JP2010014959A - Lens barrel - Google Patents
Lens barrel Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010014959A JP2010014959A JP2008174689A JP2008174689A JP2010014959A JP 2010014959 A JP2010014959 A JP 2010014959A JP 2008174689 A JP2008174689 A JP 2008174689A JP 2008174689 A JP2008174689 A JP 2008174689A JP 2010014959 A JP2010014959 A JP 2010014959A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- optical axis
- lens barrel
- group
- axis direction
- fixed cylinder
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Lens Barrels (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明はレンズ鏡筒に関し、特に、光軸方向に進退する光学要素に対する付勢手段の保護構造に関する。 The present invention relates to a lens barrel, and more particularly, to a protection structure for a biasing means for an optical element that advances and retreats in the optical axis direction.
レンズ鏡筒においては、光軸方向に移動可能な光学要素の保持部材に対して、その駆動機構の一部の機能を担わせたり、駆動機構におけるバックラッシュを取ったり、あるいは位置を安定させたりする目的で、光軸方向への付勢力が与えられることが多い。この種の付勢手段は、駆動機構の負荷軽減や動作精度向上などの観点から、光学要素の移動量あたりの荷重の変動幅が小さい方が好ましく、大型の付勢手段を用いることで、荷重の変動幅を小さくすることが可能である。例えば、付勢手段が引張ばねや圧縮ばねである場合、その伸縮方向に長いばねを用いれば荷重の変動幅を小さくできる。しかし、小型化が要求されているレンズ鏡筒においては、光軸方向に長い引張ばねや圧縮ばねを採用することが難しいという問題があった。これを解決するものとして、光学系の光軸と平行な平面に対して略直交する軸を中心に、径方向へ延出された着力部(付勢部)を揺動させるタイプの付勢手段が提案されている(特許文献1)。この付勢手段の具体的態様として、トーションばねや、揺動するレバー部材と付勢ばねの組み合わせが想定されている。
特許文献1の付勢手段は、揺動中心部から光学要素保持部材に対する着力点までの距離を大きくするにつれて荷重変動の抑制効果が高まるが、その反面、この距離を大きくすると着力部が長くなり、レンズ鏡筒を構成する他の部材と干渉する可能性が高くなるため、付勢部材を、可動部材が集中するレンズ鏡筒の径方向中心部ではなく外側に配置する必要が生じる。
The urging means of
付勢手段をレンズ鏡筒の外径側に配置すると、外側からの接触による変形や誤差発生のリスクが高まるため保護することが望ましいが、保護構造を構成することが難しい場合がある。レンズ鏡筒では一般に、各種可動部材を内部に支持した固定筒部材が最も外径側に設けられているが、この固定筒部材が、周方向に途切れのない完全な円筒形状をなしていると、その外側に配した付勢手段をさらに覆うような保護部を固定筒部材に形成することが困難であった。具体的には、外面側に付勢手段を支持する突起を有する形状の固定筒部材を樹脂成形で製造しようとした場合、光軸から離れる径方向へ向けて成形後の型抜きが行われるため、この型抜き方向の延長上に、付勢手段を覆うような形状の壁部を設けることができなかった。 If the urging means is arranged on the outer diameter side of the lens barrel, it is desirable to protect it because the risk of deformation and error generation due to contact from the outside increases, but it may be difficult to configure the protection structure. In a lens barrel, generally, a fixed cylinder member that supports various movable members is provided on the outermost diameter side, and when this fixed cylinder member has a complete cylindrical shape without any interruption in the circumferential direction, It is difficult to form a protective part on the fixed cylinder member that further covers the urging means disposed on the outside. Specifically, when an attempt is made to manufacture a fixed cylindrical member having a projection that supports the biasing means on the outer surface side by resin molding, die cutting after molding is performed in the radial direction away from the optical axis. On the extension in the die-cutting direction, a wall portion shaped so as to cover the urging means could not be provided.
本発明は以上の問題に鑑みてなされたものであり、光軸と平行な平面に対して略直交する軸を中心に揺動して光学要素保持部材を付勢する付勢手段を、固定筒部材の形状に依存せず確実に保護することが可能なレンズ鏡筒を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an urging means for urging an optical element holding member by swinging about an axis substantially orthogonal to a plane parallel to the optical axis is provided as a fixed cylinder. It is an object of the present invention to provide a lens barrel that can be reliably protected without depending on the shape of a member.
本発明のレンズ鏡筒は、撮影光学系を構成する光学要素を保持し光軸方向に移動可能な光学要素保持部材;撮影光学系を囲む固定筒部材;固定筒部材の外側に位置し、光軸と平行な平面に対して略直交する軸を中心として揺動可能で、揺動中心部から径方向に延びる着力部を介して光学要素保持部材を光軸方向に付勢する付勢手段;及び、固定筒部材とは別部材からなり、該固定筒部材に取り付けられて固定筒部材外面との間に付勢手段の収納空間を形成する保護壁部材;を備えたことを特徴としている。 The lens barrel of the present invention is an optical element holding member that holds an optical element constituting a photographing optical system and is movable in the optical axis direction; a fixed cylindrical member that surrounds the photographing optical system; An urging means that oscillates about an axis substantially orthogonal to a plane parallel to the axis, and that urges the optical element holding member in the optical axis direction via an urging portion extending radially from the oscillating center; And a protective wall member that is a member separate from the fixed cylinder member and is attached to the fixed cylinder member and forms a storage space for the urging means between the fixed cylinder member and the outer surface.
保護壁部材は、撮影光学系の結像位置に撮像素子を位置させる撮像素子保持部材からなることが好ましい。 The protective wall member is preferably composed of an image sensor holding member that positions the image sensor at the imaging position of the photographing optical system.
固定筒部材と保護壁部材のいずれか一方に、付勢手段の揺動中心部を支持する揺動支持部を設けるとよい。 A swing support portion for supporting the swing center portion of the urging means may be provided on either the fixed cylinder member or the protective wall member.
保護壁部材は、付勢部材の着力部の揺動平面と略平行な平面部を備えた形状とすることが好ましい。 It is preferable that the protective wall member has a shape including a plane portion substantially parallel to the swing plane of the force applying portion of the urging member.
付勢手段の具体例として、揺動中心部としてコイル部を備え、着力部として該コイル部から延出するアーム部とを有するトーションばねが適用可能である。 As a specific example of the urging means, a torsion spring having a coil portion as a swinging central portion and an arm portion extending from the coil portion as an applied force portion can be applied.
本発明は、固定筒部材が、その内側に位置する回転部材の光軸方向位置を制御する回転部材案内機構を内周面全体に有しているタイプのレンズ鏡筒に特に好適である。 The present invention is particularly suitable for a lens barrel of a type in which the fixed cylinder member has a rotation member guide mechanism for controlling the position in the optical axis direction of the rotation member positioned inside thereof on the entire inner peripheral surface.
以上の本発明のレンズ鏡筒によれば、光軸と平行な平面に対して略直交する軸を中心に揺動して光学要素保持部材を付勢する付勢手段が、固定筒部材と、この固定筒部材とは別部材からなる保護壁部材との間に配置されるので、固定筒部材の形状に依存せず確実に付勢部材を保護することができる。 According to the above lens barrel of the present invention, the urging means for urging the optical element holding member by oscillating about an axis substantially orthogonal to the plane parallel to the optical axis includes the fixed cylinder member, Since it is arrange | positioned between this fixed cylinder member and the protective wall member which consists of another member, an urging | biasing member can be reliably protected irrespective of the shape of a fixed cylinder member.
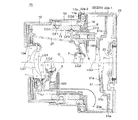
図1から図5を参照して、本発明を適用したズームレンズ鏡筒70の概略構造を説明する。このズームレンズ鏡筒70の撮像光学系は、物体(被写体)側から順に第1レンズ群LG1、第2レンズ群LG2、絞り兼用のシャッタ羽根S、第3レンズ群LG3、ローパスフィルタ25及び撮像素子71を備えており、以下の説明中で光軸方向とは、この撮影光学系の光軸Oと平行な方向を意味する。
A schematic structure of a
ローパスフィルタ25と撮像素子71はユニット化されて撮像素子ホルダ23に固定され、撮像素子ホルダ23がハウジング22の後部に固定される。ハウジング22の外側には、ズームモータ150とAFモータ160が支持されている。
The low-
第3レンズ群LG3を保持する3群レンズ枠51は、ハウジング22に対して光軸方向に移動可能に支持されていて、AFモータ160によって駆動される。
The third
ハウジング22の内側にはカム環(回転部材)11が支持されている。カム環11は、ズームモータ150の駆動力によって回転され、鏡筒収納状態(図4)から撮影状態(図5)になるまでの間は、回転しながら光軸方向に移動し、撮影状態におけるズーム域(図5上半のワイド端と図5下半のテレ端の間)では、光軸方向には定位置で回転される。より詳しくは、図12に示すように、カム環11は、光軸方向の後端部にギヤリング部11aが設けられ、ギヤリング部11a上にガイド突起11bが突設されている。ギヤリング部11aは、ズームモータ150によって回転されるズームギヤ28(図6、図7)に噛合しており、ガイド突起11bは、ハウジング22の内周面に形成したカム環ガイド溝(回転部材案内機構)22aに対して摺動可能に係合している。カム環ガイド溝22aは、光軸方向後方の螺旋溝部分22a-1と、光軸方向前方の撮影光軸Oを中心とする環状溝部分22a-2とを有し、鏡筒収納状態と撮影状態(ワイド端)の間では、ガイド突起11bがカム環ガイド溝22aの螺旋溝部分22a-1に案内されて、カム環11はハウジング22に対して回転しながら光軸方向に移動する。具体的には、カム環11は、鏡筒収納状態から撮影状態になるときに、回転しながら光軸方向前方(物体側)へ進出し、撮影状態から鏡筒収納状態になるときには逆に、回転しながら光軸方向後方へ後退する。また、ワイド端からテレ端までのズーム域では、ガイド突起11bがカム環ガイド溝22aの環状溝部分22a-2に案内されて、カム環11はハウジング22に対する光軸方向位置を変化させず、光軸方向の定位置で回転される。
A cam ring (rotating member) 11 is supported inside the
カム環11を挟んで第1繰出筒13と直進案内環10が支持されている。第1繰出筒13と直進案内環10はそれぞれハウジング22に対して光軸方向に直進案内されており、かつカム環11に対しては、相対回転は可能で光軸方向に共に移動するように結合されている。
The
直進案内環10は、2群レンズ移動枠8を光軸方向へ相対移動可能に直進案内している。2群レンズ移動枠8の内部には2群レンズ保持枠2を介して第2レンズ群LG2が保持され、第2レンズ群LG2の後部に、シャッタ羽根Sを保持するシャッタブロック100が支持されている。また、ハウジング22に対して光軸方向に直進案内された第1繰出筒13はさらに、第2繰出筒12を光軸方向へ相対移動可能に直進案内している。第2繰出筒12の内部には、1群レンズ保持枠1を介して第1レンズ群LG1が支持されている。
The
第2繰出筒12は内径方向に突出する1群用カムフォロアCF1を有し、この1群用カムフォロアCF1が、カム環11の外周面に形成した1群制御カム溝CG1に摺動可能に嵌合している。第2繰出筒12は第1繰出筒13を介して光軸方向に直進案内されているため、カム環11が回転すると、1群制御カム溝CG1の形状に従って、第2繰出筒12すなわち第1レンズ群LG1が光軸方向へ所定の軌跡で移動する。
The
カム環11の内周面に形成した2群制御カム溝CG2に対し、2群レンズ移動枠8の外周面に設けた2群用カムフォロアCF2が係合している。2群レンズ移動枠8は直進案内環10を介して光軸方向に直進案内されているため、カム環11が回転すると、2群制御カム溝CG2の形状に従って、2群レンズ移動枠8すなわち第2レンズ群LG2が光軸方向へ所定の軌跡で移動する。
The second group cam follower CF2 provided on the outer peripheral surface of the second group
2群レンズ移動枠8と第2繰出筒12の間には、圧縮ばねからなる群間付勢ばね27が挿入されており、2群レンズ移動枠8と第2繰出筒12は互いに離間する方向に付勢されている。
A
以上の構造からなるズームレンズ鏡筒70は次のように動作する。図1、図2及び図4に示す鏡筒収納状態では、図3及び図5に示す撮影状態よりも光軸方向の光学系の長さ(第1レンズ群LG1の物体側の面から撮像素子71の撮像面までの距離)が短くなっている。この鏡筒収納状態において撮影状態への移行信号(例えば、ズームレンズ鏡筒70が搭載されるカメラに設けたメインスイッチのオン)が入力されると、ズームモータ150が鏡筒繰出方向に駆動され、カム環11が回転しながら光軸方向前方へ繰り出される。直進案内環10と第1繰出筒13は、カム環11と共に前方に直進移動する。カム環11が回転すると、その内側では、直進案内環10を介して直進案内された2群レンズ移動枠8が、2群用カムフォロアCF2と2群制御カム溝CG2の関係によって光軸方向に所定の軌跡で移動される。また、カム環11が回転すると、該カム環11の外側では、第1繰出筒13を介して直進案内された第2繰出筒12が、1群用カムフォロアCF1と1群制御カム溝CG1の関係によって光軸方向に所定の軌跡で移動される。
The
すなわち、鏡筒収納状態からの第1レンズ群LG1と第2レンズ群LG2の繰出量はそれぞれ、前者が、ハウジング22に対するカム環11の前方移動量と、該カム環11に対する第2繰出筒12のカム繰出量との合算値として決まり、後者が、ハウジング22に対するカム環11の前方移動量と、該カム環11に対する2群レンズ移動枠8のカム繰出量との合算値として決まる。ズーミングは、この第1レンズ群LG1と第2レンズ群LG2が互いの空気間隔を変化させながら撮影光軸Oに沿って移動することにより行われる。収納状態から鏡筒繰出を行うと、まず図5の上半断面に示すワイド端の繰出状態になり、さらにズームモータ150を鏡筒繰出方向に駆動させると、図5の下半断面に示すテレ端の繰出状態となる。テレ端とワイド端の間のズーム領域では、カム環11は前述の定位置回転を行い、光軸方向へは進退しない。収納状態への移行信号(例えば、カメラのメインスイッチのオフ)が入力されると、ズームモータ150が鏡筒収納方向に駆動され、ズームレンズ鏡筒70は以上の繰出動作とは逆の収納動作を行う。
That is, the first lens group LG1 and the second lens group LG2 are fed out from the lens barrel retracted state by the former moving amount of the
また、第2繰出筒12の前端部には、第1レンズ群LG1の前方を開閉可能なバリヤ羽根104が設けられており、鏡筒収納状態ではバリヤ羽根104が閉じており、撮影状態への繰り出し動作に応じてバリヤ羽根104が開かれる。
Further, a
第3レンズ群LG3を支持する3群レンズ枠51は、以上のズームモータ150による第1レンズ群LG1及び第2レンズ群LG2の駆動とは独立して、AFモータ160によって光軸方向に前後移動させることができる。そして、光学系がワイド端からテレ端までのズーム域にあるとき、測距手段によって得られた被写体距離情報に応じてAFモータ160を駆動することにより、第3レンズ群LG3が光軸方向に移動してフォーカシングが実行される。
The third
続いて、3群レンズ枠(光学要素保持部材)51の位置制御機構を説明する。ハウジング22は、カム環ガイド溝22aを内周面に有する、撮影光軸Oを中心とする円筒状部(固定筒部材)22bと、円筒状部22bの後端部外側に位置するAF機構組付部22cと、AF機構組付部22cの前方に位置する前方壁部22dとを有している。図6に示すように、AFモータ160の回転出力軸に設けたピニオン160aが、ハウジング22のAF機構組付部22cの後面側に突出する。AF機構組付部22cの後面側には、ピニオン160aに噛合する中間ギヤ57と、該中間ギヤ57に噛合する従動ギヤ56が軸支されていて、ピニオン160aの回転は、このギヤ列を介して、従動ギヤ56と一体に回転するスクリューシャフト58に伝達される。スクリューシャフト58は、ハウジング22と撮像素子ホルダ23の間に、撮影光軸Oと略平行な回転軸を中心として回転可能に支持されている。スクリューシャフト58の外周面に形成した送りねじは、光軸方向に直進案内されたAFナット54に螺合しており、スクリューシャフト58を正逆に回転させることにより、AFナット54が光軸方向に進退移動される。
Next, the position control mechanism of the third group lens frame (optical element holding member) 51 will be described. The
図7ないし図9に示すように、3群レンズ枠51は、第3レンズ群LG3を保持するレンズ保持部51aから、撮影光軸Oを挟んで略対称の径方向に一対のガイド腕部51b、51cを延設させている。ハウジング22と撮像素子ホルダ23の間に撮影光軸Oと平行な3群ガイド軸52が設けられ、この3群ガイド軸52に対して、3群レンズ枠51の一方のガイド腕部51bの先端部付近に形成したガイド穴51dが摺動自在に挿通支持されている。3群レンズ枠51は、他方のガイド腕部51cの先端部に設けた回転規制キー51eを、ハウジング22内周面の回転規制溝22eに係合させて回転規制されており、3群ガイド軸52に沿う光軸方向の直進移動のみ可能に案内されている。
As shown in FIGS. 7 to 9, the third
3群レンズ枠51は、トーションばね(付勢手段)55によって光軸方向前方に付勢されている。図7、図9及び図10に示すように、トーションばね55は、コイル部(揺動中心部)55aと、該コイル部55aから外径方向に突出する支持アーム55bと付勢アーム(着力部)55cを有しており、コイル部55aが、ハウジング22に設けたばね支持突起22fに支持される。ばね支持突起22fは、ハウジング22の円筒状部22bの外側に、撮影光軸Oと平行な(撮影光軸Oを含む)上下方向平面P(図11)に対して略直交する方向へ軸線を向けて形成された円筒状の突起である。ばね支持突起22fの中心に形成されたねじ穴に対してばね留めねじ39を固定することによって、ばね支持突起22fの円筒状外面に対してトーションばね55のコイル部55aが抜け止めされた状態で保持される。この保持状態のコイル部55aの軸線は、ばね支持突起22fの軸線と概ね一致する。
The third
ハウジング22の円筒状部22bの外面には、ばね支持突起22fの近傍に位置させてばね掛け突起22g(図10)が設けられ、トーションばね55の支持アーム55bは、このばね掛け突起22gに掛けられている。一方、付勢アーム55cは、3群レンズ枠51のガイド穴51dの近傍に設けたばね掛け突起51fに掛けられている。付勢アーム55cは、コイル部55aの軸線に略一致する(すなわち撮影光軸Oと平行な上下方向平面Pに対して略直交する)揺動中心軸55xを中心(支点)として揺動することが可能な揺動着力部であって、ばね掛け突起51fに掛けられていない自由状態では図10に「55c(F)」で示す方向を向いている。そして、この自由状態から付勢アーム55cを図10中の反時計方向に約半回転させて、該付勢アーム55cの先端部付近をばね掛け突起51fの光軸方向後方の面に当て付けることにより、トーションばね55の撓み(ねじれ)量が大きくなり、その撓み解消方向の力は、付勢アーム55cがばね掛け突起51fを光軸方向前方へ押圧する荷重として作用する。すなわち、付勢アーム55cを介して3群レンズ枠51に対して光軸方向前方への付勢力が与えられる着力状態となる。
A
このようにしてトーションばね55により光軸方向前方への付勢力を与えられた3群レンズ枠51は、ガイド穴51dの近傍に設けた(すなわちガイド腕部51bの先端部付近に位置する)ナット当付部51gがAFナット54に当て付くことによって、前方への移動が規制される。すなわち、3群レンズ枠51は、トーションばね55の付勢力によってナット当付部51gをAFナット54に当接させた状態で保持され、3群レンズ枠51の光軸方向の前後位置はAFナット54に依存して決まる。前述の通り、AFナット54は、AFモータ160のピニオン160aを正逆に回転駆動することにより、スクリューシャフト58によって光軸方向へ進退移動されるため、結果として、3群レンズ枠51の光軸方向位置は、AFモータ160の駆動方向と駆動量に応じて制御される。例えば、AFモータ160によって前方にAFナット54を移動させると、AFナット54の移動分だけ、トーションばね55の付勢力によって3群レンズ枠51が追随して前方に移動する。逆に、前方の移動位置からAFナット54を後方に移動させると、該AFナット54がナット当付部51gを押し込み、3群レンズ枠51はトーションばね55の付勢力に抗して後方へ移動される。
The third
ハウジング22には、AFモータ160による3群レンズ枠51の光軸方向の後方移動端を検出する原点位置検出センサ40が設けられている。原点位置検出センサ40は、透過型フォトインタラプタからなり、二股状の投光部と受光部の間に3群レンズ枠51のセンサ通過板51hが位置した状態が、該3群レンズ枠51の後方移動端であると検知される。AFモータ160はステッピングモータからなり、フォーカシングに際しての第3レンズ群LG3の移動量は、この後方移動端を原点位置としたAFモータ160の駆動ステップ数として演算される。図10に実線で示しているのが、AFモータ160に制御される可動範囲における3群レンズ枠51の後方移動端であり、同図に二点鎖線で示しているのが、同可動範囲における3群レンズ枠51の前方移動端である。
The
以上のトーションばね55による付勢構造によると、3群レンズ枠51がAFモータ160による前後の移動端の間で移動されるときの付勢アーム55cの揺動角(トーションばね55の撓み量)は、自由状態からばね掛け突起51fに係合させる着力状態にさせるときの付勢アーム55cの揺動角(トーションばね55の撓み量)に比べて遙かに小さい。そのため、AFモータ160による3群レンズ枠51の可動範囲におけるトーションばね55の荷重の変動が小さく、3群レンズ枠51の駆動に必要とされるエネルギーが低いレベルで平均化され、AFモータ160の負担を軽減することができる。また、3群レンズ枠51の移動に応じた荷重変動が小さいので、移動範囲の全域に亘ってスムーズに駆動させることができ、AFモータ160からの駆動力を伝達するギヤ列からの異音も発生しにくくなっている。
According to the biasing structure by the
トーションばね55において荷重変動が小さく抑えられている要因として、揺動の支点であるコイル部55aから、3群レンズ枠51への着力点(作用点)であるばね掛け突起51fまでの付勢アーム55cの長さも関係している。揺動中心軸55xからばね掛け突起51fに対する着力点までの距離、すなわち付勢アーム55cの先端付近の揺動の回転半径が大きくなるほど、3群レンズ枠51の単位移動量あたりの付勢アーム55cの変位角は小さくなり、ばね荷重の変動を抑制できる。そして、トーションばね55をハウジング22の円筒状部22bの外側に位置させることで、円筒状部22b内にある他の部材と干渉することなく、付勢アーム55cにこのような長さを持たせることが可能になっている。
As a factor that suppresses the load fluctuation in the
トーションばね55をハウジング22の円筒状部22bの外側に位置させることで以上の効果が得られるが、その反面、図6に示すように、トーションばね55がハウジング22による保護を受けない状態になる。図12に示すように、ハウジング22の円筒状部22bは、内周面に設けた3つのカム環ガイド溝22aが、その周方向の略全域に亘って形成されている関係上、周方向の途中に途絶部分のない完全な円筒体である必要がある。ハウジング22は合成樹脂の成形品として形成されるが、完全円筒体である円筒状部22bの外側にさらにトーションばね55を覆う壁部を有するような二重壁構造にすることは製造上難しい。
Although the above effect can be obtained by positioning the
本実施形態のズームレンズ鏡筒70では、ハウジング22の後部に取り付けられる撮像素子ホルダ23に、トーションばね55の外側を覆う保護壁部(保護壁部材)23aが設けられている。図2、図7、図8及び図11に示すように、保護壁部23aは、トーションばね55の付勢アーム55cの揺動平面と略平行な平面状の側壁部(平面部)23bと、その下方のコイル部55aを囲む箱状部23cを有していて、側壁部23bから箱状部23cに亘る光軸方向の前縁部が、ハウジング22の前方壁部22dに当接し、箱状部23cの側縁部が、ハウジング22に設けた下方支持部22hに当接される。前方壁部22dと下方支持部22hにはそれぞれ、保護壁部23a側の当接縁部を嵌合支持する段部22d-1、22h-1が形成されている。図8に示すように、保護壁部23aの側壁部23bの内側面には、3群レンズ枠51の移動時にばね掛け突起51fとの干渉を防ぐ光軸方向溝23dが形成され、光軸方向溝23dの後部には原点位置検出センサ40を収納するセンサ収納部23eが形成されている。
In the
撮像素子ホルダ23をハウジング22に組み付けるときには、保護壁部23aにおける箱状部23cの側縁部を下方支持部22hの段部22h-1上に支持させつつ前方へスライドさせていき、撮像素子ホルダ23の本体部がハウジング22の後面部に当接すると、保護壁部23aの前縁部も前方壁部22dに当て付き段部22d-1に嵌合する。そして、ハウジング22に対して撮像素子ホルダ23をねじ留め固定することによって、図2に示すように保護壁部23aがトーションばね55の外側を完全に塞いだ保護状態になる。この保護状態では、図11に示すように、ハウジング22の円筒状部22bの外周面と、撮像素子ホルダ23の保護壁部23aとの間の収納空間Q内にトーションばね55が保持されており、トーションばね55は、ズームレンズ鏡筒70内部の可動部材に対しては円筒状部22bによって接触から保護され、ズームレンズ鏡筒70の外側からの接触も保護壁部23aによって保護される。したがって、トーションばね55、特に付勢アーム55cが、別の部材などとの接触によって、通常使用状態での弾性変形とは異なる不可逆的な変形をしてしまうおそれがなく、ズームレンズ鏡筒70が組まれた状態では、3群レンズ枠51の位置制御の精度が損なわれない。
When the
このように、ハウジング22に対して固定される撮像素子ホルダ23に、ハウジング22への取り付け状態でトーションばね55の外側を覆う保護壁部23aを設けたので、ハウジング22の外側に位置するトーションばね55を保護することができる。特に、本実施形態のように、ハウジング22において円筒状部22bが完全な円筒状をなし、この円筒状部22bの外側にトーションばね55を覆うような壁部を形成することが樹脂成形では難しい構造においても、ハウジング22の形状に依存することなく、確実にトーションばね55を保護することができる。なお、ハウジング22のうち、保護壁部23aが当接される前方壁部22dと下方支持部22hはいずれも、円筒状部22bの外周面から突出する板状の部分であり、ばね支持突起22fと同じ方向の型抜きで形成可能であるため、保護壁部23aとは異なり、ハウジング22の一部として成形が可能である。
As described above, since the
以上の実施形態では、ハウジング22の円筒状部22bの内周面に形成したカム環ガイド溝22aの螺旋溝部分22a-1によってカム環11の光軸方向移動を行わせているが、これに代えて、図13のようなヘリコイドを用いた繰出構造を用いてもよい。図13に示すハウジング22′の円筒状部22b′は、螺旋溝部分22a-1′と環状溝部分22a-2′からなるカム環ガイド溝(回転部材案内機構)22a′を内周面に有しており、このカム環ガイド溝22a′に対してカム環11′のギヤリング部11a′に設けたガイド突起11b′が嵌まっている。先の実施形態とは異なり、カム環11′の光軸方向への繰出案内は、カム環ガイド溝22a′の螺旋溝部分22a-1′とガイド突起11b′の関係ではなく、円筒状部22b′の内周面に形成した内面ヘリコイド(回転部材案内機構)22zと、カム環11′のギヤリング部11a′上に形成した外面ヘリコイド(回転部材案内機構)11zによって行われる。そして、ヘリコイド11z、22zによってカム環11′が光軸方向前方まで繰り出されると、ヘリコイド螺合が外れると共に、ガイド突起11b′がカム環ガイド溝22a′の環状溝部分22a-2′に進入し、カム環11′は光軸方向に移動されない定位置回転状態となる。この実施形態においても、カム環11′の移動制御のために、ハウジング22′の円筒状部22b′は周方向の途絶部分のない完全な円筒体とされているため、先の実施形態と同様のばね保護構造が有効である。
In the above embodiment, the
以上、図示実施形態に基づき本発明を説明したが、本発明は、この実施形態に限定されるものではない。例えば、実施形態においては、光軸方向に移動付勢される光学要素が、フォーカシングレンズ群として機能する第3レンズ群LG3であるが、本発明において付勢手段により移動付勢される光学要素は、このようなレンズ群以外のものであってもよい。 As mentioned above, although this invention was demonstrated based on illustration embodiment, this invention is not limited to this embodiment. For example, in the embodiment, the optical element that is moved and urged in the optical axis direction is the third lens group LG3 that functions as a focusing lens group, but in the present invention, the optical element that is moved and urged by the urging means is Other than such a lens group may be used.
また、実施形態の付勢手段はトーションばね55であるが、トーションばね55の付勢アーム55cに相当する着力部分を独立したレバー部材とし、このレバー部材に対して別のばね部材で付勢力を付与するタイプの付勢手段を備えたレンズ鏡筒にも、本発明は適用が可能である。
The urging means of the embodiment is the
また、実施形態のトーションばね55は、光軸方向前方への付勢力を与えるものであるが、本発明では付勢手段による付勢の方向はこれに限定されず、光軸方向後方への付勢手段であってもよい。
The
また、実施形態では、トーションばね55のコイル部55aを支持するばね支持突起22fが、ハウジング22の円筒状部22b側に設けられているが、撮像素子ホルダ23の保護壁部23a側に同様の支持突起を設けることも可能である。
In the embodiment, the
1 1群レンズ保持枠
2 2群レンズ保持枠
8 2群レンズ移動枠
10 直進案内環
11 11′ カム環(回転部材)
11a 11a′ ギヤリング部
11b 11b′ ガイド突起
11z 外面ヘリコイド(回転部材案内機構)
12 第2繰出筒
13 第1繰出筒
22 22′ ハウジング
22a 22a′ カム環ガイド溝(回転部材案内機構)
22a-1 22a-1′ 螺旋溝部分
22a-2 22a-2′ 環状溝部分
22b 円筒状部(固定筒部材)
22c AF機構組付部
22d 前方壁部
22d-1 段部
22e 回転規制溝
22f ばね支持突起
22g ばね掛け突起
22h 下方支持部
22h-1 段部
22z 内面ヘリコイド(回転部材案内機構)
23 撮像素子ホルダ
23a 保護壁部(保護壁部材)
23b 側壁部(平面部)
23c 箱状部
23d 光軸方向溝
23e センサ収納部
25 ローパスフィルタ
27 群間付勢ばね
28 ズームギヤ
39 ばね留めねじ
40 原点位置検出センサ
51 3群レンズ枠(光学要素保持部材)
51a レンズ保持部
51b 51c ガイド腕部
51d ガイド穴
51e 回転規制キー
51f ばね掛け突起
51g ナット当付部
51h センサ通過板
52 3群ガイド軸
54 AFナット
55 トーションばね(付勢手段)
55a コイル部(揺動中心部)
55b 支持アーム
55c 付勢アーム(着力部)
55x 揺動中心軸
56 従動ギヤ
57 中間ギヤ
58 スクリューシャフト
70 ズームレンズ鏡筒
71 撮像素子
100 シャッタブロック
104 バリヤ羽根
150 ズームモータ
160 AFモータ
160a ピニオン
CF1 1群用カムフォロア
CF2 2群用カムフォロア
CG1 1群制御カム溝
CG2 2群制御カム溝
LG1 第1レンズ群
LG2 第2レンズ群
LG3 第3レンズ群
O 撮影光学系の光軸
P 撮影光軸と平行な上下方向平面
S シャッタ羽根
Q ハウジングの円筒状部と撮像素子ホルダの保護壁部の間の収納空間
DESCRIPTION OF
12
22a-1 22a-1 '
22c AF
23
23b Side wall (plane part)
23c Box-shaped
51a
55a Coil (swinging center)
55x
Claims (6)
上記撮影光学系を囲む固定筒部材;
上記固定筒部材の外側に位置し、光軸と平行な平面に対して略直交する軸を中心として揺動可能で、揺動中心部から径方向に延びる着力部を介して上記光学要素保持部材を光軸方向に付勢する付勢手段;及び
上記固定筒部材とは別部材からなり、該固定筒部材に取り付けられて固定筒部材外面との間に上記付勢手段の収納空間を形成する保護壁部材;
を備えたことを特徴とするレンズ鏡筒。 An optical element holding member that holds an optical element constituting the photographing optical system and is movable in the optical axis direction;
A fixed cylinder member surrounding the imaging optical system;
The optical element holding member is located on the outer side of the fixed cylinder member and is swingable about an axis substantially orthogonal to a plane parallel to the optical axis, and via an attachment portion extending in the radial direction from the swing center portion. An urging means for urging the urging means in the direction of the optical axis; and a member separate from the fixed cylinder member, and is attached to the fixed cylinder member to form a storage space for the urging means between the fixed cylinder member and the outer surface. Protective wall member;
A lens barrel characterized by comprising:
Priority Applications (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008174689A JP5090274B2 (en) | 2008-07-03 | 2008-07-03 | Lens barrel |
| US12/263,694 US7965933B2 (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2008-11-03 | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element |
| TW097142460A TWI418913B (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2008-11-04 | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element |
| CN 200810175556 CN101430414B (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2008-11-07 | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element |
| KR1020080110449A KR101249869B1 (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2008-11-07 | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element |
| GB0820515A GB2454780B (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2008-11-10 | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element |
| DE102008056601A DE102008056601A1 (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2008-11-10 | Mechanism for positioning an optical element |
| US13/453,385 USRE44171E1 (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2012-04-23 | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008174689A JP5090274B2 (en) | 2008-07-03 | 2008-07-03 | Lens barrel |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010014959A true JP2010014959A (en) | 2010-01-21 |
| JP5090274B2 JP5090274B2 (en) | 2012-12-05 |
Family
ID=41701129
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008174689A Expired - Fee Related JP5090274B2 (en) | 2007-11-09 | 2008-07-03 | Lens barrel |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5090274B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015179239A (en) * | 2014-02-28 | 2015-10-08 | 三星電子株式会社Samsung Electronics Co.,Ltd. | Lens barrel and optical apparatus |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004240360A (en) * | 2003-02-10 | 2004-08-26 | Pentax Corp | Guide structure and finder structure of lens group |
| JP2005189516A (en) * | 2003-12-25 | 2005-07-14 | Nitto Kogaku Kk | Lens barrel driving mechanism |
| JP2007033961A (en) * | 2005-07-28 | 2007-02-08 | Nidec Copal Corp | Lens driving apparatus |
| JP2007316279A (en) * | 2006-05-25 | 2007-12-06 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | State switching mechanism |
-
2008
- 2008-07-03 JP JP2008174689A patent/JP5090274B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004240360A (en) * | 2003-02-10 | 2004-08-26 | Pentax Corp | Guide structure and finder structure of lens group |
| JP2005189516A (en) * | 2003-12-25 | 2005-07-14 | Nitto Kogaku Kk | Lens barrel driving mechanism |
| JP2007033961A (en) * | 2005-07-28 | 2007-02-08 | Nidec Copal Corp | Lens driving apparatus |
| JP2007316279A (en) * | 2006-05-25 | 2007-12-06 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | State switching mechanism |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015179239A (en) * | 2014-02-28 | 2015-10-08 | 三星電子株式会社Samsung Electronics Co.,Ltd. | Lens barrel and optical apparatus |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5090274B2 (en) | 2012-12-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101249869B1 (en) | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element | |
| JP5335259B2 (en) | Optical element position control mechanism | |
| KR20090048361A (en) | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element | |
| JP2007114528A (en) | Cam mechanism of lens barrel, and method for manufacturing rotation member used for cam mechanism | |
| US7866901B2 (en) | Lens barrel and image-pickup apparatus | |
| JP2009116222A (en) | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element | |
| JP4917075B2 (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2007033961A (en) | Lens driving apparatus | |
| JP2004233916A (en) | Optical element retreat mechanism for lens barrel | |
| JP5090274B2 (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP5056971B2 (en) | Lens barrel cam mechanism | |
| JP2009134249A (en) | Mechanism for controlling position of optical element | |
| US7944634B2 (en) | Support structure for light quantity control unit of lens barrel | |
| JP2004258641A (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2007094118A (en) | Lens driving device | |
| JP2009169285A (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2004233924A (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2004258640A (en) | Optical element withdrawing mechanism for lens barrel | |
| JP3342480B2 (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2004233922A (en) | Optical element retreat mechanism and positioning adjusting mechanism for lens barrel | |
| JP2004258639A (en) | Optical element withdrawing mechanism for lens barrel | |
| JP2004233918A (en) | Optical element retreat mechanism for lens barrel | |
| JP2007206710A (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP2016166960A (en) | Lens barrel | |
| JP6084017B2 (en) | Lens barrel and imaging device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20110518 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20120118 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120124 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120326 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20120828 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20120912 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20150921 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |