EP2749776A1 - Procédé de fabrication d'un corps de cylindre d'un vérin de commande et appareil de pompage de béton - Google Patents
Procédé de fabrication d'un corps de cylindre d'un vérin de commande et appareil de pompage de béton Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2749776A1 EP2749776A1 EP12878834.6A EP12878834A EP2749776A1 EP 2749776 A1 EP2749776 A1 EP 2749776A1 EP 12878834 A EP12878834 A EP 12878834A EP 2749776 A1 EP2749776 A1 EP 2749776A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- inner lining
- cylinder body
- lining layer
- layer
- fibrous composite
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B15/00—Fluid-actuated devices for displacing a member from one position to another; Gearing associated therewith
- F15B15/08—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit
- F15B15/14—Characterised by the construction of the motor unit of the straight-cylinder type
- F15B15/1423—Component parts; Constructional details
- F15B15/1428—Cylinders
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B15/00—Pumps adapted to handle specific fluids, e.g. by selection of specific materials for pumps or pump parts
- F04B15/02—Pumps adapted to handle specific fluids, e.g. by selection of specific materials for pumps or pump parts the fluids being viscous or non-homogeneous
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B9/00—Piston machines or pumps characterised by the driving or driven means to or from their working members
- F04B9/08—Piston machines or pumps characterised by the driving or driven means to or from their working members the means being fluid
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05C—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO MATERIALS, MATERIAL PROPERTIES OR MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS FOR MACHINES, ENGINES OR PUMPS OTHER THAN NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES
- F05C2253/00—Other material characteristics; Treatment of material
- F05C2253/04—Composite, e.g. fibre-reinforced
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05C—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO MATERIALS, MATERIAL PROPERTIES OR MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS FOR MACHINES, ENGINES OR PUMPS OTHER THAN NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES
- F05C2253/00—Other material characteristics; Treatment of material
- F05C2253/20—Resin
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F15—FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS; HYDRAULICS OR PNEUMATICS IN GENERAL
- F15B—SYSTEMS ACTING BY MEANS OF FLUIDS IN GENERAL; FLUID-PRESSURE ACTUATORS, e.g. SERVOMOTORS; DETAILS OF FLUID-PRESSURE SYSTEMS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F15B2215/00—Fluid-actuated devices for displacing a member from one position to another
- F15B2215/30—Constructional details thereof
- F15B2215/305—Constructional details thereof characterised by the use of special materials
Definitions
- the present invention relates to actuating cylinders domain, in particular to a cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, a method of manufacturing the cylinder body, and a concrete pumping apparatus having the cylinder body.
- Actuating cylinders usually include hydraulic cylinders and air cylinders, and are applied widely.
- concrete pumping apparatuses e.g., concrete pump trucks
- a hydraulic cylinder to drive a concrete cylinder to reciprocate and thereby deliver concrete.
- more and more concrete delivery work is accomplished with concrete pump trucks.
- the cylinder body of any existing hydraulic cylinder is made of alloy steel material solely.
- the self-weight of the hydraulic cylinder is high; therefore, the boom length of the concrete pump truck is severely limited, and the development of concrete pump trucks is limited. It is of great significance to develop a cylinder body of a hydraulic cylinder that can meet the strength requirement of concrete pump trucks and is light in weight, so as to extend the boom length of concrete pump trucks.
- the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder made of alloy steel solely has drawbacks such as low fatigue resistance, low corrosion resistance and high thermal expansibility, which limit the application of the actuating cylinder.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, which has high strength, light weight, high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansibility, to widen the application range of the actuating cylinder.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a method of manufacturing the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder.
- the present invention provides a cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, which comprises an inner lining layer and a first fibrous composite layer bonded on the outside of the inner lining layer, wherein, the first fibrous composite layer is composited from a first fibrous material and a substrate resin material.
- the present invention provides a concrete pumping apparatus, wherein, a cylinder body of a pumping cylinder of the concrete pumping apparatus is the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder described above.
- the present invention provides a method of manufacturing a cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, comprising: an inner lining layer forming step: forming an inner lining layer; and, a bonding step: forming a first fibrous composite layer with a first fibrous material and a substrate resin material and bonding the first fibrous composite layer on the outside of the inner lining layer.
- the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder comprises an inner lining layer and a first fibrous composite layer; owing to the fact that the fibrous composite has lighter weight when compared with existing metallic materials with the same strength as well as has high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansibility, the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder has high strength, light weight, high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansibility; therefore, the actuating cylinder can be applied more widely.
- the inner lining layer of the cylinder body can meet the requirements for leak tightness of the inner wall of the cylinder body and wear resistance when contacts with the piston, the service performance of the cylinder body will not be degraded.
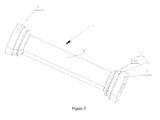
- the present invention provides a cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, which comprises an inner lining layer 1 and a first fibrous composite layer 2 bonded on the outside of the inner lining layer 1.
- the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder comprises an inner lining layer 1 and a first fibrous composite layer 2; owing to the fact that the fibrous composite has lighter weight when compared with existing metallic materials with the same strength as well as has high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansibility, the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder has high strength, light weight, high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansibility; therefore, the actuating cylinder can be applied more widely.
- the inner lining layer of the cylinder body can meet the requirements for leak tightness of the inner wall of cylinder body and wear resistance when contacts with the piston, the service performance of the cylinder body will not be degraded.
- the inner lining layer 1 may be made of an appropriate material that can meet the requirements for leak tightness of the inner wall of cylinder body and wear resistance when contacts with the piston; for example, the inner lining layer 1 may be made of an existing metallic material that is usually used to manufacture a cylinder body.
- the fibrous composite material mentioned in the present invention refers to a material composited from a fibrous material and a substrate resin material, i.e., a fiber reinforced resin composite material.
- the first fibrous composite layer 2 may be composited from any appropriate fibrous material and substrate resin material; for example, the fibrous material may be selected from one or more of fiber glass, aramid fiber, super-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and carbon fiber.
- the first fibrous composite layer 2 is made of a carbon fiber material and a substrate resin material.
- Carbon fiber composite materials have advantages such as light weight, high strength, high rigidity, high damping performance, high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance, etc.
- the carbon fiber material may be composited with a variety of substrate resin materials to form carbon fiber composite materials; for example, the substrate resin material may be unsaturated polyester, vinyl resin, phenolic resin, etc., preferably an epoxy resin system that has good machinability, high strength and high ductility.
- the fibrous materials that can be used to form the first fibrous composite layer 2 some are electroconductive materials, and others are non-electroconductive materials; in case the inner lining layer 1 and the first fibrous composite layer 2 are made of electroconductive materials (e.g., the inner lining layer 1 is made of a metallic material, and the first fibrous composite layer is made of a carbon fiber composite material), an insulating layer 3 is preferably arranged between the inner lining layer 1 and the first fibrous composite layer 2.
- the electro-chemical corrosion between the inner lining layer 1 and the first fibrous composite layer 2 can be prevented, and the service life of the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder can be prolonged.
- the insulating layer 3 may be made of any appropriate insulating material; for example, it may be selected from one or more of fiber glass, aramid fiber, super-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and basalt fiber.
- the insulating layer 3 may be bonded to the inner lining layer 1 by a high-toughness adhesive.
- a second fibrous composite layer 4 is arranged on the outside of the first fibrous composite layer 2.
- the second fibrous composite layer 4 is helpful for improving impact resistance of the cylinder body against external impacts.
- the second fibrous composite layer 4 may be composited from any appropriate fibrous material and substrate resin material; for example, the fibrous material may be selected from one or more of fiber glass, aramid fiber, super-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and basalt fiber.
- the substrate resin material for the first fibrous composite layer 2 may be identical to or different from the substrate resin material for the second fibrous composite layer 4.
- the present invention doesn't involve any change to the overall shape of the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, which is to say, the overall shape of the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder may be identical to the overall shape of the cylinder body of any existing actuating cylinder; for example, the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder may be generally in a hollow cylinder structure, with connecting thread and/or an oil port arranged on both ends, wherein, the connecting thread is mainly designed to connect an end cap of the actuating cylinder, and the oil port is mainly designed to connect a working oil circuit of the actuating cylinder, so that the working oil circuit can communicate with a working chamber within the cylinder body.
- the cylinder body comprises multiple material layers, so as to improve the strength, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance of the cylinder body and decrease the weight and thermal expansibility of the cylinder body.
- the multiple material layers of the cylinder body e.g., the above-mentioned inner lining layer 1, first fibrous composite layer 2, insulating layer 3 and second fibrous composite layer 4) may have even thickness or uneven thickness respectively.
- the inner lining layer 1 is generally in a cylindrical shape, and comprises a middle part 11 and two end parts 12 at the sides of the middle part 11, wherein, the thickness of the middle part 11 is smaller than the thickness of each end part 12.
- the middle part 11 and two end parts 12 are arranged essentially along the axial direction of the cylinder body, and the inner lining layer 1 is essentially in a structure that is bigger at both ends and smaller in the middle, which is helpful for processing and port arrangement, and provides fixing effect for the fibrous composite material formed on the outside of the two end parts 12 and the middle part 11.
- a transition part 13 is arranged between each end part 12 and the middle part 11, and the thickness of the transition part 13 transits from the thickness of the end part 12 to the thickness of the middle part 11. With the transition part 13, stress concentration incurred by abrupt change of thickness can be prevented.
- an oil port and/or connecting thread is/are arranged on the end parts 12 of the inner lining layer 1, and the first fibrous composite layer 2 is arranged on the outside of the middle part 11 and transition part 13 of the inner lining layer 1.
- the oil port and/or connecting thread of the cylinder body can be pre-formed on the end parts 12 as required, and the oil part and/or connecting thread is/are not covered by the first fibrous composite layer 2, insulating layer 3 and second fibrous composite layer 4 (if any); therefore, the cylinder body has high machinability, and it is unnecessary to work out additional oil port and/or connecting thread on any other material layer (e.g., the first fibrous composite layer 2, insulating layer 3 and second fibrous composite layer 4) except for the inner lining layer 1.
- the transition part 13 may have a ramp profile with uniformly transiting thickness, or a staged profile with thickness transiting by stages, or any other appropriate profile. More preferably, as shown in Figure 1 ⁇ 3 , the transition part 13 comprises a ramp part 131 and a raised part 132 arranged on the ramp part 131, wherein, the thickness of the ramp part 131 transits uniformly from the thickness of the end part 12 to the thickness of the middle part 11.
- the raised part 132 is helpful for bonding between the inner lining layer 1 and other material layers (e.g., the first fibrous composite layer 2) and improving the bonding force, and can prevent the inner lining layer 1 from separated from other material layers.
- the raised part 132 may be one raised continuous ring or multiple raised continuous rings (one continuous ring as shown in Figure 3 ), or may be a plurality of discrete raised bars or raised ribs.
- the present invention provides a concrete pumping apparatus, wherein, a cylinder body of a pumping cylinder of the concrete pumping apparatus is the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder described above.
- the present invention provides a method of manufacturing a cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, comprising: an inner lining layer forming step: forming an inner lining layer 1; and, a bonding step: forming a first fibrous composite layer 2 with a first fibrous material and a substrate resin material and bonding the first fibrous composite layer 2 on the outside of the inner lining layer 1.
- the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder comprises an inner lining layer 1 and a first fibrous composite layer 2; owing to the fact that the fibrous composite has lighter weight when compared with existing metallic materials with the same strength as well as has high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansibility, the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder has high strength, light weight, high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance and low thermal expansibility; therefore, the actuating cylinder can be applied more widely.
- the inner lining layer of the cylinder body can meet the requirements for leak tightness of the inner wall of cylinder body and wear resistance when contacts with the piston, the service performance of the cylinder body will not be degraded.
- the inner lining layer 1 may be made of an appropriate material that can meet the requirements for leak tightness of the inner wall of cylinder body and wear resistance when contacts with the piston; for example, the inner lining layer 1 may be made of an existing metallic material that is usually used to manufacture a cylinder body.
- the first fibrous composite layer 2 may be composited from any appropriate fibrous material and substrate resin material; for example, the fibrous material may be selected from one or more of fiber glass, aramid fiber, super-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and carbon fiber.
- the first fibrous composite layer 2 is formed from a carbon fiber and a substrate resin.
- Carbon fiber composite materials have advantages such as light weight, high strength, high rigidity, high damping performance, high fatigue resistance, high corrosion resistance, etc.
- the carbon fiber material may be composited with a variety of substrate resin materials to form carbon fiber composite materials; for example, the substrate resin material may be unsaturated polyester, vinyl resin, phenolic resin, etc., preferably an epoxy resin system that has good machinability, high strength and high ductility.
- the inner lining layer 1 is formed from a electroconductive material (e.g., a metallic material, more specifically, 27SiMn); in the bonding step, the first fibrous composite layer 2 is formed from a electroconductive material (e.g., a carbon fiber composite material); in addition, the manufacturing method further comprises an insulating layer forming step: forming an insulating layer 3 on the outside of the inner lining layer 1 before the bonding step, so that the insulating layer 3 is arranged between the inner lining layer 1 and the first fibrous composite layer 2.
- a electroconductive material e.g., a metallic material, more specifically, 27SiMn
- the first fibrous composite layer 2 is formed from a electroconductive material (e.g., a carbon fiber composite material)
- the manufacturing method further comprises an insulating layer forming step: forming an insulating layer 3 on the outside of the inner lining layer 1 before the bonding step, so that the insulating layer 3 is arranged between the inner lining layer 1 and the first fibrous
- the insulating layer 3 may be made of any appropriate insulating material; for example, it may be selected from one or more of fiber glass, aramid fiber, super-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and basalt fiber.
- the insulating layer may be formed by wrapping a piece of fiber cloth (e.g., glass fiber cloth) on the outside of the inner lining layer 1.
- the insulating layer 3 may be bonded to the inner lining layer 1 by a high-toughness adhesive.
- the first fibrous composite layer may be formed and bonded in an appropriate manner; preferably, in the bonding step, a bundle of the first fibrous material dipped with the substrate resin is wound on the outside of the inner lining layer 1 by a wet winding process. Specifically, a bundle of continuous first fiber is dipped with prepared epoxy resin, and then wound to the fixed inner lining layer 1 through a winding guide head of a winding machine, so as to accomplish fiber winding.
- a product obtained by wet winding gives full play to the properties of the composite material; therefore, the product is afforded with required structural performance as far as possible, and the forming cost is low and the process is relatively simple.
- the angle between the extension direction of the bundle of the first fibrous composite material and the axial line of the cylinder body is 70° ⁇ 90°, i.e., the winding angle of the first fibrous composite material is 70° ⁇ 90°.
- the wrapping angle is helpful for improving the radial strength of the cylinder body (i.e., improving the mechanical properties of the cylinder body) and reducing the overall thickness of the cylinder body, and thereby can provide favorable fatigue resistance performance for the cylinder body.
- the manufacturing method further comprises: forming a second fibrous composite layer 4 on the outside of the first fibrous composite layer 2.
- the second fibrous composite layer 4 is helpful for improving impact resistance of the cylinder body against external impacts.
- the second fibrous composite layer 4 may be composited from any appropriate fibrous material and substrate resin material; for example, the fibrous material may be selected from one or more of fiber glass, aramid fiber, super-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and basalt fiber.
- the second fibrous composite layer 4 may be formed by wrapping a piece of cloth made of a second fibrous material on the outside of the first fibrous composite layer 2 so as to make the substrate resin in the first fibrous composite layer 2 infiltrate into the cloth made of a second fibrous material.
- substrate resin may be added on the second fibrous material cloth additionally, instead of utilizing the substrate resin in the first fibrous composite layer 2.
- the present invention doesn't involve any change to the overall shape of the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder, which is to say, the overall shape of the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder may be identical to the overall shape of the cylinder body of any existing actuating cylinder; for example, the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder may be generally in a hollow cylinder structure, with connecting thread and/or an oil port arranged on both ends.
- the main innovative ideal of the present invention lies in: the cylinder body comprises multiple material layers, so as to improve the strength, corrosion resistance and fatigue resistance of the cylinder body and decrease the weight and thermal expansibility of the cylinder body.
- the multiple material layers of the cylinder body may have even thickness or uneven thickness respectively.
- the inner lining layer forming step comprises: providing a blank of the inner lining layer that is generally in a hollow cylinder shape; and, a machining procedure: reducing the thickness of a part of the blank of the inner lining layer by machining (e.g., turning), so that the inner lining layer 1 is formed to have a middle part 11 and two end parts 12 at the sides of the middle part 11, wherein, the thickness of the middle part 11 is smaller than the thickness of each end part 12.
- the middle part 11 and two end parts 12 are arranged essentially along the axial direction of the cylinder body, and the inner lining layer 1 is essentially in a structure that is bigger at both ends and smaller in the middle which is helpful for processing and port arrangement, and provides fixing effect for the fibrous composite material formed on the outside of the two end parts 12 and the middle part 11.
- a transition part 13 is formed between each end part 12 and the middle part 11, and the thickness of the transition part 13 transits from the thickness of the end part 12 to the thickness of the middle part 11. With the transition part 13, stress concentration incurred by abrupt change of thickness can be prevented.
- an oil port and/or connecting thread is/are formed on the end parts 12 of the inner lining layer 1, and in the bonding step, the first fibrous composite layer 2 is bonded on the outside of the middle part 11 and transition parts 13 of the inner lining layer 1.
- the oil port and/or connecting thread of the cylinder body can be pre-formed on the end parts 12 as required, and the oil part and/or connecting thread is/are not covered by the first fibrous composite layer 2, insulating layer 3 and second fibrous composite layer 4 (if any); therefore, the cylinder body has high machinability, and it is unnecessary to work out additional oil port and/or connecting thread on any other material layer (e.g., the first fibrous composite layer 2, insulating layer 3 and second fibrous composite layer 4) except for the inner lining layer 1.
- any other material layer e.g., the first fibrous composite layer 2, insulating layer 3 and second fibrous composite layer 4
- the transition part 13 may have a ramp profile with uniformly transiting thickness or a staged profile with thickness transiting by stages, or any other appropriate profile.
- the transition part 13 is formed to have a ramp part 131 and a raised part 132 arranged on the ramp part 131, wherein, the thickness of the ramp part 131 transits uniformly from the thickness of the end part 12 to the thickness of the middle part 11.
- the raised part 132 is helpful for bonding between the inner lining layer 1 and other material layers (e.g., the first fibrous composite layer 2) and improving the bonding force, and can prevent the inner lining layer 1 from separated from other material layers.
- the raised part 132 may be one raised continuous ring or multiple raised continuous rings (one continuous ring as shown in Figure 3 ), or may be a plurality of discrete raised bars or raised ribs.
- the inner lining layer forming step further comprises: a sand blasting procedure: carrying out sand blasting on the outer surface of the inner lining layer 1 formed in the machining procedure, to increase roughness of the outer surface of the inner lining layer 1. In that way, the bonding force between the inner lining layer 1 and other material layers (e.g., insulating layer 3, first fibrous composite layer 2, etc.) can be increased.
- a sand blasting procedure carrying out sand blasting on the outer surface of the inner lining layer 1 formed in the machining procedure, to increase roughness of the outer surface of the inner lining layer 1.
- other material layers e.g., insulating layer 3, first fibrous composite layer 2, etc.
- the cylinder body of an actuating cylinder and the method of manufacturing the cylinder body described above are applicable to different types of actuating cylinders, including hydraulic cylinders, gas cylinders, etc.; for example, the cylinder body may be widely used as a cylinder body of an actuating cylinder in different engineering machines, such as concrete pump trucks, lifters, excavators, fire engines, overhead working trucks, environmental sanitation vehicles, etc.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Pistons, Piston Rings, And Cylinders (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Actuator (AREA)
- Cylinder Crankcases Of Internal Combustion Engines (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201210195986.3A CN102705293B (zh) | 2012-06-14 | 2012-06-14 | 致动缸的缸体及其制造方法和混凝土泵送设备 |
| PCT/CN2012/086108 WO2013185451A1 (fr) | 2012-06-14 | 2012-12-07 | Procédé de fabrication d'un corps de cylindre d'un vérin de commande et appareil de pompage de béton |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2749776A1 true EP2749776A1 (fr) | 2014-07-02 |
Family
ID=46898285
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP12878834.6A Withdrawn EP2749776A1 (fr) | 2012-06-14 | 2012-12-07 | Procédé de fabrication d'un corps de cylindre d'un vérin de commande et appareil de pompage de béton |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2749776A1 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN102705293B (fr) |
| IN (1) | IN2014KN00740A (fr) |
| WO (1) | WO2013185451A1 (fr) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102015224913A1 (de) * | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-14 | Festo Ag & Co. Kg | Fluidaktor |
| EP3260369A1 (fr) * | 2016-06-23 | 2017-12-27 | Goodrich Corporation | Joint composite métallique |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102705293B (zh) * | 2012-06-14 | 2014-04-09 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 致动缸的缸体及其制造方法和混凝土泵送设备 |
| CN102689436A (zh) * | 2012-06-14 | 2012-09-26 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 致动缸的缸体的制造方法 |
| CN103470755B (zh) * | 2013-09-11 | 2015-12-23 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 活塞缸及活塞缸的制作方法 |
| CN103727092A (zh) * | 2014-01-24 | 2014-04-16 | 武汉理工大学 | 一种碳纤维复合材料液压缸 |
| JP6368517B2 (ja) * | 2014-03-28 | 2018-08-01 | Kyb株式会社 | 液圧回転機 |
| CN104832487A (zh) * | 2014-09-18 | 2015-08-12 | 北汽福田汽车股份有限公司 | 驱动缸的缸筒过渡连接头及具有其的驱动缸 |
| CN104454763B (zh) * | 2014-12-02 | 2017-01-04 | 荣成复合材料有限公司 | 一种复合材料液压油缸或伸缩臂的制造方法 |
| CN105587709B (zh) * | 2016-03-17 | 2018-03-06 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 液压缸 |
| CN106930998A (zh) * | 2017-05-18 | 2017-07-07 | 武汉科技大学 | 一种碳纤维复合材料增强的轻量化液压缸 |
| CN108953600A (zh) * | 2018-06-26 | 2018-12-07 | 河南德佰特机电设备制造有限公司 | 一种降低重量的缸筒 |
| CN109340209B (zh) * | 2018-10-29 | 2020-11-27 | 山西平阳重工机械有限责任公司 | 用于动车救援的碳纤维双伸缩油缸 |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3793104A (en) * | 1972-03-31 | 1974-02-19 | Lawron Ind Ltd | Process for restoring and covering suction couch shells |
| US4867044A (en) * | 1984-11-26 | 1989-09-19 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Jam resistant fluid power actuator for ballistic-damage tolerant redundant cylinder assemblies |
| US4971846A (en) * | 1987-11-16 | 1990-11-20 | Tre Corporation | Thermoplastic cylinder and process for manufacturing same |
| JPH0634047A (ja) * | 1992-07-15 | 1994-02-08 | Sumitomo Metal Ind Ltd | シリンダー装置 |
| DE19649133C1 (de) * | 1996-11-27 | 1998-03-05 | Dornier Gmbh | Hydraulik-Zylinder |
| AT502447B1 (de) * | 2004-11-25 | 2007-06-15 | Hoelzl Margit | Zylinder für hochdruckhydraulik |
| KR101274263B1 (ko) * | 2005-03-22 | 2013-06-14 | 퀵스텝 테크놀로지즈 피티와이 리미티드 | 복합재료 튜브 생산 |
| JP4669318B2 (ja) * | 2005-05-11 | 2011-04-13 | カヤバ工業株式会社 | シリンダバレル |
| CN101362387A (zh) * | 2007-08-10 | 2009-02-11 | 武济群 | 复合管制造方法 |
| CN101900246B (zh) * | 2010-07-28 | 2011-09-07 | 国营江北机械厂 | 纤维缠绕气瓶的固化方法 |
| CN102705293B (zh) * | 2012-06-14 | 2014-04-09 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 致动缸的缸体及其制造方法和混凝土泵送设备 |
| CN202597323U (zh) * | 2012-06-14 | 2012-12-12 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 致动缸的缸体和混凝土泵送设备 |
| CN102689436A (zh) * | 2012-06-14 | 2012-09-26 | 中联重科股份有限公司 | 致动缸的缸体的制造方法 |
| CN102720721A (zh) * | 2012-07-02 | 2012-10-10 | 江苏恒神纤维材料有限公司 | 碳纤维复合材料增强液压油缸 |
-
2012
- 2012-06-14 CN CN201210195986.3A patent/CN102705293B/zh active Active
- 2012-12-07 EP EP12878834.6A patent/EP2749776A1/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 2012-12-07 WO PCT/CN2012/086108 patent/WO2013185451A1/fr active Application Filing
- 2012-12-07 IN IN740KON2014 patent/IN2014KN00740A/en unknown
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See references of WO2013185451A1 * |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102015224913A1 (de) * | 2015-12-10 | 2017-06-14 | Festo Ag & Co. Kg | Fluidaktor |
| DE102015224913B4 (de) | 2015-12-10 | 2023-12-21 | Festo Se & Co. Kg | Fluidaktor |
| EP3260369A1 (fr) * | 2016-06-23 | 2017-12-27 | Goodrich Corporation | Joint composite métallique |
| US10272991B2 (en) | 2016-06-23 | 2019-04-30 | Goodrich Corporation | Metallic composite joint |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2013185451A1 (fr) | 2013-12-19 |
| CN102705293B (zh) | 2014-04-09 |
| IN2014KN00740A (fr) | 2015-10-02 |
| CN102705293A (zh) | 2012-10-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2749776A1 (fr) | Procédé de fabrication d'un corps de cylindre d'un vérin de commande et appareil de pompage de béton | |
| EP2963313A1 (fr) | Engrenage formé à partir de premier et second matériaux | |
| JP4669318B2 (ja) | シリンダバレル | |
| WO2002068844A1 (fr) | Chemise de pompe | |
| US8529361B2 (en) | Drive shaft, in particular radial shaft for a gas-turbine engine | |
| US20050089429A1 (en) | Composite material progressing cavity stators | |
| US20190310044A1 (en) | Metal-Metal-Matrix Composite Barrels | |
| US20180335077A1 (en) | Shaft and method for manufacturing a shaft | |
| KR100715427B1 (ko) | 복합재료와 금속으로 이루어진 경량 붐 어셈블리 | |
| EP2895748A1 (fr) | Cylindre hydraulique fait d'un stratifié composite hybride, en particulier pour des applications à grande puissance | |
| CN107218368B (zh) | 多孔超声波传动副 | |
| CN102689436A (zh) | 致动缸的缸体的制造方法 | |
| US20130228071A1 (en) | Piston unit | |
| US6675699B1 (en) | Composite components for use in pumps | |
| CN203297186U (zh) | 液压油缸 | |
| CN104936766A (zh) | 用于塑料部件的阻隔复合物 | |
| US9409376B2 (en) | Reinforcement integrated into the structure of wound components consisting of composite materials | |
| CN104831468A (zh) | 经编针织机的部件 | |
| CN103470755A (zh) | 活塞缸及活塞缸的制作方法 | |
| CN211343584U (zh) | 一种预应力镶嵌式组合筒结构 | |
| CN112555316A (zh) | 一种抗冲击的复合材料横向减振结构及其制造方法 | |
| EP2806185A1 (fr) | Élément de machine contenant un remplissage effective de la composition minérale et la méthode de la production du celui-ci | |
| KR100541118B1 (ko) | 콘크리트이송용복합재파이프 | |
| CN113531226B (zh) | 混凝土输送管及制备方法和混凝土泵车 | |
| CN202937545U (zh) | 致动缸的缸体和混凝土泵送设备 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20140326 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18W | Application withdrawn |
Effective date: 20150501 |