JP2006186099A - Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave driving device - Google Patents
Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave driving device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2006186099A JP2006186099A JP2004377892A JP2004377892A JP2006186099A JP 2006186099 A JP2006186099 A JP 2006186099A JP 2004377892 A JP2004377892 A JP 2004377892A JP 2004377892 A JP2004377892 A JP 2004377892A JP 2006186099 A JP2006186099 A JP 2006186099A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- piezoelectric element
- laminated
- piezoelectric
- layers
- vibrating body
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 230000003534 oscillatory effect Effects 0.000 title abstract 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 31
- 239000007772 electrode material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 19
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 18
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 20
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 34
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 34
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 16
- 230000010287 polarization Effects 0.000 description 14
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000002123 temporal effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010304 firing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000012447 hatching Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003475 lamination Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003754 machining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007650 screen-printing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003854 Surface Print Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910010293 ceramic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002783 friction material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002452 interceptive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000010363 phase shift Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- General Electrical Machinery Utilizing Piezoelectricity, Electrostriction Or Magnetostriction (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、電気−機械エネルギ変換機能を有する複数の材料の層を積層した積層圧電素子及び振動波駆動装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a laminated piezoelectric element and a vibration wave driving device in which a plurality of layers of materials having an electro-mechanical energy conversion function are laminated.
従来、電気的エネルギを機械的エネルギに変換する電気−機械エネルギ変換機能を有する代表的な材料である圧電材料は、様々な圧電素子を構成する材料として多種多様に用いられている。特に、最近では、多数層の圧電素子を積層して一体化し焼結した積層圧電素子が使われている。これは、積層化によって、単一の板状の圧電体のみから構成される圧電素子と比較し、低い印加電圧で大きな変形歪や大きな力が得られるためである。 Conventionally, piezoelectric materials, which are representative materials having an electro-mechanical energy conversion function for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, are widely used as materials constituting various piezoelectric elements. In particular, recently, laminated piezoelectric elements obtained by laminating and sintering a large number of layers of piezoelectric elements have been used. This is because a large deformation strain and a large force can be obtained with a low applied voltage by stacking as compared with a piezoelectric element composed of only a single plate-like piezoelectric body.
例えば、振動波駆動装置としての振動波モータ、特に棒状に形成された振動波モータの振動体の一部を構成する積層電気−機械エネルギ変換素子としての積層圧電素子に関しては、各種の技術が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1、特許文献2、特許文献3参照)。また、振動波モータ以外の用途についても、積層圧電素子に関する技術が数多く提案されている。
For example, various technologies have been proposed for a laminated piezoelectric element as a laminated electro-mechanical energy conversion element that constitutes a part of a vibrating body of a vibration wave motor as a vibration wave drive device, particularly a vibration wave motor formed in a rod shape. (For example, see
上記のような積層圧電素子は、複数の圧電セラミックスからなる材料の層(以下圧電層と称する)と、各圧電層の表面に設けられ、電極材料で形成された電極材料の層(以下内部電極と称する)とから構成されており、圧電層と内部電極とを複数層重ねて積層化し、焼結後、分極処理を行い積層圧電素子全体が圧電性を有するようにしていた。即ち、積層圧電素子全体に複数の内部電極が配置され、圧電層は圧電性を有する圧電活性部となった積層圧電素子が一般的であった。 The laminated piezoelectric element as described above is composed of a plurality of piezoelectric ceramic material layers (hereinafter referred to as piezoelectric layers) and electrode material layers (hereinafter referred to as internal electrodes) formed on the surface of each piezoelectric layer. And a plurality of piezoelectric layers and internal electrodes are laminated and laminated, and after sintering, a polarization treatment is performed so that the entire laminated piezoelectric element has piezoelectricity. That is, a laminated piezoelectric element in which a plurality of internal electrodes are arranged over the entire laminated piezoelectric element and the piezoelectric layer is a piezoelectric active portion having piezoelectricity is generally used.
図10は、特許文献3に開示された棒状の振動波モータの振動体に用いられる積層圧電素子を示す分解斜視図及び斜視図である。
10 is an exploded perspective view and a perspective view showing a laminated piezoelectric element used in a vibrating body of a rod-shaped vibration wave motor disclosed in
図10において、積層圧電素子40を構成する最上層の圧電層を除く複数の圧電層42の表面に、分割された内部電極43が設けられており、更に圧電層42の表面には、各内部電極43と接続されて圧電層42の外縁部まで延びる接続電極43a(図中黒色に塗りつぶしている部分)がそれぞれ形成されている。内部電極43は、外周が圧電層42の外周よりも内周側となるように配置されると共に、4分割(AG、AG、BG、BG、または、A+、A−、B+、B−)に形成されており、各内部電極43は互いに非導通となっている。
In FIG. 10, divided
接続電極43aは、内部電極43に対して、圧電層42の一層おきに積層圧電素子40の軸方向で同一位相位置となるように形成されている。同一位相位置同士の接続電極43aは、積層圧電素子40の外周部に設けられた層間の導通を図る電極である外部電極44により接続されている。
The
積層圧電素子40を構成する最上層の圧電層表面の外周部周辺には、周方向に沿って複数の表面電極45が設けられており、接続電極43aの位相位置に合わせて設けられた外部電極44と接続されている。そして、この表面電極45を介して各内部電極43に直流電圧を印加し、後述の振動波モータの駆動が可能な分極極性になるように分極処理を行う。
A plurality of
更に、図11は、上記図10に示した積層圧電素子40を棒状の振動波モータ50の振動体51に組み込んだ例を示す断面図である。
Further, FIG. 11 is a cross-sectional view showing an example in which the laminated
図11において、中央部に貫通孔を有する積層圧電素子40は、表面電極45が回路基板52と接触すると共に、振動体51を構成する中空の金属部材53と金属部材54の間に配置されている。ボルト55を金属部材53側から挿入して金属部材54にねじ込むことにより、金属部材53と金属部材54の間に積層圧電素子40と回路基板52が挟持固定される。回路基板52は、積層圧電素子40の外部電極44に接続された表面電極45と不図示の駆動回路に接続され、駆動用の高周波電圧が積層圧電素子40に印加される。
In FIG. 11, the laminated
振動体51の軸方向一方の側には、ばね56とばね支持体57を介して、金属部材54の先端部と加圧接触するロータ58が配置されており、ロータ58と一体となり回転するギヤ59により振動波モータ50の回転出力を取り出すことができる。
On one side in the axial direction of the vibrating
棒状の振動波モータ50の駆動原理は、積層圧電素子40を組み込んだ振動体51の軸方向に対して直交する2つの曲げ振動を、時間的位相差を有して発生させ、振動体51を構成する金属部材54の先端部を駆動部として、金属部材54が首振りのような運動を行い、この金属部材54に加圧接触する接触部材であるロータ58が摩擦接触により回転することにある。
The drive principle of the rod-shaped
また、直線(リニア)駆動する振動波モータとして、従来、平板状の振動体を用いるものが提案されている(例えば、特許文献4、特許文献5参照)。
Conventionally, as a vibration wave motor for linear driving, one using a plate-like vibrating body has been proposed (see, for example,
図12は、リニア駆動する振動波モータの構成を示す図であり、(a)は正面図、(b)は右側面図、(c)は平面図である。 12A and 12B are diagrams showing a configuration of a vibration wave motor that is linearly driven. FIG. 12A is a front view, FIG. 12B is a right side view, and FIG. 12C is a plan view.
図12において、振動体の一部を構成する金属製の弾性体61の一方の面には、縦振動と曲げ振動を同時に発生させる2つの圧電素子62、63が配置されている。また、弾性体61の他方の面には、2つの突起部64、65が形成されている。2つの圧電素子62、63は、接着剤により弾性体61に接着されている。
In FIG. 12, two
2つの圧電素子62、圧電素子63にそれぞれ高周波電圧A、高周波電圧Bを印加して、2つの複合振動を合成することで、突起部64、65の先端に楕円または円運動を発生させることができる。また、2つの圧電素子62、63は、互いに極性は同一方向になるように分極され、上記の高周波電圧A、高周波電圧Bは、90度の時間的な位相差を有している。
By applying the high frequency voltage A and the high frequency voltage B to the two
この結果、突起部64、65の先端を固定部66に対し加圧接触させると、振動体の一部を構成する弾性体61は固定部66に対し自走する。即ち、振動体に対して他の部材を加圧接触することで振動体との間に相対移動運動が形成され、リニア駆動が可能な振動波モータになる。ただし、この例では、圧電素子62、63は単一の板状の素子であり、積層圧電素子ではない。
上述した振動波モータは、今後、小型化や高効率化による高出力化と製造コストの低減が要求されている。 In the future, the above-described vibration wave motor is required to have a higher output and a reduced manufacturing cost due to downsizing and higher efficiency.
しかしながら、上記図11に示した棒状の振動波モータのように積層圧電素子40を金属部材間に挟持する方式や、上記図12に示したリニア駆動の振動波モータのように金属部品に圧電素子を接着した方式でも、部品点数が複数あり部品の形状も複雑である。そのため、組み立てた振動体は各部品の加工誤差が積み重なり、組み立て後の寸法と設計時の寸法との誤差が大きくなる。また、組み立てた振動体の各部品の界面や接着面での振動減衰も生じる。これらの結果、従来の振動波モータは設計時の予想よりもモータ性能の低下が起りやすいという問題があった。
However, the laminated
更に、複雑な形状の部品点数が多いことや、それらの部品の組み立てにも時間がかかるため、振動波モータの製造コストが高いことの本質的な原因となっていた。 Furthermore, since the number of parts having a complicated shape is large and it takes time to assemble these parts, it is an essential cause of the high manufacturing cost of the vibration wave motor.
本発明の目的は、基本的に圧電素子で振動体を形成することで、振動波駆動装置の性能の向上を図ると共に、小型化を容易にし製造コストの低減を可能とした積層圧電素子及び振動波駆動装置を提供することにある。 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION An object of the present invention is to provide a multilayer piezoelectric element and a vibration which can improve the performance of a vibration wave driving device by forming a vibrating body basically by a piezoelectric element, and can be easily reduced in size and reduced in manufacturing cost. It is in providing a wave drive device.
上述の目的を達成するために、本発明の積層圧電素子は、複数の層から構成される積層圧電素子であり、電気量を機械量に変換する変換機能を有する材料の層と複数に分割された電極材料の層とを複数層重ねた圧電活性部と、前記変換機能を有する材料の層を複数層重ねた圧電不活性部とを積層して一体化し、前記圧電活性部の端面の材料の層の表面に、電極材料の層を設けたことを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above-described object, the multilayer piezoelectric element of the present invention is a multilayer piezoelectric element composed of a plurality of layers, and is divided into a material layer having a conversion function for converting an electrical quantity into a mechanical quantity and a plurality of layers. A piezoelectric active portion in which a plurality of electrode material layers are stacked and a piezoelectric inactive portion in which a plurality of layers having the conversion function are stacked are stacked and integrated, and the material of the end face of the piezoelectric active portion is integrated. An electrode material layer is provided on the surface of the layer.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記圧電不活性部の厚さを前記積層圧電素子に複数の振動を発生可能な厚さとすることを特徴とする。 In the multilayer piezoelectric element of the present invention, the thickness of the piezoelectric inactive portion is set to a thickness capable of generating a plurality of vibrations in the multilayer piezoelectric element.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記圧電不活性部のみが前記振動の変位を拡大するための凹部または凸部を有することを特徴とする。 In the laminated piezoelectric element of the present invention, only the piezoelectric inactive portion has a concave portion or a convex portion for expanding the displacement of the vibration.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記電極材料の層に接続される回路基板を介して電力の供給を受けることを特徴とする。 The multilayered piezoelectric element of the present invention is characterized in that power is supplied through a circuit board connected to the electrode material layer.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記積層圧電素子を円筒形状とし、前記圧電活性部の積層方向に前記圧電不活性部を積層して一体化したことを特徴とする。 The laminated piezoelectric element of the present invention is characterized in that the laminated piezoelectric element has a cylindrical shape and is integrated by laminating the piezoelectric inactive part in the laminating direction of the piezoelectric active part.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記複数の振動は、前記積層圧電素子の積層方向に交差する少なくとも2つの曲げ振動であることを特徴とする。 The multilayer piezoelectric element of the present invention is characterized in that the plurality of vibrations are at least two bending vibrations intersecting a lamination direction of the multilayer piezoelectric element.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記積層圧電素子を平板形状とし、前記圧電活性部の積層方向の一方の側に前記圧電不活性部を積層して一体化したことを特徴とする。 The laminated piezoelectric element of the present invention is characterized in that the laminated piezoelectric element has a flat plate shape, and the piezoelectric inactive part is laminated and integrated on one side in the lamination direction of the piezoelectric active part.
また、前記圧電活性部の端面の材料の層の一部が、その表面に設けられた電極材料の層により分極処理されていることを特徴とする。 Further, a part of the material layer of the end face of the piezoelectric active part is polarized by an electrode material layer provided on the surface thereof.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記圧電不活性部の一部に凸部を形成したことを特徴とする。 The multilayer piezoelectric element of the present invention is characterized in that a convex portion is formed on a part of the piezoelectric inactive portion.
また、本発明の積層圧電素子は、前記複数の振動は、2つの曲げ振動であることを特徴とする。 In the multilayer piezoelectric element of the present invention, the plurality of vibrations are two bending vibrations.
上述の目的を達成するために、本発明の振動波駆動装置は、前記請求項1乃至6の何れかに記載の積層圧電素子を備え、前記積層圧電素子を振動体とし、前記振動体に加圧接触する接触体を回転させることを特徴とする。
In order to achieve the above object, a vibration wave driving device of the present invention comprises the multilayered piezoelectric element according to any one of
また、本発明の振動波駆動装置は、前記請求項1、2、7乃至10の何れかに記載の積層圧電素子を備え、前記積層圧電素子を振動体とし、前記振動体と前記振動体に加圧接触する接触体とを相対的に移動させることを特徴とする。 According to another aspect of the present invention, there is provided a vibration wave driving device including the multilayered piezoelectric element according to any one of the first, second, and seventh to tenth aspects, wherein the multilayered piezoelectric element is a vibrating body. It is characterized by relatively moving the contact body in pressure contact.
更に、本発明の積層圧電素子は、円筒形状の前記積層圧電素子を構成する前記圧電不活性部の外周部を周方向に沿って研削することで凹部を形成する構成としてもよい。 Furthermore, the multilayer piezoelectric element of the present invention may be configured such that a concave portion is formed by grinding an outer peripheral portion of the piezoelectric inactive portion constituting the cylindrical multilayer piezoelectric element along a circumferential direction.
更に、本発明の積層圧電素子は、平板形状の前記積層圧電素子を構成する前記圧電不活性部における前記圧電活性部との積層面とは反対側の面を研削することで複数の凸部を形成する構成としてもよい。 Furthermore, the multilayered piezoelectric element of the present invention has a plurality of convex portions by grinding a surface of the piezoelectric inactive part constituting the flat plate-shaped multilayered piezoelectric element opposite to the layered surface with the piezoelectric active part. It is good also as a structure to form.
更に、本発明の振動波駆動装置は、前記振動体と前記接触体との間に耐磨耗性を有する材料からなる部材を配設する構成としてもよい。 Furthermore, the vibration wave driving device of the present invention may be configured such that a member made of a material having wear resistance is disposed between the vibrating body and the contact body.
また、上述の目的を達成するために、本発明の振動型駆動装置は、振動体に振動を発生させ、前記振動体に加圧接触する接触体を回転させる振動波駆動装置において、前記振動体が電気量を機械量に変換する変換機能を有する材料の層と複数に分割された電極材料の層とを複数層重ねた圧電活性部と、前記変換機能を有する材料の層を少なくとも一層または複数層重ねた圧電不活性部とを積層して一体化した積層圧電素子で構成され、前記積層圧電素子の端面の表面に電極材料の層が設けられ、前記接触体が前記圧電不活性部に加圧接触することを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above-mentioned object, the vibration type driving device of the present invention is a vibration wave driving device that generates vibration in a vibrating body and rotates a contact body that is in pressure contact with the vibrating body. Includes a piezoelectric active portion in which a plurality of layers of a material having a conversion function for converting an electrical quantity into a mechanical quantity and a plurality of electrode material layers divided into a plurality of layers, and at least one or a plurality of layers of the material having the conversion function. It is composed of laminated piezoelectric elements that are laminated and integrated with a layered piezoelectric inactive part, and an electrode material layer is provided on the surface of the end face of the laminated piezoelectric element, and the contact body is added to the piezoelectric inactive part. It is characterized by pressure contact.
本発明によれば、圧電活性部と圧電不活性部とを積層して一体化しているため、積層圧電素子自体で振動体を構成し複数の振動モードを発生させることが可能となる。 According to the present invention, since the piezoelectric active part and the piezoelectric inactive part are laminated and integrated, it is possible to form a vibrating body with the laminated piezoelectric element itself and generate a plurality of vibration modes.
この結果、従来のような積層圧電素子を挟持固定するための金属部材を減らすことができ、また、圧電素子に複雑な形状の金属部材を接着剤で接着することも不要となる。 As a result, the number of metal members for sandwiching and fixing the conventional laminated piezoelectric element can be reduced, and it is not necessary to bond a complicated-shaped metal member to the piezoelectric element with an adhesive.
これにより、振動波駆動装置の性能の向上が可能であり、更に、部品点数は少なく、組立ても単純で済み、振動波駆動装置の製造コストの低減も可能となる。即ち、振動波駆動装置の性能の向上のみならず、振動波駆動装置の製造工程の短縮を図ることができると共に、部品点数及び製造コストの低減も可能となる。また、振動波駆動装置の小型化が可能となる。 As a result, the performance of the vibration wave driving device can be improved, the number of parts is small, and the assembly is simple, and the manufacturing cost of the vibration wave driving device can be reduced. That is, not only the performance of the vibration wave driving device can be improved, but also the manufacturing process of the vibration wave driving device can be shortened, and the number of parts and the manufacturing cost can be reduced. In addition, the vibration wave driving device can be reduced in size.
また、積層圧電素子の圧電活性部の端面の材料の層の表面に電極材料の層を設けているため、積層圧電素子に電極材料の層を介して電力を供給するための回路基板との導通が容易になると共に、複数の振動を積層圧電素子それ自体で効率的に起こすことが可能となる。 In addition, since the electrode material layer is provided on the surface of the material layer at the end face of the piezoelectric active portion of the multilayer piezoelectric element, conduction to the circuit board for supplying power to the multilayer piezoelectric element through the electrode material layer is provided. As a result, a plurality of vibrations can be efficiently generated by the laminated piezoelectric element itself.
また、圧電材料は金属に比べ機械加工性が良く、微細加工も容易に行うことができるため、圧電不活性部の一部に凸部や凹部を加工することで、小寸法でも高精度な振動体を形成することができる。 In addition, the piezoelectric material has better machinability than metal and can be easily micro-processed. Therefore, high-precision vibration can be achieved even in small dimensions by machining convex portions and concave portions in part of the piezoelectric inactive portion. The body can be formed.
また、積層圧電素子の圧電活性部の端面の材料の層の一部が、その表面に設けられた電極材料の層により分極処理されているため、積層圧電素子において曲げ振動を低電圧で大きな振幅で効率的に発生させることが可能となる。 In addition, since a part of the material layer of the end surface of the piezoelectric active portion of the multilayer piezoelectric element is polarized by the electrode material layer provided on the surface, bending vibration is generated at a low voltage and a large amplitude in the multilayer piezoelectric element. Can be generated efficiently.
以下、本発明の実施の形態を図面に基づき説明する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
[第1の実施の形態]
図1は、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係る積層電気−機械エネルギ変換素子である積層圧電素子の構成を示す図であり、軸線Lから右半分は断面図、軸線Lから左半分は外観図である。図2は、積層圧電素子の製造の途中段階を示すと共にその積層構造を示す斜視図である。尚、以下では製造途中段階の積層圧電素子と製造後の積層圧電素子には便宜上同じ符号を付すものとする。
[First Embodiment]
FIG. 1 is a diagram showing a configuration of a laminated piezoelectric element that is a laminated electro-mechanical energy conversion element according to a first embodiment of the present invention, in which the right half from the axis L is a sectional view and the left half from the axis L is It is an external view. FIG. 2 is a perspective view showing an intermediate stage of manufacturing the laminated piezoelectric element and showing the laminated structure. In the following description, the laminated piezoelectric element in the middle of manufacturing and the laminated piezoelectric element after manufacturing are given the same reference for convenience.
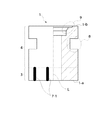
図1及び図2において、積層圧電素子1は、中央部に貫通孔が形成された円筒状の形状を有するものであり、電気的エネルギ(電気量)を機械的エネルギ(機械量)に変換する電気−機械エネルギ変換機能を有する材料の層と複数に分割された電極材料の層とを複数層重ねた圧電性を有する圧電活性部3と、圧電活性部3の軸方向に配設され、電気−機械エネルギ変換機能を有する材料の層だけを複数層重ねた圧電性を有しない圧電不活性部4とから構成されている。
1 and 2, the laminated
圧電活性部3は、複数の圧電層5から構成されている。複数の圧電層5の表面には、4分割(A+、A−、B+、B−)された内部電極6−1、4分割(AG、AG、BG、BG)された内部電極6−2がそれぞれ形成されると共に、各内部電極6−1、6−2と接続されて圧電層5の外縁部まで延びる接続電極6a(図中黒色に塗りつぶしている部分)がそれぞれ形成されている。各内部電極6−1における接続電極6aは、それぞれ積層圧電素子1の軸方向で同一位相位置に形成され、各内部電極6−2における接続電極6aは、それぞれ積層圧電素子1の軸方向で同一位相位置に形成されている。
The piezoelectric
更に、積層圧電素子1の軸方向で同一位相位置に位置する接続電極6aは、積層圧電素子1の外周部に配設された層間の導通を図る外部電極7−1により接続されている。外部電極7−1は、積層圧電素子1の軸方向で同位相位置に位置する接続電極6a毎に、積層圧電素子1の周方向に沿った状態で例えば8本形成されている。
Further, the
圧電活性部3の各内部電極6−1は、従来例と同様に、4分割された内部電極A+、A−、B+、B−から構成されており、圧電活性部3の各内部電極6−2は、4分割された内部電極AG、AG、BG、BGから構成されている。内部電極A+、A−、B+、B−と、内部電極AG、AG、BG、BGは、積層圧電素子1の軸方向で対向している。そして、圧電活性部3は、第1層から最終層まで、内部電極6−2、6−1を形成した圧電層5を交互に積層している。
Each internal electrode 6-1 of the piezoelectric
他方、圧電不活性部4は、内部電極の無い少なくとも1層以上の一体化された圧電層5から構成されている。圧電不活性部4の厚さは、積層圧電素子1の軸方向に直交する2つの曲げ振動を発生させることが可能な厚さに設定されている。この場合、圧電不活性部4の厚さが薄いと、曲げ振動を発生させることができない。
On the other hand, the piezoelectric
更に、積層圧電素子1の端面1−aの表面には、周方向に沿って複数の表面電極7−2が形成されており、それぞれの外部電極7−1と導通している。
Further, a plurality of surface electrodes 7-2 are formed along the circumferential direction on the surface of the end face 1-a of the multilayer
ここで、本実施の形態の積層圧電素子1は、例えば、外径が約10mm、内径が約2.8mm、長さが約8mmであり、圧電活性部3の圧電層5の厚さは約90μm、内部電極6−1、6−2の厚さは約2〜3μmで、内部電極の層数は25層とした。また、外部電極7−1の長さは約2mm、幅は約1mm、厚さは約0.05mmとし、圧電不活性部4の圧電層5の厚さは同様に約90μmとした。ただし、圧電不活性部4は、寸法のより厚い層を重ねることで層数を少なくするようにしても良い。また、本実施の形態では、積層圧電素子1の軸方向に直交する2つの曲げ振動を発生させることが可能な厚さであれば、端面1−aの最終層の厚さも厚い層を用いても良いし、複数の層を重ねても良い。
Here, the laminated
積層圧電素子1は、圧電層5となる圧電セラミックス粉末と有機バインダからなり、一定寸法の形状(例えば縦横約13mmの四角形)に切り出したグリーンシートを使用することで、以下の製造方法で製造される。
The laminated
最初に、図2に示すように、積層圧電素子1を構成する圧電不活性部4は、グリーンシートだけを所定枚数重ね、積層圧電素子1を構成する圧電活性部3は、内部電極6−1、6−2のパターンを銀・パラジウム粉末ペーストを用いてグリーンシート上にスクリーン印刷で形成し、該スクリーン印刷したグリーンシートの所定の枚数を順に重ね、これらを加熱しながら加圧して積層化し一体化する。
First, as shown in FIG. 2, the piezoelectric
次に、図2に示すように、上記積層化した積層圧電素子1に対し、ドリル加工により、積層圧電素子1の内径に相当する位置に貫通孔を開け、その後、所定温度(例えば1100〜1200度C)の鉛雰囲気で焼成する。焼成後、両面のラップ加工を行い、積層圧電素子1の両端面を平滑化する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 2, the laminated
次に、図1及び図2に示すように、積層圧電素子1の外径を、研削加工により円筒状に研削し、積層圧電素子1の外周部に接続電極6aを露出させる。その後、円筒形表面印刷用のスクリーン印刷機を使用し、積層圧電素子1の外周部の接続電極6aが露出した8個所に外部電極7−1を印刷し乾燥させる。更に、表面電極7−2を外部電極7−1と導通する位置に印刷し乾燥させる。印刷後は、所定温度(例えば約750度C)で加熱し、積層圧電素子1の外周部の外部電極7−1と表面電極7−2を焼き付ける。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 1 and 2, the outer diameter of the multilayer
次に、図1に示すように、圧電不活性部4の外周部に対し、機械(研削)加工により外周方向に沿って削ることで、環状の凹み部8(凹部)を形成し、また、積層圧電素子1の軸方向一方の端面1−b側の圧電不活性部4から内径を一部拡大するように削ることで、凸部9を形成する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 1, an annular recess 8 (recess) is formed on the outer periphery of the piezoelectric
ここで、凹み部8は、振動変位の拡大を目的として形成される。凹み部8を形成した部分は剛性的に弱い部分となるため、凹み部8より上の部分が振動しやすくなる。また、凸部9は、積層圧電素子1におけるロータ18(図3参照)と加圧接触する端面に部材(例えば耐摩耗性の良好な金属やセラミックス)を配設する際の位置決め用として形成される。なお、本実施の形態では振動子の振動変位の拡大を目的として凹み部8を形成したが、振動子の端部に凸部を形成し、端部の質量を増加させることによって、凸部を形成した部分が振動しやすくなるように構成してもよい。
Here, the
最後に、図2に示すように、内部電極6−1、6−2における4分割した各電極(A+、A−、B+、B−、AG、AG、BG、BG)に対し、特定の分極方向に分極処理を行う。具体的には、8本の外部電極7−1に金属コンタクトピンを押し当て、所定温度(例えば100〜150度C)のオイル中で、AG、BGをグランド(G)とし、内部電極A+、B+をプラス(+)とし、内部電極A−、B−をマイナス(-)として、それぞれ所定電圧(例えば300V)を印加して、約10分〜30分かけて分極処理を行う。 Finally, as shown in FIG. 2, a specific polarization is applied to each of the four divided electrodes (A +, A−, B +, B−, AG, AG, BG, BG) in the internal electrodes 6-1 and 6-2. Polarize in the direction. Specifically, metal contact pins are pressed against the eight external electrodes 7-1, AG and BG are grounded (G) in oil at a predetermined temperature (for example, 100 to 150 degrees C), and the internal electrodes A +, A predetermined voltage (for example, 300 V) is applied with B + as plus (+) and internal electrodes A− and B− as minus (−), respectively, and polarization is performed for about 10 to 30 minutes.
この結果、積層圧電素子1は、図2に示すように、電気的なグランドに相当する内部電極AG、BG、AG、BGに対し、内部電極A+、B+が(+)の極性に、内部電極A−、B−が(-)の極性に、異なるように分極される。
As a result, as shown in FIG. 2, the laminated
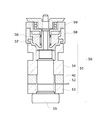
図3は、積層圧電素子1を組み込んだ棒状の振動波モータ11の構成を示す断面図である。
FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view showing a configuration of a rod-shaped
図3において、振動波モータ11(振動波駆動装置)は、積層圧電素子1を振動体10として用いている。振動体10は、ボルト12を積層圧電素子1の内径部に挿入し、ボルト12のフランジ部13とナット14−1と金属のリング状の部品14−2により積層圧電素子1を挟持し固定することで構成されている。ボルト12のフランジ部13の上側には、振動波モータ11の上部構造であるロータ部が配設されている。ロータ部は、ばね16とばね支持体17を介して振動体10の端面に加圧接触したロータ18(接触体)と、ギヤ19を備えている。ロータ18は、ギヤ19と一体に構成されており、ロータ18の回転をギヤ19から取り出すことができる。
In FIG. 3, the vibration wave motor 11 (vibration wave driving device) uses the laminated
他方、振動体10としての積層圧電素子1の端面1−aに形成された表面電極7−2(図2参照)には、回路基板15が接続され、回路基板15により表面電極7−2と駆動回路(不図示)とを電気的に接続している。端面1−aに形成された表面電極7−2により回路基板15との導通が容易で、上記のようにボルト12のフランジ部13とナット14−1と金属のリング状の部品14−2により積層圧電素子1を挟持し固定することで、信頼性も向上させることができる。尚、回路基板15は、フレキシブル基板とする構造、板状の硬い回路基板とする構造のどちらでも良い。
On the other hand, a
振動波モータ11の実際の駆動は、振動体10としての積層圧電素子1における上述の極性を有すると共に、積層圧電素子1の径方向で対向する位置関係(AGとAG、BGとBG、A+とA−、B+とB−)にある2つの内部電極において、AG相、BG相はグランドとし、A+、A−をA相とし、B+、B−をB相として、A相に振動体10の固有振動数とほぼ一致した高周波電圧を印加し、B相にはA相と位相が90度異なる高周波電圧を印加することにより行う。
The actual drive of the
上記の高周波電圧の印加により、積層圧電素子1を構成する圧電活性部3のA+、A−が交互に厚み方向で伸縮し、同様に、圧電活性部3のB+、B−も厚み方向で伸縮する。圧電活性部3の伸縮動作を、該圧電活性部3の軸方向両側に積層され一体化された圧電不活性部4で曲げ振動に変えることにより、積層圧電素子1に対し、軸方向に直交する2つの曲げ振動を発生させることが可能となる。
By applying the high-frequency voltage, A + and A− of the piezoelectric
ここで、従来例の積層圧電素子40(図10参照)は、厚み方向での伸縮しかできないが、金属部材53と金属部材54により積層圧電素子40を挟持固定することで振動体51を構成することにより、2つの曲げ振動を発生させていた(尚、積層圧電素子40は、絶縁のために最上層と最下層の1層分は分極されていない圧電不活性層を有しているが、この層は薄いので厚み方向での1つの振動(伸縮)しかできない)。
Here, the multilayer
これに対し、本実施の形態の積層圧電素子1は、従来例のように金属部材54で積層圧電素子を挟持固定する代わりに、圧電不活性部4を圧電活性部3に積層し一体化しているので、棒状の振動波モータ11を駆動するための上記2つの曲げ振動を発生させることが可能となる。この2つの曲げ振動は、振動体10としての積層圧電素子1の端面1−bを駆動部として首振り運動を行わせることができ、この駆動部に加圧接触するロータ18は摩擦により回転する。
On the other hand, in the laminated
尚、本実施の形態では、振動体10としての積層圧電素子1におけるロータ18と加圧接触する端面1−bには、耐摩耗性の良好な金属やセラミックスの小部品を配設することで、耐久性を向上させることも可能である。
In the present embodiment, a metal or ceramic small component with good wear resistance is disposed on the end surface 1-b in pressure contact with the
また、本実施の形態では、積層圧電素子1の圧電不活性部4の外周部に形成した振動変位拡大用の凹み部8の形状を環状とした場合を例に挙げたが、凹み部8の形状は、振動変位の拡大が可能な範囲で任意の形状とすることができる。
Further, in the present embodiment, the case where the shape of the
また、本実施の形態では、内部電極間の導通を外部電極により取る構成としているが、後述する第2の実施の形態のようにスルーホールで導通を取った表面電極を用いても良い。 In this embodiment, the external electrodes are electrically connected to each other by the external electrodes. However, surface electrodes that are electrically connected by through holes may be used as in the second embodiment to be described later.
以上説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、積層圧電素子1を、電気−機械エネルギ変換機能を有する材料の層と電極材料の層とを複数層重ねた圧電性を有する圧電活性部3と、電気−機械エネルギ変換機能を有する材料の層だけを複数層重ねた圧電性を有しない圧電不活性部4とから構成し、圧電不活性部4の厚さを、積層圧電素子1の軸方向に直交する2つの曲げ振動を発生可能な厚さに設定しているため、複数の振動モード(2つの曲げ振動のモード)を有することが可能となる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the laminated
また、積層圧電素子1の圧電活性部3の端面1−aに表面電極7−2を形成しているため、表面電極7−2により回路基板15との導通が容易となると共に、複数の振動を積層圧電素子それ自体で効率的に起こすことが可能となる。
Further, since the surface electrode 7-2 is formed on the end surface 1-a of the piezoelectric
また、振動波モータの性能を悪くしていた金属部材間の界面の振動減衰の原因を少なくすることができる結果、振動波モータの性能を向上させることが可能となる。 Moreover, as a result of reducing the cause of vibration attenuation at the interface between the metal members that has deteriorated the performance of the vibration wave motor, the performance of the vibration wave motor can be improved.
また、振動波モータの小型化も容易になり、振動波モータの性能の向上のみならず、振動波モータの製造工程の短縮を図ることができると共に、部品点数及びコストの低減も可能となる。 In addition, the vibration wave motor can be easily downsized, and not only the performance of the vibration wave motor can be improved, but also the manufacturing process of the vibration wave motor can be shortened, and the number of parts and the cost can be reduced.
また、積層圧電素子1を構成する圧電不活性部4の外周部を機械加工することで凹み部8を配設しているため、振動変位の拡大など設計仕様への対応や変更を的確に行うことができるばかりでなく、圧電材料は金属に比べ加工性が良く、微細加工も容易に行うことができる。また、積層圧電素子1の端面の表面電極と基板との導通は挟持し固定するので確実に行える。
Further, since the
上記のように、今後の新たな小型化及び高出力化を実現しようとする振動波モータにとって、性能面及び製造面における効果は大きい。 As described above, for vibration wave motors that intend to realize new miniaturization and higher output in the future, the effects in terms of performance and manufacturing are great.
[第2の実施の形態]
図4は、本発明の第2の実施の形態に係る積層圧電素子の構成を示す斜視図である。図5は、積層圧電素子の製造途中の段階を示すと共にその積層構造を示す斜視図である。尚、以下では製造途中段階の積層圧電素子と製造後の積層圧電素子には便宜上同じ符号を付すものとする。
[Second Embodiment]
FIG. 4 is a perspective view showing the configuration of the laminated piezoelectric element according to the second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 5 is a perspective view showing the laminated structure while showing the stage in the middle of manufacturing the laminated piezoelectric element. In the following description, the laminated piezoelectric element in the middle of manufacturing and the laminated piezoelectric element after manufacturing are given the same reference for convenience.
図5において、積層圧電素子2は、後述の研削加工前は平板状の形状を有するものであり、圧電活性部26と、圧電不活性部27−2から構成されている。圧電不活性部27−2は、一番上の第1層から第7層までが内部電極の無い圧電層22から構成されている。圧電活性部26は、第8層から最終層(最下層である第11層)までが、2分割された内部電極23−1、23−2が形成された圧電層22と、全面に内部電極23−3が形成された圧電層22とが交互に重なり積層化されることで構成されている。
In FIG. 5, the laminated
図5において、圧電活性部26と圧電不活性部27−2は、例えば同時に積層して一体化され焼成される。
In FIG. 5, the piezoelectric
各圧電層22における、2分割された内部電極23−1、23−2と、全面の内部電極23−3は、それぞれ、スルーホール24−1、24−2、24−3を介し独立して電気的に繋がれており、最下層の圧電層裏面に配設される3つに分割された表面電極25−1、25−2、25−3と導通している。そして、後述の分極処理を行い、各圧電層22には所定の分極極性を与えられる。
In each
図4に示すように、図5の圧電不活性部27−2を研削加工により削り出すことで、圧電不活性部27−1の上面には、2つの突起部21(凸部)が形成されている。加工後の圧電不活性部27−1の厚さは、積層圧電素子2において曲げ振動を発生させることが可能な厚さに設定されている。この場合、圧電不活性部27−1の厚さが薄いと、曲げ振動を発生させることができない。つまり、最終的に、振動体20は、圧電活性部26と圧電不活性部27−1、そして、2つの突起部21を備えた積層圧電素子2により構成されている。
As shown in FIG. 4, two projecting portions 21 (convex portions) are formed on the upper surface of the piezoelectric inactive portion 27-1 by grinding the piezoelectric inactive portion 27-2 in FIG. 5 by grinding. ing. The thickness of the piezoelectric inactive part 27-1 after processing is set to a thickness capable of generating bending vibration in the laminated
ここで、2つの突起部21は、振動変位の拡大を目的として形成される。ただし、2つの突起部21は積層圧電素子2と必ずしも同一の幅で角形状でなくても良い。これらは振動体の振動への影響や加工の容易さから決められる。
Here, the two
図6(a)は、図5に示した積層圧電素子2の長手方向の断面図であり、積層圧電素子に表面電極がある場合である。
FIG. 6A is a cross-sectional view in the longitudinal direction of the multilayer
図6(a)において、積層圧電素子2は、最上層の第1層(1)、第2層(2)、・・・最下層の第11層(11)の順に積層されており、内部電極23―1、23―2、23―3と、端面となる最下層の第11層(11)の表面電極25―1、25―2、25―3、そして、スルーホール24−1、24−2、24−3を備えている。斜線で示す内部電極23−1と内部電極23−3、内部電極23−2と内部電極23−3、内部電極23−3と表面電極25−1、内部電極23−3と表面電極25−2で挟まれた第8層(8)から第11層(11)までの領域は、分極処理され圧電活性化されている。
In FIG. 6A, the laminated
ここで、表面電極25−1、25−2は、内部電極23−1、23−2とほぼ同じ外形寸法である。つまり、表面電極25−1、25−2の形成された圧電層、即ち、積層圧電素子2の端面の最下層の第11層(11)(最終層)も、分極処理され圧電活性化されている。
Here, the surface electrodes 25-1 and 25-2 have substantially the same outer dimensions as the internal electrodes 23-1 and 23-2. That is, the piezoelectric layer on which the surface electrodes 25-1 and 25-2 are formed, that is, the lowermost eleventh layer (11) (final layer) on the end face of the laminated
このように、積層圧電素子2の最下層の第11層(11)が分極処理され圧電活性化されることで、伸縮できる層は斜線で示す第8層(8)から第11層(11)の4層となり、板状の積層圧電素子2においては、曲げ振動を低電圧で大きな振幅で効率的に発生させることが可能となった。
In this way, the eleventh layer (11), which is the lowermost layer of the multilayer
図6(b)は、図5に示した積層圧電素子2の長手方向の断面図であり、積層圧電素子に表面電極が無い場合である。
FIG. 6B is a longitudinal sectional view of the multilayer
図6(b)において、圧電活性部26´の分極活性化領域は、斜線で示す第8層(8)から第10層(10)の3層だけである。最終層(11´)は分極活性化されていないので、伸縮することはできず、また、逆に、この最終層(11´)は第8層(8)から第10層(10)の伸縮を拘束してしまう結果となっている。尚、従来は、表面電極は面積が小さく分極処理にだけ用いられ、その後、両面ラップ加工によって削り落とされていたので、最終層は活性領域としては用いることはなかった。
In FIG. 6B, the polarization activation region of the piezoelectric
また、本実施の形態では、図4及び図5に示すように、この表面電極を用いて、表面電極層25−1、25−2、25−3のそれぞれの端部の所定の位置に回路基板28を貼り付け導通を図ることで、駆動回路(不図示)との接続を容易に行うことができる。尚、回路基板28は、フレキシブル基板とする構造、板状の硬い回路基板とする構造のどちらでも良い。
Moreover, in this Embodiment, as shown in FIG.4 and FIG.5, using this surface electrode, it is a circuit in the predetermined position of each edge part of the surface electrode layers 25-1, 25-2, and 25-3. By attaching the
従来例と同様に、積層圧電素子2の内部電極23−1、23−2、23−3に例えば90度の時間的な位相差を有する高周波電圧を印加し、2つの曲げ振動を同時に発生させる。2つの曲げ振動からなる複合振動を合成することで、振動体20を構成する積層圧電素子2の圧電不活性部27−1の上の2つの突起部21の先端には、楕円運動または円運動を発生させることができる。
As in the conventional example, a high-frequency voltage having a temporal phase difference of 90 degrees, for example, is applied to the internal electrodes 23-1, 23-2, 23-3 of the multilayer
この結果、振動体20の突起部21の先端を固定部(不図示)に加圧接触させると、該先端に発生した楕円運動または円運動により、振動体20は固定部に対し自走する。従って、振動体20に対して他の部材(接触体)を加圧接触させることで、振動体20との間に相対移動運動が形成されるため、直線(リニア)駆動する振動波モータを構成することができる。
As a result, when the tip of the
尚、本実施の形態では、振動体20としての積層圧電素子2の圧電不活性部27−1の上の2つの突起部21における他の部材と加圧接触する端面には、極く薄い耐摩耗性の良好な金属やセラミックスを配設することで、耐久性を向上させることも可能である。
In the present embodiment, the end surfaces of the two projecting
ここで、本実施の形態の積層圧電素子2は、例えば、縦が20mm、幅が5mm、厚さが約0.44mmであり、圧電層22の厚さは40μm、内部電極の厚さは1〜2μmであり、また、スルーホールの径は0.1mmである。また、圧電不活性部27−2の圧電層22は、より厚いシートを用いて層数を少なくしても良い。
Here, in the laminated
積層圧電素子2の製造方法は、上記第1の実施の形態と基本的に同じであり、以下のような工程となる。
The manufacturing method of the laminated
最初に、内部電極を形成していないグリーンシートと内部電極を形成したグリーンシートとを積層して一体化し、その後、所定温度(例えば1100〜1200度C)の鉛雰囲気で焼成する。 First, a green sheet without an internal electrode and a green sheet with an internal electrode are laminated and integrated, and then fired in a lead atmosphere at a predetermined temperature (for example, 1100 to 1200 ° C.).
次に、図5に示すように、3本のスルーホールに繋がる表面電極25−1、25−2、25−3にそれぞれ金属コンタクトピンを押し当て、内部電極23−3と導通した表面電極25−3をグランド(G)とし、内部電極23−1、23−2にそれぞれ導通した表面電極25−1、25−2をプラス(+)として、所定温度(例えば100〜150度C)のオイル中で、所定電圧(例えば200V)を印加して、約10分〜30分かけて分極処理を行う。 Next, as shown in FIG. 5, a metal contact pin is pressed against each of the surface electrodes 25-1, 25-2, and 25-3 connected to the three through holes, and the surface electrode 25 electrically connected to the internal electrode 23-3. -3 is a ground (G), and surface electrodes 25-1 and 25-2 respectively conducted to the internal electrodes 23-1 and 23-2 are plus (+), and oil at a predetermined temperature (for example, 100 to 150 degrees C) In particular, a predetermined voltage (for example, 200 V) is applied, and the polarization process is performed for about 10 to 30 minutes.
最後に、上記の分極処理後、積層圧電素子2の圧電不活性部27−2側の片面だけラップ加工を行うことで積層圧電素子2の片面を平滑化し、図5に示す積層圧電素子2の圧電活性部27−2を研削加工し、図4に示すように圧電不活性部27−1の上に2つの凸部である突起部21を削り出す。
Finally, after the above-described polarization treatment, one surface of the multilayer
尚、本実施の形態では、積層圧電素子1の圧電不活性部27−1の上に形成した振動変位拡大用の突起部21の形状を直方体状とし配設数を2つとした場合を例に挙げたが、突起部21の形状及び配設数は、振動変位の拡大が可能な範囲で任意の形状及び任意の配設数とすることができる。
In the present embodiment, the case where the shape of the
また、本実施の形態では、内部電極間の導通をスルーホールにより取っているが、第1の実施の形態のように外部電極で導通を取った表面電極を用いても良い。 Further, in the present embodiment, the conduction between the internal electrodes is taken by the through-hole, but a surface electrode that is conducted by the external electrode as in the first embodiment may be used.
以上説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、従来は金属部材である弾性体と圧電素子の貼り合わせにより2つの曲げ振動を起こしていたが、積層圧電素子2として圧電活性部26に圧電不活性部27−2を積層し一体化すると共に、他の部材に加圧接触させるための突起部21を圧電不活性部27−2から削り出すことで形成しているため、積層圧電素子2だけで振動波モータの振動体20として使用することができ、2つの曲げ振動を同時に起こすことが可能となる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, conventionally, two bending vibrations are caused by bonding of an elastic body, which is a metal member, and a piezoelectric element. Since the inactive portion 27-2 is laminated and integrated, and the protruding
また、積層圧電素子2の最下層の第11層(11)に表面電極25−1、25−2を形成すると共に分極処理し圧電活性化することで、伸縮できる層は第8層(8)から第11層(11)の4層となり、板状の積層圧電素子2において曲げ振動を低電圧で大きな振幅で効率的に発生させることが可能となる。
In addition, the surface electrodes 25-1 and 25-2 are formed on the lowermost eleventh layer (11) of the laminated
また、積層圧電素子2の最下層の第11層(11)に表面電極25−1、25−2を配設することで、最下層の圧電層の分極のために、また、内部電極間の分極処理のための金属コンタクトピンの当たる導通部として、更に、モータ駆動時の電力供給のための回路基板との接続用の端子としての役割を果たすことができる。
Further, by disposing the surface electrodes 25-1 and 25-2 on the lowermost eleventh layer (11) of the laminated
また、従来のように、圧電素子と厚い金属部材との接着を行うことが不要となるため、振動波モータの性能を悪くしていた振動減衰の原因を取り除くことができる結果、振動減衰を非常に少なくすることが可能となり、振動波モータの性能を向上させることが可能となる。 In addition, since it is not necessary to bond the piezoelectric element and the thick metal member as in the conventional case, the cause of vibration attenuation that has deteriorated the performance of the vibration wave motor can be removed. Therefore, the performance of the vibration wave motor can be improved.
また、金属部材を使用することが不要となるため、振動波モータの小型化も容易になり、振動波モータの性能の向上のみならず、振動波モータの製造工程の短縮を図ることができると共に、部品点数及びコストの低減も図ることが可能となる。 Further, since it is not necessary to use a metal member, it is easy to reduce the size of the vibration wave motor, and not only the performance of the vibration wave motor can be improved, but also the manufacturing process of the vibration wave motor can be shortened. In addition, the number of parts and the cost can be reduced.
また、積層圧電素子2を構成する圧電不活性部27−2を研削加工することで突起部21を形成しているため、振動変位の拡大など設計仕様への対応や変更を的確に行うことができるばかりでなく、圧電材料は金属に比べ加工性が良く、微細加工も容易に行うことができる。
Further, since the projecting
[第3の実施の形態]
図7は、本発明の第3の実施の形態に係る積層圧電素子を使用した振動波モータの構成を示す斜視図である。
[Third Embodiment]
FIG. 7 is a perspective view showing a configuration of a vibration wave motor using the laminated piezoelectric element according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
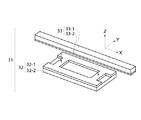
図7において、振動波モータ31は、上述した第2の実施の形態の図5に示した平板形状の積層圧電素子2を使用したリニア型の振動波モータである。振動波モータ31は、振動体32と、振動体32の接触部に加圧接触状態で保持されるスライダ33を備えている。超音波モータ31は、振動体32及びスライダ33の他に、振動体32と外部との電気的な接続を行う回路基板、振動体32の支持を行う支持部材、スライダ33のガイド部材、振動体32とスライダ33の間の加圧力を与える加圧機構等から構成される。
In FIG. 7, a
振動体32は、摩擦板32―1と積層圧電素子32―2から構成されている。振動体32は、スライダ33に対して図7に示すX方向への送り力を伝達する。スライダ33は、角棒状のスライダ基部33―1と板状の摩擦材33-2を接合して形成される。スライダ33は、振動体32から伝達される送り力により振動体32に対してX方向に相対運動を行う。
The vibrating
一方、振動体32の摩擦板32―1は、高摩擦係数と摩擦耐久性を兼ね備える材料から形成されており、本実施の形態ではSUS420J2の表面を窒化処理して所望の特性を得ることができた。加圧力を与える加圧機構等により振動体32とスライダ33とを加圧接触させることで、摩擦力を得ることができる。
On the other hand, the friction plate 32-1 of the vibrating
図8は、積層圧電素子からなる振動体32の構成を示す斜視図である。
FIG. 8 is a perspective view showing the configuration of the vibrating
図8において、振動体32は、極く薄い矩形平板状の摩擦板32−1を、上記図5に示した積層圧電素子2に相当する積層圧電素子32―2に接着等で貼り付けることにより構成されている。摩擦板32−1と積層圧電素子32―2は、X方向及びY方向の縁が略一致するように形状と位置が規定されている。振動体の長辺は20mm、短辺は5mm、厚さは0.6mmである。摩擦板32−1はSUS420J2の板材から加工され、厚さは最大0.16mmである。
In FIG. 8, a vibrating
摩擦板32−1の厚い個所は、2つの接触部32―1−aと2つの縁部32−1−bを構成している。これら接触部32−1−aと縁部32−1−bは同じ厚さ0.16mmであり表面は連続している。摩擦板32−1の他の部位は表面側から板厚が更に薄くなるように加工されており、摩擦板中央付近の薄板部32−1−c、単部付近の2つの薄板部32−1−dを構成している。 The thick portion of the friction plate 32-1 constitutes two contact portions 32-1-a and two edge portions 32-1-b. The contact portion 32-1-a and the edge portion 32-1-b have the same thickness of 0.16 mm and the surfaces are continuous. Other portions of the friction plate 32-1 are processed so that the plate thickness is further reduced from the surface side. The thin plate portion 32-1-c near the center of the friction plate and the two thin plate portions 32-1 near the single portion. -D.
これらの薄板部32−1−c、32−1−dは、板状の素材の表面側からエッチング処理により素材を除去することで形成される。薄板部32−1−c、32−1―dの厚さは0.05mmである。これらの薄板部32−1−c、32−1−dは、接触部32−1−aより凹むように構成されているので、薄板部32−1−c、32−1−dがスライダ33と干渉せずに、接触部32−1−aのみがスライダ33に当接することで、所望の送り力をスライダ33に伝達することができる。
These thin plate portions 32-1 -c and 32-1 -d are formed by removing the material from the surface side of the plate-shaped material by an etching process. The thickness of the thin plate portions 32-1-c and 32-1-d is 0.05 mm. Since the thin plate portions 32-1-c and 32-1-d are configured to be recessed from the contact portion 32-1-a, the thin plate portions 32-1-c and 32-1-d are the
積層圧電素子32−2は、上記図5に示した積層圧電素子2と同じであり、圧電活性部と圧電不活性部とから構成され、振動体32には第1及び第2の振動モードが互いの位相が略90度ずれて励起される。
The laminated piezoelectric element 32-2 is the same as the laminated
図9は、積層圧電素子からなる振動体32に励起される2つの振動モードを示す斜視図であり、(a)は第1の振動モードを示す図、(b)は第2の振動モードを示す図である。
FIG. 9 is a perspective view showing two vibration modes excited by a vibrating
図9において、これら2つの振動モードは板状の振動体32の面外曲げモードである。図9(a)に示す第1の振動モードは、図中X方向に節が生じる面外1次曲げモードであり、図9(b)に示す第2の振動モードは、図中Y方向に節が生じる面外2次曲げモードである。これら2つの振動モードは、共振周波数が略一致するように振動体の形状が設計されている。
In FIG. 9, these two vibration modes are out-of-plane bending modes of the plate-like vibrating
第1の振動モードが励起されているとき、2つの接触部32−1−aはZ方向の繰り返し上下運動を生じている。第2の振動モードが励起されているとき、2つの接触部32−1−aはX方向の繰り返し上下運動を生じている。第1の振動モードと第2の振動モードの時間的な位相を例えば90度ずれるように各々の振動モードの励起を行うと、接触部32−1−aはXZ面内で略楕円運動を生じる。この略楕円運動により、接触部32−1−aと加圧接触しているスライダ33はX方向への送り力を受けて、振動体32との間で相対移動運動を行うことができる。
When the first vibration mode is excited, the two contact portions 32-1-a repeatedly move up and down in the Z direction. When the second vibration mode is excited, the two contact portions 32-1-a repeatedly move up and down in the X direction. When excitation of each vibration mode is performed such that the temporal phases of the first vibration mode and the second vibration mode are shifted by 90 degrees, for example, the contact portion 32-1-a generates a substantially elliptical motion in the XZ plane. . By this substantially elliptical motion, the
以上説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、振動体32は積層圧電素子32−2を主体とし、その表面に薄い耐磨耗性を有する金属である摩擦板32−1を貼り付けた構成としているため、基本的に積層圧電素子32−2だけで上記の第1の振動モードと第2の振動モードを励起することが可能となる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the vibrating
1、2、32−2 積層圧電素子
1−a 端面
3、26 圧電活性部
4、27−1、27−2 圧電不活性部
5、22 圧電層
6−1、6−2、23−1、23−2、23−3 内部電極
7−1 外部電極
7−2、25−1、25−2、25−3 表面電極
8 凹み部
9 凸部
10、20、32 振動体
11、31 振動波モータ
15 回路基板
18 ロータ
21 突起部
24−1、24−2、24−3 スルーホール
33 スライダ
1, 2, 32-2 Multilayer piezoelectric element 1-a
Claims (13)
電気量を機械量に変換する変換機能を有する材料の層と複数に分割された電極材料の層とを複数層重ねた圧電活性部と、前記変換機能を有する材料の層を少なくとも一層又は複数層重ねた圧電不活性部とを積層して一体化し、
前記圧電活性部の端面の材料の層の表面に電極材料の層を設けたことを特徴とする積層圧電素子。 In a laminated piezoelectric element composed of a plurality of layers,
A piezoelectric active part in which a plurality of layers of a material having a conversion function for converting an electric quantity into a mechanical quantity and a plurality of electrode material layers divided into at least one layer or a plurality of layers of the material having a conversion function are stacked. Laminate and integrate the stacked piezoelectric inert parts,
A laminated piezoelectric element comprising an electrode material layer provided on a surface of a material layer at an end face of the piezoelectric active portion.
前記振動体が電気量を機械量に変換する変換機能を有する材料の層と複数に分割された電極材料の層とを複数層重ねた圧電活性部と、前記変換機能を有する材料の層を複数層重ねた圧電不活性部とを積層して一体化した積層圧電素子で構成され、前記積層圧電素子の端面の表面に電極材料の層が設けられ、前記接触体が前記圧電不活性部に加圧接触することを特徴とする振動波駆動装置。 In the vibration wave driving device that generates vibration in the vibrating body and rotates the contact body that is in pressure contact with the vibrating body,
The vibrator has a piezoelectric active portion in which a plurality of layers of a material having a conversion function for converting an electrical quantity into a mechanical quantity and a plurality of electrode material layers divided into a plurality of layers, and a plurality of layers of the material having a conversion function. It is composed of laminated piezoelectric elements that are laminated and integrated with a layered piezoelectric inactive part, and an electrode material layer is provided on the surface of the end face of the laminated piezoelectric element, and the contact body is added to the piezoelectric inactive part. A vibration wave drive device characterized by pressure contact.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004377892A JP2006186099A (en) | 2004-12-27 | 2004-12-27 | Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave driving device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004377892A JP2006186099A (en) | 2004-12-27 | 2004-12-27 | Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave driving device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006186099A true JP2006186099A (en) | 2006-07-13 |
| JP2006186099A5 JP2006186099A5 (en) | 2008-02-21 |
Family
ID=36738995
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004377892A Pending JP2006186099A (en) | 2004-12-27 | 2004-12-27 | Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave driving device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2006186099A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008253069A (en) * | 2007-03-30 | 2008-10-16 | Canon Inc | Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave drive device |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05175567A (en) * | 1991-12-20 | 1993-07-13 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Laminated actuator |
| JPH11220893A (en) * | 1997-11-27 | 1999-08-10 | Canon Inc | Vibration-type actuator and vibration-type drive unit |
| JP2000156988A (en) * | 1998-09-18 | 2000-06-06 | Seiko Instruments Inc | Piezoelectric actuator, and electronic apparatus fitted with the piezoelectric actuator |
| JP2001045774A (en) * | 1999-07-28 | 2001-02-16 | Canon Inc | Vibration body with electromechanical energy conversion element as vibration source, vibration wave- driving device with vibration body as drive source, device with vibration wave-driving device, and carrying device with vibration body as carrier source |
| JP2003046156A (en) * | 2001-07-31 | 2003-02-14 | Canon Inc | Laminated electro-mechanical energy transducer and oscillatory wave drive device |
| JP2004297951A (en) * | 2003-03-27 | 2004-10-21 | Olympus Corp | Ultrasonic vibrator and ultrasonic motor |
| JP2004335554A (en) * | 2003-04-30 | 2004-11-25 | Canon Inc | Method of manufacturing laminated electric energy/mechanical energy transducer |
| JP2005168281A (en) * | 2003-11-13 | 2005-06-23 | Canon Inc | Laminated piezoelectric element and vibration wave driver |
-
2004
- 2004-12-27 JP JP2004377892A patent/JP2006186099A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH05175567A (en) * | 1991-12-20 | 1993-07-13 | Olympus Optical Co Ltd | Laminated actuator |
| JPH11220893A (en) * | 1997-11-27 | 1999-08-10 | Canon Inc | Vibration-type actuator and vibration-type drive unit |
| JP2000156988A (en) * | 1998-09-18 | 2000-06-06 | Seiko Instruments Inc | Piezoelectric actuator, and electronic apparatus fitted with the piezoelectric actuator |
| JP2001045774A (en) * | 1999-07-28 | 2001-02-16 | Canon Inc | Vibration body with electromechanical energy conversion element as vibration source, vibration wave- driving device with vibration body as drive source, device with vibration wave-driving device, and carrying device with vibration body as carrier source |
| JP2003046156A (en) * | 2001-07-31 | 2003-02-14 | Canon Inc | Laminated electro-mechanical energy transducer and oscillatory wave drive device |
| JP2004297951A (en) * | 2003-03-27 | 2004-10-21 | Olympus Corp | Ultrasonic vibrator and ultrasonic motor |
| JP2004335554A (en) * | 2003-04-30 | 2004-11-25 | Canon Inc | Method of manufacturing laminated electric energy/mechanical energy transducer |
| JP2005168281A (en) * | 2003-11-13 | 2005-06-23 | Canon Inc | Laminated piezoelectric element and vibration wave driver |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008253069A (en) * | 2007-03-30 | 2008-10-16 | Canon Inc | Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave drive device |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4697929B2 (en) | Multilayer piezoelectric element and vibration wave drive device | |
| US6051911A (en) | Vibration wave actuator | |
| US8749117B2 (en) | Vibrating body of vibratory drive unit and vibratory drive unit | |
| JP2004297951A (en) | Ultrasonic vibrator and ultrasonic motor | |
| JP4891053B2 (en) | Ultrasonic motor | |
| JP4795158B2 (en) | Ultrasonic motor | |
| JP4794897B2 (en) | Ultrasonic motor | |
| US7531948B2 (en) | Stacked piezoelectric element, manufacturing method thereof and vibration wave driving apparatus | |
| JP4328113B2 (en) | Ultrasonic motor | |
| US6114798A (en) | Stacked element and vibration drive device | |
| JP2001352768A (en) | Multilayer electromechanical energy conversion element and oscillation wave driver | |
| JP5298999B2 (en) | Multilayer piezoelectric element | |
| JP2006094591A (en) | Ultrasonic motor and its operation method | |
| JP4871593B2 (en) | Vibrator and vibration wave drive device | |
| US20090039736A1 (en) | Ultrasonic actuator and method for manufacturing piezoelectric deformation portion used in the same | |
| JP2006004980A (en) | Laminated electrical-mechanical energy converting element and vibration wave driver | |
| JP2006186099A (en) | Laminated piezoelectric element and oscillatory wave driving device | |
| JP2008067539A (en) | Ultrasonic actuator and method of manufacturing its vibrator | |
| JP4658530B2 (en) | Ultrasonic vibrator and ultrasonic motor using the same | |
| JP5144097B2 (en) | Ultrasonic motor device | |
| JP4818853B2 (en) | Ultrasonic motor element | |
| JP2005150351A (en) | Laminated piezo-electric device and its manufacturing method, oscillator, and oscillating wave driving device | |
| JP2001037262A (en) | Piezoelectric crystal element and actuator using the same | |
| JP5124429B2 (en) | Ultrasonic motor | |
| JP2010193591A (en) | Ultrasonic motor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20060420 |
|
| RD05 | Notification of revocation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7425 Effective date: 20070626 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20071227 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20071227 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110901 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20111028 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111226 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20120807 |