JP2011068614A - Vitamin preparation - Google Patents
Vitamin preparation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2011068614A JP2011068614A JP2009222165A JP2009222165A JP2011068614A JP 2011068614 A JP2011068614 A JP 2011068614A JP 2009222165 A JP2009222165 A JP 2009222165A JP 2009222165 A JP2009222165 A JP 2009222165A JP 2011068614 A JP2011068614 A JP 2011068614A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vitamin
- ascorbic acid
- glucoside
- mass
- powder
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Abstract
Description
本発明は、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸類(ビタミンC類)とを含む製剤及びその製造方法、並びに製剤成分の安定化方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a preparation containing fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acids (vitamin Cs), a method for producing the same, and a method for stabilizing the preparation components.
ビタミンB1類であるフルスルチアミン塩酸塩はその優れた吸収性により、生物学的利用能の高いビタミンB1類として、数多くの医薬品、医薬部外品に配合されている。一方、ビタミンC類に属するアスコルビン酸類はビタミン補給効果、抗酸化効果、抗疲労回復効果、しみ・そばかす緩和効果などを有するビタミン類であり、アスコルビン酸類もまた数多くの医薬品、医薬部外品に配合されている。しかし、ビタミンB1類とビタミンC類は配合性が悪いことが知られており、その製剤においては、薬物の分解、製剤の変色を引き起こしやすく、その製剤化には工夫が必要である。 Due to its excellent absorbability, fursultiamine hydrochloride, which is a vitamin B1, is blended in many pharmaceuticals and quasi drugs as vitamin B1 having a high bioavailability. On the other hand, ascorbic acids belonging to vitamin C are vitamins that have vitamin supplementation effect, antioxidant effect, anti-fatigue recovery effect, stain / freckle mitigation effect, etc. Ascorbic acids are also included in many pharmaceuticals and quasi drugs Has been. However, it is known that vitamins B1 and vitamins C have poor compounding properties. In the preparation, the drug tends to cause decomposition of the drug and discoloration of the preparation.
例えば、特開昭61−257923号公報(特許文献1)には、ビタミンB1塩もしくはビタミンB1誘導体とシクロデキストリンとを含有する顆粒とビタミンCとを含有する固形状医薬組成物が開示され、ビタミンB1及びビタミンCを安定化でき着色変化も減少できることが記載されている。この特許文献1には、ビタミンCの量がビタミンB1の約1〜50倍量であり、ビタミンB1は全量に対して約0.1〜50重量%であることが記載され、実施例では、スルフルチアミン5mg及びL−アスコルビン酸(ビタミンC)100mgを含む錠剤(全量500mg)などの処方が記載されている。 For example, JP-A-61-257923 (Patent Document 1) discloses a solid pharmaceutical composition containing granules containing vitamin B1 salt or vitamin B1 derivative and cyclodextrin and vitamin C, and vitamins. It is described that B1 and vitamin C can be stabilized and the color change can be reduced. Patent Document 1 describes that the amount of vitamin C is about 1 to 50 times the amount of vitamin B1, and that vitamin B1 is about 0.1 to 50% by weight based on the total amount. Formulations such as tablets (total amount 500 mg) containing 5 mg of sulfurtiamine and 100 mg of L-ascorbic acid (vitamin C) are described.
特開2001−10955号公報(特許文献2)には、アスコルビン酸、ビタミンB1及びビオチンから選択された少なくとも一種とスクラロースとを含む内服液剤組成物が開示されている。 Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 2001-10955 (Patent Document 2) discloses an internal liquid composition containing at least one selected from ascorbic acid, vitamin B1 and biotin and sucralose.
近年、アスコルビン酸類として、アスコルビン酸2−グルコシド(AA2G)が開発された。アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドはアスコルビン酸の不安定要因である2位の水酸基がグルコースで修飾された分子構造を有しているため、安定性が極めて高いことが知られている。また、アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドは小腸、腎臓など生体内の各組織に存在するα−グルコシダーゼにより加水分解されてアスコルビン酸を遊離し、生体内でビタミンCとしての生理作用を発揮することも明らかとなっている(三皷仁志, 新規指定添加物L-アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの特性と用途, FFIジャーナル, 211, 435-444(2006))。 In recent years, ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G) has been developed as an ascorbic acid. Since ascorbic acid 2-glucoside has a molecular structure in which the hydroxyl group at the 2-position, which is an unstable factor of ascorbic acid, is modified with glucose, it is known to have extremely high stability. It is also clear that ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is hydrolyzed by α-glucosidase present in each tissue in the living body such as the small intestine and kidney to release ascorbic acid and exerts physiological action as vitamin C in vivo. (Hitoshi Mitsumata, Characteristics and Uses of Newly Specified Additive L-Ascorbic Acid 2-Glucoside, FFI Journal, 211, 435-444 (2006)).
アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの利用方法として、特開2007−63177号公報(特許文献3)には、ヒアルロン酸とL−アスコルビン酸に換算したときのL−アスコルビン酸類(L−アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドなど)との配合割合が、質量比で1:4乃至4:1である美肌用の経口摂取用組成物が開示され、この組成物は、さらに、コンドロイチン硫酸及び/又はグルコサミンを含有してもよいことも記載されている。また、経口摂取用組成物は、ビタミンB1、ビタミンB2などを含んでもよいことも記載され、実施例では、L−アスコルビン酸2−グルコシド50質量部及びチアミン0.01質量部を含む経口摂取用組成物(総量約980質量部)が記載されている。 As a method of using ascorbic acid 2-glucoside, JP-A-2007-63177 (Patent Document 3) describes L-ascorbic acids (L-ascorbic acid 2-glucoside, etc.) when converted into hyaluronic acid and L-ascorbic acid. ) And the composition for oral intake for skin beautification, wherein the composition ratio is 1: 4 to 4: 1 by mass, and this composition may further contain chondroitin sulfate and / or glucosamine. It is also described. In addition, it is also described that the composition for oral consumption may contain vitamin B1, vitamin B2, etc., and in the examples, for oral consumption containing 50 parts by mass of L-ascorbic acid 2-glucoside and 0.01 parts by mass of thiamine. The composition (total amount about 980 parts by weight) is described.
特開2006−320223号公報(特許文献4)には、チアミン類、及びビタミンC源としてアスコルビン酸グルコシドを含有するビタミンC強化チアミン類含有食品が開示され、ビタミンC強化チアミン類含有組成物に配合するビタミンC源としてアスコルビン酸グルコシドを用い、ビタミンC強化チアミン類含有組成物の熱及び/又は光に起因する異臭発生を抑制する方法も開示されている。この文献には、チアミン類としては、チアミンの他、フルスルチアミン、オクトチアミンなども記載され、食品に限らず、ビタミンC強化チアミン類含有経口組成物(ビタミンC強化チアミン類含有医薬品など)を調製することができ、この場合のアスコルビン酸グルコシドの配合割合は、組成物(医薬品など)100重量%あたり0.001〜5重量%であることも記載されている。さらに、実施例では、ジベンゾイルチアミン塩酸塩、チアミン塩酸塩、チアミン硝酸塩を用いた例が記載されている。 JP-A-2006-320223 (Patent Document 4) discloses thiamines and a vitamin C-enhanced thiamine-containing food containing ascorbic acid glucoside as a vitamin C source, and is incorporated into a vitamin C-enhanced thiamine-containing composition There is also disclosed a method for suppressing the generation of off-flavor caused by heat and / or light of a vitamin C-enhanced thiamine-containing composition using ascorbic acid glucoside as a vitamin C source. In this document, as thiamines, in addition to thiamine, fursultiamine, octothiamine and the like are described, and not only foods, but also oral compositions containing vitamin C-enhanced thiamines (medicines containing vitamin C-enhanced thiamines, etc.) It is also described that the blending ratio of ascorbic acid glucoside in this case is 0.001 to 5% by weight per 100% by weight of the composition (pharmaceutical or the like). Further, in the examples, examples using dibenzoyl thiamine hydrochloride, thiamine hydrochloride, and thiamine nitrate are described.
米国特許出願公報US 2004/0156923 A1(特許文献5)には、オイルケーキ成分と、グルコサミン成分と、酸成分と、ミネラル成分と、ビタミン成分と、機能性食品成分とを含む栄養補助食品組成物が開示され、酸成分としてアスコルビン酸、アスコルビン酸ナトリウム、アスコルビン酸グルコジトなどが記載され、ビタミン成分としてチアミンが記載されている。この文献には、アスコルビン酸ナトリウム100g、チアミン塩酸(87.4%)11.362gを含む組成物(全量880g)なども記載されている。 US Patent Application Publication US 2004/0156923 A1 (Patent Document 5) contains an oil cake component, a glucosamine component, an acid component, a mineral component, a vitamin component, and a functional food component. Ascorbic acid, sodium ascorbate, glucodite ascorbate and the like are described as the acid component, and thiamine is described as the vitamin component. This document also describes a composition containing 100 g of sodium ascorbate and 11.362 g of thiamine hydrochloride (87.4%) (total amount of 880 g).
WO 2006/022174 A1(特許文献6)には、アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを有効成分とする褐変抑制剤とこれを利用した褐変抑制方法が開示されている。この文献には、褐変抑制剤として、組成物100質量部に対してアルコルビン酸2−グルコシドをアスコルビン酸に換算して約0.0001質量部以上、望ましくは約0.001〜10質量部、さらに望ましくは約0.04〜5質量部配合したものが好適であり、組成物100質量部に対して10質量部以上配合しても、褐変抑制効果に差異はないとされている。また、ビタミンEなどの抗酸化作用の強い成分を併用してもよいことも記載されている。 WO 2006/022174 A1 (Patent Document 6) discloses a browning inhibitor containing ascorbic acid 2-glucoside as an active ingredient and a browning inhibiting method using the same. In this document, as a browning inhibitor, about 10001 parts by mass of alcorbic acid 2-glucoside is converted to ascorbic acid with respect to 100 parts by mass of the composition, preferably about 0.001 to 10 parts by mass, Desirably, about 0.04 to 5 parts by mass is blended, and even if 10 parts by mass or more is blended with respect to 100 parts by mass of the composition, there is no difference in the browning inhibiting effect. It is also described that a strong antioxidant component such as vitamin E may be used in combination.
しかし、フルスルチアミン塩酸塩の安定化について具体的には記載されていない。また、ビタミンC類(アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドなど)との併用によりビタミンB1類の種類によっては、長期間に亘る保存により、形態変化を生じ、粉末状の形態がアメ状に溶融固化した形態となり、形態安定性を損なう場合がある。 However, it does not specifically describe stabilization of fursultiamine hydrochloride. In addition, combination with vitamin C (ascorbic acid 2-glucoside, etc.), depending on the type of vitamin B1, causes a change in shape due to storage over a long period of time, and the powdery form is melted and solidified into a candy form. , The form stability may be impaired.
本発明の目的は、ビタミンB1類とビタミンC類とを含み、ビタミンB1類及びビタミンC類が安定化したビタミン製剤及びその製造方法を提供することにある。 An object of the present invention is to provide a vitamin preparation containing vitamin B1 and vitamin C, wherein vitamin B1 and vitamin C are stabilized, and a method for producing the same.
本発明の他の目的は、変色及び含量低下を抑制できるビタミン製剤、およびビタミンB1類を安定化する方法を提供することにある。 Another object of the present invention is to provide a vitamin preparation capable of suppressing discoloration and content reduction, and a method for stabilizing vitamin B1.
本発明のさらに他の目的は、ビタミンB1類とビタミンC類とを併用しても形態変化を防止できる組成物(又はビタミン製剤)を提供することにある。 Still another object of the present invention is to provide a composition (or vitamin preparation) that can prevent morphological changes even when vitamin B1 and vitamin C are used in combination.
本発明者は、ビタミンB1類とビタミンC類とを含む製剤の安定化において、ビタミンB1類としてのフルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸類(ビタミンC類)としてのアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを用いると、フルスルチアミン又はその塩が安定化し、製剤の変色及び含量低下を防止できること、特に、前記特許文献(特許文献6など)に開示の範囲とは異なる含有量でアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを用いると、褐変及び含量低下を著しく抑制できること、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを組み合わせて併用すると、長期間に亘り保存しても、これらの各成分の形態変化を防止でき、粒子状、粉末状などの形態を保持でき安定化することを見いだし、本発明を完成した。 The present inventor uses fursultiamine or a salt thereof as vitamin B1 and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside as ascorbic acid (vitamin C) in stabilizing a preparation containing vitamin B1 and vitamin C. In addition, it is possible to stabilize the fursultiamine or a salt thereof and prevent discoloration and content reduction of the preparation. In particular, ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is used in a content different from the range disclosed in the above-mentioned patent documents (eg, Patent Document 6). And, it is possible to remarkably suppress browning and content reduction, and in combination with fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside, even if stored for a long period of time, it is possible to prevent changes in the form of each of these components, The inventors have found that the particles and powders can be maintained and stabilized, and the present invention has been completed.
すなわち、本発明のビタミン製剤は、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを含む。アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの含有量は、製剤の総量100質量部中に6〜90質量部程度であってもよい。また、フルスルチアミン又はその塩1質量部に対するアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの割合は、0.01〜20質量部程度であってもよい。より具体的には、ビタミン製剤は、総量100質量部中にアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド8〜85質量部を含み、フルスルチアミン又はその塩1質量部に対してアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド0.1〜10質量部を含んでいてもよい。 That is, the vitamin preparation of the present invention contains fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside. About 6-90 mass parts may be sufficient as content of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside in 100 mass parts of total amounts of a formulation. Moreover, about 0.01-20 mass parts may be sufficient as the ratio of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside with respect to 1 mass part of fursultiamine or its salt. More specifically, the vitamin preparation contains 8-85 parts by mass of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside in a total amount of 100 parts by mass, and 0.1-0.1 parts of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside with respect to 1 part by mass of fursultiamine or a salt thereof. 10 mass parts may be included.
本発明は、製剤に、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを含有させ、ビタミン製剤を製造する方法、およびフルスルチアミン又はその塩を含む製剤にアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを含有させ、フルスルチアミン又はその塩を安定化させる方法も包含する。 The present invention allows a preparation to contain fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside to produce a vitamin preparation, and a preparation containing fursultiamine or a salt thereof to contain ascorbic acid 2-glucoside. Also included is a method of stabilizing fursultiamine or a salt thereof.
本発明では、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドのうち、少なくとも1つの成分を造粒することなく、製剤中に、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとが接触する形態(例えば、粉末状混合物の形態)で含有されていても、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)を安定化でき、各成分を粒子状又は粉末状の形態で維持できる。さらに、本発明の製剤は、ヒアルロン酸、スクラロース、グルコサミンを含まなくてもよく、コンドロイチン硫酸は必ずしも必要ではない。本発明の製剤はこのような成分を含まなくても高い安定性を示す。 In the present invention, fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside come into contact with each other in the preparation without granulating at least one component of fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside. Even if contained in a form (for example, in the form of a powdery mixture), fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative) can be stabilized, and each component can be maintained in a particulate or powdery form. Furthermore, the preparation of the present invention may not contain hyaluronic acid, sucralose, or glucosamine, and chondroitin sulfate is not necessarily required. The preparation of the present invention exhibits high stability even without such components.
本発明は、フルスルチアミン又はその塩に限らず、他のジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体にも適用できる。 The present invention is not limited to fursultiamine or a salt thereof, but can be applied to other disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivatives.
なお、本明細書において、「製剤」とは、専らヒトの疾患の予防及び/又は治療に用いる「医薬組成物」に限らず、広く栄養補助食品(サプリメントなど)などの用途にも適用できる組成物を意味する。 In the present specification, the “formulation” is not limited to a “pharmaceutical composition” used exclusively for the prevention and / or treatment of human diseases, but can be widely applied to uses such as nutritional supplements (eg supplements). Means a thing.
本発明では、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体であるフルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを含むため、ビタミンB1誘導体及びビタミンC類が安定化したビタミン製剤を得ることができる。また、製剤の変色(褐変など)を抑制できると共に、フルスルチアミン又はその塩及びアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの含量低下を抑制でき、フルスルチアミン又はその塩を安定化できる。しかも、長期間に亘り保存しても、フルスルチアミン又はその塩及びアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドが塊状に固まることがなく、粒子状、粉末状などの形態を保持できる。そのため、保存安定性(又は保管性)、取り扱い性、及び製剤の生産効率を向上できる。 In the present invention, since it contains disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside, a vitamin preparation in which vitamin B1 derivative and vitamin C are stabilized can be obtained. Moreover, while being able to suppress discoloration (browning etc.) of a formulation, the content fall of a fursultiamine or its salt and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside can be suppressed, and a fursultiamine or its salt can be stabilized. And even if it preserve | saves for a long period of time, a full sultiamine or its salt, and ascorbic-acid 2-glucoside do not harden | cure in a lump shape, and can maintain forms, such as a particulate form and a powder form. Therefore, storage stability (or storage property), handleability, and production efficiency of the preparation can be improved.
本発明のビタミン製剤(配合剤)は、ビタミンB1類としてフルスルチアミン又はその塩を含み、アスコルビン酸類(ビタミンC類)としてアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを含む。 The vitamin preparation (formulation) of the present invention contains fursultiamine or a salt thereof as vitamin B1 and contains ascorbic acid 2-glucoside as ascorbic acid (vitamin C).
フルスルチアミンの塩としては、無機酸塩(例えば、塩酸塩、硝酸塩、硫酸塩、リン酸塩など)、有機酸塩(例えば、酢酸塩、クエン酸塩など)などが例示できる。これらのフルスルチアミン又はその塩は単独で又は二種以上組み合わせて使用できる。これらのフルスルチアミン又はその塩のうち、フルスルチアミン塩酸塩などが好ましく使用される。フルスルチアミン又はその塩は、基−S−S−R(Rは2−(オキソラン−2−イル)エチル基を示す)を有するジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体に属し、ジスルフィド結合を有するため、他の成分と共存すると不安定化し易く、変色(褐変など)や含量低下を招きやすい。 Examples of the salt of fursultiamine include inorganic acid salts (for example, hydrochloride, nitrate, sulfate, phosphate, etc.), organic acid salts (for example, acetate, citrate, etc.), and the like. These fursultiamines or salts thereof can be used alone or in combination of two or more. Of these fursultiamine or salts thereof, fursultiamine hydrochloride and the like are preferably used. Fursultiamine or a salt thereof belongs to a disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative having a group —S—S—R (R represents 2- (oxolan-2-yl) ethyl group), and has a disulfide bond. When it coexists with ingredients, it tends to be unstable and easily causes discoloration (browning, etc.) and content reduction.
アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドは、アスコルビン酸の2位のヒドロキシル基がグルコースで修飾された化合物であり、加水分解によりアスコルビン酸を遊離し、生体内でビタミンCとしての生理活性を示す。アスコルビン酸類と配合すると不安定化するフルスルチアミン又はその塩であっても、アスコルビン酸2−グルコシド類と組み合わせることによりフルスルチアミン又はその塩を安定化できる。また、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド類とを併用すると、これらの成分のうち少なくとも一方の成分、特に双方の成分の形態を長期間に亘り安定して維持できる。すなわち、比較例に記載のように、ビタミンB1誘導体であるビスイブチアミン(粉末状)とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド類(粉末状)とを併用し、両者の粉末混合物を保存(例えば、室温、特に加温下で保存)すると、粉末状ビスイブチアミンと粉末状アスコルビン酸2−グルコシド類とが褐色に変色するとともに、融着してアメ状の1つの塊となり、取り扱い性を大きく低下させる。このような現象は、ビスイブチアミンとアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド類とを含む製剤においても生じる。これに対して、本発明では、粉末状フルスルチアミン又はその塩と粉末状アスコルビン酸2−グルコシド類とを混合して混合物の形態(又は両成分が接触した状態)で保存(例えば、室温、特に加温下で保存)しても、着色又は変色することがないだけでなく、粉末状の形態を長期間に亘り維持でき、形態変化を生じることがない。そのため、フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド類とを粉末混合物の形態で安定に保存でき、保存性、取り扱い性及び製剤の生産性を向上できる。 Ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is a compound in which the hydroxyl group at the 2-position of ascorbic acid is modified with glucose, liberates ascorbic acid by hydrolysis, and exhibits physiological activity as vitamin C in vivo. Even if it is a fursultiamine or a salt thereof that is destabilized when blended with ascorbic acid, it can be stabilized by combining it with an ascorbic acid 2-glucoside. Further, when fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside are used in combination, at least one of these components, particularly the form of both components can be stably maintained over a long period of time. That is, as described in the comparative example, a vitamin B1 derivative, bisibutiamine (in powder form) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (in powder form) are used in combination, and the powder mixture of both is stored (for example, at room temperature, particularly When stored under heating), the powdered bisibutiamine and the powdered ascorbic acid 2-glucosides turn brown and fuse together to form one candy-like lump, greatly reducing the handleability. Such a phenomenon also occurs in preparations containing bisibuthiamine and ascorbic acid 2-glucosides. In contrast, in the present invention, powdered fursultiamine or a salt thereof and powdered ascorbic acid 2-glucoside are mixed and stored in the form of a mixture (or in a state where both components are in contact) (for example, room temperature, Even when stored under heating in particular, not only does it not be colored or discolored, but it can also maintain a powdery form for a long period of time without causing a change in form. Therefore, fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside can be stably stored in the form of a powder mixture, and storage stability, handleability, and productivity of the preparation can be improved.
アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの含有量は、製剤の総量100質量部中、6〜90質量部(例えば、8〜85質量部)、好ましくは10〜85質量部(例えば、20〜85質量部)、さらに好ましくは25〜85質量部(例えば、30〜80質量部)程度である。アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの含有量は、製剤の総量100質量部中、20〜75質量部(例えば、25〜70質量部)、特に25〜65質量部(例えば、30〜60質量部)程度である場合が多い。 The content of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is 6 to 90 parts by mass (for example, 8 to 85 parts by mass), preferably 10 to 85 parts by mass (for example, 20 to 85 parts by mass), in a total amount of 100 parts by mass of the preparation. More preferably, it is about 25-85 mass parts (for example, 30-80 mass parts). The content of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is about 20 to 75 parts by mass (for example, 25 to 70 parts by mass), particularly about 25 to 65 parts by mass (for example, 30 to 60 parts by mass), in a total amount of 100 parts by mass of the preparation. There are many cases.
前記フルスルチアミン又はその塩に対するアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの割合は、フルスルチアミン又はその塩1質量部に対して0.01〜20質量部程度の範囲から選択でき、0.1〜15質量部(例えば、0.3〜12質量部)、好ましくは0.5〜10質量部(例えば、0.7〜8質量部)、さらに好ましくは1〜7質量部(例えば、2〜7質量部)程度である。アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの割合は、フルスルチアミン又はその塩1質量部に対して0.1〜10質量部、好ましくは0.1〜5質量部(例えば、0.5〜5質量部)、さらに好ましくは1〜5質量部(例えば、2〜5質量部)、特に2.5〜4.5質量部程度であってもよい。 The ratio of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside to the fursultiamine or a salt thereof can be selected from a range of about 0.01 to 20 parts by mass with respect to 1 part by mass of the fursultiamine or a salt thereof, and 0.1 to 15 parts by mass. (E.g. 0.3-12 parts by mass), preferably 0.5-10 parts by mass (e.g. 0.7-8 parts by mass), more preferably 1-7 parts by mass (e.g. 2-7 parts by mass). Degree. The proportion of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is 0.1 to 10 parts by weight, preferably 0.1 to 5 parts by weight (for example, 0.5 to 5 parts by weight), based on 1 part by weight of fursultiamine or a salt thereof. More preferably, it may be about 1 to 5 parts by mass (for example, 2 to 5 parts by mass), particularly about 2.5 to 4.5 parts by mass.
フルスルチアミン又はその塩とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド(アスコルビン酸換算)との総量は、製剤全体に対して6〜93重量%程度の範囲から選択でき、通常、10〜80重量%、好ましくは15〜60重量%程度であってもよい。 The total amount of fursultiamine or a salt thereof and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (ascorbic acid equivalent) can be selected from the range of about 6 to 93% by weight with respect to the whole preparation, and is usually 10 to 80% by weight, preferably 15 It may be about ˜60% by weight.
本発明では、フルスルチアミン又はその塩に代えて、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体にも適用できる。すなわち、本発明の製剤は、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを含むビタミン製剤であってもよい。 In the present invention, it can be applied to a disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative instead of fursultiamine or a salt thereof. That is, the preparation of the present invention may be a vitamin preparation containing a disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside.
ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体としては、プロスルチアミン、オクトチアミン、ビスベンチアミン、チアミンジスルフィドなどが挙げられる。これらのビタミンB1誘導体は塩(塩酸塩、硝酸塩、硫酸塩などの無機酸塩、酢酸塩などの有機酸塩)の形態であってもよい。これらのビタミンB1誘導体は単独で又は二種以上組み合わせて使用できる。これらのビタミンB1誘導体のうち、プロスルチアミン、オクトチアミン、ビスベンチアミン又はそれらの塩が好ましく使用される。特に、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体のうち、基−S−S−R(Rはプロピル基などのアルキル基、又は置換基を有するアルキル基((3−アセチルチオキシ−3−(4−メトキシカルボニルブチル)プロピル基など)を示す)を有するビタミンB1誘導体、例えば、プロスルチアミン、オクトチアミンが好ましく使用される。ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体、なかでも前記基−S−S−Rを有するジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体は、前記フルスルチアミン又はその塩と同様に、ジスルフィド結合を有するため、他の成分と共存すると不安定化し易く、変色(褐変など)や含量低下を招きやすい。 Examples of the disulfide type vitamin B1 derivative include prosultiamine, octothiamine, bisbenchamine, thiamine disulfide and the like. These vitamin B1 derivatives may be in the form of a salt (an inorganic acid salt such as hydrochloride, nitrate or sulfate, or an organic acid salt such as acetate). These vitamin B1 derivatives can be used alone or in combination of two or more. Of these vitamin B1 derivatives, prosultiamine, octothiamine, bisbenchamine or salts thereof are preferably used. In particular, among disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivatives, the group —S—S—R (where R is an alkyl group such as a propyl group, or an alkyl group having a substituent ((3-acetylthioxy-3- (4-methoxycarbonylbutyl Vitamin B1 derivatives having a propyl group, etc.), such as prosultiamine, octothiamine, etc. Disulfide type vitamin B1 derivatives, especially disulfide type vitamin B1 having the group -S-S-R Since the derivative has a disulfide bond as in the case of the aforementioned fursultiamine or a salt thereof, it tends to be unstable when coexisting with other components, and easily causes discoloration (browning, etc.) and content reduction.
不安定な前記ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体であっても、アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドと組み合わせて併用することにより、ビタミンB1誘導体を安定化できる。また、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを併用することにより、加温して保存しても、長期間に亘り各成分の形態の安定化も期待できる。 Even if the disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative is unstable, the vitamin B1 derivative can be stabilized by using it in combination with ascorbic acid 2-glucoside. In addition, by using a disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside in combination, it is possible to expect stabilization of the form of each component over a long period of time even when heated and stored.
フルスルチアミン又はその塩と前記ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体とを併用する場合、両者の割合(質量比)は、例えば、前者/後者=1/0.01〜1/10、好ましくは1/0.05〜1/5、さらに好ましくは1/0.1〜1/1程度であってもよい。 When fursultiamine or a salt thereof and the disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative are used in combination, the ratio (mass ratio) of both is, for example, the former / the latter = 1 / 0.01 to 1/10, preferably 1 / 0.0. It may be about 05 to 1/5, more preferably about 1 / 0.1 to 1/1.
ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体1質量部に対するアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの割合は、前記フルスルチアミン又はその塩に対する割合と同様であってもよい。すなわち、前記ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体に対するアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの割合は、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体1質量部に対して0.01〜20質量部程度の範囲から選択でき、0.1〜15質量部(例えば、0.3〜12質量部)、好ましくは0.5〜10質量部(例えば、0.7〜8質量部)、さらに好ましくは1〜7質量部(例えば、2〜7質量部)程度である。アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの割合は、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体1質量部に対して0.1〜10質量部、好ましくは0.1〜5質量部(例えば、0.5〜5質量部)、さらに好ましくは1〜5質量部(例えば、2〜5質量部)、特に2.5〜4.5質量部程度であってもよい。 The proportion of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside relative to 1 part by mass of the disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative may be the same as the proportion relative to the aforementioned fursultiamine or a salt thereof. That is, the ratio of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside to the disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative can be selected from a range of about 0.01 to 20 parts by mass with respect to 1 part by mass of the disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative. (E.g. 0.3-12 parts by mass), preferably 0.5-10 parts by mass (e.g. 0.7-8 parts by mass), more preferably 1-7 parts by mass (e.g. 2-7 parts by mass). Degree. The proportion of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is 0.1 to 10 parts by weight, preferably 0.1 to 5 parts by weight (for example, 0.5 to 5 parts by weight), based on 1 part by weight of the disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative. It may be preferably 1 to 5 parts by mass (for example, 2 to 5 parts by mass), particularly about 2.5 to 4.5 parts by mass.
ビタミンB1誘導体とジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド(アスコルビン酸換算)との総量も、製剤全体に対して6〜93重量%程度の範囲から選択でき、通常、10〜80重量%、好ましくは15〜60重量%程度であってもよい。 The total amount of vitamin B1 derivative, disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (ascorbic acid equivalent) can also be selected from the range of about 6 to 93% by weight with respect to the whole preparation, and usually 10 to 80% by weight, Preferably, it may be about 15 to 60% by weight.
なお、本発明のビタミン製剤において、ビタミンB1誘導体をシクロデキストリンなどで予め造粒又は顆粒とする必要はなく、ビタミンB1誘導体とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを製剤中に含有させても、ビタミンB1誘導体を有効に安定化できる。また、還元性の小さなビタミンB1誘導体であっても、ビタミンB1誘導体を有効に安定化できる。すなわち、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドのうち、少なくとも1つの成分を造粒することなく、製剤中に、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとが接触する形態(例えば、担体成分を含んでいてもよく、これらの成分の粉末状混合物の形態)で含有されていても、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)を安定化できる。そのため、結合剤、賦形剤などを用いて、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとの粉末混合物を造粒しても、安定な固形製剤を得ることができる。従って、本発明は、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを粒子状又は粉末状の形態で維持し、形態変化を防止する組成物及び防止方法をも包含する。 In the vitamin preparation of the present invention, it is not necessary to granulate or granulate the vitamin B1 derivative beforehand with cyclodextrin or the like. Even if the vitamin B1 derivative and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside are contained in the preparation, the vitamin B1 derivative Can be effectively stabilized. Moreover, even if it is a vitamin B1 derivative with small reducibility, a vitamin B1 derivative can be stabilized effectively. That is, without the granulation of at least one component of fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide type vitamin B1 derivative) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside, fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide type) Even if the vitamin B1 derivative) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside are in contact with each other (for example, a carrier component may be included or a powdery mixture of these components), fullsultiamine or a salt thereof (Or disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative) can be stabilized. Therefore, even if a powder mixture of fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide type vitamin B1 derivative) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is granulated using a binder, an excipient, etc., a stable solid preparation is obtained. be able to. Accordingly, the present invention provides a composition and a method for preventing morphological change by maintaining fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside in a particulate or powder form. Is also included.
本発明の製剤は、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)及びアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドに加えて、他の生理活性又は薬理活性成分、例えば、ビタミン類、解熱鎮痛薬、抗炎症薬、鎮咳去痰薬、抗喘息薬又は気管支拡張薬、抗アレルギー薬、副交感神経遮断薬、交感神経興奮薬又はα受容体刺激薬、消炎薬又は消炎酵素薬、中枢神経興奮薬、胃腸薬(制酸薬又は粘膜保護薬、健胃薬、消化薬を含む)、止瀉薬、生薬、アミノ酸類、ミネラル類などを含んでいてもよい。また、本発明の製剤は、γ−オリザノール、オロチン酸、ヨクイニン、グルクロン酸類(グルクロン酸、グルクロノラクトン、グルクロン酸アミドなど)、コンドロイチン硫酸ナトリウムなどを含んでいてもよい。これらの成分は単独で又は組み合わせて使用できる。 In addition to fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside, the preparation of the present invention contains other physiologically active or pharmacologically active ingredients such as vitamins, antipyretic analgesics, anti-inflammatory Drugs, antitussive expectorants, anti-asthma drugs or bronchodilators, anti-allergic drugs, parasympathomimetic drugs, sympathomimetic drugs or alpha receptor stimulants, anti-inflammatory drugs or anti-inflammatory enzymes drugs, central nervous stimulants, gastrointestinal drugs Acidic drugs or mucosal protective drugs, including stomachic drugs and digestive drugs), antidiarrheals, herbal medicines, amino acids, minerals and the like may be included. In addition, the preparation of the present invention may contain γ-oryzanol, orotic acid, yoquinin, glucuronic acid (such as glucuronic acid, glucuronolactone, glucuronic acid amide), chondroitin sodium sulfate and the like. These components can be used alone or in combination.
ビタミン類は、水溶性ビタミン類又は脂溶性ビタミン類のいずれであってもよい。ビタミン類としては、ビタミンB1類(塩酸チアミン、硝酸チアミン、塩酸ジセチアミン、シコチアミン、ベンフォチアミン、ビスイブチアミンなど)、ビタミンB2類(リボフラビン、リン酸リボフラビンナトリウム、酪酸リボフラビン、フラビンアデニンジヌクレオチドナトリウムなどのリボフラビン類など)、ビタミンB6類(ピリドキシン、ピリドキサールなどのピリドキシン類又はその塩(塩酸ピリドキシン、酢酸ピリドキシン、リン酸ピリドキサールなど))、ニコチン酸類(ニコチン酸、ニコチン酸アミドなど)、ビタミンB12類(メコバラミン、シアノコバラミン、ヒドロキソコバラミン、メチルコバラミンなどのコバラミン類又はその塩(塩酸ヒドロキソコバラミン、酢酸ヒドロキソコバラミンなど))、葉酸、パントテン酸類(パンテノール、パントテン酸又はその塩(パントテン酸カルシウム、パントテン酸カルシウムタイプSなど))、ビタミンC類(アスコルビン酸、アスコルビン酸カルシウム、アスコルビン酸ナトリウム、アスコルビン酸カリウムなど)、ビタミンA類(酢酸レチノール、パルミチン酸レチノール、ビタミンA油、肝油、強肝油など)、ビタミンD類(エルゴカルシフェロール、コレカルシフェロールなど)、ビタミンE類(d−α−トコフェロール、dl−α−トコフェロール、コハク酸d−α−トコフェロール、コハク酸dl−α−トコフェロールカルシウム、酢酸d−α−トコフェロール、酢酸dl−α−トコフェロールなど)、ビオチン、ビタミンK、ビタミンP(ヘスペリジンなど)などが挙げられる。これらのビタミン類も単独で又は二種以上組み合わせて使用でき、複合ビタミン剤を形成してもよい。 The vitamins may be either water-soluble vitamins or fat-soluble vitamins. Vitamins such as vitamin B1 (thiamine hydrochloride, thiamine nitrate, dicetiamine hydrochloride, chicotiamine, benfotiamine, bisibutiamine, etc.), vitamin B2 (riboflavin, sodium riboflavin phosphate, riboflavin butyrate, sodium flavin adenine dinucleotide, etc.) Riboflavins, etc.), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine such as pyridoxine and pyridoxal or salts thereof (pyridoxine hydrochloride, pyridoxine acetate, pyridoxal phosphate, etc.)), nicotinic acid (nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, etc.), vitamin B12 ( Mecobalamin, cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin, cobalamin such as methylcobalamin or salts thereof (hydroxocobalamin hydrochloride, hydroxocobalamin acetate, etc.)), folic acid, punt Acids (pantenol, pantothenic acid or salts thereof (calcium pantothenate, calcium pantothenate type S, etc.)), vitamin C (ascorbic acid, calcium ascorbate, sodium ascorbate, potassium ascorbate, etc.), vitamin A ( Retinol acetate, retinol palmitate, vitamin A oil, liver oil, strong liver oil, etc.), vitamin D (ergocalciferol, cholecalciferol, etc.), vitamin E (d-α-tocopherol, dl-α-tocopherol, succinic acid) and d-α-tocopherol, dl-α-tocopherol calcium succinate, d-α-tocopherol acetate, dl-α-tocopherol acetate, etc.), biotin, vitamin K, vitamin P (eg hesperidin) and the like. These vitamins may be used alone or in combination of two or more, and may form a complex vitamin preparation.
解熱鎮痛薬として、アセトアミノフェン、イブプロフェン、ケトプロフェン、アスピリン、アスピリンアルミニウム、エテンザミド、サリチルアミド、サリチル酸メチル、サリチル酸ナトリウム、ロキソプロフェンナトリウム、アンフェナクナトリウム、インドメタシンファルネシル、メフェナム酸、フルフェナム酸、ピロキシカムなどが挙げられる。 Antipyretic analgesics include acetaminophen, ibuprofen, ketoprofen, aspirin, aspirin aluminum, etenzaamide, salicylamide, methyl salicylate, sodium salicylate, loxoprofen sodium, ampenac sodium, indomethacin farnesyl, mefenamic acid, flufenamic acid, piroxicam, etc. .
鎮咳去痰薬として、リン酸コデイン、リン酸ジヒドロコデイン、臭化水素酸デキストロメトルファン、塩酸メチルエフェドリン、ノスカピン、塩酸メチルシステイン、塩酸エチルシステイン、カルボシステインなどが挙げられる。 Examples of antitussive expectorants include codeine phosphate, dihydrocodeine phosphate, dextromethorphan hydrobromide, methylephedrine hydrochloride, noscapine, methylcysteine hydrochloride, ethylcysteine hydrochloride, carbocysteine and the like.
抗喘息薬又は気管支拡張薬には、例えば、アミノフィリン、ジプロフィリン、テオフィリン、エフェドリン、塩酸エフェドリン、エピネフリン、dl−塩酸メチルエフェドリン、硫酸サルブタモール、塩酸プロカテロール、塩酸イソプレナリン、硫酸イソプロテレノール、塩酸メトキシフェナミン、硫酸オルシプレナリン、塩酸クロルプレナリン、塩酸トリメトキノール、硫酸サルブタモール、硫酸テルブタリン、硫酸ヘキソプレナリン、フマル酸フォルモテロール、塩酸ツブロブテロール、臭化水素酸フェノテロール、塩酸プロカテロール、塩酸プルブテロール、塩酸クレンブテロール、塩酸マブテロールコリンテオフィリン、プロキシフィリンなどが含まれる。 Anti-asthma drugs or bronchodilators include, for example, aminophylline, diprofylline, theophylline, ephedrine, ephedrine hydrochloride, epinephrine, dl-methylephedrine hydrochloride, salbutamol sulfate, procaterol hydrochloride, isoprenaline hydrochloride, isoproterenol sulfate, methoxyphenamine hydrochloride, Orciprenaline sulfate, chlorprenalin hydrochloride, trimethoquinol hydrochloride, salbutamol sulfate, terbutaline sulfate, hexoprenaline sulfate, formoterol fumarate, tubrobuterol hydrochloride, fenoterol hydrobromide, procaterol hydrochloride, plubuterol hydrochloride, clenbuterol hydrochloride, mabuterol choline theophylline , Including proxyphylline.
抗アレルギー薬としては、例えば、フマル酸ケトチフェン、塩酸アゼラスチン、オキサトミド、フマル酸エメダスチン、塩酸エピナスチン、エバスチン、塩酸ジフェンヒドラミン、フマル酸クレマスチン、dl−マレイン酸クロルフェニラミン、d−マレイン酸クロルフェニラミン、プランルカスト水和物、ザフィルルカスト、モンテルカストカルシウム、トシル酸スプラタスト、クロモグリク酸ナトリウム、トラニラスト、レピリナスト、イブジラスト、タザノラスト、ペミロラストカリウムなどが例示できる。 Antiallergic agents include, for example, ketotifen fumarate, azelastine hydrochloride, oxatomide, emedastine fumarate, epinastine hydrochloride, ebastine, diphenhydramine hydrochloride, clemastine fumarate, chlorpheniramine maleate, chlorpheniramine maleate, plan Examples include lucast hydrate, zafirlukast, montelukast calcium, suplatast tosilate, cromoglycate sodium, tranilast, repirinast, ibudilast, tazanolast, pemirolast potassium and the like.
副交感神経遮断薬としては、例えば、天然アルカロイド類(例えば、ベラドンナ総アルカロイド、ベラドンナエキス、アトロピン、スコポラミン、ロートエキス、ダツラエキスなど)、天然アルカロイド誘導体、ヨウ化イソプロパミド、臭化メチルベナクチジウム、臭化プロパンテリンなどが例示できる。 Examples of parasympathetic blocking agents include natural alkaloids (eg, belladonna total alkaloids, belladonna extract, atropine, scopolamine, funnel extract, duck extract, etc.), natural alkaloid derivatives, iodopropamide iodide, methylbenactidium bromide, bromide Propanthelin and the like can be exemplified.
交感神経興奮薬又はα受容体刺激薬としては、例えば、塩酸フェニルプロパノールアミン、塩酸プソイドエフェドリン、塩酸フェニレフリン、塩酸メチルエフェドリン、塩酸エフェドリン、ノルエピネフリン、硝酸ナファゾリン、ジャイロメタゾリン、ミドドリン、メトキサミン、塩酸テトラヒドロゾリンなどが例示できる。 Examples of sympathomimetic drugs or alpha receptor stimulants include phenylpropanolamine hydrochloride, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, phenylephrine hydrochloride, methylephedrine hydrochloride, ephedrine hydrochloride, norepinephrine, naphazoline nitrate, gyrometazoline, middolin, methoxamine hydrochloride, tetrahydrozoline hydrochloride, etc. It can be illustrated.
消炎薬又は消炎酵素薬としては、例えば、塩化リゾチーム、セラペプターゼ、トラネキサム酸、アズレンスルホン酸ナトリウムなどが挙げられる。 Examples of the anti-inflammatory agent or anti-inflammatory enzyme include lysozyme chloride, serrapeptase, tranexamic acid, sodium azulene sulfonate, and the like.
中枢神経興奮薬としては、例えば、カフェイン類又はキサンチン類(例えば、無水カフェイン、安息香酸ナトリウムカフェイン、カフェインサイレート、カフェイン(1水和物)など)などが例示できる。 Examples of the central nervous stimulant include caffeine or xanthines (for example, anhydrous caffeine, sodium benzoate caffeine, caffeine silate, caffeine (monohydrate), etc.) and the like.
胃腸薬として、乾燥水酸化アルミニウムゲル、ケイ酸アルミン酸マグネシウム、ケイ酸マグネシウム、合成ヒドロタルサイト、酸化マグネシウム、水酸化アルミナマグネシウム、水酸化アルミニウムゲル、水酸化アルミニウム・炭酸水素ナトリウム共沈生成物、水酸化アルミニウム・炭酸マグネシウム混合乾燥ゲル、水酸化アルミニウム・炭酸マグネシウム・炭酸カルシウム共沈生成物、水酸化マグネシウム、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸マグネシウム、沈降炭酸カルシウム、メタケイ酸アルミン酸マグネシウム、無水リン酸水素カルシウム、リン酸水素カルシウム、アミノ酢酸、ジヒドロキシアルミニウムアミノアセテート、ロートエキス、アロエ、ウイキョウ、ウコン、オウバク、オウレン、加工大蒜、コウジン、コウボク、ショウキョウ、センブリ、ケイヒ、ダイオウ、チクセツニンジン、チンピ、トウヒ、ニガキ、ニンジン、ハッカ、ホップ、ウイキョウ油、ケイヒ油、ショウキョウ油、トウヒ油、ハッカ油、レモン油、L−メントール、塩酸ベタイン、塩化カルニチン、乾燥酵母、でんぷん消化酵素、たん白消化酵素、脂肪消化酵素、繊維素消化酵素、ウルソデスオキシコール酸、胆汁末などが例示できる。 As a gastrointestinal agent, dry aluminum hydroxide gel, magnesium aluminate silicate, magnesium silicate, synthetic hydrotalcite, magnesium oxide, magnesium hydroxide alumina, aluminum hydroxide gel, aluminum hydroxide / sodium bicarbonate coprecipitation product, Aluminum hydroxide / magnesium carbonate mixed dry gel, aluminum hydroxide / magnesium carbonate / calcium carbonate coprecipitation product, magnesium hydroxide, sodium bicarbonate, magnesium carbonate, precipitated calcium carbonate, magnesium metasilicate aluminate, anhydrous calcium hydrogen phosphate , Calcium hydrogen phosphate, aminoacetic acid, dihydroxyaluminum aminoacetate, funnel extract, aloe, fennel, turmeric, oak, auren, processed daikon, kojin, kokuboku, ginger Assembly, Keihi, Daio, Chikutsutsujinjin, Chimpi, Spruce, Nigaki, Carrot, Pepper, Hop, Fennel Oil, Keihi Oil, Pepper Oil, Spruce Oil, Pepper Oil, Lemon Oil, L-Menthol, Betaine Hydrochloride, Carnitine Chloride Examples thereof include dry yeast, starch digestive enzyme, protein digestive enzyme, fat digestive enzyme, fibrin digestive enzyme, ursodeoxycholic acid, and bile powder.
止瀉薬としては、アクリノール、塩化ベルべリン、グアヤコール、クレオソート、次サリチル酸ビスマス、次硝酸ビスマス、次炭酸ビスマス、次没食子酸ビスマス、タンニン酸、カオリン、ペクチン、薬用炭、乳酸カルシウム、沈降炭酸カルシウム、リン酸水素カルシウム、塩酸パパベリン、アミノ安息香酸エチル、アズレンスルホン酸ナトリウム、アルジオキサ、L−グルタミン、銅クロロフィリンカリウム、銅クロロフィリンナトリウム、メチルメチオニンスルホニウムクロライド、ジメチルポリシロキサンなどが挙げられる。 Antidiarrheal agents include acrinol, berberine chloride, guaiacol, creosote, bismuth subsalicylate, bismuth hyponitrite, bismuth subcarbonate, bismuth subgallate, tannic acid, kaolin, pectin, medicinal charcoal, calcium lactate, precipitated calcium carbonate , Calcium hydrogen phosphate, papaverine hydrochloride, ethyl aminobenzoate, sodium azulene sulfonate, aldioxa, L-glutamine, copper chlorophyllin potassium, copper chlorophyllin sodium, methylmethionine sulfonium chloride, dimethylpolysiloxane and the like.
生薬としては、アカメガシワ、アセンヤク、アセンヤク末、アマチャ、アマチャ末、アロエ、アロエ末、アンソッコウ、イレイセン、インチンコウ、インヨウカク、ウイキョウ、ウイキョウ末、ウコン、ウヤク、ウワウルシ、エイジツ、エイジツ末、エンゴサク、オウギ、オウゴン、オウゴン末、オウセイ、オウバク、オウバク末、オウレン、オウレン末、オンジ、オンジ末、カゴソウ、カシュウ、ガジュツ、カッコン、カノコソウ、カノコソウ末、カロコン、カンキョウ、カンゾウ、カンゾウ末、カンテン、カンテン末、キキョウ、キキョウ末、キクカ、キササゲ、キジツ、キョウカツ、キョウニン、クコシ、クジン、クジン末、ケイガイ、ケイヒ、ケイヒ末、ケツメイシ、ケンゴシ、ゲンチアナ、ゲンチアナ末、ゲンノショウコウ、ゲンノショウコウ末、コウカ、コウジン、コウブシ、コウブシ末、コウボク、コウボク末、ゴオウ、ゴシツ、ゴシュユ、ゴボウシ、ゴミン、コメデンプン、コロンボ、コロンボ末、コンズランゴ、サイコ、サイシン、サフラン、サンキライ、サンキライ末、サンシシ、サンシシ末、サンシュユ、サンショウ、サンショウ末、サンソウニン、サンヤク、サンヤク末、ジオウ、シゴカ、ジコッピ、シコン、シツリシ、シャクヤク、シャクヤク末、ジャショウシ、シャゼンシ、シャゼンソウ、ジュウヤク、シュクシャ、シュクシャ末、ショウキョウ、ショウキョウ末、ショウズク、ショウマ、シンイ、セッコウ、セネガ、セネガ末、センキュウ、センキュウ末、センコツ、センソ、センナ、センナ末、センブリ、センブリ末、ソウジュツ、ソウジュツ末、ソウハクヒ、ソボク、ソヨウ、ダイオウ、ダイオウ末、ダイソウ、タクシャ、タクシャ末、チクセツニンジン、チクセツニンンジン末、チモ、チョウジ、チョウジ末、チョウトウコウ、チョレイ、チョレイ末、チンピ、テンマ、テンモンドウ、トウガシ、トウガラシ、トウガラシ末、トウキ、トウキ末、トウニン、トウニン末、トウヒ、トコン、トコン末、トチュウ、トラガント、トランガント末、ニガキ、ニガキ末、ニンジン、ニンジン末、ニンドウ、バイモ、バクモンドウ、ハチミツ、ハッカ、ハマボウフウ、ハンゲ、ビャクシ、ビャクジュツ、ビャクジュツ末、ビワヨウ、ビンロウジ、ブクリョウ、ブクリョウ末、ブシ、ブシ末、ベラドンナコン、ヘンズ、ボウイ、ボウコン、ボウフウ、ボタンピ、ボタンピ末、ホミカ、ボレイ、ボレイ末、マオウ、マクリ、マシニン、モクツウ、モッコウ、ヤクチ、ユウタン、ヨクイニン、ヨクイニン末、リュウコツ、リュウタン、リュウタン末、リョウキョウ、レンギョウ、レンニク、ロジン、ロートコンなどが挙げられる。 Herbal medicines include Akamegashiwa, Asenyaku, Asenyaku powder, Achacha, Achacha powder, Aloe, Aloe powder, Ansokkou, Ireisen, Inchinko, Yinakukaku, Fennel, Fennel powder, Turmeric, Uyaku, Uwaurushi, Ages, Ages powder, Engosaku, Ogi , Ogon powder, Ousei, Oubak, Oubak powder, Ouren, Ourem powder, Onji, Onji powder, Kagosou, Kashu, Gadju, Kakon, Kanoko, Ganoderma powder, Carocon, Citrus, Licorice, Licorice powder, Kangten, Kantou Kyoku powder, Kikuka, Kisage, Kijitsu, Kyokatsu, Kyonin, Kokushi, Kujin, Kukujin powder, Keigai, Keihi, Keihi powder, Ketsumeishi, Kengoshi, Gentiana, Gentiana powder, Gennoshokou, Gen Ginger powder, Koko, Koji, Koji, Kowushi powder, Kokuboku, Kokuboku powder, Gou, Goshitsu, Goshuyu, Goboushi, Gomin, Rice starch, Colombo, Colombo powder, Kuzurango, Psycho, Saishin, Saffron, Sankirai, Sankirai powder, Sanshishi, Sangshi powder, Sanshuyu, Salamander, Salamander powder, Sangyonin, Sanyaku, Sanyaku powder, Giant, Shigoka, Zikoppi, Sikon, Shitsurishi, Peonies, Peonies, Jashou, Shazenshi, Shazensou, Zyuyaku, Shukusha, Shukusha, Syakusha, Showa powder, Shozuk, Shouma, Shini, Gypsum, Senega, Senega powder, Senkyu, Senkyu powder, Senkotsu, Senso, Senna, Senna powder, Assembly, Assembly powder, Sojutsu powder, Sojutsu powder Sakuhakuhi, Soboku, Soyo, Daio, Daio powder, Daiso, Takusha, Takusha powder, Chikusetuninjin, Chikutsuninjinjin powder, Timo, Choji, Choji powder, Butterflyfish, Chorei, Chorei powder, Chimpi, Tenma, Tenmondou, Togashi , Red pepper, red pepper powder, red pepper, red powder, red pepper, red pepper powder, red spider, tokon, powdered red pepper, carrot, powdered carrot, powdered carrot, red pepper, honey, mint, mint, Hamaboufu, Hange, Beakshi, Byakujutsu, Byakujutsu powder, Biwayo, Binrouji, Bukuryu, Bukkyou powder, Bushi, Bushi powder, Belladon Nakhon, Hens, Bowie, Bowcon, Bowfish, Buttonpi, Buttonpi powder, Homica, Boray, Bore Examples include a powder, mah, macri, machinin, mokutsu, mokko, yak, yutan, yokoinin, yokuinin powder, ryukotsu, ryutan, ryutan powder, ryokyo, forsythia, rennik, rosin, rotokon.
アミノ酸類としては、L−システイン、アスパラギン酸カリウム・マグネシウム等量混合物、L−バリン、L−ロイシン、L−イソロシン、タウリンなどが挙げられる。 Examples of amino acids include L-cysteine, potassium / magnesium aspartate equivalent mixture, L-valine, L-leucine, L-isolosin, taurine and the like.
本発明では、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体を含む製剤にアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを含有させることにより、ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体を安定化させることができ、製剤の変色及び活性成分(ジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体など)の含量低下を有効に防止できる。 In the present invention, by containing 2-glucoside ascorbic acid in a preparation containing a disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative, the disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative can be stabilized, and the discoloration of the preparation and active ingredients (disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative, etc. ) Can be effectively prevented.
本発明の製剤は、製剤の形態に応じて慣用の方法により、フルスルチアミン又その塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)とアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドとを含有させることにより製造できる。本発明の製剤は、種々の形態、例えば、固形剤(散剤、細粒又は顆粒剤、丸剤、錠剤(素錠又は裸錠)、カプセル剤、フィルムコーティング錠(糖衣錠)などのフィルムコーティング剤など)、半固形剤(クリーム剤、ゼリー剤、軟膏剤、ゲル剤、ゲルクリーム剤、グミ剤など)及び液剤(液剤、エリキシル剤、懸濁剤、乳剤、シロップ剤、内服液剤(いわゆるドリンク剤)など)の形態であってもよい。また、製剤は、用事溶解型のドライシロップ剤、発泡剤などであってもよい。錠剤としては、素錠、フィルム錠、糖衣錠、薄層糖衣錠、シュガーレス薄層糖衣錠、口腔内速崩壊錠、チュアブル錠、チョコレート剤などが挙げられる。また、錠剤は、二層錠、三層錠、有核錠などであってもよく、顆粒剤又は細粒剤含有の錠剤などであってもよい。カプセル剤としては、硬カプセル剤、軟カプセル剤などが挙げられる。さらに、本発明の製剤は、経口投与製剤(内用剤など)であってもよく、非経口投与製剤(貼付剤などの外用剤など)であってもよい。本発明のビタミン製剤は経口投与の固形製剤である場合が多い。 The preparation of the present invention can be produced by incorporating fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide type vitamin B1 derivative) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside by a conventional method according to the form of the preparation. The preparation of the present invention can be used in various forms, for example, film coating agents such as solid preparations (powder, fine granules or granules, pills, tablets (plain tablets or uncoated tablets), capsules, film-coated tablets (sugar-coated tablets), etc. ), Semi-solid preparations (creams, jellies, ointments, gels, gel creams, gummi, etc.) and liquids (liquids, elixirs, suspensions, emulsions, syrups, internal use liquids (so-called drinks)) Etc.). Further, the preparation may be a business-soluble dry syrup, a foaming agent, or the like. Examples of the tablet include a plain tablet, a film tablet, a sugar-coated tablet, a thin-layer sugar-coated tablet, a sugarless thin-layer sugar-coated tablet, an intraoral quick disintegrating tablet, a chewable tablet, and a chocolate agent. Further, the tablet may be a bilayer tablet, a trilayer tablet, a dry-coated tablet, or the like, or a tablet containing granules or fine granules. Examples of capsules include hard capsules and soft capsules. Furthermore, the preparation of the present invention may be a preparation for oral administration (such as an internal preparation) or a preparation for parenteral administration (such as an external preparation such as a patch). The vitamin preparation of the present invention is often a solid preparation for oral administration.
本発明の製剤は、製剤の形態に応じて種々の担体成分又は添加剤を利用できる。固形製剤において、担体成分又は添加剤としては、賦形剤、結合剤及び崩壊剤のうち少なくとも一種を使用する場合が多い。 In the preparation of the present invention, various carrier components or additives can be used depending on the form of the preparation. In solid preparations, at least one of an excipient, a binder and a disintegrant is often used as a carrier component or additive.
賦形剤としては、例えば、エリスリトール、マルチトール、マンニトール、ソルビトール、キシリトール、ラクチトールなどの糖アルコール、精製白糖、白糖、トレハロース、乳糖、還元麦芽糖水アメ、粉末還元麦芽糖水アメ、ブドウ糖、麦芽糖などの糖類、コーンスターチ、結晶セルロース、粉末セルロース、リン酸一水素カルシウム、リン酸水素カルシウム、無水リン酸水素カルシウム、乳酸カルシウム、沈降炭酸カルシウム、軽質無水ケイ酸、含水二酸化ケイ素、二酸化ケイ素などが挙げられる。結合剤としては、例えば、アラビアゴム末、ヒドロキシエチルセルロース、ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース(HPC)、ヒドロキシプロピルメチルセルロース(HPMC)、メチルセルロース、カルボキシメチルセルロース、カルボキシメチルエチルセルロースなどのセルロース誘導体、ポビドン(PVP)、ビニルピロリドン共重合体(コポリビドン)、ポリビニルアルコール(PVA)、アクリル酸系高分子、プルラン、デキストリン、アルファー化デンプン、ヒドロキシプロピルスターチ、トラガント末、結晶セルロース、低置換度ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース(L−HPC)などが挙げられる。崩壊剤としては、例えば、クロスカルメロースナトリウム、低置換度ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース、カルメロースカルシウム、クロスポビドン、コーンスターチ、カルボキシメチルスターチナトリウム、ヒドロキシプロピルスターチ、部分α化デンプンなどが挙げられる。 Examples of excipients include sugar alcohols such as erythritol, maltitol, mannitol, sorbitol, xylitol, and lactitol, purified sucrose, sucrose, trehalose, lactose, reduced maltose water candy, powdered reduced maltose water candy, glucose, maltose, and the like. Examples include saccharides, corn starch, crystalline cellulose, powdered cellulose, calcium monohydrogen phosphate, calcium hydrogen phosphate, anhydrous calcium hydrogen phosphate, calcium lactate, precipitated calcium carbonate, light anhydrous silicic acid, hydrous silicon dioxide, silicon dioxide and the like. Examples of the binder include gum arabic powder, hydroxyethylcellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose (HPC), hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC), cellulose derivatives such as methylcellulose, carboxymethylcellulose, carboxymethylethylcellulose, povidone (PVP), vinylpyrrolidone copolymer Examples include coalescence (copolyvidone), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), acrylic polymer, pullulan, dextrin, pregelatinized starch, hydroxypropyl starch, tragacanth powder, crystalline cellulose, low-substituted hydroxypropylcellulose (L-HPC), and the like. . Examples of the disintegrant include croscarmellose sodium, low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, carmellose calcium, crospovidone, corn starch, sodium carboxymethyl starch, hydroxypropyl starch, and partially pregelatinized starch.
製剤において、さらに他の添加剤、例えば、滑沢剤、流動化剤、着色剤、pH調節剤、甘味剤、香料、防腐剤などを使用してもよい。他の担体成分又は添加剤としては、滑沢剤(例えば、ステアリン酸マグネシウム、ステアリン酸カルシウム、タルク、ショ糖脂肪酸エステル、グリセリン脂肪酸エステル、硬化油、マクロゴール6000など)、流動化剤(例えば、軽質無水ケイ酸、含水二酸化ケイ素、カオリンなど)、抗酸化剤(例えば、ジブチルヒドロキシトルエン(BHT)、没食子酸プロピル、ブチルヒドロキシアニソール(BHA)、トコフェロール、クエン酸など)、保存剤(パラオキシ安息香酸エステル類など)、着色剤(例えば、リボフラビン、ビタミンB12、酸化チタン、黄色三二酸化鉄、三二酸化鉄、食用赤色2号、食用赤色3号、食用赤色102号、食用赤色104号、食用赤色105号、食用赤色106号、食用黄色4号、食用黄色5号、食用緑色3号、食用青色1号、食用青色2号、銅クロロフィルナトリウム、銅クロロフィルなど)、pH調節剤(例えば、水酸化ナトリウム、クエン酸ナトリウム、塩酸、炭酸水素ナトリウム、炭酸ナトリウム、乳酸カルシウム、リン酸、リン酸二カリウム、リン酸水素ナトリウム、リン酸二水素カリウム、リン酸二水素ナトリウムなど)、甘味剤(例えば、ショ糖、マンニトール、D−ソルビトール、キシリトール、アスパルテーム、ステビア、グリチルリチン酸ジカリウム、アセスルファームK、スクラロースなど)、香料(例えば、L−メントール、ハッカ油、ユーカリ油、オレンジ油、チョウジ油、テレビン油、ウイキョウ油、バニリンなど)、界面活性剤(ポリオキシエチレン硬化ヒマシ油、モノステアリン酸グリセリン、ソルビタン脂肪酸エステル(モノステアリン酸ソルビタン、モノラウリン酸ソルビタンなど)、ポリオキシエチレンポリオキシプロピレン、ポリソルベート類、ラウリル硫酸ナトリウム、マクロゴール類、ショ糖脂肪酸エステルなど)、可塑剤(クエン酸トリエチル、ポリエチレングリコール、トリアセチン、セタノールなど)、矯味剤又は着香剤(メントールなど)、吸着剤、防腐剤、湿潤剤、帯電防止剤などが挙げられる。 In the preparation, further additives such as a lubricant, a fluidizing agent, a coloring agent, a pH adjusting agent, a sweetening agent, a fragrance, and an antiseptic may be used. Other carrier components or additives include lubricants (eg, magnesium stearate, calcium stearate, talc, sucrose fatty acid ester, glycerin fatty acid ester, hydrogenated oil, macrogol 6000, etc.), fluidizing agents (eg, light Silicic anhydride, hydrous silicon dioxide, kaolin, etc.), antioxidants (eg, dibutylhydroxytoluene (BHT), propyl gallate, butylhydroxyanisole (BHA), tocopherol, citric acid, etc.), preservatives (paraoxybenzoic acid esters) Etc.), coloring agent (for example, riboflavin, vitamin B12, titanium oxide, yellow ferric oxide, ferric oxide, edible red No. 2, edible red No. 3, edible red No. 102, edible red No. 104, edible red No. 105) , Edible red No. 106, Edible yellow No. 4, Edible yellow No. 5, Edible green No. 3, Edible Blue No. 1, Edible Blue No. 2, Copper Chlorophyll Sodium, Copper Chlorophyll, etc.), pH adjuster (eg, sodium hydroxide, sodium citrate, hydrochloric acid, sodium bicarbonate, sodium carbonate, calcium lactate, phosphoric acid) , Dipotassium phosphate, sodium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, etc.), sweeteners (eg, sucrose, mannitol, D-sorbitol, xylitol, aspartame, stevia, stevia, dipotassium glycyrrhizinate, acese LeFarm K, sucralose, etc.), flavor (for example, L-menthol, peppermint oil, eucalyptus oil, orange oil, clove oil, turpentine oil, fennel oil, vanillin, etc.), surfactant (polyoxyethylene hydrogenated castor oil, monostearin) Acid glycerin, sorbitan fat Acid esters (such as sorbitan monostearate and sorbitan monolaurate), polyoxyethylene polyoxypropylene, polysorbates, sodium lauryl sulfate, macrogol, sucrose fatty acid esters, etc., plasticizers (triethyl citrate, polyethylene glycol, triacetin) , Cetanol, etc.), flavoring agents or flavoring agents (menthol, etc.), adsorbents, preservatives, wetting agents, antistatic agents and the like.
固形剤は必要に応じて、HPC、HPMC、ポビドンなどの水溶性基剤(又は高分子)、エチルセルロースなどの不溶性基剤(又は高分子)、腸溶性基剤、胃溶性基剤、糖類などでコーティングしてもよい。 If necessary, the solid preparation may be a water-soluble base (or polymer) such as HPC, HPMC, or povidone, an insoluble base (or polymer) such as ethyl cellulose, an enteric base, a gastric base, or a saccharide. It may be coated.
固形剤は慣用の方法で製造できる。前記活性成分と担体成分とを混合して粉剤を調製してもよく、通常、活性成分と担体成分とを造粒し、必要により造粒物を整粒して粒剤(細粒剤又は顆粒剤)を調製するか、又は造粒物を含む混合物(特に、造粒物と担体成分との混合物)を打錠することにより裸錠を調製できる。カプセル剤は前記粒剤をカプセルに充填することにより調製できる。 The solid agent can be produced by a conventional method. The active ingredient and the carrier component may be mixed to prepare a powder. Usually, the active ingredient and the carrier component are granulated, and if necessary, the granulated product is granulated to give granules (fine granules or granules). An uncoated tablet can be prepared by tableting a mixture containing the granulated product (particularly a mixture of the granulated product and the carrier component). Capsules can be prepared by filling capsules with the granules.
造粒は、慣用の方法、例えば、撹拌造粒法、流動層造粒法、押出造粒法、乾式造粒法などで行うことができる。好ましい造粒法は流動層造粒法である。造粒においては、活性成分と担体成分とを、結合剤を含む溶液を用いて造粒する場合が多く、例えば、活性成分と担体成分との流動層に結合剤を含む溶液を噴霧することにより造粒できる。コーティング製剤は、フィルムコーティング機を用いて、コーティング基剤を含有するコーティング剤を未コーティング製剤(素顆粒、素錠など)に噴霧することにより得ることができる。 Granulation can be performed by a conventional method, for example, stirring granulation method, fluidized bed granulation method, extrusion granulation method, dry granulation method and the like. A preferred granulation method is a fluidized bed granulation method. In granulation, an active ingredient and a carrier component are often granulated using a solution containing a binder. For example, by spraying a solution containing a binder on a fluidized bed of the active ingredient and the carrier component. Can be granulated. The coating preparation can be obtained by spraying a coating agent containing a coating base onto an uncoated preparation (elementary granule, plain tablet, etc.) using a film coating machine.
液剤において、担体成分としては、水性媒体(精製水、エタノール含有精製水など)、アルコール類(エタノール、グリセリンなど)、水溶性高分子などが利用できる。担体成分としては、精製水、エタノール含有精製水などを用いる場合が多い。半固形製剤の担体成分としては、油性基剤(植物油などの脂質、ワセリン、流動パラフィンなど)、親水性基剤(乳剤性基剤)などが利用できる。また、添加剤としては、崩壊助剤、抗酸化剤又は酸化防止剤、界面活性剤、乳化剤、分散剤、懸濁剤、溶解補助剤、増粘剤、pH調整剤又は緩衝剤、防腐剤又は保存剤(パラベン類など)、殺菌剤又は抗菌剤、帯電防止剤、矯味剤又はマスキング剤(例えば、甘味剤など)、清涼化剤、着色剤、矯臭剤又は香料などが挙げられる。 In the liquid agent, an aqueous medium (purified water, ethanol-containing purified water, etc.), alcohols (ethanol, glycerin, etc.), a water-soluble polymer, etc. can be used as the carrier component. As the carrier component, purified water, ethanol-containing purified water and the like are often used. As the carrier component of the semi-solid preparation, an oily base (lipid such as vegetable oil, petrolatum, liquid paraffin, etc.), a hydrophilic base (emulsion base) and the like can be used. Examples of additives include disintegration aids, antioxidants or antioxidants, surfactants, emulsifiers, dispersants, suspension agents, solubilizers, thickeners, pH adjusters or buffers, preservatives or Preservatives (such as parabens), bactericides or antibacterial agents, antistatic agents, taste-masking agents or masking agents (such as sweeteners), cooling agents, coloring agents, flavoring agents, and fragrances.
液剤は、各成分を担体成分に溶解又は分散させ、必要により濾過又は滅菌処理し、所定の容器に充填することにより調製できる。半固形製剤も慣用の方法、例えば、各成分と担体成分とを混合し、必要により滅菌処理し、所定の容器に充填したり、基材に塗布することにより調製できる。 The liquid preparation can be prepared by dissolving or dispersing each component in a carrier component, filtering or sterilizing if necessary, and filling a predetermined container. A semi-solid preparation can also be prepared by a conventional method, for example, by mixing each component and a carrier component, sterilizing if necessary, filling a predetermined container, or applying to a substrate.
なお、本発明の製剤は、ヒアルロン酸、スクラロース、グルコサミンなどを含んでいてもよいが、ヒアルロン酸、スクラロース、グルコサミンを含まない場合が多い。また、コンドロイチン硫酸を含んでいてもよいが、本発明では必ずしも必要ではない。本発明の製剤はこのような成分を含まなくても高い安定性を示す。 The preparation of the present invention may contain hyaluronic acid, sucralose, glucosamine, etc., but often does not contain hyaluronic acid, sucralose, glucosamine. Moreover, although chondroitin sulfate may be included, it is not necessarily required in the present invention. The preparation of the present invention exhibits high stability even without such components.
本発明の製剤は、哺乳類に適用でき、ヒトに投与するのに適している。本発明の製剤の投与量は、症状の程度、年齢、性別、体重、投与経路などに応じて選択でき、フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)の単位投与量は、例えば、1〜300mg(例えば、10〜250mg)、好ましくは50〜200mg、さらに好ましくは75〜150mg程度であってもよい。また、アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドの単位投与量は、アスコルビン酸換算で、例えば、10〜1000mg(例えば、25〜750mg)、好ましくは50〜600mg、さらに好ましくは100〜500mg程度であってもよい。 The formulations of the present invention can be applied to mammals and are suitable for administration to humans. The dosage of the preparation of the present invention can be selected according to the degree of symptoms, age, sex, body weight, administration route, etc. The unit dosage of fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide vitamin B1 derivative) is, for example, It may be about 1 to 300 mg (for example, 10 to 250 mg), preferably 50 to 200 mg, more preferably about 75 to 150 mg. The unit dose of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside may be, for example, 10 to 1000 mg (for example, 25 to 750 mg), preferably 50 to 600 mg, and more preferably about 100 to 500 mg in terms of ascorbic acid.
フルスルチアミン又はその塩(又はジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体)及びアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド(アスコルビン酸換算)の投与量は、1日あたり、20〜1500mg、好ましくは50〜1000mg(例えば、75〜750mg)、さらに好ましくは100〜750mg(例えば、150〜600mg)程度であってもよい。 The dose of fursultiamine or a salt thereof (or disulfide type vitamin B1 derivative) and ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (ascorbic acid equivalent) is 20 to 1500 mg, preferably 50 to 1000 mg (for example, 75 to 750 mg) per day. More preferably, it may be about 100 to 750 mg (for example, 150 to 600 mg).
本発明の製剤は、1日当たり1回又は複数回(例えば、2〜6回)に分けて投与できる。 The preparation of the present invention can be administered once or a plurality of times (for example, 2 to 6 times) per day.
以下に、試験例及び実施例に基づいて本発明をより詳細に説明するが、本発明はこれらの実施例によって限定されるものではない。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail based on test examples and examples, but the present invention is not limited to these examples.
[試験例1〜4]
ビタミンC類としてのアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド(AA2G)又はアスコルビン酸(AsA)と、ビタミンB1類としてのフルスルチアミン塩酸塩(TTFD-HCL)とを、表1に示す量的割合で秤量し、乳鉢にて乾式混合し、散剤を得た。
[Test Examples 1 to 4]
Weigh ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G) or ascorbic acid (AsA) as vitamin Cs and fursultiamine hydrochloride (TTFD-HCL) as vitamins B1 at the quantitative ratios shown in Table 1, Dry-mixed in a mortar to obtain a powder.
外観安定性
試験例1〜4の散剤をガラス瓶に収容し、40℃75%RHでガラス瓶開栓状態で2週間保存し、保存後の外観変化をカラーコンピュター(S&Mカラーコンピュター、スガ試験機)により測定し、色差(ΔE)で評価した。結果を表1に示す。
Appearance stability test powders of Examples 1 to 4 were stored in a glass bottle, stored at 40 ° C. and 75% RH for 2 weeks with the glass bottle open, and the appearance change after storage was checked with a color computer (S & M color computer, Suga test machine). Measured and evaluated by color difference (ΔE). The results are shown in Table 1.
VC類の割合1:組成物100質量部に対するVC類の割合
VC類の割合2:TTFD−HCL 1質量部に対するVC類の割合
VC類:ビタミンC類
AA2G:アスコルビン酸2−グルコシド
AsA:アスコルビン酸
ΔE(AA2G):AA2Gを含む散剤の色差ΔE値
ΔE(AsA):AsAを含む散剤の色差ΔE値
表1から明らかなように、VC類としてアスコルビン酸を配合すると、そのΔEは10以上であり、変色が著しいのに対して、VC類としてアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを配合すると、そのΔEは4以下であり、変色がほとんどなく、変色を著しく抑制できる。なお、試験例1において、AA2G 100mgに代えて、AA2G 10(mg)ではΔE(AA2G)1.4であり、AA2G 50(mg)ではΔE(AA2G)1.9であり、AA2G 20000(mg)ではΔE(AA2G)2.0であり、VC類としてアスコルビン酸の代わりにアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを配合することで、変色を著しく抑制できる。これらの結果から、組成物全体100質量部に対してAA2Gの割合が6〜90質量部、TTFD−HCL 1質量部に対してAA2Gの割合が0.1〜15質量部(例えば、0.1〜5質量部)において、変色を著しく抑制できる。
Ratio of VCs 1: Ratio of VCs to 100 parts by mass of composition Ratio of VCs 2: Ratio of VCs to 1 part by mass of TTFD-HCL VCs: Vitamin Cs AA2G: Ascorbic acid 2-glucoside AsA: Ascorbic acid ΔE (AA2G): Color difference ΔE value of powder containing AA2G ΔE (AsA): Color difference ΔE value of powder containing AsA As can be seen from Table 1, when ascorbic acid is added as VCs, ΔE is 10 or more. In contrast, when the ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is added as a VC, the ΔE is 4 or less and there is almost no discoloration, and discoloration can be remarkably suppressed. In Test Example 1, instead of AA2G 100 mg, AA2G 10 (mg) has ΔE (AA2G) 1.4, AA2G 50 (mg) has ΔE (AA2G) 1.9, and AA2G 20000 (mg) Then, it is (DELTA) E (AA2G) 2.0, and discoloration can be suppressed remarkably by mix | blending ascorbic acid 2-glucoside instead of ascorbic acid as VCs. From these results, the ratio of AA2G is 6 to 90 parts by mass with respect to 100 parts by mass of the whole composition, and the ratio of AA2G is 0.1 to 15 parts by mass (for example, 0.1 to 1 part by mass of TTFD-HCL). -5 mass parts), the discoloration can be remarkably suppressed.
[試験例5]
ビタミンC類としてのアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド(AA2G)又はアスコルビン酸(AsA)と、ビタミンB1類としての硝酸チアミン(VB1)とを表2に示す量的割合で秤量し、乳鉢にて乾式混合し、散剤を得た。そして、試験例1〜4と同様に外観安定性を評価した。
[Test Example 5]
Ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G) or ascorbic acid (AsA) as vitamins C and thiamine nitrate (VB1) as vitamins B1 are weighed in the quantitative ratios shown in Table 2, and dry-mixed in a mortar. , Got powder. And external appearance stability was evaluated similarly to Test Examples 1-4.
表2から明らかなように、ビタミンB1類として硝酸チアミンを用い、VC類としてAsAを配合すると、そのΔEは21.6であり、変色が著しく、VC類としてAA2Gを配合しても、そのΔEは15.5で、変色を著しく抑制することはできない。 As can be seen from Table 2, when thiamin nitrate is used as vitamin B1 and AsA is blended as VCs, its ΔE is 21.6, discoloration is remarkable, and even when AA2G is blended as VCs, its ΔE Is 15.5, and the discoloration cannot be remarkably suppressed.
[試験例6]
ビタミンC類としてアスコルビン酸2−グルコシド(AA2G)又はアスコルビン酸(AsA)と、ビタミンB1類中のジスルフィド型ビタミンB1誘導体であるビスイブチアミン(Bis)とを表3に示す量的割合で秤量し、乳鉢にて乾式混合し、散剤を得た。そして、試験例1〜5と同様に外観安定性を評価した。
[Test Example 6]
Ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (AA2G) or ascorbic acid (AsA) as vitamin Cs and disulfide-type vitamin B1 derivative bisivethiamine (Bis) in vitamins B1 are weighed in the quantitative ratios shown in Table 3. The mixture was dry-mixed in a mortar to obtain a powder. And external appearance stability was evaluated similarly to Test Examples 1-5.
ΔE(AA2G):括弧( )内は保存後の形態を示す
ΔE(AsA):括弧( )内は保存後の形態を示す
表3から明らかなように、ビタミンB1類としてビスイブチアミンを用い、VC類としてAsAを配合すると、そのΔEは60.4であり、変色が極めて著しく、VC類としてAA2Gを配合しても、そのΔEは43.8で、変色を著しく抑制することはできない。さらには、試験例6では、40℃75%RHで開栓して2週間保存すると、いずれもペースト状となり、試験例1〜5では起きなかった形態変化を起こした。なお、ビスイブチアミンのみを40℃75%RHで開栓して2週間保存しても、形態変化は起こさず(白色粉末)、ΔEは1.2であった。
ΔE (AA2G): parentheses () indicate the form after storage ΔE (AsA): parentheses () indicate the form after storage As is clear from Table 3, bibisbutiamine was used as vitamin B1 class, When AsA is blended as VCs, its ΔE is 60.4, and the color change is extremely remarkable. Even when AA2G is blended as VCs, its ΔE is 43.8, and the color change cannot be remarkably suppressed. Furthermore, in Test Example 6, when the cap was opened at 40 ° C. and 75% RH and stored for 2 weeks, all became paste-like, and the shape change that did not occur in Test Examples 1 to 5 occurred. In addition, even when only bibisbutiamine was opened at 40 ° C. and 75% RH and stored for 2 weeks, the shape did not change (white powder), and ΔE was 1.2.
[試験例7]
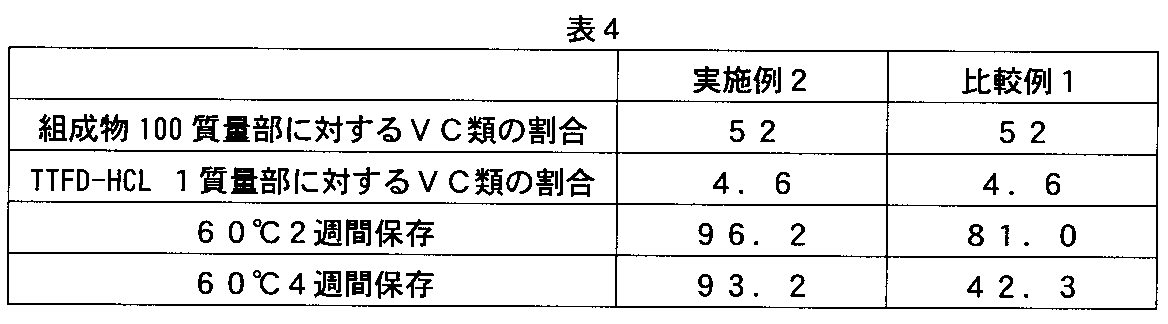
製剤例1(錠剤)
アスコルビン酸2−グルコシド 250g、フルスルチアミン塩酸塩 54.6g、結晶セルロース(セオラスPH101、旭化成)110.6gを流動層造粒機(LAB−1、パウレック)にて、6%ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース(HPC−L)水溶液240gを噴霧することにより、造粒し、乾燥後、整粒機(パワーミル、スクリーン径1.5mm)にて整粒した。得られた整粒末343.7gに結晶セルロース(セオラスPH101、旭化成)19.2g、低置換度ヒドロキシプロピルセルロース(LH31、信越化学)19.2g、ステアリン酸マグネシウム(軽質、植物性、太平化学産業)1.9gをタンブラー混合機(15L)にて回転数30rpmで、3分間混合し、混合末とした。得られた混合末をロータリー式打錠機(コレクト19K、菊水製作所)にて8.5mmφ、7Rの杵を用い、回転数20rpm、打錠圧7kNで打錠し、素錠(質量240mg、厚み4.6mm)を得た。得られた素錠の平衡相対湿度(ERH)は27.0%であった。
[Test Example 7]
Formulation Example 1 (tablet)
Ascorbic acid 2-glucoside (250 g), fursultiamine hydrochloride (54.6 g), and crystalline cellulose (Ceolus PH101, Asahi Kasei) (110.6 g) were added to a 6% hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) in a fluidized bed granulator (LAB-1, Paulek). -L) The aqueous solution 240g was granulated by spraying, dried, and then sized with a sizing machine (power mill, screen diameter 1.5 mm). 343.7 g of the obtained sized powder is added to 19.2 g of crystalline cellulose (Theorus PH101, Asahi Kasei), 19.2 g of low-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose (LH31, Shin-Etsu Chemical), magnesium stearate (light, vegetable, Taihei Chemical Industry) ) 1.9 g was mixed with a tumbler mixer (15 L) at a rotation speed of 30 rpm for 3 minutes to obtain a mixed powder. The obtained mixed powder was tableted with a rotary tableting machine (collect 19K, Kikusui Seisakusho) using a 8.5 mmφ, 7R punch at a rotation speed of 20 rpm and a tableting pressure of 7 kN, and an uncoated tablet (mass 240 mg, thickness) 4.6 mm). The obtained uncoated tablet had an equilibrium relative humidity (ERH) of 27.0%.
比較例1
アスコルビン酸2−グルコシドに代えてアスコルビン酸を用いる以外、製剤例1と同様にして素錠(質量240mg、厚み4.6mm)を得た。得られた素錠の平衡相対湿度(ERH)は27.2%であった。
Comparative Example 1
An uncoated tablet (mass 240 mg, thickness 4.6 mm) was obtained in the same manner as in Preparation Example 1 except that ascorbic acid was used instead of ascorbic acid 2-glucoside. The uncoated tablet obtained had an equilibrium relative humidity (ERH) of 27.2%.
薬物含量安定性
製剤例1及び比較例1の素錠を60℃でガラス瓶に密栓保存し、保存後の素錠中のフルスルチアミン塩酸塩含量をHPLC法にて測定し、フルスルチアミン塩酸塩残存率(%)を算出した。結果を表4に示す。
Drug content stable preparation Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 uncoated tablets were stored tightly in glass bottles at 60 ° C., and the content of fursultiamine hydrochloride in the uncoated tablets after storage was measured by HPLC method. The residual rate (%) was calculated. The results are shown in Table 4.
表4から明らかなように、アスコルビン酸の代わりにアスコルビン酸2−グルコシドを配合すると、フルスルチアミン塩酸塩を著しく安定化できる。 As is clear from Table 4, when ascorbic acid 2-glucoside is added instead of ascorbic acid, fursultiamine hydrochloride can be remarkably stabilized.
本発明の製剤は、肉体疲労、精神疲労、眼精疲労、白内障、神経痛、筋肉痛、関節痛(腰痛、肩こり、五十肩など)、首すじのこり、リウマチ、手足のしびれ、末梢神経炎、末梢神経麻痺、糖尿病性神経症、心筋代謝障害、便秘、胃腸運動障害、術後腸管麻痺、脚気、痔、しみ、そばかす、日焼け・かぶれによる色素沈着、歯茎からの出血、鼻出血、免疫機能疾患、神経機能疾患などを予防又は治療、緩和するのに有効である。また、肉体疲労時、病中病後、食欲不振、栄養障害、発熱性消耗疾患、産前産後、妊娠・授乳期、病中・病後の体力低下時、発育期、老年期、甲状腺機能亢進症、ウエルニッケ脳症、精神的・心理的変調(集中力欠如、神経質、不眠症、非強調性)などにおけるビタミンB1類及びビタミンC類の補給、栄養補給、滋養強壮、虚弱体質に有効である。 The preparation of the present invention comprises physical fatigue, mental fatigue, eye strain, cataract, neuralgia, muscle pain, joint pain (back pain, stiff shoulders, fifty shoulders, etc.), neck stiffness, rheumatism, numbness of limbs, peripheral neuritis, peripheral nerve palsy , Diabetic neuropathy, myocardial metabolism disorder, constipation, gastrointestinal motility disorder, postoperative intestinal paralysis, beriberi, hemorrhoids, blotches, freckles, pigmentation due to sunburn and rash, bleeding from gums, nasal bleeding, immune function disease, nerve function It is effective for preventing, treating, or alleviating diseases. Also, during physical fatigue, after sickness, anorexia, malnutrition, febrile wasting disease, postpartum, pregnancy / lactation, during physical / post-health decline, development, old age, hyperthyroidism, Wernicke encephalopathy, mental and psychological modulation (inability to concentrate, nervousness, insomnia, non-enhancement) supplementation of vitamin B 1 class and vitamin C in such, nutrition is effective tonic nourishment, the frail.
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009222165A JP2011068614A (en) | 2009-09-28 | 2009-09-28 | Vitamin preparation |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009222165A JP2011068614A (en) | 2009-09-28 | 2009-09-28 | Vitamin preparation |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011068614A true JP2011068614A (en) | 2011-04-07 |
Family
ID=44014259
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009222165A Withdrawn JP2011068614A (en) | 2009-09-28 | 2009-09-28 | Vitamin preparation |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2011068614A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113260415A (en) * | 2018-12-28 | 2021-08-13 | 小林制药株式会社 | Deep body temperature improving agent |
-
2009
- 2009-09-28 JP JP2009222165A patent/JP2011068614A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113260415A (en) * | 2018-12-28 | 2021-08-13 | 小林制药株式会社 | Deep body temperature improving agent |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JPWO2002096406A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition | |
| KR20030097892A (en) | Drug preparations | |
| JP2006290812A (en) | Analgesic preparation | |
| ES2635763T3 (en) | Nutritional Supplement Composition | |
| WO2012001977A1 (en) | Disintegrating composition and easily disintegrating compression molded article | |
| US20160000716A1 (en) | Method of treating vitamin b12 deficiency | |
| JP2010024181A (en) | Solid preparation and method for producing the same | |
| JP4674955B2 (en) | Amino sugar-containing preparation | |
| JP2002145779A (en) | Composition for treatment or prophylaxis of arthralgia | |
| JP2004002482A (en) | Pharmaceutical preparation containing aminosugar | |
| JP2011068614A (en) | Vitamin preparation | |
| EP3238712A1 (en) | Very rapidly disintegrating tablet, and method for producing same | |
| JP2005281324A (en) | Amino sugar-containing preparation | |
| JP2008201712A (en) | Film-coated preparation | |
| JP2013032407A (en) | Composition for treating or preventing arthralgia | |
| JP2004026846A (en) | Therapeutic or prophylactic composition for arthralgia | |
| JP2005162713A (en) | Composition for oral administration | |
| JP2018076312A (en) | Pharmaceutical composition containing acetaminophen, isopropylantipyrine and ginger-derived components | |
| WO2022133555A1 (en) | Solid pharmaceutical composition containing vitamin d and calcium salt, method for treating or preventing conditions related to low ingestion of and/or higher need for calcium, use of the solid pharmaceutical composition, and pharmaceutical product or supplement | |
| JP5329866B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition and preventive and therapeutic agent for joint disorders | |
| JP5241127B2 (en) | Analgesic composition | |
| JP2019194269A (en) | Composition for treatment or prevention of arthralgia | |
| JP2018127501A (en) | Compositions for treatment or prophylaxis of arthralgia | |
| JP5896806B2 (en) | Oral composition | |
| JP2019199486A (en) | Amino sugar-containing preparation |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A300 | Withdrawal of application because of no request for examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A300 Effective date: 20121204 |