JP2004348564A - Compression device and expansion device - Google Patents
Compression device and expansion device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2004348564A JP2004348564A JP2003146429A JP2003146429A JP2004348564A JP 2004348564 A JP2004348564 A JP 2004348564A JP 2003146429 A JP2003146429 A JP 2003146429A JP 2003146429 A JP2003146429 A JP 2003146429A JP 2004348564 A JP2004348564 A JP 2004348564A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- difference value
- order difference
- element point
- data
- value
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Processing Or Creating Images (AREA)
- Compression, Expansion, Code Conversion, And Decoders (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】地図データをより高い圧縮率で圧縮可能な圧縮装置を提供すること。
【解決手段】圧縮装置12において、中央処理部122は、前記地図画像を構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを取得した後、取得した複数の要素点の内、所定の要素点の2階差分値を算出する。2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。中央処理部122はさらに、自身が算出した2階差分値を含む圧縮データを作成する。
【選択図】 図1To provide a compression device capable of compressing map data at a higher compression ratio.
In a compression device, a central processing unit (122) acquires data including a plurality of element points for specifying a shape of an object constituting the map image, and then acquires a predetermined one of a plurality of acquired element points. Calculate the second order difference value of the element points. The second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point. The first-order difference value is a coordinate value of the predetermined element point, This is a difference value from the immediately preceding coordinate value. The central processing unit 122 further creates compressed data including the second-order difference value calculated by itself.
[Selection diagram] Fig. 1
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、地図データの圧縮装置及び伸長装置に関し、より特定的には、地図上のオブジェクトの形状がベクトル形式で表現されるデータの圧縮装置及び伸長装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
一般的に、地図データにおいて、地図を描画するために必要なオブジェクト(典型的には道路、建造物、河川及び緑地帯)はそれぞれ、そのオブジェクトの形状を特定する要素点の集まりとして、ベクトル形式で表現されている。従来、各オブジェクトの要素点は全て、典型的には正規化座標値の集まりの列で表現されていた。しかしながら、このような地図データは、そのデータ量に起因して、通信又は放送により配信するには不向きであることから、近年、様々な地図データの圧縮方法が提案されている。以下、従来の地図データの圧縮方法の一例として、特開2001−56823号公報に開示されたものについて説明する。
【0003】
上記公報の圧縮方法では、各オブジェクトの要素点は、正規化座標値及び1階差分値のいずれか一方で表現される。ここで、1階差分値とは、対象となる要素点の正規化座標値と、対象要素点に対して1個前の要素点の正規化座標値との差分値である。例えば、対象要素点の正規化座標値が(X1,Y1)で、直前の要素点の正規化座標値が(X0,Y0)である場合には、1階差分値は、(X1−X0,Y1−Y0)となる。このような1階差分値を採用することにより、各要素点を特定するためのデータ量を圧縮している。
【0004】
【特許文献1】
特開2001−56823号公報
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
今後、地図配信の需要はさらに大きくなり、小容量の記憶装置しか実装できないデータ端末装置でも、地図データを利用することが予想される。しかしながら、従来の圧縮方法では、まだデータ量の圧縮が不十分なため、このような地図データの利用拡大に対応しきれないという問題点がある。
【0006】
また、地図配信を受けるデータ端末装置の多くは、ナビゲーション装置のように移動体であるので、移動体通信網を通じて地図データを取得することになる。しかしながら、移動体通信の課金体系は未だに従量制の場合が多く、従来の圧縮方法では、データ量の圧縮が不十分なため、ユーザ側の通信費用がかさむという問題点もある。
【0007】
それ故に、本発明の目的は、地図データをより高い圧縮率で圧縮可能な圧縮装置と、それに対応した伸長装置とを提供することである。
【0008】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明の圧縮装置は、地図データを圧縮する圧縮装置であって、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを取得するデータ取得部と、データ取得部で取得された複数の要素点の内、所定の要素点の2階差分値を算出する2階差分値算出部とを備える。ここで、2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。本発明の圧縮装置はさらに、2階差分値算出部で算出された2階差分値を含む圧縮データを作成する圧縮データ作成部をさらに備える。
この構成により、地図データをより高い圧縮率で圧縮することが可能となる。
【0009】。
本発明の圧縮装置において、圧縮データ作成部は、データ取得部が取得したデータと、2階差分値算出部で算出された2階差分値とを使って、先頭の要素点の座標値と、2番目の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値とを少なくとも含む圧縮データを作成する。
この構成により、地図データをより高い圧縮率で圧縮することが可能となる。
【0010】
本発明の圧縮装置はさらに、データ取得部で取得された複数の要素点から、少なくとも1個の要素点を境界要素点として設定する要素点設定部と、要素点設定部で設定された境界要素点に基づいて、データ取得部で取得された複数の要素点を、複数のグループに分割するグループ化部とを備える。ここで、圧縮データ作成部は、グループ化部により分割されたいずれかのグループにおいて、先頭の要素点の座標値と、2番目の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値とを少なくとも含み、さらに、他のグループにおいて、先頭の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値とを少なくとも含む圧縮データを作成する。
この構成により、地図データをさらに高い圧縮率で圧縮することが可能となる。
【0011】
本発明の圧縮装置はさらに、データ取得部で取得された要素点毎に、1階差分値を表現するために必要なビット数と、2階差分値を表現するために必要なビット数とを比較部をさらに備える。ここで、要素点設定部は、2階差分値のビット数が1階差分値のビット数よりも大きい全ての要素点を、境界要素点として設定する。
この構成により、2階差分値が1階差分値より大きなビット数を持たないようにすることができるので、高い圧縮率を保った状態で、複数の要素点を最適にグループ化できるようになる。
【0012】
本発明の圧縮装置はさらに、グループ化部により分割された各グループに、対象となるグループに属する要素点の総数と、後続のグループが存在するか否かを示す継続フラグとを割り当てる情報割り当て部をさらに備える。ここで、圧縮データ作成部は、グループ化部により分割されたいずれかのグループについて、先頭の要素点の座標値と、2番目の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値と、グループ内の要素点の総数と、継続フラグとを含み、さらに、他のグループにおいて、先頭の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値と、グループ内の要素点の総数と、継続フラグとを含む圧縮データを作成する。
この構成より、オブジェクトがどのようなグループで構成されるかを特定するので、地図データの受信側で適切な伸長処理を行うことができるようになる。
【0013】
本発明の圧縮装置において、データ取得部は、道路の渋滞情報を構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータをさらに取得する。
この構成により、渋滞情報を構成するオブジェクトをより高い圧縮率で圧縮することが可能となる。
【0014】
本発明の、地図データを伸長する伸長装置は、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する要素点の位置を特定可能な2階差分値を少なくとも含む圧縮データを取得する圧縮データ取得部を備える。ここで、2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。本発明の伸長装置はさらに、圧縮データ取得部で取得された2階差分値から、対象となる要素点の1階差分値を導出する1階差分値導出部と、1階差分値導出部で導出された要素点の1階差分値を使って、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定するデータを作成するデータ作成部とをさらに備える。
この構成により、上記圧縮装置で圧縮された地図データを正確で高速に伸長することができる。
【0015】
本発明の圧縮方法は、地図データを圧縮する圧縮方法であって、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを取得するデータ取得ステップと、データ取得ステップで取得された複数の要素点の内、所定の要素点の2階差分値を算出する2階差分値算出ステップとを備える。ここで、2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。圧縮方法はさらに、2階差分値算出ステップで算出された2階差分値を含む圧縮データを作成する圧縮データ作成ステップを備える。
【0016】
本発明の伸長方法は、地図データを伸長する伸長方法であって、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する要素点の位置を特定可能な2階差分値を少なくとも含む圧縮データを取得する圧縮データ取得ステップを備える。ここで、2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。伸長方法はさらに、圧縮データ取得ステップで取得された2階差分値から、対象となる要素点の1階差分値を導出する1階差分値導出ステップと、1階差分値導出ステップで導出された要素点の1階差分値を使って、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定するデータを作成するデータ作成ステップとを備える。
【0017】
本発明のコンピュータプログラムを格納した記録媒体は、地図データを圧縮するためのコンピュータプログラムを格納する。コンピュータプログラムは、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを取得するデータ取得ステップと、データ取得ステップで取得された複数の要素点の内、所定の要素点の2階差分値を算出する2階差分値算出ステップとを備える。ここで、2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。コンピュータプログラムはさらに、2階差分値算出ステップで算出された2階差分値を含む圧縮データを作成する圧縮データ作成ステップを備える。
【0018】
本発明のコンピュータプログラムを格納した記録媒体は、地図データを伸長するためのコンピュータプログラムを格納する。コンピュータプログラムは、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する要素点の位置を特定可能な2階差分値を少なくとも含む圧縮データを取得する圧縮データ取得ステップを備える。ここで、2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。コンピュータプログラムはさらに、圧縮データ取得ステップで取得された2階差分値から、対象となる要素点の1階差分値を導出する1階差分値導出ステップと、1階差分値導出ステップで導出された要素点の1階差分値を使って、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定するデータを作成するデータ作成ステップとを備える。
【0019】
本発明のデータを格納した記録媒体は、地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを格納する。データは、少なくとも1個の基準要素点の位置を特定する正規化座標値及び絶対座標値のいずれかと、基準要素点に対して直後の要素点の位置を特定する1階差分値と、1階差分値で表現された要素点の後に続く要素点の位置を特定する2階差分値とを備える。
【0020】
本発明の地図配信システムは、地図データを圧縮して、圧縮地図データを配信する地図配信装置と、地図配信装置により配信された圧縮地図データを使って、地図画像を作成するデータ端末装置とを備える。地図配信装置は、地図画像を構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含む地図データを格納する記憶装置と、記憶装置に格納された地図データを圧縮して、所定の要素点の位置を2階差分値で表現した圧縮地図データを作成する圧縮装置とを含む。ここで、2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値である。地図配信装置はさらに、地図配信装置はさらに、圧縮装置で作成された圧縮地図データを伝送路に送出する送信装置を含む。また、データ端末装置は、送信装置から送出され、伝送路を通じて送られてくる圧縮地図データを受信する受信装置と、受信装置により受信された圧縮地図データを伸長して、少なくとも2階差分値で表現された要素点の位置を1階差分値で表現した地図データを作成する伸長装置と、伸長装置で作成された地図データを使って、地図画像を作成する描画装置とを、描画装置で作成された地図画像を表示する表示装置とを含む。
【0021】
【発明の実施の形態】
図1は、本発明の一実施形態に係る圧縮装置及び伸長装置を組み込んだ地図配信システムの全体構成を示すブロック図である。図1において、地図配信システムは、地図配信装置1と、データ端末装置2とを備えている。地図配信装置1は、有線又は無線の伝送路3を通じて、データ端末装置2に地図を提供するために、記憶装置11と、圧縮装置12と、送信装置13とを備えている。
【0022】
記憶装置11は好ましくは、後段の圧縮装置12で圧縮処理される低圧縮地図データLCDcartを格納する。低圧縮地図データLCDcartは、地図データDcartから作成され、少なくとも、地図の描画に必要な各オブジェクト(典型的には道路、建造物、河川及び緑地帯)の外形を規定する。ここで、地図データDcartは典型的には、各オブジェクトの外形を構成する複数の要素点の位置を特定するために、全要素点が正規化座標値で表現されるベクトル形式のデータである。ここで、周知のように、地図配信では、地図は予め定められたユニット毎に区切られて配信される。正規化座標値は、このようなユニット内における2次元座標値である。
なお、正規化座標値の代わりに、低圧縮地図データLCDcartは絶対座標値を含んでいても構わない。絶対座標値とは、地図上において予め定められた位置を基準として2次元座標値であり、例えば、(緯度,経度)で表現される。
【0023】
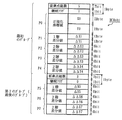
以上の低圧縮地図データLCDcartはより具体的には、好ましくは1個の正規化座標値及び1個以上の1階差分値から少なくとも構成れるデータ列を、図2に示すような低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj として含む。低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj において、正規化座標値は典型的には、データ列の先頭に配置され、オブジェクトを描画する際に基準となる要素点の2次元座標位置を特定する。なお、本実施形態では例示的に、正規化座標値は合計4バイトを使って表現される。また、各1階差分値は、上記基準要素点を除く、対象要素点の位置を特定するために、対象要素点と、データ列において1個前の要素点の正規化座標値との差分値である。なお、本実施形態では例示的に、1階差分値は合計2バイトを使って表現される。
【0024】
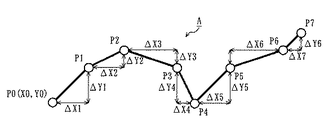
例えば、今、図3に示すように、8個の要素点P0〜P7を順番に結んで得られる線状のオブジェクトAを想定する。このようなオブジェクトAの形状を特定する場合、低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj は、図2に示すように、要素点P0の正規化座標値(X0,Y0)と、要素点P1〜P7の1階差分値(ΔX1,ΔY1)〜(ΔX7,ΔY7)とを含む。ここで、要素点P1の正規化座標値を(X1,Y1)とすると、(ΔX1,ΔY1)は、(X1−X0,Y1−Y0)である。1階差分値(ΔX2,ΔY2)〜(ΔX7,ΔY7)もまた、(ΔX1,ΔY1)と同様の方法で算出される。
【0025】
圧縮装置12は、図1に示すように、プログラム格納部121と、中央処理部122と、作業領域123とを備える。プログラム格納部121は、ROM(Random Access Memory)に代表される記憶媒体であって、後述する圧縮処理の手順が記述されているコンピュータプログラム(以下、圧縮プログラムと称する)124を格納する。以上の構成により、圧縮装置12は、圧縮プログラム124に従って、記憶装置11に格納される低圧縮地図データLCDcartをさらに圧縮して、高圧縮地図データHCDcartを生成する。なお、圧縮装置12による圧縮処理の詳細については後述する。送信装置13は、圧縮装置12で生成された高圧縮地図データHCDcartをデータ端末装置2に送信する。
【0026】
データ端末装置2は、典型的には車両用ナビゲーション装置であって、図1に示すように、受信装置21と、伸長装置22と、描画装置23と、表示装置24とを少なくとも備えている。受信装置21は、伝送路3を通じて送られてくる高圧縮地図データHCDcartを受信して、伸長装置22に送る。
【0027】
伸長装置22は、図1に示すように、プログラム格納部221と、中央処理部222と、作業領域223とを備える。プログラム格納部221は、ROMに代表される記憶媒体であって、後述する伸長処理の手順が記述されているコンピュータプログラム(以下、伸長プログラムと称する)224を格納する。以上の構成により、伸長装置22は、受信装置21から送られてくる高圧縮地図データHCDcartを、伸長プログラム224に従って処理して、本実施形態では、正規化座標列を含みかつ1階差分値及び2階差分値を含まないベクトル形式の地図データDcartを再生し描画装置23に送る。なお、伸長装置22による伸長処理の詳細については後述する。
【0028】
描画装置23は一般的には、プログラム格納部221と、中央処理部222と、作業領域223とにより実現され、伸長装置22で再生された地図データDcartを使って地図を描画する。より具体的には、描画装置23は、受け取った地図データDcartから、地図画像を表す地図画像データDmap を生成する。描画装置23はさらに、生成した地図画像データDmap を表示装置24に送る。表示装置24は、描画装置23から送られてくる地図画像データDmap に基づいて、それが表す地図画像を、自身が有するディスプレイ上に表示する。
【0029】
次に、上記構成を有する地図配信装置1及びデータ端末装置2の動作について説明する。地図配信装置1は、例えば、データ端末装置2から要求を受け付ける。この要求により、データ端末装置2は、地図配信装置1が提供可能な地図の範囲の内、データ端末装置2が現在取得したい範囲を少なくとも指定する。以上のような要求に応答して、地図配信装置1において、記憶装置11は、指定された低圧縮地図データLCDcartを読み出して圧縮装置12の作業領域123に転送する。
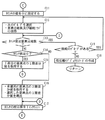
【0030】
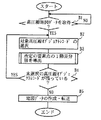
圧縮装置12において、中央処理部122は、プログラム格納部121に格納される圧縮プログラム124を実行し、図4に示す処理手順に従って、記憶装置11から取得した低圧縮地図データLCDcartをさらに圧縮する。具体的には、図4に示すように、中央処理部122は、記憶装置11からの低圧縮地図データLCDcartを取得すると(ステップA1)、取得したものから、1個の低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj を選択する(ステップA2)。なお、以下、ステップA2で選択された低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj を、対象低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj と称し、対象低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj で特定されるオブジェクトを、対象オブジェクトと称する。また、説明の便宜上、対象低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj は、図3に示すオブジェクトAの形状を特定すると仮定する。
【0031】
次に、中央処理部122は、先頭及び2番目の要素点を除く、全ての要素点の2階差分値を算出する(ステップA3)。ここで、2階差分値とは、対象となる要素点の1階差分値と、対象要素点の直前に位置する要素点の1階差分値との差分値である。上記仮定下では、要素点P2〜P7の2階差分値ΔΔP2〜ΔΔP7が算出される。例えば、2階差分値ΔΔP2は、(ΔX2−ΔX1,ΔY2−ΔY1)である。
【0032】
次に、中央処理部122は、先頭及び2番目の要素点を除く、全ての要素点について、2階差分値及び1階差分値の大きさを比較する(ステップA4)。上記仮定下では、例えば、2階差分値ΔΔP2及び1階差分値ΔP2の大きさを対比する。ここで、2階差分値の大きさとは、上記2階差分値ΔΔP2を例に挙げると、√{(ΔX2−ΔX1)2 +(ΔY2−ΔY1)2 }である。また、1階差分値の大きさとは、上記1階差分値ΔP2を例に取り上げると、√{(X2−X1)2 +(Y2−Y1)2 }である。
【0033】
ところで、一般的に、対象オブジェクトの外形線において直線に近い形状を有する区間ほど、要素点の2階差分値は、同じ要素点の1階差分値よりも小さくなる。逆に、対象オブジェクトの外形線において曲率の大きい区間ほど、要素点の2階差分値は、同じ要素点の1階差分値よりも大きくなる。ところで、地図を構成するには様々なオブジェクトが必要となる。これらオブジェクトの内、特に道路について言えば、車両が走行し易いように、可能な限り急カーブにならないように設計される。河川についても、さほど急激に曲がらない。そのため、殆どの場合、対象要素点の2階差分値と1階差分値とを比較すると、2階差分値の大きさの方が小さくなる。以上のことから、2階差分値は1階差分値よりも少ないビット数で表現可能である。本実施形態では例示的に、2階差分値は合計で、1階差分値のビット数よりも少ない12ビットで表現される。
【0034】
なお、上述のステップA4では、2階差分値及び1階差分値の大きさを比較した。これに限らず、例えば、1階差分値が(130,0)で、2階差分値が(127,−127)の場合、1階差分値の大きさは130で、2階差分値の大きさは約180となり、2階差分値の方が大きくなるが、必要なビット数は、1階差分値の場合、−255から+255の9ビットで、2階差分値の場合、−127から+127の8ビットで表現できるため、対象となる要素点を2階差分値で表現する際に必要となるビット数と、同じ要素点を1階差分値で表現する際に必要となるビット数とを比較しても構わない。
【0035】
次に、後のステップA6及びA7のために、中央処理部122は、2階差分値の方が大きい要素点があれば、そのような要素点を境界要素点として記憶する(ステップA5)。ここで、本実施形態では、図3に示すように、要素点P4の部分でオブジェクトAが大きく曲がっていることから、ステップA5では、要素点P4が境界要素点として記憶されると仮定する。
なお、上述のようにビット数で比較する場合、中央処理部122は、2階差分値で表現した方が、1階差分値で表現するよりも多くのビット数を必要とする要素点を、境界要素点として記憶する。
【0036】
次に、中央処理部122は、境界要素点があるか否かを判断し(ステップA6)、境界要素点が1つでもあれば、各境界要素点を境に、対象オブジェクトレコードRobj に含まれる要素点をグループ化する(ステップA7)。より具体的には、中央処理部122は、先頭の要素点から、最初の境界要素点の直前にある要素点を最初のグループに割り当てる。最初のグループにおいて、最初の要素点の位置は正規化座標値で、2番目の要素点の位置は1階差分値で、残りの要素点の位置は2階差分値で特定される。また、最初の境界要素点から、次の境界要素点の直前にある要素点までが、2番目のグループに割り当てられる。以降、同様にしてグループを作成していき、中央処理部122は、最後の境界要素点から、最後の要素点までを、最後のグループに割り当てる。ここで、2番目以降のグループにおいて、最初の境界要素点の位置は1階差分値で、残りの要素点の位置は2階差分値で特定される。以上のステップA7が終了すると、中央処理部122はステップA8を行う。上述の仮定下では、要素点P0からP4までが最初のグループに割り当てられ、要素点P5からP7までが第2のグループに割り当てられると仮定する。
【0037】
また、ステップA6で境界要素点がないと判断された場合には1つのグループしかできないので、中央処理部122は特にグループ化を行う必要がない。それゆえ、中央処理部122は、ステップA7をスキップして、ステップA8を行う。
【0038】
ステップA6又はA7の後、中央処理部122は、ステップA7で作成したグループのそれぞれに付加情報を割り当て、図5に示すような高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj を作成する(ステップA8)。ここで、付加情報は、要素点総数と継続フラグとを少なくとも含む。要素点総数は、対象となるグループに属する要素点総数を示し、本実施形態では例示的に7ビットで表現される。継続フラグとは、対象となるグループの後に、同じ対象オブジェクトに属するグループが続くか否かを特定するフラグであり、好ましくは1ビットで表現される。また、本実施形態では例示的に、継続フラグが1の場合には、後ろに同じ対象オブジェクトに属するグループが続く。逆に、継続フラグが0の場合には、後ろに同じ対象オブジェクトに属するグループが続かないことを示す。従って、継続フラグとしての0は、最後のグループにのみ割り当てられる。
【0039】
以上のステップA8の処理により、中央処理部122は、対象低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj を圧縮して、高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj を作成することが可能となる。ここで、図5に示すように、高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj において、多くの要素点の位置は、2階差分値を使って表現される。2階差分値は、上述から明らかなように、1階差分値よりも少ないビット数で表現可能である。これによって、従来よりも高い圧縮率で地図データDcartを圧縮することが可能となる。
【0040】
また、中央処理部122は、ステップA9で、ステップA2で未選択のオブジェクトレコードRobj が残っていないと判断するまで、ステップA2からA8で特定される処理を繰り返す。そして、未選択のオブジェクトレコードRobj がなくなると、少なくとも1つの高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj からなる高圧縮地図データHCDcartが完成したこととなり、中央処理部122は、図4の処理を終了する。
【0041】
送信装置13は、以上のようにして作成された高圧縮地図データHCDcartに周知の処理を行って、伝送路3に送出する。送出された高圧縮地図データHCDcartは、伝送路3を通じて、データ端末装置2に到着する。
データ端末装置2において、受信装置21は、到着した高圧縮地図データHCDcartを受信して、伸長装置22の作業領域223に転送する。
【0042】
伸長装置22において、中央処理部222は、プログラム格納部221に格納される伸長プログラム224を実行し、図6に示す処理手順に従って、作業領域223に格納されている高圧縮地図データHCDcartを伸長して、全要素点が正規化座標値又は絶対座標値で表現された地図データDcartを再生する。具体的には、図6に示すように、中央処理部222は、受信装置21からの高圧縮地図データHCDcartを取得すると(ステップB1)、今回取得した高圧縮地図データHCDcartから、1個の高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj を選択する(ステップB2)。なお、以下、ステップB2で選択された高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj を、対象高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj と称し、対象高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj で特定されるオブジェクトを、対象オブジェクトと称する。また、説明の便宜上、今回選択された高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj は、図5に示すものであると仮定する。
【0043】
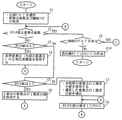
次に、中央処理部222は、対象オブジェクトの外形を規定するために、2階差分値で表現された要素点すべての1階差分値を導出する(ステップB3)。図7及び図8は、ステップB3の詳細な処理手順を示すフローチャートである。まず、図7において、中央処理部222は、対象高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj から、先頭のグループを選択した後、選択したグループに割り当てられた付加情報、つまり要素点総数及び継続フラグを取得する(ステップC1)。上記仮定下では、要素点総数として5が取得され、継続フラグとして1が取得される。
次に、中央処理部222は、処理済の要素点数をカウントするためのカウンタを0に設定した後、カウンタの指示値が、ステップC1で取得された要素点総数以上であるか否かを判断する(ステップC2)。
【0044】
ステップC2で指示値が要素点総数以上でないと判断された場合、中央処理部222は、上記カウンタの指示値が0か否かを判断し(ステップC3)、この指示値が0である場合には、対象高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj の先頭のグループから、基準要素点、つまり先頭の要素点の正規化座標値を取得する(ステップC4)。上記仮定下では、要素点P0の正規化座標値(X0,Y0)が取得される。なお、ステップC2で指示値が要素点総数以上と判断された場合の処理については後述する。
【0045】
また、中央処理部222は、ステップC3で指示値が0でない場合には、指示値が1か否かを判断する(ステップC5)。この時指示値が1であれば、中央処理部222は、先頭のグループにおける基準要素点の直後の要素点、つまり2番目の要素点の1階差分値を取得し記憶する(ステップC6)。上記仮定下では、要素点P1の1階差分値(ΔX1,ΔY1)が取得される。
【0046】
また、中央処理部222は、ステップC5で指示値が1でない場合には、この指示値が2以上であるから、ステップC7において、先頭グループにおいて、1階差分値を未導出の1個又は複数の要素点から、先頭に位置する要素点の2階差分値を取得する。その後、中央処理部222は、対象要素点の直前及び2個前に位置する要素点の正規化座標値と、今回取得した2階差分値とを使って、対象要素点の正規化座標値を導出する(ステップC7)。例えば、要素点P2の2階差分値(ΔΔX2,ΔΔY2)が取得された場合には、直前の要素点P1の1階差分値(ΔX1,ΔY1)を使って、要素点P2の1階差分値(ΔX2,ΔY2)が導出される。より具体的には、ΔX2はΔX1+ΔΔX2であり、ΔY2はΔY1+ΔΔY2である。他の要素点P3及びP4の1階差分値も同様に導出される。
【0047】
以上のステップC4、C6及びC7のいずれかが終了した後、中央処理部222は、カウンタの指示値を1だけインクリメントし(ステップC8)、ステップC2に戻る。ここで、ステップC2で指示値が要素点総数以上であれば、先頭のグループについて、2階差分値で表現された全要素点について1階差分値が導出されたことになるので、中央処理部222は、ステップC1で取得した継続フラグを参照して、後続のグループがあるか否かを判断する(ステップC9)。具体的には、継続フラグが1であれば、2番目のグループが未処理のまま残っていると判断する。
【0048】
また、ステップC9でグループが残っていないと判断すれば、中央処理部222は、今回取得した基準要素点の正規化座標値、2番目の要素点の1階差分値及び、今回導出した3番目以降の1階差分値を順番通りに並べて、さらに1階差分値で表現された要素点数を付加することにより、図2に示すような低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj を作業領域223に作成する(ステップC10)。なお、必要に応じて、ステップC10において、対象オブジェクトの描画に必要な情報(図示せず)も付加される。このような情報としては、例えば、対象オブジェクトの色や線種を特定する情報がある。
【0049】
ステップC9で後続のグループが未処理のまま残っていると判断すれば、中央処理部222は、カウンタを0に再設定し(図8のステップC11)、その後、次のグループを選択した後、選択したグループの付加情報を取得する(ステップC12)。上記仮定下では、最後のグループ(図5参照)が選択され要素点総数として3が取得され、継続フラグとして0が取得される。
次に、中央処理部222は、カウンタの指示値が、ステップC12で取得された要素点総数以上であるか否かを判断する(ステップC13)。
【0050】
ステップC13で指示値が要素点総数以上でないと判断した場合、中央処理部222は、上記カウンタの指示値が0か否かを判断し(ステップC14)、この指示値が0である場合には、現在選択されているグループから、先頭の要素点の位置を特定する1階差分値を取得する(ステップC15)。上記仮定下では、要素点P5の1階差分値(ΔX5,ΔY5)が取得される。なお、ステップC13で指示値が要素点総数以上と判断された場合の処理については後述する。
【0051】
また、中央処理部222は、ステップC14で指示値が0でない場合には、この指示値が1以上であるから、現在選択されているグループにおいて、1階差分値を未導出の1個又は複数の要素点から、先頭に位置するものの2階差分値を取得する。その後、中央処理部222は、ステップC7と同様にして、現在選択されている要素点の1階差分値を導出する(ステップC16)。
【0052】
以上のステップC14及びC16のいずれかが終了した後、中央処理部222は、カウンタの指示値を1だけインクリメントし(ステップC17)、ステップC13に戻る。ここで、ステップC13で指示値が要素点総数以上であれば、現在選択されているグループについて、全要素点の正規化座標を導出したことになるので、中央処理部222は、ステップC9と同様にして、1階差分値を導出すべき後続のグループが残っているか否かを判断する(ステップC18)。
【0053】
また、ステップC18でグループが残っていないと判断すれば、中央処理部222は、今回取得した基準要素点の正規化座標値、2番目の要素点の1階差分値及び、これまでに導出した1階差分値を順番通りに並べて、さらに1階差分値で表現された要素点数を付加することにより、図2に示すような低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj を作業領域223に作成する(ステップC19)。前述したように、ステップC10において、対象オブジェクトの描画に必要な情報(図示せず)が付加されてもよい。
【0054】
以上のステップC10及びC19のいずれかが終了した後、中央処理部222は、図7及び図8の処理から抜けて、図6のステップB4を行う。つまり、中央処理部222は、今回受け取った高圧縮地図データHCDcartに、高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj が残っているか否かを判断し(ステップB4)、残っている場合には、ステップB2に戻る。逆に、残っていない場合には、中央処理部222は、図7及び図8の処理で作成された全ての低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj を含む低圧縮地図データLCDcartを作業領域223に作成し、作成したものを描画装置23に転送する(ステップB5)。
【0055】
描画装置23は、伸長装置22で作成された低圧縮地図データLCDcartを使って、地図を描画する。より具体的には、描画装置23は、受け取った低圧縮地図データLCDcartから、各低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCRobj を選択した後、選択したものに含まれかつ正規化座標値で表現された基準要素点から、基準要素点の直後に位置しかつ1階差分値(つまり基準要素点に対する相対座標値)で表現された2個目の要素点とを繋ぐ。以降同様に、直前の要素点に対する相対座標値で特定される全要素点を線で結ぶことにより、描画装置23は、対象オブジェクトを描画する。その結果、描画装置23は、地図画像を表す地図画像データDmap を生成する。なお、この時、描画装置23は、車両のナビゲーションに必要な各種データを、地図画像上に重畳しても構わない。各種データの典型例としては、車両の現在位置を示すマーク、及び車両が目的地に至るまでの経路がある。描画装置23はさらに、生成した地図画像データDmap を表示装置24に送る。表示装置24は、描画装置23から送られてくる地図画像データDmap に基づいて、それが表す地図画像を、自身が有するディスプレイ上に表示する。
【0056】
以上説明したように、伸長装置22によれば、本願特有の圧縮装置12において高圧縮率で圧縮された高圧縮地図データHCDcartから、低圧縮地図データLCDcartを再生することができる。しかも、伸長装置22は、対象となる要素点の1階差分値を導出する際、直前の要素点の1階差分値に対象となる要素点の2階差分値を加算するだけで良いので、早い速度で、低圧縮地図データLCDcartを再生することが可能となる。
【0057】
なお、以上の実施形態において、圧縮装置12は、低圧縮地図データLCDcartから、高圧縮地図データHCDcartを作成すると説明したが、これだけに限らず、地図データDcartから高圧縮地図データHCDcartを作成しても構わない。また、以上の実施形態において、圧縮プログラム124及び伸長プログラム224は、圧縮装置12及び伸長装置22にインストールされていると説明したが、これだけに限らず、CD(Compact Disk)に代表される記憶媒体に書き込まれた状態で頒布されても構わない。さらに、圧縮プログラム124及び伸長プログラム224は、デジタルネットワークを介して頒布されても構わない。
【0058】
また、以上の実施形態において、高圧縮地図データHCDcartは、データ端末装置2に配信されるとして説明したが、これだけに限らず、CD及びDVD(Digital Versatile Disk)に代表される記憶媒体に記録された状態で頒布されても構わない。さらに、高圧縮地図データHCDcartは、一般的にデータ端末装置2がローカルに備えるCDドライブ、DVDドライブ、HDD(Hard Disk Drive )に代表される記憶装置に格納されていても構わない。この場合、伸長装置22は、このような記憶装置から、高圧縮地図データHCDcartを読み出して、伸長する。
【0059】
また、以上の実施形態では、圧縮装置12は、地図を構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する低圧縮オブジェクトレコードLCDcartを圧縮処理すると説明したが、これだけに限らず、道路の渋滞情報を構成するオブジェクト(典型的には、矢印)の形状を特定するデータを圧縮しても構わない。また、伸長装置22は、渋滞情報の形状を特定する圧縮データを取得して伸長しても構わない。
【0060】
また、以上の実施形態では、圧縮装置12は、圧縮プログラム124を実行する中央処理部122と、作業領域123とで構成されるとして説明し、さらに、伸長装置22は、伸長プログラム224を実行する中央処理部222と、作業領域223で構成されるとして説明した。しかし、これだけに限らず、圧縮装置12及び伸長装置22は、ゲートアレイに代表されるハードウェアで構成されても構わない。
【0061】
また、以上の実施形態では、伸長装置22は、2階差分値から1階差分値を導出すると説明した。しかし、これに限らず、伸長装置22は、要素点の2階差分値から1階差分値を導出した後、その要素点の正規化座標値又は絶対座標値を導出するようにしても構わない。
【0062】
また、以上の実施形態では、データ端末装置2において、描画装置23が低圧縮地図データLCDcartを使って地図画像を描画し、表示装置24は、描画された地図画像を表示している。しかし、データ端末装置2は、経路探索又は誘導案内のように、地図画像の表示を必ずしも必要としない処理(典型的には、ターンバイターンタイプのデータ端末装置2)に、低圧縮データLCDcartを使っても構わない。
【0063】
【発明の効果】
以上のように本発明は、圧縮装置に、オブジェクトの外形を規定するいくつかの要素点について2階差分値を算出する2階差分値算出部と、2階差分値算出部で算出された2階差分値を使って高圧縮地図データを作成する高圧縮データ作成部とを設けることにより、高い圧縮率で地図データを圧縮できるという効果を有する圧縮装置を提供することができるものである。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の一実施形態に係る圧縮装置12及び伸長装置22を組み込んだ地図配信システムの全体構成を示すブロック図
【図2】図1の記憶装置11に格納される低圧縮地図データLCDcartのデータ構造を示す模式図
【図3】図2の低圧縮地図データLCDにより表現される線状のオブジェクトAを示す模式図
【図4】図1に示す圧縮装置12の動作説明のためのフロー図
【図5】図1に示す圧縮装置12が作成する高圧縮オブジェクトレコードHCRobj のデータ構造を示す模式図
【図6】図1に示す伸長装置22の動作説明のためのフロー図
【図7】図6に示すステップB3の詳細な処理手順の前半を示すフロー図
【図8】図6に示すステップB3の詳細な処理手順の後半を示すフロー図
【符号の説明】
12 圧縮装置
121 プログラム格納部
122 中央処理部
123 作業領域
124 圧縮プログラム
22 伸長装置
221 プログラム格納部
222 中央処理部
223 作業領域
224 伸長プログラム[0001]
TECHNICAL FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a map data compression and decompression device, and more particularly to a data compression and decompression device in which the shape of an object on a map is expressed in a vector format.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In general, in map data, objects (typically, roads, buildings, rivers, and green belts) necessary for drawing a map are each represented by a vector format as a set of element points that specify the shape of the object. Is represented by Conventionally, all the element points of each object are typically represented by a sequence of normalized coordinate values. However, since such map data is unsuitable for distribution by communication or broadcasting due to the amount of data, various map data compression methods have been proposed in recent years. Hereinafter, an example of a conventional map data compression method disclosed in Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2001-56823 will be described.
[0003]
In the compression method disclosed in the above publication, the element point of each object is represented by one of a normalized coordinate value and a first-order difference value. Here, the first-order difference value is a difference value between the normalized coordinate value of the target element point and the normalized coordinate value of the element point immediately before the target element point. For example, when the normalized coordinate value of the target element point is (X1, Y1) and the normalized coordinate value of the immediately preceding element point is (X0, Y0), the first-order difference value is (X1-X0, Y1-Y0). By adopting such a first-order difference value, the data amount for specifying each element point is compressed.
[0004]
[Patent Document 1]
JP 2001-56823 A
[0005]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
In the future, the demand for map distribution will further increase, and it is expected that map data will be used even in data terminal devices that can only be mounted with a small-capacity storage device. However, the conventional compression method has a problem that it is not possible to cope with such expanded use of map data because the data amount is still insufficiently compressed.
[0006]
In addition, most of the data terminal devices that receive map distribution are mobile objects such as navigation devices, and thus obtain map data through a mobile communication network. However, the billing system for mobile communication is still often based on a pay-as-you-go system, and the conventional compression method has a problem that the communication cost on the user side increases due to insufficient compression of the data amount.
[0007]
Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide a compression device capable of compressing map data at a higher compression ratio and a decompression device corresponding thereto.
[0008]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
The compression device of the present invention is a compression device that compresses map data, and is obtained by a data acquisition unit that acquires data including a plurality of element points that specify the shape of an object that constitutes the map data, and a data acquisition unit that acquires the data. A second-order difference value calculating unit that calculates a second-order difference value of a predetermined element point among the plurality of element points. Here, the second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate of the predetermined element point. This is a difference value between the value and the immediately preceding coordinate value. The compression device of the present invention further includes a compressed data creation unit that creates compressed data including the second-order difference value calculated by the second-order difference value calculation unit.
With this configuration, it is possible to compress the map data at a higher compression rate.
[0009]
In the compression device according to the aspect of the invention, the compressed data creation unit uses the data acquired by the data acquisition unit and the second-order difference value calculated by the second-order difference value calculation unit to calculate a coordinate value of a first element point; Compressed data including at least a first-order difference value of the second element point and a second-order difference value of the remaining element points is created.
With this configuration, it is possible to compress the map data at a higher compression rate.
[0010]
The compression device of the present invention further includes: an element point setting unit that sets at least one element point as a boundary element point from the plurality of element points acquired by the data acquisition unit; and a boundary element set by the element point setting unit. A grouping unit that divides the plurality of element points acquired by the data acquisition unit into a plurality of groups based on the points. Here, in any one of the groups divided by the grouping unit, the compressed data creation unit determines the coordinate value of the first element point, the first-order difference value of the second element point, and the second-order difference value of the remaining element points. Compressed data including at least a difference value, and further including, in another group, at least a first-order difference value of the first element point and a second-order difference value of the remaining element points.
With this configuration, it is possible to compress the map data at a higher compression rate.
[0011]
The compression device of the present invention further calculates, for each element point acquired by the data acquisition unit, the number of bits required to represent the first-order difference value and the number of bits required to represent the second-order difference value. A comparison unit is further provided. Here, the element point setting unit sets all element points in which the number of bits of the second-order difference value is larger than the number of bits of the first-order difference value as boundary element points.
With this configuration, it is possible to prevent the second-order difference value from having a larger number of bits than the first-order difference value, so that it is possible to optimally group a plurality of element points while maintaining a high compression ratio. .
[0012]
The compression device of the present invention further includes an information allocating unit that allocates, to each group divided by the grouping unit, a total number of element points belonging to the target group and a continuation flag indicating whether or not a subsequent group exists. Is further provided. Here, for any of the groups divided by the grouping unit, the compressed data creation unit determines the coordinate value of the first element point, the first-order difference value of the second element point, and the second-order difference value of the remaining element points. A difference value, a total number of element points in the group, and a continuation flag. In other groups, a first-order difference value of the first element point, a second-order difference value of the remaining element points, Compressed data including the total number of element points and the continuation flag is created.
With this configuration, since the object is specified as a group, the map data receiving side can perform an appropriate decompression process.
[0013]
In the compression device according to the aspect of the invention, the data acquisition unit further acquires data including a plurality of element points that specify a shape of an object that constitutes traffic congestion information on the road.
With this configuration, it is possible to compress the objects constituting the traffic congestion information at a higher compression ratio.
[0014]
A decompression device that decompresses map data according to the present invention includes a compressed data acquisition unit that acquires compressed data that includes at least a second-order difference value that can specify the position of an element point that specifies the shape of an object that constitutes map data. . Here, the second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate of the predetermined element point. This is a difference value between the value and the immediately preceding coordinate value. The decompression device of the present invention further includes a first-order difference value derivation unit that derives a first-order difference value of a target element point from the second-order difference value acquired by the compressed data acquisition unit, and a first-order difference value derivation unit. A data creation unit that creates data that specifies the shape of an object constituting the map data using the derived first-order difference value of the element point.
With this configuration, the map data compressed by the compression device can be accurately and rapidly expanded.
[0015]
A compression method according to the present invention is a compression method for compressing map data, wherein the data acquisition step acquires data including a plurality of element points that specify the shape of an object constituting the map data. Calculating a second-order difference value of a predetermined element point among the plurality of element points. Here, the second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate of the predetermined element point. This is a difference value between the value and the immediately preceding coordinate value. The compression method further includes a compressed data creation step of creating compressed data including the second-order difference value calculated in the second-order difference value calculation step.
[0016]
A decompression method according to the present invention is a decompression method for decompressing map data, wherein the decompression method obtains compressed data including at least a second-order difference value capable of specifying the position of an element point that specifies the shape of an object constituting the map data. The method includes a data acquisition step. Here, the second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate of the predetermined element point. This is a difference value between the value and the immediately preceding coordinate value. The decompression method is further derived in a first-order difference value derivation step of deriving a first-order difference value of the target element point from the second-order difference value acquired in the compressed data acquisition step, and a first-order difference value derivation step. A data creating step of creating data specifying the shape of the object constituting the map data using the first-order difference value of the element point.
[0017]
The recording medium storing the computer program of the present invention stores a computer program for compressing map data. The computer program includes a data acquisition step of acquiring data including a plurality of element points that specify the shape of an object constituting the map data; and a predetermined element point of the plurality of element points acquired in the data acquisition step. Calculating a second-order difference value. Here, the second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate of the predetermined element point. This is a difference value between the value and the immediately preceding coordinate value. The computer program further includes a compressed data creation step of creating compressed data including the second-order difference value calculated in the second-order difference value calculation step.
[0018]
The recording medium storing the computer program of the present invention stores a computer program for expanding map data. The computer program includes a compressed data obtaining step of obtaining compressed data including at least a second-order difference value that can specify the position of an element point that specifies the shape of an object forming the map data. Here, the second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate of the predetermined element point. This is a difference value between the value and the immediately preceding coordinate value. The computer program is further derived in a first-order difference value derivation step of deriving a first-order difference value of a target element point from the second-order difference value acquired in the compressed data acquisition step, and a first-order difference value derivation step. A data creating step of creating data specifying the shape of the object constituting the map data using the first-order difference value of the element point.
[0019]
The recording medium storing the data of the present invention stores data including a plurality of element points for specifying the shape of the object constituting the map data. The data includes one of a normalized coordinate value and an absolute coordinate value specifying the position of at least one reference element point, a first-order difference value specifying the position of an element point immediately after the reference element point, and a first-order difference value. And a second-order difference value that specifies the position of an element point that follows the element point represented by the difference value.
[0020]
The map distribution system of the present invention includes a map distribution device that compresses map data and distributes compressed map data, and a data terminal device that creates a map image using the compressed map data distributed by the map distribution device. Prepare. The map distribution device includes a storage device that stores map data including a plurality of element points that specify a shape of an object that forms a map image, and compresses the map data stored in the storage device to determine a position of a predetermined element point. And a compression device that generates compressed map data expressing the second map as a second-order difference value. Here, the second-order difference value is a difference value between the first-order difference value of the predetermined element point and the first-order difference value of the immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate of the predetermined element point. This is a difference value between the value and the immediately preceding coordinate value. The map distribution device further includes a transmission device for transmitting the compressed map data created by the compression device to a transmission path. Further, the data terminal device receives the compressed map data transmitted from the transmitting device and transmitted through the transmission path, and expands the compressed map data received by the receiving device to obtain at least a second-order difference value. A decompression device that creates map data that expresses the position of the expressed element point by the first-order difference value and a rendering device that creates a map image using the map data created by the decompression device is created by the rendering device. And a display device for displaying the generated map image.
[0021]
BEST MODE FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of a map distribution system incorporating a compression device and a decompression device according to an embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 1, the map distribution system includes a
[0022]
The
Instead of the normalized coordinate values, the low-compression map data LCDcart may include absolute coordinate values. The absolute coordinate value is a two-dimensional coordinate value based on a predetermined position on the map, and is represented by, for example, (latitude, longitude).
[0023]
More specifically, the above-described low-compression map data LCDcart preferably stores a data string composed of at least one normalized coordinate value and one or more first-order difference values in a low-compression object record as shown in FIG. Included as LCRob. In the low-compression object record LCRobj, the normalized coordinate value is typically placed at the head of the data string, and specifies the two-dimensional coordinate position of an element point that is used as a reference when drawing an object. In the present embodiment, the normalized coordinate values are exemplarily represented using a total of 4 bytes. In addition, each first-order difference value is a difference value between the target element point and the normalized coordinate value of the previous element point in the data sequence in order to specify the position of the target element point excluding the reference element point. It is. In the present embodiment, the first-order difference value is exemplarily represented using a total of 2 bytes.
[0024]
For example, as shown in FIG. 3, a linear object A obtained by sequentially connecting eight element points P0 to P7 is assumed. When specifying the shape of such an object A, as shown in FIG. 2, the low-compression object record LCRobj includes a normalized coordinate value (X0, Y0) of the element point P0 and a first-order difference between the element points P1 to P7. Values (ΔX1, ΔY1) to (ΔX7, ΔY7). Here, assuming that the normalized coordinate value of the element point P1 is (X1, Y1), (ΔX1, ΔY1) is (X1-X0, Y1-Y0). The first-order difference values (ΔX2, ΔY2) to (ΔX7, ΔY7) are also calculated in the same manner as (ΔX1, ΔY1).
[0025]
As illustrated in FIG. 1, the
[0026]
The data
[0027]
As shown in FIG. 1, the
[0028]
The
[0029]
Next, operations of the
[0030]
In the
[0031]
Next, the
[0032]
Next, the
[0033]
By the way, in general, in a section having a shape closer to a straight line in the outline of the target object, the second-order difference value of the element point is smaller than the first-order difference value of the same element point. Conversely, the second-order difference value of the element point is larger than the first-order difference value of the same element point in a section having a larger curvature in the outline of the target object. By the way, various objects are required to construct a map. Of these objects, especially on the road, the vehicle is designed so as not to be as sharp as possible so that the vehicle can travel easily. Even rivers do not turn very sharply. Therefore, in most cases, when the second-order difference value of the target element point is compared with the first-order difference value, the magnitude of the second-order difference value is smaller. From the above, the second-order difference value can be represented by a smaller number of bits than the first-order difference value. In the present embodiment, for example, the second-order difference value is expressed in total as 12 bits, which is smaller than the number of bits of the first-order difference value.
[0034]
In step A4, the magnitudes of the second-order difference value and the first-order difference value were compared. For example, when the first-order difference value is (130, 0) and the second-order difference value is (127, -127), the magnitude of the first-order difference value is 130, and the magnitude of the second-order difference value is 130. The second order difference value is about 180, and the second order difference value is larger. However, the required number of bits is 9 bits from -255 to +255 in the case of the first order difference value, and -127 to +127 in the case of the second order difference value. Since the number of bits required to represent the target element point by the second-order difference value and the number of bits required to represent the same element point by the first-order difference value You may compare.
[0035]
Next, for subsequent steps A6 and A7, if there is an element point having a larger second-order difference value, the
In the case where the comparison is performed by the number of bits as described above, the
[0036]
Next, the
[0037]
If it is determined in step A6 that there is no boundary element point, only one group can be formed, so that the
[0038]
After step A6 or A7, the
[0039]
Through the processing in step A8, the
[0040]
The
[0041]
The
In the data
[0042]
In the
[0043]
Next, the
Next, after setting the counter for counting the number of processed element points to 0, the
[0044]
If it is determined in step C2 that the indicated value is not equal to or greater than the total number of element points, the
[0045]
If the indicated value is not 0 in step C3, the
[0046]
If the indicated value is not 1 in step C5, the
[0047]
After any of the above steps C4, C6 and C7 is completed, the
[0048]
If it is determined in step C9 that no group remains, the
[0049]
If it is determined in step C9 that the subsequent group remains unprocessed, the
Next, the
[0050]
If it is determined in step C13 that the indicated value is not equal to or greater than the total number of element points, the
[0051]
When the indicated value is not 0 in step C14, the
[0052]
After any of steps C14 and C16 described above is completed, the
[0053]
If it is determined in step C18 that no group remains, the
[0054]
After any of the above steps C10 and C19 is completed, the
[0055]
The
[0056]
As described above, according to the
[0057]
In the above-described embodiment, the
[0058]
In the above embodiment, the high-compression map data HCDcart has been described as being distributed to the data
[0059]
In the above embodiment, the
[0060]
In the above embodiment, the
[0061]
Further, in the above embodiment, it has been described that the
[0062]
In the above embodiment, in the data
[0063]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, in the compression device, the second-order difference value calculation unit that calculates the second-order difference value for some element points that define the outer shape of the object, and the two-dimensional difference value calculated by the second-order difference value calculation unit By providing a high-compression data creation unit that creates high-compression map data using a floor difference value, it is possible to provide a compression device that has the effect of enabling map data to be compressed at a high compression rate.
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the overall configuration of a map distribution system incorporating a
FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram showing a data structure of low-compression map data LCDcart stored in a
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing a linear object A represented by the low-compression map data LCD of FIG. 2;
FIG. 4 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the
FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram showing a data structure of a high-compression object record HCRob created by the
FIG. 6 is a flowchart for explaining the operation of the
7 is a flowchart showing the first half of a detailed processing procedure of step B3 shown in FIG. 6;
FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing the latter half of the detailed processing procedure of step B3 shown in FIG. 6;
[Explanation of symbols]
12 Compressor
121 Program storage
122 Central processing unit
123 work area
124 compression program
22 Stretching device
221 Program storage
222 central processing unit
223 Work area
224 Decompression program
Claims (13)
前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを取得するデータ取得部と、
前記データ取得部で取得された複数の要素点の内、所定の要素点の2階差分値を算出する2階差分値算出部とを備え、
前記2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、前記1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値であり、
前記2階差分値算出部で算出された2階差分値を含む圧縮データを作成する圧縮データ作成部をさらに備える、圧縮装置。A compression device for compressing map data,
A data acquisition unit that acquires data including a plurality of element points that specify the shape of an object that constitutes the map data;
A second-order difference value calculation unit that calculates a second-order difference value of a predetermined element point among the plurality of element points acquired by the data acquisition unit;
The second-order difference value is a difference value between a first-order difference value of a predetermined element point and a first-order difference value of an immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate value of a predetermined element point. And the difference value between the coordinate value immediately before and
A compression device, further comprising a compressed data creation unit that creates compressed data including the second-order difference value calculated by the second-order difference value calculation unit.
前記要素点設定部で設定された境界要素点に基づいて、前記データ取得部で取得された複数の要素点を、複数のグループに分割するグループ化部とをさらに備え、
前記圧縮データ作成部は、前記グループ化部により分割されたいずれかのグループにおいて、先頭の要素点の座標値と、2番目の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値とを少なくとも含み、さらに、他のグループにおいて、先頭の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値とを少なくとも含む圧縮データを作成する、請求項2に記載の圧縮装置。An element point setting unit configured to set at least one element point as a boundary element point from the plurality of element points acquired by the data acquisition unit;
Based on the boundary element points set in the element point setting unit, a plurality of element points acquired by the data acquisition unit, further comprising a grouping unit to divide into a plurality of groups,
In any one of the groups divided by the grouping unit, the compressed data creation unit may calculate a coordinate value of a first element point, a first-order difference value of a second element point, and a second-order difference value of a remaining element point. 3. The compressed data according to claim 2, wherein compressed data including at least a first-order difference value of a first element point and a second-order difference value of a remaining element point is created in another group. apparatus.
前記要素点設定部は、2階差分値のビット数が1階差分値のビット数よりも大きい全ての要素点を、境界要素点として設定する、請求項3に記載の圧縮装置。A comparison unit configured to compare the number of bits required to represent a first-order difference value with the number of bits required to represent a second-order difference value for each element point acquired by the data acquisition unit; ,
The compression device according to claim 3, wherein the element point setting unit sets all element points in which the number of bits of the second-order difference value is larger than the number of bits of the first-order difference value as boundary element points.
前記圧縮データ作成部は、前記グループ化部により分割されたいずれかのグループについて、先頭の要素点の座標値と、2番目の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値と、グループ内の要素点の総数と、継続フラグとを含み、さらに、他のグループにおいて、先頭の要素点の1階差分値と、残りの要素点の2階差分値と、グループ内の要素点の総数と、継続フラグとを含む圧縮データを作成する、請求項4に記載の圧縮装置。Each group divided by the grouping unit, further includes an information allocating unit that allocates a total number of element points belonging to the target group and a continuation flag indicating whether or not a subsequent group exists,
The compressed data creation unit is configured to determine, for any of the groups divided by the grouping unit, a coordinate value of a leading element point, a first-order difference value of a second element point, and a second-order difference value of a remaining element point. Values, the total number of element points in the group, and the continuation flag. In other groups, the first-order difference value of the first element point, the second-order difference value of the remaining element points, and the The compression device according to claim 4, wherein the compression device generates compressed data including a total number of element points and a continuation flag.
前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する要素点の位置を特定可能な2階差分値を少なくとも含む圧縮データを取得する圧縮データ取得部を備え、
前記2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、前記1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値であり、
前記圧縮データ取得部で取得された2階差分値から、対象となる要素点の1階差分値を導出する1階差分値導出部と、
前記1階差分値導出部で導出された要素点の1階差分値を使って、前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定するデータを作成するデータ作成部とをさらに備える、伸長装置。An expansion device for expanding map data,
A compressed data acquisition unit that acquires compressed data that includes at least a second-order difference value that can specify the position of an element point that specifies the shape of an object that constitutes the map data;
The second-order difference value is a difference value between a first-order difference value of a predetermined element point and a first-order difference value of an immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate value of a predetermined element point. And the difference value between the coordinate value immediately before and
A first-order difference value derivation unit that derives a first-order difference value of a target element point from the second-order difference value acquired by the compressed data acquisition unit;
A decompression device further comprising: a data creation unit that creates data specifying a shape of an object constituting the map data using a first-order difference value of an element point derived by the first-order difference value derivation unit.
前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを取得するデータ取得ステップと、
前記データ取得ステップで取得された複数の要素点の内、所定の要素点の2階差分値を算出する2階差分値算出ステップとを備え、
前記2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、前記1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値であり、
前記2階差分値算出ステップで算出された2階差分値を含む圧縮データを作成する圧縮データ作成ステップをさらに備える、圧縮方法。A compression method for compressing map data,
A data acquisition step of acquiring data including a plurality of element points for specifying a shape of an object constituting the map data;
A second-order difference value calculating step of calculating a second-order difference value of a predetermined element point among the plurality of element points obtained in the data obtaining step,
The second-order difference value is a difference value between a first-order difference value of a predetermined element point and a first-order difference value of an immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate value of a predetermined element point. And the difference value between the coordinate value immediately before and
A compression method, further comprising a compressed data creation step of creating compressed data including the second-order difference value calculated in the second-order difference value calculation step.
前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する要素点の位置を特定可能な2階差分値を少なくとも含む圧縮データを取得する圧縮データ取得ステップを備え、
前記2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、前記1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値であり、
前記圧縮データ取得ステップで取得された2階差分値から、対象となる要素点の1階差分値を導出する1階差分値導出ステップと、
前記1階差分値導出ステップで導出された要素点の1階差分値を使って、前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定するデータを作成するデータ作成ステップとをさらに備える、伸長方法。An expansion method for expanding map data,
A compressed data obtaining step of obtaining compressed data including at least a second-order difference value capable of specifying a position of an element point specifying a shape of an object constituting the map data,
The second-order difference value is a difference value between a first-order difference value of a predetermined element point and a first-order difference value of an immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate value of a predetermined element point. And the difference value between the coordinate value immediately before and
A first-order difference value deriving step of deriving a first-order difference value of a target element point from the second-order difference value obtained in the compressed data obtaining step;
A data creation step of creating data for specifying a shape of an object constituting the map data using a first-order difference value of an element point derived in the first-order difference value derivation step.
前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含むデータを取得するデータ取得ステップと、
前記データ取得ステップで取得された複数の要素点の内、所定の要素点の2階差分値を算出する2階差分値算出ステップとを備え、
前記2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、前記1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値であり、
前記2階差分値算出ステップで算出された2階差分値を含む圧縮データを作成する圧縮データ作成ステップをさらに備える、コンピュータプログラムを格納した記録媒体。A recording medium storing a computer program for compressing map data,
A data acquisition step of acquiring data including a plurality of element points for specifying a shape of an object constituting the map data;
A second-order difference value calculating step of calculating a second-order difference value of a predetermined element point among the plurality of element points obtained in the data obtaining step,
The second-order difference value is a difference value between a first-order difference value of a predetermined element point and a first-order difference value of an immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate value of a predetermined element point. And the difference value between the coordinate value immediately before and
A recording medium storing a computer program, further comprising a compressed data creating step of creating compressed data including the second order difference value calculated in the second order difference value calculating step.
前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する要素点の位置を特定可能な2階差分値を少なくとも含む圧縮データを取得する圧縮データ取得ステップを備え、
前記2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、前記1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値であり、
前記圧縮データ取得ステップで取得された2階差分値から、対象となる要素点の1階差分値を導出する1階差分値導出ステップと、
前記1階差分値導出ステップで導出された要素点の1階差分値を使って、前記地図データを構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定するデータを作成するデータ作成ステップとをさらに備える、コンピュータプログラムを格納した記録媒体。A recording medium storing a computer program for expanding map data,
A compressed data obtaining step of obtaining compressed data including at least a second-order difference value capable of specifying a position of an element point specifying a shape of an object constituting the map data,
The second-order difference value is a difference value between a first-order difference value of a predetermined element point and a first-order difference value of an immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate value of a predetermined element point. And the difference value between the coordinate value immediately before and
A first-order difference value deriving step of deriving a first-order difference value of a target element point from the second-order difference value obtained in the compressed data obtaining step;
Using a first-order difference value of an element point derived in the first-order difference value deriving step to create data for specifying a shape of an object constituting the map data. Recording medium.
少なくとも1個の基準要素点の位置を特定する正規化座標値及び絶対座標値のいずれかと、
前記基準要素点に対して直後の要素点の位置を特定する1階差分値と、
前記1階差分値で表現された要素点の後に続く要素点の位置を特定する2階差分値とを備える、データを格納した記録媒体。A recording medium storing data including a plurality of element points for specifying the shape of an object constituting map data,
One of a normalized coordinate value and an absolute coordinate value specifying the position of at least one reference element point;
A first-order difference value specifying the position of an element point immediately after the reference element point;
And a second-order difference value for specifying the position of an element point following the element point represented by the first-order difference value.
地図データを圧縮して、圧縮地図データを配信する地図配信装置と、
前記地図配信装置により配信された圧縮地図データを使って、地図画像を作成するデータ端末装置とを備え、
前記地図配信装置は、
前記地図画像を構成するオブジェクトの形状を特定する複数の要素点を含む地図データを格納する記憶装置と、
前記記憶装置に格納された地図データを圧縮して、所定の要素点の位置を2階差分値で表現した圧縮地図データを作成する圧縮装置とを含み、
前記2階差分値は、所定の要素点の1階差分値と、その直前の要素点の1階差分値との差分値であって、前記1階差分値は、所定の要素点の座標値と、その直前の座標値との差分値であり、
前記地図配信装置はさらに、前記圧縮装置で作成された圧縮地図データを伝送路に送出する送信装置を含み、
前記データ端末装置は、
前記送信装置から送出され、前記伝送路を通じて送られてくる圧縮地図データを受信する受信装置と、
前記受信装置により受信された圧縮地図データを伸長して、少なくとも2階差分値で表現された要素点の位置を1階差分値で表現した地図データを作成する伸長装置と、
前記伸長装置で作成された地図データを使って、地図画像を作成する描画装置とを、
前記描画装置で作成された地図画像を表示する表示装置とを含む、地図配信システム。A map distribution system,
A map distribution device that compresses the map data and distributes the compressed map data;
A data terminal device that creates a map image using the compressed map data distributed by the map distribution device,
The map distribution device,
A storage device for storing map data including a plurality of element points for specifying the shape of an object constituting the map image,
A compression device that compresses the map data stored in the storage device to create compressed map data in which the position of a predetermined element point is represented by a second-order difference value,
The second-order difference value is a difference value between a first-order difference value of a predetermined element point and a first-order difference value of an immediately preceding element point, and the first-order difference value is a coordinate value of a predetermined element point. And the difference value between the coordinate value immediately before and
The map distribution device further includes a transmission device that transmits the compressed map data created by the compression device to a transmission path,
The data terminal device,
A receiving device that receives compressed map data transmitted from the transmitting device and transmitted through the transmission path;
A decompression device that decompresses the compressed map data received by the receiving device and creates map data in which at least the position of an element point represented by a second-order difference value is represented by a first-order difference value;
Using the map data created by the decompression device, a drawing device that creates a map image,
A display device for displaying a map image created by the drawing device.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003146429A JP2004348564A (en) | 2003-05-23 | 2003-05-23 | Compression device and expansion device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003146429A JP2004348564A (en) | 2003-05-23 | 2003-05-23 | Compression device and expansion device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004348564A true JP2004348564A (en) | 2004-12-09 |
Family
ID=33533285
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003146429A Withdrawn JP2004348564A (en) | 2003-05-23 | 2003-05-23 | Compression device and expansion device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2004348564A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112751568A (en) * | 2020-12-21 | 2021-05-04 | 青岛鼎信通讯股份有限公司 | Fault waveform self-adaptive compression method for fault indicator |
-
2003
- 2003-05-23 JP JP2003146429A patent/JP2004348564A/en not_active Withdrawn
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112751568A (en) * | 2020-12-21 | 2021-05-04 | 青岛鼎信通讯股份有限公司 | Fault waveform self-adaptive compression method for fault indicator |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3772853B1 (en) | Method and device for point cloud coding | |
| US20050128305A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for image-classifying, and recording medium storing computer-readable program for the same | |
| JP5740149B2 (en) | Display control device, display layer synthesis program | |
| JP2011166750A (en) | Apparatus for transmitting and receiving map data and method of operating navigation system | |
| US10277729B2 (en) | Apparatus and method for transmitting and receiving handwriting animation message | |
| US12475630B2 (en) | Image rendering method and related apparatus | |
| CN100545884C (en) | Method and device for providing time variable geographic information and corresponding user equipment | |
| CN105243119A (en) | Determination of to-be-superimposed region of image, superimposition of images and image display method and apparatus | |
| CN101742395B (en) | Method for downloading and displaying map data by mobile phone | |
| US8437563B2 (en) | Vector-based image processing | |
| US7633641B2 (en) | Image transmission apparatus using information on rendered range | |
| CN113607182A (en) | Vehicle driving route navigation method and device, storage medium and terminal | |
| JP2004535644A (en) | Wavelet coding method for mesh-like objects | |
| JP2009265277A (en) | Map working device, program, map display apparatus, and geographical information system | |
| JP2009210400A (en) | Guidance information transmission apparatus, guidance system, guidance information transmission method, guidance information providing method, and computer program | |
| JP2004348564A (en) | Compression device and expansion device | |
| US7418145B2 (en) | Compression device and decompression device | |
| CN115588086A (en) | Map dividing method, map dividing device, computer readable storage medium and processor | |
| CN111435089A (en) | Map data compiling method, device, medium and server | |
| JP2007132972A (en) | Information processing apparatus, information processing method, and program | |
| KR101511907B1 (en) | Contents retargeting method and apparatus | |
| JP2006227744A (en) | Information generation device, search device, distribution device, and information distribution system | |
| CN112015832B (en) | Road network prediction tree visualization method, device, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN114666657A (en) | Video editing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| JP2008090518A (en) | Data update system, terminal device, server device, and data update method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20060320 |
|
| A761 | Written withdrawal of application |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A761 Effective date: 20080610 |