JP2008188177A - Image processor - Google Patents
Image processor Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2008188177A JP2008188177A JP2007024698A JP2007024698A JP2008188177A JP 2008188177 A JP2008188177 A JP 2008188177A JP 2007024698 A JP2007024698 A JP 2007024698A JP 2007024698 A JP2007024698 A JP 2007024698A JP 2008188177 A JP2008188177 A JP 2008188177A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- image
- region
- interest
- images
- frame
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000009966 trimming Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 abstract description 31
- 238000002059 diagnostic imaging Methods 0.000 abstract description 11
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003902 lesion Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000001015 abdomen Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002699 waste material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は、画像処理装置に係り、特に取得された画像を処理して視認性を向上させる画像処理装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an image processing apparatus, and more particularly to an image processing apparatus that processes an acquired image to improve visibility.
医療施設では、医用画像撮像装置で撮影された画像、医用画像診断装置やワークステーション等で作成された画像等がフィルムに出力され又はモニタに表示され、その画像を用いて読影医が観察又は診断をしている。 In a medical facility, an image taken by a medical imaging device, an image created by a medical image diagnostic device, a workstation, or the like is output on a film or displayed on a monitor, and an image interpretation doctor observes or diagnoses using the image. I am doing.
近年、画像診断装置が高性能化し、短時間で長距離の撮影ができるようになったことにより、取り扱う画像枚数が爆発的に増えたことや、三次元やMPR(Multi Planer Reconstruction)などの画像解析技術が高度になったことにより、これらの画像を用いて観察や診断をする機会がますます増えている。 In recent years, the performance of diagnostic imaging equipment has improved, and it has become possible to shoot long distances in a short time, so the number of images handled has increased explosively and images such as 3D and MPR (Multi Planer Reconstruction) As analysis techniques become more advanced, there are more and more opportunities for observation and diagnosis using these images.
このような状況にあって、読影医が観察や診断をするにあたっての視認性、見読性を向上させるために、所望の画像を効果的かつ効率的にモニタに表示したりフィルムに出力したりする工夫が望まれている。 Under these circumstances, in order to improve the visibility and readability of the interpretation doctor for observation and diagnosis, the desired image can be effectively and efficiently displayed on the monitor or output to the film. The idea to do is desired.
特許文献1には、画像の関心領域を指定し、その関心領域を画像出力媒体の最大出力サイズに合わせて変倍する方法が提案されている。
しかしながら、特許文献1に記載の画像出力方法では、複数の画像を一度に扱うことが考慮されていないという問題がある。そのため、1つの媒体を任意の領域に分割して各分割領域に画像を出力する、ということについても考慮されていない。 However, the image output method described in Patent Document 1 has a problem that it is not considered to handle a plurality of images at once. Therefore, it is not considered that one medium is divided into arbitrary areas and an image is output to each divided area.
本発明は、上記事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、柔軟かつ簡便に利用できる画像処理装置であって、所望の画像を効果的かつ効率的に出力できる画像処理装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above circumstances, and an object thereof is to provide an image processing apparatus that can be used flexibly and easily, and that can output a desired image effectively and efficiently. To do.
前記課題を解決するために、請求項1に記載の画像処理装置は、複数のフレームがレイアウトされているテンプレートの各フレーム内に複数の画像をそれぞれ合成し、出力画像を作成する医用画像処理装置において、医用画像撮影装置で撮影された複数の画像を入力する入力手段と、前記入力手段により入力された複数の画像に対して関心領域を指定する関心領域指定手段と、前記複数の画像から前記関心領域指定手段によって指定された関心領域を、その関心領域が内接するトリミング領域にしたがって画像領域として抽出する抽出手段と、前記抽出手段によって前記複数の画像から抽出された複数の画像領域像を前記テンプレートの各フレーム内に合成して出力画像を作成する合成処理手段と、を備えたことを特徴としている。 In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, the image processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein a plurality of images are combined in each frame of a template in which a plurality of frames are laid out to create an output image. The input means for inputting a plurality of images captured by the medical image capturing apparatus, the region of interest specifying means for specifying the region of interest for the plurality of images input by the input means, and the plurality of images from the plurality of images. Extraction means for extracting a region of interest designated by the region of interest designation means as an image region according to a trimming region inscribed in the region of interest, and a plurality of image region images extracted from the plurality of images by the extraction means And a composition processing means for composing within each frame of the template to create an output image.
請求項1に記載の画像処理装置によれば、医用画像撮影装置で撮影された複数の画像が画像処理装置に入力され、その各画像に対して関心領域を指定し、関心領域が内接する部分を画像領域として抽出する。画像領域をフレームに合成する処理を全ての画像領域に対して行うことにより、画像領域とフレームとが合成された出力画像を作成し、モニタ、フィルム等に出力する。これにより、所望の画像を効率的かつ効果的にモニタやフィルムに出力することができ、ユーザの視認性を高めることができる。 According to the image processing device of claim 1, a plurality of images photographed by the medical image photographing device are input to the image processing device, a region of interest is designated for each image, and the region of interest is inscribed Are extracted as image regions. By performing the process of combining the image area with the frame on all the image areas, an output image in which the image area and the frame are combined is created and output to a monitor, a film, or the like. Thereby, a desired image can be output to a monitor and a film efficiently and effectively, and a user's visibility can be improved.
請求項2に記載の画像処理装置は、請求項1に記載の画像処理装置において、前記合成処理手段は、前記複数の画像領域が前記テンプレートの各フレーム内で最大の大きさになるように各画像領域を変倍することを特徴としている。
The image processing apparatus according to
請求項2に記載の画像処理装置によれば、合成処理手段は、画像領域がフレームに最大の大きさで表示されるように、画像領域を変倍し、変倍された矩形画像がフレームに合成される。これにより、画像を最適化(例えば、最大化)してフレームに表示することができ、所望の画像をできるだけ大きく表示させることができる。 According to the image processing apparatus of the second aspect, the composition processing unit scales the image area so that the image area is displayed with the maximum size in the frame, and the scaled rectangular image is displayed in the frame. Synthesized. Thereby, an image can be optimized (for example, maximized) and displayed in a frame, and a desired image can be displayed as large as possible.
請求項3に記載の画像処理装置は、請求項1に記載の画像処理装置において、前記複数の画像は、時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある一連の画像を含み、前記合成処理手段は、前記一連の画像の各関心領域の画像間の撮影倍率が一致するように各矩形画像を変倍することを特徴としている。
The image processing device according to
請求項3に記載の画像処理装置によれば、時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある一連の画像が入力された場合には、合成処理手段は、関心領域の画像間の撮影倍率が一致するように各矩形画像を変倍し、変倍された矩形画像がフレームに合成される。これにより、時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある一連の画像(複数枚の画像)を取り扱う場合において、関心領域の大きさが異なることで腫瘍の大きさが異なる等、観察や読影がしにくく、誤診を招く危険性がある場合においても、一連の画像の関心領域の大きさを揃えることで誤診を招く危険性を低下させることができる。
According to the image processing apparatus of
請求項4に記載の画像処理装置は、請求項1から3のいずれかに記載の画像処理装置において、前記複数の画像は、時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある一連の画像を含み、前記合成処理手段は、前記テンプレートのフレームの中心と前記画像領域の中心とが一致するように各画像領域を各フレーム内に合成することを特徴としている。 The image processing device according to claim 4 is the image processing device according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the plurality of images include a series of temporally or spatially related images, and the synthesis is performed. The processing means synthesizes each image area in each frame so that the center of the frame of the template matches the center of the image area.
請求項4に記載の画像処理装置によれば、時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある一連の画像が入力された場合には、合成処理手段は、フレームの中心と画像領域の中心とが一致するように各画像領域を各フレーム内に合成する。これにより、患者の状態が悪く動かすことが困難である等により、被写体の中心位置が画像診断装置に対してずれた状態で撮影せざるを得ない場合等、一連の画像の関心領域の中心位置がずれてしまうことで視認性が低下して観察や読影がしにくい場合においても、一連の画像の関心領域の位置と大きさとを同一にすることで視認性の低下を防ぎ、観察や読影をしやすくすることができる。 According to the image processing apparatus of the fourth aspect, when a series of images that are temporally or spatially related are input, the synthesis processing means matches the center of the frame with the center of the image area. In this way, each image region is synthesized in each frame. As a result, the center position of the region of interest in a series of images, such as when the subject's center position is displaced with respect to the diagnostic imaging apparatus due to the patient's poor condition and difficult movement, etc. Even if it is difficult to observe or interpret because the visibility is reduced due to the shift, it is possible to prevent the degradation of visibility by making the position and size of the region of interest in the series of images the same, and to observe and interpret Can be easier.
請求項5に記載の画像処理装置は、請求項1から4のいずれかに記載の画像処理装置において、複数のテンプレートを記憶する記憶手段と、 前記記憶されているテンプレートの中から、前記合成処理手段において画像領域が合成されるテンプレートを選択する選択手段と、を更に備え、前記記憶手段は、フレームの大きさ及び配置を任意に設定することによって作成されたテンプレート及び/又はフレームが水平方向と垂直方向とに規則的に配置されたテンプレートを複数記憶することを特徴としている。 The image processing device according to claim 5 is the image processing device according to any one of claims 1 to 4, wherein a storage unit that stores a plurality of templates, and the combination processing among the stored templates. Selecting means for selecting a template with which the image area is synthesized in the means, wherein the storage means is configured so that the template and / or the frame created by arbitrarily setting the size and arrangement of the frame is horizontal. A plurality of templates regularly arranged in the vertical direction are stored.
請求項5に記載の画像処理装置によれば、フレームの大きさ及び配置を任意に設定することによって作成されたテンプレート及び/又はフレームが水平方向と垂直方向とに規則的に配置されたテンプレートの複数のテンプレートがあらかじめ記憶されており、その中から出力画像を作成する基となるテンプレートを選択して使用する。これにより、様々なテンプレートが用いられる場合においても、その中から最適なテンプレートを使用することができる。 According to the image processing apparatus of claim 5, a template created by arbitrarily setting the size and arrangement of the frame and / or a template in which the frame is regularly arranged in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction. A plurality of templates are stored in advance, and a template serving as a basis for creating an output image is selected and used. Thereby, even when various templates are used, an optimal template can be used.
本発明によれば、柔軟かつ簡便に利用できる画像処理装置であって、所望の画像を効果的かつ効率的に出力できる画像処理装置を提供することができる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, it is an image processing apparatus which can be utilized flexibly and simply, Comprising: The image processing apparatus which can output a desired image effectively and efficiently can be provided.
以下、本発明を実施するための最良の形態を添付図面に基づいて説明する。 The best mode for carrying out the present invention will be described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
図1は、本発明に係る画像処理装置10の構成を示すブロック図である。画像処理装置10は、被検体の断層像を撮影する医用画像撮影装置2、医用画像撮影装置2で撮影された画像等が保存されている画像データベース3、プリンタ4とLAN等のネットワーク1によって接続される。医用画像撮影装置2は、X線CT装置、MR装置、超音波撮影装置等の被検体の断層像を撮影可能な装置により構成される。本実施の形態では、X線CT装置によって、被検体の頭部又は腹部の断層像が撮影された場合を例に説明する。
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of an
画像処理装置10は、主として、各構成要素の動作を制御する制御装置としての中央処理装置(CPU)11と、装置の制御プログラムが格納されたり、プログラム実行時の作業領域となったりする主メモリ12と、オペレーティングシステム(OS)、周辺機器のデバイスドライブ、各種アプリケーションソフト等が格納される磁気ディスク13と、表示用データを一時記憶する表示メモリ14と、この表示メモリ14からのデータに基づいて画像を表示するCRTモニタ、液晶モニタ等のディスプレイ15と、操作者が指示を入力するためのキーボード16と、ディスプレイ15上のソフトスイッチを操作するためのマウス17と、マウス17の状態を検出してディスプレイ15上のマウスポインタの位置やマウス17の状態等の信号をCPU11に出力するコントローラ18と、上記各構成要素を接続する共通バス19とから構成される。
The
画像処理プログラムとして、磁気ディスク13には、画像診断装置等で作成した画像をモニタに表示するためのプログラム(ビューワ)、及び画像をフィルムに出力するプログラム(フィルミング)が格納されている。CPU11は、上記プログラム(ビューワ又はフィルミング)を磁気ディスク13から読み出して主メモリ12にロードし、実行する。
As the image processing program, the
ビューワは、磁気ディスク13又は画像データベース3に格納されている画像やその付帯情報を主メモリ12に読み込み、それらのデータを主メモリ12に展開する。そして、ビューワは、主メモリ12に展開したデータ、主メモリ12に展開したデータを基に作成された表示データ等をディスプレイ15上に出力して表示させたり、画像を解析して主メモリ12に展開したデータを更新したり、解析したデータを磁気ディスク13に保存したりすることができる。ディスプレイ15で表示された画像は、ネットワーク1を介して別の画像診断装置やワークステーションに転送することができる。転送された画像は、別の画像診断装置やワークステーションで受信され、その画像が画面に表示されたり画像処理されたりする。
The viewer reads an image stored in the
フィルミングは、磁気ディスク13又は画像データベース3に格納されている画像やその付帯情報を主メモリ12に読み込み、それらのデータを処理してフィルムデータを作成する。そして、そのフィルムデータを磁気ディスク13又は主メモリ12に保存したり、ディスプレイ15上に表示したり、ネットワーク1を介して接続されているプリンタ4に出力したりすることができる。ネットワーク1を介してプリンタ4に転送されたフィルムデータは、フィルムや紙等の媒体に印刷される。
In filming, an image stored in the
なお、本実施例では、主メモリ12以外の記憶装置として磁気ディスク13が接続されているが、磁気ディスク13以外の記憶装置として、例えば、画像処理装置10に内蔵又は外付けされたメモリ、取り出し可能な外部メディアに対してデータの書き込みや読み出しを行う装置、外部記憶装置とネットワークを介してデータを送受信する装置等を適用してもよい。
In the present embodiment, the
上記のように構成された画像処理装置においては、(1)診断上有用な関心領域を抜き出す(トリミングと同義)、(2)抜き出された画像領域をビューワまたはフィルミングの画像表示領域(フレーム)に合わせて変倍してフレームと合成する、の2つの手段により、所望の画像を効果的かつ効率的にモニタに表示させるためのデータ(表示データ)又はフィルムに出力するためのデータ(フィルムデータ)が作成される。以下、上記2つの手段について順番に説明する。なお、以下に説明する上記2つの手段における処理は、キーボード16等により処理を行う対象となる画像が選択され、CPU11にその選択された画像について画像処理を行う旨の指示が入力された後に、CPU11によって行われる。
In the image processing apparatus configured as described above, (1) a diagnostically useful region of interest is extracted (synonymous with trimming), and (2) the extracted image region is displayed as a viewer or filming image display region (frame). ) In order to display the desired image effectively and efficiently on the monitor (display data) or data to be output to the film (film). Data) is created. Hereinafter, the two means will be described in order. Note that the processing in the two means described below is performed after an image to be processed is selected by the
なお、関心領域は、一般的に多角形や楕円形で指定することが可能であるが、観察や読影をする際、ビューワやフィルミングのフレームは矩形であることが最も視認性が良く、また、無駄な空間が存在しないため、本実施の形態では、関心領域、フレームを矩形として説明する。 The region of interest can generally be specified as a polygon or an ellipse. However, when viewing or interpreting, the viewer or filming frame is most rectangular and has the highest visibility. In this embodiment, the region of interest and the frame are described as rectangles because there is no useless space.
<診断上有用な関心領域を抜き出す(トリミング)処理について>
関心領域を指定する方法としては、閾値処理と呼ばれる方法により自動的に関心領域を指定する方法、及びユーザが手動で関心領域を指定する方法(自動的に指定した関心領域を調整する方法も含む)の2つがある。なお、閾値処理については、既に公知の様々な方法を使用することができる。
<About extracting (trimming) areas of interest useful for diagnosis>
As a method of designating a region of interest, a method of automatically designating a region of interest by a method called threshold processing, and a method of manually designating a region of interest by a user (including a method of automatically adjusting a region of interest designated) There are two). For the threshold processing, various known methods can be used.
まず、自動的に関心領域を指定してトリミングする方法について説明する。 First, a method for automatically specifying a region of interest and performing trimming will be described.
[1枚の画像に対して処理を行う場合]
一般的に、X線CT装置やMRI装置、ワークステーションなどで撮影又は作成された画像の関心領域は、画像の中央付近に存在する。そこで、画像の各辺の中央から対辺に向かって所定の閾値を超える画素を走査していき、閾値を超える最も外側の画素を矩形の辺として領域が抜き出される。
[When processing one image]
In general, a region of interest of an image captured or created by an X-ray CT apparatus, an MRI apparatus, a workstation, or the like exists near the center of the image. Therefore, pixels exceeding a predetermined threshold are scanned from the center of each side toward the opposite side, and an area is extracted with the outermost pixel exceeding the threshold as a rectangular side.
すなわち、図2に示すように、水平方向の中心位置において、画像の上辺から下方向に所定の閾値を超える最初の画素が探索される。そして、水平方向の中心位置から左右方向に、残りの画素についても同様の作業が行われる。その結果、閾値を超える画素が最も上にある画素位置が、抜き出される関心領域の上辺と設定される。画像の下辺、左辺、右辺についても同様の処理が行われることにより、関心領域の下辺、左辺、右辺が設定される。これにより、図3(a)に示すように、最適な関心領域が指定される。 That is, as shown in FIG. 2, the first pixel exceeding a predetermined threshold value is searched from the upper side of the image downward in the horizontal center position. The same operation is performed for the remaining pixels from the horizontal center position to the left and right. As a result, the pixel position where the pixel exceeding the threshold value is at the top is set as the upper side of the region of interest to be extracted. Similar processing is performed on the lower side, left side, and right side of the image, thereby setting the lower side, left side, and right side of the region of interest. Thereby, as shown to Fig.3 (a), an optimal region of interest is designated.
その後、このように指定された関心領域が内接する矩形のトリミング領域にしたがって、矩形の画像領域(矩形画像)が抽出される。本実施の形態では、矩形の関心領域を指定したため、関心領域と矩形画像とは一致した領域となる。 Thereafter, a rectangular image region (rectangular image) is extracted according to a rectangular trimming region inscribed by the region of interest designated in this way. In the present embodiment, since the rectangular region of interest is designated, the region of interest and the rectangular image coincide with each other.
これにより、画像が撮影されている部分のみ、すなわち観察したい部分のみをフレーム一杯に表示することができるため、読影しやすい表示データ又はフィルムデータを作成することができる。また、フィルム一杯に画像が印刷されるため、フィルムの無駄を減らすことができる。 As a result, since only the part where the image is taken, that is, only the part to be observed can be displayed in a full frame, display data or film data that is easy to interpret can be created. Further, since the image is printed on the entire film, the waste of the film can be reduced.
なお、図3(a)においては、出来るだけ大きな関心領域をとるために、画像が撮影されている領域を抜き出す例について説明したが、閾値を変えることにより、病変部のみを抜き出したり、特定の臓器を抜き出したりすることもできる。 In FIG. 3A, an example in which an area where an image is captured is extracted in order to take as large a region of interest as possible has been described. However, by changing a threshold, only a lesion is extracted or a specific area is extracted. You can also extract organs.
[時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある複数枚の画像(一連の画像)に対して処理を行う場合]
時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある一連の画像を扱う場合、視認性・見読性を向上させるために、一連の画像の関心領域を同じ大きさにすることが望まれている。また、回転させた(様々な角度で作成した)一連の三次元画像の位置と大きさを揃えることで視認性を向上させることも望まれている。これは一連の画像の大きさがそれぞれ異なると、画像ごとに腫瘍等の大きさが変わってしまい、誤診を招く危険性があるからである。もちろん、被写体の長さを示す目盛りなどが各フレームに表示されているであろうが、直感的にはわかりにくい。
[When processing multiple images (series of images) that are temporally or spatially related]
When dealing with a series of images that are temporally or spatially related, in order to improve visibility and legibility, it is desired to make the region of interest of the series of images the same size. It is also desired to improve visibility by aligning the position and size of a series of three-dimensional images that have been rotated (created at various angles). This is because if the size of a series of images is different, the size of a tumor or the like changes for each image, which may cause a misdiagnosis. Of course, a scale indicating the length of the subject will be displayed on each frame, but it is difficult to understand intuitively.
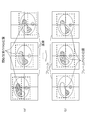
このような場合には、図3(b)に示すように、一連で扱う個々の画像における所定の閾値を越えるすべての画素を抱合する大きさの関心領域が指定される。例えば、一連の画像全てに対して、上記のような角画像に最適な関心領域を指定する処理が行われ、その中で最も大きな関心領域が、一連の画像の関心領域として指定される。その結果、一連の画像すべてに対して関心領域の大きさと位置とを同一にすることができる。 In such a case, as shown in FIG. 3 (b), a region of interest having a size for merging all pixels exceeding a predetermined threshold in each series of images handled is designated. For example, the process of designating the region of interest that is optimal for the corner image as described above is performed on all the series of images, and the largest region of interest is designated as the region of interest of the series of images. As a result, the size and position of the region of interest can be the same for all the series of images.
これにより、同じシリーズに属する全画像の大きさ又は回転させた複数の三次元画像の大きさを揃えることができるため、読影しやすいという効果がある。なお、指定された関心領域から矩形画像を抽出する方法は、1枚の画像に対して処理を行う場合と同様である。 Thereby, the size of all the images belonging to the same series or the size of a plurality of rotated three-dimensional images can be made uniform, so that there is an effect that interpretation is easy. Note that a method for extracting a rectangular image from a designated region of interest is the same as the case of processing a single image.
なお、自動的に関心領域を指定する場合において、関心領域を指定する前にトリミング処理を適用する画像の範囲を指定することにより、1枚の画像に対して関心領域を指定するか、一連の画像に対して関心領域を指定するか、全ての画像に対して関心領域を指定するか等を設定することができる。 When the region of interest is automatically specified, the region of interest is specified for one image by specifying the range of the image to which the trimming process is applied before the region of interest is specified, or a series of It is possible to set whether a region of interest is designated for an image, a region of interest is designated for all images, or the like.
また、自動的に関心領域を指定する場合において、矩形の関心領域を指定した場合について説明したが、楕円形等の矩形以外の形の関心領域を指定した場合には、楕円形等の関心領域が内接する矩形のトリミング領域を矩形画像として抽出することにより、矩形以外の関心領域にも適応することができる。 In addition, in the case of automatically specifying a region of interest, a case has been described in which a rectangular region of interest is specified. However, when a region of interest other than a rectangle, such as an ellipse, is specified, a region of interest such as an ellipse is used. By extracting a rectangular trimming region inscribed as a rectangular image, it is possible to adapt to a region of interest other than a rectangle.
また、自動的に関心領域を指定する場合において、図4に示すように、抜き出された関心領域に余白を設定することも可能である。この場合には、余白を設定すること及び余白の幅をあらかじめ設定しておく。余白を設定することにより視認性を良くすることができる。また、閾値よりわずかに下回った画素部分を関心領域に含むことができる。これによりフレーム画面での編集(後述)が不要になり、より柔軟かつ簡便に表示データまたはフレームデータを作成することができる。 Further, when the region of interest is automatically designated, it is also possible to set a margin for the extracted region of interest as shown in FIG. In this case, the margin is set and the margin width is set in advance. Visibility can be improved by setting a margin. In addition, a pixel portion slightly below the threshold can be included in the region of interest. This eliminates the need for editing (described later) on the frame screen, so that display data or frame data can be created more flexibly and easily.
次に、ユーザが手動で関心領域を指定する方法について説明する。 Next, a method for manually specifying a region of interest by the user will be described.
手動で関心領域を指定する方法は、基本的には、上記方法により自動的に指定された関心領域を修正する場合に用いられる。 The method of manually designating a region of interest is basically used for correcting a region of interest automatically designated by the above method.
抜き出された関心領域は、ビューワまたはフィルミングの画像表示領域(フレーム)に出力される(詳細は後述)。しかし、被写体の下に写っているテーブルが関心領域に含まれている等、フレームに出力された関心領域がユーザの希望と異なっている場合が考えられる。このような場合には、フレームに出力された関心領域が以下の方法により手動で調整される。 The extracted region of interest is output to a viewer or filming image display region (frame) (details will be described later). However, there may be a case where the region of interest output in the frame is different from the user's wish, for example, the table of interest under the subject is included in the region of interest. In such a case, the region of interest output to the frame is manually adjusted by the following method.
ユーザが、フレームに出力された画像のうち、関心領域を手動で指定したい画像をマウス17等で選択すると、図5に示すように、関心領域指定画面がディスプレイ15に表示される。画面中央の画像表示部には、関心領域が抜き出される前の画像と、関心領域を示す枠とが表示されている。
When the user selects an image for which the region of interest is desired to be manually designated from among the images output to the frame, the region of interest designation screen is displayed on the
そして、画像表示部の下に表示されるHorizontalメニューやVerticalメニュー等により、又はマウス17等で枠の各線を水平方向及び垂直方向に移動させたり、枠の大きさや位置を変えたりすることにより、枠で囲まれた関心領域が新たな関心領域として指定される。
Then, by moving each line of the frame in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction with the
これにより、ユーザが手動で希望する関心領域を指定することができる。例えば、テーブルが写っている画像の場合には、被写体の中心位置が関心領域の中心に対して上に上がるのを防止することができる。また、被写体内部の病変部位等、部分的な関心領域の選択も容易となる。 Thereby, the region of interest desired by the user can be designated manually. For example, in the case of an image showing a table, it is possible to prevent the center position of the subject from rising upward with respect to the center of the region of interest. In addition, it becomes easy to select a partial region of interest such as a lesion site inside the subject.
なお、画像表示部の下に表示されるScopeメニューにより手動で関心領域を指定する処理を適用する範囲を指定することにより、1枚の画像に対して関心領域を指定するか、一連の画像に対して関心領域を指定するか、全ての画像に対して関心領域を指定するか等を設定することができる。 In addition, by designating the range to which the process of manually designating the region of interest is applied using the Scope menu displayed below the image display unit, the region of interest can be designated for one image, or a series of images On the other hand, it is possible to set whether to specify a region of interest or to specify a region of interest for all images.
<抜き出された矩形画像をビューワまたはフィルミングの画像表示領域(フレーム)に合わせて変倍してフレームと合成する処理について>
(1)設定されたテンプレートを読み出す、(2)矩形画像をフレームに合わせて変倍する、(3)矩形画像をフレームに出力する、の3つの手段により、抜き出された矩形画像がフレームに合成された出力画像(表示データ又はフィルムデータ)が作成される。以下、上記3つの手段について順番に説明する。
<About the process of scaling the extracted rectangular image to fit the image display area (frame) of the viewer or filming and compositing with the frame>
The extracted rectangular image is converted into a frame by three means: (1) reading the set template, (2) scaling the rectangular image to fit the frame, and (3) outputting the rectangular image to the frame. A synthesized output image (display data or film data) is created. Hereinafter, the three means will be described in order.
[読み出されるテンプレートを設定する方法について]
テンプレートとは、1つ以上の画像表示領域(フレーム)が配置されているものであり、あらかじめ作成されたものが磁気ディスク13に保存されている。画像を効果的かつ効率的にディスプレイ15又はフィルムに表示するために、データの種類(表示データ又はフィルムデータ)によって異なるテンプレートが作成されている。また、フィルムデータの場合には、フィルムのサイズによっても異なるテンプレートが作成されている。なお、テンプレートには、フレームの大きさ及び配置を任意に設定することによって作成されたテンプレート(図6テンプレート選択画面上段参照、詳細は後述)とフレームが水平方向と垂直方向とに規則的に配置されたテンプレート(図6テンプレート選択画面下段参照)とがある。
[How to set the template to be read]
The template is one in which one or more image display areas (frames) are arranged, and a template created in advance is stored on the
テンプレートを読み出す場合には、ユーザがデータの種類、フィルムのサイズ等を入力すると、入力されたデータの種類又はフィルムのサイズに該当するテンプレートが磁気ディスク13から読み出され、図6に示すようなテンプレート選択画面がディスプレイ15上に表示される。ユーザが所望のテンプレートを選択して、マウス17等でOKボタンを押すことにより、選択されたテンプレートが設定されたテンプレートとして磁気ディスク13から読み出され、主メモリ12に展開される。
When reading the template, when the user inputs the data type, film size, etc., the template corresponding to the input data type or film size is read from the
テンプレート選択画面に希望するテンプレートが無い場合には、新たなテンプレートを作成することができる。図6に示すようなテンプレート選択画面において、マウス17等でAddボタンを押すことにより、図7に示すようなテンプレート作成画面がディスプレイ15に表示される。
If there is no desired template on the template selection screen, a new template can be created. In the template selection screen as shown in FIG. 6, when the Add button is pressed with the
図7に示すようなテンプレート作成画面において、テンプレート作成領域は複数のブロックに分割されている。なお、ブロックの大きさは、ブロックサイズ変更領域で選択されたブロックの大きさとなる。テンプレート作成領域において、マウス17等でブロックをドラッグアンドドロップすることにより、フレームの大きさと位置とが決定される。フレームの形状は正方形、長方形が作成できるが、断層像を表示させる場合には横長のフレームを作成し、長尺画像を表示させる場合には縦長のフレームを作成する等、出力したい画像をイメージしてフレームを作成するのが好ましい。なお、作成されたテンプレートは磁気ディスク13に保存され、これ以降に表示されるテンプレート選択画面に追加表示される。
In the template creation screen as shown in FIG. 7, the template creation area is divided into a plurality of blocks. The block size is the size of the block selected in the block size change area. In the template creation area, the size and position of the frame are determined by dragging and dropping the block with the
これにより、ユーザがフレームのサイズや配置を任意に設定することができる。なお、新規にテンプレートを作成するのみでなく、既に作成されているテンプレートを微調整して新たなテンプレートを作成することもできる。これは、図6に示すようなテンプレート選択画面で、微調整したいテンプレートを選択してModifyボタンを押すことによって可能となる。 Thereby, the user can arbitrarily set the size and arrangement of the frame. In addition to creating a new template, a new template can also be created by finely adjusting a template that has already been created. This can be done by selecting a template to be finely adjusted and pressing the Modify button on the template selection screen as shown in FIG.
[矩形画像をフレームに合わせて変倍する方法について]
まず、上記方法により設定されたテンプレートにおける、所定の画像の出力先となるフレームの縦横比を算出する。なお、所定の画像の出力先のフレームは、手動又は自動であらかじめ選択されている。
[How to scale a rectangular image to fit a frame]
First, the aspect ratio of the frame that is the output destination of a predetermined image in the template set by the above method is calculated. Note that the output destination frame of the predetermined image is selected in advance manually or automatically.
次に、矩形画像の縦横比を変更しないように、かつ矩形画像全体がフレームに表示されるように、矩形画像が変倍される。フレームは任意の縦横比を持つ矩形であり、矩形画像の縦横比とフレームの縦横比とが一致しない場合がある。そこで、図8に示すように、矩形画像の縦横比とフレームの縦横比とが一致しない場合には、矩形画像の辺の長さとフレームの辺の長さとの比を縦と横とで算出し、その比が大きい方を基準として矩形画像が変倍される。これにより、矩形画像全体が必ずフレーム内に収まるように、矩形画像をフレームに合わせて変倍することができる。 Next, the rectangular image is scaled so that the aspect ratio of the rectangular image is not changed and the entire rectangular image is displayed in the frame. The frame is a rectangle having an arbitrary aspect ratio, and the aspect ratio of the rectangular image may not match the aspect ratio of the frame. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 8, when the aspect ratio of the rectangular image does not match the aspect ratio of the frame, the ratio of the side length of the rectangular image to the side length of the frame is calculated in the vertical and horizontal directions. The rectangular image is scaled based on the larger ratio. As a result, the rectangular image can be scaled to fit the frame so that the entire rectangular image always fits within the frame.
[矩形画像をフレームに出力する方法について]
上記方法により変倍された矩形画像をフレームに出力する場合には、矩形画像の中心位置とフレームの中心位置とを一致させるようにする。
[How to output a rectangular image to a frame]
When a rectangular image scaled by the above method is output to a frame, the center position of the rectangular image is matched with the center position of the frame.
これにより、図8に示すように、変倍された矩形画像の縦横比とフレームの縦横比とが一致しない場合においても、矩形画像がフレームの中央に表示される。なお、図8においては、矩形画像をフレームに合わせて変倍するときに縦方向の長さを基準としたため、フレームの左右に空白ができているが、矩形画像をフレームに合わせて変倍するときに横方向の長さを基準とする場合には、フレームの上下に空白ができるし、矩形画像の縦横比とフレームの縦横比とが一致する場合には、空白は発生しない。 As a result, as shown in FIG. 8, even when the aspect ratio of the scaled rectangular image does not match the aspect ratio of the frame, the rectangular image is displayed at the center of the frame. In FIG. 8, since the length in the vertical direction is used as a reference when scaling the rectangular image to fit the frame, there are blanks on the left and right of the frame, but the rectangular image is scaled to fit the frame. Sometimes when the length in the horizontal direction is used as a reference, blanks are formed at the top and bottom of the frame, and when the aspect ratio of the rectangular image matches the aspect ratio of the frame, no blank is generated.
ただし、図9(a)に示すように、一連の画像の中に被写体の中心位置が画像診断装置に対してずれた状態で撮影された画像が含まれている場合には、一連の画像の矩形画像の中心位置もずれてしまう。このままの画像をビューワに表示したりフィルムに出力したりすると、矩形画像の配置が不均等になることでユーザのストレスを誘発して視認性が低下する要因となり得る。そこで、図9(b)に示すように、各画像の矩形画像の中心とフレームの中心とを一致させることで、一連の画像の矩形画像の中心位置がずれている場合においても、矩形画像をフレームに均等に配置することができる。 However, as shown in FIG. 9A, when a series of images includes images taken with the center position of the subject shifted from the diagnostic imaging apparatus, The center position of the rectangular image is also shifted. If the image as it is is displayed on the viewer or output to the film, the arrangement of the rectangular images becomes uneven, which may cause a stress on the user and reduce visibility. Therefore, as shown in FIG. 9B, by matching the center of the rectangular image of each image with the center of the frame, the rectangular image can be converted even when the center position of the rectangular image of the series of images is shifted. It can be evenly arranged on the frame.
次に、抜き出された矩形画像がフレームに合成された出力画像(表示データ又はフィルムデータ)の例について説明する。 Next, an example of an output image (display data or film data) obtained by combining the extracted rectangular image into a frame will be described.
(例1)
図10は、一つ一つの画像に対して最適な関心領域を指定してフレームに出力する場合を示している。この場合、各画像は出力するフレームに最大サイズで出力することができる。
(Example 1)
FIG. 10 shows a case where an optimum region of interest is designated for each image and output to a frame. In this case, each image can be output in the maximum size in the output frame.
(例2)
図11は、一連の画像の関心領域の大きさを同一にしてフレームに出力する場合を示している。この場合、一連の画像は出力する大きさを揃えて出力することができる。
(Example 2)
FIG. 11 shows a case where a region of interest in a series of images has the same size and is output to a frame. In this case, a series of images can be output with the same output size.
(例3)
図12は、被写体の中心位置が画像診断装置に対してずれた状態で撮影された場合において、一つ一つの画像に対して最適な関心領域を指定し、なおかつ、矩形画像の中心とフレームの中心を一致させてビューワまたはフィルミングのフレームに出力する場合を示している。この場合、各画像は出力するフレームに最大サイズで出力することができ、なおかつ、関心領域の大きさを均等に出力することができる。
(Example 3)
FIG. 12 shows an example in which an optimal region of interest is designated for each image when the center position of the subject is taken with respect to the diagnostic imaging apparatus, and the center of the rectangular image and the frame It shows a case where the centers are matched and output to a viewer or filming frame. In this case, each image can be output at the maximum size in the output frame, and the size of the region of interest can be output uniformly.
(例4)
図13は被写体の中心位置が画像診断装置に対してずれた状態で撮影された場合において、一連の画像の関心領域の位置と大きさを同一にし、なおかつ、矩形画像の中心とフレームの中心を一致させてビューワまたはフィルミングのフレームに出力する場合を示している。この場合、一連の画像は出力する大きさを揃えて出力することができ、なおかつ、関心領域の配置を均等にして出力することができる。
(Example 4)
FIG. 13 shows that when the image is taken with the center position of the subject deviated from the diagnostic imaging apparatus, the position and size of the region of interest in the series of images are the same, and the center of the rectangular image and the center of the frame are the same. It shows the case of matching and outputting to the viewer or filming frame. In this case, the series of images can be output with the same output size, and the arrangement of the regions of interest can be output uniformly.
なお、図13に示す出力画像の例は、上記方法以外に、体軸の中心位置と画像の中心位置を揃えることによっても可能である。以下、体軸の中心位置と画像の中心位置を揃える方法について、図14を用いて説明する。 The example of the output image shown in FIG. 13 can also be obtained by aligning the center position of the body axis with the center position of the image, in addition to the above method. Hereinafter, a method of aligning the center position of the body axis and the center position of the image will be described with reference to FIG.
まず、図14(a)に示すように、各画像を閾値処理することにより関心領域が算出され、それぞれの関心領域を含む矩形画像の中心位置が求められる。そして、図14(b)に示すように、算出された矩形画像のうち、縦横それぞれの最大値を持つ矩形画像(最大の矩形画像)が算出され、その中心位置が求められる。最後に、図14(c)に示すように、図14(a)で算出された矩形画像の中心位置と、図14(b)で算出された最大の矩形画像の中心位置とが合わせられる。これにより、撮影時に患者が斜めになっていた場合においても、体軸の中心位置を自動的にフレームの中央に配置することができる。 First, as shown in FIG. 14A, a region of interest is calculated by performing threshold processing on each image, and the center position of a rectangular image including each region of interest is obtained. Then, as shown in FIG. 14B, among the calculated rectangular images, a rectangular image having the maximum value in each of the vertical and horizontal directions (maximum rectangular image) is calculated, and the center position is obtained. Finally, as shown in FIG. 14C, the center position of the rectangular image calculated in FIG. 14A and the center position of the maximum rectangular image calculated in FIG. 14B are matched. Thereby, even when the patient is inclined at the time of imaging, the center position of the body axis can be automatically arranged at the center of the frame.
これにより、抜き出された関心領域をビューワまたはフィルミングのフレームに合わせて変倍して、フレームに出力することができる。 Accordingly, the extracted region of interest can be scaled according to the viewer or filming frame and output to the frame.
なお、図10〜図13に示すような出力画像のフレームに表示された関心領域のみを拡大表示することもできる。所定のフレームをマウス17等で選択することにより、図15に示すような、そのフレーム全体が拡大表示されているフレーム画面がディスプレイ15に表示されることにより行われる。
Note that only the region of interest displayed in the frame of the output image as shown in FIGS. 10 to 13 can be enlarged and displayed. By selecting a predetermined frame with the
本実施の形態によれば、目的に応じた様々なテンプレートを作成し、テンプレート中のフレームに表示したい画像の関心領域(本実施の形態においては、矩形画像と同じ)を変倍(最大化)して表示することで、効率的かつ効果的な表示データ又はフィルムデータを作成することができる。また、表示データ又はフィルムデータを用いることで、ユーザの視認性を高めることができる。 According to the present embodiment, various templates according to the purpose are created, and the region of interest (same as the rectangular image in the present embodiment) of the image to be displayed in the frame in the template is scaled (maximized). Thus, efficient and effective display data or film data can be created. Moreover, a user's visibility can be improved by using display data or film data.
また、本実施の形態によれば、時間的あるいは空間的に関連のある一連の画像を取り扱う場合には、一連の画像の関心領域の大きさが揃えられた表示データ又はフィルムデータを作成することにより、誤診を招く危険性を低下させることができる。 In addition, according to the present embodiment, when a series of images that are temporally or spatially related are handled, display data or film data in which the size of the region of interest of the series of images is aligned is created. Thus, the risk of misdiagnosis can be reduced.
また、本実施の形態によれば、患者の状態が悪く動かすことが困難である場合等、被写体の中心位置が画像診断装置に対してずれた状態で撮影せざるを得ない状況においても、一連の画像の関心領域の位置と大きさを同一にした表示データ又はフィルムデータを作成することで、視認性の低下を防ぎ、観察や読影をしやすくすることができる。 Further, according to the present embodiment, even in a situation where it is difficult to move the patient because the patient is in a bad condition, the center position of the subject must be photographed with a deviation from the diagnostic imaging apparatus. By creating display data or film data in which the position and size of the region of interest in the image are the same, it is possible to prevent deterioration in visibility and facilitate observation and interpretation.
また、本実施の形態によれば、画像の種類等により、様々なテンプレートの中から最適なテンプレートを使用し、かつ最大化された関心領域を表示させるか、一連の画像に共通の関心領域を表示させるかを選択して表示データ又はフィルムデータを作成することにより、ディスプレイやフィルムなどの限られた領域に、診断上有用な部分である関心領域が大きくかつ効率よく表示された表示データ又はフィルムデータを柔軟かつ簡便に作成することができる。 Further, according to the present embodiment, an optimum template is used from various templates depending on the type of image and the maximized region of interest is displayed, or a region of interest common to a series of images is displayed. Display data or film in which a region of interest, which is a diagnostically useful part, is large and efficiently displayed in a limited area such as a display or film by selecting display or creating display data or film data Data can be created flexibly and easily.
なお、本実施の形態では、関心領域を抜き出した後でその関心領域をフレームに出力することで、表示データ又はフィルムデータを作成したが、表示させる画像や画像診断の目的によっては、自動的に関心領域の抜き出しをしないで、すなわち画像全体を関心領域として画像全体をフレームに出力し、その後改めて手動で関心領域を指定するようにしてもよい。 In this embodiment, after extracting the region of interest, the region of interest is output to the frame to create display data or film data. However, depending on the image to be displayed and the purpose of image diagnosis, it may be automatically It is also possible to output the entire image as a region of interest without extracting the region of interest, that is, the entire image, and then manually specify the region of interest again.
また、本実施の形態では、関心領域をフレームに出力する前に、テンプレートの新規作成及びテンプレートの微調整を行うようにしたが、関心領域をフレームに出力した後で、フレームを分割する線の微調整等のテンプレートの編集ができるようにしてもよい。これは、関心領域が出力されたテンプレートがディスプレイ15などに表示されている場合において、フレームを分割する線をマウス17等で動かす事等によって行われる。これにより、より効率的な表示データ又はフィルムデータをより柔軟かつ簡便に作成することができる。
In this embodiment, a new template is created and a template is finely adjusted before the region of interest is output to the frame. However, after the region of interest is output to the frame, the line dividing the frame is displayed. The template may be edited such as fine adjustment. This is performed by moving a line that divides the frame with the
また、本実施の形態では、矩形画像を例にして説明したが、台形、円形などの医用画像が呈する形状となる可能性のある形状は本発明の実施として全て含まれる。 Further, in the present embodiment, a rectangular image has been described as an example. However, shapes that may be shapes exhibited by medical images such as trapezoids and circles are all included as embodiments of the present invention.
1:ネットワーク、2:医用画像撮影装置、3:画像データベース、4:プリンタ、10:画像処理装置、11:中央処理装置(CPU)、12:主メモリ、13:磁気ディスク、14:表示メモリ、15:ディスプレイ、16:キーボード、17:マウス、18:コントローラ、19:共通バス 1: network, 2: medical imaging device, 3: image database, 4: printer, 10: image processing device, 11: central processing unit (CPU), 12: main memory, 13: magnetic disk, 14: display memory, 15: Display, 16: Keyboard, 17: Mouse, 18: Controller, 19: Common bus
Claims (5)
医用画像撮影装置で撮影された複数の画像を入力する入力手段と、
前記入力手段により入力された複数の画像に対して関心領域を指定する関心領域指定手段と、
前記複数の画像から前記関心領域指定手段によって指定された関心領域を、その関心領域が内接するトリミング領域にしたがって画像領域として抽出する抽出手段と、
前記抽出手段によって前記複数の画像から抽出された複数の画像領域を前記テンプレートの各フレーム内に合成して出力画像を作成する合成処理手段と、
を備えたことを特徴とする画像処理装置。 In a medical image processing apparatus for creating an output image by combining a plurality of images in each frame of a template in which a plurality of frames are laid out,
Input means for inputting a plurality of images photographed by the medical image photographing device;
A region-of-interest specifying unit that specifies a region of interest for a plurality of images input by the input unit;
Extracting means for extracting the region of interest designated by the region of interest designating means from the plurality of images as an image region according to a trimming region inscribed by the region of interest;
Synthesis processing means for creating an output image by synthesizing a plurality of image regions extracted from the plurality of images by the extraction means in each frame of the template;
An image processing apparatus comprising:
前記合成処理手段は、前記一連の画像の各関心領域の画像間の撮影倍率が一致するように各矩形画像を変倍することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の画像処理装置。 The plurality of images includes a series of temporally or spatially related images,
The image processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the composition processing unit scales each rectangular image so that photographing magnifications between images of each region of interest in the series of images coincide with each other.
前記合成処理手段は、前記テンプレートのフレームの中心と前記画像領域の中心とが一致するように各画像領域を各フレーム内に合成することを特徴とする請求項1から3のいずれかに記載の画像処理装置。 The plurality of images includes a series of temporally or spatially related images,
4. The image processing apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the synthesis processing unit synthesizes each image area in each frame so that a center of the frame of the template matches a center of the image area. 5. Image processing device.
前記記憶されているテンプレートの中から、前記合成処理手段において画像領域が合成されるテンプレートを選択する選択手段と、
を更に備え、
前記記憶手段は、フレームの大きさ及び配置を任意に設定することによって作成されたテンプレート及び/又はフレームが水平方向と垂直方向とに規則的に配置されたテンプレートを複数記憶することを特徴とする請求項1から4のいずれかに記載の画像処理装置。 Storage means for storing a plurality of templates;
Selecting means for selecting a template with which the image processing area is synthesized in the synthesis processing means from the stored templates;
Further comprising
The storage means stores a plurality of templates created by arbitrarily setting the size and arrangement of frames and / or templates in which frames are regularly arranged in the horizontal and vertical directions. The image processing apparatus according to claim 1.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007024698A JP2008188177A (en) | 2007-02-02 | 2007-02-02 | Image processor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007024698A JP2008188177A (en) | 2007-02-02 | 2007-02-02 | Image processor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008188177A true JP2008188177A (en) | 2008-08-21 |
| JP2008188177A5 JP2008188177A5 (en) | 2010-03-04 |
Family
ID=39748842
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007024698A Pending JP2008188177A (en) | 2007-02-02 | 2007-02-02 | Image processor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2008188177A (en) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008271547A (en) * | 2007-04-16 | 2008-11-06 | General Electric Co <Ge> | Systems and methods for multi-source video distribution and composite display |
| JP2010167188A (en) * | 2009-01-26 | 2010-08-05 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image diagnostic apparatus, image data output device, and control program for outputting image data |
| JP2011056024A (en) * | 2009-09-09 | 2011-03-24 | Canon Inc | Radiographic apparatus and radiography method and program |
| JP2013192601A (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-30 | Konica Minolta Inc | Medical image display system |
| JP2014004252A (en) * | 2012-06-26 | 2014-01-16 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image display device |
| US20150055887A1 (en) * | 2013-08-23 | 2015-02-26 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Image Processing Apparatus and Storage Medium |
| WO2016052289A1 (en) * | 2014-10-03 | 2016-04-07 | 株式会社 日立メディコ | X-ray fluoroscopy device and x-ray projection condition setting method |
| JP2017045030A (en) * | 2015-08-26 | 2017-03-02 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image display device |
| JP2017158757A (en) * | 2016-03-09 | 2017-09-14 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image display apparatus, method, and program |
| US9875256B2 (en) | 2015-02-19 | 2018-01-23 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. | Control method of information terminal and recording medium |
| JP2019527876A (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2019-10-03 | ベックマン コールター, インコーポレイテッド | Image atlas system and method |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07148155A (en) * | 1993-11-26 | 1995-06-13 | Toshiba Corp | Computerized tomographic apparatus |
| JP2000115513A (en) * | 1998-09-30 | 2000-04-21 | Canon Inc | Picture processing system, its controlling method, photographing system, its controlling method and computer readable memory |
| JP2002008005A (en) * | 2000-06-20 | 2002-01-11 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Method and device for outputting medical image |
| JP2003210414A (en) * | 2002-01-17 | 2003-07-29 | Konica Corp | Medical image processor, medical image processing method, program, and recording medium |
| JP2005312774A (en) * | 2004-04-30 | 2005-11-10 | Soft Quality:Kk | Medical image display system and method of displaying the same |
| JP2006094095A (en) * | 2004-09-24 | 2006-04-06 | Noritsu Koki Co Ltd | Photograph processing device |
-
2007
- 2007-02-02 JP JP2007024698A patent/JP2008188177A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07148155A (en) * | 1993-11-26 | 1995-06-13 | Toshiba Corp | Computerized tomographic apparatus |
| JP2000115513A (en) * | 1998-09-30 | 2000-04-21 | Canon Inc | Picture processing system, its controlling method, photographing system, its controlling method and computer readable memory |
| JP2002008005A (en) * | 2000-06-20 | 2002-01-11 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | Method and device for outputting medical image |
| JP2003210414A (en) * | 2002-01-17 | 2003-07-29 | Konica Corp | Medical image processor, medical image processing method, program, and recording medium |
| JP2005312774A (en) * | 2004-04-30 | 2005-11-10 | Soft Quality:Kk | Medical image display system and method of displaying the same |
| JP2006094095A (en) * | 2004-09-24 | 2006-04-06 | Noritsu Koki Co Ltd | Photograph processing device |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008271547A (en) * | 2007-04-16 | 2008-11-06 | General Electric Co <Ge> | Systems and methods for multi-source video distribution and composite display |
| JP2010167188A (en) * | 2009-01-26 | 2010-08-05 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image diagnostic apparatus, image data output device, and control program for outputting image data |
| JP2011056024A (en) * | 2009-09-09 | 2011-03-24 | Canon Inc | Radiographic apparatus and radiography method and program |
| JP2013192601A (en) * | 2012-03-16 | 2013-09-30 | Konica Minolta Inc | Medical image display system |
| JP2014004252A (en) * | 2012-06-26 | 2014-01-16 | Toshiba Corp | Medical image display device |
| US20150055887A1 (en) * | 2013-08-23 | 2015-02-26 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Image Processing Apparatus and Storage Medium |
| US10460421B2 (en) * | 2013-08-23 | 2019-10-29 | Brother Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Image processing apparatus and storage medium |
| JPWO2016052289A1 (en) * | 2014-10-03 | 2017-07-13 | 株式会社日立製作所 | X-ray fluoroscopy apparatus and X-ray irradiation condition setting method |
| WO2016052289A1 (en) * | 2014-10-03 | 2016-04-07 | 株式会社 日立メディコ | X-ray fluoroscopy device and x-ray projection condition setting method |
| US9875256B2 (en) | 2015-02-19 | 2018-01-23 | Panasonic Intellectual Property Management Co., Ltd. | Control method of information terminal and recording medium |
| JP2017045030A (en) * | 2015-08-26 | 2017-03-02 | キヤノン株式会社 | Image display device |
| JP2017158757A (en) * | 2016-03-09 | 2017-09-14 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image display apparatus, method, and program |
| WO2017154640A1 (en) * | 2016-03-09 | 2017-09-14 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | Image display device, method, and program |
| US10307124B2 (en) | 2016-03-09 | 2019-06-04 | Fujifilm Corporation | Image display device, method, and program for determining common regions in images |
| JP2019527876A (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2019-10-03 | ベックマン コールター, インコーポレイテッド | Image atlas system and method |
| JP2021177407A (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2021-11-11 | ベックマン コールター, インコーポレイテッド | Image atlas systems and methods |
| US11448583B2 (en) | 2016-06-24 | 2022-09-20 | Beckman Coulter, Inc. | Image atlas systems and methods |
| JP7275202B2 (en) | 2016-06-24 | 2023-05-17 | ベックマン コールター, インコーポレイテッド | Image atlas system and method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2008188177A (en) | Image processor | |
| JP2007282656A (en) | Medical image display | |
| JP2006268120A (en) | Medical image display device | |
| WO2013125276A1 (en) | X-ray ct device, image display device, and image display method | |
| JP4640384B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and image processing method | |
| JP2001167251A (en) | Medical image processor | |
| CN107633478B (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer readable medium | |
| JP4722500B2 (en) | Medical image filming device | |
| JP2008245832A (en) | Medical image display device and method | |
| US20080136815A1 (en) | Image display controlling apparatus, image display controlling program and image display controlling method | |
| JP4794993B2 (en) | Image diagnosis support apparatus and image display method | |
| US10102638B2 (en) | Device and method for image registration, and a nontransitory recording medium | |
| JP6738631B2 (en) | Medical image processing apparatus, medical image processing method, and medical image processing program | |
| JP6433190B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and program | |
| JP5305635B2 (en) | Medical image display device | |
| JP4595594B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and program | |
| JP6085435B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus and region of interest setting method | |
| JP5262649B2 (en) | Medical image display apparatus and program | |
| JP2009005840A (en) | Image processor and image processing method | |
| JP2014000182A (en) | Medical image generating device and program | |
| JP2006340939A (en) | Method for generating projection image | |
| JP6643433B2 (en) | Supporting apparatus for creating an interpretation report and its control method | |
| JP4661209B2 (en) | Medical image output system | |
| JP2007125102A (en) | Medical image display device and medical image diagnostic apparatus | |
| JP2005173818A (en) | Medical image diagnostic support system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20090721 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20090727 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100120 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100120 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120522 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120713 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120821 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20121218 |