JP2010121831A - Refrigerating cycle - Google Patents
Refrigerating cycle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010121831A JP2010121831A JP2008294844A JP2008294844A JP2010121831A JP 2010121831 A JP2010121831 A JP 2010121831A JP 2008294844 A JP2008294844 A JP 2008294844A JP 2008294844 A JP2008294844 A JP 2008294844A JP 2010121831 A JP2010121831 A JP 2010121831A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- temperature
- expansion valve
- refrigerant
- compressor
- low
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B40/00—Subcoolers, desuperheaters or superheaters
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B41/00—Fluid-circulation arrangements
- F25B41/30—Expansion means; Dispositions thereof
- F25B41/31—Expansion valves
- F25B41/33—Expansion valves with the valve member being actuated by the fluid pressure, e.g. by the pressure of the refrigerant
- F25B41/335—Expansion valves with the valve member being actuated by the fluid pressure, e.g. by the pressure of the refrigerant via diaphragms
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2309/00—Gas cycle refrigeration machines
- F25B2309/06—Compression machines, plants or systems characterised by the refrigerant being carbon dioxide
- F25B2309/061—Compression machines, plants or systems characterised by the refrigerant being carbon dioxide with cycle highest pressure above the supercritical pressure
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2341/00—Details of ejectors not being used as compression device; Details of flow restrictors or expansion valves
- F25B2341/06—Details of flow restrictors or expansion valves
- F25B2341/068—Expansion valves combined with a sensor
- F25B2341/0683—Expansion valves combined with a sensor the sensor is disposed in the suction line and influenced by the temperature or the pressure of the suction gas
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2700/00—Sensing or detecting of parameters; Sensors therefor
- F25B2700/21—Temperatures
- F25B2700/2115—Temperatures of a compressor or the drive means therefor
- F25B2700/21151—Temperatures of a compressor or the drive means therefor at the suction side of the compressor
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Temperature-Responsive Valves (AREA)
- Compression-Type Refrigeration Machines With Reversible Cycles (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、カーエアコン等に使用される冷凍サイクルに係り、特に、圧縮機、凝縮器、蒸発器、内部熱交換器、及び、膨張弁を備え、内部熱交換器において、凝縮器から膨張弁に導かれる高温の冷媒と蒸発器から圧縮機の吸入側に導かれる低温の冷媒との間で熱交換を行うようにされた冷凍サイクル関する。 The present invention relates to a refrigeration cycle used for a car air conditioner and the like, and in particular, includes a compressor, a condenser, an evaporator, an internal heat exchanger, and an expansion valve. This relates to a refrigeration cycle in which heat is exchanged between the high-temperature refrigerant introduced to the refrigerant and the low-temperature refrigerant introduced from the evaporator to the suction side of the compressor.
カーエアコン等に使用される冷凍サイクルにおいて、冷却能力等を向上させるため、従来、例えば,図9に示される如くのものが提案ないし実用に供されている。すなわち、図示例の冷凍サイクル10は、圧縮機101、凝縮器102、蒸発器103、内部熱交換器104、及び、膨張弁110(後述)を備え、内部熱交換器104において、凝縮器102から膨張弁110に導かれる高温高圧の冷媒(液相)と蒸発器103から圧縮機101の吸入側に導かれる低温低圧の冷媒(気相)との間で熱交換を行うようにしたものである(例えば、下記特許文献1、2も参照)。
In order to improve the cooling capacity and the like in a refrigeration cycle used for a car air conditioner or the like, conventionally, for example, the one shown in FIG. 9 has been proposed or put into practical use. That is, the
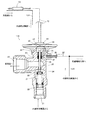
かかる冷凍サイクル10に使用されている膨張弁110の一例を図10に示す。図示例の膨張弁110は、弁本体20の下部に内部熱交換器104からの高温冷媒を導入するための流入口21と弁シート部25(弁口26)を有する弁室24が設けられるとともに、中央部に流出口22が設けられ、また、弁本体20の上部左右に感温用流入口31及び流出口32が設けられ、弁本体20の最上部には、感温用流入口31から流出口32へ流れる冷媒の温度変化及び圧力変化に応動する感温感圧応動手段としてのダイアフラム装置40が取り付けられている。
An example of the
前記弁室24には、前記弁口26を開閉するボール弁体30と該ボール弁体30を閉弁方向に付勢するコイルばね27が配在されている。
A
前記ダイアフラム装置40は、前記ボール弁体30を駆動ロッド35及び連結体36を介して開閉方向(上下方向)に駆動するためのダイアフラム42を有し、該ダイアフラム42を隔壁としてその上下には、上側圧力室43と下側圧力室44とが画成されている。上側圧力室43は所定圧力のガスが封入されてキャップ46で密閉されている。下側圧力室44は、連通開口部45を介して前記感温用流入口31及び流出口32に連通しており、前記ダイアフラム42の下面側には、蒸発器103から内部熱交換器104に導かれる低温冷媒の圧力が作用するようになっている。
The
なお、前記下側圧力室44、感温用流入口31及び流出口32と前記冷媒流出口22との連通・流通を遮断すべく、弁本体20における駆動ロッド35が通される内部中央付近に穴38が設けられるとともに、この穴38の内周面と駆動ロッド35の外周面との間にはシール材としてのOリング39が介装されている。また、弁室24の下部には、ばね圧調節用ナット28が螺合せしめられ、このばね圧調節用ナット28の非螺合部分と弁室24内周面との間にはシール材としてのOリング29が介装されている。
The
したがって、かかる構成の膨張弁110では、流出口22から前記蒸発器103へ導出される冷媒の流量(圧力降下度及び温度降下度)を、前記内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行う前の低温冷媒の温度及び圧力に応じて調整するようになっている。
Therefore, in the
しかしながら、前記内部熱交換器104や膨張弁110を備えた冷凍サイクル10では、内部熱交換器104において熱交換が行われることにより、圧縮機101に吸入される冷媒の温度が上昇し、これに伴い圧縮機内部(吐出)温度が高くなり過ぎる場合があり、冷媒中に含まれるオイルが劣化して焼付等の不具合が発生するおそれがあった。
However, in the
かかる不具合の発生を防止すべく、前記特許文献1には、圧縮機吸入側の冷媒温度を感知して、三方弁で内部熱交換器を流れる冷媒量を調整する方策が提案されているが、かかる方策では、三方弁が必要とされるので、配管系が複雑になるとともに、部品点数等も増加する嫌いがある。 In order to prevent the occurrence of such inconvenience, Patent Document 1 proposes a method of detecting the refrigerant temperature on the compressor suction side and adjusting the amount of refrigerant flowing through the internal heat exchanger with a three-way valve. In such a measure, since a three-way valve is required, the piping system is complicated and the number of parts is increased.
また、前記特許文献2には、膨張弁にバイパス通路を設けて冷媒を冷却する方策が提案されているが、かかる方策では、負荷が変動した場合、圧縮機吸入側の冷媒温度をコントロールすることができないし、膨張弁の構造が複雑になり、コストアップを招く。 Patent Document 2 proposes a measure for cooling the refrigerant by providing a bypass passage in the expansion valve. In this measure, when the load fluctuates, the refrigerant temperature on the compressor suction side is controlled. And the structure of the expansion valve becomes complicated, resulting in an increase in cost.
本発明は、上記事情に鑑みてなされたもので、その目的とするところは、配管系や膨張弁の構造を複雑にすることなく、圧縮機吸入側の冷媒温度が過度に上昇することを確実かつ効果的に抑えることのできる冷凍サイクルを提供することにある。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and the object thereof is to ensure that the refrigerant temperature on the compressor suction side excessively increases without complicating the structure of the piping system and the expansion valve. Another object of the present invention is to provide a refrigeration cycle that can be effectively suppressed.
前記の目的を達成すべく、本発明に係る冷凍サイクルは、基本的には、圧縮機、凝縮器、蒸発器、内部熱交換器、及び、膨張弁を備え、前記内部熱交換器内において前記凝縮器から前記膨張弁に導かれる高温の冷媒と前記蒸発器から前記圧縮機の吸入側に導かれる低温の冷媒との間で熱交換を行うようにされ、前記圧縮機の吸入側に導かれる、前記内部熱交換器で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の温度及び/又は圧力を感知すべく、前記膨張弁に感温筒及び/又は外部圧力導入管が付設され、前記膨張弁において、前記蒸発器へ導出される冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度及び/又は圧力に応じて調整するようにされていることを特徴としている。 In order to achieve the above object, a refrigeration cycle according to the present invention basically includes a compressor, a condenser, an evaporator, an internal heat exchanger, and an expansion valve, and the internal heat exchanger includes the above-mentioned Heat is exchanged between a high-temperature refrigerant led from the condenser to the expansion valve and a low-temperature refrigerant led from the evaporator to the suction side of the compressor, and led to the suction side of the compressor. In order to sense the temperature and / or pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant after heat exchange with the internal heat exchanger, the expansion valve is provided with a temperature sensing tube and / or an external pressure introduction pipe, The flow rate of the refrigerant led out to the evaporator is adjusted according to the temperature and / or pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant after the heat exchange.
好ましい態様では、前記膨張弁は、前記外部圧力導入管を介して導入される熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の圧力変化に応動して弁体を開閉方向に駆動するダイアフラム装置等の駆動手段を備える。 In a preferred embodiment, the expansion valve is a driving means such as a diaphragm device that drives the valve body in the opening / closing direction in response to a pressure change of the low-temperature refrigerant after performing heat exchange introduced through the external pressure introduction pipe. Is provided.
他の好ましい態様では、前記膨張弁は、前記感温筒により感知される熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の温度変化に応動して弁体を開閉方向に駆動するダイアフラム装置等の駆動手段を備える。 In another preferred embodiment, the expansion valve includes a driving means such as a diaphragm device that drives the valve body in an opening / closing direction in response to a temperature change of the low-temperature refrigerant after performing heat exchange detected by the temperature sensing cylinder. Prepare.
本発明に係る冷凍サイクルでは、熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度及び圧力は、熱交換前のそれに比して高くなることを考慮して、圧縮機の吸入側に導かれる、内部熱交換器で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の温度及び/又は圧力を感知するための感温筒及び/又は外部冷媒圧力導入管が備えられ、膨張弁において、蒸発器へ導出する冷媒の流量(圧力降下度及び温度降下度)を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度及び/又は圧力に応じて調整するようにされているので、配管系や膨張弁の構造を複雑にすることなく、圧縮機吸入側の冷媒温度が過度に上昇することを確実かつ効果的に抑えることができる。そのため、圧縮機内部(吐出)温度が過度に上昇することを未然に防止でき、冷媒中に含まれるオイルが劣化して焼付等の不具合が発生する事態を確実に防止できる。 In the refrigeration cycle according to the present invention, in consideration of the fact that the temperature and pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant after heat exchange are higher than that before heat exchange, an internal heat exchanger led to the suction side of the compressor. A temperature sensing tube and / or an external refrigerant pressure introduction pipe for sensing the temperature and / or pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant after heat exchange is provided, and the refrigerant flow rate (pressure drop) to the evaporator is provided in the expansion valve. The temperature and the temperature drop degree) are adjusted according to the temperature and / or pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant after the heat exchange, so that the compressor intake side can be obtained without complicating the structure of the piping system and the expansion valve. It is possible to reliably and effectively suppress the refrigerant temperature from rising excessively. Therefore, it is possible to prevent an excessive rise in the compressor internal (discharge) temperature, and it is possible to reliably prevent the occurrence of problems such as seizure due to deterioration of the oil contained in the refrigerant.
また、本発明の冷凍サイクルは、既存の冷凍サイクル及びそれに使用されている膨張弁に極僅かに改造を加えるだけで、前記した効果が得られるので、大きなコストアップには繋がらないという利点も有する。 In addition, the refrigeration cycle of the present invention has the advantage that it does not lead to a significant increase in cost because the above-described effect can be obtained by making a slight modification to the existing refrigeration cycle and the expansion valve used therein. .
以下、本発明の冷凍サイクルの実施形態を図面を参照しながら説明する。
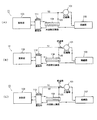
図1(A)、(B)、(C)は、本発明に係る冷凍サイクルの第1実施例、第2実施例、第3実施例を示している。また、図2、図3、図4は、それぞれ第1、第2、第3実施例で使用されている膨張弁111、112、113を示している。図1(A)、(B)、(C)に示される冷凍サイクル11、12、13並びに図2〜図4に示される膨張弁111、112、113については、前記した図9、図10に示される従来例の冷凍サイクル10並びに膨張弁110の各部に対応する部分には同一の符号が付されており、以下においては、従来例との相異点を重点的に説明する。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the refrigeration cycle of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
1A, 1B, and 1C show a first embodiment, a second embodiment, and a third embodiment of a refrigeration cycle according to the present invention. 2, 3 and 4 show the
第1実施例の冷凍サイクル11は、圧縮機101の吸入側に導かれる、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の圧力を感知すべく、内部熱交換器104と圧縮機101の吸入側とを結ぶ導管125の途中に外部圧力導入管50の一端部を連結するとともに、外部圧力導入管50の他端部を膨張弁111の下側圧力室44の底部近くに設けられた圧力導入通路54に接続し、膨張弁111において、蒸発器103へ導出される冷媒の流量(圧力降下度及び温度降下度)を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の圧力に応じて調整するようにしたものである。
In the refrigeration cycle 11 of the first embodiment, the
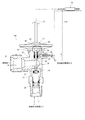
より詳細には、本第1実施例の冷凍サイクル11で使用される膨張弁111は、図2に示される如くに、下側圧力室44と感温用流入口31及び流出口32との連通を遮断すべく、従来例の連通開口部45を小径のロッド挿通穴62に変更し、このロッド挿通穴62と駆動ロッド35との間にシール材としてのOリング63を介装するとともに、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の圧力を前記外部圧力導入管50及び圧力導入通路54を介して前記下側圧力室44に導入するようにされている。
More specifically, the
このように本実施例の冷凍サイクル11では、熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度及び圧力は、熱交換前のそれに比して高くなることを考慮して、圧縮機101の吸入側に導かれる、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の圧力を感知するための外部冷媒圧力導入管50が備えられ、膨張弁111において、蒸発器103へ導出する冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の圧力に応じて調整するようにされているので、配管系や膨張弁の構造を複雑にすることなく、圧縮機101の吸入側の冷媒温度が過度に上昇することを確実かつ効果的に抑えることができる。そのため、圧縮機内部(吐出)温度が過度に上昇することを未然に防止でき、冷媒中に含まれるオイルが劣化して焼付等の不具合が発生する事態を確実に防止できる。
Thus, in the refrigeration cycle 11 of the present embodiment, the temperature and pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant after heat exchange are led to the suction side of the
また、本実施例の冷凍サイクルは、既存の冷凍サイクル及びそれに使用されている膨張弁に極僅かに改造を加えるだけで、前記した効果が得られるので、大きなコストアップには繋がらないという利点も有する。 In addition, the refrigeration cycle of the present embodiment has the advantage that it does not lead to a significant increase in cost because the above-described effects can be obtained by making a slight modification to the existing refrigeration cycle and the expansion valve used therein. Have.
第2実施例の冷凍サイクル12は、圧縮機101の吸入側に導かれる、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の温度を感知すべく、感温筒70を内部熱交換器104と圧縮機101の吸入側とを結ぶ導管125に近接配置するとともに、図3に示される如くに、感温筒70と膨張弁112の上側圧力室43とをキャピラリーチューブ72で結び、膨張弁112において、蒸発器103へ導出される冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度に応じて調整するようにしたものである。
In the
このような構成の冷凍サイクル12では、圧縮機101の吸入側に導かれる、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の温度を感知するための感温筒70が備えられ、膨張弁112において、蒸発器103へ導出する冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度に応じて調整するようにされているので、第1実施例と同様に、配管系や膨張弁の構造を複雑にすることなく、圧縮機101の吸入側の冷媒温度が過度に上昇することを確実かつ効果的に抑えることができる。そのため、圧縮機内部(吐出)温度が過度に上昇することを未然に防止でき、冷媒中に含まれるオイルが劣化して焼付等の不具合が発生する事態を確実に防止できる。
In the
また、本実施例の冷凍サイクルは、既存の冷凍サイクル及びそれに使用されている膨張弁に極僅かに改造を加えるだけで、前記した効果が得られるので、大きなコストアップには繋がらないという利点も有する。 In addition, the refrigeration cycle of the present embodiment has the advantage that it does not lead to a significant increase in cost because the above-described effects can be obtained by making a slight modification to the existing refrigeration cycle and the expansion valve used therein. Have.
第3実施例の冷凍サイクル13は、第1実施例の冷凍サイクル11及び第2実施例の冷凍サイクル12を組み合わせたもので、外部圧力導入管50及び感温筒70の両方を備えており、それに使用される膨張弁113の下側圧力室44周りは第1実施例のものと略同様であり、上側圧力室43周りは第2実施例のものと略同様に構成されていて、膨張弁113において、蒸発器103へ導出される冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の圧力及び温度に応じて調整するようにしたものである。
The
このような構成の冷凍サイクル13においても、第1実施例及び第2実施例と同様に、
圧縮機内部(吐出)温度が過度に上昇することを未然に防止でき、冷媒中に含まれるオイルが劣化して焼付等の不具合が発生する事態を確実に防止できる。
Also in the
It is possible to prevent the compressor internal (discharge) temperature from rising excessively, and to reliably prevent the occurrence of problems such as seizure due to deterioration of the oil contained in the refrigerant.
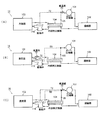
図5(A)、(B)、(C)は、本発明に係る冷凍サイクルの第4実施例、第5実施例、第6実施例を示している。また、図6は、第4実施例で使用されている膨張弁114を示し、図7は、第5実施例で使用されている膨張弁115を示し、図8は第6実施例で使用されている膨張弁116を示している。図5(A)、(B)、(C)に示される冷凍サイクル14、15、16並びに図6、図7、図8に示される膨張弁114、115、116については、前述した第1、第2、第3実施例の冷凍サイクル11、12、13並びに膨張弁111、112、113の各部に対応する部分には同一の符号が付されており、以下においては、それらとの相異点を重点的に説明する。
5A, 5B, and 5C show a fourth embodiment, a fifth embodiment, and a sixth embodiment of the refrigeration cycle according to the present invention. 6 shows the
第4、第5、第6実施例の冷凍サイクル14、15、16に使用されている膨張弁114、115、116は、前述した第1、第2、第3実施例の冷凍サイクル11、12、13に使用されている膨張弁111、112、113では設けられていた感温用流入口31及び流出口32は設けられておらず、蒸発器103からの低温の冷媒は、膨張弁114、115(116)内を通らずに直接内部熱交換器104に導かれるようになっている。
The
第4実施例の冷凍サイクル14は、前述した第2実施例の冷凍サイクル12と同様に、
圧縮機101の吸入側に導かれる、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の温度を感知すべく、感温筒70を内部熱交換器104と圧縮機101の吸入側とを結ぶ導管125に近接配置するとともに、図6に示される如くに、感温筒70と膨張弁112の上側圧力室43とをキャピラリーチューブ72で結び、膨張弁114において、蒸発器103へ導出される冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度に応じて調整するようにしたものである。また、この例で使用されている膨張弁114の弁本体20には、下側圧力室44と流出口22とを連通する内部圧力通路66が設けられている。
The
In order to sense the temperature of the low-temperature refrigerant after the heat exchange by the
なお、このタイプの膨張弁では、通常、感温筒で蒸発器103の出口近傍の冷媒温度を感知するようにされている(図5(B)参照)が、本実施例は、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の冷媒温度を感温筒70で感知するようにしたこと、つまり、感温筒70の配置部位を変更したことを特徴としている。
In this type of expansion valve, the temperature of the refrigerant in the vicinity of the outlet of the
このような構成の冷凍サイクル14おいても、第2実施例の冷凍サイクル12と略同様な作用効果が得られる。
In the
第5実施例の冷凍サイクル15は、前述した第1実施例の冷凍サイクル11と同様に、
圧縮機101の吸入側に導かれる、内部熱交換器104で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の圧力を感知すべく、内部熱交換器104と圧縮機101の吸入側とを結ぶ導管125の途中に外部圧力導入管50の一端部を連結するとともに、外部圧力導入管50の他端部を膨張弁115の下側圧力室44と外部とを連通するL形状の圧力導入通路54に接続し、膨張弁115において、蒸発器103へ導出される冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の圧力に応じて調整するようにしたものである。なお、ここでは、感温筒70を蒸発器103と内部熱交換器104とを結ぶ導管124(蒸発器103の出口近傍)に近接配置し、感温筒70と膨張弁112の上側圧力室43とがキャピラリーチューブ72で結ばれている。
The
A
このような構成の冷凍サイクル15おいても、第1実施例の冷凍サイクル11と略同様な作用効果が得られる。
Also in the
第6実施例の冷凍サイクル16は、第4実施例の冷凍サイクル14及び第5実施例の冷凍サイクル14を組み合わせたもので、外部圧力導入管50及び感温筒70の両方を備えており、それに使用される膨張弁113の下側圧力室44周りは第5実施例のものと略同様であり、上側圧力室43周りは第4実施例のものと略同様に構成されていて、膨張弁116において、蒸発器103へ導出される冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の圧力及び温度に応じて調整するようにしたものである。
The
このような構成の冷凍サイクル16においても、第1実施例及び第2実施例と同様に、
圧縮機内部(吐出)温度が過度に上昇することを未然に防止でき、冷媒中に含まれるオイルが劣化して焼付等の不具合が発生する事態を確実に防止できる。
Also in the
It is possible to prevent the compressor internal (discharge) temperature from rising excessively, and to reliably prevent the occurrence of problems such as seizure due to deterioration of the oil contained in the refrigerant.
11〜16 冷凍サイクル
101 圧縮機
102 凝縮器
103 蒸発器
104 内部熱交換器
111〜116 膨張弁
20 弁本体
21 流入口
22 流出口
24 弁室
30 ボール弁体
40 ダイアフラム装置
43 上側圧力室
44 下側圧力室
50 外部圧力導入管
54 圧力導入通路
70 感温筒
72 キャピラリーチューブ
11-16
Claims (3)
前記圧縮機の吸入側に導かれる、前記内部熱交換器で熱交換を行った後の低温冷媒の温度及び/又は圧力を感知すべく、前記膨張弁に感温筒及び/又は外部圧力導入管が付設され、前記膨張弁において、前記蒸発器へ導出される冷媒の流量を前記熱交換後の低温冷媒の温度及び/又は圧力に応じて調整するようにされていることを特徴とする冷凍サイクル。 A compressor, a condenser, an evaporator, an internal heat exchanger, and an expansion valve, and a high-temperature refrigerant led from the condenser to the expansion valve in the internal heat exchanger and the evaporator to the compressor. A refrigeration cycle adapted to exchange heat with a low-temperature refrigerant guided to the suction side,
In order to sense the temperature and / or pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant, which is guided to the suction side of the compressor and has undergone heat exchange with the internal heat exchanger, the expansion valve is provided with a temperature sensing tube and / or an external pressure introduction pipe. And the expansion valve adjusts the flow rate of the refrigerant led to the evaporator in accordance with the temperature and / or pressure of the low-temperature refrigerant after the heat exchange. .
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008294844A JP2010121831A (en) | 2008-11-18 | 2008-11-18 | Refrigerating cycle |
| EP09175357.4A EP2187150A3 (en) | 2008-11-18 | 2009-11-09 | Refrigerating Cycle |
| CN200910226504A CN101737987A (en) | 2008-11-18 | 2009-11-18 | refrigerating cycle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008294844A JP2010121831A (en) | 2008-11-18 | 2008-11-18 | Refrigerating cycle |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010121831A true JP2010121831A (en) | 2010-06-03 |
| JP2010121831A5 JP2010121831A5 (en) | 2012-01-05 |
Family
ID=41818427
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008294844A Pending JP2010121831A (en) | 2008-11-18 | 2008-11-18 | Refrigerating cycle |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2187150A3 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2010121831A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101737987A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113654284A (en) * | 2020-05-12 | 2021-11-16 | 浙江三花制冷集团有限公司 | Temperature sensing part and refrigerating system with same |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8931305B2 (en) | 2010-03-31 | 2015-01-13 | Denso International America, Inc. | Evaporator unit |
| CN102530803B (en) * | 2012-01-12 | 2013-06-05 | 苏权兴 | Refrigerant subpackage equipment |
| CN103017409B (en) * | 2013-01-15 | 2015-12-02 | 吴秀华 | Efficient energy-saving freezes, heats all-in-one |
| EP2977244B1 (en) * | 2014-07-24 | 2016-06-29 | C.R.F. Società Consortile per Azioni | Air conditioning system for motor-vehicles |
| FR3028016A1 (en) * | 2014-10-30 | 2016-05-06 | Valeo Systemes Thermiques | THERMAL MANAGEMENT DEVICE FOR A MOTOR VEHICLE |
| FR3028015A1 (en) * | 2014-10-30 | 2016-05-06 | Valeo Systemes Thermiques | THERMAL MANAGEMENT DEVICE FOR A MOTOR VEHICLE |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02561U (en) * | 1988-06-13 | 1990-01-05 | ||
| JPH06241580A (en) * | 1993-02-18 | 1994-08-30 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | Freezing cycle device |
| JP2008122034A (en) * | 2006-11-15 | 2008-05-29 | Sanden Corp | Air conditioner for vehicle |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2902853B2 (en) * | 1992-04-27 | 1999-06-07 | 三洋電機株式会社 | Air conditioner |
| KR20000053279A (en) * | 1996-11-19 | 2000-08-25 | 니센 게오르그 | Process for regulating a refrigerating system, refrigerating system and expansion valve |
| JP2000346466A (en) | 1999-06-02 | 2000-12-15 | Sanden Corp | Vapor compression type refrigerating cycle |
| JP4323619B2 (en) * | 1999-06-17 | 2009-09-02 | 株式会社日本クライメイトシステムズ | Air conditioner for vehicles |
| US6460358B1 (en) * | 2000-11-13 | 2002-10-08 | Thomas H. Hebert | Flash gas and superheat eliminator for evaporators and method therefor |
| JP4246189B2 (en) * | 2005-09-07 | 2009-04-02 | 株式会社デンソー | Refrigeration cycle equipment |
| JP2007240041A (en) * | 2006-03-07 | 2007-09-20 | Tgk Co Ltd | Expansion valve |
-
2008
- 2008-11-18 JP JP2008294844A patent/JP2010121831A/en active Pending
-
2009
- 2009-11-09 EP EP09175357.4A patent/EP2187150A3/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2009-11-18 CN CN200910226504A patent/CN101737987A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH02561U (en) * | 1988-06-13 | 1990-01-05 | ||
| JPH06241580A (en) * | 1993-02-18 | 1994-08-30 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | Freezing cycle device |
| JP2008122034A (en) * | 2006-11-15 | 2008-05-29 | Sanden Corp | Air conditioner for vehicle |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113654284A (en) * | 2020-05-12 | 2021-11-16 | 浙江三花制冷集团有限公司 | Temperature sensing part and refrigerating system with same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101737987A (en) | 2010-06-16 |
| EP2187150A2 (en) | 2010-05-19 |
| EP2187150A3 (en) | 2014-01-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2010121831A (en) | Refrigerating cycle | |
| CN100567780C (en) | The heating power expansion valve of band safety structure | |
| JPWO2011141959A1 (en) | Switching device and air conditioner | |
| JP2011208860A (en) | Air conditioner | |
| US20080202156A1 (en) | Air-conditioning system for vehicles | |
| CN104279804A (en) | Gas-liquid separator, air conditioner and air conditioner liquid return control method | |
| CN102589217A (en) | Refrigerant quantity control device and method and air conditioning unit with control device | |
| CN104345743A (en) | Refrigerant liquid level control method of flooded air-conditioning system | |
| US20190257562A1 (en) | Cooling system with adjustable internal heat exchanger | |
| JPWO2006126396A1 (en) | Refrigeration cycle equipment | |
| JP2010112616A (en) | Thermal expansion valve | |
| CN103913005B (en) | The air-conditioning of refrigeration system and control method thereof and this refrigeration system of tool | |
| US7549389B2 (en) | Ball valve apparatus having a moisture indicator | |
| JP5157580B2 (en) | Refrigeration equipment | |
| JP2007271181A (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2008051373A (en) | Gas-liquid separator | |
| JP2010121831A5 (en) | ||
| CN201193710Y (en) | Thermostatic expansion valve with safety structure | |
| JP7496817B2 (en) | Cooling System | |
| KR100557760B1 (en) | Air conditioner | |
| JP2008249157A (en) | Reversible thermostatic expansion valve | |
| KR200420568Y1 (en) | outlet structure of low prssure of internal heat exchanger | |
| CN105605673B (en) | Air conditioning apparatus | |
| JP2008039262A (en) | Expansion valve | |
| JP2012163299A (en) | Oil returning mechanism of flooded-evaporator, and refrigeration apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111114 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20111114 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130226 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130305 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130507 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20131015 |