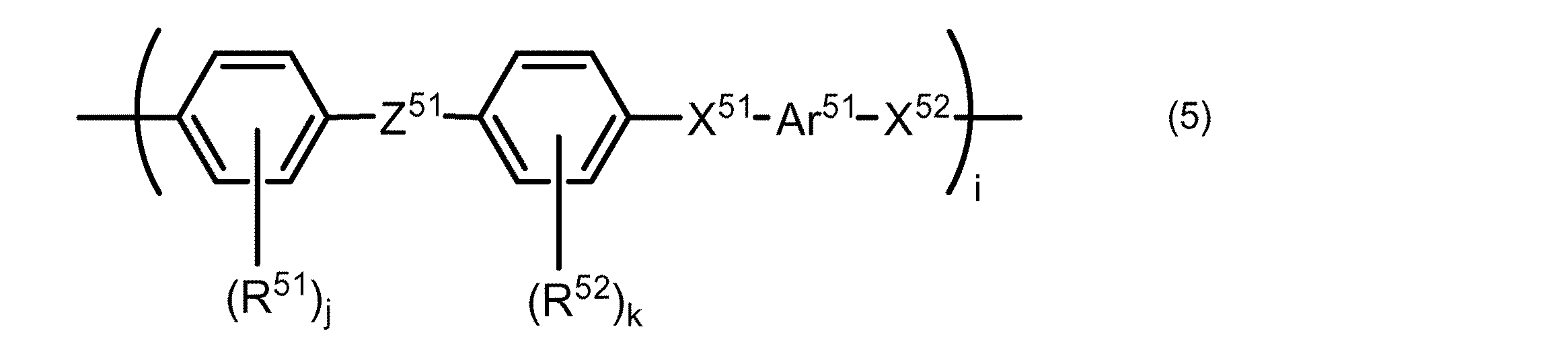JP2007106986A - Block copolymer and method for producing the same, polymer electrolyte, catalytic composition, polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane/electrode assembly and fuel cell - Google Patents
Block copolymer and method for producing the same, polymer electrolyte, catalytic composition, polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane/electrode assembly and fuel cell Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007106986A JP2007106986A JP2006244692A JP2006244692A JP2007106986A JP 2007106986 A JP2007106986 A JP 2007106986A JP 2006244692 A JP2006244692 A JP 2006244692A JP 2006244692 A JP2006244692 A JP 2006244692A JP 2007106986 A JP2007106986 A JP 2007106986A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- group
- polymer compound
- block copolymer
- carbon atoms
- polymer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 0 Cc1ccc(*c2ccc(*)cc2)cc1 Chemical compound Cc1ccc(*c2ccc(*)cc2)cc1 0.000 description 2
- DDTHUSRGGGQLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(C)C1=C[I]=CC=C1 Chemical compound CC(C)(C)C1=C[I]=CC=C1 DDTHUSRGGGQLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XIAJWWWCYMMOMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C)(c(cc1)ccc1OC)c(cc1)ccc1Oc(cc1)ccc1S(c1ccc(C)cc1)(=O)=O Chemical compound CC(C)(c(cc1)ccc1OC)c(cc1)ccc1Oc(cc1)ccc1S(c1ccc(C)cc1)(=O)=O XIAJWWWCYMMOMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/30—Hydrogen technology
- Y02E60/50—Fuel cells
Abstract
Description
本発明は、ブロック共重合体及びその製造方法、高分子電解質、触媒組成物、高分子電解質膜、膜−電極接合体及び燃料電池に関する。 The present invention relates to a block copolymer and a method for producing the same, a polymer electrolyte, a catalyst composition, a polymer electrolyte membrane, a membrane-electrode assembly, and a fuel cell.
固体高分子型の燃料電池におけるプロトン伝導膜に用いられるプロトン伝導性の高分子電解質としては、従来、パーフルオロアルキルスルホン酸系高分子が、燃料電池としての特性に優れることから主として使用されている。しかしながら、この材料は非常に高価であることから、燃料電池を用いる発電システムをより広範に普及させるために、より安価に提供し得る高分子電解質用の材料が盛んに開発されている。 Conventionally, as a proton conductive polymer electrolyte used for a proton conductive membrane in a solid polymer fuel cell, a perfluoroalkylsulfonic acid polymer is mainly used because of its excellent characteristics as a fuel cell. . However, since this material is very expensive, a material for a polymer electrolyte that can be provided at a lower cost has been actively developed in order to spread a power generation system using a fuel cell more widely.
パーフルオロアルキルスルホン酸系高分子に代わる高分子電解質用の材料としては、例えば、耐熱性に優れ、しかも、フィルム強度が高い芳香族ポリエーテルにスルホン酸基を導入した材料が提案されている。例えば、スルホン化ポリエーテルケトン系(特許文献1)、スルホン化ポリエーテルスルホン系(特許文献2、3)等が開示されている。また、イオン交換基が導入されたセグメントとイオン交換基が導入されていないセグメントからなるブロック共重合体は、優れたプロトン伝導性を示す高分子電解質を形成し得る材料として知られている(特許文献4、5)。
近年では、住宅用や自動車用等の用途における発電機として、固体高分子型の燃料電池の実用化が期待されており、かかる燃料電池に対しては、従来にも増して高い効率での運転が可能であることが求められている。燃料電池の高効率化のためには、プロトン伝導膜に用いる高分子電解質のプロトン伝導性を高めることが有効であり、上記従来の高分子電解質用材料に対しても、更なるプロトン伝導性の向上が求められている。 In recent years, solid polymer fuel cells are expected to be put to practical use as generators for residential and automotive applications. For such fuel cells, operation with higher efficiency than before is expected. Is required to be possible. In order to increase the efficiency of the fuel cell, it is effective to increase the proton conductivity of the polymer electrolyte used for the proton conducting membrane, and even higher proton conductivity than the above-mentioned conventional polymer electrolyte materials. There is a need for improvement.
そこで、本発明はこのような事情に鑑みてなされたものであり、優れたプロトン伝導性を有する高分子電解質を構成し得るブロック共重合体を製造する方法を提供することを目的とする。本発明はまた、かかる製造方法から得られたブロック共重合体、これを含む高分子電解質及び高分子電解質膜、この高分子電解質を含む触媒組成物、これらを高分子電解質膜又は触媒層に用いた膜−電極接合体、並びにこの膜−電極接合体を備える燃料電池を提供することを特徴とする。 Then, this invention is made | formed in view of such a situation, and it aims at providing the method of manufacturing the block copolymer which can comprise the polymer electrolyte which has the outstanding proton conductivity. The present invention also provides a block copolymer obtained from such a production method, a polymer electrolyte and a polymer electrolyte membrane containing the block copolymer, a catalyst composition containing the polymer electrolyte, and a polymer electrolyte membrane or a catalyst layer. And a fuel cell including the membrane-electrode assembly.
上記目的を達成するために、本発明者らが鋭意研究を行ったところ、上記高分子電解質を構成するブロック共重合体において、イオン交換基が導入されたセグメント、及び、イオン交換基が導入されていないセグメントをそれぞれ高分子量化することによって、優れたプロトン伝導性を発揮し得るブロック共重合体が得られることを見出した。 In order to achieve the above-mentioned object, the present inventors have conducted intensive research. As a result, in the block copolymer constituting the polymer electrolyte, a segment into which an ion-exchange group has been introduced, and an ion-exchange group have been introduced. It was found that a block copolymer capable of exhibiting excellent proton conductivity can be obtained by increasing the molecular weight of each segment that is not present.
通常、ブロック共重合体は、各セグメントを形成するための高分子化合物をブロック共重合させることで合成することができるが、上記のようにセグメントを高分子量化するためには、各セグメントを形成するための高分子化合物として、従来以上に高分子量のものを用いる必要がある。しかしながら、本発明者らの検討結果によると、各セグメントを形成するための高分子化合物は、上述のような高分子量化によって単一の溶媒中に溶解し難くなり、これらをブロック共重合させる際には、いずれかの高分子化合物のみが溶媒中に析出してしまう等の不都合が生じ易くなる傾向にあることが判明した。このため、各セグメントの高分子量化を図った場合、ブロック共重合が十分に進行し難くなり、良好なブロック共重合体が得られない場合も少なくなかった。 Usually, a block copolymer can be synthesized by block copolymerization of a polymer compound for forming each segment, but in order to increase the molecular weight of the segment as described above, each segment is formed. It is necessary to use a polymer compound having a higher molecular weight than the conventional polymer compound. However, according to the study results of the present inventors, the polymer compound for forming each segment becomes difficult to dissolve in a single solvent due to the increase in the molecular weight as described above. Therefore, it has been found that there is a tendency that only one of the polymer compounds is likely to be precipitated in the solvent. For this reason, when the molecular weight of each segment is increased, block copolymerization does not proceed sufficiently, and there are many cases in which a good block copolymer cannot be obtained.
そこで、本発明者らが更に検討を行った結果、ブロック共重合に用いる溶媒として、複数種のものを組み合わせて用いることで、上述したような高分子量化された高分子化合物であっても良好にブロック共重合させることが可能となることを見出し、本発明を完成させるに至った。 Therefore, as a result of further investigation by the present inventors, it is possible to use a polymer compound having a high molecular weight as described above by using a combination of a plurality of solvents as a solvent used for block copolymerization. The inventors have found that block copolymerization can be carried out, and have completed the present invention.
すなわち、本発明のブロック共重合体の製造方法は、2種以上の溶媒を含む混合溶媒中で、イオン交換基を有する第1の高分子化合物と、イオン交換基を実質的に有しない第2の高分子化合物と、が結合した重合体を得る工程を有することを特徴とする。 That is, the method for producing a block copolymer of the present invention includes a first polymer compound having an ion exchange group in a mixed solvent containing two or more solvents, and a second substantially free of an ion exchange group. It has the process of obtaining the polymer which couple | bonded with the high molecular compound.
このように、本発明の製造方法においては、2種以上の溶媒を含む混合溶媒を用いているため、ブロック共重合体の各セグメントを形成するための高分子化合物として、単一の溶媒ではいずれかが析出してしまうような組み合わせを用いた場合であっても、これらを良好に溶解することができるようになり、これらの高分子化合物のブロック共重合反応を良好に行うことが可能となる。その結果、イオン交換基が導入されたセグメント、及び、イオン交換基が導入されていないセグメントがそれぞれ高分子量化されたブロック共重合体が得られるようになり、これにより優れたプロトン伝導性を有する高分子電解質が得られるようになる。 As described above, in the production method of the present invention, since a mixed solvent containing two or more solvents is used, any single solvent can be used as the polymer compound for forming each segment of the block copolymer. Even in the case of using a combination that causes precipitation, these can be dissolved satisfactorily, and the block copolymerization reaction of these polymer compounds can be performed satisfactorily. . As a result, a block copolymer in which a segment having an ion exchange group introduced therein and a segment having no ion exchange group introduced therein are respectively increased in molecular weight can be obtained, thereby having excellent proton conductivity. A polymer electrolyte is obtained.
上記混合溶媒は、第1の高分子化合物の良溶媒を含むと好ましい。これにより、混合溶媒中への第1の高分子化合物の溶解が有利となり、ブロック共重合がより良好に進行するようになる。また、混合溶媒は、第2の高分子の良溶媒を含むとより好ましい。こうすれば、第2の高分子化合物も混合溶媒に良好に溶解することとなり、各セグメントが高分子量化されたブロック共重合体が確実に得られるようになる。 The mixed solvent preferably contains a good solvent for the first polymer compound. Thereby, dissolution of the first polymer compound in the mixed solvent becomes advantageous, and block copolymerization proceeds more favorably. The mixed solvent more preferably contains a good solvent for the second polymer. By doing so, the second polymer compound is also well dissolved in the mixed solvent, and a block copolymer in which each segment has a high molecular weight can be reliably obtained.
より具体的には、混合溶媒は、第1の高分子化合物の良溶媒を20質量%以上含むと好ましい。また、第2の高分子化合物の良溶媒を20質量%以上含むと更に好ましい。こうすれば、第1及び/又は第2の高分子化合物が混合溶媒に更に良好に溶解することとなり、各セグメントが高分子量化されたブロック共重合の生成が更に有利となる。 More specifically, the mixed solvent preferably contains 20% by mass or more of the good solvent for the first polymer compound. Further, it is more preferable that the good solvent for the second polymer compound is contained in an amount of 20% by mass or more. In this way, the first and / or second polymer compound is more satisfactorily dissolved in the mixed solvent, and the production of block copolymer in which each segment has a high molecular weight is further advantageous.
ここで、「第1(又は第2)の高分子化合物の良溶媒」とは、25℃において100g中に当該高分子化合物を5質量%以上の濃度となるように溶解し得る溶媒をいうものとする。なお、第1(又は第2)の高分子化合物が複数種類含まれている場合は、それらの合計の溶解量(g)を基準とする。また、ここでいう「溶解」とは、高分子化合物と溶媒とが均一な液相を形成した状態を意味する。 Here, the “good solvent for the first (or second) polymer compound” refers to a solvent that can dissolve the polymer compound in 100 g at 25 ° C. to a concentration of 5% by mass or more. And In addition, when multiple types of 1st (or 2nd) high molecular compounds are contained, the total amount (g) of those dissolutions is used as a reference. The term “dissolved” as used herein means a state where the polymer compound and the solvent form a uniform liquid phase.
上記第1の高分子化合物が有しているイオン交換基としては、陽イオン交換基が好ましい。これにより、得られるブロック共重合体が陽イオン交換基を含むセグメントを有するようになる。このようなブロック共重合体は、高分子電解質として用いた場合に優れたプロトン伝導性を発揮し得るようになる。なかでも、陽イオン交換基としては、スルホン酸基が好ましい。 The ion exchange group possessed by the first polymer compound is preferably a cation exchange group. Thereby, the obtained block copolymer comes to have a segment containing a cation exchange group. Such a block copolymer can exhibit excellent proton conductivity when used as a polymer electrolyte. Especially, as a cation exchange group, a sulfonic acid group is preferable.
また、本発明においては、第1及び第2の高分子化合物のうちの少なくとも一方は芳香族高分子化合物であると好ましい。特に、第1及び第2の高分子化合物の両方が芳香族高分子化合物であるとより好ましい。こうすれば、より優れた耐熱性やガスバリア性を有する高分子電解質が得られやすくなる。なお、本明細書において、「芳香族高分子化合物」とは、当該化合物を主として構成している繰り返し単位のうちの50%以上がその主鎖に芳香環を有している化合物をいうものとする。 In the present invention, at least one of the first and second polymer compounds is preferably an aromatic polymer compound. In particular, it is more preferable that both the first and second polymer compounds are aromatic polymer compounds. If it carries out like this, it will become easy to obtain the polymer electrolyte which has the more excellent heat resistance and gas barrier property. In the present specification, the “aromatic polymer compound” refers to a compound in which 50% or more of the repeating units mainly constituting the compound have an aromatic ring in the main chain. To do.
さらに、上記第1の高分子化合物は、その分子量が2000以上であると好ましい。また、第2の高分子化合物も、その分子量が2000以上であると好ましい。こうすれば、得られるブロック共重合体における各セグメントがより高分子量化されたものとなり、更にプロトン伝導性に優れる高分子電解質を得ることが可能となる。 Furthermore, the first polymer compound preferably has a molecular weight of 2000 or more. Also, the second polymer compound preferably has a molecular weight of 2000 or more. If it carries out like this, each segment in the obtained block copolymer will become what became high molecular weight, and also it will become possible to obtain the polymer electrolyte which is excellent in proton conductivity.
また、本発明の製造方法においては、第1の高分子化合物の良溶媒の比誘電率が40.0以上であり、第2の高分子化合物の良溶媒の比誘電率が40.0未満であると好ましい。こうすれば、第1及び第2の高分子化合物の両方が混合溶媒中に良好に溶解され、その結果、各セグメントが高分子量化されたブロック共重合体が良好に得られるようになる。また、この場合、第1の高分子化合物の良溶媒の比誘電率と第2の高分子化合物の良溶媒の比誘電率との差が、5.0以上であると、両高分子化合物の混合溶媒への溶解が更に良好となるため、好ましい。 In the production method of the present invention, the relative permittivity of the good solvent of the first polymer compound is 40.0 or more, and the relative permittivity of the good solvent of the second polymer compound is less than 40.0. It is preferable. In this way, both the first and second polymer compounds are dissolved well in the mixed solvent, and as a result, a block copolymer in which each segment has a high molecular weight can be obtained favorably. In this case, if the difference between the relative permittivity of the good solvent of the first polymer compound and the relative permittivity of the good solvent of the second polymer compound is 5.0 or more, This is preferable because dissolution in a mixed solvent is further improved.
より具体的には、第1の高分子化合物の良溶媒がジメチルスルホキシド(DMSO)であると好ましい。こうすれば、特に、第1の高分子化合物が上述した陽イオン交換基、なかでもスルホン酸基を有する場合に、当該化合物の混合溶媒への溶解が有利となる。また、第2の高分子化合物の良溶媒は、N−メチルピロリドンであると更に好ましい。こうすれば、第2の高分子化合物が、混合溶媒中に更に良好に溶解することとなる。 More specifically, the good solvent for the first polymer compound is preferably dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). In this case, particularly when the first polymer compound has the above-described cation exchange group, particularly a sulfonic acid group, dissolution of the compound in a mixed solvent is advantageous. The good solvent for the second polymer compound is more preferably N-methylpyrrolidone. If it carries out like this, a 2nd high molecular compound will melt | dissolve more favorably in a mixed solvent.
上述した第1の高分子化合物は、具体的には、下記一般式(7)で表される構造を有し、且つ、この構造中にイオン交換基を有する化合物であると好適である。
[式中、Ar71は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X71は、直接結合、酸素原子、硫黄原子、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、dは5以上の整数である。]
Specifically, the first polymer compound described above is preferably a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (7) and having an ion exchange group in the structure.
[In the formula, Ar 71 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. A divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group, X 71 represents a direct bond, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and d is an integer of 5 or more. ]
より具体的には、第1の高分子化合物は、下記一般式(1a)、(1b)又は(1c)で表される構造を有し、且つ、この構造中にイオン交換基を有する化合物であるとより好ましい。
[式中、Ar11、Ar12、Ar13、Ar14、Ar15、Ar16及びAr17(以下、「Ar11〜Ar17」のように表記する)は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X11〜X15は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、Y11及びY12は、それぞれ独立に、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、p、q及びrは、それぞれ独立に、5以上の整数である。]
More specifically, the first polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (1a), (1b) or (1c) and having an ion exchange group in this structure. More preferably.
[In the formula, Ar 11 , Ar 12 , Ar 13 , Ar 14 , Ar 15 , Ar 16 and Ar 17 (hereinafter referred to as “Ar 11 to Ar 17 ”) are each independently represented by 1 to Divalent which may have 20 alkyl groups, C1-C20 alkoxy groups, C6-C20 aryl groups, C6-C20 aryloxy groups, or C2-C20 acyl groups X 11 to X 15 each independently represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, Y 11 and Y 12 each independently represent a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and p, q and r Are each independently an integer of 5 or more. ]
より具体的には、第1の高分子化合物は、下記一般式(2)で表される構造を有する化合物であるとより好ましい。
[式中、Y21は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、s及びtは、それぞれ独立に0又は1であって少なくともいずれか一方が1であり、uは0、1又は2であり、vは1又は2であり、wは5以上の整数である。]
More specifically, the first polymer compound is more preferably a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (2).
[Wherein Y 21 represents a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, s and t are each independently 0 or 1, at least one of which is 1, u is 0, 1 or 2; Is 1 or 2, and w is an integer of 5 or more. ]
さらに、上記第1の高分子化合物は、下記一般式(17)で表される構造を有する化合物であると一層好ましい。
[式中、X171は、直接結合又は有機基であり、fは1からX171における置換可能な部位の数までの整数であり、gは1又は2であり、lは5以上の整数である。]
Furthermore, the first polymer compound is more preferably a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (17).
[ Wherein X 171 is a direct bond or an organic group, f is an integer from 1 to the number of substitutable sites in X 171 , g is 1 or 2, and l is an integer of 5 or more. is there. ]
一方、第2の高分子化合物は、下記一般式(3)で表される構造を有する化合物であるであると好ましい。
[式中、Ar31は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X31は、直接結合、酸素原子、硫黄原子、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、zは5以上の整数である。]
On the other hand, the second polymer compound is preferably a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (3).
[In the formula, Ar 31 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. And X 31 represents a direct bond, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and z is an integer of 5 or more. ]
また、このような第2の高分子化合物は、下記一般式(4)で表される構造を有する化合物であってもよい。
[式中、Ar41、Ar42及びAr43は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X41及びX42は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、Z41は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、hは5以上の整数である。]
Such a second polymer compound may be a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (4).
[Wherein, Ar 41 , Ar 42 and Ar 43 each independently represent an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 6 to 20 carbon atoms. An aryloxy group or a divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms, X 41 and X 42 each independently represent an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and Z 41 Represents a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and h is an integer of 5 or more. ]
より具体的には、第2の高分子化合物としては、下記一般式(5)で表される構造を有する化合物が好適である。
[式中、Ar51は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X51及びX52は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、R51及びR52は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を示し、Z51は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、j及びkは、それぞれ独立に、0〜4の整数であり、iは、5以上の整数である。]
More specifically, the second polymer compound is preferably a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (5).
[In the formula, Ar 51 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. A divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group, X 51 and X 52 each independently represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and R 51 and R 52 each independently represent a carbon atom. C 1 -
本発明はまた、上記本発明の製造方法により得ることのできるブロック共重合体を提供する。このようなブロック共重合体は、上述の如く、それぞれ従来に比して高い分子量を有するイオン交換基を有するセグメントと、イオン交換基を実質的に有しないセグメントとを有するものとなり、優れたプロトン伝導性を有する高分子電解質を形成し得る。 The present invention also provides a block copolymer obtainable by the production method of the present invention. As described above, such a block copolymer has a segment having an ion exchange group having a higher molecular weight than the conventional one and a segment having substantially no ion exchange group. A conductive polymer electrolyte can be formed.
かかる本発明のブロック共重合体は、イオン交換容量が0.1〜4meq/gであると好ましい。このようなイオン交換容量を有するブロック共重合体は、更に優れたプロトン伝導性を有する高分子電解質を形成し得る。これらの本発明のブロック共重合体をプロトン伝導成分として含むことで、本発明の高分子電解質が構成される。 Such a block copolymer of the present invention preferably has an ion exchange capacity of 0.1 to 4 meq / g. A block copolymer having such an ion exchange capacity can form a polymer electrolyte having further excellent proton conductivity. By containing these block copolymers of the present invention as proton conducting components, the polymer electrolyte of the present invention is constituted.
本発明は更に、上記本発明の高分子電解質と触媒とを含有する触媒組成物を提供する。このような触媒組成物は、燃料電池を構成する膜−電極接合体において、プロトン伝導膜に隣接して配置される触媒層の構成材料として好適である。 The present invention further provides a catalyst composition containing the polymer electrolyte of the present invention and a catalyst. Such a catalyst composition is suitable as a constituent material of the catalyst layer disposed adjacent to the proton conducting membrane in the membrane-electrode assembly constituting the fuel cell.
本発明はまた、上記本発明の高分子電解質からなる高分子電解質膜を提供する。このような高分子電解質膜は、優れたプロトン伝導性を有するため、かかる高分子電解質をプロトン伝導膜として用いた燃料電池は、極めて高効率なものとなる。 The present invention also provides a polymer electrolyte membrane comprising the polymer electrolyte of the present invention. Since such a polymer electrolyte membrane has excellent proton conductivity, a fuel cell using such a polymer electrolyte as a proton conducting membrane is extremely efficient.
また、本発明は、上記本発明の高分子電解質を用いた、燃料電池に適用するための膜−電極接合体を提供する。すなわち、本発明の膜−電極接合体は、高分子電解質膜と、この高分子電解質膜上に形成された触媒層とを備え、高分子電解質膜が、上記本発明の高分子電解質を含有することを特徴とする。かかる膜−電極接合体を備える燃料電池は、高効率で発電可能なものとなる。 The present invention also provides a membrane-electrode assembly that uses the polymer electrolyte of the present invention and is applied to a fuel cell. That is, the membrane-electrode assembly of the present invention includes a polymer electrolyte membrane and a catalyst layer formed on the polymer electrolyte membrane, and the polymer electrolyte membrane contains the polymer electrolyte of the present invention. It is characterized by that. A fuel cell including such a membrane-electrode assembly can generate power with high efficiency.
さらに、本発明は、上記本発明の高分子電解質を触媒層に用いた膜−電極接合体を提供する。すなわち、本発明の膜−電極接合体は、高分子電解質膜と、この高分子電解質膜上に形成された触媒層とを備え、触媒層が、上記本発明の高分子電解質及び触媒を含有することを特徴とする。かかる膜−電極接合体は、触媒層も高プロトン伝導性を発現し得るものとなる。このため、この膜−電極接合体を備える燃料電池は、極めて高効率なものとなる。 Furthermore, the present invention provides a membrane-electrode assembly using the polymer electrolyte of the present invention as a catalyst layer. That is, the membrane-electrode assembly of the present invention comprises a polymer electrolyte membrane and a catalyst layer formed on the polymer electrolyte membrane, and the catalyst layer contains the polymer electrolyte and catalyst of the present invention. It is characterized by that. In such a membrane-electrode assembly, the catalyst layer can also exhibit high proton conductivity. For this reason, a fuel cell provided with this membrane-electrode assembly becomes extremely efficient.
さらにまた、本発明は、上記本発明の膜−電極接合体を備える燃料電池を提供する。すなわち、本発明の燃料電池は、一対のセパレータと、この一対のセパレータ間に配置された膜−電極接合体とを備え、膜−電極接合体が上記本発明の膜−電極接合体であることを特徴とする。このような燃料電池は、上記本発明の膜−電極接合体を備えることから、極めて高効率での運転が可能となる。 Furthermore, the present invention provides a fuel cell comprising the membrane-electrode assembly of the present invention. That is, the fuel cell of the present invention includes a pair of separators and a membrane-electrode assembly disposed between the pair of separators, and the membrane-electrode assembly is the membrane-electrode assembly of the present invention. It is characterized by. Since such a fuel cell includes the membrane-electrode assembly of the present invention, it can be operated with extremely high efficiency.
本発明によれば、優れたプロトン伝導性を有するプロトン伝導膜を形成し得る高分子電解質用材料であるブロック共重合体を提供することが可能となる。また、かかるプロトン共重合体を含み、高プロトン伝導性を有する高分子電解質及び高分子電解質膜、これを備える膜−電極接合体、並びに、かかる膜−電極接合体を備え、高効率での運転が可能な燃料電池を提供することが可能となる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, it becomes possible to provide the block copolymer which is a material for polymer electrolytes which can form the proton conductive film | membrane which has the outstanding proton conductivity. Further, a polymer electrolyte and a polymer electrolyte membrane including such a proton copolymer and having high proton conductivity, a membrane-electrode assembly including the same, and a high-efficiency operation including the membrane-electrode assembly It is possible to provide a fuel cell capable of performing the above.
以下、必要に応じて図面を参照しながら、本発明の好適な実施形態について説明する。
[ブロック共重合体の製造方法]
Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings as necessary.
[Method for producing block copolymer]
まず、好適な実施形態に係るブロック共重合体の製造方法について説明する。本実施形態においては、イオン交換基を有するセグメントと、イオン交換基を実質的に有しないセグメントとを有するブロック共重合体を製造する。ここで、「セグメント」とは、ブロック共重合体において所定の繰り返し単位が複数連結してなる高分子構造単位をいう。そして、「ブロック共重合体」とは、2種以上のセグメントが直接又は連結基を介して結合した状態の高分子化合物をいう。 First, the manufacturing method of the block copolymer which concerns on suitable embodiment is demonstrated. In this embodiment, a block copolymer having a segment having an ion exchange group and a segment having substantially no ion exchange group is produced. Here, the “segment” refers to a polymer structural unit formed by connecting a plurality of predetermined repeating units in a block copolymer. The “block copolymer” refers to a polymer compound in which two or more types of segments are bonded directly or via a linking group.
本実施形態において、好適な場合、上記ブロック共重合体におけるイオン交換基を有するセグメントは、イオン交換基を有する高分子化合物(第1の高分子化合物)から構成され、イオン交換基を実質的に有しないセグメントは、イオン交換基を実質的に有しない高分子化合物(第2の高分子化合物)から構成される。すなわち、ブロック共重合体は、第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とが結合した重合体によって構成される。そして、本実施形態においては、2種以上の溶媒を含む混合溶媒中で上記重合体を合成する。なお、本明細書における高分子化合物とは、所定の繰り返し単位を複数含む化合物を意味しており、オリゴマー及びポリマーの両方を含む。 In this embodiment, when preferred, the segment having an ion exchange group in the block copolymer is composed of a polymer compound having an ion exchange group (first polymer compound), and the ion exchange group is substantially The segment which does not have is comprised from the high molecular compound (2nd high molecular compound) which does not have an ion exchange group substantially. That is, the block copolymer is constituted by a polymer in which a first polymer compound and a second polymer compound are bonded. And in this embodiment, the said polymer is synthesize | combined in the mixed solvent containing 2 or more types of solvents. In addition, the high molecular compound in this specification means the compound containing two or more predetermined repeating units, and includes both an oligomer and a polymer.
(第1の高分子化合物)
まず、第1の高分子化合物について説明する。第1の高分子化合物の有するイオン交換基としては、陽イオン交換基及び陰イオン交換基のどちらも適用でき、これらのイオン交換基は、その一部又は全部が対イオンとの塩を形成していてもよい。
(First polymer compound)
First, the first polymer compound will be described. As the ion exchange group possessed by the first polymer compound, either a cation exchange group or an anion exchange group can be applied. These ion exchange groups partially or entirely form a salt with a counter ion. It may be.
このようなイオン交換基としては、例えば、−SO3H、−COOH、−PO(OH)2、−POH(OH)、−SO2NHSO2−、−Ph(OH)(Phはフェニル基を表す)、下記一般式(6)で示される基(かかる構造を有する基を、以下「オキソカーボン基」という)等の陽イオン交換基、−NH2、−NHR、−NRR’、−NRR’R’’+、−NH3 +等(R、R’及びR’’は、それぞれ独立に、アルキル基、シクロアルキル基又はアリール基を示す)等の陰イオン交換基等が挙げられる。
[式中、X61及びX62は、それぞれ独立に−O−、−S−又は−NR−を表し、Z61は−CO−、−C(S)−、−C(NR63)−、置換基を有していてもよいアルキレン基又は置換基を有していてもよいアリーレン基を表す。また、上記NR63におけるR63は、水素原子、置換基を有していてもよい炭素数1〜6のアルキル基又は置換基を有していてもよい炭素数6〜10のアリール基を表す。aは、繰り返しの数を表わし、a=0〜10の整数を表わす。なお、a個のZ61はそれぞれ同一であってもよく、異なっていてもよい。)
Examples of such ion-exchange groups, for example, -SO 3 H, -COOH, -PO (OH) 2, -POH (OH), - SO 2 NHSO 2 -, - Ph a (OH) (Ph represents a phenyl group A cation exchange group such as a group represented by the following general formula (6) (a group having such a structure is hereinafter referred to as an “oxocarbon group”), —NH 2 , —NHR, —NRR ′, —NRR ′ Anion exchange groups such as R ″ + , —NH 3 + and the like (R, R ′ and R ″ each independently represents an alkyl group, a cycloalkyl group or an aryl group) and the like can be mentioned.
[Wherein, X 61 and X 62 each independently represent —O—, —S— or —NR—, and Z 61 represents —CO—, —C (S) —, —C (NR 63 ) —, It represents an alkylene group which may have a substituent or an arylene group which may have a substituent. Further, R 63 in the above NR 63 represents a hydrogen atom, 1 to 6 carbon atoms which may have a substituent alkyl or optionally substituted aryl group having 6 to 10 carbon atoms . a represents the number of repetitions, and a represents an integer of 0 to 10. The a Z 61 may be the same or different. )
なかでも、イオン交換基としては、陽イオン交換基が好ましく、−SO3H、−PO(OH)2、−POH(OH)、−SO2NHSO2−又はオキソカーボン基がより好ましく、−SO3H、−PO(OH)2又はオキソカーボン基が更に好ましく、−SO3Hが特に好ましい。 Among them, the ion exchange group is preferably a cation exchange group, more preferably —SO 3 H, —PO (OH) 2 , —POH (OH), —SO 2 NHSO 2 — or an oxocarbon group. 3 H, —PO (OH) 2 or an oxocarbon group is more preferable, and —SO 3 H is particularly preferable.
第1の高分子化合物において、イオン交換基は、当該高分子化合物を構成している繰り返し単位1個あたり平均して0.5個以上含まれていることが好ましく、0.8個以上含まれていることがより好ましく、1.0個以上含まれていることが更に好ましい。イオン交換基の含有量が、繰り返し単位1個当たり0.5個未満であると、第1の高分子化合物からなるセグメント中のイオン交換基の量が不十分となり、ブロック共重合体のプロトン伝導性が不十分となる傾向にある。 In the first polymer compound, the ion exchange group is preferably contained in an average of 0.5 or more per repeating unit constituting the polymer compound, and is contained in 0.8 or more. It is more preferable that 1.0 or more are included. When the content of ion exchange groups is less than 0.5 per repeating unit, the amount of ion exchange groups in the segment comprising the first polymer compound becomes insufficient, and the proton conductivity of the block copolymer. Tend to be insufficient.
第1の高分子化合物としては、芳香族高分子化合物が好ましく、例えば、ポリフェニレン、ポリフェニレンエーテル、ポリフェニレンスルフィド、ポリエーテルケトン、ポリエーテルスルホン又はこれらを構成する繰り返し単位の共重合体であって、これらの繰り返し単位中に上記の条件を満たすようにイオン交換基が導入された化合物が挙げられる。第1の高分子化合物である芳香族高分子化合物において、イオン交換基の結合位置は特に限定されないが、合成の容易さ等の観点から、繰り返し単位中の芳香環(特にベンゼン環)に結合していると好ましい。 The first polymer compound is preferably an aromatic polymer compound, such as polyphenylene, polyphenylene ether, polyphenylene sulfide, polyether ketone, polyether sulfone, or a copolymer of repeating units constituting them, In the repeating unit, a compound in which an ion exchange group is introduced so as to satisfy the above-mentioned condition can be mentioned. In the aromatic polymer compound as the first polymer compound, the bonding position of the ion exchange group is not particularly limited, but it is bonded to the aromatic ring (particularly the benzene ring) in the repeating unit from the viewpoint of ease of synthesis and the like. It is preferable.
より具体的には、第1の高分子化合物としては、下記一般式(7)で表される構造を有し、且つ、繰り返し単位の少なくとも一部に、上述したようなイオン交換基が導入された化合物が挙げられる。
[式中、Ar71は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X71は、直接結合、酸素原子、硫黄原子、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、dは5以上の整数である。]
More specifically, the first polymer compound has a structure represented by the following general formula (7), and an ion exchange group as described above is introduced into at least a part of the repeating unit. Compounds.
[In the formula, Ar 71 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. A divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group, X 71 represents a direct bond, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and d is an integer of 5 or more. ]
かかる第1の高分子化合物は、その分子量が、2000以上であると好ましく、4000以上であるとより好ましく、6000以上であると更に好ましく、8000以上であると一層好ましく、10000以上であると特に好ましい。第1の高分子化合物の分子量が2000以上であると、得られるブロック共重合体を含む高分子電解質のプロトン伝導性が良好となる。なお、かかる分子量の値は、例えば、ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー(GPC)による分析によって求めることができる。 The molecular weight of the first polymer compound is preferably 2000 or more, more preferably 4000 or more, still more preferably 6000 or more, still more preferably 8000 or more, and particularly preferably 10,000 or more. preferable. When the molecular weight of the first polymer compound is 2000 or more, the proton conductivity of the polymer electrolyte containing the resulting block copolymer is good. In addition, the value of this molecular weight can be calculated | required by the analysis by a gel permeation chromatography (GPC), for example.
第1の高分子化合物の分子量は、例えば、重縮合により第1の高分子化合物を合成する場合(例えば、ジハロゲノモノマーとジオールモノマーとの重縮合)には、これらのモノマーの物質量の比率を調整することで制御することができ、また、連鎖重合により合成する場合には、開始剤とモノマーとの物質量の比率を調整することによって制御することができる。 For example, when the first polymer compound is synthesized by polycondensation (for example, polycondensation of a dihalogeno monomer and a diol monomer), the molecular weight of the first polymer compound is a ratio of the substance amounts of these monomers. It is possible to control by adjusting the ratio, and when synthesizing by chain polymerization, it can be controlled by adjusting the ratio of the amount of the initiator to the monomer.
このような第1の高分子化合物としては、具体的には、下記一般式(1a)、(1b)又は(1c)で表される構造を有し、且つ、かかる構造中にイオン交換基を有する化合物が挙げられる。
[式中、Ar11〜Ar17は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X11〜X15は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、Y11及びY12は、それぞれ独立に、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、p、q及びrは、それぞれ独立に、5以上の整数である。]
Specifically, such a first polymer compound has a structure represented by the following general formula (1a), (1b) or (1c), and an ion exchange group is present in the structure. The compound which has is mentioned.
[In the formula, Ar 11 to Ar 17 are each independently an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or an aryloxy having 6 to 20 carbon atoms. A divalent aromatic group optionally having a C 2-20 acyl group, X 11 to X 15 each independently represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and Y 11 and Y 12 Each independently represents a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and p, q, and r are each independently an integer of 5 or more. ]
上記式(1a)、(1b)、(1c)中、p、q及びrは、それぞれ独立に5〜250の整数であると好ましく、10〜200の整数であるとより好ましく、15〜150の整数であると更に好ましい。また、これらの構造を有する第1の高分子化合物の末端構造は、当該化合物を合成する際に用いる原料モノマーに依存し、例えば、ヒドロキシ基等が挙げられる。なお、上記式(1a)、(1b)及び(1c)で表される構造において、Ar11〜Ar17、X11〜X15、Y11〜Y12で表される基は、それぞれ繰り返し単位ごとに同じ基であってもよく、異なっていてもよい。但し、合成の容易さ等の観点からは、これらは繰り返し単位ごとに同じであることが好ましい。 In the above formulas (1a), (1b) and (1c), p, q and r are each independently preferably an integer of 5 to 250, more preferably an integer of 10 to 200, and 15 to 150. More preferably, it is an integer. Further, the terminal structure of the first polymer compound having these structures depends on the raw material monomer used when the compound is synthesized, and examples thereof include a hydroxy group. In the structures represented by the above formulas (1a), (1b), and (1c), groups represented by Ar 11 to Ar 17 , X 11 to X 15 , and Y 11 to Y 12 are each a repeating unit. The same group may be different from each other. However, from the viewpoint of ease of synthesis, etc., these are preferably the same for each repeating unit.
上記式(1a)、(1b)及び(1c)において、Ar11〜Ar17で表される基としては、例えば、1,3−フェニレン、1,4−フェニレン等の2価の単環性炭化水素芳香族基、1,3−ナフタレンジイル、1,4−ナフタレンジイル、1,5−ナフタレンジイル、1,6−ナフタレンジイル、1,7−ナフタレンジイル、2,6−ナフタレンジイル、2,7−ナフタレンジイル等の2価の縮合系炭化水素芳香族基、3,3’−ビフェニリレン、3,4’−ビフェニリレン、4,4’−ビフェニリレン、ジフェニルメタン−4’,4’−ジイル、2,2−ジフェニルプロパン−4’,4’’−ジイル、1,1,1,3,3,3−ヘキサフルオロ−2,2−ジフェニルプロパン−4’,4’’−ジイル等の2価の多環系炭化水素系芳香族基、ピリジンジイル、キノキサリンジイル、チオフェンジイル等のヘテロ環系芳香族基等が挙げられる。なかでも、2価の炭化水素系芳香族基が好ましい。 In the above formulas (1a), (1b) and (1c), examples of the group represented by Ar 11 to Ar 17 include bivalent monocyclic carbonization such as 1,3-phenylene and 1,4-phenylene. Hydrogen aromatic group, 1,3-naphthalenediyl, 1,4-naphthalenediyl, 1,5-naphthalenediyl, 1,6-naphthalenediyl, 1,7-naphthalenediyl, 2,6-naphthalenediyl, 2,7 -Divalent condensed hydrocarbon aromatic groups such as naphthalenediyl, 3,3'-biphenylylene, 3,4'-biphenylylene, 4,4'-biphenylylene, diphenylmethane-4 ', 4'-diyl, 2,2 -Divalent polycyclic rings such as diphenylpropane-4 ′, 4 ″ -diyl, 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2,2-diphenylpropane-4 ′, 4 ″ -diyl Hydrocarbon aromatic group, pyridine Yl, quinoxalinediyl, heterocyclic aromatic groups such as thiophenediyl. Of these, divalent hydrocarbon aromatic groups are preferred.
また、これらの基は、上述の如く、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基で置換されていてもよい。ここで、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基としては、例えば、メチル基、エチル基、n−プロピル基、イソプロピル基、アリル基、n−ブチル基、sec−ブチル基、tert−ブチル基、イソブチル基、n−ペンチル基、2,2−ジメチルプロピル基、シクロペンチル基、n−ヘキシル基、シクロヘキシル基、2−メチルペンチル基、2−エチルヘキシル基等の炭素数1〜20のアルキル基や、これらのアルキル基にフッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子等のハロゲン原子や、ヒドロキシル基、ニトリル基、アミノ基、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、イソプロピルオキシ基、フェニル基、フェノキシ基等が置換し、かかる置換基を含み全炭素数が1〜20であるアルキル基等が挙げられる。 Moreover, as above-mentioned, these groups are a C1-C20 alkyl group, a C1-C20 alkoxy group, a C6-C20 aryl group, a C6-C20 aryloxy group, or carbon number. It may be substituted with 2 to 20 acyl groups. Here, examples of the alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms include a methyl group, an ethyl group, an n-propyl group, an isopropyl group, an allyl group, an n-butyl group, a sec-butyl group, a tert-butyl group, and an isobutyl group. Alkyl groups having 1 to 20 carbon atoms such as n-pentyl group, 2,2-dimethylpropyl group, cyclopentyl group, n-hexyl group, cyclohexyl group, 2-methylpentyl group, 2-ethylhexyl group, and the like. Substituents are substituted with halogen atoms such as fluorine atom, chlorine atom, bromine atom, hydroxyl group, nitrile group, amino group, methoxy group, ethoxy group, isopropyloxy group, phenyl group, phenoxy group, etc. Examples include alkyl groups having 1 to 20 carbon atoms.
炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基としては、例えばメトキシ基、エトキシ基、n−プロピルオキシ基、イソプロピルオキシ基、n−ブチルオキシ基、sec−ブチルオキシ基、tert−ブチルオキシ基、イソブチルオキシ基、n−ペンチルオキシ基、2,2−ジメチルプロピルオキシ基、シクロペンチルオキシ基、n−ヘキシルオキシ基、シクロヘキシルオキシ基、2−メチルペンチルオキシ基、2−エチルヘキシルオキシ基等の炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基や、これらのアルコキシ基にフッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子等のハロゲン原子や、ヒドロキシル基、ニトリル基、アミノ基、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、イソプロピルオキシ基、フェニル基、フェノキシ基等が置換し、この置換基を含み全炭素数が1〜20であるアルコキシ基等が挙げられる。 Examples of the alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms include methoxy group, ethoxy group, n-propyloxy group, isopropyloxy group, n-butyloxy group, sec-butyloxy group, tert-butyloxy group, isobutyloxy group, and n-pentyl. An alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms such as oxy group, 2,2-dimethylpropyloxy group, cyclopentyloxy group, n-hexyloxy group, cyclohexyloxy group, 2-methylpentyloxy group, 2-ethylhexyloxy group, These alkoxy groups are substituted with halogen atoms such as fluorine atom, chlorine atom, bromine atom, hydroxyl group, nitrile group, amino group, methoxy group, ethoxy group, isopropyloxy group, phenyl group, phenoxy group, etc. An alkoxy group containing 1 to 20 carbon atoms It is below.
炭素数6〜20のアリール基としては、例えば、フェニル基、ナフチル基等の炭素数6〜20のアリール基や、これらのアリール基にフッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子等のハロゲン原子や、ヒドロキシル基、ニトリル基、アミノ基、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、イソプロピルオキシ基、フェニル基、フェノキシ基等が置換し、この置換基を含み全炭素数が1〜20であるアリール基等が挙げられる。 Examples of the aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms include an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms such as a phenyl group and a naphthyl group, a halogen atom such as a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom and a bromine atom, and a hydroxyl group. A group, a nitrile group, an amino group, a methoxy group, an ethoxy group, an isopropyloxy group, a phenyl group, a phenoxy group, and the like, and an aryl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms including the substituent.
また、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基としては、例えば、フェノキシ基、ナフチルオキシ基等の炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基や、これらのアリールオキシ基にフッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子等のハロゲン原子や、ヒドロキシル基、ニトリル基、アミノ基、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、イソプロピルオキシ基、フェニル基、フェノキシ基等が置換し、この置換基を含み全炭素数が6〜20であるアリールオキシ基等が挙げられる。 Moreover, as an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, for example, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms such as a phenoxy group and a naphthyloxy group, a fluorine atom, a chlorine atom, a bromine atom, etc. Substituted with a halogen atom, a hydroxyl group, a nitrile group, an amino group, a methoxy group, an ethoxy group, an isopropyloxy group, a phenyl group, a phenoxy group, etc. Groups and the like.
さらに、炭素数2〜20のアシル基としては、例えば、アセチル基、プロピオニル基、ブチリル基、イソブチリル基、ベンゾイル基、1−ナフトイル基、2−ナフトイル基等の炭素数2〜20のアシル基や、これらの基にフッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子等のハロゲン原子、ヒドロキシル基、ニトリル基、アミノ基、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、イソプロピルオキシ基、フェニル基、ナフチル基、フェノキシ基、ナフチルオキシ基等が置換し、この置換基を含み全炭素数が2〜20であるアシル基等が挙げられる。 Furthermore, examples of the acyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms include an acyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms such as an acetyl group, a propionyl group, a butyryl group, an isobutyryl group, a benzoyl group, a 1-naphthoyl group, and a 2-naphthoyl group. In these groups, fluorine atoms, chlorine atoms, halogen atoms such as bromine atoms, hydroxyl groups, nitrile groups, amino groups, methoxy groups, ethoxy groups, isopropyloxy groups, phenyl groups, naphthyl groups, phenoxy groups, naphthyloxy groups, etc. And an acyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms in total including this substituent.
このような第1の高分子化合物としては、例えば、下記に示すような構造を有する化合物が挙げられる。すなわち、上記一般式(1a)で表される構造としては、例えば、下記式8−1〜8−7で表される構造が好ましい。なお、下記式中、nは好ましくは10以上の整数であり、より好ましくは10〜250の整数であり、更に好ましくは15〜150の整数である。n’は好ましくは5以上の整数であり、より好ましくは5〜250の整数であり、更に好ましくは10〜200の整数であり、特に好ましくは15〜150の整数である。また、式中、イオン交換基としてはスルホン酸基を例示したが、スルホン酸基以外のイオン交換基であってもよい。
また、上記一般式(1b)で表される構造としては、下記式9−1〜9−15で表される構造が好ましい。式中のn’は上記と同義である。なお、式中、イオン交換基としてはスルホン酸基を示したが、スルホン酸基以外のイオン交換基であってもよい。
Moreover, as a structure represented by the said general formula (1b), the structure represented by following formula 9-1 to 9-15 is preferable. N 'in a formula is synonymous with the above. In the formula, a sulfonic acid group is shown as the ion exchange group, but an ion exchange group other than the sulfonic acid group may be used.
上述したなかでも、上記一般式(1b)で表される構造としては、下記一般式(2)で表される構造が好ましい。かかる構造は、上述した9−1〜4、9−13及び9−14で表される構造を包含する。
[式中、Y21は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、s及びtは、それぞれ独立に0又は1であって少なくともいずれか一方は1であり、uは0、1又は2であり、vは1又は2であり、wは5以上の整数である。]
Among the structures described above, the structure represented by the general formula (1b) is preferably a structure represented by the following general formula (2). Such a structure includes the structures represented by 9-1 to 4, 9-13, and 9-14.
[Wherein Y 21 represents a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, s and t are each independently 0 or 1, at least one is 1, u is 0, 1 or 2; Is 1 or 2, and w is an integer of 5 or more. ]
さらに、上記一般式(1c)で表される構造としては、下記式10−1〜10−10で表される構造が挙げられる。式中のn及びn’は上記と同義である。なお、式中、イオン交換基としてはスルホン酸基を示したが、スルホン酸基以外のイオン交換基であってもよい。
さらにまた、第1の高分子化合物としては、下記一般式(17)で表される構造を有するものも好適である。
[式中、X171は、直接結合又は有機基であり、fは1からX171における置換可能な部位の数までの整数であり、gは1又は2であり、lは5以上の整数である。gが2である場合、2つのX171、f及びgは、それぞれ同一であっても、異なっていてもよい。]
Furthermore, as the first polymer compound, those having a structure represented by the following general formula (17) are also suitable.
[ Wherein X 171 is a direct bond or an organic group, f is an integer from 1 to the number of substitutable sites in X 171 , g is 1 or 2, and l is an integer of 5 or more. is there. When g is 2, two X 171 , f and g may be the same or different. ]
X171で表される基が有機基である場合、X171は、f個のスルホン酸基が結合した有機基であり、スルホン酸基以外の置換基を更に有していてもよい。かかる有機基としては、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数1〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基が挙げられる。これらの有機基に置換していてもよい基としては、フッ素原子、塩素原子、臭素原子等のハロゲン原子や、ヒドロキシル基、ニトリル基、アミノ基、メトキシ基、エトキシ基、イソプロピルオキシ基、フェニル基、フェノキシ基等が例示できる。なお、上記式中、gが2である場合、2つのX171は、それぞれ同じでも異なっていてもよい。 When the group represented by X 171 is an organic group, X 171 is an organic group to which f sulfonic acid groups are bonded, and may further have a substituent other than the sulfonic acid group. Examples of the organic group include an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, and an acyl having 2 to 20 carbon atoms. Groups. Examples of the group that may be substituted with these organic groups include halogen atoms such as fluorine atom, chlorine atom, bromine atom, hydroxyl group, nitrile group, amino group, methoxy group, ethoxy group, isopropyloxy group, and phenyl group. And a phenoxy group. In the above formula, when g is 2, two X 171s may be the same or different.
X171で表される有機基としては芳香環を一つ以上含む基が好ましい。この場合、式(17)においてX171に結合しているスルホン酸基は、X171に含まれる芳香環に直接又は所定の基を介して結合していることが好ましく、X171が芳香環を複数有している場合にはこれらのうちの複数の芳香環に結合していてもよい。芳香環としては、ベンゼン環や縮合環(ナフタレン環等)が挙げられる。 The organic group represented by X 171 is preferably a group containing one or more aromatic rings. In this case, the sulfonic acid group bonded to X 171 in formula (17) is preferably bonded directly to the aromatic ring contained in X 171 or via a predetermined group, and X 171 has an aromatic ring. When there are a plurality of them, they may be bonded to a plurality of these aromatic rings. Examples of the aromatic ring include a benzene ring and a condensed ring (such as a naphthalene ring).
X171で表される基が芳香環を含む有機基である場合、上記一般式(17)で表される構造は、下記一般式(18a)で表されるような構造であると好ましい。
[式中、X181及びX182はそれぞれ独立に直接結合、酸素原子又はカルボニル基であり、Ar181及びAr182はそれぞれ独立に芳香環であり、Qは、スルホン酸基を含む基であり、eは0〜3の整数であり、y及びy’はそれぞれ独立に0〜3の整数であってそれらの合計が1以上となる数である。なお、l及びgは上記と同義である。ただし、eが2以上である場合、複数のX181及びAr181は、それぞれ同じであっても異なっていてもよい。
When the group represented by X 171 is an organic group containing an aromatic ring, the structure represented by the general formula (17) is preferably a structure represented by the following general formula (18a).
Wherein X 181 and X 182 are each independently a direct bond, an oxygen atom or a carbonyl group, Ar 181 and Ar 182 are each independently an aromatic ring, and Q is a group containing a sulfonic acid group, e is an integer of 0 to 3, and y and y ′ are each independently an integer of 0 to 3, and the sum thereof is 1 or more. Here, l and g are as defined above. However, when e is 2 or more, the plurality of X 181 and Ar 181 may be the same or different.
また、上記一般式(17)で表される高分子化合物としては、一般式(17)におけるX171が直接結合である構造を有するものも好ましい。このような構造は、具体的には、下記一般式(18b)で表される。
[式中、lは上記と同義である。]
Moreover, as a high molecular compound represented by the said General formula (17), what has a structure where X171 in General formula (17) is a direct bond is preferable. Such a structure is specifically represented by the following general formula (18b).
[Wherein l is as defined above. ]
また、上記一般式(18a)におけるスルホン酸基を含む基であるQとしては、具体的には、下記(19a)〜(19f)で表される基を挙げることができる。
式(19e)及び(19f)中、X19は酸素原子、硫黄原子、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基であり、b及びb´はそれぞれ独立に0〜12の整数である。]
Specific examples of Q that is a group containing a sulfonic acid group in the general formula (18a) include groups represented by the following (19a) to (19f).
In the formulas (19e) and (19f), X 19 is an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and b and b ′ are each independently an integer of 0 to 12. ]
上記一般式(17)で表される構造を有する化合物を構成する構造単位としては、具体的には、下記式20−1〜20−11で表される化合物が挙げられる。下記式中、Q、y及びy’は上記と同義であり、y及びy’はそれぞれ1〜3であると好適である。y’’は0〜2の整数である。
第1の高分子化合物を構成する上記構造のなかでも、上記一般式(2)で表される構造が好ましく、その中でも、上記式9−1、9−2、9−13又は9−14で表される構造がより好ましく、上記式9−13又は9−14で表される構造が更に好ましく、上記式9−13で表される構造が特に好ましい。 Among the above structures constituting the first polymer compound, the structure represented by the general formula (2) is preferable, and among them, the above formulas 9-1, 9-2, 9-13, or 9-14 The structure represented is more preferable, the structure represented by the formula 9-13 or 9-14 is more preferable, and the structure represented by the formula 9-13 is particularly preferable.
(第2の高分子化合物)
次に、第2の高分子化合物について説明する。第2の高分子化合物は、イオン交換基を実質的に含有しない高分子化合物である。ここで、「イオン交換基を実質的に含有しない」とは、第2の高分子化合物を主として構成する繰り返し単位の殆どがイオン交換基を有していないことを意味し、具体的には、イオン交換基が、当該高分子化合物を構成している繰り返し単位1個あたり平均して0.1個以下であり、0.05個以下であると好ましく、繰り返し単位中にイオン交換基を有していないことが更に好ましい。
(Second polymer compound)
Next, the second polymer compound will be described. The second polymer compound is a polymer compound that does not substantially contain an ion exchange group. Here, “substantially free of ion exchange groups” means that most of the repeating units mainly constituting the second polymer compound have no ion exchange groups, specifically, The average number of ion-exchange groups per repeating unit constituting the polymer compound is 0.1 or less, preferably 0.05 or less, and has an ion-exchange group in the repeating unit. More preferably not.
第2の高分子化合物としては、芳香族高分子化合物が好ましく、例えば、ポリフェニレン、ポリフェニレンエーテル、ポリフェニレンスルフィド、ポリエーテルケトン、ポリエーテルスルホン又はこれらを構成する繰り返し単位の共重合体であって、イオン交換基を実質的に含有しない化合物が挙げられる。 The second polymer compound is preferably an aromatic polymer compound, such as polyphenylene, polyphenylene ether, polyphenylene sulfide, polyether ketone, polyether sulfone, or a copolymer of repeating units constituting these, The compound which does not contain an exchange group substantially is mentioned.
かかる第2の高分子化合物は、その分子量が、2000以上であると好ましく、4000以上であるとより好ましく、6000以上であると更に好ましく、8000以上であると一層好ましく、10000以上であると特に好ましい。第2の高分子化合物の分子量が2000以上であると、得られるブロック共重合体を含む高分子電解質のプロトン伝導性が良好となる。なお、かかる分子量の値は、上記第1の高分子化合物と同様にして求めることができる。 The molecular weight of the second polymer compound is preferably 2000 or more, more preferably 4000 or more, further preferably 6000 or more, still more preferably 8000 or more, and particularly preferably 10,000 or more. preferable. When the molecular weight of the second polymer compound is 2000 or more, the proton conductivity of the polymer electrolyte containing the resulting block copolymer is good. The molecular weight value can be determined in the same manner as in the first polymer compound.
より具体的には、第2の高分子化合物としては、下記一般式(3)で表される構造を有する化合物が挙げられる。なお、第2の高分子化合物は、上述の如くイオン交換基を実質的に有しないものであり、上記の定義を満たす範囲であれば、下記式(3)の構造中、イオン交換基を一部に有していても構わない。これは、以下に例示する各種の第2の高分子化合物においても同様である。
[式中、Ar31は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X31は、直接結合、酸素原子、硫黄原子、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、zは5以上の整数である。]
More specifically, examples of the second polymer compound include compounds having a structure represented by the following general formula (3). The second polymer compound does not substantially have an ion exchange group as described above. If the second polymer compound satisfies the above definition, one ion exchange group is not included in the structure of the following formula (3). You may have in a part. The same applies to the various second polymer compounds exemplified below.
[In the formula, Ar 31 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. And X 31 represents a direct bond, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and z is an integer of 5 or more. ]
このような第2の高分子化合物としては、下記一般式(4)で表される構造を有する化合物が好適である。
[式中、Ar41、Ar42及びAr43は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X41及びX42は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、Z41は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、hは5以上の整数である。]
As such a second polymer compound, a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (4) is suitable.
[Wherein, Ar 41 , Ar 42 and Ar 43 each independently represent an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 6 to 20 carbon atoms. An aryloxy group or a divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms, X 41 and X 42 each independently represent an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and Z 41 Represents a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and h is an integer of 5 or more. ]
上記一般式(4)で表される化合物において、Ar41〜Ar43で表される基としては、上記Ar11〜Ar17で表される基と同様のものが挙げられ、なかでも、フェニレン基が好ましい。また、X41及びX42としては、オキシ基(−O−)が好ましい。さらに、hは、10〜500の整数であると好ましい。なお、上記式(4)で表される構造において、Ar41〜Ar43、X41及びX42又はZ41で表される基は、繰り返し単位ごとに異なっていてもよく、同じであってもよい。 In the compound represented by the general formula (4), examples of the group represented by Ar 41 to Ar 43 include the same groups as the groups represented by Ar 11 to Ar 17 , and among them, a phenylene group Is preferred. X 41 and X 42 are preferably an oxy group (—O—). Furthermore, h is preferably an integer of 10 to 500. In the structure represented by the above formula (4), the groups represented by Ar 41 to Ar 43 , X 41 and X 42 or Z 41 may be different for each repeating unit or may be the same. Good.
第2の高分子化合物を構成する上記構造としては、特に、下記一般式(5)で表される構造が好ましい。
[式中、Ar51は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X51及びX52は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、R51及びR52は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を示し、Z51は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、j及びkは、それぞれ独立に、0〜4の整数であり、iは、5以上の整数である。]
As the structure constituting the second polymer compound, a structure represented by the following general formula (5) is particularly preferable.
[In the formula, Ar 51 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. A divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group, X 51 and X 52 each independently represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and R 51 and R 52 each independently represent a carbon atom. C 1 -
式中、Ar51、X51、X52及びZ51としては、それぞれ上記Ar43、X41、X42及びZ41と同様の基が好ましく、なかでも、Ar51としては、フェニレン基又はビフェニレン基が好ましい。また、iは、5〜500の整数であると好ましい。さらに、R51又はR52としては、上述したAr11〜Ar17に置換していてもよい基等の官能基が挙げられる。また、上記j及びkは0であることが特に好ましい。 In the formula, each of Ar 51 , X 51 , X 52 and Z 51 is preferably the same group as Ar 43 , X 41 , X 42 and Z 41, and Ar 51 is preferably a phenylene group or a biphenylene group. Is preferred. Moreover, i is preferably an integer of 5 to 500. Furthermore, as R 51 or R 52 , a functional group such as a group that may be substituted with Ar 11 to Ar 17 described above may be mentioned. The j and k are particularly preferably 0.
このような第2の高分子化合物としては、例えば、Z41(Z51)がカルボニル基(−CO−)である場合、置換基を有していてもよいポリエーテルエーテルケトンが挙げられ、Z41(Z51)がスルホニル基(−SO2−)である場合、置換基を有していてもよいポリエーテルエーテルスルホンが挙げられ、両方を含む場合、置換基を有していてもよいポリエーテルエーテルケトンエーテルエーテルスルホン等が挙げられる。 Examples of such second polymer compound include polyether ether ketone which may have a substituent when Z 41 (Z 51 ) is a carbonyl group (—CO—), and Z When 41 (Z 51 ) is a sulfonyl group (—SO 2 —), examples thereof include polyether ether sulfone which may have a substituent. When both are included, poly which may have a substituent Examples include ether ether ketone ether ether sulfone.
より具体的には、第2の高分子化合物としては、例えば、下記式11−1〜11−18で表される構造を有するものが好ましい。下記式中、mは上記h又はiと同義である。
なかでも、第2の高分子化合物を構成する構造としては、上記式11−1〜10及び11−15〜18で表される構造のうちの少なくとも1種が好ましく、上記式11−1、3、11−5〜7及び11−15〜18で表される構造のうちの少なくとも1種がより好ましく、上記式11−1又は11−15で表される構造が更に好ましく、上記式11−15で表される構造が特に好ましい。 Especially, as a structure which comprises a 2nd high molecular compound, at least 1 sort (s) of the structure represented by said Formula 11-1-10 and 11-15-18 is preferable, and said Formula 11-1, 3 is preferable. , 11-5 to 7 and 11-15 to 18 are more preferable, and a structure represented by Formula 11-1 or 11-15 is more preferable, and Formula 11-15 is used. The structure represented by is particularly preferable.
(混合溶媒)
次に、混合溶媒について説明する。混合溶媒は、上記の如く、2種以上の溶媒を混合した溶媒であり、例えば、比誘電率が異なる2種以上の溶媒の組み合わせが挙げられる。なかでも、混合溶媒としては、第1の高分子化合物の良溶媒(以下、「第1の良溶媒」という)及び第2の高分子化合物の良溶媒(以下、「第2の良溶媒」という)のうち少なくとも1種を含むものが好ましく、これらの両方を含むものがより好ましい。なお、第1の高分子化合物又は第2の高分子化合物を複数種類用いる場合は、第1及び第2の良溶媒として複数種類を組み合わせて用いてもよい。
(Mixed solvent)
Next, the mixed solvent will be described. As described above, the mixed solvent is a solvent in which two or more solvents are mixed, and examples thereof include a combination of two or more solvents having different relative dielectric constants. In particular, the mixed solvent includes a good solvent for the first polymer compound (hereinafter referred to as “first good solvent”) and a good solvent for the second polymer compound (hereinafter referred to as “second good solvent”). ) Including at least one type is preferable, and including both of these is more preferable. When a plurality of types of the first polymer compound or the second polymer compound are used, a plurality of types may be used in combination as the first and second good solvents.
例えば、混合溶媒中に第1の良溶媒が含まれている場合、かかる良溶媒の含有量は、混合溶媒中、10質量%以上であると好ましく、20質量%以上であるとより好ましく、30質量%以上であると更に好ましく40質量%以上であると特に好ましい。また、第2の良溶媒が含まれている場合、かかる良溶媒の含有量は、混合溶媒中、10質量%以上であると好ましく、20質量%以上であるとより好ましく、30質量%以上であると更に好ましく40質量%以上であると特に好ましい。そして、これらの両方を含む場合も、両方の溶媒が上記条件を満たしていると更に好ましい。混合溶媒中の第1又は第2の良溶媒の含有量が10質量%未満であると、いずれかの高分子化合物が混合溶媒中に溶解され難くなり、ブロック共重合中に析出して良好にブロック共重合体が得られ難くなる傾向にある。 For example, when the first good solvent is contained in the mixed solvent, the content of the good solvent is preferably 10% by mass or more, more preferably 20% by mass or more in the mixed solvent, 30 More preferably, it is more preferably 40% by mass or more. When the second good solvent is contained, the content of the good solvent in the mixed solvent is preferably 10% by mass or more, more preferably 20% by mass or more, and 30% by mass or more. More preferably, it is more preferably 40% by mass or more. Even in the case where both of these are included, it is more preferable that both of the solvents satisfy the above conditions. When the content of the first or second good solvent in the mixed solvent is less than 10% by mass, any of the polymer compounds is hardly dissolved in the mixed solvent, and precipitates during block copolymerization. It tends to be difficult to obtain a block copolymer.
また、ブロック共重合の際の混合溶媒中の第1及び第2の高分子化合物の濃度、すなわち、100×[{第1の高分子化合物の重量(g)}+{第2の高分子化合物の重量(g)}]/[ブロック共重合溶液の重量(g)]の値は、1〜50質量%とすることが好ましく、3〜40質量%とすることがより好ましく、5〜30質量%とすることが更に好ましく、7〜20質量%とすることが特に好ましい。こうすれば、ブロック共重合中も第1及び第2の高分子化合物が混合溶媒に十分に溶解され、良好にブロック共重合が進行するようになる。 The concentration of the first and second polymer compounds in the mixed solvent during block copolymerization, that is, 100 × [{weight of the first polymer compound (g)} + {second polymer compound The weight (g)}] / [weight (g) of block copolymer solution] is preferably 1 to 50% by mass, more preferably 3 to 40% by mass, and 5 to 30% by mass. % Is more preferable, and 7 to 20% by mass is particularly preferable. By doing so, the first and second polymer compounds are sufficiently dissolved in the mixed solvent even during the block copolymerization, and the block copolymer proceeds well.
また、第1の良溶媒としては、比誘電率が好ましくは40.0以上である溶媒が挙げられる。また、第2の良溶媒としては、比誘電率が好ましくは40.0未満である溶媒が挙げられる。なお、第1及び第2の高分子化合物の両方を良好に溶解するためには、両者の比誘電率の差は、5.0以上であると好ましい。この比誘電率の値を満たす第1及び第2の良溶媒を組み合わせた混合溶媒によれば、第1及び第2の高分子化合物が十分に溶解され、これらのブロック共重合が良好に進行するようになる。 The first good solvent includes a solvent having a relative dielectric constant of preferably 40.0 or more. The second good solvent includes a solvent having a relative dielectric constant of preferably less than 40.0. In order to dissolve both the first and second polymer compounds satisfactorily, the difference in relative dielectric constant between them is preferably 5.0 or more. According to the mixed solvent in which the first and second good solvents satisfying the relative dielectric constant are combined, the first and second polymer compounds are sufficiently dissolved, and the block copolymerization proceeds well. It becomes like this.
より具体的には、第1の良溶媒としては、例えば、アルコール系溶媒、エーテル系溶媒、スルホキシド系溶媒、アミド系溶媒、炭酸エステル類、オリゴアルキレングリコール類や、これらにフッ素置換基を導入してなる溶媒等が挙げられる。これらの溶媒は、第1の高分子化合物の種類、特に、当該化合物が有するイオン交換基の種類に応じて適宜用いることが好ましい。 More specifically, examples of the first good solvent include alcohol solvents, ether solvents, sulfoxide solvents, amide solvents, carbonates, oligoalkylene glycols, and fluorine substituents introduced into these solvents. And the like. These solvents are preferably used as appropriate according to the type of the first polymer compound, in particular, the type of ion exchange group possessed by the compound.
アルコール系溶媒としてはメタノール、エタノール、イソプロパノール、ブタノール等が挙げられる。エーテル系溶媒としてはジエチルエーテル、ジブチルエーテル、ジフェニルエーテル、テトラヒドロフラン(THF)、ジオキサン、ジオキソラン、エチレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、エチレングリコールモノエチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノエチルエーテル等が挙げられる。 Examples of alcohol solvents include methanol, ethanol, isopropanol, butanol and the like. Examples of ether solvents include diethyl ether, dibutyl ether, diphenyl ether, tetrahydrofuran (THF), dioxane, dioxolane, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, propylene glycol monomethyl ether, propylene glycol monoethyl ether, and the like.
スルホキシド系溶媒としてはジメチルスルホキシド(DMSO)が挙げられる。アミド系溶媒としてはN,N−ジメチルアセトアミド(DMAc)、N−メチルアセトアミド、N,N−ジメチルホルムアミド(DMF)、N−メチルホルムアミド、ホルムアミド、N−メチルピロリドン(NMP)等が挙げられる。 Examples of the sulfoxide solvent include dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Examples of the amide solvent include N, N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), N-methylacetamide, N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF), N-methylformamide, formamide, N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) and the like.
炭酸エステル類としてはプロピレンカーボネート、エチレンカーボネート、ジメチルカーボネート、ジエチルカーボネート、エチルメチルカーボネート、4−トリフルオロメチル−1,3−ジオキソラン−2−オン、1,2−ジ(メトキシカルボニルオキシ)エタン等が、エステル類としてはギ酸メチル、酢酸メチル、γ−ブチロラクトン等が、ニトリル類としてはアセトニトリル、ブチロニトリル等が、オリゴアルキレングリコール類としてはオリゴ(エチレングリコール)、オリゴ(プロピレングリコール)、オリゴ(ブチレングリコール)等が挙げられる。 Carbonic acid esters include propylene carbonate, ethylene carbonate, dimethyl carbonate, diethyl carbonate, ethyl methyl carbonate, 4-trifluoromethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one, 1,2-di (methoxycarbonyloxy) ethane and the like. Esters include methyl formate, methyl acetate, and γ-butyrolactone, nitriles include acetonitrile and butyronitrile, and oligoalkylene glycols include oligo (ethylene glycol), oligo (propylene glycol), and oligo (butylene glycol). Etc.
上述したなかでも、第1の良溶媒としては、アルコール系溶媒、スルホキシド系溶媒又はアミド系溶媒が好ましく、スルホキシド系溶媒又はアミド系溶媒がより好ましく、スルホキシド系溶媒が更に好ましく、DMSOが特に好ましい。DMSOは、第1の高分子化合物がイオン交換基としてスルホン酸基を有する場合に、当該化合物を良好に溶解し得るため特に好ましい。 Among the above, the first good solvent is preferably an alcohol solvent, a sulfoxide solvent or an amide solvent, more preferably a sulfoxide solvent or an amide solvent, still more preferably a sulfoxide solvent, and particularly preferably DMSO. DMSO is particularly preferable because the compound can be dissolved well when the first polymer compound has a sulfonic acid group as an ion exchange group.
また、第2の良溶媒としては、ケトン系溶媒、エーテル系溶媒、ハロゲン系溶媒、スルホキシド系溶媒、スルホン系溶媒、アミド系溶媒、炭酸エステル類、エステル類、ニトリル類、オリゴアルキレングリコール類や、これらにフッ素置換基を導入してなる溶媒等が挙げられる。 As the second good solvent, ketone solvents, ether solvents, halogen solvents, sulfoxide solvents, sulfone solvents, amide solvents, carbonates, esters, nitriles, oligoalkylene glycols, Examples thereof include a solvent obtained by introducing a fluorine substituent.
ケトン系溶媒としては、アセトン、メチルイソブチルケトン、メチルエチルケトン、ベンゾフェノン等が挙げられる。エーテル系溶媒としてはジエチルエーテル、ジブチルエーテル、ジフェニルエーテル、テトラヒドロフラン(THF)、ジオキサン、ジオキソラン、エチレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、エチレングリコールモノエチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノエチルエーテル等が挙げられる。 Examples of the ketone solvent include acetone, methyl isobutyl ketone, methyl ethyl ketone, and benzophenone. Examples of ether solvents include diethyl ether, dibutyl ether, diphenyl ether, tetrahydrofuran (THF), dioxane, dioxolane, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, propylene glycol monomethyl ether, propylene glycol monoethyl ether, and the like.
ハロゲン系溶媒としてはクロロホルム、ジクロロメタン、1,2−ジクロロエタン、1,1,2,2−テトラクロロエタン、クロロベンゼン、ジクロロベンゼン等が、スルホキシド系溶媒としてはDMSOが挙げられる。スルホン系溶媒としてはジフェニルスルホン、スルホラン等が、アミド系溶媒としてはDMAc、N−メチルアセトアミド、DMF、N−メチルホルムアミド、ホルムアミド、NMP等が挙げられる。 Examples of the halogen-based solvent include chloroform, dichloromethane, 1,2-dichloroethane, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane, chlorobenzene, dichlorobenzene, and the like, and examples of the sulfoxide-based solvent include DMSO. Examples of the sulfone solvent include diphenyl sulfone and sulfolane, and examples of the amide solvent include DMAc, N-methylacetamide, DMF, N-methylformamide, formamide, and NMP.
炭酸エステル類としてはプロピレンカーボネート、エチレンカーボネート、ジメチルカーボネート、ジエチルカーボネート、エチルメチルカーボネート、4−トリフルオロメチル−1,3−ジオキソラン−2−オン、1,2−ジ(メトキシカルボニルオキシ)エタン等が、エステル類としてはギ酸メチル、酢酸メチル、γ−ブチロラクトン等が、ニトリル類としてはアセトニトリル、ブチロニトリル等が、オリゴアルキレングリコール類としてはオリゴ(エチレングリコール)、オリゴ(プロピレングリコール)、オリゴ(ブチレングリコール)等が挙げられる。 Carbonic acid esters include propylene carbonate, ethylene carbonate, dimethyl carbonate, diethyl carbonate, ethyl methyl carbonate, 4-trifluoromethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one, 1,2-di (methoxycarbonyloxy) ethane and the like. Esters include methyl formate, methyl acetate, and γ-butyrolactone, nitriles include acetonitrile and butyronitrile, and oligoalkylene glycols include oligo (ethylene glycol), oligo (propylene glycol), and oligo (butylene glycol). Etc.
上述した中でも、第2の良溶媒としては、ケトン系溶媒、スルホキシド系溶媒、スルホン系溶媒又はアミド系溶媒が好ましく、スルホキシド系溶媒又はアミド系溶媒がより好ましく、アミド系溶媒が更に好ましく、NMPが特に好ましい。 Among the above-described solvents, the second good solvent is preferably a ketone solvent, a sulfoxide solvent, a sulfone solvent or an amide solvent, more preferably a sulfoxide solvent or an amide solvent, still more preferably an amide solvent, and NMP. Particularly preferred.
なお、第1の良溶媒と第2の良溶媒とは、それぞれが第1及び第2の高分子化合物に対して良溶媒である限り同種の構造を有するものであってもよいが、この場合には、同種の構造を有するもののうち、特性等の異なる溶媒を組み合わせて用いる。具体的には、アミド系溶媒は、上述したとおり、第1及び第2の高分子化合物の両方の良溶媒であるが、例えば、第1の良溶媒としてDMAcを用いる場合は、第2の良溶媒としてDMAc以外の溶媒であるDMFやNMP等を選択する。 The first good solvent and the second good solvent may have the same kind of structure as long as each is a good solvent for the first and second polymer compounds. Are used in combination with solvents having different characteristics among those having the same kind of structure. Specifically, as described above, the amide solvent is a good solvent for both the first and second polymer compounds. For example, when DMAc is used as the first good solvent, the second good solvent is used. A solvent other than DMAc, such as DMF or NMP, is selected as the solvent.
第1の良溶媒と第2の良溶媒との好適な組み合わせとしては、第1の良溶媒がスルホキシド系溶媒であり、第2の良溶媒がアミド系溶媒である組み合わせが好ましく、具体的には、第1の良溶媒がDMSOであり、第2の良溶媒がNMPである組み合わせが特に好ましい。 A preferred combination of the first good solvent and the second good solvent is preferably a combination in which the first good solvent is a sulfoxide solvent and the second good solvent is an amide solvent. A combination in which the first good solvent is DMSO and the second good solvent is NMP is particularly preferable.
なお、混合溶媒としては、上述した第1の良溶媒及び第2の良溶媒のほか、第1及び第2の高分子化合物の混合溶媒への溶解性を低下させない範囲で、その他の溶媒を更に含有していてもよい。このようなその他の溶媒としては、例えば、共沸脱水のためのベンゼン、トルエン、キシレン等の芳香族炭化水素溶媒や、クロロベンゼン、ジクロロベンゼン等のハロゲン化芳香族炭化水素溶媒等が挙げられる。 As the mixed solvent, in addition to the first good solvent and the second good solvent described above, other solvents may be further added as long as the solubility of the first and second polymer compounds in the mixed solvent is not lowered. You may contain. Examples of such other solvents include aromatic hydrocarbon solvents such as benzene, toluene, and xylene for azeotropic dehydration, and halogenated aromatic hydrocarbon solvents such as chlorobenzene and dichlorobenzene.
(ブロック共重合)
本実施形態においては、第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とからなる重合体を、上述した混合溶媒中で合成してブロック共重合体を得る。この場合、重合反応は、はじめから混合溶媒中で行ってもよく、単一の溶媒中で開始させた後、途中で他の種類の溶媒を添加するようにして行ってもよい。但し、得られるブロック共重合体の分子量分布等を均質化するためには、反応開始から混合溶媒を用いることが好ましい。
(Block copolymerization)
In the present embodiment, a block copolymer is obtained by synthesizing a polymer composed of a first polymer compound and a second polymer compound in the above-described mixed solvent. In this case, the polymerization reaction may be carried out in a mixed solvent from the beginning, or may be carried out by adding another type of solvent in the middle after starting in a single solvent. However, in order to homogenize the molecular weight distribution of the obtained block copolymer, it is preferable to use a mixed solvent from the start of the reaction.
より好適なブロック共重合の方法としては、例えば、下記(A)、(B)又は(C)の方法が挙げられる。すなわち、
(A)混合溶媒中で第1の高分子化合物及び第2の高分子化合物のうちのいずれか一方の高分子化合物を合成した後、この混合溶媒中で、得られた上記一方の高分子化合物と他の高分子化合物とをブロック共重合させてブロック共重合体を得る方法、
(B)混合溶媒中で第1の高分子化合物及び第2の高分子化合物のうちのいずれか一方の高分子化合物の合成を行うとともに、上記のうちいずれか他方の高分子化合物を共存させることで、上記一方の高分子化合物の合成を行いながら、これと上記他方の高分子化合物とのブロック共重合を同時に進行させ、ブロック共重合体を得る方法、
(C)単独の溶媒中で第1の高分子化合物を合成した反応溶液と、これとは別の単独溶媒中で第2の高分子化合物を合成した反応溶液と、を混合し、この混合した溶液中で第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とをブロック共重合させてブロック共重合体を得る方法、が挙げられる。
As a more suitable block copolymerization method, for example, the following method (A), (B) or (C) can be mentioned. That is,
(A) After synthesizing one of the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound in a mixed solvent, the one polymer compound obtained in the mixed solvent Block copolymerization of the polymer with other polymer compounds to obtain a block copolymer,
(B) Synthesizing one of the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound in a mixed solvent, and causing the other polymer compound to coexist. Then, while synthesizing the one polymer compound, the block copolymer of this and the other polymer compound is simultaneously advanced to obtain a block copolymer,
(C) A reaction solution obtained by synthesizing the first polymer compound in a single solvent and a reaction solution obtained by synthesizing the second polymer compound in another single solvent were mixed and mixed. And a method in which a block copolymer is obtained by block copolymerization of a first polymer compound and a second polymer compound in a solution.
(A)の方法において、第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とのブロック共重合は、(A−1)第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物との縮合反応や、(A−2)第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とを連結基として機能する化合物を介して結合させる方法等により生じさせることができる。 In the method (A), the block copolymerization of the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound is carried out by (A-1) a condensation reaction between the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound, (A-2) The first polymer compound and the second polymer compound can be produced by a method of bonding via a compound that functions as a linking group.
(A−1)の方法としては、例えば、以下に示すものが例示できる。すなわち、まず、末端にヒドロキシル基を有する高分子化合物及び末端にハロゲノ基を有する高分子化合物のうち、いずれか一方を第1の高分子化合物とし、他方を第2の高分子化合物として用い、これらを塩基触媒の存在下に求核置換的に縮合させる方法が挙げられる。 Examples of the method (A-1) include the following. That is, first, one of the polymer compound having a hydroxyl group at the terminal and the polymer compound having a halogeno group at the terminal is used as the first polymer compound and the other is used as the second polymer compound. And nucleophilic substitution condensation in the presence of a base catalyst.
また、第1及び第2の高分子化合物として、一方の末端にヒドロキシル基を有し、他方の末端にハロゲノ基を有する高分子化合物をそれぞれ用い、これらを塩基触媒の存在下に求核置換的に縮合させる方法も挙げられる。さらに、末端にハロゲノ基を有する化合物を第1及び第2の高分子化合物として用い、これらを脱ハロゲン縮合反応により結合させる方法も挙げられる。 Further, as the first and second polymer compounds, polymer compounds having a hydroxyl group at one end and a halogeno group at the other end are used, respectively, and these are nucleophilically substituted in the presence of a base catalyst. The method of condensing to is also mentioned. Furthermore, a method of using a compound having a halogeno group at the terminal as the first and second polymer compounds and bonding them by a dehalogenation condensation reaction is also included.
一方、(A−2)の方法としては、第1及び第2の高分子化合物として末端にヒドロキシル基を有する高分子化合物をそれぞれ用い、これらを、4,4’−ジフルオロベンゾフェノン、デカフルオロビフェニル、ヘキサフルオロベンゼン、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン等の、上記両高分子化合物と縮合反応を生じて連結基を形成し得る化合物を介して結合する方法が挙げられる。また、第1及び第2の高分子化合物として末端にハロゲノ基を有する高分子化合物をそれぞれ用い、これらを、4,4’−ジヒドロキシビフェニル、ビスフェノールA、4,4’−ジヒドロキシベンゾフェノン、4、4’−ジヒドロキシジフェニルスルホン等の、上記両高分子化合物と縮合反応を生じて連結基を形成し得る化合物を介して結合する方法も例示できる。 On the other hand, as the method (A-2), a polymer compound having a hydroxyl group at the terminal is used as each of the first and second polymer compounds, and these are used as 4,4′-difluorobenzophenone, decafluorobiphenyl, Examples thereof include a method of bonding via a compound capable of forming a linking group by causing a condensation reaction with the above-described both polymer compounds, such as hexafluorobenzene and 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone. Moreover, the polymer compound which has a halogeno group at the terminal is used as the first and second polymer compounds, respectively, and these are used as 4,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl, bisphenol A, 4,4′-dihydroxybenzophenone, 4, 4 Examples of the method include bonding with a compound capable of forming a linking group by causing a condensation reaction with the above-described both polymer compounds, such as' -dihydroxydiphenylsulfone.
(A)の方法においては、混合溶媒中で第1の高分子化合物を合成した後、これと第2の高分子化合物とを上述した方法により結合させるが、第1の高分子化合物の合成は、例えば、上記と同様の縮合反応等を生じ得るモノマー及び/又は高分子化合物を重合させる方法によって行うことができる。この場合、第1の高分子化合物中にイオン交換基を導入する方法としては、上記重合により得られた重合体にイオン交換基を付加する方法や、この重合体の形成前のモノマーや高分子化合物としてイオン交換基を有するものを用いる方法の両方が適用できる。 In the method (A), after synthesizing the first polymer compound in a mixed solvent, this and the second polymer compound are bonded together by the method described above. For example, it can be carried out by a method of polymerizing monomers and / or polymer compounds capable of causing the same condensation reaction as described above. In this case, as a method of introducing an ion exchange group into the first polymer compound, a method of adding an ion exchange group to the polymer obtained by the above polymerization, a monomer or a polymer before the formation of this polymer, Both methods using compounds having an ion exchange group can be applied.
前者の方法によって、例えば、上記一般式(1a)、(1b)又は(1c)で表される構造にスルホン酸基を導入する方法としては、上記一般式(1a)、(1b)又は(1c)で表される構造を有する化合物を濃硫酸又は発煙硫酸に溶解又はサスペンドするか、或いは、この化合物を有機溶媒に少なくとも部分的に溶解させた後、これに濃硫酸、クロロ硫酸、発煙硫酸又は三酸化硫黄等を作用させる方法が例示できる。 As a method for introducing a sulfonic acid group into the structure represented by the general formula (1a), (1b) or (1c) by the former method, for example, the general formula (1a), (1b) or (1c Or a compound having a structure represented by) is dissolved or suspended in concentrated sulfuric acid or fuming sulfuric acid, or at least partially dissolved in an organic solvent, and then concentrated sulfuric acid, chlorosulfuric acid, fuming sulfuric acid or The method of making sulfur trioxide etc. act can be illustrated.
また、(A−2)の方法のように連結基を介して第1及び第2の高分子化合物を結合させる場合には、連結基を形成すべき化合物として、3官能以上の化合物、例えば、デカフルオロビフェニル、ヘキサフルオロベンゼン等の多官能性の化合物を用いると、反応条件を適切に制御することで、分岐構造を有するブロック共重合体を合成することも可能となる。この場合、第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物との仕込み組成を変化させることで、直鎖構造のブロック共重合体と分岐構造のブロック共重合体を作り分けることもできる。 In addition, when the first and second polymer compounds are bonded via a linking group as in the method (A-2), a compound having three or more functional groups, for example, When a polyfunctional compound such as decafluorobiphenyl or hexafluorobenzene is used, a block copolymer having a branched structure can be synthesized by appropriately controlling the reaction conditions. In this case, by changing the charged composition of the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound, a linear block copolymer and a branched block copolymer can be produced separately.
一方、(B)の方法における、第1の高分子化合物及び第2の高分子化合物のうちのいずれか一方の高分子化合物の合成は、例えば、縮合可能な官能基を有するモノマーを塩基触媒の存在下で求核置換的に縮合させて、当該モノマー同士を重合させることにより行うことができる。かかる縮合としては、上記(A−1)で挙げたようなものが挙げられ、縮合可能な官能基としては、ヒドロキシル基又はハロゲノ基が例示できる。かかる重合において第1の高分子化合物を合成する場合には、モノマーとしてイオン交換基を有するものを用いることが好ましい。 On the other hand, in the method (B), the synthesis of any one of the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound is performed by, for example, using a monomer having a condensable functional group as a base catalyst. It can be carried out by condensation in the presence of nucleophilic substitution and polymerizing the monomers. Examples of such condensation include those described above in (A-1), and examples of the condensable functional group include a hydroxyl group or a halogeno group. In the case of synthesizing the first polymer compound in such polymerization, it is preferable to use a monomer having an ion exchange group.
また、この合成中に共存させる第1及び第2の高分子化合物のうちのいずれか他方の高分子化合物としては、上述したモノマーが有している縮合可能な官能基との縮合が可能な官能基(ヒドロキシル基又はハロゲノ基)を有するものが挙げられる。これにより、この高分子化合物と上記合成中のモノマーとが縮合反応により結合される。その結果、一方の高分子化合物が合成されるのと同時に、これと他方の高分子化合物とのブロック共重合が進行する。 In addition, any one of the first and second polymer compounds coexisting during the synthesis includes a functional group capable of condensing with the condensable functional group of the above-described monomer. Those having a group (hydroxyl group or halogeno group) are mentioned. As a result, the polymer compound and the monomer under synthesis are combined by a condensation reaction. As a result, simultaneously with the synthesis of one polymer compound, block copolymerization of the polymer compound with the other polymer compound proceeds.
より具体的には、(B)の方法としては、以下に示す方法が挙げられる。すなわち、まず、(B−1)末端にヒドロキシル基を有する一方の高分子化合物の共存下で、ハロゲノ基を2つ有するモノマーとヒドロキシル基を2つ有するモノマーとを、塩基触媒下で求核置換的に縮合させて、他方の高分子化合物を合成する方法が挙げられる。また、(B−2)末端にヒドロキシル基を有する一方の高分子化合物の共存下で、ハロゲノ基とヒドロキシル基の両方を有するモノマー同士を、塩基触媒下で求核置換的に縮合させて、他方の高分子化合物を合成する方法も挙げられる。 More specifically, examples of the method (B) include the following methods. That is, (B-1) nucleophilic substitution of a monomer having two halogeno groups and a monomer having two hydroxyl groups in the presence of one polymer compound having a hydroxyl group at the terminal is carried out under a base catalyst. A method of synthesizing the other polymer compound to synthesize the other polymer compound. (B-2) In the presence of one polymer compound having a hydroxyl group at the terminal, monomers having both a halogeno group and a hydroxyl group are condensed with each other in a nucleophilic substitution manner under a base catalyst, A method of synthesizing the above polymer compound is also included.
さらに、(B−3)末端にハロゲノ基を有する一方の高分子化合物の存在下で、ハロゲノ基を2つ有するモノマーとヒドロキシル基を2つ有するモノマーとを、塩基触媒下で求核置換的に縮合させて、他方の高分子化合物を合成する方法も例示できる。さらにまた、(B−4)末端にハロゲノ基を有する一方の高分子化合物の存在下で、ハロゲノ基とヒドロキシル基の両方を有するモノマー同士を、塩基触媒下で求核置換的に縮合させて、他方の高分子化合物を合成する方法も挙げられる。 Further, (B-3) in the presence of one polymer compound having a halogeno group at the terminal, a monomer having two halogeno groups and a monomer having two hydroxyl groups are nucleophilically substituted under a base catalyst. A method of synthesizing the other polymer compound by condensation is also exemplified. Furthermore, in the presence of one polymer compound having a halogeno group at the terminal (B-4), monomers having both a halogeno group and a hydroxyl group are condensed in a nucleophilic substitution manner under a base catalyst, A method of synthesizing the other polymer compound is also included.
また、(C)の方法においては、それぞれ異なる単独溶媒中で第1の高分子化合物及び第2の高分子化合物を別に合成した後、これらを混合して反応することで、混合溶媒中での第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とのブロック共重合を行うものである。かかるブロック共重合の形態としては、上記(A)の方法と同様に、(C−1)第1の高分子化合物と第1の高分子化合物との縮合反応、及び、(C−2)第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とを連結基として機能する化合物を介して結合させる方法が挙げられ、これらは、各高分子化合物の合成時に単独溶媒を用いること以外は、上記(A)の方法と同様にして実施することができる。 In the method (C), the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound are separately synthesized in different solvents, and then mixed to react with each other. Block copolymerization of the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound is performed. As the form of such block copolymerization, (C-1) the condensation reaction of the first polymer compound and the first polymer compound, and (C-2) the same as in the method (A) above, Examples include a method in which a polymer compound of 1 and a second polymer compound are bonded via a compound that functions as a linking group, except that a single solvent is used during the synthesis of each polymer compound. It can be carried out in the same manner as in the method A).
(ブロック共重合体)
上述したように、混合溶媒中で、第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とを反応させることによって、イオン交換基を有するセグメントと、イオン交換基を実質的に有しないセグメントとを有するブロック共重合体が得られる。
(Block copolymer)
As described above, by reacting the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound in a mixed solvent, a segment having an ion exchange group and a segment having substantially no ion exchange group are obtained. The block copolymer which has is obtained.
このようなブロック共重合体としては、例えば、上記一般式(1a)、(1b)又は(1c)で表される構造であって、当該構造中にイオン交換基を有する構造を有するセグメントと、上記一般式(3)で表される構造を有するセグメントとを有するものが例示できる。 As such a block copolymer, for example, a segment having the structure represented by the general formula (1a), (1b) or (1c) having a structure having an ion exchange group in the structure; What has the segment which has a structure represented by the said General formula (3) can be illustrated.
そして、このようなブロック共重合体の具体例としては、例えば、下記式12−1〜12−12で表されるものが例示できる。なお、下記式における「block」の記載は、第1の高分子化合物に由来するセグメント及び第2の高分子化合物に由来するセグメントをそれぞれ一つ以上有することを表している。すなわち、下記式で表されるブロック共重合体は、上記の両セグメントを一つずつのみ有するものには限定されない。
本実施形態により得られるブロック共重合体としては、上述したなかでも、12−2、12−8、12−9〜12−12で表される化合物が好ましく、12−9〜12−12で表される化合物がより好ましく、12−9又は12−10で表される化合物が更に好ましく、12−10で表される化合物が特に好ましい。 Among the block copolymers obtained by the present embodiment, compounds represented by 12-2, 12-8, and 12-9 to 12-12 are preferable, and represented by 12-9 to 12-12. The compound represented by 12-9 or 12-10 is more preferred, and the compound represented by 12-10 is particularly preferred.
このようなブロック共重合体におけるイオン交換基を有するセグメントと、イオン交換基を実質的に有しないセグメントとの質量組成比は、特に制限はないが、質量%を単位として、3:97〜70:30であると好ましく、5:95〜60:40であるとより好ましく、10:90〜50:50であるとさらに好ましく、20:80〜40:60であると特に好ましい。イオン交換基を有するセグメントの組成比が上記の範囲であると、得られるブロック共重合体を用いた高分子電解質膜が優れたプロトン伝導性を有し、耐水性も良好となるため好ましい。このようなブロック共重合体はとりわけ燃料電池用高分子電解質膜として好適に機能する。 The mass composition ratio between the segment having an ion exchange group and the segment having substantially no ion exchange group in such a block copolymer is not particularly limited, but is 3:97 to 70 in terms of mass%. : 30, preferably 5:95 to 60:40, more preferably 10:90 to 50:50, and particularly preferably 20:80 to 40:60. When the composition ratio of the segment having an ion exchange group is in the above range, the resulting polymer electrolyte membrane using the block copolymer is preferable because it has excellent proton conductivity and good water resistance. Such a block copolymer particularly suitably functions as a polymer electrolyte membrane for fuel cells.
また、ブロック共重合体全体としてのイオン交換基の導入量は、ブロック共重合体1g当たり0.1mmol〜4mmolであると好ましい。すなわち、ブロック共重合体のイオン交換容量は、0.1meq/g〜4.0meq/gであると好ましい。より良好なプロトン伝導性を得る観点からは、ブロック共重合体のイオン交換容量は、0.8meq/g〜3.0meq/gがより好ましく、1.3meq/g〜2.5meq/gが更に好ましい。ブロック共重合体のイオン交換容量が0.1meq/gよりも少ないと、プロトン伝導性が低くなり、燃料電池用の高分子電解質としての機能が不十分となる場合がある。一方、4meq/gよりも多いと、耐水性が低下する傾向にある。なお、このようなイオン交換基の導入量は、ブロック共重合体の製造時において、第1の高分子化合物中のイオン交換基の含有量、第1の高分子化合物の分子量(数平均分子量)、或いは、第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物との配合比等を調整することで制御することができる。 In addition, the amount of ion exchange groups introduced as a whole block copolymer is preferably 0.1 mmol to 4 mmol per 1 g of the block copolymer. That is, the ion exchange capacity of the block copolymer is preferably 0.1 meq / g to 4.0 meq / g. From the viewpoint of obtaining better proton conductivity, the ion exchange capacity of the block copolymer is more preferably 0.8 meq / g to 3.0 meq / g, and further preferably 1.3 meq / g to 2.5 meq / g. preferable. If the ion exchange capacity of the block copolymer is less than 0.1 meq / g, proton conductivity may be low, and the function as a polymer electrolyte for a fuel cell may be insufficient. On the other hand, if it exceeds 4 meq / g, the water resistance tends to decrease. The amount of such ion exchange groups introduced is the content of the ion exchange groups in the first polymer compound and the molecular weight of the first polymer compound (number average molecular weight) during the production of the block copolymer. Alternatively, it can be controlled by adjusting the blending ratio of the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound.
さらに、本実施形態で得られたブロック共重合体の分子量は、5000〜1000000であると好ましく、15000〜200000であると更に好ましい。このような分子量としては、ゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー(GPC)により測定したポリスチレン換算の数平均分子量が適用できる。 Furthermore, the molecular weight of the block copolymer obtained in the present embodiment is preferably 5000 to 1000000, and more preferably 15000 to 200000. As such molecular weight, a polystyrene-equivalent number average molecular weight measured by gel permeation chromatography (GPC) can be applied.
このなかで、イオン交換基を有するセグメントの平均分子量は、上記ポリスチレン換算の数平均分子量で、2000以上であると好ましく、4000以上であるとより好ましく、6000以上であると更に好ましく、8000以上であると一層好ましく、10000以上であると特に好ましい。なお、この上限値は100000であると好ましく、50000であるとより好ましい。また、イオン交換基を実質的に有しないセグメントの平均分子量は、上記ポリスチレン換算の数平均分子量で、2000以上であると好ましく、4000以上であるとより好ましく、6000以上であると更に好ましく、8000以上であると一層好ましく、10000以上であると特に好ましい。なお、この上限値は200000であると好ましく、100000であると更に好ましい。 Among these, the average molecular weight of the segment having an ion-exchange group is preferably 2000 or more, more preferably 4000 or more, further preferably 6000 or more, and more preferably 8000 or more in terms of the number average molecular weight in terms of polystyrene. More preferably, it is more preferably 10,000 or more. In addition, this upper limit is preferably 100,000, and more preferably 50,000. Further, the average molecular weight of the segment having substantially no ion exchange group is the above-mentioned polystyrene-equivalent number average molecular weight, preferably 2000 or more, more preferably 4000 or more, still more preferably 6000 or more, and 8000. More preferably, it is more preferably 10,000 or more. The upper limit is preferably 200,000, and more preferably 100,000.
なお、本実施形態で得られるブロック共重合体は、上述の如く、イオン交換基を有するセグメントと、イオン交換基を実質的に有しないセグメントとを有するものであるが、これらのセグメントを一つずつ有するブロック共重合体であってもよく、いずれか一方のセグメントを2つ以上有するブロック共重合体であってもよく、両方のセグメントを2つ以上有するマルチブロック共重合体のいずれであってもよい。 As described above, the block copolymer obtained in this embodiment has a segment having an ion exchange group and a segment having substantially no ion exchange group. Each of which may be a block copolymer, may be a block copolymer having two or more of any one segment, and may be any of a multi-block copolymer having two or more of both segments. Also good.
また、ブロック共重合体は、上述した2つのセグメント以外のセグメントを更に有するものであってもよく、例えば、繰り返し単位1個あたりのイオン交換基の数が、平均して0.1個よりも大きく0.5個よりも小さいセグメントを有していてもよい。このようなセグメントは、ブロック共重合の際、かかるイオン交換基の条件を満たす高分子化合物を原料として添加することで、ブロック共重合体中に導入することができる。
[燃料電池]
Further, the block copolymer may further have a segment other than the two segments described above. For example, the number of ion-exchange groups per repeating unit is more than 0.1 on average. It may have a segment larger than 0.5. Such a segment can be introduced into the block copolymer by adding, as a raw material, a polymer compound that satisfies the condition of the ion exchange group at the time of block copolymerization.
[Fuel cell]
次に、上記本発明の製造方法により得られたブロック共重合体を含む高分子電解質を用いた燃料電池について説明する。 Next, a fuel cell using a polymer electrolyte containing a block copolymer obtained by the production method of the present invention will be described.
図1は、好適な実施形態に係る燃料電池の断面構成を模式的に示す図である。図1に示すように、燃料電池10は、高分子電解質膜12(プロトン伝導膜)の両側に、これを挟むように触媒層14a,14b、ガス拡散層16a,16b及びセパレータ18a,18bが順に形成されている。高分子電解質膜12と、これを挟む一対の触媒層14a,14bとから、膜−電極接合体(以下、「MEA」と略す)20が構成されている。
FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing a cross-sectional configuration of a fuel cell according to a preferred embodiment. As shown in FIG. 1, the
高分子電解質膜12は、上記実施形態の製造方法により得られたブロック共重合体を含む高分子電解質から構成されるものである。かかる高分子電解質は、主としてプロトン伝導成分であるブロック共重合体から構成されている。
The
このような高分子電解質膜12は、高分子電解質をフィルム状に加工することで得ることができ、加工方法としては、例えば、高分子電解質を溶液状態として製膜する方法(溶液キャスト法)等が挙げられる。具体的には、高分子電解質を適当な溶媒に溶解し、得られた溶液を、ガラス板上に流延塗布した後、溶媒を除去することにより製膜することができる。
Such a
製膜に用いる溶媒は、高分子電解質を溶解可能であり、製膜後に除去することが可能な溶媒であれば特に制限はなく、N,N−ジメチルホルムアミド(DMF)、N,N−ジメチルアセトアミド(DMAc)、N−メチル−2−ピロリドン(NMP)、ジメチルスルホキシド(DMSO)等の非プロトン性極性溶媒や、ジクロロメタン、クロロホルム、1,2−ジクロロエタン、クロロベンゼン、ジクロロベンゼン等の塩素系溶媒、メタノール、エタノール、プロパノール等のアルコール類、エチレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、エチレングリコールモノエチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノメチルエーテル、プロピレングリコールモノエチルエーテル等のアルキレングリコールモノアルキルエーテル、テトラヒドロフラン、1,3−ジオキソラン、1,4−ジオキサン、1,3−ジオキサン、テトラヒドロピラン、ジブチルエーテル、tert−ブチルメチルエーテル、ジフェニルエーテル、クラウンエーテル類等のエーテル系溶媒等が好適である。これらは単独で用いてもよく、必要に応じて2種以上を混合して用いてもよい。 The solvent used for film formation is not particularly limited as long as it can dissolve the polymer electrolyte and can be removed after film formation. N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF), N, N-dimethylacetamide (DMAc), N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), aprotic polar solvents such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), chlorinated solvents such as dichloromethane, chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane, chlorobenzene and dichlorobenzene, methanol , Alcohols such as ethanol and propanol, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, ethylene glycol monoethyl ether, propylene glycol monomethyl ether, alkylene glycol monoalkyl ether such as propylene glycol monoethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, 1, - dioxolane, 1,4-dioxane, 1,3-dioxane, tetrahydropyran, dibutyl ether, tert- butyl methyl ether, diphenyl ether, ether solvents such as crown ethers are preferred. These may be used alone or as a mixture of two or more as required.
これらのなかでも、製膜用の溶媒としては、ジメチルスルホキシド、N,N−ジメチルホルムアミド、N,N−ジメチルアセトアミド、N−メチルピロリドン、テトラヒドロフラン、1,3−ジオキソラン等が高分子電解質の溶解性に優れるため、好ましい。 Of these, dimethyl sulfoxide, N, N-dimethylformamide, N, N-dimethylacetamide, N-methylpyrrolidone, tetrahydrofuran, 1,3-dioxolane and the like are used as membrane-forming solvents for the solubility of the polymer electrolyte. Is preferable.
高分子電解質膜12を構成するフィルムの厚さは、特に制限はないが、10〜300μmであると好ましく、20〜100μmであるとより好ましい。この厚さが10μmよりも薄いと、高分子電解質膜12としての実用的な強度が十分に得られない場合があり、300μmより厚いと、膜抵抗が大きくなり燃料電池10の特性が低下する傾向にある。この膜厚は、溶液の濃度や基板上への塗布厚によって制御することができる。
Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular in the thickness of the film which comprises the
なお、高分子電解質膜12を構成する高分子電解質は、上述したブロック共重合体の他、必要に応じて通常の高分子に使用される可塑剤、安定剤、離型剤等を含んでいてもよい。また、燃料電池の用途においては、含水量の管理を容易にするために、無機又は有機の微粒子を保水剤として添加してもよい。さらに、高分子電解質膜12は、混合共キャスト等により、上記ブロック共重合体と他のポリマーとの複合アロイ化されたものであってもよい。これらのブロック共重合体以外の成分は、高分子電解質膜12の特性(プロトン伝導性等)を低下させない範囲で使用できる。
The polymer electrolyte constituting the
なお、高分子電解質膜12は、上記の製膜後、機械的強度の向上等を目的として、電子線・放射線等を照射することにより更に架橋されたものであってもよい。また、高分子電解質膜12は、上記のような高分子電解質を製膜したもの以外に、多孔性のフィルムやシートに高分子電解質を含浸して複合化させたものや、ファイバーやパルプを混合することにより補強されたものであってもよい。
The
高分子電解質膜12に隣接する触媒層14a,14bは、燃料電池における電極層として機能する層であり、これらのいずれか一方がアノード触媒層となり、他方がカソード触媒層となる。かかる触媒層14a,14bとしては、上記高分子電解質と触媒とを含む触媒組成物から形成されたものが好適である。
The catalyst layers 14a and 14b adjacent to the
触媒としては、水素又は酸素との酸化還元反応を活性化できるものであれば特に制限はなく、例えば、貴金属、貴金属合金、金属錯体、金属錯体を焼成してなる金属錯体焼成物等が挙げられる。なかでも、触媒としては、白金の微粒子が好ましく、触媒層14a,14bは、活性炭や黒鉛等の粒子状または繊維状のカーボンに白金の微粒子が担持されてなるものであってもよい。 The catalyst is not particularly limited as long as it can activate a redox reaction with hydrogen or oxygen, and examples thereof include noble metals, noble metal alloys, metal complexes, and fired metal complex products obtained by firing metal complexes. . Of these, platinum fine particles are preferable as the catalyst, and the catalyst layers 14a and 14b may be formed by supporting fine particles of platinum on particulate or fibrous carbon such as activated carbon or graphite.
ガス拡散層16a,16bは、MEA20の両側を挟むように設けられており、触媒層14a,14bへの原料ガスの拡散を促進するものである。このガス拡散層16a,16bは、電子伝導性を有する多孔質材料により構成されるものが好ましく、例えば、多孔質性のカーボン不織布やカーボンペーパーが、原料ガスを触媒層14a,14bへ効率的に輸送することができるため、好ましい。
The gas diffusion layers 16a and 16b are provided so as to sandwich both sides of the
これらの高分子電解質膜12、触媒層14a,14b及びガス拡散層16a,16bから膜−電極−ガス拡散電極接合体(MEGA)が構成されている。このようなMEGAは、例えば、以下に示す方法により製造することができる。すなわち、まず、高分子電解質を含む溶液と触媒とを混合して触媒組成物のスラリーを形成する。これを、ガス拡散層16a,16bを形成するためのカーボン不織布やカーボンペーパー等の上に塗布し、溶媒等を蒸発させることで、ガス拡散層上に触媒層が形成された積層体を得る。そして、得られた一対の積層体をそれぞれの触媒層が対向するように配置するとともに、これらの間に高分子電解質膜12を配置し、これらを圧着させる。こうして、上述した構造のMEGAが得られる。
These
なお、カーボン不織布やカーボンペーパー上に触媒層を形成する方法、及び、これを高分子電解質膜と接合させる方法は、例えば、J.Electrochem.Soc.:Electrochemical Science and Technology,1988,135(9),2209に記載されている方法等を適用することができる。 A method for forming a catalyst layer on a carbon non-woven fabric or carbon paper, and a method for bonding it to a polymer electrolyte membrane are described in, for example, J. Pat. Electrochem. Soc. : Methods described in Electrochemical Science and Technology, 1988, 135 (9), 2209 can be applied.
セパレータ18a,18bは、電子伝導性を有する材料で形成されており、かかる材料としては、例えば、カーボン、樹脂モールドカーボン、チタン、ステンレス等が挙げられる。
そして、燃料電池10は、上述したようなMEGAを、一対のセパレータ18a,18bで挟み込み、これらを接合することで得ることができる。
The
なお、本発明の燃料電池は、必ずしも上述した構成を有するものに限られず、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜異なる構成を有していてもよい。例えば、上記燃料電池10では、上記本発明の製造方法により得られたブロック共重合体を含む高分子電解質が、高分子電解質膜12及び触媒層14a,14bの両方に含まれていたが、これに限定されず、これらのいずれか一方に含まれていればよい。ただし、高効率の燃料電池を得る観点からは、これらの両方に含まれていることが好ましい。また、燃料電池10は、上述した構造を有するものを、ガスシール体等で封止したものであってもよい。
The fuel cell of the present invention is not necessarily limited to the above-described configuration, and may have a different configuration as long as it does not depart from the spirit of the fuel cell. For example, in the
以下、本発明を実施例により更に詳細に説明するが、本発明はこれらの実施例に限定されるものではない。
[4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウムの合成]
EXAMPLES Hereinafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention still in detail, this invention is not limited to these Examples.
[Synthesis of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3′-disulfonate dipotassium]
まず、後述する合成に用いる4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウムを、以下に示すようにして合成した。すなわち、まず、攪拌機を備えた反応器に、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン467gと30%発煙硫酸3500gとを加え、100℃で5時間反応させた。得られた反応混合物を冷却した後、大量の氷水中に加え、これに更に50%水酸化カリウム水溶液470mLを滴下した。 First, dipotassium 4,4'-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3'-disulfonate used in the synthesis described below was synthesized as shown below. That is, first, 467 g of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone and 3500 g of 30% fuming sulfuric acid were added to a reactor equipped with a stirrer, and reacted at 100 ° C. for 5 hours. The obtained reaction mixture was cooled and then added to a large amount of ice water, and 470 mL of a 50% aqueous potassium hydroxide solution was further added dropwise thereto.
次いで、析出した固体を濾過して集め、エタノールで洗浄した後、乾燥させた。得られた固体を脱イオン水6.0Lに溶解させ、50%水酸化カリウム水溶液を加えて、pH7.5に調整した後、塩化カリウム460gを加えた。析出した固体を濾過して集め、エタノールで洗浄した後、乾燥させた。 Next, the precipitated solid was collected by filtration, washed with ethanol, and dried. The obtained solid was dissolved in 6.0 L of deionized water, 50% aqueous potassium hydroxide solution was added to adjust the pH to 7.5, and then 460 g of potassium chloride was added. The precipitated solid was collected by filtration, washed with ethanol, and dried.
その後、得られた固体をDMSO2.9Lに溶解させ、不溶の無機塩を濾過で除き、残渣をDMSO300mLでさらに洗浄した。得られた濾液に酢酸エチル/エタノール=24/1の溶液6.0Lを滴下し、析出した固体をメタノールで洗浄し、100℃で乾燥させて、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウムの固体482gを得た。
[参考試験:第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物との溶解性の比較]
Thereafter, the obtained solid was dissolved in 2.9 L of DMSO, insoluble inorganic salts were removed by filtration, and the residue was further washed with 300 mL of DMSO. To the obtained filtrate, 6.0 L of a solution of ethyl acetate / ethanol = 24/1 was added dropwise, and the precipitated solid was washed with methanol, dried at 100 ° C., and 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3. 482 g of dipotassium dipotassium disulfonate was obtained.
[Reference test: Comparison of solubility between the first polymer compound and the second polymer compound]
(参考例1)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウム81.69g、2,5−ジヒドロキシベンゼンスルホン酸カリウム(三星化学工業株式会社製)31.26g、ジメチルスルホキシド(DMSO)493g、及び、トルエン77gを加え、これらを室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Reference Example 1)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, 81.69 g of dipotassium 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3′-disulfonate, potassium 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate (Samsung Chemical Co., Ltd.) under an argon atmosphere. 31.26 g, 493 g of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 77 g of toluene were added, and argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour while stirring them at room temperature.
その後、得られた混合物に、炭酸カリウムを19.91g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを留去しながら加熱を続け、高分子化合物のDMSO溶液を得た。総加熱時間は14時間であった。得られた溶液の一部をサンプリングし、これをメタノールに注いで高分子化合物を析出させ、さらにメタノール洗浄を繰り返して精製した後、乾燥して、下記式(13)で表される繰り返し単位を有する高分子化合物(A)を得た。この高分子化合物(A)は、数平均分子量(Mn)が9.0×103であり、重量平均分子量(Mw)が1.7×104であった。
得られたイオン交換基を有する高分子化合物(A)(第1の高分子化合物)は、25℃において、10gのDMSOに対して2.0g以上溶解したが、NMPにはほとんど溶解しなかった。 The obtained polymer compound (A) (first polymer compound) having an ion exchange group was dissolved in an amount of 2.0 g or more in 10 g of DMSO at 25 ° C., but was hardly dissolved in NMP. .
(参考例2)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン76.12g、2,6−ジヒドロキシナフタレン51.62g、N−メチルピロリドン(NMP)557g、及び、トルエン94gを加え、これらを室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Reference Example 2)
A flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus was charged with 76.12 g of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone, 51.62 g of 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene, 557 g of N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP), and 94 g of toluene under an argon atmosphere. In addition, argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour while stirring at room temperature.
その後、得られた混合物に、炭酸カリウムを49.02g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを留去しながら加熱を続けた。総加熱時間は5時間であった。得られた溶液を室温にて放冷し、高分子化合物のNMP溶液を得た。この溶液をメタノールに注いで高分子化合物を析出させ、さらにメタノールで洗浄することによって精製した後、乾燥して、下記式(14)で表される繰り返し単位を有する高分子化合物(B)を得た。この高分子化合物(B)は、Mnが2.0×104であり、Mwが3.8×104であった。
得られたイオン交換基を有しない高分子化合物(B)(第2の高分子化合物)は、25℃において、10gのNMPに対して2.0g以上溶解したが、DMSOにはほとんど溶解しなかった。また、この高分子化合物(B)は、NMP5gとDMSO5gからなる混合溶媒には2.0g以上溶解した。 The obtained polymer compound (B) having no ion exchange group (second polymer compound) was dissolved in an amount of 2.0 g or more in 10 g of NMP at 25 ° C., but hardly dissolved in DMSO. It was. In addition, 2.0 g or more of this polymer compound (B) was dissolved in a mixed solvent composed of 5 g of NMP and 5 g of DMSO.
以上の参考試験の結果から、イオン交換基を有する高分子化合物(A)、及び、イオン交換基を有しない高分子化合物(B)とは、DMSOとNMPからなる混合溶媒に対して溶解し得ることが確認された。
[実施例1]
From the results of the above reference test, the polymer compound (A) having an ion exchange group and the polymer compound (B) having no ion exchange group can be dissolved in a mixed solvent composed of DMSO and NMP. It was confirmed.
[Example 1]
(第1の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウム313.37g、2,5−ジヒドロキシベンゼンスルホン酸カリウム120.05g、DMSO1892g、及び、トルエン297gを加え、これらを室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of the first polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, under an argon atmosphere, 313.37 g of dipotassium 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3′-disulfonate, 120.05 g of potassium 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate, 1892 g of DMSO, And 297 g of toluene was added, and argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour, stirring these at room temperature.
その後、得られた混合物に、炭酸カリウムを76.55g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを留去しながら加熱を続け、第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液を得た。総加熱時間は14時間であった。得られた溶液は室温にて放冷した。この第1の高分子化合物は、Mnが9.0×103であり、Mwが1.8×104であった。 Thereafter, 76.55 g of potassium carbonate was added to the obtained mixture, and azeotropic dehydration was performed by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while distilling off toluene to obtain a DMSO solution of the first polymer compound. Total heating time was 14 hours. The resulting solution was allowed to cool at room temperature. This first polymer compound had Mn of 9.0 × 10 3 and Mw of 1.8 × 10 4 .
(第2の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン250.40g、2,6−ジヒドロキシナフタレン177.78g、DMSO953g、NMP953g、及び、トルエン310gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of second polymer compound)
To a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, 250.40 g of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone, 177.78 g of 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene, 953 g of DMSO, 953 g of NMP, and 310 g of toluene were added under an argon atmosphere at room temperature. While stirring, argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour.
その後、得られた混合物に、炭酸カリウムを169.81g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを留去しながら加熱を続けた。総加熱時間は5時間であった。得られた溶液を室温にて放冷し、第2の高分子化合物のNMP/DMSO混合溶液を得た。この第2の高分子化合物のMnは1.7×104であり、Mwは3.0×104であった。 Thereafter, 169.81 g of potassium carbonate was added to the obtained mixture, and the mixture was stirred at 140 ° C. for azeotropic dehydration. Thereafter, heating was continued while toluene was distilled off. Total heating time was 5 hours. The resulting solution was allowed to cool at room temperature to obtain an NMP / DMSO mixed solution of the second polymer compound. The Mn of this second polymer compound was 1.7 × 10 4 and the Mw was 3.0 × 10 4 .
(ブロック共重合体の合成)
得られた第2の高分子化合物のNMP/DMSO混合溶液を攪拌しながら、これに、上記第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液の全量とNMP1035gを加え、150℃にて40時間ブロック共重合反応を行った。
(Synthesis of block copolymer)
While stirring the resulting NMP / DMSO mixed solution of the second polymer compound, the total amount of the DMSO solution of the first polymer compound and NMP1035 g were added thereto, and block copolymerization reaction was performed at 150 ° C. for 40 hours. Went.
得られた反応液を大量の2N塩酸に滴下し、1時間浸漬した。その後、生成した沈殿物を濾別した後、再度2N塩酸に1時間浸漬した。得られた沈殿物を濾別、水洗した後、95℃の大量の熱水に1時間浸漬した。そして、熱水から濾別した後、80℃で1晩乾燥させて、ブロック共重合体を得た。ブロック共重合反応時の溶媒組成を表1に示す。 The obtained reaction solution was dropped into a large amount of 2N hydrochloric acid and immersed for 1 hour. Thereafter, the produced precipitate was filtered off and then immersed again in 2N hydrochloric acid for 1 hour. The obtained precipitate was filtered and washed with water, and then immersed in a large amount of hot water at 95 ° C. for 1 hour. And after filtering off from hot water, it dried at 80 degreeC overnight and the block copolymer was obtained. Table 1 shows the solvent composition during the block copolymerization reaction.
(高分子電解質膜の作製)
得られたブロック共重合体を、約20重量%のNMP溶液とし、これをガラス板上に展開した後、80℃で溶媒を乾燥させた。乾燥後、ガラス板上に形成された膜を、2N塩酸水溶液に浸漬処理した後、洗浄水が中性になるまで脱イオン水で水洗し、乾燥させて厚さ33μmの実施例1の高分子電解質膜を得た。この高分子電解質膜は、Mnが8.6×104であり、Mwが23.4×104であった。
[実施例2]
(Production of polymer electrolyte membrane)
The obtained block copolymer was made into an NMP solution of about 20% by weight and developed on a glass plate, and then the solvent was dried at 80 ° C. After drying, the film formed on the glass plate was immersed in a 2N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, then washed with deionized water until the washing water became neutral, dried, and then the polymer of Example 1 having a thickness of 33 μm. An electrolyte membrane was obtained. This polymer electrolyte membrane had Mn of 8.6 × 10 4 and Mw of 23.4 × 10 4 .
[Example 2]
(第1の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウム313.37g、2,5−ジヒドロキシベンゼンスルホン酸カリウム120.05g、DMSO1892g、及び、トルエン297gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。その後、炭酸カリウムを76.55g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを留去しながら加熱を続け、第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液を得た。総加熱時間は14時間であった。得られた溶液は室温にて放冷した。得られた第1の高分子化合物のMnは9.0×103であり、Mwは1.8×104であった。
(Synthesis of the first polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, under an argon atmosphere, 313.37 g of dipotassium 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3′-disulfonate, 120.05 g of potassium 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate, 1892 g of DMSO, Then, 297 g of toluene was added, and argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour while stirring at room temperature. Thereafter, 76.55 g of potassium carbonate was added and subjected to azeotropic dehydration by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while distilling off toluene to obtain a DMSO solution of the first polymer compound. Total heating time was 14 hours. The resulting solution was allowed to cool at room temperature. The obtained first polymer compound had Mn of 9.0 × 10 3 and Mw of 1.8 × 10 4 .
(第2の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン292.34g、2,6−ジヒドロキシナフタレン198.21g、DMSO1070g、NMP1070g、及び、トルエン348gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。その後、炭酸カリウムを189.33g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを留去しながら加熱を続けた。総加熱時間は5時間であった。室温にて放冷し、第2の高分子化合物のNMP/DMSO混合溶液を得た。得られた第2の高分子化合物のMnは1.9×104であり、Mwは3.6×104であった。
(Synthesis of second polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, 292.34 g of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone, 198.21 g of 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene, 1070 g of DMSO, 1070 g of NMP, and 348 g of toluene are added under an argon atmosphere at room temperature While stirring, argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour. Thereafter, 189.33 g of potassium carbonate was added and subjected to azeotropic dehydration by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while toluene was distilled off. Total heating time was 5 hours. The mixture was allowed to cool at room temperature to obtain an NMP / DMSO mixed solution of the second polymer compound. The obtained second polymer compound had Mn of 1.9 × 10 4 and Mw of 3.6 × 10 4 .
(ブロック共重合体の合成)
得られた第2の高分子化合物のNMP/DMSO混合溶液を攪拌しながら、これに第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液の全量とNMP1035gを加え、150℃にて41時間ブロック共重合反応を行った。
(Synthesis of block copolymer)
While stirring the obtained NMP / DMSO mixed solution of the second polymer compound, the total amount of DMSO solution of the first polymer compound and 1035 g of NMP were added thereto, and a block copolymerization reaction was performed at 150 ° C. for 41 hours. It was.
得られた反応液を大量の2N塩酸に滴下し、1時間浸漬した。その後、生成した沈殿物を濾別した後、再度2N塩酸に1時間浸漬した。得られた沈殿物を濾別、水洗した後、95℃の大量の熱水に1時間浸漬した。そして、熱水から濾別した後、80℃で1晩乾燥させて、ブロック共重合体を得た。ブロック共重合反応時の溶媒組成を表1に示す。 The obtained reaction solution was dropped into a large amount of 2N hydrochloric acid and immersed for 1 hour. Thereafter, the produced precipitate was filtered off and then immersed again in 2N hydrochloric acid for 1 hour. The obtained precipitate was filtered and washed with water, and then immersed in a large amount of hot water at 95 ° C. for 1 hour. And after filtering off from hot water, it dried at 80 degreeC overnight and the block copolymer was obtained. Table 1 shows the solvent composition during the block copolymerization reaction.
(高分子電解質膜の作製)
得られたブロック共重合体を、約20重量%のNMP溶液とし、これをガラス板上に展開した後、80℃で溶媒を乾燥させた。乾燥後、ガラス板上に形成された膜を、2N塩酸水溶液に浸漬処理した後、洗浄水が中性になるまで脱イオン水で水洗し、乾燥させて厚さ22μmの実施例2の高分子電解質膜を得た。この高分子電解質膜は、Mnが8.3×104であり、Mwが20.9×104であった。
[実施例3]
(Production of polymer electrolyte membrane)
The obtained block copolymer was made into an NMP solution of about 20% by weight and developed on a glass plate, and then the solvent was dried at 80 ° C. After drying, the film formed on the glass plate was immersed in a 2N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, then washed with deionized water until the washing water became neutral, and dried to give a polymer of Example 2 having a thickness of 22 μm. An electrolyte membrane was obtained. This polymer electrolyte membrane had Mn of 8.3 × 10 4 and Mw of 20.9 × 10 4 .
[Example 3]
(第1の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウム81.69g、2,5−ジヒドロキシベンゼンスルホン酸カリウム31.26g、DMSO493g、及び、トルエン77gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of the first polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, in an argon atmosphere, 81.69 g of dipotassium 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3′-disulfonate, 31.26 g of potassium 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate, 493 g of DMSO, And 77g of toluene was added, and argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour, stirring at room temperature.
その後、炭酸カリウムを19.91g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを溜去しながら加熱を続け、第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液を得た。総加熱時間は14時間であった。得られた溶液は室温にて放冷した。得られた第1の高分子化合物のMnは9.0×103であり、Mwは1.7×104であった。 Thereafter, 19.91 g of potassium carbonate was added, and azeotropic dehydration was performed by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while distilling off the toluene to obtain a DMSO solution of the first polymer compound. Total heating time was 14 hours. The resulting solution was allowed to cool at room temperature. Mn of the obtained 1st high molecular compound was 9.0 * 10 < 3 >, and Mw was 1.7 * 10 < 4 >.
(第2の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン62.43g、2,6−ジヒドロキシナフタレン43.12g、NMP460g、及び、トルエン77gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of second polymer compound)
To a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, 62.43 g of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone, 43.12 g of 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene, 460 g of NMP and 77 g of toluene are added under an argon atmosphere, and the mixture is stirred at room temperature. Then, argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour.
その後、炭酸カリウムを40.93g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを溜去しながら加熱を続けた。総加熱時間は3時間であった。室温にて放冷し、第2の高分子化合物のNMP溶液を得た。得られた第2の高分子化合物のMnは1.9×104であり、Mwは3.5×104であった。 Thereafter, 40.93 g of potassium carbonate was added and subjected to azeotropic dehydration by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while distilling off toluene. The total heating time was 3 hours. The mixture was allowed to cool at room temperature to obtain an NMP solution of the second polymer compound. The obtained second polymer compound had Mn of 1.9 × 10 4 and Mw of 3.5 × 10 4 .
(ブロック共重合体の合成)
得られた第2の高分子化合物のNMP溶液を撹拌しながら、これに、第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液の全量とNMP274gを加え、150℃にて21時間加熱撹拌した。
(Synthesis of block copolymer)
While stirring the obtained NMP solution of the second polymer compound, the total amount of the DMSO solution of the first polymer compound and 274 g of NMP were added thereto, and the mixture was heated and stirred at 150 ° C. for 21 hours.
得られた反応液を大量の2N塩酸に滴下し、1時間浸漬した。その後、生成した沈殿物を濾別した後、再度2N塩酸に1時間浸漬した。得られた沈殿物を濾別、水洗した後、95℃の大量の熱水に1時間浸漬した。そして、熱水から濾別した後、80℃で1晩乾燥させて、ブロック共重合体を得た。ブロック共重合反応時の溶媒組成を表1に示す。 The obtained reaction solution was dropped into a large amount of 2N hydrochloric acid and immersed for 1 hour. Thereafter, the produced precipitate was filtered off and then immersed again in 2N hydrochloric acid for 1 hour. The obtained precipitate was filtered and washed with water, and then immersed in a large amount of hot water at 95 ° C. for 1 hour. And after filtering off from hot water, it dried at 80 degreeC overnight and the block copolymer was obtained. Table 1 shows the solvent composition during the block copolymerization reaction.
(高分子電解質膜の作製)
得られたブロック共重合体を、約20重量%のNMP溶液とし、これをガラス板上に展開した後、80℃で溶媒を乾燥させた。乾燥後、ガラス板上に形成された膜を、2N塩酸水溶液に浸漬処理した後、洗浄水が中性になるまで脱イオン水で水洗し、乾燥させて厚さ28μmの高分子電解質膜を得た。得られた高分子電解質膜は、Mnが8.0×104、Mwが20.4×104であった。
[実施例4]
(Production of polymer electrolyte membrane)
The obtained block copolymer was made into an NMP solution of about 20% by weight and developed on a glass plate, and then the solvent was dried at 80 ° C. After drying, the membrane formed on the glass plate is immersed in a 2N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, washed with deionized water until the washing water becomes neutral, and dried to obtain a polymer electrolyte membrane having a thickness of 28 μm. It was. The obtained polymer electrolyte membrane had Mn of 8.0 × 10 4 and Mw of 20.4 × 10 4 .
[Example 4]
(第1の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウム83.78g、2,5−ジヒドロキシベンゼンスルホン酸カリウム32.01g、DMSO505g、及び、トルエン79gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of the first polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, in an argon atmosphere, 83.78 g of dipotassium 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3′-disulfonate, 32.01 g of potassium 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate, 505 g of DMSO, And 79g of toluene was added, and argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour, stirring at room temperature.
その後、得られた混合物に炭酸カリウムを20.39g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを溜去しながら加熱を続け、第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液を得た。総加熱時間は19時間であった。得られた溶液は室温にて放冷した。得られた第1の高分子化合物のMnは9.0×103であり、Mwは1.7×104であった。 Thereafter, 20.39 g of potassium carbonate was added to the obtained mixture, and azeotropic dehydration was performed by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while distilling off the toluene to obtain a DMSO solution of the first polymer compound. Total heating time was 19 hours. The resulting solution was allowed to cool at room temperature. Mn of the obtained 1st high molecular compound was 9.0 * 10 < 3 >, and Mw was 1.7 * 10 < 4 >.
(第2の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン69.22g、2,6−ジヒドロキシナフタレン47.45g、NMP509g、及び、トルエン86gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of second polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, 69.22 g of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone, 47.45 g of 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene, 509 g of NMP and 86 g of toluene are added under an argon atmosphere, and the mixture is stirred at room temperature. Then, argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour.
その後、得られた混合物に炭酸カリウムを45.06g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを溜去しながら加熱を続けた。総加熱時間は3時間であった。室温にて放冷し、第2の高分子化合物のNMP溶液を得た。得られた第1の高分子化合物のMnは1.6×104であり、Mwは3.3×104であった。 Thereafter, 45.06 g of potassium carbonate was added to the obtained mixture, followed by azeotropic dehydration by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while distilling off toluene. The total heating time was 3 hours. The mixture was allowed to cool at room temperature to obtain an NMP solution of the second polymer compound. The obtained first polymer compound had Mn of 1.6 × 10 4 and Mw of 3.3 × 10 4 .
(ブロック共重合体の合成)
得られた第2の高分子化合物のNMP溶液を撹拌しながら、これに、上記第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液の全量とDMSO290gを加え、150℃にて24時間ブロック共重合反応を行った。
(Synthesis of block copolymer)
While stirring the obtained NMP solution of the second polymer compound, the total amount of the DMSO solution of the first polymer compound and 290 g of DMSO were added thereto, and a block copolymerization reaction was performed at 150 ° C. for 24 hours. .
得られた反応液を大量の2N塩酸に滴下し、1時間浸漬した。その後、得られた沈殿物を濾別した後、再度2N塩酸に1時間浸漬した。そして、得られた沈殿物を濾別、水洗した後、95℃の大量の熱水に1時間浸漬した。その後、熱水から濾別した後、80℃で1晩乾燥させて、ブロック共重合体を得た。ブロック共重合反応時の溶媒組成を表1に示す。 The obtained reaction solution was dropped into a large amount of 2N hydrochloric acid and immersed for 1 hour. Thereafter, the obtained precipitate was filtered off and then immersed again in 2N hydrochloric acid for 1 hour. The resulting precipitate was filtered off and washed with water, and then immersed in a large amount of hot water at 95 ° C. for 1 hour. Then, after separating from hot water, it was dried at 80 ° C. overnight to obtain a block copolymer. Table 1 shows the solvent composition during the block copolymerization reaction.
(高分子電解質膜の作製)
得られたブロック共重合体を、約20重量%のNMP溶液とし、これをガラス板上に展開した後、80℃で溶媒を乾燥させた。乾燥後、ガラス板上に形成された膜を、2N塩酸水溶液に浸漬処理した後、洗浄水が中性になるまで脱イオン水で水洗し、乾燥させて厚さ30μmの実施例4の高分子電解質膜を得た。得られた高分子電解質膜は、Mnが9.1×104であり、Mwが21.5×104であった。
[比較例1]
(Production of polymer electrolyte membrane)
The obtained block copolymer was made into an NMP solution of about 20% by weight and developed on a glass plate, and then the solvent was dried at 80 ° C. After drying, the film formed on the glass plate was immersed in a 2N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, washed with deionized water until the washing water became neutral, and dried to give a polymer of Example 4 having a thickness of 30 μm. An electrolyte membrane was obtained. The obtained polymer electrolyte membrane had Mn of 9.1 × 10 4 and Mw of 21.5 × 10 4 .
[Comparative Example 1]
(第1の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン−3,3’−ジスルホン酸ジカリウム313.59g、2,5−ジヒドロキシベンゼンスルホン酸カリウム120.07g、DMSO1892g、及び、トルエン297gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of the first polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, an argon atmosphere was charged with 31.59 g of dipotassium 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone-3,3′-disulfonate, 120.07 g of potassium 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate, 1892 g of DMSO, Then, 297 g of toluene was added, and argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour while stirring at room temperature.
その後、得られた混合物に、炭酸カリウムを76.34g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを溜去しながら加熱を続け、第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液を得た。総加熱時間は15時間であった。得られた溶液は室温にて放冷した。得られた第1の高分子化合物のMnは9.0×103であり、Mwは1.7×104であった。 Thereafter, 76.34 g of potassium carbonate was added to the obtained mixture, and azeotropic dehydration was performed by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while distilling off the toluene to obtain a DMSO solution of the first polymer compound. Total heating time was 15 hours. The resulting solution was allowed to cool at room temperature. Mn of the obtained 1st high molecular compound was 9.0 * 10 < 3 >, and Mw was 1.7 * 10 < 4 >.
(第2の高分子化合物の合成)
共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジフルオロジフェニルスルホン304.55g、2,6−ジヒドロキシナフタレン205.78g、ジメチルスルホキシド2225g、及び、トルエン350gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスを1時間バブリングした。
(Synthesis of second polymer compound)
To a flask equipped with an azeotropic distillation apparatus, 304.55 g of 4,4′-difluorodiphenylsulfone, 205.78 g of 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene, 2225 g of dimethyl sulfoxide and 350 g of toluene were added under an argon atmosphere at room temperature. While stirring, argon gas was bubbled for 1 hour.
その後、得られた混合物に炭酸カリウムを195.10g加え、140℃にて加熱撹拌して共沸脱水した。その後トルエンを留去しながら加熱を続けた。総加熱時間は5時間であった。得られた溶液を室温にて放冷したところ、第2の高分子化合物はDMSO中で析出しており、第2の高分子化合物のDMSO分散液が得られた。得られた第2の高分子化合物のMnは2.2×104であり、Mwは4.1×104であった。 Thereafter, 195.10 g of potassium carbonate was added to the obtained mixture, followed by azeotropic dehydration by heating and stirring at 140 ° C. Thereafter, heating was continued while toluene was distilled off. Total heating time was 5 hours. When the resulting solution was allowed to cool at room temperature, the second polymer compound was precipitated in DMSO, and a DMSO dispersion of the second polymer compound was obtained. The obtained second polymer compound had Mn of 2.2 × 10 4 and Mw of 4.1 × 10 4 .
(ブロック共重合体の合成)
第2の高分子化合物のDMSO分散液を撹拌しながら、これに第1の高分子化合物のDMSO溶液の全量を加え、120℃にて2時間、さらに150℃にて4時間ブロック共重合反応を行った。反応中、系内は2相に分離しており不均一系となっていた。
(Synthesis of block copolymer)
While stirring the DMSO dispersion of the second polymer compound, the whole amount of the DMSO solution of the first polymer compound was added thereto, and a block copolymerization reaction was performed at 120 ° C. for 2 hours and further at 150 ° C. for 4 hours. went. During the reaction, the inside of the system was separated into two phases and became a heterogeneous system.
反応後の反応液を大量の2N塩酸に滴下し、1時間浸漬した。その後、生成した沈殿物を濾別した後、再度2N塩酸に1時間浸漬した。得られた沈殿物を濾別、水洗した後、95℃の大量の熱水に1時間浸漬した。そして、熱水から濾別した後、80℃で1晩乾燥させて、ブロック共重合体を得た。ブロック共重合反応時の溶媒組成を表1に示す。 The reaction solution after the reaction was dropped into a large amount of 2N hydrochloric acid and immersed for 1 hour. Thereafter, the produced precipitate was filtered off and then immersed again in 2N hydrochloric acid for 1 hour. The obtained precipitate was filtered and washed with water, and then immersed in a large amount of hot water at 95 ° C. for 1 hour. And after filtering off from hot water, it dried at 80 degreeC overnight and the block copolymer was obtained. Table 1 shows the solvent composition during the block copolymerization reaction.
(高分子電解質膜の作製)
得られたブロック共重合体を、約20重量%のNMP溶液とし、これをガラス板上に展開した後、80℃で溶媒を乾燥させた。乾燥後、ガラス板上に形成された膜を、2N塩酸水溶液に浸漬処理した後、洗浄水が中性になるまで脱イオン水で水洗し、乾燥させて厚さ26μmの比較例1の高分子電解質膜を得た。この高分子電解質膜は、Mnが11.0×104であり、Mwが38.3×104であった。
[実施例5]
(Production of polymer electrolyte membrane)
The obtained block copolymer was made into an NMP solution of about 20% by weight and developed on a glass plate, and then the solvent was dried at 80 ° C. After drying, the film formed on the glass plate was immersed in a 2N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, then washed with deionized water until the washing water became neutral, dried, and polymer of Comparative Example 1 having a thickness of 26 μm. An electrolyte membrane was obtained. This polymer electrolyte membrane had Mn of 11.0 × 10 4 and Mw of 38.3 × 10 4 .
[Example 5]
(第1の高分子化合物の合成)
特開2005‐248143に記載の方法にしたがって重合を行い、下記式(15)で表される繰り返し単位を有する第1の高分子化合物(C)を得た。この高分子化合物(C)のMnは11.8×104であり、Mwは30.5×104であった。
Polymerization was performed according to the method described in JP-A-2005-248143 to obtain a first polymer compound (C) having a repeating unit represented by the following formula (15). Mn of this polymer compound (C) was 11.8 × 10 4 , and Mw was 30.5 × 10 4 .
(第2の高分子化合物の合成)
減圧共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、4,4’−ジクロロジフェニルスルホン(東京化成工業株式会社製)23.79g、2,2−ビス(4−ヒドロキシフェニル)プロパン(東京化成工業株式会社製)18.02g、NMP184g、及び、トルエン48gを加え、室温にて撹拌しながらアルゴンガスをバブリングした。
(Synthesis of second polymer compound)
In a flask equipped with a reduced-pressure azeotropic distillation apparatus, 23.79 g of 4,4′-dichlorodiphenylsulfone (manufactured by Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd.), 2,2-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) propane (Tokyo Chemical Industry) under an argon atmosphere. Kogyo Co., Ltd.) 18.02 g, NMP 184 g and toluene 48 g were added, and argon gas was bubbled while stirring at room temperature.
その後、得られた混合物に、炭酸カリウムを11.67g加え、100℃にて加熱撹拌して減圧共沸脱水した。トルエンを留去し、180℃に昇温し、7時間加熱撹拌した。その後、炭酸カリウムを0.38g加え、1.5時間加熱撹拌した。総加熱時間は8.5時間であった。得られた反応混合物を大量のメタノールに滴下し、高分子化合物を析出させ、さらにメタノール及び、水で洗浄することによって精製した後、乾燥して、下記式(16)で表される繰り返し単位を有する第2の高分子化合物(D)を得た。この高分子化合物(D)のMnは1.6×104であり、Mwは3.0×104であった。
(第1及び第2の高分子化合物の溶解性評価)
上記で得られたイオン交換基を有する第1の高分子化合物(C)は25℃において、0.95gのDMSOに対して0.05g以上溶解したが、0.95gのNMPに対しては0・05gが完全には溶解しなかった。また、この高分子化合物は、DMSO0.76gとNMP0.19gからなる混合溶媒には0.05g以上溶解した。
(Evaluation of solubility of first and second polymer compounds)
The first polymer compound (C) having an ion exchange group obtained above was dissolved in an amount of 0.05 g or more in 0.95 g of DMSO at 25 ° C., but 0 in 0.95 g of NMP. -05g was not completely dissolved. Further, 0.05 g or more of this polymer compound was dissolved in a mixed solvent composed of 0.76 g of DMSO and 0.19 g of NMP.
一方、イオン交換基を有しない第2の高分子化合物(D)は、25℃において、9.5gのNMPに対して0.5g以上溶解したが、9.5gのDMSOに対しては0.5gが完全には溶解しなかった。また、この高分子化合物は、NMP1.9gとDMSO7.6gからなる混合溶媒には0.5g以上溶解した。以上の結果から、高分子化合物(C)及び高分子化合物(D)は、MDSOとNMPからなる混合溶媒に溶解し得ることが確認された。 On the other hand, the second polymer compound (D) having no ion-exchange group was dissolved in an amount of 0.5 g or more in 9.5 g of NMP at 25 ° C., but in the case of 9.5 g of DMSO, it was 0.8. 5 g was not completely dissolved. In addition, 0.5 g or more of this polymer compound was dissolved in a mixed solvent composed of 1.9 g of NMP and 7.6 g of DMSO. From the above results, it was confirmed that the polymer compound (C) and the polymer compound (D) can be dissolved in a mixed solvent composed of MDSO and NMP.
(ブロック共重合体の合成)
減圧共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、上記第2の高分子化合物(D)2.03g、上記第1の高分子化合物(C)の原料モノマーである2,5’−ジクロロベンゼンスルホン酸ナトリウム5.68g、2,2’−ビピリジル(和光純薬工業株式会社製)8.55g、DMSO104g、NMP28g、及び、トルエン53gを加え、100℃にて加熱撹拌して、減圧共沸脱水した。その後、トルエンを留去し、70℃に冷却した。次いで、これにビス(1,5−シクロオクタジエン)ニッケル(0)(関東化学株式会社製)15.06gを加えて3時間攪拌した。これにより、第1の高分子化合物(C)を合成するとともに、第1の高分子化合物(C)と第2の高分子化合物(D)との共重合反応を生じさせた。
(Synthesis of block copolymer)
In a flask equipped with a reduced pressure azeotropic distillation apparatus, in an argon atmosphere, 2.03 g of the second polymer compound (D) and 2,5′-di, which is a raw material monomer of the first polymer compound (C). 5.68 g of sodium chlorobenzenesulfonate, 8.55 g of 2,2′-bipyridyl (manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.), 104 g of DMSO, 28 g of NMP, and 53 g of toluene were added, and the mixture was heated and stirred at 100 ° C., followed by azeotropic distillation under reduced pressure. Dehydrated. Then, toluene was distilled off and cooled to 70 ° C. Next, 15.06 g of bis (1,5-cyclooctadiene) nickel (0) (manufactured by Kanto Chemical Co., Inc.) was added thereto and stirred for 3 hours. Thus, the first polymer compound (C) was synthesized and a copolymerization reaction between the first polymer compound (C) and the second polymer compound (D) was caused.
得られた反応液を大量のメタノールに滴下し、ポリマーを析出させて濾別した。その後、6mol/L塩酸による洗浄・ろ過操作を数回繰り返した後、濾液が中性になるまで水洗し、次いで95℃の大量の熱水に1時間浸漬した。そして、熱水から濾別した後、乾燥することによってブロック共重合体を得た。ブロック共重合反応時の溶媒組成を表1に示す。 The obtained reaction solution was dropped into a large amount of methanol, and a polymer was precipitated and separated by filtration. Then, after washing and filtering with 6 mol / L hydrochloric acid were repeated several times, the filtrate was washed with water until it became neutral, and then immersed in a large amount of hot water at 95 ° C. for 1 hour. And after filtering off from hot water, the block copolymer was obtained by drying. Table 1 shows the solvent composition during the block copolymerization reaction.
(高分子電解質膜の作製)
得られたブロック共重合体を、約10重量%のNMP溶液とし、これをガラス板上に展開した後、80℃で溶媒を乾燥させた。乾燥後、ガラス板上に形成された膜を、2N塩酸水溶液に浸漬処理した後、洗浄水が中性になるまで脱イオン水で水洗し、乾燥させて厚さ20μmの実施例5の高分子電解質膜を得た。得られた高分子電解質膜は、Mnが9.5×104であり、Mwが18.5×104であった。
[比較例2]
(Production of polymer electrolyte membrane)
The obtained block copolymer was made into an about 10% by weight NMP solution, which was spread on a glass plate, and then the solvent was dried at 80 ° C. After drying, the film formed on the glass plate was immersed in a 2N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, then washed with deionized water until the washing water became neutral, and dried to dry the polymer of Example 5 having a thickness of 20 μm. An electrolyte membrane was obtained. The obtained polymer electrolyte membrane had Mn of 9.5 × 10 4 and Mw of 18.5 × 10 4 .
[Comparative Example 2]
(ブロック共重合体の合成)
減圧共沸蒸留装置を備えたフラスコに、アルゴン雰囲気下、上記第2の高分子化合物(D)2.34g、上記第1の高分子化合物(C)の原料モノマーである2,5’−ジクロロベンゼンスルホン酸ナトリウム5.65g、2,2’−ビピリジル9.29g、NMPの141g、及び、トルエン59gを加え、100℃にて加熱撹拌して、減圧共沸脱水した。その後、トルエンを留去し、70℃に冷却した。次いで、これにビス(1,5−シクロオクタジエン)ニッケル(0)14.87gを加え、3時間攪拌した。これにより、第1の高分子化合物(C)を合成するとともに、この第1の高分子化合物(C)と第2の高分子化合物(D)との共重合反応を生じさせた。
(Synthesis of block copolymer)
In a flask equipped with a vacuum azeotropic distillation apparatus, in an argon atmosphere, 2.34 g of the second polymer compound (D) and 2,5′-di, which is a raw material monomer of the first polymer compound (C). 5.65 g of sodium chlorobenzenesulfonate, 9.29 g of 2,2′-bipyridyl, 141 g of NMP, and 59 g of toluene were added, and the mixture was heated and stirred at 100 ° C. to perform azeotropic dehydration under reduced pressure. Then, toluene was distilled off and cooled to 70 ° C. Next, 14.87 g of bis (1,5-cyclooctadiene) nickel (0) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred for 3 hours. Thus, the first polymer compound (C) was synthesized, and a copolymerization reaction between the first polymer compound (C) and the second polymer compound (D) was caused.
得られた反応液を大量のメタノールに滴下し、ポリマーを析出させて濾別した。その後、6mol/L塩酸による洗浄・ろ過操作を数回繰り返した後、濾液が中性になるまで水洗し、次いで95℃の大量の熱水に1時間浸漬した。そして、熱水から濾別した後、乾燥することによりブロック共重合体を得た。ブロック共重合反応時の溶媒組成を表1に示す。 The obtained reaction solution was dropped into a large amount of methanol, and a polymer was precipitated and separated by filtration. Then, after washing and filtering with 6 mol / L hydrochloric acid were repeated several times, the filtrate was washed with water until it became neutral, and then immersed in a large amount of hot water at 95 ° C. for 1 hour. And after filtering off from hot water, the block copolymer was obtained by drying. Table 1 shows the solvent composition during the block copolymerization reaction.
(高分子電解質膜の作製)
得られたブロック共重合体を、約25重量%のNMP溶液とし、これをガラス板上に展開した後、80℃で溶媒を乾燥させた。乾燥後、ガラス板上に形成された膜を、2N塩酸水溶液に浸漬処理した後、洗浄水が中性になるまで脱イオン水で水洗し、乾燥させて厚さ44μmの比較例2の高分子電解質膜を得た。得られた高分子電解質膜は、Mnが2.7×104であり、Mwが5.4×104であった。
(Production of polymer electrolyte membrane)
The obtained block copolymer was made into an about 25 wt% NMP solution, which was developed on a glass plate, and then the solvent was dried at 80 ° C. After drying, the film formed on the glass plate was immersed in a 2N hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, then washed with deionized water until the washing water became neutral, dried, and the polymer of Comparative Example 2 having a thickness of 44 μm. An electrolyte membrane was obtained. The obtained polymer electrolyte membrane had Mn of 2.7 × 10 4 and Mw of 5.4 × 10 4 .
[特性評価]
[Characteristic evaluation]
実施例1〜5及び比較例1〜2の高分子電解質膜を用い、以下に示す方法にしたがって、これらのプロトン伝導度、イオン交換容量、吸水率及び分子量を測定した。得られた結果をまとめて表2に示す。 Using the polymer electrolyte membranes of Examples 1 to 5 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2, the proton conductivity, ion exchange capacity, water absorption rate, and molecular weight were measured according to the following method. The results obtained are summarized in Table 2.
(プロトン伝導度(σ)の測定)
各高分子電解質膜を、幅1.0cmの短冊状膜試料とし、その表面に白金板(幅:5.0mm)を間隔が1.0cmになるように押しあて、80℃、相対湿度90%の恒温恒湿槽中に試料を保持し、白金板間の106〜10-1Hzにおける交流インピーダンスを測定した。そして、得られた値を、下記式に代入して、各高分子電解質膜のプロトン伝導度(σ)(S/cm)を算出した。
σ(S/cm)=1/(R×d)
[式中、コール・コールプロット上において、複素インピーダンスの虚数成分が0の時の、複素インピーダンスの実数成分をR(Ω)とする。dは短冊状膜試料の膜厚(cm)を表す。]
(Measurement of proton conductivity (σ))
Each polymer electrolyte membrane is a strip-shaped membrane sample having a width of 1.0 cm, and a platinum plate (width: 5.0 mm) is pressed against the surface so that the interval is 1.0 cm, and 80 ° C. and a relative humidity of 90%. The sample was held in a constant temperature and humidity chamber, and the AC impedance between the platinum plates at 10 6 to 10 −1 Hz was measured. Then, the obtained value was substituted into the following formula to calculate the proton conductivity (σ) (S / cm) of each polymer electrolyte membrane.
σ (S / cm) = 1 / (R × d)
[In the equation, the real component of the complex impedance when the imaginary component of the complex impedance is 0 on the Cole-Cole plot is R (Ω). d represents the film thickness (cm) of the strip-shaped film sample. ]
(イオン交換容量の測定)
実施例1〜5及び比較例1〜2の高分子電解質膜の所定量を秤量した後、これらをそれぞれ0.1Nの水酸化ナトリウム標準水溶液中に2時間浸漬した。その後、この溶液を、0.1Nの塩酸水溶液を用いて滴定し、その中和点から各高分子電解質膜のイオン交換容量(meq/g)を算出した。
(Measurement of ion exchange capacity)
After weighing a predetermined amount of each of the polymer electrolyte membranes of Examples 1 to 5 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2, they were each immersed in a 0.1N sodium hydroxide standard aqueous solution for 2 hours. Thereafter, this solution was titrated with a 0.1N aqueous hydrochloric acid solution, and the ion exchange capacity (meq / g) of each polymer electrolyte membrane was calculated from the neutralization point.
(吸水率の測定)
実施例1〜5及び比較例1〜2の高分子電解質膜を充分に乾燥させ、その重量を測定した。また、この十分に乾燥させた膜を、100℃の水に2時間浸漬した後、その重量を測定した。そして、膜を水に浸漬する前後の重量変化を求め、その変化率を吸水率とした。
(Measurement of water absorption)
The polymer electrolyte membranes of Examples 1 to 5 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2 were sufficiently dried and their weights were measured. The fully dried membrane was immersed in water at 100 ° C. for 2 hours, and its weight was measured. And the weight change before and behind immersing a film | membrane in water was calculated | required, and the change rate was made into the water absorption rate.
(数平均分子量及び重量平均分子量の測定、及び、高分子電解質膜の分子量分布の評価)
実施例1〜5及び比較例1〜2における第1の高分子化合物、第2の高分子化合物及び高分子電解質膜について、それぞれ以下に示すようにして数平均分子量(Mn)及び重量平均分子量(Mw)を測定した。すなわち、参考例1、実施例1〜4及び比較例1の第1の高分子化合物については下記(1)の条件で、また、参考例2、実施例1〜4及び比較例1の第2の高分子化合物及び高分子電解質については下記(2)の条件で、さらに、実施例5及び比較例2の第1及び第2の高分子化合物については下記(3)の条件で、それぞれゲルパーミエーションクロマトグラフィー(GPC)による分析を行い、ポリスチレン換算のMn及びMwを算出した。
(Measurement of number average molecular weight and weight average molecular weight, and evaluation of molecular weight distribution of polymer electrolyte membrane)
For the first polymer compound, the second polymer compound, and the polymer electrolyte membrane in Examples 1 to 5 and Comparative Examples 1 and 2, the number average molecular weight (Mn) and the weight average molecular weight ( Mw) was measured. That is, the first polymer compound of Reference Example 1, Examples 1 to 4 and Comparative Example 1 was subjected to the following condition (1), and the second polymer of Reference Example 2, Examples 1 to 4 and Comparative Example 1 was used. For the polymer compound and the polymer electrolyte, the gel permeation was performed under the condition (2) below, and for the first and second polymer compounds of Example 5 and Comparative Example 2 under the condition (3) below. The analysis by an oscillation chromatography (GPC) was performed and Mn and Mw of polystyrene conversion were computed.
そして、得られた値から、各高分子電解質膜の分子量分布(Mw/Mn)を算出した。実施例1〜5及び比較例1〜2における第1の高分子化合物、第2の高分子化合物及び高分子電解質膜のMn及びMwについては上記で示したとおりである。また、各高分子電解質膜の分子量分布は、まとめて表2に示した。 And the molecular weight distribution (Mw / Mn) of each polymer electrolyte membrane was computed from the obtained value. The Mn and Mw of the first polymer compound, the second polymer compound, and the polymer electrolyte membrane in Examples 1 to 5 and Comparative Examples 1 to 2 are as described above. The molecular weight distribution of each polymer electrolyte membrane is shown in Table 2 together.
<GPC測定条件>
条件(1)
GPC測定装置:日立L−6200低圧
カラム :TSKgel α−M
カラム温度 :40℃
移動相溶媒 :50mM酢酸アンモニウム/水:アセトニトリル=7:3
溶媒流量 :0.6mL/min
条件(2)
GPC測定装置:TOSOH社製 HLC−8220
カラム :Shodex社製 AT−80Mを2本直列に接続
カラム温度 :40℃
移動相溶媒 :DMAc(LiBrを10mmol/dm3になるように添加)
溶媒流量 :0.5mL/min
条件(3)
GPC測定装置:島津製作所製 Prominence GPCシステム
カラム :TOSOH社製 TSKgel GMHHR−M
カラム温度 :40℃
移動相溶媒 :DMF(LiBrを10mmol/dm3になるように添加)
溶媒流量 :0.5mL/min
<GPC measurement conditions>
Condition (1)
GPC measuring device: Hitachi L-6200 low pressure column: TSKgel α-M
Column temperature: 40 ° C
Mobile phase solvent: 50 mM ammonium acetate / water: acetonitrile = 7: 3
Solvent flow rate: 0.6 mL / min
Condition (2)
GPC measuring device: HLC-8220 manufactured by TOSOH
Column: Two AT-80Ms manufactured by Shodex are connected in series Column temperature: 40 ° C
Mobile phase solvent: DMAc (added LiBr to 10 mmol / dm 3 )
Solvent flow rate: 0.5 mL / min
Condition (3)
GPC measuring device: Prominence GPC system column manufactured by Shimadzu Corporation: TSKgel GMH HR- M manufactured by TOSOH
Column temperature: 40 ° C
Mobile phase solvent: DMF (LiBr added to 10 mmol / dm 3 )
Solvent flow rate: 0.5 mL / min
表2より、第1の高分子化合物と第2の高分子化合物とを混合溶媒中でブロック共重合させたブロック共重合体からなる実施例1〜5の高分子電解質膜は、高いプロトン伝導性を有しており、また、分子量分布が小さく均質な膜であることが判明した。 From Table 2, the polymer electrolyte membranes of Examples 1 to 5 comprising a block copolymer obtained by block copolymerization of a first polymer compound and a second polymer compound in a mixed solvent have high proton conductivity. In addition, the film was found to be a homogeneous film having a small molecular weight distribution.
10…燃料電池、12…高分子電解質膜、14a,14b…触媒層、16a,16b…ガス拡散層、18a,18b…セパレータ、20…MEA。
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (30)
[式中、Ar71は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X71は、直接結合、酸素原子、硫黄原子、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、dは5以上の整数である。] The first polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (7) and having an ion exchange group in the structure. A method for producing a block copolymer according to claim 1.
[In the formula, Ar 71 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. A divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group, X 71 represents a direct bond, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and d is an integer of 5 or more. ]
[式中、Ar11、Ar12、Ar13、Ar14、Ar15、Ar16及びAr17は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X11、X12、X13、X14及びX15は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、Y11及びY12は、それぞれ独立に、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、p、q及びrは、それぞれ独立に、5以上の整数である。] The first polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (1a), (1b) or (1c), and having an ion exchange group in the structure. The manufacturing method of the block copolymer as described in any one of Claims 1-15.
[In formula, Ar < 11 >, Ar < 12 >, Ar < 13 >, Ar < 14 >, Ar < 15 >, Ar < 16 > and Ar < 17 > are respectively independently a C1-C20 alkyl group, a C1-C20 alkoxy group, carbon number A divalent aromatic group optionally having 6 to 20 aryl groups, 6 to 20 aryloxy groups or 2 to 20 carbon atoms acyl groups, X 11 , X 12 , X 13 , X 14 and X 15 each independently represent an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, Y 11 and Y 12 each independently represent a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and p, q and r each independently represent 5 It is an integer above. ]
[式中、Y21は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、s及びtは、それぞれ独立に0又は1であって少なくともいずれか一方が1であり、uは0、1又は2であり、vは1又は2であり、wは5以上の整数である。] The method for producing a block copolymer according to any one of claims 1 to 15, wherein the first polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (2). .
[Wherein Y 21 represents a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, s and t are each independently 0 or 1, at least one of which is 1, u is 0, 1 or 2; Is 1 or 2, and w is an integer of 5 or more. ]
[式中、X171は、直接結合又は有機基であり、fは1からX171における置換可能な部位の数までの整数であり、gは1又は2であり、lは5以上の整数である。] The method for producing a block copolymer according to any one of claims 1 to 15, wherein the first polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (17). .
[ Wherein X 171 is a direct bond or an organic group, f is an integer from 1 to the number of substitutable sites in X 171 , g is 1 or 2, and l is an integer of 5 or more. is there. ]
[式中、Ar31は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X31は、直接結合、酸素原子、硫黄原子、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、zは5以上の整数である。] The method for producing a block copolymer according to any one of claims 1 to 19, wherein the second polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (3). .
[In the formula, Ar 31 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. And X 31 represents a direct bond, an oxygen atom, a sulfur atom, a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and z is an integer of 5 or more. ]
[式中、Ar41、Ar42及びAr43は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X41及びX42は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、Z41は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、hは5以上の整数である。] The method for producing a block copolymer according to any one of claims 1 to 19, wherein the second polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (4). .
[Wherein, Ar 41 , Ar 42 and Ar 43 each independently represent an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 6 to 20 carbon atoms. An aryloxy group or a divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms, X 41 and X 42 each independently represent an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and Z 41 Represents a carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, and h is an integer of 5 or more. ]
[式中、Ar51は、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を有していてもよい2価の芳香族基を示し、X51及びX52は、それぞれ独立に、酸素原子又は硫黄原子を示し、R51及びR52は、それぞれ独立に、炭素数1〜20のアルキル基、炭素数1〜20のアルコキシ基、炭素数6〜20のアリール基、炭素数6〜20のアリールオキシ基又は炭素数2〜20のアシル基を示し、Z51は、カルボニル基又はスルホニル基を示し、j及びkは、それぞれ独立に、0〜4の整数であり、iは、5以上の整数である。] The method for producing a block copolymer according to any one of claims 1 to 19, wherein the second polymer compound is a compound having a structure represented by the following general formula (5). .
[In the formula, Ar 51 represents an alkyl group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryloxy group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, or 2 to 20 carbon atoms. A divalent aromatic group optionally having an acyl group, X 51 and X 52 each independently represents an oxygen atom or a sulfur atom, and R 51 and R 52 each independently represent a carbon atom. C 1 -C 20 alkyl group, an alkoxy group having 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group having 6 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group or an acyl group having 2 to 20 carbon atoms having from 6 to 20 carbon atoms, Z 51 is , A carbonyl group or a sulfonyl group, j and k are each independently an integer of 0 to 4, and i is an integer of 5 or more. ]
前記高分子電解質膜が、請求項25記載の高分子電解質を含有することを特徴とする膜−電極接合体。 A polymer electrolyte membrane, and a catalyst layer formed on the polymer electrolyte membrane,
The membrane-electrode assembly, wherein the polymer electrolyte membrane contains the polymer electrolyte according to claim 25.
前記触媒層が、請求項25記載の高分子電解質及び触媒を含有することを特徴とする膜−電極接合体。 A polymer electrolyte membrane, and a catalyst layer formed on the polymer electrolyte membrane,
The membrane-electrode assembly, wherein the catalyst layer contains the polymer electrolyte according to claim 25 and a catalyst.
前記膜−電極接合体が請求項28又は29記載の膜−電極接合体であることを特徴とする燃料電池。
A pair of separators, and a membrane-electrode assembly disposed between the pair of separators,
30. A fuel cell, wherein the membrane-electrode assembly is the membrane-electrode assembly according to claim 28 or 29.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006244692A JP2007106986A (en) | 2005-09-16 | 2006-09-08 | Block copolymer and method for producing the same, polymer electrolyte, catalytic composition, polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane/electrode assembly and fuel cell |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005270755 | 2005-09-16 | ||
| JP2006244692A JP2007106986A (en) | 2005-09-16 | 2006-09-08 | Block copolymer and method for producing the same, polymer electrolyte, catalytic composition, polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane/electrode assembly and fuel cell |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007106986A true JP2007106986A (en) | 2007-04-26 |
Family
ID=38033097
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006244692A Pending JP2007106986A (en) | 2005-09-16 | 2006-09-08 | Block copolymer and method for producing the same, polymer electrolyte, catalytic composition, polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane/electrode assembly and fuel cell |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2007106986A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009005055A1 (en) * | 2007-07-02 | 2009-01-08 | Kaneka Corporation | Polymer electrolyte, polymer electrolyte membrane, catalyst layer binder for fuel cell, and its use |
| WO2009096574A1 (en) * | 2008-02-01 | 2009-08-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Polyelectrolyte composition, method of production of same, and fuel cell |
| WO2011046234A1 (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-21 | 住友化学株式会社 | Polyarylene copolymer and uses thereof |
| EP2568524A2 (en) | 2011-09-07 | 2013-03-13 | Hitachi Ltd. | Electrolyte material, and proton conductive polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane electrode assembly and polymer electrolyte fuel cell using the same |
| JP2013064125A (en) * | 2011-08-31 | 2013-04-11 | Toray Ind Inc | Block copolymer and method for producing the same, and polymer electrolyte material, polymer electrolyte molding and solid polymer fuel cell using block copolymer |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003017090A (en) * | 2001-07-03 | 2003-01-17 | Sumitomo Chem Co Ltd | Polymer electrolyte membrane and fuel cell using it |
| JP2004031307A (en) * | 2001-11-29 | 2004-01-29 | Ube Ind Ltd | Polyelectrolyte composition |
| JP2004359925A (en) * | 2003-04-07 | 2004-12-24 | Mitsui Chemicals Inc | Proton conductive block copolymer and proton conductive film |
| JP2005139432A (en) * | 2003-10-17 | 2005-06-02 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Block copolymer and use thereof |
| JP2005190675A (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-14 | Jsr Corp | Solid polyelectrolyte film and solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell |
| JP2005206807A (en) * | 2003-12-25 | 2005-08-04 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Polymer electrolyte and use of the same |
| WO2006095919A1 (en) * | 2005-03-10 | 2006-09-14 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Polyarylene block copolymer and use thereof |
| JP2006313740A (en) * | 2005-04-05 | 2006-11-16 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Cross-linked polymer electrolyte and its manufacturing method |
| JP2007109638A (en) * | 2005-09-16 | 2007-04-26 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Polymer electrolyte, and polymer electrolyte membrane using same, membrane-electrode assembly and fuel cell using same |
-
2006
- 2006-09-08 JP JP2006244692A patent/JP2007106986A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003017090A (en) * | 2001-07-03 | 2003-01-17 | Sumitomo Chem Co Ltd | Polymer electrolyte membrane and fuel cell using it |
| JP2004031307A (en) * | 2001-11-29 | 2004-01-29 | Ube Ind Ltd | Polyelectrolyte composition |
| JP2004359925A (en) * | 2003-04-07 | 2004-12-24 | Mitsui Chemicals Inc | Proton conductive block copolymer and proton conductive film |
| JP2005139432A (en) * | 2003-10-17 | 2005-06-02 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Block copolymer and use thereof |
| JP2005190675A (en) * | 2003-12-24 | 2005-07-14 | Jsr Corp | Solid polyelectrolyte film and solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell |
| JP2005206807A (en) * | 2003-12-25 | 2005-08-04 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Polymer electrolyte and use of the same |
| WO2006095919A1 (en) * | 2005-03-10 | 2006-09-14 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Polyarylene block copolymer and use thereof |
| JP2006313740A (en) * | 2005-04-05 | 2006-11-16 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Cross-linked polymer electrolyte and its manufacturing method |
| JP2007109638A (en) * | 2005-09-16 | 2007-04-26 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Polymer electrolyte, and polymer electrolyte membrane using same, membrane-electrode assembly and fuel cell using same |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2009005055A1 (en) * | 2007-07-02 | 2009-01-08 | Kaneka Corporation | Polymer electrolyte, polymer electrolyte membrane, catalyst layer binder for fuel cell, and its use |
| WO2009096574A1 (en) * | 2008-02-01 | 2009-08-06 | Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | Polyelectrolyte composition, method of production of same, and fuel cell |
| WO2011046234A1 (en) * | 2009-10-16 | 2011-04-21 | 住友化学株式会社 | Polyarylene copolymer and uses thereof |
| JP2013064125A (en) * | 2011-08-31 | 2013-04-11 | Toray Ind Inc | Block copolymer and method for producing the same, and polymer electrolyte material, polymer electrolyte molding and solid polymer fuel cell using block copolymer |
| EP2568524A2 (en) | 2011-09-07 | 2013-03-13 | Hitachi Ltd. | Electrolyte material, and proton conductive polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane electrode assembly and polymer electrolyte fuel cell using the same |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5858129B2 (en) | Method for producing polymer electrolyte molded body | |
| JP4424129B2 (en) | Block copolymer and use thereof | |
| JP3724064B2 (en) | Polymer electrolyte for fuel cell and fuel cell | |
| JP4375170B2 (en) | Block copolymer and use thereof | |
| KR101341274B1 (en) | Process for producing polymer electrolyte molded product, polymer electrolyte material, polymer electrolyte membrane, and solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell | |
| JP5740030B2 (en) | Copolymer of sulfonated polyethersulfone containing hydroxy group and method for producing the same, polymer electrolyte membrane for fuel cell, and membrane electrode assembly including the same | |
| JP2007177197A (en) | Polyarylene-based block copolymer and its use | |
| WO2005030840A1 (en) | Block copolymers and use thereof | |
| JP5892653B2 (en) | POLYMER ELECTROLYTE AND USE THEREOF | |
| JP2005248143A (en) | Polymer compound and its producting method | |
| JP2007109638A (en) | Polymer electrolyte, and polymer electrolyte membrane using same, membrane-electrode assembly and fuel cell using same | |
| WO2005037892A1 (en) | Block copolymer and use thereof | |
| JP2007106986A (en) | Block copolymer and method for producing the same, polymer electrolyte, catalytic composition, polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane/electrode assembly and fuel cell | |
| EP3021395A1 (en) | Electrolyte membrane, membrane-electrode assembly, and solid polymer fuel cell | |
| EP2284844A1 (en) | Polymer electrolyte, crosslinked polymer electrolyte, polymer electrolyte membrane and use of the same | |
| EP1519435A1 (en) | Polymeric laminates, processes for producing the same, and use thereof | |
| US20100167165A1 (en) | Copolymer, polymer electrolyte, and use thereof | |
| JP5309822B2 (en) | Aromatic sulfonic acid derivative, sulfonated polymer, polymer electrolyte material and polymer electrolyte fuel cell using the same | |
| JP2012114049A (en) | Solid polymer electrolyte membrane, method for manufacturing the same, and membrane-electrode assembly and fuel cell using the same | |
| JP2007191694A (en) | Copolymer, polymer electrolyte, and use thereof | |
| CA2634062A1 (en) | Copolymer, polymer electrolyte and use thereof | |
| EP4317257A1 (en) | Polymer electrolyte membrane, block copolymer, polymer electrolyte material, polymer electrolyte molded body, electrolyte membrane with catalyst layer, membrane electrode composite, solid polymer fuel cell, and water electrolytic hydrogen generator | |
| JP2007149653A (en) | Electrolyte for direct methanol fuel cell and direct methanol fuel cell using same | |
| TWI645609B (en) | Polymer electrolyte membrane, membrane electrode bonding element, and solid polymer-type fuel cell | |
| WO2013153696A1 (en) | High-molecular-weight electrolyte and use thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090713 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120724 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20121113 |