JP2006207648A - Liquid hose - Google Patents
Liquid hose Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006207648A JP2006207648A JP2005018091A JP2005018091A JP2006207648A JP 2006207648 A JP2006207648 A JP 2006207648A JP 2005018091 A JP2005018091 A JP 2005018091A JP 2005018091 A JP2005018091 A JP 2005018091A JP 2006207648 A JP2006207648 A JP 2006207648A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- inner layer
- thermoplastic elastomer
- hose
- water
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Rigid Pipes And Flexible Pipes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
技術分野
この発明は、一般住宅用ホース、各種産業用ホースとして用いられる液体用ホースに係り、特に、給湯装置と浴槽との間又は各種機器間を繋ぐ液体用ホースに関する。
TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a general housing hose and a liquid hose used as various industrial hoses, and more particularly to a liquid hose connecting between a hot water supply device and a bathtub or between various devices.
従来、一般住宅等に設置されている浴槽には、浴槽への給湯又は追い焚きを行うために、給湯装置と浴槽とをホースによって接続している。このようなホースには、2本のホースを独立的に用いるか、予め並列して接合された2本のホースをツイン管として用いられる。そして、これらのホースは、金属あるいは架橋ポリエチレンによって製造されている。
2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, a hot water supply device and a bathtub are connected to a bathtub installed in a general house or the like by a hose in order to supply or recharge the bathtub. For such a hose, two hoses are used independently, or two hoses joined in parallel in advance are used as a twin pipe. These hoses are made of metal or cross-linked polyethylene.
しかしながら、上記金属製ホースや架橋ポリエチレンホースの場合には、柔軟性に劣り、施工する際に作業性が悪く、また金具への組み付けが難しいという問題があった。そこで、塩化ビニル製ホースが使用されてきたが、塩化ビニルは、耐熱性に劣るために高温の温水を通すことができなかった。そのために、高温の温水で効率よく給湯したり、追い焚きしたりすることができなかった。 However, in the case of the metal hose or the cross-linked polyethylene hose, there is a problem that the flexibility is inferior, the workability is poor at the time of construction, and the assembly to the metal fitting is difficult. Accordingly, vinyl chloride hoses have been used, but vinyl chloride cannot pass hot water because of its poor heat resistance. For this reason, it has not been possible to efficiently supply hot water with hot water or catch up.
これらの問題を解決し高温の温水を通すことができるように、耐水性合成ゴムからなる内面ゴム層と、合成繊維によって網状に形成された補強層と、耐油性合成ゴムからなる中間ゴム層と、熱可塑性樹脂からなる外面層の4層構造からなるツインホースが開示されている。
しかしながら、上記特開平11−336955号公報記載の温水配管用ホースは、2本のホースを並列に配したツイン管とするために、外面層には、通常溶着性の良い塩化ビニル系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPVC)が使用される。塩化ビニル系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPVC)は、廃棄処理の際にハロゲンが遊離することがあるなど環境に影響を与えるおそれがある。従って、上記公報記載の温水配管用ホースは、高温の温水を通すことができるものの、近年高まっている環境問題に対応することができない。 However, the hot water piping hose described in the above-mentioned JP-A-11-336955 is a twin pipe in which two hoses are arranged in parallel. (TPVC) is used. Vinyl chloride thermoplastic elastomer (TPVC) may affect the environment, for example, halogen may be liberated during disposal. Therefore, although the hot water piping hose described in the above publication can pass hot hot water, it cannot cope with environmental problems that have been increasing in recent years.
また、上記温水配管用ホースは、内面に加硫ゴム層を有しているために、ホース自体の臭いが強く温水を通したとき温水に臭いが移行しやすく、また、混合されている物質が抽出されることによる色水(黒水)が発生し易いという問題がある。 In addition, since the hose for hot water piping has a vulcanized rubber layer on the inner surface, the smell of the hose itself is strong and the odor is likely to shift to hot water when it passes through hot water. There is a problem that colored water (black water) is likely to be generated by extraction.
この発明は、かかる現状に鑑みてされたものであり、環境問題の原因となる塩化ビニル樹脂などのハロゲン含有物を含まず、また、水等への臭いの移行や色水(黒)の発生がなく、しかも軽量化、柔軟性、耐熱性、耐久性及び金具組み付け性に優れた液体用ホースを提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the present situation, does not include halogen-containing materials such as vinyl chloride resin, which cause environmental problems, and transfers odors to water and the like, and generation of colored water (black). In addition, an object of the present invention is to provide a liquid hose that is excellent in weight reduction, flexibility, heat resistance, durability, and metal fitting assembly.
この発明は上記目的を達成するために次のような構成とした。即ち、この発明に係る液体用ホースは、内側層となる内層にポリプロピレン(PP)とエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)からなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)を用い、内層の外周面に編み組又は巻き付けによる補強層を設け、外側層となる外層にオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)を用い、内層と外層とは補強層を介して直接融着していることを特徴とする。そして、前記内層のオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)は、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)であることが好ましい。
前記補強層は、内層と外層が直接融着するように編み目の間が開いていることが好ましく、そのために編角度又は巻き付け角度45〜60°であることが好ましい。
In order to achieve the above object, the present invention is configured as follows. That is, the liquid hose according to the present invention uses an olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPO) made of polypropylene (PP) and ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) for the inner layer serving as the inner layer, and braided or formed on the outer peripheral surface of the inner layer. A reinforced layer by winding is provided, and an olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPO) is used for the outer layer serving as the outer layer, and the inner layer and the outer layer are directly fused via the reinforcing layer. The olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPO) of the inner layer is a dynamically cross-linked olefin in which ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) of 5 μm or less is completely dispersed in a polypropylene (PP) matrix (continuous layer). A thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) is preferred.
The reinforcing layer preferably has an opening between the stitches so that the inner layer and the outer layer are directly fused. Therefore, the knitting angle or the winding angle is preferably 45 to 60 °.
前記ホースは単体で使用することができるが、2本以上を並列に配し、外周面の少なくとも一部を接合してなる複数管として使用することができる。前記ホースは、水、温水、あるいは不凍液を通す一般住宅の液体用ホースとして使用することができる。 Although the hose can be used alone, it can be used as a plurality of tubes in which two or more are arranged in parallel and at least a part of the outer peripheral surface is joined. The hose can be used as a liquid hose for ordinary houses through which water, warm water, or antifreeze liquid passes.
上記構成により、環境問題の原因となる塩化ビニル樹脂などのハロゲン含有樹脂を含まないから環境に影響を与えることがない。また、内層には、加硫ゴムではなく臭いの発生のない熱可塑性エラストマーを用いたから、液体への臭いの移行がなく、混合物の抽出による色水(黒水)の発生もない。また、内層、外層とも低比重(0.96〜1.00)の材料を用いたから、軽量化、柔軟性、耐熱性、耐久性及び金具組み付け性に優れた液体用ホースを得ることができる。 The above configuration does not affect the environment because it does not contain a halogen-containing resin such as vinyl chloride resin that causes environmental problems. In addition, since a thermoplastic elastomer that does not generate odor is used for the inner layer instead of vulcanized rubber, there is no odor transfer to the liquid, and there is no generation of colored water (black water) due to extraction of the mixture. Moreover, since the material of low specific gravity (0.96-1.00) was used for the inner layer and the outer layer, the liquid hose excellent in weight reduction, a softness | flexibility, heat resistance, durability, and metal fitting | attachment property can be obtained.
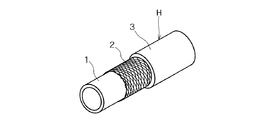
以下に、この発明に係る液体用ホースの実施形態について詳細に説明する。図1に示すように、ホースHは、内側層となる内層1と、その外側に補強層2を介して外層3を設けてなる複層構造のホースである。前記内層1は、ポリプロピレン(PP)とエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)からなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)により形成してなり、内層1の外周面に編み組による補強層2を設け、外側層となる外層3にオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)により形成し、内層と外層とは補強層の網目を介して直接融着している。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the liquid hose according to the present invention will be described in detail. As shown in FIG. 1, the hose H is a multi-layered hose in which an
前記内層1に用いるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)は、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)であることが好ましい。このように、オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)を、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させたものとすることによって、耐抽出性を向上させることができる。
The olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPO) used for the
前記補強層2は、内層1を成形後、ブレード又はスパイラル等の任意の方法で編み組みを行い、チューブに予熱を与えた後外層を押出することによりホースを成形することができる。また、1つの金型の中で内層、補強層、外層を成形してもよい。編み目は、内層1と外層3が溶着できるように開いていることが好ましく、編角度は45〜60°とする。編角度60°以上では、網目が小さくなり内層1と外層3の樹脂が直接溶着することができなくなり、接着力が低下するからである。一方、編角度45°以下では、常温では問題がないものの、例えば80℃雰囲気中では耐圧性を保持できなくなるおそれがあるからである。
The reinforcing
上記構成のホースは、内層1と外層3をオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマーにより形成することとしたから、内層1と外層3とを溶着することが可能であり、加硫工程が不要である。また、編角度を45〜60°とすることにより編み目を開けることができるから、内層1と外層3とが直接溶着することができる。従って、接着層や中間層が不要となり、工程を簡素化して安価なホースとすることができる。
In the hose having the above-described configuration, the
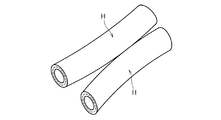
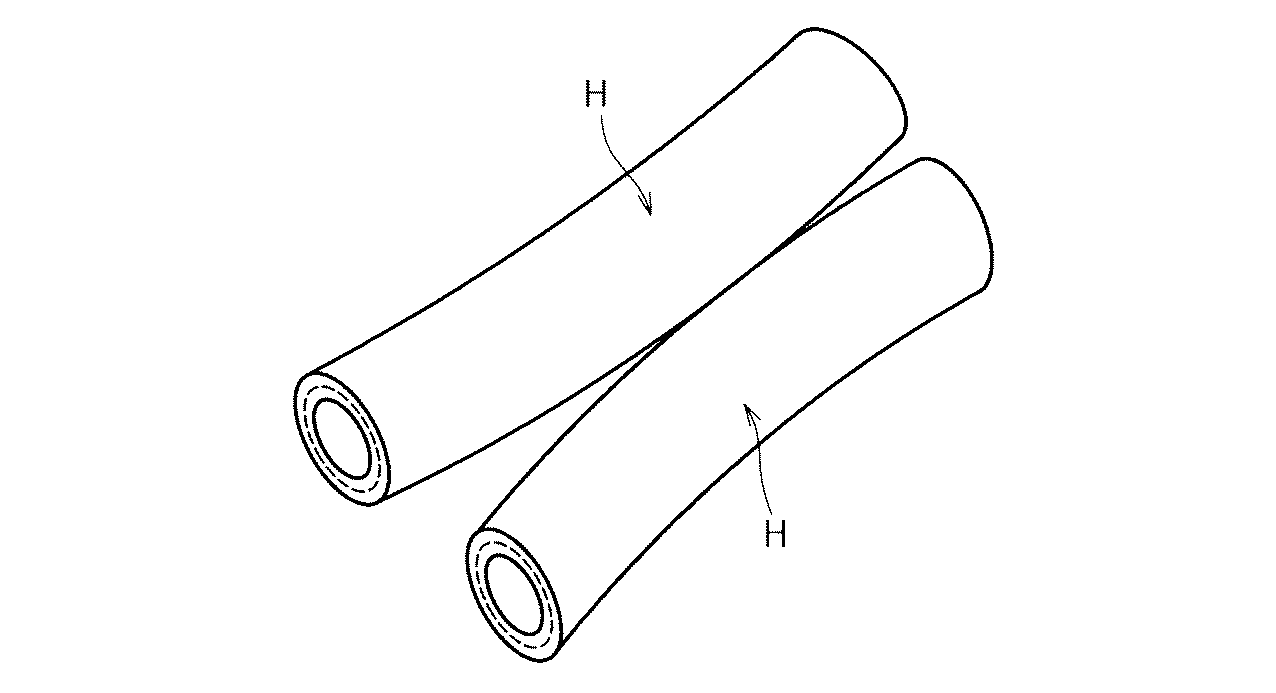
上記ホースHは、単体で使用することができるのは勿論であるが、図2に示すように、同じ長さの2本のホースを並列させて外層3同士の一部を溶着によって接合し一体化した複数管として使用してもよい。複数管とするには、200〜400℃の熱風を外層の接合部にあて、2本または3本以上のホースを圧着後冷却することにより得られる。また、熱板を接合部に直接あて溶着するなど任意の方法で複数管とすることができる。この発明に係る液体用ホースは、図示するのを省略したが、両端部に接続金具を取り付けて使用される。次に実施例と比較例について説明する。
(実施例1〜3)
Of course, the hose H can be used alone, but as shown in FIG. 2, two hoses having the same length are juxtaposed and a part of the outer layers 3 are joined together by welding. It may be used as a multiple tube. In order to obtain a plurality of tubes, hot air of 200 to 400 ° C. is applied to the joint portion of the outer layer, and two or three or more hoses are crimped and then cooled. Moreover, it can be set as a several pipe | tube by arbitrary methods, such as applying a hot plate directly to a junction part and welding. Although the liquid hose according to the present invention is not shown in the drawing, it is used with connecting fittings attached to both ends. Next, examples and comparative examples will be described.
(Examples 1-3)
次に、内層1に用いるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマーについて各種試験を行った。実施例1は、ポリプロピレン(PP)とエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)からなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)として、プラス・テク社製の「アムゼル7KFR059−1」を用い、射出成型にて厚さ2mmに成型した試験片を用いた。
Next, various tests were performed on the olefinic thermoplastic elastomer used for the
実施例2は、ポリプロピレン(PP)とエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)からなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)であって、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)を使用した。前記TPVには、エーイーエス社製の商品名「サントプレン101−73」を用い、射出成型にて厚さ2mmに成型した試験片を用いた。 Example 2 is an olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPO) made of polypropylene (PP) and ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM), and is completely or partially crosslinked to a polypropylene (PP) matrix (continuous layer) of 5 μm or less. A dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) in which ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) was dispersed was used. As the TPV, a product name “Santoprene 101-73” manufactured by AES was used, and a test piece molded to a thickness of 2 mm by injection molding was used.
実施例3は、実施例2と同じポリプロピレン(PP)にエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)を使用した。前記TPVには、DSM社製の商品名「サーリンク4175」を射出成型にて厚さ2mmに成型した試験片を用いた。 In Example 3, a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) in which ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) was dispersed in the same polypropylene (PP) as in Example 2 was used. For the TPV, a test piece obtained by molding a product name “Sirlink 4175” manufactured by DSM to a thickness of 2 mm by injection molding was used.
比較例1及び比較例2は、実際に温水配管用ホースとして使用されている材料を用いた。比較例1には、エチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を適宜加硫し、厚さ2mmに成型した試験片を用い、比較例2には、塩化ビニル系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPVC)を厚さ2mmに成型した試験片を用いた。 In Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2, a material actually used as a hot water piping hose was used. In Comparative Example 1, a test piece obtained by vulcanizing ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) as appropriate and molded to a thickness of 2 mm was used. In Comparative Example 2, a vinyl chloride thermoplastic elastomer (TPVC) was made to a thickness of 2 mm. A molded test piece was used.
上記実施例1〜3、及び比較例1〜2について、次の各種試験を行った。
<耐水性>
JISK6258(加硫ゴムの浸せき試験方法) に準じて、試験片を精製水に浸漬して70℃で300h〜1000h促進老化させた後、体積変化率を測定した。
<耐塩素水性>
JISK6258(加硫ゴムの浸せき試験方法) に準じて、試験片を塩素水(0.3%塩素水を水で希釈) 200ppmに浸漬して70℃で300h〜1000h促進老化させた後、体積変化率を測定した。
<耐不凍液性>
JISK6258(加硫ゴムの浸せき試験方法)に準じて、試験片を調整済み不凍液 KTブラインP−34(プロピレングリコール29〜33%)に浸漬して100℃で300h〜1000h促進老化させた後、体積変化率を測定した。
<耐熱性>
JISK6257(加硫ゴムの老化試験方法) に準じて、試験片を80℃および100℃にて100h〜1000h老化させた後、硬さ変化、引張強さ変化、伸び変化を測定した。
<熱間時物性>
雰囲気温度80℃および100℃にてJISK6251およびJISK6253に準じて、硬さ、引張強さおよび伸びを測定した。
<耐抽出性>
JISK6258(加硫ゴムの浸せき試験方法)に準じて、試験片を精製水、塩素水(0.3%塩素水を水で希釈) 200ppmおよび調整済み不凍液KTブラインP−34(プロピレングリコール29〜33%)に浸漬し、精製水、塩素水は80℃、不凍液は100℃で300h〜1000h促進老化させた後、試験液の変色を確認した。
測定結果を表1に示す。
About the said Examples 1-3 and Comparative Examples 1-2, the following various tests were done.
<Water resistance>
According to JISK6258 (a vulcanized rubber immersion test method), the test piece was immersed in purified water and subjected to accelerated aging at 70 ° C. for 300 h to 1000 h, and then the volume change rate was measured.
<Chlorine resistant water>
According to JISK6258 (Method of immersion test for vulcanized rubber), the test piece was immersed in 200 ppm of chlorine water (0.3% chlorine water diluted with water) and accelerated aging at 70 ° C. for 300 h to 1000 h, followed by volume change. The rate was measured.
<Antifreeze resistance>
According to JISK6258 (vulcanized rubber immersion test method), the test piece was immersed in an adjusted antifreeze KT brine P-34 (propylene glycol 29-33%) and accelerated aging at 100 ° C. for 300 h to 1000 h, and then volume. The rate of change was measured.
<Heat resistance>
According to JISK6257 (vulcanized rubber aging test method), the test piece was aged at 80 ° C. and 100 ° C. for 100 h to 1000 h, and then the change in hardness, change in tensile strength, and change in elongation were measured.
<Hot physical properties>
Hardness, tensile strength and elongation were measured according to JISK6251 and JISK6253 at an atmospheric temperature of 80 ° C and 100 ° C.
<Extraction resistance>
According to JISK6258 (Method of immersion test for vulcanized rubber), the test piece was purified water, chlorinated water (0.3% chlorinated water diluted with water) 200 ppm and adjusted antifreeze KT brine P-34 (propylene glycol 29-33) %), Purified water and chlorine water were subjected to accelerated aging at 80 ° C. and antifreeze solution at 100 ° C. for 300 to 1000 hours, and then the discoloration of the test solution was confirmed.
The measurement results are shown in Table 1.
上記試験結果は、実施例1、2、3は、温水配管用ホース材料として適していることを示している。
実施例1は温水配管用ホース材料として使用可能であるが、80℃以上での熱間時物性が実施例2、3の方が優れており、近年の高温の湯で効率よく給湯または追焚きを行うという用途を考えると、ポリプロピレン(PP)とエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)からなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)は温水配管用ホースとして使用可能であるが、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)を用いることがより好ましい。
The said test result has shown that Example 1, 2, 3 is suitable as a hose material for hot water piping.
Although Example 1 can be used as a hose material for hot water piping, the hot physical properties at 80 ° C. or higher are superior to those in Examples 2 and 3, and hot water supply or reheating is efficiently performed with hot water in recent years. The olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPO) composed of polypropylene (PP) and ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) can be used as a hot water pipe hose, but a polypropylene (PP) matrix (continuous layer) It is more preferable to use a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) in which a completely crosslinked or partially crosslinked ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) is dispersed.
また、実施例1、2、3は、水、塩素水、不凍液での耐抽出性に優れており、発明者らは種々の材料について検討を行う中でポリプロピレン(PP)とエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)からなるオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPO)が、水、塩素水、不凍液での耐抽出性に優れていることを発見した。また、上記動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)を用いることによりさらに耐抽出性を良くすることが出来ることが分かる。さらに、外観の悪化、機械的物性を考えると上記動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)はポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連結層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)とすることがより好ましい。また、耐抽出性は架橋度に影響を受けることより、完全架橋された動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)とすることがさらに好ましい。
(実施例4〜8)
In addition, Examples 1, 2, and 3 are excellent in extraction resistance in water, chlorinated water, and antifreeze, and the inventors investigated polypropylene and polypropylene (PP) and ethylene propylene diene rubber ( It has been discovered that an olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPO) made of EPDM has excellent extraction resistance in water, chlorinated water and antifreeze. Moreover, it turns out that extraction resistance can be improved further by using the said dynamically crosslinked olefin type thermoplastic elastomer (TPV). Furthermore, considering the deterioration of the appearance and mechanical properties, the above dynamically crosslinked olefin thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) is an ethylene propylene diene rubber (TPM) that is 5 μm or less fully or partially crosslinked ethylene propylene diene rubber (TP). It is more preferable to use a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) in which EPDM) is dispersed. Moreover, it is more preferable to use a dynamically crosslinked olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) that is completely crosslinked, because the extraction resistance is affected by the degree of crosslinking.
(Examples 4 to 8)
次に、実際にホースを作成し、各種試験を行った。ホースは、実施例2,3と同様に、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)として、AES社製の商品名「サントプレン101−73」を用い、補強層としてポリエステル繊維2200dexを編み角度40〜65°にて編み込み、外層に動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)として、AES社製の商品名「サントプレン8221−70」を用いて作成した。なお、編み角度と編組中心外径は、次式により算出した。
編み角度=tan−1(編組中心外径 ×π(円周率)/編組ピッチ)
編組中心外径= (編組外径+チューブ外径) /2
Next, a hose was actually made and various tests were performed. As in Examples 2 and 3, the hose is a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic in which a polypropylene (PP) matrix (continuous layer) is dispersed with 5 μm or less of completely or partially crosslinked ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM). The product name “Santoprene 101-73” manufactured by AES is used as an elastomer (TPV), polyester fiber 2200 dex is knitted at a knitting angle of 40 to 65 ° as a reinforcing layer, and a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) is formed in an outer layer. ) As a product name “Santoprene 8221-70” manufactured by AES. The knitting angle and the braid center outer diameter were calculated by the following equations.
Knitting angle = tan −1 (braid center outer diameter × π (circumferential ratio) / braid pitch)
Braid center outer diameter = (braid outer diameter + tube outer diameter) / 2
編み角度は、実施例4を40°、実施例5を45°、実施例6を50°、実施例7を60°、実施例8を65°とした。 The knitting angles were 40 ° in Example 4, 45 ° in Example 5, 50 ° in Example 6, 60 ° in Example 7, and 65 ° in Example 8.
上記実施例4〜8について、次の各種試験を行った。
<接着性試験>
JIS K6330−6(第6部:接着試験)に準じて内層と外層の間の接着力を測定した。
<耐圧性>
JIS K6330−2(第2部:耐圧性試験)の7.1項(耐圧試験)に準じて試験圧力0.3MPa、試験時間は5分にて試験後、漏れ等異常の有無を確認した。なお、雰囲気温度はRT(室温)および80℃中にて試験を実施した。
測定結果を表2に示す。
About the said Examples 4-8, the following various tests were done.
<Adhesion test>
The adhesive force between the inner layer and the outer layer was measured according to JIS K6330-6 (Part 6: Adhesion test).
<Pressure resistance>
According to JIS K6330-2 (Part 2: pressure resistance test) Section 7.1 (pressure resistance test), the test pressure was 0.3 MPa and the test time was 5 minutes. The test was conducted at RT (room temperature) and 80 ° C.
The measurement results are shown in Table 2.
上記結果から、外層をオレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマーにより形成することによって、加硫工程が不用で、また接着層や中間層が不用となり工程を簡素化することが出来る。また、上記結果から、内層と外層の接着力は1.2kN/m以上とすることが好ましく、編角度を60°以上とした場合網目が小さくなり、内層と外層の溶着面積が小さくなることにより接着力が低下する。また、温水配管用ホースとして使用する場合、耐圧性は0.3Mpa以上とすることが好ましく、編み角度を45°以下とした場合常温では問題ないものの80℃雰囲気中で金具抜けが発生するなど、80℃の温水を流した場合耐圧性を保持できない可能性がある。従って、編角度は45°〜60°とすることがより好ましい。
(実施例9、10)
From the above results, by forming the outer layer from an olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer, the vulcanization process is unnecessary, and the adhesive layer and the intermediate layer are unnecessary, thereby simplifying the process. Further, from the above results, the adhesive force between the inner layer and the outer layer is preferably 1.2 kN / m or more, and when the knitting angle is 60 ° or more, the mesh becomes smaller, and the welding area of the inner layer and the outer layer becomes smaller. Adhesive strength decreases. In addition, when used as a hot water piping hose, the pressure resistance is preferably 0.3 Mpa or more, and when the knitting angle is 45 ° or less, there is no problem at room temperature, but metal fittings occur in an 80 ° C atmosphere. When hot water at 80 ° C. is flowed, pressure resistance may not be maintained. Accordingly, the knitting angle is more preferably 45 ° to 60 °.
(Examples 9 and 10)
次に、実施例4〜8と同様にホースを作成し、各種試験を行った。実施例9の内層には、実施例4〜8と同じく、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)として、AES社製の商品名「サントプレン101−73」を用い、補強層としてポリエステル繊維2200dexを編み角度53°にて編み込み、外層に動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)として、AES社製の商品名「サントプレン8221−70」を用いてホースを作成した。 Next, the hose was created similarly to Examples 4-8, and various tests were done. In the inner layer of Example 9, as in Examples 4 to 8, dynamic crosslinking in which ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) of 5 μm or less was completely or partially crosslinked in a polypropylene (PP) matrix (continuous layer) was dispersed. The product name “Santoprene 101-73” manufactured by AES is used as the olefinic thermoplastic elastomer (TPV), polyester fiber 2200dex is knitted at a knitting angle of 53 ° as a reinforcing layer, and the dynamically crosslinked olefinic thermoplastic elastomer is formed in the outer layer. As (TPV), a hose was created using a trade name “Santoprene 8221-70” manufactured by AES.
実施例10の内層には、ポリプロピレン(PP)マトリックス(連続層)に5μm以下の完全架橋あるいは部分架橋されたエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を分散させた動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)として、DSM社製の商品名「サーリンク4175」を用い、補強層としてポリエステル繊維2200dexを編み角度53°にて編み込み、外層に動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)として、DSM社製の商品名「サーリンク4165」を用いてホースを作成した。比較例3の内層にはエチレンプロピレンジエンゴム(EPDM)を用い、比較例4の内層には、塩化ビニル系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPVC)を用いた温水配管用ホースを作成した。比較例3,4には、市販されている温水配管用ホースと同じ材質である。 The inner layer of Example 10 is a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) in which ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) of 5 μm or less is dispersed in a polypropylene (PP) matrix (continuous layer). As a reinforcing layer, polyester fiber 2200 dex is knitted at a knitting angle of 53 °, and a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) is used as an outer layer by DSM. A hose was created using the trade name “Cirlink 4165”. A hot water piping hose using ethylene propylene diene rubber (EPDM) for the inner layer of Comparative Example 3 and a vinyl chloride thermoplastic elastomer (TPVC) for the inner layer of Comparative Example 4 was prepared. Comparative Examples 3 and 4 are made of the same material as a commercially available hot water piping hose.
上記実施例9、10及び比較例3,4について、次の各種試験を行った。
<臭気性>
ホース10mに精製水を封入し、80℃の雰囲気中に24時間放置後、封入液を採取し環境庁大気保全局大気生活環境室編集臭覚測定法マニュアル(排出水資料編)に準じ三点比較式フラスコ法により臭気濃度を測定した。
<汚染性>
ホースに塩素水(0.3%塩素水を水で希釈)200ppmを封入し、80℃の雰囲気中に200h放置後、封入液の変色を観察した。また、その後ホースを2つ割にして、ホース内面を綿棒にてふきとり付着物の色を観察した。
<最小曲げ半径>
ホースを折り曲げたとき外径変化率が10%となる曲げ半径を最小曲げ半径として求めた。外径変化率(%)は、次の式により求めた。
外径変化率(%)=(初期のホース外径-折り曲げ後のホース外径)/初期のホース外径×100
<加速試験>
ホースを継手金具に組み付け80℃または100℃雰囲気中でエアーにて0.3MPaにて加圧し、漏れ等の異常の発生する時間を求めた。
<ツイン接着性>
2本のホースを並列に配し溶着によりツイン管とし、2本のホースを引き裂くのに必要な荷重(接着力)を求めた。
測定結果を表3に示す。
The following various tests were performed on Examples 9 and 10 and Comparative Examples 3 and 4.
<Odor>
Purified water is sealed in a 10m hose, left in an atmosphere at 80 ° C for 24 hours, and then the liquid is collected and compared in three points according to the Manual for Odor Measurement Method (Air Discharge Data) edited by the Air Quality Environment Office of the Environment Agency. The odor concentration was measured by the formula flask method.
<Contamination>
200 ppm of chlorinated water (0.3% chlorinated water diluted with water) was sealed in the hose, and after being left in an atmosphere at 80 ° C. for 200 hours, discoloration of the sealed solution was observed. Further, the hose was divided into two, and the inner surface of the hose was wiped off with a cotton swab to observe the color of the deposit.
<Minimum bending radius>
The bending radius at which the rate of change in outer diameter was 10% when the hose was bent was determined as the minimum bending radius. The outer diameter change rate (%) was obtained by the following formula.
Rate of change in outer diameter (%) = (initial hose outer diameter−hose outer diameter after bending) / initial hose outer diameter × 100
<Acceleration test>
The hose was assembled to the fitting and pressurized at 0.3 MPa with air in an atmosphere of 80 ° C. or 100 ° C., and the time for occurrence of abnormality such as leakage was determined.
<Twin adhesion>
Two hoses were arranged in parallel to form a twin pipe by welding, and a load (adhesive force) necessary to tear the two hoses was determined.
Table 3 shows the measurement results.
実施例9、10は比較例3、4に比べて格段に臭気性(臭気濃度)に優れている。従って、得られたホースは、水または温水への臭いの移行が少なく実際に温水配管用ホースとして使用した場合、水または温水に臭いが移ることはほとんど無い。また、実施例9、10は比較例3、4に比べて汚染性に優れており、水道水など塩素を含む水または温水に使用した場合に、ホース内で水が滞留し塩素濃度が上昇した場合などを考慮しても色水(黒水)の発生がない。さらに、実施例9、10は、最小曲げ半径、加速試験においても良好な結果を示し、また内層および外層に使用する材料が低比重(0.96〜1.00)であることより、軽量化、柔軟性、耐熱性、耐久性および金具組付性に優れたホースである。 Examples 9 and 10 are much more excellent in odor (odor concentration) than Comparative Examples 3 and 4. Therefore, the obtained hose has little transfer of odor to water or hot water, and when it is actually used as a hose for hot water piping, the odor hardly transfers to water or hot water. In addition, Examples 9 and 10 were superior in contamination compared to Comparative Examples 3 and 4, and when used for water containing chlorine such as tap water or warm water, water stayed in the hose and the chlorine concentration increased. There is no generation of colored water (black water) even when considering the case. Furthermore, Examples 9 and 10 showed good results in the minimum bending radius and acceleration test, and the material used for the inner layer and the outer layer had a low specific gravity (0.96 to 1.00). It is a hose excellent in flexibility, heat resistance, durability, and metal fitting assembly.
また、上記結果から、実施例9、10は、ツイン管として使用するために十分なツイン接着力を有しており、外層に動的架橋オレフィン系熱可塑性エラストマー(TPV)を用いたことにより、溶着により2本または3本以上のホースを接合することが可能である。 In addition, from the above results, Examples 9 and 10 have sufficient twin adhesive strength to be used as a twin tube, and by using a dynamically crosslinked olefin-based thermoplastic elastomer (TPV) as an outer layer, It is possible to join two or more hoses by welding.
1:内層
2:補強糸層
3:外層
1: Inner layer 2: Reinforcement yarn layer 3: Outer layer
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005018091A JP2006207648A (en) | 2005-01-26 | 2005-01-26 | Liquid hose |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005018091A JP2006207648A (en) | 2005-01-26 | 2005-01-26 | Liquid hose |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006207648A true JP2006207648A (en) | 2006-08-10 |
Family
ID=36964747
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005018091A Pending JP2006207648A (en) | 2005-01-26 | 2005-01-26 | Liquid hose |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006207648A (en) |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013037972A (en) * | 2011-08-10 | 2013-02-21 | Suzuki Motor Corp | Water hose for fuel cell |
| DE202013104202U1 (en) * | 2013-09-16 | 2014-06-16 | Nikles Inter AG | Plastic hose |
| KR101485091B1 (en) * | 2013-08-09 | 2015-01-22 | 주식회사 한승켐 | Hose to transfer fluid |
| JP2015218741A (en) * | 2014-05-14 | 2015-12-07 | 積水化学工業株式会社 | Multilayer pipe |
| JP2018500510A (en) * | 2014-12-18 | 2018-01-11 | フィット エッセピア | Extensible flexible hose and its continuous production method and continuous production line |
| KR20180031343A (en) * | 2016-09-20 | 2018-03-28 | 주식회사 경신전선 | Insulation material |
| US20180347851A1 (en) * | 2015-06-23 | 2018-12-06 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Drain hose and air conditioner including the same |
| WO2020191393A1 (en) * | 2019-03-21 | 2020-09-24 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Pipe including a thermoplastic vulcanizate composition |
| CN112997033A (en) * | 2018-09-14 | 2021-06-18 | 埃克森美孚化学专利公司 | Thermoplastic vulcanizate composition, its preparation and use in flexible tubular pipes |
| IT202000032297A1 (en) * | 2020-12-23 | 2022-06-23 | Fitt Spa | RECYCLABLE REINFORCED FLEXIBLE HOSE |
| JP2024056946A (en) * | 2018-08-21 | 2024-04-23 | テーイー オートモーティブ(フルダブリュック) ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Multi-layer automotive temperature control tube |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62502851A (en) * | 1985-05-15 | 1987-11-12 | アルペ−プラスト クンストシユトツフフエルアルバイツング ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | water pipe for plant irrigation |
| JPH11336955A (en) * | 1998-05-22 | 1999-12-07 | Hatano Seisakusho:Kk | Paired hose |
| JP2000119536A (en) * | 1998-10-20 | 2000-04-25 | Sumitomo Rubber Ind Ltd | Thermoplastic elastomer composition and joint for piping using the same thermoplastic elastomer composition |
| JP2003049977A (en) * | 2001-08-06 | 2003-02-21 | Kakuichi Technical Service Kk | Water supply hose and water supply hose for washing machine |
| JP2004082413A (en) * | 2002-08-23 | 2004-03-18 | Tokai Rubber Ind Ltd | Spiral knitting hose |
| JP2004144180A (en) * | 2002-10-24 | 2004-05-20 | Bridgestone Corp | Hose having kink resistance |
-
2005
- 2005-01-26 JP JP2005018091A patent/JP2006207648A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62502851A (en) * | 1985-05-15 | 1987-11-12 | アルペ−プラスト クンストシユトツフフエルアルバイツング ゲゼルシヤフト ミツト ベシユレンクテル ハフツング | water pipe for plant irrigation |
| JPH11336955A (en) * | 1998-05-22 | 1999-12-07 | Hatano Seisakusho:Kk | Paired hose |
| JP2000119536A (en) * | 1998-10-20 | 2000-04-25 | Sumitomo Rubber Ind Ltd | Thermoplastic elastomer composition and joint for piping using the same thermoplastic elastomer composition |
| JP2003049977A (en) * | 2001-08-06 | 2003-02-21 | Kakuichi Technical Service Kk | Water supply hose and water supply hose for washing machine |
| JP2004082413A (en) * | 2002-08-23 | 2004-03-18 | Tokai Rubber Ind Ltd | Spiral knitting hose |
| JP2004144180A (en) * | 2002-10-24 | 2004-05-20 | Bridgestone Corp | Hose having kink resistance |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013037972A (en) * | 2011-08-10 | 2013-02-21 | Suzuki Motor Corp | Water hose for fuel cell |
| KR101485091B1 (en) * | 2013-08-09 | 2015-01-22 | 주식회사 한승켐 | Hose to transfer fluid |
| DE202013104202U1 (en) * | 2013-09-16 | 2014-06-16 | Nikles Inter AG | Plastic hose |
| JP2015218741A (en) * | 2014-05-14 | 2015-12-07 | 積水化学工業株式会社 | Multilayer pipe |
| JP2018500510A (en) * | 2014-12-18 | 2018-01-11 | フィット エッセピア | Extensible flexible hose and its continuous production method and continuous production line |
| US11287066B2 (en) | 2014-12-18 | 2022-03-29 | Fitt S.P.A. | Extensible flexible hose, and method and production line for continuously manufacturing thereof |
| US10359130B2 (en) | 2014-12-18 | 2019-07-23 | Fitt S.P.A. | Extensible flexible hose, and method and production line for continuously manufacturing thereof |
| US11118809B2 (en) * | 2015-06-23 | 2021-09-14 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Drain hose and air conditioner including the same |
| US20180347851A1 (en) * | 2015-06-23 | 2018-12-06 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Drain hose and air conditioner including the same |
| KR102023001B1 (en) | 2016-09-20 | 2019-09-20 | 주식회사 경신전선 | Insulation material |
| KR20180031343A (en) * | 2016-09-20 | 2018-03-28 | 주식회사 경신전선 | Insulation material |
| JP2024056946A (en) * | 2018-08-21 | 2024-04-23 | テーイー オートモーティブ(フルダブリュック) ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Multi-layer automotive temperature control tube |
| CN112997033A (en) * | 2018-09-14 | 2021-06-18 | 埃克森美孚化学专利公司 | Thermoplastic vulcanizate composition, its preparation and use in flexible tubular pipes |
| CN112997033B (en) * | 2018-09-14 | 2023-07-25 | 国际人造丝公司 | Thermoplastic vulcanizate composition, its preparation and use in flexible tubular pipes |
| WO2020191393A1 (en) * | 2019-03-21 | 2020-09-24 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Pipe including a thermoplastic vulcanizate composition |
| CN113748166A (en) * | 2019-03-21 | 2021-12-03 | 埃克森美孚化学专利公司 | Pipe comprising thermoplastic vulcanizate composition |
| IT202000032297A1 (en) * | 2020-12-23 | 2022-06-23 | Fitt Spa | RECYCLABLE REINFORCED FLEXIBLE HOSE |
| WO2022137119A1 (en) * | 2020-12-23 | 2022-06-30 | Fitt S.P.A. | Reinforced recyclable flexible hose |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2006207648A (en) | Liquid hose | |
| JPH01141047A (en) | Refrigerant transport hose | |
| US20250058533A1 (en) | Fiber reinforced composite materials, articles and related methods | |
| JP2012189129A (en) | Refrigerant transportation hose | |
| JP2020046047A (en) | Heat resistant flexible tube | |
| JP4815039B2 (en) | Water supply / hot water supply hose | |
| JP2010516496A (en) | Fluid transfer duct | |
| JP4618584B2 (en) | Fluid hose | |
| JP5611521B2 (en) | Hose and method of manufacturing hose | |
| JP2009228753A (en) | Flexible hose | |
| JP2005076849A (en) | Resin hose | |
| JP6857445B2 (en) | Hose and its manufacturing method | |
| JP2008137358A (en) | Hot water supply hose | |
| CA3001849C (en) | Fuel hose with rubber cover layer | |
| JP4267395B2 (en) | Water supply / hot water supply hose | |
| JP4587300B2 (en) | hose | |
| JPH01152061A (en) | Hose for transporting refrigerant | |
| JP2004144180A (en) | Hose having kink resistance | |
| JP2007190769A (en) | Hose for supplying water and hot water | |
| JP4587291B2 (en) | hose | |
| JP2006144875A (en) | Hose for water supply/hot water supply | |
| JP5255269B2 (en) | hose | |
| JP2019007605A (en) | Hose and manufacturing method of hose | |
| JPH09178058A (en) | Hose for supplying cold and hot water | |
| JP4898084B2 (en) | Water supply / hot water supply hose |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A625 | Written request for application examination (by other person) |
Effective date: 20071122 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A625 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20091216 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20091221 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Effective date: 20100412 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 |