JP2002164239A5 - - Google Patents
Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2002164239A5 JP2002164239A5 JP2001279656A JP2001279656A JP2002164239A5 JP 2002164239 A5 JP2002164239 A5 JP 2002164239A5 JP 2001279656 A JP2001279656 A JP 2001279656A JP 2001279656 A JP2001279656 A JP 2001279656A JP 2002164239 A5 JP2002164239 A5 JP 2002164239A5
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- less
- magnet
- content
- rare earth
- amount
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Description
【特許請求の範囲】
【請求項1】 R−T−B系(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上であり、TはFe又はFe及びCoである)の希土類焼結磁石用合金粗粉を非酸化性雰囲気中で平均粒径1〜10μmに微粉砕し、得られた微粉を鉱油、合成油及び植物油から選択される少なくとも1種の油と、脂肪酸の1価アルコールエステル、多塩基酸の1価アルコールエステル、多価アルコールの脂肪酸エステル及びそれらの誘導体のうちから選択される少なくとも1種からなる潤滑剤とからなる非酸化性液中に回収してスラリーを作製し、次いで前記スラリーにより成形し、得られた成形体を脱油後焼結し、得られた焼結体を熱処理することを特徴とする希土類焼結磁石の製造方法。
【請求項2】 前記潤滑剤の添加量は、(R−T−B系合金微粉):(潤滑剤)=99.99〜99.5重量部:0.01〜0.5重量部となる範囲である請求項1に記載の希土類焼結磁石の製造方法。
【請求項3】 重量%で、R(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上である):28〜33%、B:0.8〜1.5%、Co:5%以下(0を含む)、Cu:0.3%以下(0を含む)及び残部:Feの主要成分、ならびに不可避的不純物を含有するR−T−B系(TはFe又はFe及びCoである)焼結磁石からなるアークセグメント磁石であって、
前記アークセグメント磁石の全重量に対し不可避的に含有される酸素量が0.3%以下であり、厚みが1〜4mmの薄肉形状に形成され、密度が7.50 Mg/m3(g/cm3)以上であり、室温において1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上の保磁力iHc及び96%以上の異方性付与方向の配向度(Br/4πImax)を有することを特徴とするアークセグメント磁石。
【請求項4】 平行異方性を有する請求項3に記載のアークセグメント磁石。
【請求項5】 長さが40〜100mmの長尺形状に形成された請求項3又は4に記載のアークセグメント磁石。
【請求項6】 (105)面からのX線回折ピーク強度:I(105)と(006)面からのX線回折ピーク強度:I(006)との比率が、I(105)/I(006)=0.5〜0.8である請求項3乃至5のいずれかに記載のアークセグメント磁石。
【請求項7】 重量%で、R(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上である):28〜33%、B:0.8〜1.5%、Co:5%以下(0を含む)、Cu:0.3%以下(0を含む)及び残部:Feの主要成分、ならびに不可避的不純物を含有するR−T−B系(TはFe又はFe及びCoである)焼結磁石からなるアークセグメント磁石であって、
前記アークセグメント磁石の全重量に対し不可避的に含有される酸素量が0.3%以下であり、かつ前記アークセグメント磁石はラジアル異方性が付与されたアーク断面形状に形成され、内径が100mm以下であり、密度が7.50 Mg/m3(g/cm3)以上であり、室温における保磁力iHcが1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上であり、室温におけるラジアル方向の残留磁束密度(Br//)とラジアル方向に垂直な長さ方向の残留磁束密度(Br⊥)とで定義する配向度:[(Br//)/(Br//+ Br⊥)×100(%)] が85.5%以上であることを特徴とするアークセグメント磁石。
【請求項8】 厚みが1〜4mmの薄肉形状に形成された請求項7に記載のアークセグメント磁石。
【請求項9】 長さが40〜100mmの長尺形状に形成された請求項7又は8に記載のアークセグメント磁石。
【請求項10】 重量%で、R(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上である):28〜33%,B:0.8〜1.5%,Co:5%以下(0を含む),Cu:0.3%以下(0を含む)及び残部:Feの主要成分、ならびに不可避的不純物を含有するR−T−B系(TはFe又はFe及びCoである)焼結磁石からなるリング磁石であって、
前記リング磁石の全重量に対し不可避的に含有される酸素量が0.3%以下であり、かつ前記リング磁石は内径が100mm以下であり、ラジアル異方性を有し、密度が7.50 Mg/m3(g/cm3)以上であり、室温の保磁力iHcが1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上であり、室温におけるラジアル方向の残留磁束密度(Br//)とラジアル方向に垂直な長さ方向の残留磁束密度(Br⊥)とで定義する配向度:[(Br//)/(Br//+ Br⊥)×100(%)] が85.5%以上であることを特徴とするリング磁石。
[Claims]
1. A the R-T-B-based (R is at least one of rare earth elements including Y, Pr occupying in R is 50 atomic% or more, T is a Fe or Fe and Co) rare earth The alloy coarse powder for a sintered magnet is pulverized in a non-oxidizing atmosphere to an average particle size of 1 to 10 μm, and the obtained fine powder is mixed with at least one oil selected from mineral oil, synthetic oil and vegetable oil, and one of fatty acids. hydric alcohols esters, multi monohydric alcohol esters of polybasic acid, polyhydric alcohol fatty acid esters and the slurry was collected in a non-oxidizing liquid consisting of lubricant and comprising at least one selected from among the derivatives thereof prepared, then molded by the slurry, the resulting molded body is sintered after deoiling method for producing a rare earth sintered magnet characterized by heat-treating the obtained sintered body.
2. The amount of the lubricant to be added is in the range of (RTB based alloy fine powder) :( lubricant) = 99.99 to 99.5 parts by weight: 0.01 to 0.5 part by weight. Of manufacturing rare earth sintered magnets.
3. In% by weight, R (R is at least one kind of rare earth element including Y and Pr occupies at least 50 atomic%): 28 to 33% , B: 0.8 to 1.5% , Co: 5% or less (including 0) , Cu: 0.3% or less (including 0) and the balance: a main component of Fe, and an RTB system containing unavoidable impurities (T is Fe or Fe and Co An arc segment magnet comprising a sintered magnet,
The amount of oxygen inevitably contained is 0.3% or less with respect to the total weight of the arc segment magnet, is formed into a thin shape having a thickness of 1 to 4 mm, and has a density of 7.50 Mg / m 3 (g / cm 3 ) or more. An arc segment magnet having a coercive force iHc of 1.1 MA / m (14 kOe) or more at room temperature and a degree of orientation (Br / 4πI max ) of 96% or more in an anisotropic direction at room temperature.
4. The arc segment magnet according to claim 3, which has a parallel anisotropy.
5. The arc segment magnet according to claim 3, wherein the arc segment magnet is formed in a long shape having a length of 40 to 100 mm.
6. The ratio of the X-ray diffraction peak intensity from the (105) plane: I (105) to the X-ray diffraction peak intensity from the (006) plane: I (006) is I (105) / I ( 006) = 0.5 to 0.8, the arc segment magnet according to any one of claims 3 to 5.
7. In% by weight, R (R is at least one kind of rare earth element including Y and Pr occupies at least 50 atomic%): 28 to 33% , B: 0.8 to 1.5% , Co: 5% or less (including 0) , Cu: 0.3% or less (including 0) and the balance: a main component of Fe, and an RTB system containing unavoidable impurities (T is Fe or Fe and Co An arc segment magnet comprising a sintered magnet,
The amount of oxygen inevitably contained relative to the total weight of the arc segment magnets Ri Ah at 0.3% or less, and said arc segment magnets is formed in an arc sectional shape radial anisotropy imparted, inner diameter less than 100mm The density is 7.50 Mg / m 3 (g / cm 3 ) or more, the coercive force iHc at room temperature is 1.1 MA / m (14 kOe) or more, and the residual magnetic flux density in the radial direction (Br //) at room temperature And the degree of orientation defined by the residual magnetic flux density (Br⊥) in the length direction perpendicular to the radial direction: [(Br //) / (Br // + Br⊥) × 100 (%)] is 85.5% or more. An arc segment magnet characterized in that:
8. The arc segment magnet according to claim 7 , wherein the arc segment magnet is formed in a thin shape having a thickness of 1 to 4 mm.
Arc segment magnets according to claim 9 according to claim 7 or 8 length is formed in a long shape of 40 to 100 mm.
10. In% by weight, R (R is at least one kind of rare earth element including Y, and Pr occupies 50 atomic% or more in R): 28 to 33%, B: 0.8 to 1.5%, Co: 5% or less (including 0), Cu: 0.3% or less (including 0) and the balance: a main component of Fe, and an RTB system containing unavoidable impurities (T is Fe or Fe and Co A) ring magnet comprising a sintered magnet,
The amount of oxygen inevitably contained is 0.3% or less based on the total weight of the ring magnet, and the ring magnet has an inner diameter of 100 mm or less, has radial anisotropy, and has a density of 7.50 Mg / m 3. (G / cm 3 ) or more, the coercive force iHc at room temperature is 1.1 MA / m (14 kOe) or more, the residual magnetic flux density (Br //) in the radial direction at room temperature and the length in the length direction perpendicular to the radial direction. A ring magnet, wherein the degree of orientation defined by residual magnetic flux density (Br⊥): [(Br //) / (Br // + Br⊥) × 100 (%)] is 85.5% or more.
【0002】
【従来の技術】
R−T−B系焼結磁石(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種、Tは遷移金属)は、所定組成のR−T−B系合金を粗粉砕し、次いでN2等の不活性ガス中で微粉砕し、得られた平均粒径1〜10μmの微粉末を磁場中成形し、次いで焼結し、熱処理することにより製造される。また、特開平10−303008号に記載されているように、Rの元素としてPrを50原子%以上用いたR−T−B系合金は液体窒素冷却温度近傍でスピン再配列を示すことなく高い磁気特性を保持可能であることが知られており、高速回転を必要とする流体機械や工作機械、余剰電力をフライホイールの運動エネルギーに変換して貯蔵する電力貯蔵装置等に用いることが検討されている。
これらの用途において、残留磁束密度Brおよび最大エネルギー積(BH)maxを高めるには含有酸素量の低減が極めて重要である。このため、本出願人は前記微粉の酸化の進行を阻止する作用の顕著な鉱油や合成油を発見し、それら油中に前記微粉を回収してスラリー化し、このスラリーを成形し、次いで得られた成形体を脱油し、焼結し、熱処理することにより低酸素含有量、高密度型の高性能R−T−B系焼結磁石を得られる製造プロセスを提案した(特許第2731337号等参照)。この製造プロセスは前記微粉末及び成形体を前記油で被覆し大気と遮断することにより酸化の進行を実質的に抑えられるという特徴を有し、脱油し、焼結して得られたR−T−B系焼結体の含有酸素量が微粉砕前のR−T−B系合金粗粉に相当する低水準に保持される。よってR−T−B系焼結体中のR元素が酸化物化し、実質的に滅失して生じる有効希土類量の減少が小さく抑えられ、粒界相を形成する希土類リッチ相は健全に保持される。有効希土類量の実質的な滅失が小さい分だけR含有量を低く設定できるので従来に比べて余剰のRリッチ相及び希土類酸化物が低減でき、同時に強磁性相のR2Fe14B型結晶粒(主相)の体積比率を高められるのでBr,(BH)maxが顕著に向上する。
[0002]
[Prior art]
(At least one rare earth element R containing Y, T is a transition metal) the R-T-B-based sintered magnet, coarsely crushed an R-T-B type alloy having a predetermined composition, and then such as N 2 non It is manufactured by pulverizing in an active gas and molding the obtained fine powder having an average particle size of 1 to 10 μm in a magnetic field, followed by sintering and heat treatment. Further, as described in JP-A-10-303008, an RTB-based alloy using 50 atomic% or more of Pr as an element of R is high without exhibiting spin rearrangement near a liquid nitrogen cooling temperature. are known to be capable of retaining the magnetic properties, the fluid machinery and machine tools requiring high speed rotation, is Rukoto have use in the power storage apparatus that stores and converts the excess power into kinetic energy of the flywheel Are being considered.
In these applications, reduction of the oxygen content is extremely important to increase the residual magnetic flux density Br and the maximum energy product (BH) max. For this reason, the present applicant has discovered mineral oil or synthetic oil having a remarkable effect of inhibiting the progress of the oxidation of the fine powder, recovering the fine powder in the oil to form a slurry, molding the slurry, and then obtaining the slurry. Proposed a manufacturing process to obtain a high-performance, high-density type RTB-based sintered magnet with low oxygen content and high density by deoiling, sintering and heat-treating the compact (Patent No. 2731337, etc.). reference). This manufacturing process has a feature that the progress of oxidation can be substantially suppressed by coating the fine powder and the molded body with the oil and shielding the air from the atmosphere. The oxygen content of the TB-based sintered body is maintained at a low level corresponding to the RTB-based alloy coarse powder before fine pulverization. Therefore, the R element in the RTB-based sintered body is oxidized, and the reduction in the amount of effective rare earth caused by substantial loss is suppressed, and the rare earth rich phase forming the grain boundary phase is kept sound. You. Since the R content can be set lower by the amount that the substantial loss of the effective rare earth is small, the excess R-rich phase and rare earth oxide can be reduced as compared with the prior art, and at the same time, the R 2 Fe 14 B type crystal grains of the ferromagnetic phase Since the volume ratio of the (main phase) can be increased, Br and (BH) max are significantly improved.
【0005】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記課題を解決した本発明の希土類焼結磁石の製造方法は、R−T−B系(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上であり、TはFe又はFe及びCoである)の希土類焼結磁石用合金粗粉を非酸化性雰囲気中で平均粒径1〜10μmに微粉砕し、得られた微粉を鉱油、合成油及び植物油から選択される少なくとも1種の油と、脂肪酸の1価アルコールエステル、多塩基酸の1価アルコールエステル、多価アルコールの脂肪酸エステル及びそれらの誘導体のうちから選択される少なくとも1種からなる潤滑剤とからなる非酸化性液中に回収してスラリーを作製し、次いで前記スラリーにより成形し、得られた成形体を脱油後焼結し、得られた焼結体を熱処理することを特徴とする。
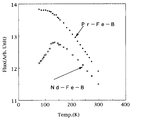
前記潤滑材の添加量は、(R−T−B系合金微粉):(潤滑剤)=99.99〜99.5重量部:0.01〜0.5重量部となる範囲であることが好ましい。RがPr系のものとNd系の磁束量の温度依存性を図6に示す。Nd系のR−T−B系希土類焼結磁石の方では約130K以下になると磁束量が低下する。対してPr系では80K近傍まで環境温度を下げても磁束量が増加しつづけており、高速回転を必要とする流体機械や工作機械、余剰電力をフライホイールの運動エネルギーに変換して貯蔵する電力貯蔵装置等に適用しても高特性のものを得る事が可能である。
[0005]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
Method for producing a rare earth sintered magnet of the present invention which solves the above-mentioned problems, R-T-B system (R is at least one of rare earth elements including Y, Pr occupying the R is at least 50 atom%, T is finely ground to an average particle size of 1~10μm rare earth sintered alloy coarse powder for a magnet and is) Fe or Fe and Co in a non-oxidizing atmosphere, select a resultant fine mineral, synthetic oils and vegetable oils at least one oil, monohydric alcohol esters of fatty acids, monohydric alcohol esters of polybasic acids, a lubricant consisting of at least one selected from among polyhydric alcohol fatty acid esters and their derivatives made and collected in a non-oxidizing liquid slurry prepared, then molded by the slurry, the resulting molded body is sintered after deoiling, characterized by heat-treating the obtained sintered body.
The amount of the lubricant added is preferably in the range of (R-T-B-based alloy fine powder) :( lubricant) = 99.99 to 99.5 parts by weight: 0.01 to 0.5 part by weight. FIG. 6 shows the temperature dependence of the amount of magnetic flux in the case where R is Pr-based and in the case of Nd-based. In the case of the Nd-based RTB-based rare earth sintered magnet, the magnetic flux amount decreases when the temperature is reduced to about 130K or less. On the other hand, in the Pr system, the amount of magnetic flux continues to increase even if the environmental temperature is lowered to around 80K, and the fluid machinery and machine tools that require high-speed rotation and the surplus power that is converted into kinetic energy of the flywheel and stored Even if it is applied to a storage device or the like, it is possible to obtain a product with high characteristics.
又、本発明のアークセグメント磁石は、重量%で、R(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上である):28〜33%、B:0.8〜1.5%、Co:5%以下(0を含む)、Cu:0.3%以下(0を含む)及び残部:Feの主要成分、ならびに不可避的不純物を含有するR−T−B系(TはFe又はFe及びCoである)焼結磁石からなるアークセグメント磁石であって、前記アークセグメント磁石の全重量に対し不可避的に含有される酸素量が0.3%以下であり、厚みが1〜4mmの薄肉形状に形成され、密度が7.50 Mg/m3(g/cm3)以上であり、室温において1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上の保磁力iHc及び96%以上の異方性付与方向の配向度(Br/4πImax)を有することを特徴とする。
前記アークセグメント磁石は、平行異方性を有するものとすることが可能であり、また形状として長さが40〜100mmの長尺形状に形成されたものを製造可能である。この配向性の良好なアークセグメント磁石においては、(105)面からのX線回折ピーク強度:I(105)と(006)面からのX線回折ピーク強度:I(006)との比率が、I(105)/I(006)=0.5〜0.8であるという特徴を持つ。
The arc segment magnet of the present invention has a weight percentage of R (R is at least one kind of rare earth element including Y and Pr occupying 50 at% or more in R): 28 to 33% , B: 0.8 to 1.5% , Co: 5% or less (including 0) , Cu: 0.3% or less (including 0) and the balance: a main component of Fe, and an RTB system containing unavoidable impurities (T is An arc segment magnet comprising a sintered magnet ( which is Fe or Fe and Co) , wherein the amount of oxygen inevitably contained is 0.3% or less with respect to the total weight of the arc segment magnet, and the thickness is 1 to 4 mm. It is formed in a thin shape, has a density of 7.50 Mg / m 3 (g / cm 3 ) or more, and has a coercive force iHc of 1.1 MA / m (14 kOe) or more at room temperature and an orientation degree of 96% or more in the anisotropic direction. (Br / 4πI max ).
The arc segment magnet can have parallel anisotropy, and can be manufactured in a long shape having a length of 40 to 100 mm. In this arc segment magnet having good orientation, the ratio of the X-ray diffraction peak intensity from the (105) plane: I (105) to the X-ray diffraction peak intensity from the (006) plane: I (006) is It has a feature that I (105) / I (006) = 0.5 to 0.8.
又、本発明の他のアークセグメント磁石は、重量%で、R(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上である):28〜33%,B:0.8〜1.5%,Co:5%以下(0を含む),Cu:0.3%以下(0を含む)及び残部:Feの主要成分、ならびに不可避的不純物を含有するR−T−B系(TはFe又はFe及びCoである)焼結磁石からなるアークセグメント磁石であって、前記アークセグメント磁石の全重量に対し不可避的に含有される酸素量が0.3%以下であり、かつ前記アークセグメント磁石はラジアル異方性が付与されたアーク断面形状に形成され、内径が100mm以下であり、密度が7.50 Mg/m3(g/cm3)以上であり、室温における保磁力iHcが1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上であり、室温におけるラジアル方向の残留磁束密度(Br//)とラジアル方向に垂直な長さ方向の残留磁束密度(Br⊥)とで定義する配向度:[(Br//)/(Br//+ Br⊥)×100(%)]が85.5%以上であることを特徴とする。
前記アークセグメント磁石は、厚みが1〜4mmの薄肉形状、さらには長さが40〜100mmの長尺形状に形成することが可能である。
Further, the other arc segment magnet of the present invention is, by weight%, R (R is at least one kind of rare earth element including Y and Pr occupying at least 50 atomic%): 28 to 33%, B: 0.8~1.5%, Co: 5 % or less (including 0), Cu: 0.3% or less (including 0), and the balance: principal component, and the R-T-B-based containing unavoidable impurities Fe ( T is Fe or Fe and Co) a arc segment magnet made of a sintered magnet, the amount of oxygen inevitably contained relative to the total weight of the arc segment magnets Ri Ah at 0.3% or less, and said arc The segment magnet is formed in an arc cross-sectional shape provided with radial anisotropy, has an inner diameter of 100 mm or less, has a density of 7.50 Mg / m 3 (g / cm 3 ) or more, and has a coercive force iHc of 1.1 MA at room temperature. / m (14 kOe) or more, residual magnetic flux in the radial direction at room temperature The degree of orientation defined by the density (Br //) and the residual magnetic flux density (Br⊥) in the length direction perpendicular to the radial direction: [(Br //) / (Br // + Br ×) × 100 (%) ] Is 85.5% or more.
The arc segment magnet can be formed in a thin shape having a thickness of 1 to 4 mm and further in a long shape having a length of 40 to 100 mm.
又本発明のリング磁石は、重量%で、R(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上である):28〜33%,B:0.8〜1.5%,Co:5%以下(0を含む),Cu:0.3%以下(0を含む)及び残部:Feの主要成分、ならびに不可避的不純物を含有するR−T−B系(TはFe又はFe及びCoである)焼結磁石からなるリング磁石であって、前記リング磁石の全重量に対し不可避的に含有される酸素量が0.3%以下であり、かつ前記リング磁石は内径が100mm以下であり、ラジアル異方性を有し、密度が7.50 Mg/m3(g/cm3)以上であり、室温の保磁力iHcが1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上であり、室温におけるラジアル方向の残留磁束密度(Br//)とラジアル方向に垂直な長さ方向の残留磁束密度(Br⊥)とで定義する配向度:[(Br//)/(Br//+ Br⊥)×100(%)] が85.5%以上であることを特徴とする。
In the ring magnet of the present invention, R (R is at least one kind of rare earth element including Y and Pr occupies at least 50 atomic%) is 28 to 33%, and B is 0.8 to 0.8% by weight. R-T-B system containing 1.5%, Co: 5% or less (including 0), Cu: 0.3% or less (including 0) and the balance: a main component of Fe, and inevitable impurities (T is Fe or A ring magnet comprising a sintered magnet ( Fe and Co) , wherein the amount of oxygen inevitably contained is 0.3% or less with respect to the total weight of the ring magnet, and the ring magnet has an inner diameter of 100 mm or less. Has a radial anisotropy, a density of 7.50 Mg / m 3 (g / cm 3 ) or more, a coercive force iHc at room temperature of 1.1 MA / m (14 kOe) or more, and a radial residual at room temperature. Degree of orientation defined by magnetic flux density (Br //) and residual magnetic flux density (Br⊥) in the length direction perpendicular to the radial direction: [(Br //) / (Br // + Br⊥) × 100 (%)] is not less than 85.5% .
R元素としてPrを主とした希土類焼結磁石では、R2Fe14B金属間化合物(RはYを含む希土類元素の少なくとも1種であり、Rに占めるPrが50原子%以上である)を主相とする場合、主要成分組成を、重量%で、R:28〜33%.B:0.8〜1.5%、M1:0〜0.6%(M1はNb,Mo,W,V,Ta,Cr,Ti,Zr及びHfから選択される少なくとも1種である), M2:0〜0.6%(M2はAl,Ga及びCuから選択される少なくとも1種)及び残部Fe(但し、R+B+Fe+M1+M2=100重量%とした場合)とするのが好ましい。以下、単に%と記すのは重量%を意味するものとする。
R量は28〜33%が好ましい。良好な耐食性を具備するために、R量は28〜32%がより好ましく、28〜31%が特に好ましい。R量が28%未満では所定のiHcを得られず、33%超ではBrが著しく低下する。所定のBr及び配向度を得るために、RはPr、又はPrとDy、又はNdとDyとPr及び不可避的R成分からなることが好ましい。即ちRに占めるPrを50原子%以上とし、Dy含有量を0.3〜10%にするのが好ましい。又Rに占めるPrを90原子%以上とし、Dy含有量を0.5〜8%にするのがより好ましい。Rに占めるPrが50原子%未満では液体窒素温度付近でスピン再配列が顕著になり、磁気特性が大きく低下する。Dy含有量が0.3%未満ではDyの含有効果が得られず、10%超ではBrが低下し所定の配向度を得られない。
B量は0.8〜1.5%が好ましく、0.85〜1.2%がより好ましい。B量が0.8%未満では1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上のiHcを得ることが困難であり、B量が1.5%超ではBrが著しく低下する。
Nb,Mo,W,V,Ta,Cr,Ti,Zr及びHfの少なくとも1種からなる高融点金属元素M1を0.01〜0.6%含有することが磁気特性を高めるために好ましい。M1を0.01〜0.6%含有することにより、焼結過程での主相結晶粒の過度の粒成長が抑制され、1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上のiHcを安定して得ることができる。しかし、M1を0.6%超含有すると逆に主相結晶粒の正常な粒成長が阻害され、Brの低下を招く。又M1含有量が0.01%未満では磁気特性を改良する効果が得られない。
M2元素(Al,Ga及びCuの少なくとも1種)の含有量は0.01〜0.6%が好ましい。Alの含有によりiHcが向上し、耐食性が改善されるが、Al含有量が0.6%超ではBrが大きく低下し、0.01%未満ではiHc及び耐食性を高める効果が得られない。より好ましいAl含有量は0.05〜0.3%である。Gaの含有によりiHcが顕著に向上するが、Ga含有量が0.6%超ではBrが大きく低下し、0.01%未満ではiHcを高める効果が得られない。より好ましいGa含有量は0.05〜0.2%である。Cuの微量添加は耐食性の改善及びiHcの向上に寄与するが、Cu含有量が0.3%超ではBrが大きく低下し、0.01%未満では耐食性及びiHcを高める効果が得られない。より好ましいCu含有量は0.05〜0.3%である。
Coの含有により耐食性が改善され、キュリー点が上昇し、希土類焼結磁石の耐熱性が向上するが、Co含有量が5%超では磁気特性に有害なFe−Co相が形成され、あるいはR2(Fe,Co)14B相が形成されてBr及びiHcが大きく低下する。従って、Co含有量は5%以下が好ましい。一方、Co含有量が0.5%未満では耐食性及び耐熱性の向上効果が得られない。よって、Co含有量は0.5〜5%が好ましい。
Coを0.5〜5%及びCuを0.01〜0.3%含有するときに1.1MA/m(14kOe)以上の室温のiHcを得られる第2次熱処理の許容温度が広がる効果を得られ、特に好ましい。
Alを0.01〜0.3%含有させると保磁力向上に寄与するとともに、熱処理温度のばらつきによる保磁力の変動を低減することが可能である。またNbを0.01〜0.08%含有させると焼結過程での結晶粒成長を抑制し、粗大粒の形成を抑制することができる。
不可避に含有される酸素量は0.3%以下が好ましく、0.2%以下がより好ましく、0.18%以下が特に好ましい。酸素含有量を0.3%以下に低減することにより焼結体密度を略理論密度まで高めることができる。R2Fe14B金属間化合物を主相とする場合の焼結体密度はPr2Fe14B金属間化合物の理論密度(7.54g/cm3)に近い7.50g/cm3以上が得られる。
又不可避に含有される炭素量は0.10%以下が好ましく、0.07%以下がより好ましい。炭素含有量の低減により希土類炭化物の生成が抑えられ、有効希土類量が増大し、iHc及び(BH)max等を高めることができる。
又不可避に含有される窒素量は0.15%以下が好ましい。窒素量が0.15%を超えるとBrが大きく低下する。本発明の磁石には公知の表面処理被膜(Niめっき等)が被覆され、実用に供されるが、R量が28〜32%でかつ窒素量が0.002〜0.15%のときに良好な耐食性が付与されるのでより好ましい。
又、原料合金としてCaを還元剤とする還元拡散法により作製したものを用いて本発明の磁石を作製した場合、所定のiHc及び配向度を得るために、前記磁石の全重量を100重量%としてCa含有量を0.1重量%以下(0を含まず)に抑えることが好ましく、0.03重量%以下(0を含まず)に抑えることがより好ましい。
In a rare earth sintered magnet mainly containing Pr as an R element, an R 2 Fe 14 B intermetallic compound (R is at least one rare earth element including Y and Pr in R is 50 atomic% or more) is used. When the main phase is used, the composition of the main component is represented by R: 28 to 33%. B: 0.8 to 1.5%, M 1 : 0 to 0.6% (M 1 is at least one selected from Nb, Mo, W, V, Ta, Cr, Ti, Zr and Hf), M 2 : 0 to 0.6% (M 2 is Al, at least one selected from Ga and Cu), and the balance Fe (However, when the R + B + Fe + M 1 + M 2 = 100 wt%) preferably with. Hereinafter, simply writing% means weight%.
The amount of R is preferably 28 to 33%. In order to provide good corrosion resistance, the R amount is more preferably from 28 to 32%, particularly preferably from 28 to 31%. If the amount of R is less than 28%, a predetermined iHc cannot be obtained, and if it exceeds 33%, Br is remarkably reduced. In order to obtain a predetermined Br and orientation degree, R is preferably composed of Pr, or Pr and Dy, or Nd, Dy, Pr, and an unavoidable R component. That is, it is preferable that the ratio of Pr to R be 50 atomic% or more and the Dy content be 0.3 to 10%. Further, it is more preferable that the ratio of Pr in R is 90 atomic% or more and the Dy content is 0.5 to 8%. When Pr occupying less than 50 atomic% of R, spin rearrangement becomes remarkable near the temperature of liquid nitrogen, and the magnetic properties are greatly reduced. If the Dy content is less than 0.3%, the effect of containing Dy cannot be obtained, and if it exceeds 10%, Br decreases and the predetermined degree of orientation cannot be obtained.
The B content is preferably from 0.8 to 1.5%, more preferably from 0.85 to 1.2%. If the amount of B is less than 0.8%, it is difficult to obtain iHc of 1.1 MA / m (14 kOe) or more, and if the amount of B exceeds 1.5%, Br is significantly reduced.
Nb, Mo, W, V, Ta, Cr, Ti, it is preferable to enhance the magnetic properties of the refractory metal element M 1 consisting of at least one of Zr and Hf containing 0.01 to 0.6%. By containing M 1 0.01 to 0.6%, is suppressed main phase crystal grains of excessive grain growth in the sintering process, can be obtained stably 1.1MA / m (14kOe) or more iHc. However, normal grain growth of the reverse main phase crystal grains when the M 1 ultra containing 0.6% is inhibited, leading to reduction in Br. The M 1 content can not be obtained the effect of improving the magnetic properties is less than 0.01%.
The content of M 2 element (Al, at least one of Ga and Cu) is preferably 0.01 to 0.6%. The content of Al improves iHc and improves corrosion resistance. However, when the Al content exceeds 0.6%, Br is greatly reduced, and when the Al content is less than 0.01%, the effect of increasing iHc and corrosion resistance cannot be obtained. A more preferred Al content is 0.05 to 0.3%. The content of Ga significantly improves iHc, but when the content of Ga exceeds 0.6%, Br is greatly reduced, and when the content of Ga is less than 0.01%, the effect of increasing iHc cannot be obtained. A more preferable Ga content is 0.05 to 0.2%. The addition of a small amount of Cu contributes to the improvement of corrosion resistance and iHc, but when the Cu content exceeds 0.3%, Br is greatly reduced, and when the Cu content is less than 0.01%, the effect of increasing corrosion resistance and iHc cannot be obtained. A more preferred Cu content is 0.05 to 0.3%.
The content of Co improves the corrosion resistance, raises the Curie point, and improves the heat resistance of the rare earth sintered magnet. However, if the Co content exceeds 5%, a Fe—Co phase harmful to magnetic properties is formed, or R 2 (Fe, Co) 14 B phase is formed and Br and iHc are greatly reduced. Therefore, the Co content is preferably 5% or less. On the other hand, if the Co content is less than 0.5%, the effect of improving corrosion resistance and heat resistance cannot be obtained. Therefore, the Co content is preferably 0.5 to 5%.
When 0.5 to 5% of Co and 0.01 to 0.3% of Cu are contained, the allowable temperature of the second heat treatment for obtaining iHc at room temperature of 1.1 MA / m (14 kOe) or more is obtained, which is particularly preferable.
When Al is contained in an amount of 0.01 to 0.3%, it contributes to the improvement of the coercive force, and it is possible to reduce the variation of the coercive force due to the variation of the heat treatment temperature. When Nb is contained in an amount of 0.01 to 0.08%, crystal grain growth during the sintering process is suppressed, and formation of coarse grains can be suppressed.
The amount of oxygen inevitably contained is preferably 0.3% or less, more preferably 0.2% or less, and particularly preferably 0.18% or less. By reducing the oxygen content to 0.3% or less, the density of the sintered body can be increased to approximately the theoretical density. When the R 2 Fe 14 B intermetallic compound is used as the main phase, the sintered body density is 7.50 g / cm 3 or more, which is close to the theoretical density (7.54 g / cm 3 ) of the Pr 2 Fe 14 B intermetallic compound.
Further, the unavoidable carbon content is preferably 0.10% or less, more preferably 0.07% or less. The reduction of the carbon content suppresses the formation of rare earth carbides, increases the effective rare earth amount, and can increase iHc and (BH) max.
The amount of nitrogen unavoidably contained is preferably 0.15% or less . When the amount of nitrogen exceeds 0.15%, Br is greatly reduced. The magnet of the present invention is coated with a known surface treatment film (Ni plating or the like) and put to practical use. However, when the R amount is 28 to 32% and the nitrogen amount is 0.002 to 0.15%, good corrosion resistance is obtained. It is more preferable because it is provided.
When the magnet of the present invention was manufactured using a material alloy manufactured by a reduction diffusion method using Ca as a reducing agent, the total weight of the magnet was reduced to 100% by weight in order to obtain a predetermined iHc and orientation degree. The Ca content is preferably suppressed to 0.1% by weight or less (excluding 0), and more preferably 0.03% by weight or less (excluding 0).
鉱油、合成油又は植物油として、脱油及び成形性の点から、分留点が350℃以下のものがよい。又室温の動粘度が10cSt以下のものがよく、5cSt以下のものがさらに好ましい。
As a mineral oil , a synthetic oil or a vegetable oil, those having a fractionation point of 350 ° C. or lower are preferred from the viewpoint of deoiling and moldability. The kinematic viscosity at room temperature is preferably 10 cSt or less, more preferably 5 cSt or less.
以下に極異方性を有する、R−T−B系焼結リング磁石を作製し、評価した実施例を説明する。
(実施例11)
重量%で、主要成分組成がPr:29.5%,Dy:1.0%,B:1.05%、Ga:0.08%、Nb:0.2%,Al:0.05%,Cu:0.13%,Co:2.0%及び残部FeからなるR−T−B系原料合金粗粉(320メッシュアンダー)を酸素濃度が1ppm未満(体積比)の窒素雰囲気中でジェットミル粉砕し、得られた平均粒径3.8μmの微粉を用いた以外は実施例1と同様にしてスラリーを作製した。得られたスラリーを、図2に示す成形機のキャビティ59に充填後、成形圧力:78.4MPa(0.8ton/cm2)及び100Vのパルス磁場で極異方性が付与されるよう磁場中成形し、成形体を得た。成形体を真空度が約66.5Pa(5×10-1Torr)、200℃の条件で1時間加熱し脱油後、続いて約4.0×10-3Pa(3×10-5Torr)、1060℃の条件で2時間焼結後室温まで冷却し焼結体を得た。次に、アルゴン雰囲気中で900℃で1時間加熱後550℃まで冷却し、次いで550℃で2時間加熱後さらに室温まで冷却する熱処理を行った。次に所定寸法に加工後、電着により平均膜厚12μmのエポキシ樹脂膜をコーティングし、外径48mm、内径30mm及び高さ11mmの8極の極異方性リングを得た。
次に上記の極異方性リングの外径面における磁極間中央部からX線回折用の試料を切り出し、その試料を理学電気(株)製のX線回折装置(RU-200BH)にセットし、2θ−θ走査法によりX線回折した。X線源にはCuKα1線(λ=0.15405nm)を用い、ノイズ(バックグラウンド)は装置に内蔵されたソフトにより除去した。主な回折ピークは主相であるR2T14B型金属間化合物の、2θ=29.08°の(004)面、38.06°の(105)面、44.34°の(006)面であり、(006)面からのX線回折ピーク強度:I(006)を100%として、I(004)/I(006)=0.33,I(105)/I(006)=0.63であった。結果を表6に示す。表中のBoは磁極部で測定した表面磁束密度を示す。
(比較例11)
実施例11のスラリーに替えて、比較例1のスラリーにより極異方性が付与されるよう磁場中成形した以外は実施例11と同様にして比較例の極異方性リングを作製した。以後は実施例11と同様に比較例11の極異方性リングのX線回折を行なった。結果を表6に示す。主な回折ピークは実施例11と同様であったが、I(004)/I(006)=0.32,I(105)/I(006)=0.96であった。又前記極異方性リングの酸素量は0.13重量%であり、炭素量は0.05重量%であり、窒素量は0.003重量%であった。
An example in which an RTB based sintered ring magnet having polar anisotropy is manufactured and evaluated will be described below.
(Example 11)
By weight, the main component composition is Pr: 29.5%, Dy: 1.0%, B: 1.05%, Ga: 0.08%, Nb: 0.2%, Al: 0.05%, Cu: 0.13%, Co: 2.0% and the balance Fe RTB-based raw material alloy coarse powder (320 mesh under) consisting of the following was milled by a jet mill in a nitrogen atmosphere having an oxygen concentration of less than 1 ppm (volume ratio), and the obtained fine powder having an average particle diameter of 3.8 µm was used. A slurry was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except for the above. The resulting slurry, after filling the cavity 59 of the molding machine shown in FIG. 2, the molding pressure: 78.4MPa (0.8ton / cm 2) and polar anisotropy in a pulse magnetic field of 100V is molded in a magnetic field to be applied To obtain a molded product. The compact was heated at 200 ° C. for 1 hour at a degree of vacuum of about 66.5 Pa (5 × 10 −1 Torr), and after deoiling, subsequently, about 4.0 × 10 −3 Pa (3 × 10 −5 Torr), 1060 After sintering at a temperature of 2 ° C. for 2 hours, the mixture was cooled to room temperature to obtain a sintered body. Next, heat treatment was performed in an argon atmosphere at 900 ° C. for 1 hour, followed by cooling to 550 ° C., and then heating at 550 ° C. for 2 hours and further cooling to room temperature. Then after processing into a predetermined size, by coating the epoxy resin film having an average thickness of 12μm by electrodeposition, to obtain an outer diameter 48 mm, the 8-pole pole anisotropic ring having an inner diameter of 30mm and height 11 mm.
Then cut the sample for X-ray diffraction from the inter-pole center portion in the radially outer surface of the pole anisotropic ring, sets its sample X-ray diffraction apparatus manufactured by Rigaku Denki (Ltd.) (RU-200BH) X-ray diffraction was performed by a 2θ-θ scanning method. A CuKα1 ray (λ = 0.15405 nm) was used as an X-ray source, and noise (background) was removed by software built in the apparatus. The main diffraction peaks are the (004) plane at 2θ = 29.08 °, the (105) plane at 38.06 °, the (006) plane at 44.34 °, and the (006) plane of the R2T14B type intermetallic compound as the main phase. X-ray diffraction peak intensity: I (004) / I (006) = 0.33 and I (105) / I (006) = 0.63, where I (006) was 100%. Table 6 shows the results. Bo in the table indicates the surface magnetic flux density measured at the magnetic pole portion.
(Comparative Example 11)
Instead of the slurry of Example 11, polar anisotropic properties except molded in a magnetic field to be applied to produce a polar anisotropic ring of the comparative example in the same manner as in Example 11 by a slurry of Comparative Example 1. Thereafter it was subjected to X-ray diffraction of the polar anisotropic property ring of Comparative Example 11 in the same manner as in Example 11. Table 6 shows the results. The main diffraction peaks were the same as in Example 11, but I (004) / I (006) = 0.32 and I (105) / I (006) = 0.96. The oxygen content of the polar anisotropic property ring is 0.13 wt%, the carbon content is 0.05 wt%, nitrogen content was 0.003 wt%.
表4の実施例11及び比較例11の結果より、本発明によれば、極異方性を有し、密度が7.50 Mg/m3(g/cm3)以上であり、リング外径面での磁極間中心部表面位置で測定した(105)面からのX線回折ピーク強度:I(105)と(006)面からのX線回折ピーク強度:I(006)との比率が、I(105)/I(006)=0.5〜0.8である極異方性リングを提供できることがわかる。
From the results of Example 11 and Comparative Example 11 in Table 4, according to the present invention, the material has polar anisotropy, has a density of 7.50 Mg / m 3 (g / cm 3 ) or more, and has a ring outer diameter surface. The ratio between the X-ray diffraction peak intensity from the (105) plane: I (105) and the X-ray diffraction peak intensity from the (006) plane: I (006) measured at the surface position of the center between the magnetic poles is I ( 105) / I (006) = 0.5~0.8 a polar anisotropic ring it can be seen that can provide.
【0036】
【発明の効果】
以上記述の通り、本発明によれば、低酸素含有量であり、高い焼結体密度を有し、従来に比べて配向度を高めた高性能の希土類焼結磁石を得られる製造方法を提供することができる。
又、低酸素含有量であり、高い焼結体密度を有し、従来に比べて配向度を高めた、薄肉形状又は薄肉、長尺形状の平行異方性又はラジアル異方性を有する高性能のR−T−B系焼結アークセグメント磁石を提供することができる。
又、低酸素含有量であり、高い焼結体密度を有し、従来に比べてラジアル方向の配向度を高めた、ラジアル異方性を有する高性能のR−T−B系焼結リング磁石を提供することができる。
[0036]
【The invention's effect】
As described above , according to the present invention , there is provided a manufacturing method capable of obtaining a high-performance rare-earth sintered magnet having a low oxygen content, a high sintered body density, and a higher degree of orientation than in the past. it is Ru can be.
In addition, it has low oxygen content, high sintered body density, high degree of orientation compared to conventional, high performance with parallel or radial anisotropy of thin or thin, long shape. Ru can provide the R-T-B based sintered arc segment magnets.
Also, a high performance R-T-B sintered ring magnet having a low oxygen content, a high sintered body density, and a higher degree of radial orientation than before, and having a radial anisotropy. Ru can provide.
【符号の説明】
1 ダイス、2 下パンチ、3 キャビティ、4 シリンダー、6 スラリー供給管、9 供給ヘッド、10 ポンプ、11 配管、13 タンク、15 スラリー供給装置、30,40 アークセグメント磁石、51 ダイス強磁性部、52 ダイス、53 コア、59 キャビティ、70 ラジアルリング。
[Explanation of symbols]
1 die, 2 lower punches, 3 cavities, 4 cylinders, 6 slurry supply pipe, 9 supply head, 10 pumps, 11 piping, 13 tanks, 15 slurry supply device, 30, 40 arc segment magnet, 51 die ferromagnetic section, 52 Dies, 53 cores, 59 cavities, 70 radial rings.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001279656A JP2002164239A (en) | 2000-09-14 | 2001-09-14 | Manufacturing method of rare earth sintered magnet, ring magnet, and arc segment magnet |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000280104 | 2000-09-14 | ||
| JP2000-280104 | 2000-09-14 | ||
| JP2001279656A JP2002164239A (en) | 2000-09-14 | 2001-09-14 | Manufacturing method of rare earth sintered magnet, ring magnet, and arc segment magnet |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2002164239A JP2002164239A (en) | 2002-06-07 |
| JP2002164239A5 true JP2002164239A5 (en) | 2007-03-01 |
Family
ID=26600003
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001279656A Pending JP2002164239A (en) | 2000-09-14 | 2001-09-14 | Manufacturing method of rare earth sintered magnet, ring magnet, and arc segment magnet |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2002164239A (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7192493B2 (en) * | 2002-09-30 | 2007-03-20 | Tdk Corporation | R-T-B system rare earth permanent magnet and compound for magnet |
| US7311788B2 (en) | 2002-09-30 | 2007-12-25 | Tdk Corporation | R-T-B system rare earth permanent magnet |
| CN100334662C (en) * | 2002-09-30 | 2007-08-29 | Tdk株式会社 | Method for producing r-t-b based rare earth element permanent magnet |
| CN100431062C (en) * | 2002-10-08 | 2008-11-05 | 日立金属株会社 | Sintered R-Fe-B series permanent magnet and its manufacturing method |
| US7314531B2 (en) | 2003-03-28 | 2008-01-01 | Tdk Corporation | R-T-B system rare earth permanent magnet |
| JP2009225608A (en) | 2008-03-18 | 2009-10-01 | Nitto Denko Corp | Permanent magnet for motor and method of manufacturing the permanent magnet for motor |
| JP5266523B2 (en) * | 2008-04-15 | 2013-08-21 | 日東電工株式会社 | Permanent magnet and method for manufacturing permanent magnet |
| JP5266522B2 (en) * | 2008-04-15 | 2013-08-21 | 日東電工株式会社 | Permanent magnet and method for manufacturing permanent magnet |
| JP5298180B2 (en) * | 2011-11-24 | 2013-09-25 | 日東電工株式会社 | Permanent magnet for motor and method for manufacturing permanent magnet for motor |
| CN107430921B (en) * | 2015-03-24 | 2020-03-10 | 日东电工株式会社 | Sintered body for forming rare earth magnet and rare earth sintered magnet |
| JP6848736B2 (en) * | 2016-07-15 | 2021-03-24 | Tdk株式会社 | RTB series rare earth permanent magnet |
| CN107610861A (en) * | 2017-09-26 | 2018-01-19 | 北京京磁电工科技有限公司 | The high remanent magnetism preparation technology of neodymium iron boron magnetic body |
-
2001
- 2001-09-14 JP JP2001279656A patent/JP2002164239A/en active Pending
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5767788B2 (en) | R-T-B rare earth permanent magnet, motor, automobile, generator, wind power generator | |
| JP6274216B2 (en) | R-T-B system sintered magnet and motor | |
| JP5392400B2 (en) | Rare earth sintered magnet, manufacturing method thereof, motor, and automobile | |
| JP4805998B2 (en) | Permanent magnet and permanent magnet motor and generator using the same | |
| JP5120710B2 (en) | RL-RH-T-Mn-B sintered magnet | |
| US20110233455A1 (en) | Sintered nd-fe-b permanent magnet with high coercivity for high temperature applications | |
| JPWO2015020182A1 (en) | R-T-B system sintered magnet and motor | |
| JP5501828B2 (en) | R-T-B rare earth permanent magnet | |
| CN103730227B (en) | A kind of nano biphase isotropic composite permanent magnet and preparation method thereof | |
| US6635120B2 (en) | Method for producing sintered rare earth magnet and sintered ring magnet | |
| JP2002164239A5 (en) | ||
| JP4951703B2 (en) | Alloy material for RTB-based rare earth permanent magnet, method for manufacturing RTB-based rare earth permanent magnet, and motor | |
| JP6613730B2 (en) | Rare earth magnet manufacturing method | |
| JP4433282B2 (en) | Rare earth magnet manufacturing method and manufacturing apparatus | |
| USRE40348E1 (en) | Arc segment magnet, ring magnet and method for producing such magnets | |
| JP4900085B2 (en) | Rare earth magnet manufacturing method | |
| JP5288276B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of RTB-based permanent magnet | |
| JP5743458B2 (en) | Alloy material for RTB-based rare earth permanent magnet, method for manufacturing RTB-based rare earth permanent magnet, and motor | |
| JP2002164239A (en) | Manufacturing method of rare earth sintered magnet, ring magnet, and arc segment magnet | |
| JP5299737B2 (en) | Quenched alloy for RTB-based sintered permanent magnet and RTB-based sintered permanent magnet using the same | |
| JP2018160669A (en) | R-t-b based rare earth magnet | |
| JP6691667B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing RTB magnet | |
| JP3059188B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing permanent magnet and permanent magnet | |
| WO2021193334A1 (en) | Anisotropic rare earth sintered magnet and method for producing same | |
| JP2002164238A5 (en) |