JP2005295310A - Radio communication method, radio communication system, radio terminal, program and recording medium - Google Patents
Radio communication method, radio communication system, radio terminal, program and recording medium Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005295310A JP2005295310A JP2004109029A JP2004109029A JP2005295310A JP 2005295310 A JP2005295310 A JP 2005295310A JP 2004109029 A JP2004109029 A JP 2004109029A JP 2004109029 A JP2004109029 A JP 2004109029A JP 2005295310 A JP2005295310 A JP 2005295310A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- wireless
- energy source
- terminal
- remaining amount
- finite energy
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Description
本発明は、無線通信技術に関し、特に、マルチホップ無線通信システムおよびそれを構成する無線端末等に適用して有効な技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a radio communication technique, and more particularly, to a technique effective when applied to a multi-hop radio communication system and radio terminals constituting the multi-hop radio communication system.
たとえば、携帯電話のような移動通信システムでは、無線端末が最寄りの基地局と一対一に通信することが基本であるが、地下道やビルの谷間など、地理的には基地局の管轄範囲であるにもかかわらず、局所的に通信困難となる領域、すなわちデッドスポットが存在することが問題となる。 For example, in a mobile communication system such as a mobile phone, it is basic that a wireless terminal communicates with the nearest base station on a one-to-one basis, but geographically, such as an underpass or a valley of a building, is within the jurisdiction range of the base station Nevertheless, there is a problem that a region where communication is difficult locally, that is, a dead spot exists.
このため、無線端末が基地局と通信するだけでなく、無線端末同士が直接通信をしながらネットワークを形成するマルチホップ無線通信網が考えられている。このマルチホップ無線通信網を用いることで、無線端末がデッドスポット内にある時でも通信が可能となり、さらには有線網や固定基地局を介することなく、無線端末のみでネットワークを構成できる可能性があり、盛んに研究されている。 For this reason, a multi-hop wireless communication network in which a wireless terminal forms a network while communicating directly with each other as well as with a base station is considered. By using this multi-hop wireless communication network, communication is possible even when the wireless terminal is in a dead spot, and there is a possibility that the network can be configured with only the wireless terminal without using a wired network or a fixed base station. Yes, it has been actively researched.
従来のマルチホップ無線通信システムでは、無線端末が保持している経路情報および信頼性情報を基に、伝送するパケットの最適な転送経路が決定され、中継転送が行われる。
このとき、通信経路の信頼性値は、無線端末間で通信する各端末の経路情報の着信率に従い決定されるものがある。例えば、特許文献1の様な方法がある。
In a conventional multi-hop wireless communication system, an optimum transfer route of a packet to be transmitted is determined based on route information and reliability information held by a wireless terminal, and relay transfer is performed.
At this time, the reliability value of the communication path is determined according to the incoming rate of the path information of each terminal communicating between wireless terminals. For example, there is a method as described in
上記のようなマルチホップ無線通信システムを電池駆動した場合、経路ごとに無線端末の電池の消耗量が異なるため、この消耗量を偏りなく分散することが必要となる。
すなわち、従来の方式では、無線端末が管理する経路情報により、パケットを中継伝送する中継先の無線端末を選択し、中継伝送する。このとき経路の選択には最終目的の端末までの中継段数と中継先の端末間の通信の信頼性値をもとに、最適な経路が選択される。このため、通信異常等の要因で通信経路の変更がある場合を除き、通常は中継段数が最小で信頼性値が最大となる一部の通信経路が常時使用され、無線システム全体のその他の経路と比較して、この経路上の各中継端末の電池消耗量が大きくなってしまう。特に複数の通信経路として使用される中継端末はこの電池消耗量が特に大きく、これら一部の中継端末の電池残量がなくなることにより動作不可となり、中継経路自体が使用できない場合があり得る。
When the multi-hop wireless communication system as described above is battery-powered, the consumption amount of the battery of the wireless terminal is different for each route. Therefore, it is necessary to distribute the consumption amount evenly.
That is, in the conventional system, a relay destination wireless terminal that relays and transmits a packet is selected and relayed based on route information managed by the wireless terminal. At this time, an optimum route is selected based on the number of relay stages up to the final target terminal and the reliability value of communication between relay destination terminals. For this reason, unless there is a change in the communication path due to a communication error, etc., some communication paths with the minimum number of relay stages and the maximum reliability value are normally used, while other paths in the entire wireless system are used. In comparison with the above, the battery consumption of each relay terminal on this route becomes large. In particular, relay terminals used as a plurality of communication paths have a particularly large amount of battery consumption, and some of the relay terminals may become inoperable due to the remaining battery power remaining, and the relay paths themselves may not be usable.
これを解決すべく電池消耗量を分散させる従来の経路選択方式としては、特許文献2で示されているように、個々の無線端末の電池消耗量の情報を各無線端末間で交換し、この情報に基づいて経路を選択する方式がある。
As a conventional route selection method for distributing the battery consumption to solve this, as shown in
しかしながら、この特許文献2の方式では通常の経路情報のほかに電池の残量を示す情報や経路毎の送信所用電力量等の情報を付加して無線端末間で交換する必要がある。このため、ネットワーク全体としての通信量が増加し、また電池残量の管理も複雑になる。とくに、ネットワーク上の無線端末の台数が多くなるほど、この問題は顕著になる。
本発明の目的は、無線端末間の通信データ量を増大させることなく、マルチホップ無線通信システム全体での通信経路毎の各無線端末の有限エネルギー源の消耗量の偏りを防止して、安定なマルチホップ無線通信を実現することにある。 An object of the present invention is to prevent a bias in the consumption amount of the finite energy source of each wireless terminal for each communication path in the entire multihop wireless communication system without increasing the amount of communication data between wireless terminals, and to stabilize It is to realize multi-hop wireless communication.
本発明の他の目的は、個々の無線端末における有限エネルギー源の複雑な残量管理を必要とすることなく、マルチホップ無線通信システム全体での通信経路毎の各無線端末の有限エネルギー源の消耗量の偏りを防止して、安定なマルチホップ無線通信を実現することにある。 Another object of the present invention is to consume the finite energy source of each wireless terminal for each communication path in the entire multi-hop wireless communication system without requiring complicated remaining amount management of the finite energy source in each wireless terminal. The object is to realize a stable multi-hop wireless communication by preventing a bias in amount.
本発明の第1の観点は、有限エネルギー源で動作する複数の無線端末が、相互に送受信される経路情報に基づいて伝送パケットを相互に中継伝送するマルチホップ方式の無線通信方法であって、個々の前記無線端末は、前記有限エネルギー源の残量に応じて前記経路情報の送信間隔を変化させることで、他の前記無線端末に自無線端末の前記有限エネルギー源の残量を認識させる無線通信方法を提供する。 A first aspect of the present invention is a multi-hop wireless communication method in which a plurality of wireless terminals operating with a finite energy source relay and transmit a transmission packet based on path information transmitted and received between each other, Each of the wireless terminals changes the transmission interval of the route information according to the remaining amount of the finite energy source, thereby allowing other wireless terminals to recognize the remaining amount of the finite energy source of the own wireless terminal. A communication method is provided.
本発明の第2の観点は、有限エネルギー源で動作する複数の無線端末が、前記無線端末を経由する通信路を定義する経路情報を相互に送受信し、前記経路情報および前記通信路の信頼性値に基づいて伝送パケットを相互に中継伝送するマルチホップ方式の無線通信方法であって、個々の前記無線端末において、前記有限エネルギー源の残量に応じて前記経路情報の送信間隔を変化させる無線通信方法を提供する。 According to a second aspect of the present invention, a plurality of wireless terminals operating with a finite energy source mutually transmit / receive path information defining a communication path passing through the wireless terminal, and the path information and the reliability of the communication path A multi-hop wireless communication method for relaying transmission packets to each other based on a value, wherein each wireless terminal changes a transmission interval of the route information according to the remaining amount of the finite energy source A communication method is provided.
本発明の第3の観点は有限エネルギー源で動作する複数の無線端末が、前記無線端末を経由する通信路を定義する経路情報を相互に送受信し、前記経路情報および前記通信路の信頼性値に基づいて伝送パケットを相互に中継伝送するマルチホップ無線通信システムであって、個々の前記無線端末は、前記有限エネルギー源の残量を検出する第1機能と、前記残量に応じて前記経路情報の送信間隔を変化させる第2機能とを備えた無線通信システムを提供する。 According to a third aspect of the present invention, a plurality of wireless terminals operating with a finite energy source mutually transmit / receive path information defining a communication path passing through the wireless terminal, and the path information and the reliability value of the communication path A multi-hop wireless communication system that relays transmission packets based on each other, wherein each of the wireless terminals has a first function for detecting a remaining amount of the finite energy source, and the route according to the remaining amount. Provided is a radio communication system having a second function for changing an information transmission interval.
本発明の第4の観点は、マルチホップ無線通信システムを構成し、有限エネルギー源で動作する無線端末であって、前記有限エネルギー源の残量を検出する第1機能と、前記残量に応じて経路情報の送信間隔を変化させる第2機能とを備えた無線端末を提供する。 According to a fourth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a wireless terminal that constitutes a multi-hop wireless communication system and operates with a finite energy source, wherein a first function for detecting a remaining amount of the finite energy source and the remaining amount A wireless terminal having a second function for changing the transmission interval of the route information is provided.
本発明の第5の観点は、マルチホップ無線通信システムを構成し有限エネルギー源で動作するコンピュータを備えた無線端末を制御するプログラムであって、前記コンピュータに、前記有限エネルギー源の残量を検出する第1機能と、前記残量に応じて経路情報の送信間隔を変化させる第2機能とを実現させるプログラムを提供する。 According to a fifth aspect of the present invention, there is provided a program for controlling a wireless terminal comprising a computer that constitutes a multi-hop wireless communication system and operates with a finite energy source, and detects the remaining amount of the finite energy source in the computer. And a second function for changing a transmission interval of route information in accordance with the remaining amount.
本発明の第6の観点は、マルチホップ無線通信システムを構成し有限エネルギー源で動作する無線端末に備えられたコンピュータを制御するプログラムであって、前記コンピュータに、前記有限エネルギー源の残量を検出する第1機能と、前記残量に応じて経路情報の送信間隔を変化させる第2機能とを実現させるプログラムが格納されたコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体を提供する。 A sixth aspect of the present invention is a program for controlling a computer included in a wireless terminal that constitutes a multi-hop wireless communication system and operates with a finite energy source, the remaining amount of the finite energy source being stored in the computer. Provided is a computer-readable recording medium storing a program for realizing a first function to be detected and a second function for changing a transmission interval of route information according to the remaining amount.
上記した本発明によれば、各無線端末は駆動電源としての電池等の有限エネルギー源の残量を計測し、無線端末内に保持している電池残量の低下を閾値等で判定して、通信経路を選択するための自端末が保持している経路情報の送信間隔を大きくすることで、自無線端末の電池残量の情報を他の無線端末に伝達できる。あるいは、経路情報の送信処理を間欠的に動作させることで電池残量の情報を伝達しても良い。この場合、経路情報の送信間隔が変化するだけで無線端末間の通信情報量は全く増加しない。 According to the present invention described above, each wireless terminal measures the remaining amount of a finite energy source such as a battery as a driving power source, determines a decrease in the remaining battery level held in the wireless terminal by a threshold or the like, By increasing the transmission interval of the route information held by the own terminal for selecting the communication route, the information on the remaining battery level of the own wireless terminal can be transmitted to other wireless terminals. Alternatively, the remaining battery information may be transmitted by intermittently operating the route information transmission process. In this case, the amount of communication information between wireless terminals does not increase at all, only by changing the transmission interval of route information.
そして、周囲の経路情報を受信する無線端末において、電池残量の変動した無線端末を中継端末として経由する経路情報の着信率(単位時間当たりの受信回数)が低くなる。この着信率の大小を当該経路情報の発信元の無線端末の信頼性値の大小の目安とする場合、経路情報テーブル上において、電池残量が低下した無線端末を中継器とする経路の信頼性値が変化し、目的局に対して同一の中継段数の他の経路より信頼性値が低くなることにより、この無線端末を含む通信経路の使用優先度が下がる。これにより、パケットを伝送する際に、電池残量の低下した無線端末を中継端末として経由する経路の使用頻度が相対的に低下し、この経路上の中継端末の電池の消耗量を低くすることができる。 Then, in the wireless terminal that receives the surrounding route information, the incoming rate (the number of receptions per unit time) of the route information that passes through the wireless terminal whose battery level has changed as a relay terminal is low. When the size of the incoming call rate is used as a measure of the reliability value of the wireless terminal that is the source of the route information, the reliability of the route using the wireless terminal whose battery remaining amount is reduced as a repeater on the route information table When the value changes and the reliability value becomes lower than that of the other route having the same number of relay stages with respect to the target station, the use priority of the communication route including the wireless terminal is lowered. As a result, when packets are transmitted, the frequency of use of a route through which a wireless terminal having a low remaining battery capacity is routed as a relay terminal is relatively reduced, and the battery consumption of the relay terminal on this route is reduced. Can do.
この結果、特定の無線端末に中継路が継続的に集中して電池の消耗量が大きく偏って動作不能に陥ることが回避され、安定なマルチホップ無線通信を実現することができる。
また、電池残量に応じて経路情報の送信間隔を変化させることで、相手側に自無線端末の信頼性を認識させるので、個々の無線端末にて、他の無線端末の各々における電池消耗量をデータとして管理する等の煩雑な処理は全く不要であり、個々の無線端末における複雑な電池の残量管理を必要とすることなく、マルチホップ無線通信システム全体での通信経路毎の各無線端末の電池消耗量の偏りを防止して、安定なマルチホップ無線通信を実現することができる。
As a result, it is possible to avoid a situation in which relay paths are continuously concentrated on a specific wireless terminal and the consumption of the battery is greatly biased to become inoperable, and stable multi-hop wireless communication can be realized.
In addition, by changing the transmission interval of the route information according to the remaining battery level, the other party can recognize the reliability of the own wireless terminal, so that the amount of battery consumption in each of the other wireless terminals at each wireless terminal No complicated processing such as managing data as data is required, and each wireless terminal for each communication path in the entire multi-hop wireless communication system does not require complicated battery remaining amount management in each wireless terminal. Thus, it is possible to realize a stable multi-hop wireless communication by preventing an uneven battery consumption amount.
本発明によれば、無線端末間の通信データ量を増大させることなく、マルチホップ無線通信システム全体での通信経路毎の各無線端末の有限エネルギー源の消耗量の偏りを防止して、安定なマルチホップ無線通信を実現することができる。 According to the present invention, without increasing the amount of communication data between wireless terminals, it is possible to prevent a bias in the consumption amount of the finite energy source of each wireless terminal for each communication path in the entire multihop wireless communication system and Multihop wireless communication can be realized.
また、個々の無線端末における有限エネルギー源の複雑な残量管理を必要とすることなく、マルチホップ無線通信システム全体での通信経路毎の各無線端末の有限エネルギー源の消耗量の偏りを防止して、安定なマルチホップ無線通信を実現することができる。 Further, it is possible to prevent uneven consumption of the finite energy source of each wireless terminal for each communication path in the entire multi-hop wireless communication system without requiring complicated remaining amount management of the finite energy source in each wireless terminal. Thus, stable multi-hop wireless communication can be realized.
以下、図面を参照しながら、本発明の実施の形態について詳細に説明する。
図1は、本発明の一実施の形態であるマルチホップ無線通信システムによる無線ネットワークの構成の一例を示す概念図であり、図2は、本実施の形態のマルチホップ無線通信システムを構成する無線端末の構成の一例を示す概念図、図3は、本実施の形態の無線端末がもつ経路情報テーブルの構成の一例を示す概念図、図4は、本実施の形態の無線端末がもつ送信間隔制御テーブルの構成の一例を示す概念図である。
Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
FIG. 1 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example of a configuration of a wireless network using a multi-hop wireless communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention, and FIG. 2 is a wireless configuration of the multi-hop wireless communication system according to the present embodiment. FIG. 3 is a conceptual diagram illustrating an example of a configuration of a route information table included in the wireless terminal according to the present embodiment. FIG. 4 is a transmission interval included in the wireless terminal according to the present embodiment. It is a conceptual diagram which shows an example of a structure of a control table.
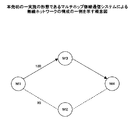
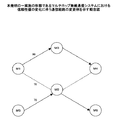
図1に例示される本実施の形態のマルチホップ無線通信システムは、各々が無線端末10からなる端末M1〜端末M4によって無線通信ネットワークを構成している。図1において、点線は無線区間で通信路として成立している通信経路、経路上の数値は通信経路の信頼性値を示している。この例では、端末M1から端末M4への通信は、端末M3を経由する通信経路と端末M2を経由する通信経路とが考えられる。
In the multi-hop wireless communication system of the present embodiment illustrated in FIG. 1, a wireless communication network is configured by terminals M <b> 1 to M <b> 4 each including a
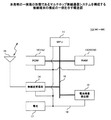
図2に例示されるように、端末M1〜端末M4の各々を構成する無線端末10は、マイクロプロセッサ11と、このマイクロプロセッサ11を制御して後述の制御動作を行わせる制御プログラム12aが格納されたROM(Read Only Memory)12(記録媒体)と、マイクロプロセッサ11がアクセスする後述の経路情報テーブル20や送信間隔制御テーブル30等の情報が格納されるRAM(Random Access Memory)13と、アンテナ19を経由した無線通信にて外部とデータの授受を行う無線送受信部14と、電池残量検出部15と、これらを相互に接続する情報伝送路としてのバス16からなるコンピュータで構成されている。
As illustrated in FIG. 2, the
この無線端末10には、給電線18を介して上述の各部に動作電力を供給する電池17が設けられており、電池残量検出部15は、この電池17の残量を検出して、マイクロプロセッサ11に通知する機能を備えている。
The
有限エネルギー源としての電池17は、たとえば、一次電池、二次電池、燃料電池、その他あらゆる電池型の電源を含む。一次電池、二次電池の場合、電池の残量は、出力電圧、出力電流の変化等にて計測され、燃料電池の場合には、燃料の残量として計測できる。
The
制御プログラム12aは、後述の経路情報テーブル20の経路情報および信頼性値等に基づいて、無線送受信部14を介して他の無線端末10との間で情報通信を制御する機能、経路情報の単位時間当たりの受信頻度(着信率)に基づいて当該経路情報の送信元の無線端末10の信頼性値を決定する(着信率が高いほど信頼性が高いと判定する)機能(第3機能)、電池残量検出部15を介して自無線端末10における電池17の残量を検出する機能(第1機能)、自無線端末10における電池17の残量と、後述の送信間隔制御テーブル30の設定内容に基づいて、経路情報の同報送信の送信間隔を制御する機能(第2機能)等をマイクロプロセッサ11に実行させるように構成されている。
The
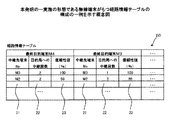
図3は、本実施の形態における無線端末10(この図3は、端末M1の例)の管理する経路情報テーブル20の構成例を示す。経路情報テーブル20は、通信先の最終目的端末毎に、中継先端末番号21と、中継段数22と、信頼性値23とが対応付けられて格納されている。
FIG. 3 shows a configuration example of the route information table 20 managed by the wireless terminal 10 (this FIG. 3 is an example of the terminal M1) in the present embodiment. The route information table 20 stores a relay
また、個々の無線端末10は、図4に例示される送信間隔制御テーブル30を備えている。この送信間隔制御テーブル30は、電池17の残量に応じて、経路情報を他の無線端末10に送信する間隔を制御するためのものであり、たとえば百分率で示された複数段階の電池残量31と、それに対応した経路情報送信間隔32とが対応付けて設定されている。
Each
すなわち、図4の設定例では、電池残量が100%の場合は、単位時間T当たりに10回(送信間隔=T/10)だけ経路情報の送信を行い、電池残量が10%の場合は、単位時間T当たりに1回(送信間隔=T)だけ経路情報の送信を行うように設定されており、マイクロプロセッサ11は、経路情報テーブル20に格納されている経路情報の送信を行う際に、電池残量検出部15から得られる電池残量と、送信間隔制御テーブル30の設定状態とに基づいて、送信間隔を決定する。
That is, in the setting example of FIG. 4, when the remaining battery level is 100%, the route information is transmitted 10 times per unit time T (transmission interval = T / 10), and the remaining battery level is 10%. Is set so as to transmit the path information once per unit time T (transmission interval = T), and the
なお、本実施の形態では、10/Tは、マルチホップ無線通信のプロトコル等で推奨される標準的な頻度とすることにより、電池残量の減少とともに頻度が低くなるようにすることで、経路情報自体の送信頻度増大によってデータ量が増加することはない。 In this embodiment, 10 / T is set to a standard frequency recommended in a multi-hop wireless communication protocol or the like, so that the frequency decreases as the remaining battery level decreases, thereby reducing the path. The amount of data does not increase due to an increase in the transmission frequency of the information itself.
以下、本実施の形態の作用について説明する。本実施の形態では、無線端末10の制御プログラム12aは、図5に示すように、一定間隔で自端末のもつ経路情報をブロードキャスト(同報送信)し、周囲の端末は単位時間の経路情報の着信率を元に経路の信頼性値を判定する。パケットを伝送する端末はこの経路情報テーブル20上の各経路の中継段数22と信頼性値23を元に通信に使用する経路を選択する。
Hereinafter, the operation of the present embodiment will be described. In the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. 5, the
図1の場合、端末M1から端末M4への通信経路は図3の経路情報テーブル20の端末M4を最終目的局とする中継端末(中継先端末番号21)の中で、中継段数22の少ない経路をまず選択する。このとき、同一の中継段数に複数の経路が存在した場合は、経路の信頼性値23の高い経路(図1、図3の例の場合、端末M3への経路)を優先的に選択する。この場合の経路は、端末M1→端末M3→端末M4となる。 In the case of FIG. 1, the communication path from the terminal M1 to the terminal M4 is a path with a small number of relay stages 22 among relay terminals (relay destination terminal number 21) having the terminal M4 in the path information table 20 of FIG. Select first. At this time, when a plurality of routes exist with the same number of relay stages, a route having a high route reliability value 23 (in the example of FIGS. 1 and 3, a route to the terminal M3) is preferentially selected. The route in this case is terminal M1 → terminal M3 → terminal M4.
このとき、各端末のマイクロプロセッサ11の制御プログラム12aは、自端末の電池残量を計測し、自端末の電池残量が低下した場合は、上述の図4ように、あらかじめ端末内に保持している電池残量に対する経路情報の送信間隔制御テーブル30の設定情報にしたがい、経路情報の送信間隔を制御する。例えば、端末M3の電池残塁が80%以下となった場合、送信間隔制御テーブル30の情報に従い、図6に例示されるように、単位時間T内に経路情報K1〜経路情報K8の8回だけ経路情報が同報送信され、周囲の端末への経路情報の送信間隔はT/8に延長される。
At this time, the
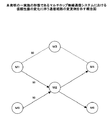
これにより、周囲の端末(たとえば端末M1や端末M4)は端末M3からの経路情報の着信率(単位時間T当たりの経路情報の受信回数)が低下する。このため、端末M1や端末M4から見た場合、端末M3を使用する経路の信頼性値情報が低下するために、端末M3を中継端末とする経路の優先順位が、端末M2を中継端末とする経路に対して低くなり、この経路の使用頻度が低くなる。 As a result, peripheral terminals (for example, the terminal M1 and the terminal M4) have a lower rate of incoming route information from the terminal M3 (number of times route information is received per unit time T). For this reason, when viewed from the terminal M1 and the terminal M4, since the reliability value information of the route using the terminal M3 is lowered, the priority order of the route having the terminal M3 as a relay terminal is the terminal M2 as the relay terminal. It becomes low with respect to a path | route, and the frequency of use of this path | route becomes low.
図7に端末M1内の更新された経路情報テーブル20を示す。図3の状態に比較して、たとえば最終目的端末が端末M4の場合、中継先端末番号21が端末M3の信頼性値23の値が100%から80%に低下しており、端末M2の90%よりも小さくなり、端末M3を経由する経路は選択されなくなる。これにより、端末M1では目的端末M4への経路テーブル上の各経路の優先順位が変動し、この結果、マイクロプロセッサ11は、端末M2を中継先と変更して転送する。すなわち、図7の経路情報テーブル20に対応した端末M1から端末M4への転送経路は、図8に例示されるように、端末M1→端末M2→端末M4に変化する。
FIG. 7 shows the updated route information table 20 in the terminal M1. Compared to the state of FIG. 3, for example, when the terminal terminal is the terminal M4, the relay
また、図9のように、図1の構成に対して端末M5、端末M6が追加され、端末M5から端末M6への通信(転送経路:端末M5→端末M2→端末M6)が同時に行なわれた場合、端末M2の電池残量はさらに低下し、これに伴い上記の送信間隔制御テーブル30の情報に基づき、経路情報の送信間隔が広がることにより、端末M1で管理する端末M2を中継端末とした経路の信頼性値は低くなる。このとき目的端末M4への経路情報テーブル上の経路で、端末M3を中継先とする経路の信頼性値より低くなった場合は、図10の経路情報テーブル20のように優先順位が変更され、再度、端末M1から端末M4への転送経路は端末M1→端末M3→端末M4となる、このとき端末M5から端末M6への経路は1つしか存在しないため、図11のように、端末M5→端末M2→端末M6を使用し続ける。これにより、図9のように端末M2に集中していた負荷が、図11のように端末M3に分散されて軽減され、端末M2の電池17が短時間に消耗して中継不能となるような障害が確実に防止され、安定にマルチホップ無線通信を継続することが可能となる。
Further, as shown in FIG. 9, terminal M5 and terminal M6 are added to the configuration of FIG. 1, and communication from the terminal M5 to the terminal M6 (transfer route: terminal M5 → terminal M2 → terminal M6) is performed simultaneously. In this case, the remaining battery level of the terminal M2 further decreases, and accordingly, the transmission interval of the route information is widened based on the information of the transmission interval control table 30. Accordingly, the terminal M2 managed by the terminal M1 is used as a relay terminal. The reliability value of the route is low. At this time, when the route on the route information table to the target terminal M4 becomes lower than the reliability value of the route having the terminal M3 as a relay destination, the priority is changed as in the route information table 20 of FIG. Again, the transfer path from the terminal M1 to the terminal M4 is terminal M1 → terminal M3 → terminal M4. At this time, since there is only one path from the terminal M5 to the terminal M6, as shown in FIG. 11, the terminal M5 → Continue to use terminal M2 → terminal M6. As a result, the load concentrated on the terminal M2 as shown in FIG. 9 is reduced by being distributed to the terminal M3 as shown in FIG. 11, so that the
また、上記の例では電池17の残量に応じて経路情報の送信間隔を可変とした場合を例示したが、図12に示すように、送信間隔T/10で、当該T/10以上の休止期間が挟まれるように間欠的に送信する方式でも良い。
In the above example, the case where the transmission interval of the route information is made variable according to the remaining amount of the
以上説明したように、本発明の実施の形態によれば、個々の無線端末10において、電池17の残量に応じて、経路情報の同報送信の送信間隔を変動させ、各端末の経路情報上の信頼性値を制御し、たとえば、電池17の残量が少ない端末を経由する通信経路の選択頻度が低くなるように経路の優先度を制御することにより、マルチホップ無線通信システムを構成する複数の端末M1〜端末M6の間で電池17の消耗量が偏らないで均等化されるような中継経路の選択が可能になる。
As described above, according to the embodiment of the present invention, each
これにより、特定の端末に中継経路が集中して電池17の消耗が促進されて中継不能となるような通信障害が回避され、安定なマルチホップ無線通信が可能となる。
また、電池17の消耗度に応じた経路情報の送信間隔の変更にて経路の優先度を制御するので、たとえば、すべての端末の電池17の消耗量のデータを相互に交換する場合のように、データ量が増加することもなく、マルチホップ無線通信網における通信負荷の増大が発生することもない。さらに、個々の無線端末にて他のすべての無線端末の電池17の残量を管理する等の複雑な処理も不要である。
As a result, a communication failure such that the relay routes are concentrated on a specific terminal, the
Further, since the priority of the route is controlled by changing the transmission interval of the route information according to the degree of consumption of the
なお、上述の説明では、有限エネルギー源として電池を用いる場合を例にとって説明したが、使用とともにエネルギー残量が減少する一般の有限エネルギー源を用いる場合にも本発明は適用することができる。 In the above description, the case where a battery is used as a finite energy source has been described as an example. However, the present invention can also be applied to a case where a general finite energy source whose remaining energy decreases with use is used.
10 無線端末
11 マイクロプロセッサ
12 ROM
12a 制御プログラム
13 RAM
14 無線送受信部
15 電池残量検出部
16 バス
17 電池
18 給電線
19 アンテナ
20 経路情報テーブル
21 中継先端末番号
22 中継段数
23 信頼性値
30 送信間隔制御テーブル
31 電池残量
32 経路情報送信間隔
K1〜K10 経路情報
M1〜M6 端末
T 単位時間
10
14 Wireless transmission /
Claims (10)
個々の前記無線端末は、前記有限エネルギー源の残量に応じて前記経路情報の送信間隔を変化させることで、他の前記無線端末に自無線端末の前記有限エネルギー源の残量を認識させることを特徴とする無線通信方法。 A multi-hop wireless communication method in which a plurality of wireless terminals operating with a finite energy source relay transmission packets to each other based on path information transmitted and received between each other,
Each of the wireless terminals causes other wireless terminals to recognize the remaining amount of the finite energy source of the own wireless terminal by changing the transmission interval of the route information according to the remaining amount of the finite energy source. A wireless communication method characterized by the above.
個々の前記無線端末において、前記有限エネルギー源の残量に応じて前記経路情報の送信間隔を変化させることを特徴とする無線通信方法。 A plurality of wireless terminals operating with a finite energy source mutually transmit / receive path information defining a communication path passing through the wireless terminal, and transmit packets to each other based on the path information and the reliability value of the communication path A multi-hop wireless communication method for relay transmission,
A wireless communication method, wherein each of the wireless terminals changes a transmission interval of the route information according to a remaining amount of the finite energy source.
個々の前記無線端末は、前記有限エネルギー源の残量を検出する第1機能と、前記残量に応じて前記経路情報の送信間隔を変化させる第2機能とを備えていることを特徴とする無線通信システム。 A plurality of wireless terminals operating with a finite energy source mutually transmit / receive path information defining a communication path passing through the wireless terminal, and transmit packets to each other based on the path information and the reliability value of the communication path A multi-hop wireless communication system for relay transmission,
Each of the wireless terminals has a first function of detecting the remaining amount of the finite energy source and a second function of changing a transmission interval of the route information according to the remaining amount. Wireless communication system.
前記第2機能は、前記有限エネルギー源の前記残量の減少に比例して前記経路情報の送信間隔を長くし、他の前記無線端末にて認識される自無線端末の前記信頼性値を低くすることにより、前記有限エネルギー源の残量の少ない前記無線端末を経由した前記通信路の使用頻度が相対的に低くなるようにしたことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の無線通信システム。 Each of the wireless terminals further includes a third function of determining the reliability value of the communication path that passes through the wireless terminal that is the transmission source of the route information based on the reception frequency of the route information within a unit time. ,
The second function increases a transmission interval of the route information in proportion to a decrease in the remaining amount of the finite energy source, and lowers the reliability value of the own wireless terminal recognized by the other wireless terminals. The wireless communication system according to claim 4, wherein the use frequency of the communication path via the wireless terminal with a small remaining amount of the finite energy source is relatively reduced.
前記第2機能は、前記有限エネルギー源の前記残量の減少に比例して前記経路情報の送信間隔を長くし、他の前記無線端末にて認識される自無線端末の前記信頼性値を低くすることにより、前記有限エネルギー源の残量の少ない自無線端末を経由した前記通信路の使用頻度が相対的に低くなるように制御することを特徴とする請求項7に記載の無線端末。 A third function of determining a reliability value of a communication path that passes through the wireless terminal that is the transmission source of the route information based on a reception frequency of the route information within a unit time;
The second function increases a transmission interval of the route information in proportion to a decrease in the remaining amount of the finite energy source, and lowers the reliability value of the own wireless terminal recognized by the other wireless terminals. The wireless terminal according to claim 7, wherein control is performed so that the frequency of use of the communication path via the own wireless terminal with a small remaining amount of the finite energy source is relatively low.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004109029A JP2005295310A (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2004-04-01 | Radio communication method, radio communication system, radio terminal, program and recording medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004109029A JP2005295310A (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2004-04-01 | Radio communication method, radio communication system, radio terminal, program and recording medium |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005295310A true JP2005295310A (en) | 2005-10-20 |
Family
ID=35327739
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004109029A Pending JP2005295310A (en) | 2004-04-01 | 2004-04-01 | Radio communication method, radio communication system, radio terminal, program and recording medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2005295310A (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008193136A (en) * | 2007-01-31 | 2008-08-21 | Ntt Docomo Inc | Communication terminal and communication control method |
| JP2010537565A (en) * | 2007-08-17 | 2010-12-02 | クゥアルコム・インコーポレイテッド | Ad hoc service provider's ability to serve wireless networks |
| US7924758B2 (en) | 2006-09-26 | 2011-04-12 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Energy-aware routing apparatus and method |
| US9179367B2 (en) | 2009-05-26 | 2015-11-03 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Maximizing service provider utility in a heterogeneous wireless ad-hoc network |
| US9392445B2 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2016-07-12 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Handoff at an ad-hoc mobile service provider |
| JP2018157640A (en) * | 2017-03-16 | 2018-10-04 | 株式会社富士通エフサス | Management device and control method |
| JP2020170908A (en) * | 2019-04-01 | 2020-10-15 | 京セラ株式会社 | Communication device, communication system, and communication method |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03220828A (en) * | 1990-01-25 | 1991-09-30 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Wireless monitoring equipment |
| JPH09149079A (en) * | 1995-11-20 | 1997-06-06 | Nec Corp | Path selection system for communication equipment |
| JP2001036459A (en) * | 1999-07-22 | 2001-02-09 | Canon Inc | Wireless communication device |
| JP2001189689A (en) * | 1999-12-28 | 2001-07-10 | Toshiba Corp | Communication device and control method thereof |
| JP2003511950A (en) * | 1999-10-13 | 2003-03-25 | テレフオンアクチーボラゲツト エル エム エリクソン | Wireless transceiver |
| JP2003283560A (en) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-03 | Tama Tlo Kk | Information distribution system and distribution method therefor |
| WO2004023241A2 (en) * | 2002-09-04 | 2004-03-18 | Harris Corporation | Intelligent communication node object beacon framework in a mobile ad hoc network |
| JP2005217548A (en) * | 2004-01-27 | 2005-08-11 | Nec Corp | Method and system for radio communication and radio terminal |
| JP2005526416A (en) * | 2001-08-03 | 2005-09-02 | ハネウェル・インターナショナル・インコーポレーテッド | Energy recognition network management |
-
2004
- 2004-04-01 JP JP2004109029A patent/JP2005295310A/en active Pending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH03220828A (en) * | 1990-01-25 | 1991-09-30 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Wireless monitoring equipment |
| JPH09149079A (en) * | 1995-11-20 | 1997-06-06 | Nec Corp | Path selection system for communication equipment |
| JP2001036459A (en) * | 1999-07-22 | 2001-02-09 | Canon Inc | Wireless communication device |
| JP2003511950A (en) * | 1999-10-13 | 2003-03-25 | テレフオンアクチーボラゲツト エル エム エリクソン | Wireless transceiver |
| JP2001189689A (en) * | 1999-12-28 | 2001-07-10 | Toshiba Corp | Communication device and control method thereof |
| JP2005526416A (en) * | 2001-08-03 | 2005-09-02 | ハネウェル・インターナショナル・インコーポレーテッド | Energy recognition network management |
| JP2003283560A (en) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-03 | Tama Tlo Kk | Information distribution system and distribution method therefor |
| WO2004023241A2 (en) * | 2002-09-04 | 2004-03-18 | Harris Corporation | Intelligent communication node object beacon framework in a mobile ad hoc network |
| JP2005217548A (en) * | 2004-01-27 | 2005-08-11 | Nec Corp | Method and system for radio communication and radio terminal |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7924758B2 (en) | 2006-09-26 | 2011-04-12 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Energy-aware routing apparatus and method |
| JP2008193136A (en) * | 2007-01-31 | 2008-08-21 | Ntt Docomo Inc | Communication terminal and communication control method |
| JP2010537565A (en) * | 2007-08-17 | 2010-12-02 | クゥアルコム・インコーポレイテッド | Ad hoc service provider's ability to serve wireless networks |
| US8644206B2 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2014-02-04 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Ad hoc service provider configuration for broadcasting service information |
| US9167426B2 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2015-10-20 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Ad hoc service provider's ability to provide service for a wireless network |
| US9392445B2 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2016-07-12 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Handoff at an ad-hoc mobile service provider |
| US9398453B2 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2016-07-19 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Ad hoc service provider's ability to provide service for a wireless network |
| US9179367B2 (en) | 2009-05-26 | 2015-11-03 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Maximizing service provider utility in a heterogeneous wireless ad-hoc network |
| JP2018157640A (en) * | 2017-03-16 | 2018-10-04 | 株式会社富士通エフサス | Management device and control method |
| JP2020170908A (en) * | 2019-04-01 | 2020-10-15 | 京セラ株式会社 | Communication device, communication system, and communication method |
| JP7104654B2 (en) | 2019-04-01 | 2022-07-21 | 京セラ株式会社 | Communication devices, communication systems, and communication methods |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9681327B2 (en) | Wireless sensor network system | |
| ElBatt et al. | Power management for throughput enhancement in wireless ad-hoc networks | |
| EP3085160B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for data packet transmission | |
| US11558299B2 (en) | Method for utilization-based traffic throttling in a wireless mesh network | |
| US7924758B2 (en) | Energy-aware routing apparatus and method | |
| US7277414B2 (en) | Energy aware network management | |
| US8098615B2 (en) | Network protocol | |
| US8103316B2 (en) | Power management system for a field device on a wireless network | |
| US7619998B2 (en) | Multi-hop communication system, radio control station, radio station and multi-hop communication method | |
| JP5338567B2 (en) | Wireless terminal and wireless system | |
| JP7057670B2 (en) | Configurable communication module for flexible communication in energy-limited wireless systems | |
| WO2008079471A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for maintaining traffic flow in a mesh network | |
| Femila et al. | Optimizing transmission power and energy efficient routing protocol in MANETs | |
| JP2005295310A (en) | Radio communication method, radio communication system, radio terminal, program and recording medium | |
| JP2010199742A (en) | Radio communication system | |
| JP6015072B2 (en) | Communication system, communication apparatus, route switching method, and route switching program | |
| JP5870285B2 (en) | Multi-hop communication method, multi-hop communication system, and communication terminal | |
| Djidi et al. | Adaptive relaying for wireless sensor networks leveraging wake-up receiver | |
| KR101137653B1 (en) | Addaptive Topology Operation System And Method Thereof | |
| JP2006345414A (en) | Route setting method, data aggregation node, data transmission node, and communication system | |
| JP5870286B2 (en) | Multi-hop communication method, multi-hop communication system, and communication terminal | |
| JP5796214B2 (en) | Multi-hop communication method and multi-hop communication system | |
| KR100770878B1 (en) | How to set up routing routes in mobile ad hoc networks | |
| Geetha et al. | Hop Count Based Energy Saving Dynamic Source Routing Protocol for Ad Hoc Network | |
| WO2012028918A1 (en) | Multi-hop communication system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070116 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090410 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090609 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20091020 |