JP2007242304A - Valve, valve control device, and fuel cell system - Google Patents
Valve, valve control device, and fuel cell system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007242304A JP2007242304A JP2006060128A JP2006060128A JP2007242304A JP 2007242304 A JP2007242304 A JP 2007242304A JP 2006060128 A JP2006060128 A JP 2006060128A JP 2006060128 A JP2006060128 A JP 2006060128A JP 2007242304 A JP2007242304 A JP 2007242304A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- valve
- tank
- injector
- fuel cell
- gas
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C13/00—Details of vessels or of the filling or discharging of vessels
- F17C13/04—Arrangement or mounting of valves
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K1/00—Lift valves or globe valves, i.e. cut-off apparatus with closure members having at least a component of their opening and closing motion perpendicular to the closing faces
- F16K1/30—Lift valves or globe valves, i.e. cut-off apparatus with closure members having at least a component of their opening and closing motion perpendicular to the closing faces specially adapted for pressure containers
- F16K1/304—Shut-off valves with additional means
- F16K1/305—Shut-off valves with additional means with valve member and actuator on the same side of the seat
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K31/00—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices
- F16K31/02—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices electric; magnetic
- F16K31/06—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices electric; magnetic using a magnet, e.g. diaphragm valves, cutting off by means of a liquid
- F16K31/0644—One-way valve
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16K—VALVES; TAPS; COCKS; ACTUATING-FLOATS; DEVICES FOR VENTING OR AERATING
- F16K31/00—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices
- F16K31/02—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices electric; magnetic
- F16K31/06—Actuating devices; Operating means; Releasing devices electric; magnetic using a magnet, e.g. diaphragm valves, cutting off by means of a liquid
- F16K31/0644—One-way valve
- F16K31/0648—One-way valve the armature and the valve member forming one element
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04082—Arrangements for control of reactant parameters, e.g. pressure or concentration
- H01M8/04089—Arrangements for control of reactant parameters, e.g. pressure or concentration of gaseous reactants
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04082—Arrangements for control of reactant parameters, e.g. pressure or concentration
- H01M8/04201—Reactant storage and supply, e.g. means for feeding, pipes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04223—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids during start-up or shut-down; Depolarisation or activation, e.g. purging; Means for short-circuiting defective fuel cells
- H01M8/04228—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids during start-up or shut-down; Depolarisation or activation, e.g. purging; Means for short-circuiting defective fuel cells during shut-down
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04298—Processes for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems
- H01M8/04694—Processes for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems characterised by variables to be controlled
- H01M8/04746—Pressure; Flow
- H01M8/04753—Pressure; Flow of fuel cell reactants
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2201/00—Vessel construction, in particular geometry, arrangement or size
- F17C2201/01—Shape
- F17C2201/0104—Shape cylindrical
- F17C2201/0109—Shape cylindrical with exteriorly curved end-piece
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2201/00—Vessel construction, in particular geometry, arrangement or size
- F17C2201/05—Size
- F17C2201/056—Small (<1 m3)
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2203/00—Vessel construction, in particular walls or details thereof
- F17C2203/06—Materials for walls or layers thereof; Properties or structures of walls or their materials
- F17C2203/0602—Wall structures; Special features thereof
- F17C2203/0604—Liners
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2203/00—Vessel construction, in particular walls or details thereof
- F17C2203/06—Materials for walls or layers thereof; Properties or structures of walls or their materials
- F17C2203/0602—Wall structures; Special features thereof
- F17C2203/0612—Wall structures
- F17C2203/0614—Single wall
- F17C2203/0619—Single wall with two layers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2203/00—Vessel construction, in particular walls or details thereof
- F17C2203/06—Materials for walls or layers thereof; Properties or structures of walls or their materials
- F17C2203/0634—Materials for walls or layers thereof
- F17C2203/0658—Synthetics
- F17C2203/066—Plastics
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2203/00—Vessel construction, in particular walls or details thereof
- F17C2203/06—Materials for walls or layers thereof; Properties or structures of walls or their materials
- F17C2203/0634—Materials for walls or layers thereof
- F17C2203/0658—Synthetics
- F17C2203/0663—Synthetics in form of fibers or filaments
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0302—Fittings, valves, filters, or components in connection with the gas storage device
- F17C2205/0305—Bosses, e.g. boss collars
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0302—Fittings, valves, filters, or components in connection with the gas storage device
- F17C2205/0311—Closure means
- F17C2205/0317—Closure means fusing or melting
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0302—Fittings, valves, filters, or components in connection with the gas storage device
- F17C2205/0323—Valves
- F17C2205/0326—Valves electrically actuated
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0302—Fittings, valves, filters, or components in connection with the gas storage device
- F17C2205/0323—Valves
- F17C2205/0332—Safety valves or pressure relief valves
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0302—Fittings, valves, filters, or components in connection with the gas storage device
- F17C2205/0323—Valves
- F17C2205/0335—Check-valves or non-return valves
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0302—Fittings, valves, filters, or components in connection with the gas storage device
- F17C2205/0338—Pressure regulators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0388—Arrangement of valves, regulators, filters
- F17C2205/0391—Arrangement of valves, regulators, filters inside the pressure vessel
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2205/00—Vessel construction, in particular mounting arrangements, attachments or identifications means
- F17C2205/03—Fluid connections, filters, valves, closure means or other attachments
- F17C2205/0388—Arrangement of valves, regulators, filters
- F17C2205/0394—Arrangement of valves, regulators, filters in direct contact with the pressure vessel
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2221/00—Handled fluid, in particular type of fluid
- F17C2221/01—Pure fluids
- F17C2221/012—Hydrogen
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2221/00—Handled fluid, in particular type of fluid
- F17C2221/03—Mixtures
- F17C2221/032—Hydrocarbons
- F17C2221/033—Methane, e.g. natural gas, CNG, LNG, GNL, GNC, PLNG
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2223/00—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel
- F17C2223/01—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel characterised by the phase
- F17C2223/0107—Single phase
- F17C2223/0123—Single phase gaseous, e.g. CNG, GNC
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2223/00—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel
- F17C2223/03—Handled fluid before transfer, i.e. state of fluid when stored in the vessel or before transfer from the vessel characterised by the pressure level
- F17C2223/036—Very high pressure (>80 bar)
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2225/00—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel
- F17C2225/01—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel characterised by the phase
- F17C2225/0107—Single phase
- F17C2225/0123—Single phase gaseous, e.g. CNG, GNC
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2225/00—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel
- F17C2225/03—Handled fluid after transfer, i.e. state of fluid after transfer from the vessel characterised by the pressure level
- F17C2225/036—Very high pressure, i.e. above 80 bars
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2227/00—Transfer of fluids, i.e. method or means for transferring the fluid; Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/01—Propulsion of the fluid
- F17C2227/0128—Propulsion of the fluid with pumps or compressors
- F17C2227/0135—Pumps
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2227/00—Transfer of fluids, i.e. method or means for transferring the fluid; Heat exchange with the fluid
- F17C2227/01—Propulsion of the fluid
- F17C2227/0128—Propulsion of the fluid with pumps or compressors
- F17C2227/0157—Compressors
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2250/00—Accessories; Control means; Indicating, measuring or monitoring of parameters
- F17C2250/03—Control means
- F17C2250/032—Control means using computers
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2250/00—Accessories; Control means; Indicating, measuring or monitoring of parameters
- F17C2250/04—Indicating or measuring of parameters as input values
- F17C2250/0404—Parameters indicated or measured
- F17C2250/043—Pressure
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2250/00—Accessories; Control means; Indicating, measuring or monitoring of parameters
- F17C2250/04—Indicating or measuring of parameters as input values
- F17C2250/0404—Parameters indicated or measured
- F17C2250/0439—Temperature
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2250/00—Accessories; Control means; Indicating, measuring or monitoring of parameters
- F17C2250/06—Controlling or regulating of parameters as output values
- F17C2250/0605—Parameters
- F17C2250/0626—Pressure
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2250/00—Accessories; Control means; Indicating, measuring or monitoring of parameters
- F17C2250/06—Controlling or regulating of parameters as output values
- F17C2250/0605—Parameters
- F17C2250/0636—Flow or movement of content
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2260/00—Purposes of gas storage and gas handling
- F17C2260/01—Improving mechanical properties or manufacturing
- F17C2260/015—Facilitating maintenance
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2260/00—Purposes of gas storage and gas handling
- F17C2260/01—Improving mechanical properties or manufacturing
- F17C2260/018—Adapting dimensions
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/01—Applications for fluid transport or storage
- F17C2270/0102—Applications for fluid transport or storage on or in the water
- F17C2270/0105—Ships
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/01—Applications for fluid transport or storage
- F17C2270/0165—Applications for fluid transport or storage on the road
- F17C2270/0168—Applications for fluid transport or storage on the road by vehicles
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/01—Applications for fluid transport or storage
- F17C2270/0165—Applications for fluid transport or storage on the road
- F17C2270/0168—Applications for fluid transport or storage on the road by vehicles
- F17C2270/0173—Railways
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/01—Applications for fluid transport or storage
- F17C2270/0165—Applications for fluid transport or storage on the road
- F17C2270/0184—Fuel cells
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/05—Applications for industrial use
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/05—Applications for industrial use
- F17C2270/0518—Semiconductors
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17C—VESSELS FOR CONTAINING OR STORING COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED OR SOLIDIFIED GASES; FIXED-CAPACITY GAS-HOLDERS; FILLING VESSELS WITH, OR DISCHARGING FROM VESSELS, COMPRESSED, LIQUEFIED, OR SOLIDIFIED GASES
- F17C2270/00—Applications
- F17C2270/07—Applications for household use
- F17C2270/0763—Fuel cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04082—Arrangements for control of reactant parameters, e.g. pressure or concentration
- H01M8/04089—Arrangements for control of reactant parameters, e.g. pressure or concentration of gaseous reactants
- H01M8/04097—Arrangements for control of reactant parameters, e.g. pressure or concentration of gaseous reactants with recycling of the reactants
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04223—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids during start-up or shut-down; Depolarisation or activation, e.g. purging; Means for short-circuiting defective fuel cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04298—Processes for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems
- H01M8/04313—Processes for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems characterised by the detection or assessment of variables; characterised by the detection or assessment of failure or abnormal function
- H01M8/0432—Temperature; Ambient temperature
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M8/00—Fuel cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M8/04—Auxiliary arrangements, e.g. for control of pressure or for circulation of fluids
- H01M8/04298—Processes for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems
- H01M8/04313—Processes for controlling fuel cells or fuel cell systems characterised by the detection or assessment of variables; characterised by the detection or assessment of failure or abnormal function
- H01M8/0438—Pressure; Ambient pressure; Flow
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/30—Hydrogen technology
- Y02E60/32—Hydrogen storage
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/30—Hydrogen technology
- Y02E60/50—Fuel cells
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Fuel Cell (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、二次側への流体の流量を調整可能に構成されたバルブ、バルブ制御装置及び燃料電池システムに関する。 The present invention relates to a valve, a valve control device, and a fuel cell system configured to be able to adjust a flow rate of a fluid to a secondary side.
従来、タンクに貯蔵した燃料を燃料消費装置に供給する供給システムが広く知られている。例えば、特許文献1に記載の供給システムでは、タンクに貯蔵した水素化物流体を半導体製造設備に供給している。このタンクには、タンク外に供給される水素化物流体の圧力を調整する機械式のレギュレータが設けられている。
しかしながら、タンクに付随するレギュレータでは、タンク外への燃料の放出流量を精緻に調整することができなかった。また、機械式のレギュレータであるため、応答性が比較的低かった。 However, the regulator attached to the tank cannot precisely adjust the fuel discharge flow rate to the outside of the tank. Moreover, since it is a mechanical regulator, the response was relatively low.
本発明は、タンク外への流体の放出流量を精度良く調整できるバルブ、バルブ制御装置及び燃料電池システムを提供することを目的とする。 An object of this invention is to provide the valve | bulb which can adjust the discharge | release flow volume of the fluid out of a tank accurately, a valve control apparatus, and a fuel cell system.
上記目的を達成するための本発明のバルブは、二次側への流体の流量を調整可能に構成されたバルブであって、二次側がタンク内からの流体の放出側となるようにタンクに設けられ、タンク内からの流体の放出流量をデューティ制御により調整可能に構成されたものである。 In order to achieve the above object, the valve of the present invention is a valve configured to be able to adjust the flow rate of the fluid to the secondary side, and in the tank so that the secondary side becomes the fluid discharge side from the inside of the tank. It is provided and configured to be able to adjust the fluid discharge flow rate from the tank by duty control.
この構成によれば、流体の流量をデューティ制御により調整可能なバルブをタンクに設けているので、タンク外への流体の放出流量を精度良く調整することができる。 According to this configuration, since the tank is provided with the valve capable of adjusting the fluid flow rate by duty control, the fluid discharge flow rate to the outside of the tank can be accurately adjusted.
ここで、バルブをタンクに設ける構成としては、例えばバルブをタンクの内部に配置する構成、バルブをタンクの構成要素に直接的に又は間接的に取り付けながらタンクの外部に配置する構成、又は、バルブの一部をタンク内に配置し且つバルブの他の部分をタンク外に配置する構成を採用できる。これらのバルブの配置方法としては、バルブをタンクの口金に取り付けてもよいし、あるいは、バルブ及びその他のバルブをバルブアッセンブリとして構成し、バルブアッセンブリをタンクの口金にねじ込むように取り付けてもよい。 Here, as a configuration in which the valve is provided in the tank, for example, a configuration in which the valve is disposed inside the tank, a configuration in which the valve is directly or indirectly attached to the component of the tank, and is disposed outside the tank, or a valve It is possible to adopt a configuration in which a part of the valve is disposed in the tank and the other part of the valve is disposed outside the tank. As a method of arranging these valves, the valves may be attached to the base of the tank, or the valves and other valves may be configured as a valve assembly so that the valve assembly is screwed into the base of the tank.
本発明のバルブは、放出流量をデューティ制御により調整する流量調整機構を有し、流量調整機構は、タンク内からの流体の放出を遮断可能に構成されていることが好ましい。 The valve of the present invention preferably has a flow rate adjustment mechanism that adjusts the discharge flow rate by duty control, and the flow rate adjustment mechanism is preferably configured to be able to block the release of fluid from the tank.
この構成によれば、バルブを遮断弁としても機能させることができる。 According to this configuration, the valve can also function as a shutoff valve.
ここで、バルブの流量調整機構は、弁体と、弁体が離接可能な弁座と、弁体を弁座に対して離接方向に移動させるソレノイドと、を備えることができる。この構成では、通常、バルブの軸線方向は、弁体の離接方向に合致する。また、弁座は、バルブの基体又は弁体よりも弾性を有することが好ましく、こうすることで、バルブの遮断弁としての機能を高めることができる。さらに、バルブは、弁体がタンクの圧力(一次圧)により弁座に当接して、流体の流出を遮断する構成であることが好ましい。 Here, the flow rate adjusting mechanism of the valve can include a valve body, a valve seat to which the valve body is detachable, and a solenoid that moves the valve body in a detaching direction with respect to the valve seat. In this configuration, normally, the axial direction of the valve coincides with the contact / separation direction of the valve body. Moreover, it is preferable that the valve seat has more elasticity than the base or valve body of the valve, and by doing so, the function of the valve as a shut-off valve can be enhanced. Further, the valve is preferably configured such that the valve body abuts against the valve seat by the pressure (primary pressure) of the tank to block outflow of fluid.
好ましくは、バルブの軸線とタンクの軸線とは、略平行である又は合致する。 Preferably, the valve axis and the tank axis are substantially parallel or coincident.
この構成によれば、バルブを自己清浄し易い構造とし得る。例えばバルブを上記のように構成した場合に、弁体の移動時に発生し得る磨耗粉などのコンタミを、一次側から二次側への流体の流れによって二次側へと排出することが可能となる。 According to this configuration, the valve can be configured to be easily cleaned. For example, when the valve is configured as described above, it is possible to discharge contamination such as abrasion powder that may be generated when the valve body moves to the secondary side by the flow of fluid from the primary side to the secondary side. Become.
一方で、一般に、バルブは全体としてみれば軸線方向に長さを長くとる傾向にある。このため、バルブの軸線方向とタンクの軸線方向とを合致させると、バルブ及びタンクの全体の長さが長くなり易い。 On the other hand, generally, the valve tends to have a long length in the axial direction as a whole. For this reason, if the axial direction of a valve and the axial direction of a tank are made to correspond, the whole length of a valve and a tank tends to become long.
そこで、バルブ及びタンクの全体の長さを比較的短くする観点からすれば、本発明のバルブはタンクのボディよりも外側に位置し、バルブの軸線とタンクの軸線とは略直交する構成であってもよい。 Therefore, from the viewpoint of relatively shortening the overall length of the valve and the tank, the valve of the present invention is located outside the tank body, and the valve axis and the tank axis are substantially orthogonal to each other. May be.
この構成によれば、バルブ及びタンクが設置される設置スペースを大きく占有しないで済むようになる。 According to this configuration, it is not necessary to occupy a large installation space in which the valve and the tank are installed.
本発明の一態様によれば、タンクにはバルブとは別体の主止弁が設けられ、主止弁はバルブの一次側に位置していることが好ましい。 According to one aspect of the present invention, the tank is provided with a main stop valve that is separate from the valve, and the main stop valve is preferably located on the primary side of the valve.
この構成によれば、主止弁を閉じることで、バルブに作用する流体圧を抑制することができる。また、フェールセーフも達成できる。 According to this configuration, the fluid pressure acting on the valve can be suppressed by closing the main stop valve. Fail safe can also be achieved.
この場合、主止弁がタンク口金よりもタンク内側に位置し、且つバルブがタンクのボディよりも外側に位置することが好ましい。 In this case, it is preferable that the main stop valve is located on the inner side of the tank than the tank base, and the valve is located on the outer side of the tank body.
上記目的を達成するための本発明のバルブ制御装置は、上記した本発明のバルブをデューティ制御するものである。 In order to achieve the above object, a valve control device of the present invention performs duty control on the above-described valve of the present invention.
この構成によれば、バルブを適切にデューティ制御でき、タンク外への流体の放出流量を精緻に調整することができる。 According to this configuration, the valve can be appropriately duty-controlled, and the discharge flow rate of the fluid to the outside of the tank can be precisely adjusted.
上記目的を達成するための本発明の燃料電池システムは、上記した本発明のバルブ及びタンクと、酸化ガス及び燃料ガスが供給される燃料電池とを備えた燃料電池システムであって、タンク内の前記流体は燃料ガスである。 In order to achieve the above object, a fuel cell system of the present invention is a fuel cell system comprising the above-described valve and tank of the present invention, and a fuel cell to which an oxidizing gas and a fuel gas are supplied. The fluid is a fuel gas.
この構成によれば、バルブにより放出流量が調整された燃料ガスを燃料電池に供給することができる。これにより、燃料電池における燃料ガスの消費量に対応して、タンクから所望の燃料ガスを応答性良く供給することができる。 According to this structure, the fuel gas whose discharge flow rate is adjusted by the valve can be supplied to the fuel cell. Thereby, the desired fuel gas can be supplied from the tank with high responsiveness in accordance with the consumption amount of the fuel gas in the fuel cell.
本発明のバルブ、バルブ制御装置及び燃料電池システムによれば、タンク外への流体の放出流量を精度良く調整することができる。 According to the valve, the valve control device, and the fuel cell system of the present invention, the fluid discharge flow rate to the outside of the tank can be accurately adjusted.
以下、添付図面を参照して、本発明のバルブを備えた燃料電池システムについて説明する。この燃料電池システムは、デューティ制御されるバルブをタンクに設け、タンク外への燃料ガスの放出流量を調整するようにしたものである。以下では、デューティ制御されるバルブとして、インジェクタを例に説明する。 Hereinafter, a fuel cell system including a valve of the present invention will be described with reference to the accompanying drawings. In this fuel cell system, a duty-controlled valve is provided in a tank to adjust the flow rate of fuel gas discharged to the outside of the tank. Hereinafter, an injector will be described as an example of a valve that is duty controlled.
<第1実施形態>
図1は、燃料電池システムの構成図である。
燃料電池システム1は、燃料電池2と、酸化ガスとしての空気(酸素)を燃料電池2に供給する酸化ガス配管系3と、燃料ガスとしての水素ガスを燃料電池2に供給する燃料ガス配管系4と、システム全体を統括制御する制御部7と、を備えている。
<First Embodiment>
FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a fuel cell system.
The fuel cell system 1 includes a
燃料電池2は、例えば固体高分子電解質型で構成され、多数の単セルを積層したスタック構造を備えている。燃料電池2の単セルは、イオン交換膜からなる電解質の一方の面に空気極を有し、他方の面に燃料極を有し、さらに空気極及び燃料極を両側から挟みこむように一対のセパレータを有している。一方のセパレータの燃料ガス流路に燃料ガスが供給され、他方のセパレータの酸化ガス流路に酸化ガスが供給され、このガス供給により燃料電池2は電力を発生する。
The
酸化ガス配管系3は、燃料電池2に供給される酸化ガスが流れる供給路11と、燃料電池2から排出された酸化オフガスが流れる排出路12と、を有している。供給路11には、フィルタ13を介して酸化ガスを取り込むコンプレッサ14と、コンプレッサ14により圧送される酸化ガスを加湿する加湿器15と、が設けられている。排出路12を流れる酸化オフガスは、背圧調整弁16を通って加湿器15で水分交換に供された後、最終的に排ガスとしてシステム外の大気中に排気される。
The oxidizing
燃料ガス配管系4は、燃料供給源としての水素タンク21と、水素タンク21から燃料電池2に供給される水素ガスが流れる供給路22と、燃料電池2から排出された水素オフガス(燃料オフガス)を供給路22の合流点Aに戻すための循環路23と、循環路23内の水素オフガスを供給路22に圧送するポンプ24と、循環路23に分岐接続された排出路25と、を有している。
The fuel
水素タンク21は、例えば35MPa又は70MPaの水素ガスを貯留可能に構成されている。水素タンク21の主止弁26を開くと、供給路22に水素ガスが流出する。その後、水素ガスは、インジェクタ29により流量及び圧力を調整された後、さらに下流において機械式の調圧弁27その他の減圧弁により、最終的に例えば200kPa程度まで減圧されて、燃料電池2に供給される。主止弁26及びインジェクタ29は、図1において点線の枠線で示すバルブアッセンブリ30に組み込まれ、バルブアッセンブリ30が水素タンク21に接続されている(詳細は後述する)。
The
供給路22の合流点Aの上流側には、遮断弁28が設けられている。水素ガスの循環系は、供給路22の合流点Aの下流側流路と、燃料電池2のセパレータに形成される燃料ガス流路と、循環路23とを順番に連通することで構成されている。排出路25上のパージ弁33が燃料電池システム1の稼動時に適宜開弁することで、水素オフガス中の不純物が水素オフガスと共に図示省略した水素希釈器に排出される。パージ弁33の開弁により、循環路23内の水素オフガス中の不純物の濃度が下がり、循環供給される水素オフガス中の水素濃度が上がる。
A
制御部7は、内部にCPU,ROM,RAMを備えたマイクロコンピュータとして構成される。CPUは、制御プラグラムに従って所望の演算を実行して、インジェクタ29の流量制御など、種々の処理や制御を行う。ROMは、CPUで処理する制御プログラムや制御データを記憶する。RAMは、主として制御処理のための各種作業領域として使用される。制御部7は、ガス系統(3,4)や図示省略の冷媒系統に用いられる各種の圧力センサや温度センサなどの検出信号を入力し、各構成要素に制御信号を出力する。後述するように、制御部7は、インジェクタ29をデューティ制御するバルブ制御装置として機能するものである。
The
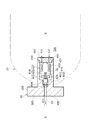
図2は、水素タンク21に設けられたインジェクタ29周りの断面図である。
先ず、水素タンク21について説明する。
水素タンク21は、水素タンク21のボディを構成する密閉円筒状のタンク本体101と、タンク本体101の長手方向の一端部に位置する口金部102と、を備えている。タンク本体101の内部は、水素ガスを高圧で貯留する貯留空間104となっている。タンク本体2は、ガスバリア性を有する内側の樹脂ライナー107と、樹脂ライナー107の外側を覆うFRPからなるシェル108と、の二層構造を有している。
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view around the
First, the
The
口金部102(口部)は、例えばステンレスなどの金属で形成され、タンク本体101の球面状をした端壁部の中心に設けられている。口金部102の内周面に形成されためねじを介して、バルブアッセンブリ30を口金部102にねじ込み接続することができるように構成されている。
The base part 102 (mouth part) is formed of a metal such as stainless steel, for example, and is provided at the center of the spherical end wall part of the
バルブアッセンブリ30は、水素タンク21の内外に亘るように設けられ、水素タンク21におけるガス排出部を構成している。バルブアセンブリ30は、例えば単一のハウジング300を有し、ハウジング300には、上記の主止弁26及びインジェクタ29が直列に組み込まれている。本実施形態では、ハウジング300は、水素タンク21内部に挿入される第1の領域301に主止弁26を組み込むと共に、水素タンク21外部に露出する第2の領域302にインジェクタ29を組み込んでいる。ハウジング300は、例えばSUSやアルミなどの金属により形成されている。
The
なお、図2では、本発明の要部であるインジェクタ29及び主止弁26を中心に表したが、ハウジング300には、インジェクタ29等以外に、安全弁(リリーフ弁、溶栓弁)や逆止弁など他のバルブが設けられてもよい。また、ハウジング300には、通常、図示省略した水素ガスの充填通路などが形成される。さらに、ハウジング300は、単一の部材又は複数の部材の組み合わせにより構成されてもよい。また、ハウジング300は、主止弁26及びインジェクタ29のボディ(基体)を兼ねているが、これら26,29のボディを別個に形成し、それぞれのボディをハウジング300に組み付けてもよい。
In FIG. 2, the
ハウジング300内には、貯留空間104と外部の供給路22とを連通するバルブ内流路310が形成されている。バルブ内流路310は、貯留空間104側から順に、第1流路311、第2流路312、及び第3流路313を連ねて構成されている。第1流路311と第2流路312との間は、主止弁26により連通又は遮断される。第2流路312はインジェクタ29の一次側の流路となり、第3流路313は、インジェクタ29の二次側の流路となって、外部の供給路22に連なっている。
In the
主止弁26(開閉弁)は、水素タンク21に対して元弁として機能し、水素タンク21内から供給路22への流体(水素ガス)の流動を遮断する。主止弁26は、電磁弁式の遮断弁で構成されている。主止弁26は、例えば、ソレノイドの励磁により弁棒321(可動子)がその軸方向に進出し、弁棒321の先端部の弁体322が弁座323に当接すると、バルブ内流路310を遮断する。一方、ソレノイドの消磁により弁棒321が軸方向に退避し、弁体322が弁座323から離間すると、貯留空間104からの水素ガスの流出が許容される。弁棒321及び弁体322の軸線方向X―Xは、水素タンク21の軸線方向に合致している。なお、主止弁26の軸線方向とは、弁体322の移動方向を意味し、この場合弁体322の軸線方向X―Xに相当する。
The main stop valve 26 (open / close valve) functions as a main valve for the
インジェクタ29は、タンク本体101の外周面よりも外側に位置し、制御部7に電気的に接続されている。インジェクタ29は、弁体401を電磁駆動力で直接的に所定の駆動周期で駆動して弁座402から離隔させることにより、水素ガスの流量や圧力を調整することが可能な電磁駆動式の開閉弁である。インジェクタ29は、弁体401の駆動周期を高応答の領域まで制御できるため、機械式の調圧弁に比べて高い応答性を有している。
The
インジェクタ29は、二次側への水素ガスの流量及び圧力を調整可能な流量調整機構を有する。流量調整機構は、大別すると、主弁部分410とソレノイド部分420とにより構成されている。これら主弁部分410及びソレノイド部分420は、ハウジング300の第2領域302内に設けられており、水素タンク21内からの水素ガスの放出流量をデューティ制御により調整する。
The
主弁部分410は、上記の弁体401及び弁座402からなる。弁体401は、ポペットタイプからなり、金属で形成されている。弁体401の軸線方向Y−Yは、水素タンク21の軸線方向X−Xに直交している。なお、インジェクタ26の軸線方向とは、弁体401の移動方向を意味し、この場合弁体401の軸線方向Y−Yに相当する。
The
弁座402は、シール性及び耐圧性を有する環状の樹脂部材からなり、ハウジング300(基体)よりも高い弾性率を有している。弁座402の中心は、開口しており、二次側に水素ガスを噴射する噴射孔404として機能する。噴射孔404の開口面積は、弁体401の軸方向の位置によって可変される。弁体401が弁座402に当接した状態では、噴射孔404の開口面積はゼロとなり、二次側への水素ガスの流出が遮断される。上記したように、弁座402に弾性特性をもたせているため、弁体401を弁座402に強密着させるように当接させることができ、水素ガスの二次側への流出をシール性良く遮断できる。
The
ソレノイド部分420は、Iプランジャ型など各種の基本構造で構成されることができ、ここではいわゆる平板型で構成されている。具体的には、ソレノイド部分420は、コイル421と、鉄心422と、弁体401と一体形成された平板状のプランジャ423と、で構成されている。鉄心422とプランジャ423との間には、隙間があると共に、弁体401と同軸上(Y−Y方向)にスプリング425が設けられている。スプリング425は、弁体401を弁座402に向けて付勢する。
The
インジェクタ29では、コイル421に通電することで、磁化された鉄心422がプランジャ423及び弁体401を吸引する。これにより、弁体401が、スプリング425に抗して弁座402から離れる方向に移動する。逆に、コイル421への通電を停止、すなわちソレノイド部420を消磁すると、弁体401がスプリング425のバネ力により弁座402に当接する方向に移動する。コイル421に供給される電流は、パルス状励磁電流である。
In the
このように、インジェクタ29は、コイル421に給電されるパルス状励磁電流のオン・オフにより、噴射孔404の開口時間(開弁時間)又は開口面積を2段階、多段階、連続的(無段階)、又はリニアに切り替え可能に構成されている。そして、インジェクタ29は、制御部7から出力される制御信号によって噴射口404からのガス噴射の時間及びタイミングが制御されることにより、水素ガスの流量及び圧力を高精度に調整する。この場合のインジェクタ29の制御方法としては、パルス状励磁電流のデューティ比を変化させるデューティ制御が用いられる。ここで、デューティ比とは、パルス状励磁電流のON時間を、パルス状励磁電流のON時間とOFF時間とを加算したスイッチング周期で除したものである。デューティ比を変えることにより、インジェクタ29は、0から一次圧(タンク内圧)までの任意の圧力に、二次圧を調整することができる。
In this way, the
図2に示すように、インジェクタ29には、ソレノイド部分420に隣接してハンドル部430が設けられている。ハンドル部430の一部は、オペレータが操作可能なように、ハウジング300の外表面よりも外側に位置している。ハンドル部430の軸線方向は、軸線方向Y−Yと合致している。ハンドル部430の外周面の一部には、ハウジング300にねじ込み接続されるようにおねじ431が形成されている。ハンドル部430をハウジング300から取り外すことで、インジェクタ29の主弁部分410及びソレノイド部分420を調整することができるようになっている。
As shown in FIG. 2, the
以上説明した本実施形態によれば、水素タンク21にインジェクタ29を設け、水素タンク21から供給路22へと水素ガスを流出させる際に、インジェクタ29で水素ガスの流量及び圧力を調整することができる。これにより、機械式の調圧弁を水素タンク21に設ける場合に比べて、水素タンク21から燃料電池2への水素ガスの放出流量(供給流量)を精緻に調整できる。加えて、インジェクタ29は、機械式の調圧弁に比べて応答性が高いので、燃料電池2の発電量、水素ガスの消費状態又は運転状態に応じた流量の水素ガスを燃料電池2に応答性良く供給することができる。
According to the present embodiment described above, the
また、インジェクタ29は、二次側への水素ガスの流出を遮断することもでき、インジェクタ29自体をタンク元弁としても機能させることができる。特に、遮断時には、プランジャ423の鉄心422に対向する面に一次側の水素ガス圧(タンク内圧)が作用するため、弁体401はプランジャ423を介して閉弁方向の推力を作用される。これにより、弁体401と弁座402との密着度が高まり、インジェクタ29内における流路の遮断性を高めることができる。
Further, the
一方、本実施形態では、インジェクタ29の一次側に、タンク元弁として主止弁26を設けている。このため、燃料電池システム1の停止時(水素ガス供給停止時)に主止弁26を閉じることで、インジェクタ29にタンク内圧を直接作用させることを抑制できる。また、インジェクタ29の遮断特性が低下した場合にも、水素タンク21からの水素ガスの流出を主止弁26で遮断することができ、フェールセールを好適に達成することもできる。
On the other hand, in this embodiment, the
さらに、インジェクタ29の配置の観点では、以下のような作用効果がある。
すなわち、インジェクタ29を水素タンク21の外側に配置したため、インジェクタ29の取扱い性や保守性を高めることができる。また、インジェクタ29は外気との熱交換が容易となるため、ガス放出時における水素タンク21の温度低下の影響を抑制できる。
さらに、インジェクタ29の軸線方向Y−Yを水素タンク21の軸線方向X−Xに直交させているため、水素タンク21にバルブアッセンブリ30が設けられた状態の構造の全長を比較的短くできる。これにより、全体として小型化でき、水素タンク21等の設置スペースの占有領域を小さくできる。限られる設置スペースとの関係からすれば、相対的ではあるが、水素タンク21を長手方向に伸長させることができ、水素ガスの貯蔵容量を増やすことができる。なお、インジェクタ29の軸線方向Y−Yを水素タンク21の軸線方向X−Xを交差させる構成であってもよい。
Further, from the viewpoint of the arrangement of the
That is, since the
Furthermore, since the axial direction YY of the
<第2実施形態>
次に、図3を参照して、第2実施形態に係るインジェクタ29(バルブ)について相違点を中心に説明する。第1実施形態との相違点は、バルブアッセンブリ30におけるインジェクタ29の配置を同軸形に変更したことである。なお、第1実施形態と共通する構成については、第1実施形態と同一の符号を付してその詳細な説明を省略する。
Second Embodiment
Next, an injector 29 (valve) according to the second embodiment will be described with a focus on the differences with reference to FIG. The difference from the first embodiment is that the arrangement of the
インジェクタ29は、主弁部分410、ソレノイド部分420、及びハンドル部分430を有し、これら410,420及び430は、これらは水素タンク21の軸線方向X−Xに沿って順にバルブアッセンブリ30の第1の領域301に配置されている。つまり、本実施形態では、弁体401の軸線方向に相当するインジェクタ29の軸線方向は、水素タンク21の軸線方向X−Xに合致している。
The
ハンドル部分430には、環状又は複数の水素ガスの流路451が貫通形成されている。流路451は、軸線方向X−Xに延在し、ハウジング300内の流路453に連通している。流路453は、水素ガスがソレノイド部分420の外周を流れるように軸線方向X−Xに延在しており、インジェクタ29の二次側の流路455に連通している。流路455は、ハウジング300内に形成されており、供給路22に連通している。したがって、貯留空間104内の水素ガスは、インジェクタ29において、流路451、流路453、噴射孔404及び流路455を順に流れて、供給路22に流出する。
An annular or plurality of hydrogen
本実施形態が第1実施形態に比べて有用となる点は、インジェクタ29を水素タンク21と同軸上に設けていることにより、インジェクタ29が自己清浄し易くなることである。
The point that this embodiment is useful compared with the first embodiment is that the
具体的には、弁体401の軸方向の移動時に発生し得る磨耗粉などのコンタミは、流路453を流れる水素ガスと共に流路455へと排出され得る。これにより、インジェクタ29内のソレノイド部分420の周囲にコンタミを滞留させなくて済み、インジェクタ29を簡易な構造で自己清浄することができる。このような自己清浄効果は、プランジャ423の外周面又は弁体401の外周面がハウジング300の内壁に摺動する場合に特に有用となる。なお、図3では、プランジャ423の外周面又は弁体401の外周面が摺動するような態様では表されていない。
Specifically, contamination such as abrasion powder that may be generated when the
本実施形態の変形例として、インジェクタ29の軸線方向が、水素タンク21の軸線方向X−Xに合致していなくても良く、例えば両者が平行であってもよい。この場合も、上記と同様の作用効果を奏することができる。また、バルブアッセンブリ30において、主止弁26を省略したが、もちろんインジェクタ29の一次側に主止弁26を設けてもよい。
As a modification of the present embodiment, the axial direction of the
なお、第1実施形態及び第2実施形態で説明したインジェクタ29は、二次側へのガス圧の調整を行えることから、調圧弁(減圧弁、レギュレータ)と解釈することもできる。
The
以上説明した本発明の燃料電池システム1は、二輪または四輪の車両、電車、航空機、船舶、ロボットその他の移動体に搭載することができる。また、燃料電池システム1は、定置用ともすることができ、コージェネレーションシステムに組み込むことができる。さらに、インジェクタ29が設けられるタンクは、水素吸蔵合金用のタンクであってもよいし、炭化水素系の他の燃料ガスを貯蔵するものであってもよい。例えば、タンクは、圧縮天然ガスを例えば20MPaで貯蔵するものであってもよく、貯蔵する流体が気体であるか液体であるかなど、その種類が限定されるものではない。
The fuel cell system 1 of the present invention described above can be mounted on a two-wheeled or four-wheeled vehicle, a train, an aircraft, a ship, a robot, or other moving bodies. Further, the fuel cell system 1 can be used for stationary use and can be incorporated into a cogeneration system. Furthermore, the tank in which the
1:燃料電池システム、2:燃料電池、21:水素タンク、26:主止弁、29:インジェクタ 1: Fuel cell system, 2: Fuel cell, 21: Hydrogen tank, 26: Main stop valve, 29: Injector
Claims (7)
二次側がタンク内からの流体の放出側となるように当該タンクに設けられ、当該タンク内からの流体の放出流量をデューティ制御により調整可能に構成されたバルブ。 A valve configured to adjust the flow rate of fluid to the secondary side,
A valve that is provided in the tank so that the secondary side is the side from which the fluid is discharged from the tank, and is configured such that the flow rate of the fluid discharged from the tank can be adjusted by duty control.
前記流量調整機構は、前記タンク内からの流体の放出を遮断可能に構成されている、請求項1に記載のバルブ。 A flow rate adjusting mechanism for adjusting the discharge flow rate by duty control;
The valve according to claim 1, wherein the flow rate adjusting mechanism is configured to be able to block the release of fluid from the tank.
当該バルブの軸線と前記タンクの軸線とは、略直交する、請求項1又は2に記載のバルブ。 The valve is located outside the tank body,
The valve according to claim 1 or 2, wherein an axis of the valve and an axis of the tank are substantially orthogonal to each other.
前記主止弁は、当該バルブの一次側に位置している、請求項1ないし4のいずれか一項に記載のバルブ。 The tank is provided with a main stop valve separate from the valve,
The valve according to any one of claims 1 to 4, wherein the main stop valve is located on a primary side of the valve.
酸化ガス及び燃料ガスが供給される燃料電池と、を備えた燃料電池システムであって、
前記タンク内の前記流体は、燃料ガスである、燃料電池システム。
The valve and the tank according to any one of claims 1 to 5,
A fuel cell system provided with an oxidizing gas and a fuel gas,
The fuel cell system, wherein the fluid in the tank is a fuel gas.
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006060128A JP2007242304A (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2006-03-06 | Valve, valve control device, and fuel cell system |
| PCT/JP2007/052438 WO2007102297A1 (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2007-02-06 | Valve, valve controller and fuel cell system |
| US12/223,484 US20090014089A1 (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2007-02-06 | Valve, Valve Controller, and Fuel Cell System |
| CNA2007800080108A CN101395423A (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2007-02-06 | Valve, valve controller and fuel cell system |
| DE112007000513T DE112007000513T5 (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2007-02-06 | Valve, valve control and fuel cell system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006060128A JP2007242304A (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2006-03-06 | Valve, valve control device, and fuel cell system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007242304A true JP2007242304A (en) | 2007-09-20 |
| JP2007242304A5 JP2007242304A5 (en) | 2008-10-30 |
Family
ID=38474739
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006060128A Withdrawn JP2007242304A (en) | 2006-03-06 | 2006-03-06 | Valve, valve control device, and fuel cell system |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20090014089A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2007242304A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101395423A (en) |
| DE (1) | DE112007000513T5 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2007102297A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102011114728A1 (en) * | 2011-10-01 | 2013-04-04 | Daimler Ag | Device for storing a gaseous fuel |
| DE102012005689B3 (en) | 2012-03-21 | 2013-08-22 | Audi Ag | Method for supplying a drive unit |
| DE202013004126U1 (en) * | 2012-12-19 | 2014-03-24 | Erwin Weh | Gas handling unit |
| LU92385B1 (en) * | 2014-02-27 | 2015-08-28 | Luxembourg Patent Co Sa | Valve for LPG storage tank |
| JP6137126B2 (en) * | 2014-11-13 | 2017-05-31 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Valve control device and valve control method |
| KR102496178B1 (en) | 2016-12-15 | 2023-02-03 | 현대자동차주식회사 | The method for controlling of hydrogen cut-off valve |
| JP7090042B2 (en) * | 2019-02-25 | 2022-06-23 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Fuel cell system and fuel cell vehicle |
| FR3095848B1 (en) * | 2019-05-07 | 2021-07-30 | Faurecia Systemes Dechappement | Tank head for pressurized gas |
| DE102020200679A1 (en) | 2020-01-22 | 2021-07-22 | Robert Bosch Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Method for opening a valve assembly for a fuel tank |
| DE102020112830A1 (en) * | 2020-05-12 | 2021-11-18 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Control unit and method for operating a pressure vessel valve of a pressure vessel |
| CN112879614B (en) * | 2021-01-16 | 2022-06-28 | 新乡市赛特钢瓶有限公司 | Constant pressure process valve for preparing porous packing of acetylene cylinder |
| KR20240005278A (en) * | 2022-07-04 | 2024-01-12 | 현대자동차주식회사 | Fuel supply device |
| DE102022207249A1 (en) * | 2022-07-15 | 2024-01-18 | Robert Bosch Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Fuel gas tank system |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6041762A (en) * | 1996-08-16 | 2000-03-28 | Impco Technologies, Inc. | Control module for natural gas fuel supply for a vehicle |
| US6101816A (en) | 1998-04-28 | 2000-08-15 | Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. | Fluid storage and dispensing system |
| JP4824853B2 (en) * | 2000-07-18 | 2011-11-30 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Gas supply device for fuel cell |
| JP2002256980A (en) * | 2001-03-05 | 2002-09-11 | Fujitsu Ten Ltd | Fuel cutoff valve control device |
| JP2003090499A (en) * | 2001-09-19 | 2003-03-28 | Samtec Kk | High pressure tank device |
| JP4042518B2 (en) * | 2002-10-10 | 2008-02-06 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Excess pressure release structure of gas fuel tank |
| JP4552399B2 (en) * | 2003-08-07 | 2010-09-29 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Tank system comprising multiple tanks and control method thereof |
| JP4779301B2 (en) * | 2004-02-10 | 2011-09-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Fuel cell system |
| US20070240770A1 (en) * | 2004-08-23 | 2007-10-18 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | High-Pressure Tank and Valve Assembly |
-
2006
- 2006-03-06 JP JP2006060128A patent/JP2007242304A/en not_active Withdrawn
-
2007
- 2007-02-06 US US12/223,484 patent/US20090014089A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2007-02-06 DE DE112007000513T patent/DE112007000513T5/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2007-02-06 CN CNA2007800080108A patent/CN101395423A/en active Pending
- 2007-02-06 WO PCT/JP2007/052438 patent/WO2007102297A1/en active Search and Examination
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20090014089A1 (en) | 2009-01-15 |
| DE112007000513T5 (en) | 2009-06-18 |
| WO2007102297A1 (en) | 2007-09-13 |
| CN101395423A (en) | 2009-03-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2007242304A (en) | Valve, valve control device, and fuel cell system | |
| JP5438745B2 (en) | Fluid supply system | |
| EP2276096B1 (en) | Fuel cell system and mobile article | |
| JP4962777B2 (en) | Gas supply system | |
| JP2010001916A (en) | Solenoid shutoff valve | |
| JP2013089307A (en) | Pressure-reducing valve with injector, and fuel cell system equipped with the same | |
| JP6868371B2 (en) | High pressure fluid control valve and fuel cell system | |
| US8671981B2 (en) | Freeze robust anode valve and passage design | |
| JP2010135189A (en) | Fuel cell system | |
| JP6724736B2 (en) | High pressure fluid control valve control device and abnormality diagnosis method | |
| JP2010053983A (en) | On-off valve | |
| JP2009068648A (en) | Reactant gas-supplying device of fuel cell | |
| JP2012189108A (en) | Tank valve with injector and fuel cell system | |
| JP2006331850A (en) | Reaction gas supply device of fuel cell | |
| JP4398349B2 (en) | Electromagnetic shut-off valve for fuel cell | |
| JP2009168166A (en) | Valve device for high-pressure tank and fuel cell system | |
| JP4533114B2 (en) | Electromagnetic shut-off valve for fuel cell | |
| JP2008071669A (en) | Fuel cell system | |
| JP5380760B2 (en) | Fuel cell control device | |
| JP2019108924A (en) | Relief valve and gas fuel supply unit | |
| JP2006302612A (en) | Fuel cell system | |
| JP2012219949A (en) | Fluid supply system | |
| JP2010255746A (en) | Gas supply system | |
| JP2017004887A (en) | Hydrogen supply device | |
| JP2009146669A (en) | Valve for fuel cell |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080916 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20080916 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20110419 |