JP2005290580A - Woven fabric and woven fabric processed product - Google Patents
Woven fabric and woven fabric processed product Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2005290580A JP2005290580A JP2004103704A JP2004103704A JP2005290580A JP 2005290580 A JP2005290580 A JP 2005290580A JP 2004103704 A JP2004103704 A JP 2004103704A JP 2004103704 A JP2004103704 A JP 2004103704A JP 2005290580 A JP2005290580 A JP 2005290580A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- woven fabric
- sheath
- thermoplastic resin
- fiber
- component
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000002759 woven fabric Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 79
- 239000000306 component Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 239000008358 core component Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 claims description 50
- 229920005992 thermoplastic resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 35
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 claims description 31
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 31
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 24
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000011162 core material Substances 0.000 description 23
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 17
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 17
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 14
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 14
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 13
- -1 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 11
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 7
- 125000004805 propylene group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([*:1])C([H])([H])[*:2] 0.000 description 7
- 239000005871 repellent Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229920001684 low density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000004702 low-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 5
- QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene Natural products CC=C QQONPFPTGQHPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 230000002940 repellent Effects 0.000 description 5
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000004711 α-olefin Substances 0.000 description 4
- VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethene Chemical compound C=C VGGSQFUCUMXWEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000005977 Ethylene Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 3
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920001384 propylene homopolymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- VXNZUUAINFGPBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Butene Chemical compound CCC=C VXNZUUAINFGPBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine atom Chemical compound [F] YCKRFDGAMUMZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001400 block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004566 building material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920005674 ethylene-propylene random copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001125 extrusion Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920005672 polyolefin resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229920005606 polypropylene copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000012805 post-processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920005604 random copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000009941 weaving Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001644 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- WSSSPWUEQFSQQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-methyl-1-pentene Chemical compound CC(C)CC=C WSSSPWUEQFSQQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101100420946 Caenorhabditis elegans sea-2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000089 Cyclic olefin copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl urethane Chemical compound CCOC(N)=O JOYRKODLDBILNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000106 Liquid crystal polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004977 Liquid-crystal polymers (LCPs) Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004677 Nylon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002216 antistatic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003490 calendering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011203 carbon fibre reinforced carbon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000092 linear low density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004707 linear low-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002074 melt spinning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000655 nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001778 nylon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012466 permeate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001707 polybutylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001225 polyester resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004645 polyester resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D1/00—Woven fabrics designed to make specified articles
- D03D1/0035—Protective fabrics
- D03D1/0041—Cut or abrasion resistant
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/28—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like while mixing different spinning solutions or melts during the spinning operation; Spinnerette packs therefor
- D01D5/30—Conjugate filaments; Spinnerette packs therefor
- D01D5/34—Core-skin structure; Spinnerette packs therefor
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01F—CHEMICAL FEATURES IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE MANUFACTURE OF CARBON FILAMENTS
- D01F8/00—Conjugated, i.e. bi- or multicomponent, artificial filaments or the like; Manufacture thereof
- D01F8/04—Conjugated, i.e. bi- or multicomponent, artificial filaments or the like; Manufacture thereof from synthetic polymers
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D15/00—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used
- D03D15/20—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the material of the fibres or filaments constituting the yarns or threads
- D03D15/283—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the material of the fibres or filaments constituting the yarns or threads synthetic polymer-based, e.g. polyamide or polyester fibres
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D15/00—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used
- D03D15/20—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the material of the fibres or filaments constituting the yarns or threads
- D03D15/292—Conjugate, i.e. bi- or multicomponent, fibres or filaments
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D15/00—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used
- D03D15/40—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the structure of the yarns or threads
- D03D15/44—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the structure of the yarns or threads with specific cross-section or surface shape
- D03D15/46—Flat yarns, e.g. tapes or films
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D15/00—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used
- D03D15/50—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the properties of the yarns or threads
- D03D15/573—Tensile strength
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D15/00—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used
- D03D15/50—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the properties of the yarns or threads
- D03D15/587—Woven fabrics characterised by the material, structure or properties of the fibres, filaments, yarns, threads or other warp or weft elements used characterised by the properties of the yarns or threads adhesive; fusible
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2321/00—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- D10B2321/02—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds polyolefins
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2321/00—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- D10B2321/02—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds polyolefins
- D10B2321/021—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds polyolefins polyethylene
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2321/00—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds
- D10B2321/02—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds polyolefins
- D10B2321/022—Fibres made from polymers obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds polyolefins polypropylene
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2331/00—Fibres made from polymers obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polycondensation products
- D10B2331/02—Fibres made from polymers obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polycondensation products polyamides
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2331/00—Fibres made from polymers obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polycondensation products
- D10B2331/04—Fibres made from polymers obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polycondensation products polyesters, e.g. polyethylene terephthalate [PET]
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2401/00—Physical properties
- D10B2401/04—Heat-responsive characteristics
- D10B2401/041—Heat-responsive characteristics thermoplastic; thermosetting
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2401/00—Physical properties
- D10B2401/06—Load-responsive characteristics
- D10B2401/063—Load-responsive characteristics high strength
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T442/00—Fabric [woven, knitted, or nonwoven textile or cloth, etc.]
- Y10T442/30—Woven fabric [i.e., woven strand or strip material]
- Y10T442/3146—Strand material is composed of two or more polymeric materials in physically distinct relationship [e.g., sheath-core, side-by-side, islands-in-sea, fibrils-in-matrix, etc.] or composed of physical blend of chemically different polymeric materials or a physical blend of a polymeric material and a filler material
- Y10T442/3163—Islands-in-sea multicomponent strand material
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Woven Fabrics (AREA)
- Multicomponent Fibers (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
- Nonwoven Fabrics (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Yarns And Mechanical Finishing Of Yarns Or Ropes (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、織布およびその織布加工品に関する。さらに詳しくは、建築用資材カバーなどのカバー類、防水シートなどのシート類、テント、包装袋、フレキシブルコンテナなどのシート状物として用いられる織布、およびその織布加工品に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a woven fabric and a processed product of the woven fabric. More specifically, the present invention relates to a cover such as a building material cover, a sheet such as a waterproof sheet, a woven fabric used as a sheet-like material such as a tent, a packaging bag, and a flexible container, and a woven fabric processed product thereof.
従来、シート状の織布は、マルチフィラメントを収束した繊維束を織ることにより作製されており、そして、織るためには、マルチフィラメントに対する油剤(帯電防止剤)の表面付着処理と、マルチフィラメントの撚り加工が必須であった。しかしながら、撚り加工を行うと、織布中の繊維束が不揃いになりやすく、その結果、良好な物性、特に強い引張り強度、低い伸度を有する織布を得ることは困難であった。
また、前記織布に防水性機能を付与する場合、織布表面に撥水処理を施しているが、このようにして得られた防水性織布は、単繊維間への吸水や、織布の端面、破損部への水分侵入が発生するという問題があった。
Conventionally, a sheet-like woven fabric is produced by weaving a bundle of fibers in which multifilaments are converged, and in order to weave, a surface adhesion treatment of an oil agent (antistatic agent) on the multifilament, Twisting was essential. However, when twisting is performed, the fiber bundles in the woven fabric tend to be uneven, and as a result, it has been difficult to obtain a woven fabric having good physical properties, particularly strong tensile strength and low elongation.
In addition, when the waterproof function is imparted to the woven fabric, the surface of the woven fabric is subjected to water repellency treatment. The waterproof woven fabric thus obtained can absorb water between single fibers, There is a problem that moisture permeates into the end face and the damaged part of the glass.
そこで、このような問題に対処するために、例えば紡糸油剤にフッ素系撥水剤を使用したポリエチレンテレフタレート(PET)繊維からなる基布(例えば、特許文献1参照)や、ターポリンの基布を構成するポリエステル系繊維からなる繊維束を、主としてフッ素系撥水剤およびポリエステル系ウレタンからなるエマルジョンで処理すること(例えば、特許文献2参照)など、各マルチフィラメント表面に撥水処理を施すことが開示されている。 Therefore, in order to cope with such a problem, for example, a base fabric made of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fiber using a fluorine-based water repellent as a spinning oil (see, for example, Patent Document 1) or a tarpaulin base fabric is configured. Disposing water repellent treatment on the surface of each multifilament, such as treating a fiber bundle composed of polyester fibers to be treated with an emulsion mainly composed of a fluorine-based water repellent and a polyester-based urethane (for example, see Patent Document 2). Has been.
しかしながら、これらの場合、処理剤やその工程数が増えてコストが高くなることや、前記織布の問題点がそのままであることに加え、繊維や繊維束の撥水処理加工によって、得られる織布は、組織(織り)が乱れ、製品の品質、外観が悪くなる。
さらに、前記防水性織布の少なくとも片面に、樹脂を被覆した樹脂被覆加工布が提案されている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。この公報には、目ずれしないように、からみ織やからみ糸を使用して目ずれ防止を行っている粗目組織の基布に対して、効果を発揮することが開示されている。これは、一方で、撥水性表面の織布と被覆樹脂との接着性が低下するため、粗目組織のすき間で、上下の被覆樹脂同士が融着することによって、はじめて接着性を保持していることが推察される。この場合、加工布全体が一体になっておらず、高い物性を有する防水性織布の加工品が得られにくいことが考えられる。
However, in these cases, the number of treatment agents and the number of processes increases, the cost increases, the problem of the woven fabric remains as it is, and the weave obtained by the water-repellent treatment of fibers and fiber bundles. The fabric (texture) is disturbed, and the quality and appearance of the product deteriorate.
Further, a resin-coated processed cloth in which at least one surface of the waterproof woven cloth is coated with a resin has been proposed (see, for example, Patent Document 1). This gazette discloses that an effect is exerted on a base fabric having a coarse structure in which stitch misalignment and string yarn are used to prevent misalignment so as not to cause misalignment. On the other hand, since the adhesiveness between the woven fabric on the water-repellent surface and the coating resin is lowered, the adhesiveness is maintained only when the upper and lower coating resins are fused with each other in the gap of the coarse texture. It is inferred. In this case, it is conceivable that the processed fabric is not integrated and the processed product of the waterproof woven fabric having high physical properties is difficult to obtain.
本発明は、このような事情のもとで、強力が高く、伸度が低いなど、良好な物性を有すると共に、その良好な物性を保持したままで、防水性も良好な織布、およびその織布加工品を安価に提供することを目的とするものである。 Under such circumstances, the present invention has a good physical property such as high strength and low elongation, and also has a good waterproof property while maintaining the good physical property, and its The object is to provide a processed fabric product at a low cost.
本発明者は、前記目的を達成するために鋭意研究を重ねた結果、鞘成分が芯成分よりも融点が20℃以上低い熱可塑性樹脂からなり、かつ撚り加工を行わない鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を、特定の条件で延伸処理して得られた繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体を用いて得られた織布により、その目的を達成し得ることを見出し、この知見に基づいて本発明を完成するに至った。 As a result of intensive studies to achieve the above object, the present inventor has made a sheath core type composite spun fiber in which the sheath component is made of a thermoplastic resin having a melting point lower than that of the core component by 20 ° C. or more and does not undergo twist processing. Has been found to be able to achieve its purpose with a woven fabric obtained by using a fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin filament obtained by stretching under specific conditions, and the present invention has been completed based on this finding. It came to do.
すなわち、本発明は、
(1)収束された鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を、鞘成分の融点以上、かつ芯成分の融点未満の温度で延伸すると共に、前記鞘成分を融合させてなる繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体を用いて得られた織布であって、前記の鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維として、鞘成分が芯成分の融点より20℃以上低い熱可塑性樹脂からなり、かつ撚り加工を行わないストレートの鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を用いたことを特徴とする織布、
(2)下記の式(I)で表される強力寄与率が80%以上である請求項1に記載の織布、
強力寄与率(%)=(B/A)×100 ・・・(I)
[ただし、Aは繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体から計算される引張り強力(N/3cm)。該線状体の強力(N)×織布の打ち込み本数(本)/2.54cm×3cmの式によって計算される。Bは織布の引張り強力(N/3cm)。]
(3)目付けが50〜500g/m2である上記(1)または(2)項に記載の織布、
(4)熱可塑性樹脂がポリオレフィンである上記(1)ないし(3)項のいずれか1項に記載の織布、
(5)上記(1)ないし(4)項のいずれか1項に記載の織布を加工処理してなる織布加工品、
(6)加工処理が加熱プレス処理である上記(5)項に記載の織布加工品、
(7)加工処理が少なくとも片面に熱可塑性樹脂被覆層を新たに形成する処理である上記(5)または(6)項に記載の織布加工品、
(8)JIS L 1907のバイレック法によって測定される、端面における10分間放置後の水の上昇高さが10mm以下である上記(1)ないし(4)項のいずれか1項に記載の織布を含む防水性シート状物、および
(9)JIS L 1907のバイレック法によって測定される、端面における10分間放置後の水の上昇高さが10mm以下である上記(5)ないし(7)項のいずれか1項に記載の織布加工品を含む防水性シート状物、
を提供するものである。
That is, the present invention
(1) A fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body obtained by stretching the converged sheath-core type composite spun fiber at a temperature not lower than the melting point of the sheath component and lower than the melting point of the core component and fusing the sheath component. The sheath-core type composite spun fiber obtained by using the sheath-core-type composite spun fiber, wherein the sheath component is made of a thermoplastic resin that is lower by 20 ° C. or more than the melting point of the core component, and does not undergo twist processing A woven fabric characterized by using a composite spun fiber,
(2) The woven fabric according to
Strong contribution ratio (%) = (B / A) × 100 (I)
[However, A is the tensile strength (N / 3 cm) calculated from the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body. It is calculated by the formula of the strength of the linear body (N) × the number of driven woven fabrics (pieces) /2.54 cm × 3 cm. B is the tensile strength (N / 3cm) of the woven fabric. ]
(3) The woven fabric according to (1) or (2), wherein the basis weight is 50 to 500 g / m 2 ;
(4) The woven fabric according to any one of (1) to (3) above, wherein the thermoplastic resin is polyolefin.
(5) A woven fabric processed product obtained by processing the woven fabric according to any one of (1) to (4) above,
(6) The woven fabric processed product according to (5) above, wherein the processing treatment is a heat press treatment,
(7) The woven fabric processed product according to (5) or (6) above, wherein the processing treatment is a treatment for newly forming a thermoplastic resin coating layer on at least one surface;
(8) The woven fabric according to any one of the above items (1) to (4), wherein the rising height of the water after standing for 10 minutes on the end face is 10 mm or less, as measured by the Bayrec method of JIS L 1907 And (9) the rising height of the water after standing for 10 minutes at the end face measured by the Bayrec method of JIS L 1907 is 10 mm or less. A waterproof sheet-like material comprising the processed woven fabric according to any one of the above items,
Is to provide.
本発明によれば、強力が高く、伸度が低いなど、良好な物性を有し、その良好な物性を保持したままで、防水性も良好な織布、およびその織布加工品を安価に提供することができる。 According to the present invention, a woven fabric having good physical properties such as high strength and low elongation, and maintaining good physical properties, and having good waterproof properties, and processed woven fabrics thereof at low cost. Can be provided.
本発明の織布は、収束された鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を、鞘成分の融点以上、かつ芯成分の融点未満の温度で延伸すると共に、前記鞘成分を融合させてなる繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体を用いて作製されたものである。
前記の鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維における芯成分(高融点成分)としては、結晶性プロピレン系重合体、ポリエチレンテレフタレートやポリブチレンテレフタレートなどの結晶性ポリエステル、ポリアミド(ナイロン)、芳香族ポリエステル樹脂(液晶ポリマー)などを用いることができ、これらは1種を単独で用いてもよく、2種以上を組み合わせて用いてもよい。これらの中で、リサイクル性などを考慮すると、後述の鞘成分がポリオレフィン系樹脂である場合には、同種のポリオレフィン系樹脂である結晶性プロピレン系重合体が好ましい。
The woven fabric of the present invention is a fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin obtained by stretching a converged sheath-core type composite spun fiber at a temperature not lower than the melting point of the sheath component and lower than the melting point of the core component, and fusing the sheath component. It was produced using a linear body.
As the core component (high melting point component) in the sheath-core type composite spun fiber, crystalline propylene polymer, crystalline polyester such as polyethylene terephthalate and polybutylene terephthalate, polyamide (nylon), aromatic polyester resin (liquid crystal polymer) Etc.), and these may be used alone or in combination of two or more. Among these, in consideration of recyclability and the like, when the sheath component described later is a polyolefin resin, a crystalline propylene polymer which is the same kind of polyolefin resin is preferable.
この結晶性プロピレン系重合体としては、アイソタクチックポリプロピレン系樹脂が好ましく用いられる。中でもアイソタクチックペンタッド分率(IPF)が、好ましくは85%以上、より好ましくは90%以上のものが有利である。また、分子量分布の指標であるQ値(重量平均分子量/数平均分子量Mw/Mn比)は6以下、メルトインデックスMI(温度230℃、荷重2.16kg)は3〜50g/10分の範囲が好ましい。上記IPFが85%未満では立体規則性が不充分で結晶性が低く、得られる線状体における強度などの物性に劣る。 As this crystalline propylene polymer, an isotactic polypropylene resin is preferably used. Among them, those having an isotactic pentad fraction (IPF) of preferably 85% or more, more preferably 90% or more are advantageous. The Q value (weight average molecular weight / number average molecular weight Mw / Mn ratio), which is an index of molecular weight distribution, is 6 or less, and the melt index MI (temperature 230 ° C., load 2.16 kg) ranges from 3 to 50 g / 10 min. preferable. If the IPF is less than 85%, the stereoregularity is insufficient and the crystallinity is low, and the physical properties such as strength in the obtained linear body are inferior.
なお、アイソタクチックペンタッド分率(IPF)(一般にmmmm分率ともいわれる)は、任意の連続する5つのプロピレン単位で構成される炭素−炭素結合による主鎖に対して、側鎖である5つのメチル基がいずれも同方向に位置する立体構造の割合を示すものであって、同位体炭素核磁気共鳴スペクトル(13C−NMR)にけるPmmmm(プロピレン単位が5個連続してアイソタクチック結合した部位における第3単位目のメチル基に由来する吸収強度)およびPw(プロピレン単位の全メチル基に由来する吸収強度)から、式
IPF(%)=(Pmmmm/Pw)×100
によって求めることができる。
The isotactic pentad fraction (IPF) (generally also referred to as mmmm fraction) is a side chain with respect to the main chain of carbon-carbon bonds composed of any five consecutive propylene units. This shows the proportion of the three-dimensional structure in which two methyl groups are located in the same direction. Pmmmm (5 propylene units are isotactic) in the isotope carbon nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum ( 13 C-NMR). From the absorption intensity derived from the methyl group of the third unit at the bonded site and Pw (absorption intensity derived from all methyl groups of the propylene unit), the formula IPF (%) = (Pmmmm / Pw) × 100
Can be obtained.
また、このポリプロピレン系樹脂は、プロピレンの単独重合体であってもよいし、プロピレンとα−オレフィン(例えばエチレン、ブテン−1など)との共重合体であってもよい。
すなわち、結晶性プロピレン系重合体としては、例えば結晶性を有するアイソタクチックプロピレン単独重合体、エチレン単位の含有量の少ないエチレン−プロピレンランダム共重合体、プロピレン単独重合体からなるホモ部とエチレン単位の含有量の比較的多いエチレン−プロピレンランダム共重合体からなる共重合部とから構成されたプロピレンブロック共重合体、さらに前記プロピレンブロック共重合体における各ホモ部または共重合部が、さらにブテン−1などのα−オレフィンを共重合したものからなる結晶性プロピレン−エチレン−α−オレフィン共重合体などが挙げられる。
The polypropylene resin may be a propylene homopolymer or a copolymer of propylene and an α-olefin (for example, ethylene, butene-1, etc.).
That is, as the crystalline propylene polymer, for example, isotactic propylene homopolymer having crystallinity, ethylene-propylene random copolymer having a small ethylene unit content, homo-part consisting of propylene homopolymer and ethylene unit A propylene block copolymer composed of a copolymer part composed of an ethylene-propylene random copolymer having a relatively large content, and each homo part or copolymer part in the propylene block copolymer further comprises a butene- Examples thereof include crystalline propylene-ethylene-α-olefin copolymers formed by copolymerizing α-olefin such as 1.
一方、鞘成分(低融点成分)としては、前記芯成分の融点よりも20℃以上低い融点をもつ熱可塑性樹脂が用いられる。このような熱可塑性樹脂としては、各種のオレフィン系重合体や、低融点ポリエチレンテレフタレートなどが挙げられる。上記オレフィン系重合体としては、例えば高密度、中密度、低密度ポリエチレンや直鎖状低密度ポリエチレンなどのエチレン系重合体、プロピレンと他のα−オレフィンとの共重合体、具体的にはプロピレン−ブテン−1ランダム共重合体、プロピレン−エチレン−ブテン−1ランダム共重合体、あるいは軟質ポリプロピレンなどの非結晶性プロピレン系重合体、ポリ4−メチルペンテン−1などを挙げることができる。これらのオレフィン系重合体は、1種を単独で用いてもよいし、2種以上を組み合わせて用いてもよい。
特に、芯成分がポリプロピレンで、鞘成分がポリエチレンであるものは、価格的に安価で好ましい。
On the other hand, as the sheath component (low melting point component), a thermoplastic resin having a melting point lower by 20 ° C. or more than the melting point of the core component is used. Examples of such thermoplastic resins include various olefin polymers and low melting point polyethylene terephthalate. Examples of the olefin polymer include ethylene polymers such as high density, medium density, low density polyethylene and linear low density polyethylene, copolymers of propylene and other α-olefins, specifically propylene. Examples thereof include a -butene-1 random copolymer, a propylene-ethylene-butene-1 random copolymer, an amorphous propylene-based polymer such as soft polypropylene, and poly-4-methylpentene-1. One of these olefin polymers may be used alone, or two or more thereof may be used in combination.
In particular, it is preferable that the core component is polypropylene and the sheath component is polyethylene because it is inexpensive.
本発明で用いる鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維は、前記の芯成分とそれを被覆する鞘成分とから構成されたものであり、その製造方法については特に制限はなく、従来、鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維の製造において使用されている公知の方法を用いることができる。例えば、前記の鞘成分および芯成分を用い、押出し機2台と鞘芯型繊維用ノズルを備えた複合紡糸装置により、紡糸温度200〜260℃程度で溶融紡糸することにより、鞘心構造の複合紡糸繊維が得られる。
このようにして得られた鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維における芯/鞘断面積比は、通常40/60〜80/20の範囲で選定される。
The sheath-core type composite spun fiber used in the present invention is composed of the core component and the sheath component covering the core component, and the production method is not particularly limited. Conventionally, the sheath-core type composite spun fiber is used. The well-known method currently used in manufacture of can be used. For example, by using the above-mentioned sheath component and core component, and melt spinning at a spinning temperature of about 200 to 260 ° C. by a composite spinning apparatus equipped with two extruders and a sheath core type fiber nozzle, a composite with a sheath core structure is obtained. A spun fiber is obtained.
The core / sheath cross-sectional area ratio in the sheath-core type composite spun fiber thus obtained is usually selected in the range of 40/60 to 80/20.
本発明においては、前記の鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を、撚り加工せずにストレートの形で収束し、これを鞘成分の融点以上、かつ芯成分の融点未満の温度で延伸すると共に、該鞘成分を融合させて、繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体を作製する。
この延伸処理方法としては、所望の繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体が得られる方法であればよく、特に制限はないが、加圧飽和水蒸気中で、前記鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を延伸処理することが、良好な物性を有する繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体が得られるので好ましい。
本発明においては、加圧飽和水蒸気中での延伸処理を行う前に、所望により予備延伸処理を行ってもよい。
In the present invention, the sheath-core type composite spun fiber is converged in a straight form without being twisted, and stretched at a temperature not lower than the melting point of the sheath component and lower than the melting point of the core component. The components are fused to produce a fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body.
The stretching method may be any method as long as a desired fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body can be obtained, and is not particularly limited. However, the sheath-core composite spun fiber is stretched in pressurized saturated steam. It is preferable because a fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body having good physical properties can be obtained.
In the present invention, a preliminary stretching treatment may be performed as desired before performing the stretching treatment in pressurized saturated steam.
この予備延伸工程においては、続いて行われる本延伸工程における延伸温度よりも低い温度で複合紡糸繊維の延伸処理が行われる。この予備延伸処理方法としては、例えば一般的に知られている金属加熱ロールや金属加熱板などを用いた接触加熱延伸、あるいは温水、常圧〜0.2MPa程度の水蒸気や熱風などの加熱流体、遠赤外線などの熱線を用いた非接触加熱延伸などの方法を適用することができる。さらに、本延伸工程で使用する高圧蒸気延伸槽と同じシステムにより、本延伸工程における延伸温度よりも低い温度で予備延伸処理することも可能である。 In this preliminary drawing step, the composite spun fiber is drawn at a temperature lower than the drawing temperature in the subsequent main drawing step. As this pre-stretching treatment method, for example, generally known contact heating stretching using a metal heating roll or a metal heating plate, or heated fluid such as warm water, steam of normal pressure to 0.2 MPa or hot air, A method such as non-contact heating stretching using heat rays such as far infrared rays can be applied. Furthermore, it is also possible to perform a preliminary stretching treatment at a temperature lower than the stretching temperature in the main stretching step by the same system as the high-pressure steam stretching tank used in the main stretching step.
この予備延伸工程における延伸倍率としては、本延伸処理を含めた全延伸倍率の25〜90%の範囲が適しており、予備延伸装置のシステム、延伸状態などによって、延伸条件を適宜選択すればよい。特に、予備延伸処理を1段で行ったのち、本延伸処理を行う2段階延伸の場合、予備延伸倍率は、全延伸倍率の25〜85%の範囲が好ましく、さらに35〜80%の範囲が好ましい。また、該予備延伸処理は1段階で行ってもよいし、2段以上の多段階で行なってもよく、多段階で行う場合には、延伸温度を一定とし、予備延伸倍率を多段階にする方法や、延伸温度に勾配を与えながら、延伸倍率を多段階にする方法を用いることができる。
一方、本延伸工程は、複合紡糸繊維または前述の予備延伸工程で得られた複合紡糸繊維の予備延伸処理物を、鞘成分の融点以上、芯成分の融点未満の温度を有する加圧飽和水蒸気により直接加熱して、本延伸処理する工程である。
本延伸倍率は、複合紡糸繊維またはその予備延伸処理物の繊度に応じて適宜選定されるが、通常全延伸倍率が5〜20倍、好ましくは7〜17倍になるように選定される。
なお、加圧飽和水蒸気による延伸方法および延伸装置に関しては、特開平11−350283号公報に、その詳細が記載されている。
As the draw ratio in this pre-stretching step, a range of 25 to 90% of the total draw ratio including the main stretching process is suitable, and the stretching conditions may be appropriately selected depending on the system of the pre-stretching apparatus, the stretching state, and the like. . In particular, in the case of two-stage stretching in which the main stretching process is performed after the preliminary stretching process is performed in one stage, the preliminary stretching ratio is preferably in the range of 25 to 85% of the total stretching ratio, and more preferably in the range of 35 to 80%. preferable. Further, the preliminary stretching treatment may be performed in one stage, or may be performed in multiple stages of two or more stages. In the case of performing in multiple stages, the stretching temperature is constant and the preliminary stretching ratio is multistage. The method and the method of making a draw ratio multistage, giving a gradient to extending | stretching temperature can be used.
On the other hand, the present drawing step is performed by applying pressurized presaturated steam having a temperature not lower than the melting point of the sheath component and lower than the melting point of the core component to the pre-stretched product of the composite spun fiber or the composite spun fiber obtained in the above-described pre-stretching step. This is a step of directly heating and performing the main stretching treatment.
The main draw ratio is appropriately selected according to the fineness of the composite spun fiber or its pre-drawn product, but is usually selected so that the total draw ratio is 5 to 20 times, preferably 7 to 17 times.
The details of the stretching method and stretching apparatus using pressurized saturated steam are described in JP-A No. 11-350283.
このようにして得られた繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体は、一般に以下に示す性状を有している。
繊度は、通常50〜5000dTex程度、好ましくは100〜3000dTex、より好ましくは500〜1500dTexの範囲である。また、芯部繊維の繊度断面形状は、1〜70dTex(最大径が10μm〜100μm)であることが好ましく、柔軟性を求められるときは30dTex程度以下が好ましい。
The fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body thus obtained generally has the following properties.
The fineness is usually in the range of about 50 to 5000 dTex, preferably 100 to 3000 dTex, more preferably 500 to 1500 dTex. The fineness cross-sectional shape of the core fiber is preferably 1 to 70 dTex (the maximum diameter is 10 μm to 100 μm), and preferably about 30 dTex or less when flexibility is required.
最大径は、10μm未満であると、芯部繊維が細くなりすぎるため、形態を維持することが困難になり、シート化後の物性が低下しやすく、100μmを超えると繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体自体が太くなりすぎるため、柔軟性が損なわれるおそれがある。好ましくは、最大径は15μm〜40μmである。 If the maximum diameter is less than 10 μm, the core fiber becomes too thin, so that it becomes difficult to maintain the form, and the physical properties after forming into a sheet are liable to deteriorate, and if it exceeds 100 μm, the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear shape Since the body itself becomes too thick, flexibility may be impaired. Preferably, the maximum diameter is 15 μm to 40 μm.
また、繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体は複合繊維未延伸糸を複数本集束しつつ延伸して製造されるが、集束する本数は20〜500本が好ましい。20本未満であると、複合糸単繊維が太くなり紡糸性が悪化するおそれがあり、500本を超えると、紡糸ノズル密度が増加するとともに、複合単繊維が細くなり紡糸性、延伸性共に悪化するおそれがある。更に好ましくは、100〜300本である。引張り強度は、通常4cN/dTex以上が好ましいが、概ね4〜12cN/dTexの範囲である。さらに、伸度は、通常5〜30%程度、好ましくは10〜25%、より好ましくは15〜20%の範囲である。
なお、上記の引張り強度および伸度は、JIS L 1096に準じて測定した値である。
The fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body is produced by drawing a plurality of unstretched composite fiber yarns while being bundled, and the number of fibers to be bundled is preferably 20 to 500. If the number is less than 20, the composite yarn single fiber may become thick and the spinnability may be deteriorated. If the number exceeds 500, the spinning nozzle density increases and the composite single fiber becomes thin and both the spinnability and stretchability deteriorate. There is a risk. More preferably, it is 100-300. The tensile strength is usually preferably 4 cN / dTex or more, but is generally in the range of 4 to 12 cN / dTex. Furthermore, the elongation is usually in the range of about 5 to 30%, preferably 10 to 25%, more preferably 15 to 20%.
In addition, said tensile strength and elongation are the values measured according to JISL1096.
また、この繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体の内部構造は、延伸処理しながら、前記鞘成分を融合させた結果、鞘成分が融合した海に芯成分が島状に配置された海島構造となっている。また、形状については特に制限はなく、断面形状が円、楕円、扁平状など、任意の形状をとることができる。 Further, the internal structure of the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body is a sea-island structure in which the core component is arranged in an island shape in the sea where the sheath component is fused as a result of fusing the sheath component while stretching. ing. Moreover, there is no restriction | limiting in particular about a shape, A cross-sectional shape can take arbitrary shapes, such as a circle, an ellipse, and flat shape.
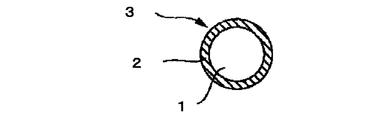
図1は、本発明において用いられる鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維の1例を示す断面図であり、鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維3は、芯成分1の表面全周が、鞘成分2によって被覆された構造を有している。
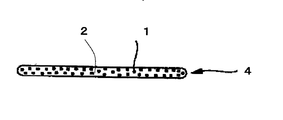
図2は、本発明において用いられる繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体の1例を示す要部断面図であり、繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体4は鞘成分が融合した海2’に芯成分1が島状に配置された構造を有している。
FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view showing an example of a sheath-core type composite spun fiber used in the present invention. In the sheath-core type composite spun
FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of an essential part showing an example of a fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body used in the present invention. The fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin
本発明においては、このようにして得られた繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体を用いて、織布を製造する。織布の製造については、特に制限はなく、従来公知の方法の中から、任意の方法を選択して用いることができる。この際、仕込み本数や目付けなどは、用途および必要物性に応じて適宜選定することができるが、目付けは、通常50〜500g/m2、好ましくは100〜400g/m2、より好ましくは150〜300g/m2である。目付けが50〜500g/m2の範囲にあれば、引張り強力や引張り強度などの物性が良好であると共に、織布の厚さも実用的である。
また、織布組織については、特に制限はなく、例えば平織、斜文織、シュス(朱子)織の原組織、およびこれらの原組織の変形組織などの中から、用途に応じて適宜選択することができる。
In the present invention, a woven fabric is produced using the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body thus obtained. There is no restriction | limiting in particular about manufacture of a woven fabric, Arbitrary methods can be selected and used from a conventionally well-known method. At this time, the number of preparations and the basis weight can be appropriately selected according to the use and necessary physical properties, but the basis weight is usually 50 to 500 g / m 2 , preferably 100 to 400 g / m 2 , more preferably 150 to 300 g / m 2 . If the basis weight is in the range of 50 to 500 g / m 2 , physical properties such as tensile strength and tensile strength are good, and the thickness of the woven fabric is also practical.
In addition, the woven fabric structure is not particularly limited, and may be appropriately selected according to the use from, for example, a plain weave, a diagonal weave, an original texture of shusu, and a deformed structure of these original textures. Can do.
本発明の織布は、前記の繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体の引張り強力を維持し、良好な物性を有しており、強力寄与率が、通常80%以上、好ましくは85%以上である。なお、この強力寄与率は、下記の式(I)
強力寄与率(%)=(B/A)×100 …(I)
[ただし、Aは、繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体から計算される引張り強力(N/3cm)であり、該線状体の強力(N)×織布の打ち込み本数(本)/2.54cm×3cmの式によって計算される。Bは織布の引張り強力(N/3cm)である。]
から算出される値である。ここで、引張り強力は、JIS L 1096に準じて測定した値である。
The woven fabric of the present invention maintains the tensile strength of the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body and has good physical properties, and the strength contribution ratio is usually 80% or more, preferably 85% or more. . In addition, this strong contribution rate is the following formula (I)
Strong contribution ratio (%) = (B / A) × 100 (I)
[However, A is the tensile strength (N / 3 cm) calculated from the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body, and the linear body's strength (N) × the number of woven fabrics (pieces) /2.54 cm Calculated by the formula x3 cm. B is the tensile strength (N / 3 cm) of the woven fabric. ]
It is a value calculated from Here, the tensile strength is a value measured according to JIS L 1096.
また、本発明の織布は、撥水処理を施さなくとも、良好な防水性を有している。
本発明はまた、前記織布を加工処理して得られた織布加工品をも提供する。
この織布加工品としては、例えば前記織布を加熱プレス処理してなるシート、あるいは、このシートや前記織布の少なくとも片面に熱可塑性樹脂被覆層を有する織布加工品などを挙げることができる。
Further, the woven fabric of the present invention has a good waterproof property without being subjected to a water repellent treatment.
The present invention also provides a woven fabric processed product obtained by processing the woven fabric.
Examples of the woven fabric processed product include a sheet obtained by heat-pressing the woven fabric, or a woven fabric processed product having a thermoplastic resin coating layer on at least one surface of the sheet or the woven fabric. .
樹脂被覆層の形成に用いられる樹脂に特に制限はないが、例えば前述の鞘成分として例示したものの中から、適宜1種以上を選択して用いることができる。特に、融点や接着性などを考慮すると、織布の原材料として用いた鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維の鞘成分と同じものを使用することが好ましい。 Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular in resin used for formation of a resin coating layer, For example, 1 or more types can be selected suitably from what was illustrated as an above-mentioned sheath component, for example. In particular, considering the melting point, adhesiveness, etc., it is preferable to use the same sheath component as the sheath-core composite spun fiber used as the raw material of the woven fabric.
樹脂被覆層を設ける方法に特に制限はなく、従来公知の方法を用いることができる。例えば、バッチ式の場合では、加熱プレス法や加熱ローラー法を採用することができる。また、連続式の場合では、押出しラミネート法、ドライラミネート法、カレンダー加工法などを採用することができるが、押出しラミネート法が好ましい。樹脂被覆層の厚さに特に制限はないが、通常50〜500μm程度、好ましくは100〜300μm、より好ましくは150〜200μmの範囲である。
さらに、本発明の織布および織布加工品は、熱可塑性樹脂からなることから、必要に応じて、加熱プレスなどの処理によって幅継ぎが可能である。
There is no restriction | limiting in particular in the method of providing a resin coating layer, A conventionally well-known method can be used. For example, in the case of a batch type, a heating press method or a heating roller method can be employed. In the case of a continuous type, an extrusion laminating method, a dry laminating method, a calendering method or the like can be adopted, but an extrusion laminating method is preferable. Although there is no restriction | limiting in particular in the thickness of a resin coating layer, Usually, about 50-500 micrometers, Preferably it is the range of 100-300 micrometers, More preferably, it is the range of 150-200 micrometers.
Furthermore, since the woven fabric and the woven fabric processed product of the present invention are made of a thermoplastic resin, they can be spliced by a treatment such as a hot press, if necessary.
このような織布加工品は、前記の織布と同様に、繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体の引張り強力を維持し、良好な物性を有しており、強力寄与率が、通常80%以上、好ましくは85%以上である。また、防水性も良好であり、前記の織布と同様に織布加工品の防水性は、JIS L 1907のバイレック法によって測定される、端面における10分間放置後における水の上昇高さが10mm以下、好ましくは5mm以下、さらに好ましくは3mm以下であり、表面および端面や破損部からの吸水が生じない。 Such a woven fabric processed product maintains the tensile strength of the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body, has good physical properties, and has a strength contribution ratio of usually 80% or more, like the woven fabric. , Preferably 85% or more. Also, the waterproof property is good, and the waterproof property of the woven fabric processed product is measured by the birec method of JIS L 1907, and the rising height of the water after standing for 10 minutes on the end surface is 10 mm. Hereinafter, it is preferably 5 mm or less, more preferably 3 mm or less, and water absorption from the surface, the end face, or the damaged portion does not occur.
次に、本発明を、実施例により、さらに詳細に説明するが、本発明は、これらの例によってなんら限定されるものではない。
なお、各物性は以下に示す方法に従って求めた。
(1)引張り強力、引張り強度および伸度
JIS L 1096に準じて測定した。また、前記式(I)より、強力寄与率を算出した。
(2)吸水性
JIS L 1096のバイレック法により、端面における10分間放置後の水の上昇高さ(mm)によって評価した。
実施例1
(1)繊維および繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体の作製
芯材として、ポリプロピレン(PP)[日本ポリケム社製、商品名「SA02」、メルトインデックス(MI)=20g/10分、融点=164℃]を、鞘材として、低密度ポリエチレン[旭化成工業社製、商品名「サンテックLD M7620」、メルトフローレート(MFR)=20g/10分、融点=113℃]]を用い、紡糸温度240℃にて、芯成分/鞘成分断面積比が55/45の鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を得た。
引き続き、前記の鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維を150本収束し、スピンドロー方式(紡糸延伸直結法)にて、G1=23m/min、延伸温度=145℃(高圧蒸気)、G2速度=322m/min、延伸倍率=14倍の条件で延伸処理し、PP強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体を得た。
この線状体の物性は、繊度=2200dTex(PP繊度=1210dTex)、引張り強力=131N、引張り強度=6.0cN/dTex、伸度=14.3%であった。
EXAMPLES Next, although an Example demonstrates this invention further in detail, this invention is not limited at all by these examples.
In addition, each physical property was calculated | required according to the method shown below.
(1) Tensile strength, tensile strength and elongation Measured according to JIS L 1096. Moreover, the strong contribution rate was computed from said Formula (I).
(2) Water absorption It evaluated by the rising height (mm) of the water after leaving for 10 minutes in an end surface by the birec method of JISL1096.
Example 1
(1) Production of fiber and fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body As a core material, polypropylene (PP) [trade name “SA02” manufactured by Nippon Polychem Co., Ltd., melt index (MI) = 20 g / 10 min, melting point = 164 ° C. ] As a sheath material, using low density polyethylene [manufactured by Asahi Kasei Kogyo Co., Ltd., trade name “Suntech LD M7620”, melt flow rate (MFR) = 20 g / 10 min, melting point = 113 ° C.]] at a spinning temperature of 240 ° C. Thus, a sheath-core type composite spun fiber having a core component / sheath component cross-sectional area ratio of 55/45 was obtained.
Subsequently, 150 sheath-core type composite spun fibers are converged, and G1 = 23 m / min, stretching temperature = 145 ° C. (high pressure steam), G2 speed = 322 m / min by a spin draw method (spinning stretching direct coupling method). The film was stretched under the condition of a stretching ratio = 14 to obtain a PP reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body.
The physical properties of the linear body were as follows: fineness = 2200 dTex (PP fineness = 1210 dTex), tensile strength = 131 N, tensile strength = 6.0 cN / dTex, and elongation = 14.3%.
(2)織布の作製
上記(1)で得られたPP強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体を用い、打ち込み本数=14×14本/インチ(2.54cm)、目付け=250g/m2の平織布を作製した。なお、前記線状体は、鞘成分が溶融し、一体化しているため、撚り加工なしで織布の作製が可能であった。
(2) Fabrication of Woven Fabric Plain weaving using the PP reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body obtained in (1) above, the number of driven = 14 × 14 / inch (2.54 cm), and the basis weight = 250 g / m 2 A fabric was made. In addition, since the sheath component was melted and integrated with the linear body, it was possible to produce a woven fabric without twisting.
(3)後加工(シート加工)
(イ)シートの作製
上記(2)で得られた織布を、120℃、0.41MPaの条件で加熱プレスし、低密度ポリエチレンを押し広げて、厚さ0.35mmのシートを作製した。
(ロ)樹脂被覆シートの作製
上記(1)で得られたシートの両面に、低密度ポリエチレン[旭化成工業社製、商品名「サンテックLD M7620」、MFR=20g/10分]を、それぞれ厚さ150μmずつ被覆し、樹脂被覆シートを作製した。
(3) Post-processing (sheet processing)
(I) Production of Sheet The woven fabric obtained in (2) above was heated and pressed under the conditions of 120 ° C. and 0.41 MPa, and low-density polyethylene was spread to produce a sheet having a thickness of 0.35 mm.
(B) Preparation of resin-coated sheet Low-density polyethylene [manufactured by Asahi Kasei Kogyo Co., Ltd., trade name “Suntech LD M7620, MFR = 20 g / 10 min]” on each side of the sheet obtained in the above (1) was thickened. Each 150 μm was coated to prepare a resin-coated sheet.
(4)物性の評価
上記(2)で得られた織布、(3)で得られたシート及び樹脂被覆シートについて、それぞれ物性を評価した。その結果は以下のとおりである。
(4) Evaluation of physical properties The physical properties of the woven fabric obtained in (2) above, the sheet obtained in (3), and the resin-coated sheet were evaluated. The results are as follows.
織 布 シート 樹脂被覆シート
引張り強力 1951N/3cm 1981N/3cm 1930N/3cm
強力寄与率 90.1% 91.5% 89.1%
伸度 22% 21% 23%
いずれも、強力寄与率[加工後の強力/線状体から計算された強力(131(線状体の強力)×14(織布の打ち込み本数)/2.54cm×3cm=2166N/3cm)]が80%を超える高い値を示し、良好な物性を維持していることが確認された。
また、吸水性能はいずれも0mmであり、撥水処理を行わないにもかかわらず、いずれも優れた防水性を示した。
Woven cloth sheet Resin coated sheet Tensile strength 1951N / 3cm 1981N / 3cm 1930N / 3cm
Strong contribution 90.1% 91.5% 89.1%
Elongation 22% 21% 23%
In any case, strength contribution ratio [strength after processing / strength calculated from linear body (131 (strength of linear body) × 14 (number of woven fabrics) /2.54 cm × 3 cm = 2166 N / 3 cm)] Shows a high value exceeding 80%, and it was confirmed that good physical properties were maintained.
In addition, the water absorption performance was 0 mm in all cases, and all of them exhibited excellent water resistance despite no water repellent treatment.
比較例1
(1)繊維の作製
ポリプロピレン(PP)[日本ポリケム社製、商品名「SA02」、MI=20g/10分]を紡糸温度225℃で紡糸したのち、この単一型紡糸繊維を120本収束し、スピンドロー方式にて、G1=45m/min、延伸温度=162℃(高圧蒸気)、G2速度=423m/min、延伸倍率=9.4倍の条件で延伸処理し、PPマルチフィラメントを得た。なお、収束性を付与するために、界面活性剤を付与した。
このマルチフィラメントの物性は、繊度=757dTex、引張り強力=70.6N、引張り強度=9.3cN/dTex、伸度=16.5%であった。
Comparative Example 1
(1) Preparation of fiber After spinning polypropylene (PP) [manufactured by Nippon Polychem, trade name “SA02”, MI = 20 g / 10 min] at a spinning temperature of 225 ° C., 120 single-type spun fibers converged. In the spin draw method, a stretching process was performed under the conditions of G1 = 45 m / min, stretching temperature = 162 ° C. (high pressure steam), G2 speed = 423 m / min, stretching ratio = 9.4 times, and a PP multifilament was obtained. . In addition, in order to provide convergence property, surfactant was provided.
The physical properties of the multifilament were fineness = 757 dTex, tensile strength = 70.6 N, tensile strength = 9.3 cN / dTex, and elongation = 16.5%.
(2)織布の作製
上記(1)で得られたPPマルチフィラメントを用い、繊維の収束性をあげるために、100ターン/mの撚り加工を行ったのち、織布を作成した。打ち込み本数=20×20本/インチ(2.54cm)、目付け=120g/m2の平織布を作製した。
(2) Fabrication of Woven Fabric Using the PP multifilament obtained in (1) above, twisting was performed at 100 turns / m in order to increase the fiber convergence, and then a woven fabric was fabricated. A plain woven fabric having a driving number = 20 × 20 / inch (2.54 cm) and a basis weight = 120 g / m 2 was produced.
(3)後加工
上記(2)で得られた平織布の両面に、低密度ポリエチレン[旭化成工業社製、商品名「サンテックLD M7620」、MFR=20g/10分]を、それぞれ厚さ150μmで張り合わせ、シートを作製した。
(3) Post-processing Low-density polyethylene (trade name “Suntech LD M7620”, MFR = 20 g / 10 min, manufactured by Asahi Kasei Kogyo Co., Ltd.) on both sides of the plain woven fabric obtained in (2) above is 150 μm in thickness. To make a sheet.
(4)物性の評価
上記(2)で得られた織布、および(3)で得られたシートについて、それぞれ物性を評価した。その結果は以下のとおりである。
織 布 シート
引張り強力 1305N/3cm 1262N/3cm
強力寄与率 78.2% 75.6%
伸度 16.5% 15.8%
いずれも、強力寄与率[加工後の強力/原糸から計算される強力(70.6(線状体の強力)×20(織布の打ち込み本数)/2.54cm×3cm=1668N/3cm)]が80%未満と低い値を示し、良好な物性を維持できていないことが確認できた。
また、吸水性能はいずれも200mmを超える値であった。
(4) Evaluation of physical properties The physical properties of the woven fabric obtained in (2) and the sheet obtained in (3) were evaluated. The results are as follows.
Woven cloth sheet Tensile strength 1305N / 3cm 1262N / 3cm
Strong contribution rate 78.2% 75.6%
Elongation 16.5% 15.8%
In any case, the strength contribution ratio [the strength after processing / the strength calculated from the raw yarn (70.6 (strength of the linear body) × 20 (number of woven fabrics) /2.54 cm × 3 cm = 1668 N / 3 cm) ] Was a low value of less than 80%, and it was confirmed that good physical properties could not be maintained.
Further, the water absorption performance was a value exceeding 200 mm.
本発明の織布および織布加工品は、良好な物性と防水性を有し、例えば建築用資材カバーなどのカバー類、防水シートなどのシート類、テント、包装袋、フレキシブルコンテナなどに好適に用いられる。 The woven fabric and woven fabric processed product of the present invention have good physical properties and waterproofness, and are suitable for, for example, covers such as building material covers, sheets such as waterproof sheets, tents, packaging bags, flexible containers, etc. Used.
1 芯成分
2 鞘成分
2’鞘成分が融合した海
3 鞘芯型複合紡糸繊維
4 繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (9)
強力寄与率(%)=(B/A)×100 ・・・(I)
[ただし、Aは繊維強化熱可塑性樹脂線状体から計算される引張り強力(N/3cm)。該線状体の強力(N)×織布の打ち込み本数(本)/2.54cm×3cmの式によって計算される。Bは織布の引張り強力(N/3cm)。] The woven fabric according to claim 1, wherein the strength contribution represented by the following formula (I) is 80% or more.
Strong contribution ratio (%) = (B / A) × 100 (I)
[However, A is the tensile strength (N / 3 cm) calculated from the fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin linear body. It is calculated by the formula of the strength of the linear body (N) × the number of driven woven fabrics (pieces) /2.54 cm × 3 cm. B is the tensile strength (N / 3cm) of the woven fabric. ]
The waterproof sheet containing the woven fabric processed product according to any one of claims 5 to 7, wherein the rising height of the water after standing for 10 minutes at the end face is 10 mm or less, as measured by the JIS L 1907 birec method. State.
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004103704A JP4365249B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Woven fabric and its woven fabric processed products |
| US11/547,170 US20080274657A1 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2005-03-25 | Woven Fabric and Articles Made by Using the Same |
| CA 2560779 CA2560779A1 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2005-03-25 | Woven fabric and articles made by using the same |
| EP05728051A EP1731641A4 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2005-03-25 | Woven fabric and articles made by using the same |
| CNA2005800106490A CN1989281A (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2005-03-25 | Woven fabric and articles made by using the same |
| PCT/JP2005/006430 WO2005095691A1 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2005-03-25 | Woven fabric and articles made by using the same |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004103704A JP4365249B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Woven fabric and its woven fabric processed products |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005290580A true JP2005290580A (en) | 2005-10-20 |
| JP2005290580A5 JP2005290580A5 (en) | 2007-03-22 |
| JP4365249B2 JP4365249B2 (en) | 2009-11-18 |
Family
ID=35063814
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004103704A Expired - Fee Related JP4365249B2 (en) | 2004-03-31 | 2004-03-31 | Woven fabric and its woven fabric processed products |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20080274657A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1731641A4 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP4365249B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN1989281A (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2560779A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2005095691A1 (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009127159A (en) * | 2007-11-27 | 2009-06-11 | Kuraray Co Ltd | Sheet=type fiber construct made from polypropylene fiber |
| JP2015030129A (en) * | 2013-07-31 | 2015-02-16 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin flat shape composite material having water-absorption property and coloring discrimination function |
| JP2015030130A (en) * | 2013-07-31 | 2015-02-16 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin flat shape colored composite material |
| JP2015112784A (en) * | 2013-12-11 | 2015-06-22 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fabric-reinforced resin molding, and fabric-reinforced resin molding |
| JP2015112785A (en) * | 2013-12-11 | 2015-06-22 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fabric-reinforced resin molding, and fabric-reinforced resin molding |
| JP2016130374A (en) * | 2015-01-13 | 2016-07-21 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Reinforcement material for thermoplastic resin molding and thermoplastic resin molding using the same |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US8372495B2 (en) | 2010-05-26 | 2013-02-12 | Apple Inc. | Electronic device enclosure using sandwich construction |
| FR2974819B1 (en) * | 2011-05-05 | 2014-08-22 | Porcher Ind | TEXTILE REINFORCING YARN FOR AN INFLATABLE SAIL, AS WELL AS A SAILING CURTAIN COMPRISING SUCH TEXTILE REINFORCING YARNS |
| BE1020490A3 (en) * | 2012-02-02 | 2013-11-05 | Vertical Ecosystem Sprl | SYSTEM FOR FORMING A VEGETABLE TEXTILE ELEMENT. |
| WO2013154072A1 (en) * | 2012-04-10 | 2013-10-17 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | Absorbent article |
| CA2881347C (en) * | 2012-08-09 | 2017-04-04 | Fujikura Ltd. | Binder fiber for optical fiber unit |
| US10407955B2 (en) | 2013-03-13 | 2019-09-10 | Apple Inc. | Stiff fabric |
| TWI626345B (en) | 2013-12-20 | 2018-06-11 | 蘋果公司 | Woven fibric band, method of generating a securement mechanism for a woven fibric band and method for generating a woven fibric band for securement to an object |
| CN104562361A (en) * | 2015-02-03 | 2015-04-29 | 湖州市菱湖重兆金辉丝织厂 | High-strength multifunctional silk shell fabric |
| CA3060311C (en) * | 2017-05-02 | 2022-05-24 | Invista Textiles (U.K.) Limited | Low permeability and high strength woven fabric and methods of making the same |
| CN109402832A (en) * | 2017-08-16 | 2019-03-01 | 曾凱熙 | Cloth of reinforcement fibers, protective plate and the method for preparing protective plate |
| US10864686B2 (en) | 2017-09-25 | 2020-12-15 | Apple Inc. | Continuous carbon fiber winding for thin structural ribs |
| JP7095967B2 (en) * | 2017-09-27 | 2022-07-05 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Composite fiber and molded body |
| US11889877B2 (en) * | 2018-05-31 | 2024-02-06 | Nike, Inc. | Garment with adaptive ventilation |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4053433A (en) * | 1975-02-19 | 1977-10-11 | Minnesota Mining And Manufacturing Company | Method of tagging with color-coded microparticles |
| US4285748A (en) * | 1977-03-11 | 1981-08-25 | Fiber Industries, Inc. | Selfbonded nonwoven fabrics |
| US4211816A (en) * | 1977-03-11 | 1980-07-08 | Fiber Industries, Inc. | Selfbonded nonwoven fabrics |
| JPS5940938B2 (en) * | 1978-11-15 | 1984-10-03 | チッソ株式会社 | Manufacturing method of rod-shaped fiber molded body |
| JPS62250261A (en) * | 1986-04-23 | 1987-10-31 | チッソ株式会社 | Production of tubular fiber molded body |
| US5407623A (en) * | 1994-01-06 | 1995-04-18 | Polteco, Inc. | Process for obtaining ultra-high modulus line products with enhanced mechanical properties |
| JPH07324249A (en) * | 1994-05-31 | 1995-12-12 | Unitika Ltd | Production of waterproof cloth |
| EP0831763B1 (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 2001-10-31 | Gillette Canada Company | Dental floss |
| US5875797A (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 1999-03-02 | Gillette Canada Inc. | Dental floss |
| US5845652A (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 1998-12-08 | Tseng; Mingchih M. | Dental floss |
| JPH10130991A (en) * | 1996-10-31 | 1998-05-19 | Nippon Porikemu Kk | Nonwoven fabric or woven or knitted fabric having thermally bonded crossing part of warp and weft and laminate using the same |
| US5677056A (en) * | 1996-11-07 | 1997-10-14 | Murdock Webbing Company, Inc. | Webbing having a catch cord fabricated from biocomponent yarn |
| US20020122940A1 (en) * | 1998-02-10 | 2002-09-05 | Gunn Robert T. | Fibers having low and high coefficients of friction surfaces |
| JP3678637B2 (en) * | 2000-09-01 | 2005-08-03 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | Method and apparatus for opening continuous filament |
| US20020104548A1 (en) * | 2000-12-01 | 2002-08-08 | Vipul Bhupendra Dave | Monofilament tape |
| US20020193030A1 (en) * | 2001-04-20 | 2002-12-19 | Li Yao | Functional fibers and fibrous materials |
| JP3934061B2 (en) * | 2002-01-10 | 2007-06-20 | 宇部日東化成株式会社 | Method for producing polyolefin-based drawn fiber |
| JP4084955B2 (en) * | 2002-05-09 | 2008-04-30 | 宇部日東化成株式会社 | Fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin-made linear or rod-shaped composite material and method for producing the same |
| EP2298522B1 (en) * | 2002-07-18 | 2014-10-08 | Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd. | Prepreg and methods for the production of fiber-reinforced composite materials |
| WO2005021844A2 (en) * | 2003-08-21 | 2005-03-10 | Filtrona Richmond, Inc. | Polymeric fiber rods for separation applications |
| US7290668B2 (en) * | 2004-03-01 | 2007-11-06 | Filtrona Richmond, Inc. | Bicomponent fiber wick |
-
2004
- 2004-03-31 JP JP2004103704A patent/JP4365249B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2005
- 2005-03-25 WO PCT/JP2005/006430 patent/WO2005095691A1/en active Application Filing
- 2005-03-25 CN CNA2005800106490A patent/CN1989281A/en active Pending
- 2005-03-25 EP EP05728051A patent/EP1731641A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2005-03-25 CA CA 2560779 patent/CA2560779A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2005-03-25 US US11/547,170 patent/US20080274657A1/en not_active Abandoned
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009127159A (en) * | 2007-11-27 | 2009-06-11 | Kuraray Co Ltd | Sheet=type fiber construct made from polypropylene fiber |
| JP2015030129A (en) * | 2013-07-31 | 2015-02-16 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin flat shape composite material having water-absorption property and coloring discrimination function |
| JP2015030130A (en) * | 2013-07-31 | 2015-02-16 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fiber-reinforced thermoplastic resin flat shape colored composite material |
| JP2015112784A (en) * | 2013-12-11 | 2015-06-22 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fabric-reinforced resin molding, and fabric-reinforced resin molding |
| JP2015112785A (en) * | 2013-12-11 | 2015-06-22 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Method for producing fabric-reinforced resin molding, and fabric-reinforced resin molding |
| JP2016130374A (en) * | 2015-01-13 | 2016-07-21 | 宇部エクシモ株式会社 | Reinforcement material for thermoplastic resin molding and thermoplastic resin molding using the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2005095691A1 (en) | 2005-10-13 |
| CA2560779A1 (en) | 2005-10-13 |
| EP1731641A1 (en) | 2006-12-13 |
| EP1731641A4 (en) | 2009-08-12 |
| US20080274657A1 (en) | 2008-11-06 |
| CN1989281A (en) | 2007-06-27 |
| JP4365249B2 (en) | 2009-11-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4365249B2 (en) | Woven fabric and its woven fabric processed products | |
| WO1997013020A1 (en) | Water jet intertwined nonwoven cloth and method of manufacturing the same | |
| US6818091B1 (en) | Cut and puncture resistant laminated fabric | |
| US8114507B2 (en) | Multi-layered fiber | |
| US20080045109A1 (en) | Process for Producing Nonwoven Fabric and Nonwoven Fabric | |
| RU2008102372A (en) | INTEGRATED PACKAGE | |
| EP2135984A1 (en) | A process of producing soft and absorbent non woven fabric | |
| JP4544600B2 (en) | Drawn composite fiber | |
| JPH10130991A (en) | Nonwoven fabric or woven or knitted fabric having thermally bonded crossing part of warp and weft and laminate using the same | |
| JP4967627B2 (en) | Leather-like sheet and method for producing the same | |
| EP3017100B1 (en) | Nonwoven material | |
| US3846205A (en) | Method for producing laminated materials of fibers | |
| KR20170079656A (en) | Method for Manufacturing Polypropylene Yarn, Polyolefin-based Composite, and Method for Manufacturing The Same | |
| EP2735442A2 (en) | Eco-friendly high pressure hose fabric and eco-friendly high pressure hose using same | |
| JPH08109564A (en) | Long-fiber water jet-interlaced nonwoven fabric and its production | |
| US20030045196A1 (en) | Composite nonwoven fabric having high strength and superior printability and fabrication method of the same | |
| JP2997404B2 (en) | Reinforced spunbond nonwoven | |
| JPH02308824A (en) | Material for thermoplastic composite | |
| JP4379127B2 (en) | Thermal adhesive composite fiber, method for producing the same, and fiber molded body using the composite fiber | |
| JP3464544B2 (en) | Method for producing thin and lightweight reinforced hydroentangled nonwoven fabric | |
| KR100677786B1 (en) | A Stretch Recoverable Nonwoven Fabric and a Process for Making | |
| JPS633968B2 (en) | ||
| JP2854771B2 (en) | Stretchable waterproof sheet and manufacturing method thereof | |
| EP3638832A2 (en) | Breathable light weight unidirectional laminates | |
| WO2023106272A1 (en) | Napped artificial leather and method for producing napped artificial leather |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070205 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070205 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090407 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090529 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090616 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090716 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20090818 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20090820 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120828 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 4365249 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120828 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120828 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R371 | Transfer withdrawn |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R371 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120828 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120828 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R371 | Transfer withdrawn |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R371 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120828 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120828 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130828 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |