JP2010091502A - Alcohol detector - Google Patents
Alcohol detector Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010091502A JP2010091502A JP2008263617A JP2008263617A JP2010091502A JP 2010091502 A JP2010091502 A JP 2010091502A JP 2008263617 A JP2008263617 A JP 2008263617A JP 2008263617 A JP2008263617 A JP 2008263617A JP 2010091502 A JP2010091502 A JP 2010091502A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- alcohol
- hydrogen gas
- electrode
- solid electrolyte
- electrolyte layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims abstract description 144
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 117
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 112
- 239000007784 solid electrolyte Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 55
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- HUUOUJVWIOKBMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N bismuth;oxygen(2-);vanadium Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[V].[Bi+3] HUUOUJVWIOKBMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- -1 oxygen ion Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 61
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 36
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 30
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 7
- 206010021079 Hypopnoea Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 239000010416 ion conductor Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000029058 respiratory gaseous exchange Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000000391 vinyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])=C([H])[H] 0.000 description 3
- 229920002554 vinyl polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229910001020 Au alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 2
- CETPSERCERDGAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N ceric oxide Chemical compound O=[Ce]=O CETPSERCERDGAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910000422 cerium(IV) oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910001416 lithium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910001415 sodium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910001233 yttria-stabilized zirconia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910015902 Bi 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 206010039203 Road traffic accident Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000968352 Scandia <hydrozoan> Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000416 bismuth oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000011088 calibration curve Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- TYIXMATWDRGMPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibismuth;oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Bi+3].[Bi+3] TYIXMATWDRGMPF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N divanadium pentaoxide Chemical compound O=[V](=O)O[V](=O)=O GNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000035622 drinking Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 1
- LNTHITQWFMADLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N gallic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1 LNTHITQWFMADLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052746 lanthanum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- FZLIPJUXYLNCLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N lanthanum atom Chemical compound [La] FZLIPJUXYLNCLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 210000004072 lung Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- HJGMWXTVGKLUAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);scandium(3+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Sc+3].[Sc+3] HJGMWXTVGKLUAQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910002077 partially stabilized zirconia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- FKTOIHSPIPYAPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N samarium(iii) oxide Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Sm+3].[Sm+3] FKTOIHSPIPYAPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910002076 stabilized zirconia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Measuring Oxygen Concentration In Cells (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Biological Materials (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、呼気に含まれるアルコール濃度を検知するアルコール検出器に関するものである。 The present invention relates to an alcohol detector that detects an alcohol concentration contained in exhaled breath.
近年、飲酒による交通事故の増大に伴い、運転手の呼気中のアルコール濃度を測定する酒気帯び運転調査が頻繁に行われるようになっている。又、自動車等の車両にアルコール検出器を搭載し、呼気中のアルコール濃度が多い場合は運転できないよう、イグニッションにインターロックを掛けるアルコール・イグニッション・インターロックシステムが提案されている。
しかしながら、運転手(被験者)が自身の息の代わりに大気をビニル袋等に捕集してアルコール検出器に吹き付けたり、浅い呼吸をして肺に近い深部の呼気が出ないようにして、不正な測定結果を得ることがあり、対策が必要になっている。
In recent years, with the increase in traffic accidents due to drinking, drunk driving surveys for measuring the alcohol concentration in the driver's breath have been frequently conducted. In addition, an alcohol / ignition / interlock system has been proposed in which an alcohol detector is mounted on a vehicle such as an automobile and the ignition is interlocked so that the vehicle cannot be operated when the alcohol concentration in the exhalation is high.
However, if the driver (subject) collects air in a vinyl bag instead of his breath and blows it on an alcohol detector, or breathes shallowly and does not emit deep breaths close to the lungs, it is illegal. Measures may be obtained and countermeasures are required.
このようなことから、呼気中アルコール濃度の測定の際、併せて呼気中のCO2ガス濃度をも測定し、CO2ガス濃度に応じてアルコール濃度の測定結果を補正する技術が提案されている(例えば特許文献1参照)。
又、ガスセンサと音声センサとを呼気測定器に併設し、音声センサを用いて被験者の声の調子が一定になった時に、呼気が一定の吹付状態になったと判定してアルコール濃度を測定する提案されている(例えば特許文献2参照)。
For this reason, a technique for measuring the concentration of CO 2 gas in exhaled breath and measuring the concentration of alcohol in accordance with the CO 2 gas concentration has been proposed. (For example, refer to Patent Document 1).
Also, a gas sensor and a voice sensor are installed in the breath measuring device, and when the tone of the subject's voice becomes constant using the voice sensor, it is determined that the breath is in a constant blowing state and the alcohol concentration is measured. (See, for example, Patent Document 2).
しかしながら、特許文献1記載の技術の場合、CO2ガス濃度の測定に赤外線吸収式の装置を用いると、装置が高価で大型となり測定が容易に行えない。一方、CO2ガスセンサとして、Liイオン伝導体やNaイオン導電体の固体電解質を用いたものが存在するが、長期安定性が低いという問題がある。
又、特許文献2記載の技術の場合、被験者が一定の声の調子を出すのが難しく、測定に習熟する時間を要するという問題がある。又、戸外等の騒音の大きい環境では正確な測定が行えない可能性がある。
そこで、本発明は、呼気が正常に測定されたか否かを判定し、呼気に含まれるアルコール濃度を簡易かつ正確に検知することができるアルコール検出器を提供することを目的とする。
However, in the case of the technique described in Patent Document 1, if an infrared absorption type apparatus is used for measuring the CO 2 gas concentration, the apparatus becomes expensive and large and cannot be measured easily. On the other hand, there are CO 2 gas sensors using a solid electrolyte of Li ion conductor or Na ion conductor, but there is a problem that long-term stability is low.
In the case of the technique described in
Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an alcohol detector that can determine whether or not exhalation has been normally measured and can easily and accurately detect the alcohol concentration contained in the exhalation.
上記課題を解決するため、本発明のアルコール検出器は、アルコール検知電極と第1基準電極と第1固体電解質層とを有し、呼気中のアルコールを選択的に検知するアルコール検知部と、水素ガス検知電極と第2基準電極と第2固体電解質層とを有し、前記呼気中の水素ガスを検知する水素ガス検知部と、前記水素ガス検知部の検知結果に応じて、前記呼気が正常に測定されたか否かを判定する判定部とを備えたことを特徴としている。
このようにすると、呼気中に水素ガスが含まれていることを利用し、同質の固体電解質層を用いた水素ガス検知部により呼気が正常に測定されたか否かを判定できる。このため、従来の別方式の呼気中のCO2ガス濃度を測定する場合に比べ、アルコール検出器の構成を簡略化できる。又、戸外等の騒音の大きい環境でも測定が行え、故意に呼気を吹き込まない等の測定異常を検出し、呼気に含まれるアルコール濃度を簡易かつ正確に検知することができる。また、酸素イオン導電性の固体電解質を用いる事で、従来のLiイオン導電体やNaイオン導電体の固体電解質を用いたものよりも長期安定性を向上する事ができる。
In order to solve the above problems, an alcohol detector according to the present invention includes an alcohol detection electrode, a first reference electrode, and a first solid electrolyte layer, and an alcohol detection unit that selectively detects alcohol in breath, hydrogen A gas detection electrode, a second reference electrode, and a second solid electrolyte layer; a hydrogen gas detection unit that detects hydrogen gas in the exhalation; and the expiration is normal according to a detection result of the hydrogen gas detection unit And a determination unit for determining whether or not the measurement is performed.
If it does in this way, it can judge whether exhalation was measured normally by the hydrogen gas detection part using the solid electrolyte layer of the same quality using the fact that hydrogen gas is contained in exhalation. For this reason, the configuration of the alcohol detector can be simplified as compared with the conventional case of measuring the CO 2 gas concentration in the exhaled breath. In addition, measurement can be performed even in a noisy environment such as outdoors, and a measurement abnormality such as intentional inhalation cannot be detected, and the alcohol concentration contained in the exhalation can be detected easily and accurately. Further, by using an oxygen ion conductive solid electrolyte, the long-term stability can be improved as compared with a conventional Li ion conductor or Na ion conductor solid electrolyte.
前記判定部は、前記水素ガス検知部が検知した水素ガス濃度が閾値以上である場合に、前記呼気が正常に測定されたと判定するとよい。
このようにすると、呼気には水素ガスが1ppm程度以上含まれているにも関わらず、呼気が正常に吹き込まれていない(不正に呼気を吹き込まない場合の他、呼吸が浅い等による測定の失敗も含む)状態を判定部が識別できるので、アルコール濃度を正確に検知することができる。
The determination unit may determine that the exhalation has been normally measured when the hydrogen gas concentration detected by the hydrogen gas detection unit is greater than or equal to a threshold value.
In this case, although exhaled breath contains hydrogen gas of about 1 ppm or more, exhaled breath is not normally blown (in the case of not breathing improperly, measurement failure due to shallow breathing, etc.) In addition, since the determination unit can identify the state, the alcohol concentration can be accurately detected.
前記判定部は、前記水素ガス検知部が検知した水素ガス濃度が前記閾値以上で所定時間維持された場合に、前記呼気が正常に測定されたと判定するとよい。
このようにすると、一旦吹き込んだ呼気を止める等の異常な状態(不正に呼気を止める他、呼吸が浅い等による測定の失敗も含む)に起因して水素ガス濃度が低下したことを判定部が識別できるので、アルコール濃度をより正確に検知することができる。
The determination unit may determine that the exhalation has been normally measured when the hydrogen gas concentration detected by the hydrogen gas detection unit is maintained at a predetermined value or more for a predetermined time.
In this way, the determination unit determines that the hydrogen gas concentration has decreased due to an abnormal state such as stopping exhaled breathing (including stopping breathing illegally, including measurement failures due to shallow breathing, etc.). Since it can be identified, the alcohol concentration can be detected more accurately.
前記アルコール検知電極は、下地電極と、該下地電極を覆いビスマスバナジウム酸化物を主成分とする選択反応層とから構成されているか、又は前記アルコール検知電極はビスマスバナジウム酸化物を主成分とするとよい。
このようにすると、水素ガスとアルコールの混合ガスから、アルコールのみを選択的に検知することができる。これは、ビスマスバナジウム酸化物により、水素ガスが燃焼するためと考えられる。このため、アルコール検知部の構成が簡易になり、アルコール濃度の測定精度も向上する。
The alcohol detection electrode is composed of a base electrode and a selective reaction layer that covers the base electrode and mainly contains bismuth vanadium oxide, or the alcohol detection electrode preferably contains bismuth vanadium oxide as a main component. .
In this way, only alcohol can be selectively detected from a mixed gas of hydrogen gas and alcohol. This is considered because hydrogen gas burns by bismuth vanadium oxide. For this reason, the configuration of the alcohol detector is simplified, and the alcohol concentration measurement accuracy is improved.
前記第1固体電解質層と前記第2固体電解質層とが共通になっていてもよい。
このようにすると、共通の固体電解質層上に、アルコール検知部及び水素ガス検知部が形成され、全体として1つの検知部を構成しているため、検知部がコンパクトになり、コスト低減の他、測定の安定性にも優れる。
The first solid electrolyte layer and the second solid electrolyte layer may be common.
In this way, since the alcohol detector and the hydrogen gas detector are formed on the common solid electrolyte layer and constitute one detector as a whole, the detector becomes compact, in addition to cost reduction, Excellent measurement stability.
前記第1基準電極と前記第2基準電極とが共通になっていてもよい。
このようにすると、アルコール検知部及び水素ガス検知部の基準電極をも共通としたので、検知部がさらにコンパクトになる。
The first reference electrode and the second reference electrode may be common.
If it does in this way, since the reference electrode of the alcohol detection part and the hydrogen gas detection part was also made common, a detection part becomes still more compact.
この発明によれば、呼気が正常に測定されたか否かを判定し、呼気に含まれるアルコール濃度を簡易かつ正確に検知することができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to determine whether or not exhalation has been normally measured, and to easily and accurately detect the alcohol concentration contained in the exhalation.
以下、本発明の実施形態について説明する。
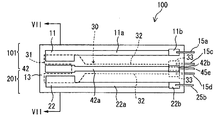
図1は、本発明の第1の実施形態に係るアルコール検出器の断面図を示す。
アルコール検出器1は、箱状の筐体2と、筐体2内に収容される回路基板4と、回路基板4に実装されるアルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20と、回路基板4に実装される制御部5とを備えている。なお、制御部5が特許請求の範囲における「判定部」に相当する。
アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20は、詳しくは後述する固体電解質層を用いた板状センサであり、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の一端からそれぞれ突出する端子15a〜15d及び端子25a〜25dを介し、回路基板4に実装されている。そして、回路基板の上面からアルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20が突出し、それぞれアルコール及び水素ガスを検知するようになっている。又、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の周囲が円筒状の金属網7でそれぞれ覆われ、各検知部10,20を保護している。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described.
FIG. 1 shows a cross-sectional view of an alcohol detector according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
The alcohol detector 1 includes a box-
The
筐体2上面のうち、回路基板4からアルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20が突出している部分は、この突出部を囲むように円筒状に張り出す測定室2aを構成し、測定室2a上端が縮径して呼気導入口2bを形成している。又、呼気導入口2bと各検知部10,20との間における測定室2a内部にはガスフィルタ3が介装され、ガスフィルタ3より下側の測定室2aの側壁に排気穴2cが開口している。そして、呼気導入口2bから導入された呼気がアルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20でそれぞれ測定に供された後、排気穴2から流出するようになっている。
A portion of the upper surface of the
制御部5は、CPU(中央演算処理装置)、メモリ(ROM、RAM)を備え、ROM等に予め格納されたプログラムがCPUにより実行されるマイクロコンピュータである。
又、回路基板4には電源スイッチ8及び表示部(ディスプレイ)9が実装され、電源スイッチ8が筐体2上面に露出し、アルコール検出器1の電源のオンオフを行えるようになっている。さらに、筐体2上面には表示部9を露出させるための表示窓2dが開口している。
The
In addition, a
図2は、アルコール検出器1の構成を示すブロック図である。制御部5はアルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の動作を制御すると共に、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の検知結果を受信して、後述する判定を行い、判定結果を表示部9に表示する。
又、制御部5はアルコール検知部10が有するヒータを制御するヒータ制御回路6aを制御し、アルコール検知部10を動作温度に加熱する。同様に、制御部5は水素ガス検知部20が有するヒータを制御するヒータ制御回路6bを制御し、水素ガス検知部20を動作温度に加熱する。
FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a configuration of the alcohol detector 1. The
Further, the
図3は、アルコール検知部10の構成を示す平面図である。アルコール検知部10は、長尺平板状の第1固体電解質層13と、第1固体電解質層13の片面に併設されるアルコール検知電極11及び第1基準電極12とを備えている。アルコール検知電極11及び第1基準電極12は、第1固体電解質層13の一端側に配置されている。
アルコール検知電極11から第1固体電解質層13の長手方向に沿ってリード部11aが延び、リード部11aの末端が第1固体電解質層13の他端側に位置している。リード部11aの末端には電極パッド11bが接続され、電極パッド11bから第1固体電解質層13の外部に端子15aが突出している。
同様に、第1基準電極12から第1固体電解質層13の長手方向に沿ってリード部12aが延び、リード部12aの末端が第1固体電解質層13の他端側に位置している。リード部12aの末端には電極パッド12bが接続され、電極パッド12bから第1固体電解質層13の外部に端子15bが突出している。
FIG. 3 is a plan view showing the configuration of the
A
Similarly, the
一方、第1固体電解質層13の反対面には図示しない絶縁層が積層され、この絶縁層内に発熱抵抗体30が埋設され、全体としてヒータを構成している。発熱抵抗体30は、アルコール検知電極11と第1基準電極12の直下に位置する蛇行線状の発熱部31と、発熱部31から第1固体電解質層13の長手方向に沿って延びる一対のリード部32と、各リード部32の末端にそれぞれ接続された2個の電極パッド33とを有する。各電極パッド33から第1固体電解質層13の外部にそれぞれ端子15c、15dが突出している。
なお、上記した各端子15a〜15dは、それぞれ対応する電極パッドにロウ付けされている。そして、アルコール検知部10を図1の回路基板4に実装する際には、突出した各端子15a〜15dを回路基板4の対応する孔に挿入し、はんだ付け固定される。
On the other hand, an insulating layer (not shown) is laminated on the opposite surface of the first
The
図4は、図3のIV−IV線に沿う断面図である。アルコール検知電極11は、下地電極11xと、下地電極11xを覆いビスマスバナジウム酸化物を主成分とする選択反応層11yとから構成されている。又、絶縁層14が第1固体電解質層13の下面に積層され、絶縁層14内部に発熱抵抗体30が埋設されている。
4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line IV-IV in FIG. The
下地電極11xはAuを主成分とし、第1基準電極12はPtを主成分としている。又、選択反応層11yに用いるビスマスバナジウム酸化物の組成としては特に限定されないが、例えばBiVO4が挙げられる。なお、本発明において「主成分」とは、含有率が50%以上のことを指す。選択反応層11yはガスを通過させるため、多孔質体である必要があるが、ビスマスバナジウム酸化物を焼成することで多孔質体を形成することができる。又、アルコール検知電極11がビスマスバナジウム酸化物を主成分とする一層であってもよい。なお、BiVO4は、酸化バナジウム(V2O5)粉末及び酸化ビスマス(Bi2O3)粉末を1:1(モル比)混合して得られる。
ビスマスバナジウム酸化物を含む選択反応層11yを設けると、水素ガスとアルコールの混合ガスから、アルコールのみを選択的に検知することができる。これは、ビスマスバナジウム酸化物により水素ガスが燃焼するためと考えられる。
The
When the
各リード部11a、12a、32、各電極パッド11b、12b、33、発熱抵抗体30は、例えばPtやPdを主成分(合金含む)としている。各端子15a〜15dは、各種の導電線を用いることができる。
第1固体電解質層13は、例えば部分安定化ジルコニアを主成分とし、ヒータの加熱によって活性化されて酸素イオン伝導性を示す。第1固体電解質層13としては、例えばYSZ(イットリア安定化ジルコニア)、ScSZ(スカンジア安定化ジルコニア)、GDC(ガドニアドープドセリア)、SDC(サマリアドープドセリア)、ランタンガーレートを主成分とすることができる。
絶縁層14は、例えばアルミナ等のセラミックからなる。
Each
The first
The insulating
水素ガス検知部20は、アルコール検知部10のアルコール検知電極11に代えて、水素ガス検知電極を用いること以外は、アルコール検知部10と同一の構成を有するので、説明を省略する。水素ガス検知電極としては、例えば下地電極11xと同様、Auを主成分としたもの(Au合金を含む)を用いることができる。
なお、図1において、水素ガス検知部20の各端子25a〜25dは、それぞれアルコール検知部10の各端子15a〜15dに相当する。
Since the hydrogen
In FIG. 1, the
次に、図5を参照して、制御部(判定部)5による判定処理の一例について説明する。
まず、制御部5は、被験者が電源スイッチ8をONしたことを検知し(ステップS2)、ヒータ制御回路6a、6bを動作させ、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20をヒータ加熱する(ステップS4)。又、制御部5は、表示部9に「WARM UP(待機中)」を表示する(ステップS6)。そして、制御部5は、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20が所定の動作温度になったと判断すると、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の出力に基づき、アルコール濃度及び水素ガス濃度を測定する(ステップS8)。
次に、制御部5は、ステップS8で測定したアルコール濃度及び水素ガス濃度がそれぞれ閾値以下か否かを判定し(ステップS10)、閾値を超えている(「No」)場合はステップS8に戻る。これは、前回測定時の被験者の呼気が測定室2aに残存して次の測定に影響を与えるのを防止するためである。又、アルコール濃度についての閾値Th1と、水素ガス濃度についての閾値Th2はそれぞれ異なる。
Next, an example of determination processing by the control unit (determination unit) 5 will be described with reference to FIG.
First, the
Next, the
一方、アルコール濃度及び水素ガス濃度がそれぞれ閾値以下(ステップS10で「Yes」)であれば、制御部5は、表示部9に「READY(測定準備完了)」を表示し(ステップS12)、被験者に測定(呼気吹き込み)を促す。この状態で呼気が吹き込まれるので、次に水素ガス検知部20の出力に基づき、水素ガス濃度を測定する(ステップS14)。
そして、制御部5は、ステップS14で測定した水素ガス濃度が閾値以上か否かを判定する(ステップS16)。ステップS16で閾値未満の(「No」)の場合、ステップS14に戻る。これは、通常、呼気には水素ガスが1ppm程度以上含まれているにも関わらず、被験者が吹き込んだ呼気中の水素ガスが閾値未満であるのは、呼気が正常に吹き込まれていない(不正に呼気を吹き込まない場合の他、呼吸が浅い等による測定の失敗も含む)と考えられるからである。なお、ステップS16での閾値は、ステップS10での閾値Th2と同一でもよく、異なっていてもよい。
On the other hand, if the alcohol concentration and the hydrogen gas concentration are each equal to or less than the threshold values (“Yes” in step S10), the
And the
ステップS16で水素ガス濃度が閾値以上(「Yes」)の場合、次に制御部5は、タイマーをスタートさせる(ステップS18)。さらに、制御部5は、表示部9に「MEASURE(測定)」を表示し(ステップS20)、水素ガス検知部20の出力に基づき、制御部5は水素ガス濃度を測定する(ステップS22)。
次に、制御部5は、ステップS22で測定した水素ガス濃度が閾値以上か否かを判定する(ステップS24)。ステップS24はステップS16と同様な処理であるが、被験者がステップS16で呼気を吹き込んだ後、呼気を止めることを防止するため、ステップS22を設けている。
ステップS24で閾値未満(「No」)の場合、制御部5は、表示部9に「NG」を表示し(ステップS28)、処理を終了する。
If the hydrogen gas concentration is greater than or equal to the threshold value (“Yes”) in step S16, the
Next, the
When it is less than the threshold value (“No”) in step S24, the
ステップS24で水素ガス濃度が閾値以上(「Yes」)の場合、次に制御部5は、所定時間維持されたか否かを判定する(ステップS26)。ステップS26で所定時間を経過する前(「No」)場合、ステップS22に戻る。ステップ22〜26の処理により、水素ガス濃度が閾値以上で所定時間維持されたか否かを判断できる。これは、アルコール濃度を正確に測定するためには、呼気が所定時間継続して吹き込まれる必要があり、呼気を止める等の異常な状態(不正に呼気を止める他、呼吸が浅い等による測定の失敗も含む)に起因して水素ガス濃度が低下したことを検出するためである。
When the hydrogen gas concentration is equal to or higher than the threshold value (“Yes”) in step S24, the
そして、ステップS26で所定時間を経過しても水素ガス濃度が閾値以上(「Yes」)の場合、呼気が正常に吹き込まれたとみなし、制御部5は、アルコール検知部10の出力に基づき、アルコール濃度を測定し(ステップS30)、測定結果を表示部9に表示して(ステップS32)処理を終了する。
If the hydrogen gas concentration is equal to or higher than the threshold value (“Yes”) even after the predetermined time has elapsed in step S26, it is considered that exhaled breath has been normally blown, and the
以上のように、本発明のアルコール検出器は、呼気中に水素ガスが含まれていることを利用し、固体電解質層を用いた水素ガス検知部(水素ガスセンサ)により呼気が正常に測定されたか否かを判定している。このため、呼気中のCO2ガス濃度を測定する場合に比べ、水素ガス検知部が簡易でコンパクトとなるので、アルコール検出器自体も簡易でコンパクトとなる。又、戸外等の騒音の大きい環境でも測定が行え、故意に呼気を吹き込まない等の測定異常を検出し、呼気に含まれるアルコール濃度を簡易かつ正確に検知することができる。 As described above, the alcohol detector according to the present invention utilizes the fact that hydrogen gas is contained in exhaled gas, and has the exhaled gas measured normally by the hydrogen gas detection unit (hydrogen gas sensor) using the solid electrolyte layer? It is determined whether or not. For this reason, compared with the case where the CO 2 gas concentration in the exhalation is measured, the hydrogen gas detection unit is simple and compact, and the alcohol detector itself is simple and compact. In addition, measurement can be performed even in a noisy environment such as outdoors, and a measurement abnormality such as intentional inhalation cannot be detected, and the alcohol concentration contained in the exhalation can be detected easily and accurately.
又、制御部5がステップS16で水素ガス濃度が閾値以上であるか否かを判定するようにした場合、呼気には水素ガスが1ppm程度以上含まれているにも関わらず、呼気が正常に吹き込まれていない(不正に呼気を吹き込まない場合の他、呼吸が浅い等による測定の失敗も含む)状態を識別し、アルコール濃度を正確に検知することができる。
さらに、制御部5がステップS26で、水素ガス濃度がこの閾値以上で所定時間維持されたか否かを判定するようにした場合、呼気を止める等の異常な状態(不正に呼気を止める他、呼吸が浅い等による測定の失敗も含む)に起因して水素ガス濃度が低下したことを識別し、アルコール濃度をより正確に検知することができる。
又、アルコール検知電極11が、下地電極11xと、下地電極11xを覆いビスマスバナジウム酸化物を主成分とする選択反応層11yとから構成されていると、水素ガスとアルコールの混合ガスから、アルコールのみを選択的に検知することができる。これは、ビスマスバナジウム酸化物により、水素ガスが燃焼するためと考えられる。このため、アルコール検知部10の構成が簡易になる。
Further, when the
Furthermore, when the
Further, when the
次に、本発明の第2の実施形態に係るアルコール検出器について、図6、図7を参照して説明する。但し、第2の実施形態に係るアルコール検出器は、アルコール検知部及び水素ガス検知部以外の構成(筐体2、回路基板4、制御部5等)は、第1の実施形態に係るアルコール検出器と同一であるので、アルコール検知部及び水素ガス検知部についてのみ説明する。
又、図6において、図3に示したものと同一の構成部分については、同一符号を付して説明を省略する。
Next, an alcohol detector according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. However, the alcohol detector according to the second embodiment has a configuration other than the alcohol detection unit and the hydrogen gas detection unit (the
In FIG. 6, the same components as those shown in FIG. 3 are denoted by the same reference numerals and description thereof is omitted.
図6は、アルコール検知部101及び水素ガス検知部201の構成を示す平面図である。第2の実施形態においては、共通の第1固体電解質層13上に、アルコール検知部101及び水素ガス検知部201が形成されており、全体として1つの検知部(マルチセンサ)100を構成している。
FIG. 6 is a plan view showing configurations of the
アルコール検知部101は、長尺平板状の第1固体電解質層13と、第1固体電解質層13の片面に併設されるアルコール検知電極11及び共通基準電極42とを備えている。アルコール検知電極11及び共通基準電極42は、第1固体電解質層13の一端側のうち、長手方向に沿う上半分の位置に設けられている。又、アルコール検知電極11が第1固体電解質層13の長辺に沿う外側に位置し、共通基準電極42が内側に位置している。
アルコール検知電極11から第1固体電解質層13の長手方向に沿ってリード部11aが延び、リード部11aの末端が第1固体電解質層13の他端側に位置している。リード部11aの末端には電極パッド11bが接続され、電極パッド11bから第1固体電解質層13の外部に端子15aが突出している。
同様に、共通基準電極42から第1固体電解質層13の長手方向に沿ってリード部42aが延び、リード部42aの末端が第1固体電解質層13の他端側に位置している。リード部42aの末端には電極パッド42bが接続され、電極パッド42bから第1固体電解質層13の外部に端子45eが突出している。
なお、共通基準電極42及びリード部42aは、第1固体電解質層13の長手方向の中心線上に配置されている。
The
A
Similarly, the
The
水素ガス検知部201は、第1固体電解質層13と、第1固体電解質層13の片面に併設される水素ガス検知電極22及び共通基準電極42とを備えている。水素ガス検知電極22及び共通基準電極42は、第1固体電解質層13の一端側のうち、長手方向に沿う上半分の位置に設けられている。又、水素ガス検知電極22が第1固体電解質層13の長辺に沿う外側に位置し、共通基準電極42が内側に位置している。
なお、共通基準電極42は、特許請求の範囲における「第1基準電極」及び「第2基準電極」に相当する。
水素ガス検知電極22から第1固体電解質層13の長手方向に沿ってリード部22aが延び、リード部22aの末端が第1固体電解質層13の他端側に位置している。リード部22aの末端には電極パッド22bが接続され、電極パッド22bから第1固体電解質層13の外部に端子25bが突出している。
The hydrogen
The
A
水素ガス検知電極22としては、Auを主成分としたもの(Au合金を含む)を用いることができる。又、共通基準電極42はPtを主成分としている。リード部22a、42a、各電極パッド22b、42bは、例えばPtやPdを主成分(合金含む)としている。各端子25b、45eは、各種の導電線を用いることができる。
As the hydrogen
一方、第1固体電解質層13の反対面には図示しない絶縁層が積層され、この絶縁層内に、発熱抵抗体30が埋設され、全体としてヒータを構成している。発熱抵抗体30については、図3の発熱抵抗体30と同一構成であるため、説明を省略する。
なお、上記した各端子15a、25b、15c、15d、45eは、それぞれ対応する電極パッドにロウ付けされている。そして、マルチセンサ100を図1の回路基板4に実装する際には、突出した各端子15a、25b、15c、15d、45eを回路基板4の対応する孔に挿入し、はんだ付け固定される。
On the other hand, an insulating layer (not shown) is laminated on the opposite surface of the first
The
図7は、図6のVII−VII線に沿う断面図である。アルコール検知電極11は、下地電極11xと、下地電極11xを覆いビスマスバナジウム酸化物を主成分とする選択反応層11yとから構成され、図7の左端に位置している。共通基準電極42が図7の中心に位置し、水素ガス検知電極22が右端に位置している。
マルチセンサ100は、アルコール検知電極11と共通基準電極42の間の電圧V2を測定してアルコール濃度を検知し、水素ガス検知電極22と共通基準電極42の間の電圧V1を測定して水素ガス濃度を検知する。
7 is a cross-sectional view taken along line VII-VII in FIG. The
The multisensor 100 measures the voltage V2 between the
第2の実施形態に係るアルコール検出器によれば、共通の第1固体電解質層13上に、アルコール検知部101及び水素ガス検知部201が形成され、全体として1つの検知部を構成しているため、検知部がコンパクトになり、コスト低減の他、測定の安定性にも優れる。さらに、アルコール検知部101及び水素ガス検知部201の基準電極42を共通とすれば、検知部がさらにコンパクトになる。
According to the alcohol detector according to the second embodiment, the
本発明は上記実施形態に限定されず、本発明の思想と範囲に含まれる様々な変形及び均等物に及ぶことはいうまでもない。 It goes without saying that the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, but extends to various modifications and equivalents included in the spirit and scope of the present invention.
次に、実施例を挙げて本発明をさらに詳細に説明するが、本発明はこれらに限定されるものではない。 EXAMPLES Next, although an Example is given and this invention is demonstrated further in detail, this invention is not limited to these.
(感度特性)
図1〜図4に示したアルコール検出器1を用意した。このアルコール検出器1をモデルガス発生装置に接続し、モデルガス発生装置のモデルガスを呼気導入口2bから導入した。モデルガスとして、相対湿度50%のベースガスに対し、アルコールガス(エタノール)又は水素ガスをそれぞれ100ppm添加し、温度25℃としたものを用いた。
アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20をヒータで650℃に保持した状態で、モデルガスを呼気導入口2bから導入し、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の出力電圧を測定した。
得られた結果を図8に示す。アルコール検知部10にベースガスとアルコールからなるモデルガスを吹き込んだところ、アルコールガスを検知した。一方、アルコール検知部10にベースガスと水素ガスからなるモデルガスを吹き込んだところ、水素ガスをまったく検知せず、アルコールを選択的に検知できることがわかった。
水素ガス検知部20にベースガスとアルコールからなるモデルガスを吹き込んだところ、アルコールガスを若干検知した。一方、水素ガス検知部20にベースガスと水素ガスからなるモデルガスを吹き込んだところ、水素ガスを検知した。なお、アルコールと水素ガスの混合ガスに対しては、アルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の各ガス濃度に応じた出力電圧を検量線として予め求めておき、アルコール検知部10で判明したアルコール濃度を、水素ガス検知部20で検知したアルコールと水素ガスの出力から差引くことにより、水素ガス濃度を求めることができる。
(Sensitivity characteristics)
The alcohol detector 1 shown in FIGS. 1 to 4 was prepared. The alcohol detector 1 was connected to a model gas generator, and the model gas of the model gas generator was introduced from the
With the
The obtained result is shown in FIG. When model gas comprising base gas and alcohol was blown into the
When model gas composed of base gas and alcohol was blown into the
(呼気の判定)
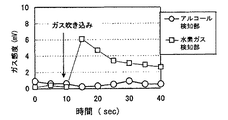
上記アルコール検出器1の呼気導入口2bへ、被験者の呼気を吹き込み、上記と同様にしてアルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の出力電圧を測定した。各検知部の測定を開始してから10秒後に呼気を吹き込んだ。
次に、大気を捕集したビニル袋を、上記アルコール検出器1の呼気導入口2bへ接続し、ビニル袋を押しつぶして大気を呼気導入口2bへ導入した。同様にアルコール検知部10及び水素ガス検知部20の出力電圧を測定した。
得られた結果を図9、図10に示す。呼気を吹き込んだ場合(図9)、水素ガスを検知したのに対し、大気を導入した場合(図10)、水素ガスを検知しなかった。これより、水素ガス検知部20の水素ガス濃度の出力の閾値を3mV程度に設定しておけば、呼気が正常に吹き込まれたか否かを判定することができる。
(Exhalation judgment)
The subject's breath was blown into the
Next, the vinyl bag which collected air was connected to the
The obtained results are shown in FIGS. When exhalation was blown (FIG. 9), hydrogen gas was detected, but when the atmosphere was introduced (FIG. 10), hydrogen gas was not detected. Thus, if the output threshold of the hydrogen gas concentration of the
1 アルコール検出器
5 判定部(制御部)
10 アルコール検知部
11 アルコール検知電極
11x 下地電極
11y 選択反応層
12 第1基準電極
13 第1固体電解質層、第2固体電解質層
20 水素ガス検知部
22 水素ガス検知電極
42 第2基準電極(共通電極)
1
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
水素ガス検知電極と第2基準電極と酸素イオン導電性の第2固体電解質層とを有し、前記呼気中の水素ガスを検知する水素ガス検知部と、
前記水素ガス検知部の検知結果に応じて、前記呼気が正常に測定されたか否かを判定する判定部とを備えたアルコール検出器。 An alcohol detection unit that includes an alcohol detection electrode, a first reference electrode, and an oxygen ion conductive first solid electrolyte layer, and that selectively detects alcohol in the breath;
A hydrogen gas detection unit having a hydrogen gas detection electrode, a second reference electrode, and an oxygen ion conductive second solid electrolyte layer, and detecting hydrogen gas in the exhalation;
An alcohol detector comprising: a determination unit that determines whether or not the exhalation has been normally measured according to a detection result of the hydrogen gas detection unit.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008263617A JP5119118B2 (en) | 2008-10-10 | 2008-10-10 | Alcohol detector |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008263617A JP5119118B2 (en) | 2008-10-10 | 2008-10-10 | Alcohol detector |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010091502A true JP2010091502A (en) | 2010-04-22 |
| JP5119118B2 JP5119118B2 (en) | 2013-01-16 |
Family
ID=42254352
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008263617A Active JP5119118B2 (en) | 2008-10-10 | 2008-10-10 | Alcohol detector |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5119118B2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4785994B1 (en) * | 2011-02-03 | 2011-10-05 | 東海電子株式会社 | Breath alcohol meter |
| WO2017158846A1 (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2017-09-21 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Expiration gas detection device and expiration gas detection method |
| JP2021085715A (en) * | 2019-11-26 | 2021-06-03 | 株式会社タニタ | Exhalation component measurement device and method for determining abnormality |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10186A (en) * | 1996-06-17 | 1998-01-06 | Mitoreeben Kenkyusho:Kk | Method and device of analyzing specified gas component in expired air |
| JP2000304715A (en) * | 1999-04-23 | 2000-11-02 | Tanita Corp | Foul odor constituent-measuring instrument |
| JP2002039981A (en) * | 2000-07-24 | 2002-02-06 | Shimadzu Corp | Expired air measuring device and microphone-applied device having function of the same |
| JP2004501374A (en) * | 2000-06-19 | 2004-01-15 | エンビテック−ウィスマール ゲー・エム・ベー・ハー | Alcohol detector |
| JP2004279228A (en) * | 2003-03-17 | 2004-10-07 | Toshikawa Takara | Method and apparatus for measuring concentration of component gas in exhalation |
| JP2006075447A (en) * | 2004-09-13 | 2006-03-23 | Hitachi Ltd | Portable health checking apparatus and exhalation analysis service method using the same |
-
2008
- 2008-10-10 JP JP2008263617A patent/JP5119118B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10186A (en) * | 1996-06-17 | 1998-01-06 | Mitoreeben Kenkyusho:Kk | Method and device of analyzing specified gas component in expired air |
| JP2000304715A (en) * | 1999-04-23 | 2000-11-02 | Tanita Corp | Foul odor constituent-measuring instrument |
| JP2004501374A (en) * | 2000-06-19 | 2004-01-15 | エンビテック−ウィスマール ゲー・エム・ベー・ハー | Alcohol detector |
| JP2002039981A (en) * | 2000-07-24 | 2002-02-06 | Shimadzu Corp | Expired air measuring device and microphone-applied device having function of the same |
| JP2004279228A (en) * | 2003-03-17 | 2004-10-07 | Toshikawa Takara | Method and apparatus for measuring concentration of component gas in exhalation |
| JP2006075447A (en) * | 2004-09-13 | 2006-03-23 | Hitachi Ltd | Portable health checking apparatus and exhalation analysis service method using the same |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4785994B1 (en) * | 2011-02-03 | 2011-10-05 | 東海電子株式会社 | Breath alcohol meter |
| WO2017158846A1 (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2017-09-21 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Expiration gas detection device and expiration gas detection method |
| JPWO2017158846A1 (en) * | 2016-03-18 | 2018-07-05 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Exhalation gas detection device and expiration gas detection method |
| JP2021085715A (en) * | 2019-11-26 | 2021-06-03 | 株式会社タニタ | Exhalation component measurement device and method for determining abnormality |
| WO2021106783A1 (en) * | 2019-11-26 | 2021-06-03 | 株式会社タニタ | Exhaled-air component measurement device and abnormality determination method |
| JP7489083B2 (en) | 2019-11-26 | 2024-05-23 | 株式会社タニタ | Exhaled breath component measuring device and abnormality determination method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5119118B2 (en) | 2013-01-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20130344609A1 (en) | Chemical sensor in a portable electronic device | |
| US20060266098A1 (en) | Hydrogen sulfide generator for sensor calibration | |
| US10241107B2 (en) | Concentration measurements with a mobile device | |
| KR101484581B1 (en) | Interactive alcometry | |
| WO1998012550A1 (en) | Gas sensor | |
| EP0990895A3 (en) | Gas sensor with electrically conductive hydrophobic membranes | |
| WO2007083350A1 (en) | Apparatus for examining component of expiratory air | |
| JP5119118B2 (en) | Alcohol detector | |
| US20110077544A1 (en) | Method for optimizing the gas conversion rate in a respiratory gas analyzer | |
| JP2006201097A (en) | Checker and method for detecting driving while intoxicated | |
| JP4557059B2 (en) | Breath alcohol concentration detector | |
| JP5141524B2 (en) | Gas component detector | |
| WO2010013023A1 (en) | Device for measuring air quality | |
| JP6535413B2 (en) | Exhalation gas detection device and exhalation gas detection method | |
| JP2005530994A (en) | Electrochemical gas detection apparatus and method including a permeable membrane and an aqueous electrolyte | |
| JP2014119943A (en) | Exhalation component measurement system, exhalation component measurement method, computer program and exhalation component measurement device | |
| KR20110029749A (en) | A drunkometer | |
| JPH03282247A (en) | Detection of flammable gas | |
| KR101182756B1 (en) | Breath Alcohol Analyzer | |
| JPH06197897A (en) | Alcohol detecting device | |
| JP2011149732A (en) | METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING NOx SENSOR | |
| JP5240677B2 (en) | Vehicle control device | |
| JP4625261B2 (en) | Sensor element of gas sensor | |
| JP2009008499A (en) | Alcohol sensor | |
| JP2010091503A (en) | Alcohol detector |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110902 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120919 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120924 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121022 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5119118 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20151026 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |