to recondition dielectric window in icp plasmas | |
| JP5970268B2 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus and processing method | |
| JP2011175977A (en) | Plasma treatment device and coupling window construction for producing uniform process rates | |
| JP2008251764A (en) | Plasma treatment equipment | |
| KR102106382B1 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP2012222295A (en) | Method for cleaning plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method | |
| WO2012033191A1 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP2016506592A (en) | Capacitively coupled plasma device with uniform plasma density | |
| US20160118284A1 (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| US20150200078A1 (en) | Plasma etching apparatus | |
| JP3276514B2 (en) | Plasma processing equipment | |
| JP5701050B2 (en) | Plasma processing equipment | |
| JP2004342984A (en) | Substrate holding mechanism and plasma processor | |
| JP2016143616A (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| KR102229990B1 (en) | Member for plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing apparatus | |
| JPWO2010092758A1 (en) | Thin film forming apparatus and thin film forming method | |
| CN110770880B (en) | Plasma processing apparatus | |
| JP2014072508A (en) | Plasma processing apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20121107 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20121107 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130612 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130717 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130723 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20131210 |