JP2005296434A - Spectral image analysis method and apparatus - Google Patents
Spectral image analysis method and apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005296434A JP2005296434A JP2004118884A JP2004118884A JP2005296434A JP 2005296434 A JP2005296434 A JP 2005296434A JP 2004118884 A JP2004118884 A JP 2004118884A JP 2004118884 A JP2004118884 A JP 2004118884A JP 2005296434 A JP2005296434 A JP 2005296434A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- spectral
- image
- spectral data
- data
- pixel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Eye Examination Apparatus (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】眼底の分光画像から、眼底にわずかな変化をもつ病変部があっても、その位置を正確に特定することができるようにする。
【解決手段】スリットの長手方向に垂直なライン位置での眼底のスリット像の分光データが、各ラインごとに取得され、この各ラインでのスリット像の分光データから各画素(Pi、Qj)ごとの分光データが求められる。各画素での分光データは、病変(A)の分光データと比較され、それにほぼ一致又は近い分光データを有する画素像の位置が特定され、その位置が眼底像とともにモニタ40に表示される。このような構成では、見落としがちなわずかな変化をもつ病変部も検出できるようになり、早期発見や正確な診断が可能となる。
【選択図】図3An object of the present invention is to make it possible to accurately identify the position of a lesion having a slight change in the fundus from a spectral image of the fundus.
Spectral data of a fundus slit image at a line position perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the slit is acquired for each line, and each pixel (Pi, Qj) is obtained from the spectral data of the slit image in each line. Spectral data is required. The spectroscopic data at each pixel is compared with the spectroscopic data of the lesion (A), the position of the pixel image having spectroscopic data substantially coincident with or close to the spectroscopic data is specified, and the position is displayed on the monitor 40 together with the fundus image. With such a configuration, it becomes possible to detect a lesion having a slight change that tends to be overlooked, and early detection and accurate diagnosis are possible.
[Selection] Figure 3
Description
本発明は、分光画像解析方法及び装置、更に詳細には、被検眼眼底などの被写体の分光画像を取得して分光解析する分光画像解析方法及びその装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a spectral image analysis method and apparatus, and more particularly to a spectral image analysis method and apparatus for acquiring and spectrally analyzing a spectral image of a subject such as a fundus of a subject's eye.
従来から被検者の診断方法として、患部をカラー撮影して病変のある部分を検出しその部分を表示することにより診断を行うことが行われている。例えば、被検者の眼底を撮影し、眼底撮影画像から特定の色成分だけを抽出して画像診断することが行われている。しかし、そのためには、画像読影法と呼ばれる特殊な読影術を身に付ける必要があった。 2. Description of the Related Art Conventionally, as a method for diagnosing a subject, diagnosis is performed by color imaging of an affected area, detecting a lesioned portion, and displaying that portion. For example, the fundus of a subject is photographed, and only a specific color component is extracted from the fundus photographed image for image diagnosis. However, for that purpose, it was necessary to acquire a special interpretation called image interpretation.
そこで、被写体の分光画像を取得して分光画像を解析することが行われている(特許文献1、特許文献2)。しかしながら、これらの文献に記載のものは、被写体の温度分布を求めたり(特許文献1)、病変部の分光パターンを表示するもので(特許文献2)、分光画像から病変部の位置を正確に特定することができないという欠点がある。
Thus, a spectral image of a subject is acquired and the spectral image is analyzed (
また、特許文献3から、眼球内のスリット像の分光画像を、複数スリット位置ごとに記録することができる眼底カメラが知られている。この眼底カメラから得られた画像は、各画素ごとに分光情報を有しているので、波長の特有な変化を評価することができるが、異変部を特定するには、画像読影法と同様な技術が必要となる、という欠点がある。
本発明の課題は、上述した従来の問題点を解決するためになされたもので、被写体の分光画像を解析し、被写体にわずかな変化をもつ異変部があっても、その位置を正確に特定することができるようにすることである。 An object of the present invention is to solve the above-mentioned conventional problems. By analyzing a spectral image of a subject, even if there is an anomalous portion having a slight change in the subject, the position can be accurately identified. Is to be able to do that.
本発明(請求項1)は、
被写体の分光データを取得して分光解析する分光画像解析方法であって、
被写体の分光画像を取り込んで被写体の各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求め、
被写体の各画素像の分光データを、参照画素像の分光データと比較し、
比較結果に基づき参照画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データを有する画素像の位置を特定することを特徴とする。
The present invention (Claim 1)
A spectral image analysis method for acquiring spectral data of a subject and performing spectral analysis,
Capture the spectral image of the subject, obtain the spectral data of the pixel image for each pixel of the subject,
Compare the spectral data of each pixel image of the subject with the spectral data of the reference pixel image,
Based on the comparison result, the position of the pixel image having spectral data substantially coincident with or close to the spectral data of the reference pixel image is specified.
また、本発明(請求項8)は、
被写体の分光データを取得して分光解析する分光画像解析装置であって、
被写体の分光画像を取り込んで被写体の各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求める演算手段と、
被写体の各画素像の分光データと、参照画素像の分光データを比較する比較手段と、
比較結果に基づき参照画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データを有する画素像の位置を特定する特定手段とを有することを特徴とする。
The present invention (Claim 8)
A spectral image analysis device for acquiring spectral data of a subject and performing spectral analysis,
Computing means for capturing a spectral image of the subject and obtaining spectral data of the pixel image for each pixel of the subject;
Comparison means for comparing the spectral data of each pixel image of the subject and the spectral data of the reference pixel image;
And a specifying means for specifying the position of a pixel image having spectral data that substantially matches or is close to the spectral data of the reference pixel image based on the comparison result.
本発明では、スリットの長手方向に垂直なライン位置での被写体のスリット像の分光データを取り込んで、取り込んだスリット像の分光データを各ラインごとに記憶する記憶手段が設けられ、演算手段は、記憶手段に記憶されている各ラインでのスリット像の分光データを読み込んで、各ラインを所定数の画素に分割し、各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求める。 In the present invention, there is provided storage means for capturing spectral data of a slit image of a subject at a line position perpendicular to the longitudinal direction of the slit, and storing the spectral data of the captured slit image for each line. The spectral data of the slit image at each line stored in the storage means is read, each line is divided into a predetermined number of pixels, and the spectral data of the pixel image is obtained for each pixel.
本発明では、被写体の分光画像から被写体の各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求め、その各画素像の分光データと、参照画素像の分光データの比較結果に基づいて、参照画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データを有する画素像の位置を特定するようにしているので、被写体の異変部(病変部)の位置を、画素単位で特定することができ、正確な診断が可能となる。 In the present invention, the spectral data of the pixel image is obtained for each pixel of the subject from the spectral image of the subject, and the spectral of the reference pixel image is obtained based on the comparison result between the spectral data of each pixel image and the spectral data of the reference pixel image. Since the position of the pixel image having spectral data that substantially matches or is close to the data is specified, the position of the abnormal part (lesioned part) of the subject can be specified in units of pixels, and accurate diagnosis is possible. Become.
本発明の分光画像解析装置は、被写体の分光画像から病変部など特異な部分の位置を特定するのもので、被写体として被検眼の眼底を例にして説明するので、分光画像を取得するのに、眼底カメラが用いられる。しかし、本発明は、被写体が眼底だけに限定されるものではなく、他の被写体の分光画像の解析にも適用できるものである。 The spectral image analysis apparatus of the present invention specifies the position of a specific portion such as a lesion from the spectral image of the subject, and will be described by taking the fundus of the eye to be examined as an example of the subject. A fundus camera is used. However, the present invention is not limited to the fundus only, but can be applied to analysis of spectral images of other subjects.
以下、図面に示す実施例に基づいて本発明を詳細に説明する。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail based on embodiments shown in the drawings.
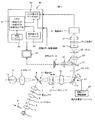
図1に示す眼底カメラでは、ハロゲンランプなどの光源1から発せられた光は、コンデンサーレンズ2、ストロボ3、リング状照明を形成するためのリングスリット4、レンズ5、対物レンズ9の反射を除去するための黒点ガラス6、リレーレンズ7を通過し、中心に穴の開いた穴あき全反射ミラー8で反射されてから対物レンズ9を経て、被検眼10の瞳より眼底10aに入射し、眼底を照明する。
In the fundus camera shown in FIG. 1, light emitted from a
眼底10aからの反射光は再び被検眼の瞳から対物レンズ9を介して受光され、穴あき全反射ミラー8の穴を通過してその背後に配置された撮影絞り14で絞られ、フォーカスレンズ15、結像レンズ16を通過して、回転ミラー17に入射する。回転ミラー17で反射された光は、眼底と共役な位置に配置されたマスク18を通過した後、ミラー19で反射され、レンズ20を通過して観察用の赤外CCD21に入射する。赤外CCD21は、観察光学系において眼底と共役な位置に配置されるので、検者は、この赤外CCDで結像された眼底像をモニタ40を介して観察でき、アライメントや合焦操作を行うことができる。なお、この観察モードのときは、赤外を透過し、可視光をカットするフィルタ1’を照明光路に挿入し、無散瞳で赤外CCD21による観察ができるようにする。
The reflected light from the fundus 10a is received again from the pupil of the eye to be examined through the objective lens 9, is passed through the hole of the perforated total reflection mirror 8, and is narrowed by the photographing aperture 14 disposed behind it, and the focus lens 15 Then, the light passes through the
分光画像を取得する時には、ミラー19が光路から離脱され、光源1で照明された眼底像は、マスク18で一旦結像された後、レンズ22を通過して、紙面に垂直な方向に延びるスリット23の位置に再結像される。そして、スリット像となった眼底像は、レンズ24、分光素子25、レンズ26からなる分光光学系を介して白黒CCDなどから構成される撮像素子27に入射する。
When acquiring a spectral image, the
分光素子25は、上記特許文献3に記載されたプリズム・グレーティング・プリズム(PGP)と同様な構成であり、スリット23によりスリット像となった眼底像は、スリットの長手方向と垂直方向に所定の波長帯域幅に渡って分光されるので、撮像素子27は、眼底のスリット像の分光画像を、撮影することができる。
The spectroscopic element 25 has a configuration similar to that of the prism / grating / prism (PGP) described in
また、回転ミラー17は、例えばステッピングモータなどで構成される回転ミラー駆動機構28により軸17aを中心に所定ステップづつ回転されるので、その回転に応じてスリット23に結像される眼底像のライン位置が変化し、回転ミラーの位置に応じて、眼底の各ライン位置でのスリット像の分光データが撮影される。
Further, the
撮像素子27で撮像された各ライン位置での眼底のスリット像の分光データは、分光画像解析装置30に入力され、回転ミラー駆動機構28から得られる眼底のライン位置に同期してスリット像分光データメモリ(記憶手段)32にラインごとに記憶される。分光画像解析装置30のCPU31は、スリット像分光データメモリ32に記憶されている眼底のスリット像の分光データを読み込み、各ラインを所定数の画素に分割して、各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを演算する(演算手段)。これら求められた各ラインでの画素ごとの分光データは、画素ごとに画素像分光データメモリ(記憶手段)33に記憶される。
Spectral data of the fundus slit image at each line position imaged by the image sensor 27 is input to the
また、眼底の病変あるいは異変のある部分の画素像の分光データが予め測定され、種々の病変部の画素像の分光データが、病変ごとに参照画素像の分光データとして分光画像解析装置30の病変ライブラリ(メモリ)34に登録される。CPU31は、画素像分光データメモリ33に記憶されている各画素像の分光データを順次読み出し、病変ライブラリ34に記憶されている病変の分光データと比較し(比較手段)、比較結果に基づき参照画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データを有する画素像の位置を特定する(位置特定手段)。
Further, the spectral data of the pixel image of the fundus lesion or the part having an abnormality is measured in advance, and the spectral data of the pixel image of various lesions is used as the spectral data of the reference pixel image for each lesion. It is registered in the library (memory) 34. The
また、分光画像解析装置30には、モニタ40が接続され、特定された病変部の位置が、明るさもしくは所定の色を割り付けて眼底の画像とともに表示される。
In addition, a
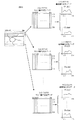
このような構成において、被検眼に対してアライメントや合焦動作が終了すると、撮影準備完了となるので、シャッタボタン(不図示)を操作する。これにより、ミラー19が光路から離脱し、光源1で照明された眼底像がスリット23に結像される。最初、回転ミラー17の位置は、図2に示すように、眼底の最上部のライン位置P1でのスリット像が撮影されるように位置決めされるので、スリット23には、ラインP1での眼底スリット像が結像される。分光素子25は、スリット像を波長λ1〜λkにスペクトル分解するので、撮像素子27は、図2の中央上部に示されたように、ラインP1のスリット像の波長λ1〜λkでのスペクトル強度を分光画像(分光波形)として撮像する。この分光画像は、A/D変換されて、分光画像解析装置30のスリット像分光データメモリ32に回転ミラー駆動機構28からの信号に同期してラインP1での分光データとして記憶される。
In such a configuration, when the alignment or focusing operation is completed for the eye to be examined, imaging preparation is completed, and a shutter button (not shown) is operated. As a result, the
回転ミラー17は、所定量づつ回転されるので、ラインP2.....Pnでの眼底スリット像の分光データが順次撮影され、各ラインでのスリット像の分光データが、回転ミラーの各位置ごとに、すなわち各ラインごとにメモリ32に記憶される。このラインP2、.....Pnでのスリット像の分光データが図2の中央に図示されている。なお、各ラインP1.....Pnの幅は、そのラインのスリット23での像幅が、スリット23のスリット幅と等しくなるように選ばれるので、回転ミラー27は、スリット幅に応じた量だけステップ的に回転され、眼底の全領域がスリット幅に応じたライン幅で隙間なく走査されることになる。
Since the
このようにして、各ライン位置での眼底スリット像の分光画像が取り込まれると、分光画像処理装置のCPU31は、スリット像分光データメモリ32から、ラインP1でのスリット像の分光データを読み出し、そのラインを所定数の画素Q1、Q2、.....Qm(例えばm=768)に分割し、各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求める。このようにして求められたラインP1での画素像の分光データが、各画素(P1、Q1)、.....(P1、Qm)の分光波形として図2の右上に図示されいる。
In this way, when the spectral image of the fundus slit image at each line position is captured, the
CPU31は、続いて、ラインP2、.....Pnでのスリット像の分光データを順次読み出し、同様に、各ラインを画素Q1、Q2、.....Qmに分割し、各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求める。このようにして求められた各ラインでの画素像の分光データが、図2の右側に図示されおり、これらの分光データは、画素(Pi、Qj)(i=1、.....n;Q=1、.....m)ごとに画素像分光データメモリ33に記憶される。
The
ここで、画素Qの画素数mを、撮像素子27のライン方向の有効画素数と同じにし、また、分光波長λの数(k)を撮像素子のライン方向と直交する方向の有効画素数と同じにすると、最高分解能の分光データが得られるが、データ量が膨大になる場合には、適当に圧縮することができる。例えば、ラインを撮像素子のライン方向の複数個(例えば、2個)の画素に対応する大きさの画素に分割し、撮像素子のライン方向と直交する方向の複数個(例えば、2個)の画素での各波長のスペクトル強度の平均値を、その波長の平均値のスペクトル強度とすることにより、データ量を圧縮することができる。 Here, the number m of pixels Q is the same as the number of effective pixels in the line direction of the image sensor 27, and the number (k) of spectral wavelengths λ is the number of effective pixels in the direction orthogonal to the line direction of the image sensor. If the same, spectral data with the highest resolution can be obtained, but if the amount of data becomes enormous, it can be compressed appropriately. For example, the line is divided into pixels having a size corresponding to a plurality of (for example, two) pixels in the line direction of the image sensor, and a plurality of (for example, two) pixels in a direction orthogonal to the line direction of the image sensor. By setting the average value of the spectral intensity of each wavelength in the pixel as the spectral intensity of the average value of the wavelength, the data amount can be compressed.
続いて、分光画像処理装置のCPU31は、画素像分光データメモリ33に記憶されている各ラインでの各画素像の分光データを順次読み出し、病変ライブラリ34に登録されている病変部の画素像の分光データと比較する。
Subsequently, the
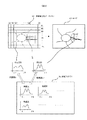
この状態が図3に図示されており、例えば、眼底に病変Aがある位置を知りたい場合には、病変ライブラリ34に登録されている病変Aの分光データが、参照画素像分光データとして読み出され、画素像分光データメモリ33から読み出された各画素像(Pi、Qj)の分光データと順次比較される。
This state is shown in FIG. 3. For example, when it is desired to know the position where the lesion A is on the fundus, the spectral data of the lesion A registered in the
例えば、各波長λ1〜λkでのスペクトル強度の差(あるいはその2乗)の平均値を求め、その値が所定値以下のときは、所定位置(Pi,Qj)にある画素像の分光データが、病変Aの画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データと判断する。平均値を求めるとき、各波長で異なる重み係数を付した加重平均値を求めるようにしてもよく、病変に特有な波長領域では、その重み係数を大きくしておくと、良好な判定結果を得ることができる。また、分光データは、パターンとして現れるので、病変Aの画素像の分光パターンをテンプレートとし、公知のテンプレートマッチングのアルゴリズムを用いて、各ラインでの各画素像の分光パターンと、病変Aのテンプレートとのパターンマッチングを行い、その相関値を求めることにより両分光データの比較を行うようにしてもよい。 For example, an average value of spectral intensity differences (or squares thereof) at the respective wavelengths λ1 to λk is obtained, and when the value is equal to or smaller than a predetermined value, the spectral data of the pixel image at the predetermined position (Pi, Qj) is obtained. Then, it is determined that the spectral data substantially coincides with or close to the spectral data of the pixel image of the lesion A. When obtaining an average value, a weighted average value obtained by assigning a different weighting factor to each wavelength may be obtained. In a wavelength region peculiar to a lesion, if the weighting factor is increased, a good determination result is obtained. be able to. Since the spectral data appears as a pattern, the spectral pattern of the pixel image of the lesion A is used as a template, and the spectral pattern of each pixel image on each line, the template of the lesion A, and the like using a known template matching algorithm. Both spectral data may be compared by performing the pattern matching and obtaining the correlation value.
上記差の平均値が所定値以下、及び/又は相関値が所定値以上で、位置(Pi,Qj)にある画素像の分光データが、病変Aの画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データと判断された場合は、画素位置(Pi,Qj)に病変があると判断し、その位置を特定して眼底像を表示するモニタ40の対応する位置に表示する。その表示は、図3のモニタ40で太目の実線で示したように、相関の大きさに従い明るさを変えて、あるいはその相関値に応じた特定の色で着色して行われるので、眼底の病変部が強調して画像化されることになる。従って、検者は、見落としがちなわずかな変化をもつ病変部も検出できるようになり、早期発見や正確な診断が可能となる。
Spectral data of the pixel image at the position (Pi, Qj) substantially equal to or close to the spectral data of the pixel image of the lesion A when the average value of the differences is not more than a predetermined value and / or the correlation value is not less than the predetermined value. If it is determined as data, it is determined that there is a lesion at the pixel position (Pi, Qj), and the position is specified and displayed at a corresponding position on the
なお、上記両分光データの比較は、分光データのうち特徴となる分光特性を有する特徴点のデータ、例えば、分光波形の変曲点、あるいは予め指定された分光波形上の点のデータを比較することにより行うことができる。 In addition, the comparison between the two spectral data is performed by comparing data of characteristic points having spectral characteristics that are characteristic among the spectral data, for example, data of inflection points of spectral waveforms or data on points specified in advance in the spectral waveforms. Can be done.
また、病変Aだけでなく、他の種々の病変B、.....Xに対しても、予めその病変に特有な分光データを測定しておき、病変ライブラリ34に登録しておくことにより、他の病変B、.....Xがある場合には、同様に、その位置を特定して対応した表示を行うことができる。また、参照画素像の分光データは、このように予め用意され登録されている分光データではなく、メモリ33に記憶されている画素像の分光データから選択された分光データとすることもできる。
In addition to the lesion A, other various lesions B,. . . . . For X, spectral data peculiar to the lesion are measured in advance and registered in the
なお、撮像素子27で眼底の分光画像を撮像するとき、可視光の光源1で眼底を照射するようにしたが、単色光、赤外光、あるいは所定の帯域幅の波長の光束で眼底を照明するようにしてもよい。その場合には、分光が所定波長領域だけで行われるので、演算量を減少させることができる。
Note that when the spectral image of the fundus is captured by the image sensor 27, the fundus is irradiated by the visible
10 被検眼
25 分光素子
27 撮像素子
30 分光画像分析装置
31 CPU
32 スリット像分光データメモリ
33 画素像分光データメモリ
34 病変ライブラリ
40 モニタ
DESCRIPTION OF
32 Slit image
Claims (14)
被写体の分光画像を取り込んで被写体の各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求め、
被写体の各画素像の分光データを、参照画素像の分光データと比較し、
比較結果に基づき参照画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データを有する画素像の位置を特定することを特徴とする分光画像解析方法。 A spectral image analysis method for acquiring spectral data of a subject and performing spectral analysis,
Capture the spectral image of the subject, obtain the spectral data of the pixel image for each pixel of the subject,
Compare the spectral data of each pixel image of the subject with the spectral data of the reference pixel image,
A spectral image analysis method characterized by identifying a position of a pixel image having spectral data substantially coincident with or close to spectral data of a reference pixel image based on a comparison result.
被写体の分光画像を取り込んで被写体の各画素ごとに画素像の分光データを求める演算手段と、
被写体の各画素像の分光データと、参照画素像の分光データを比較する比較手段と、
比較結果に基づき参照画素像の分光データにほぼ一致又は近い分光データを有する画素像の位置を特定する特定手段と、
を有することを特徴とする分光画像解析装置。 A spectral image analysis device for acquiring spectral data of a subject and performing spectral analysis,
Computing means for capturing a spectral image of the subject and obtaining spectral data of the pixel image for each pixel of the subject;
Comparison means for comparing the spectral data of each pixel image of the subject and the spectral data of the reference pixel image;
A specifying means for specifying a position of a pixel image having spectral data substantially matching or close to the spectral data of the reference pixel image based on the comparison result;
A spectral image analysis apparatus comprising:
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004118884A JP2005296434A (en) | 2004-04-14 | 2004-04-14 | Spectral image analysis method and apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004118884A JP2005296434A (en) | 2004-04-14 | 2004-04-14 | Spectral image analysis method and apparatus |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005296434A true JP2005296434A (en) | 2005-10-27 |
Family
ID=35328690
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004118884A Pending JP2005296434A (en) | 2004-04-14 | 2004-04-14 | Spectral image analysis method and apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005296434A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007330558A (en) * | 2006-06-15 | 2007-12-27 | Topcon Corp | Spectral fundus measuring apparatus and measuring method thereof |
| JP2007330557A (en) * | 2006-06-15 | 2007-12-27 | Topcon Corp | Spectral fundus measuring apparatus and measuring method thereof |
| JP2009119173A (en) * | 2007-11-19 | 2009-06-04 | Panasonic Electric Works Co Ltd | Optical scanning measurement device |
| JP2012152279A (en) * | 2011-01-24 | 2012-08-16 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope system |
| JP2021505340A (en) * | 2017-12-06 | 2021-02-18 | ジリア,インコーポレイテッド | Spectral reflection interference system with pointer mode for combined imaging and spectroscopic analysis |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6133639A (en) * | 1984-07-26 | 1986-02-17 | 熊谷 博彰 | Spectroscopic pattern image display apparatus of organism tissue |
| JPH11500832A (en) * | 1995-12-12 | 1999-01-19 | スペクトラル ダイアグノスティック リミテッド | Spectroscopic biological imaging, fluorescence hybridization and cell classification methods for biological research, medical diagnosis and therapy |
| JP2002224041A (en) * | 2001-01-31 | 2002-08-13 | Nidek Co Ltd | Ophthalmologic apparatus |
-
2004
- 2004-04-14 JP JP2004118884A patent/JP2005296434A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6133639A (en) * | 1984-07-26 | 1986-02-17 | 熊谷 博彰 | Spectroscopic pattern image display apparatus of organism tissue |
| JPH11500832A (en) * | 1995-12-12 | 1999-01-19 | スペクトラル ダイアグノスティック リミテッド | Spectroscopic biological imaging, fluorescence hybridization and cell classification methods for biological research, medical diagnosis and therapy |
| JP2002224041A (en) * | 2001-01-31 | 2002-08-13 | Nidek Co Ltd | Ophthalmologic apparatus |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007330558A (en) * | 2006-06-15 | 2007-12-27 | Topcon Corp | Spectral fundus measuring apparatus and measuring method thereof |
| JP2007330557A (en) * | 2006-06-15 | 2007-12-27 | Topcon Corp | Spectral fundus measuring apparatus and measuring method thereof |
| JP2009119173A (en) * | 2007-11-19 | 2009-06-04 | Panasonic Electric Works Co Ltd | Optical scanning measurement device |
| JP2012152279A (en) * | 2011-01-24 | 2012-08-16 | Fujifilm Corp | Endoscope system |
| JP2021505340A (en) * | 2017-12-06 | 2021-02-18 | ジリア,インコーポレイテッド | Spectral reflection interference system with pointer mode for combined imaging and spectroscopic analysis |
| JP7230052B2 (en) | 2017-12-06 | 2023-02-28 | ジリア,インコーポレイテッド | Spectral reflectance interferometry system and method with pointer mode for combined imaging and spectroscopic analysis |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US6992775B2 (en) | Hyperspectral retinal imager | |
| US7568800B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for spectrally measuring fundus | |
| JP7246541B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for measuring tear film thickness | |
| US8315692B2 (en) | Multi-spectral imaging spectrometer for early detection of skin cancer | |
| US20080007692A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for spectrally measuring fundus | |
| US9913581B2 (en) | Photography apparatus and photography method | |
| JP3723082B2 (en) | Ophthalmic equipment | |
| JP2002078683A (en) | Device and method for inspecting surface | |
| JP7517147B2 (en) | Fundus image processing device and fundus image processing program | |
| JP7063961B2 (en) | Tear layer thickness measuring device and method | |
| JP4585814B2 (en) | Ophthalmic equipment | |
| JP2005296434A (en) | Spectral image analysis method and apparatus | |
| JP5408527B2 (en) | Creating a melanoma diagnostic image | |
| JP4505852B2 (en) | Fundus spectral imaging device | |
| JP2020146105A (en) | Ophthalmologic apparatus, control method of ophthalmologic apparatus and program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070309 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20100212 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100309 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20100713 |